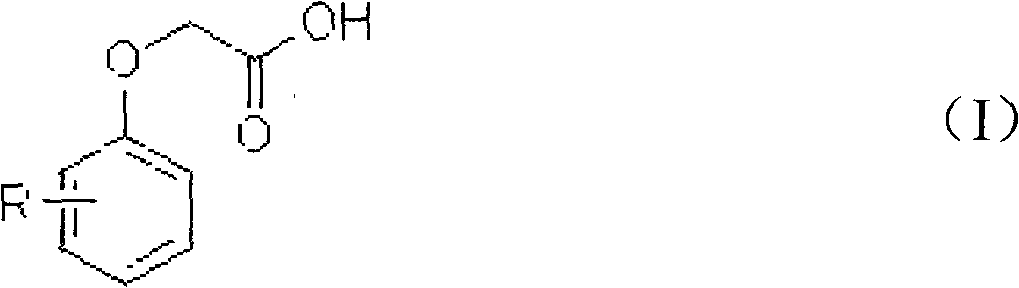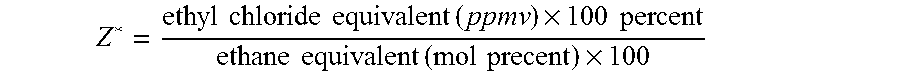Patents
Literature
697 results about "Ethane Dichloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
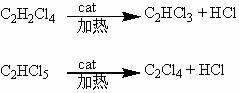
The chemical compound 1, 2-dichloroethane, commonly known by its old name of ethylene dichloride (EDC), is a chlorinated hydrocarbon, mainly used to produce vinyl chloride monomer (VCM, chloroethene), the major precursor for PVC production.
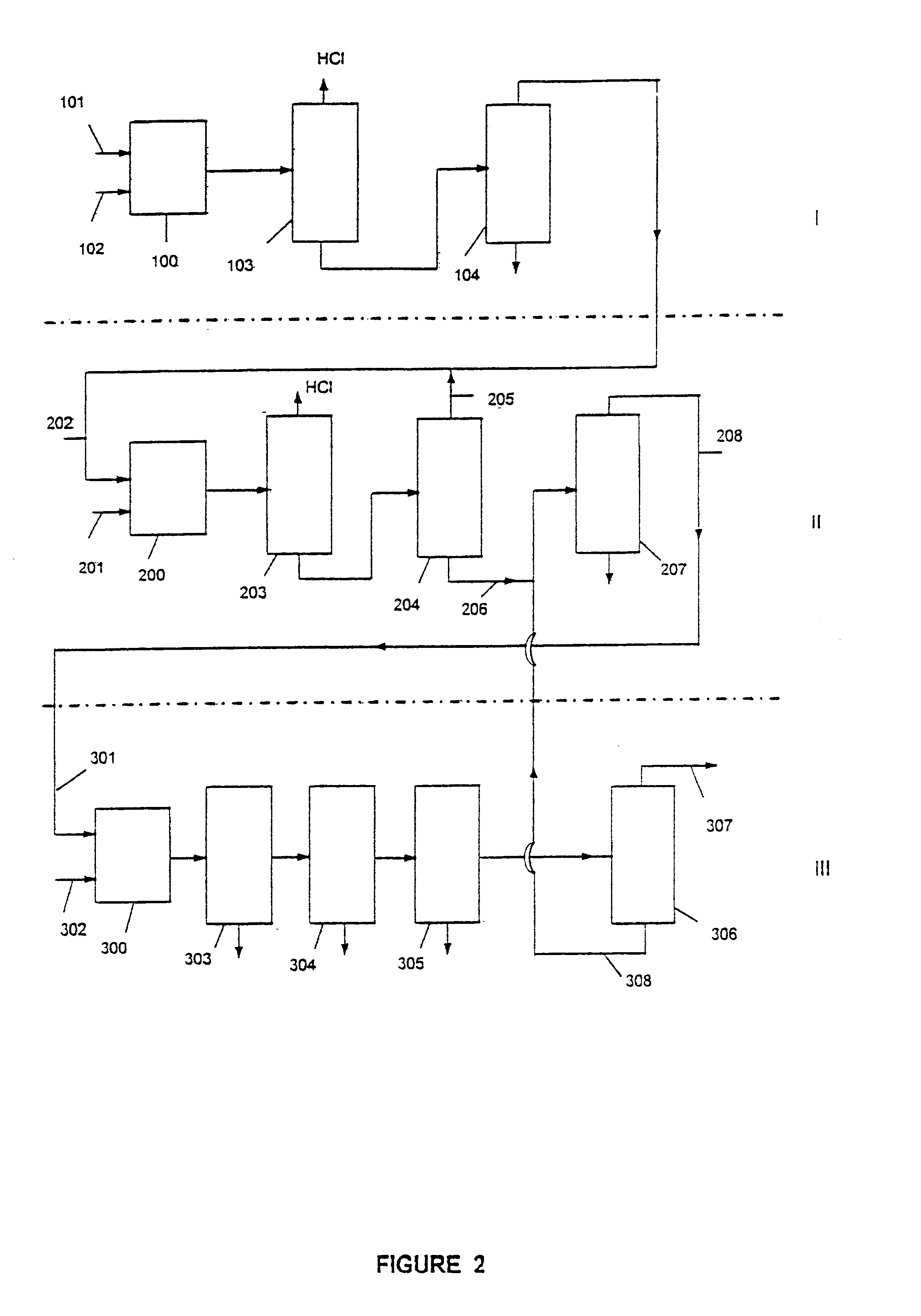
Method and device for producing 1,2-dichlorethane by means of direct chlorination
ActiveUS7579509B2Excellent part-load performanceReduce stressFlow mixersMixing methodsLiquid stateStatic mixer
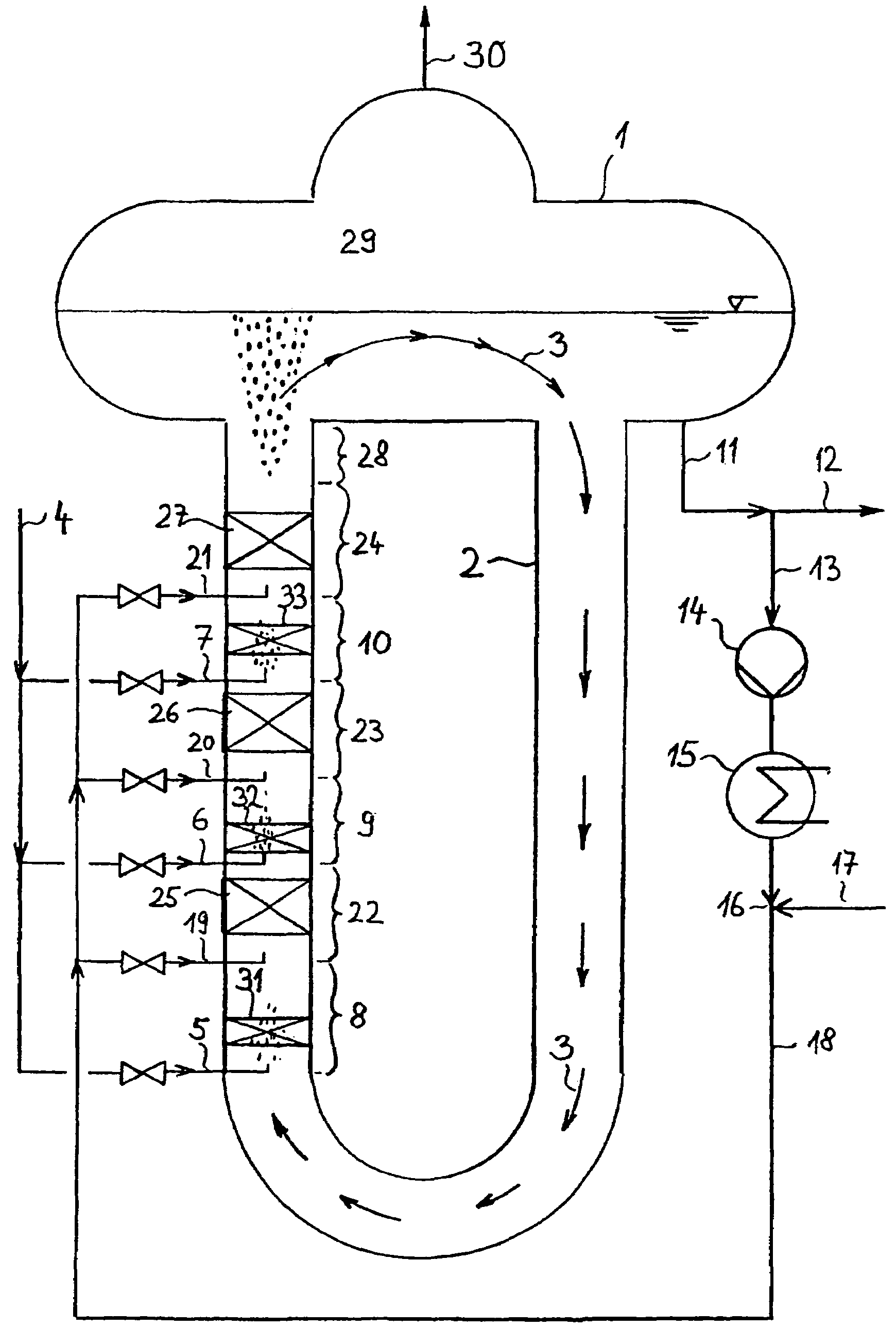
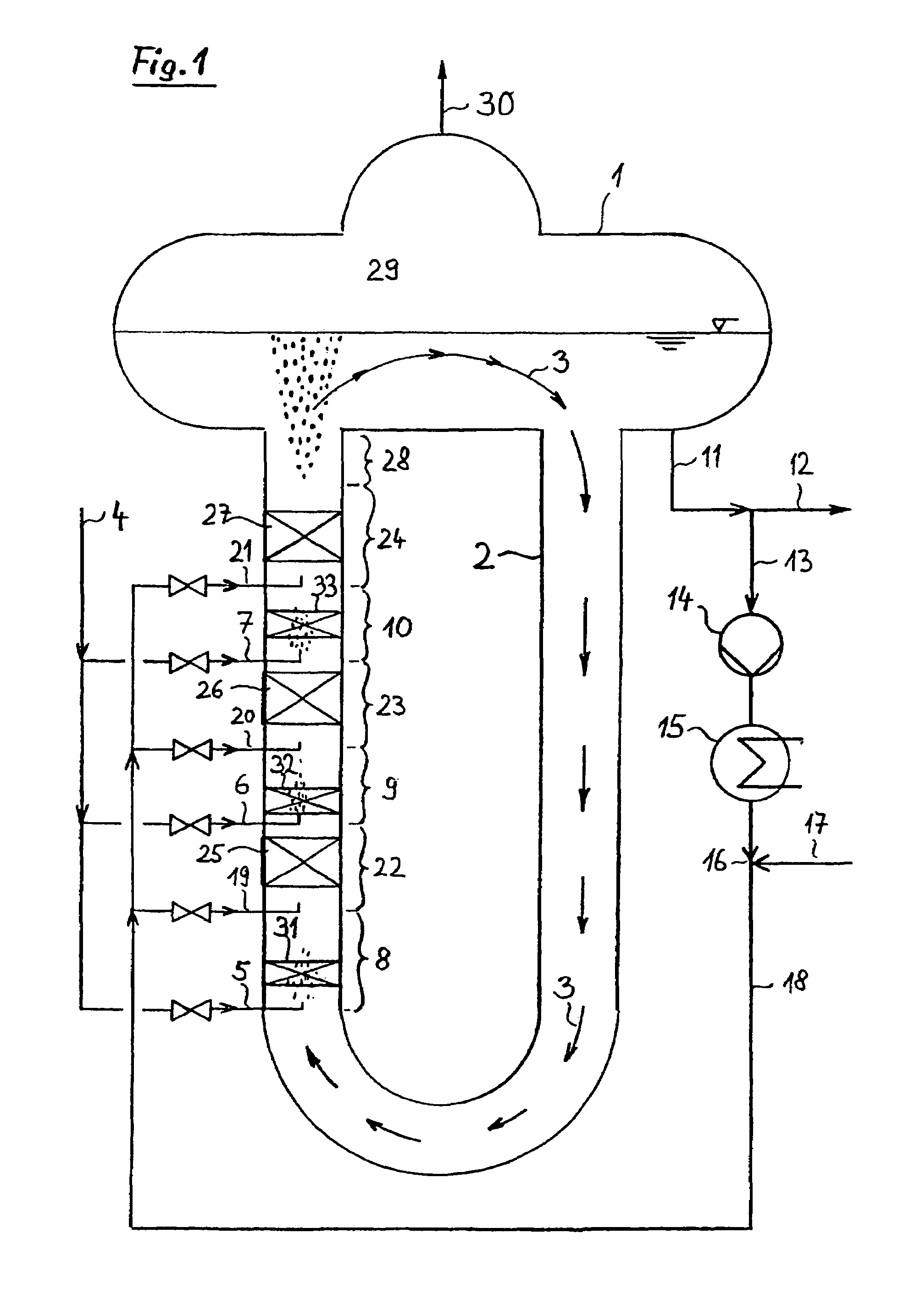
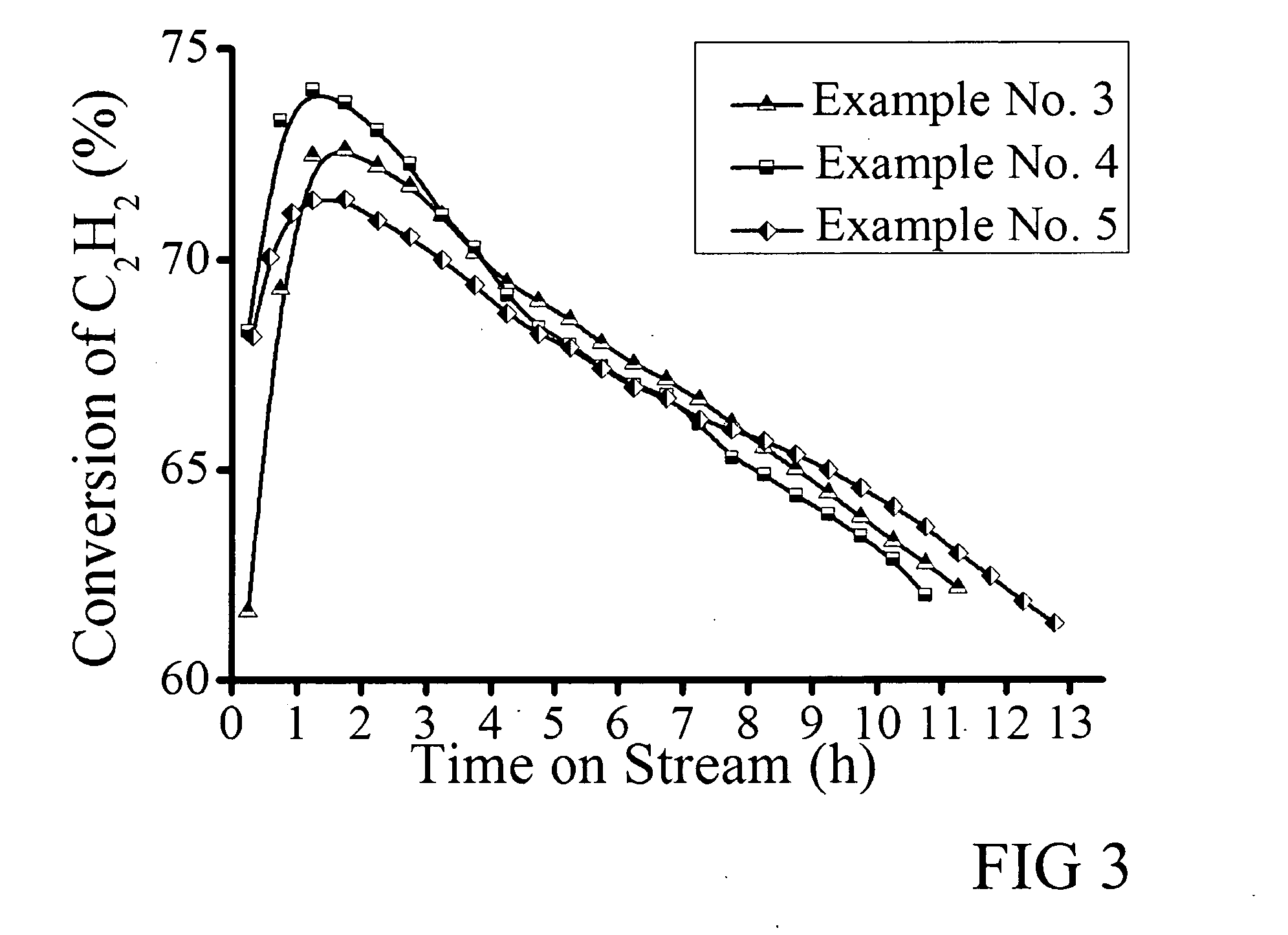
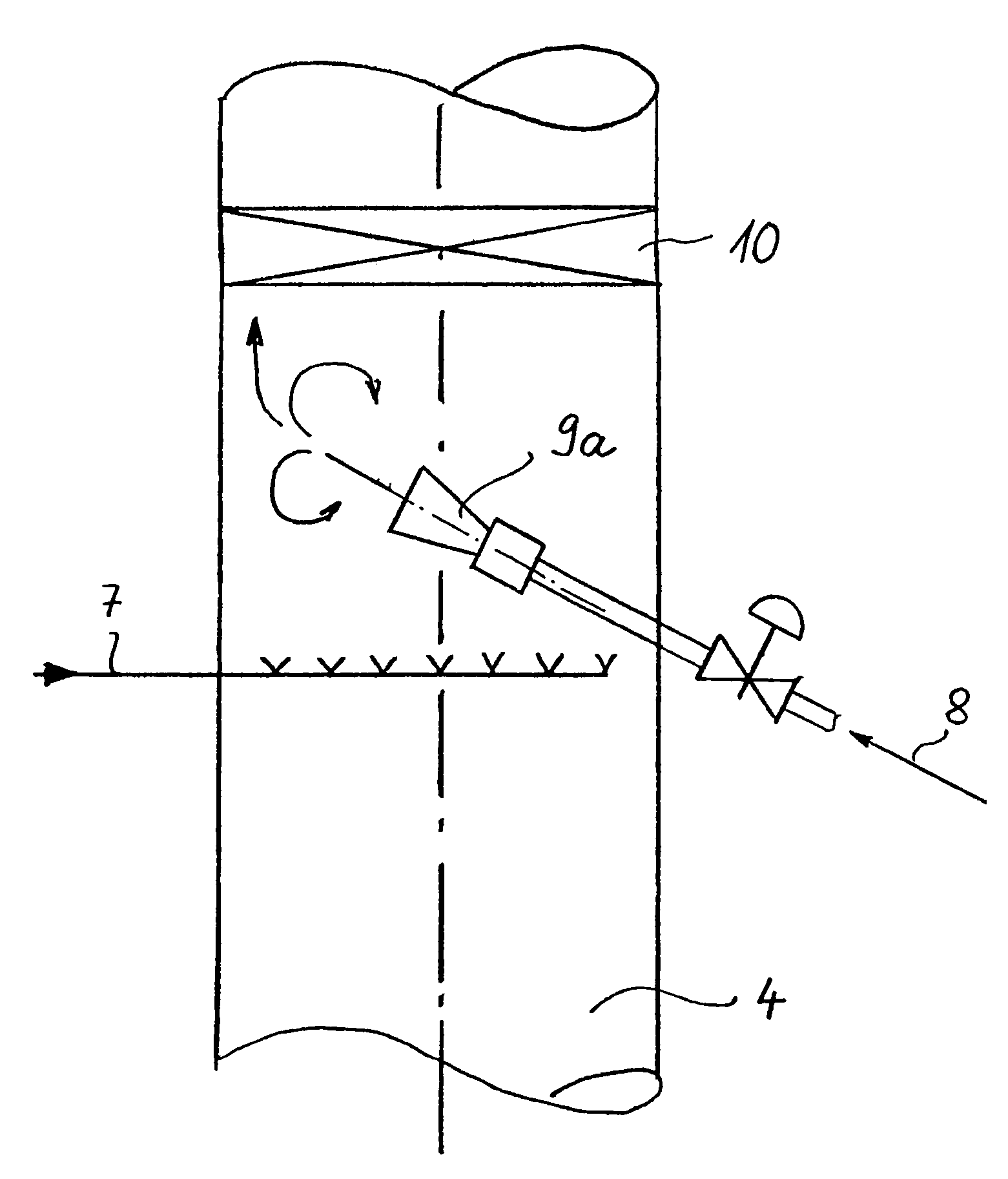
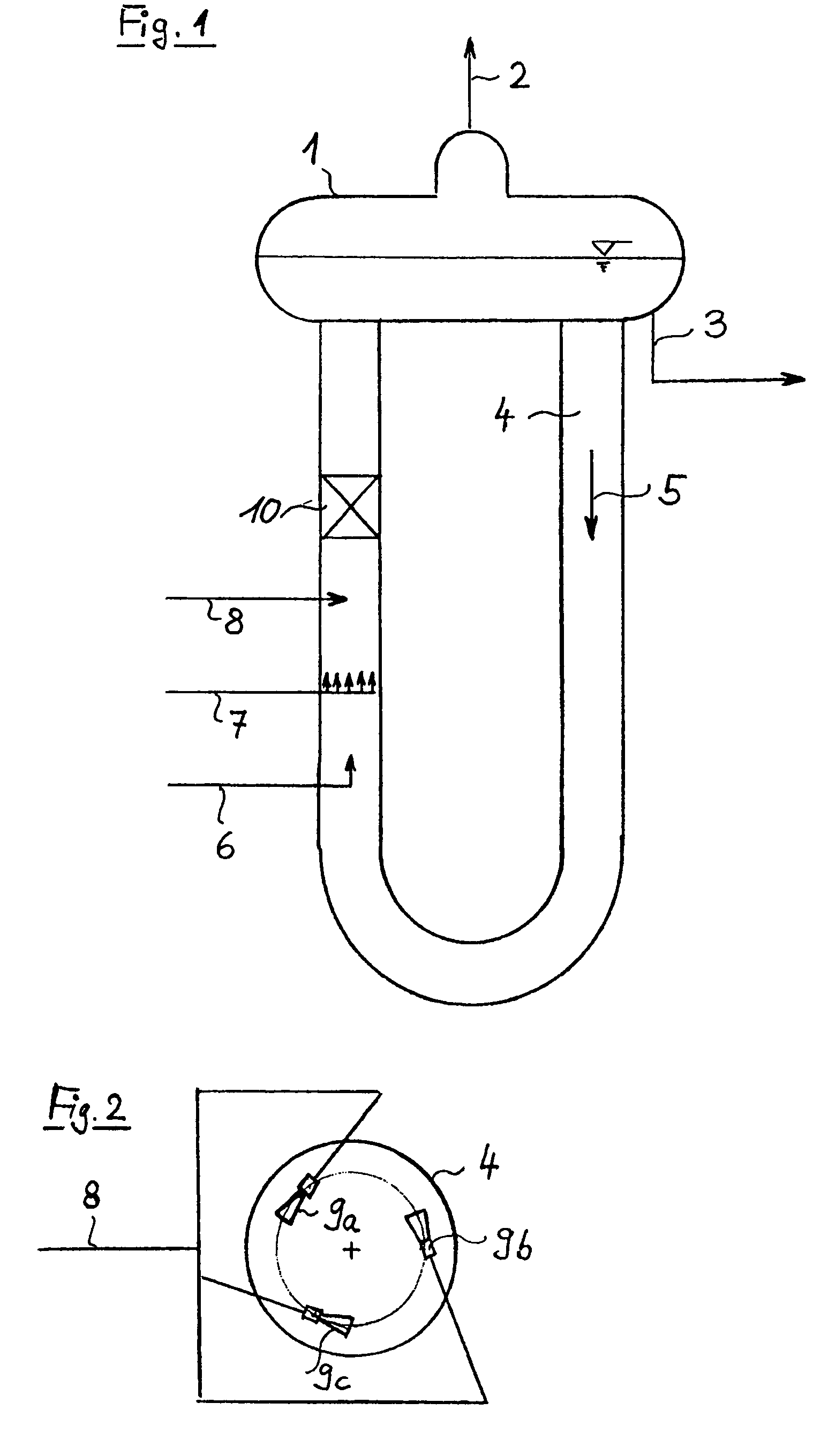
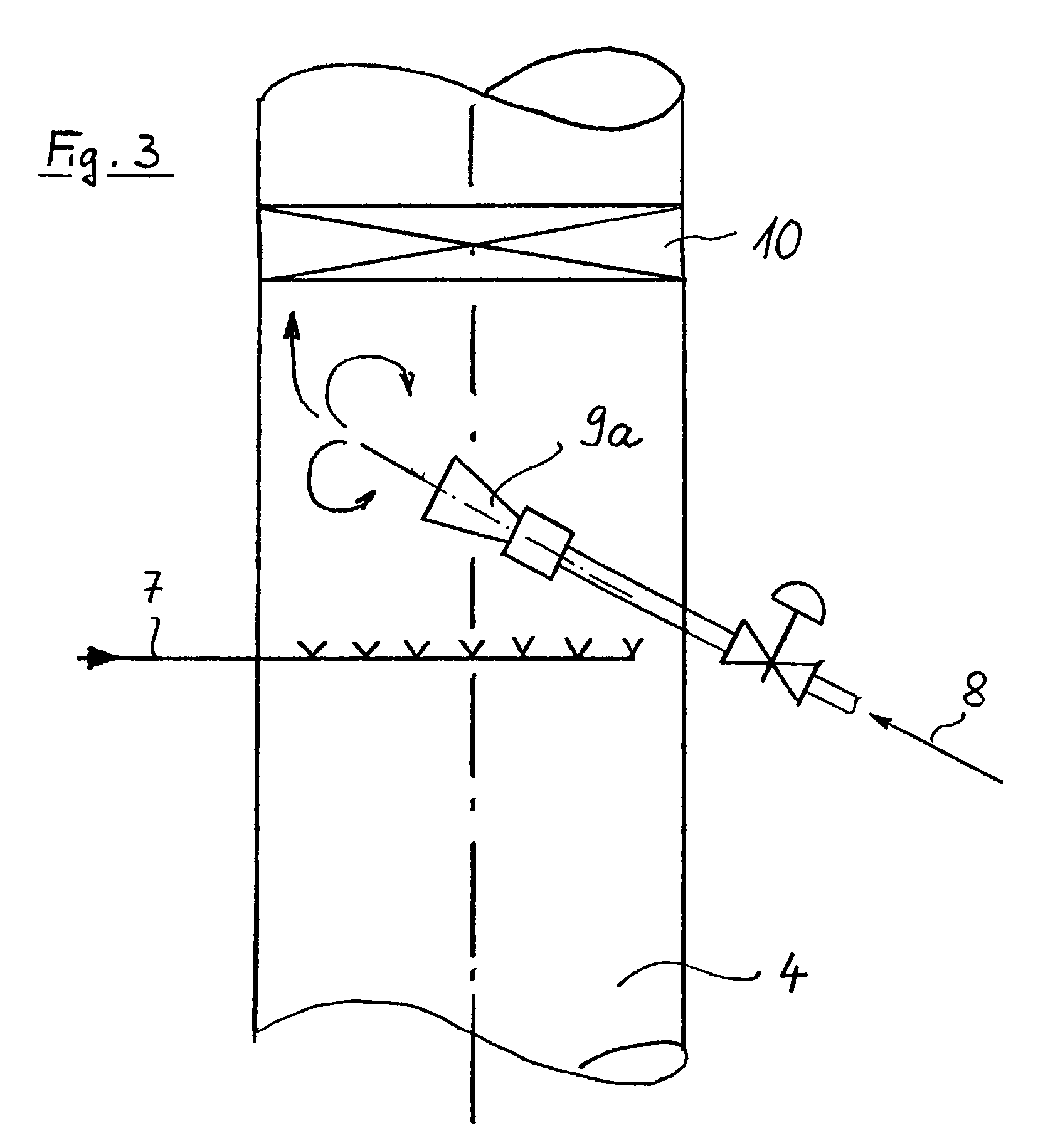
The invention refers to a process for the production of high-purity 1,2-dichloroethane from dissolved chlorine and dissolved ethylene, which are brought into contact with each other in a circulating liquid reaction fluid, which mainly consists of 1,2-dichlorethane and a catalyst and flows through at least one vertically arranged loop-type reaction section, both legs of the loop being connected to an overhead degassing vessel from where the reaction product is withdrawn either in gaseous or in liquid state or in both gaseous and liquid state, and numerous admixing sections being arranged in the leg of the loop in which the liquid rises, and each of these admixing sections having one upstream feed point for dissolved or gaseous ethylene and one downstream feed point for dissolved chlorine and, if required, the admixing sections featuring static mixers.
Owner:UHDE GMBH +1
Gold-based catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination
InactiveUS20140213437A1Molecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrogenChemical compound
Powder catalysts that comprise particles of chemical compounds of Au and Cu deposited on acid-washed carbon-based supports are effective catalysts in ethyne hydrochlorination to produce vinyl chloride monomers (VCMs). They give a high selectivity and productivity of VCM and decreased amounts of the byproducts of chloroethane, dichloroethane and others. Thiocyanates are used as complexing agents to extend the catalyst lifetime. The activity of the catalyst is enhanced by doping nitrogen atoms into the support.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing 1,2-dichloroethane by means of direct chlorination
ActiveUS7671244B2Increase capacityDouble the conversion rate according to reactionGaseous chemical processesPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offGas phaseEthane Dichloride
The invention relates to a method for producing high-purity 1,2-dichloroethane from dissolved chlorine and dissolved ethylene which are brought into contact with each other using a circulating liquid reaction medium which essentially consists of 1,2-dichloroethane and a catalyst and passes through at least one reaction loop. The two limbs of the loop are connected to a gas-phase stripping container which is arranged at the top and from which the reaction product is outwardly transferred either in a gaseous or liquid form or both in a gaseous form and in a liquid form. The addition points for the addition of chlorine and dissolved ethylene are arranged in the limb of the loop in which the liquid rises. The addition point for dissolved chlorine is always arranged downstream of the ethylene addition point. At least one addition point for liquid 1,2-dichloroethane follows each chlorine addition point, and the addition of the liquid 1,2-dichloroethane is carried out under kinetic energy which is high enough to enable a vigorous mixture of 1,2-dichloroethane, dissolved chlorine and ethylene to be carried out. Preferably, the liquid 1,2-dichloroethane is added by means of at least one jet mixer.
Owner:UHDE GMBH
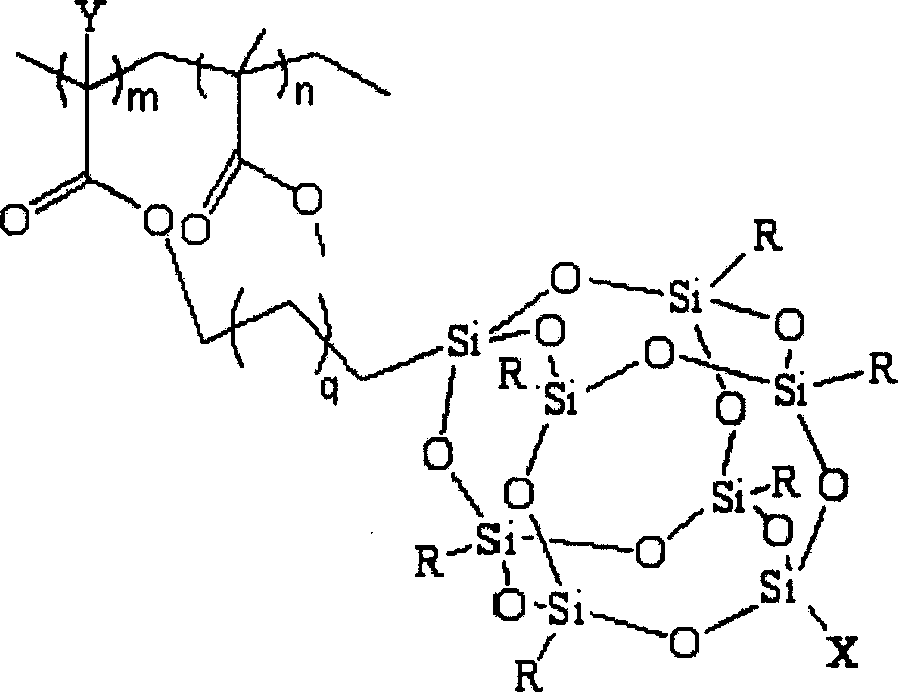
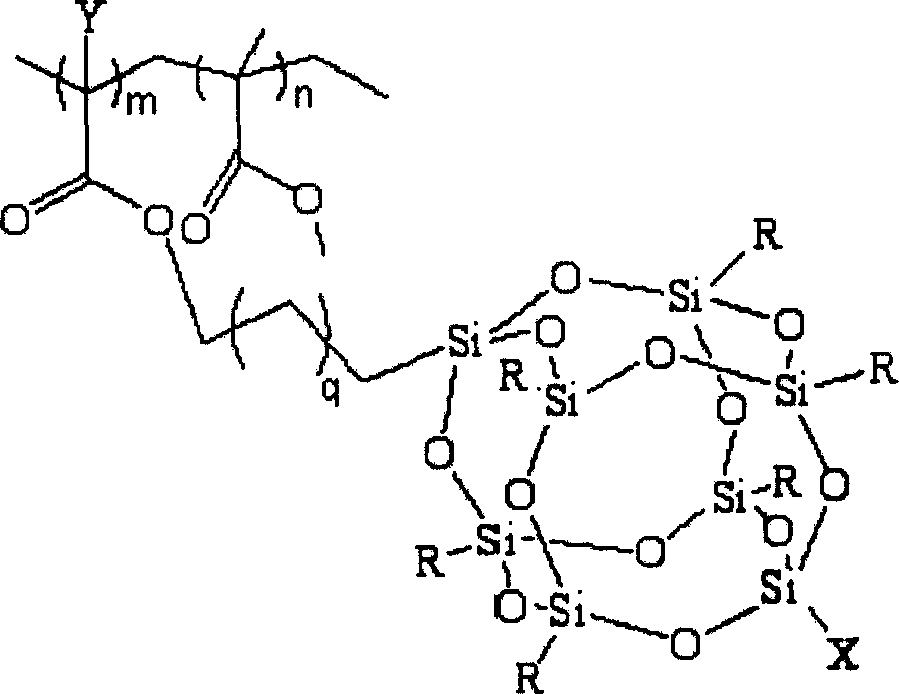
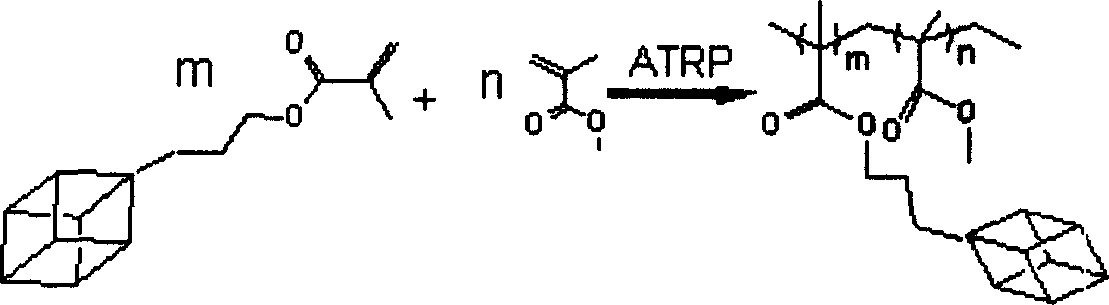
Fluoride POSS acrylic ester block multipolymer resin and its synthesis
InactiveCN101029137AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove hydrophobicityCyclohexanonePolymer science
A fluoride POSS acrylic resin block copolymer resin and its synthesis are disclosed. The molecular-weight of copolymer Mn is 20000-60000, Mn / Mw is 1.1-1.5, contact angle between coating and water is 85-120degree. The process is carried out by adding components into reactor to obtain methyl acrylate performed polymer with Br end capping, reacting with CuBr, PMDETA and F-POSS, removing catalyst from reactant, depositing while filtering by methanol, vacuum drying to constant weight to obtain the final product. The polymer powders can be dissolved into acetic ether, acetone, 1,2-dichloroethane, dioxane and cyclohexanone or their mixtures, then it can be used for coating or filming.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing chloroethylene by catalytic reforming
InactiveCN101817723ASolve the problem of high temperature energy consumptionSolve pollutionPhysical/chemical process catalystsHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationCatalytic reformingActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for preparing chloroethylene by catalytic reforming, which relates to a method for preparing the chloroethylene. The method comprises: a step of preparing a catalyst by using active carbon as a carrier, in which a barium salt is used as a catalyst, the active carbon is used as the catalyst carrier, and the barium salt is dissolved in water, absorbed by the active carbon and dried to obtain the catalyst carried by the active carbon; and a step of synthesizing the chloroethylene, in which acetylene gas and dichloroethane vapour are mixed and introduced to a reactor containing the catalyst carried by the active carbon to react, the reaction effluent is cooled to room temperature, unreacted dichloroethane is condensed to be separated out, and the remaining gas is compressed and frozen to give liquid chloroethylene. In the invention, a mercury free catalyst is adopted, the mercury pollution of the chloroethylene production industry is eliminated, and the reaction is performed spontaneously with little energy consumption.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIGONG SHANGHAI CHEM TECH CO LTD
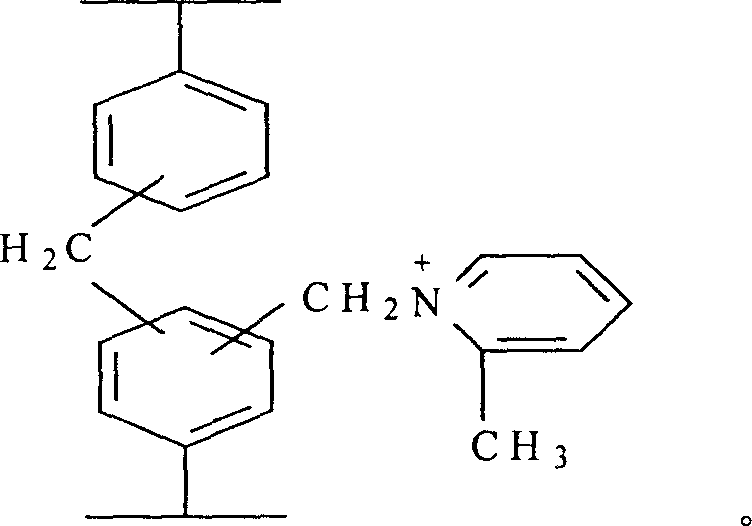
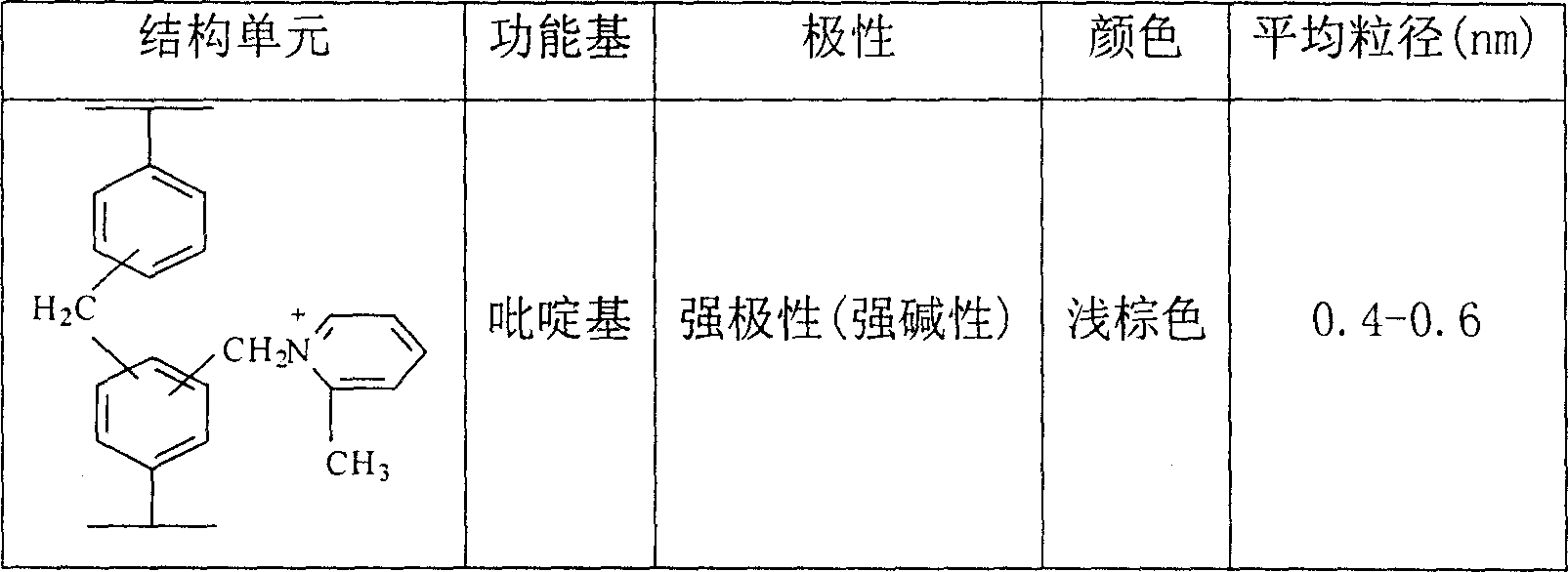
Pyridyl modified composite function super high crosslinked adsorptive resin and its preparing method
InactiveCN1858088AImprove temperature resistanceImprove thermal stabilityOther chemical processesCross-linkBenzoyl peroxide
The produce discloses a kind of pyridyl modified composite functional adsorption resin with very high crosslinking degree and pyridyl radical as functional radical and its preparation process. The preparation process includes polymerization with styrene as monomer, divinyl benzene as cross-linking agent, liquid wax as pore-creating agent, magnesium carbonate as dispersant and benzoyl peroxide as initiator to produce low crosslinking degree macroporous polystyrene; the subsequent cross-liking reaction with swellant of nitrobenzene, etc. and catalyst Lewis acid, etc. to obtain composite functional resin precursor with different crosslinking degree; and final adding alpha-methyl pyridine for reaction to prepare the pyridyl modified composite functional adsorption resin. The resin has both adsorbing and ion exchanging functions, and may find its wide application in medicine separation, food decoloring, water treatment, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer as well preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel functionalized organic porous polymer and particularly relates to an ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer and a preparation method thereof. The ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer is prepared by reacting the following components in a molar ratio: 0.5-10% of a crosslinking agent, 10-70% of an imidazole ionic liquid and 10-80% of a monomer, wherein the used solvent is 1,2-dichloroethane; the monomer used in the ionic liquid functionalized ultra-crosslinking polymer is one or a combination of two or more of benzene, biphenyl, pyrrole, thiophene, furan, 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene or p-chloromethyl styrene, preferably, p-chloromethyl styrene. The porous polymer can be applicable to gas adsorption, especially capture and separation of CO2 gas.
Owner:HANGZHOU REWARD TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
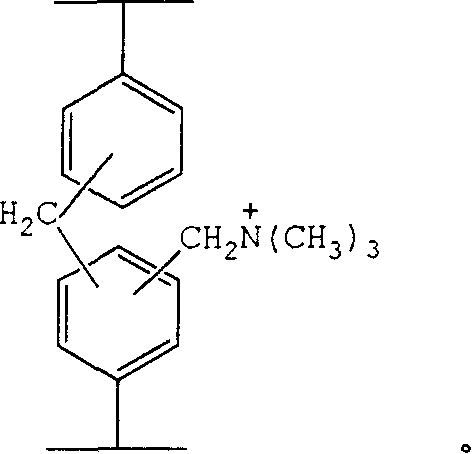
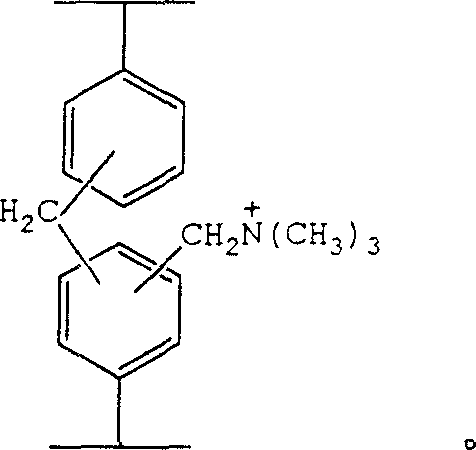
Composite functional super high cross-linked adsorption resin containing quaternary amine group, and its preparation method
ActiveCN1865302AHighlight hydrogen bondsProminent electrostatic effectOther chemical processesDibenzoyl PeroxideDisperser
The invention discloses a super high cross-linking adsorption resin with quaternary amines base composite function and making method, which comprises the following steps: utilizing phenylethene as monomer, diphenyl ethylene as cross linking agent, liquid wax as hole-sealing agent, magnesium carbonate as disperser, benzoyl peroxide as initiator; adopting nitrobenzene, substituted nitrobenzene, dichloroethanes or orthodichlorobenzene as swelling agent in the cross-linking reaction course of chloromethylation low cross-linking large-hole polyphenylacetylene; using zinc chloride, ferric chloride or tin tetrachloride as catalyst to produce different cross linking composite functional resin priority in the preset time and temperature condition; adding trimethylamine to aminate to produce the product. The resin possesses double functions of adsorption and ion exchanging, which can be applied in drug separation, little polluted water source and organic chemical waste water harnessing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Preparation method of regenerated cellulose material
ActiveCN104130425AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove toughnessBulk chemical productionCarboxylic acidEthane Dichloride
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a regenerated cellulose material and discloses a preparation method of the regenerated cellulose material. A employed solvent is a carboxylic acid type ionic liquid or is a co-solvent which is composed of the carboxylic acid type ionic liquid and an active-proton-free polar organic solvent, wherein the carboxylic acid type ionic liquid is preferably selected from 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate, 1-propyl-3-methylimidazole acetate or 1-butyl-3- methylimidazole acetate; an auxiliary solvent is selected from one or more of DMF, DMAc, DMI, DMSO, pyrrodine, acetone, dichloromethane and dichloroethane; and a solidifying agent is preferably selected from alcohol organic solvents. The carboxylic acid type ionic liquid is most preferably selected from the 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate and the 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate; the auxiliary solvent is most preferably DMF; and the solidifying agent is preferably ethanol; wherein a mass ration of the carboxylic acid type ionic liquid to the auxiliary solvent is 5:5. By means of the preparation method, mechanical performances of a regenerated cellulose product can be significantly improved and environmental pollution can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,2-dichloroethane
InactiveUS7053252B2Good choicePreparation by halogen halide additionOrganic chemistry methodsHydrogen fluoridePolymer science
The invention relates to a process for preparing 1,1,1-trifluoro-2,2-dichloroethane (F123).This process consists in placing 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane (F133a) in contact with chlorine in the presence of hydrogen fluoride and a fluorination catalyst.F133a may be obtained by fluorination of trichloroethylene, and the F123 may be subsequently fluorinated to F125.
Owner:ATOFINA
Process for the manufacture of 1,2-dichloroethane
InactiveUS8058490B2Low costHigh purityPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offChemical recyclingCatalytic oxidationEthane Dichloride
Process for the manufacture of 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) starting from a stream of ethane which is subjected to a catalytic oxydehydrogenation (ODH) thus producing a gas mixture containing ethylene which is then dried and conveyed to a chlorination reactor supplied with a flow of chlorine so that at least 10% of the ethylene is converted to DCE. The stream of products derived from the chlorination reactor is then conveyed to an oxychlorination reactor in which the majority of the balance of ethylene is converted to DCE.
Owner:SOLVAY SA
Catalyst applied to preparation of vinyl chloride by catalytic cracking of 1,2-dichloroethane as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
InactiveCN104289247AGood dispersionLow cracking temperaturePreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhysical/chemical process catalystsActivated carbonEthane Dichloride
The invention relates to a nitrogen-doped active carbon catalyst applied to preparation of vinyl chloride by catalytic cracking of 1,2-dichloroethane and in particular relates to active carbon, wherein the inner surface and the outer surface of the active carbon are doped with nitrogen; the doping content of nitrogen is 0.1-10wt%; furthermore, meal is loaded on the nitrogen-doped active carbon catalyst and exists in the form of a metal compound; the loading content of the metal compound is 0.1-10wt%. According to the catalyst, the preparation method is simple, the process is short, materials are easily available, and the cost is relatively low; the nitrogen doped in the active carbon has a small possibility of losing and inactivating; the nitrogen is doped in the nitrogen-doped active carbon catalyst loaded with the metal compound, so that the dispersion of the metal component on the active carbon can be effectively improved; the catalytic activity is improved; the cracking temperature of dichloroethane can be greatly reduced under the catalytic action of the catalyst prepared by the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
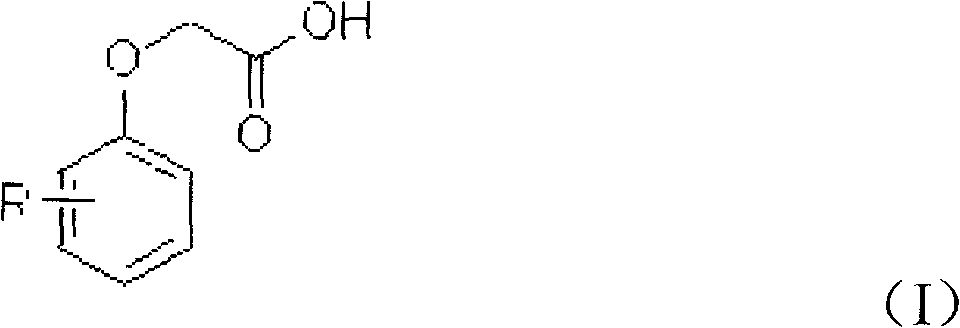
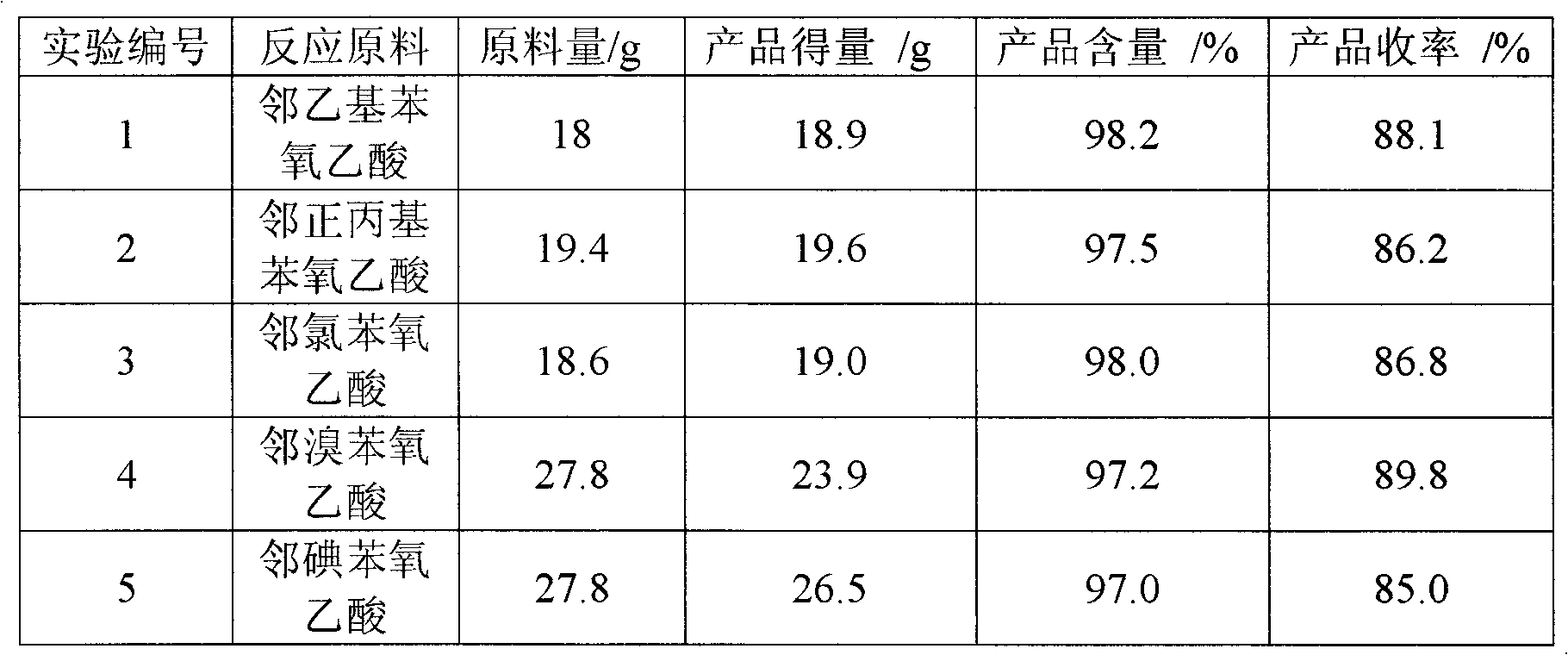
Chloration method for phenoxyacetic acid and derivatives thereof
InactiveCN102336654AEasy to industrializeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationChlorobenzeneIndustrial waste water
The invention provides a chloration method for phenoxyacetic acid and derivatives thereof, which comprises the following steps that: raw materials of the phenoxyacetic acid or the derivatives of the phenoxyacetic acid and chlorinating agents take reaction at a certain temperature in organic solvents under the effect of catalysts, wherein the chlorinating agents can be chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite and sulfuryl chloride, the catalysts can be lewis acid and sulfurated substances, and solvents can be dichloromethane, dichloroethane, trichloromethane, carbon tetrachloride, formic acid, ethyl acetate, benzene, toluene, dimethylbenzene, chlorobenzene and o-dichlorobenzene. The method has the advantages that the operation can be carried out under the waterless condition, the generation of a large amount of industrial waste water is avoided, the used catalysts are safe and are easy to obtain, the solvents can be cyclically used, and the industrialization is easy.
Owner:DALIAN RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Catalyst for preparing vinyl chloride by cracking 1,2-dichloroethane as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
InactiveCN105833892AImprove catalytic performanceRaw materials are cheap and easy to getPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhysical/chemical process catalystsActivated carbonNitrogen
The invention relates to a catalyst for cracking 1,2-dichloroethane to prepare vinyl chloride and its preparation method and application. The catalyst uses activated carbon as a carrier and supports nitrogen-containing compounds. The catalyst is based on the total mass of the catalyst. The mass percentage of nitrogen-containing compounds is 16.7% to 44.4%. The catalyst prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention has better catalytic performance, can reduce the temperature for preparing vinyl chloride from 450-500°C in the current industrial pyrolysis to 280-300°C, and increase the single-pass conversion rate of dichloroethane from 50%. The selectivity of vinyl chloride can reach 93%, and the selectivity of vinyl chloride can also reach 99.3%, and has a long service life of nearly 100 hours, and the catalyst raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, and the preparation process is simple. The catalyst is not only suitable for the cracking of dichloroethane, but also suitable for the reforming of acetylene dichloroethane to prepare vinyl chloride.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Process for preparing brominated polystyrene
The invention provides a preparation method of bromized polystyrene. The method is characterized in that sulfur is taken as the scavenging agent of a small amount of water in the electrophilic bromination reaction of the polystyrene and as the quencher of free radical in the electrophilic bromination reaction of the polystyrene, and the mass of the sulfur is 0.1 to 12 percent of that of the polystyrene. In the organic solvent of dichloroethane, chloroform, bromochloromethane, carbon tetrachloride or tetrachloroethane, the anhydrous aluminium trichloride, the anhydrous ferric chloride, the titanium tetrachloride, the antimonous chloride, the aluminum powder, the zinc powder or the iron powder is taken as the catalyst, the sulfur is taken as the scavenging agent of the small amount of water and as the quencher of the free radical, and the bromized polystyrene is prepared by the electrophilic bromination reaction between the polystyrene and the bromine.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
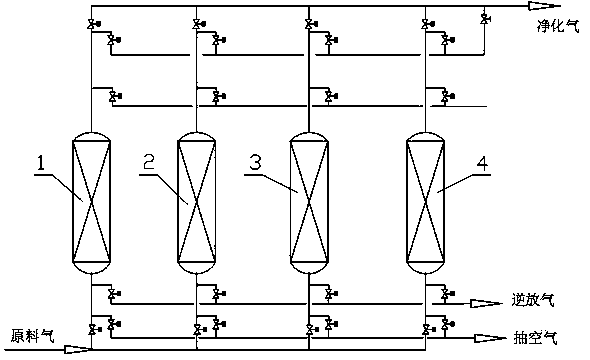
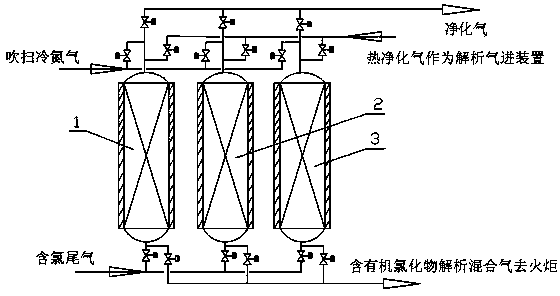
Method for purifying and removing chlorides contained in chlorine-containing industrial mixed gas and recovering light hydrocarbon
ActiveCN103357242ATo achieve the purpose of removalDispersed particle separationOrganic chloride compoundSorbent
The invention discloses a method for purifying and removing chlorides contained in a chlorine-containing industrial mixed gas and recovering light hydrocarbon, and the method comprises a pressure-swing adsorption and / or temperature swing adsorption method. An adsorptive separation system which comprises two or more than two adsorption towers filled with adsorbents and a series of program control valves absorbs and fine removes the chlorine-containing industrial mixed gas; a tail gas is respectively subjected to the following steps of: adsorption, reverse release, normal-temperature evacuation or heating flushing and filling increase in the adsorption towers under the action of the program control valves; the adsorption towers is operated according to a sequence circulating and time sequence alternating mode; the outlets positioned on the upper ends of the adsorption towers control the total content of the chlorides to be less than 5 ppm, so that a purified gas or other target product gases are obtained after the chlorides are purified and removed. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for fine purifying and removing various organic chlorides, chlorine hydride and chlorine which are contained in a dichloroethane synthetic tail gas synthesized by directly chloridizing a refining and chemical dry gas and dilute ethylene or other chlorine-containing industrial mixed gases and recovering the light hydrocarbon or the other target product gases.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Method for preparing vinyl chloride through catalyzing acetylene and dichloroethane
ActiveCN104326865AHigh conversion rate of acetyleneHigh selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offActivated carbonNitrogen
The invention discloses a method for preparing vinyl chloride through catalyzing acetylene and dichloroethane to react. The method comprises the steps: mixing acetylene and dichloroethane steam according to a molar ratio of 1:1-1:4, then introducing into a fixed bed reactor provided with a nitrogen modified catalyst, and carrying out a reaction with the reaction temperature of 180-300 DEG C and the air speed of 20-120 h<-1>. The nitrogen modified catalyst takes active carbon as a carrier, and is loaded with a metal salt compound and a nitrogen-containing compound; based on the total mass of the catalyst, the mass percentage of the metal salt compound is 0.01-10%, and the mass percentage of the nitrogen-containing compound is 0.01-10%. Vinyl chloride prepared by the method has the characteristics of high acetylene conversion rate and high vinyl chloride selectivity; and the nitrogen modified catalyst preparation process adopted in the process method is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
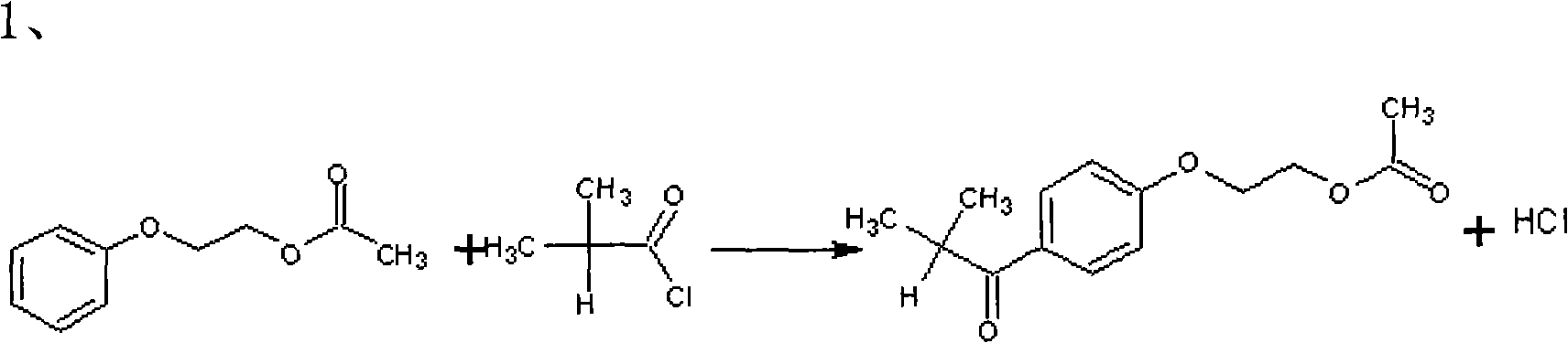
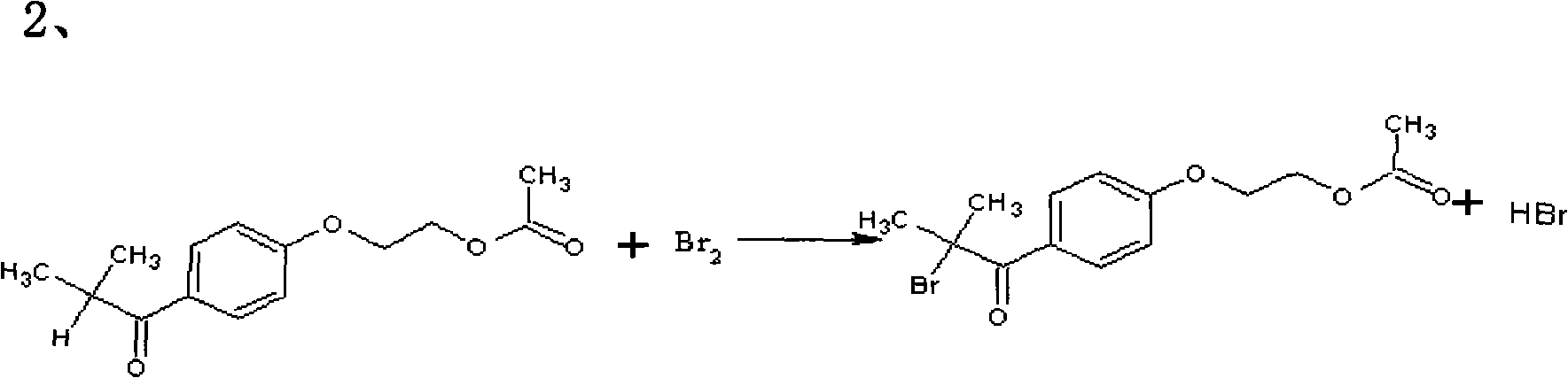
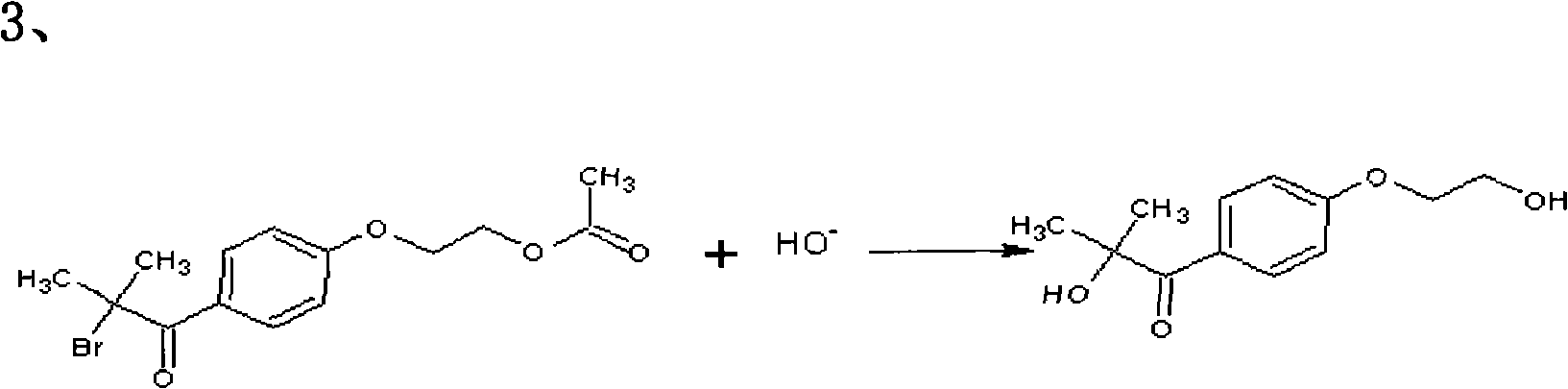
Preparation method of 2-hydroxyl-1-{4-(2-hydroxyethyl) phenyl}-2-methyl-1-acetone
InactiveCN101811951AShorten the timeSimple processOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationN dimethylformamidePhenyl Ethers
The invention relates to a preparation method of 2-hydroxyl-1-{4-(2-hydroxyethyl) phenyl}-2-methyl-1-acetone, which comprises the following steps that: ethylene glycol phenyl ether acetate serves as the raw material and carries out friedel-crafts reaction with isobutyl chloride with the molar ratio of 1 to 1.2 times of equivalent under the catalysis of lewis acid, the reaction temperature is -5 to 5DEG C, and the reaction time is 3 to 6h; bromination is carried out under the catalysis of N, N-dimethylformamide or iodine; at room temperature, phase transfer catalyst is used for carrying out catalysis and hydrolysis to a brominated product; and finally the product is prepared through purification and crystallization. The preparation method of 2-hydroxyl-1-{4-(2-hydroxyethyl) phenyl}-2-methyl-1-acetone adopts dichloromethane or dichloroethane as the solvent during the bromination process, does not use acetic acid any more, carries out reaction under the catalysis of DMF or I2, so that the reaction time is greatly shortened. The phase transfer catalyst is introduced during the hydrolysis process, so that the intermediate brominated product directly has reaction with alkali in water, thereby preventing using a large amount of ethanol as the solvent, simplifying the process, reducing the production cost and improving the yield.
Owner:GANSU JINDUN CHEM
Method of increasing hydrophilicity of complex function adsorption resin and reinforcing adsorbability of the complex function adsorption resin
InactiveCN101033305AImprove hydrophilicityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCross-linkPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for improving a composite resin adsorption function and strengthening its hydrophilic properties of adsorption. The steps include: (A) it bulges the chlorine-ball in the nitrobenzene or dichloroethane, and adds the catalyst, and accesses to the oxidant, and gradually warms up to 20 ~ 120deg.C, then it determines the response end by controlling the residual chlorine content of resin to achieve the high crosslinked polystyrene resin. (B) After the reaction, it pumps out the liquor of reaction, and washes the oxygenated high crosslinked polystyrene resin with organic solvent, and then it directly adds a functional reagent to further react with the residue chloromethyl on internal and external surface of resin to achieve the oxygen high crosslinked polystyrene resin. In which, the amount of the functional reagent is 0.5 to 3 times of the high amount of cross-linked polystyrene resin.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
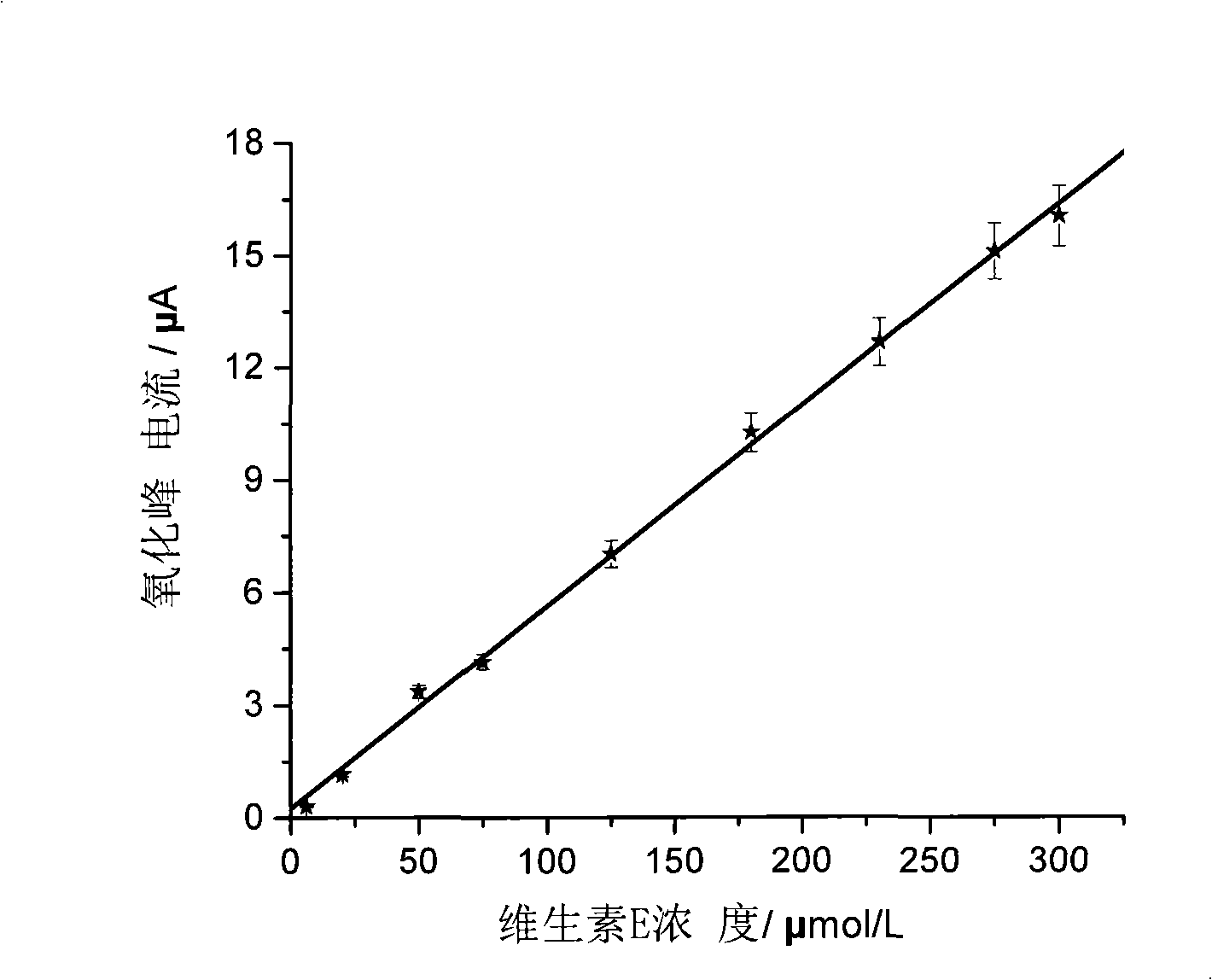
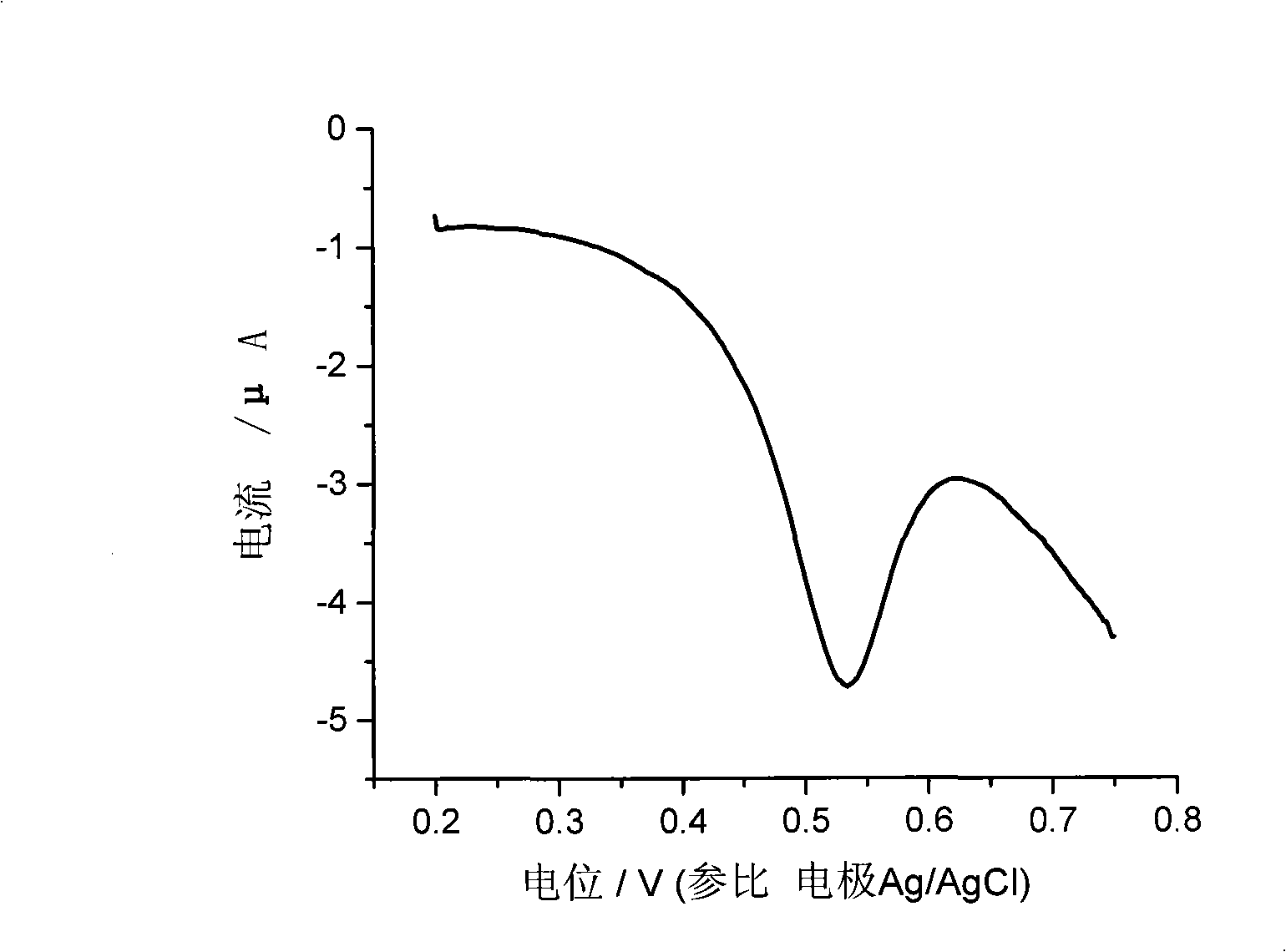
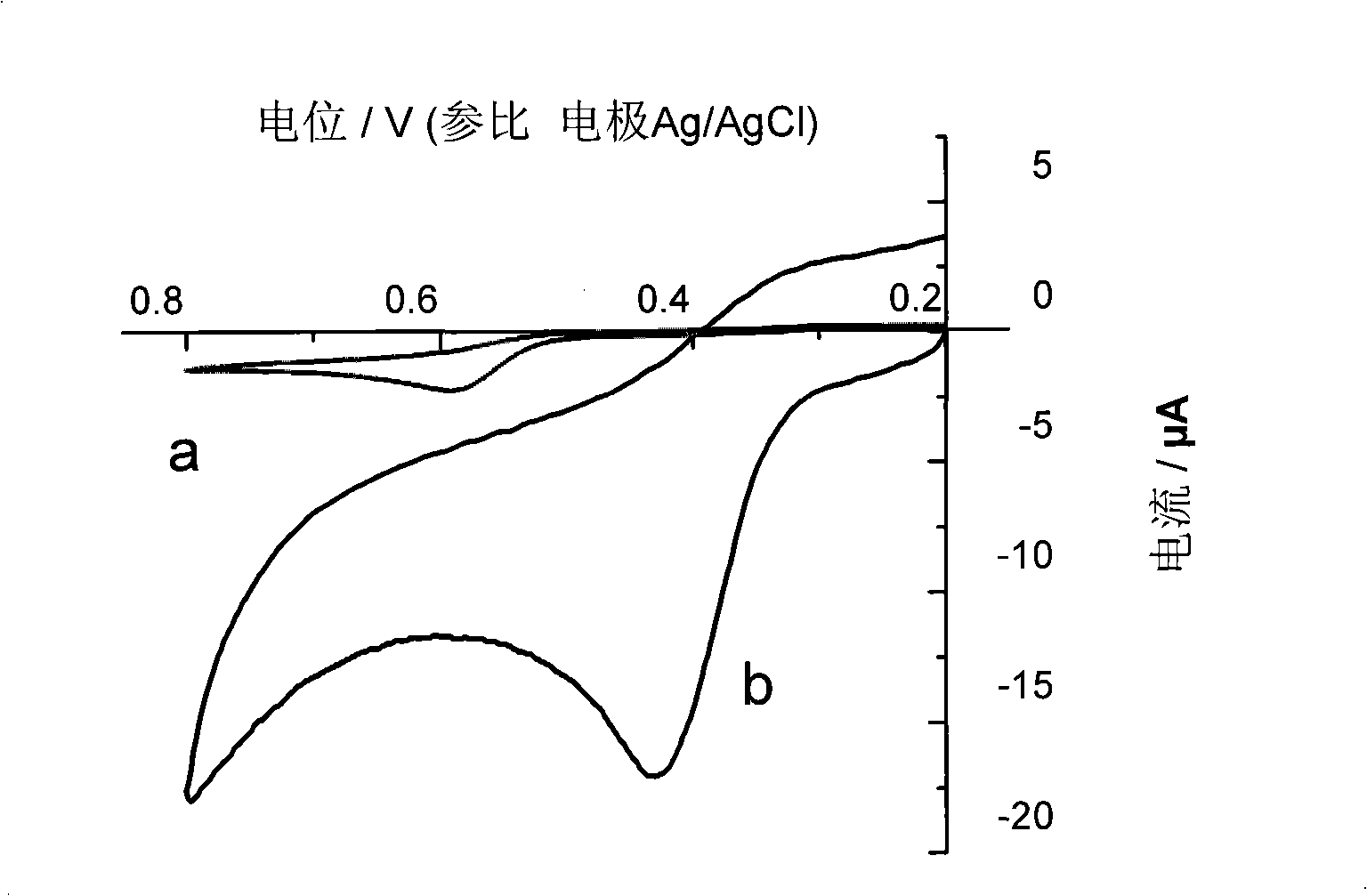
Method for fast detecting vitamin E content
InactiveCN101320015AImprove stabilityStrong anti-interferenceMaterial electrochemical variablesVegetable oilDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention relates to a poly-pyrrole modified electrode doped with p-toluene sulphonic acid and provides a method using the modified electrode for rapidly detecting the content of vitamin E. the method comprises: 1) using experimental conditions which are the same with the detecting conditions of a sampler for drawing a standard curve of the content of vitamin E and oxidation peak current; 2) dissolving the sample in the mixed solvent of ethanol-1 and 2 dichloroethane and regulating the pH value to be 2-5 to obtain the sample solution; 3) arranging the modified electrode in the sample solution, detecting the oxidation peak current through a differential pulse voltammetry and calculating the concentration of vitamin E in the sample. The method can be used for rapidly detecting the content of vitamin E in vegetable oil and has the advantages of simple sample preparation, convenience, fast speed, strong anti-interference ability and accurate detecting result which is identical with the detecting result of a liquid chromatography.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Iridium catalyzed enantiotropic hydrosubstituting process of aromatic pyridine ring and pyrazine ring
InactiveCN1468852AHigh enantiomeric excessMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistry methodsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIridiumQuinoxaline
The iridium catalyzed enantiotropic hydrosubstituting process of aromatic pyridine ring and pyrazine ring uses catalyst system comprising chiral coordination compound of iridium and additive compound. The reaction conditions includes temperature of 0-80 deg.c; solvent of dichloromethane, toluene, tetrahydrofuaran, 1, 2-dichloro ethane, isopropanol, etc.; additive compound of tetrabutyl ammonium iodide, iodine, amine, etc.; pressure of 1-100 atm; substrate / catalyst ratio up to 5000; and chiral coordination compound of diphosphine, N-P compound, S-P compound, etc. The catalyst system is prepared through reaction of iridium precursor and chiral compound in the said solvent and the addition of the additive compound while stirring; and can produce asymmetrical induction up to 96 %. The process of the present invention is environment friendly.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for the production of alkylene oxide using a gas-phase promoter system
ActiveUS7615655B2Improve performanceImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryChemical recyclingGas phaseEthylene Dichloride
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Ink detergent
InactiveCN1640958AReduce volatilityFast cleaningChemical paints/ink removersMethane DichlorideCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides one kind of ink cleaning agent comprising organic solvent 35-55 vol%, organic carboxylic acid 10-25 vol% and ethanol 30-40 vol%. The organic solvent is selected from methane dichloride, ethylidene dichloride and ethylidene trichloride; and the organic carboxylic acid is selected from formic acid and acetic acid. In addition, liquid paraffin may in 1-3 vol% be also added to inhibit solvent volatilization. The organic reagent of the present invention has fast ink cleaning speed, less volatilization, no corrosion to base material, and high cleaning effect.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Catalyst for polymerization or copolymerization of propylene and its preparation and application
The active component of the catalyst is prepared through dissolving magnesium halide in organic epoxide, organic phosphide and inert diluent to form homogeneous solution, mixing the solution with titanium tetrahalide or its derivative to separate solid matter in the presence of separate assistant, and washing the solid matter with the same inert solvent as that in forming magnesium halide solution, rather than more poisonous ethane dichloride. The preparation has no trouble of two kinds of solvent to form hard to separate azeotrope during solvent recovery, and has short technological process, high solvent recovering rate and low catalyst producing cost.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Transition metal sulfonate complex thick oil water thermo-catalysis viscosity reducer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a viscosity reducer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method for the transition metal sulfonate complex thick oil water thermo-catalysis viscosity reducer is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) adding fatty acid alkyl ester and dichloroethane into a container in a molar mass ratio of 1:2.0-3.0; 2) placing the container into an ice water bath, dripping chlorosulfonic acid in a molar mass ratio of the fatty acid alkyl ester to the chlorosulfonic acid of 1:1.3-2.0, performing sulfonation reaction, and performing ageing after the sulfonation is finished to obtain an intermediate product; and 3) adding a transition metal oxide into the intermediate product in a molar mass ratio of the fatty acid alkyl ester to the transition metal oxide of 1:0.17-0.25, performing complex reaction for 1 to 2 hours, standing and demixing after the reaction is finished, and removing the water of the upper layer, wherein the paste of the lower layer is the transition metal sulfonate complex thick oil water thermo-catalysis viscosity reducer. The viscosity reducer prepared by the method has good viscosity reducing effect at the temperature of 200 DEG C, and simultaneously has the characteristics of easily obtained raw materials and simple preparation process.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN) +1
Method for regenerating a palladium catalyst
InactiveCN1541769AEffective recoveryPromote recoveryCatalyst regeneration/reactivationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPalladium catalystEthane Dichloride
The regeneration process of supported Pd catalyst includes intermittent or continuous contact between the Pd catalyst with activity lowered in the hydrogenation reaction of unsaturated organic compound and organic solvent, which is one or several selected from toluene, benzene, n-hexane, methane dichloride, ethane dichloride, ethanol and cyclohexane, and CO2 successively or simultaneously; and processing organic solvent and CO2 after contacted with Pd catalyst through separating for reuse. The said method can restore Pd catalyst with activity lowered in the interaction with organic matter, especially Pd catalyst with activity lowered by 70 % or more, effectively.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Adsorbent resin used for treating phenolic wastewater and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105504128AUniform chloromethylationGood effectOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesBenzoyl peroxidePolystyrene
The invention provides a preparing method of high-specific-surface-area macroporous adsorbent resin used for treating phenolic wastewater. The preparing method includes the steps that a water solution of polyvinyl alcohol and sodium chloride is used as a water phase, a methylene blue solution is added, and styrene and divinyl benzene mixed liquor and a pore-foaming agent are used as an oil phase, wherein BPO (benzoyl peroxide) is dissolved in the mixed liquor, macroporous crosslinked polystyrene is obtained through a suspension polymerization method, the pore-foaming agent is recovered, and a polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer is obtained through drying; the polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer is expanded with chloromethylation solvent, a catalyst is added to carry out a chloromethylation reaction, and a chloromethylated polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer is obtained after washing and drying; the chloromethylated polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer is expanded with dichloroethane and reacts under the action of a catalyst, an expanding agent is recovered, and the resin is obtained through washing and acid adjusting. The resin obtained through the method has a remarkable effect of treating the phenolic wastewater, the maximum treatment capacity can reach 500 mg / L or above, in addition, the preparing method is simple and easy to implement, and equipment and a feeding method in the prior art continue to be used.
Owner:NINGBO ZHENGGUANG RESIN CO LTD
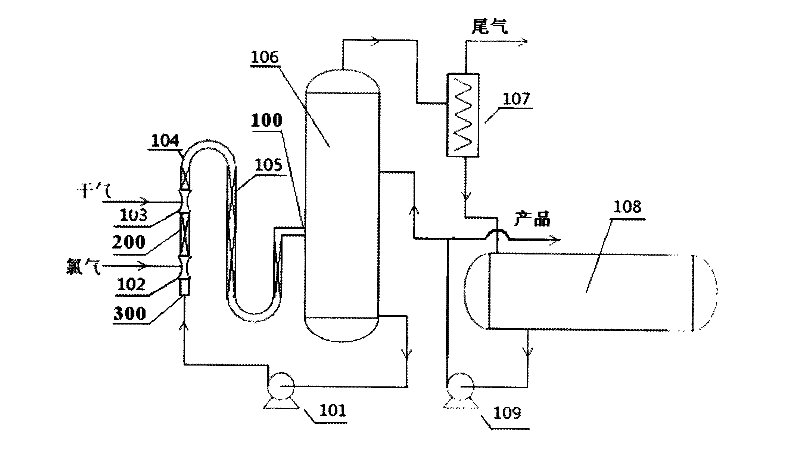
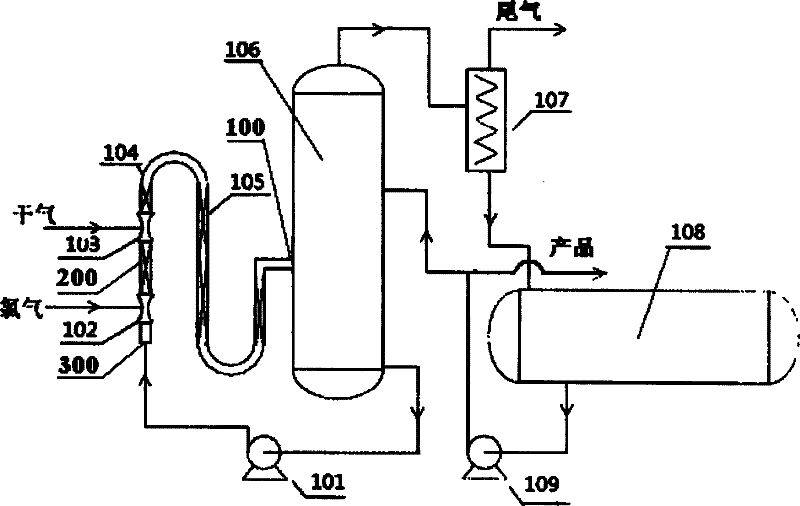
Method for preparing dichloroethane through direct chlorination by using dry gas
The invention provides a method for preparing dichloroethane through direct chlorination by using dry gas, which includes the following steps that chlorine used as a raw material is fed into a pipeline reactor through a chlorine inlet nozzle, simultaneously dichloroethane mother liquor at the bottom of a bubble tower enters the pipeline reactor from a dichloroethane mother liquor inlet, the dry gas is fed into the pipeline reactor through a dry gas inlet nozzle, and dichloroethane is produced through reactions. The dichloroethane enters the bubble tower through a pipeline reactor outlet, steam on top of the bubble tower enters a condenser, tail gas is fed to following sections to be processed, condensed liquid of the dichloroethane enters a storage tank, partial dichloroethane enters the bubble tower through a pump to be recycled, partial dichloroethane is used as products, and the dichloroethane mother liquor at the bottom of the bubble tower is returned to the pipeline reactor to be recycled through a mother liquor pump. By means of the method, weight concentration of the obtained dichloroethane can reach more than 90%, ethylene conversion rate in the dry gas is larger than 95%, reaction selectivity of ethylene is larger than 98%, and the obtained dichloroethane can be used as a basic raw material for preparing polyvinyl chloride.
Owner:SHANDONG HAIHUA GRP CO LTD +2
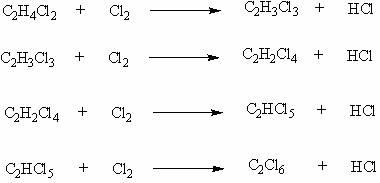
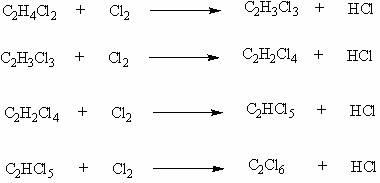
A kind of method that takes dichloroethane as raw material to produce trichloroethylene and tetrachloroethylene
InactiveCN102267863ATo satisfy the market's needsSimple processPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offTetrachloroethaneEthylene Dichloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene from dichloroethane as a raw material. The existing method has the defects of difficult realization and large amount of investment. The method of the invention comprises the following steps that dichloroethane undergoes chlorination to produce a mixture of dichloroethane, trichloroethane, tetrachloroethane, pentachloroethane and hexachloroethane, and hydrogen chloride gas under a dichloroethane gaseous or liquid phase; the mixture is transferred into a rectifying tower to be rectified; a tetrachloroethane / pentachloroethane mixture fraction with a top temperature of 147 to 162 DEG C is collected; the collected tetrachloroethane / pentachloroethane mixture fraction is vaporized and then is fed into a fixedbed reactor to form a trichloroethylene / perchloroethylene gas mixture; the trichloroethylene / perchloroethylene gas mixture is condensed into a liquid mixture; the liquid mixture and hydroquinone are fed into a rectifying tower to be rectified; a fraction with a top temperature of 86 to 87.5 DEG C is collected to obtain trichloroethylene finished products; and a fraction with a top temperature of 120 to 121.5 DEG C is collected to obtain perchloroethylene finished products. The method has the advantages of simple process, good controllability, easy acquirement of raw materials, low cost and little or no process wastewater or waste residue.
Owner:内蒙古磐迅科技有限责任公司
Preparation method of sulfoacid-type cation exchange resin catalyst
InactiveCN103638973AEfficient conversionShort reaction timeFatty acid esterificationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDivinylbenzenePolystyrene
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sulfoacid-type cation exchange resin catalyst. The preparation method of the sulfoacid-type cation exchange resin catalyst comprises the following steps: swelling for 10 minites-3 hours at 20-80 DEG C by taking a macropore crosslinked polystyrene-divinylbenzene copolymer as a sulfonation carrier and taking dichloroethane as a solvent, reacting for 1.0-6.0 hours at 70-95 DEG C by taking methanesulfonic acid as a sulfonation reagent, warming up to 100-150 DEG C, and reacting for 0.5-3.0 hours; and then removing dichloroethane, washing, and drying to obtain a target product. The reaction time is short; the preparation process is simple; the exchange capacity of the obtained high-activity sulfoacid-type cation exchange resin catalyst is even greater than 5.5mg / g; the sulfoacid-type cation exchange resin catalyst can catalyze esterification reaction efficiently, can efficiently convert free fatty acid, is high in thermal stability, and is not affected by water generated in the esterification.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com