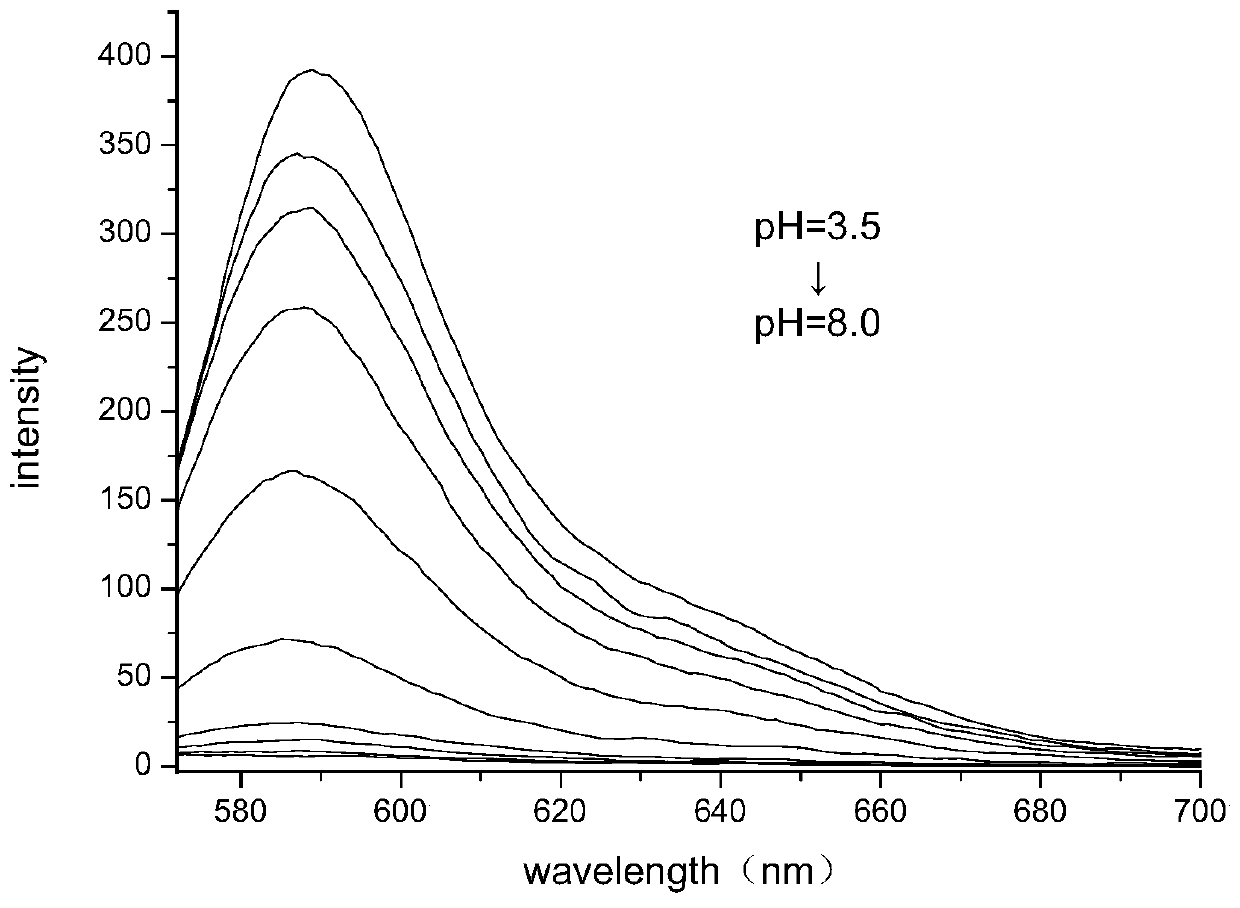
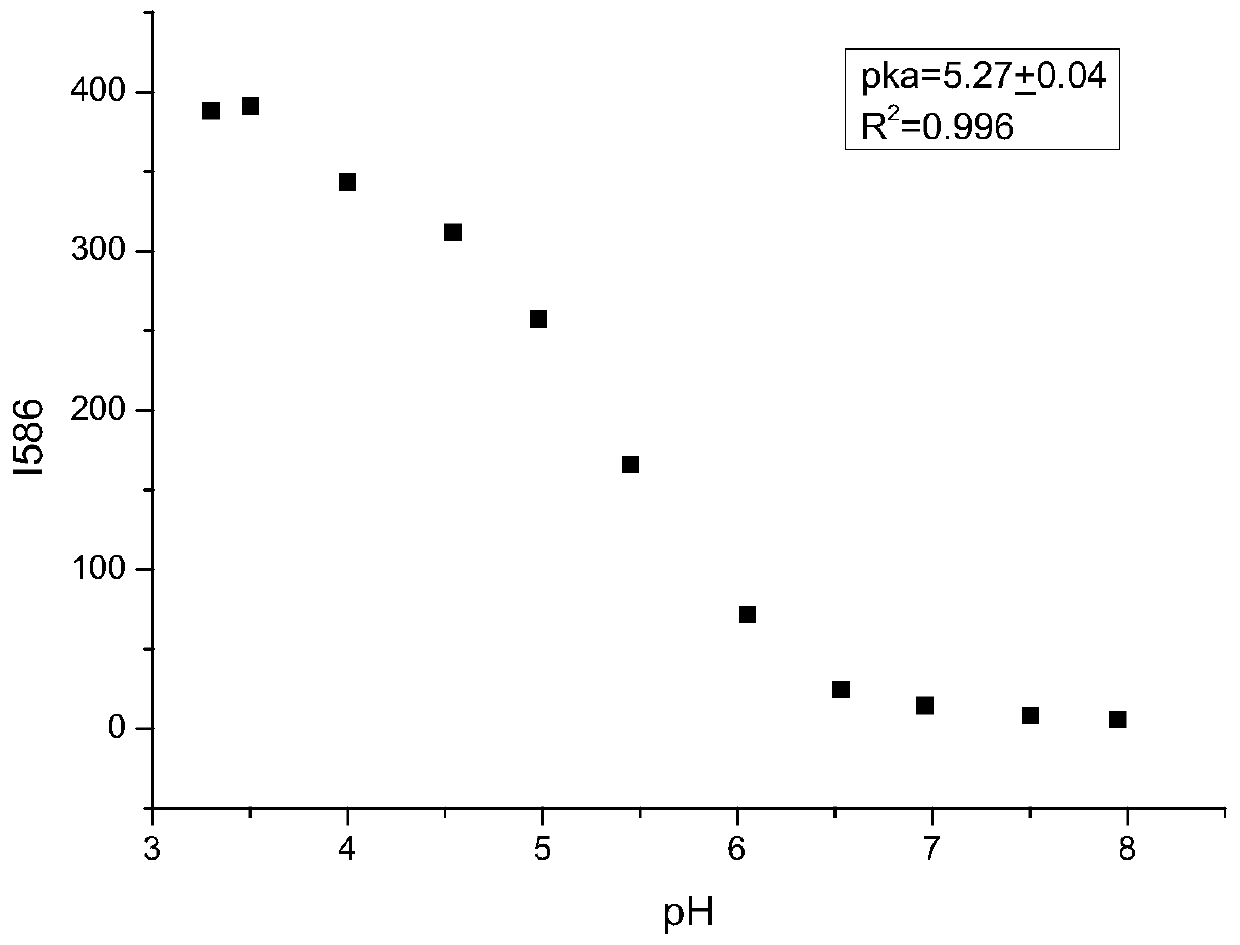
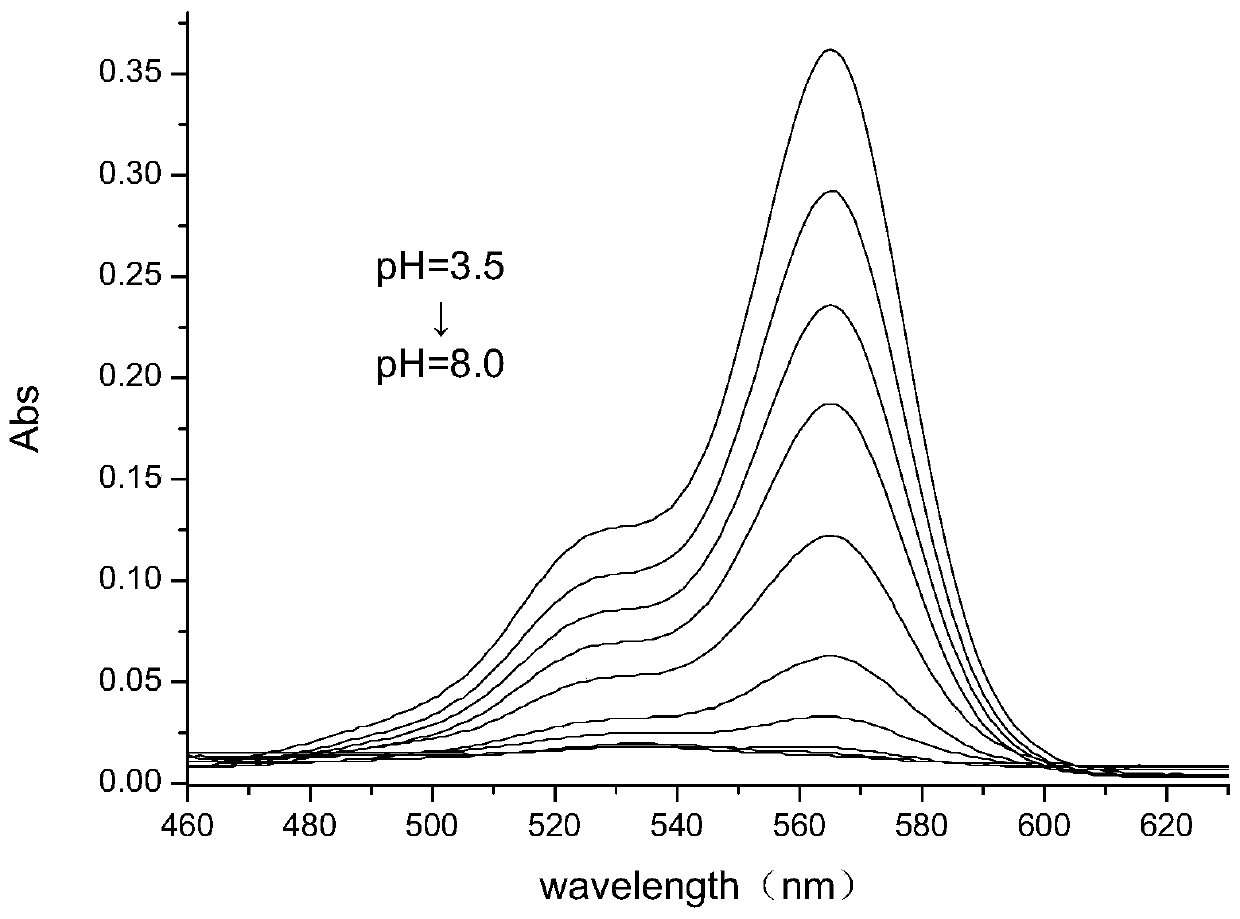
Six-membered spiro rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator containing urea structure and application thereof
A fluorescent indicator, the technology of six-membered spiro, which is applied in the field of six-membered spirocyclic rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator to achieve the effects of high sensitivity, good acid-base reversibility and rapid response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Six-membered spirocyclic rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator containing urea structure——Rh-NH1
[0031] The reaction formula is as follows:
[0032]
[0033] Mix 1 mole of rhodamine B with 3 moles of POCl 3 Add it into dry 1,2-dichloroethane, heat and reflux at 90°C for 3-5 hours, cool to room temperature, remove the solvent 1,2-dichloroethane, then add sodium azide in acetone aqueous solution ( Dissolve 0.5 mL of an aqueous solution containing 1.3 moles of sodium azide in 30 mL of acetone), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, extract the reaction solution with dichloromethane, take the lower layer, dry it with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and evaporate it under reduced pressure After solvent, dissolve the reactant with dry acetonitrile and move it into the reaction kettle, add excess ammonia water, react in an oil bath at 100°C for 10 hours, extract the resulting reaction liquid with dichloromethane, take the lower layer, dry it with anhydrous magnesium...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Six-membered spirocyclic rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator containing urea structure——Rh-NH2
[0036]
[0037] Mix 1 molar amount of Rhodamine 6G with 3 molar amounts of POCl 3 Add it into dry 1,2-dichloroethane, heat and reflux at 90°C for 3-5 hours, cool to room temperature, remove the solvent 1,2-dichloroethane, then add sodium azide in acetone aqueous solution ( Dissolve 0.5 mL of an aqueous solution containing 1.3 moles of sodium azide in 30 mL of acetone), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, extract the reaction solution with dichloromethane, take the lower layer, dry it with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and evaporate it under reduced pressure After the solvent, the reactant was dissolved in dry acetonitrile and moved into a reaction kettle, and excess ammonia water was added, and reacted in an oil bath at 100°C for 10 hours. The resulting reaction liquid was extracted with dichloromethane, and the lower layer was taken and dried with anhydrous ma...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3 Six-membered spirocyclic rhodamine pH fluorescent indicator containing urea structure——Rh-NH3
[0039]
[0040] Add 1 mole of tetramethylrhodamine TMR and 3 moles of POCl3 into dry 1,2-dichloroethane, heat and reflux at 90°C for 3-5 hours, cool to room temperature, remove the solvent 1,2 -Dichloroethane, then add the aqueous acetone solution of sodium azide (dissolve 0.5 mL of the aqueous solution containing 1.3 molar amounts of sodium azide in 30 mL of acetone), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, and extract the reaction solution with dichloromethane , remove the lower layer, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure, dissolve the reactant with dry acetonitrile and move it into a reaction kettle, add excess ammonia water, and react in an oil bath at 100°C for 10 hours. The reaction solution was extracted with dichloromethane, and the lower layer was taken and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Purify by si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com