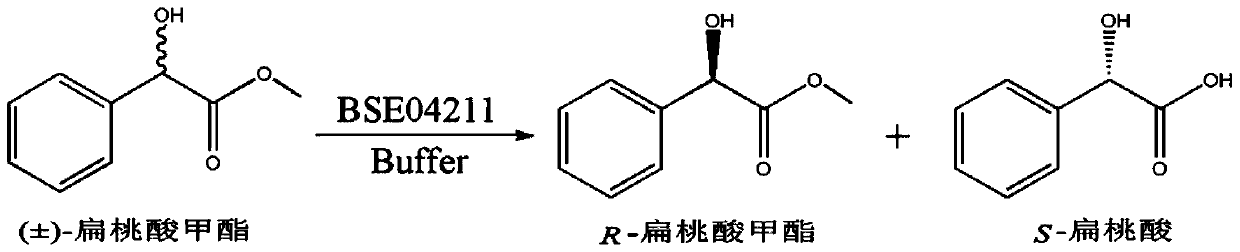
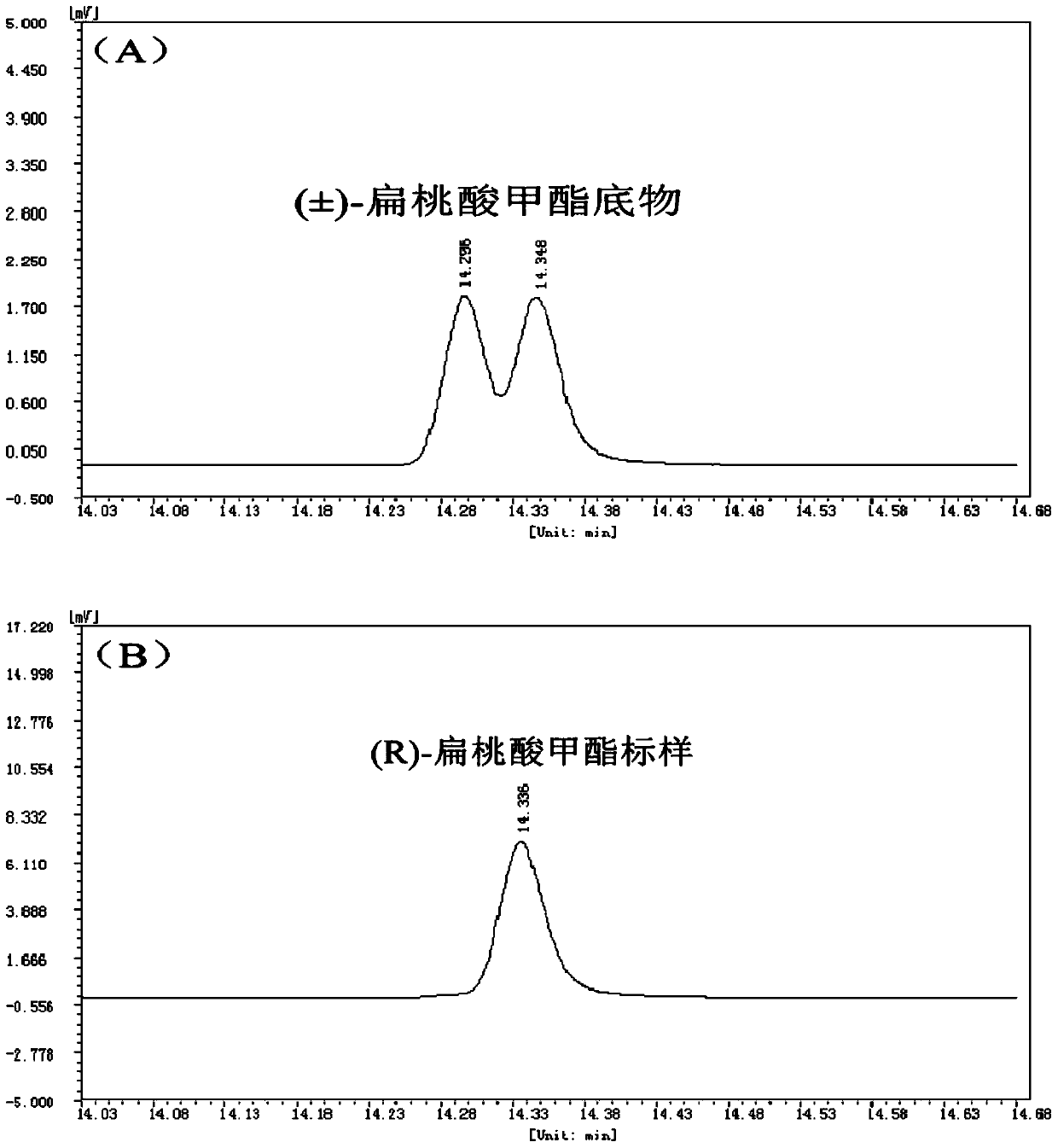
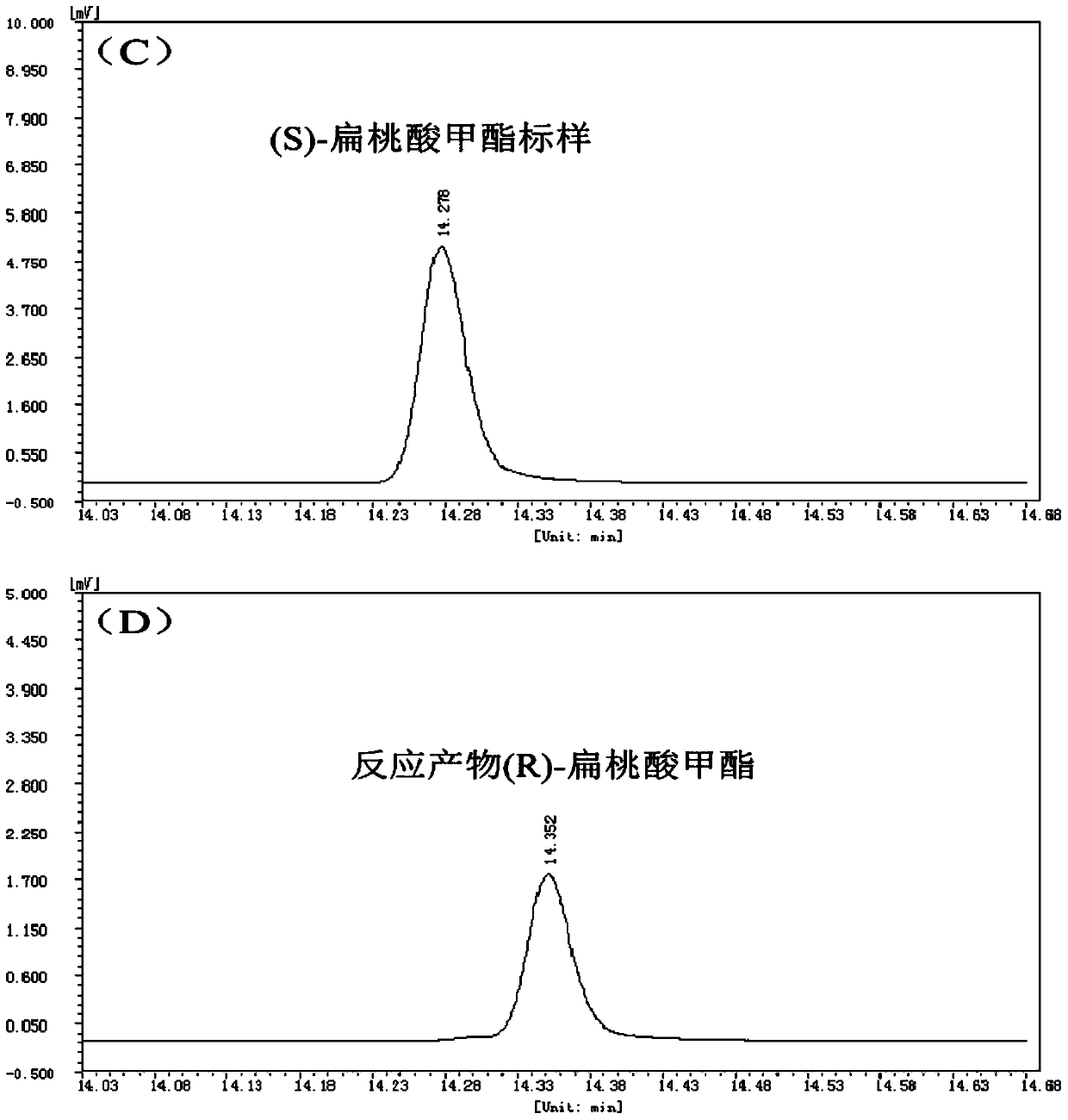
A method for splitting (±)-methyl mandelate with esterase
A technology of methyl mandelic acid and mandelic acid, which is applied in the field of biocatalysis, can solve the problems of expensive reagents, pollute the environment, and low purity, and achieve the effects of high enantiomeric excess value, strong stereoselectivity, and mild reaction conditions
Active Publication Date: 2018-04-03
SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
View PDF1 Cites 2 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
The traditional preparation process of optically pure mandelic acid series compounds is to chemically synthesize racemic products and then perform chiral chemical resolution. This method is expensive in reagents, pollutes the environment, and the purity is not high
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1. Analysis of the influence of esterase EST04211 on the hydrolysis of (±)-methyl mandelate at different temperatures. The process equation for the hydrolysis of (±)-methyl mandelate catalyzed by esterase EST04211 is as follows figure 1 shown.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention discloses a method for splitting (±)-methyl mandelate by esterase. It hydrolyzes (±)-methyl mandelate in the presence of esterase EST04211, and esterase EST04211 catalyzes S-methyl mandelate to generate S-mandelic acid, and then reacts R-methyl mandelate and S ‑Mandelic acid is separated, and the amino acid sequence of the esterase EST04211 is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with the traditional chemical resolution, the present invention has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, no pollution, and high enantiomeric excess value; compared with the currently reported enzymatic catalytic resolution, the esterase EST04211 used preferentially hydrolyzes the S-configuration Methyl mandelate yields optically pure R-mandelic acid methyl ester and S-mandelic acid with strong stereoselectivity. The obtained product can be used for the synthesis of corresponding drugs after simple purification.
Description
Technical field: [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of biocatalysis, and in particular relates to a method for splitting (±)-methyl mandelate by esterase. Background technique: [0002] The enantiomers of mandelic acid and its derivatives are a very important class of pharmaceutical intermediates, which are widely used in the synthesis of various drugs, such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cyclomandelic esters, antitumor agents, coenzyme A, etc. The traditional preparation process of optically pure mandelic acid series compounds is to chemically synthesize racemic products and then perform chiral chemical resolution. This method has expensive reagents, pollutes the environment, and the purity is not high. The preparation of chiral compounds by biocatalysis is an emerging method integrating biotechnology and chemical engineering. This method has the advantages of high efficiency, strong selectivity, and environmental friendliness. It has become the focus and ...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12P41/00C12N9/18C12P7/62C12P7/42
Inventor 胡云峰梁甲元孙爱君张云邓盾
Owner SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com