Method for forecasting acute toxicity of organic compounds by building quantitative structure-activity relationship model with quantum chemistry method
A quantitative structure-activity relationship, organic compound technology, applied in chemical property prediction, instrumentation, calculation, etc., can solve problems such as time lag, and achieve important social and economic value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
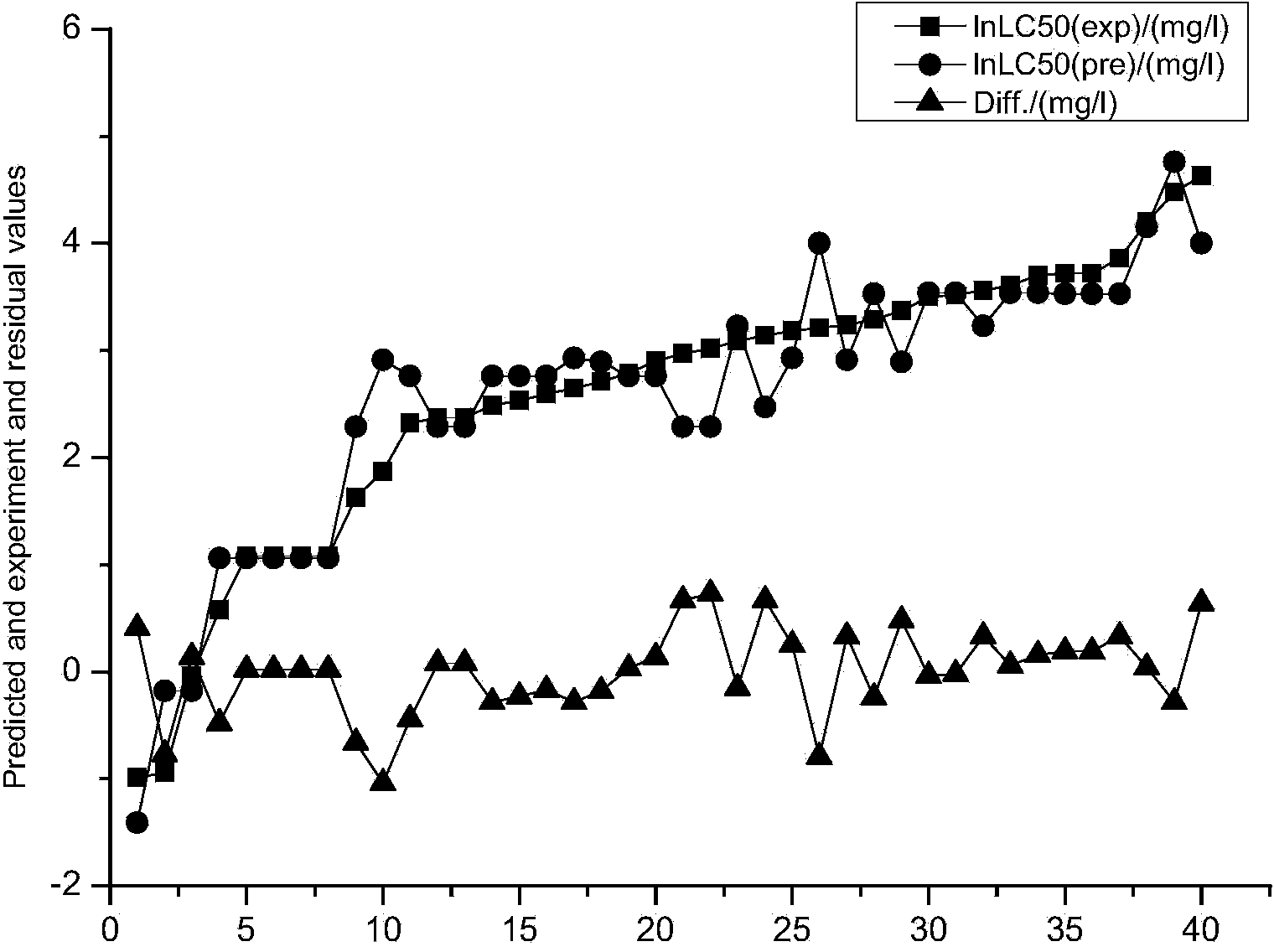
[0024] Example 1: Constructing a predictive model of the acute toxicity of aniline derivatives to black-headed minnows by means of quantum chemistry.
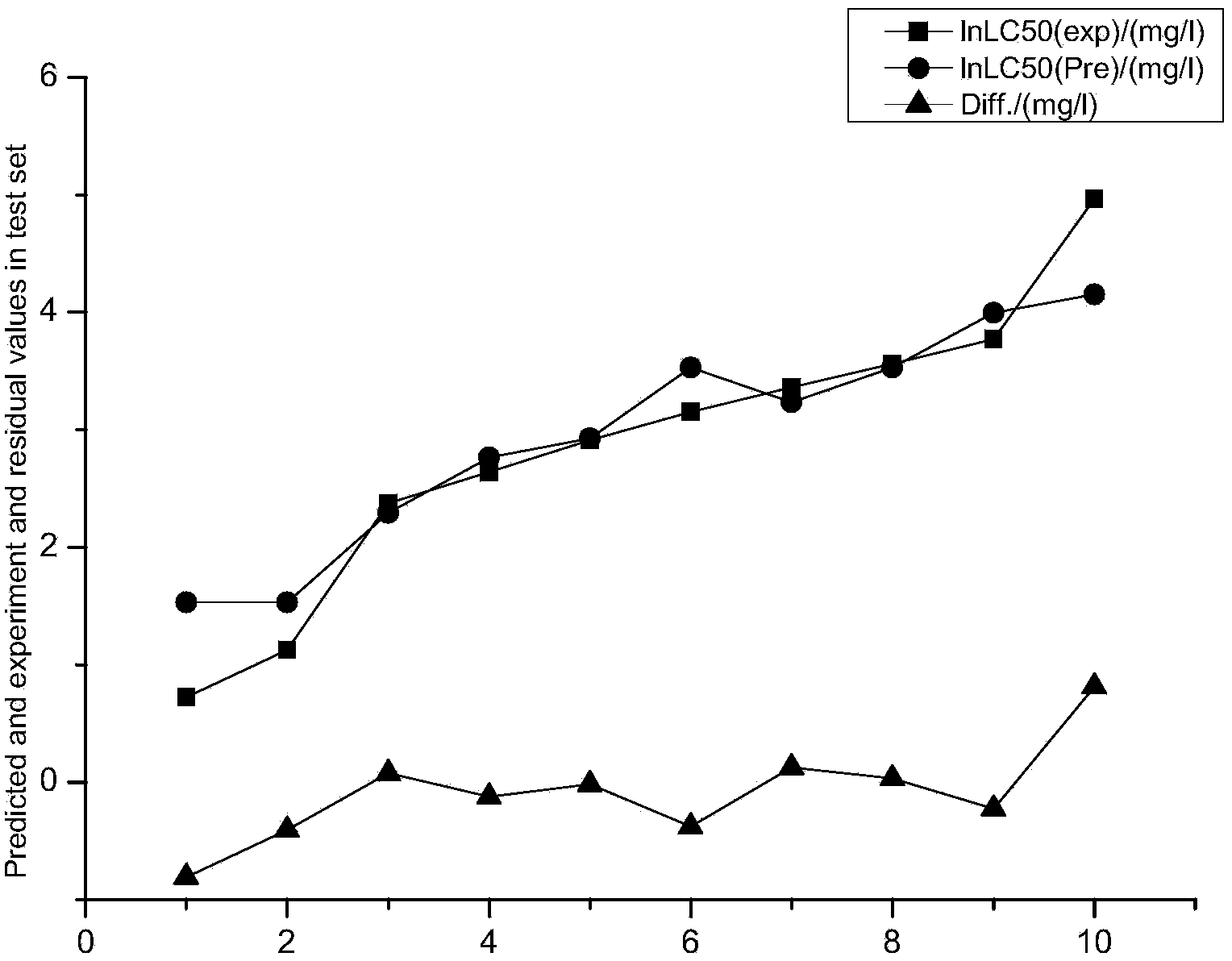
[0025] The acute toxicity data LC50 of 50 aniline derivatives to black-headed minnows was obtained from the QSAR toolbox, and every five substances were selected as the verification set data after being arranged according to their toxicity. as a training set.
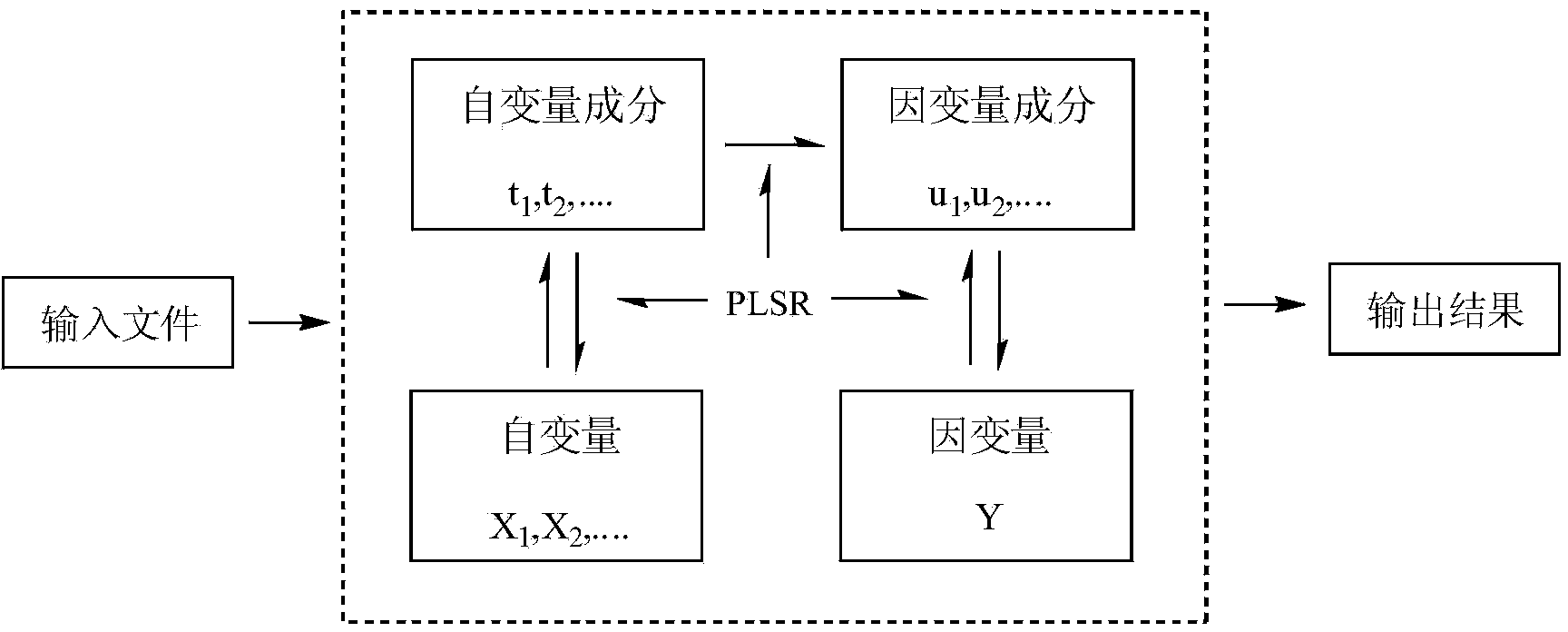
[0026] Using the quantum chemistry software Gaussian, select the molecular volume MV, relative molecular mass MW, and the highest molecular orbital energy E HOMO , the lowest unoccupied orbital energy E LUMO, frontier orbital energy level difference ΔE, molecular dipole moment μ, molecular solvation energy E sol , the electron energy E of the molecule T , the most positive atomic net charge Q+ of the molecule, the most negative atomic net charge Q- of the molecule, and the most positive hydrogen atom net charge Q of the molecule H More than a dozen quantum chemical p...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Constructing a predictive model of the acute toxicity of halogenated benzene derivatives to Daphnia magna by means of quantum chemistry.
[0033] The acute toxicity data LC50 of 40 halogenated benzene derivatives to Daphnia magna was obtained from the QSAR toolbox, and every five substances were selected as the verification set data after being arranged according to their toxicity. Toxicity as the training set.
[0034] (Variable selection and judgment criteria are the same as Example 1)
[0035] The fitting formula is: lnLC50=-1.180logp+5.529
[0036] (R 2 =0.730, F=75.883, Q 2 ext =0.839, n=32)
[0037] (Accompanying drawing is similar to embodiment 1).
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Construction of a predictive model for the acute toxicity of organophosphorus pesticides to green algae by means of quantum chemistry.
[0039] The acute toxicity data LC50 of 40 organophosphorus pesticides to green algae was obtained from the QSAR toolbox, and every five substances were selected as the verification set data after being arranged according to their toxicity. Training set. (Variable selection and judgment criteria are the same as Example 1)
[0040] The fitting formula is: lnEC50=-1.886log p+0.027MV+2.64
[0041] (R 2 =0.805,F=53.537,Q 2ex t=0.706,n=32)
[0042] (The accompanying drawing is similar to Example 1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com