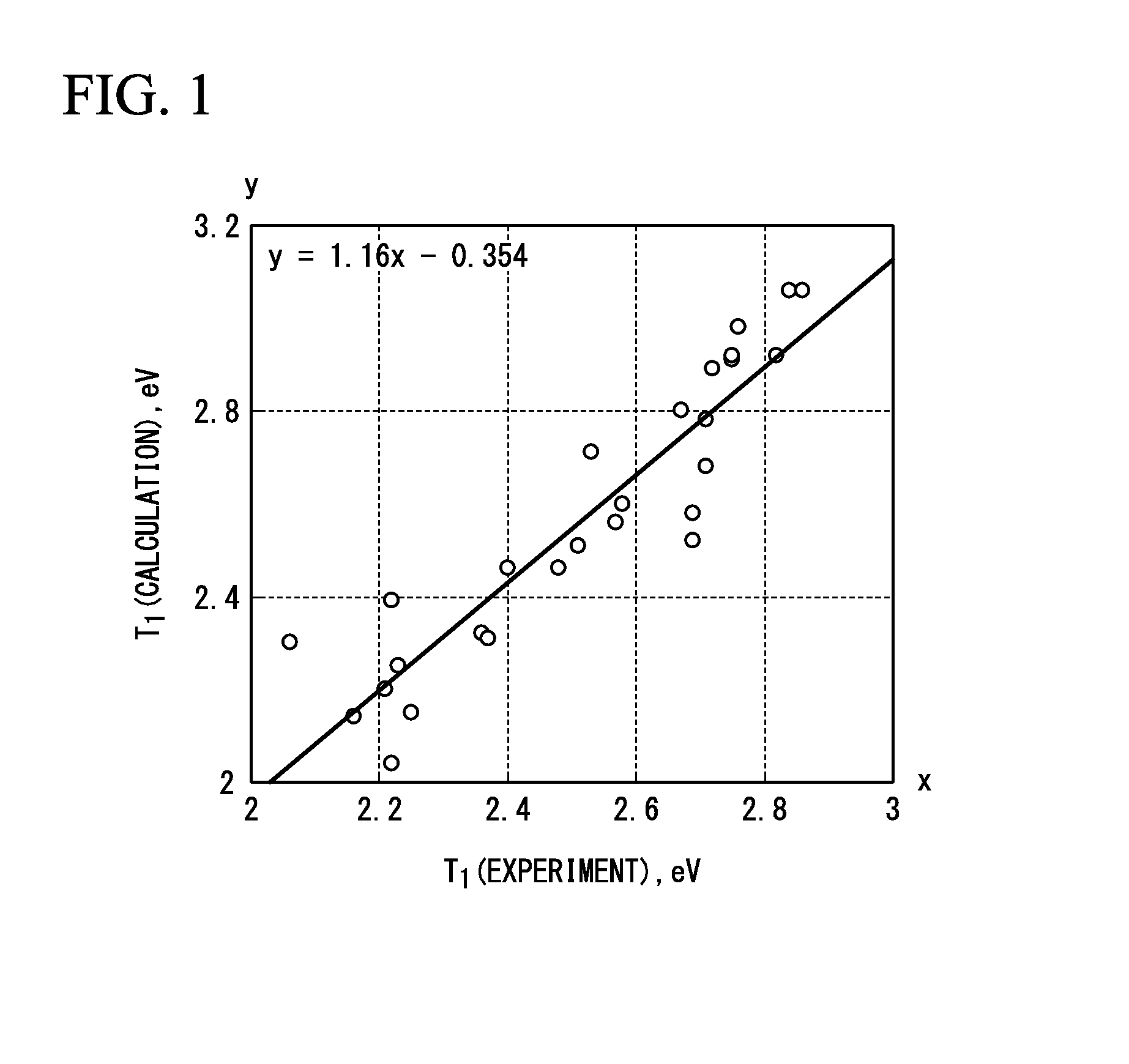
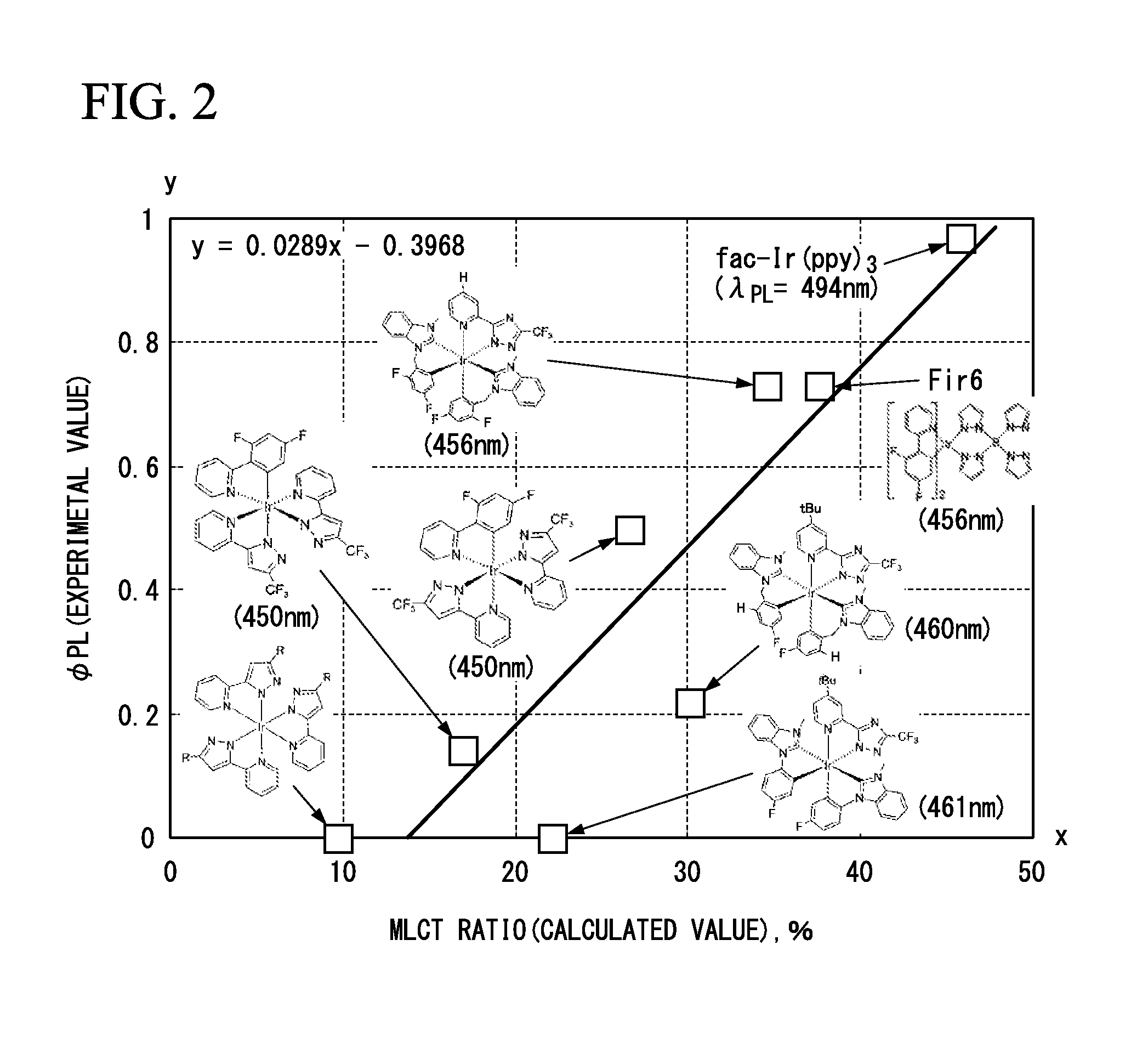
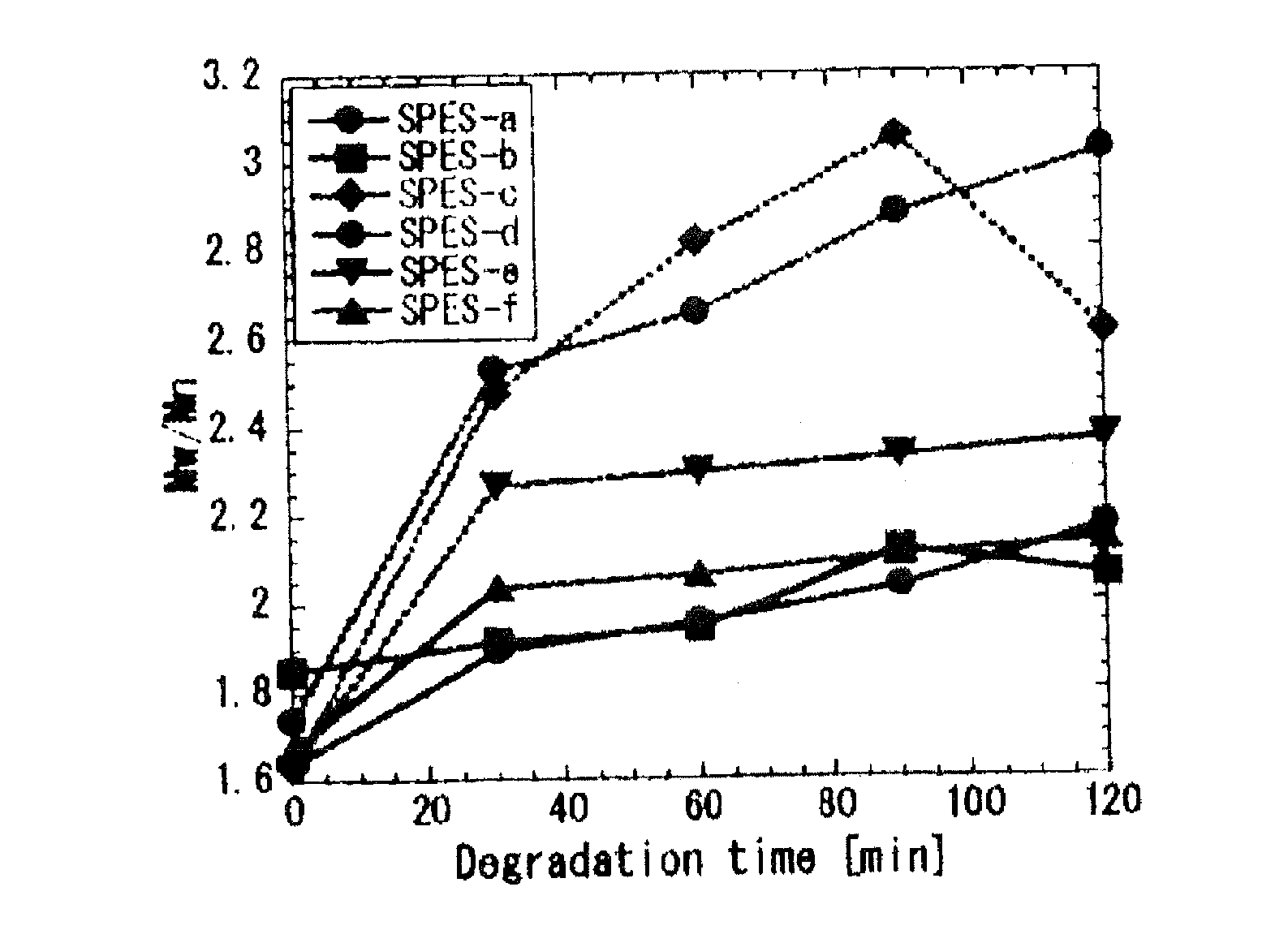
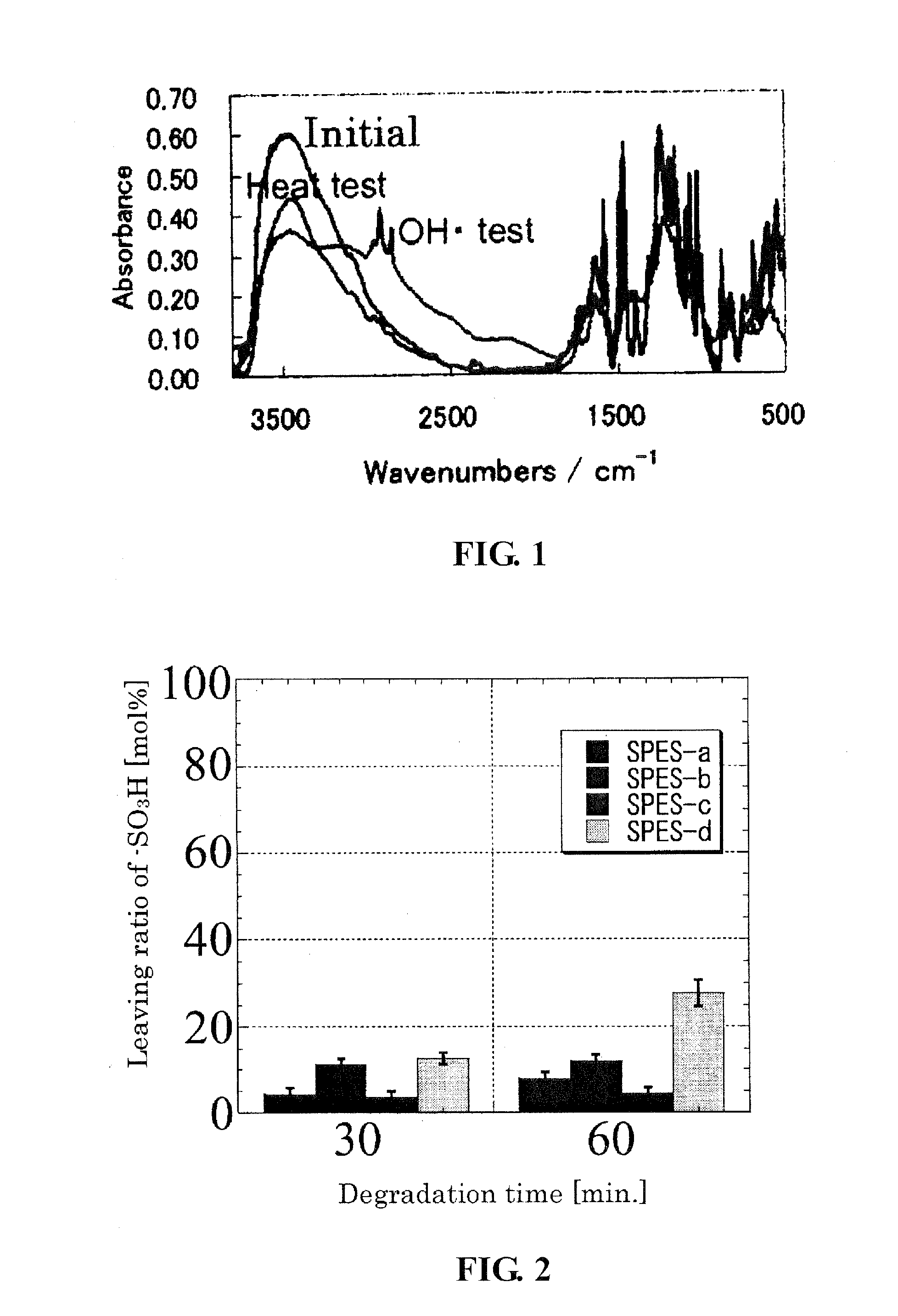
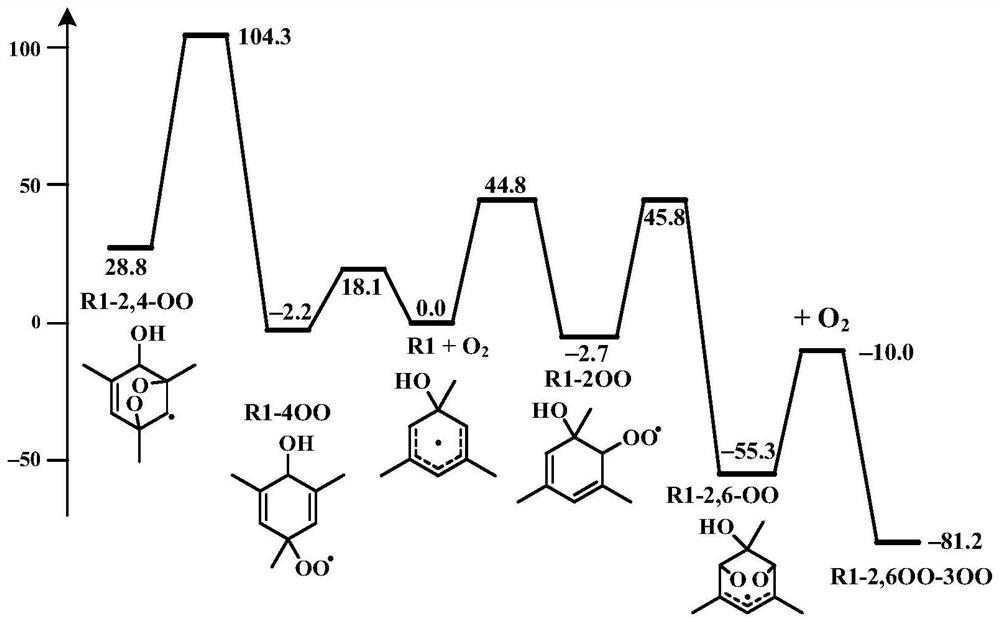
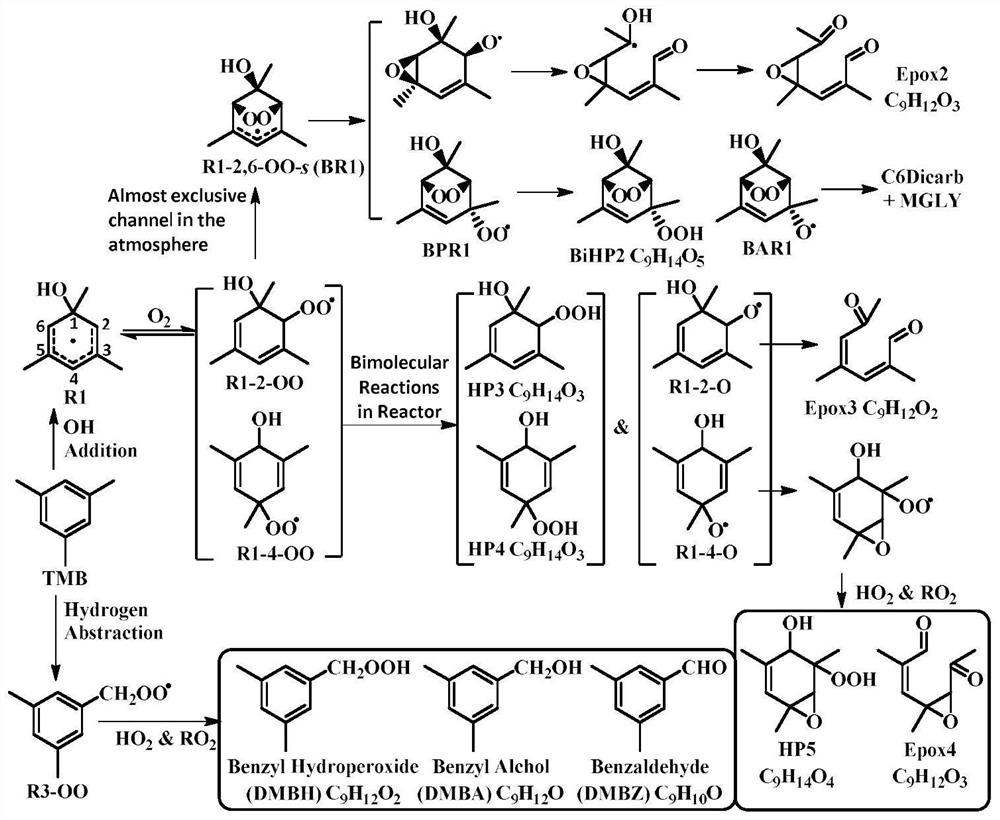
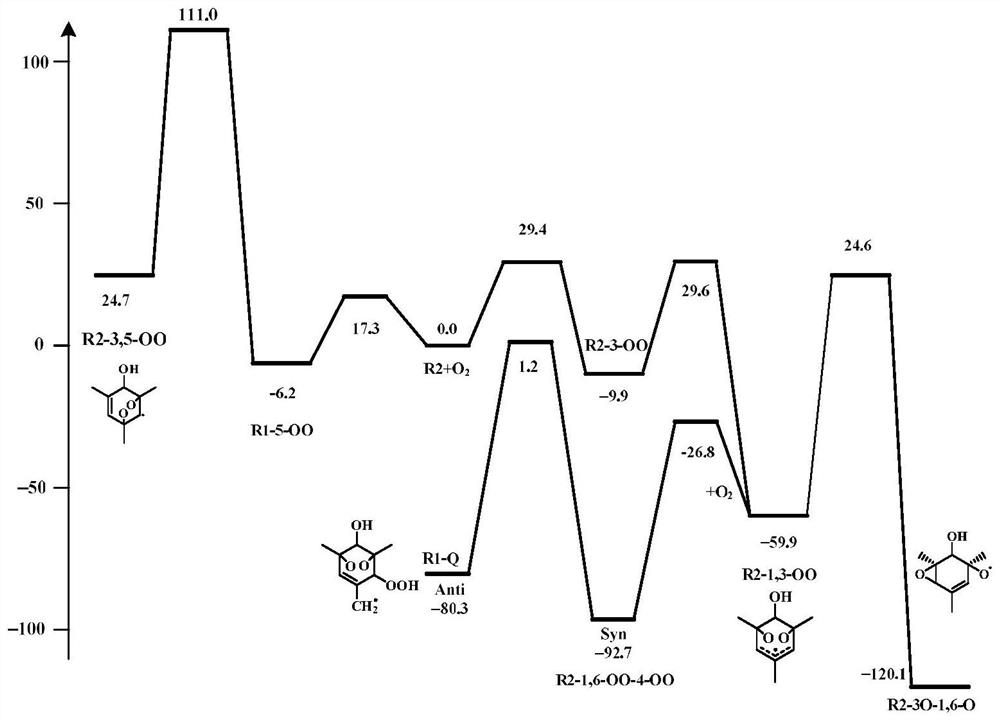
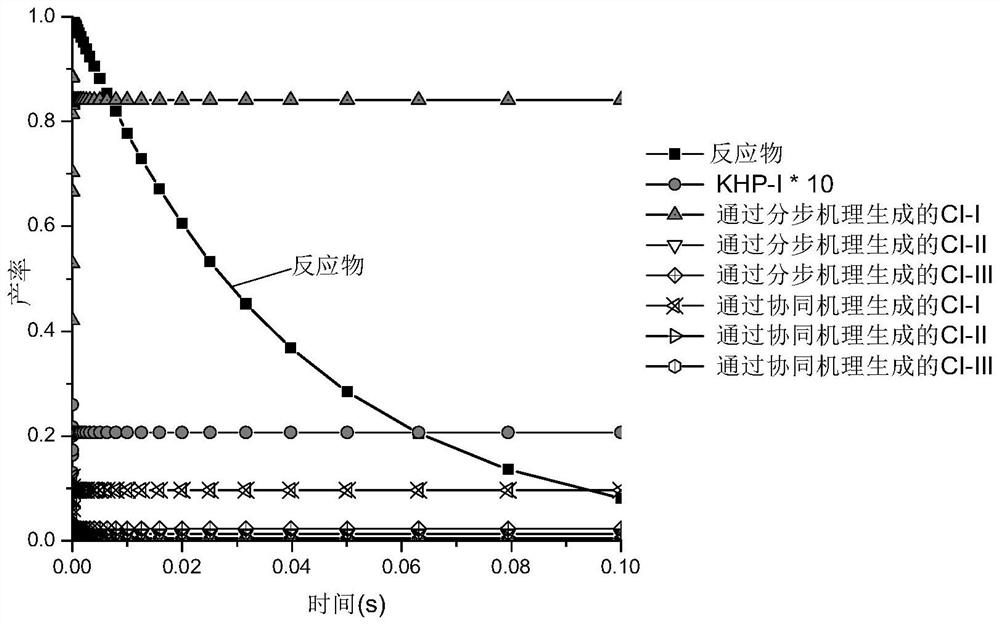
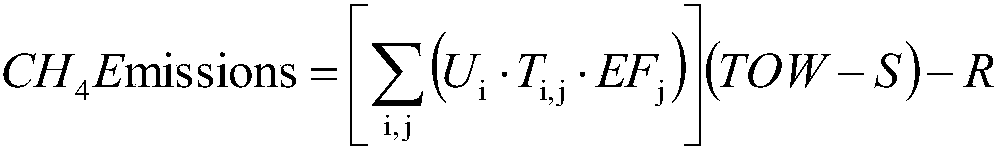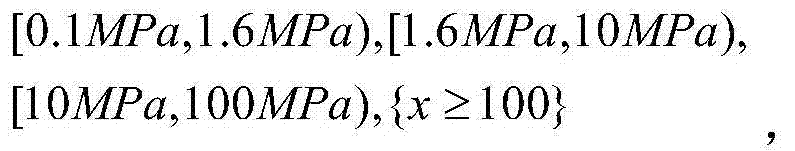Patents
Literature
40 results about "Quantum chemical" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
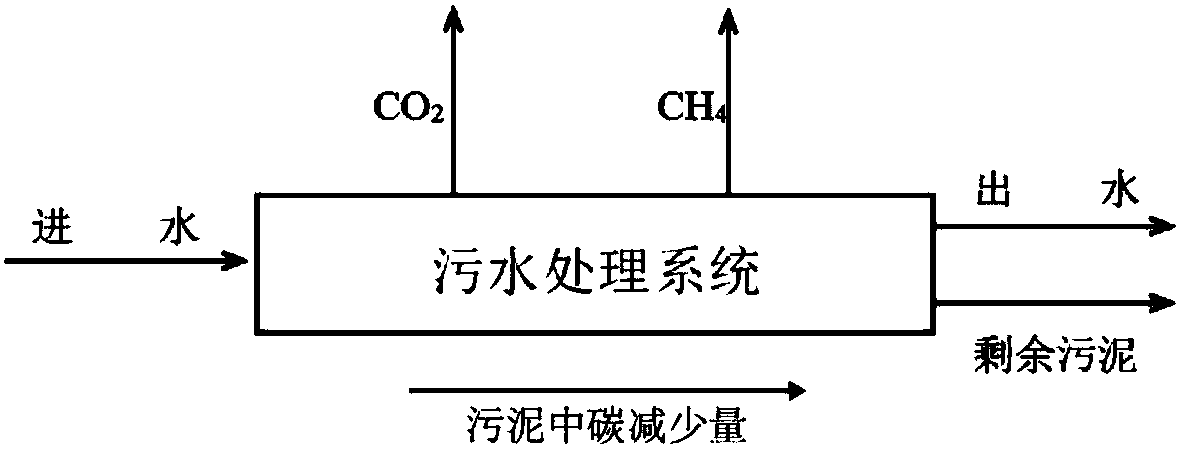
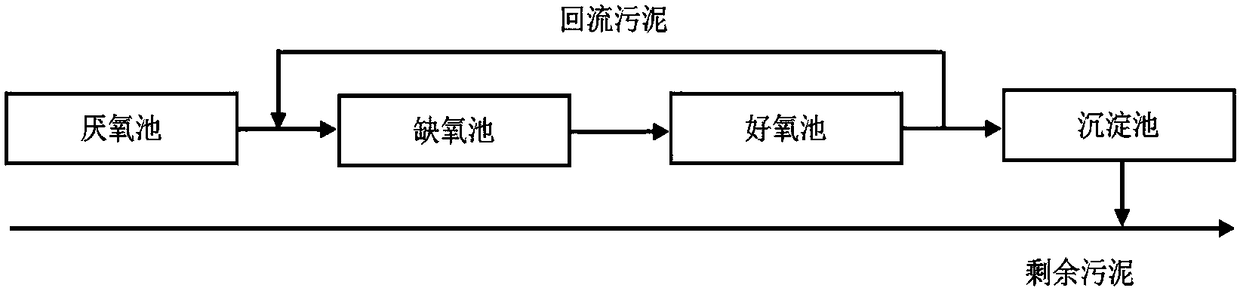
Sewage treatment plant carbon emission quantum chemical calculation method
InactiveCN108182344AAccurate carbon emissions dataGood practical valueChemical machine learningSpecial data processing applicationsIndirect emissionsQuantum chemical
The invention discloses a sewage treatment plant carbon emission quantum chemical calculation method. The sewage treatment plant carbon emission quantum chemical calculation method comprises the stepsof determining the operation time of a sewage treatment plant, working out the sewage treatment plant carbon direct emission EZ, the sewage treatment plant carbon indirect emission EJ, the sewage treatment plant carbon other emission EQ and the sewage treatment plant carbon recycling type emission ER within the operation time separately, and then obtaining a sewage treatment plant carbon emissionquantum chemical calculation result EC. According to the carbon emission quantum chemical calculation method, by delimiting the boundary conditions and calculating period, compared with an existing accounting method, the single sewage treatment plant has the pertinence, powerful data supporting can be provided for sewage treatment plant carbon emission reduction, the obtained carbon emission datais more accurate, and the method is more particularly to a single sewage treatment plant and has the good practical value.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Luminescent material, and organic light-emitting element, wavelength-converting light-emitting element, light-converting light-emitting element, organic laser diode light-emitting element, dye laser, display device, and illumination device using same
InactiveUS20130303776A1Improve efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic laserQuantum chemical
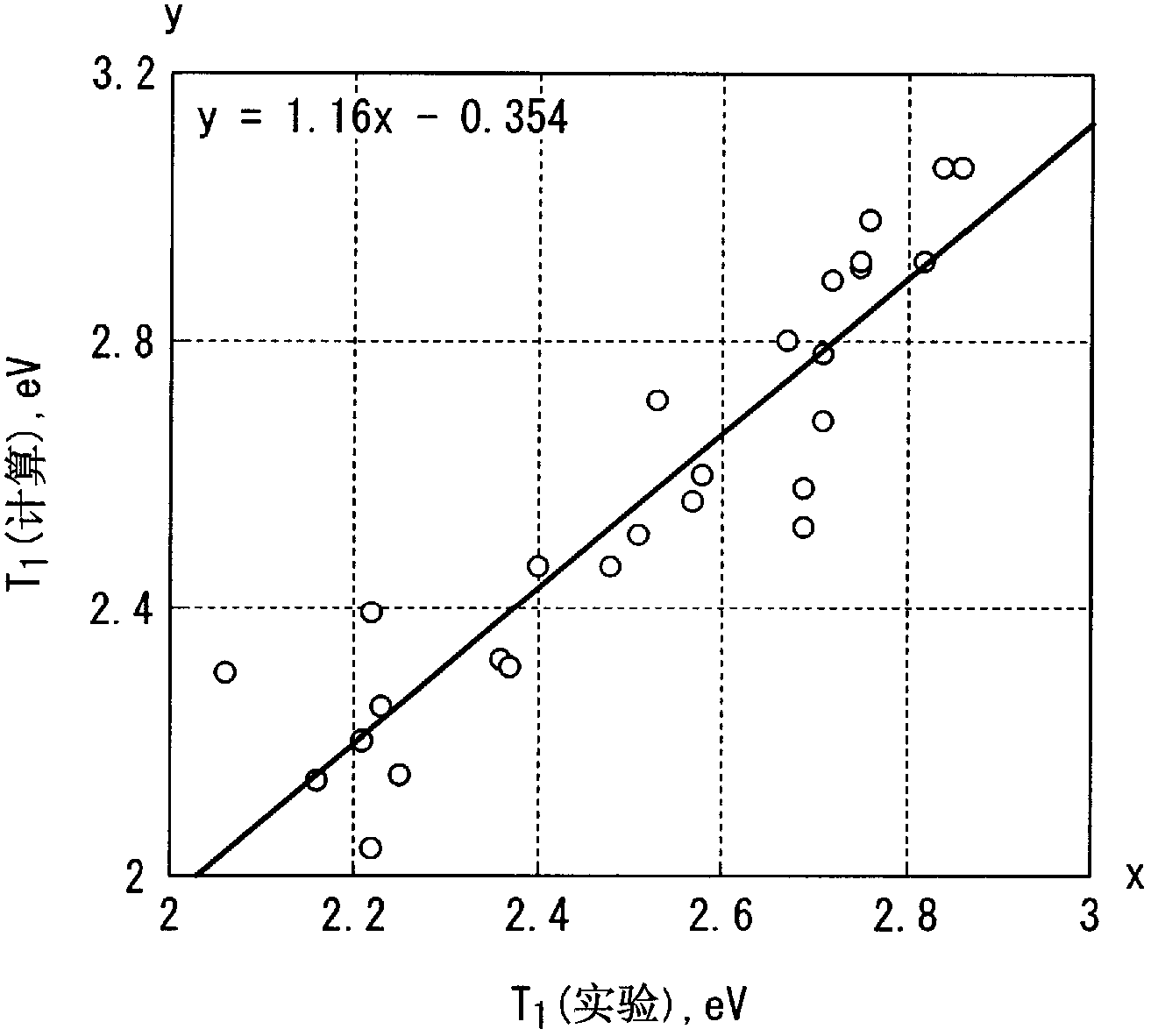
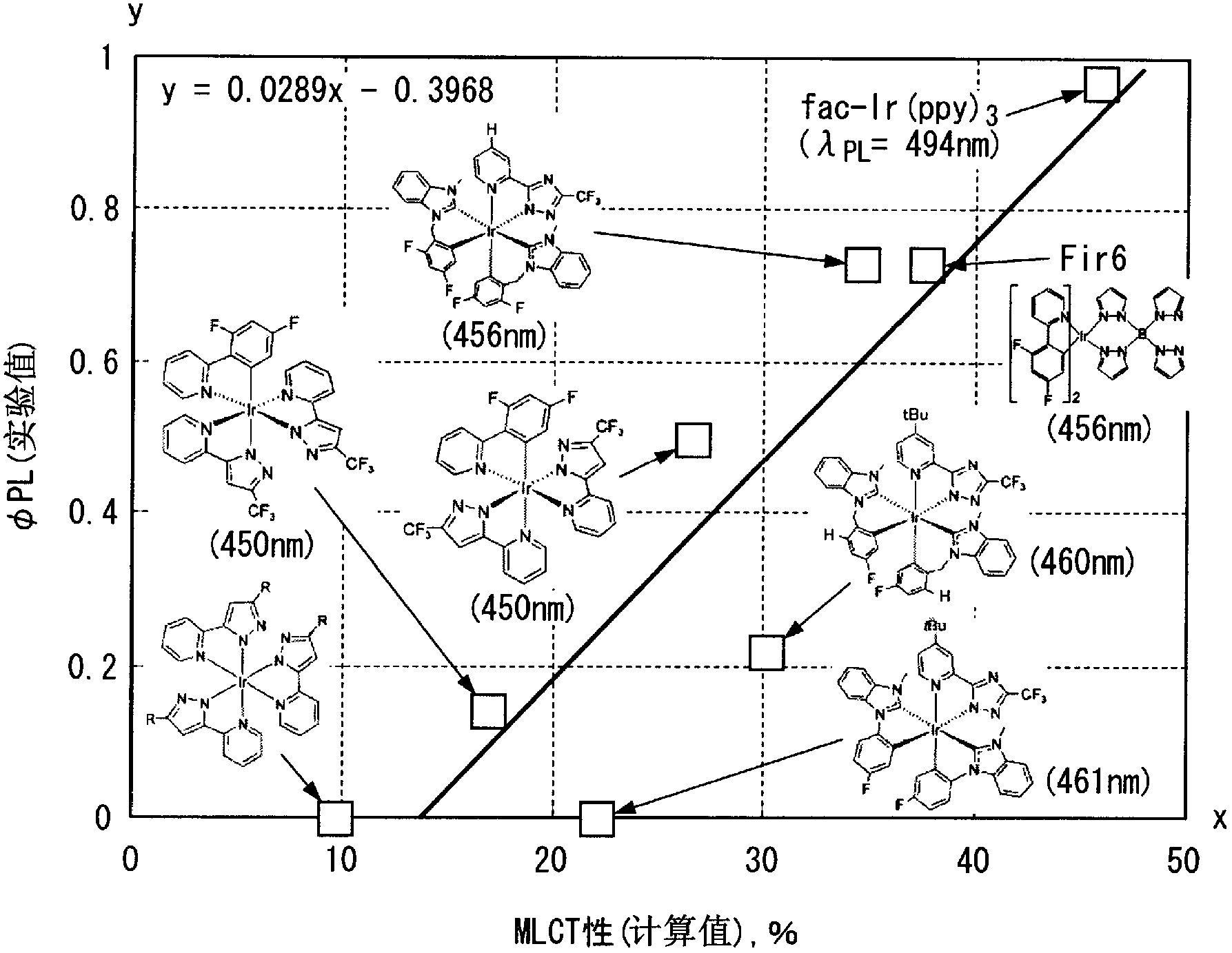
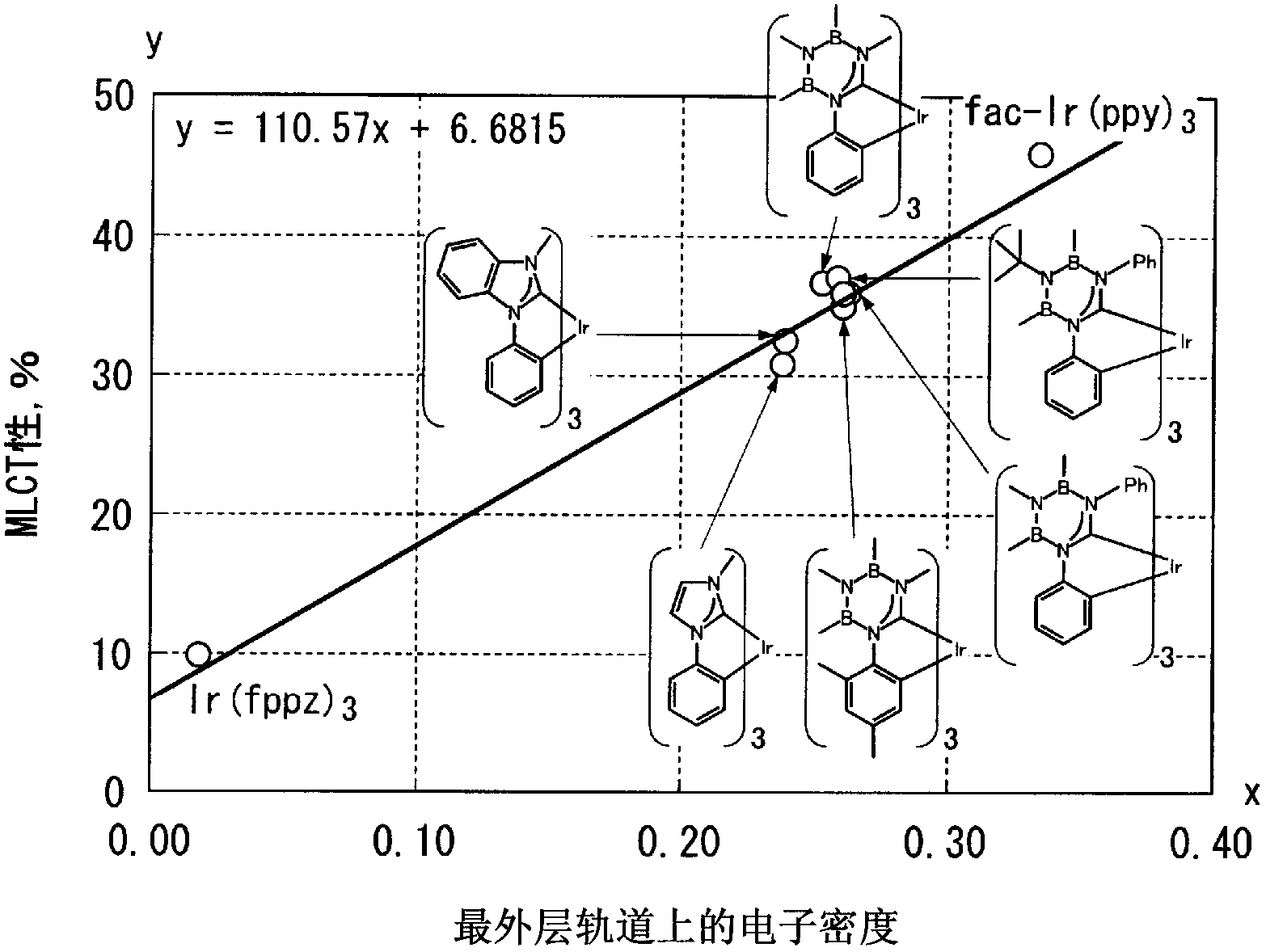
A luminescent material includes transition metal complex comprising a ligand in which an electron density of a p orbital of a highest occupied molecular orbital level is higher than 0.239 and lower than 0.711 when the electron density is calculated according to quantum chemical calculation (Gaussian09 / DFT / RB3LYP / 6-31G), the p orbital being in the outermost shell of an element coordinated to the metal.
Owner:SHARP KK
Hydrocarbon-based polymer for use of a fuel cell
InactiveUS20080044708A1Increased durabilityResist attackSolid electrolytesBiological testingOligomerFuel cells
The present invention provides a hydrocarbon-based polymer for use in an electrolyte membrane of a fuel cell having high durability, an electrolyte membrane of a fuel cell using the polymer, a fuel cell using the electrolyte membrane. The present invention provides a hydrocarbon-based polymer comprising a repeating unit, wherein a value of an HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital), obtained according to a quantum chemical calculation, of a calculated oligomer having four successive units, each of which is the repeating unit, is lower than a control HOMO value, obtained according to the quantum chemical calculation, of a control oligomer having four successive repeating units, each of which is represented by the formula (I):
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
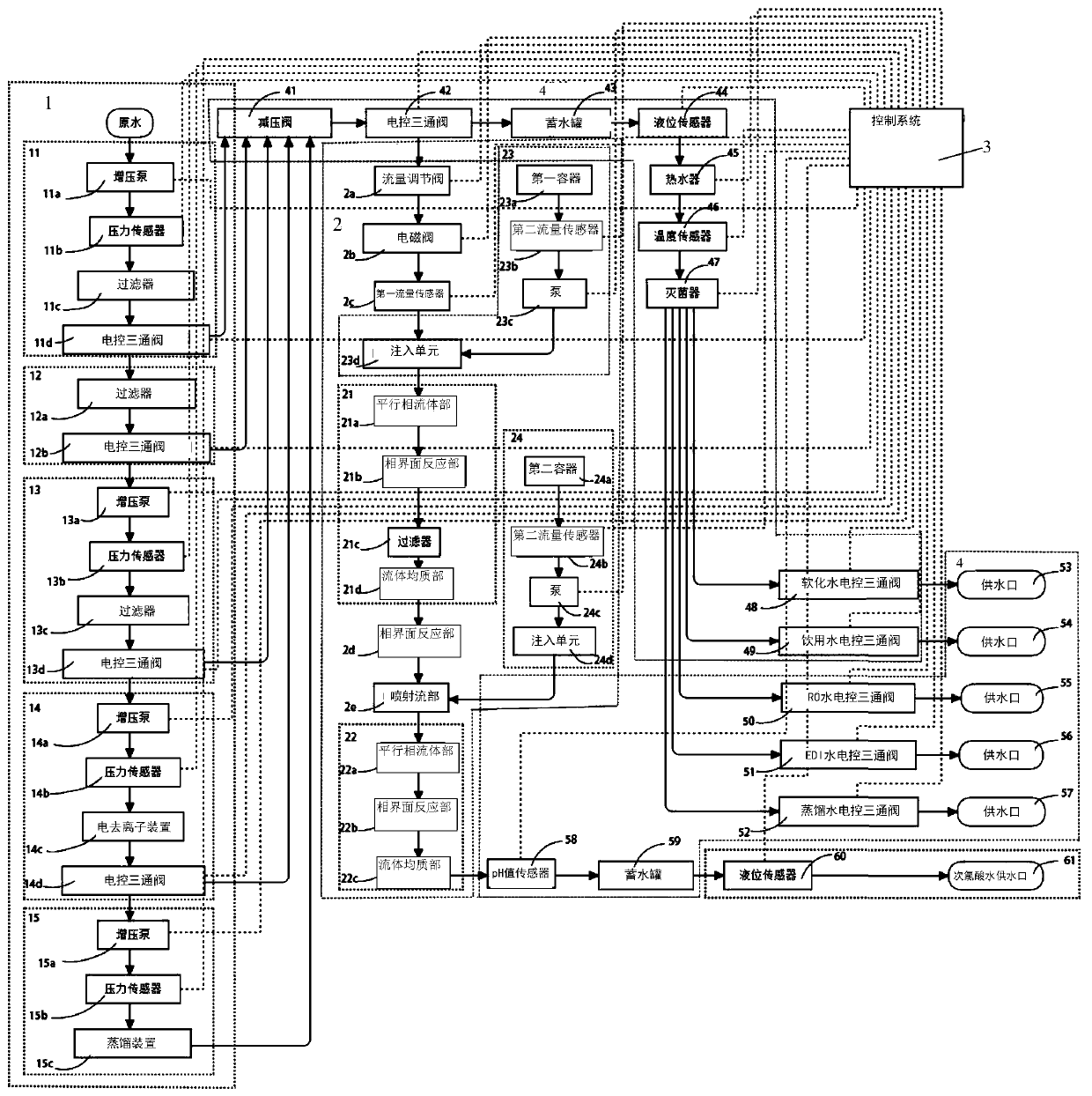
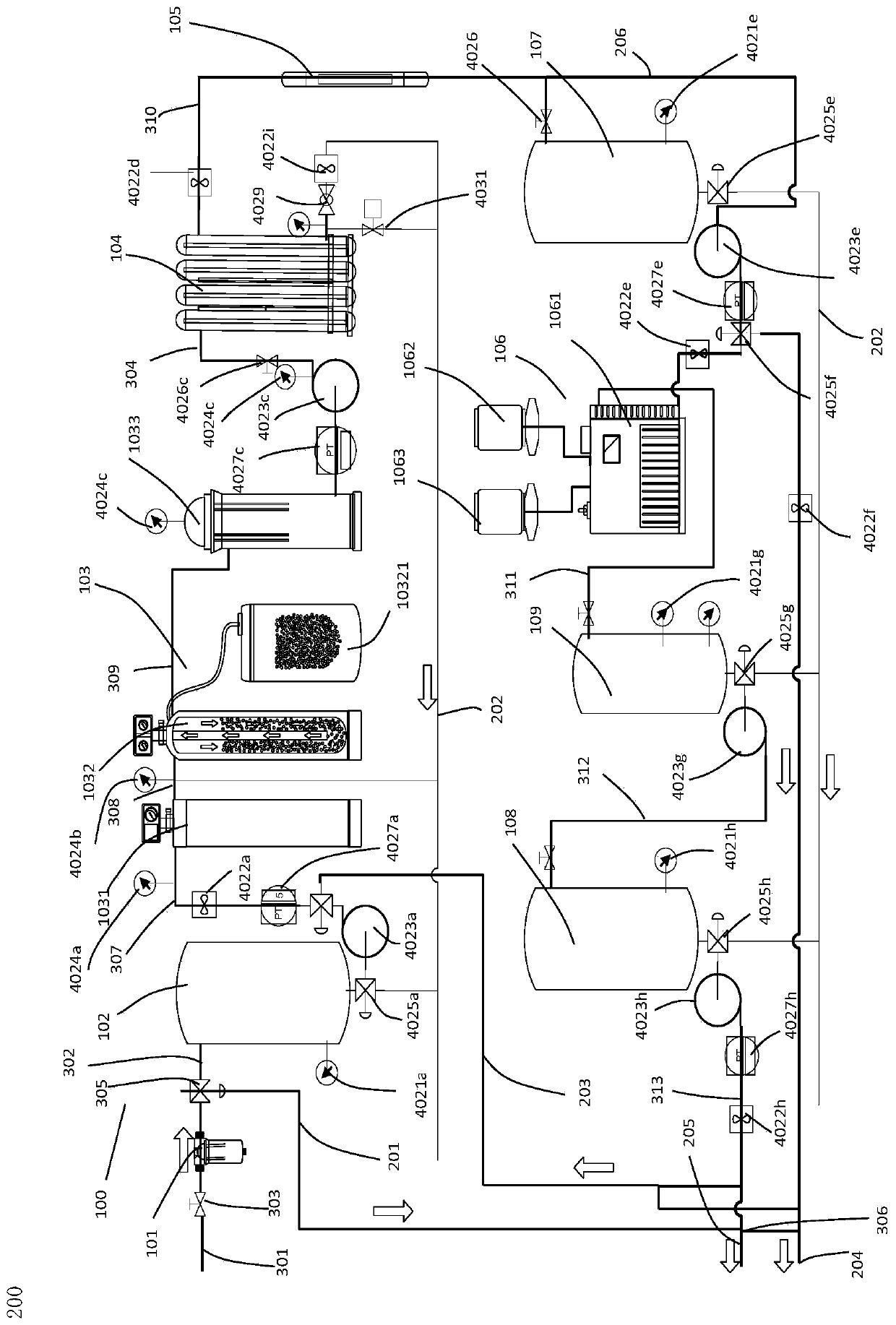
Generation equipment and generation method for non-electrolytic slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water
PendingCN110282807AStrong weather resistanceEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideWater treatment parameter controlQuantum chemicalHypochlorous acid
The invention discloses a generation equipment and generation method for non-electrolytic slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water. The concentration of the slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water can be lower than 200 ppm, especially be lower than 60 ppm; the pH value ranges from 6.20 to 6.80, the pH fluctuation range is controlled to be within plus or minus 0.05 at any value therebetween, and stable storage can be performed for 18 months. The generation equipment comprises at least one stage of purification device, a slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water generation device, a control system and water supply ports. The purification device is used for purifying raw water from a raw water supply system. The slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water generation device is located in the down stream of the purification device, and is provided with reaction devices, a water inlet and addition agent injection devices. The reaction devices are used for performing a quantum chemical reaction on addition agents and water from the purification device, and controlling H hydrated protons by stage to reach the stable saturated solubility of H ions, thereby processing into the slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water with stable pH. The control system is electrically connected with the slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water generation device, and is arranged to accurately control a whole generation process. The water outlets of the purification devices and the water outlet of the slightly-acidic hypochlorous acid water generation device are connected to the water supply ports through corresponding pipelines in a switchable way. The equipment can provide various functional water with different uses, and can switch water taking types according to user needs.
Owner:SHANGHAI WANLAY ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
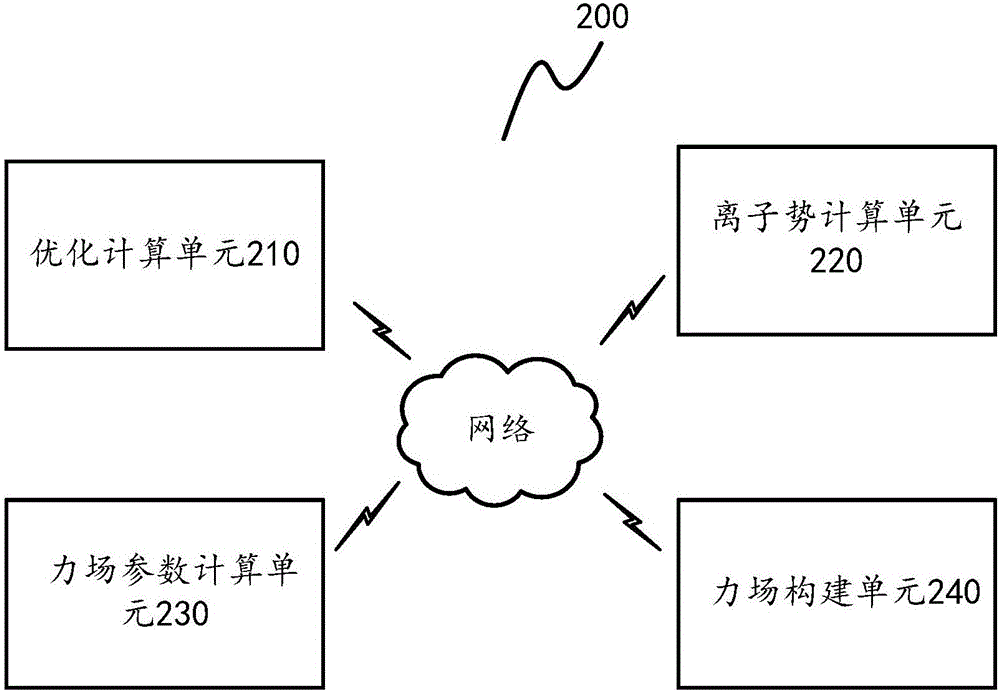
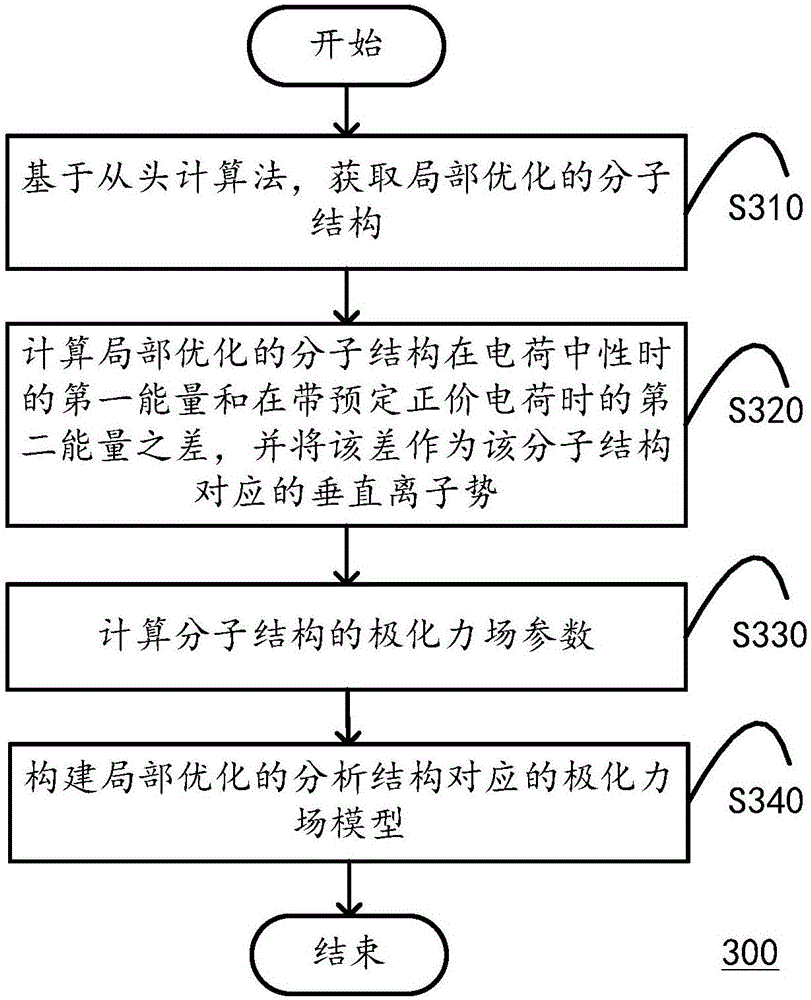
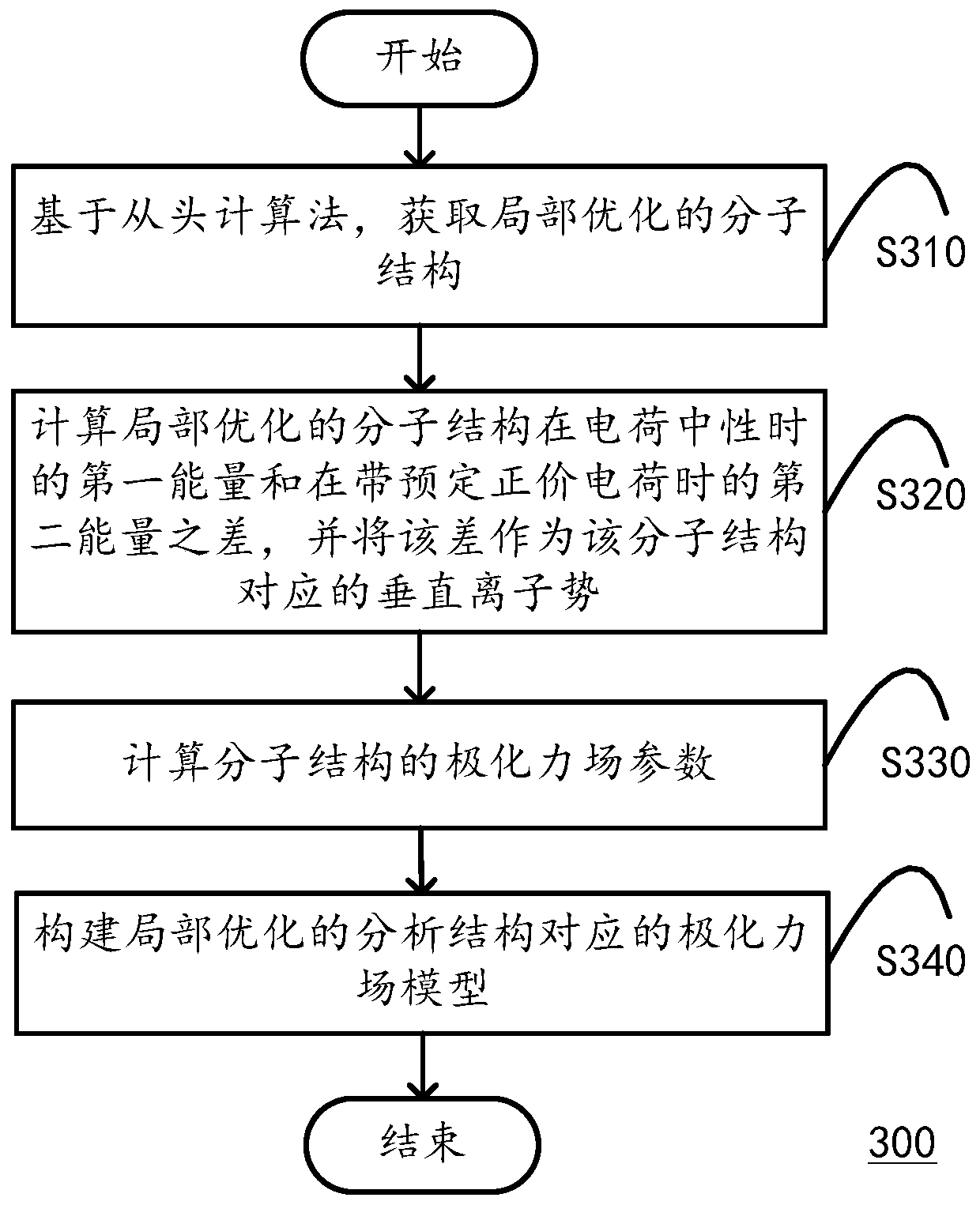
Method and application for constructing polarized force fields and method and system for predicting drug crystal forms
ActiveCN106372400APrecise Design DirectionHigh chemical precisionChemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryAb initio quantum chemistry methodsQuantum chemical
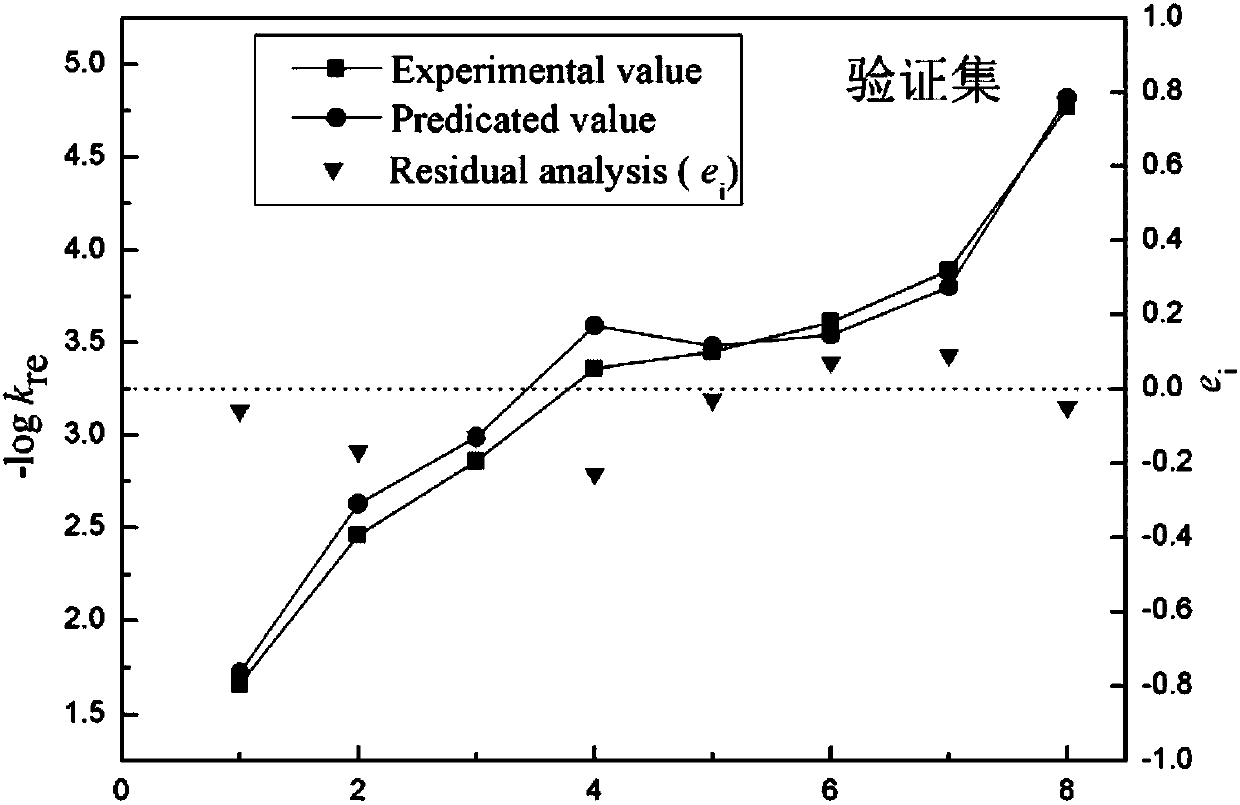
The invention discloses a method and application for constructing polarized force fields and a method and system for predicting drug crystal forms. The method for constructing chemical molecule polarized force fields is suitable for being executed in one or more computation apparatuses, and comprises the following steps of: carrying out optimization computation on a quantum chemical structure of a chemical molecule on the basis of an ab initio calculation method so as to obtain a locally optimized molecular structure; calculating the difference between first energy of the locally optimized molecular structure when the charge of the molecular structure is neutral and second energy of the locally optimized molecular structure when the molecular structure has a predetermined positive-valence charge, and taking the difference as a vertical ion potential corresponding to the molecular structure; calculating polarized force field parameters of the molecular structure on the basis of the vertical ion potential and the locally optimized molecular structure, wherein the polarized force field parameters comprise a multi-pole vector of atom distribution, a multi-pole polarization rate of the atom distribution and a frequency-related polarization rate; and constructing a corresponding polarized force field model on the basis of the locally optimized molecular structure and the calculated polarized force field parameters.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
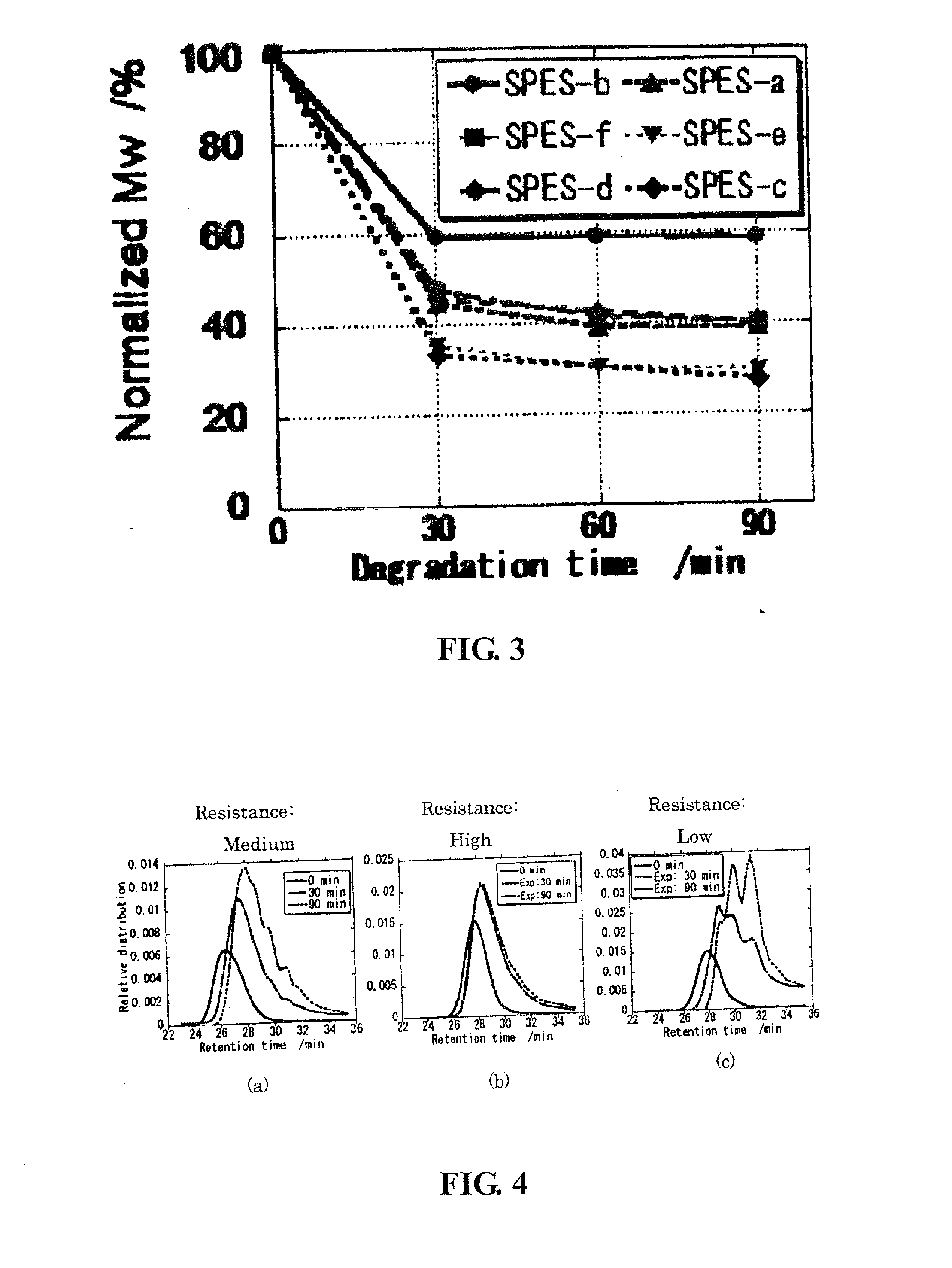
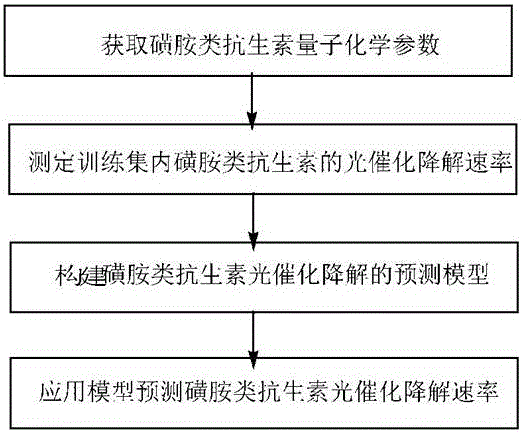
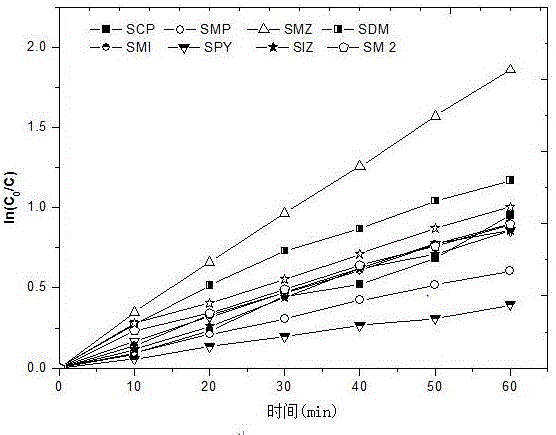
Method for predicting photocatalytic degradation rate of sulfonamide antibiotics
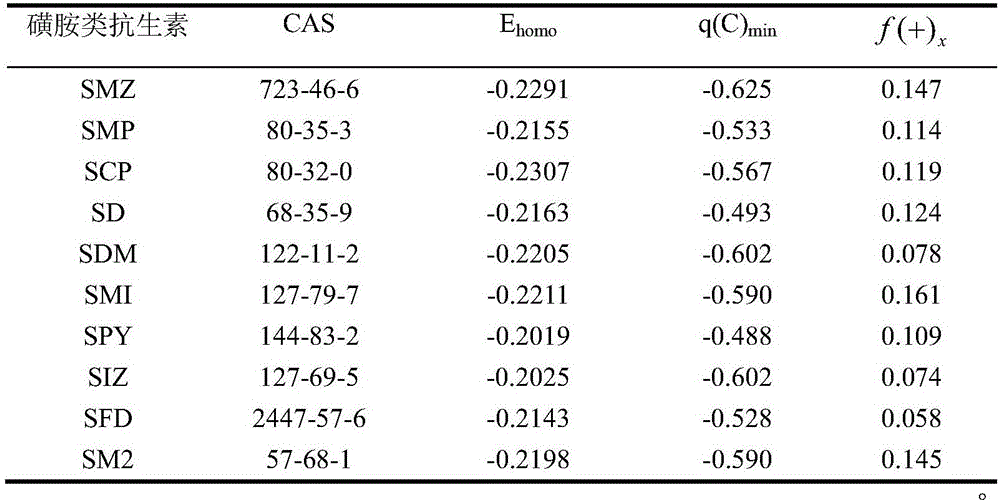
InactiveCN106124659ALarge predicted throughputReduce investmentComponent separationQuantum chemicalAntibiotic Y
A method for predicting photocatalytic degradation rate of sulfonamide antibiotics includes the steps of acquiring quantum-chemical parameters of the sulfonamide antibiotics; constructing a photocatalytic system, and measuring photocatalytic degradation rate of the sulfonamide antibiotics in a training set; establishing a prediction model for photocatalytic degradation of the sulfonamide antibiotics; using the model to predict the photocatalytic degradation rate of the sulfonamide antibiotics. The method of the invention is widely applicable, requires no complex detection apparatus, causes no experimental and environmental pollution, can accurately predict photocatalytic degradation characteristics of sulfonamide antibiotics, provides scientific basis for implementing emission and ecological risk evaluation for sulfonamide antibiotics, and has the advantages such as high prediction flux, low input, low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
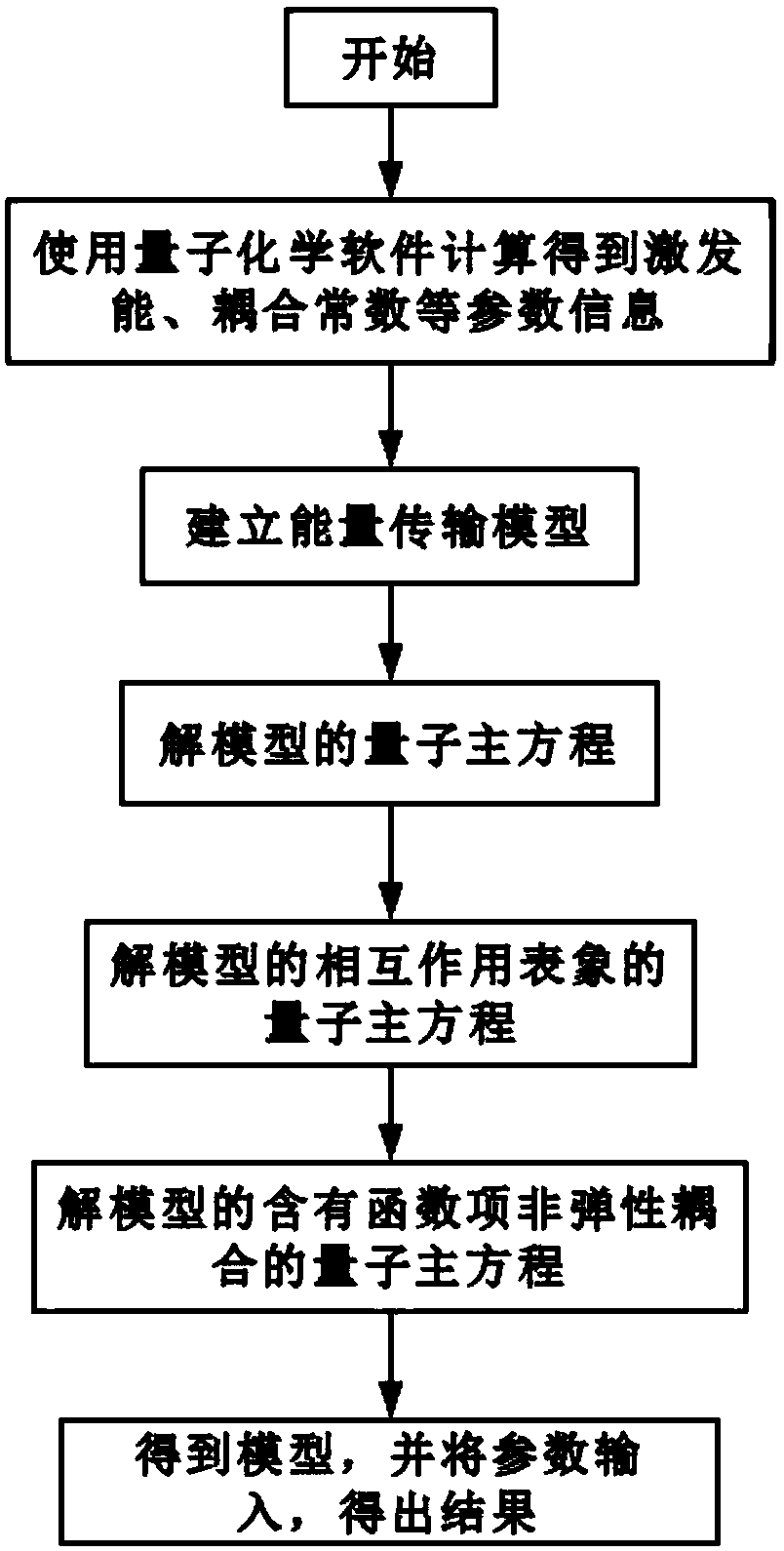
A coherent resonance energy transfer method considering inelastic coupling
InactiveCN109033736AMeet coherenceMeet the flexibilityComplex mathematical operationsEnergy transferQuantum master equation
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
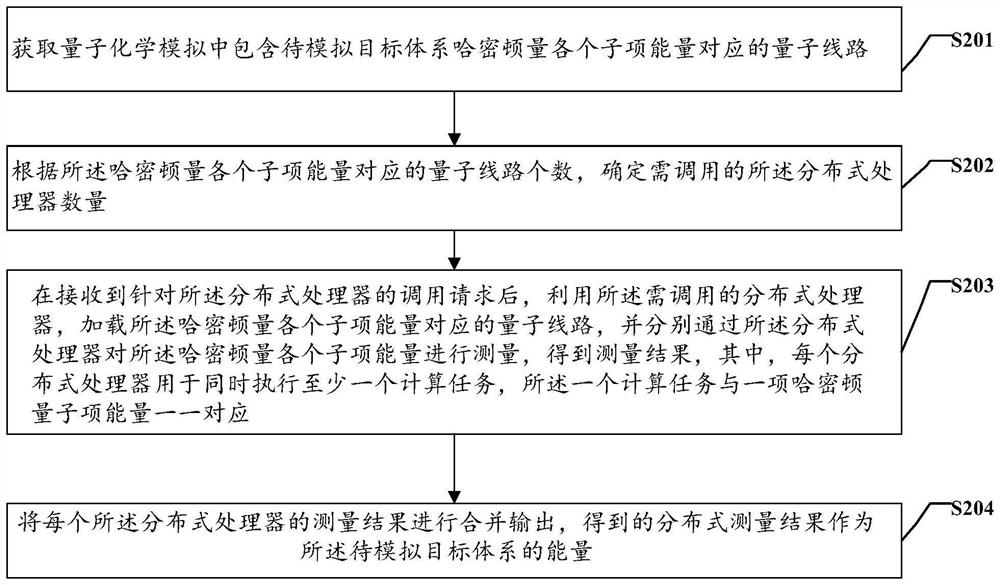
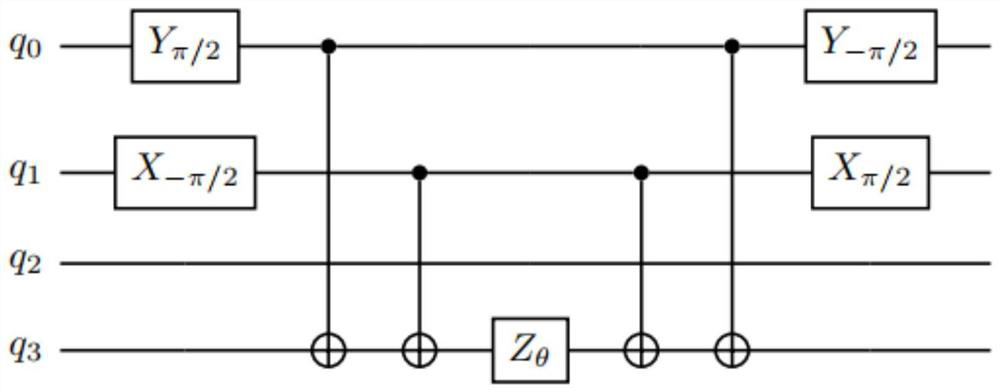
Method and device for simulating energy of target system based on quantum calculation and medium
The invention discloses a method and device for simulating target system energy based on quantum computation.The method comprises the steps that quantum circuits corresponding to all subitem energy of the Hamiltonian amount of a to-be-simulated target system in quantum chemical simulation are obtained, and the number of the quantum circuits corresponding to all subitem energy of the Hamiltonian amount is calculated according to the number of the quantum circuits corresponding to all subitem energy of the Hamiltonian amount; the method comprises the steps of determining the number of distributed processors needing to be called, after receiving a calling request for the distributed processors, utilizing the distributed processors needing to be called to load quantum circuits corresponding to the energy of all subitems of the Hamiltonian, and measuring the energy of all the subitems of the Hamiltonian through the distributed processors to obtain measurement results; finally, the measurement results of all the distributed processors are combined and output, the obtained distributed measurement results serve as the energy of the to-be-simulated target system, support can be provided for calculation of the energy of the target system, the calculation speed is increased, the depth of a quantum circuit is reduced, and further development of quantum chemistry simulation application is promoted.
Owner:ORIGIN QUANTUM COMPUTING TECH (HEFEI) CO LTD
Process for preparing high-oxygen bath lotion
InactiveCN1164251CImprove work efficiencyImprove learning efficiencyBathing devicesDiseaseQuantum chemical
A process for preparing high-oxygen water bathing solution features that the light-quantum chemical oxygen-dissolving mechanism is used to dissolve a great deal of oxygen in water. The high-oxygen water bathing solution so prepared can provide oxygen to human body, relieve fatigue, beautify face and prevent diseases.
Owner:和光学 +1
Cross-scale simulation method for predicting gelation process of water-based alumina precursor
PendingCN114023393AStructural solutionTroubleshoot Fluid Performance VariationsMolecular entity identificationCheminformatics data warehousingQuantum chemistryChemical physics
The invention discloses a cross-scale simulation method for predicting a gelation process of a water-based alumina precursor. The method comprises the following steps: (1) calculating and determining an Al-containing oligomer molecular structure by using a DFT theory; (2) constructing a colloid structure model containing different proportions of oligomers; (3) balancing and optimizing a colloid structure, and calculating a more stable oligomer molecular proportion; (4) on the basis of the proportions, constructing structure models of different solvent proportions; (5) simulating specific setting parameters in combination with experiments and molecular dynamics to improve the reliability of the model; (6) calculating the free volume of the model to obtain flow characteristics; and (7) outputting a result file, and ending. According to the method, by combining quantum chemical calculation and molecular dynamics calculation, synchronous experiment and simulation of specific parameters, calculation and experiment are mutually guided and supported, higher theoretical reliability and experiment extension possibility are provided for controlling the gelation problem, and the method can be used for guiding industrial production after being optimized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
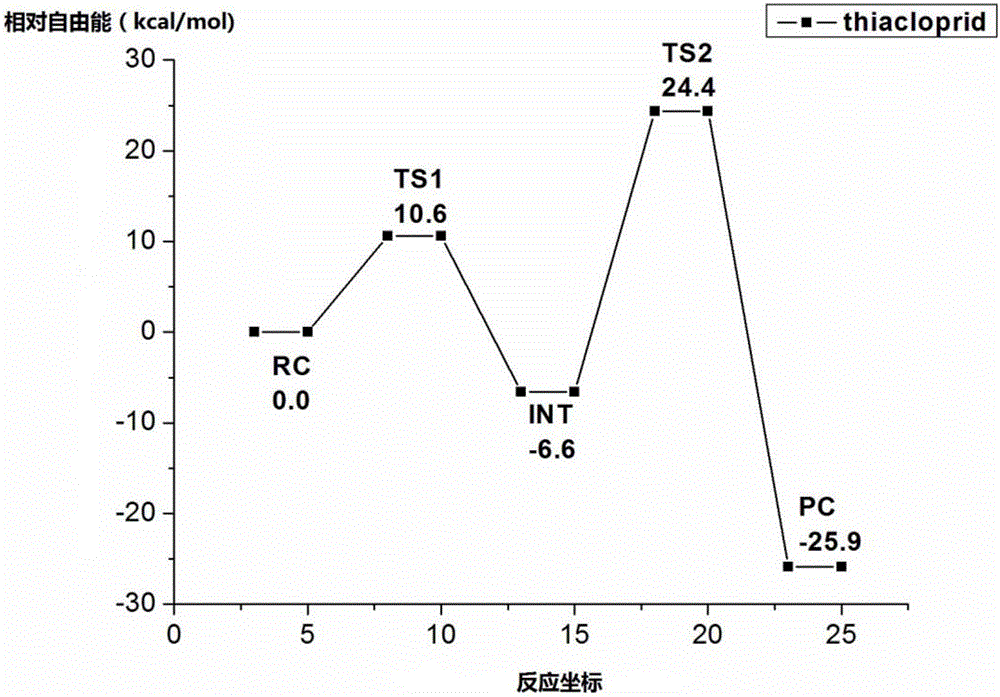
Evaluation method related to hydrolysis reaction activity of neonicotinoid insecticides
ActiveCN106198847AEasy to operateConsistent conclusionChemical methods analysisGibbs free energyQuantum chemical
The invention discloses an evaluation method related to hydrolysis reaction activity of neonicotinoid insecticides, which includes the steps of: 1) establishment a calculation model of the hydrolysis reaction of the neonicotinoid insecticides: selecting an X-ray diffraction crystal structure of the molecules of a to-be-evaluated neonicotinoid insecticide, inserting water molecules into an activated locus, and performing structural optimization to obtain the calculation model of the hydrolysis reaction; 2) selecting parameters; 3) quantum chemical analysis: calculating the electron energy E of each stationary point of the molecule along with the process of the hydrolysis reaction, and calculating the frequencies to obtain the Gibbs free energy G of the stationary points; and 4) evaluation on the hydrolysis reaction activity of the neonicotinoid insecticides: calculating the activation free energy barrier change [delta]G in a rate determination step. The lower is the [delta]G, the higher is the hydrolysis reaction activity of the neonicotinoid insecticide. The method is simple and reasonable, is easy to carry out and is low in cost, has high practical value and has a reference meaning of development of varieties of the neonicotinoid insecticides.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
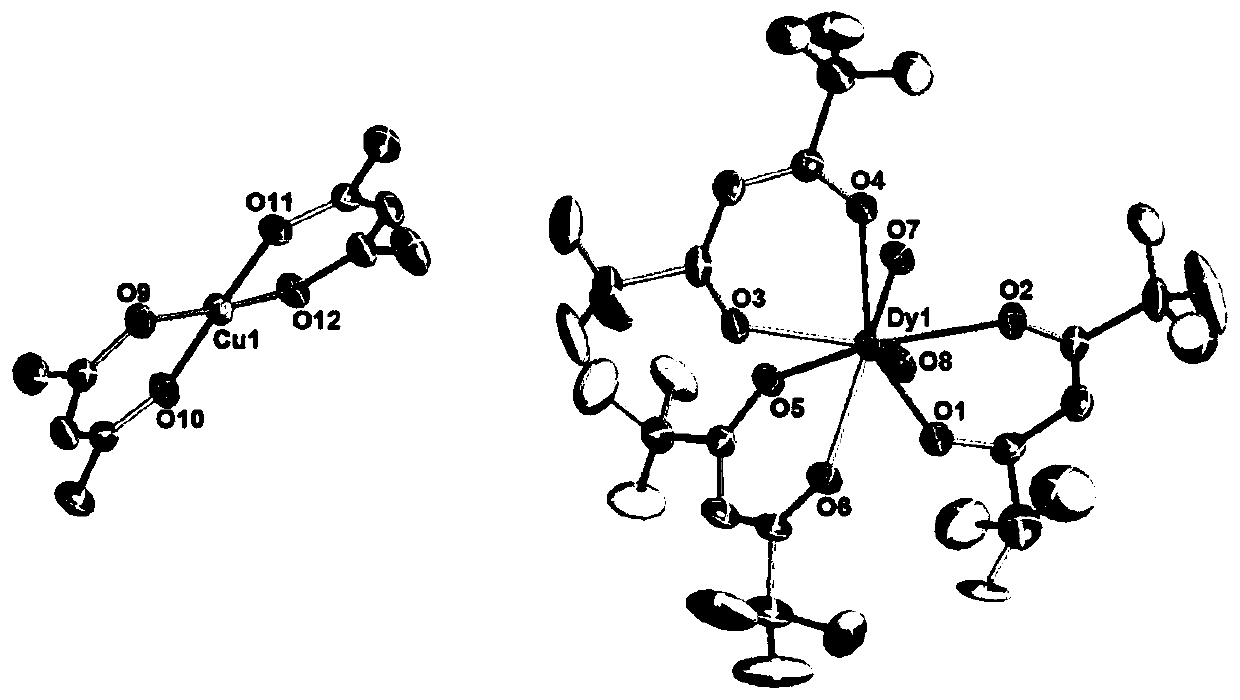
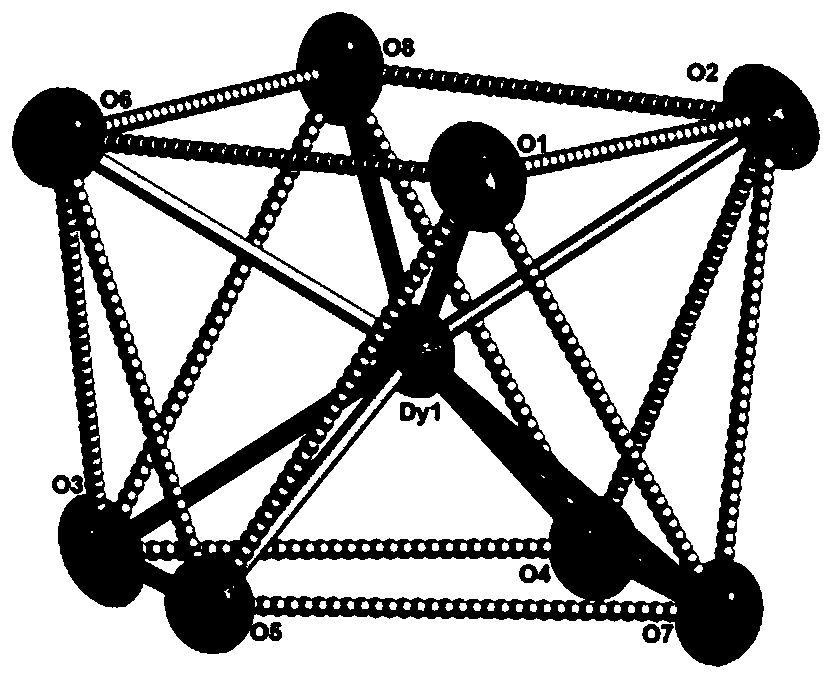
Dy (III)-Cu (II) eutectic monomolecular magnet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111116343ASimple filterSimple processOrganic chemistry methodsOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismMetallurgyQuantum chemical
The invention discloses a Dy (III)-Cu (II) eutectic monomolecular magnet and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the Dy (III)-Cu (II) eutectic monomolecular magnet is [Dy(hfac)3(H2O)2]-[Cu(acac)2], wherein hfac is a hexafluoroacetylacetone anion, and acac is an acetylacetone anion. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a methanol solution dissolved with Dy(hfac)3(H2O)2 into a dichloromethane solution dissolved with Cu(acac)2, performing room-temperature stirring for 15-20 min, filtering to obtain a clear solution, naturally volatilizing the clear solution for 3 d to obtain dark green crystals, filtering, and washing and drying the dark green crystals to obtain the Dy (III)-Cu (II) eutectic monomolecular magnet. The Dy (III)-Cu (II) eutectic molecular material has the performance of a single-molecule magnet, and has a wide application prospect in the aspects of high-density information storage equipment, quantum chemical calculation, spintronicsand the like as a molecular-based magnetic material.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Luminescent material, and organic light-emitting element, wavelength-converting light-emitting element, light-converting light-emitting element, organic laser diode light-emitting element, dye laser, display device, and illumination device using same
InactiveCN103154189AImprove efficiencyLaser detailsIndium organic compoundsQuantum chemicalOrganic laser
A luminescent material contains a transition metal complex having at least one ligand in which the electron density in the p-orbital, which is in the outermost shell of a coordination element site of a metal at the level of the highest occupied molecular orbital calculated according to quantum chemical calculation (Gaussian09 / DFT / RB3LYP / 6-31G), is greater than 0.239 and less than 0.711.
Owner:SHARP KK
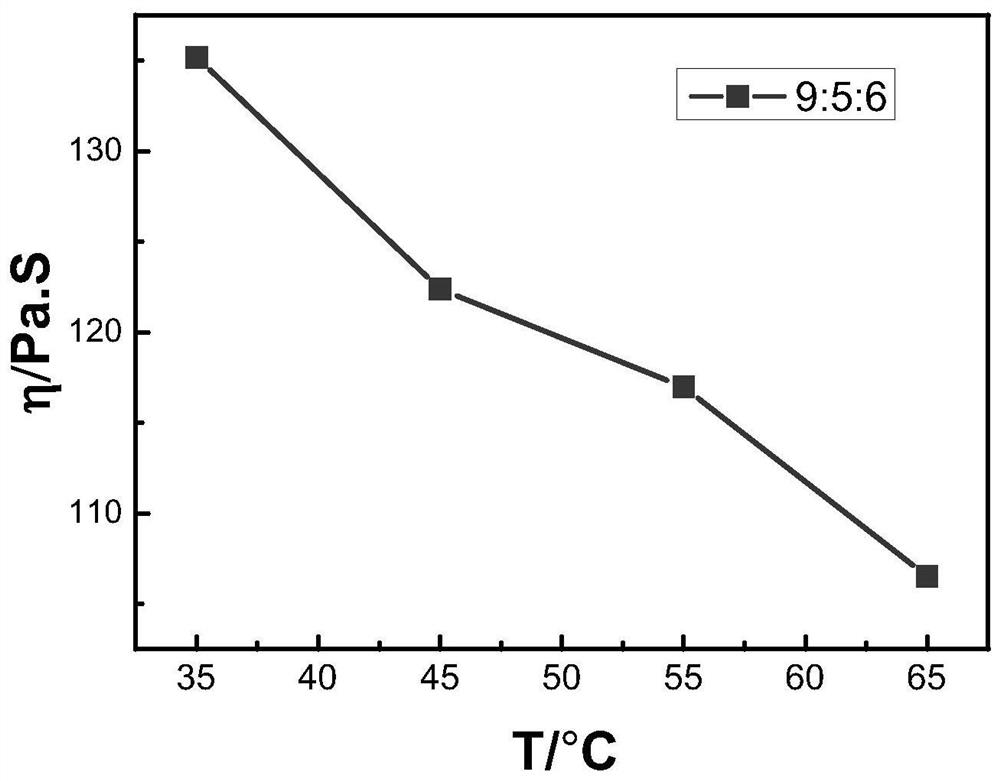
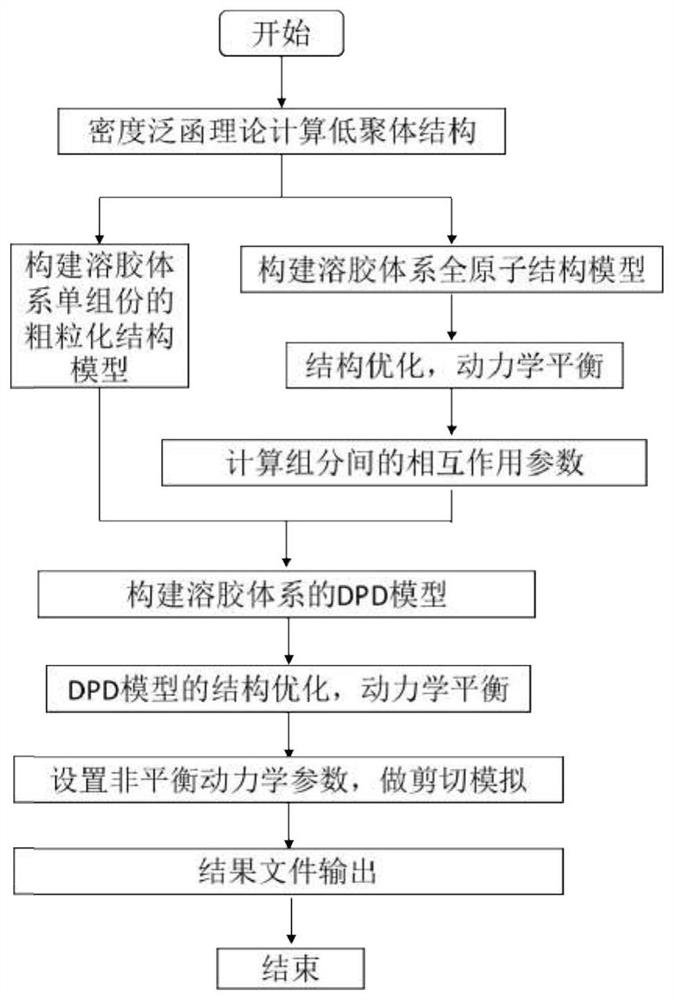
Cross-scale simulation method for predicting microstructure evolution in colloid shear motion process
ActiveCN113223624AResolution timeSolve space problemsChemical processes analysis/designComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemicalDynamic balance
The invention discloses a cross-scale simulation method for predicting microstructure evolution in a colloid shear motion process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) calculating an oligomer structure according to a density functional theory; (2) respectively constructing a sol system single-component coarse-grained structure model and a full-atom structure model; (3) carrying out structure optimization and dynamic balance on the full-atom model; (4) calculating interaction parameters among the components based on a full-atom model; (5) constructing a DPD model of a sol system by using a single-component coarse graining structure; (6) optimizing the structure of the DPD model and balancing dynamics; (7) setting unbalanced dynamic parameters, and performing shear simulation; and (8) outputting a result file, and ending the whole process. By combining quantum chemical calculation, molecular dynamics and dissipative particle dynamics, the fluid problem on time and space scales from microcosmic to mesoscopic, which cannot be solved by experiments, is solved; meanwhile, the method can be used for guiding industrial production after being optimized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
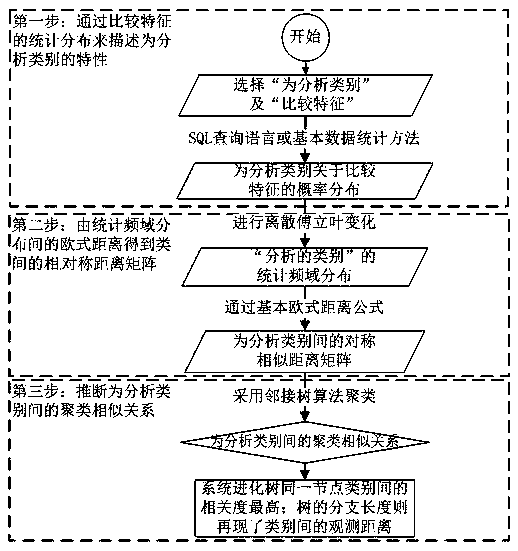
College data-based data analyzing and processing method and employment trend data analyzing and processing method
ActiveCN108052560ATroubleshoot difficult decisionsIntuitive and clear visual representationResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsDistance matrixQuantum chemical
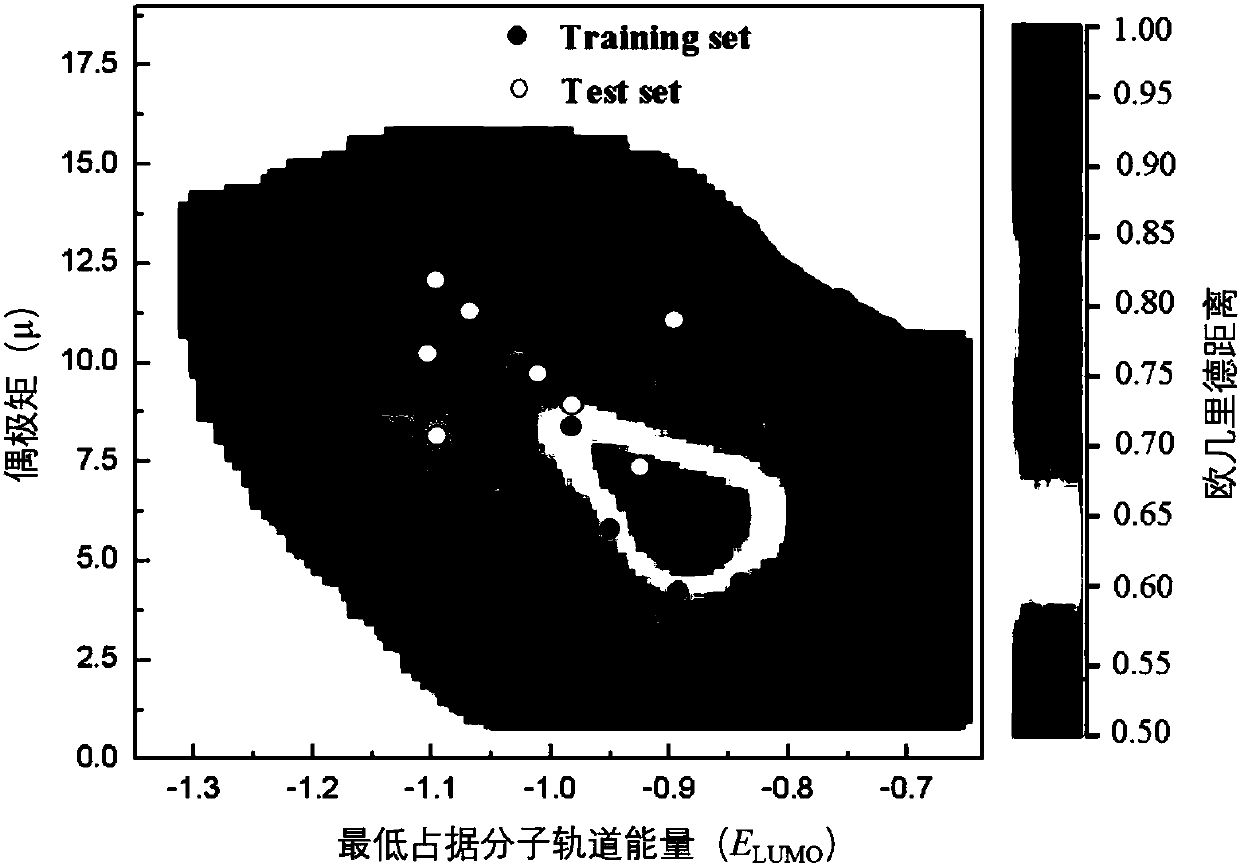
The invention provides a college data-based data analyzing and processing method and an employment trend data analyzing and processing method. The college data-based data analyzing and processing method comprises the following steps of: describing characteristics of analysis categories through comparing statistical distributions of features; obtaining a symmetric Euclidean distance matrix among the analysis categories via Euclidean distances between statistical frequency domain distributions; and carrying out visualized clustering, comparison and analysis on the symmetric Euclidean distance matrix. Quantum chemical calculation can be carried out by using standard Euclidean distances between statistical feature distributions to obtain a symmetric similar distance matrix which is displayed in an adjacent generation tree form, so that statistical features can be intuitionally and clearly represented in a visualization manner, the problem that related organizations and principals are difficult to carry out decision processing is solved, and the characteristics of being rapid and robust in analysis are provided.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Cellulose nanowhisker, synthetic fiber, cement-based composite material and reinforcing method
PendingCN114694761ACreativeWith technical effectFibre typesCharacter and pattern recognitionCelluloseQuantum chemical
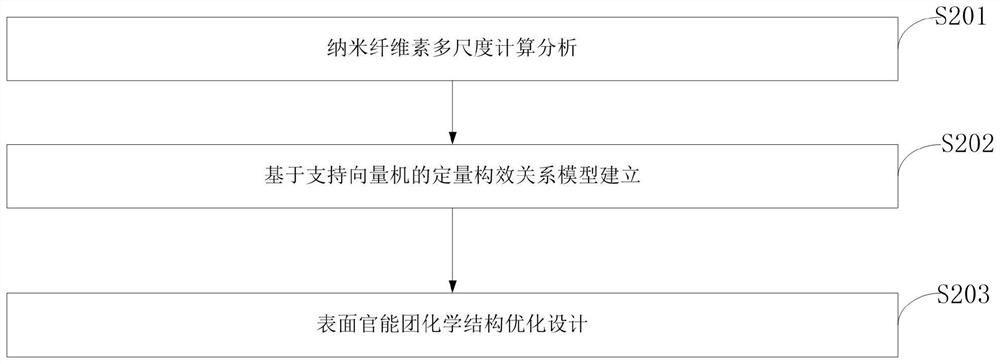
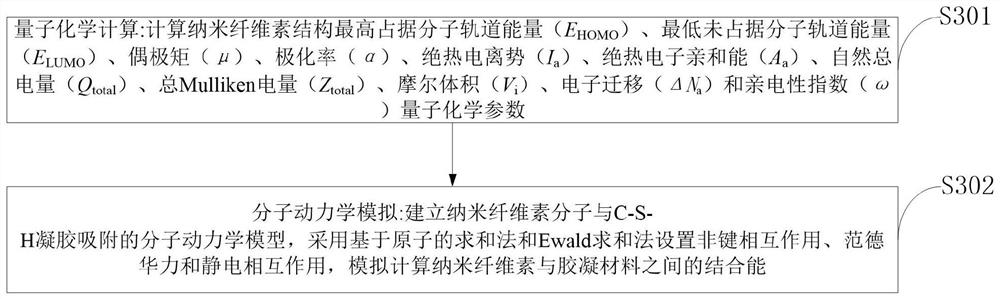
The invention belongs to the technical field of fiber surface modification, and discloses cellulose nanowhiskers, synthetic fibers, a cement-based composite material and a reinforcing method. According to the functionalized cellulose nanowhisker, surface functional groups are optimally designed through quantum chemical calculation, molecular dynamics simulation and machine learning, and the cellulose nanowhisker with better surface activity is formed. The functionalized cellulose nanowhisker provided by the invention has relatively large specific surface area and reaction activity and optimal adsorption performance with a cement-based material. And the cement can be promoted to hydrate, and the compactness, the mechanical property and the durability of the cement-based material are improved. The functionalized cellulose nanowhisker can be used as a coupling agent to improve the bonding between the fiber and a cement matrix. The existence of the functionalized cellulose nanowhiskers provides chemical activity for the fiber surface, changes the chemical characteristics of the fiber surface, and is more beneficial to improving the interface bonding force.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for predicting reduction rate constant of nitroaromatic compound
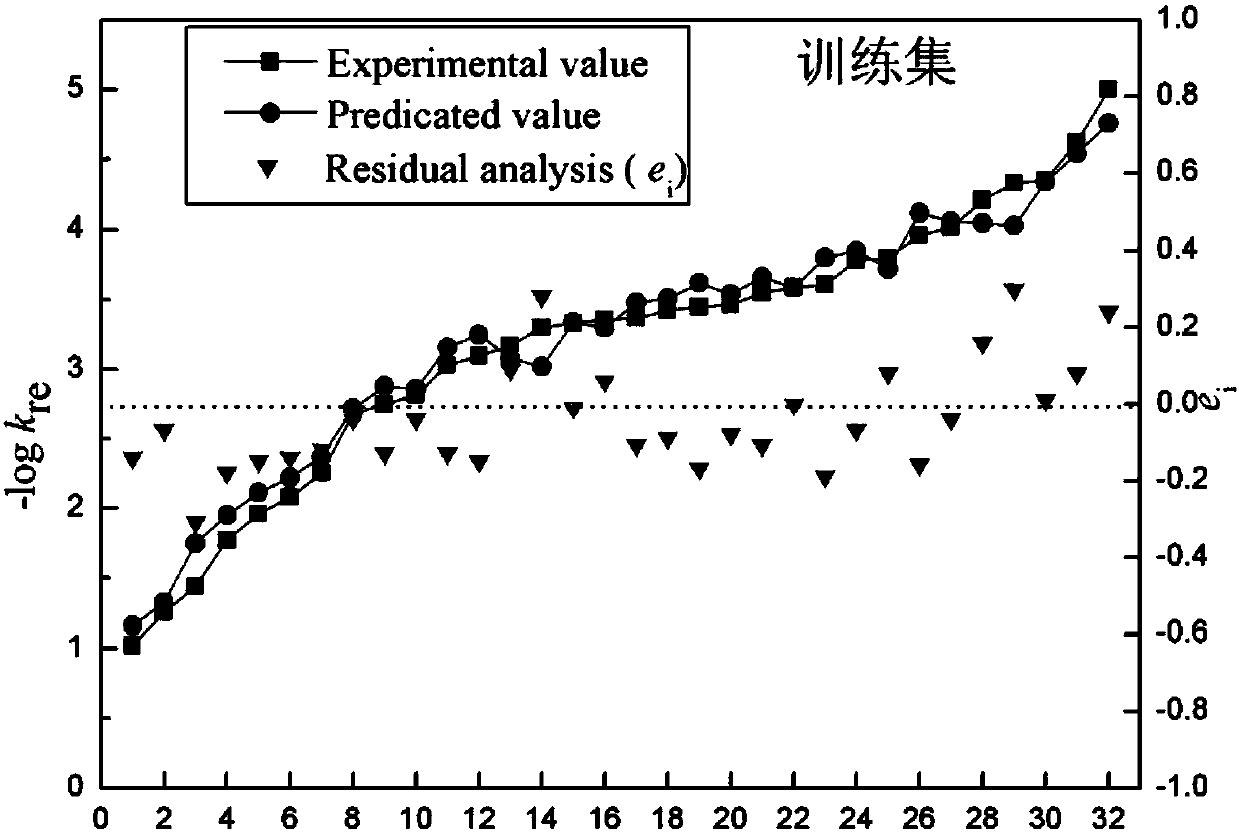
ActiveCN108536992AEffective predictionLow costChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsQuantum chemicalChemical products
The invention discloses a method for predicting the reduction rate constant of a nitroaromatic compound. The method is characterized in that on the basis that a compound structure is known, a Gaussiansoftware program package is used to perform geometric full optimization on the molecular structure of the nitroaromatic compound to obtain quantum chemical parameters such as molecule volume Vm, EHOMO (energy of highest occupied molecular orbital), ELUMO (energy of highest unoccupied molecular orbital), frontier orbital energy level difference delta E, dipole moment mu, molecular polarizability alpha, IP (ionization potential) and compound total energy to serve as structure descriptors, the obtained structure descriptors are combined with reduction rate data, a partial least squares stepwiselinear regression method is used to build a quantitative relation equation between the structure descriptors and the reduction rates, and model verification is performed to guaranteed model predictingability. By the method, the reduction rate constant of the to-be-researched nitroaromatic compound can be effectively predicted, and necessary basic data can be provided for the durability, ecological risk evaluation and monitoring of nitroaromatic compound chemical products.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and application of constructing polarized force field, method and system of predicting drug crystal form
ActiveCN106372400BPrecise Design DirectionHigh chemical precisionChemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designAb initio quantum chemistry methodsQuantum chemical
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
Light-emitting material and organic light-emitting element using the same, wavelength conversion light-emitting element, light-conversion light-emitting element, organic laser diode light-emitting element, pigment laser, display device, and lighting device
InactiveCN103154189BImprove efficiencyLaser detailsIndium organic compoundsOrganic laserQuantum chemical
The luminescent material comprises a transition metal coordination compound having at least one metal-coordinated element site with the highest occupied orbital energy level calculated by quantum chemical calculation (Gaussian09 / DFT / RB3LYP / 6-31G) A ligand whose electron density in the outermost p orbital is greater than 0.239 and less than 0.711.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for predicting reaction activity and carcinogenicity of cyclic organic matters by quantum chemistry calculation
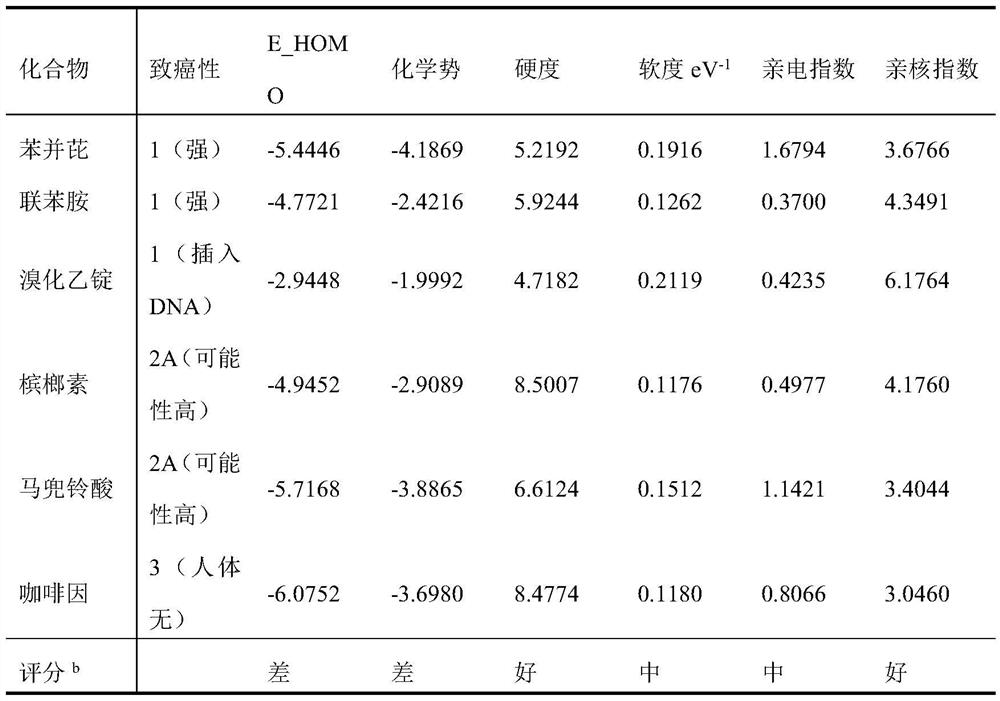
PendingCN112466406AHigh reactivityAchieving carcinogenicityChemical structure searchComputational theoretical chemistrySimple Organic CompoundsQuantum chemistry
The invention discloses a method for predicting reaction activity and carcinogenicity of cyclic organic matters by quantum chemistry calculation, which comprises the following steps of: optimizing energy and structures of various structures according to molecular structures of a plurality of organic compounds in an IARC database, performing energy and wave function calculation of different electronic states on the basis, and comparing obtained parameters to establish quantitative index prediction and carcinogenicity prediction of the reaction activity of the cyclic organic matter. Based on wave function analysis of a concept density functional theory (CDFT), quantum chemical parameters such as a global index, a real space function and an atomic index of a compound are calculated to serve as prediction descriptors, classification is carried out in combination with an IARC database, and five optimal descriptors are screened out. The model is clear in application domain and has good robustness and prediction capability. The prediction method provided by the invention can accurately and efficiently complete prediction of toxicity and carcinogenicity of the compound, and provides an effective method for health hazard evaluation of the organic compound.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
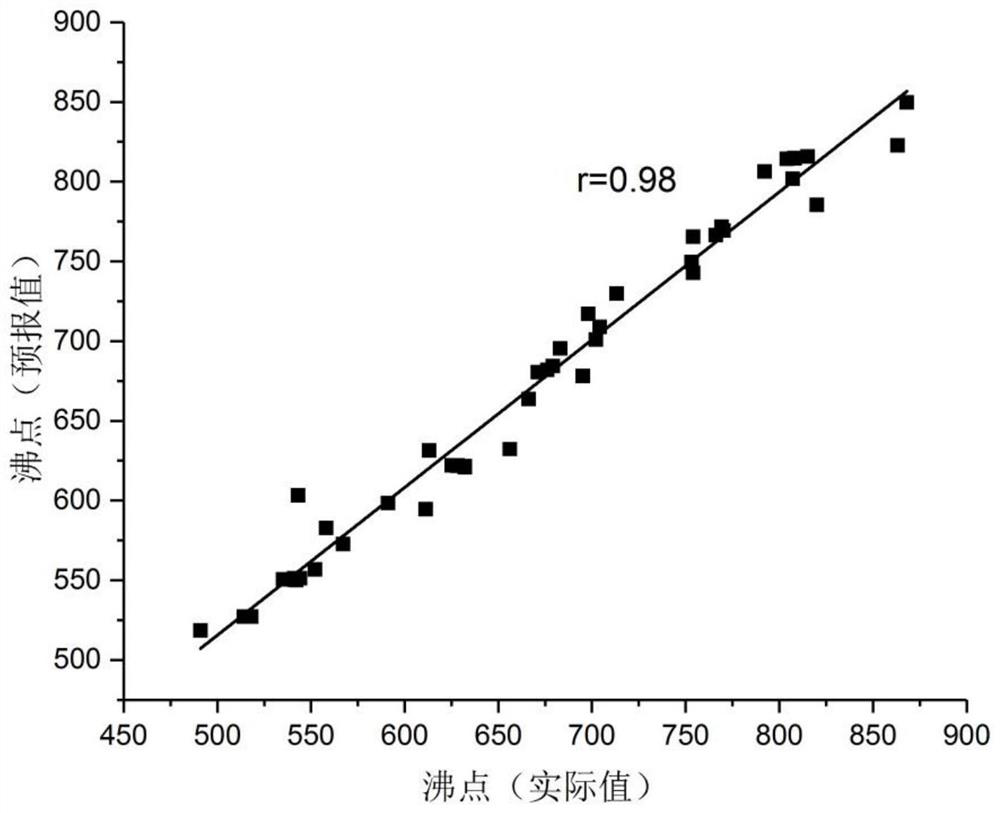
Method for predicting boiling point of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound based on molecular energy data
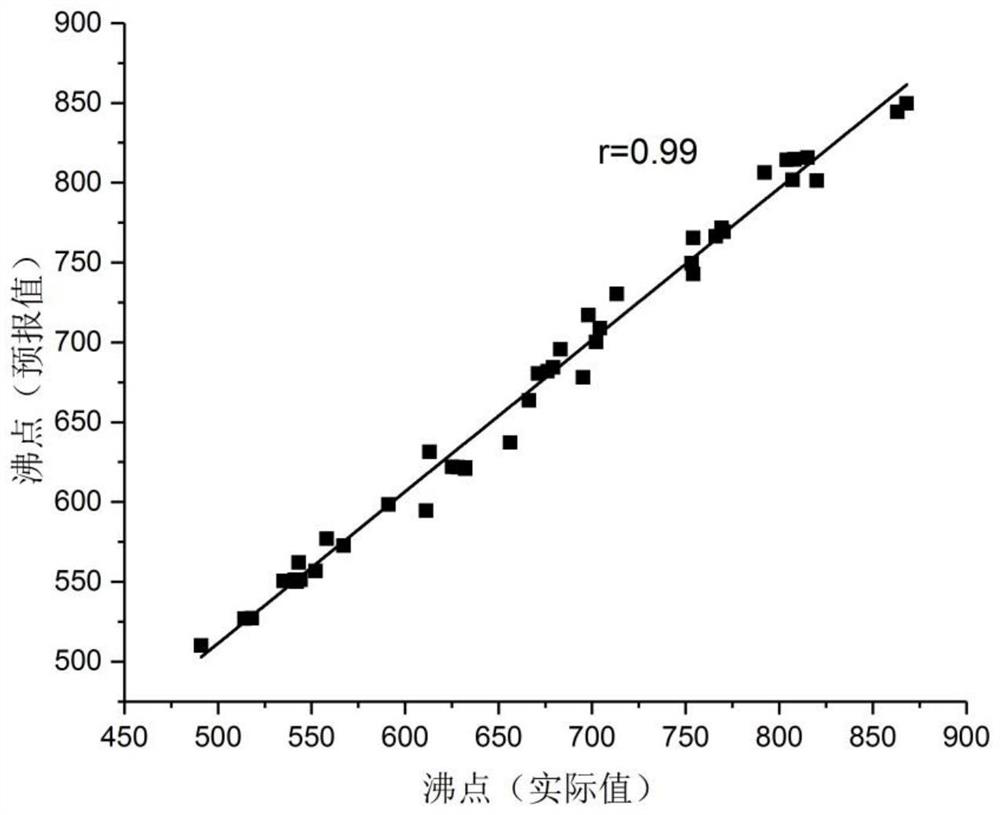
InactiveCN113707238AShorten the timeAvoid experimentationChemical property predictionKernel methodsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonQuantum chemical
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon refers to a compound in which more than two benzene rings are connected in a condensed ring form, and is an organic pollutant widely existing in the environment. Data reports related to physicochemical properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in literatures are few, and even if data recorded in the literatures are insufficient in precision. The main reason is that the experiment for detecting the physicochemical properties of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is complicated and more difficult. In order to overcome the defects of a traditional method, molecular structures and electronic structures of a plurality of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are calculated in a full-optimization manner by utilizing a first principle density functional theory method, basic data of energy descriptors of quantum chemistry are obtained, and then the basic data are mapped and combined to obtain intermediate data of the energy descriptors; and a structure-activity relationship model between the boiling point of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the quantum chemical energy parameters is established by using a support vector regression method based on the intermediate data, and finally the boiling point of the newly collected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon sample is forecasted by using the established structure-activity relationship model.
Owner:上海真谱信息科技有限公司
Environment risk source evaluation method for retail industry of fuel for motor vehicle life
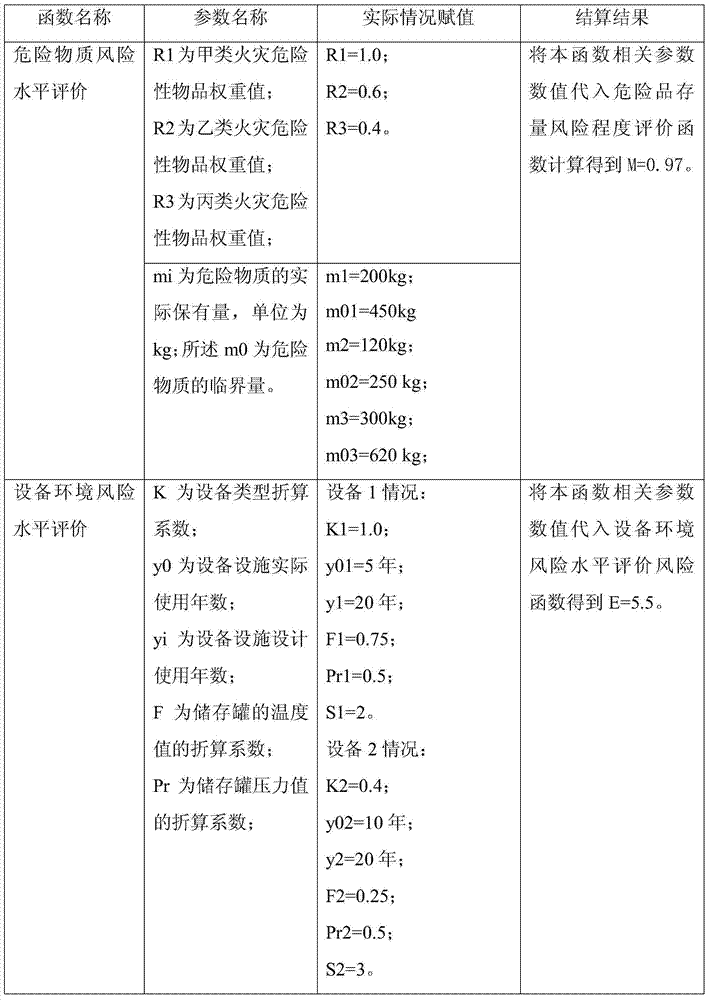
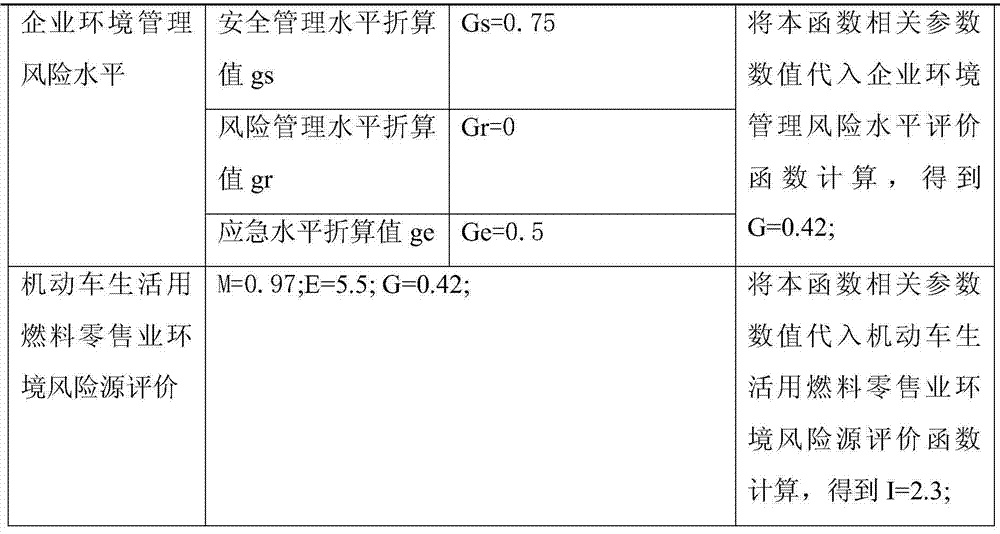
InactiveCN103488895AImprove management efficiencySystematizeSpecial data processing applicationsQuantum chemicalEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of environment risk evaluation and particularly relates to an environment risk source evaluation method for a retail industry of fuel for motor vehicle life. The method includes first respectively utilizing a dangerous substance risk level function, a device environment risk level function and an enterprise environment management risk level function to calculate a substance risk value M, the device facility risk degree K and an enterprise risk management risk level value G, substituting the value M, the value K and the value G into an environment risk source evaluation function for the retail industry of the fuel for the motor vehicle life to conduct calculation to obtain an environment risk source value I for the retail industry of the fuel for the motor vehicle life. By means of the method, quantum chemical calculation of environment risk source evaluation for the retail industry of the fuel for the motor vehicle life is achieved, evaluation is standardized and scientific, and an evaluation result is reliable.
Owner:柳州市博源环科科技有限公司
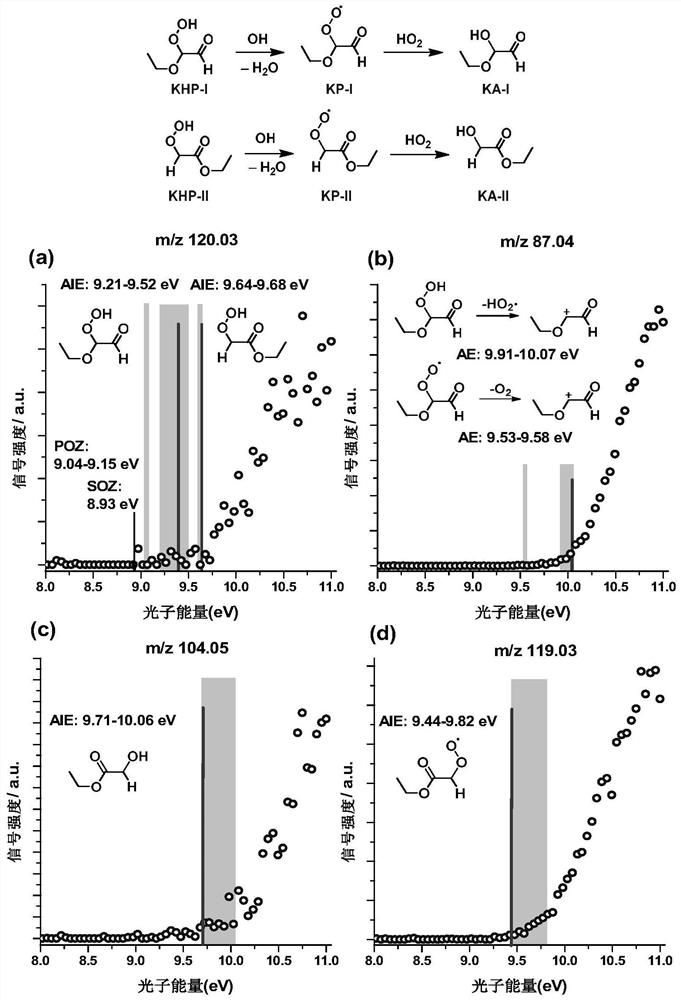
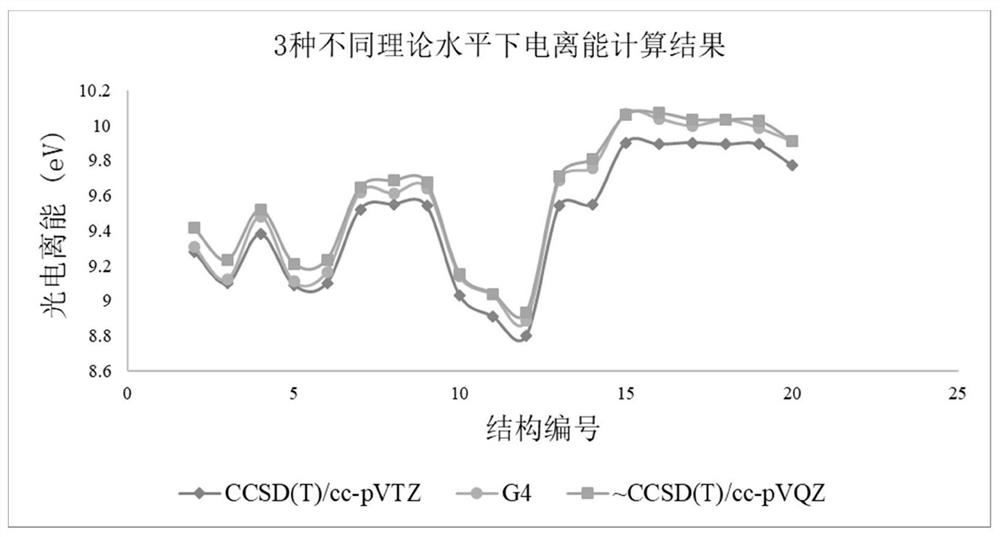
Verification method for calculating atmospheric oxidative degradation path of mesitylene by adopting high-level quantum chemistry
PendingCN114724638AEasy to distinguishSolve the problem of poor reproducibility of atmospheric oxidation processForecastingComputational theoretical chemistryQuantum chemistryQuantum chemical
The invention relates to a verification method for calculating an atmospheric oxidative degradation path of mesitylene by adopting high-level quantum chemistry. The verification method comprises the following steps: 1, calculating by using high-level quantum chemistry to obtain a transition state of an atmospheric oxidative degradation path of mesitylene; 2, predicting the atmospheric oxidative degradation path of mesitylene through a transition state energy barrier; 3, obtaining ionization energy of products in the prediction path through quantum chemistry calculation; and 4, verifying and calculating data through photoionization mass spectrometry. The method solves the problem that unstable products and free radicals are difficult to detect in the atmospheric oxidation process of mesitylene, prediction of the free radicals of the unstable products in the atmospheric oxidation process of mesitylene is achieved through high-level quantum chemistry calculation, and calculation correctness is verified through experiments. The atmospheric oxidation path of mesitylene can be well predicted through high-level quantum chemical calculation, and the problem of poor reproducibility of the atmospheric oxidation process of mesitylene is solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining vinyl ether ozonization single-molecule reaction product based on high-level quantum chemistry calculation method and experiment
PendingCN114724637AAvoid wastingLow costChemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designVinyl etherQuantum chemical
The invention discloses a method for determining a vinyl ethyl ether ozonization single-molecule reaction product based on a high-level quantum chemical calculation method in combination with an experiment. According to the method, the first principle density functional theory is combined with the de novo calculation theory, reaction kinetics simulation is adopted, existence of specific products is proved theoretically, and experiment condition setting is guided through simulation results; and determining ionization energy by comparing theoretical ionization energy and experimental signals under three different high-level quantum chemical calculation methods so as to determine the existence of the product, thereby perfecting the product identification method of the substance ozonization reaction. According to the invention, high-level quantum chemical calculation and dynamic simulation are used to verify the reaction feasibility, and a simulation result is used to guide the setting of an important experimental condition-reaction time, so that the cost is saved, the waste of drugs and instrument energy is avoided, and the method accords with the green chemistry concept.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A Method for Predicting the Skin Permeability Coefficient of Organic Chemicals
ActiveCN104376221BSave human effortSave moneySpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataQuantum chemical
The invention relates to the field of health risk assessment testing strategies, in particular to a method for predicting the skin permeability coefficient of organic chemicals. On the basis of obtaining the molecular structure of the compound, the quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) is used to construct a prediction model by calculating the descriptors that characterize the structural features. Compared with the traditional test method for measuring skin penetration parameters, it is in line with animal welfare protection and reduces test time and cost. , which can quickly and effectively predict the skin permeability coefficient. The present invention is strictly in accordance with the 5 standards proposed by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) for the construction and use of QSAR models, by calculating the physical and chemical properties, electrical properties, topology and quantum chemical parameters of compounds as predictive descriptors, and using K-S grouping to The original data is classified, and 7 optimal descriptors are screened out. Using the clear, simple, fast, and transparent GA-MLR algorithm, the model application domain is clear, and it has good fitting effect, robustness, and predictive ability. The skin permeability coefficient prediction model can accurately and efficiently predict the skin permeability coefficient of compounds, and provides an effective method for the health hazard assessment of organic compounds.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Novel quantum chemical molecule performance prediction method and system
PendingCN114420217AFast predictionPredictive fastChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationQuantum chemistryQuantum chemical
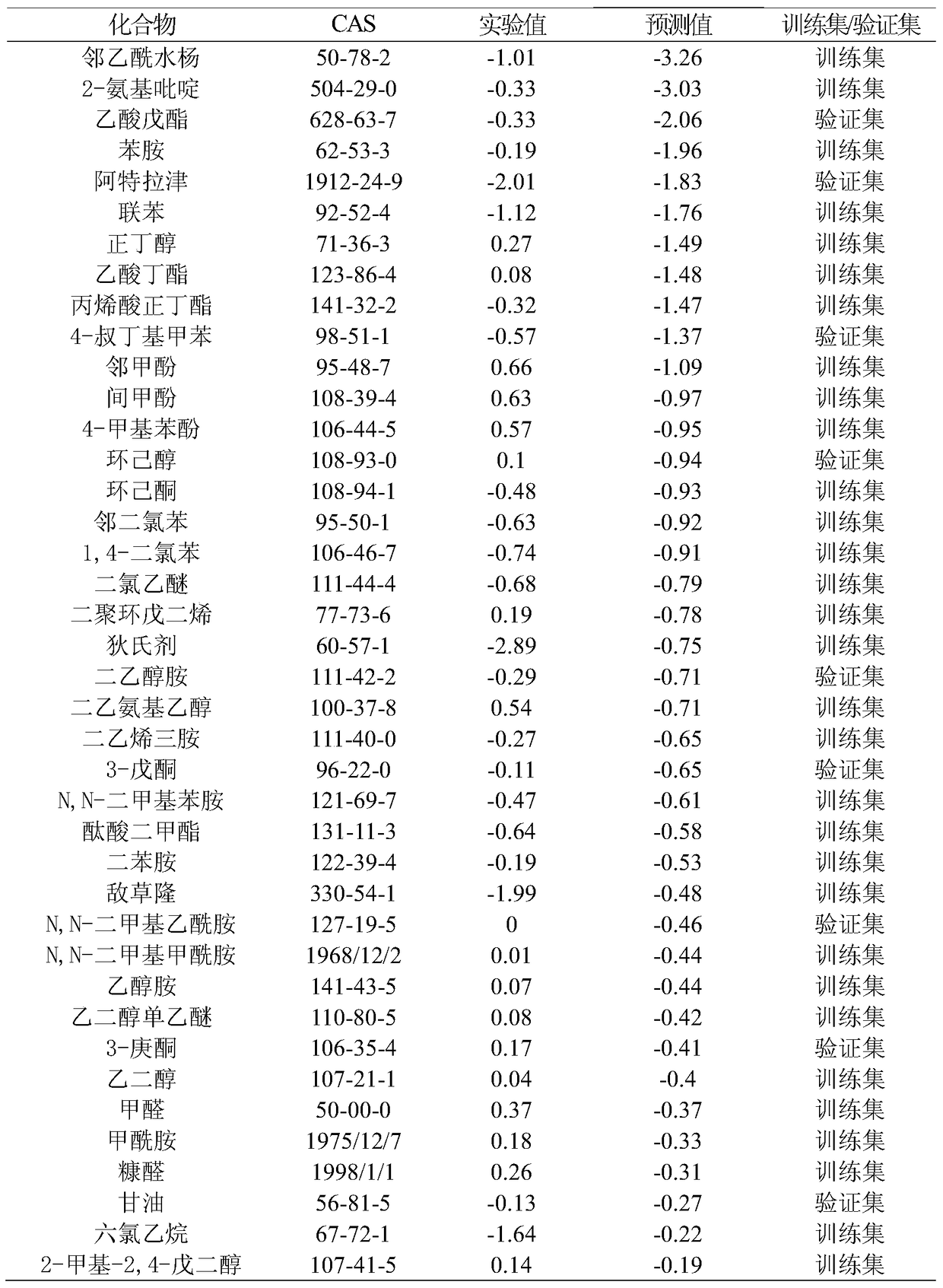
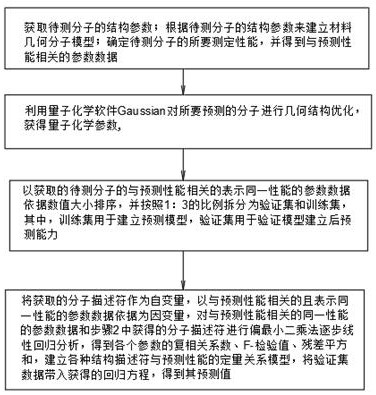
The invention discloses a novel quantum chemical molecule performance prediction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining structure parameters of chemical molecules to be tested; obtaining parameter data related to the prediction performance; performing geometric structure optimization on the chemical molecules to be predicted by using quantum chemistry software Gaussian to obtain quantum chemistry parameters; the obtained parameter data, related to the prediction performance and representing the same performance, of the chemical molecules to be tested are sorted according to the numerical value size and divided into a verification set and a training set according to the proportion of 1: 3, and the training set is used for establishing a prediction model; and taking the obtained molecular descriptors as independent variables, taking parameter data basis which is related to the predicted performance and represents the same performance as dependent variables, establishing a quantitative relation model of various structure descriptors and the predicted performance, and substituting verification set data into an obtained regression equation to obtain a predicted value. According to the method, various performances of molecules can be quickly predicted through a quantum chemical calculation method, and the method has the characteristics of high prediction speed and high prediction efficiency.
Owner:苏州鸣石量子信息技术有限公司
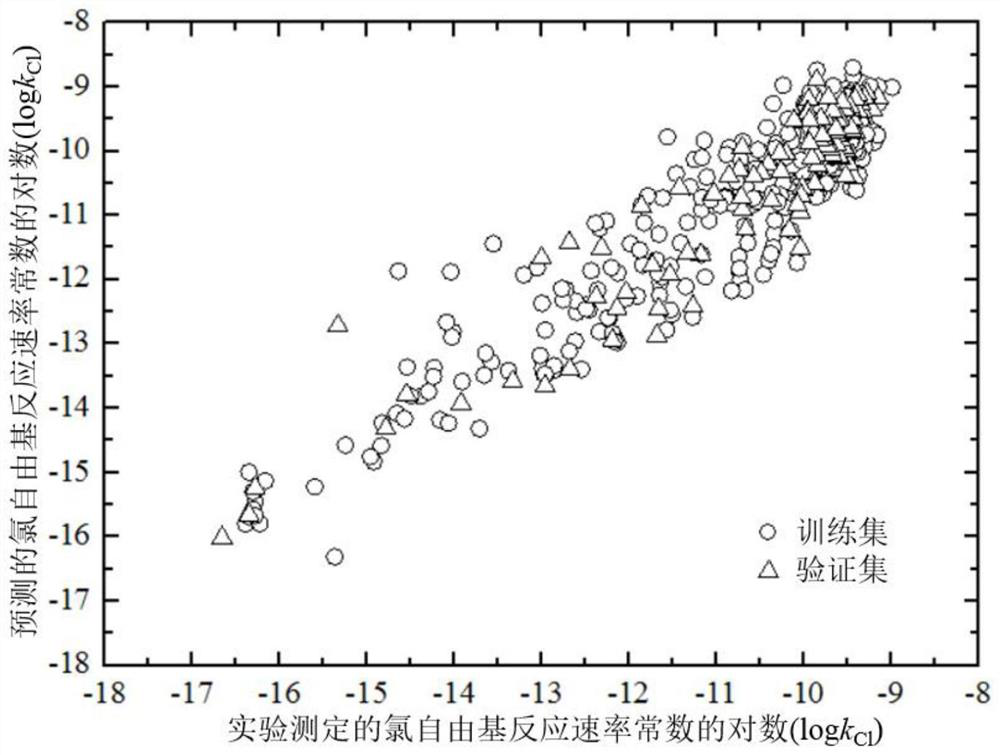
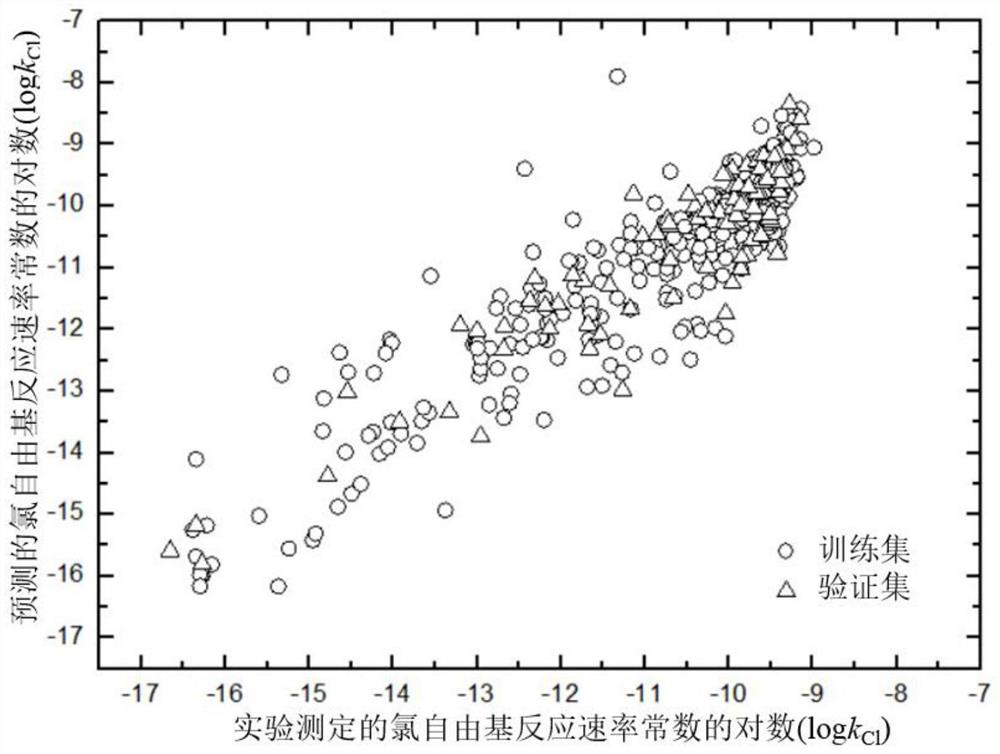
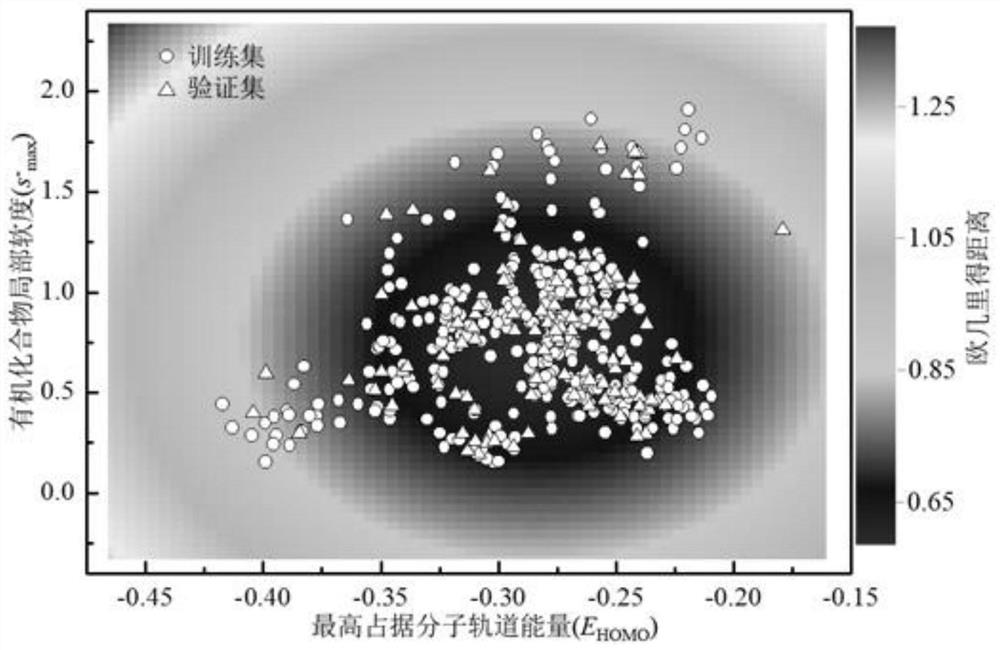
A Method for Predicting Chlorine Radical Reaction Rate Constants of Organic Chemicals Using a Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Model
ActiveCN107563133BMechanism explanatoryLow costChemical machine learningIn silico combinatorial chemistryQuantum chemistryQuantum chemical
The invention discloses a method for predicting the reaction rate constant of chlorine free radicals of organic chemicals by using a quantitative structure-activity relationship model. Only through the basic molecular structure information of organic chemicals, calculate the quantum chemical descriptors with structural characteristics, and use the constructed QSAR prediction model to quickly and efficiently predict the k of organic chemicals Cl value. The method follows the QSAR model construction and verification guidelines promulgated by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD): using genetic algorithm-multiple linear stepwise regression analysis (GA-MLR) and support vector machine-multiple linear stepwise regression analysis ( SVM-MLR), high transparency and easy to apply; GA-MLR models all use quantum chemical descriptors, so the physical meaning of the descriptors is clear; it has a clear application domain and is applicable to a wide variety of organic compounds; it has good fit and robustness It is easy to program and can provide important data support for the environmental risk assessment and management of organic chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
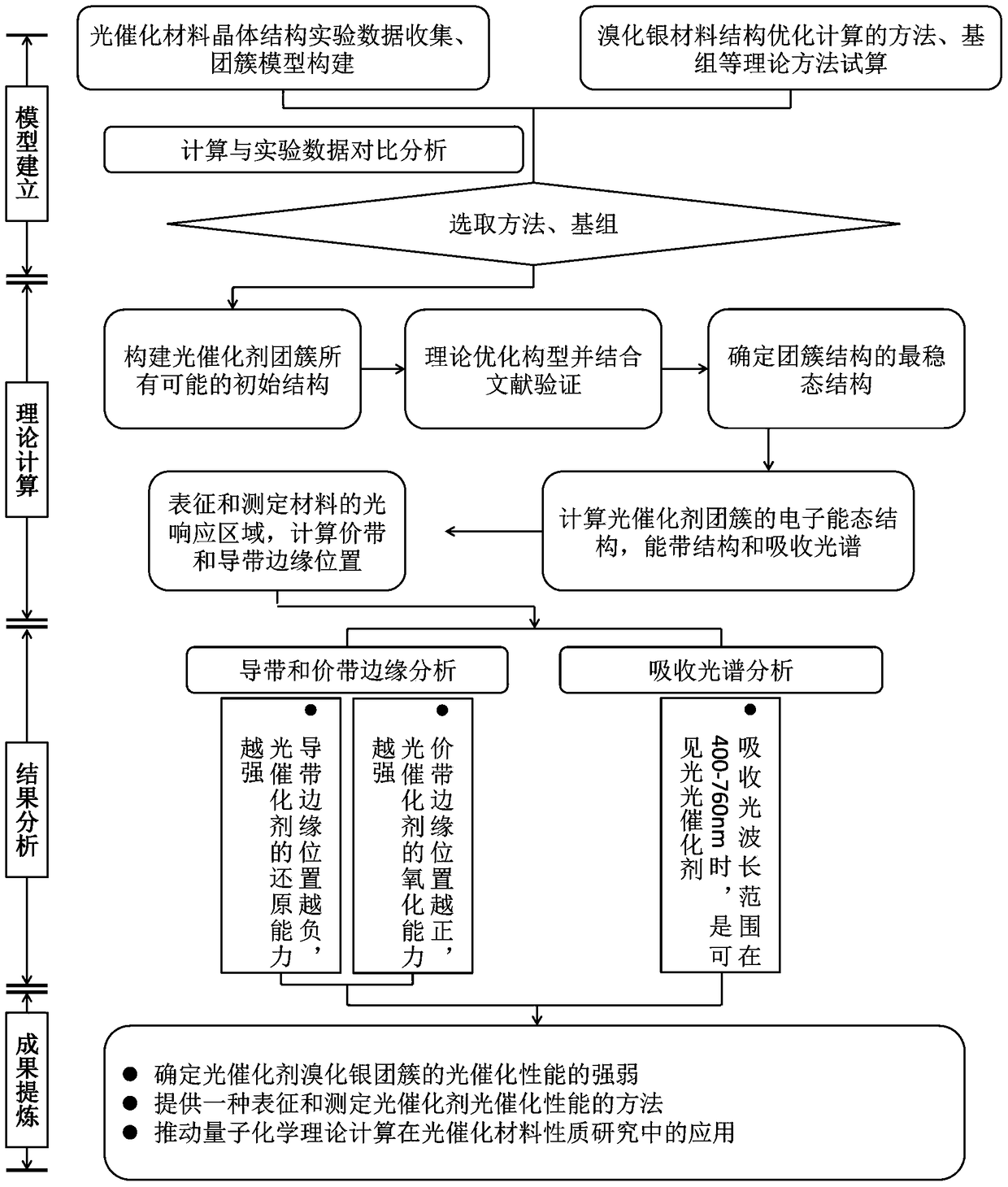
A method for quantitatively analyzing the photocatalytic performance of silver bromide clusters
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Quantum Chemical Reaction Optimization Multi-Relay Selection Method for Cognitive Relay Networks
ActiveCN107454604BSolve the problem of multiple relay selectionFast convergenceHigh level techniquesNetwork planningQuantum chemistryQuantum chemical
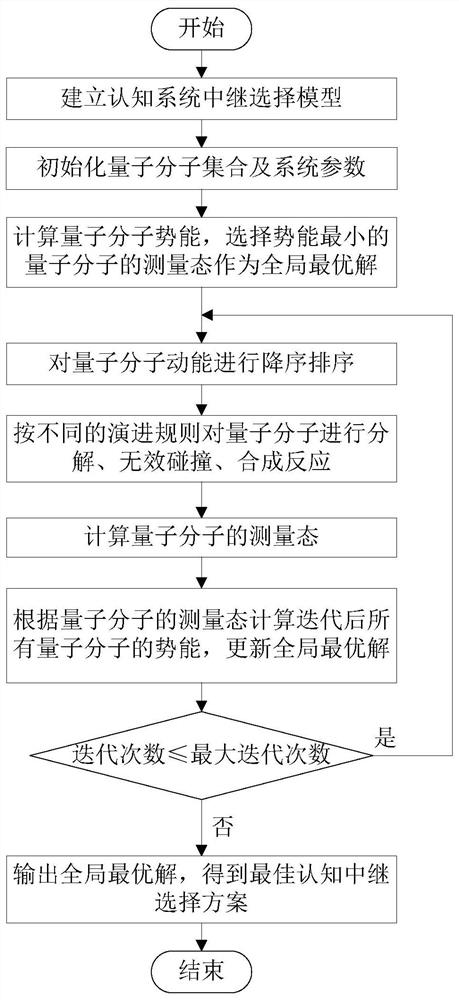
The invention provides a quantum chemistry reaction optimization multi-relay selection method of a cognitive relay network. The method comprises steps of: 1, establishing a cognitive system relay selection model; 2, initializing a quantum molecule set and a system parameter; 3, evaluating the potential energy of all quantum molecules in the set and selecting the measurement state of the quantum molecule with the lowest potential energy as a global optimal solution; 4, arranging the kinetic energy of quantum molecules in a descending order, and performing decomposition reaction, invalid collision, and synthetic reaction; 5, evaluating the potential energy of newly generated quantum molecules, and if the minimum potential energy of the newly generated quantum molecules is less than the minimum potential energy of the previous generation, marking the newly generated quantum molecules as a new global optimal solution; and 6, if the number of iteration times is less than a preset maximum number of iteration times, returning to step 4, otherwise, outputting the global optimal solution. The method balances the primary user constraint condition and non-primary user constraint condition of the cognitive relay network, and chooses a relay selection scheme that maximizes the system throughput based on a quantum chemistry reaction mechanism.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com