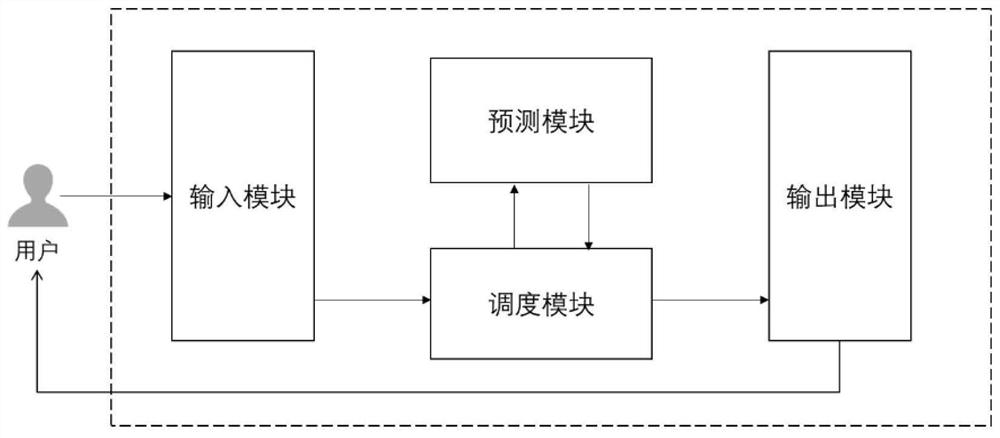
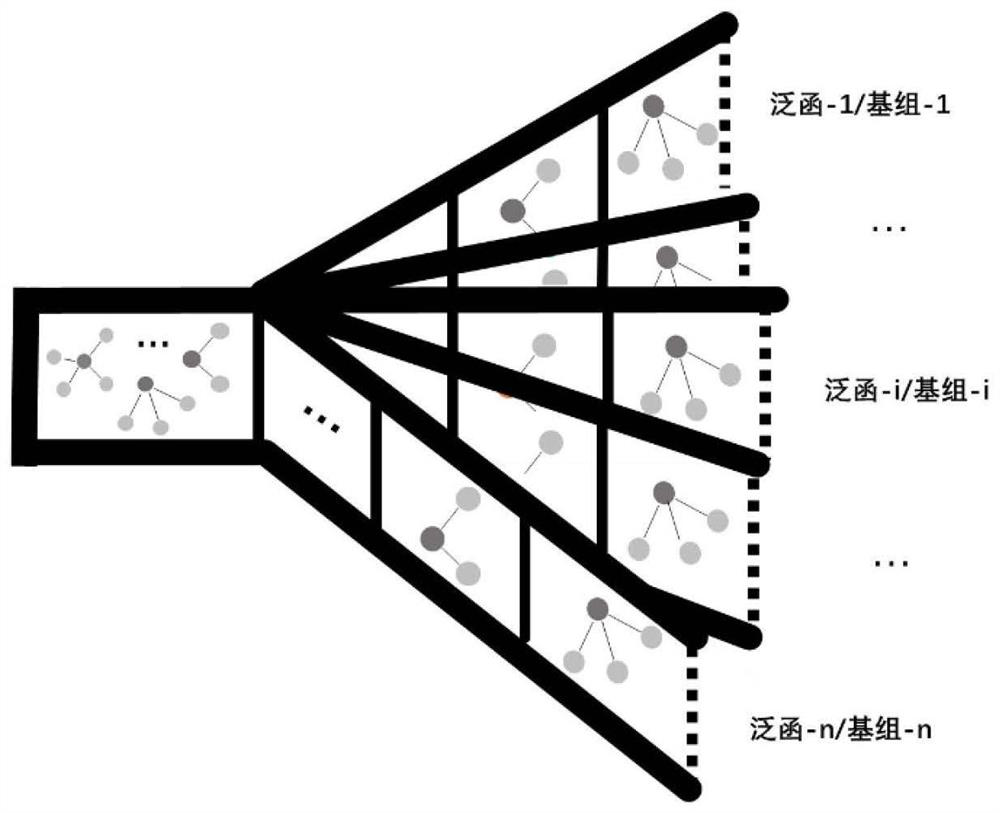
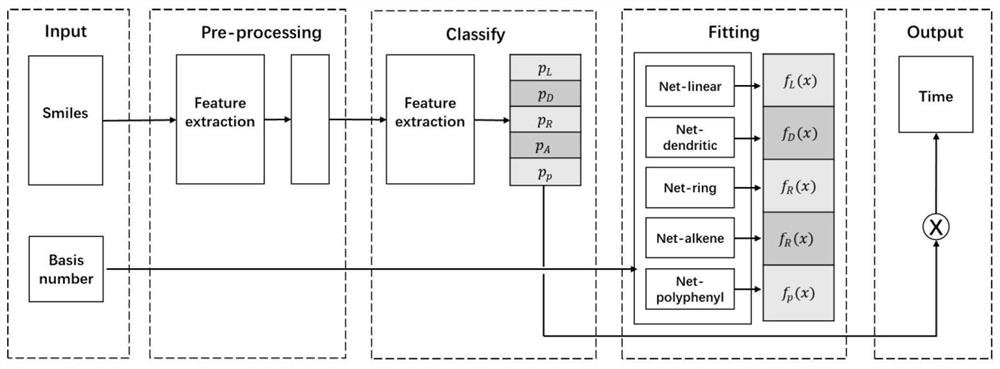
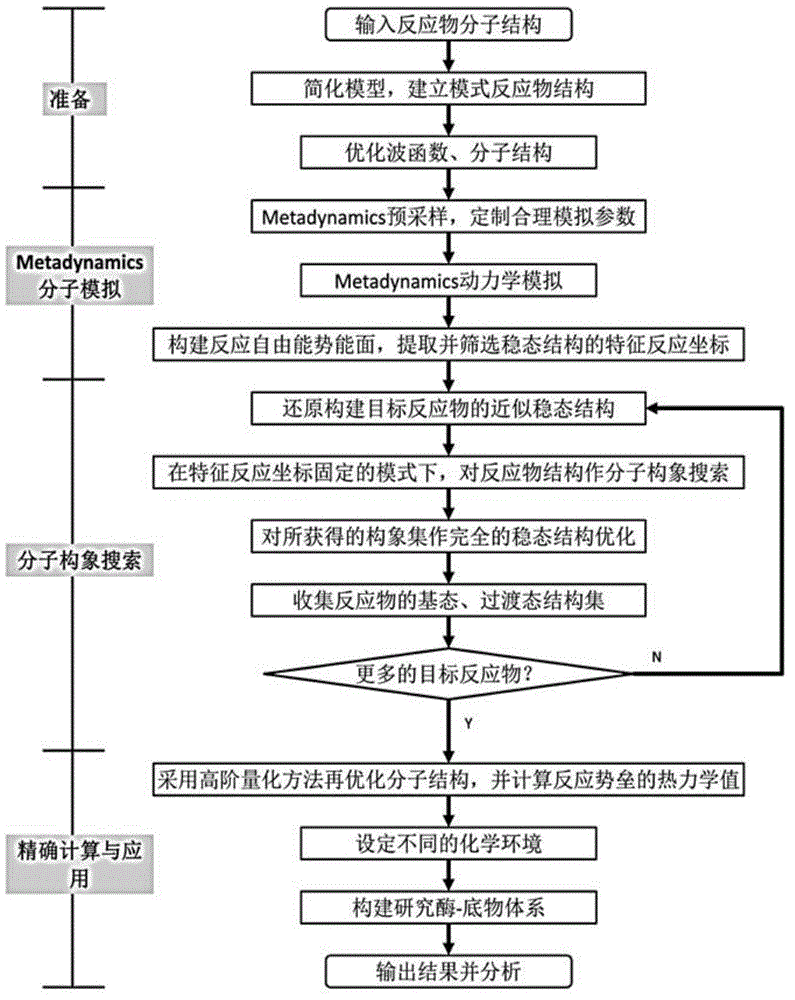
Patents
Literature
91 results about "Quantum chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
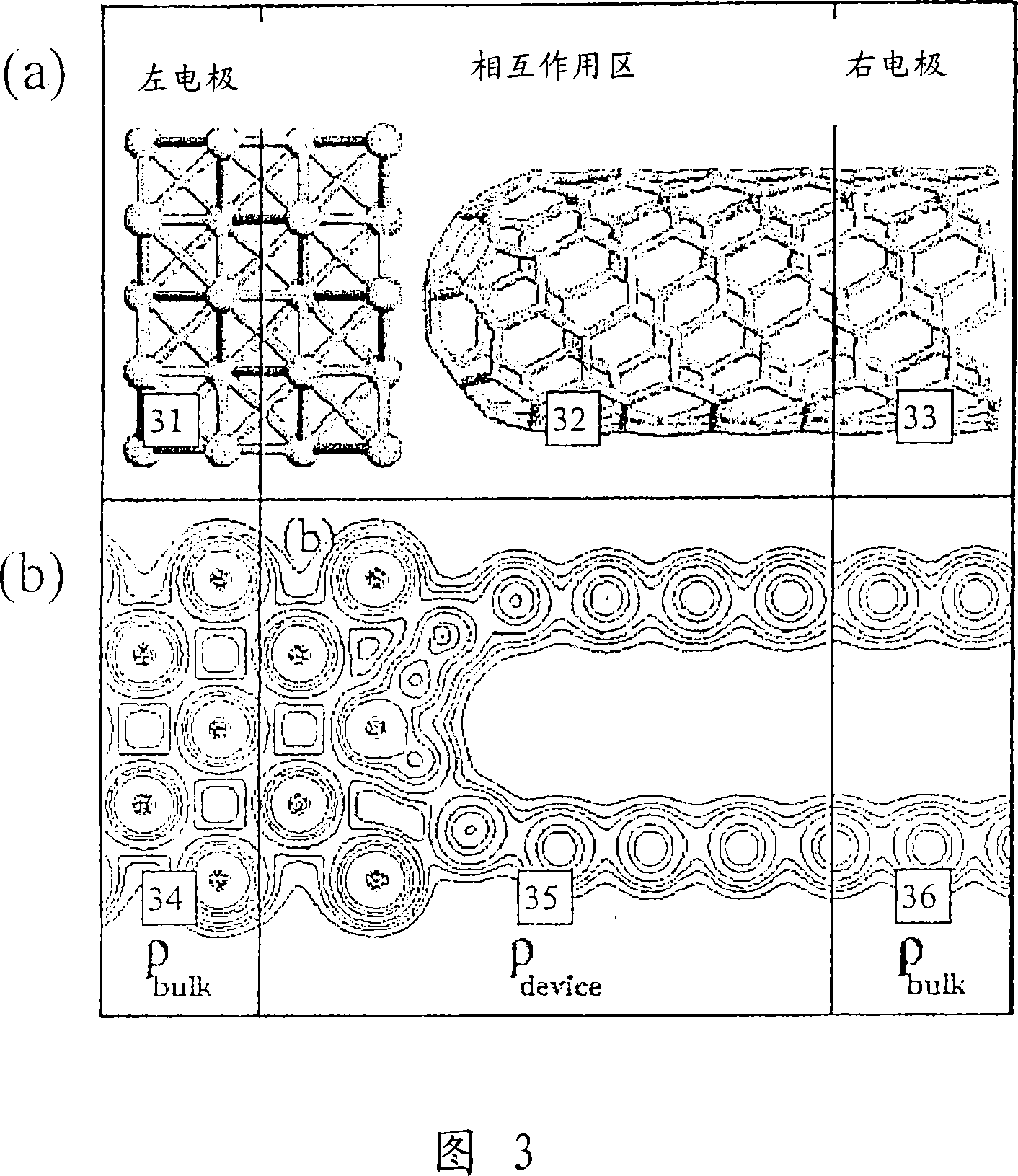
Quantum chemistry is a branch of chemistry whose primary focus is the application of quantum mechanics in physical models and experiments of chemical systems. It is also called molecular quantum mechanics.
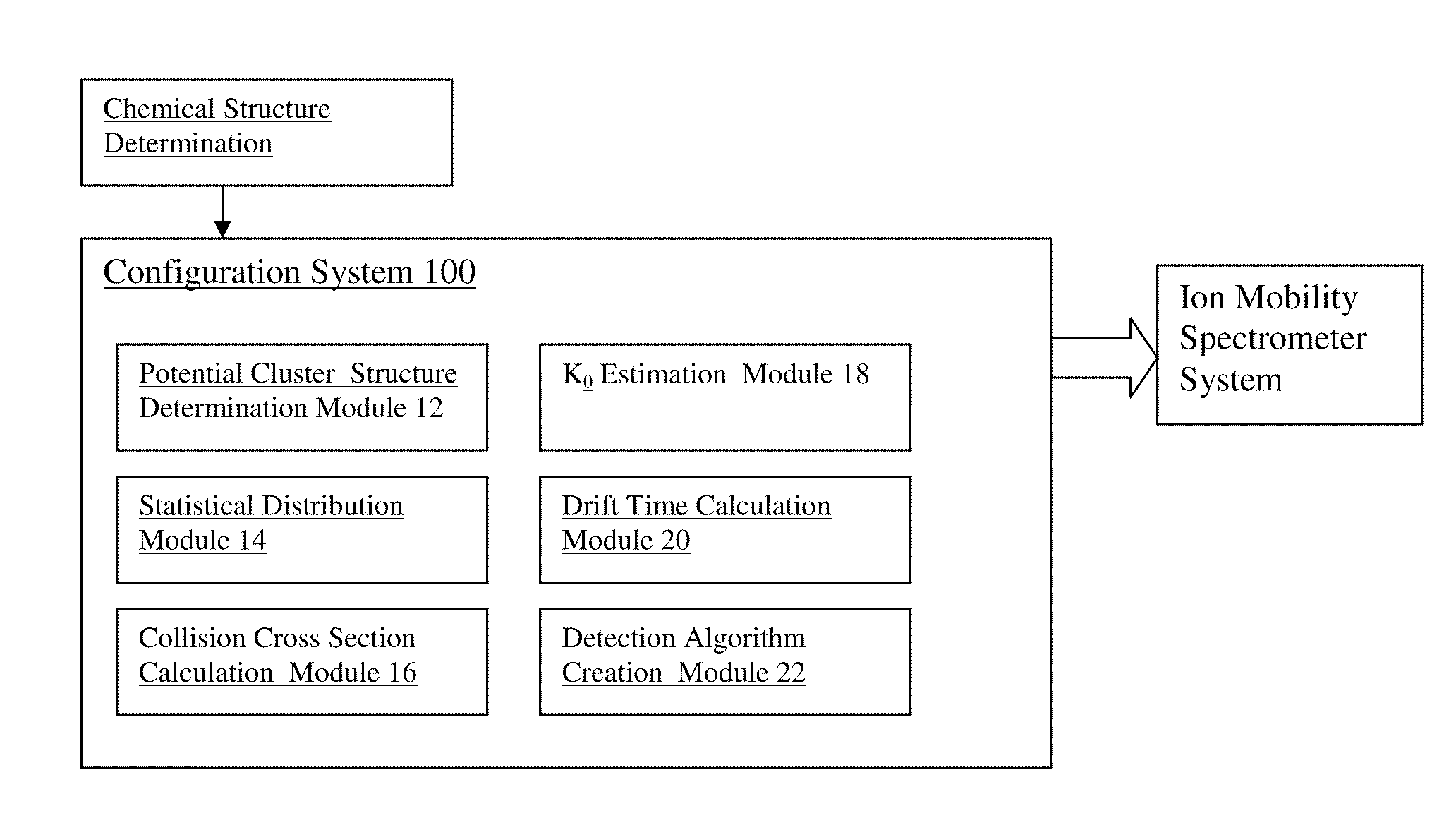
Method for configuring an ion mobility spectrometer system
InactiveUS20100224770A1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhysicsIon-mobility spectrometry
This invention relates to a method of configuring an ion mobility spectrometer system, particularly for detecting a target analyte. The method involves using quantum chemical techniques to estimate the Ko values of the target analyte, and configure the ion mobility spectrometer system based upon a detection algorithm.
Owner:ENSCO INC
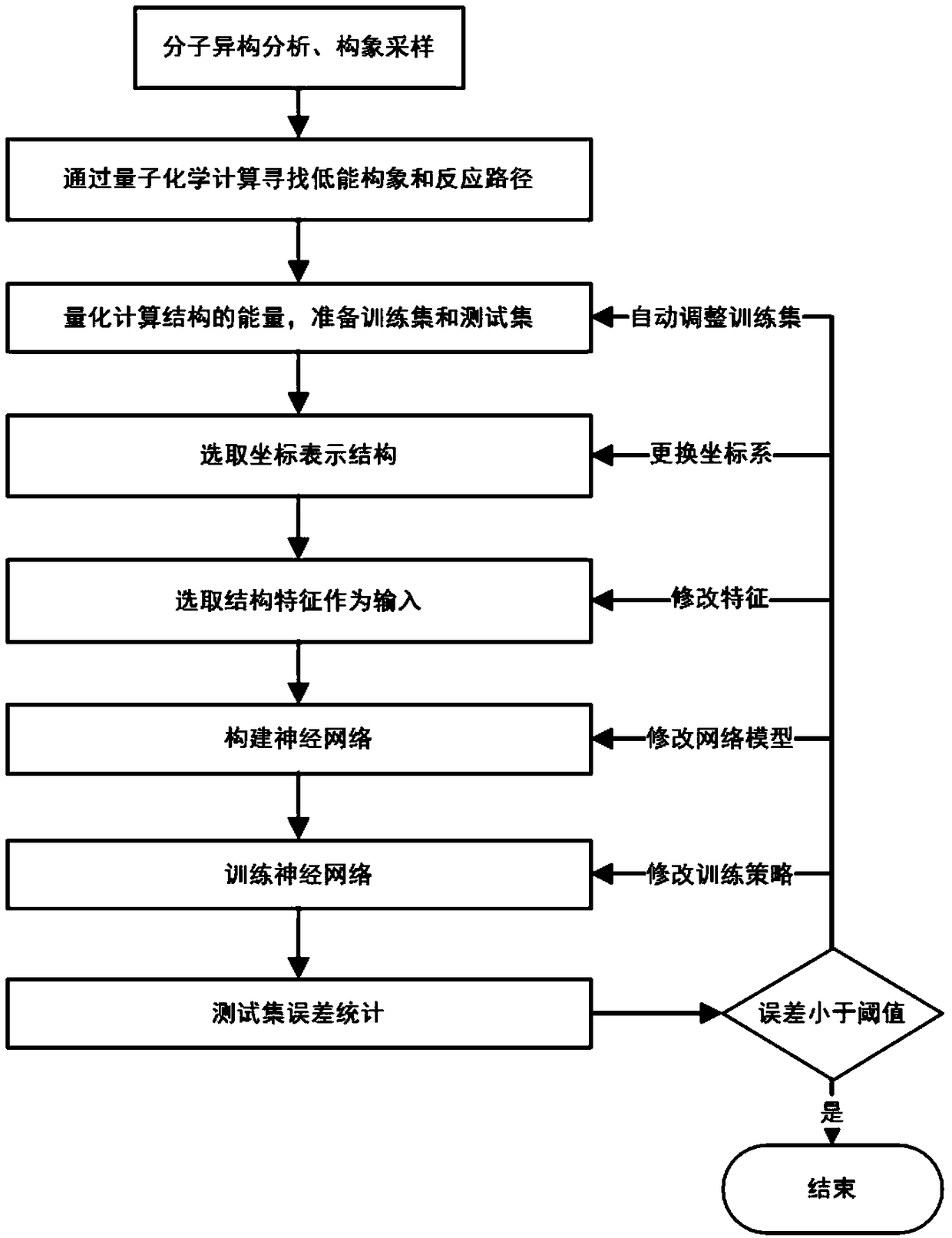
Molecular structure and chemical reaction energy function building method based on neural network
ActiveCN108804869AHigh precisionImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsQuantum chemistryChemical reaction
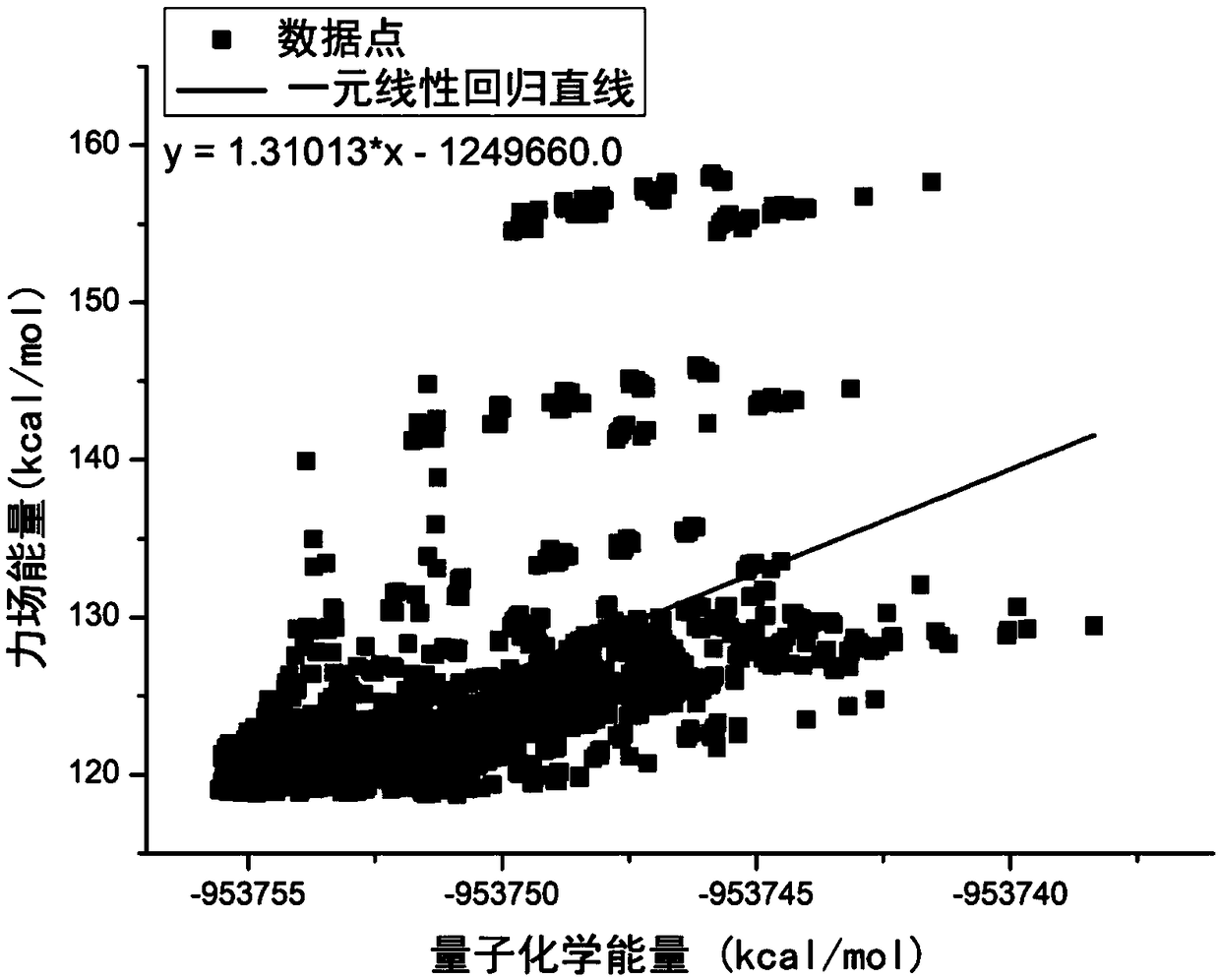
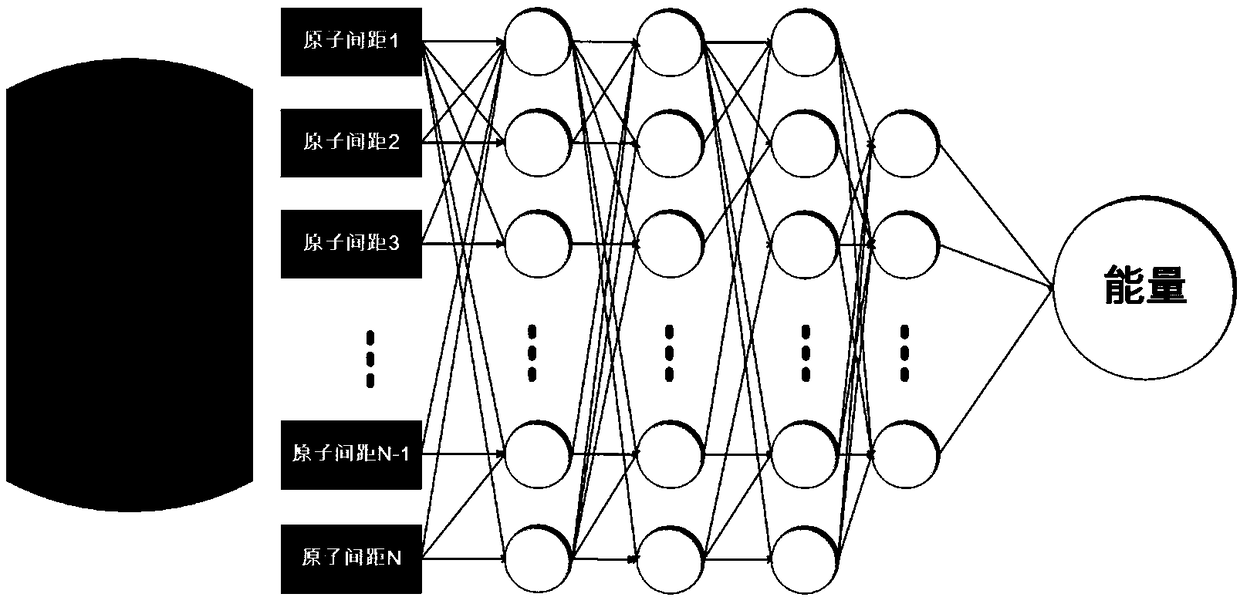
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum chemistry, and particularly relates to a molecular structure and chemical reaction energy function building method based on a neural network. The method comprises the steps of performing sampling on each degree of freedom of a molecular or chemical reaction; searching for a low-energy conformation structure through quantitative calculation; performing energy calculation on the structure, and preparing a training set and a test set; selecting a proper coordinate representation structure; according to different coordinates, constructing different features to describe the structure; selecting a proper neural network; selecting a proper method to train the neural network; after the training is completed, performing error statistics on thetest set, and when an error is smaller than 1.0 kcal / mol, ending the training; and if the error is greater than 1.0 kcal / mol, following a re-searching model. The precision of obtained conformation energy, reaction energy and the like is higher; the method can be widely applied to the quantum dynamics and molecular dynamics processes; and not only a single molecule conformation but also the chemical reaction including intramolecular or intermolecular bond breaking and generating can be simulated.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD +1
Method for forecasting acute toxicity of organic compounds by building quantitative structure-activity relationship model with quantum chemistry method
InactiveCN103646180APredict toxicityChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular orbital energyAb initio quantum chemistry methods
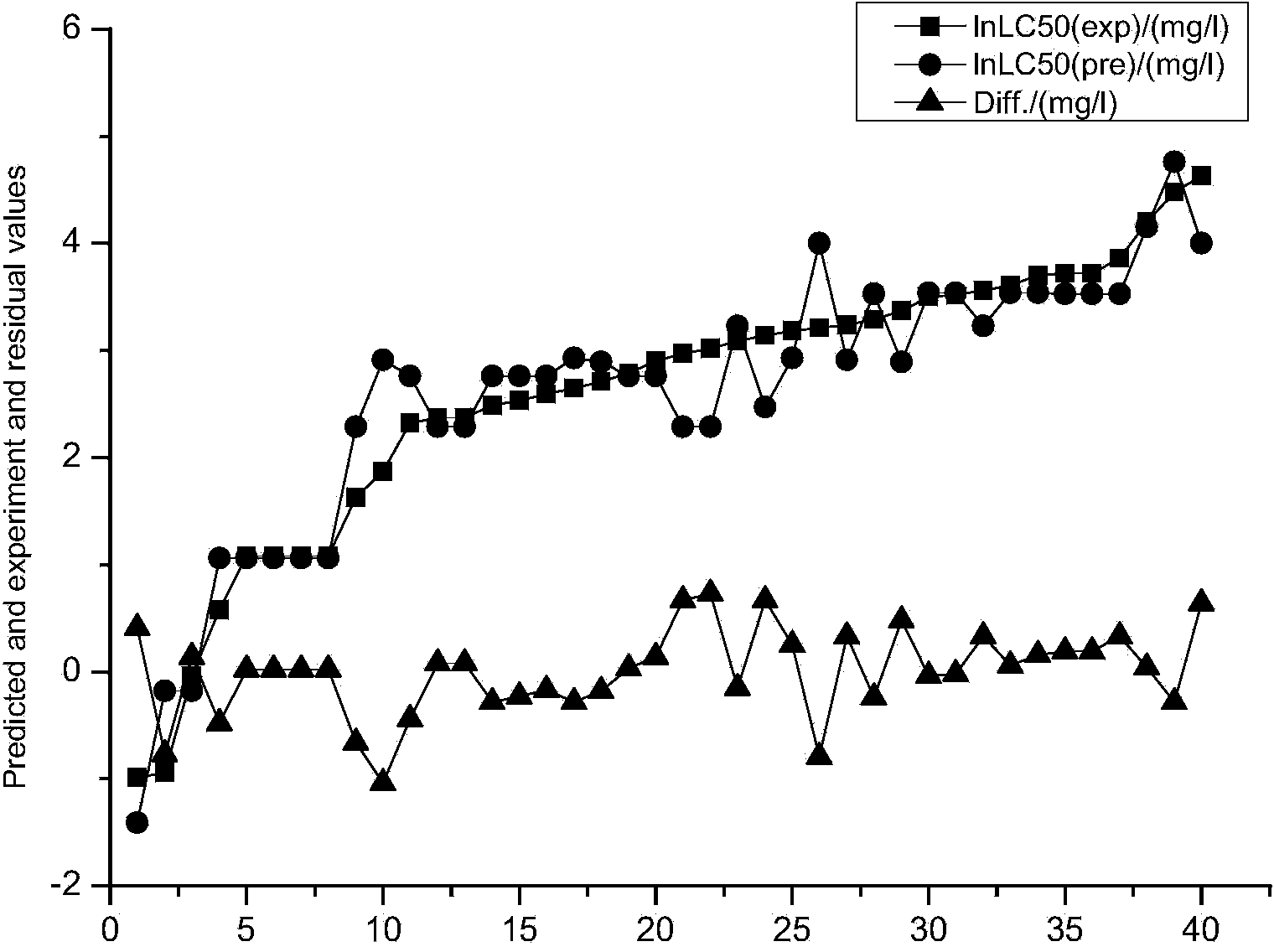
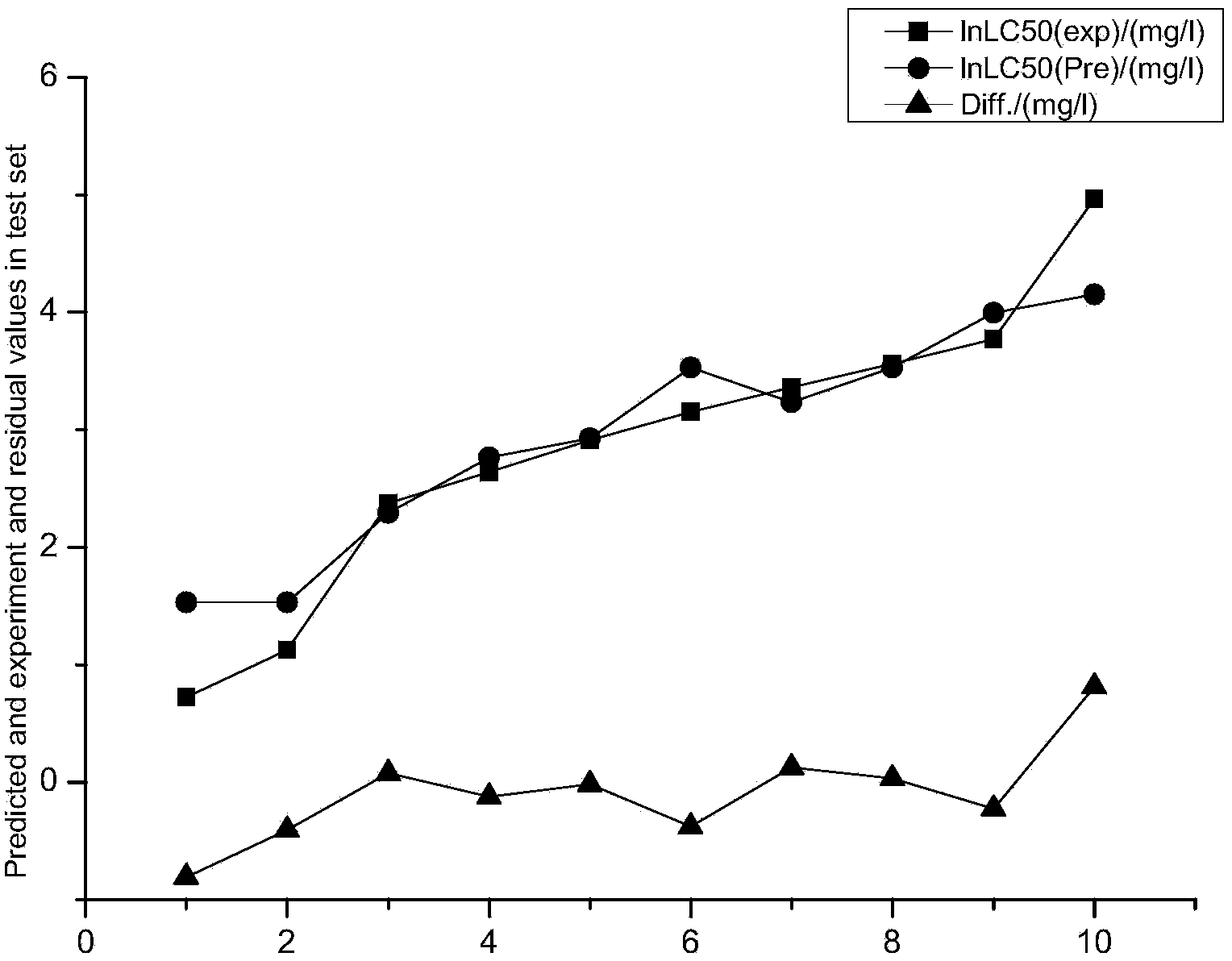
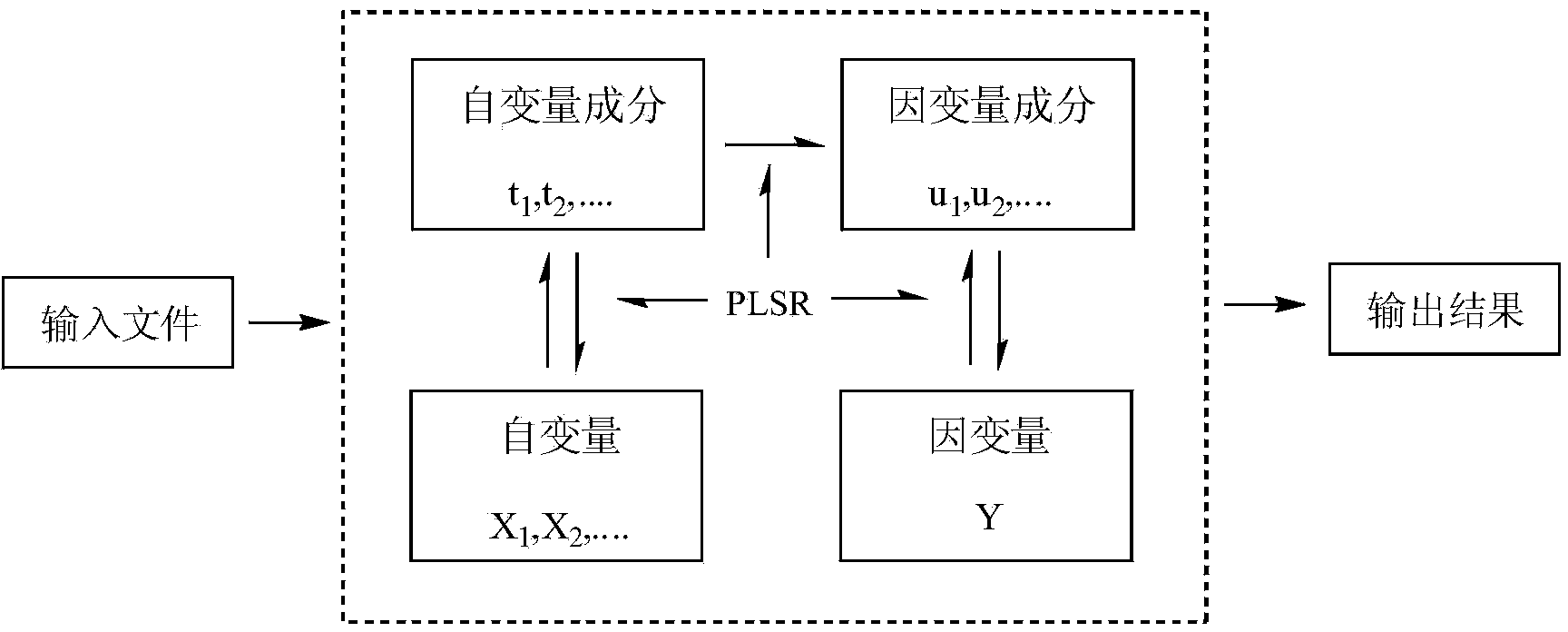
The invention discloses a method for forecasting the acute toxicity of organic compounds by building a quantitative structure-activity relationship model with a quantum chemistry method. The method fully geometrically optimizes compound structures by using a Gaussian procedure so as to obtain quantum chemistry parameters including molecular volume, relative molecular mass, highest occupied molecular orbital energy, lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy, energy gaps of frontier molecular orbital, dipole moment, solvation energy, electron energy and the like; using the quantum chemistry parameters and a hydrophobicity parameter as structural descriptors; in combination with toxicity data, quantitative relationship equations between various structural descriptors and toxicity are established according to a written procedure based on partial least square stepwise linear regression to obtain the multiple correlation coefficient, F-test value and sum of squared residuals, and then the model is verified so as to guarantee the external predictive ability. Therefore, the method can quickly and effectively forecast the toxicity of organic compounds to be studied, and provide necessary basic data for risk assessment and supervision of chemicals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
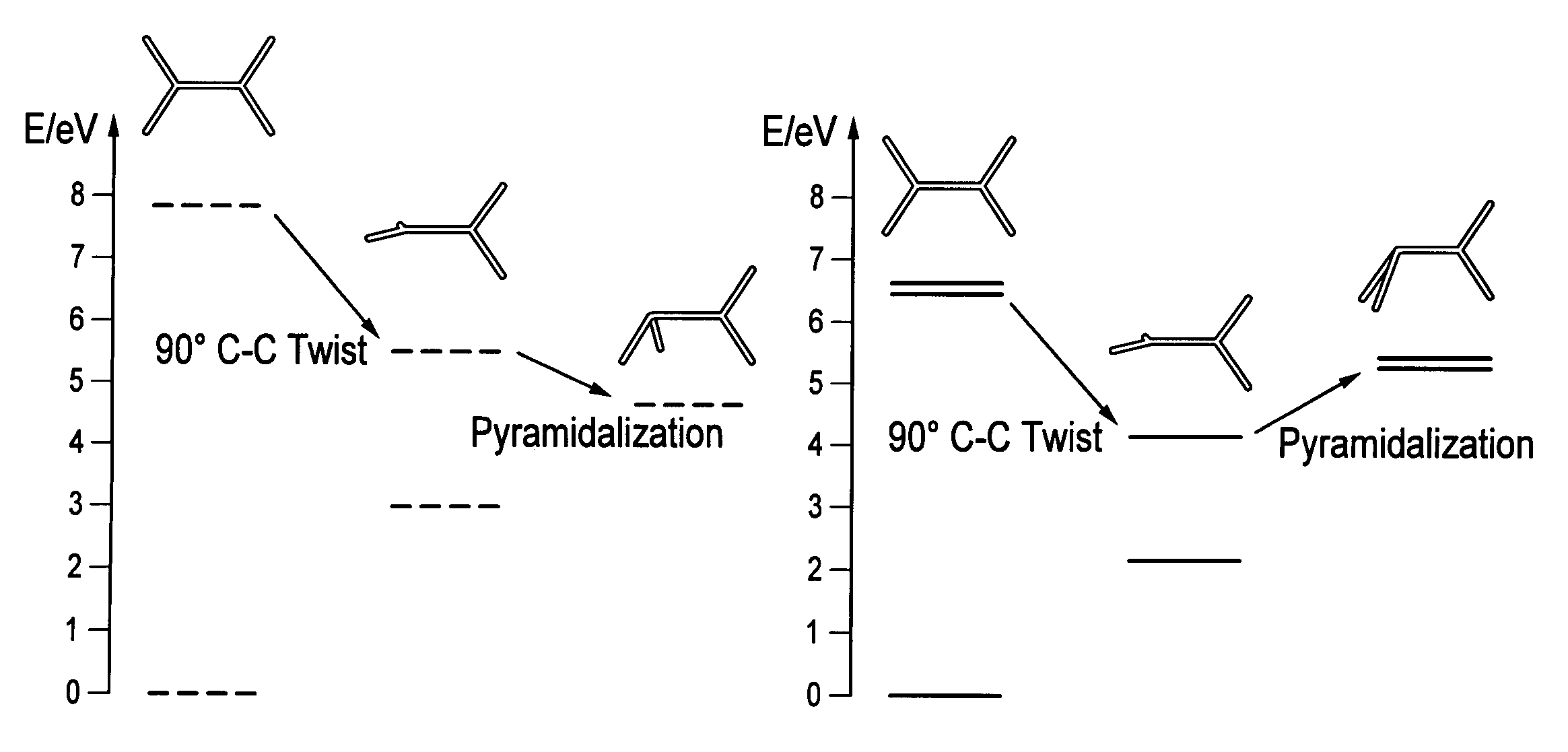
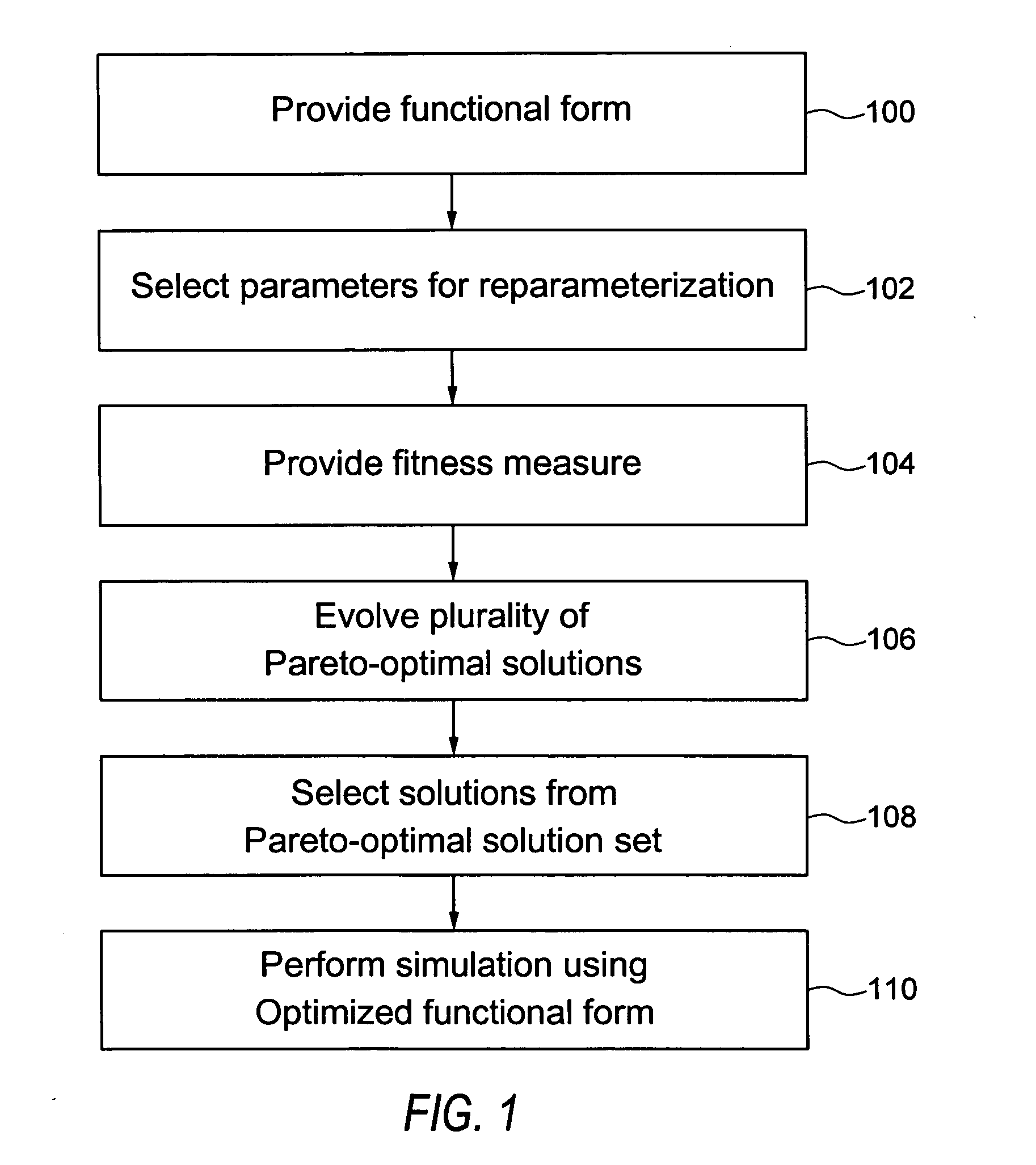
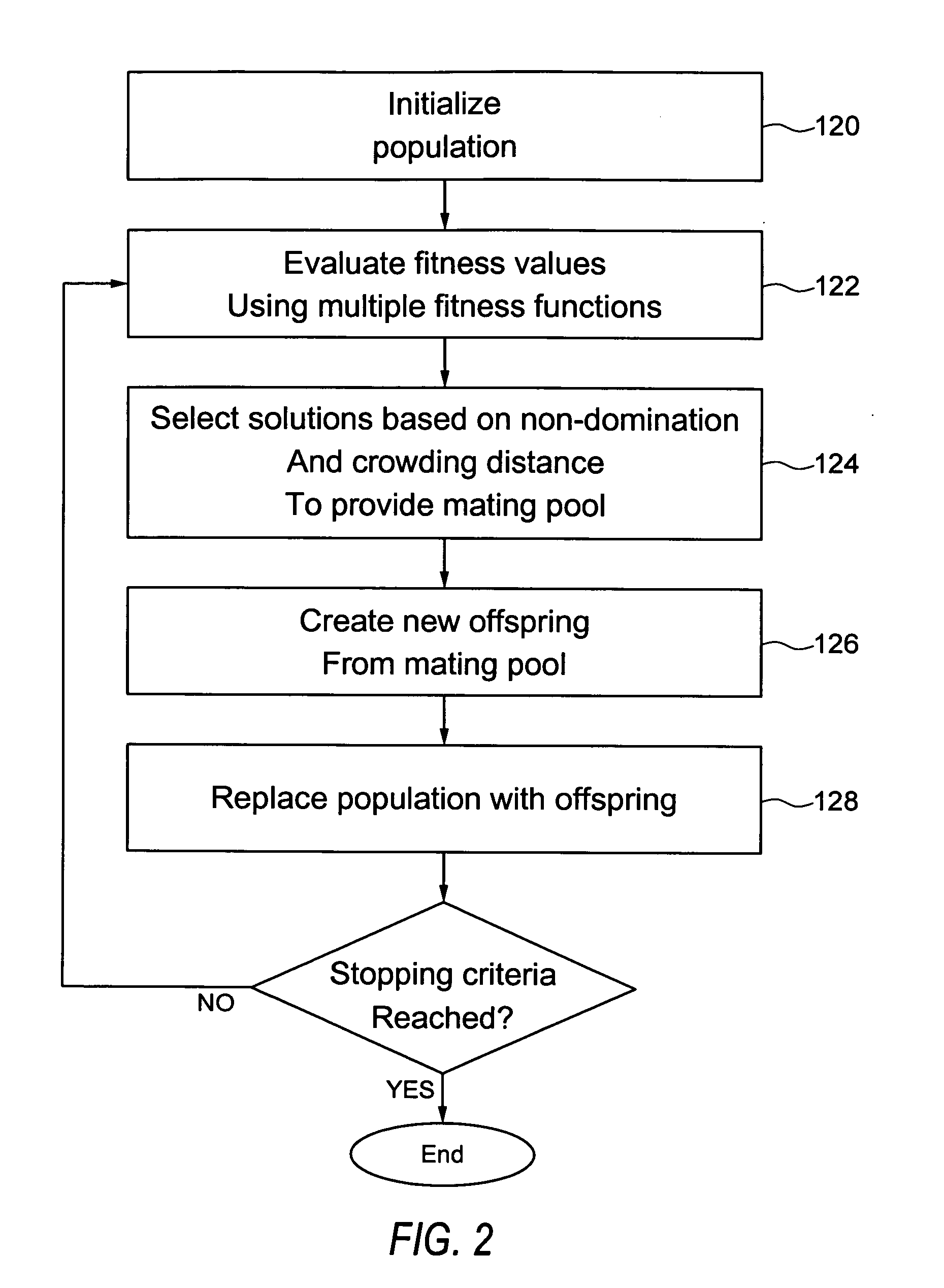
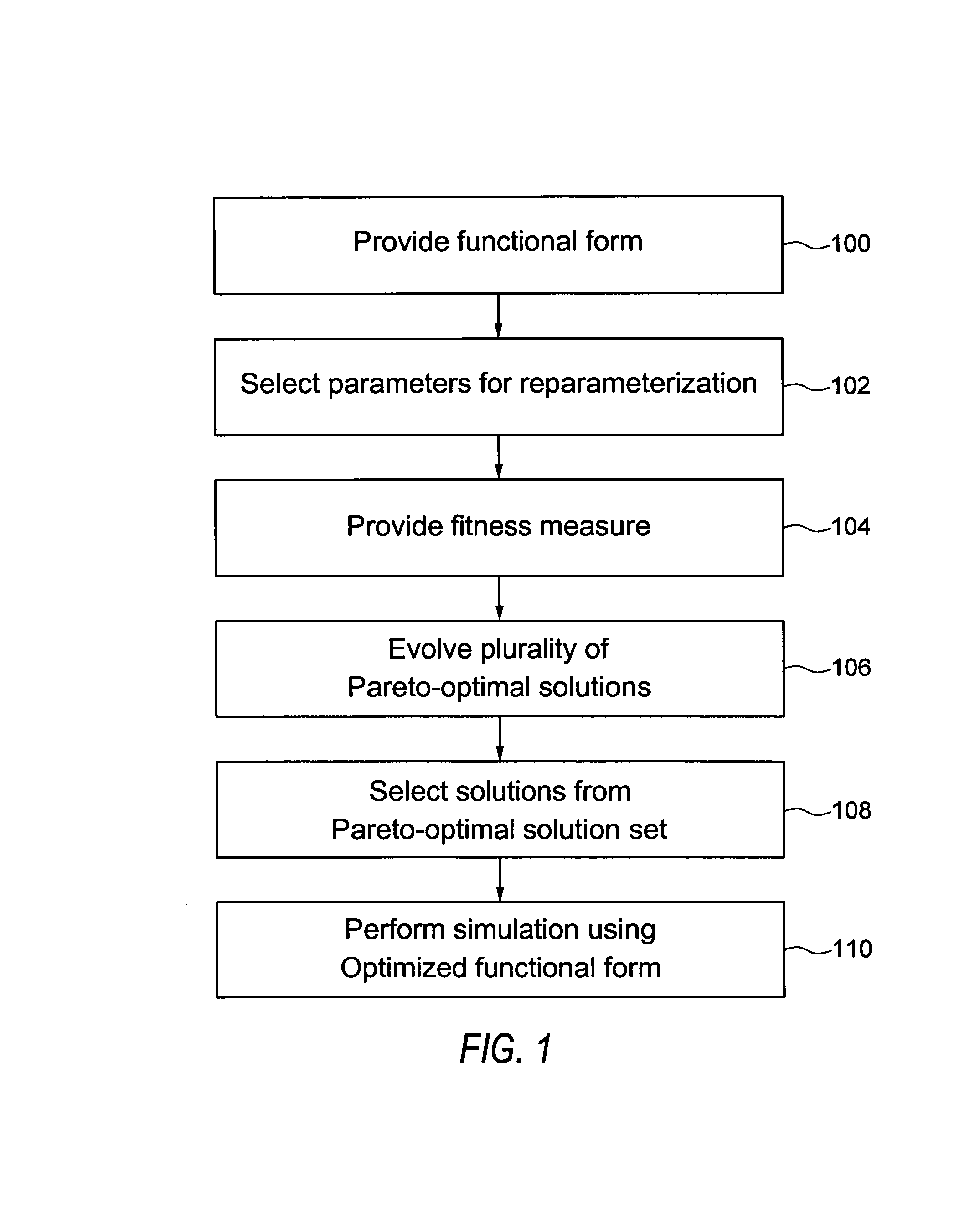
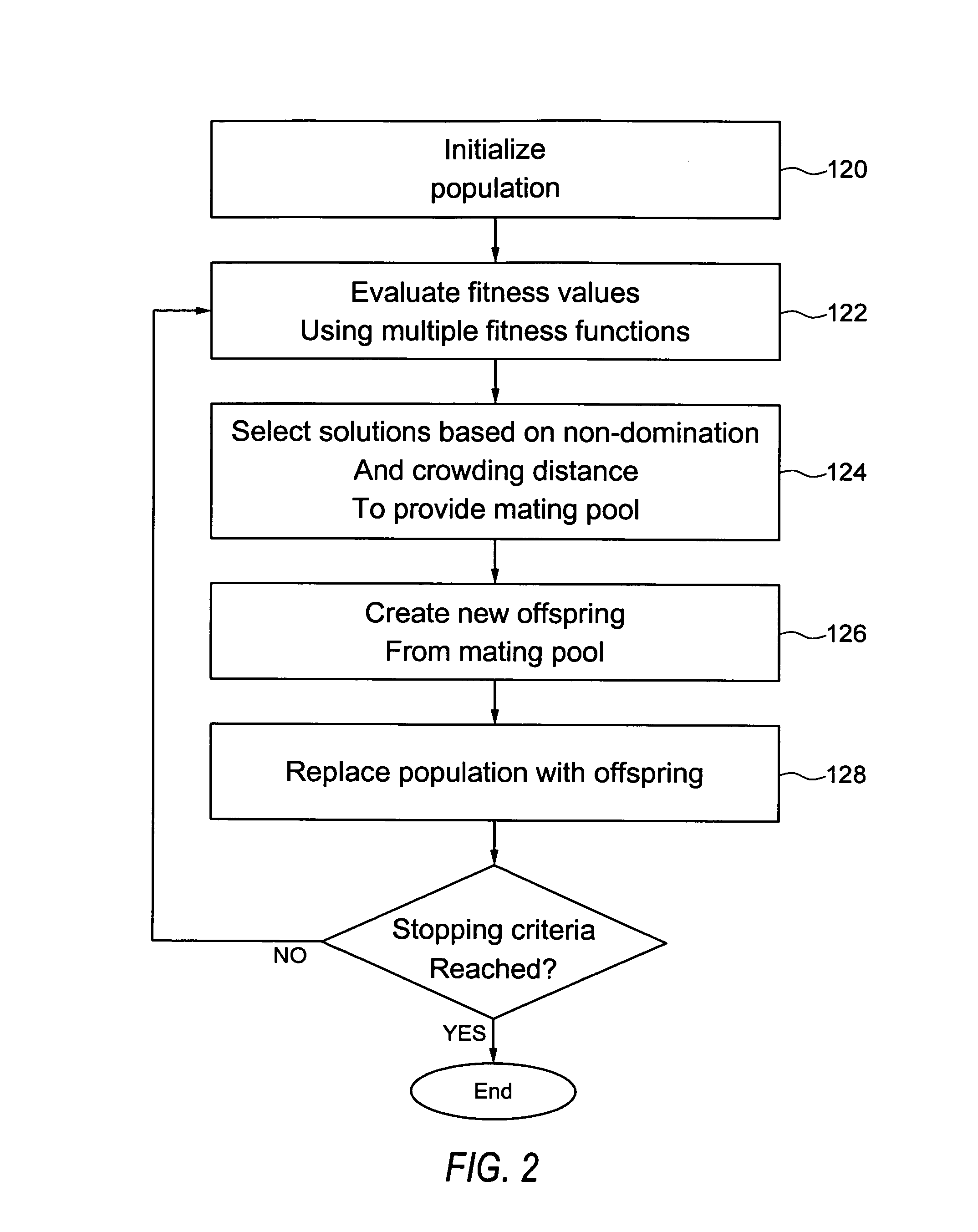
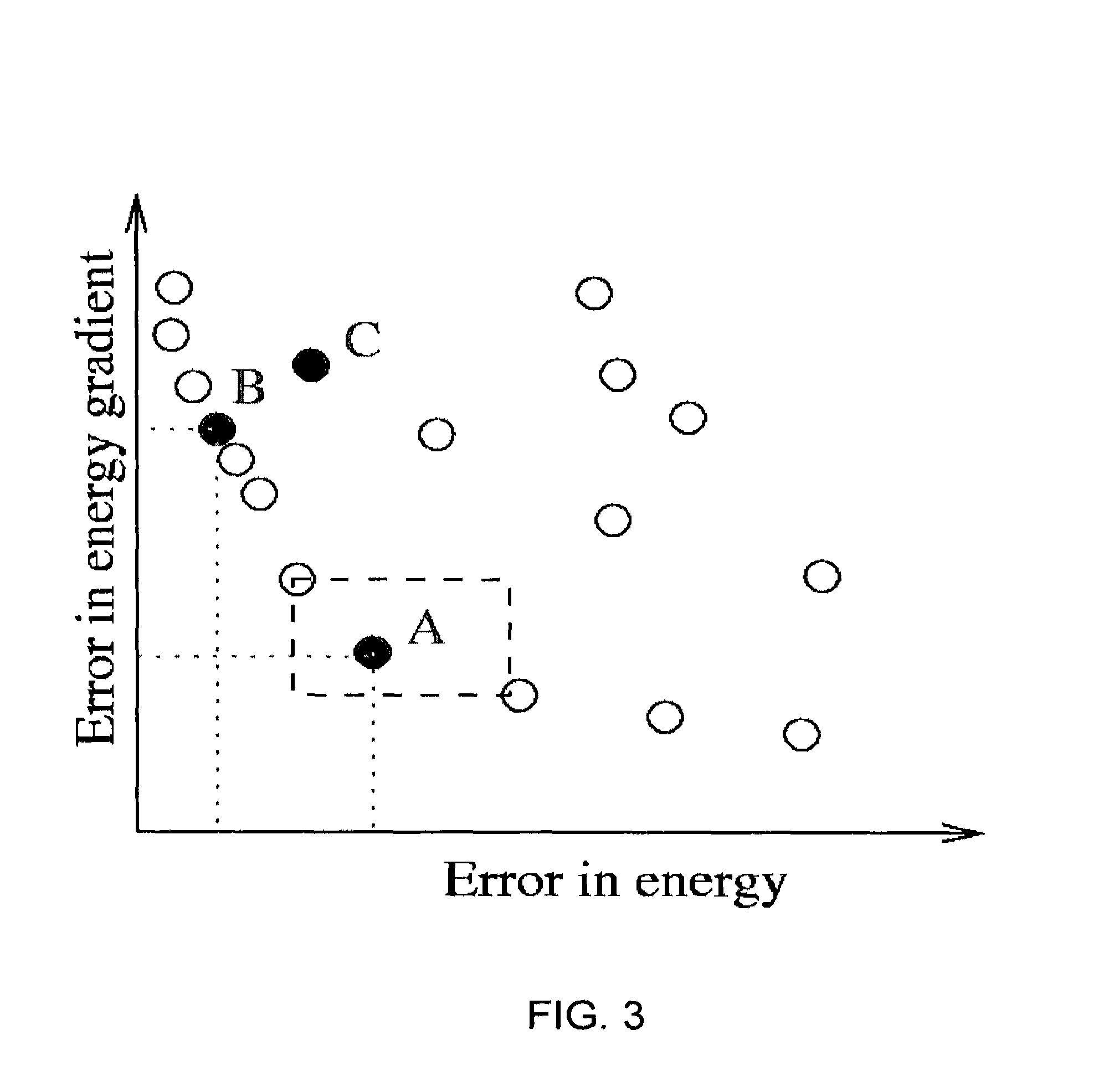
Quantum chemistry simulations using optimization methods
ActiveUS20080312895A1Chemical property predictionDigital data processing detailsQuantum chemistryEnergy gradient
Embodiments of the present invention provide, among other things, methods, apparatus, and systems for tuning a semiempirical process for predicting energy for different molecular configurations. In an example method, an energy value and an energy gradient are determined for each of a plurality of molecular configurations using an accurate method. A functional form of the semiempirical process is optimized using the determined energy values and energy gradients via multiobjective optimization. The functional form relates one or more parameters to energy values and energy gradients.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINIOS THE
Molecular property prediction method and system
ActiveCN111710375AThe regression analysis method is accurateChemical property predictionChemical machine learningCheminformaticsQuantum chemistry
The invention provides a molecular property prediction method and system, and relates to the fields of quantum chemistry / computational chemistry, chemical informatics and machine learning / artificial intelligence. Under the framework of chemical multi-world explanation, a density functional theory, chemical informatics and machine learning / artificial intelligence means are used, information such asa molecular structure, a base group, a functional and the like is used as input, and a prediction result of molecular property is output through a machine learning model. According to the method, anytype of molecular structure and any calculation strategy can be predicted, and the method is more accurate than a common experience method and a regression analysis method.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Complex system reaction access calculating system and implementing method thereof
ActiveCN104021265AIncrease productivityImprove responseSpecial data processing applicationsReaction coordinateCritical structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical and molecular structure information, and provides a complex system reaction access calculating system and an implementing method thereof. The calculating system comprises a molecular simulation and quantum chemistry calculating module, a molecular conformation searching module and a refined calculation and application module. A molecular structure simplified pattern reaction system is constructed, a characteristic reaction path is analyzed, and relevant key structures comprising ground states and transient states of reactions of a target reaction system are searched for. Based on a low-dimensional characteristic potential energy surface in a pattern system, a reaction network access is set up, and reaction coordinates of local minimum points and saddle points of a potential energy surface in a network are recorded; based on information of the reaction coordinates, molecule grafting restoring the pattern system (simple) to the target system (complex) is achieved. Through the molecular conformation searching technology, under the condition of characteristic coordinate restraint, a conformation set of reaction objects of the target system is searched for, and molecules in the conformation set are structurally optimized; effective ground state and transient state molecular structures of the reaction objects are collected according to the reaction characteristics of the characteristic coordinates on the reaction path.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and computer system for quantum chemical modelling of molecules under non-equilibrium conditions
InactiveCN101019122ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic structureQuantum chemistry
Owner:ATOMISTIX
Quantum chemistry reaction optimization multi-relay selection method of cognitive relay network
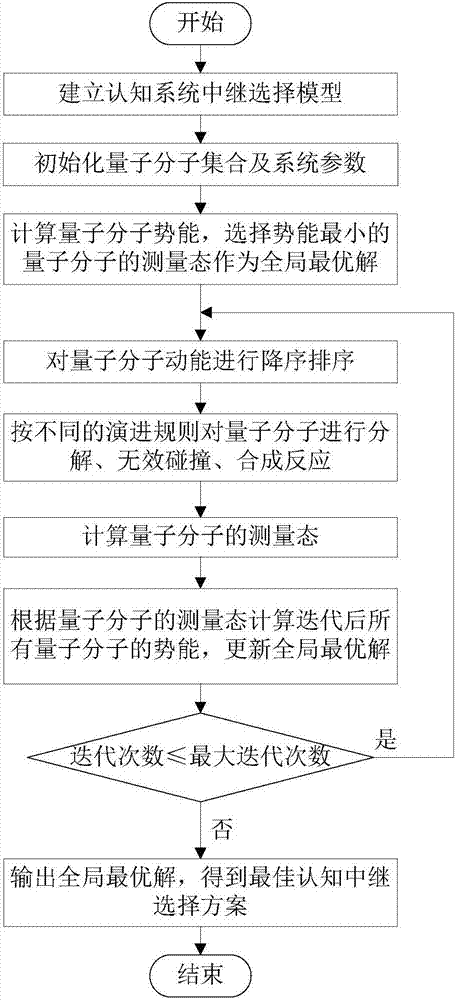
ActiveCN107454604ASolve the problem of multiple relay selectionFast convergenceNetwork planningHigh level techniquesChemical reactionCognitive systems
The invention provides a quantum chemistry reaction optimization multi-relay selection method of a cognitive relay network. The method comprises steps of: 1, establishing a cognitive system relay selection model; 2, initializing a quantum molecule set and a system parameter; 3, evaluating the potential energy of all quantum molecules in the set and selecting the measurement state of the quantum molecule with the lowest potential energy as a global optimal solution; 4, arranging the kinetic energy of quantum molecules in a descending order, and performing decomposition reaction, invalid collision, and synthetic reaction; 5, evaluating the potential energy of newly generated quantum molecules, and if the minimum potential energy of the newly generated quantum molecules is less than the minimum potential energy of the previous generation, marking the newly generated quantum molecules as a new global optimal solution; and 6, if the number of iteration times is less than a preset maximum number of iteration times, returning to step 4, otherwise, outputting the global optimal solution. The method balances the primary user constraint condition and non-primary user constraint condition of the cognitive relay network, and chooses a relay selection scheme that maximizes the system throughput based on a quantum chemistry reaction mechanism.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
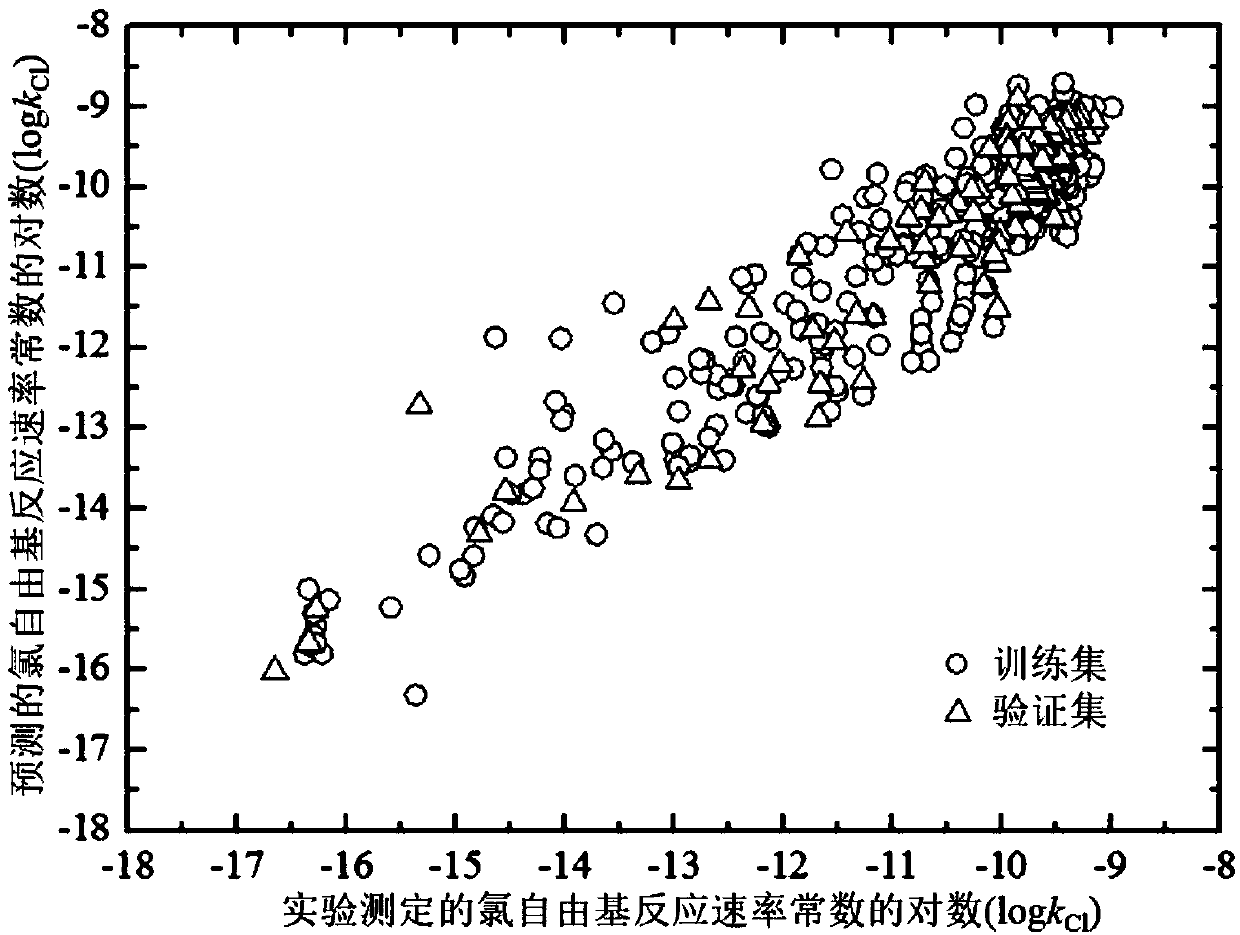
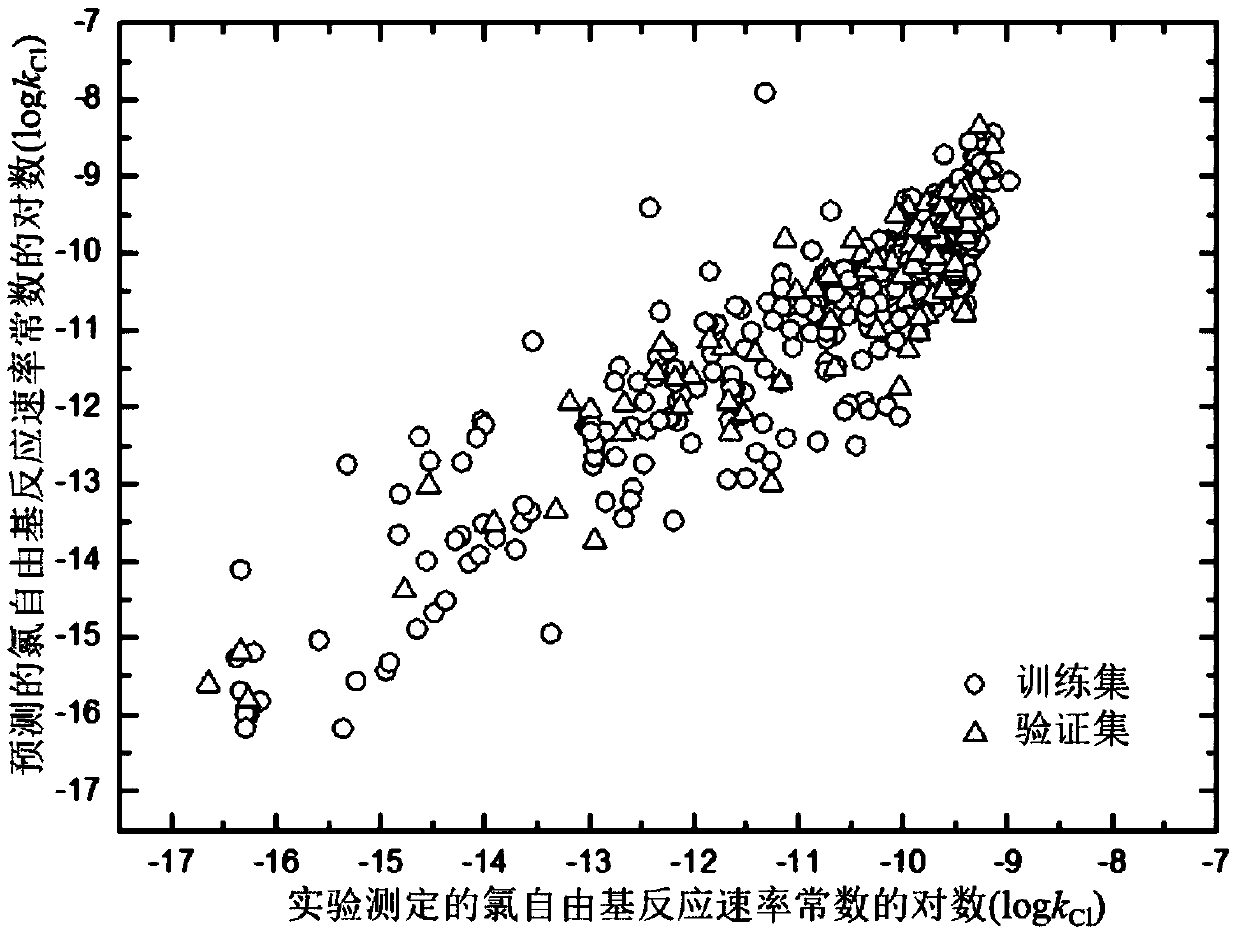
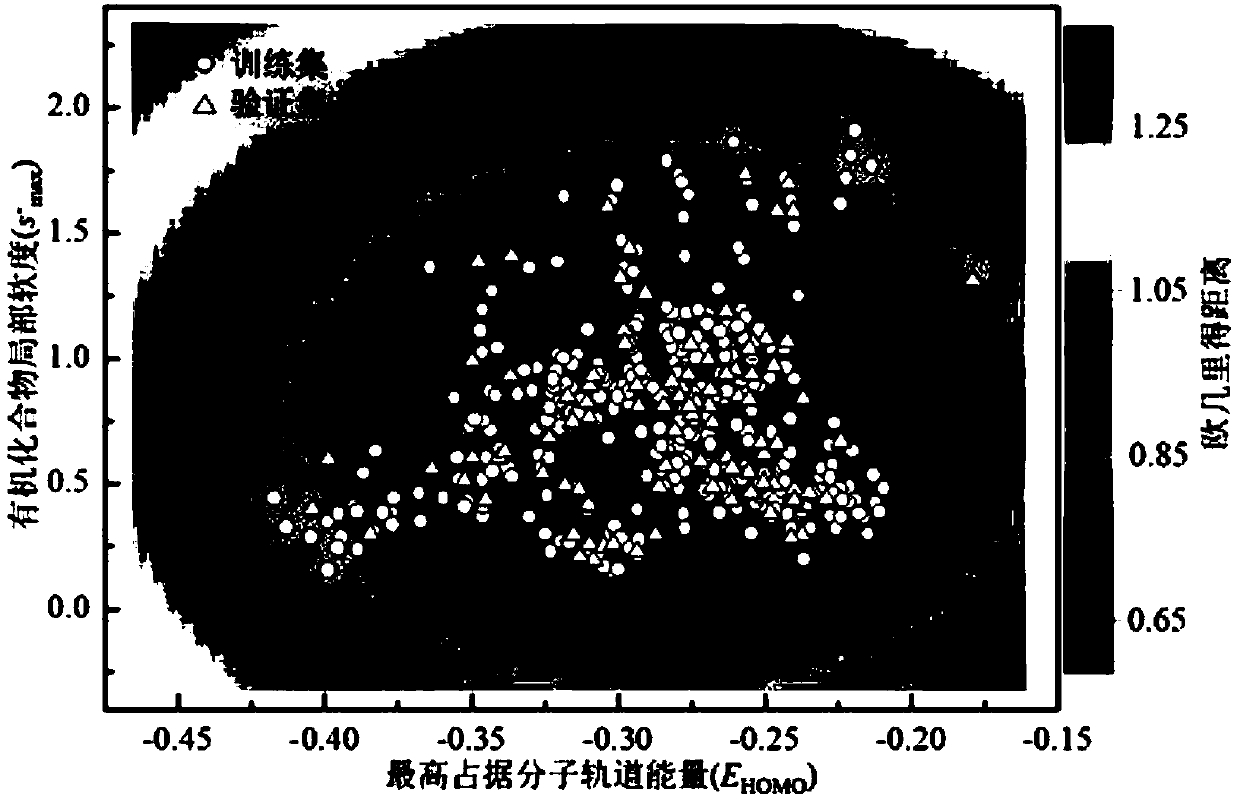
Method for adopting quantitative structure-activity relation model to predict reaction rate constant of chlorine free radical of organic chemicals
ActiveCN107563133AMechanism explanatoryLow costSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelComputational chemistry
The invention discloses a method for adopting a quantitative structure-activity relation model to predict a reaction rate constant of chlorine free radical of organic chemicals. According to the method, a quantum chemistry descriptor with structural characters is figured out only by means of basic molecular structure information of the organic chemicals, and by adopting a constructed QSAR prediction model, a kCl value of the organic chemicals can be predicted quickly and efficiently. The method follows a guide rule issued for the construction and verification of a QSAR model by the Organization For Economic Co-Operation And Development (OECD). According to the method, by adopting a genetic algorithm-multiple linear stepwise regression analysis combination use method (GA-MLR) and a supportvector machine-multiple linear stepwise regression analysis combination use method (SVM-MLR), the transparency degree is high and more convenience is provided for application; since quantum chemistrydescriptors are adopted in all GA-MLR models, the physical meaning of the descriptors is clear; the method has a specific application domain, and is applicable to abundant organic varieties, excellentin goodness of fit, robustness and prediction capability, easy to program and capable of supplying important data support to environmental risk evaluation and management of the organic chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
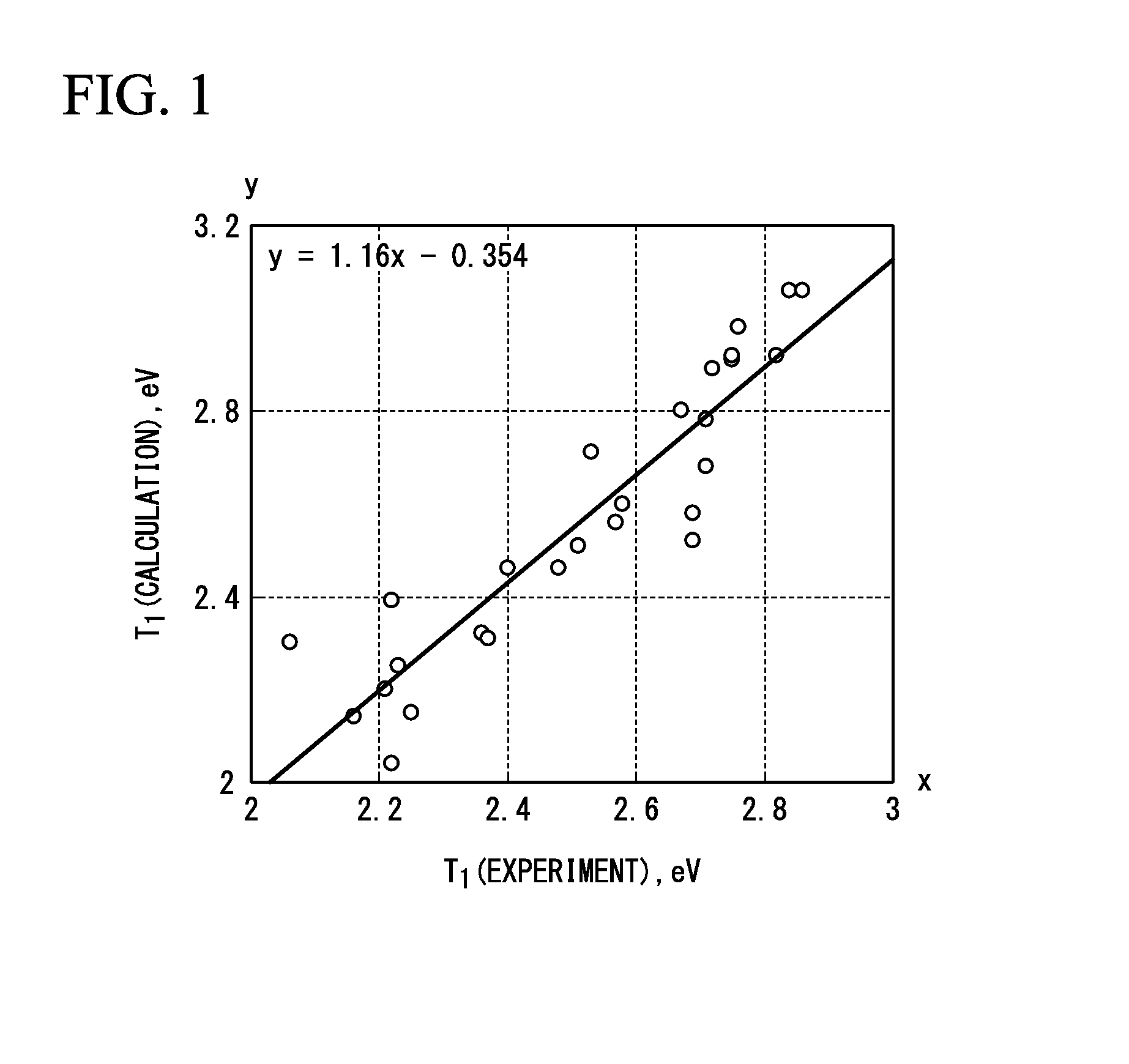
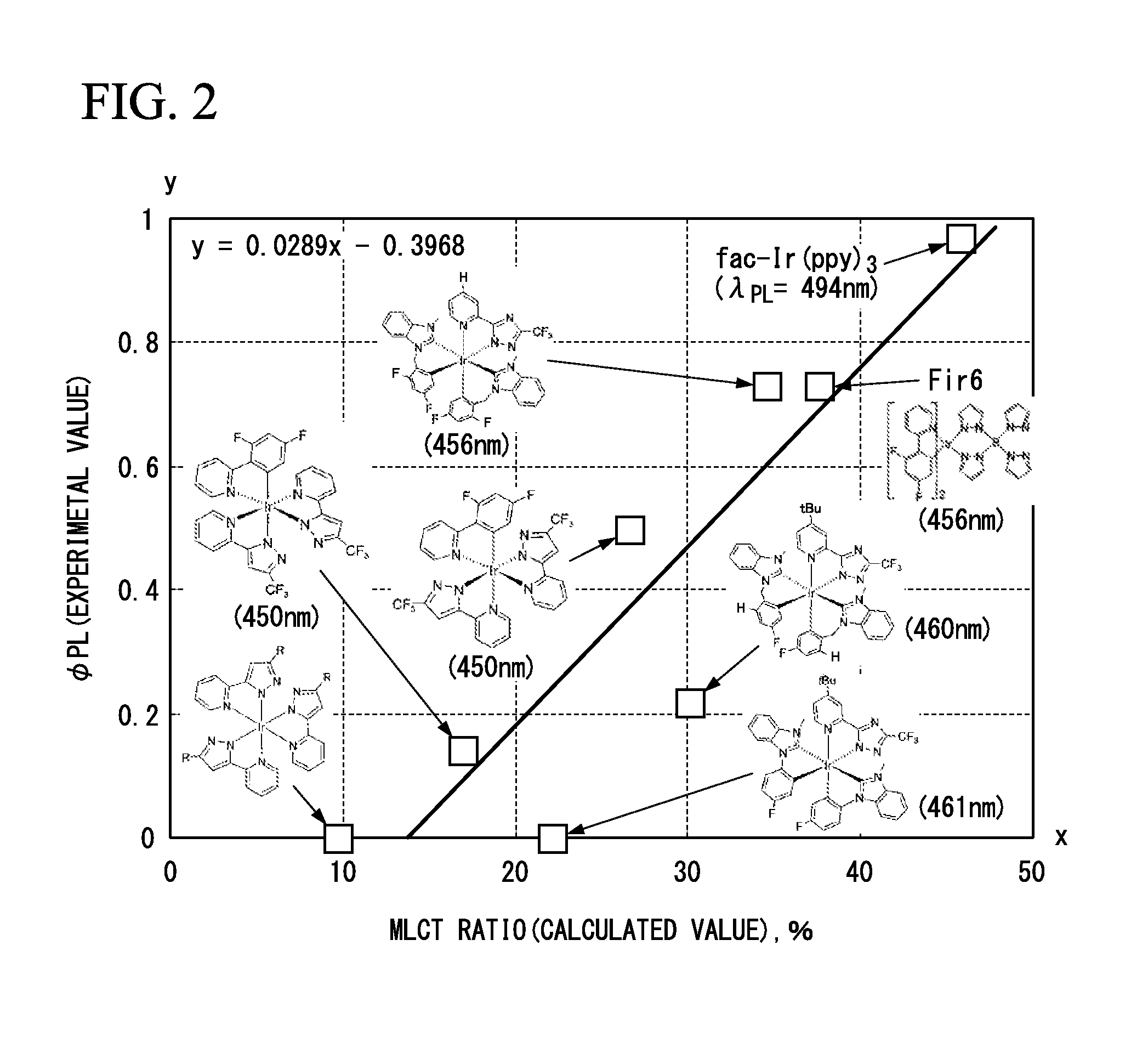
Luminescent material, and organic light-emitting element, wavelength-converting light-emitting element, light-converting light-emitting element, organic laser diode light-emitting element, dye laser, display device, and illumination device using same
InactiveUS20130303776A1Improve efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic laserQuantum chemical
A luminescent material includes transition metal complex comprising a ligand in which an electron density of a p orbital of a highest occupied molecular orbital level is higher than 0.239 and lower than 0.711 when the electron density is calculated according to quantum chemical calculation (Gaussian09 / DFT / RB3LYP / 6-31G), the p orbital being in the outermost shell of an element coordinated to the metal.
Owner:SHARP KK
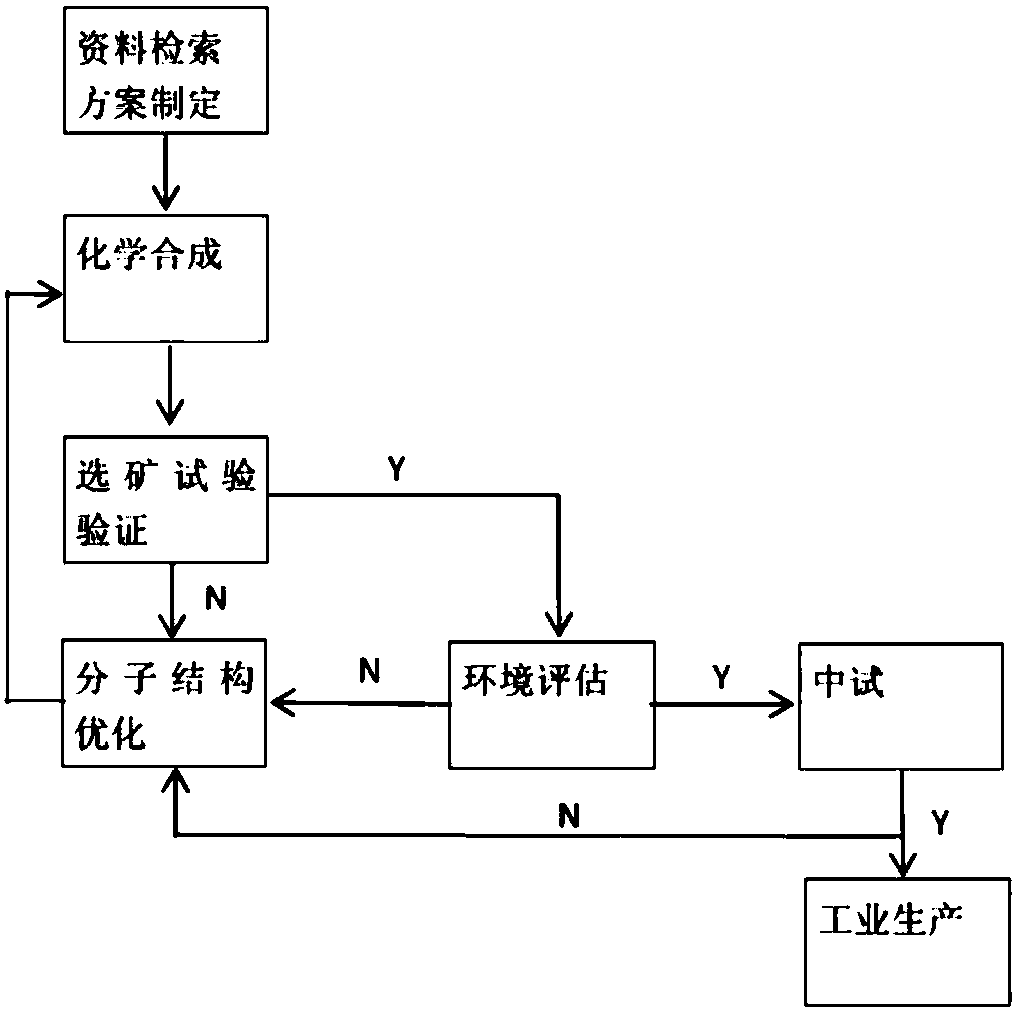
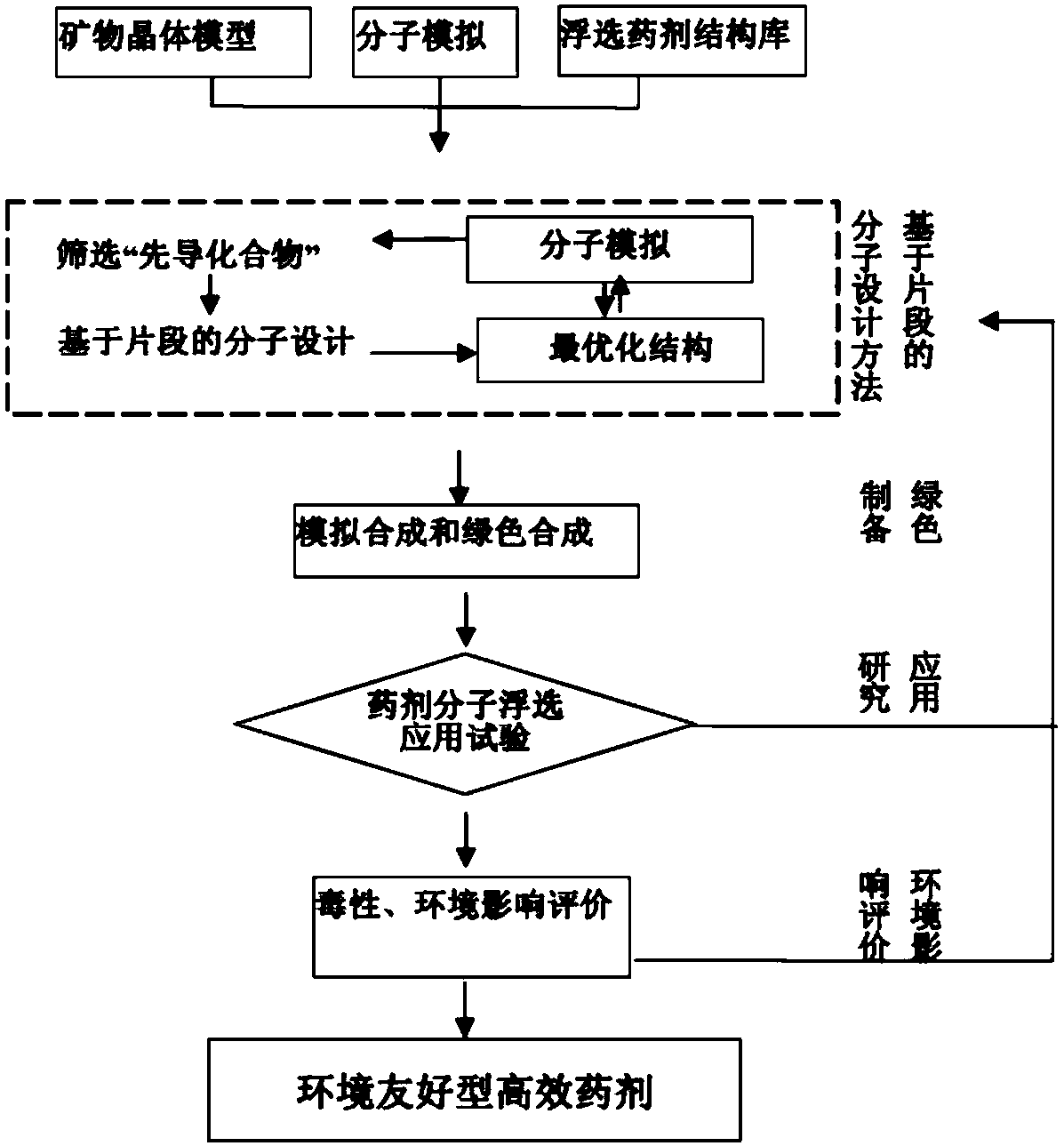
Method for designing flotation reagent molecules based on fragments
ActiveCN108304691AMention the success rate of off-the-shelf medicineMentioned success rateCheminformatics data warehousingCheminformatics programming languagesQuantum chemistryComputer-aided
The invention discloses a method for designing flotation reagent molecules based on fragments. With the help of a computer auxiliary molecule design technique, molecular mechanics and quantum chemistry calculation, the active fragments which are small in molecular weight and high in relative combination efficiency are obtained by sieving through detection, then flotation reagent molecular structures high in activity are obtained after the methods of producing, splicing and fusing are utilized for optimizing the active fragments, and the flotation reagent molecules are obtained through the steps that a fragment molecular compound library is established, active fragment molecules are sieved, and lead compounds are sieved. The dual advantages of high efficiency of the computer auxiliary molecule design technique and the flexibility of a molecule assembly technology are combined; the inspection range for the molecules is scaled to the inspection range for the molecular fragments, in this way, the success rate of reagent formulation is greatly increased for the reagent molecules, the designing efficiency is effectively promoted for the flotation reagent molecules, and the new method isfurther provided for designing flotation reagent.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
Method of evaluating collecting performance of floatation collecting agent to andalusite
The invention relates to a method of for evaluating the collecting performance of a floatation collecting agent to andalusite. The technical scheme is: firstly establishing an andalusite crystal structural model and a floatation collecting agent molecular structural model, so that total energy ET (andalusite) and ET (collecting agent) of the andalusite crystal structural model and the floatation collecting agent molecular structural model can be obtained by adopting a specific Hareree-Fock-Roothaan method of quantum chemistry Ab initio method; then carrying out molecule geometry optimization calculation on the structural models of an andalusite-floatation collecting agent system, thus the total energy ET (andalusite-collecting agent) of the andalusite-floatation collecting agent system isobtained; and finally acquiring the emitted heat amount delta ET when the floatation collecting agent is absorbed on the andalusite, if the absolute value of the delta ET is greater, the collecting capability of the floatation collecting agent to the andalusite is high. According to the size of the bond order of the andalusite-floatation collecting agent, the property and instensity of the bond formed by the surface of the andalusite and the floatation collecting agent are evalued. The method provided by the invention is simple and reasonable, is easy to operate, has low cost, and has practical value.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for constructing complex organic macromolecular average molecular structure model
InactiveCN106777958AGood for analyzing structureGood for analytical reactivityComponent separationInformaticsInfraredQuantum chemistry
The invention relates to a method for constructing a complex organic macromolecular average molecular structure model and belongs to a method for constructing an organic macromolecular structure model. The method for constructing the complex organic macromolecular average molecular structure model by adopting an in-situ process comprises the following steps: (1) analyzing elements; (2) analyzing peak slit of an infrared spectrum; (3) performing thermal gas chromatography and mass spectrometry analysis; and (4) performing quantum chemistry calculation. According to the method, the construction for the complex organic macromolecular average molecular structure model, such as, coal, can be realized. The invention has the advantages that an in-situ structure presentation method is utilized to acquire the parameters and segments of a complex macromolecular structure; a comprehensive theoretical calculation method is adopted for constructing a complex macromolecular structure model; the infrared spectrum information acquired through theoretical calculation is compared with experimental spectrum information and the macromolecular structure model is constantly corrected, so that the constructed macromolecular structure is more objective and can reflect the true structure information of the macromolecular structure model; and the research on the property, utilization and conversion of the complex macromolecular material, such as, coal, can be benefited.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for testing activity of methanol fuel cell anode material
InactiveCN103869045ASolve impossible puzzlesEasy to buildMaterial analysisPartial density of statesQuantum chemistry
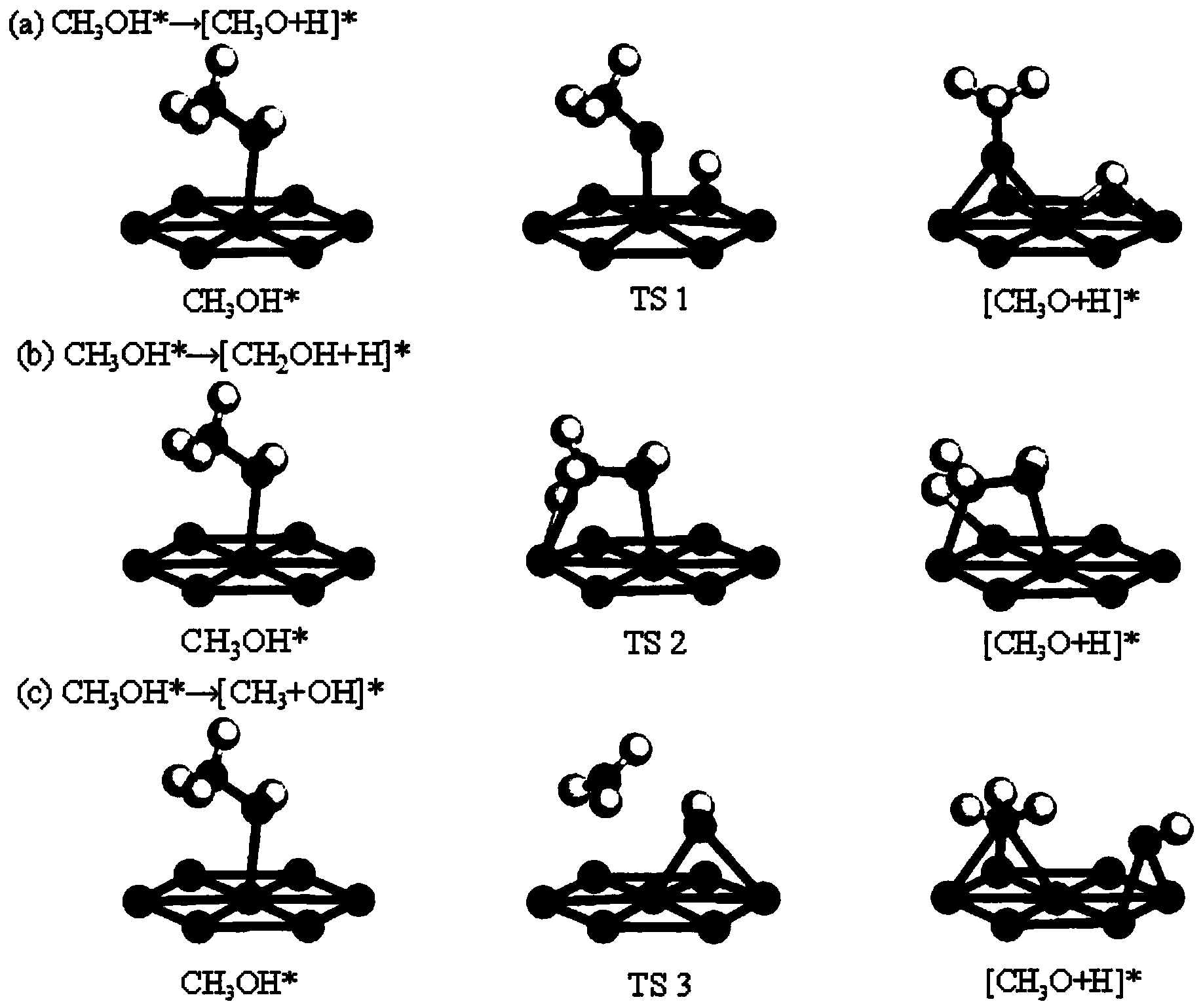
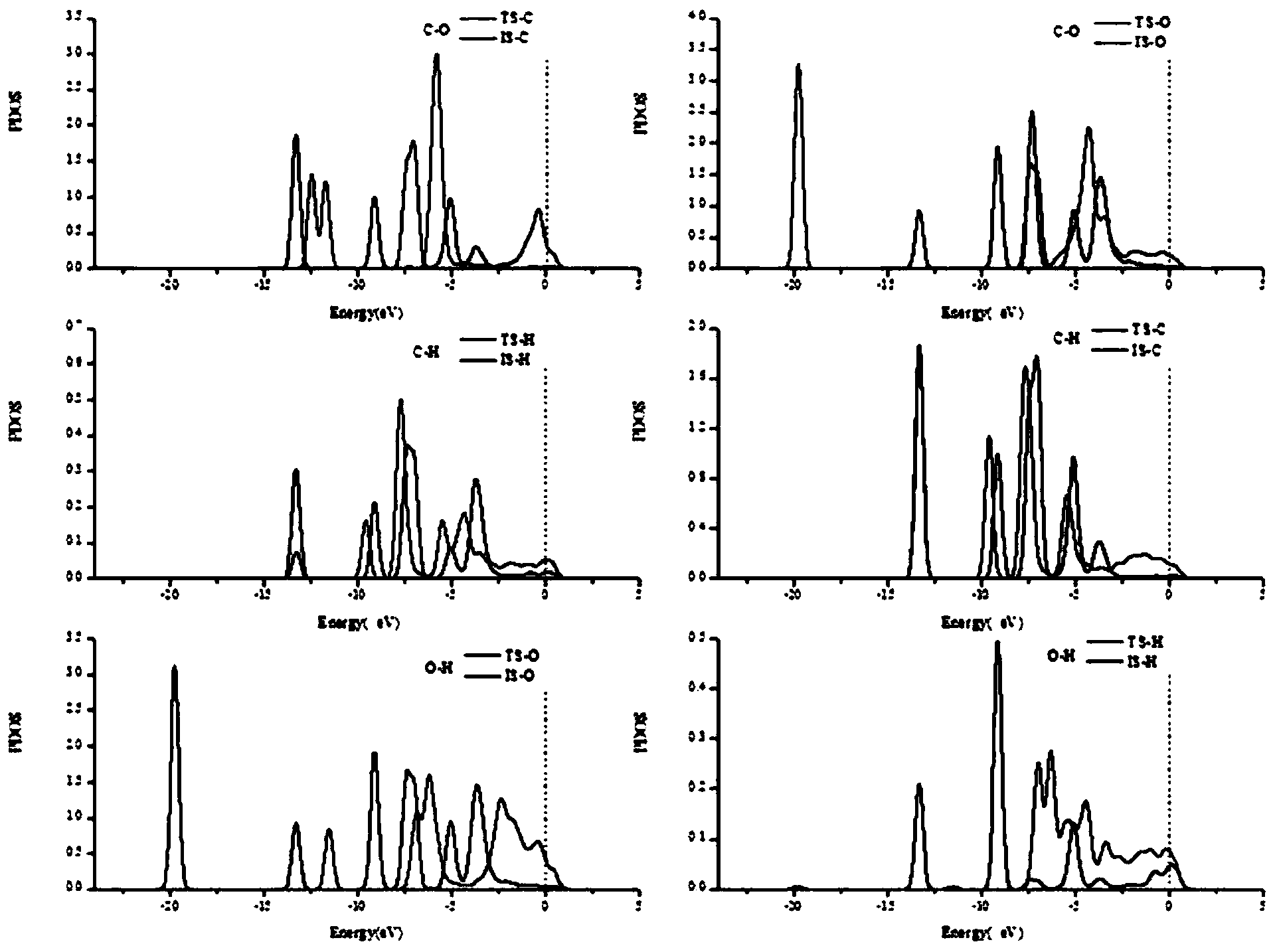
The invention discloses a method for testing activity of a methanol fuel cell anode material. The method is characterized in that the activity of the cell anode material is tested through special quantum chemistry calculation simulation for improving the accuracy of judging the activity and the efficiency of a cell. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, analyzing an adsorption structure, thermodynamics and kinetics parameters of an elementary reaction, and the like by researching the adsorption of the methanol on the surface of the anode material and three broken bond reaction principles of methanol; and secondly, performing comparative analysis on an energy barrier obtained by using calculation, a PDOS (Partial Density Of States) graph and an electrochemical potential to judge the activity of a catalyst. The activity of the methanol fuel cell anode material is conveniently, rapidly and accurately researched by using the method; resources are saved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
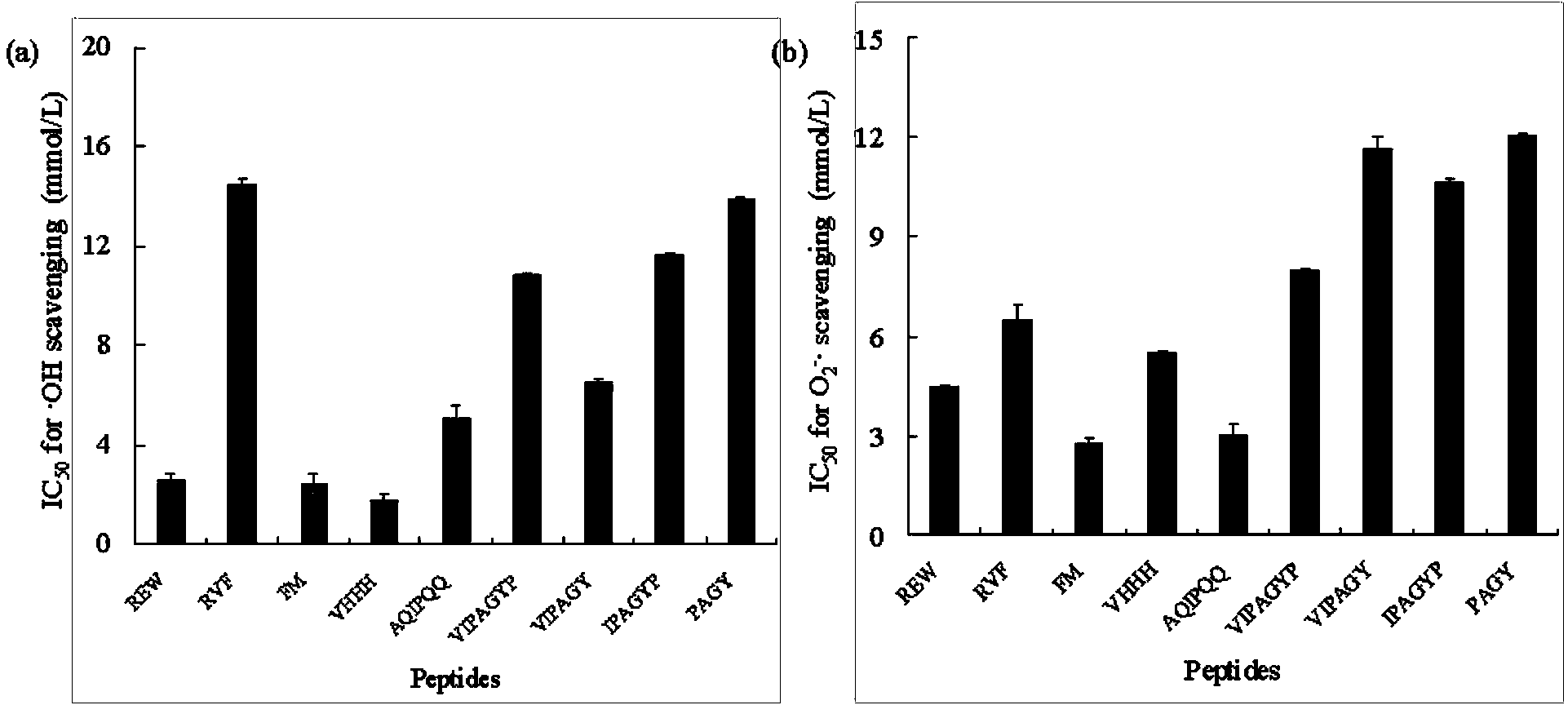
Construction method for food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model
ActiveCN103714266AGood correlationSpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a construction method and application for a food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model. The method comprises the steps of using a food-borne polypeptide with known activity as a research object, utilizing the three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship technology for establishing the food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model, and adopting the MM+ method the semi-empirical quantum chemistry method AM1, the DFT method and other quantum chemistry technologies to obtain quantum chemistry parameters. According to the construction method, analysis and statistics are carried out on the food-borne polypeptide quantum chemistry parameters, the antioxidant activity sites of the food-borne polypeptide are determined, and quantitative structure-activity model is constructed by utilizing the bond length, charge distribution, frontier molecular orbit energy parameters of the activity sites and food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity values. The constructed model can rapidly and accurately predict the activity value of the food-borne polypeptide with the unknown activity, and the relationship between the antioxidant activity and structural features can be reasonably explained; compared with a traditional high throughput screening technology, the screening efficiency is greatly improved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Calculation method and device for molecular ionization collision cross-section
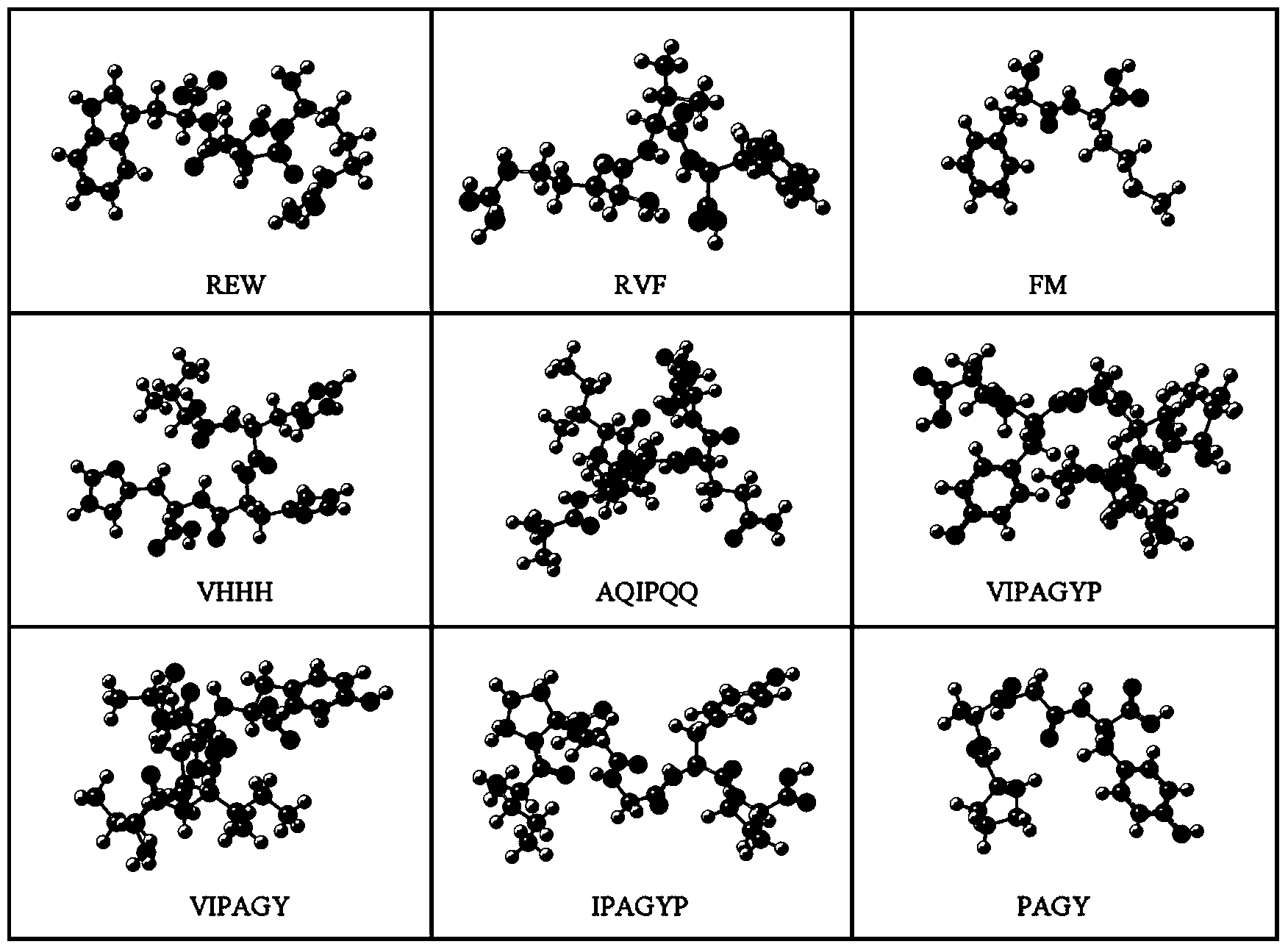
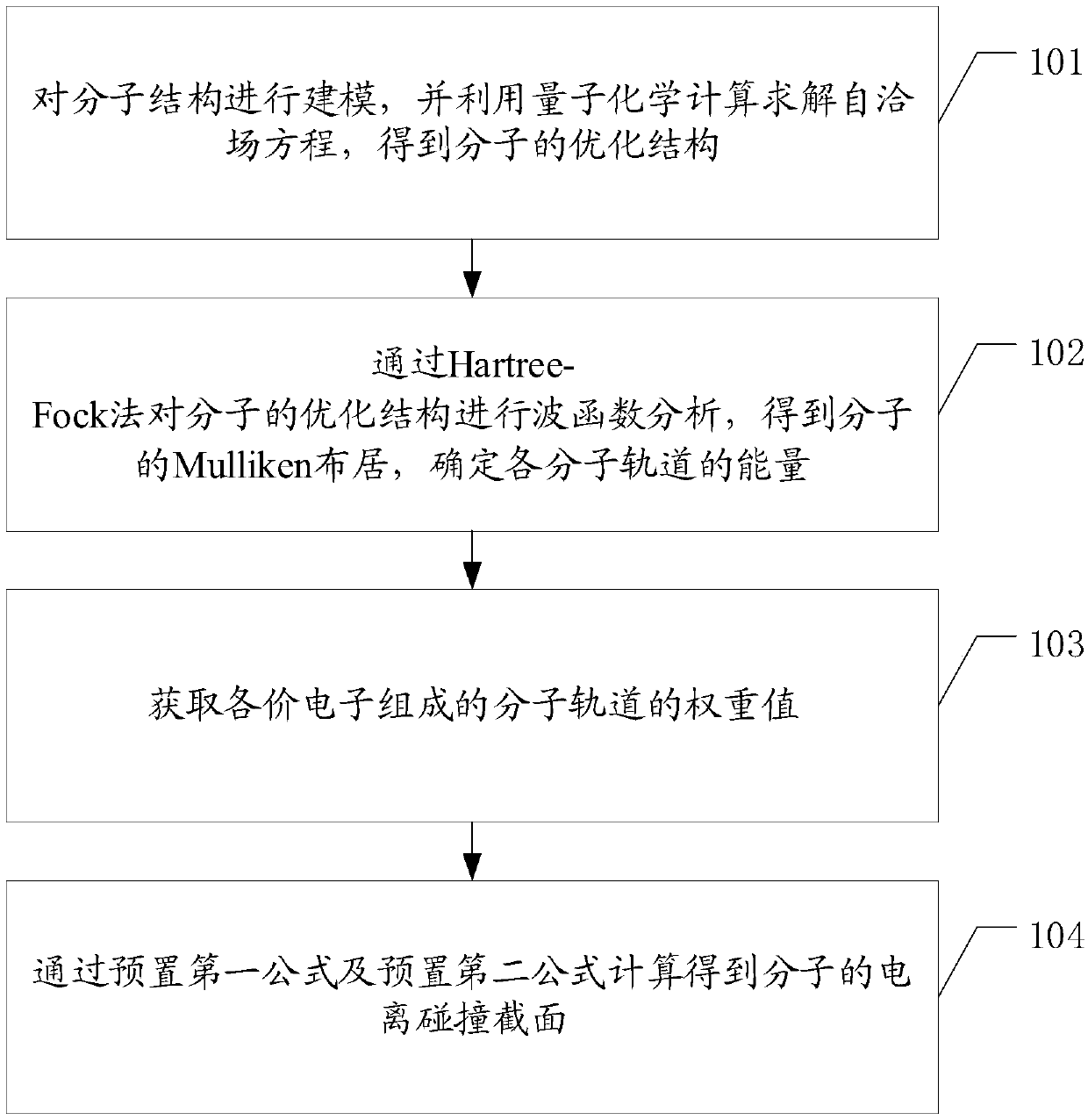
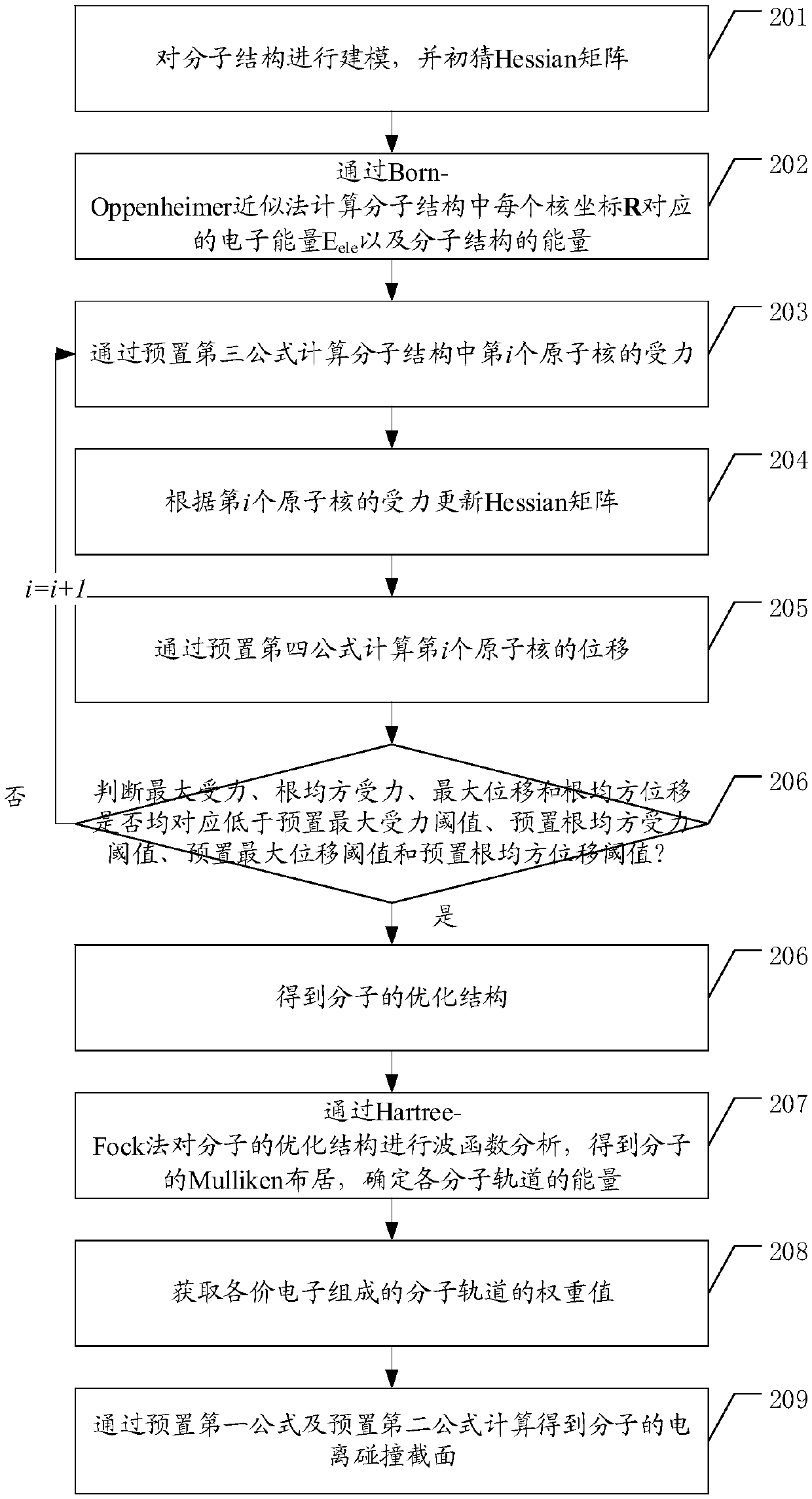
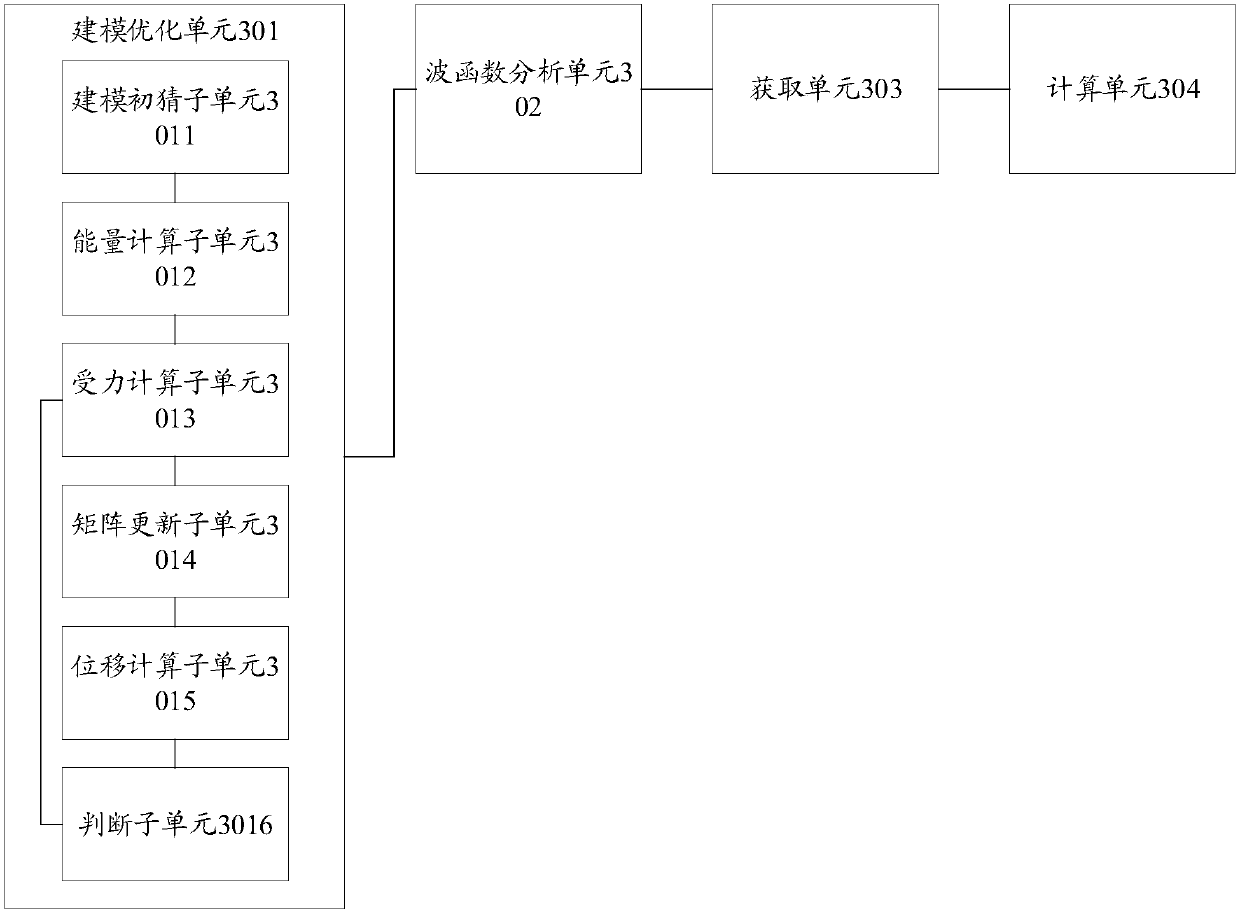
ActiveCN108595820ASimple structureImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsValence electronSelf consistent
The invention discloses a calculation method and device for a molecular ionization collision cross-section. On the basis of a DM formula, the calculation level of quantum chemistry is determined, andan optimal method for a specific system is proposed. The method comprises the steps that S1, modeling is performed on a molecular structure, and quantum chemistry calculation is utilized to solve a self-consistent field equation to obtain an optimal structure of molecules; S2, wave function analysis is performed on the optimal structure of the molecules through a Hartree-Fock method, a Mulliken population of the molecules is obtained, and energy of each molecular orbit is determined; S3, weight values of the molecular orbits composed of all valence electrons are acquired; and S4, the ionization collision cross-section of the molecules is obtained through calculation by use of a preset first formula and a preset second formula.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
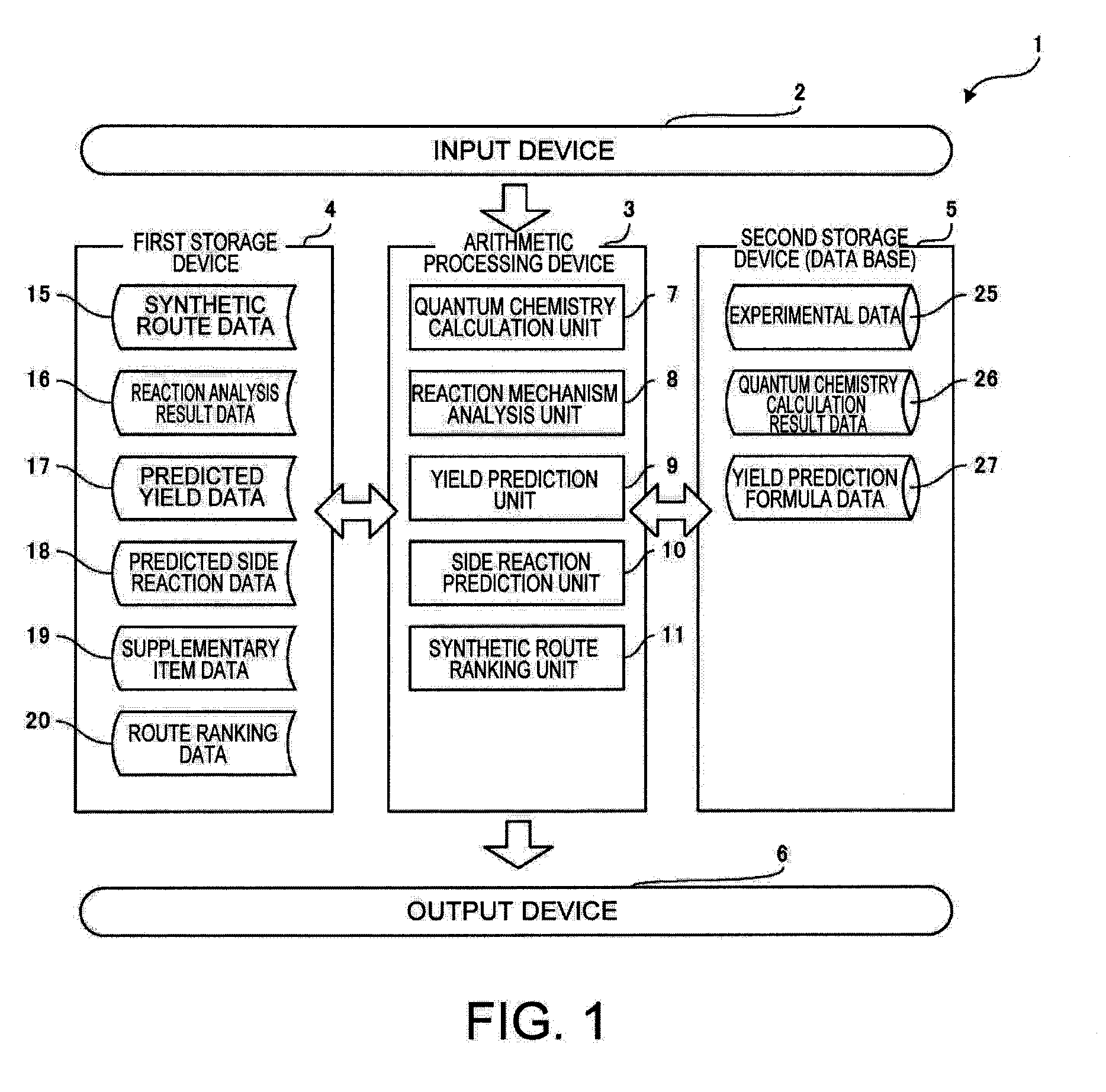
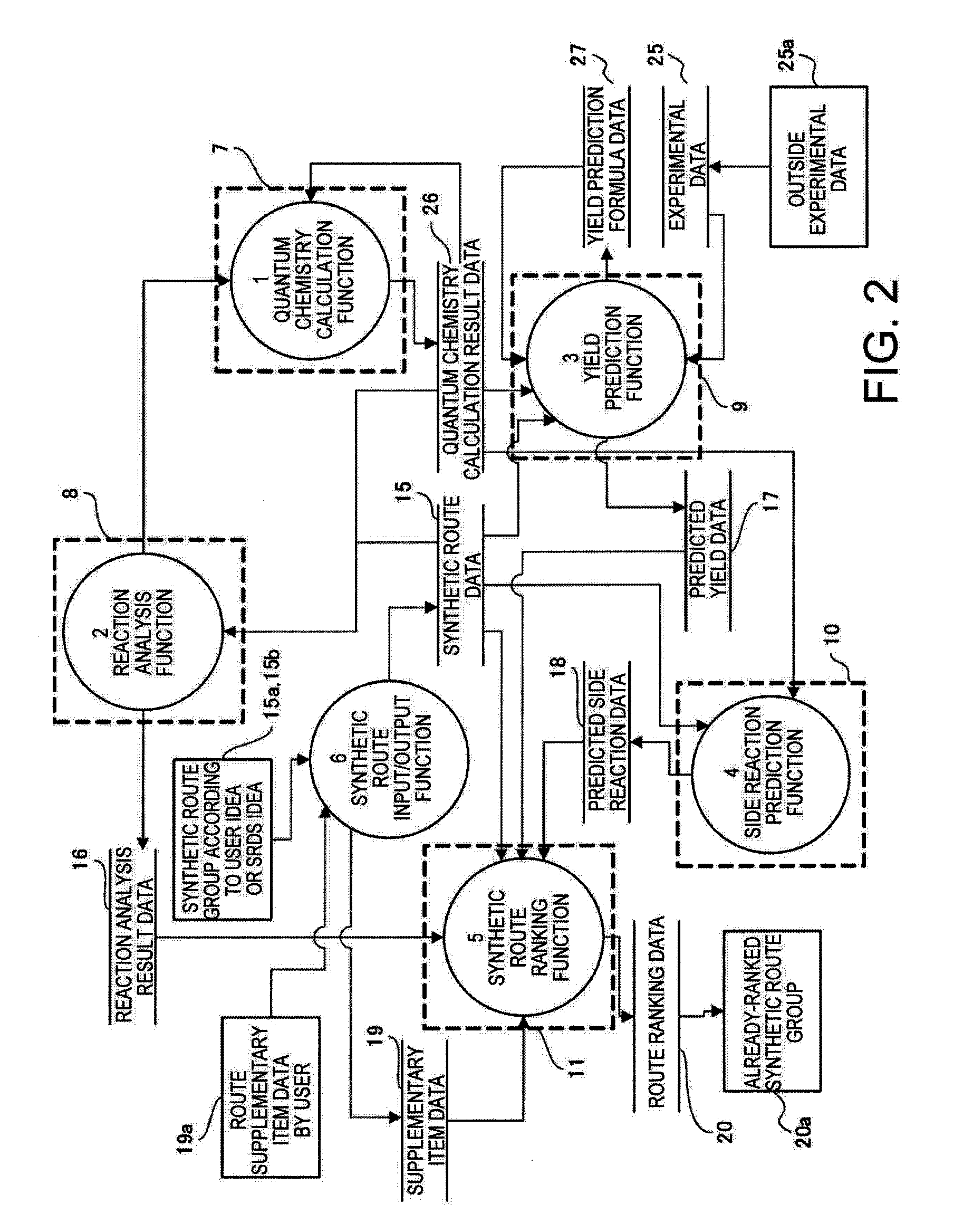
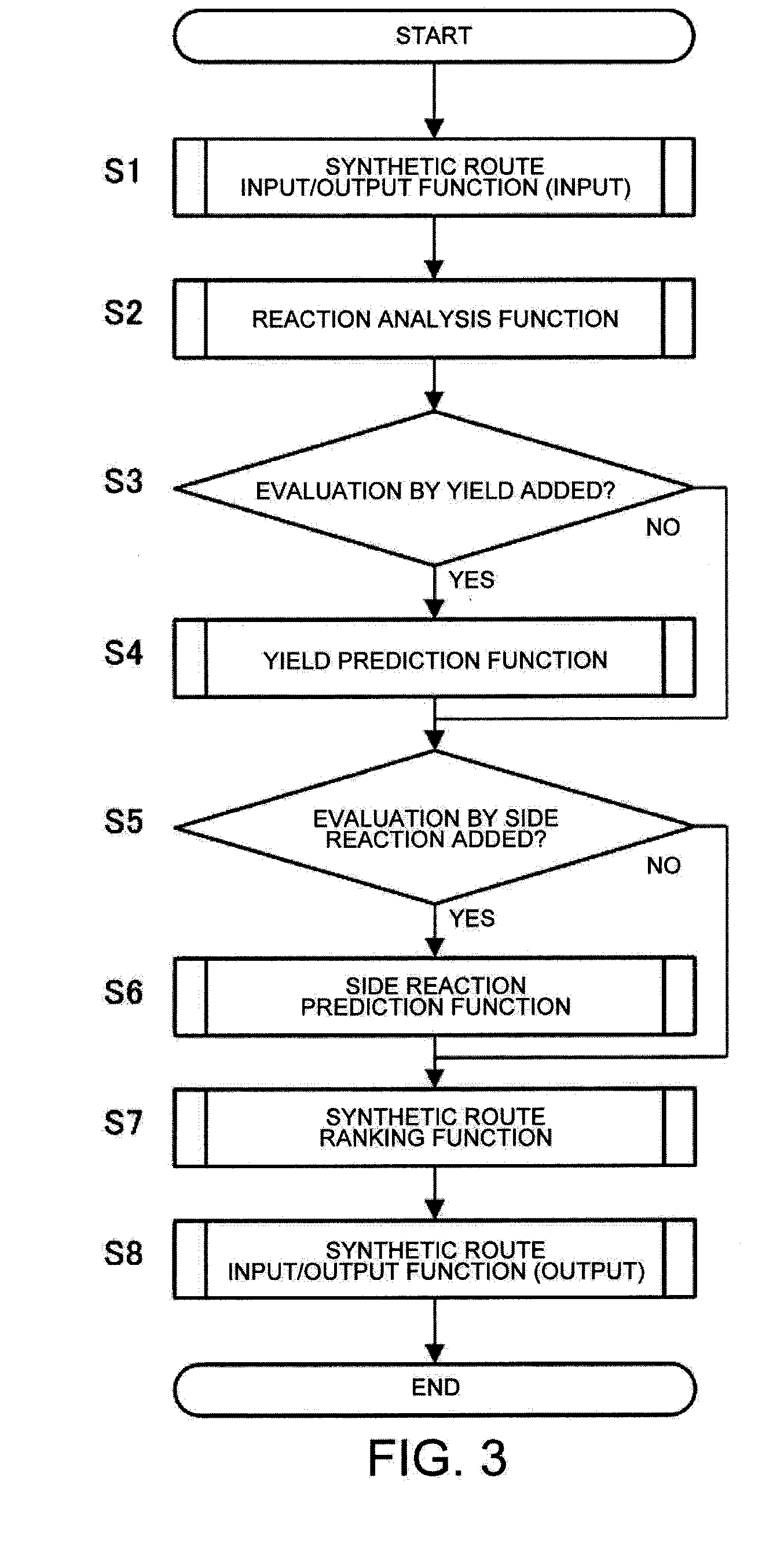
Synthesis path evaluation system and method and program thereof
InactiveUS20110106794A1Shorten development timeReduce development costsDigital data processing detailsOrganic chemistry methodsQuantum chemistryEvaluation system
A synthetic route evaluation system extracts an optimal synthetic route from a plurality of synthetic routes for a target compound to be synthetically produced. The synthetic route evaluation system includes an arithmetic processing device, which is composed of a quantum chemistry calculation unit, a reaction mechanism analysis unit, and a synthetic route ranking unit, and a storage device for storing data relative to the synthetic routes.
Owner:YAMAGUCHI UNIV
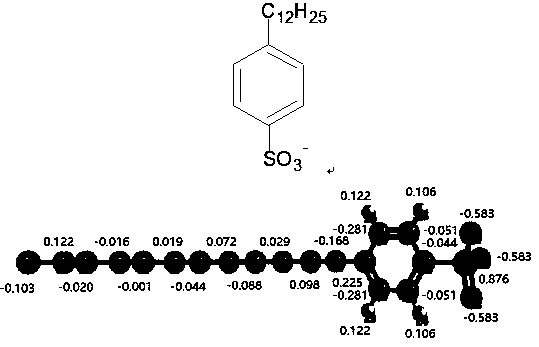
Evaluation method for simulating oil-water interface characteristics of alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactant based on molecular dynamics
PendingCN111028891AThe evaluation result is accurateEvaluation time period is shortChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationActive agentOil phase
The invention discloses an evaluation method for simulating oil-water interface characteristics of an alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactant based on molecular dynamics. The method comprises establishing amolecular structure model of alkylbenzene sulfonate by adopting software; then, performing quantum chemistry calculation by utilizing software to obtain optimized molecular conformation and all-atomic structure charge parameters of alkylbenzene sulfonate; optimizing the molecular structure of alkylbenzene sulfonate to obtain optimized molecular topological structure parameters of the bond length,the bond angle and the dihedral angle; establishing a system model of oil-phase molecules, water molecules and alkylbenzene sulfonate by utilizing molecular accumulation software; and finally carrying out molecular dynamics calculation on a simulation system by utilizing molecular dynamics calculation software to evaluate the oil-water interface characteristics of alkylbenzene sulfonate. According to the method, the oil-water interface microcosmic action mechanism of the alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactant for chemical flooding can be clarified from molecular and atomic scales, and certain theoretical guidance is provided for application of alkylbenzene sulfonate in the field of oilfield chemical flooding.
Owner:NANJING POLYTECHNIC INSITUTE
Fe-C-Cr-W-Mo-Mn-V-Si-Ni high carbon medium-alloy steel
InactiveCN102517514AMeet the performance requirementsMeet performance requirementsHeat treatment process controlQuantum chemistryCell binding
A Fe-C-Cr-W-Mo-Mn-V-Si-Ni high carbon medium-alloy steel relates to an alloy steel. The alloy steel is determinated according to matrix martensite cell binding energy calculation, yield strength prediction, quenching and tempering hardness calculation, toughness estimation and non-carbide forming elements alloy components by the use of quantum chemistry procedure combined with interatomic potentials. The alloy steel contains the following components of: by weight, 93.08% of Fe, 0.56% of C, 1.42% of Cr, 2.21% of W, 0.95% of Mo, 0.34% of Mn, 0.53% of V, 0.62% of Si and 0.29% of Ni. The alloy steel can be quenched at a low temperature, has carbides with fine microstructure distribution, simultaneously has high hardness and toughness, and is a high carbon medium-alloy tool and die steel which can satisfy the demand of using performance.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
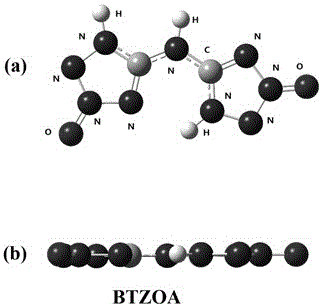
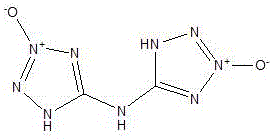
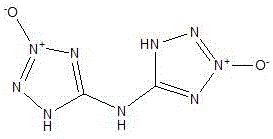
Bis(tetrazole-2-oxy-4-hydro)amine, design method, and application thereof
InactiveCN106588802AImprove thermal stabilityReduce sensitivityOrganic chemistryExplosivesQuantum chemistryHigh energy
The invention belongs to the crossing field of energetic material and quantum chemistry and particularly relates to a bis(tetrazole-2-oxy-4-hydro)amine, a design method, and an application thereof. 1-hydro-tetrazole-3-oxy is employed as a mother compound and two 1-hydro-tetrazole-3-oxy compounds are combined through connection of an NH bridge group, and then through structure optimization, a planar conjugated molecule is formed; through energy containing property calculation, thermostability calculation and sensitivity calculation, comprehensive performance of the product is evaluated. The bis(tetrazole-2-oxy-4-hydro)amine has high energy and low sensitivity and can be used as a substitute of hexogen and octogen.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Method for calculating crystal morphology of energetic material in solution
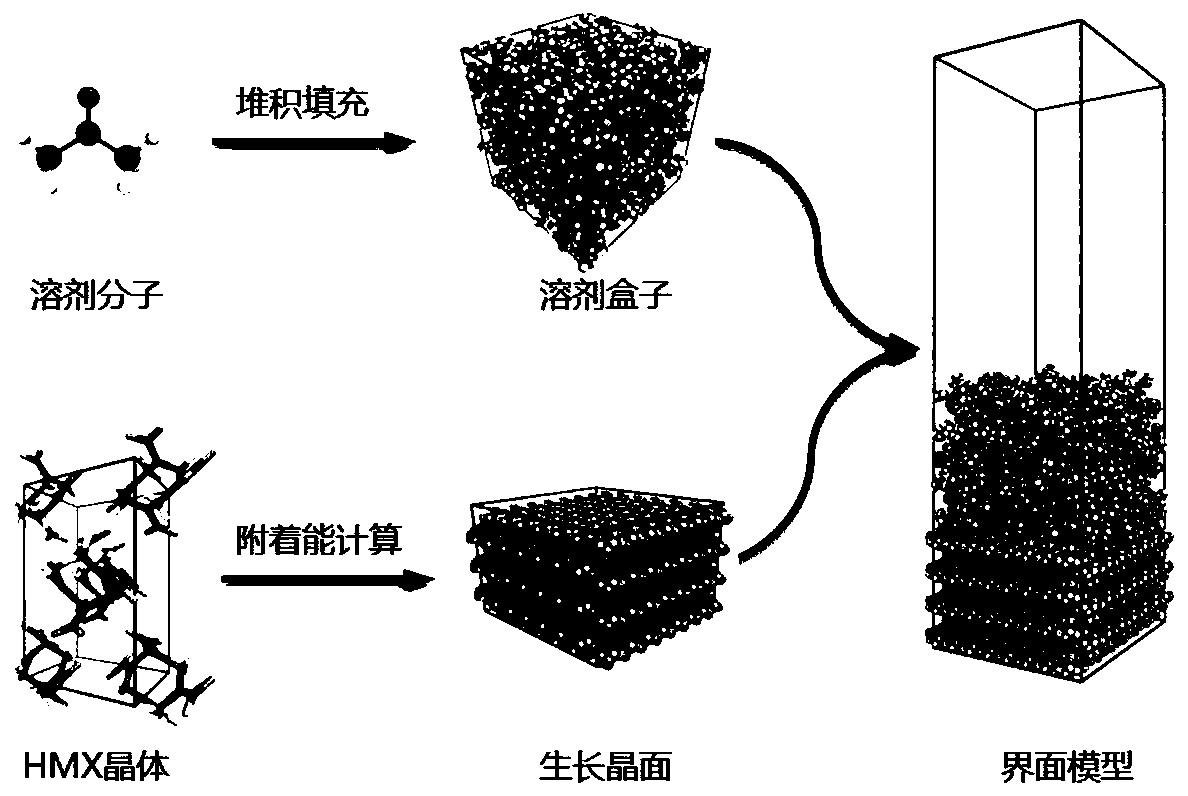
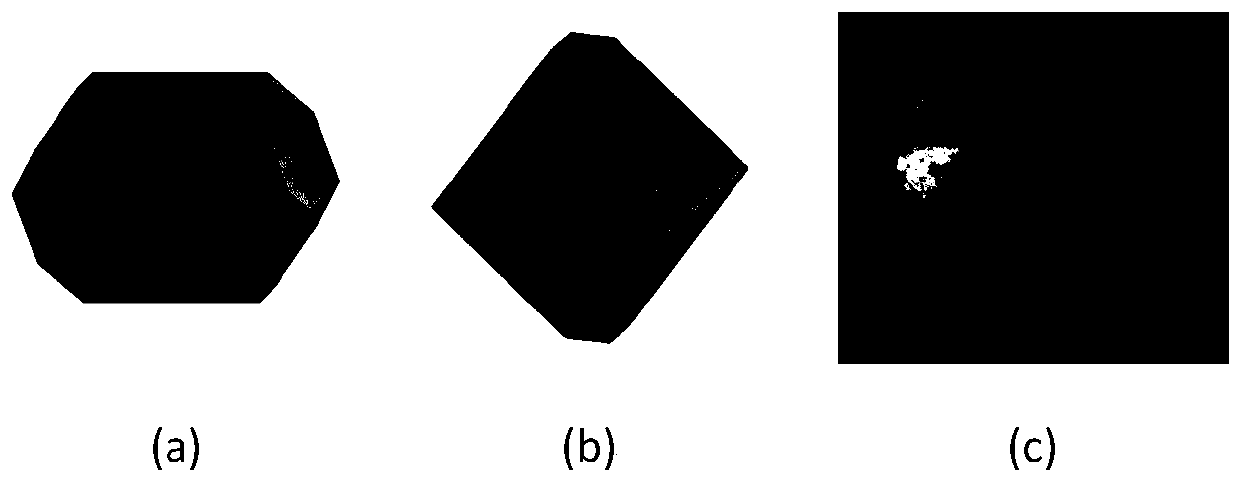
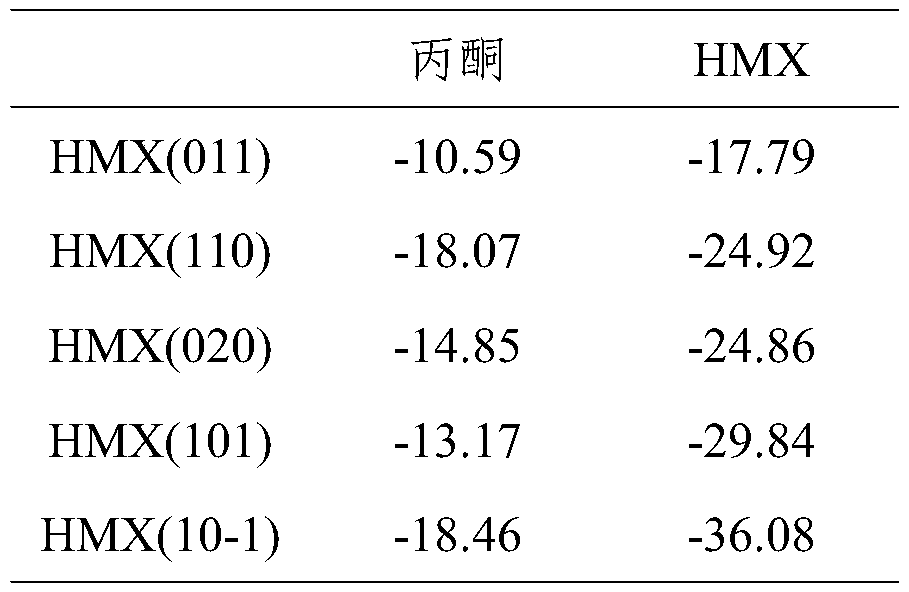
ActiveCN110867217AInhibition reasonably describedStrong growth inhibitory effectComputational theoretical chemistryInstrumentsQuantum chemistryCrystal morphology
The invention discloses a method for calculating the crystal morphology of an energetic material in a solution. According to the method, an adsorption site of a solvent on a growth crystal face is found through molecular dynamics simulation, binding energy at the adsorption site is calculated through adoption of a quantum chemistry method, and the binding energy is used for replacing 'averaged' solvent-crystal face interaction energy in an adhesion energy model, so that the inhibition effect of the solvent on solute growth is described more reasonably. Compared with the prediction result of the original adhesion energy model, the crystal morphology predicted based on the method is greatly improved, and is well matched with experimental data. The method provides an early-stage theoretical prediction and scientific basis for crystallization morphology control of energetic materials.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
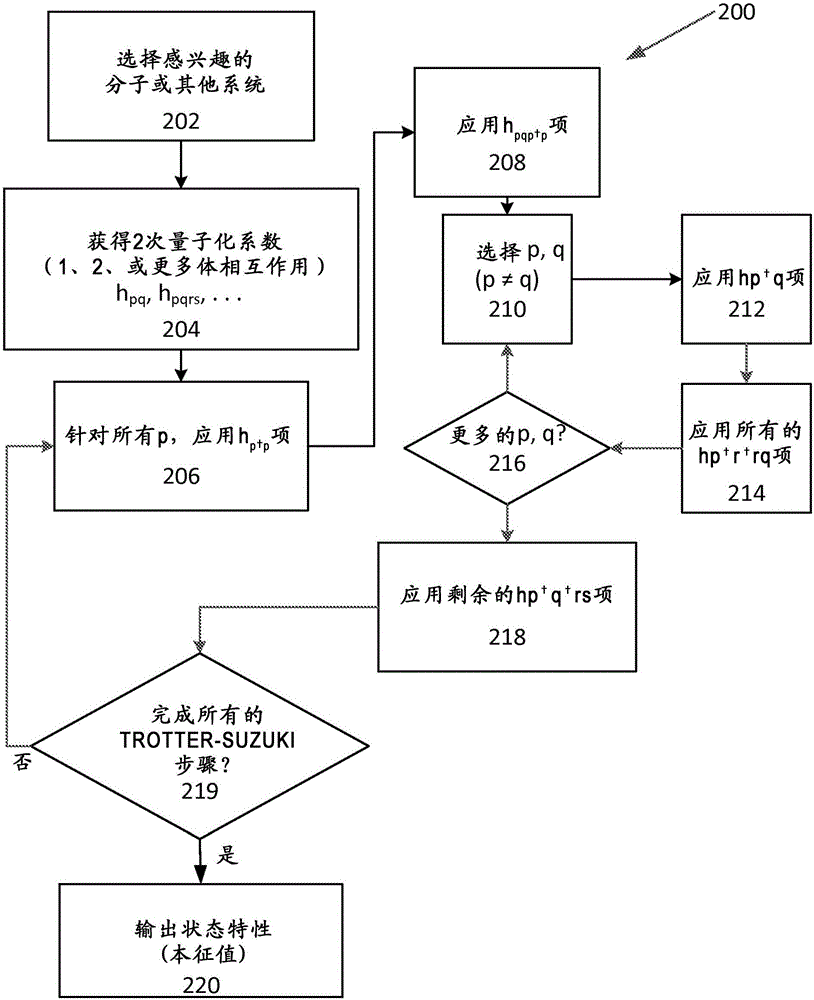
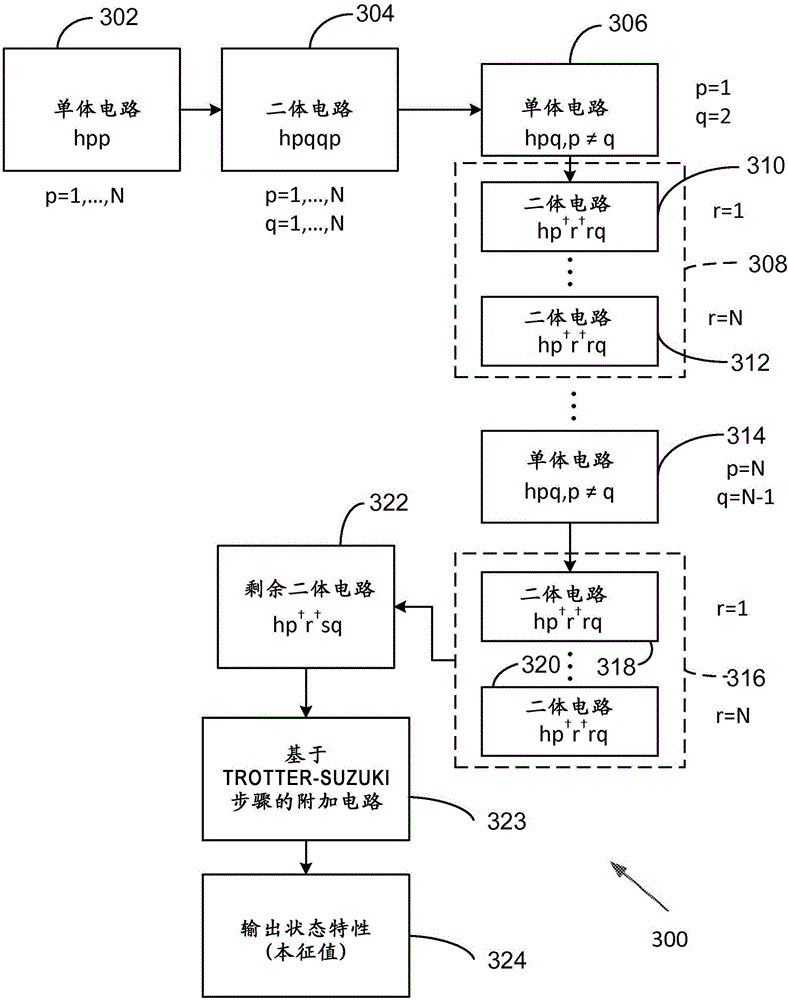
Classical simulation constants and ordering for quantum chemistry simulation
Quantum computations based on second quantization are performed by applying one body and two body terms in a selected order. Typically, terms associated with operators that commute are applied prior to application of other terms. In a particular example, one body terms of the form h pp are applied first, followed by two body terms of the form h prrp .
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
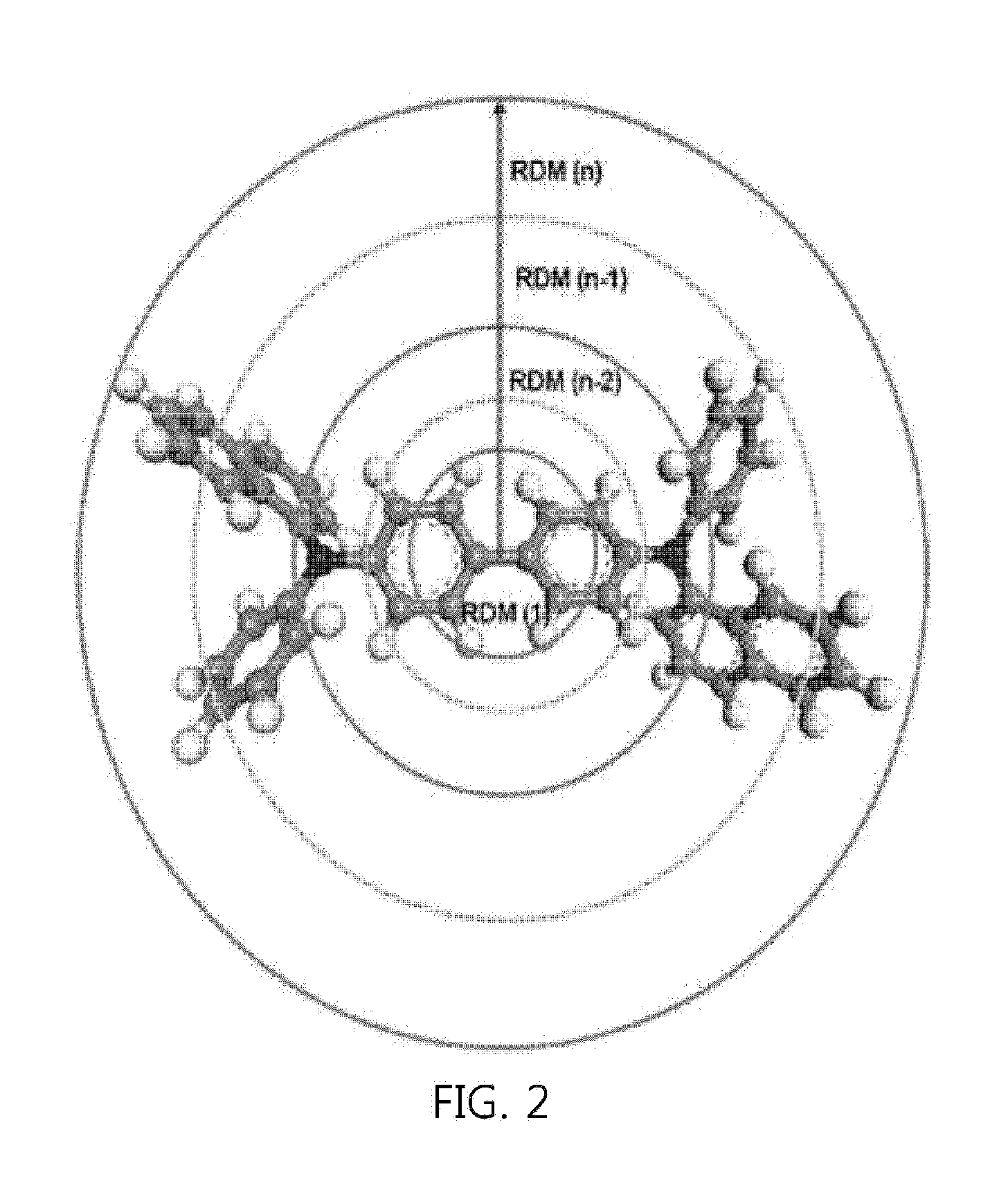
Quantitative comparative analysis method for molecular orbital distribution, and system using same
InactiveUS20160371467A1Organic chemistry methodsComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemistryUsage analysis
Disclosed herein are a method for quantitatively analyzing a molecular orbital distribution, and a quantitative analysis system of molecular orbital distributions using the same. The method comprise a) selecting two molecular orbitals to be compared for molecular orbital distributions and computing molecular orbital distributions by quantum chemistry calculation; b) calculating structural properties of each molecular orbital by means of an RDM (radially discrete mesh) calculation method, followed by matching with the molecular orbital distributions computed in step a) to obtain molecular orbital distributions according to the structural properties; and c) comparing the two molecular orbital distributions according to structural properties, obtained by RDM in step b), using a profiling method.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
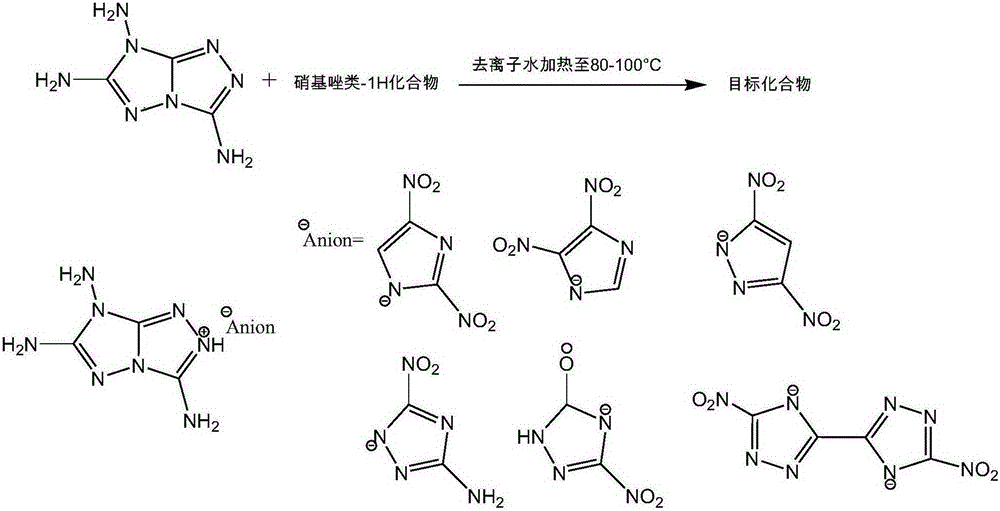
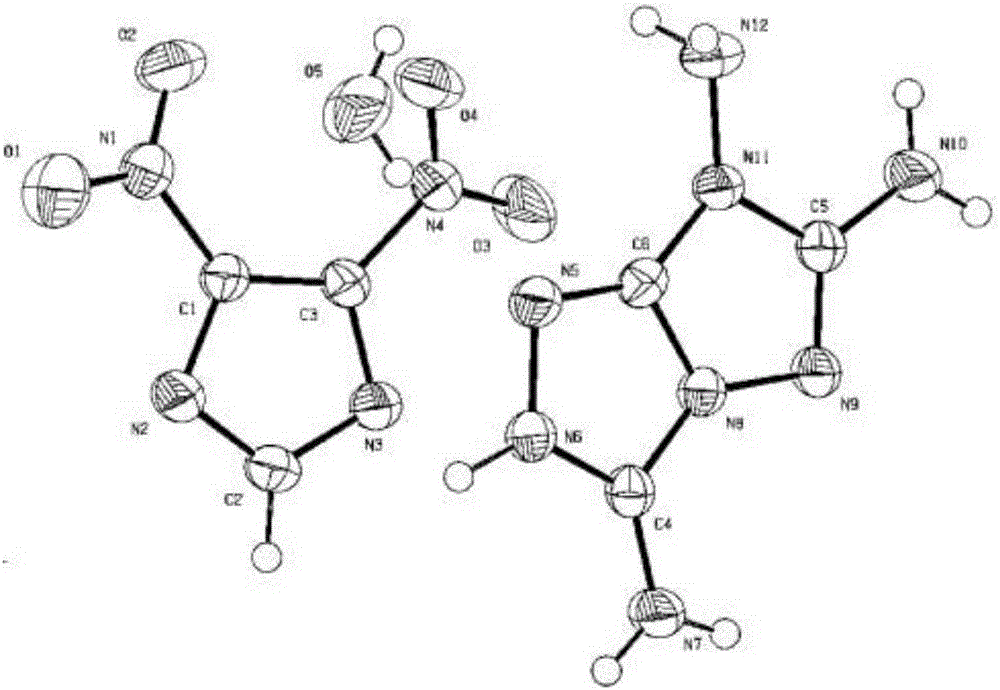
3,6,7-triamino-1,2,4-triazolocycle ionic type nitroazole compound and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a 3,6,7-triamino-1,2,4-triazolocycle ionic type nitroazole compound and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the 3,6,7-triamino-1,2,4-triazolocycle ionic type nitroazole compound comprises the following steps: dispersing a 3,6,7-triamino-1,2,4-triazolocycle compound and a nitroazole type-1H compound in right amount of deionized water, heating, reacting, then standing, filtering out a solid after temperature is reduced to normal temperature, washing the solid, and drying, so that the 3,6,7-triamino-1,2,4-triazolocycle ionic type nitroazole compound is obtained, wherein the nitroazole type-1H compound is one of 2,4-dinitroimidazole-1H, 4,5-dinitroimidazole-1H, 3,5-dinitroparazole-1H, 3-amino-5-nitro-1,2,4-triazole-1H, 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazole-5-one and 5,5'-dinitro-3,3'-bi-triazole-1H,1'H. The preparation method of the 3,6,7-triamino-1,2,4-triazolocycle ionic type nitroazole compound is simple, no toxic substance or byproduct is produced, conditions are mild, yield is high, and detonation velocity, through quantum chemistry calculation, of the obtained product is 8500-9200m / s.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
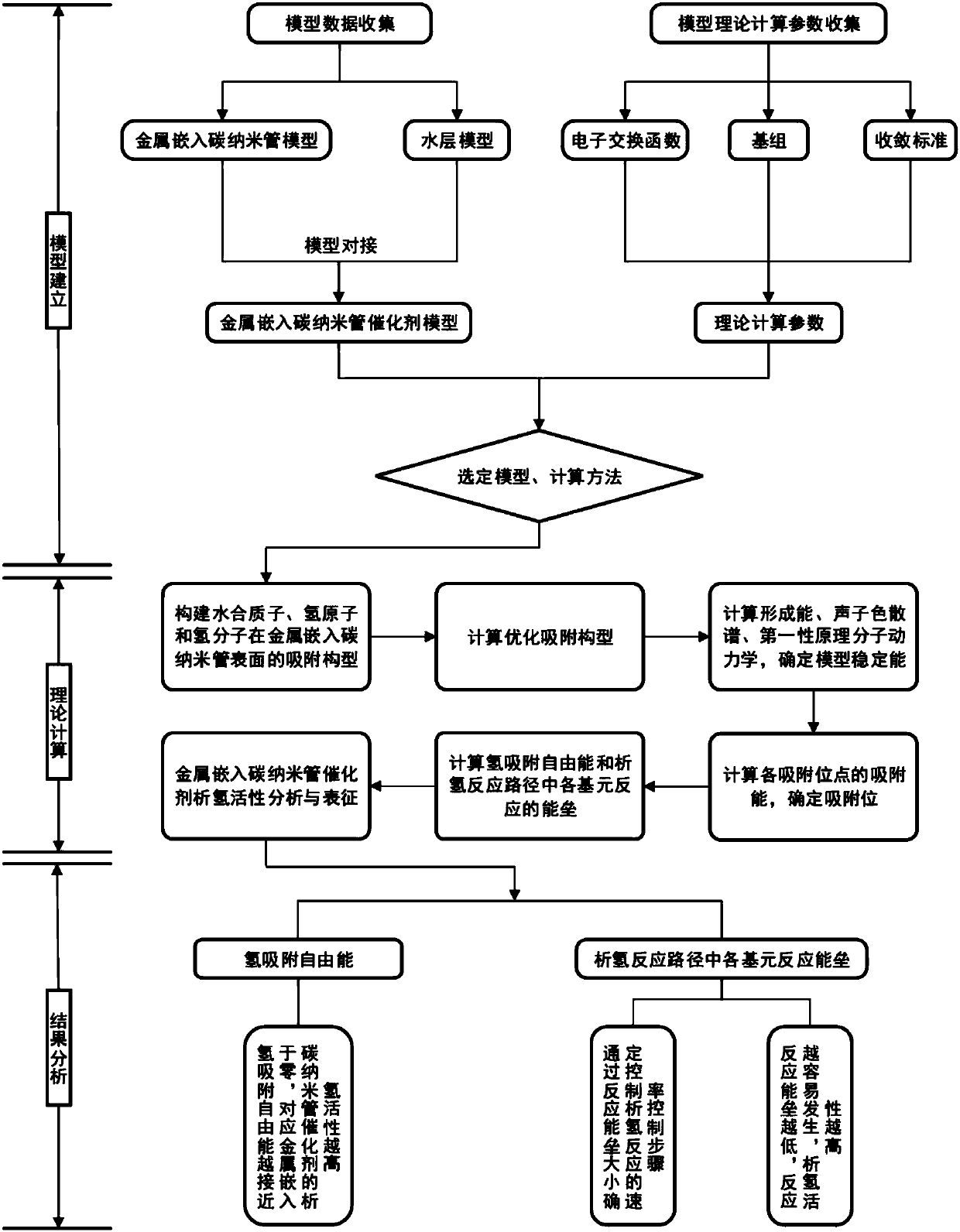
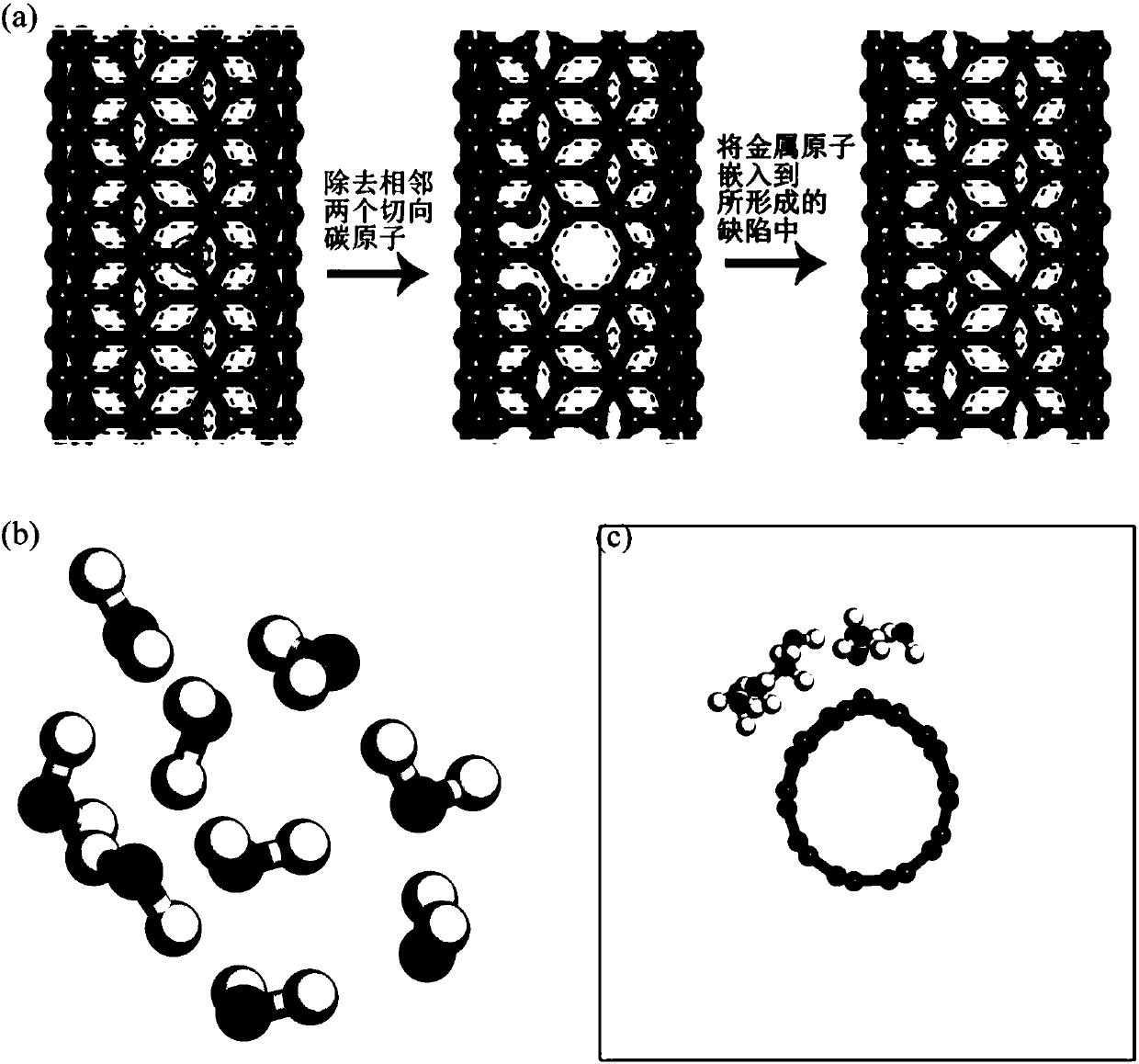
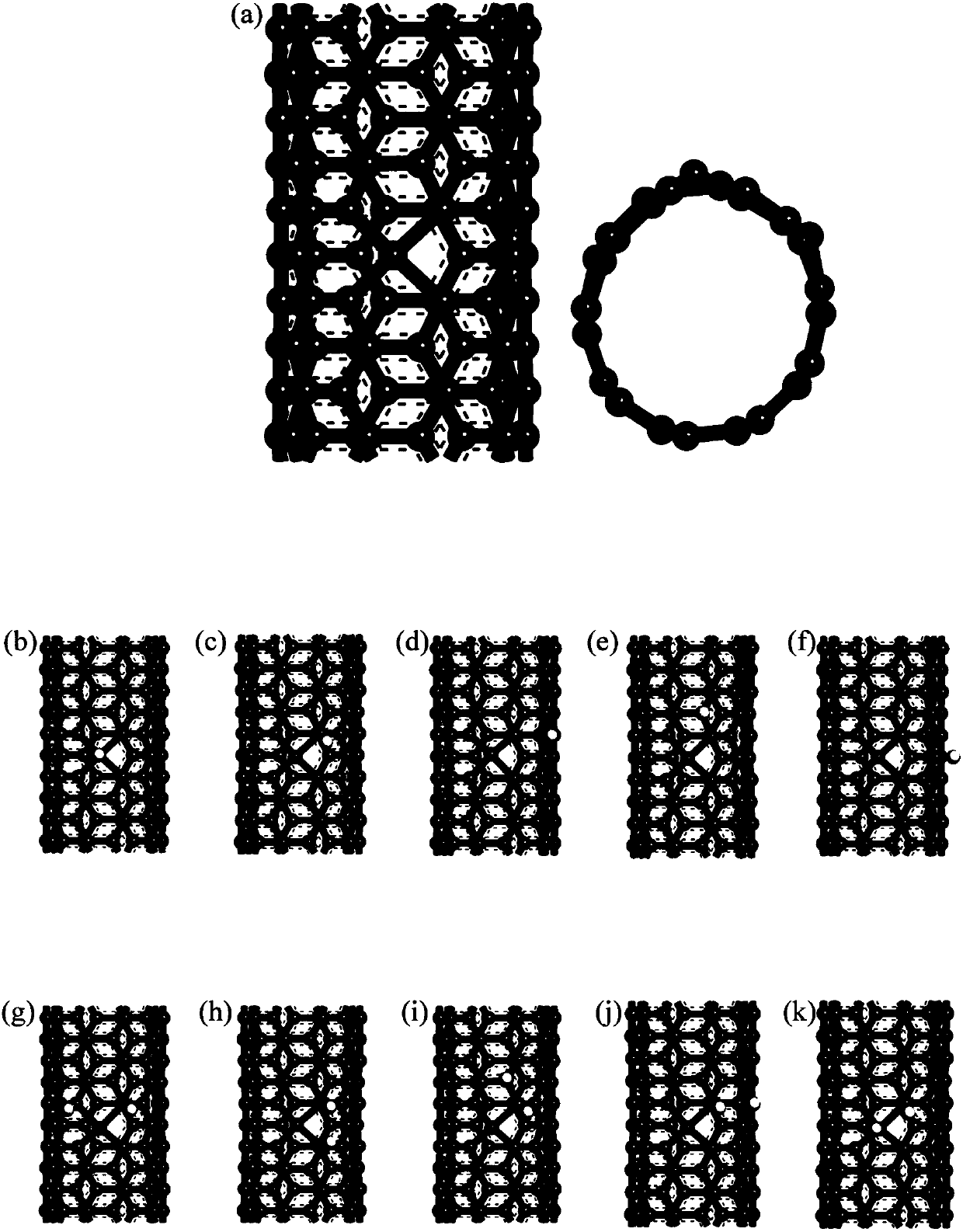
Method for quantitatively analyzing hydrogen evolution activity of MCNT catalyst
InactiveCN108573124AOvercome blindnessChemoinformaticsComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemistryFree energies
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing hydrogen evolution activity of an MCNT catalyst. The method quantitatively analyzes the hydrogen evolution activity of the MCNT catalyst on the basis of quantum chemistry density functional theory simulation. Through stability study of an MCNT model, stable existence of the model in a hydrogen evolution reaction process is determined; the specific position of a hydrogen evolution reaction on the surface of the catalyst is determined according to adsorption potential screening; the hydrogen evolution activity of the MCNT catalyst isquantitatively analyzed in combination with calculation of hydrogen adsorption free energy and a hydrogen evolution reaction route. The method comprises steps including construction of an MCNT catalyst model, optimization of the model structure, stability calculation, adsorption potential screening, calculation of hydrogen adsorption free energy and the hydrogen evolution reaction route as well asanalysis and representation of the hydrogen evolution activity. The hydrogen evolution activity of the MCNT catalyst can be quantitatively analyzed without actual experiments and actual synthesis ofthe catalyst.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Simulation method for optimizing molecular structure of biosurfactant
InactiveCN105718719APrecise molecular configurationReasonable and stable molecular configurationMolecular entity identificationComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemistryComputer science
The invention discloses a simulation method for optimizing molecular structure of biosurfactant. Through a specific quantum chemistry geometry optimization method, the molecular structure of the biosurfactant is optimized for making the stable configuration of a biosurfactant molecule in molecular dynamics simulation clear. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, through Materials Studio software, constructing an initial configuration of the biosurfactant molecule; secondly, utilizing Calculation in the DMol3Tools module of the Materials Studio software to carry out a molecular structure optimization process on the biosurfactant; and finally, through vibration frequency obtained by calculation, judging the stable configuration of the biosurfactant. The simulation method provides a stable and accurate molecular model for the molecular dynamics simulation of biosurfactant property, and guarantees the accuracy and the reliability of simulation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
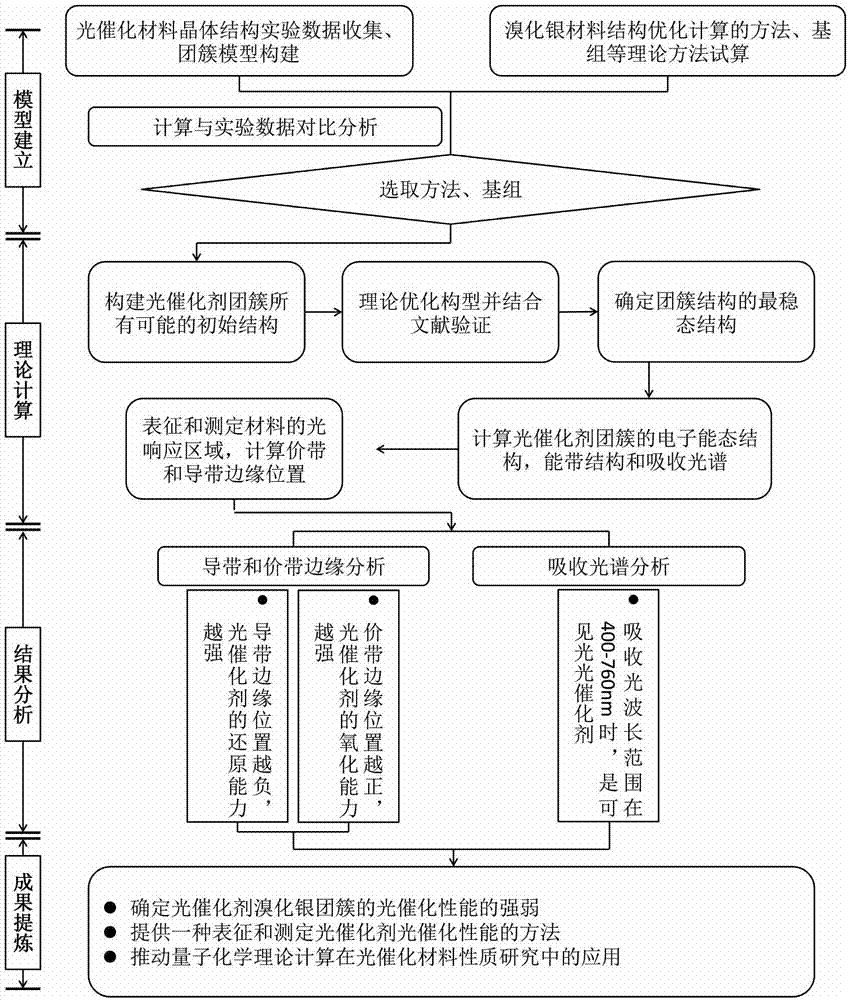
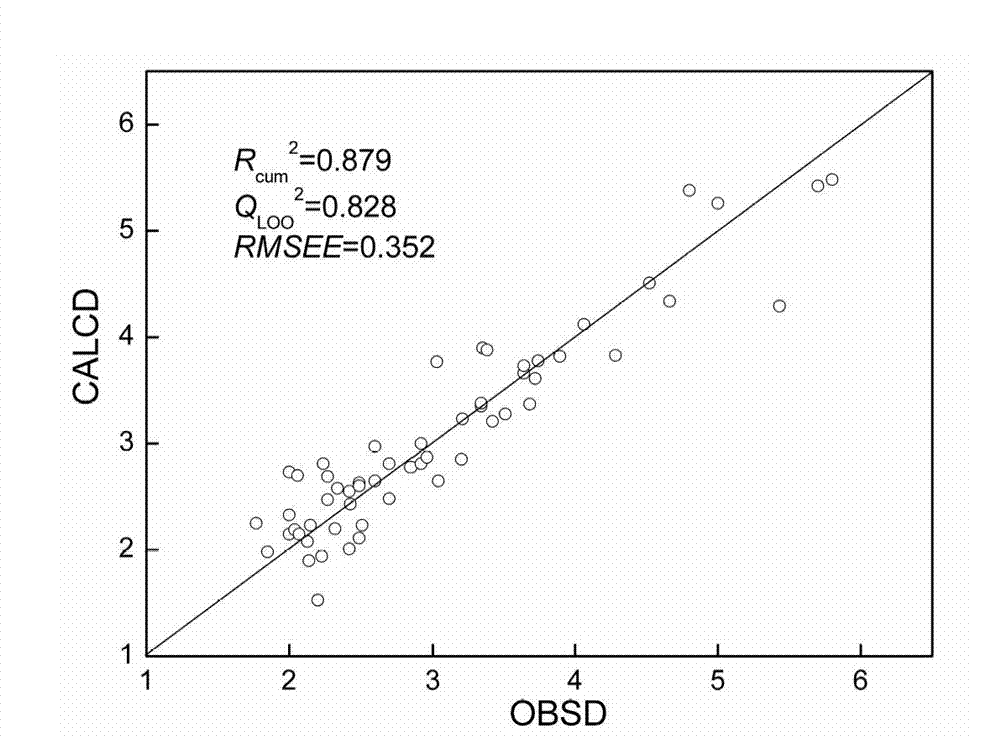
Method for quantitative analysis of photocatalytic performance of silver bromide cluster
The invention discloses a method for quantitative analysis of photocatalytic performance of a silver bromide cluster. The method is used for representing and determining the photocatalytic performance of the silver bromide cluster on the basis of density functional theories of quantum chemistry; a stable structure is determined through structure study of the silver bromide cluster; an electronic structure of the silver bromide cluster, an absorption spectrum, and positions of a valence band and a conduction band are analyzed according to the band theory; and the photocatalytic performance of the silver bromide cluster is finally determined. A method for representing and determining the photocatalytic performance of the cluster is concluded and summarized by combining related experiment research literatures. The method does not need any experiment; the photocatalytic performance of the silver bromide cluster can be represented by using a quantum chemistry theory calculation method; and the method can be expanded to determination and representation of the photocatalytic performances of other photocatalysts.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for predicting activity of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
InactiveCN103207947AEasy accessEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsQuantum chemistryAngiotensin-converting enzyme
A method for predicting activity of an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor comprises the steps of selecting quantum chemistry parameters of natural amino acids, obtaining 19 principal components by principal component analysis, enabling the principal components to serve as principal component amino acid quantization parameters for describing every amino acid, utilizing amino acid quantum chemistry parameter scores to perform representation on an amino acid sequence of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, enabling medicine activity of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor to serve as to a dependent variable for establishing a model, utilizing a step-by-step linear regression method to perform variable selection, finding out amino acid quantum chemistry parameter components remarkably associated with the dependent variable, utilizing step-by-step linear regression to process all the quantum chemistry parameter components of the amino acids obtained in every step, sequentially utilizing a method of partial least squares to construct medicine activity models of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor according to an importance sequence of all the quantum chemistry parameter components, and adopting a leave-one-out method to perform cross check and external validation on predicating capability of the evaluation models. The method for predicting the activity of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor has the advantages of being simple to operate and uniform in form and enabling data to be obtained easily and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Small molecular complex structure searching method based on genetic algorithm
The invention discloses a global search method based on genetic algorithm, which takes small molecular complexes as objects, and aims to find the structure with the lowest energy and consistent with experimental facts. Including the following steps: building a complex model, chromosome coding; initialization, generating the possible structure of the complex; local optimization using quantum chemical methods; genetic operations, including replication, hybridization, mutation, etc.; repeating the above two steps until the number of iterations is reached ; Read the result and analyze it. This method limits the generation of new structures, and selects a more reasonable method during genetic manipulation, so it can search a wider range in a shorter time and find the correct structure of the corresponding small molecule complexes more effectively.
Owner:渠汇
Quantum chemistry simulations using optimization methods
ActiveUS8301390B2Chemical property predictionDigital data processing detailsQuantum chemistryEnergy gradient
Embodiments of the present invention provide, among other things, methods, apparatus, and systems for tuning a semiempirical process for predicting energy for different molecular configurations. In an example method, an energy value and an energy gradient are determined for each of a plurality of molecular configurations using an accurate method. A functional form of the semiempirical process is optimized using the determined energy values and energy gradients via multiobjective optimization. The functional form relates one or more parameters to energy values and energy gradients.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINIOS THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com