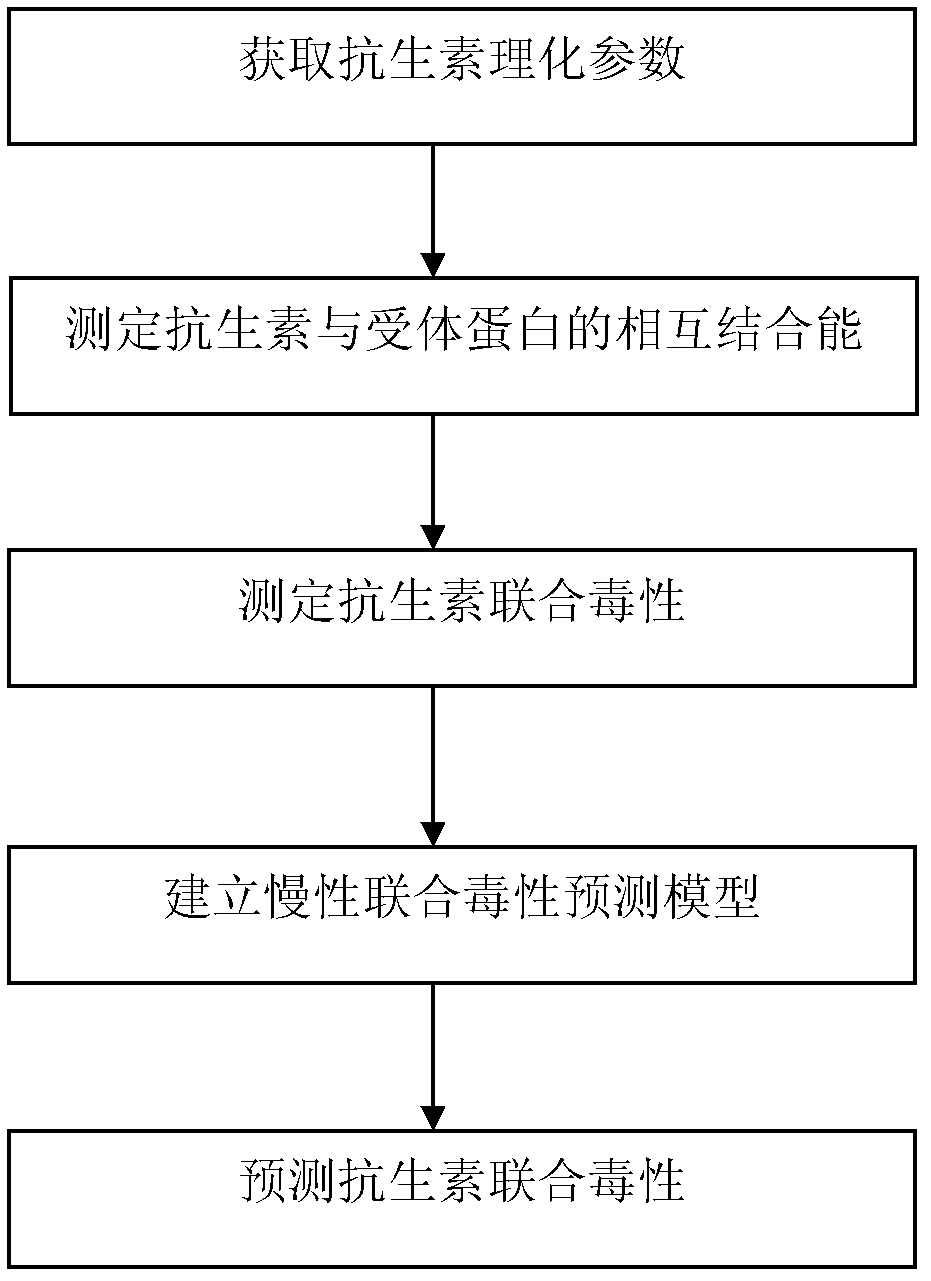
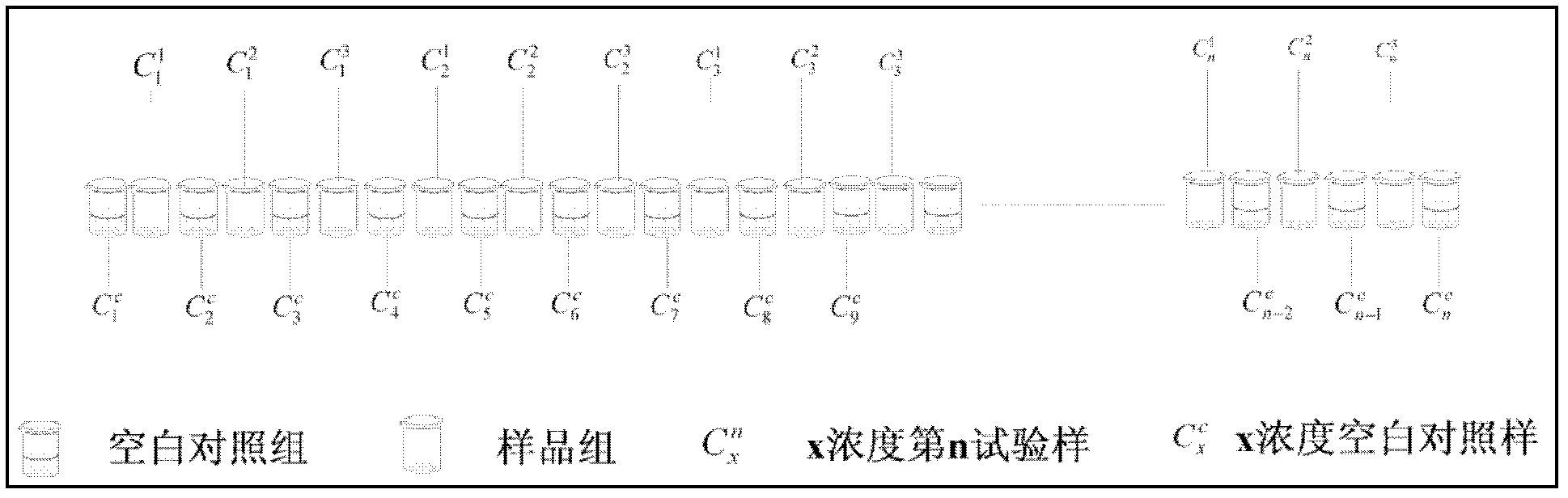
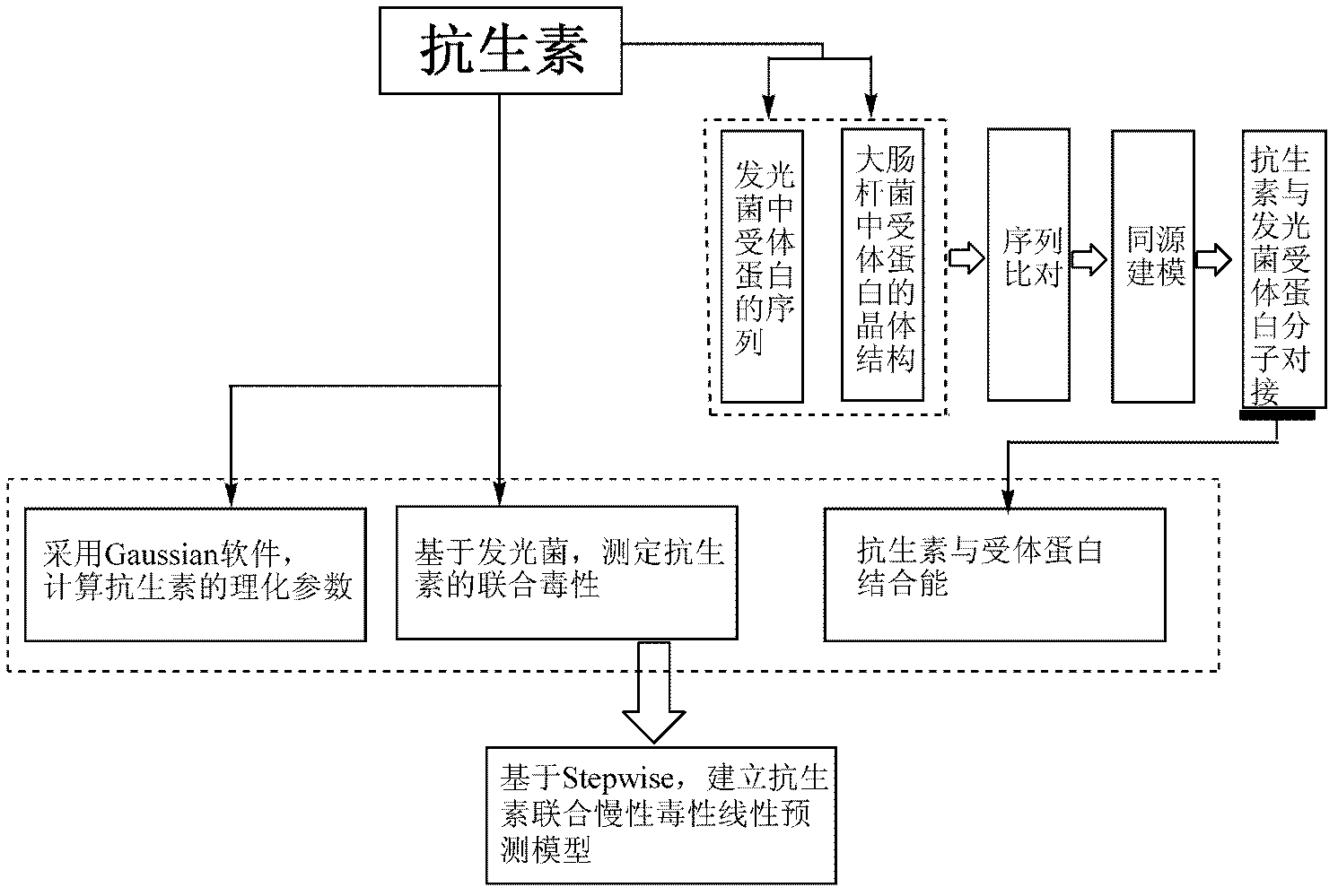
Method for predicting combined chronic toxicity of antibiotic pollutant
A technology of chronic toxicity and combined toxicity, applied in the field of environmental pollution detection, can solve the problems of organism drug resistance, endanger human health, neglect chronic effects, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing uncertainty, reducing experimental costs, and wide application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098] Example 1: Combined Toxicity Prediction of Sulfonamide Antibiotics and Trimethoprim
[0099] (1) Acquisition of physical and chemical parameters
[0100]According to step (1), the physical and chemical parameters of sulfa antibiotics and trimethoprim (TMP) were obtained, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0101] Table 1 Physicochemical parameters of tested antibiotics
[0102]
[0103]
[0104] (2) Acquisition and construction of receptor protein
[0105] The crystal structure of Escherichia coli-related proteins was compared with the gene sequence of the photobacteria protein, and based on the generated sequence alignment files, the receptor proteins folate dihydrogen synthase (DHPS) and TMP receptors of sulfonamide antibiotics were respectively constructed The model of protein folate dihydrogen reductase (DHFR), and the evaluation results of the model are shown in Table 2.
[0106] Table 2 Evaluation results of the established homology model
[0107] ...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: Prediction of combined toxicity of sulfa antibiotics (3#Sulfamonomethoxine) and binary complex systems of other sulfa antibiotics
[0125] (1) Acquisition of physical and chemical parameters
[0126] (2) Acquisition and construction of receptor protein
[0127] (3) Calculation of the interaction (kcal / mol) between the antibiotic and the receptor protein, all of the above adopts all the data in Example 1;
[0128] (4) Determination of combined toxicity of sulfonamide antibiotic binary compound system
[0129] The combined toxicity of the binary complex system of sulfonamide antibiotics was determined, and the results are shown in Table 6.
[0130] Table 6 Combined toxicity of sulfonamide binary complex system
[0131]
[0132] (5) Prediction of combined toxicity of antibiotics
[0133] - log ( EC 50 M C ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com