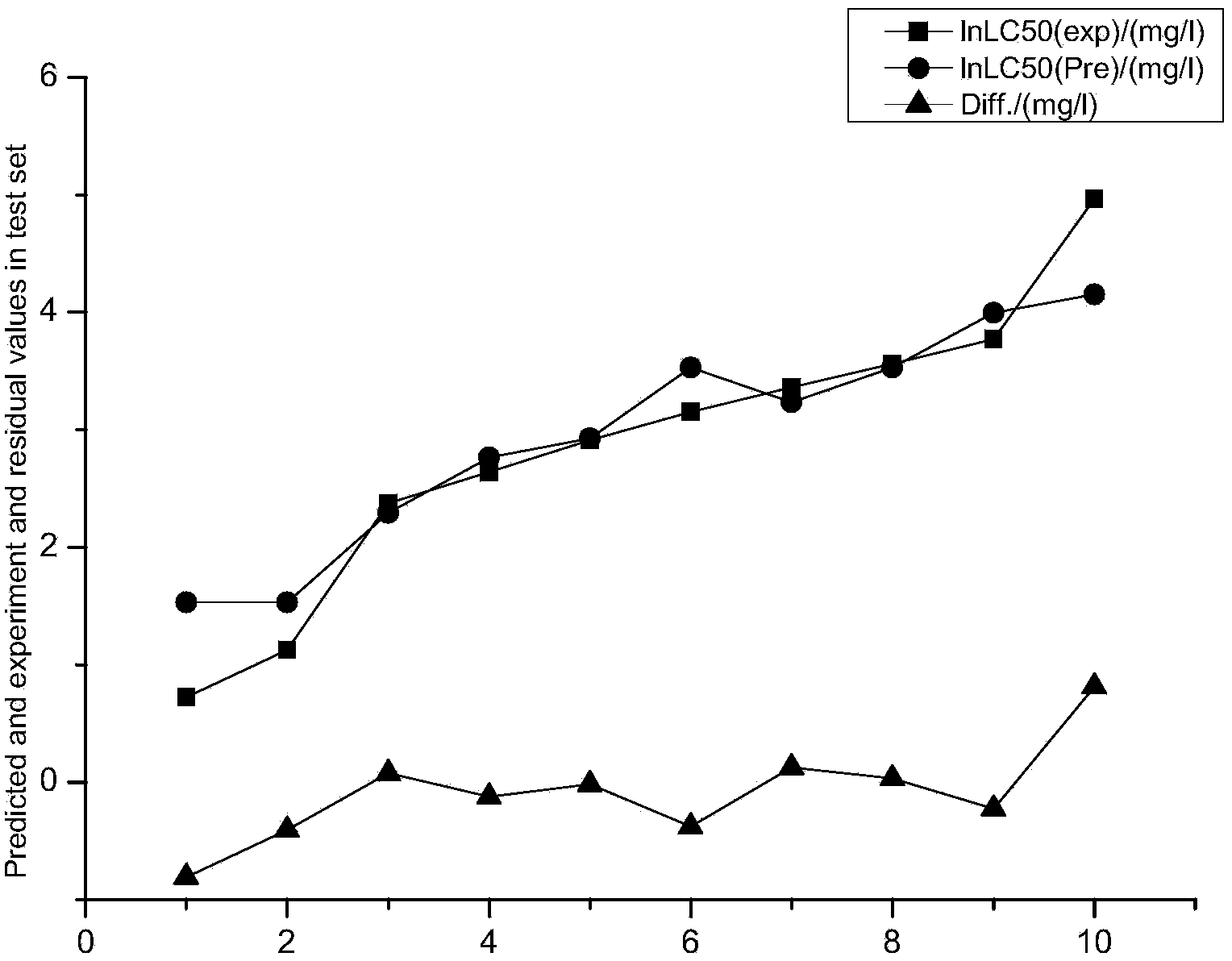
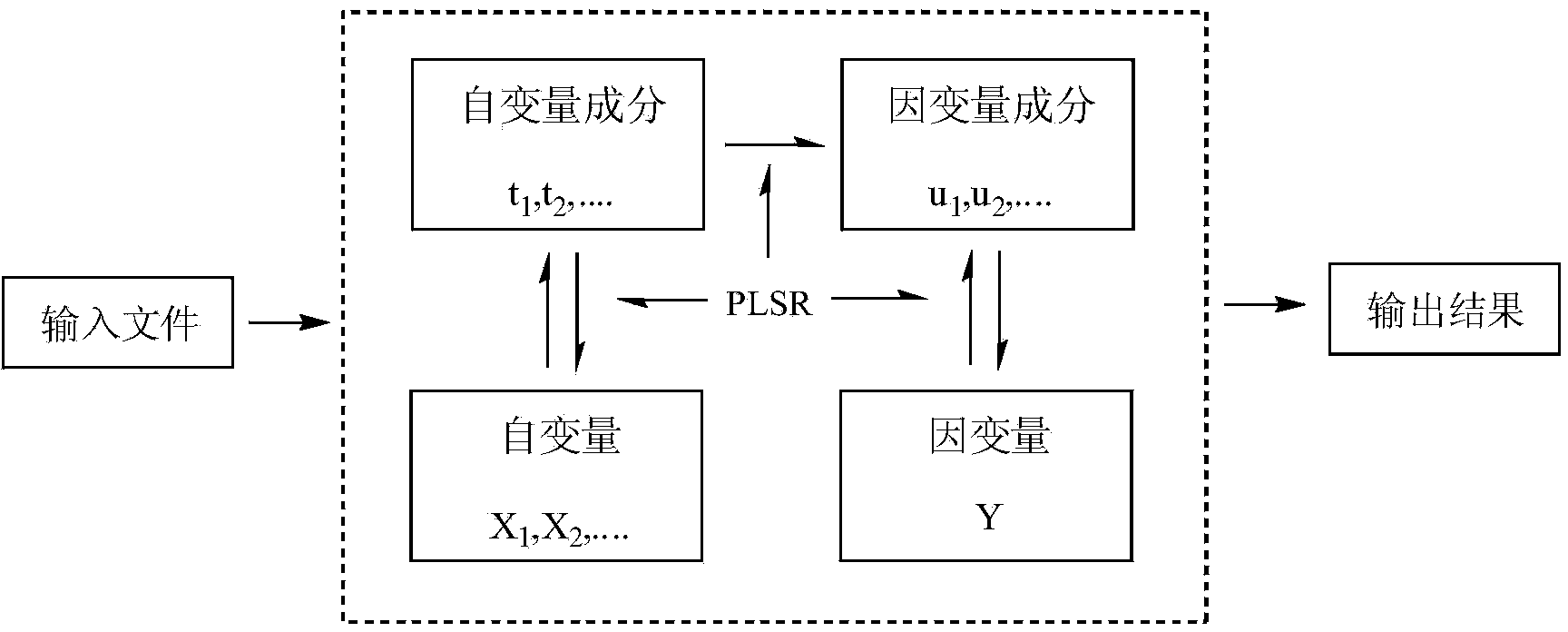
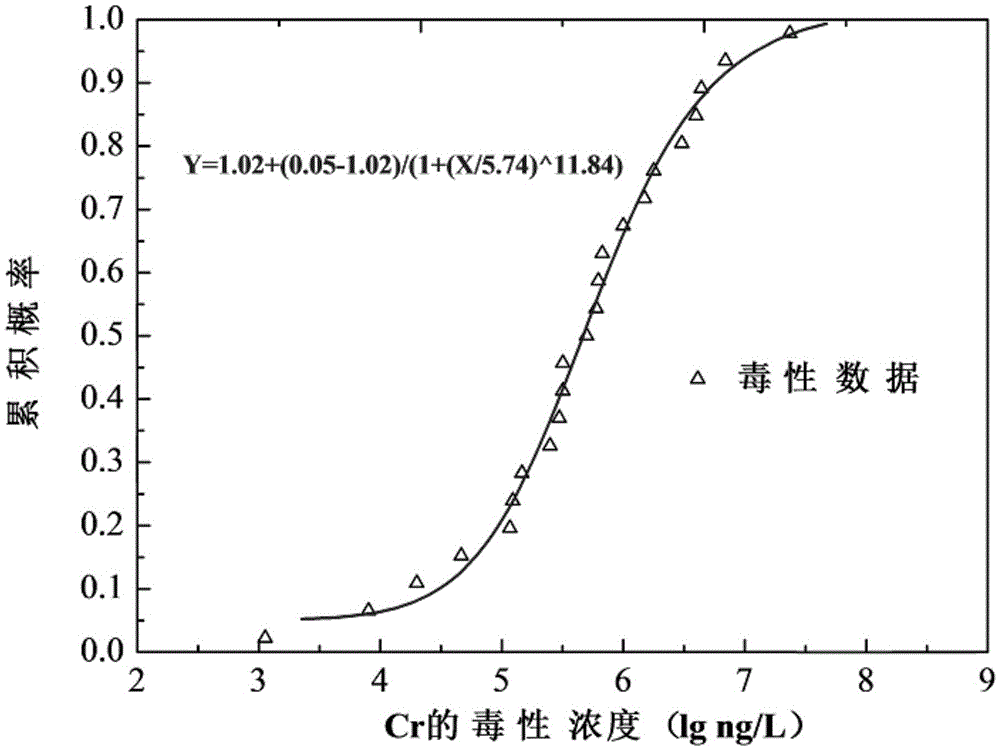
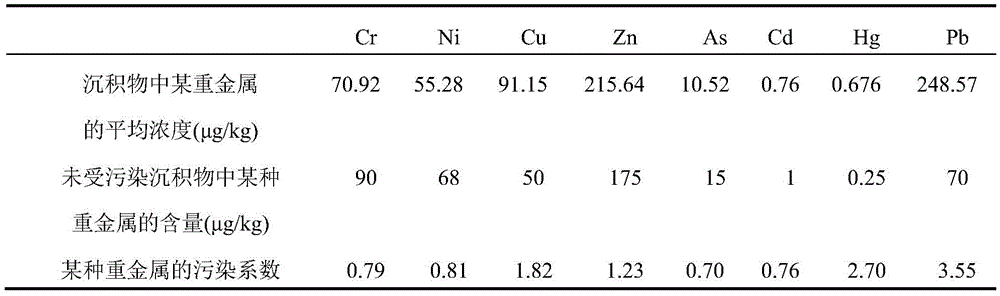
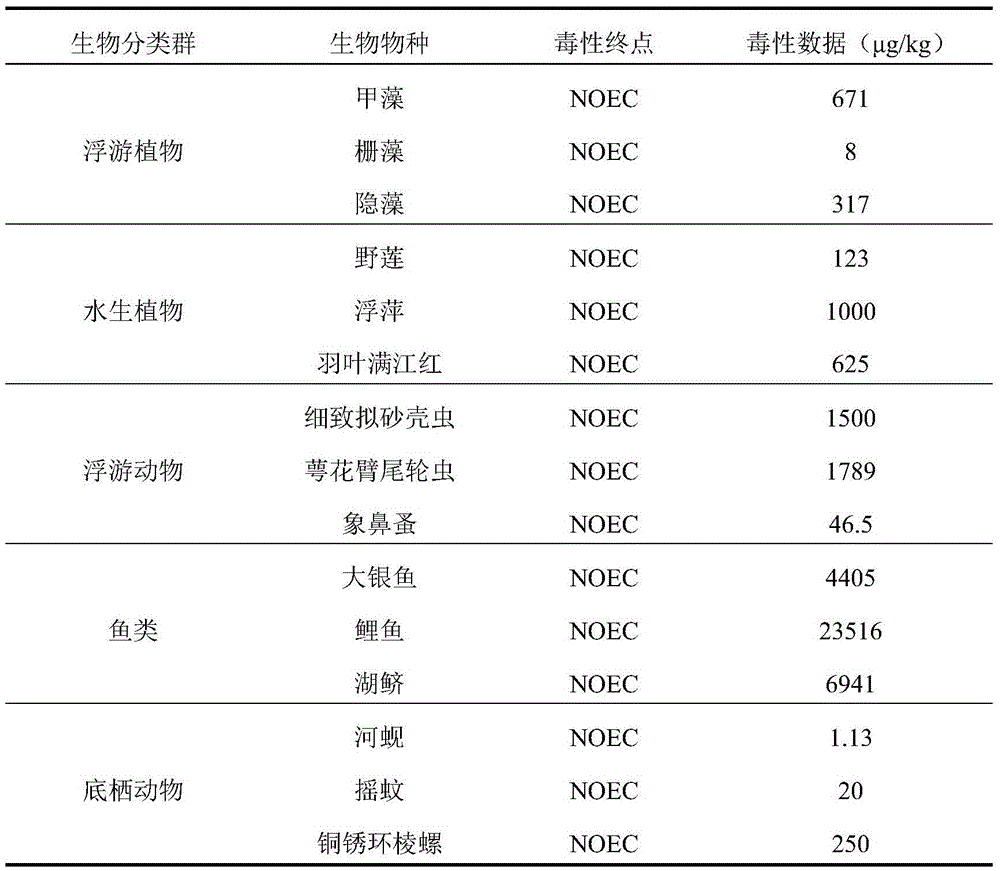
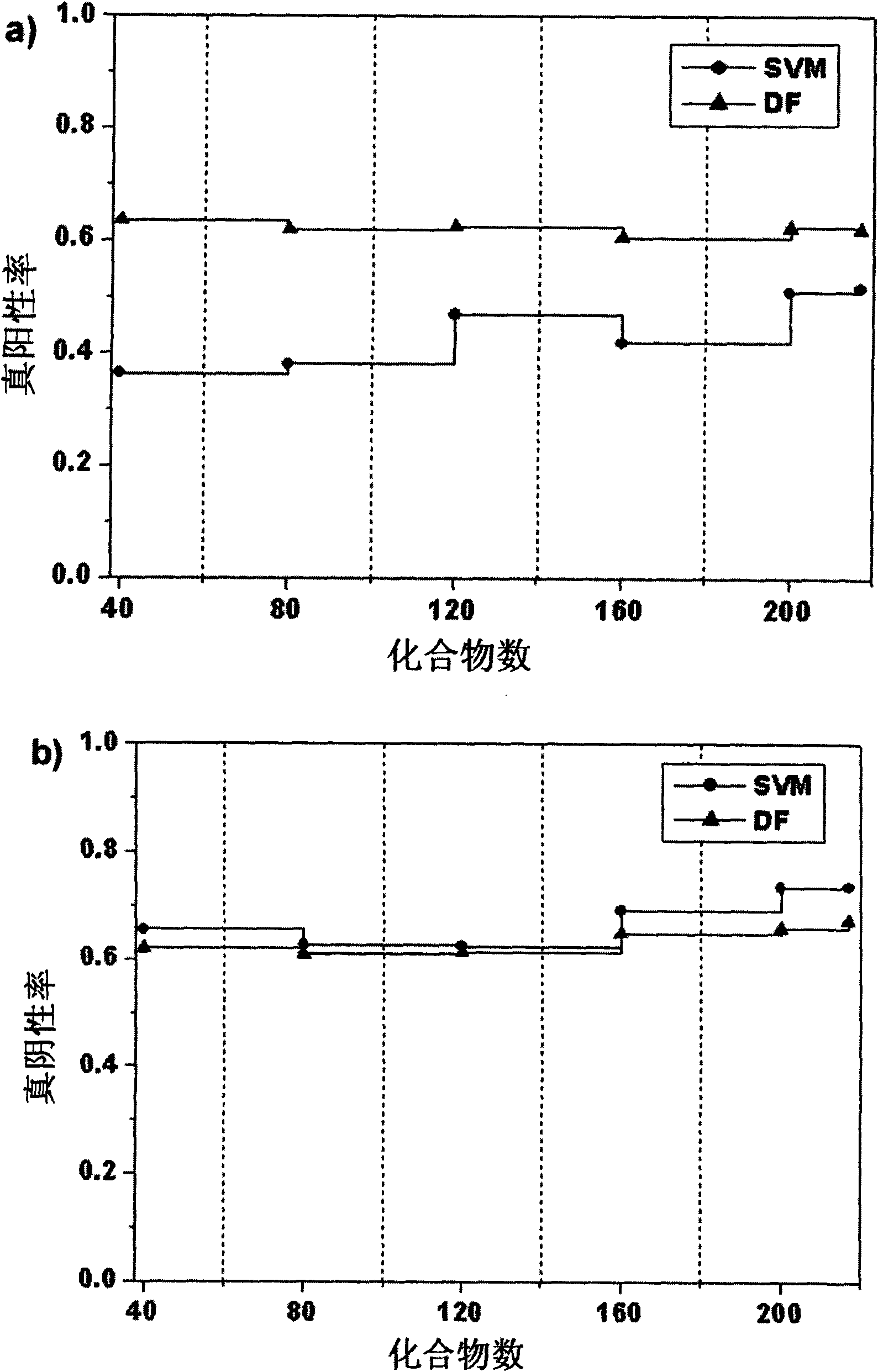
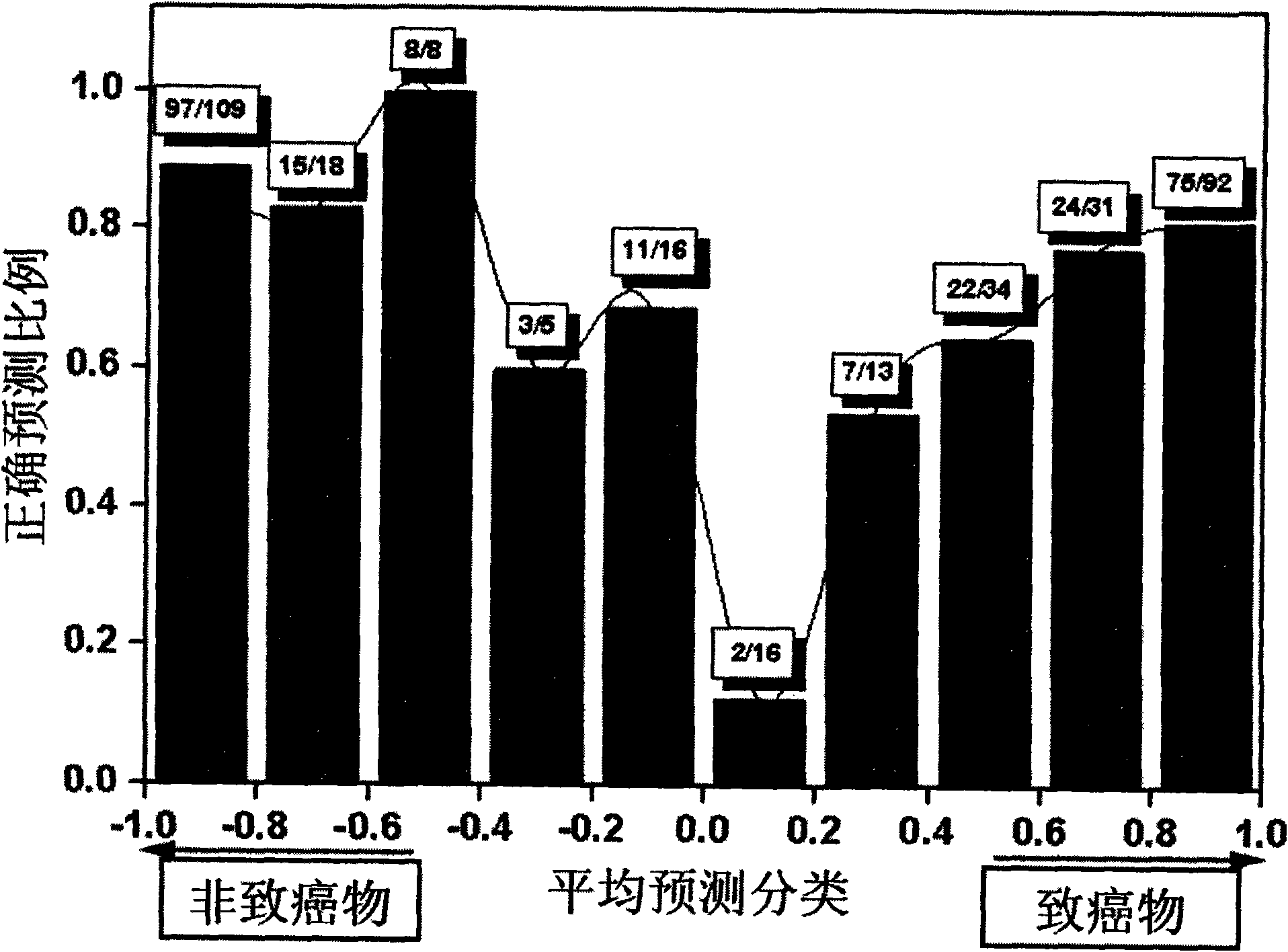
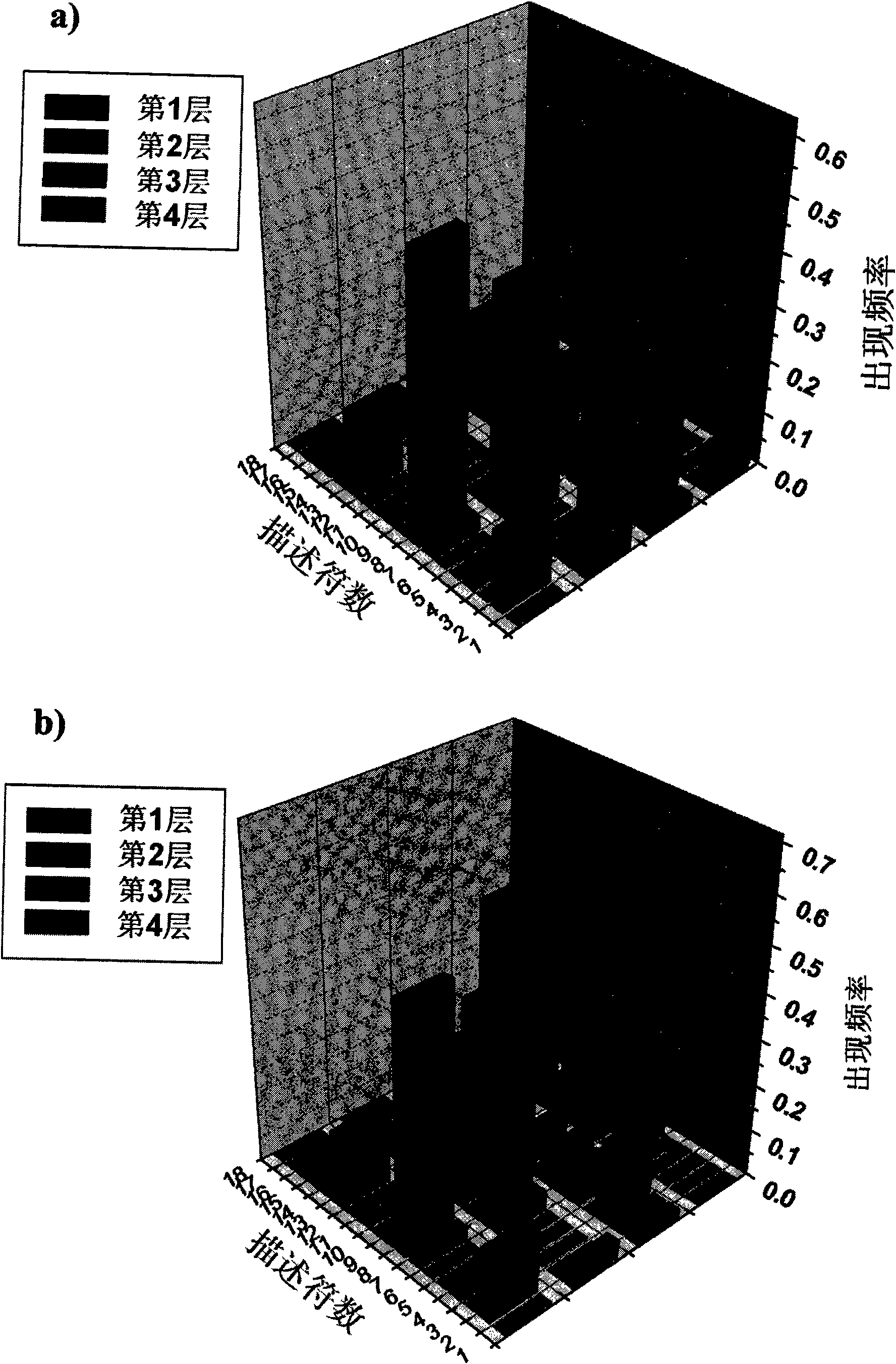
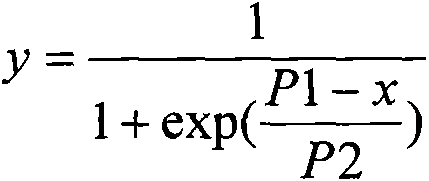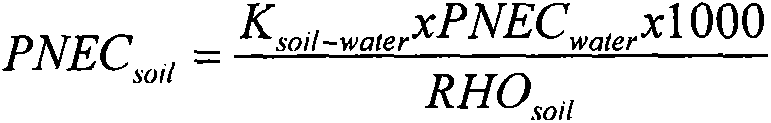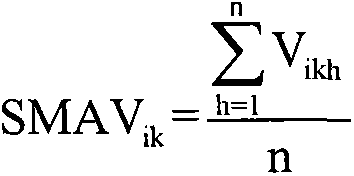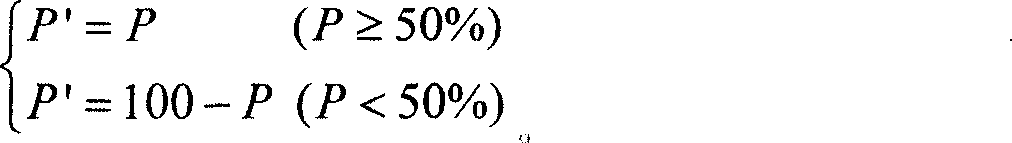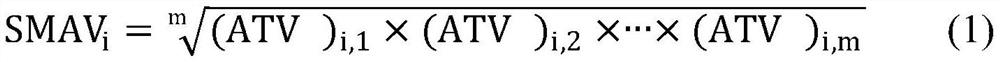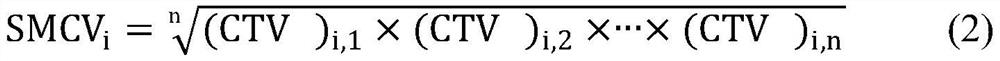Patents
Literature
70 results about "Toxicity data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
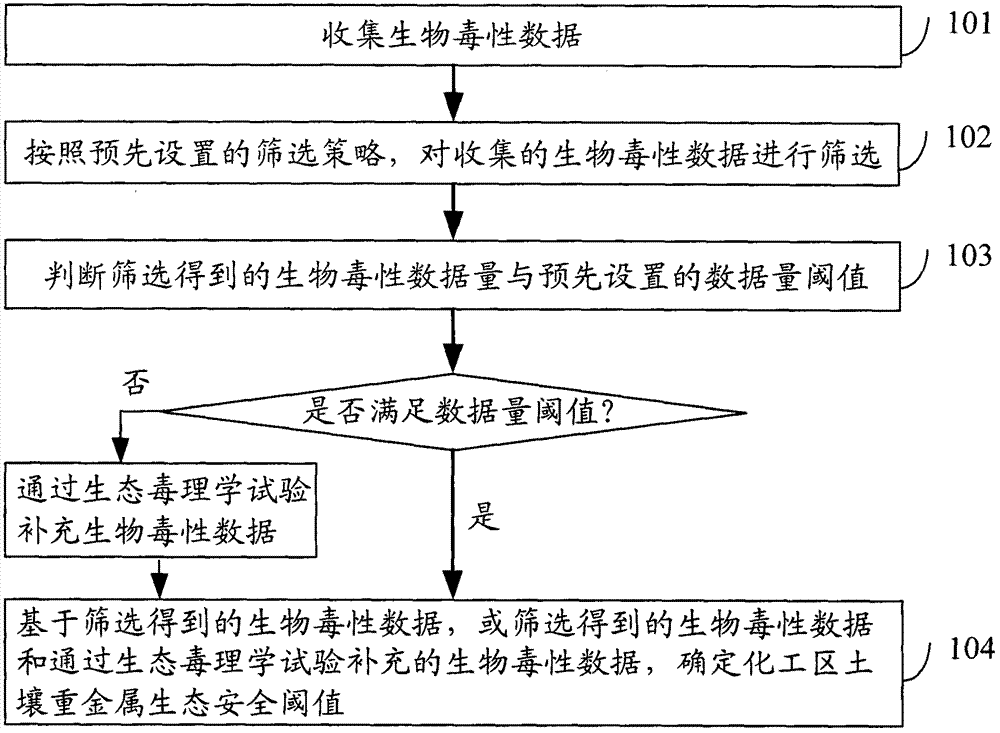
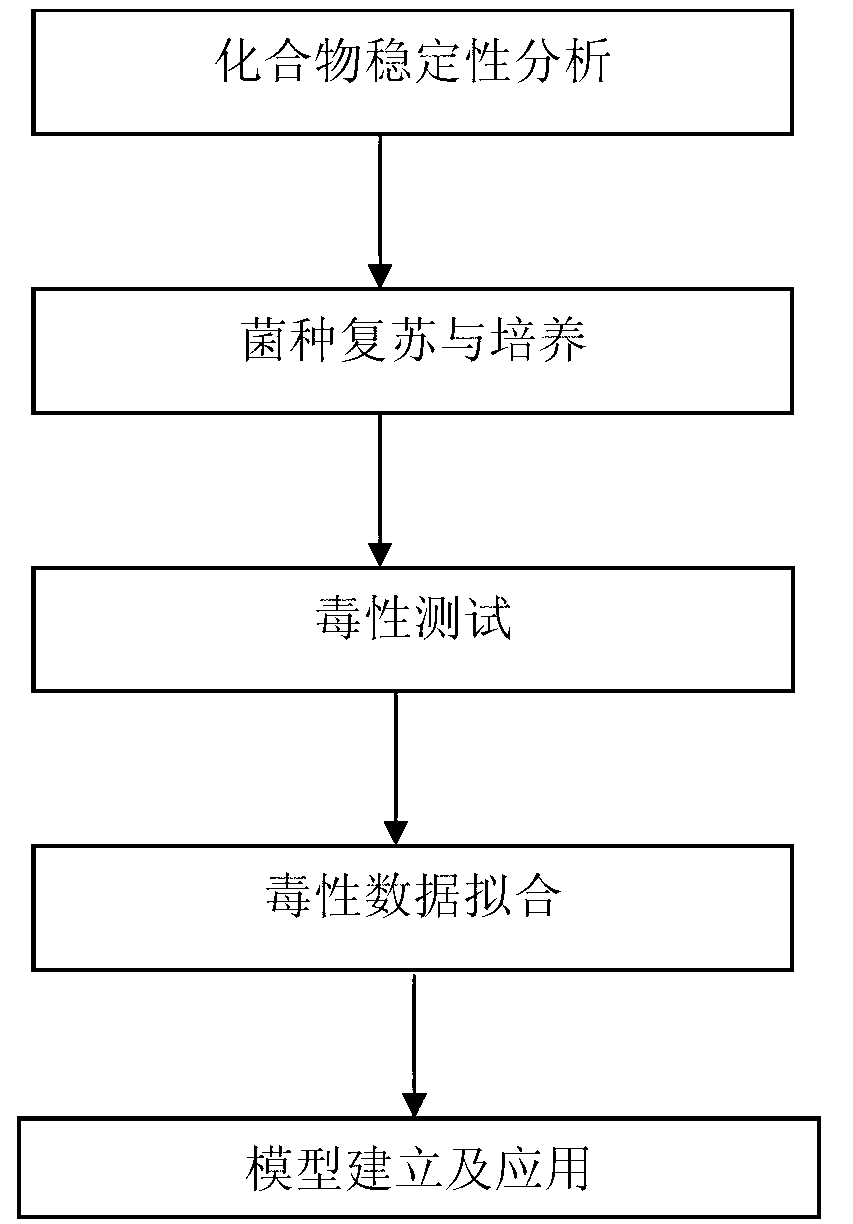
Method for determining ecological safety threshold of heavy metal in chemical engineering area
The invention discloses a method for determining an ecological safety threshold of heavy metal in chemical engineering areas. The method comprises the following steps: A1, collecting biological toxicity data; A2, screening the collected biological toxicity data according to the preset screening strategy; A3, determining whether the screened biological toxicity data quantity meets a preset data amount threshold; if it is, implementing step A4; and otherwise, supplementing biological toxicity data through the ecotoxicological test, and then implementing the step A4; and A4, based on the screened biological toxicity data, or screened toxicity data and biological toxicity data supplemented by ecotoxicological test, determining the ecological safety threshold of soil heavy metal in the chemical engineering area. The method of the invention can effectively evaluate the soil ecological risk caused by heavy metal pollutants.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
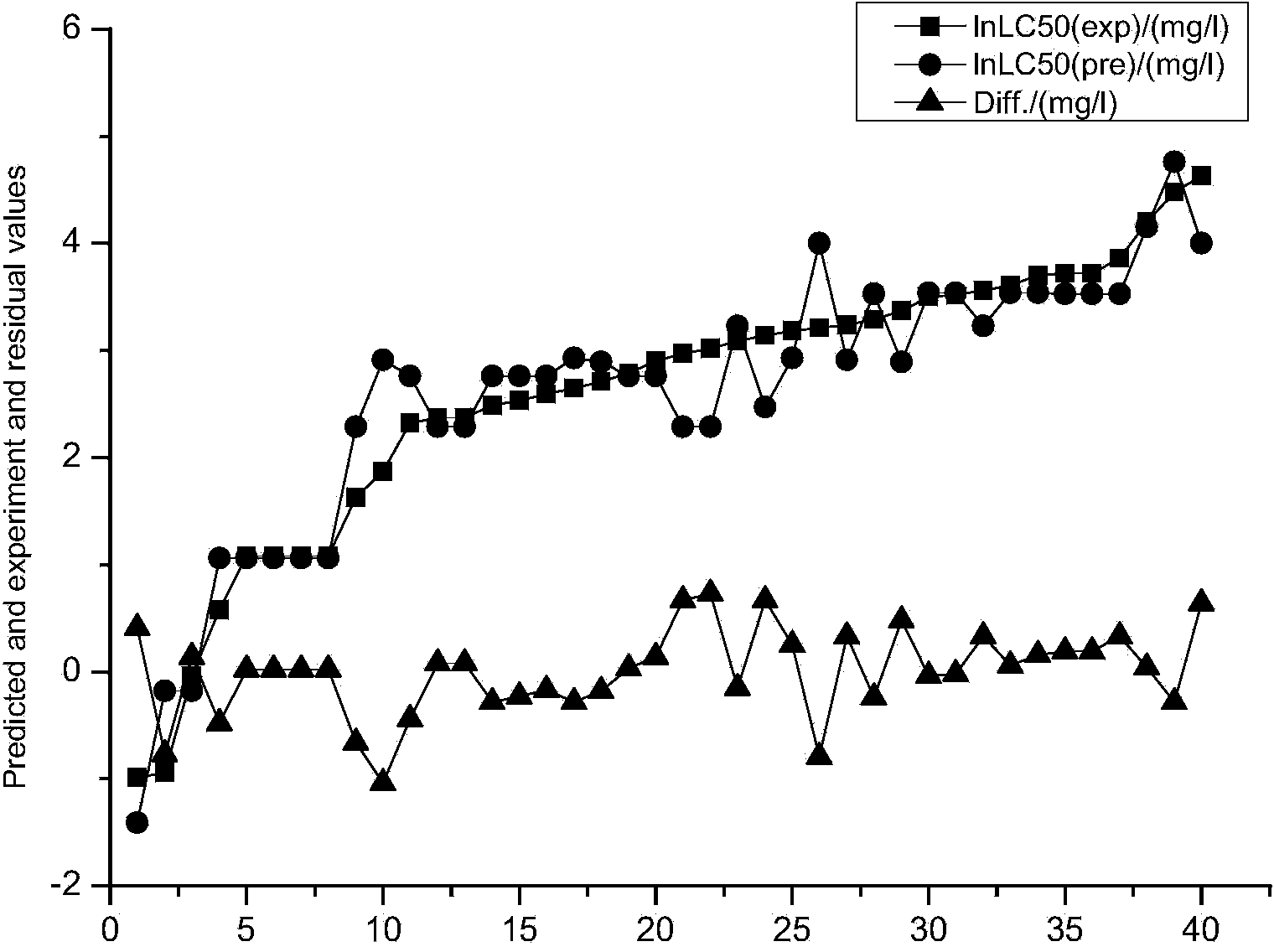
Method for forecasting acute toxicity of organic compounds by building quantitative structure-activity relationship model with quantum chemistry method
InactiveCN103646180APredict toxicityChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular orbital energyAb initio quantum chemistry methods
The invention discloses a method for forecasting the acute toxicity of organic compounds by building a quantitative structure-activity relationship model with a quantum chemistry method. The method fully geometrically optimizes compound structures by using a Gaussian procedure so as to obtain quantum chemistry parameters including molecular volume, relative molecular mass, highest occupied molecular orbital energy, lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy, energy gaps of frontier molecular orbital, dipole moment, solvation energy, electron energy and the like; using the quantum chemistry parameters and a hydrophobicity parameter as structural descriptors; in combination with toxicity data, quantitative relationship equations between various structural descriptors and toxicity are established according to a written procedure based on partial least square stepwise linear regression to obtain the multiple correlation coefficient, F-test value and sum of squared residuals, and then the model is verified so as to guarantee the external predictive ability. Therefore, the method can quickly and effectively forecast the toxicity of organic compounds to be studied, and provide necessary basic data for risk assessment and supervision of chemicals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Ecological risk assessment method of heavy metal in river basin sediment based on toxicity effect
ActiveCN105608324AAccurate reflection of riskHealth-index calculationEarth material testingEcological riskNatural abundance
The invention relates to a method for determining ecological risks, particularly to an ecological risk assessment method of heavy metal in river basin sediment based on the toxicity effect. The assessment method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, screening main aquatic organisms in the river basin, 2, sampling sediment, and determining and detecting types of heavy metal, 3, detecting the heavy metal concentration in the sediment, 4, collecting the heavy metal release coefficient, 5, collecting heavy metal toxicity data and fitting the data, 6, determining the heavy metal HC5 value according to a fitted equation, 7, calculating the heavy metal toxicity coefficient, 8, calculating the heavy metal toxicity response coefficient, and 9, calculating the heavy metal ecological risk index, and the method can further comprise a step 10 of calculating the comprehensive ecological risk index of various types of heavy metal. Compared with the prior art that the crustal abundance is adopted to indirectly and roughly estimate the metal toxicity effect, the assessment method provided by the invention can more accurately reflect the ecological risks, caused by the heavy metal in the sediment, to the aquatic organisms in the river basin.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for predicting compound carcinogenic toxicity based on complex sampling and improved decision forest algorithm
InactiveCN101587510AEquilibrium predictive powerSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual screeningAlgorithm
The invention relates to a method for predicting compound carcinogenic toxicity based on complex sampling and an improved decision forest algorithm. The method is suitable for calculating carcinogenic toxicity evaluation and virtual selection on a compound according to an organic small molecular structure, and comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting a relative force field to molecules with the molecular structure to carry out optimization and charge calculation, carrying out complex sampling to the compound with centralized original training to be used for generating a training subset, and fixing various relative descriptors in composition calculation molecules of descriptors according to a complex sampling algorithm result; secondly, optimizing a descriptor pool by using a method based on relative matrix analysis and factor analysis; and finally, carrying out data mining on carcinogenic toxicity data and corresponding chemical characteristics thereof of training set molecules by using the improved decision forest method to obtain a classified prediction confidence interval, a carcinogenic toxicity prediction mold and a judgment rule. The method has favorable application prospect in high throughput virtual selection and calculating the carcinogenic toxicity evaluation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in river basin sediment based on toxicity effect
ActiveUS20190004024A1Not at risk of errorHealth-index calculationEarth material testingEcological riskToxicity data
A method for determining ecological risk, particularly a method for the ecological risk assessment of a heavy metal in a river basin sediment based on a toxicity effect. The assessment method includes screening the main aquatic organisms in a river basin; sampling a sediment, and determining and detecting the heavy metal type; measuring the concentration of the heavy metal in the sediment; collecting the heavy metal release coefficient; collecting the heavy metal toxicity data and fitting the data; determining the heavy metal HCsi value according to a fitting equation; calculating the heavy metal toxicity response coefficient; calculating the ecological risk index of the heavy metal. This method can further include calculating the comprehensive ecological risk index of various types of heavy metals. The method can accurately reflect the ecological risk of a heavy metal on aquatic organisms in a river basin.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
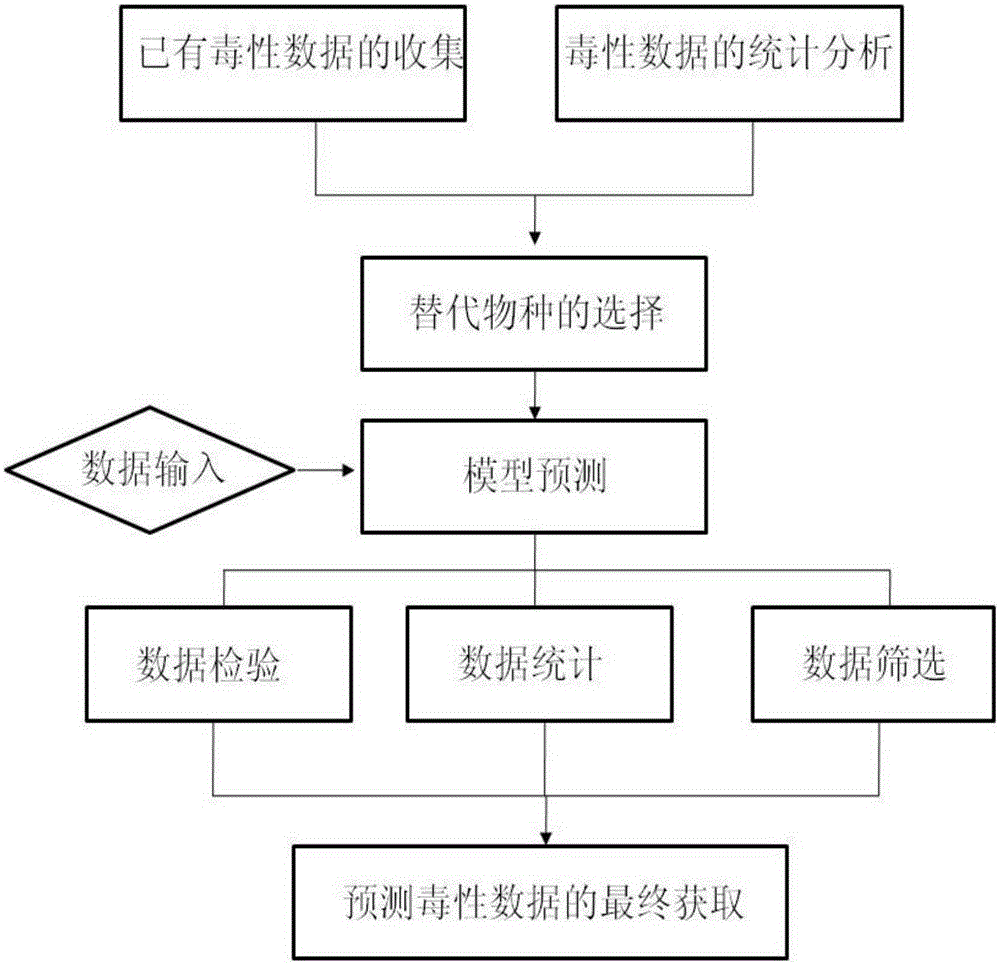
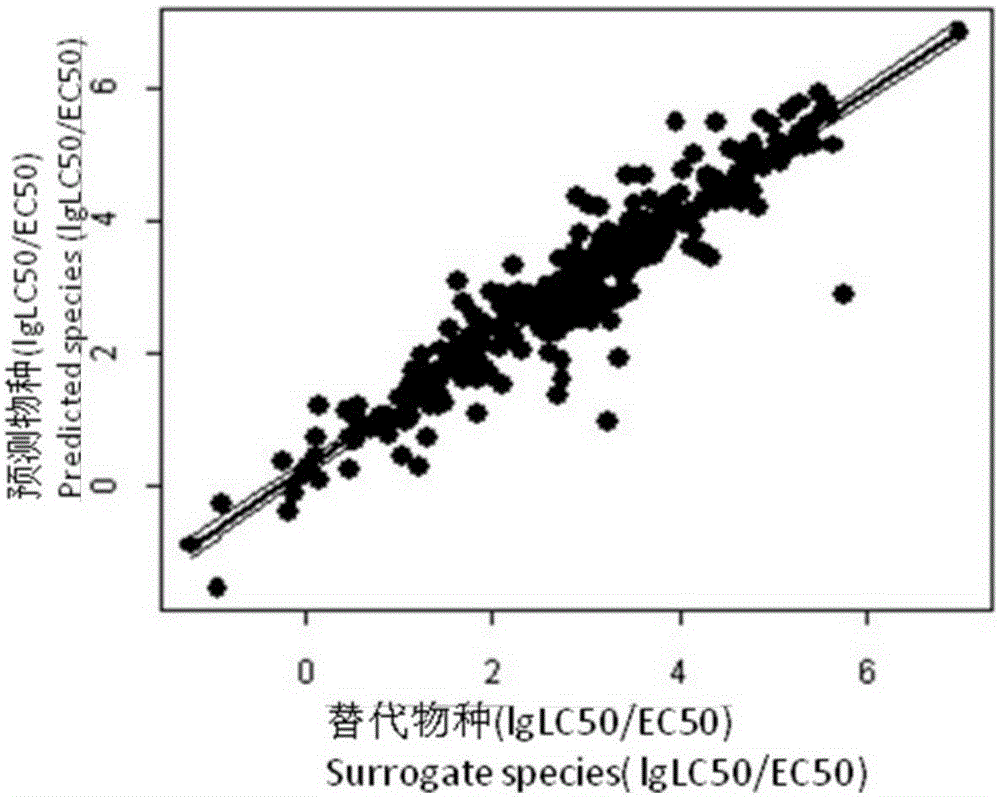
Model-estimation-based biological toxicity estimation method
InactiveCN105205322AAvoid damageReduce pollutionSpecial data processing applicationsWater qualityToxic material
The invention relates to the field of estimation of toxic substances in environments, and specifically discloses a model-estimation-based biological toxicity estimation method, which comprises the following steps of 1, selecting a surrogate species; 2, performing toxicity estimation to obtain toxicity data of an unknown species by virtue of the surrogate species; 3, screening estimation data. The biological toxicity estimation method is applied to toxicity researches on species, and a water quality criterion deduction case research on zinc laterally proves feasibility in toxicity estimation of a species with an ICE (Interspecies Correction Estimation) model, so that the problem of incapability of accurately deducing a water quality criterion due to insufficient toxicity data of a part of pollutants is solved; damage to an experimental organism is avoided, and environmental pollution is reduced, so that a rapid, simple and environment-friendly biological toxicity research method is provided; under the condition of water quality criterion and risk assessment and the like with a requirement on a large amount of biological toxicity data for analysis, if data of a part of pollutants is insufficient, the toxicity estimation method is more economical and convenient.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
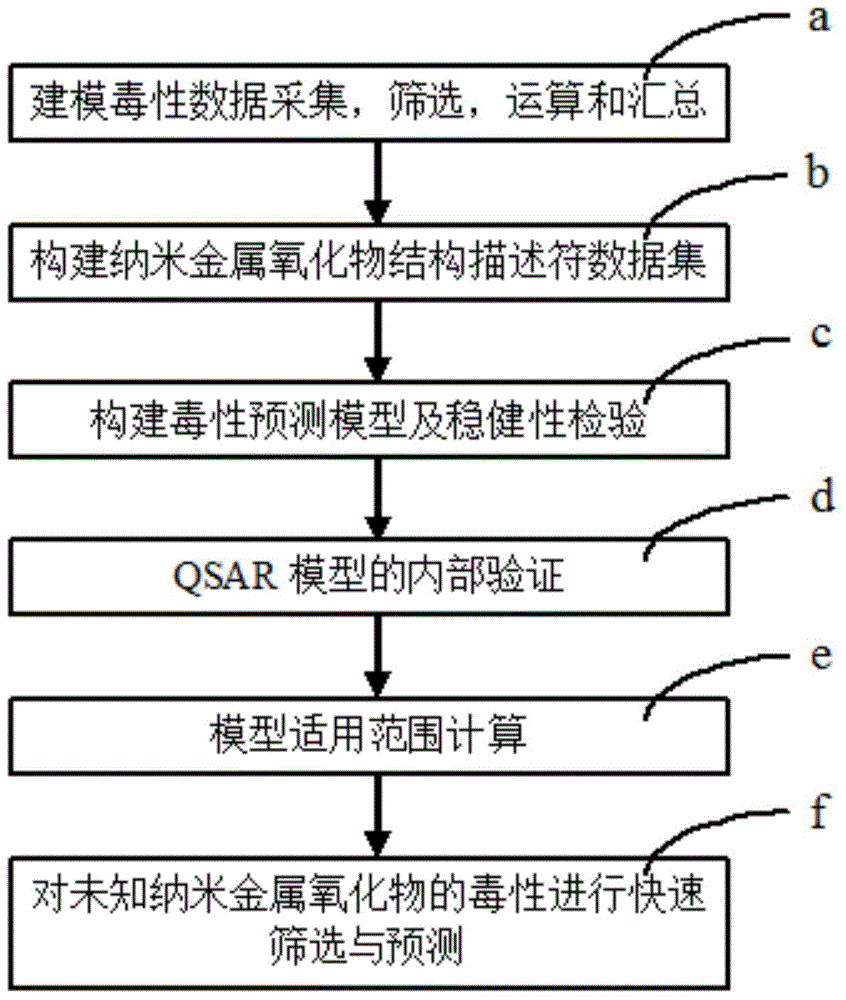
QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) toxicity prediction method for evaluating health effect of nano-crystalline metal oxide
The invention relates to the field of toxic substance prediction in an environment, in particular to a QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) toxicity prediction method for evaluating the health effect of nano-crystalline metal oxide. The method comprises the steps of predicting the toxicity endpoint of unknown metallic oxide according to a quantitative relation between structural features and cytotoxicity effect of the nano-crystalline metal oxide; building a nano-crystalline metal oxide prediction model by combining the physicochemical structure parameter and a special mechanism of toxication of the nano-crystalline metal oxide, and applying the nano-crystalline metal oxide prediction model to predict the toxicity endpoint of the unknown metallic oxide. According to the QSAR toxicity prediction method provided by the invention, based on a function model and the toxicity prediction method of the nano-crystalline metal oxide, and the nano-crystalline metal oxide prediction model can be built to predict an unknown toxicity value through the QSAR model method, therefore the toxicity endpoint prediction of various compounds lack of toxicity data can be completed quickly and simply with less dependency.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
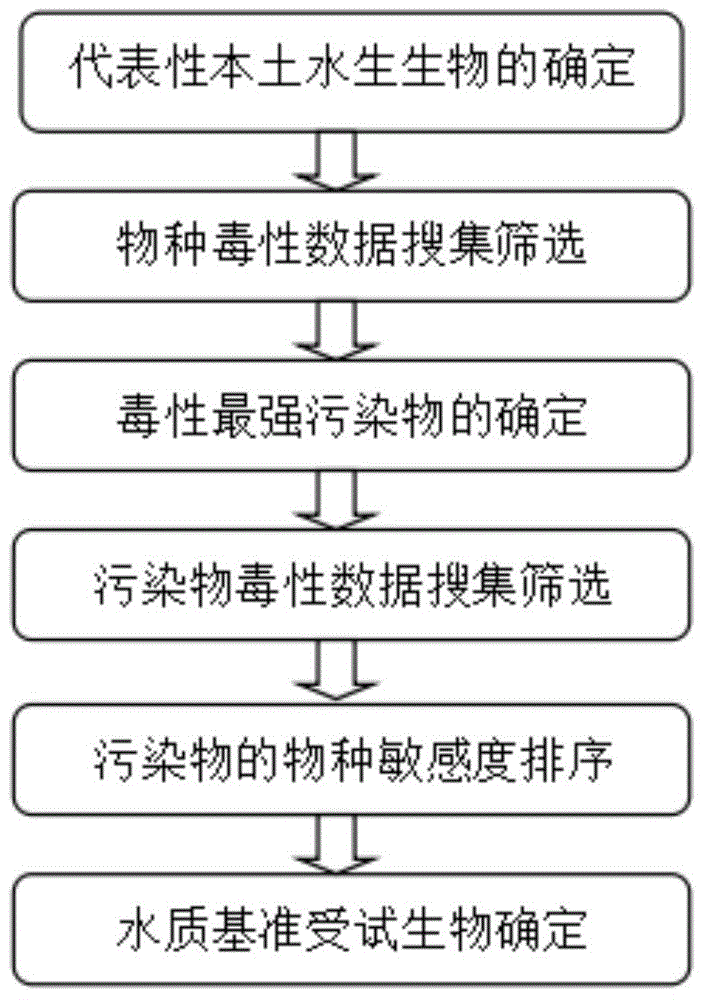
Method for screening water quality criteria testing organism
The invention discloses a method for screening a water quality criteria testing organism. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, determining a local representative aquatic organism; 2, collecting and screening species toxicity data, and determining a pollutant with the highest toxicity; 3, collecting and screening the toxicity data of the pollutant, and sequencing the species sensitivity of the pollutant; 4, determining the water quality criteria testing organism. By adopting the method, the water quality criteria testing organism can be quickly determined, and the support is provided for national water environment protection and water quality criteria study.
Owner:闫振广
Determination method for ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in water body
InactiveCN103645286AResolve uncertaintyAchieving Cumulative RiskGeneral water supply conservationTesting organic contamination in waterPyreneEnvironmental geology
The invention discloses a determination method for ecological risks of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in a water body and belongs to the field of determination of ecological risks. The determination method comprises the following steps: (1) representative species of a water ecological system in a region are screened; (2) toxicity data of benzoapyrene is obtained; (3) benzoapyrene concentration values HC5 of 95% of species of the water ecological system are calculated; (4) the varieties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants and corresponding environmental concentrations are determined by sampling and concentration distribution characteristics of various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are analyzed; (5) ecological risk quotient values RQi of the specific polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants are calculated; and (6) a total ecological risk quotient value RQt is calculated and the specific ecological risks are defined. According to the determination method, whether potential risks of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants can be accepted or not can be analyzed and whether the total level of the ecological risks of the water body needs to be controlled or not can be judged so that scientific evidences and the like is provided for making protection measures for the water ecological system and making control measures for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
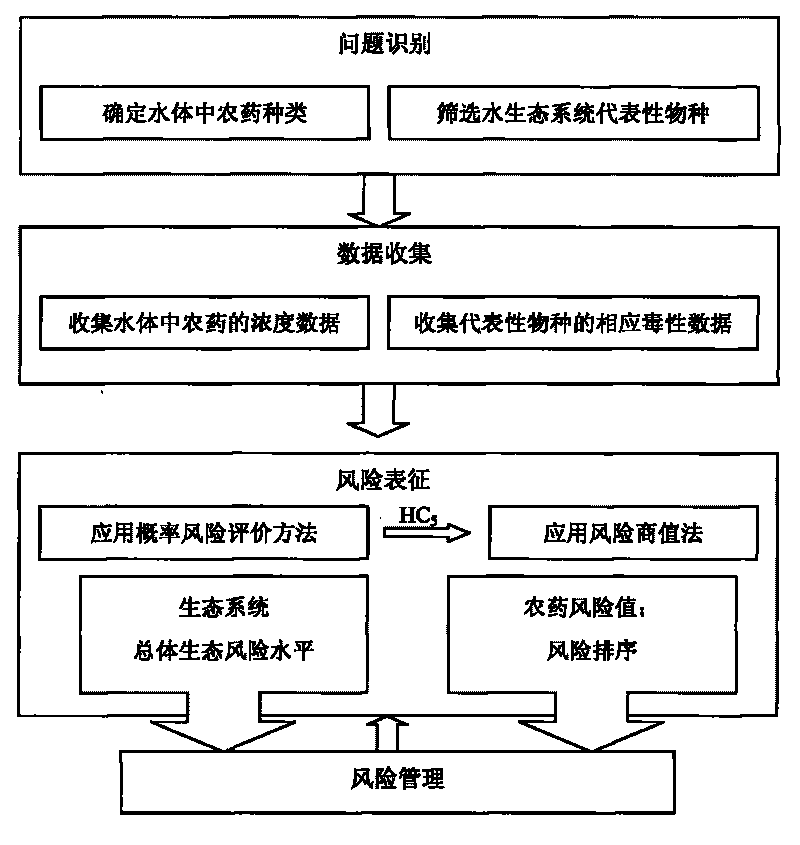
Method for identifying ecological risks of pesticides in water body
ActiveCN101713774AEasy to operateTesting waterSpecial data processing applicationsAquatic ecosystemEcological risk
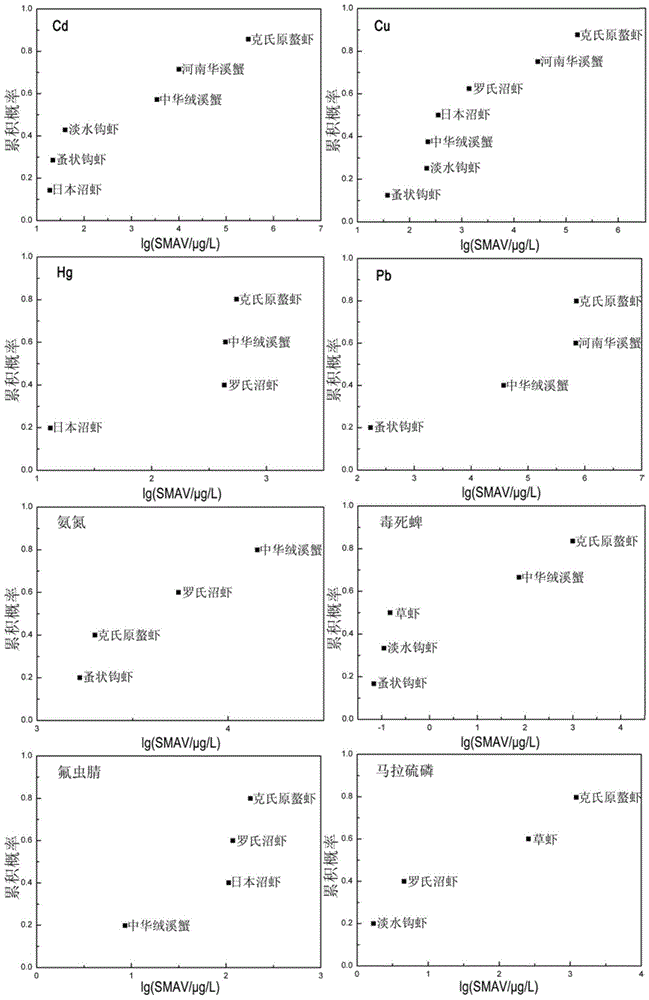
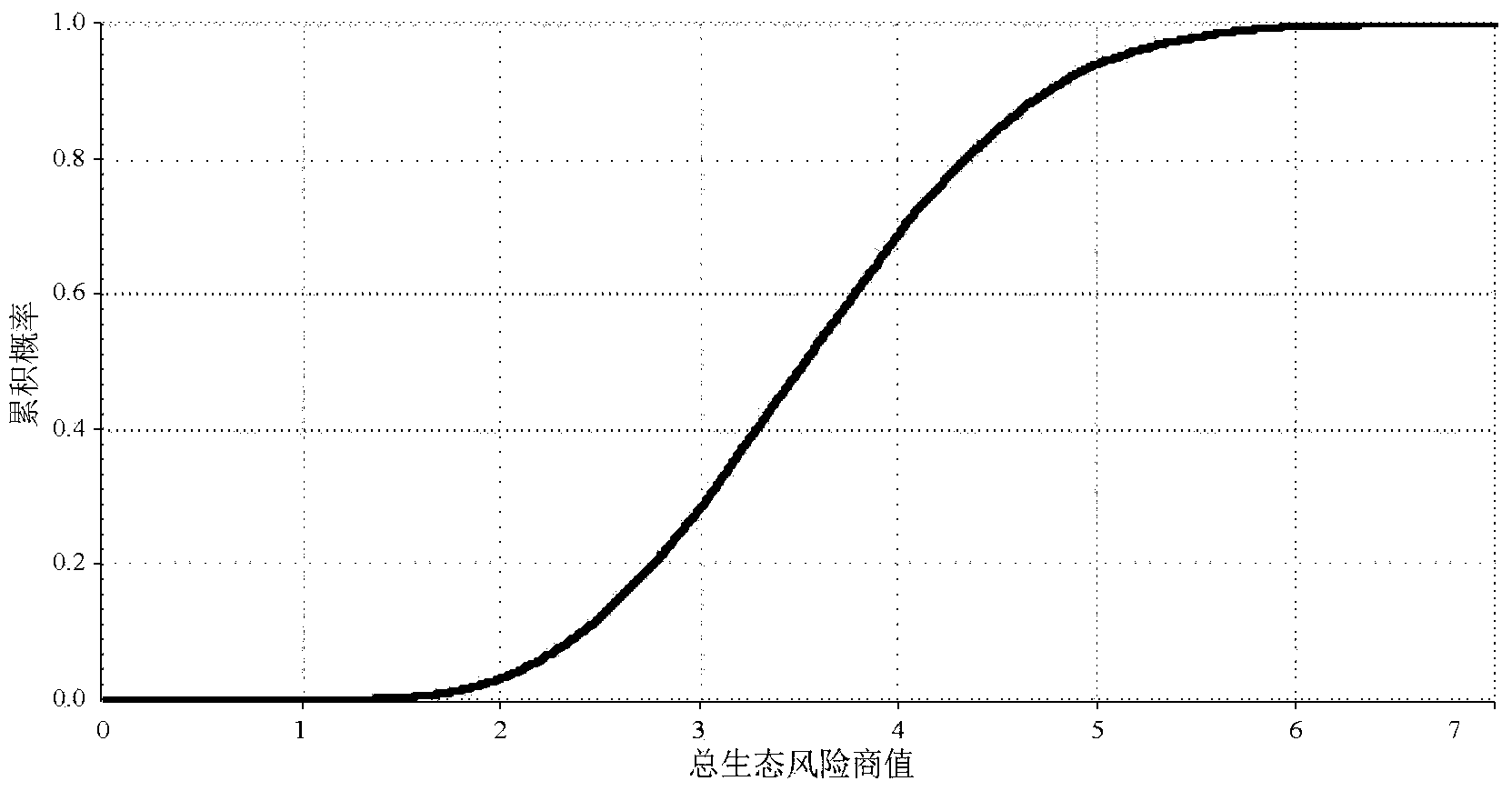
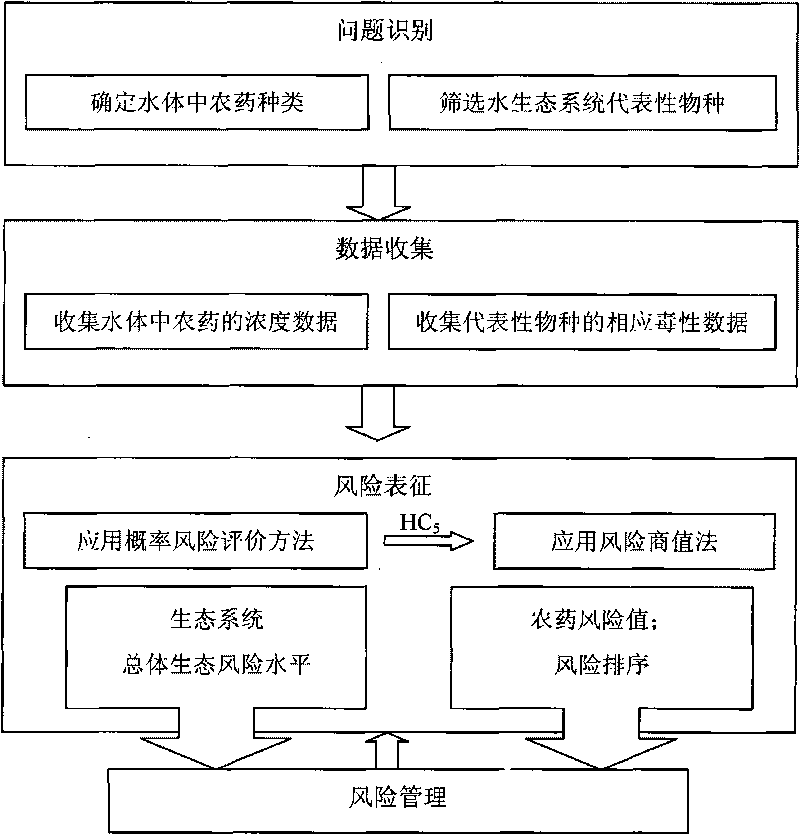
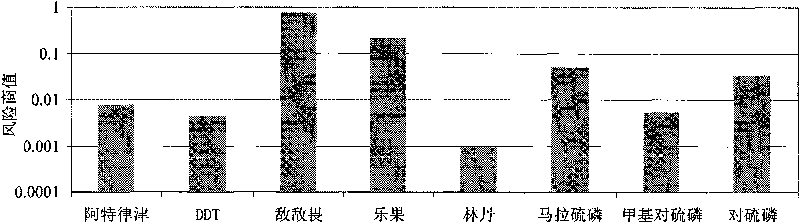
The invention discloses a method for identifying ecological risks of pesticides in water body, and belongs to the field of ecological risk identification. The method comprises the following steps: determining the types of the pesticides in the water body; screening representative biological species in an aquatic ecosystem; acquiring toxicity data of the pesticides in an area to be identified; andcalculating a concentration value HC5 for protecting 95 percent of the species in the aquatic ecosystem by a probability risk assessment method; calculating risk quotients of various pesticides and performing risk prioritizing; applying the toxicity data to the probability risk assessment method to calculate the total level of the ecological risks of the pesticides in the area to be identified; and identifying according to a result. The method combines the conventional risk quotient method and probability risk assessment method, and realizes the quantification of the total level of the ecological risks of the pesticides in the water body by screening the representative biological species in the aquatic ecosystem and utilizing less toxicity data so as to provide decisive basis for protecting the aquatic ecosystem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method and system for generating spatially and temporally controllable concentration gradients
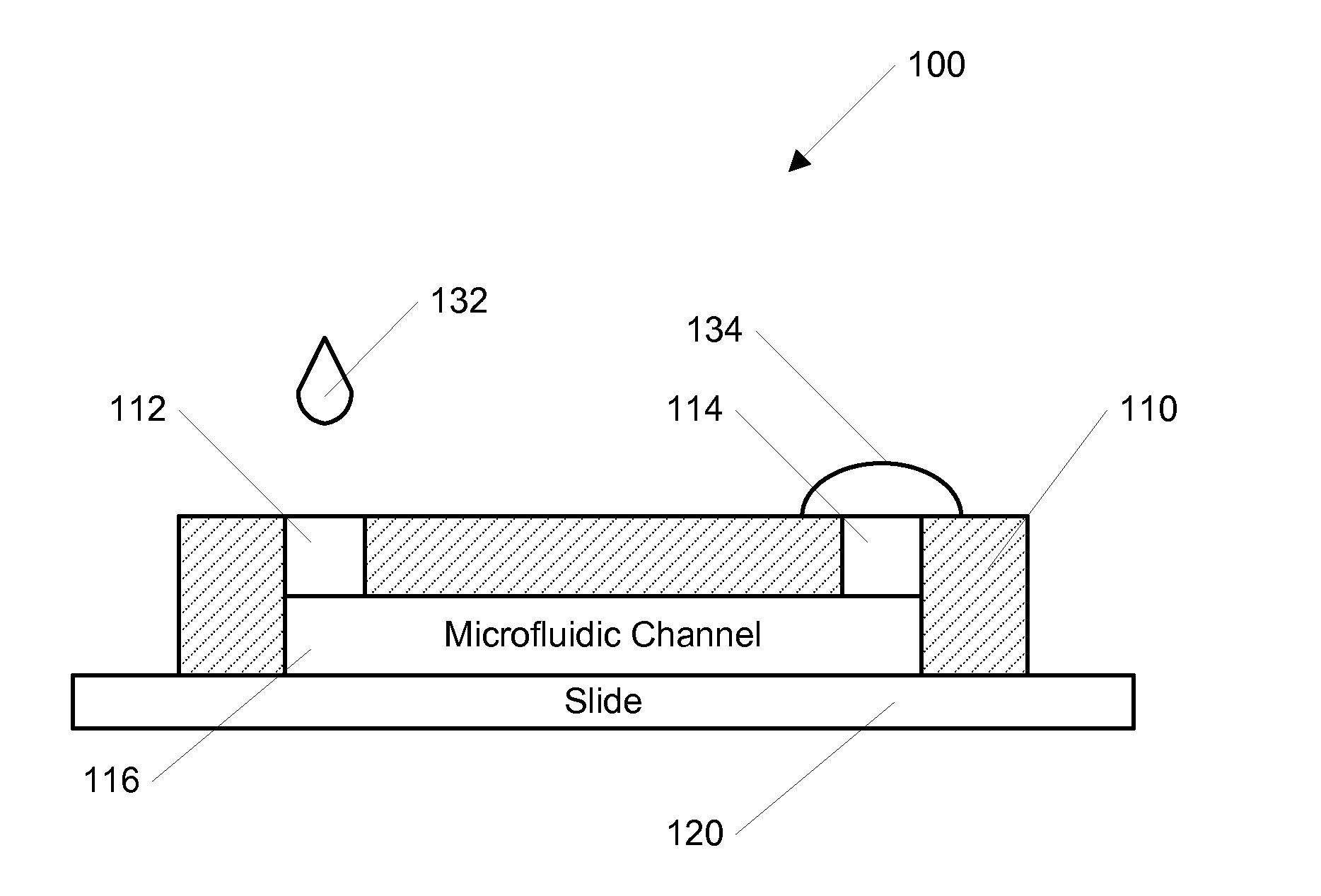
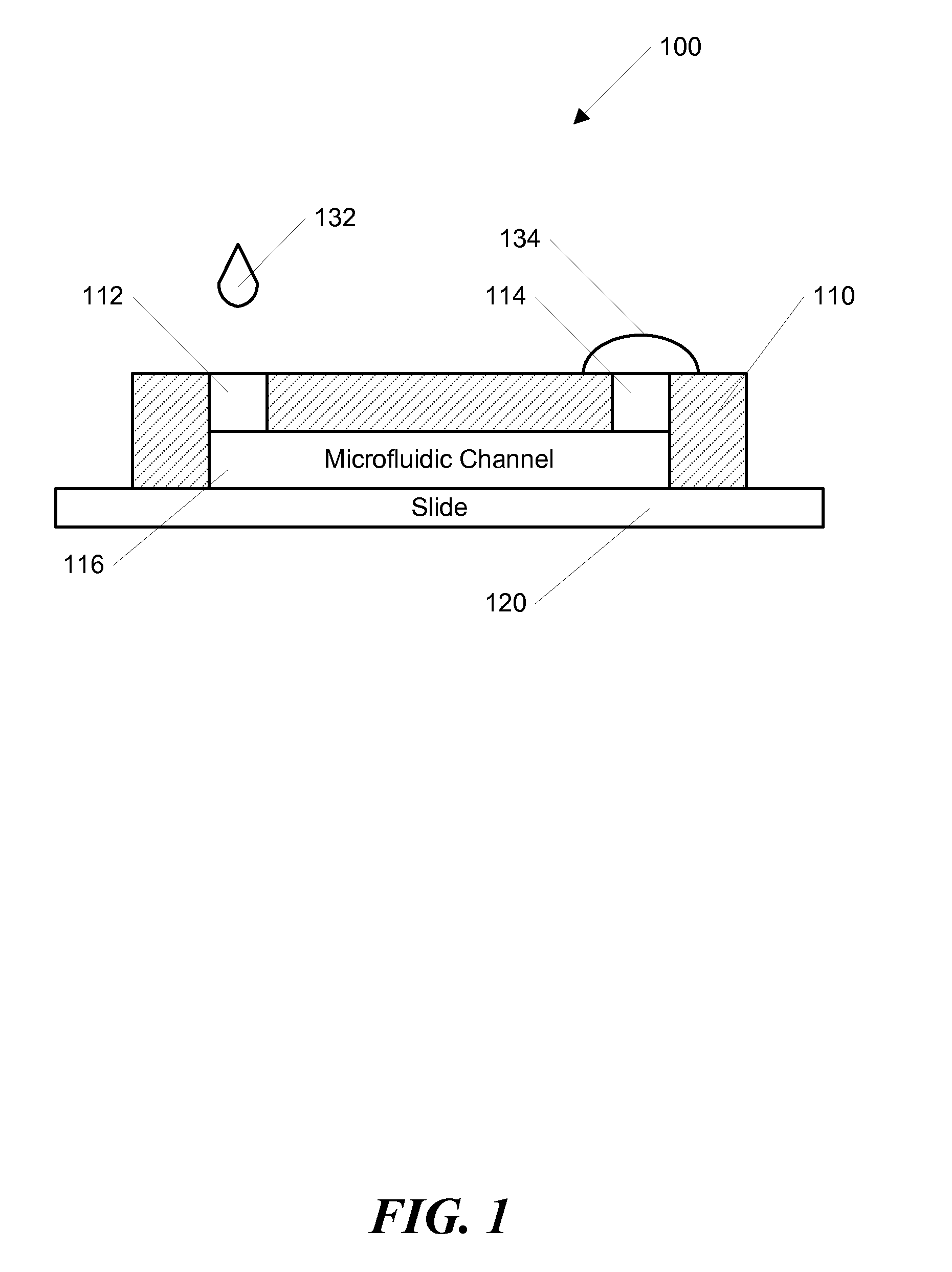
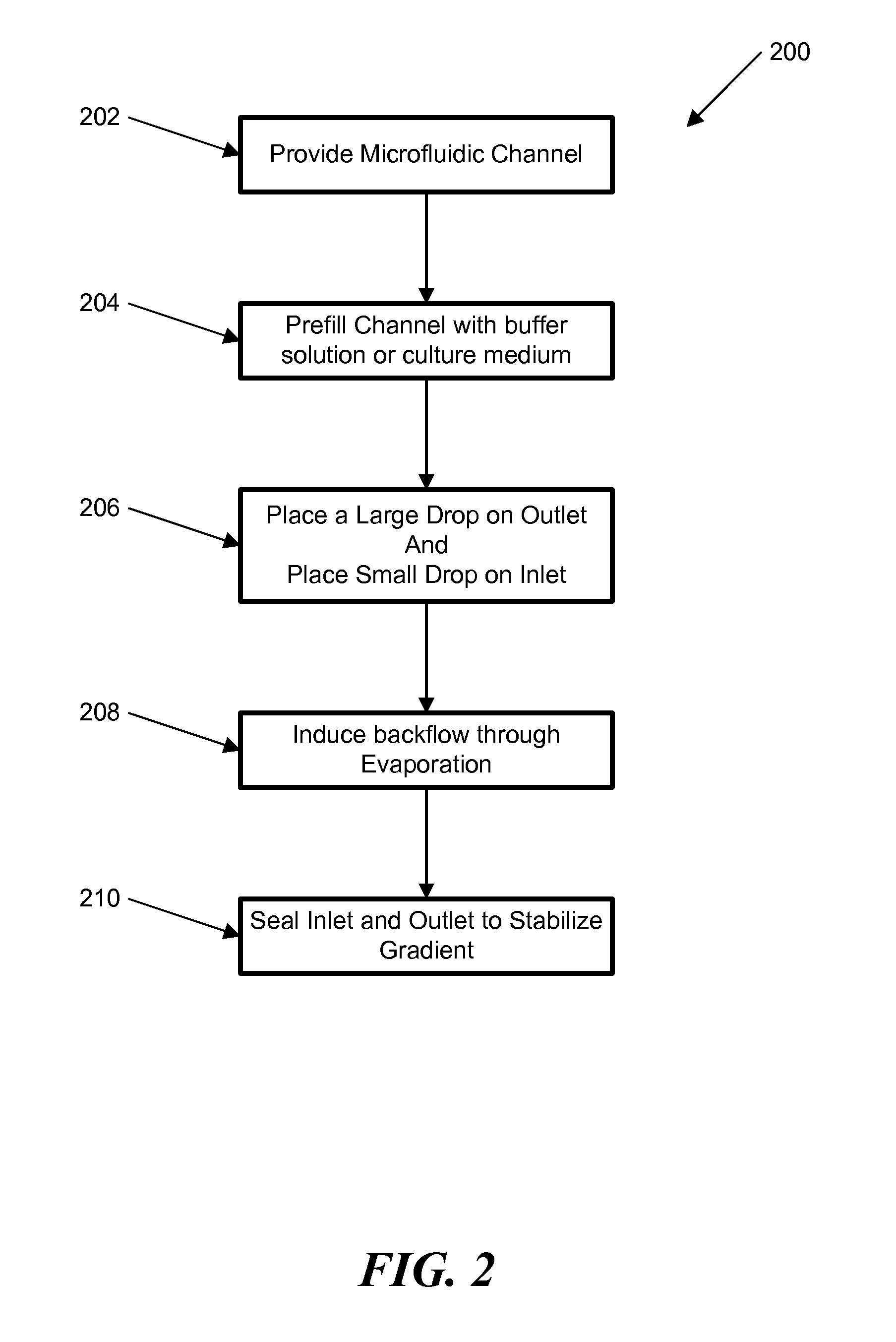
InactiveUS20110300570A1Regulate cellular responseProfile can be stabilizedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological studiesCardiac cell
The ability to rapidly generate concentration gradients of diffusible molecules has important applications in many chemical and biological studies. The present invention is directed to methods and systems for generating spatially and temporally controllable concentration gradients of molecules (i.e. proteins or toxins) in a portable microfluidic device. The formation of the concentration gradients can be initiated by an induced forward flow and further optimized during an induced backward flow. The forward and backward flows can be either passively induced and / or actively pumped. The centimeter-length gradients along the microfluidic channel can be spatially and temporally controlled by the backward flow. The gradient profile was stabilized by stopping the flow. In one example, a stabilized concentration gradient of a cardiac toxin, Alpha-cypermethrin, generated according to the invention was used to test the response of HL-1 cardiac cells in the microfluidic device, which correlated with toxicity data obtained from multi-well plates. The invention can be useful for bio-logical and chemical processes that require rapid generation of concentration gradients in a portable microfluidic device.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
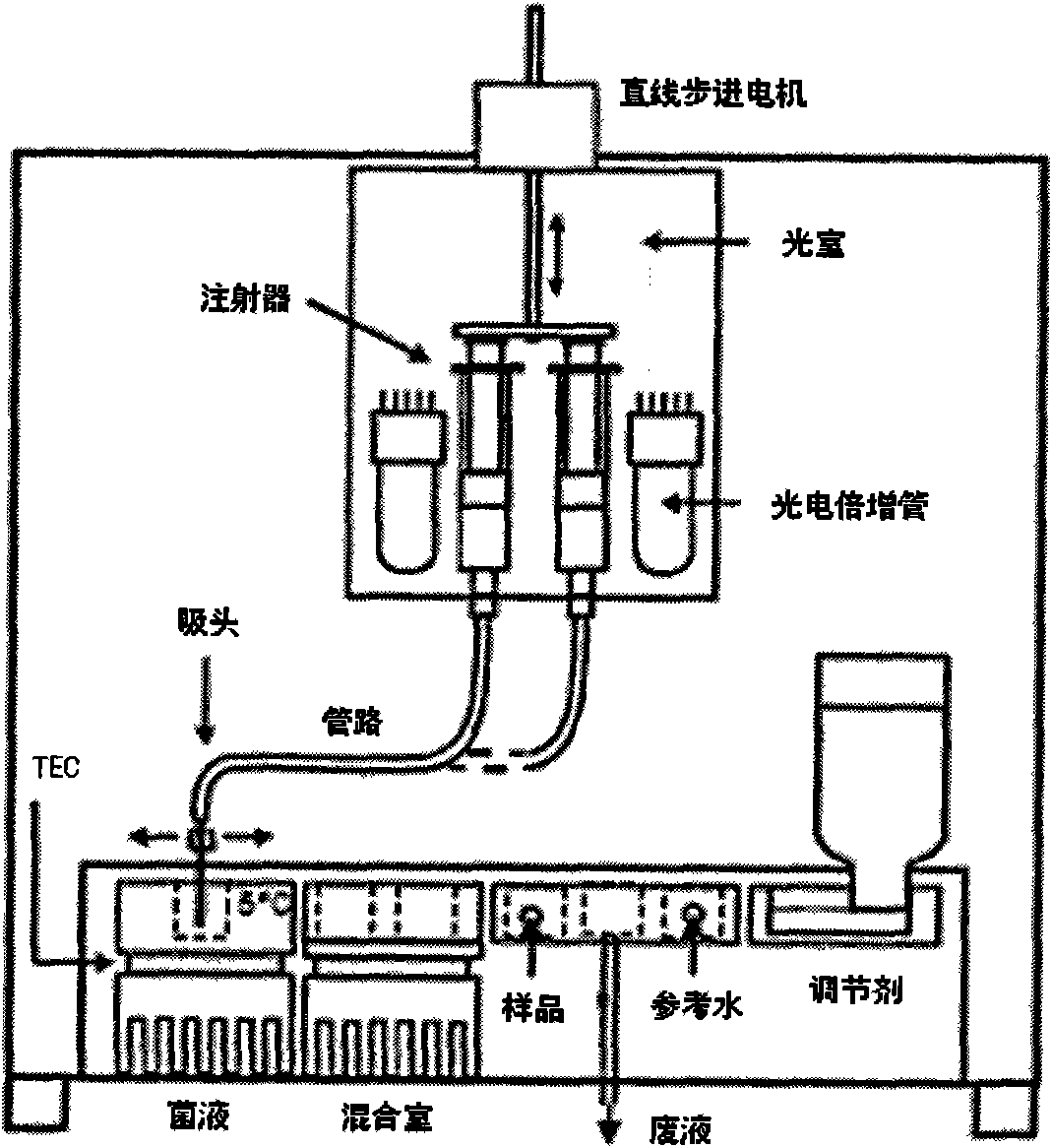
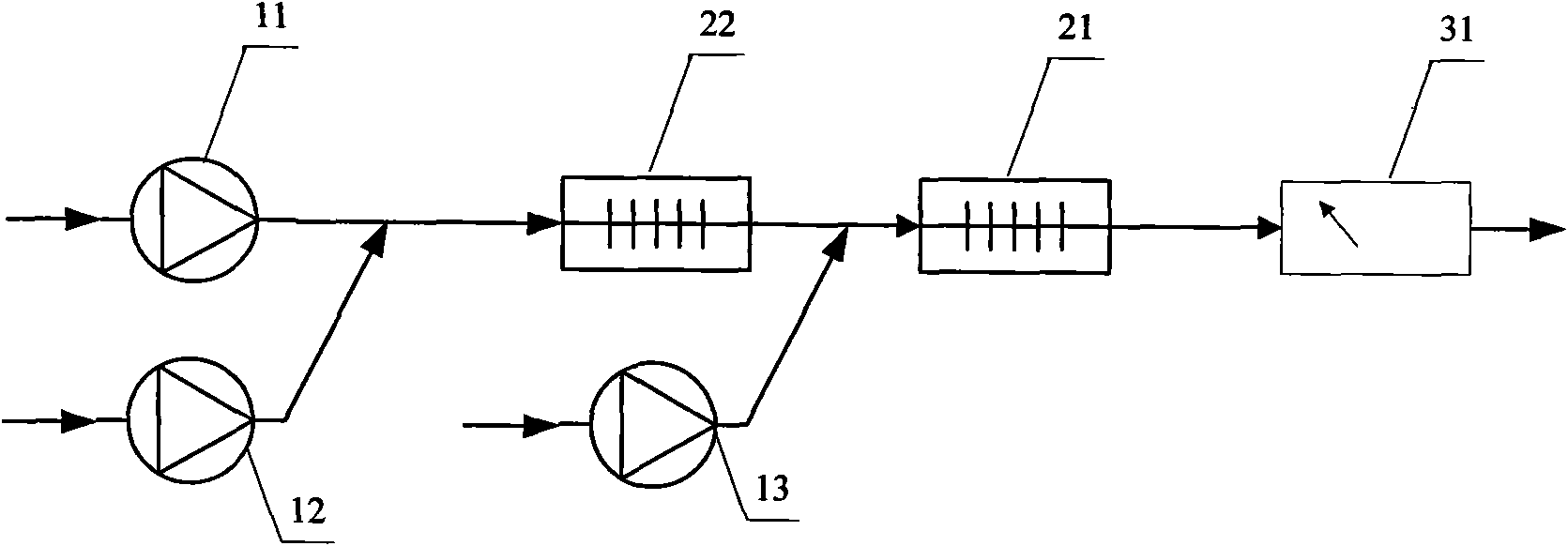
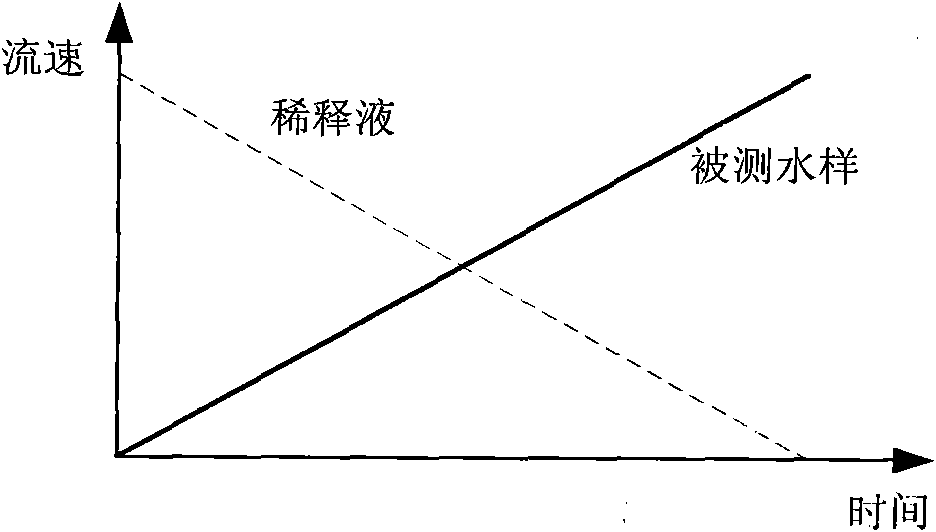
Method and device for analyzing water toxicity
ActiveCN101936910AEnables serially varying dilutionsGranular and rich toxicity measurementsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDiluentWater quality
The invention relates to a method for analyzing water toxicity, which comprises the following steps: a, introducing a tested water sample and diluents into an analysis flow path, and adjusting the flow ratio of the tested water sample and the diluents to obtain water samples of different dilutions; b, introducing test solution into the analysis flow path, and mixing the test solution and the water samples of different dilutions to obtain mixed solution; and c, testing and analyzing the signal of the mixed solution to acquire toxicity data corresponding to the water samples of different dilutions and determining the toxic characteristics of the tested water sample. The invention also provides a device for implementing the method. The method and the device can determine the toxic characteristics of the tested water sample comprehensively.
Owner:云南聚光科技有限公司
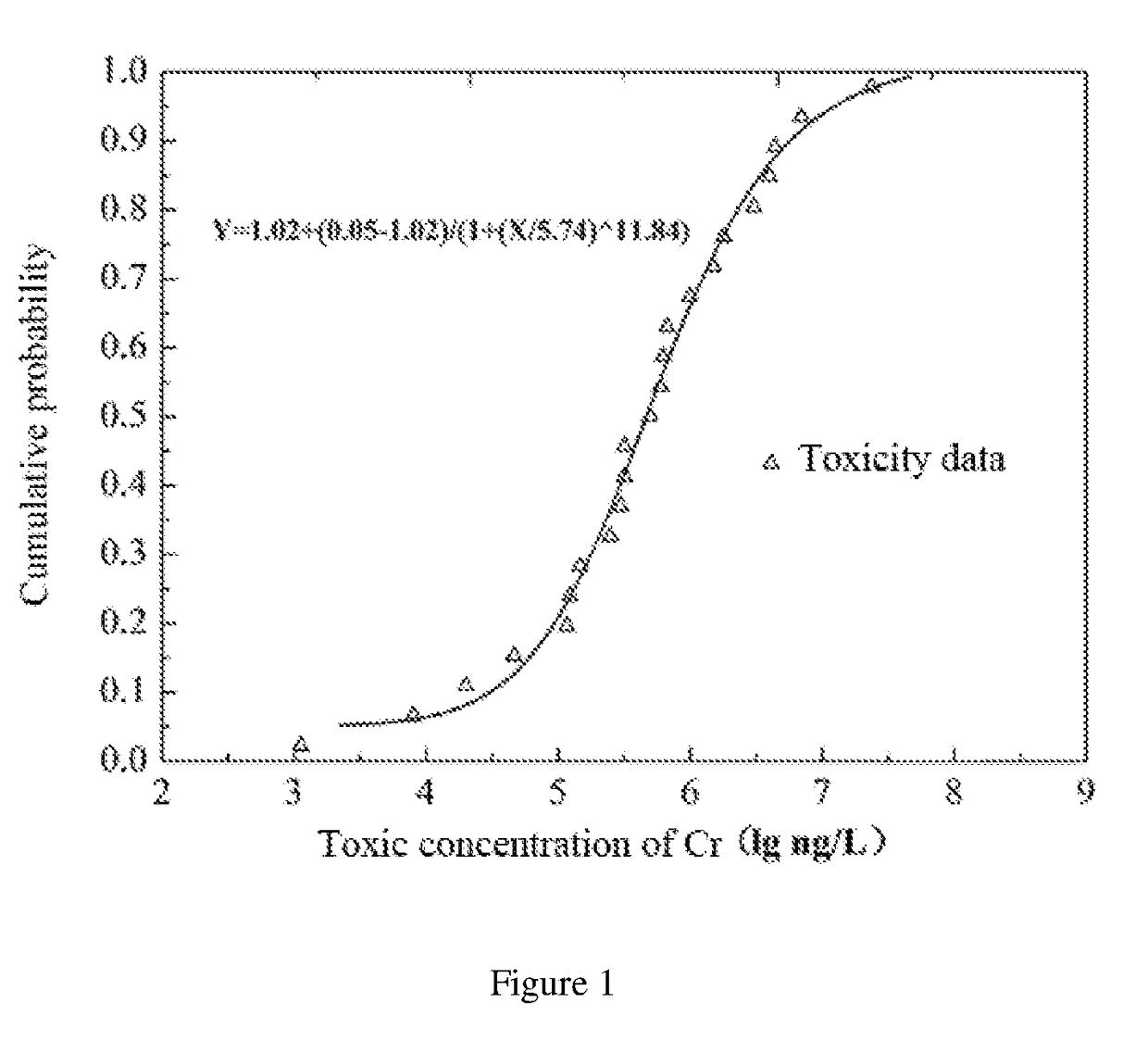
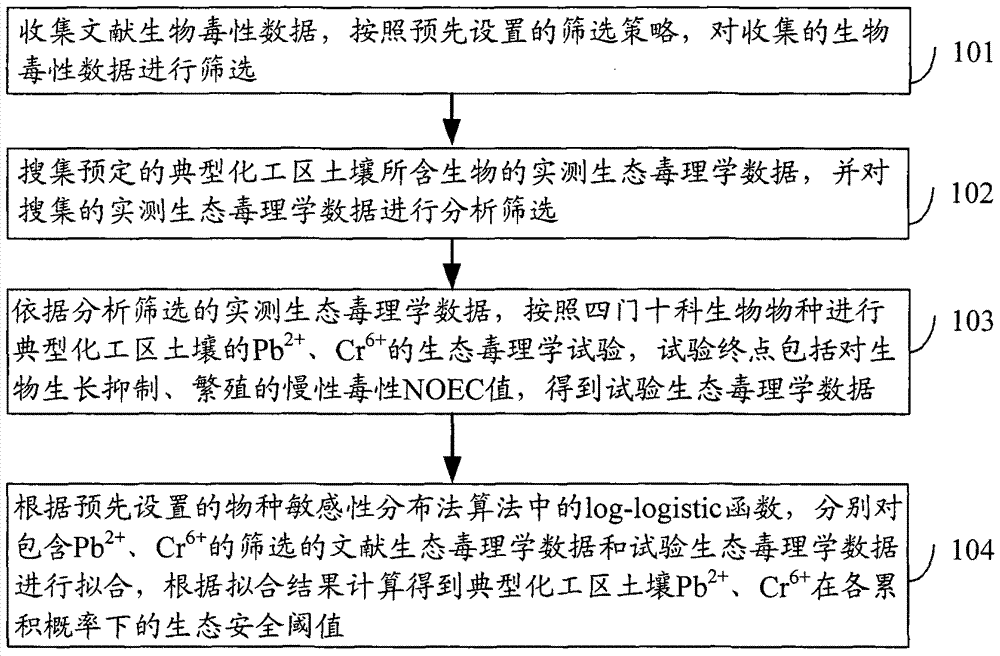
Four phyla and ten families based method for obtaining ecological safety thresholds of lead and chromium in soil
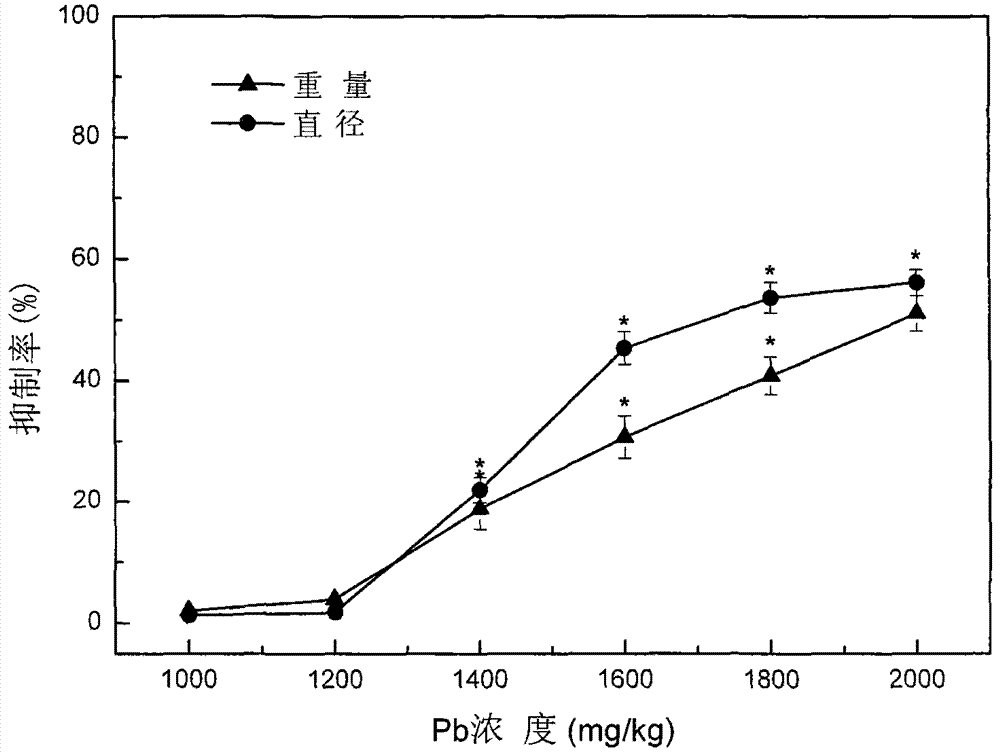
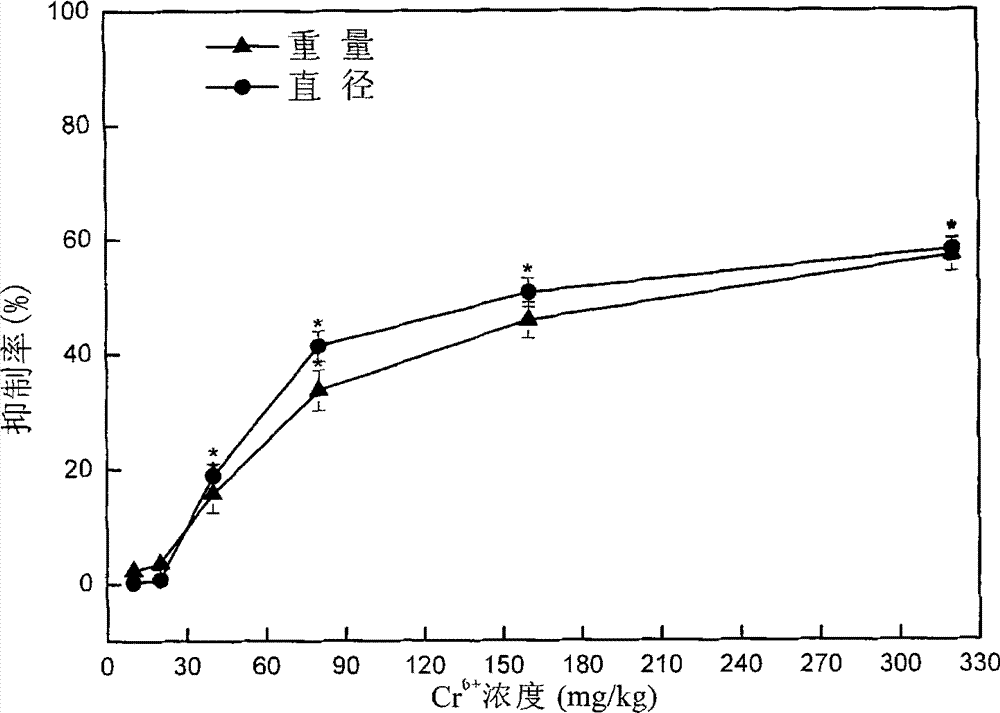
The invention discloses a four phyla and ten families based method for obtaining ecological safety thresholds of lead and chromium in soil. The method includes the steps of: screening the collected biological toxicity data; analyzing and screening the collected measured ecotoxicological data; according to the screened and analyzed measured ecotoxicological data, conducing ecotoxicological tests of Pb<2+> and Cr<6+> in the soil of a typical chemical industry zone and endpoints in accordance with four phyla and ten families, wherein test terminal points include chronic toxicity NOEC values on biological growth inhibition and reproduction; and according to a log-logistic function in a preset species sensitivity distribution method, respectively fitting the screened literature ecotoxicological data and ecotoxicological test data, and calculating the ecological safety threshold values of Pb<2+> and Cr<6+> in the soil of the typical chemical industry zone under each cumulative probability according to the fitting results. The method of the invention can effectively evaluate the soil ecological risk caused by heavy metal pollutants.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Determining method for aquatic organism protection water quality standard of bioaccumulation substance
InactiveCN105738590AConservation scienceGeneral water supply conservationTesting waterAquatic ecosystemWater quality
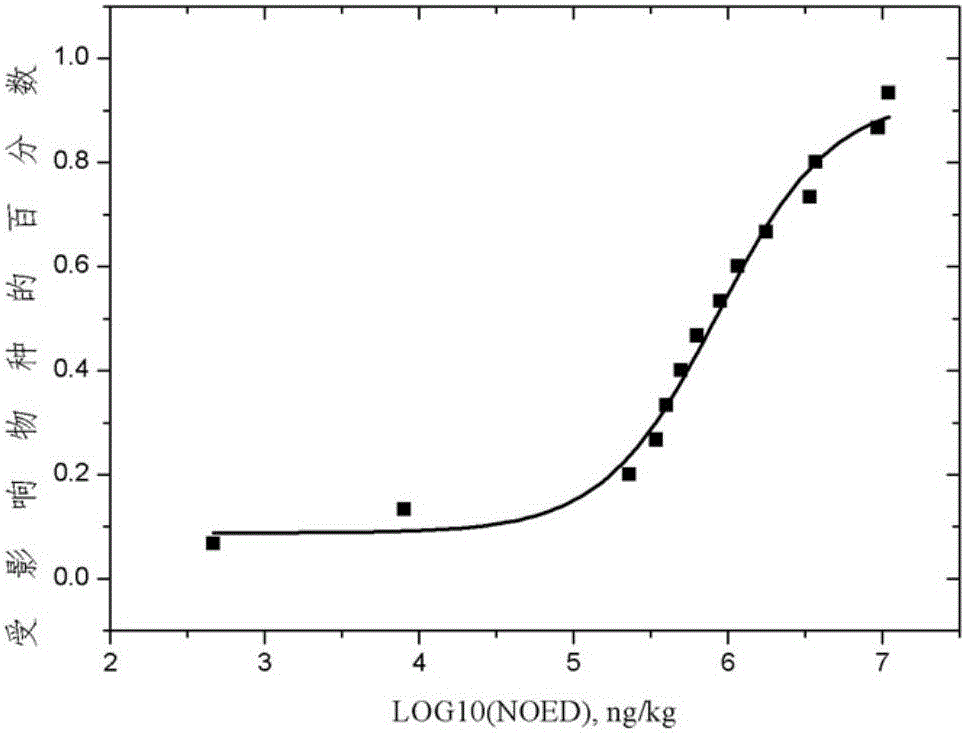
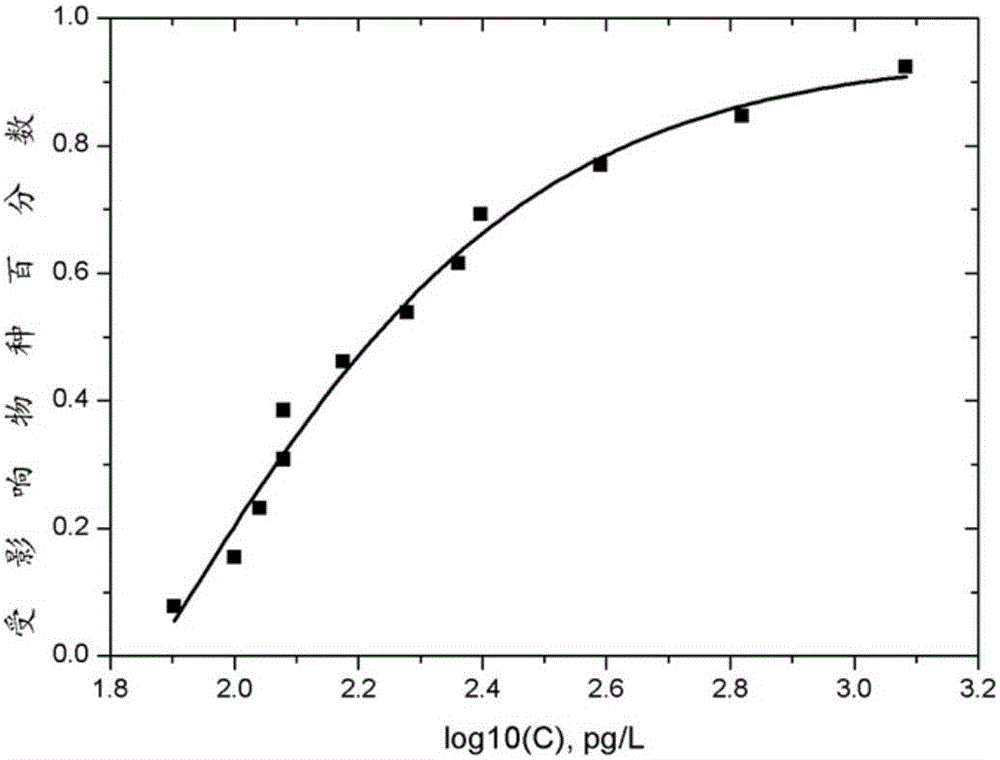
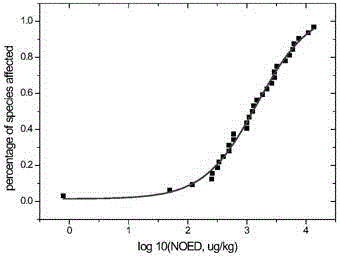
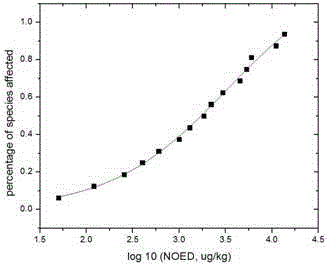
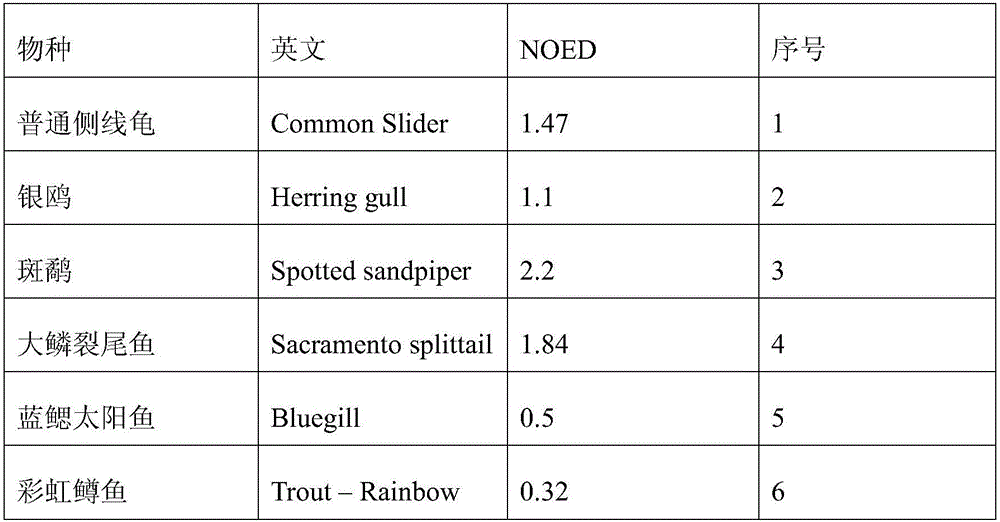
The invention belongs to the technical field of water quality protection, and particularly relates to a determining method for an aquatic organism protection water quality standard of a bioaccumulation substance. The method includes the following steps of collecting and screening toxicity data NOED; obtaining the optimal fitted equation through fitting; obtaining a reference value BTC based on tissue through the optimal fitted equation; obtaining an aquatic organism protection water quality criteria WQC of the bioaccumulation substance; obtaining predicted environment concentration PEC; determining the aquatic organism protection water quality standard WQS of the bioaccumulation substance. The aquatic organism protection water quality standard WQS of the bioaccumulation substance can be scientifically determined, the aquatic ecosystem of China can be protected more scientifically, and a new thought and method are provided for formulating the water quality standard in China.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Water sudden pollution accidental risk assessment method and apparatus
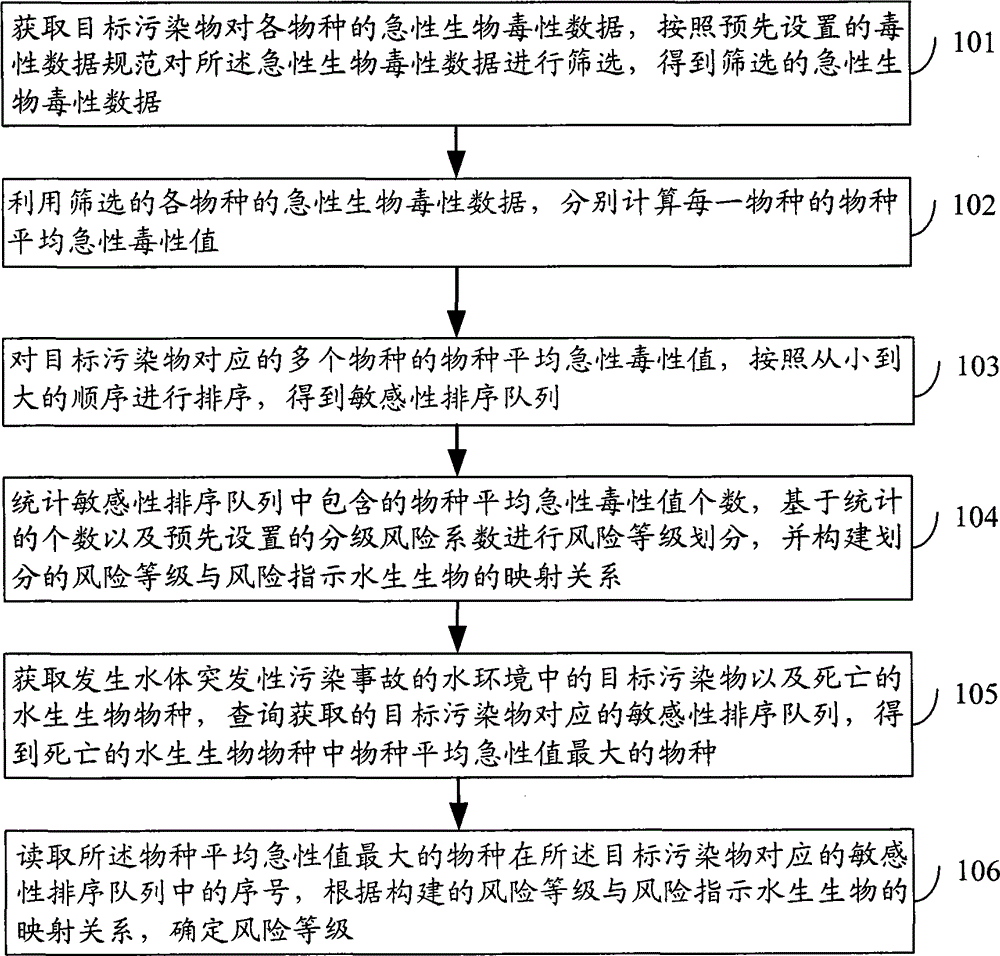
InactiveCN105224781AShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsPresent methodAcute toxicity testing
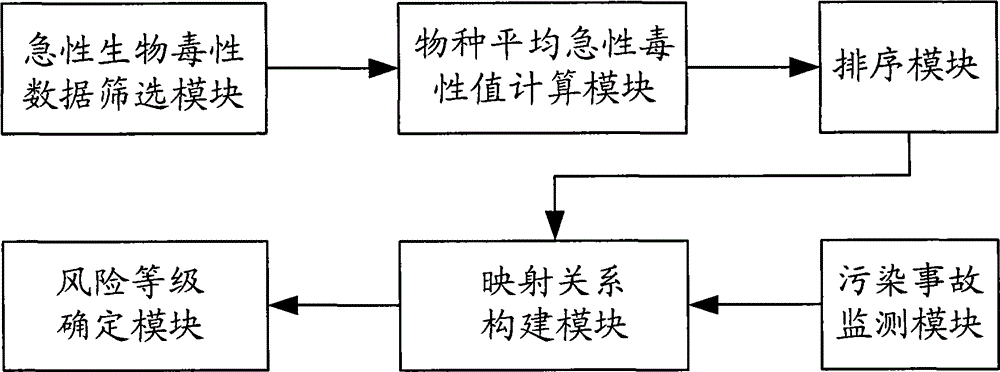
The present method discloses a water sudden pollution accidental risk assessment method and apparatus. The method comprises: obtaining acute biotoxicity data of a targeted contaminant on all species, screening on the acute biotoxicity data according to a preset toxicity data regulation, and obtaining screened acute biotoxicity data; using screened acute biotoxicity data of all species, calculating a species average acute toxicity value of each species respectively; as for the species average acute toxicity value of a plurality of species corresponding to the targeted contaminant, sorting in an ascending order, and obtaining a sensitive sorting queue; and performing statistic on quantity of species average acute toxicity value contained in the sensitive sorting queue, performing risk grades dividing based on statistical quantity and a preset classified risk coefficient, and constructing a mapping relationship between a divided risk grade and a risk indicated aquatic organism. According to the method, risk assessment efficiency for the sudden water environmental pollution accident is improved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
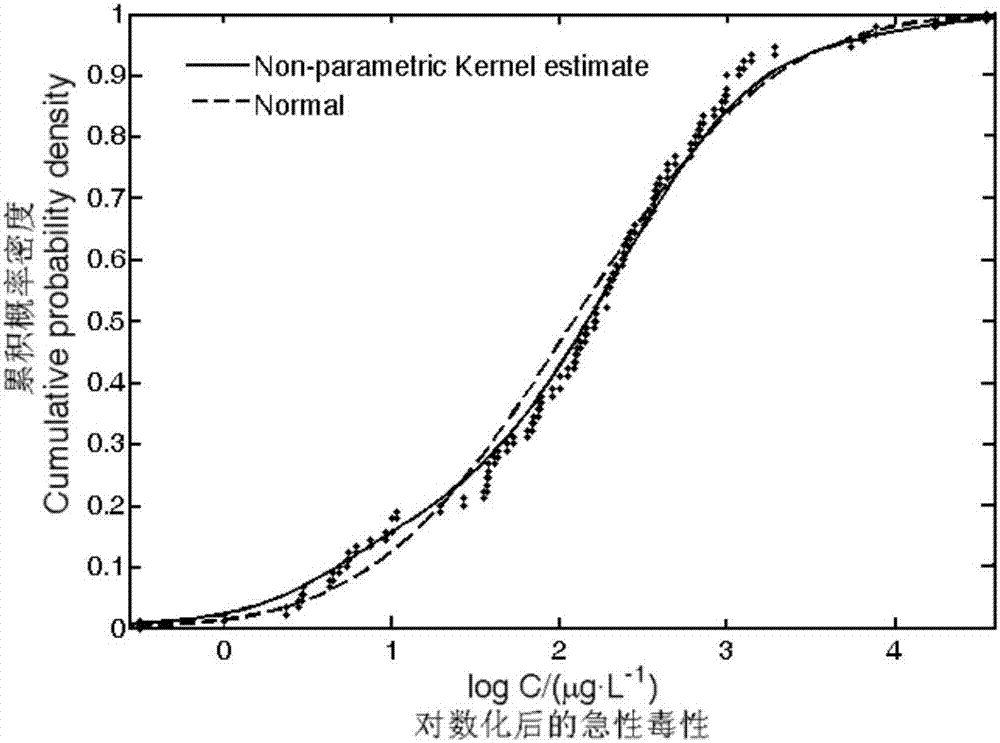
Nonparametric kernel density determination method for emergent environment event emergency disposal limit values
InactiveCN106919789ASolve the problem of missing standardsAddressing the Effects of Criterion DeterminationData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsVariable kernel density estimationLimit value
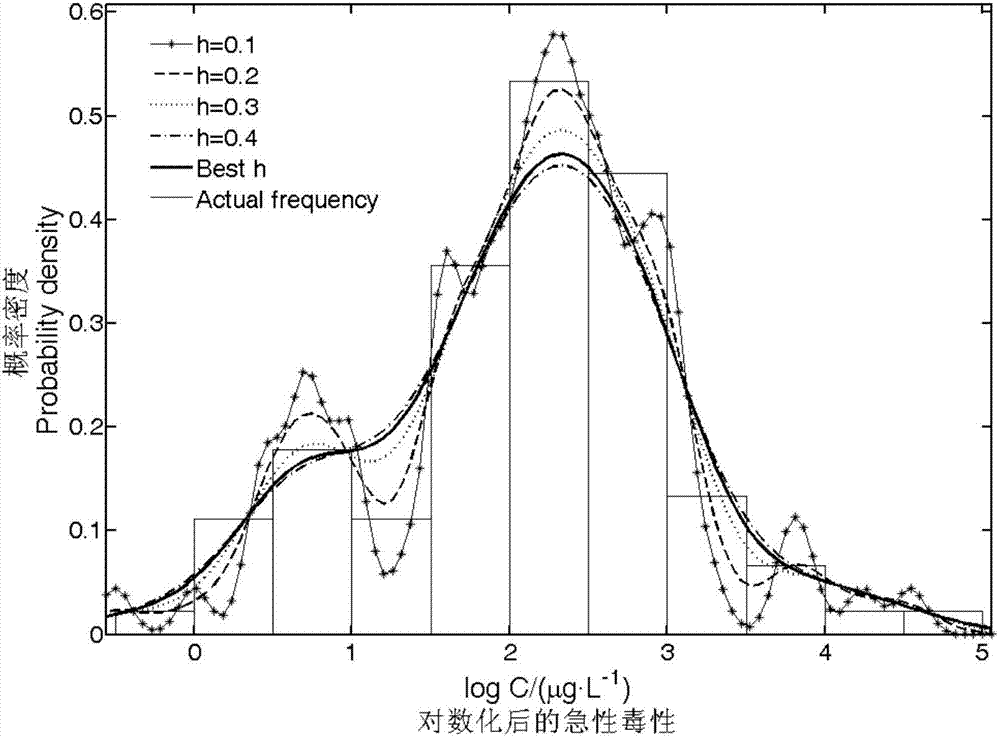
The invention relates to a determination method for emergent environment event emergency disposal limit values and specifically discloses a nonparametric kernel density determination method for emergent environment event emergency disposal limit values. The method comprises following steps: step 1. toxicity data screening; step 2. Gauss kernel function window width selecting; step 3. Gauss kernel function calculating of toxicity data; step 4. nonparametric kernel density estimation and determination of the toxicity data of distribution of species sensitivity based on Gauss kernel function; step 5. model verifying; and step 6. environment concentration limit values determination. According to the method of the invention, the fitting method of distribution curves of species sensitivity is improved; due to the improvement, the distribution features of toxicity data can be well estimated unbiasedly and accurate environment concentration limit values can be obtained so as to realize standard determination in emergent environment event emergency disposal.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
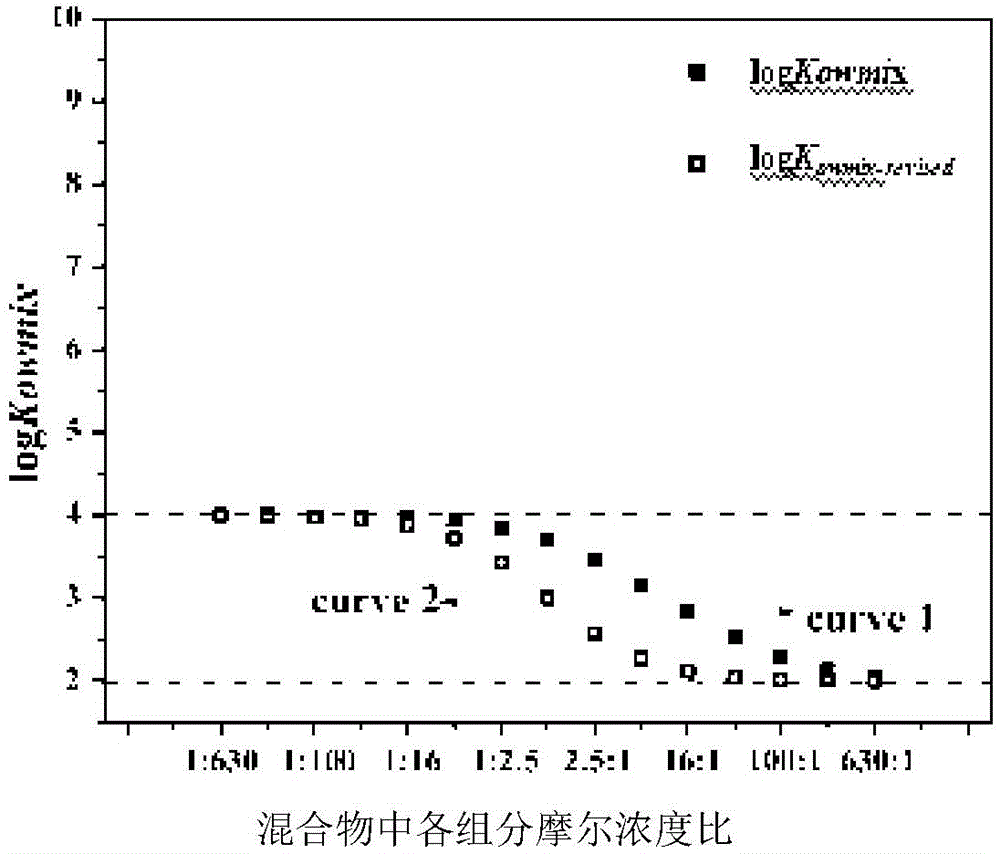
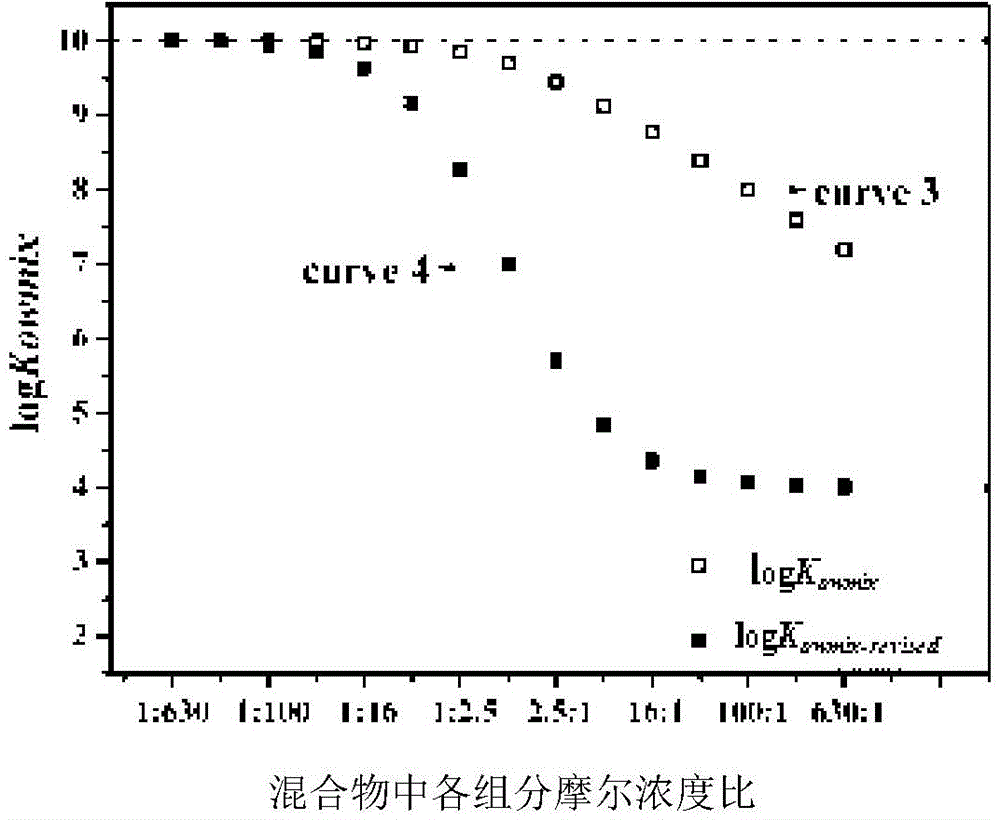
Method for determining n-octanol / water partition coefficient of mixture
InactiveCN104102826AGood correlationShow accuracySpecial data processing applicationsLinear correlationInteraction energy
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment pollution detection and relates to an optimizing method for determining an n-octanol / water partition coefficient of mixture. The method includes the steps of detecting single toxicity data and mixed toxicity data; acquiring the interaction energy Ebinding of a single compound and a phospholipid bilayer membrane; establishing a linear equation in two unknowns of the mixed toxicity and Ebinding; establishing the linear relationship of the Ebinding and logKow; acquiring the linear relationship of the mixed toxicity and logKow; acquiring the logKowmix optimizing method as follows: log (Kowmix-revised) = Sigma xilogKowi. The parameter calculating method is simple and has wide application range, a complex detecting equipment is omitted, experimental and environmental pollution is avoided, the total hydrophobicity of the mixture can be predicted accurately, and scientific basis is provided for the ecological risk assessment of mixed pollutants.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
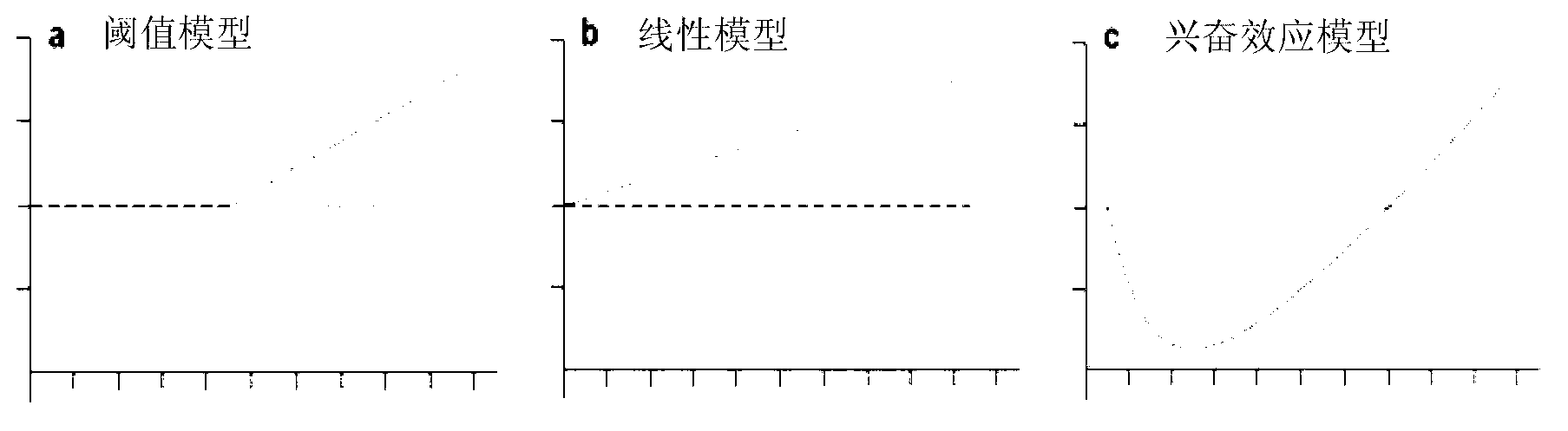
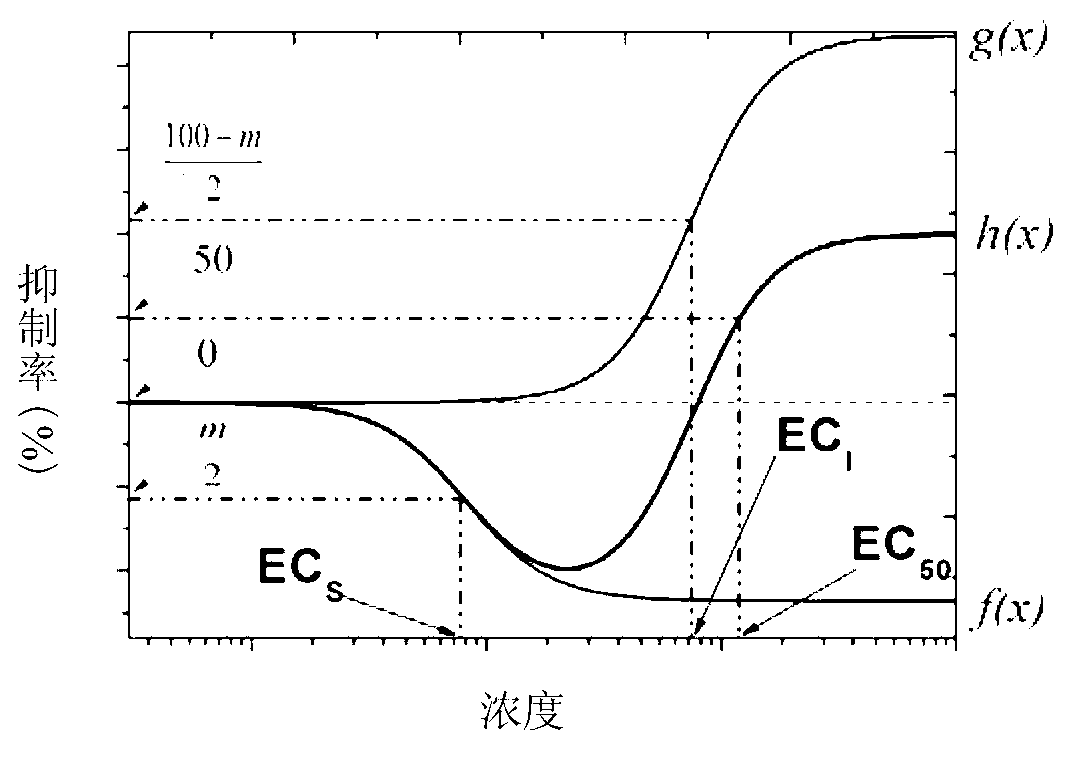
Method of establishing Hormesis dose-effect fitting model
InactiveCN103014116ASimple initializationEasy to initializeMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute toxicity testingHypothesis
The invention belongs to the field of environment pollution detection technology and relates to a method of establishing a Hormesis dose-effect fitting model, namely a Bilogistic model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) analyzing the stability of a compound; (2) recovering and culturing strains; (3) conducting toxicity test including acute toxicity test and chronic toxicity test; (4) calculating the inhibition ratio of the compound analyzed in the step (1) to the strains recovered and cultured in the step (2) by applying the experiment result obtained in the step (3), and conducting toxicity representation by taking inhibition ratio as an index; and (5) fitting the toxicity data to obtain the Bilogistic model. The data fitting is more convenient through the model; parameters in the model are initialized simply; the model is established based on a receptor mechanism hypothesis, thereby having great biological significance; good fitting can be conducted under the condition of high stimulatory effect; the Hormesis effect can be effectively guided to the application in the drug design.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
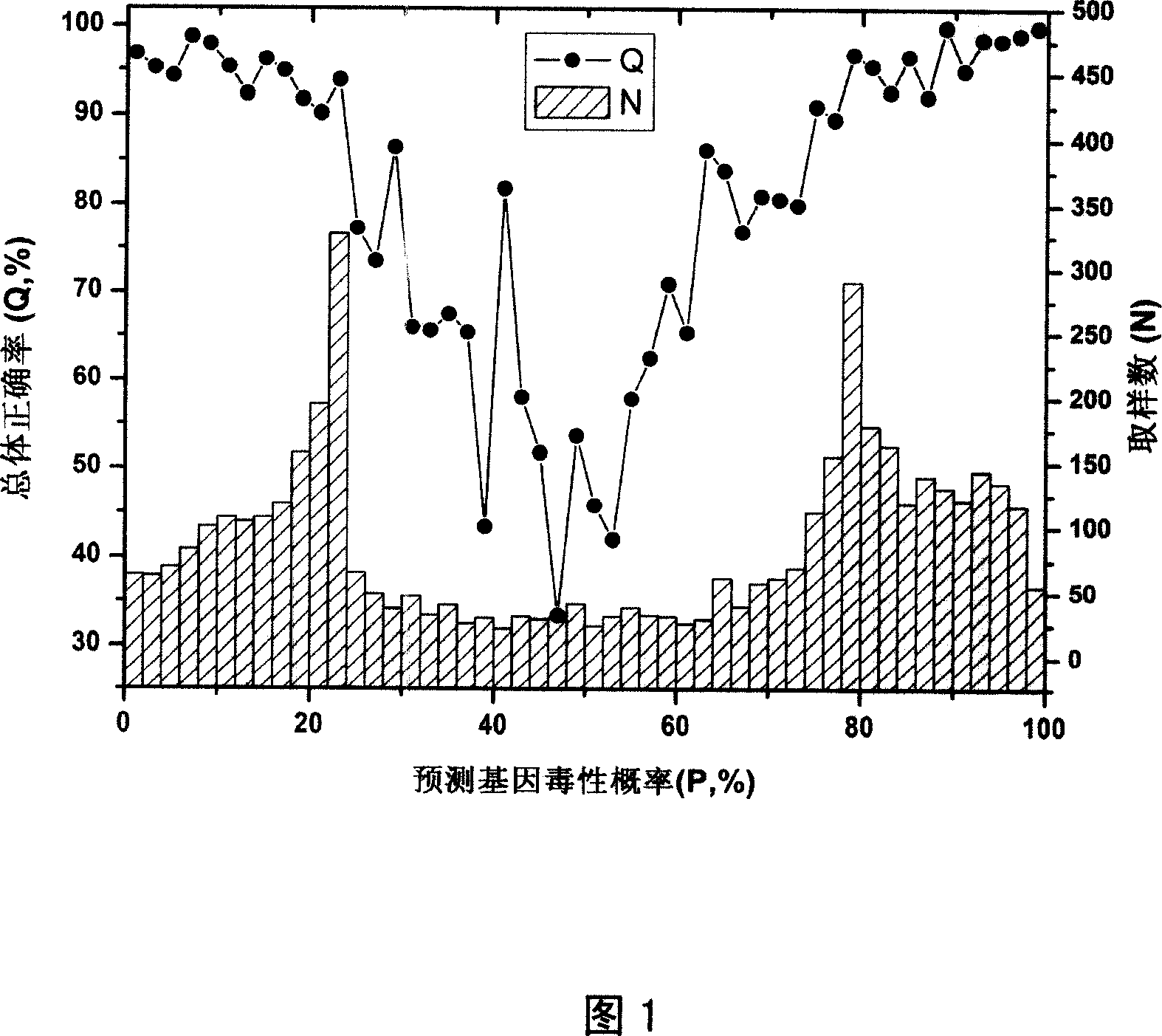
Gene toxicity probability forecasting method based on molecule electrophilic vector and extend supporting vector machine
InactiveCN101131391AInhibition biasPredictableMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsChemical structureElectron density
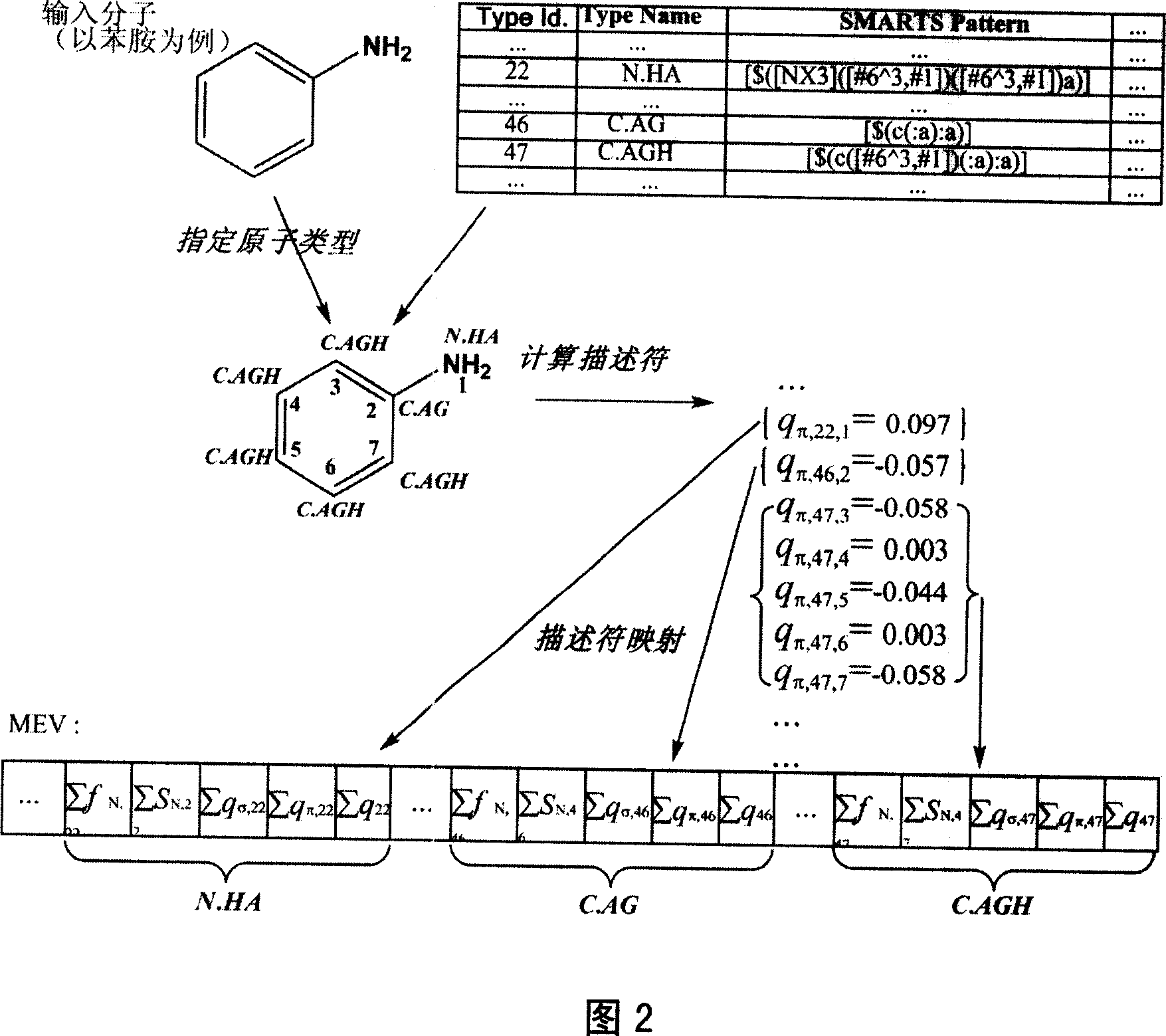
The invention relates to the gene toxicity probability preparation method based on the MEV and SVM which is proper for the dummy toxicity appraise and selection according to the organic compound molecule structure information. Firstly, it classifies the molecule structure based on the SMARTS and PATTY according to predefine rule; then to compute the atom descriptor (front track electron density, electron superdelocalizability and atom pi-charge) of every atom type according to the H¿˜ckel method and set the MEV to descript the electrophilicity; Last to statistic the gene toxicity data and MEV according to the SVM and get the posterior probability estimation of the molecule gene toxicity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
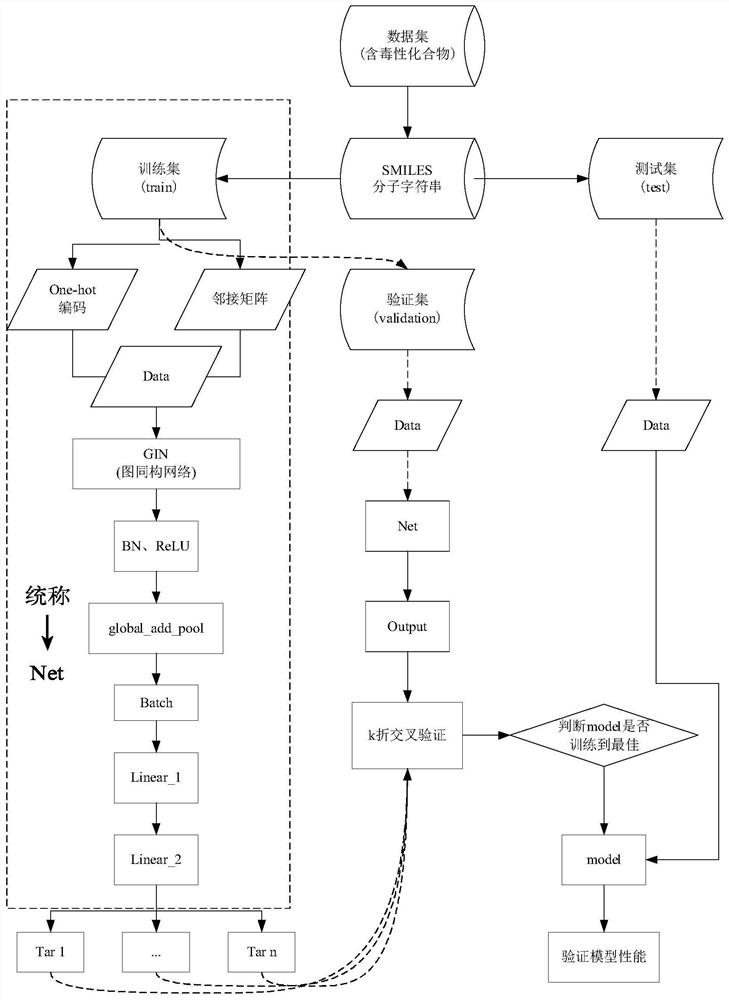
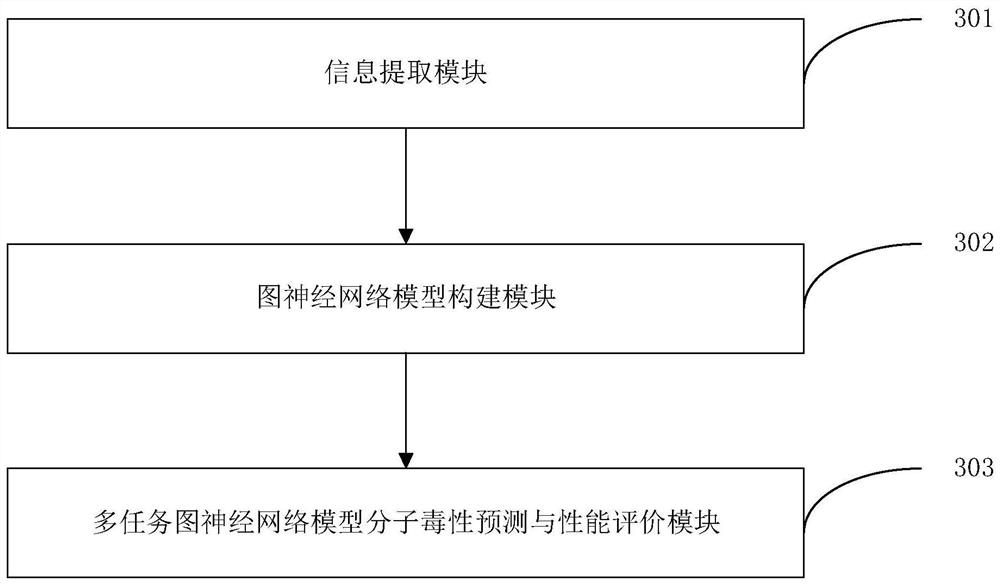
Method and apparatus for molecular toxicity prediction based on multi-task graph neural network
ActiveCN113257369ACombined associativityImprove performanceNeural architecturesChemical machine learningMulti-task learningGraph neural networks
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for molecular toxicity prediction based on a multi-task graph neural network. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a toxicity data set, and obtaining toxicity data represented by a chemical molecule standard expression; S2, generating an atomic node eigenvector by using the toxicity data which is obtained in the step S1 and represented by the chemical molecule standard expression; S3, generating a side information eigenvector by using the toxicity data which is obtained in the step S1 and represented by the chemical molecule standard expression; S4, on the basis of the atomic node eigenvector obtained in the step S2 and the side information eigenvector obtained in the step S3, constructing a molecular toxicity prediction model based on a multi-task graph neural network; S5, verifying performance of the model. According to the multi-task graph neural network designed for molecular toxicity datasets, an automatic learning molecular graph structure information model is constructed, and the performance of a toxicity prediction task can be improved by using a multi-task learning method in combination with the relevance between molecular toxicity tasks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
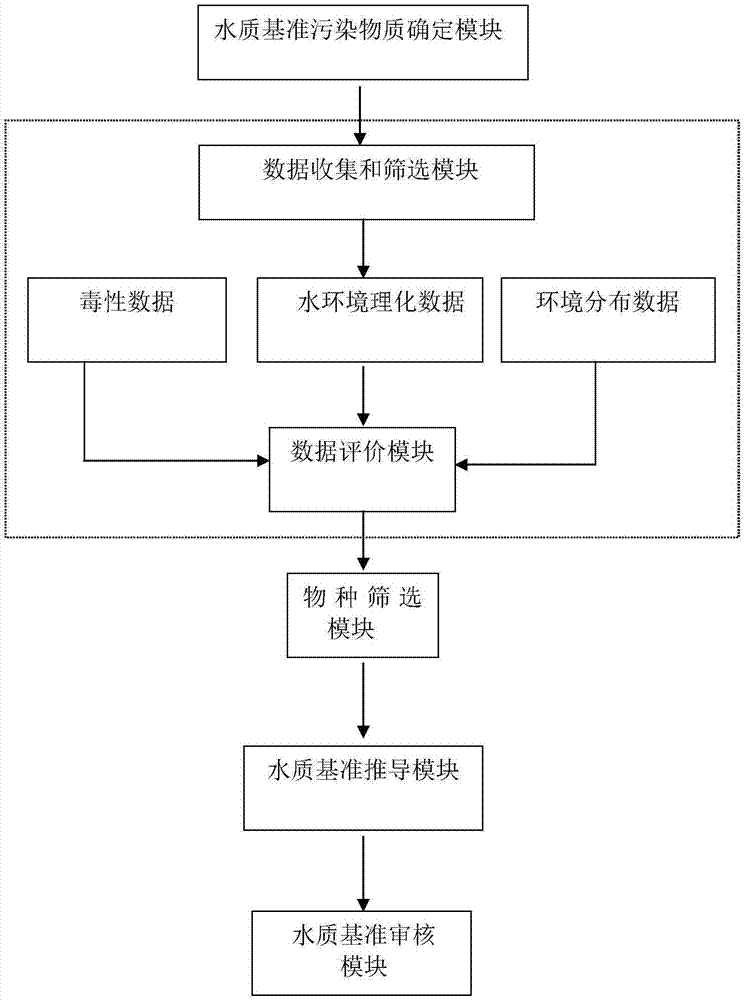
System for water quality reference prediction of fresh water organisms
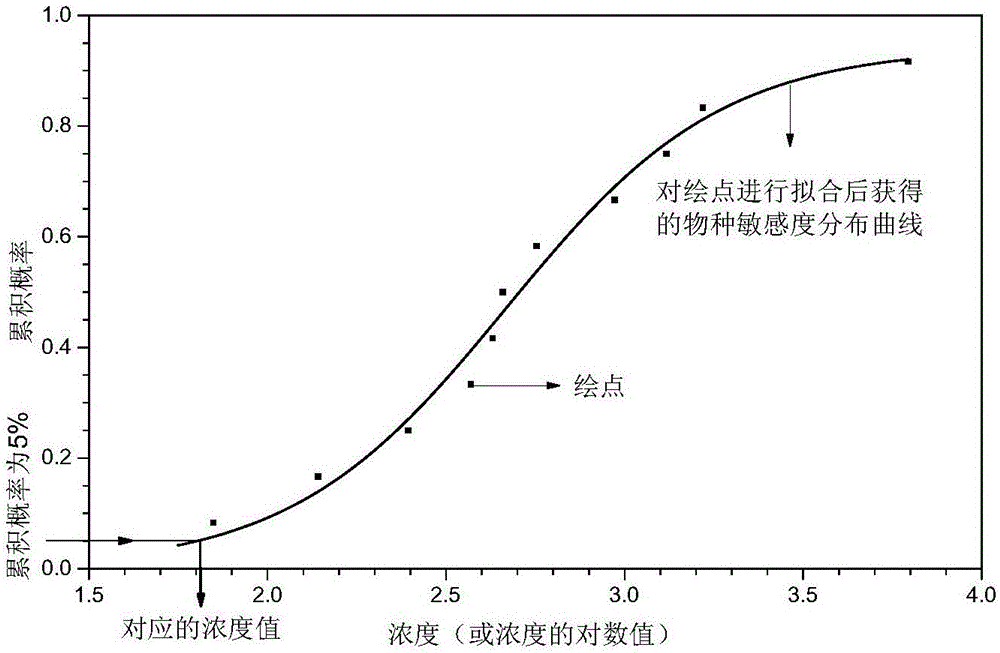
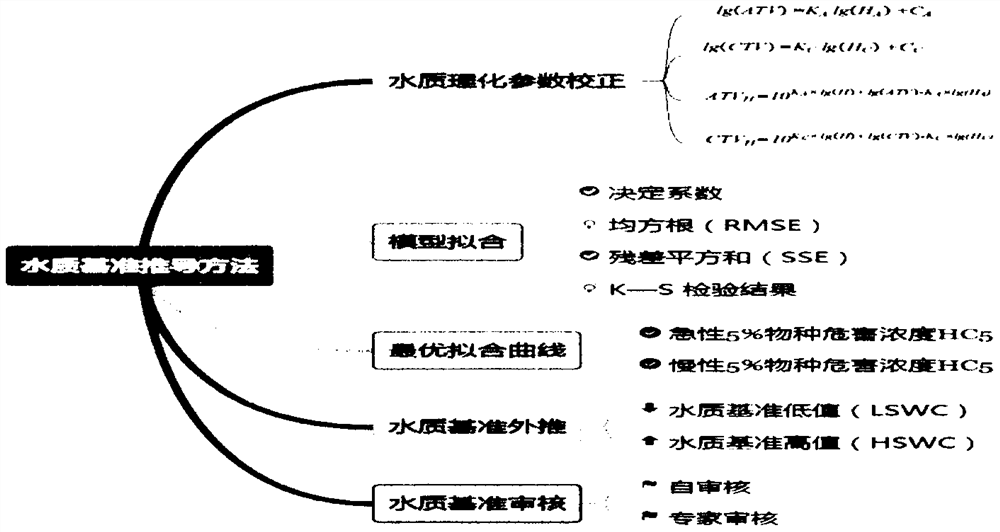
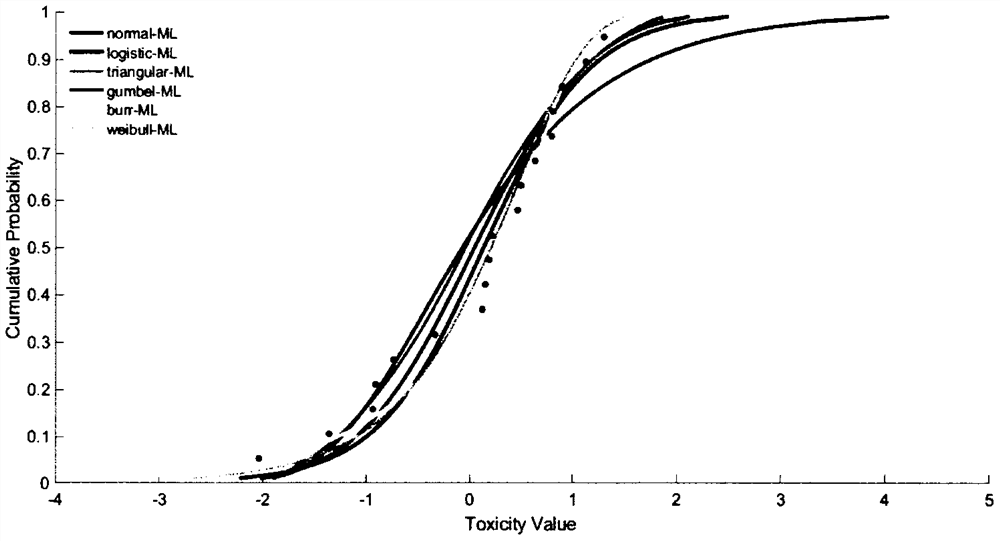
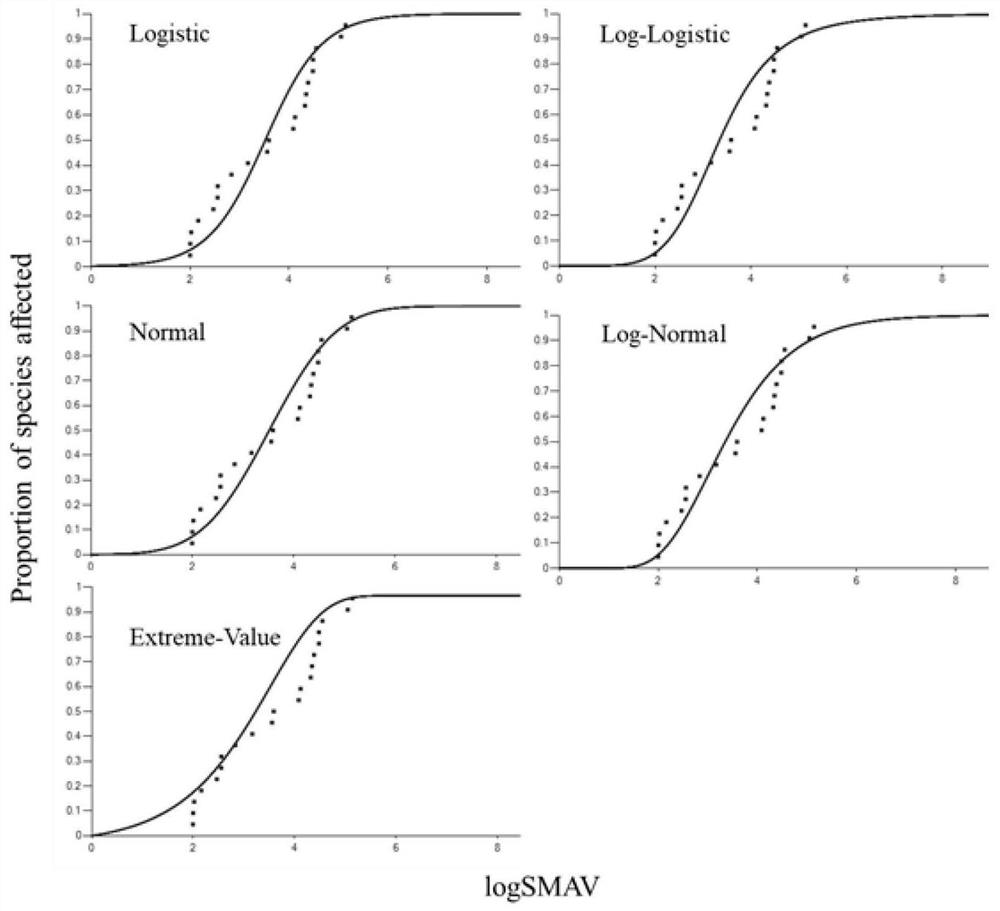
The invention discloses a system for water quality reference prediction of fresh water organisms, and the system comprises a water quality reference pollutant determining module, a data collection and screening module, a data evaluation module, a kind screening module, a water quality reference deducing module and a water quality reference checking module. The water quality reference deducing module comprises a toxicity data distribution verification module, a cumulative probability calculating module, a model fitting and evaluation module, a water quality reference extrapolation module and a water quality reference result description module. The model fitting and evaluation module employs a logistic distribution model, a normal distribution model or an extreme value distribution model for data fitting, obtains an SSD (species sensitivity distribution), and respectively evaluates the fitting degrees of the models according to the fitting goodness-of-fit evaluation parameters of the models. The water quality reference extrapolation module employs the concentration HC5 corresponding to the cumulative probability of 5% on the SSD curve to divide an evaluation factor, and determines a final fresh water organism water quality reference.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Medicine for treating poultry lice
InactiveCN109221111ASafety Toxicity DataPrevent intrusionBiocideAnimal repellantsKetoneNitrilotriacetic acid
The invention discloses a medicine for treating poultry lice. The medicine contains the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 4% of C9-11 ethanol+8-mole ethylene oxide, 4.5% of quaternary amine compound or dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride or chloride, 3% of didecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, 0.9% of coconut imide oxime glycine ester, 1.5% of N-(3-aminopropyl)-N-dodecyl-1,3-propylenediamine, 0.8% of sodium carbonate, 0.02% of 1,2-benzisothiazole-3(2H)-ketone, 6% of N- methylglycine or N-methyl imino acetic acid or nitrilotriacetic acid trisodium salt, 0.3% of lavender flavor and 78.98% of water. The medicine disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the problem of the drug resistance of poultry red mites, related to of traditional acaricide, is overcome; compared withthe traditional acaricide, the medicine has safer toxicity data and is more friendly to environment; and the medicine is fast in effect and lasting in effect and has no adverse effect on poultry.
Owner:柯林森哈德罗休
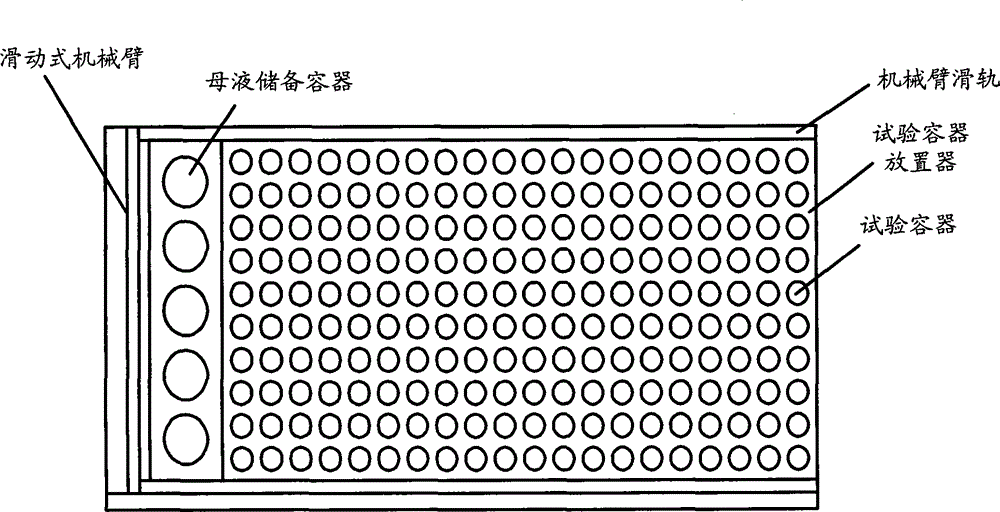
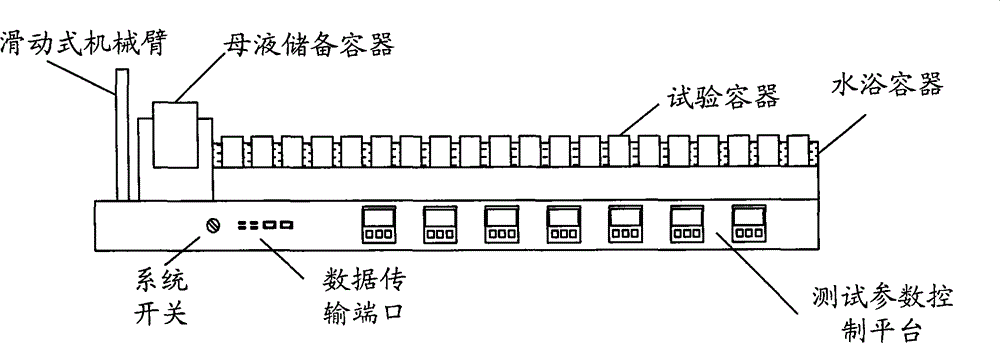
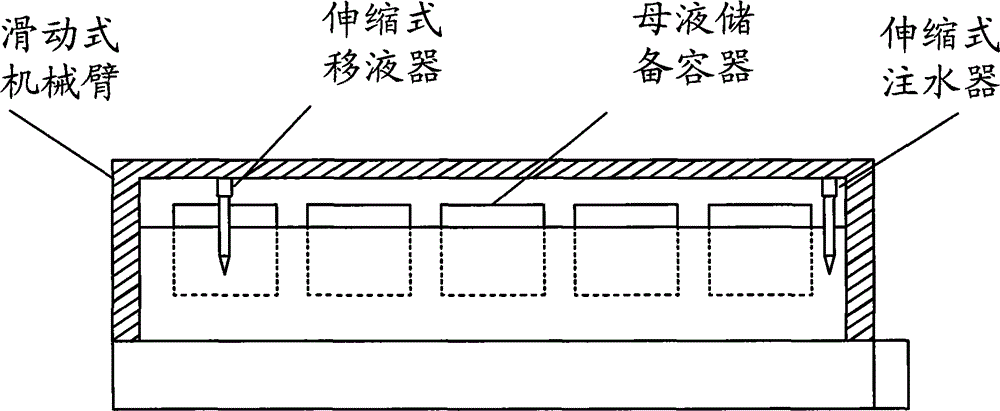
High-throughput fish ecotoxicity test system
InactiveCN105301212AImprove accuracyRealize automatic observationTesting waterBiological testingPipetteData transmission
The invention discloses a high-throughput fish ecotoxicity test system. The system comprises experiment vessels, an experiment vessel placing device, mother liquid storage vessels, a sliding mechanical arm, a telescopic injector, a telescopic pipette, a data transmission port and a test parameter control platform, wherein the experiment vessel placing device is connected with the telescopic injector and the data transmission port separately; the mother liquid storage vessels are connected with the telescopic pipette; the sliding mechanical arm is connected with the telescopic injector, the telescopic pipette and the data transmission port separately; the data transmission port is also connected with the test parameter control platform. Through the adoption of the system, the output efficiency of ecotoxicological toxicity data can be improved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Aquatic organism base value detection method
InactiveCN106556683AImprove selection efficiencyHigh precisionTesting waterSpecies selectionNon randomness
The invention relates to an aquatic organism base value deriving method. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a species, screening toxicity data, calculating the cumulative probability, acquiring a base value, and carrying out nonlocal species utilization and later sample adding when the toxic data of the species is insufficient. The method effectively solves the non-randomness problem of the toxicity data, and also solves the problem brought by scarcity of the toxicity data of the local species in China.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for obtaining water quality standard of estuary aquatic organisms
PendingCN111242442AAccurate SSD curveGeneral water supply conservationResourcesWater qualityMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for obtaining a water quality standard of estuary aquatic organisms. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining priority control pollutants and commonpollutants in a scoring manner; after determination of contaminants, aiming at the pollutant screening estuary tested biological species, providing the tested species screening method suitable for the estuary region, and preliminarily determining the estuary water quality reference tested biological recommendation list according to the relationship between the sensitivity of different species andthe cumulative probability of main pollutants, wherein the list is different from the species in fresh water and seawater; after the tested biological species are determined, providing a toxicity data collection and screening principle suitable for the estuary environment of China; after toxicity data is obtained, adopting a species sensitivity distribution method to derive a reference thresholdvalue. Five models are adopted to be used for toxicity data fitting, corresponding evaluation criteria are provided, a model most suitable for the pollutant can be selected according to the evaluationcriteria, and therefore the more accurate reference threshold value is obtained.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
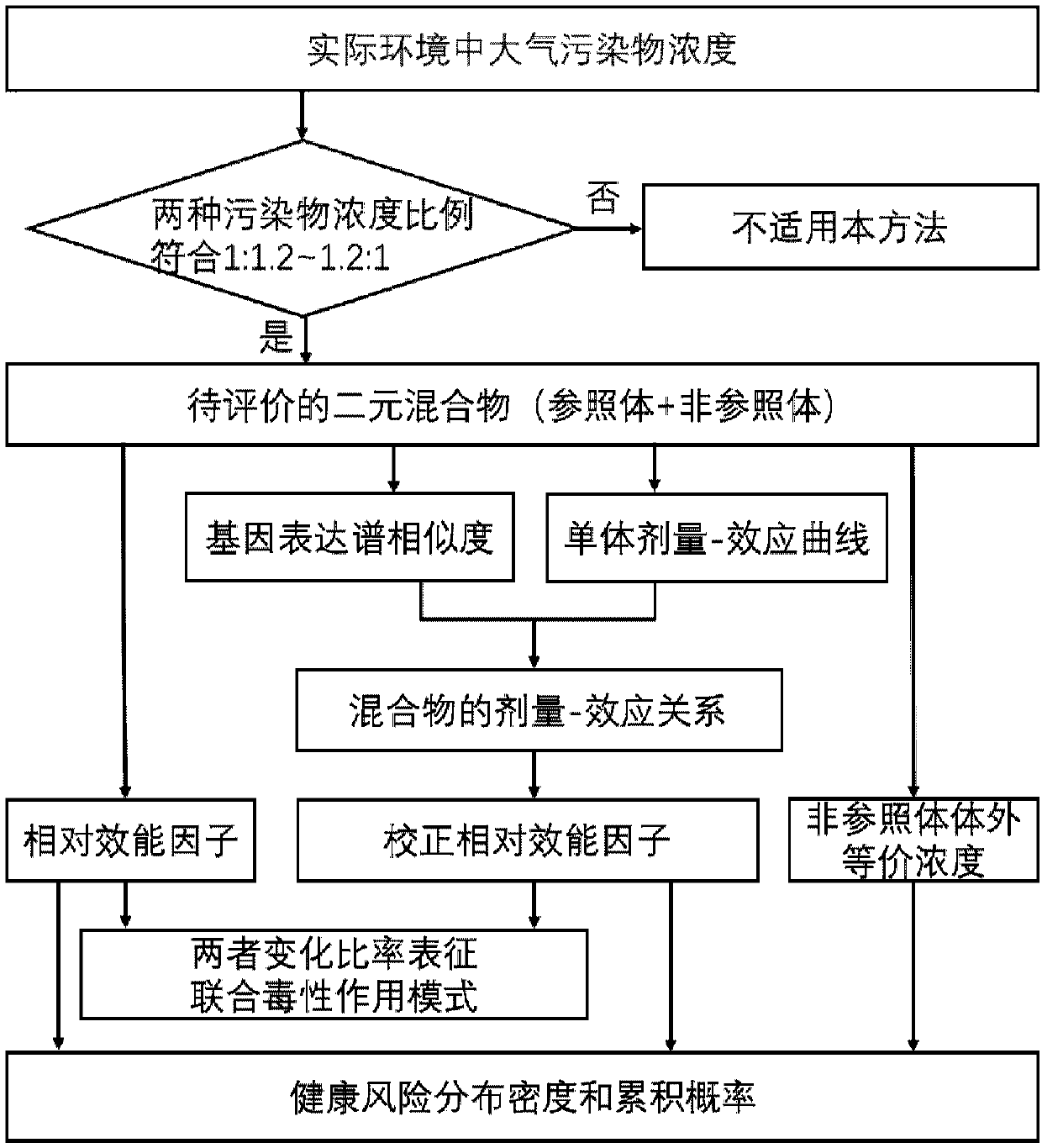
An atmospheric pollution binary mixture health risk evaluation method
ActiveCN109583662AScientifically Reasonable Health Risk EstimatesSave labor costHealth-index calculationForecastingMaterial resourcesRelative efficacy
A novel atmospheric pollution binary mixture health risk evaluation method comprises the following steps: obtaining atmospheric pollutant concentration from literature or actual environment monitoring, selecting pollutants with approximate concentration as binary mixed components to be evaluated, and converting the actual environment exposure concentration into in-vitro equivalent concentration; Obtaining transcriptome data of each pollutant and in-vitro biological test information of a specific path from a public database or literature, calculating a mixed effect value of the transcriptome data and the in-vitro biological test information, and correcting a relative efficacy factor and a combined toxicity action mode; Monte Carlo simulation is carried out on the equivalent concentration invitro of the pollutants, relative efficiency factors are coupled and corrected, and the health risk of the mixed pollutants is evaluated. The method is established on the basis of the environmental exposure concentration and the biological test data of the pollutant monomer, can evaluate the health risk of the pollutant monomer without depending on the mixture toxicity data, saves the manpower and material resource cost, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of practical environmental hybrid exposure health risk evaluation, environmental safety evaluation and the like.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heavy metal seawater aquatic organism water quality reference value derivation method
PendingCN111861242AAvoid Water Quality BenchmarksFully consider the complexity factorGeneral water supply conservationResourcesWater qualityZoology
The invention discloses a heavy metal seawater aquatic organism water quality reference value derivation method. The method comprises the following steps: collecting and screening toxicity data, screening tested species, and correcting the hardness of a water body; importing the corrected toxicity data into an SSDToolbox, taking a toxicity value as an abscissa, and taking cumulative probability asan ordinate, determining an optimal fitting model according to a K-S inspection result to obtain acute / chronic 5% species hazard concentration (HC5), and performing reference extrapolation to obtaina sea area water quality reference high value (HSWC) / low value (LSWC). In the derivation process, the influence of environmental factors on toxicity under sea area features is fully considered, the heavy metal seawater aquatic organism water quality reference value derivation method which is high in area pertinence and adapts to the current water environment management requirement is provided, themethod is more suitable for the current water environment management requirement of China, and over-protection and under-protection can be effectively avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Water quality reference derivation method for selenium and water quality safety evaluation method
InactiveCN105738591AConservation scienceAvoid effectivenessTesting waterBiological testingWater qualityToxicity data
The invention discloses a water quality reference derivation method for selenium and a water quality safety evaluation method. According to the method, the reference based on tissues is derived through toxicity data based on tissues, and then biological accumulation factors of representative species are used for converting the reference based on the tissues into a water quality reference based on water. By means of the water quality reference derivation method for selenium and the water quality safety evaluation method, the aquatic organism protecting water quality reference of accumulative substances is determined scientifically, the defects that the traditional water quality reference does not take biological accumulation and biological effectiveness into consideration are avoided, and the water ecosystem of China can be protected more scientifically.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Regional protection aquatic organism water quality benchmark derivation method for optimally controlling heavy metal pollutant chromium
PendingCN113406287AApplicable protectionConservation science is effectiveData processing applicationsGeneral water supply conservationWater qualityEnvironmental engineering
The invention provides a regional protection aquatic organism water quality benchmark derivation method for optimally controlling heavy metal pollutant chromium, which comprises the following steps: collecting and screening toxicity data, screening tested species, importing the screened toxicity data into China-WQC, carrying out model fitting by taking lgSMAV as an abscissa and cumulative probability as an ordinate, determining an optimal fitting model according to a determination coefficient r2, a root mean square RMSE, a residual sum of squares SSE and a K-S test result of model fitting, obtaining a 5% species hazard concentration HC5, selecting an evaluation factor 2, and determining a short-term reference value CMC and a long-term reference value CCC of the fresh water aquatic organisms in combination with a corresponding acute-chronic ratio. According to the method, the difference of water quality standards under different biological zones is fully considered in the derivation process, the national conditions and water environment management criteria of China are better met, and over-protection and under-protection can be effectively avoided. A reference can be provided for deriving a regional heavy metal protection aquatic organism water quality standard.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
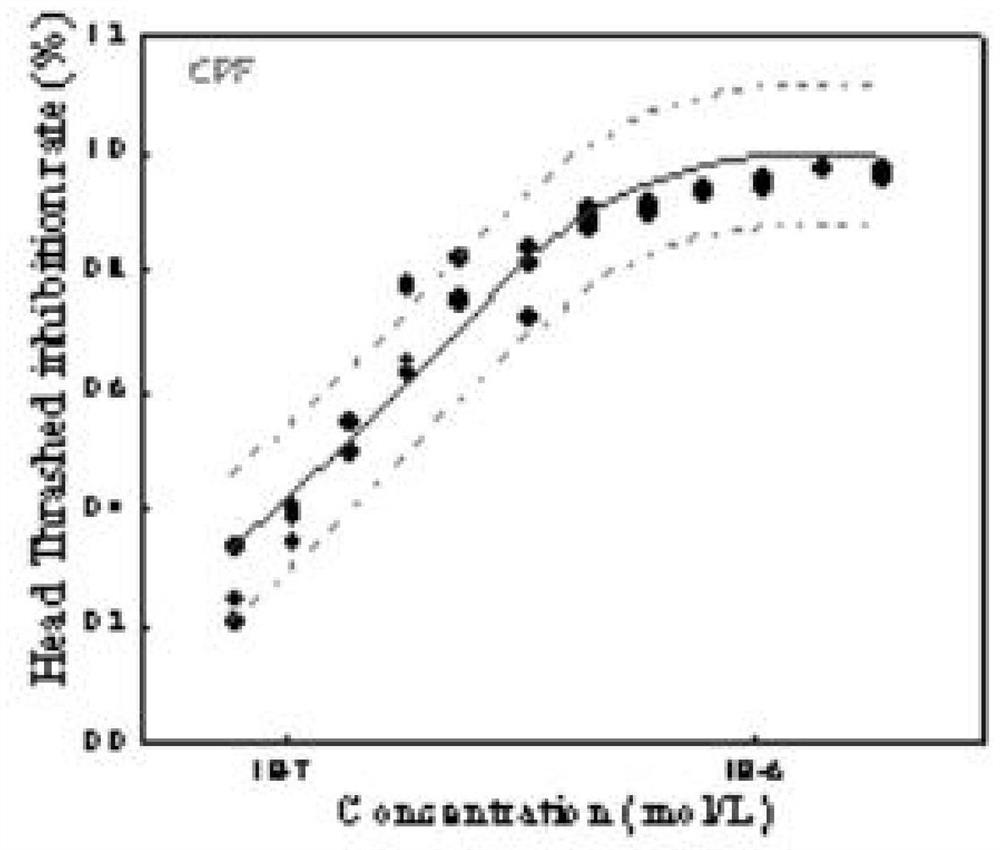
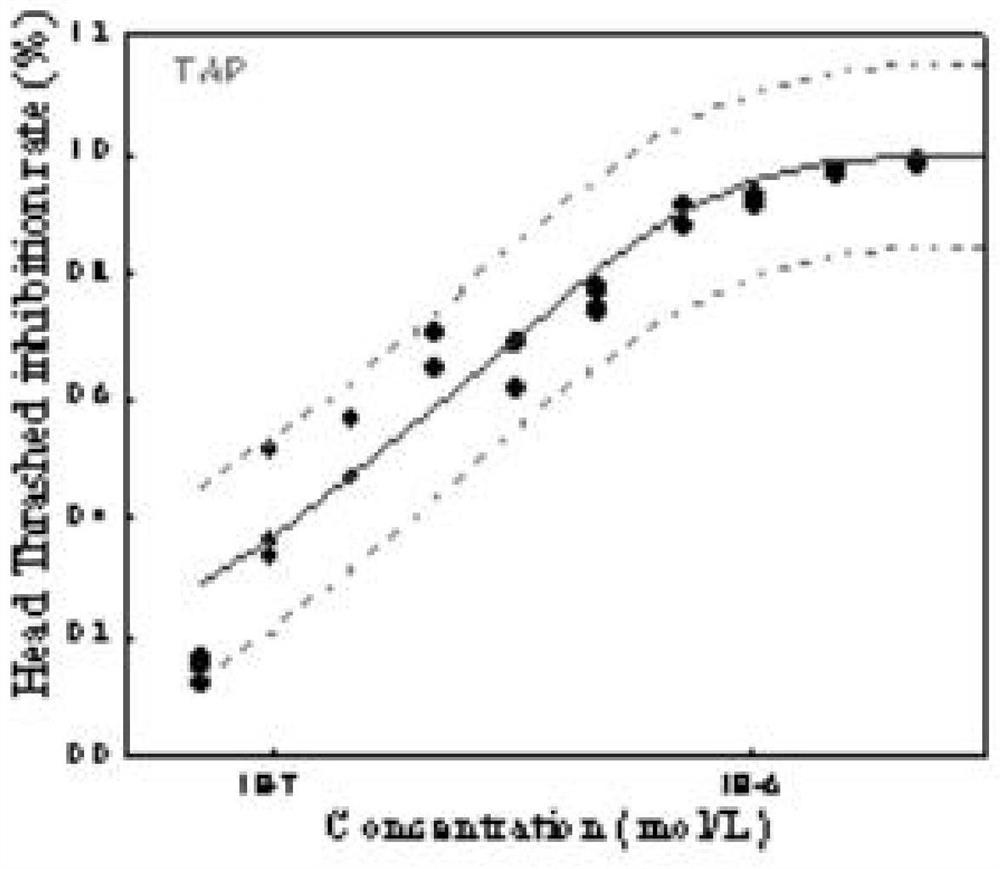
Method for analyzing caenorhabditis elegans head swing inhibition rate of pollutants
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the caenorhabditis elegans head swing inhibition rate of pollutants. A plurality of concentration gradients are set to perform high-flux toxicity exposure on caenorhabditis elegans respectively, toxicity data of a plurality of concentration points are acquired by setting a plurality of parallel groups and repeatedly measuring the toxicity of the samepollutant for multiple times, and a dose-effect curve of a target pollutant is fitted. The method mainly comprises the following steps: preparing a caenorhabditis elegans growth medium; preparing an escherichia coli OP50 culture medium; obtaining a synchronized caenorhabditis elegans stock solution; obtaining environmental pollutant sample solutions with different concentration gradients; carryingout a caenorhabditis elegans toxicity exposure experiment and acquiring toxicity data; and fitting data. According to the method, the neurotoxicity of the environmental pollutants to caenorhabditis elegans can be accurately calculated, and a more scientific theoretical support is provided for evaluating the safety of the environmental pollutants to an ecological system and human health.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com