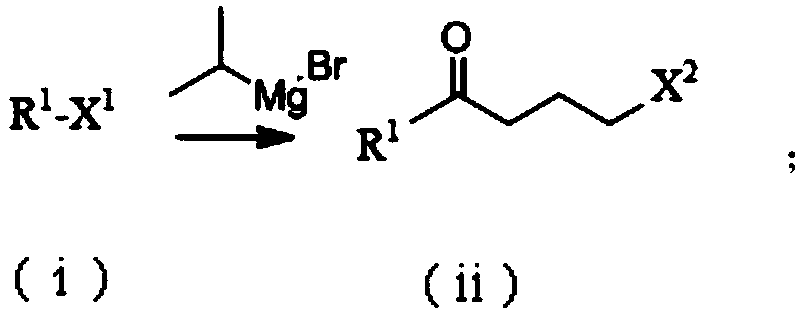
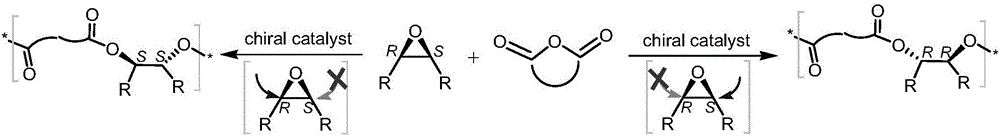
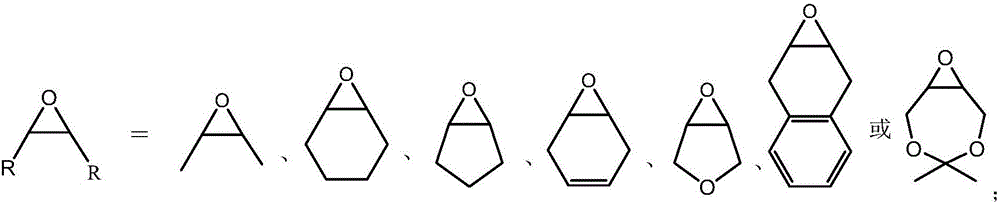
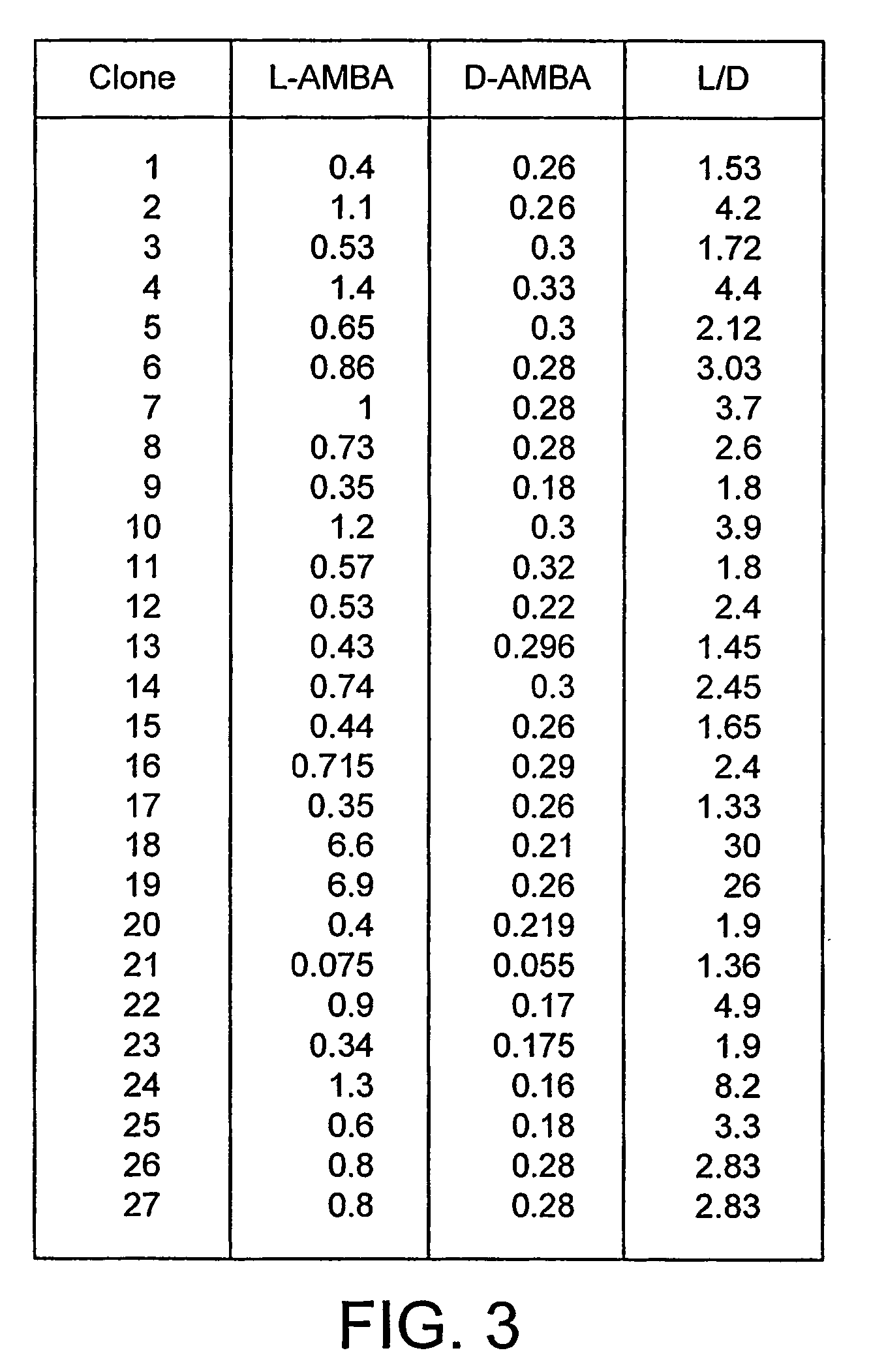
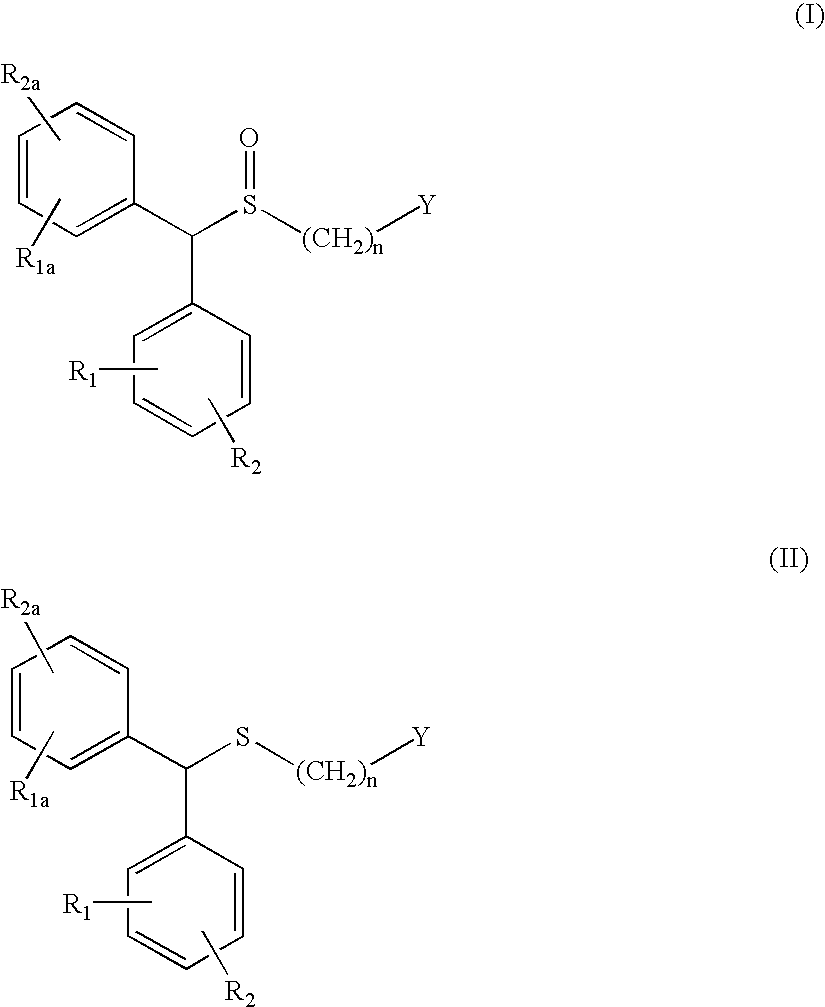
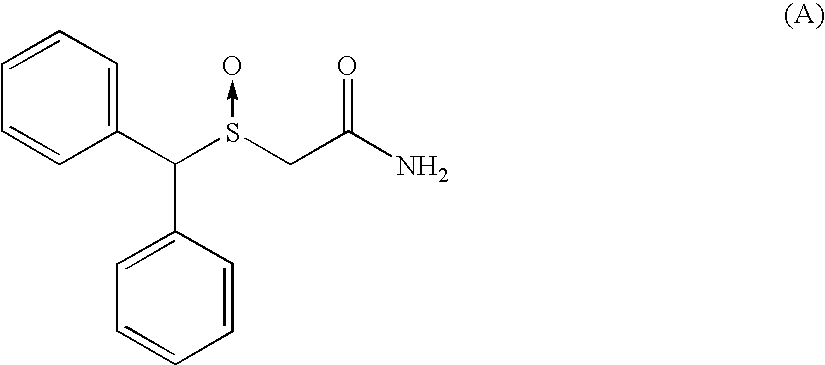
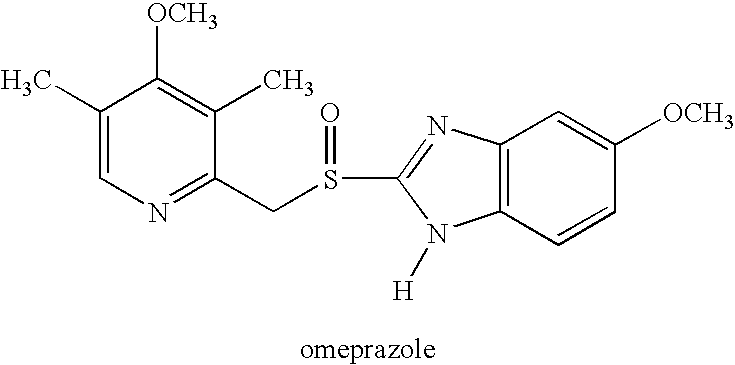
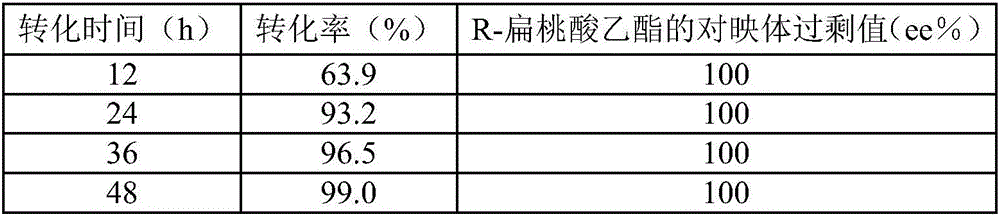
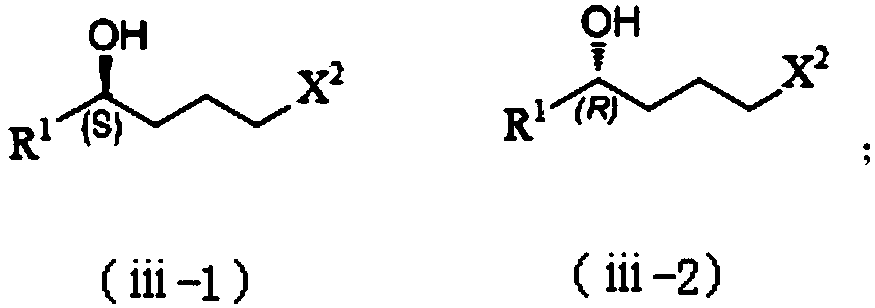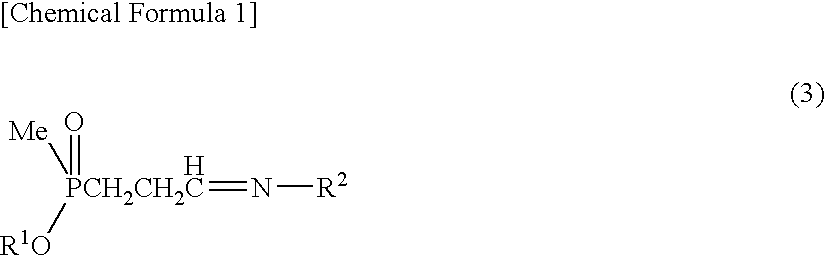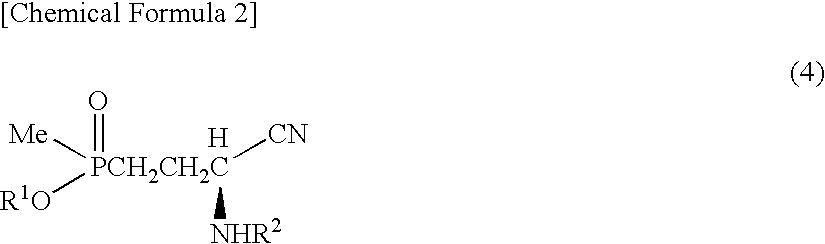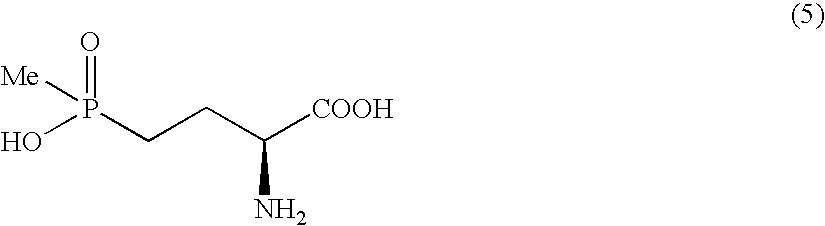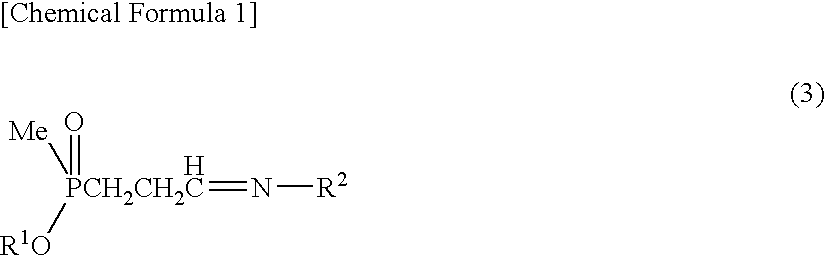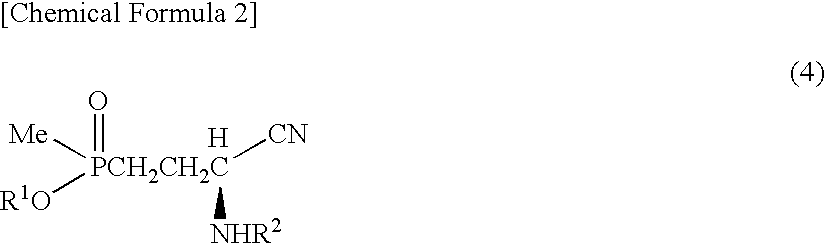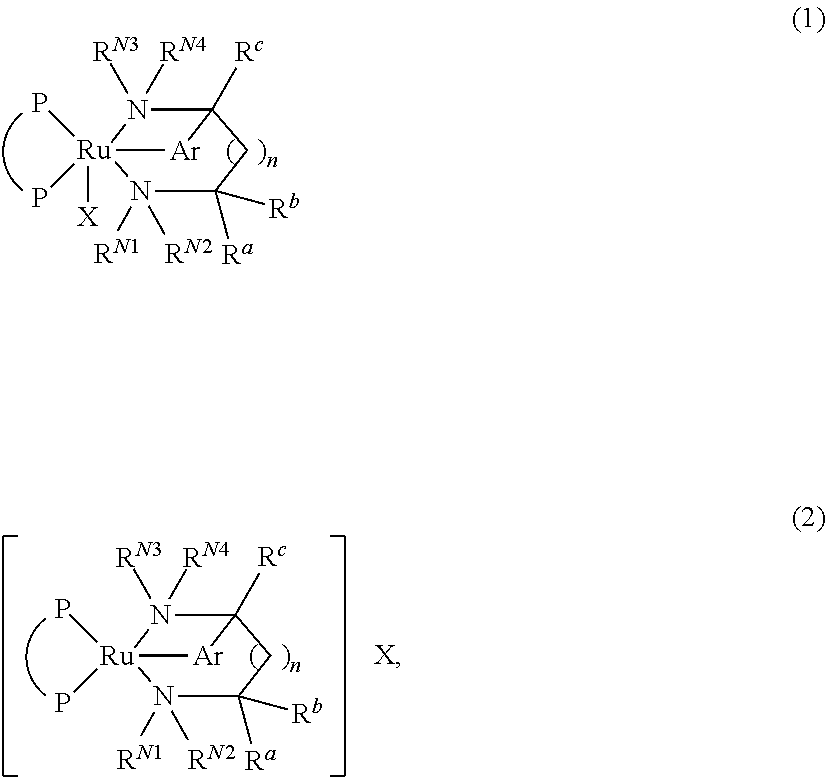Patents
Literature
76results about How to "High enantiomeric excess" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bimetallic catalyst for synthetizing vertical structure regular makrolon
ActiveCN103102480AMild reaction conditionsThe process is simple and convenientActivated carbonPolycarbonate
The invention relates to a bimetallic catalyst for synthetizing vertical structure regular makrolon through catalyzing and activating carbon dioxide to be copolymerized with internal compensation alkyleneoxide. The catalyst is a dual four-tooth or dual three-tooth Schiff alkali complex, of which two metal centers are connected through a biphenyl skeleton. Under the action of single or nucleophilicity co-catalyst, the catalyst can be used for catalyzing the carbon dioxide efficiently to be copolymerized with the internal compensation alkyleneoxide under mild condition and lower concentration of the catalyst to prepare the makrolon, the makrolon can be regulated when the catalyst efficiency is 104-106g polymer / mole catalyst and the polymer molecular weight is between 103 and 105, the makrolon can be regulated when the molecular weight distribution is less than 2 and the vertical structure regularity is between 60-100%, an alternate structure exceeds 98% and the makrolon can be degraded into a small molecular compound. The product selectivity and structure selectivity of the polymer compounds of the catalyst system using a chiral ligand are all above 98%, the enantiomer excess value of the mellow obtained by degradation reaches as high as 99%, so that the bimetallic catalyst provides a broad prospect for industrial application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis process of chiral pyrrolidine and intermediates
The invention discloses a synthesis process of chiral pyrrolidine and intermediates. The synthesis process adopts 2, 5-difluorohalobenze or 5-fluoro-3 halogenated pyridine as the raw material substrate, and employs a chiral catalyst to induce chiral reaction so as to reduce a ketone compound into a corresponding chiral alcohol compound, and then carries out substitution reaction to introduce an easily leavable group to an alcoholic hydroxyl group so as to facilitate ring formation reaction (or carry out ring formation reaction directly). The process provided by the invention has the advantagesof significant increase of product yield and reduction of cost, also the reaction temperature is mild, and the process is easy to control and industrialize.
Owner:上海鑫凯化学科技有限公司
Iridium catalyzed enantiotropic hydrosubstituting process of aromatic pyridine ring and pyrazine ring
InactiveCN1468852AHigh enantiomeric excessMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistry methodsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIridiumQuinoxaline
The iridium catalyzed enantiotropic hydrosubstituting process of aromatic pyridine ring and pyrazine ring uses catalyst system comprising chiral coordination compound of iridium and additive compound. The reaction conditions includes temperature of 0-80 deg.c; solvent of dichloromethane, toluene, tetrahydrofuaran, 1, 2-dichloro ethane, isopropanol, etc.; additive compound of tetrabutyl ammonium iodide, iodine, amine, etc.; pressure of 1-100 atm; substrate / catalyst ratio up to 5000; and chiral coordination compound of diphosphine, N-P compound, S-P compound, etc. The catalyst system is prepared through reaction of iridium precursor and chiral compound in the said solvent and the addition of the additive compound while stirring; and can produce asymmetrical induction up to 96 %. The process of the present invention is environment friendly.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Synthesis method for stereoregularity polyester and bi-metallic catalyst
The invention relates to a synthesis method for stereoregularity polyester and a bi-metallic catalyst. The catalyst is a bi-nuclear metal complex formed by connecting two metal centers through a biphenyl or dinaphthalene framework. The catalyst can efficiently catalyze a cyclic anhydride and internal compensation epoxyalkane polymerization reaction under the mild condition and low catalyst concentration to prepare polyester under the effect of a nucleophilic co-catalyst, the catalysis efficiency is 103-106 g of a polymer per mole of the catalyst, the molecular weight of the polymer can be adjusted within the range of 103-105, the molecular weight distribution is smaller than 2, stereoregularity can be adjusted within the range of 60-100%, the alternative structure exceeds 98%, and polyester can be degraded into a small molecular compound under a certain condition. A chiral ligand catalytic system is used, the product selectivity and alternative structure selectivity of the polymer are both higher than 98%, the excess value of enantiomer of diol obtained after degradation is higher than 70%, and wide prospects are provided for industrial application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for enantioselective synthesis of single enantiomers of modafinil by asymmetric oxidation
InactiveUS7368591B2High enantioselectivityHigh yieldBiocideOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventEnantiomer
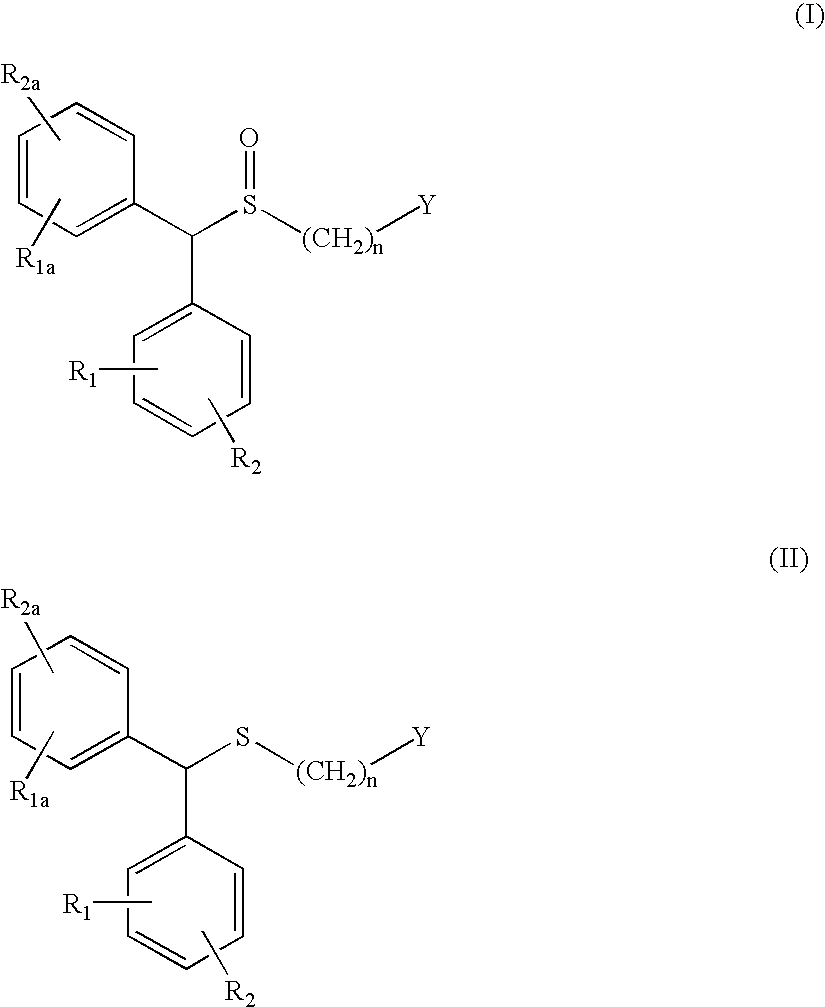
The invention relates to a method for preparing a sulphoxide compound of formula (I) either as a single enantiomer or in an enantiomerically enriched form, comprising the steps of:a) contacting a pro-chiral sulphide of formula (II) with a metal chiral complex, a base and an oxidizing agent in an organic solvent; and optionallyb) isolating the obtained sulphoxide of formula (I).wherein n, Y, R1, R1a, R2 and R2a are as defined in claim 1.
Owner:TEVA SANTE
Method for producing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid
ActiveCN101974603AShorten the growth cycleLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationThermal denaturationHydroxybutyric acid
The invention discloses a method for producing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing complete cell suspension containing NAD independent hydroxy acid dehydrogenase or coarse enzyme liquid thereof with pseudomonas; (2) carrying out thermotropy on the complete cell suspension or the coarse enzyme liquid thereof prepared by the thermal denaturation step (1) to deactivate the NAD independent D-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase so as to obtain a biocatalyst only containing the NAD independent L-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase activity; (3) separating the racemic alpha-hydroxybutyric acid by the biocatalyst prepared in the step (2) to obtain the conversion fluid containing D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid sodium salt and alpha-ketobutyric acid sodium salt; (4) pre-treating the conversion fluid; (5) acidifying the pre-treated conversion fluid; (6) separating the D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid form the alpha ketobutyric acid; and (7) refining the D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid. The method of the invention has the characteristics of simple components of culture medium, short growth period, low cost, easy subsequent separation and extraction, high enantiomeric excess of the product D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid and the like and lays a foundation for efficient production of the D-alpha-hydroxybutyric acid.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
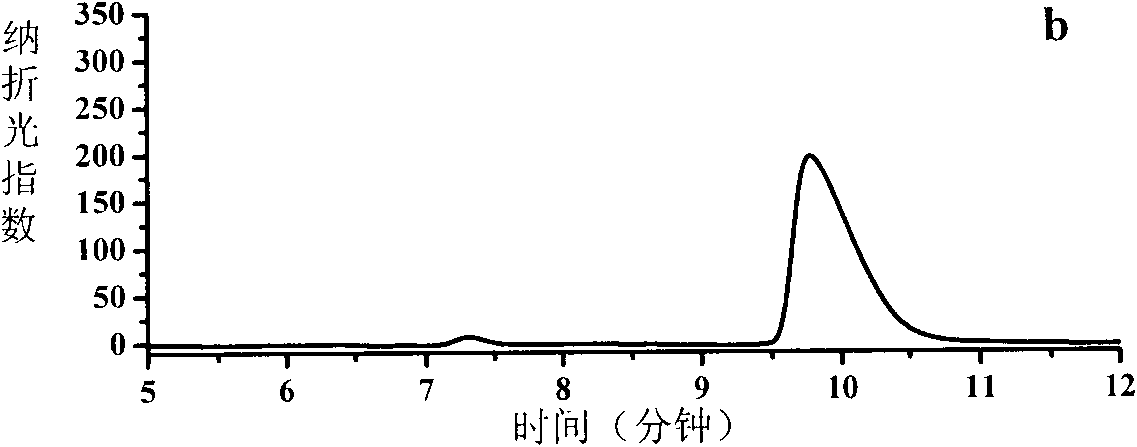
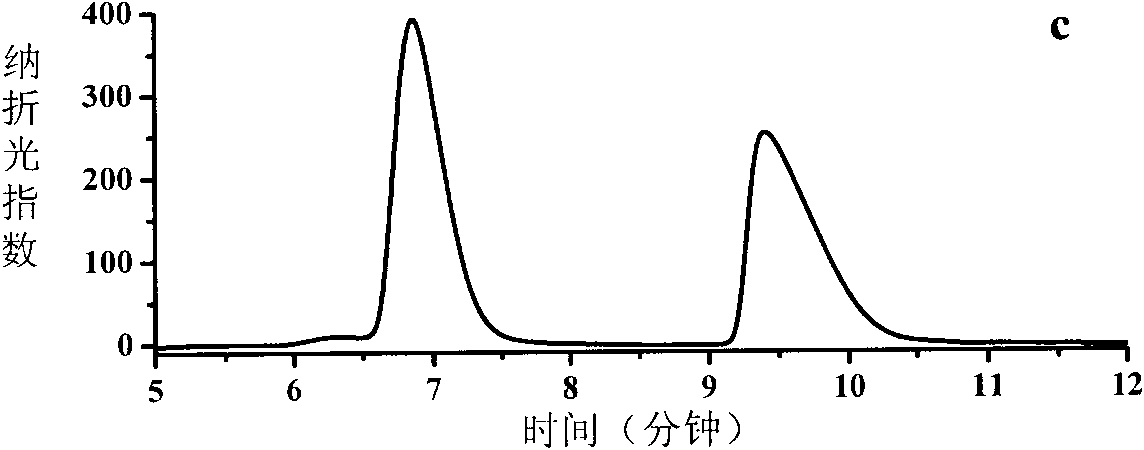
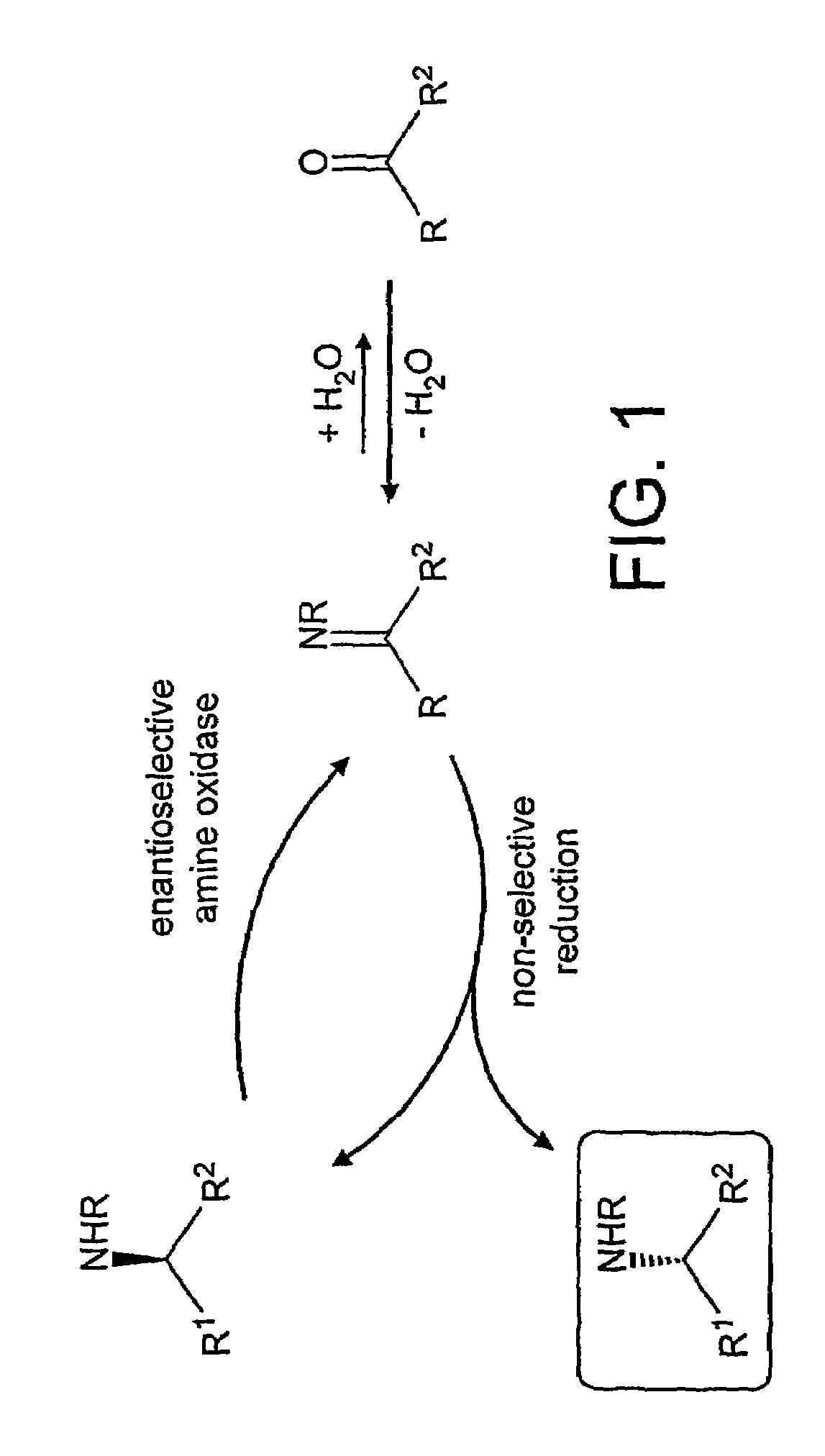
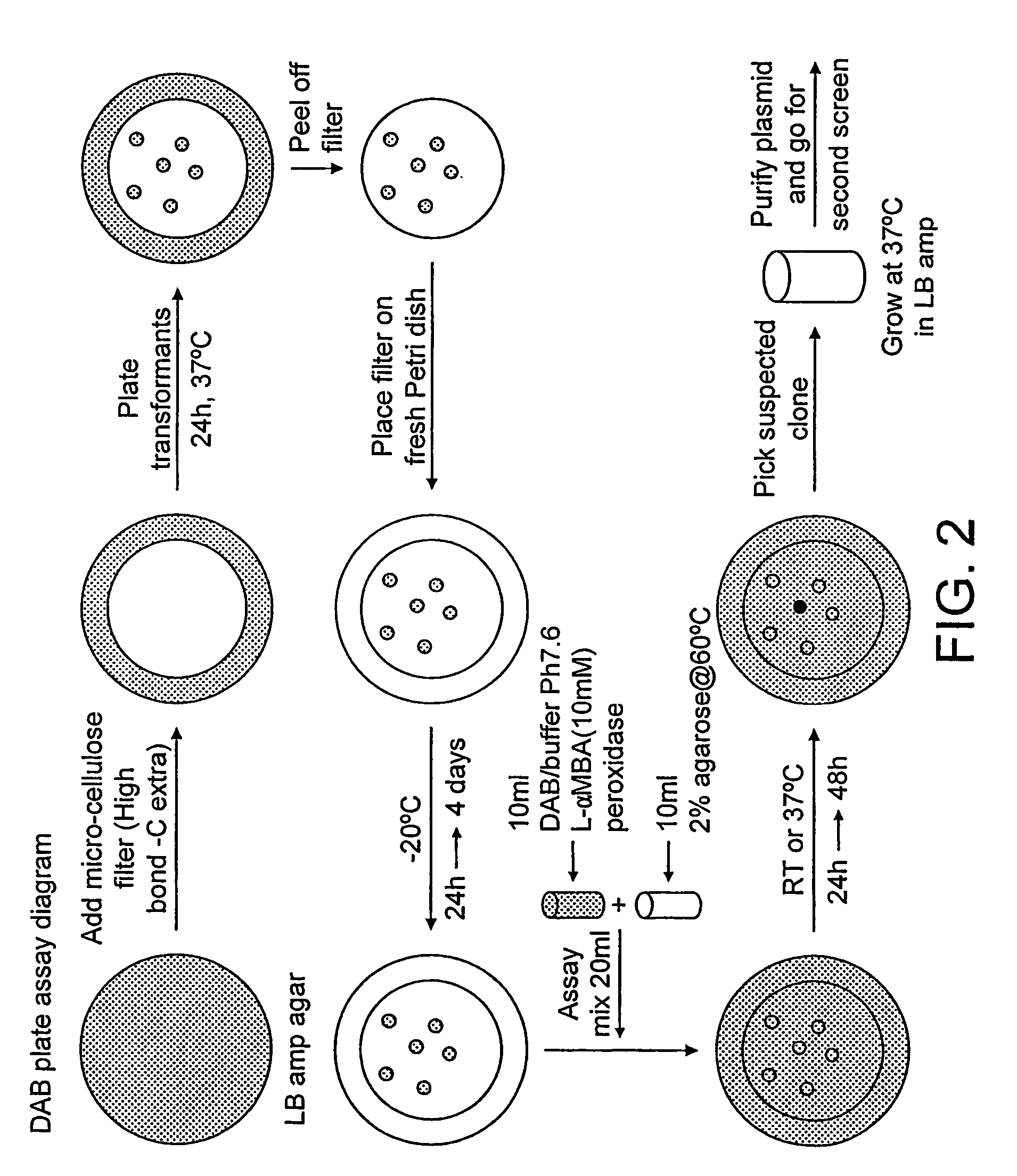
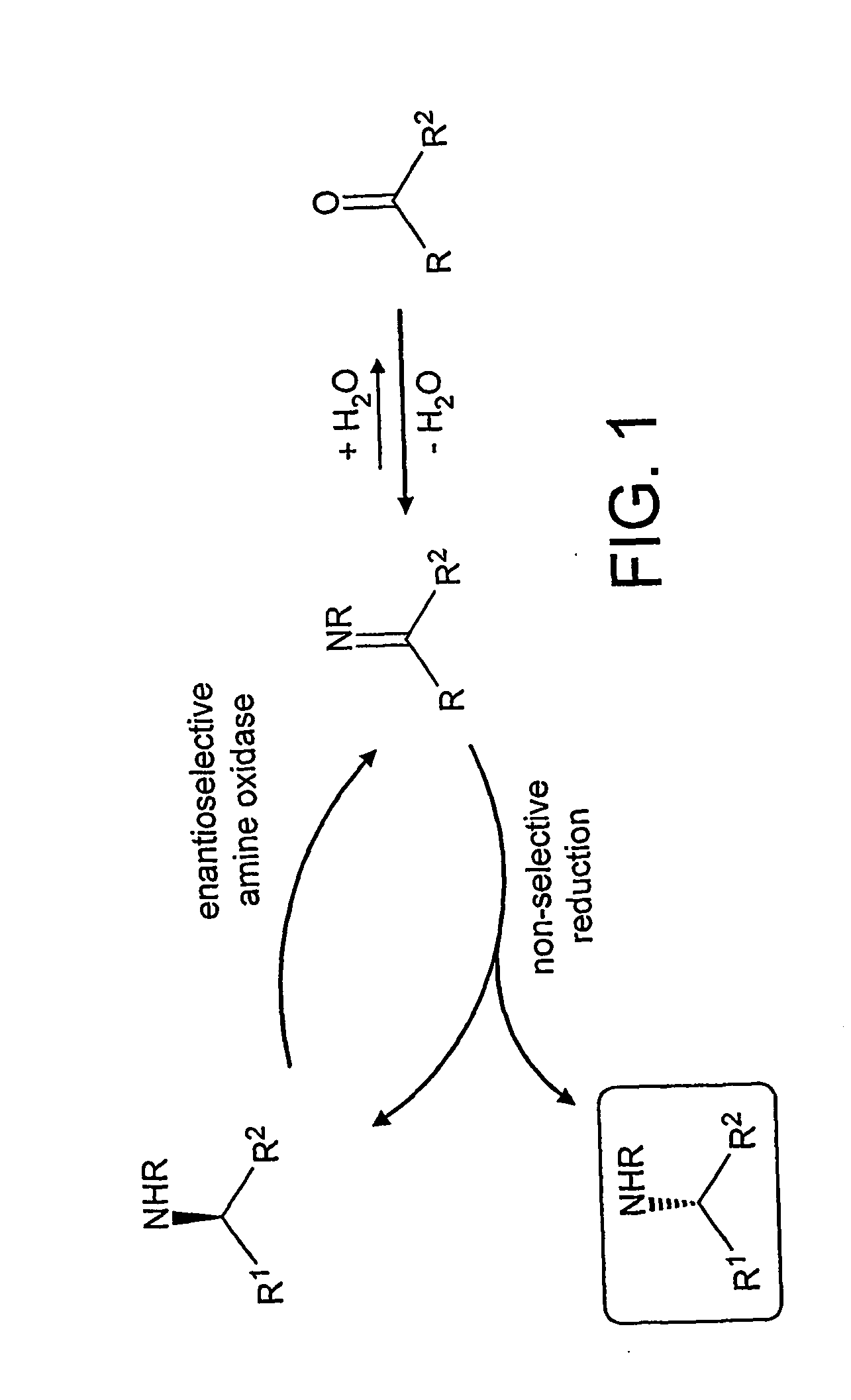
Deracemisation of amines
InactiveUS7208302B2Easy to separateHigh enantiomeric excessSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationAmine oxidaseChiral amine
The present invention relates to a method for the deracemisation or chiral inversion of chiral amines by enzymatic treatment. The method employs a stereoselective enzymatic conversion and either a non-selective or partially selective chemical or enzymatic conversion, simultaneously or sequentially. The invention also provides a method for selecting a suitable enzyme, particularly a suitable amine oxidase, and for the generation of novel enzymes suitable for use in the deracemisation method.
Owner:INGENZA
Method for producing α-amino acid including phosphorus and production intermediates thereof
ActiveUS7795464B2High enantiomeric excessEfficient processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsAcid hydrolysisBenzylamine
Owner:MMAG CO LTD
Process for enantioselective synthesis of single enantiomers of modafinil by asymmetric oxidation
InactiveUS20050222257A1High enantioselectivityHigh yieldBiocideOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventEnantioselective synthesis
The invention relates to a method for preparing a sulphoxide compound of formula (I) either as a single enantiomer or in an enantiomerically enriched form, comprising the steps of: a) contacting a pro-chiral sulphide of formula (II) with a metal chiral complex, a base and an oxidizing agent in an organic solvent; and optionally b) isolating the obtained sulphoxide of formula (I). wherein n, Y, R1, R1a, R2 and R2a are as defined in claim 1.
Owner:TEVA SANTE
Method for Producing L-2-Amino-4-(Hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-Butanoic Acid
InactiveUS20080146837A1Efficiently produceEfficient productionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAsymmetric syntheses1,5-CyclooctadieneMethyl group
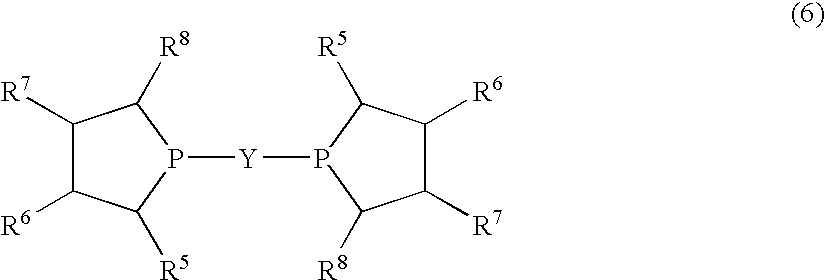
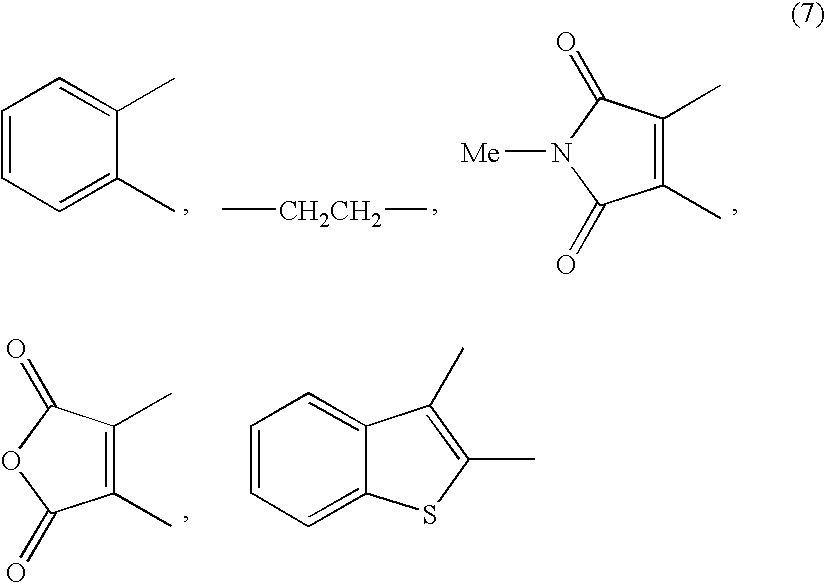
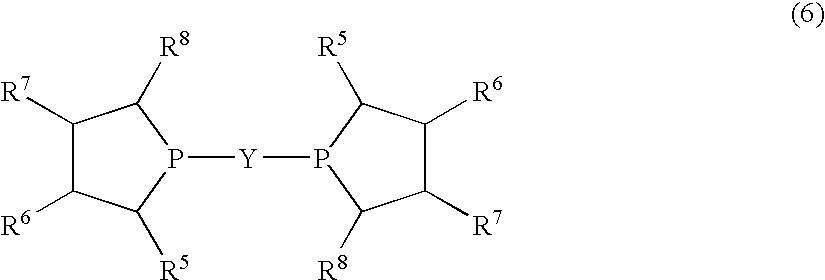
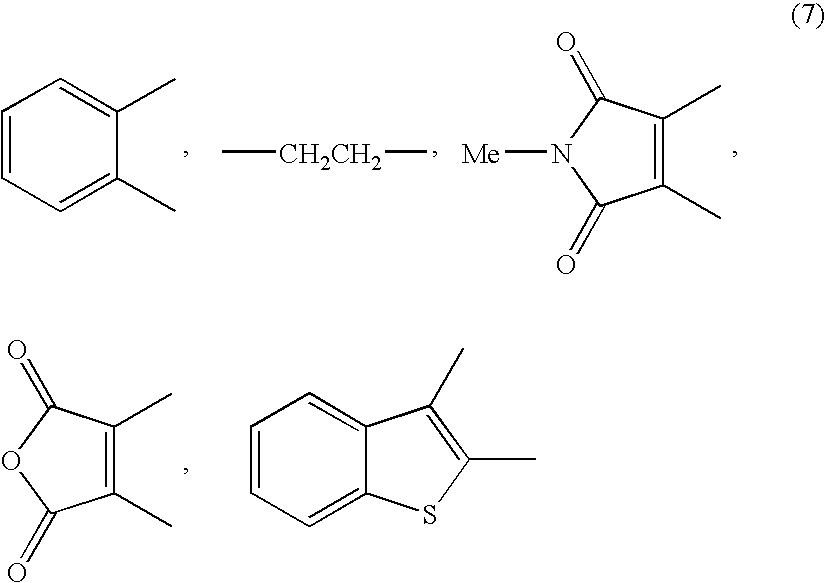
Disclosed is a method for efficiently and highly selectively producing L-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butanoic acid, which is useful as a herbicide, through a catalytic asymmetric synthesis reaction. Specifically disclosed is a method for producing L-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butanoic acid which is characterized in that a dehydroamino acid is subjected to an asymmetric hydrogenation by using a rhodium catalyst represented by the formula (2) below and having an optically active cyclic phosphine ligand, and then the resulting product is subjected to hydrolysis:[Rh(R4)(L)]X (2)[where R4 represents 1,5-cyclooctadien or norbornadien; L represents a substance represented by the following formula (6):(wherein R5 and R8 respectively represent a C1-4 alkyl group; R6 and R7 respectively represent hydrogen atom or hydroxyl group; and Y represents a group selected from groups represented by the following formula (7):(where Me represents methyl group)).].
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Process for producing optically active sulfoxide
A process for preparing an optically active cyclic sulfoxide, by reacting a cyclic thioether with cumene hydroperoxide or isopropylcumyl hydroperoxide in the presence of alcohol, water or a mixture of water and alcohol and in the presence of a complex of an optically active tartaric acid diester and a titanium (IV) alkoxide in an inert solvent.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
Method for producing L-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butanoic acid
InactiveUS7772426B2Efficient productionHigh enantiomeric excessOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHydrogen atomAsymmetric hydrogenation
Disclosed is a method for efficiently and highly selectively producing L-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butanoic acid, which is useful as a herbicide, through a catalytic asymmetric synthesis reaction. Specifically disclosed is a method for producing L-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butanoic acid which is characterized in that a dehydroamino acid is subjected to an asymmetric hydrogenation by using a rhodium catalyst represented by the formula (2) below and having an optically active cyclic phosphine ligand, and then the resulting product is subjected to hydrolysis:[Rh(R4)(L)]X (2)[where R4 represents 1,5-cyclooctadien or norbornadien; L represents a substance represented by the following formula (6):(wherein R5 and R8 respectively represent a C1-4 alkyl group; R6 and R7 respectively represent hydrogen atom or hydroxyl group; and Y represents a group selected from groups represented by the following formula (7):(where Me represents methyl group)).].
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Method for producing an optically active beta-amino acid
InactiveUS7015348B2Improve performanceHigh enantiomeric excessOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsSynthesis methodsAsymmetric hydrogenation
To provide a producing method of an optically active β-amino acid useful as intermediate for the production of medicines, agricultural chemicals and physiologically active substances, by means of a catalytic and asymmetric synthesis method of high performance and a high enantiomeric excess, without requiring additional procedures such as introduction and removal of protecting group and so on.A producing method of an optically active β-amino acids which comprises subjecting an enamine to an asymmetric hydrogenation.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
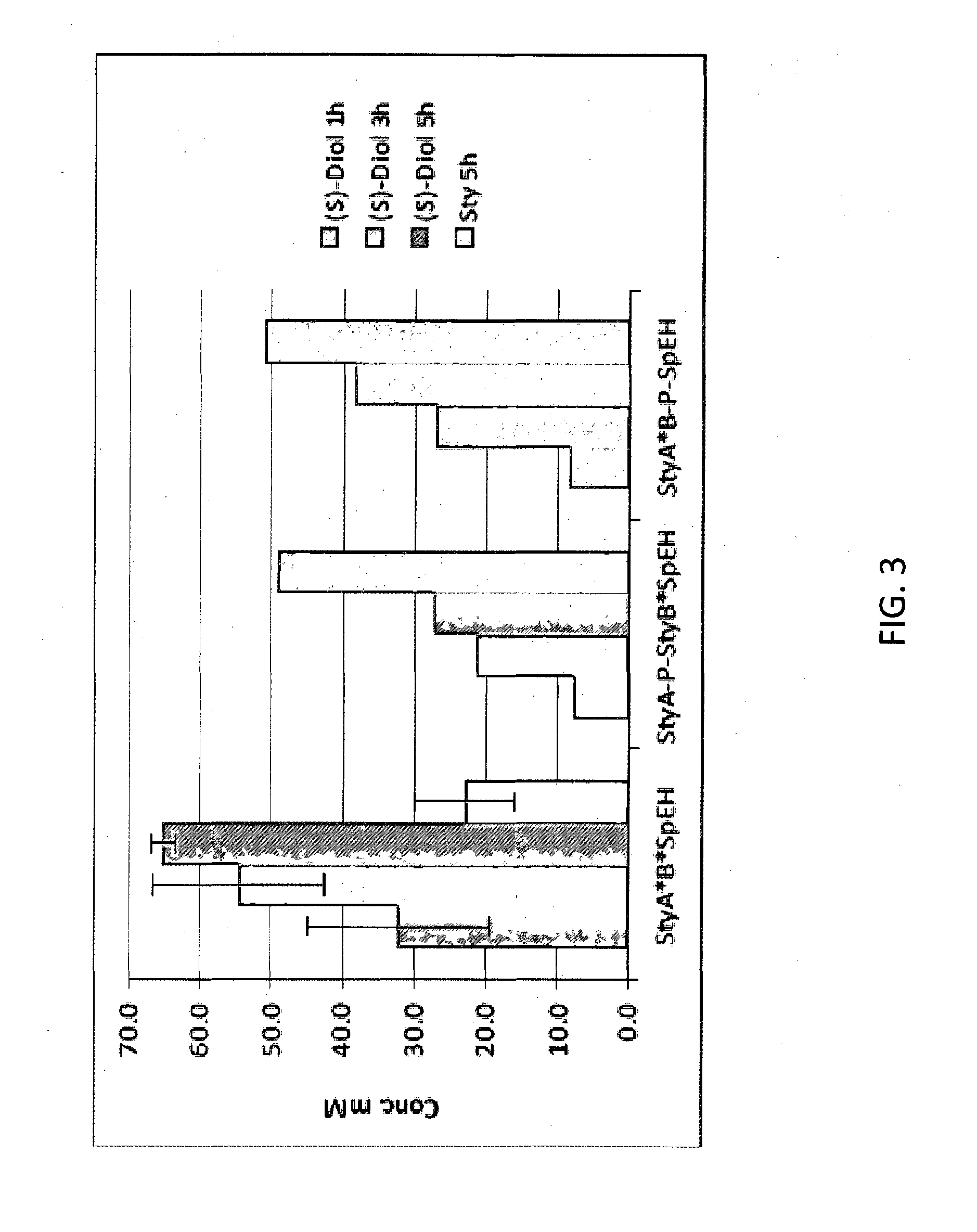
Production Of Enantiopure alpha-Hydroxy Carboxylic Acids From Alkenes By Cascade Biocatalysis
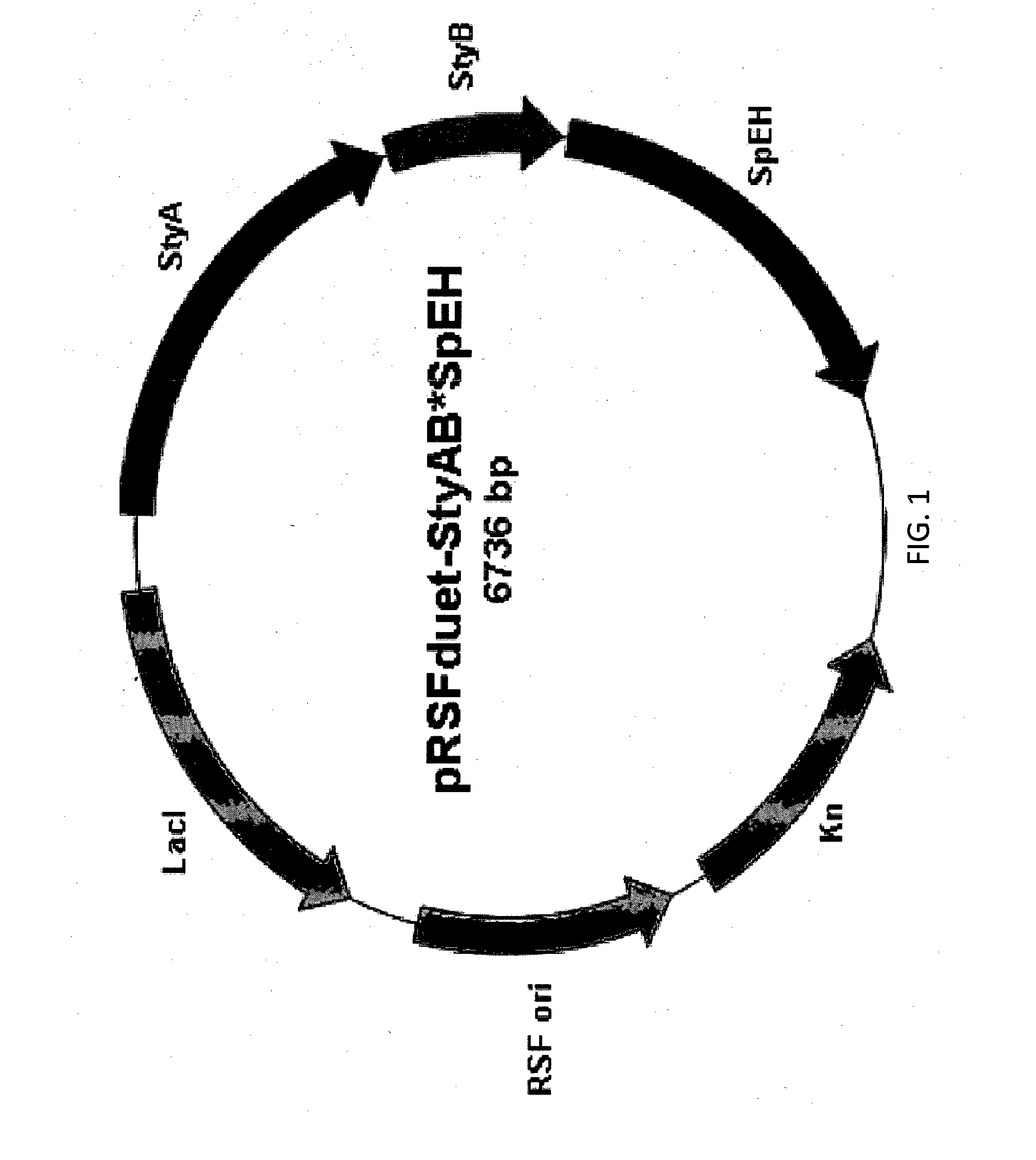
The invention provides compositions comprising an alkene epoxidase and a selective epoxide hydrolase, such as a recombinant microorganism comprising a first heterologous nucleic acid encoding an alkene epoxidase and a second heterologous nucleic acid encoding a selective epoxide hydrolase. Exemplary alkene epoxidases include StyAB, while exemplary selective epoxide hydrolases include epoxide hydrolases from Sphingomonas, Solanum tuberosum, or Aspergillus. The invention also provides non-toxic methods of making enantiomerically pure vicinal diols or enantiomerically pure alpha-hydroxy carboxylic acids using these compositions and microorganisms.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Method for producing alpha - amino acid including phosphorus and production intermediates thereof
ActiveUS20090270647A1High selectivityHigh enantiomeric excessOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsAcid hydrolysisBenzylamine
A method for efficiently producing L-2-amino-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butanoic acid, useful as a herbicide, by a catalytic asymmetric synthesis reaction with a high asymmetric yield. The method includes a step in which a compound represented by the below formula (1) and a benzylamine are reacted in the presence of dehydrating agent, then the resulting mass is reacted with hydrogen cyanide in the presence of an asymmetric catalyst, followed by acid hydrolysis, further followed by elimination of a protective group. [chemical formula 1] (1) (where, R1 represents a C1-4 alkyl group.)
Owner:MMAG CO LTD
Deracemisation of amines
InactiveUS20060257978A1Increase productionChange to enzyme activitySugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationCombinatorial chemistryOxidative enzyme
The present invention relates to a method for the deracemisation or chiral inversion of chiral amines by enzymatic treatment. The method employs a stereoselective enzymatic conversion and either a non-selective or partially selective chemical or enzymatic conversion, simultaneously or sequentially. The invention also provides a method for selecting a suitable enzyme, particularly a suitable amine oxidase, and for the generation of novel enzymes suitable for use in the deracemisation method.
Owner:INGENZA
Engineering bacteria for expressing L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution and application thereof
ActiveCN102559570BIncrease vitalityAchieve preparationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for expressing L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution, which is engineering escherichia coli capable of heterologously expressing NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) independent L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution. The engineering bacteria can highly express corresponding mutant protein on the basis of commercial escherichia coli C43 (DE3) and through transporting an expression vector pETDuet-1-mlldD containing the mutant NAD independent L-lactate dehydrogenase, and has the S-mandelic acid degrading activity. The invention also discloses an application of the engineering bacteria in the resolution of racemic mandelic acid. The racemic mandelic acid is conducted through taking intact cells of the constructed engineering bacteria as a catalyst, and meanwhile, homochiral R-mandelic acid and benzoyl formic acid are produced. The engineering bacteria has the advantages of high substrate utilization rate, high product concentration, high optical purity, simplicity and convenience in future extraction, and the like.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
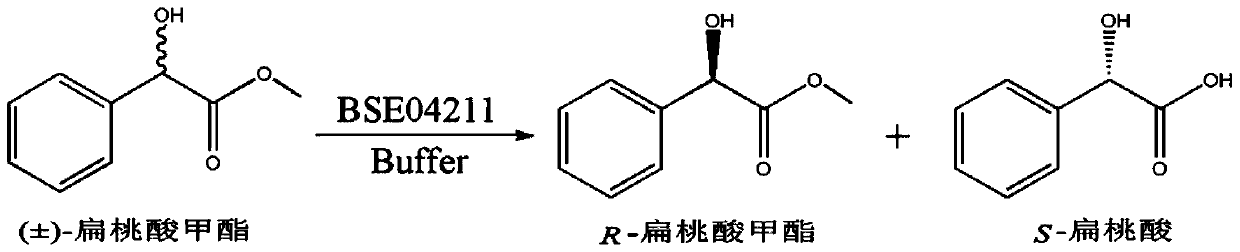
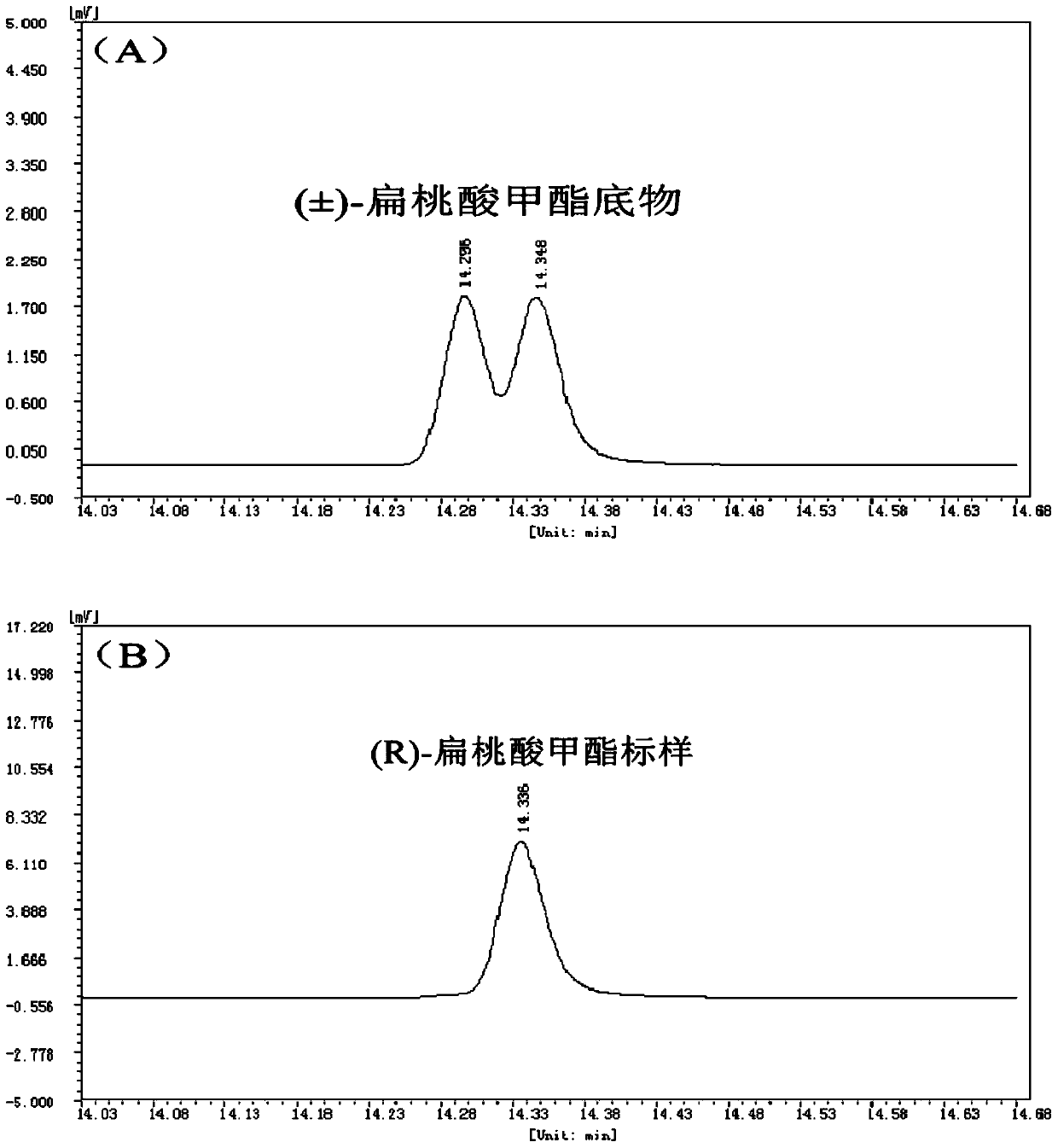
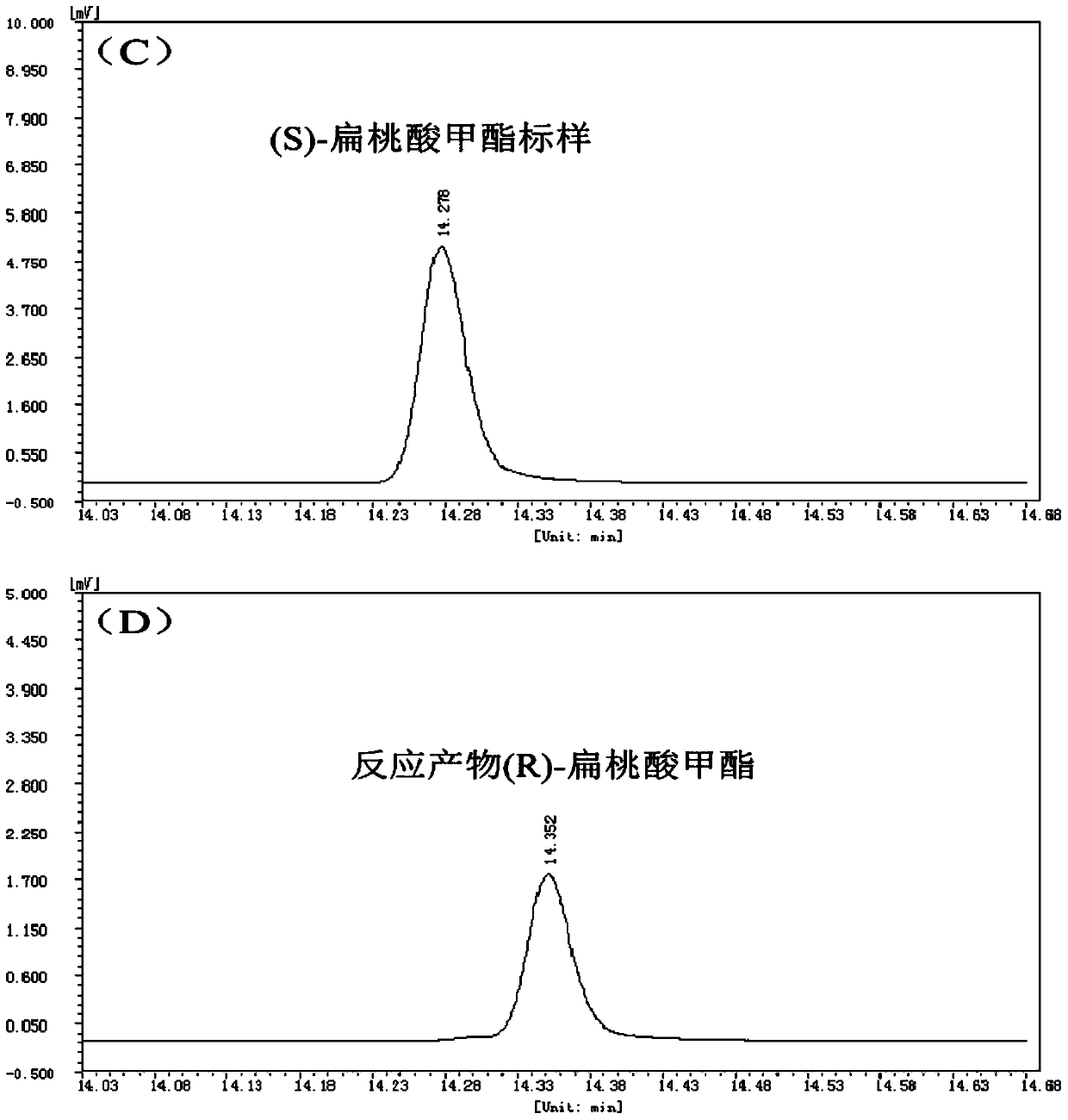
A method for splitting (±)-methyl mandelate with esterase
ActiveCN104830944BMild reaction conditionsNo pollution in the processHydrolasesFermentationMandelic acidMethyl mandelic acid
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for synthesizing optical activity 2,3-allenes secondary alcohol
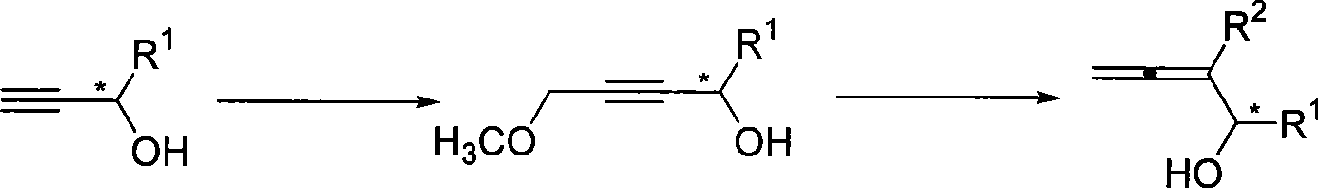
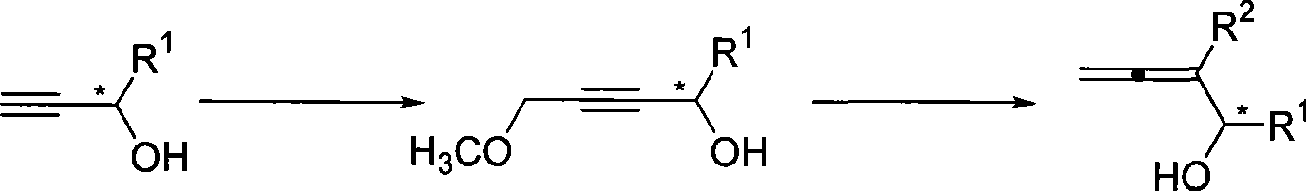
InactiveCN101503339AHigh enantiomeric excessEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationChloromethyl EtherGrignard reagent
The invention relates to a synthetic method of optical activity 2, 3-allenes disubstituted carbinol with high enantiomeric excess; optical activity propiolic alcohol reacts with n-butyllithium and chloromethyl ether to generate optical activity 4- hydroxyl-4- aryl-2- butynyl methyl ether which then reacts with grignard reagent (ethyl ether solution) under the catalysis of cuprous bromide, so that the optical activity 2, 3-allenes disubstituted carbinol with high enantiomeric excess can be synthesized. The operation of the method is simple, the raw materials and the reagents are easy to obtain, and the product has high enantioselectivity. The method can simultaneously introduce multiple substitutional groups which are easy to separate and purify, so as to be applicable to synthesizing various substitutional optical activity 2, 3-allenes disubstituted carbinols.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing optically active 2-arylpiperidinium salt
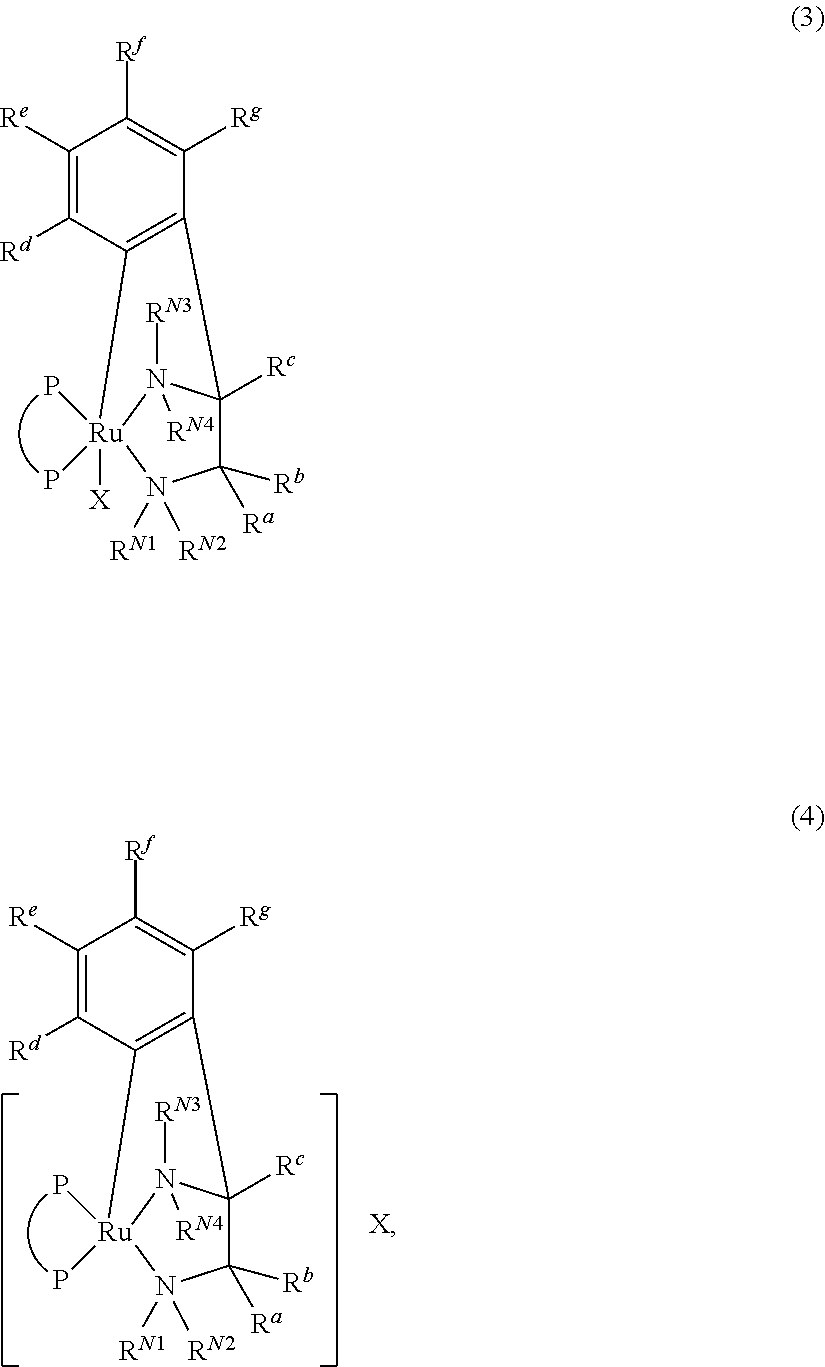
Disclosed is a method for producing an optically active 2-arylpiperidinium salt, comprising asymmetrically hydrogenating a pyridinium salt in the presence of an iridium complex and hydrogen, the 2-arylpiperidinium salt being represented by the following general formula (1):wherein R1, R2, X, *, and m are as described in Description, the pyridinium salt being represented by the following general formula (2):wherein R1, R2, X, and m are as described in Description, and the iridium complex being represented by the following general formula (3):IrH(Z)(Q)(PP*) (3),wherein Z, PP*, and Q are as described in Description, or the following general formula (4):[{IrH(PP*)}2(μ-Z)3]Z (4),wherein Z and PP* are as described in Description.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Hydrogenation of imines
ActiveUS20110054217A1Improve conversion efficiencyHigh enantiomeric excessOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPtru catalystAsymmetric hydrogenation
The present invention relates to a process for the asymmetric hydrogenation of imines with hydrogen under elevated pressure in the presence of a catalyst system. In particular the present invention relates to the use of the said catalytic system for the enantioselective hydrogenation of prochiral ketimines to asymmetric amines leading to the formation of herbicides.
Owner:UNITED PHOSPHORUS LTD
Method for producing an optically active beta-amino acid
InactiveUS20060122418A1Improve performanceHigh enantiomeric excessOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsGreek letter betaSynthesis methods
The Problem to Be Solved: To provide a producing method of an optically active β-amino acid useful as intermediate for the production of medicines, agricultural chemicals and physiologically active substances, by means of a catalytic and asymmetric synthesis method of high performance and a high enantiomeric excess, without requiring additional procedures such as introduction and removal of protecting group and so on. Means to Solve the Problems: A producing method of an optically active β-amino acids which comprises subjecting an enamine to an asymmetric hydrogenation.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Method for producing R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate by using 1, 2-butanediol as substrate
ActiveCN103103222ASuccessful stereospecific synthesisAchieve stereospecific synthesisMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,2-butanediol by using R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate as a substrate. The method comprises steps of: culturing Gluconobacter oxydans DSM 2003 by a conventional method to prepare a biological catalyst; mixing the biological catalyst with a substrate 1,2-butylene glycol aqueous solution; adding ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid and oscillating for 1-30 h under condition of 20-50 DEG C and pH of 4.0-10.0 to obtain a transformation liquid; and preparing a solution containing R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate through the transformation liquid. The method provided by the invention has the following characteristics: (1) the method employs biological catalysis, has simple reaction system, mild reaction conditions, short steps and simple operation; and the biological catalyst can be easily removed, so as to facilitate subsequent separation and purification; (2) the method has a short reaction period, and the product R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate can accumulate to a high concentration; (3) the substrate 1,2-butanediol has low price, and is easy to acquire; and (4) product enantiomer has high excessive rate reaching higher than 99%, so as to lay foundation for the efficient production of R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Method for preparing (S)-1-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol by microbial transformation
InactiveCN101519674BHigh enantiomeric excessHigh excessMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobial transformationCandida tropicalis
The invention provides a method for preparing (S)-1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol by microbial transformation. The (S)-1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol is prepared according to The invention provides a method for preparing (S)-1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol by microbial transformation. The (S)-1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol is prepared according tothe following steps: 1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol functioning as substrate is catalyzed by fermentation products of Candida tropicalis 104 functioning as enzyme source so as to be reducthe following steps: 1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol functioning as substrate is catalyzed by fermentation products of Candida tropicalis 104 functioning as enzyme source so as to be reduced asymmetrically at 28-34 DEG C, and transformation solution is separated and purified after the asymmetric reduction reaction. The Candida tropicalis 104 is chosen to be used as enzyme-producing stred asymmetrically at 28-34 DEG C, and transformation solution is separated and purified after the asymmetric reduction reaction. The Candida tropicalis 104 is chosen to be used as enzyme-producing strain after optimum strain seeking, and 1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol is catalyzed to be reduced asymmetrically in a single-phase aqueous system so as to generate (S)-1-(3,5-bis (trifluoroain after optimum strain seeking, and 1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol is catalyzed to be reduced asymmetrically in a single-phase aqueous system so as to generate (S)-1-(3,5-bis (trifluoromethyl)) phenylethanol which has an enantiomeric excess value of over 99 percent and can be well applied.methyl)) phenylethanol which has an enantiomeric excess value of over 99 percent and can be well applied.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
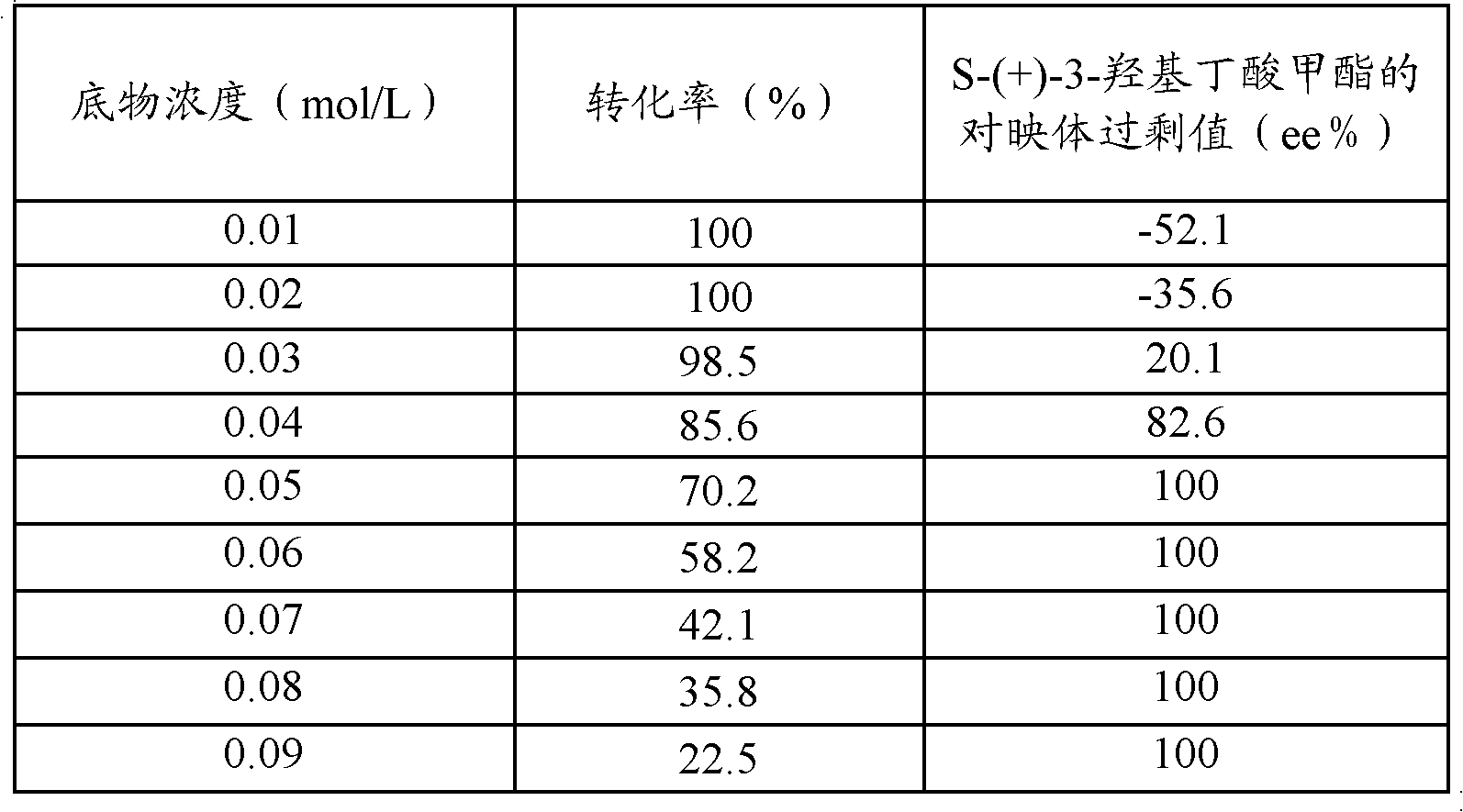
Method for preparing S-(+)-3-methyl hydroxybutyrate through microbial transformation
InactiveCN102071227AHigh molar conversionHigh enantiomeric excessMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidAcetic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing S-(+)-3-methyl hydroxybutyrate through microbial transformation, which comprises the following steps that: in phosphate buffer solution with the pH value being 5.0 to 8.0, methyl acetoacetate is used as substrates, enzyme-containing strains obtained through fermenting saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No. 2266 are used as microbial catalysts, conversion region is carried out for 8 to 40h at 25 to 45 DEG C, after the reaction is completed, and conversion liquid is prepared into the S-(+)-3-methyl hydroxybutyrate through separation and purification. The method provided by the invention has the main beneficial effects that 1. produced strains are safe and innoxious and are easy to be cultured in a large scale; 2. a large number of biological catalysts can be obtained, and the cost is low; 3. the reaction conditions are mild, and the environmental-friendly effect is realized; 4. the operation is simple and convenient, and the addition of coenzymes with a high price is not needed in the reaction process; and 5. the large-scale industrialized production is easy to realize, and the mol conversion rate is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
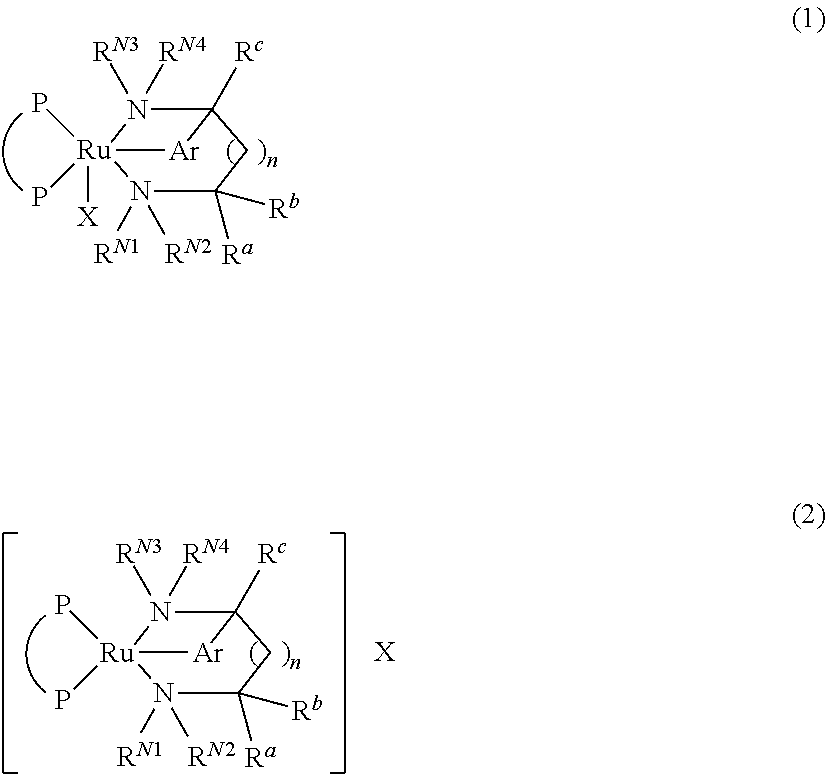
Process for producing optically active amine
ActiveUS9328079B2Improve efficiencyHigh enantiomeric excessAsymmetric synthesesAsymmetric hydrogenationDouble bond
A process for producing an optically active amine compound, characterized by asymmetrically hydrogenating a prochiral carbon-nitrogen double bond in the presence of a ruthenium complex represented by general formula (1) or (2) (wherein P represents an optically active diphosphine, X represents an anionic group, and Ar represents an optionally substituted arylene group).
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Method of preparing a don prodrug from l-glutamic acid
PendingUS20220089522A1Easily and effectively purifiedPreventing cyclizationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCombinatorial chemistryOrganic chemistry
The present disclosure provides methods of preparing a compound of Formula (1): wherein R1, R2, and R3 are as defined as set forth in the application. In one embodiment, a compound of Formula (1) is prepared in >95% chemical purity and >95% enantiomeric excess.
Owner:DRACEN PHARMA INC
Engineering bacteria for expressing L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution and application thereof
ActiveCN102559570AIncrease vitalityAchieve preparationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMutated protein
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for expressing L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution, which is engineering escherichia coli capable of heterologously expressing NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) independent L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution. The engineering bacteria can highly express corresponding mutant protein on the basis of commercial escherichia coli C43 (DE3) and through transporting an expression vector pETDuet-1-mlldD containing the mutant NAD independent L-lactate dehydrogenase, and has the S-mandelic acid degrading activity. The invention also discloses an application of the engineering bacteria in the resolution of racemic mandelic acid. The racemic mandelic acid is conducted through taking intact cells of the constructed engineering bacteria as a catalyst, and meanwhile, homochiral R-mandelic acid and benzoyl formic acid are produced. The engineering bacteria has the advantages of high substrate utilization rate, high product concentration, high optical purity, simplicity and convenience in future extraction, and the like.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Method for preparing R-mandelic acid by aid of two-step microbial transformation processes
ActiveCN106086090AEasy to grow on a large scaleIn situ regenerationMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolventBacillus cereus
The invention discloses a method for preparing R-mandelic acid by the aid of two-step microbial transformation processes. The method includes carrying out transformation reaction on ethyl benzoylformate, first thalli and buffer solution with a pH (potential of hydrogen) value of 6-8 under conditions of the temperature of 20-45 DEG C and the speed of 100-200 rpm to obtain R-ethyl mandelate; carrying out reaction on the R-ethyl mandelate, second thalli, organic solvents and buffer solution with a pH value of 7-9 under conditions of the temperature of 20-40 DEG C and the speed of 100-200 rpm to obtain the R-mandelic acid. The ethyl benzoylformate is used as a substrate during the transformation reaction, the first thalli are obtained by means of fermentation cultivation by the aid of saccharomyces cerevisiae and are used as catalysts during the transformation reaction, and the buffer solution with the pH value of 6-8 is used as a reaction medium during the transformation reaction. The R-ethyl mandelate is used as a substrate during the reaction, the second thalli are obtained by means of fermentation cultivation by the aid of bacillus cereus and are used as catalysts during the reaction, the organic solvents are used as complex solubilizers during the reaction, and the buffer solution with the pH value of 7-9 is used as a reaction medium during the reaction. The method has the advantages that the method is low in cost and is environmentally friendly, and the reaction conditions are mild; the R-mandelic acid is easy to industrially produce on a large scale; the method is easy and convenient to implement and high in molar transformation rate; the yield can be increased and can reach 99.8%, and the ee value can be increased and can reach 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com