Method for purifying and removing chlorides contained in chlorine-containing industrial mixed gas and recovering light hydrocarbon
A mixed gas and chloride technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, dispersed particle separation, etc., can solve the problems of no supply, increased adaptability, low recovery rate, etc., and achieve the effect of wide adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
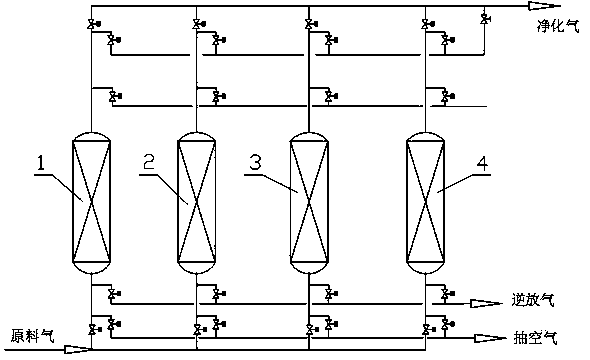
[0031] see figure 1 , the flow process of the present invention includes: the feed gas enters the adsorption separation system composed of four adsorption towers from the bottom of the tower 1, the chloride is adsorbed on the adsorbent, and the purified product gas from the removal of the chloride is discharged from the adsorption separation system from the top of the tower 1 , when the chloride content in the purified product gas reaches the control index, the raw gas is switched to tower 2, and tower 1 stops feeding raw gas, then tower 1 and another adsorption tower 3 that is in boosting pressure enter equal pressure, and tower 1 depressurizes , Tower 3 boosts the pressure, and after the end of the equal pressure drop in Tower 1, it reverses the pressure drop from the feed gas inlet to normal pressure. The adsorption tower 3 carries out the pressure equalization, the tower 1 boosts the pressure, and the tower 3 depressurizes. After the towers 1 and 3 are pressure equalized, ...
Embodiment 2
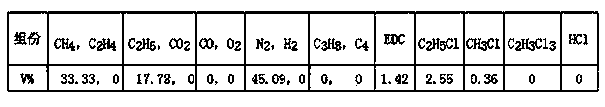
[0045] see figure 1 , In this example, the composition of dichloroethane synthesis tail gas (raw material gas) is shown in Table 3:
[0046] Table 3 Composition of dichloroethane synthesis tail gas (feed gas)
[0047]
[0048] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0049] 1. Adsorption: Dichloroethane synthesis tail gas enters from the bottom of the adsorption tower into the adsorption separation system of the composite adsorption bed with a silica gel: activated carbon ratio of 5:1. Adsorption, control the total chloride content in the purified gas at the outlet of the adsorption tower to <5ppm, and recover the purified target product gas from the top of the adsorption tower;
[0050] 2. Reverse release: After the adsorption is completed, the pressure is reversed from the bottom of the adsorption tower to normal pressure;
[0051] 3. Evacuation: After being reversed to normal pressure, the adsorption tower is evacuated and desorbed through the vacuum pump co...
Embodiment 3
[0058] see figure 1 , the present embodiment purifies and removes the high-altitude exhaust gas from the production of methane chloride, and its composition is shown in Table 5:
[0059] Table 5 Composition of high-altitude exhaust gas for the production of methane chloride (V%)
[0060]
[0061] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0062] 1. Adsorption: Synthetic tail gas enters from the bottom of the adsorption tower into the adsorption separation system of the composite adsorption bed with a silica gel: alumina ratio of 4:3. The total chloride content in the purified gas at the outlet of the adsorption tower is less than 5ppm, and the purified target product gas is recovered from the top of the adsorption tower;
[0063] 2. Reverse release: After the adsorption is completed, the pressure is reversed from the bottom of the adsorption tower to normal pressure;
[0064] 3. Evacuation: After being reversed to normal pressure, the adsorption tower is evacuate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com