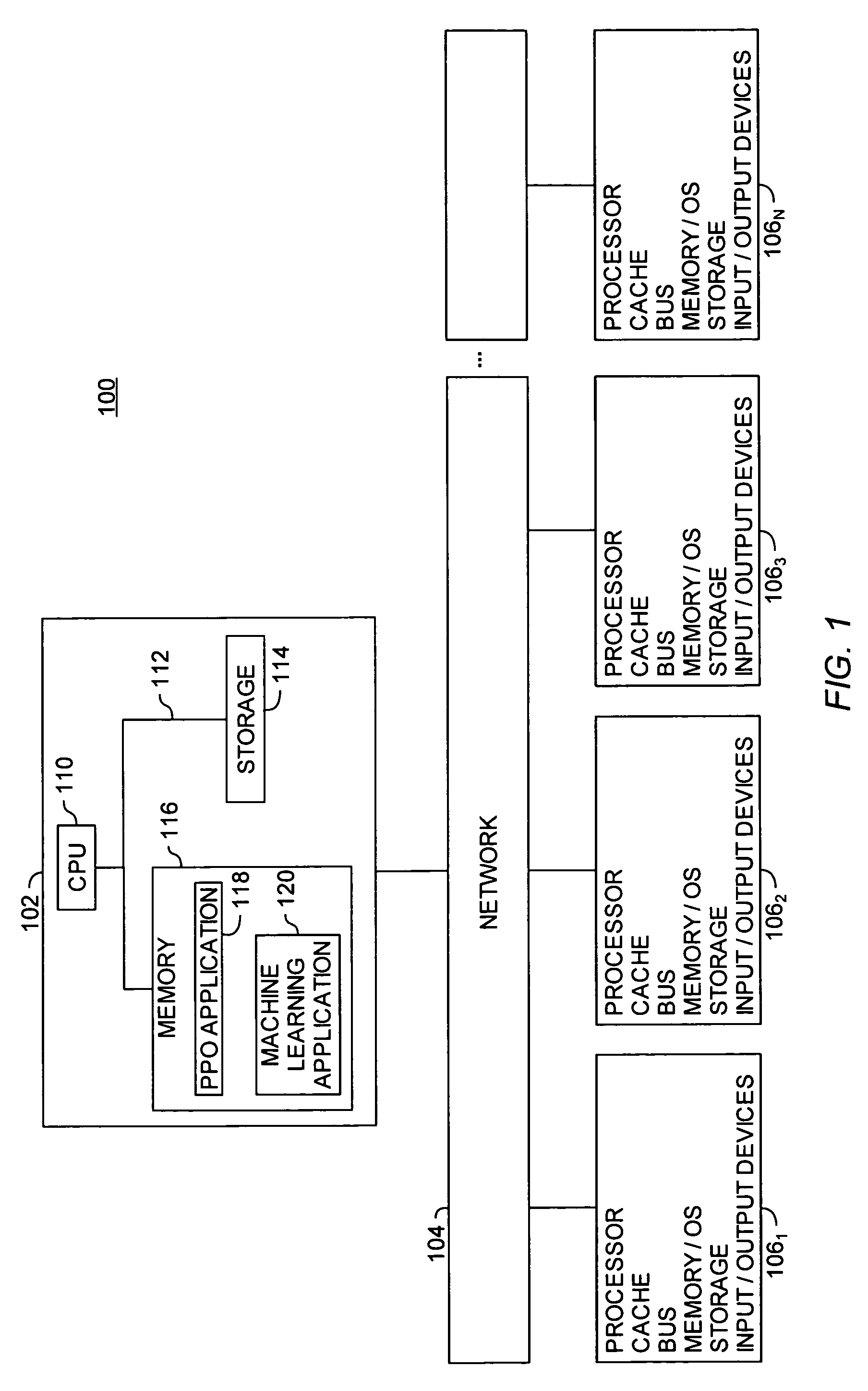
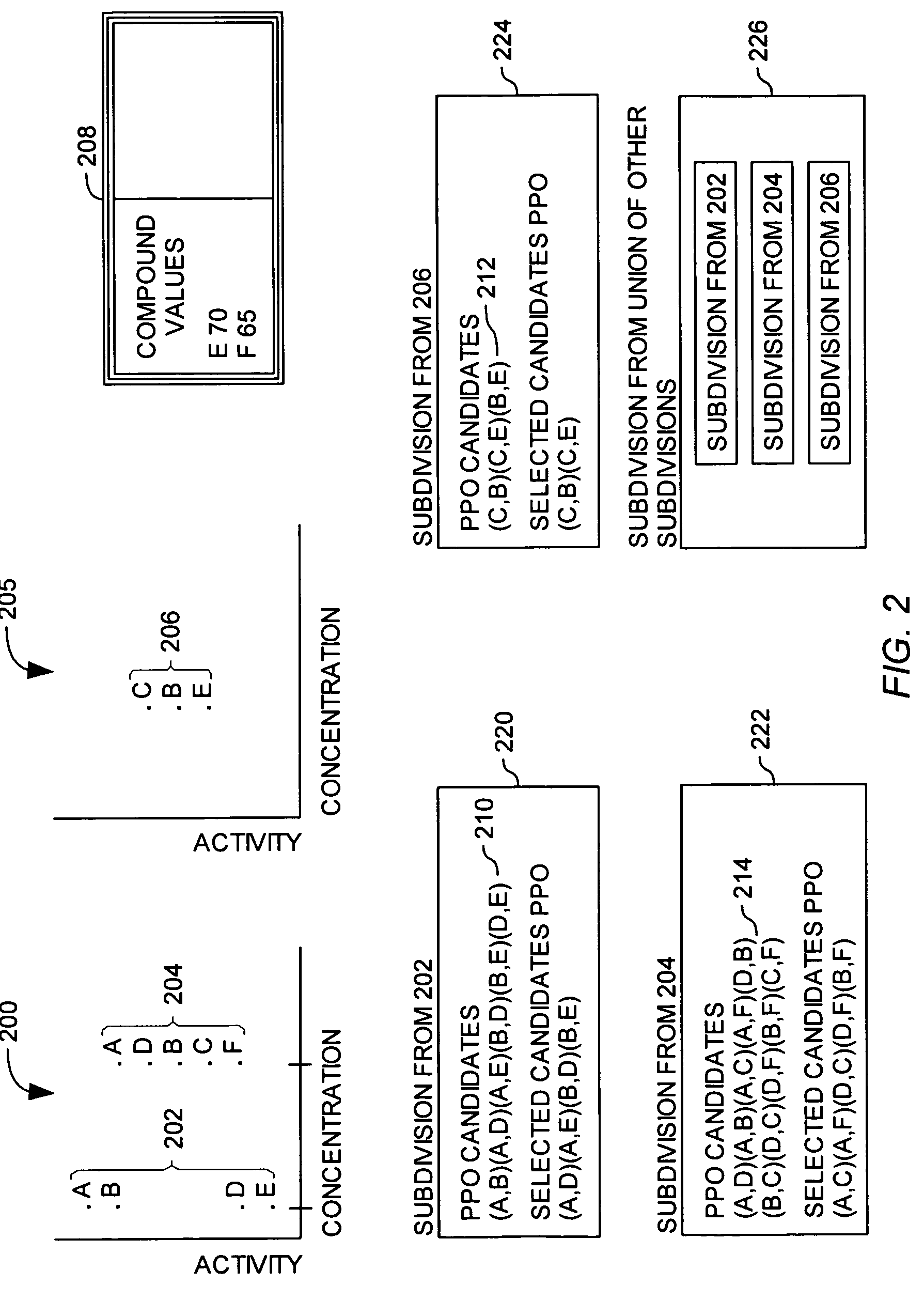
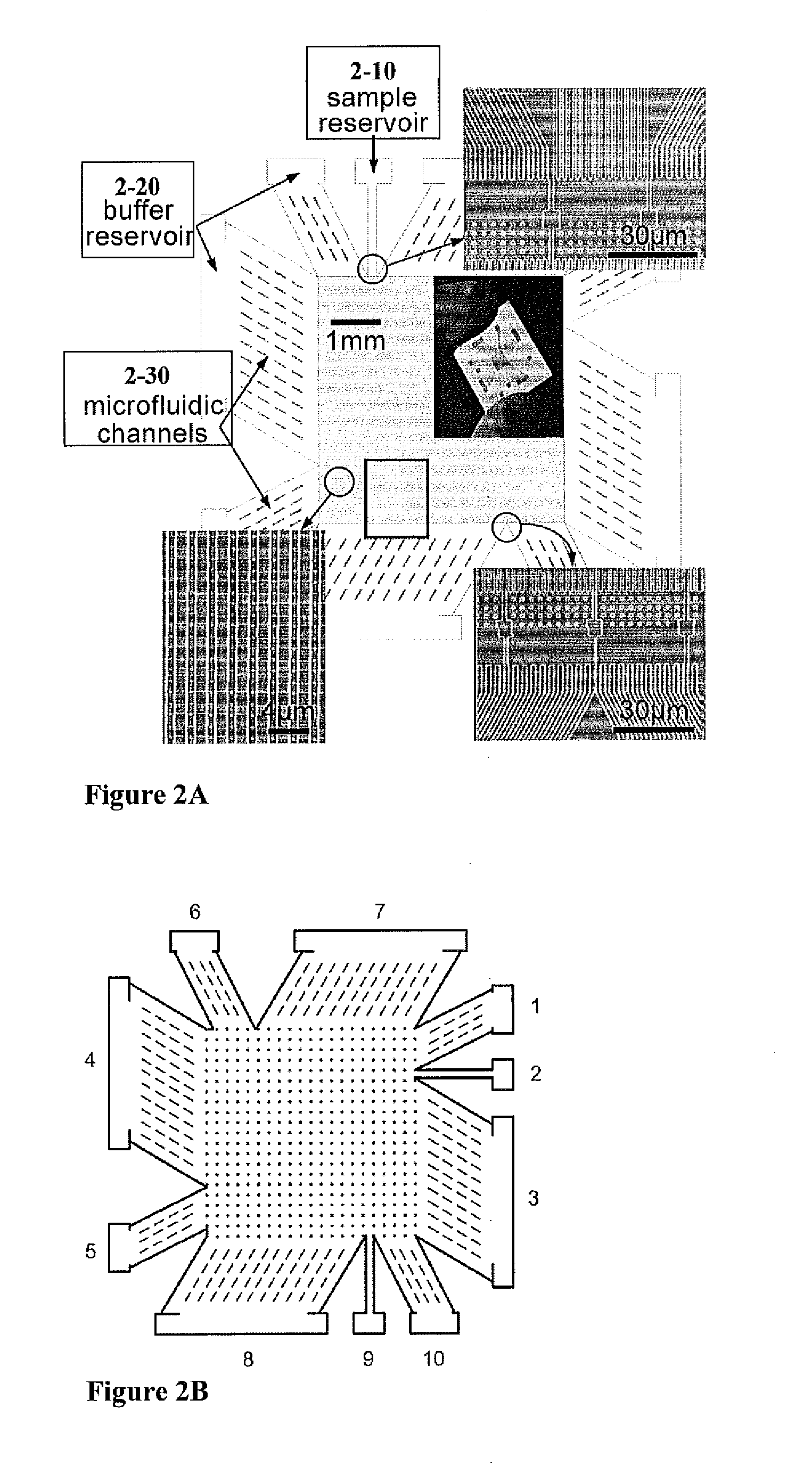
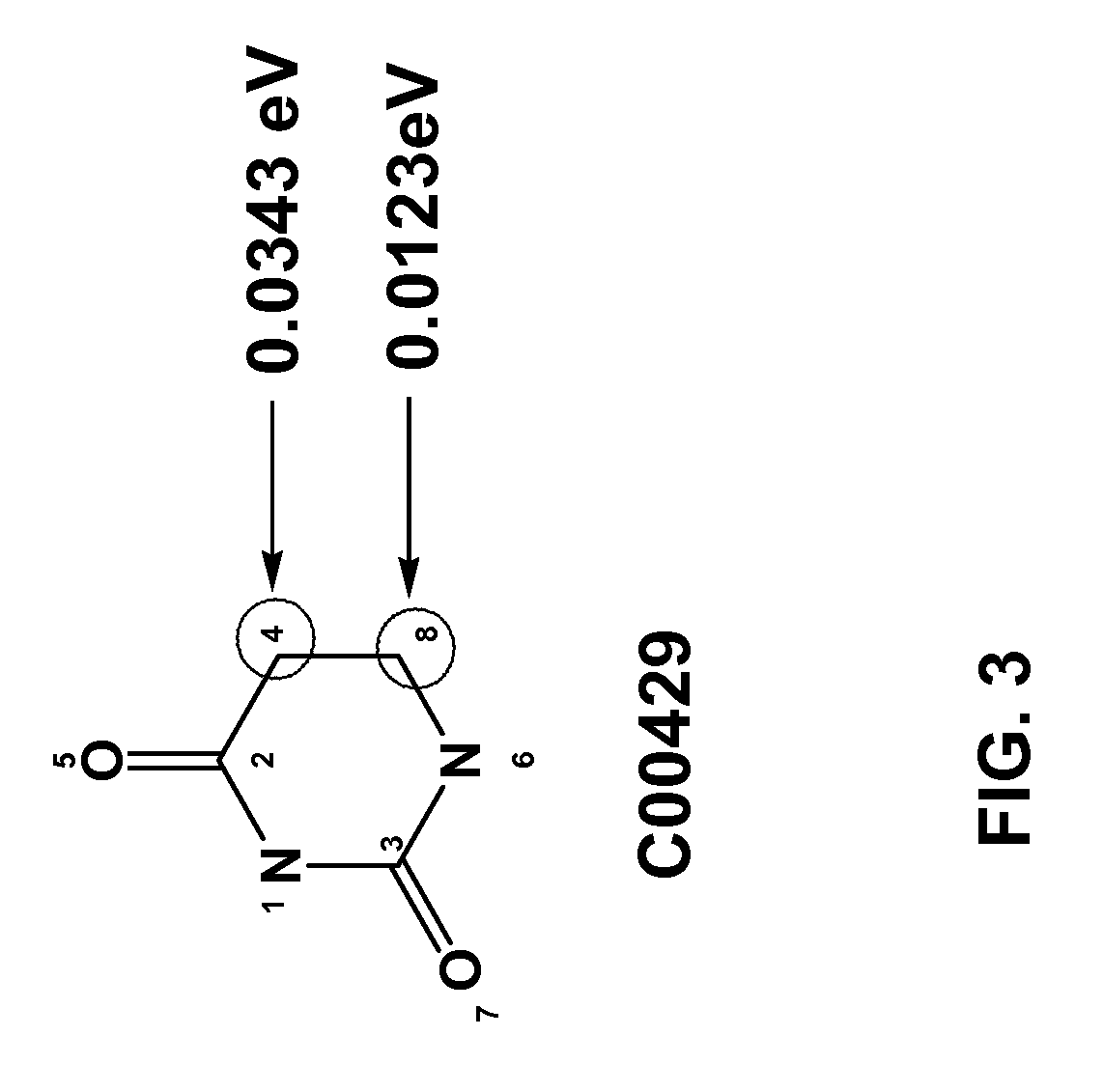
Patents
Literature
73 results about "Molecular property" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular properties include the chemical properties, physical properties, and structural properties of molecules, including drugs. Molecular properties typically do not include pharmacological or biological properties of a chemical compound.
Latex processes
InactiveUS6503680B1Improve performanceImprove featuresDevelopersEmulsion paintsGlass transitionPolymer chemistry
A process for the preparation of a latex polymer consistent with E / A (emulsion / aggregation / coalescence) toner manufacture. The process utilizes a standard (universal) latex composition and involves chain-transfer agent partitioning, emulsion polymerization that provides a latex polymer with a wide range of molecular properties. In particular, the process customizes a wide range Mw (weight average molecular weight) latex, without substantially varying the Mn (number average molecular weight) and hence, without substantially varying Tg (glass transition temperature) such that good toner performance is maintained. In a preferred process, a latex polymer is prepared by mixing a seed particle latex, generated by aqueous emulsion polymerization of a first portion of a monomer emulsion, with a second portion of the monomer emulsion and at least one chain-transfer agent. The mixing is done in the presence of a free-radical initiator and heated, and wherein the monomer emulsion comprises a mixture of polymerization reagents of at least one monomer, at least one chain-transfer agent, at least one surfactant, and water. This process may be applied to core-shell polymerization as well. These latex polymers are ideally suited in the manufacture of toner and developer for electrophotographic imaging and printing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
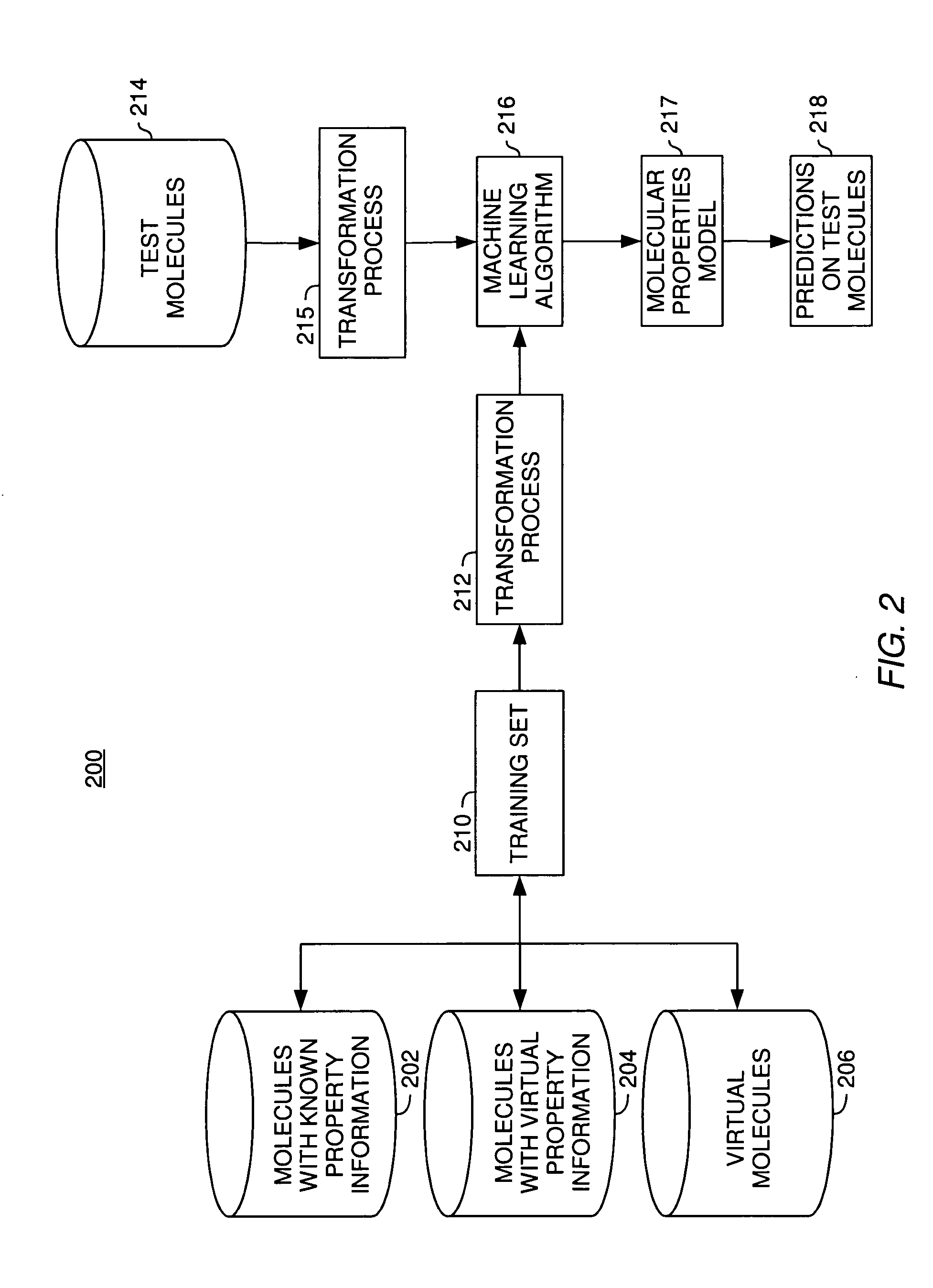
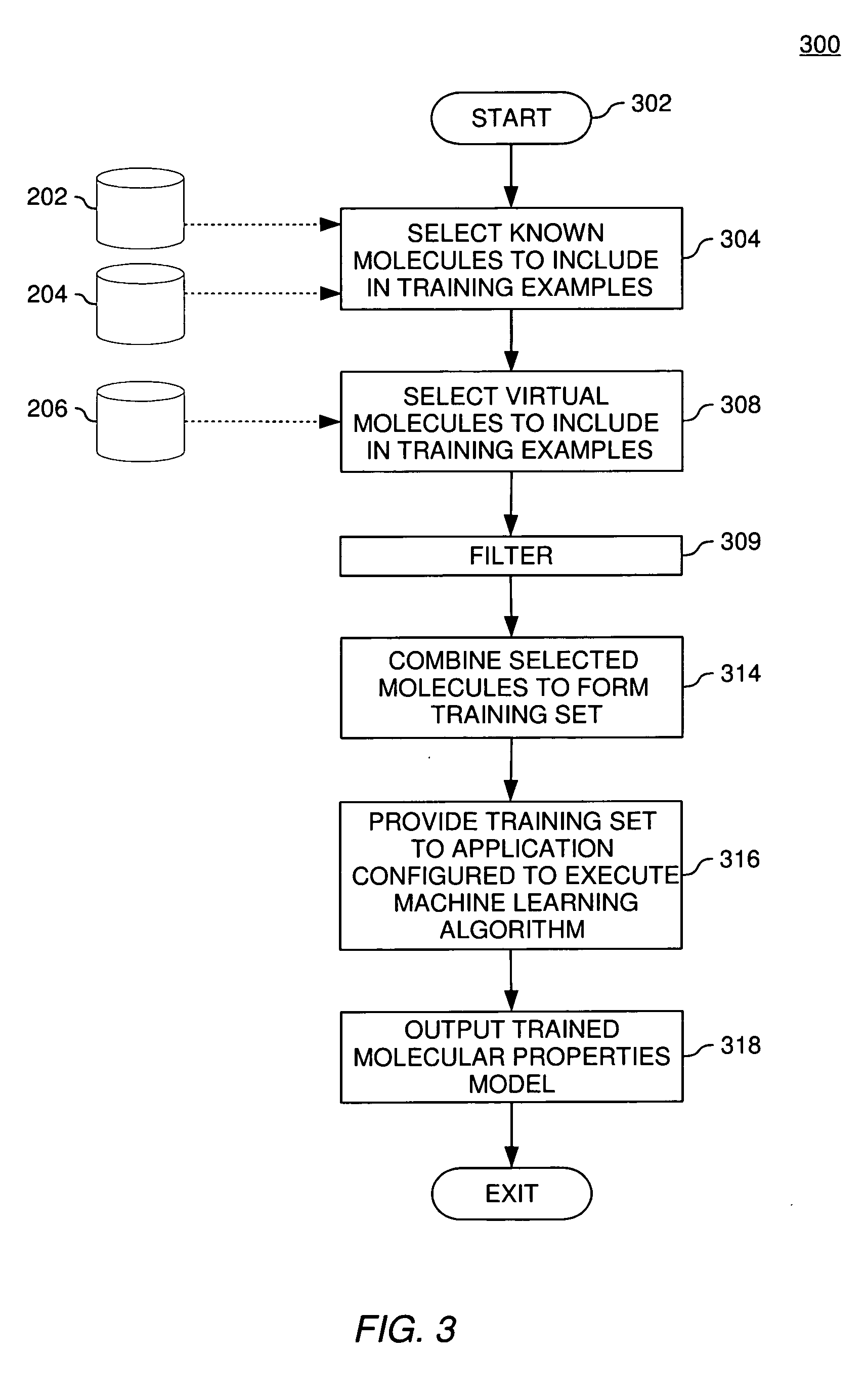
Methods for molecular property modeling using virtual data
InactiveUS20050278124A1Chemical property predictionBiological testingComputer scienceMolecular property
Embodiments of the invention provide methods, systems, and articles of manufacture for modeling molecular properties based on information obtained from sources other than direct empirical measurements of the properties. Embodiments of the invention use “virtual data” related to molecular properties to train a molecular properties model. Virtual data about a molecule may include real-valued data (e.g. measurement values falling along a continuous range) or a positive or negative assertion about whether a molecule exhibits a property of interest. Virtual data may be generated using a variety of techniques and may be further characterized by confidence in the accuracy of the virtual data. In addition to virtual data, embodiments of the invention may use “virtual molecules” paired with “virtual data” to train a molecular properties model. The virtual molecules may themselves be generated in a variety of ways.
Owner:NUMERATE
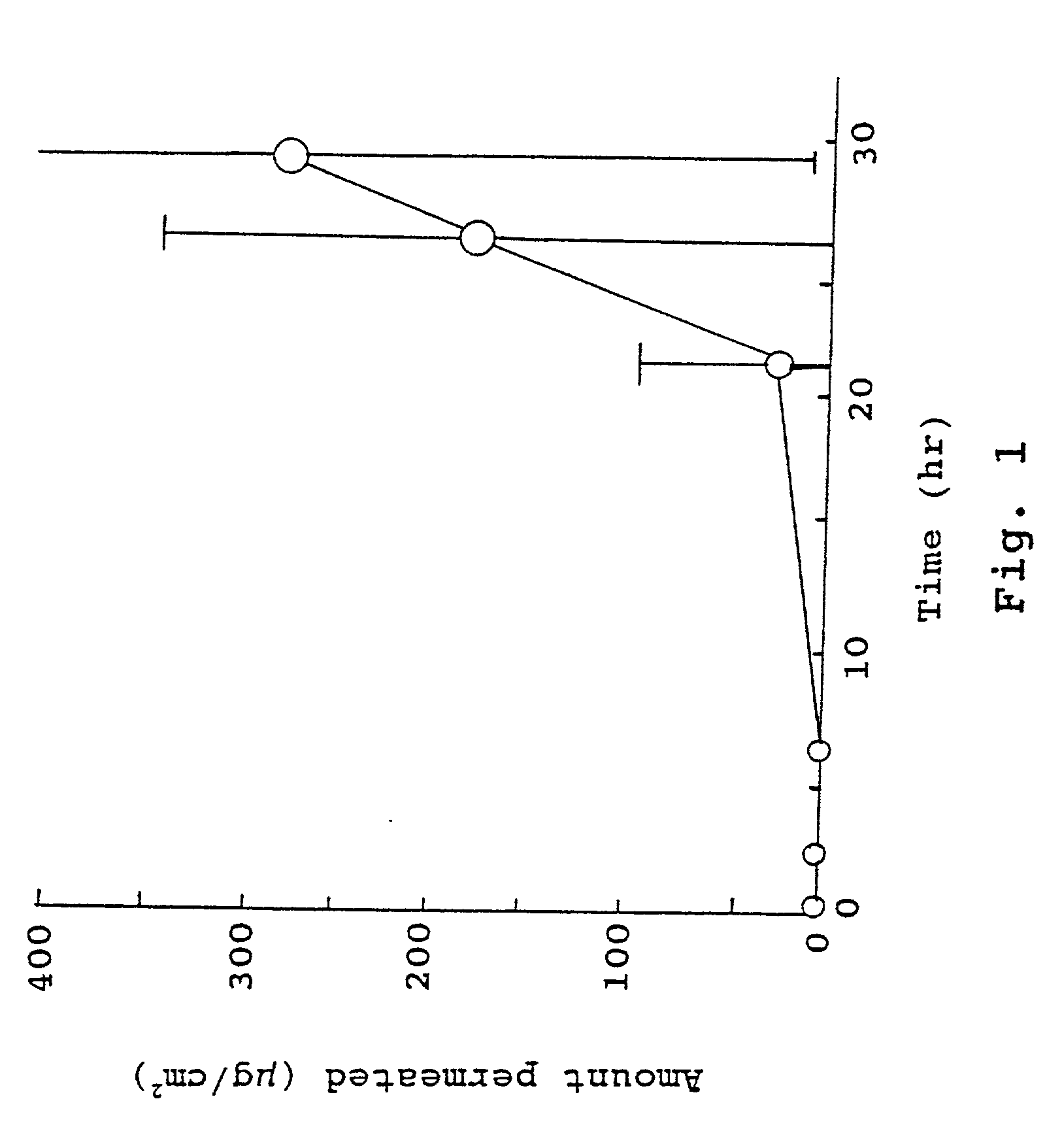
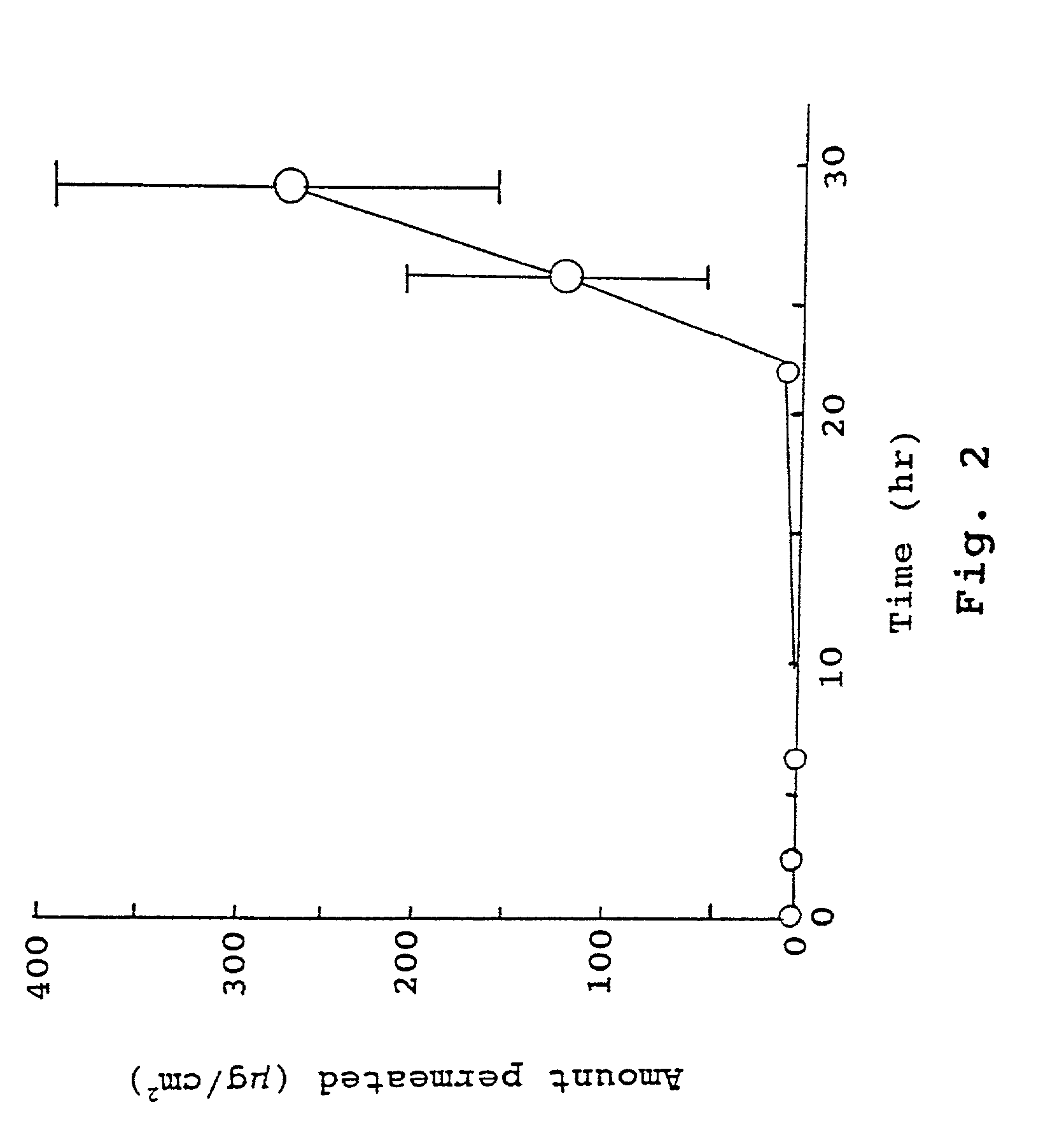
Compositions for rapid and non-irritating transdermal delivery of pharmaceutically active agents and methods for formulating such compositions and delivery thereof
InactiveUS20030104040A1Effective and safe and rapid transmigrationIntact skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsActive agentDrug activity
A transdermal delivery system (TDS) for use in treatment of living bodies may be applied as an open (liquid, gel) or closed (patch) article. The TDS is composed of a particular active agent which dictates an associated selection of certain solvents, solvent modifiers, solute modifiers and skin stabilizers with which the medicament forms a true solution that rapidly crosses the skin barrier. The associated selection of the particular solvents, solvent modifiers, solute modifiers and skin stabilizers is based on a balancing of the molecular properties of all the components against the molecular properties of all the components plus the particular active agent. The TDS may also include a source of cellular energy to induce CAMP or cGMP. The TDS improves delivery of active agents having a molecular weight greater than 340 Daltons and increases dosage above 0.25 mg / day for such active agents.
Owner:TRANSDERMAL DELIVERY SOLUTIONS
Computer-aided design system for energy-containing compound
InactiveCN101504679AWidely applicable designIncrease flexibilitySpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignDetonation
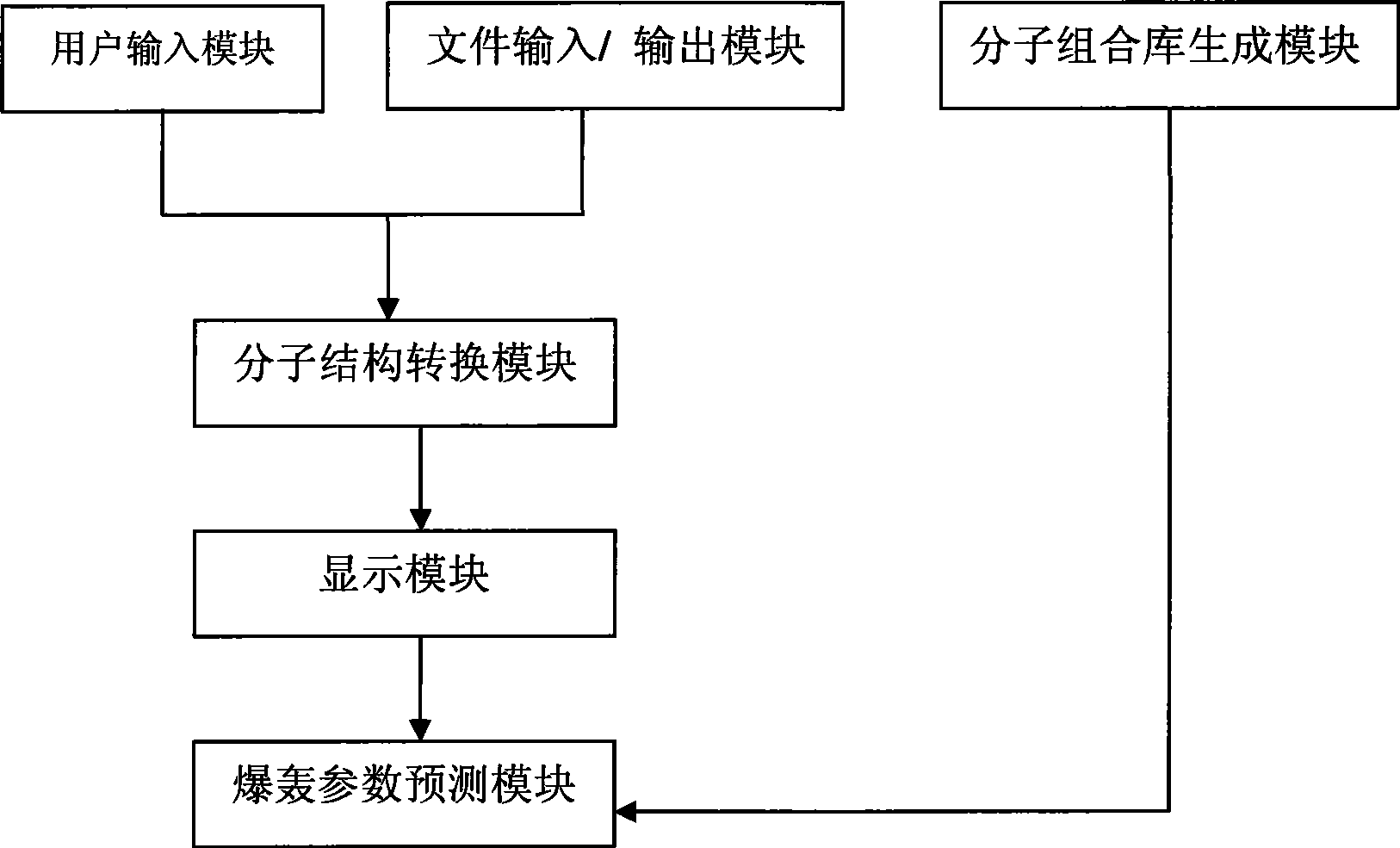
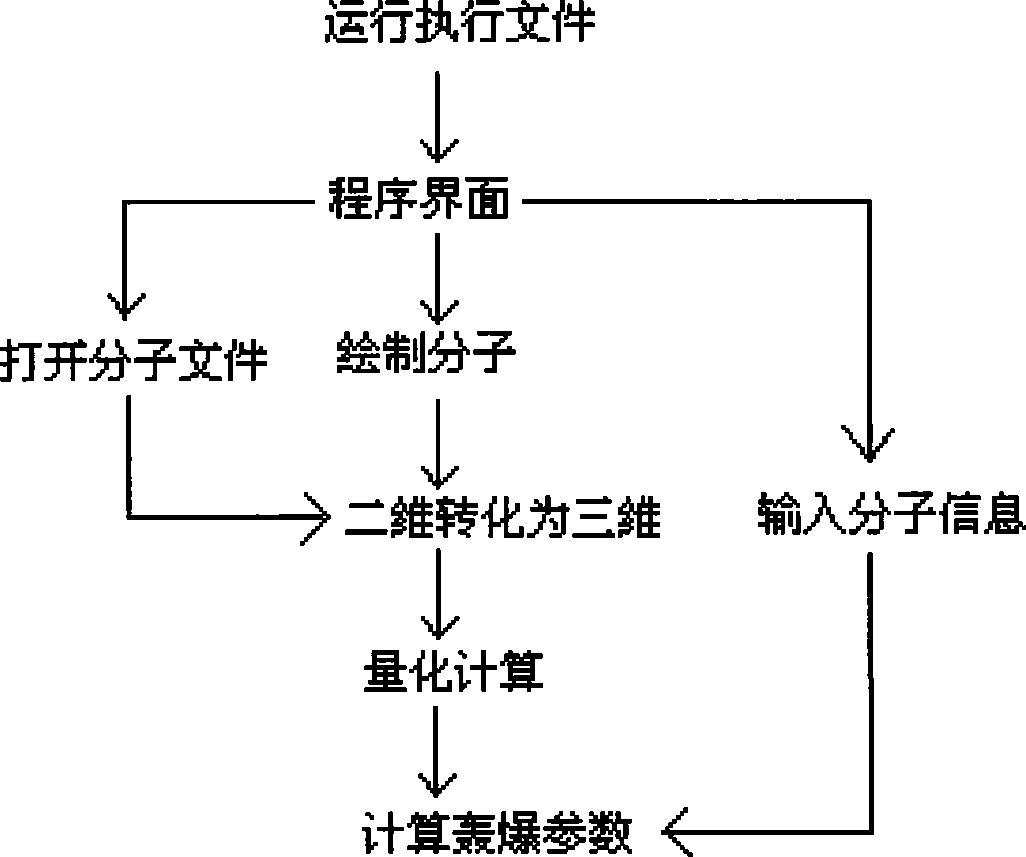
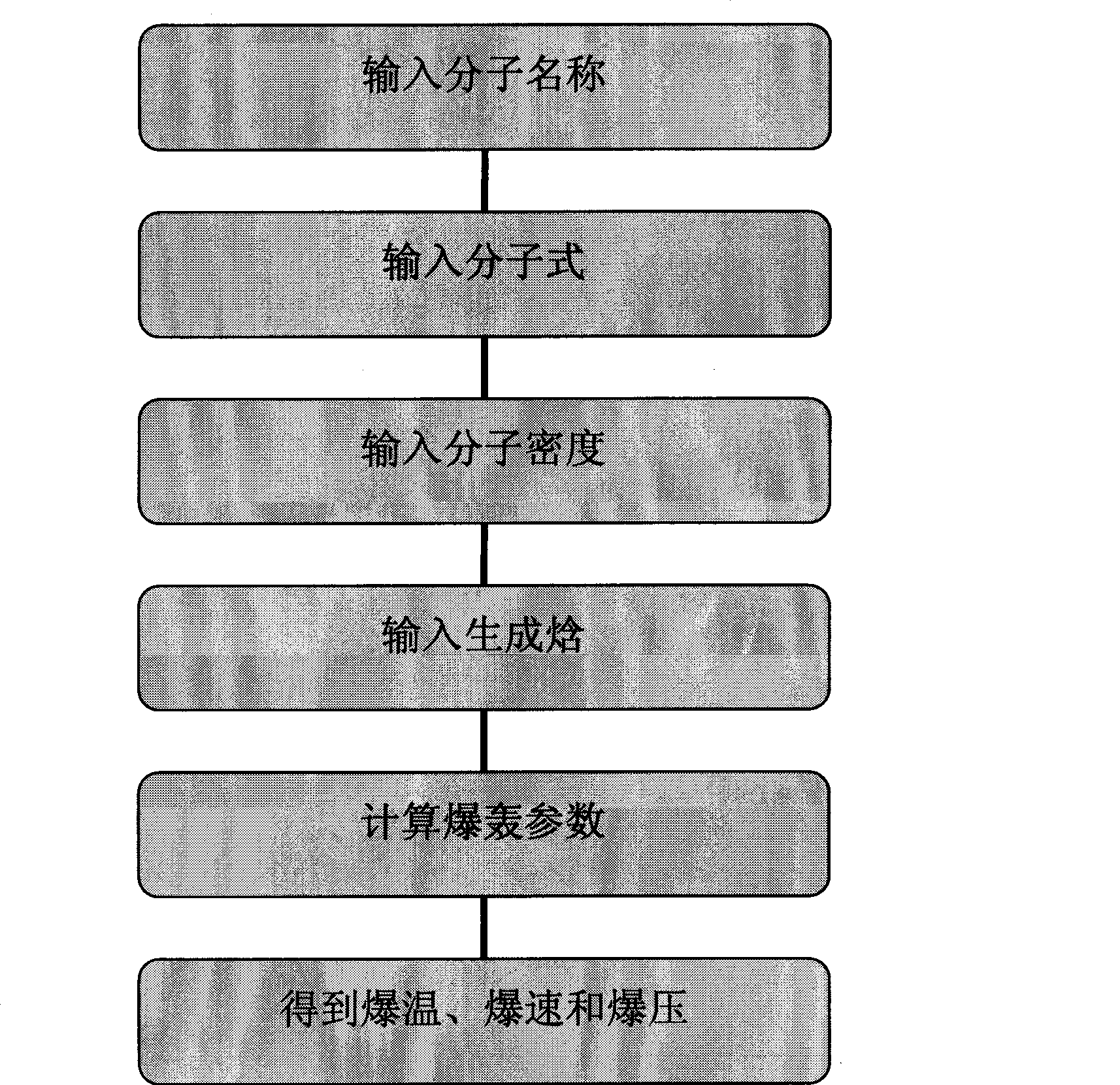
The invention discloses a system for computer-aided design of energetic compound molecules. The system is used for aided design and development of a novel energetic compound molecular structure and forecasting the detonation property of the novel energetic compound molecular structure. The system at least comprises a user input module, a file input / output module, a molecular structure conversion module, a display module, a detonation parameter predicting module and a molecular combination library generating module, wherein the user input module is used for drawing a molecular planar structure; the file input / output module can read, correct and store known file formats; the molecular structure conversion module can convert the molecular planar structure drawn by a user into a three-dimensional structure; the display module can display an opened molecular structure file or the molecular structure drawn by the user; the detonation parameter predicting module can predict the detonation parameter according to the molecular properties; and the molecular combination library generating module utilizes a combinatorial chemistry principle to generate an energetic compound molecular combination library.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Biaxially-oriented polypropylene film for capacitor, metal deposition film thereof and cast raw sheet
InactiveCN101906228AHigh crystallinityImprove heat resistanceFixed capacitor dielectricMetal layered productsTan deltaPolypropylene
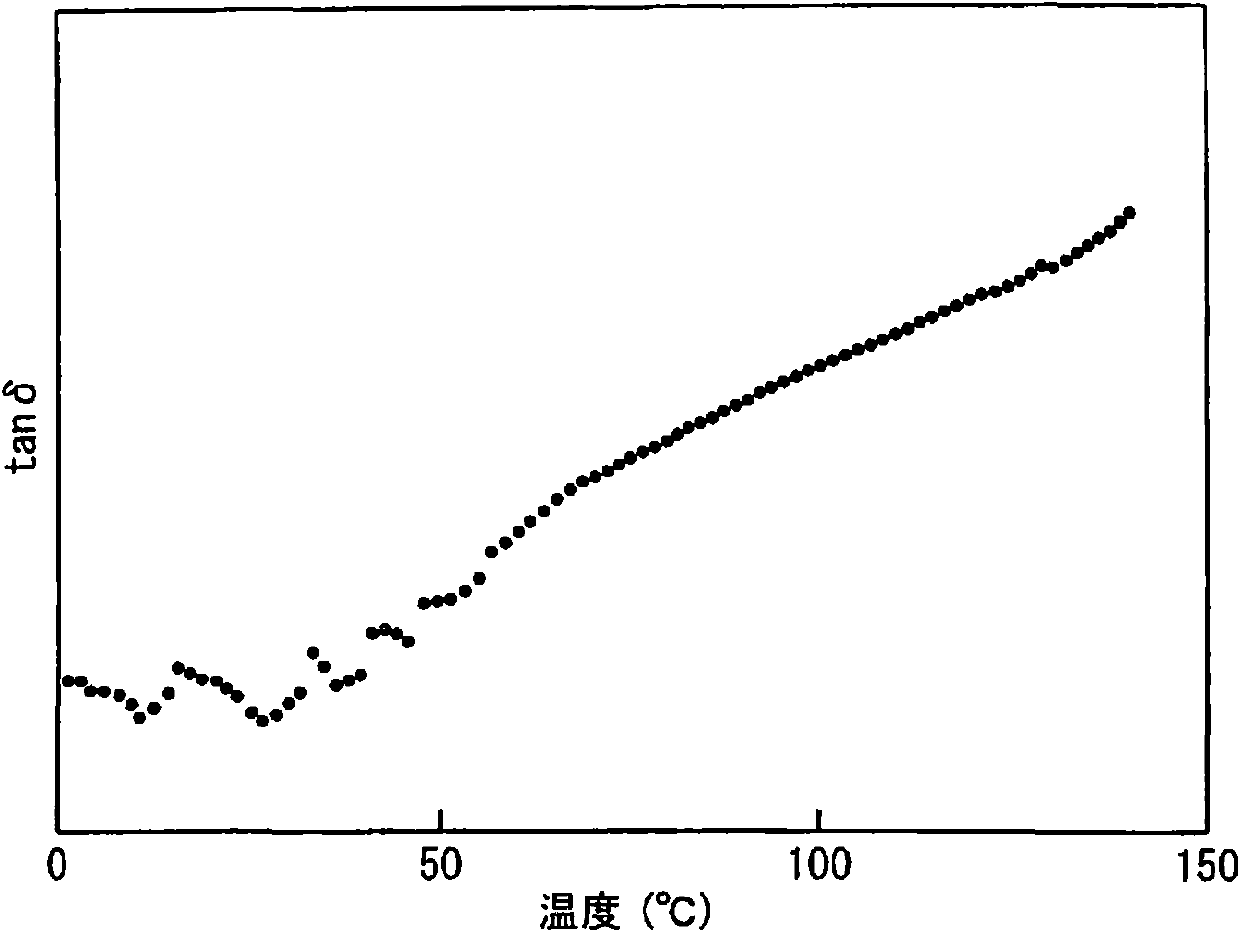
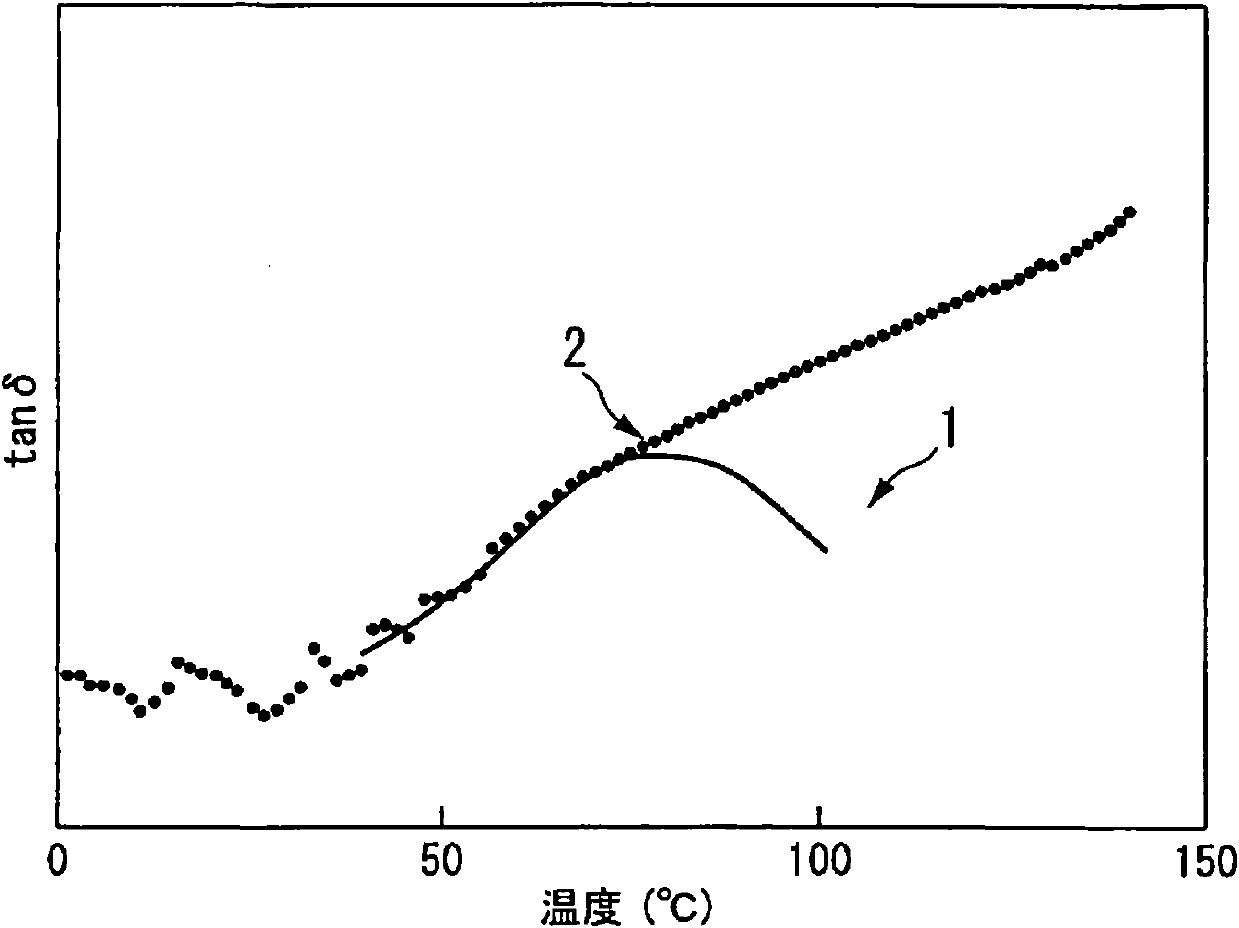
Provided is a biaxially-oriented polypropylene film for a capacitor, metal evaporated film using the capacitor and cast raw sheet for obtaining the same. The biaxially-oriented polypropylene film for a capacitor is obtained by adding 92-95% of addition resin B in a quantity ([mmmm]) of 1-20 mass% in relation to the total mass of the resin mixture, in a main resin A with the internal compensation five unit group percentage ([mmmm]). The film is a biaxially-oriented polypropylene film composed of more than two kinds of different stereoregularity in the isotactic polypropylene resin with molecular properties. The temperature of a mechanical dispersion peak (crystal dispersion) (tan delta ) in a temperature loss tangent curve, which is obtained by a dynamic solid viscoelasticity measurement at a heating rate of 2[deg] C / minutes with a frequency of 0.5 Hz, is >= 80[deg] C.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD +1
Hyperbranched polysiloxane and preparation method thereof
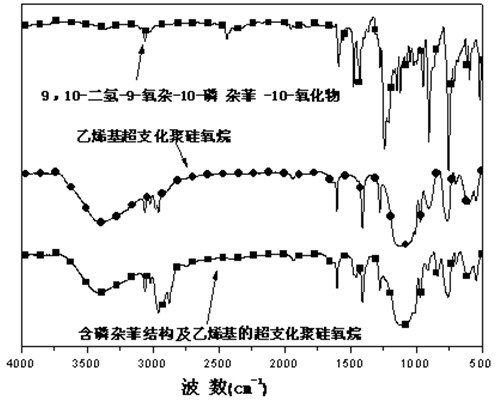
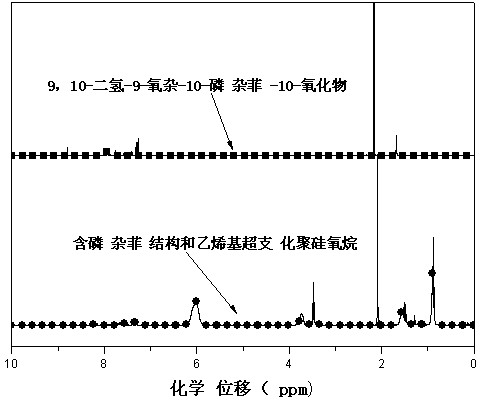
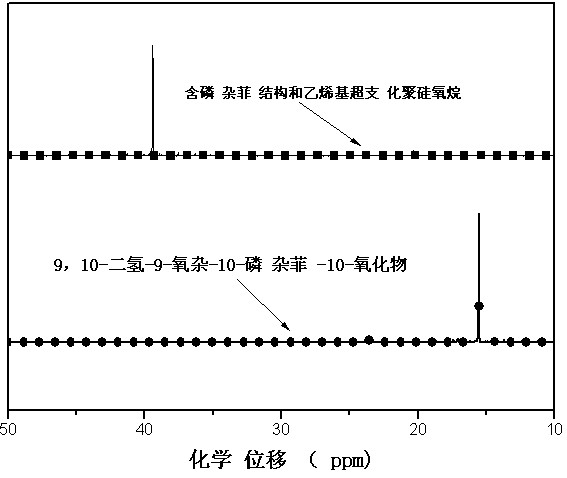
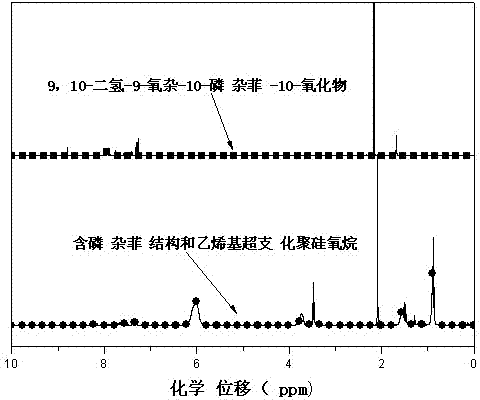
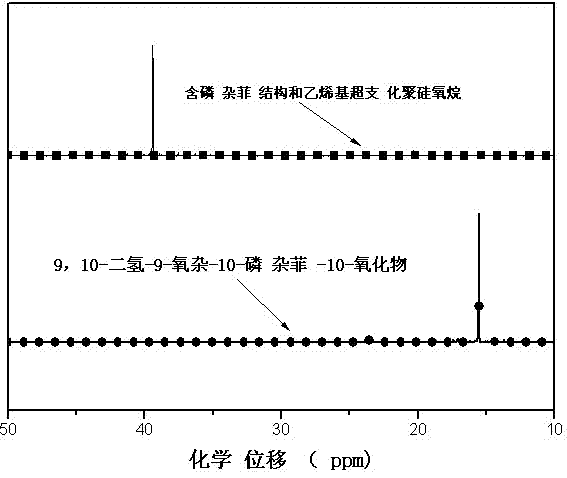
The invention discloses a phosphaphenanthrene structure and vinyl containing-hyperbranched polysiloxane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of evenly mixing distilled water with vinyl-containing trialkoxysilane, dropwise adding catalyst slowly under the stirring condition, and increasing temperature to 50-60 DEG C, thus obtaining vinyl-containing hyperbranched polysiloxane; and mixing the vinyl-containing hyperbranched polysiloxane with 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide, adding initiator and alcohol solvent, increasing temperature to 95-100 DEG C, and carrying out purification, filtering, reduced pressure distillation and vacuum drying after reaction is finished, thus obtaining phosphaphenanthrene structure and vinyl containing-hyperbranched polysiloxane. The phosphaphenanthrene structure and vinyl containing-hyperbranched polysiloxane integrates molecular properties of hyperbranched polysiloxane, 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide and vinyl, thus having wide application prospects on polymer modification aspect. The preparation method adopted has the advantages of wide applicability and simple operation process.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
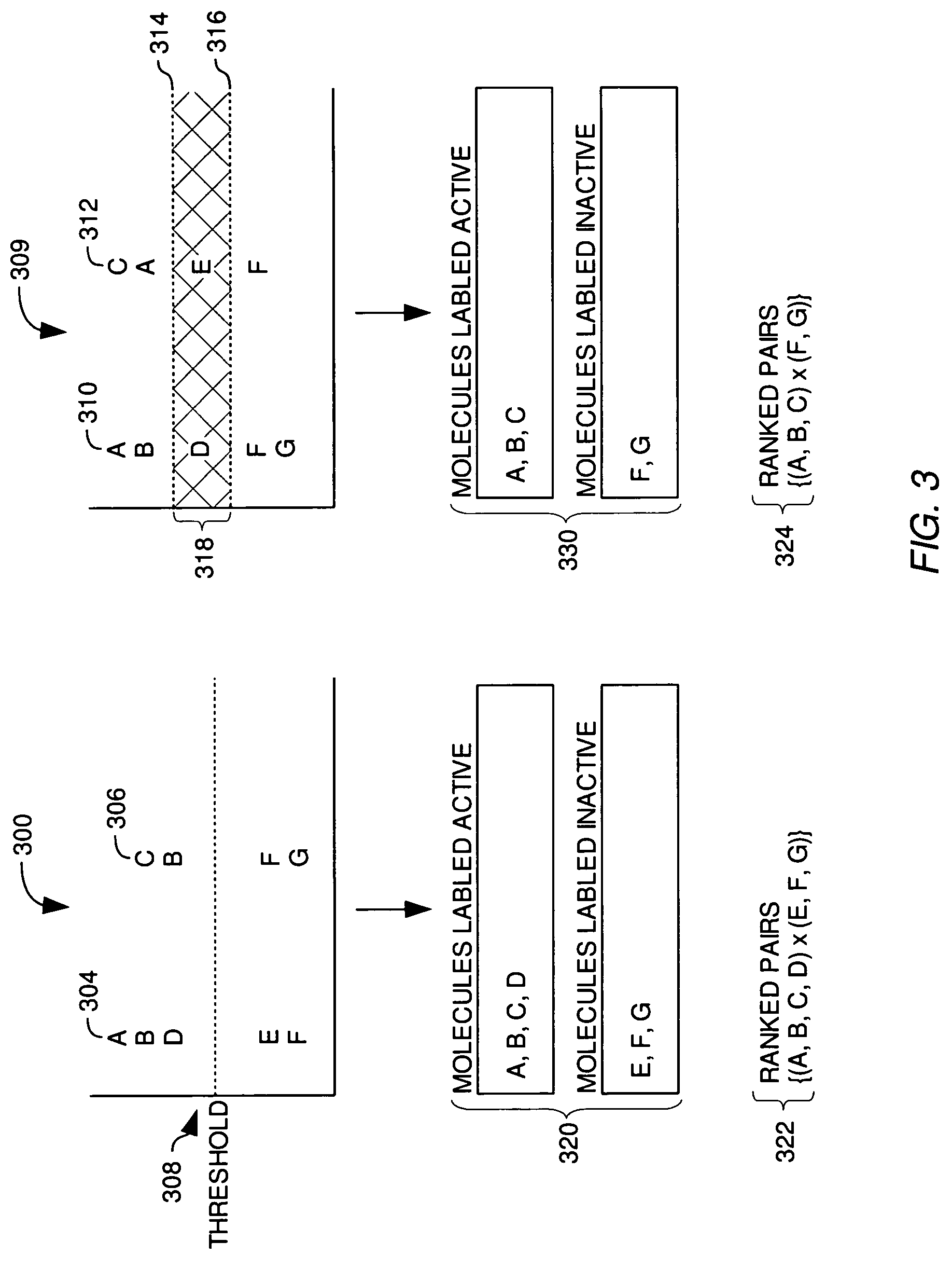
Molecular property modeling using ranking
Methods and articles of manufacture for modeling molecular properties using data regarding the partial orderings of compound properties, or by considering measurements of compound properties in terms of partial orderings are disclosed. One embodiment provides for constructing such partial orderings from data that is not already in an ordered form by processing training data to produce a partial ordering of the compounds with respect to a property of interest. Another embodiment of the invention may process the modified training data to construct a model that predicts the property of interest for arbitrary compounds.
Owner:VALO HEALTH INC
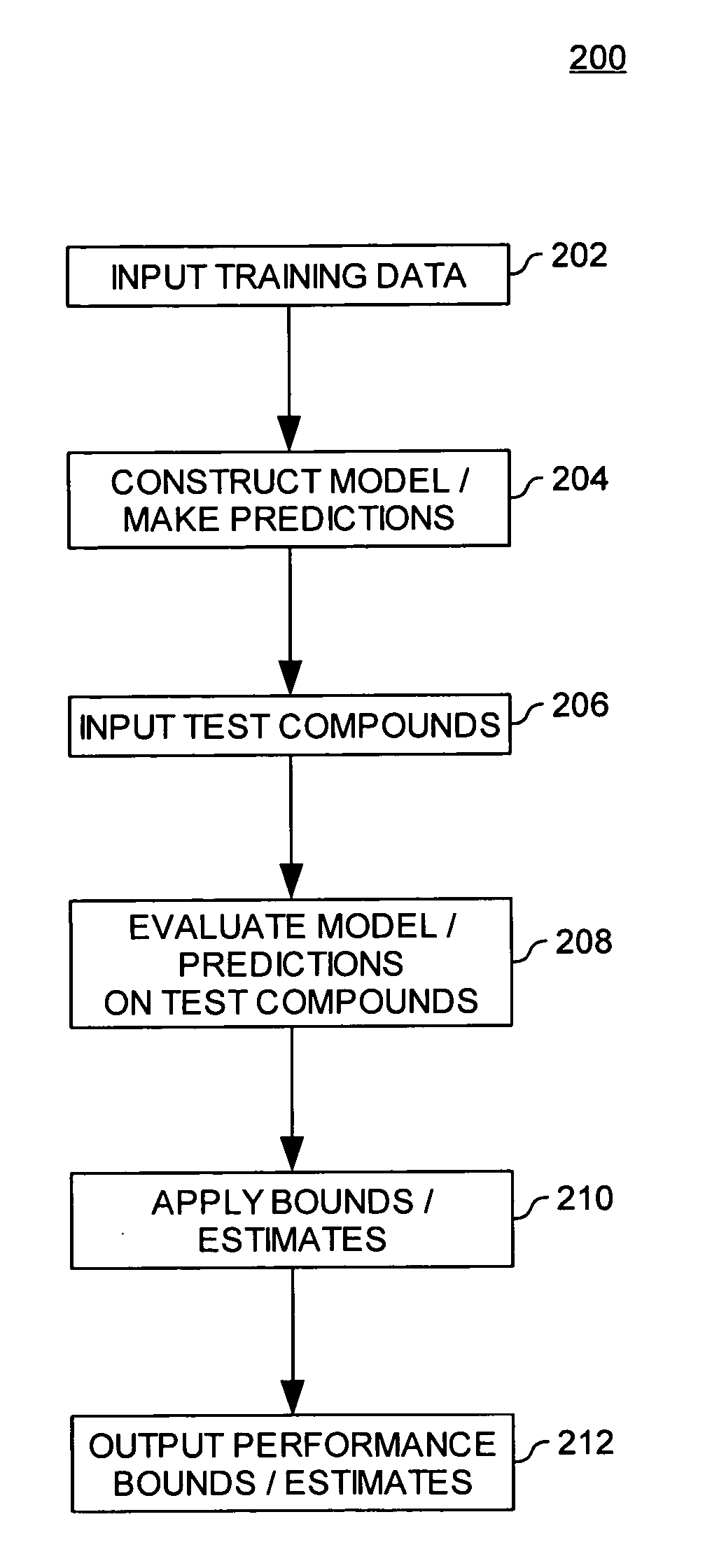
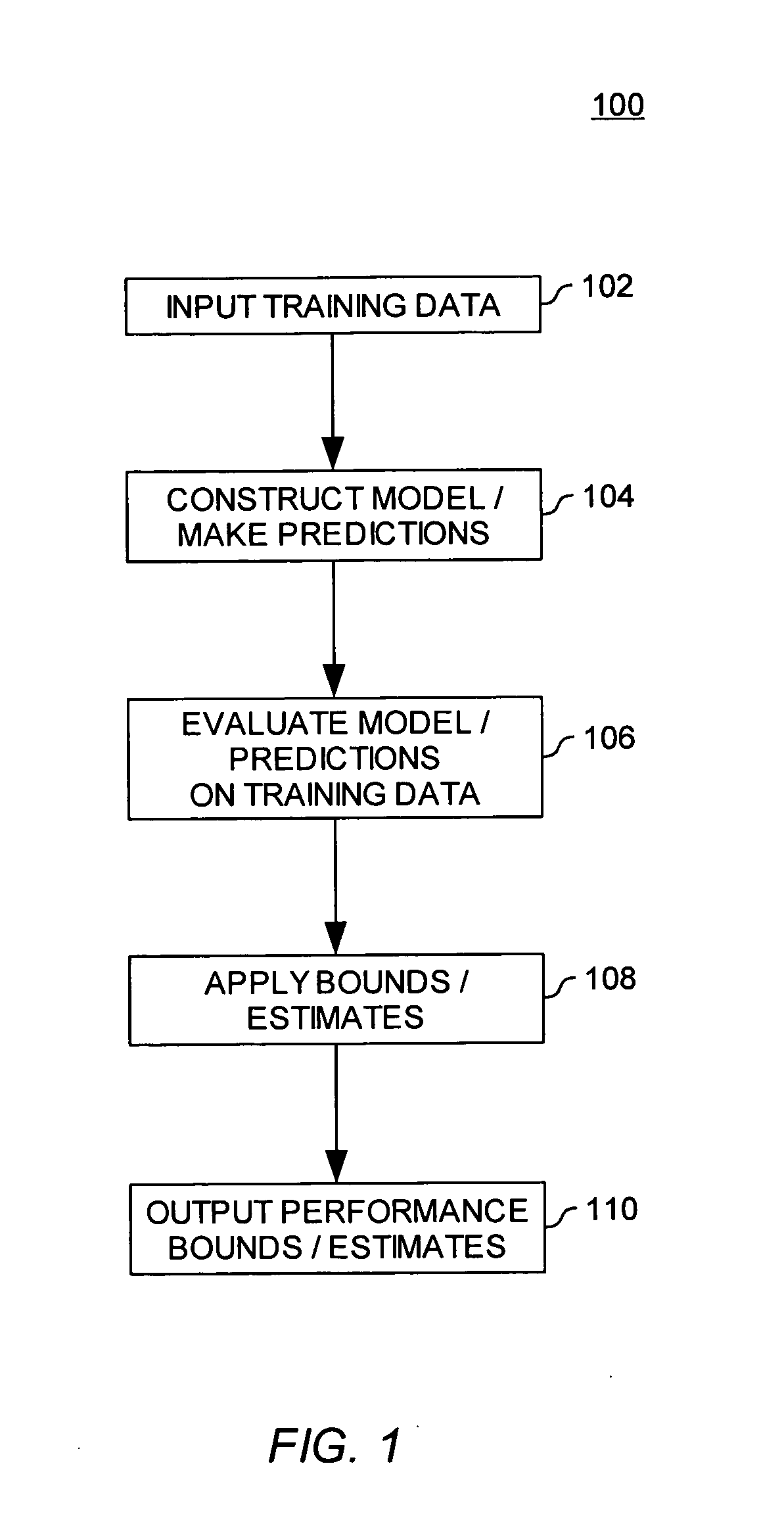
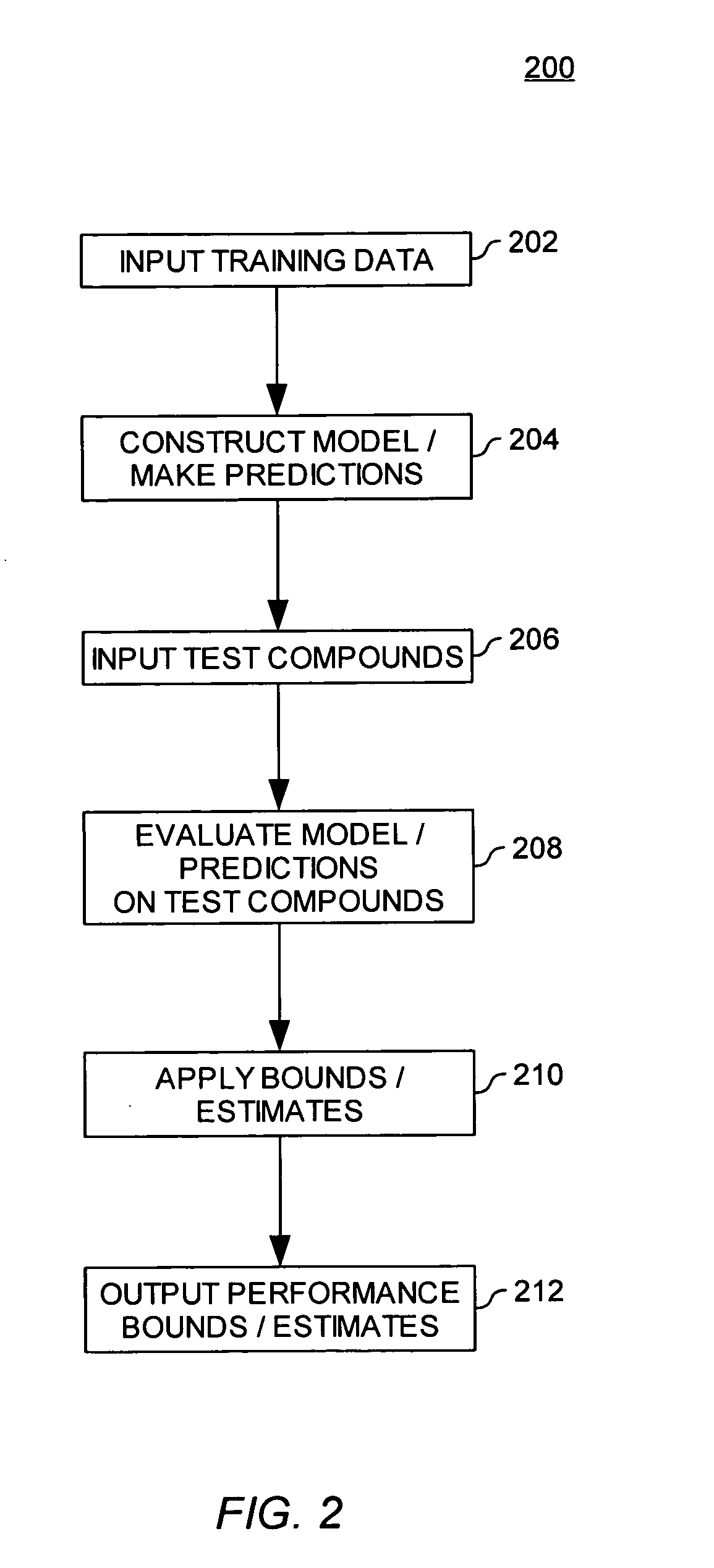
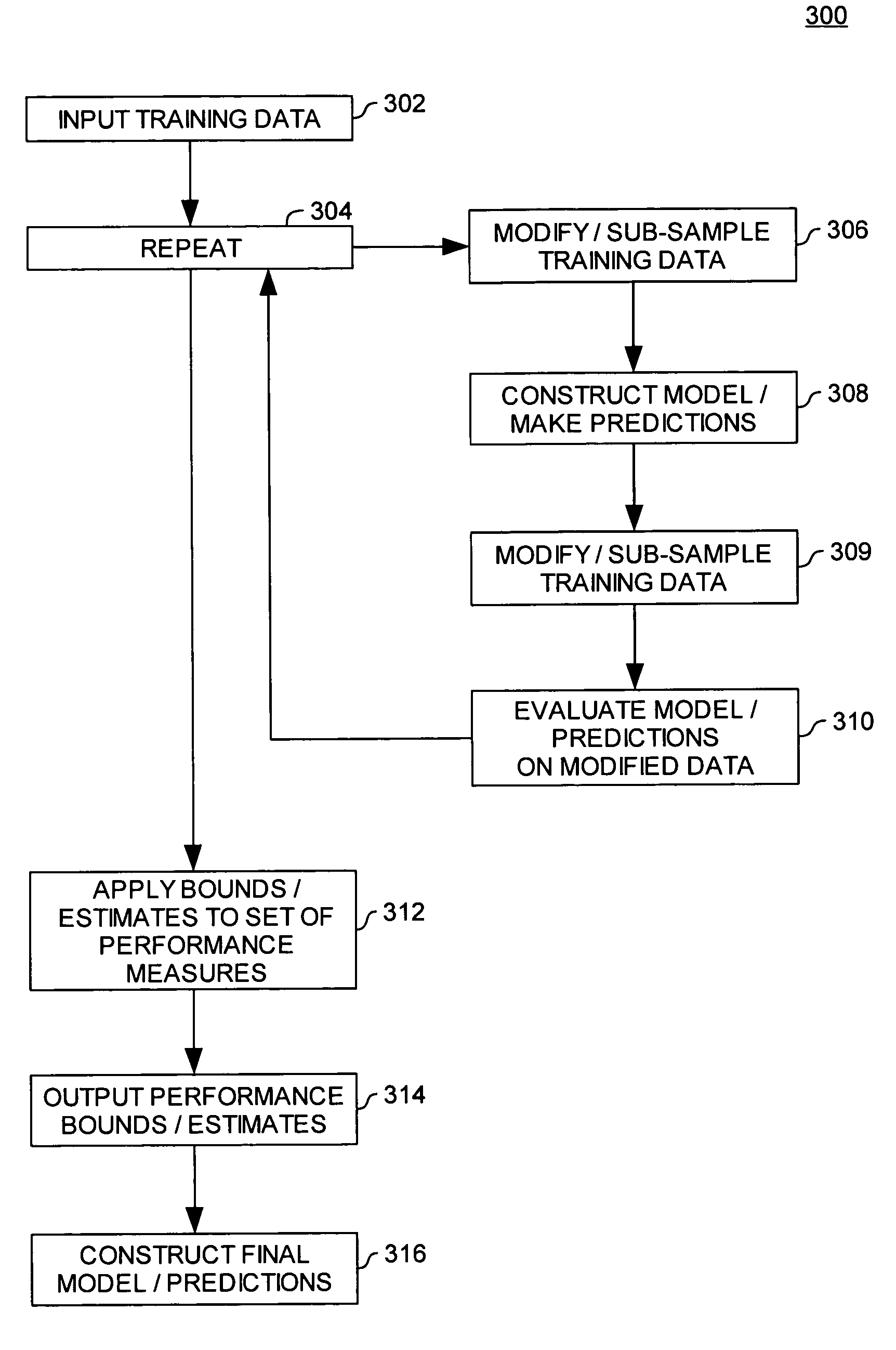
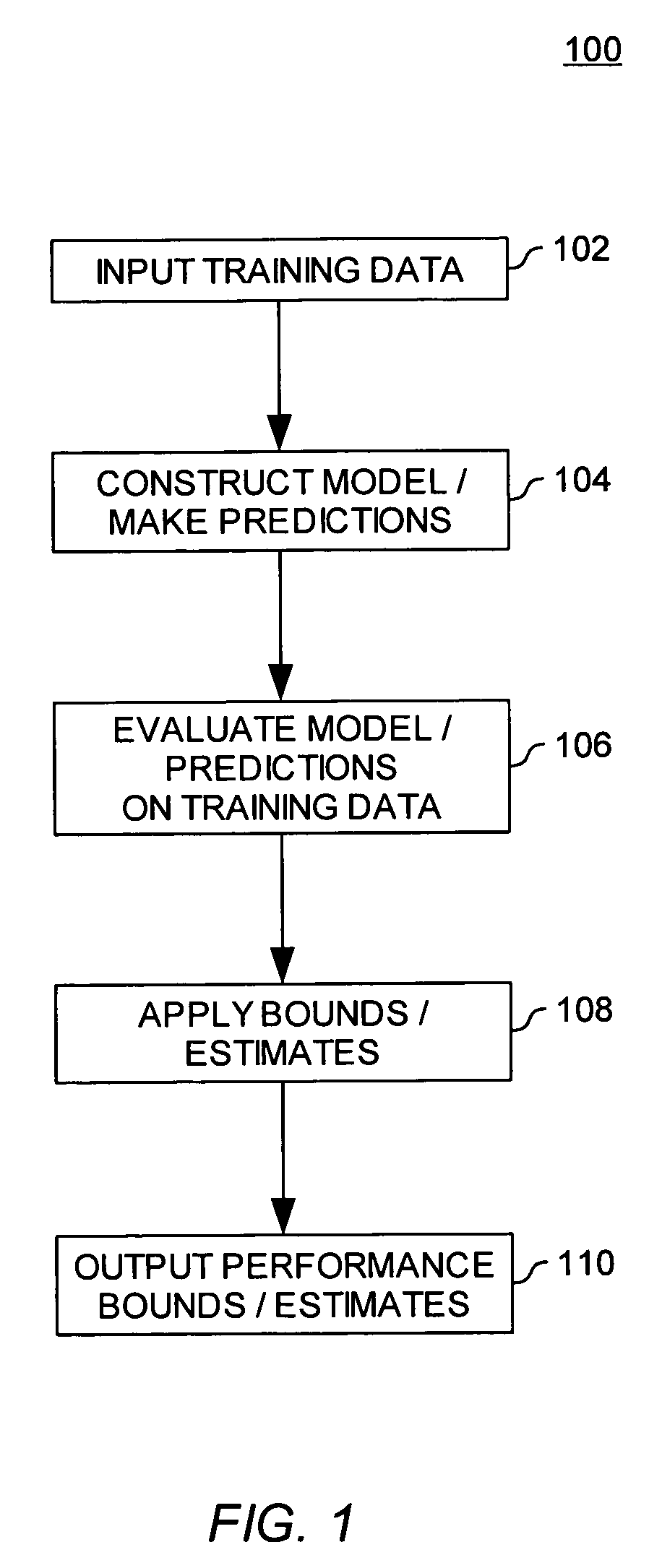
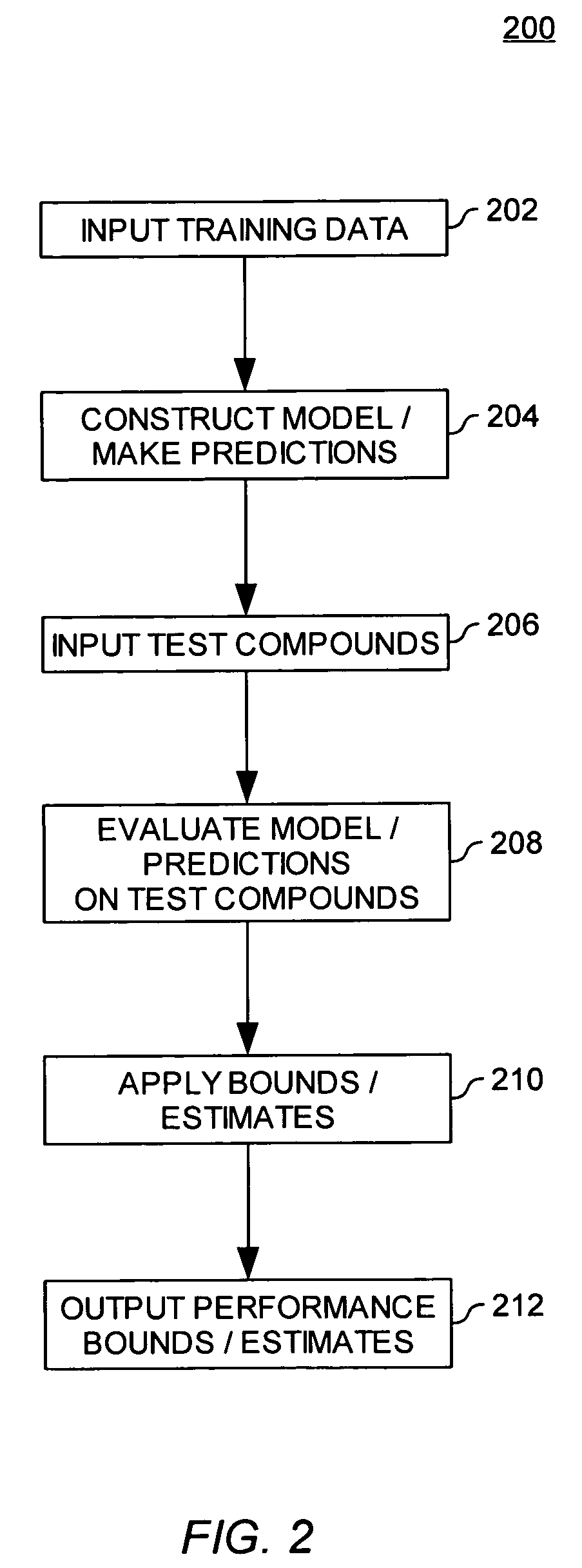
Estimating the accuracy of molecular property models and predictions
ActiveUS20050288871A1Improve accuracyAccuracy of estimationChemical property predictionPreparing sample for investigationData setComputer science
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for evaluating the accuracy of a molecular model properties model (or predictions generated using a molecular properties model). The accuracy of a molecular properties model may be evaluated using three general approaches, (i) by using the same data set to both train the model and to estimate the accuracy of the model, (ii) by using distinct data sets to train and subsequently test a model, and (iii) by using multiple models (or sets of predictions).
Owner:VALO HEALTH INC
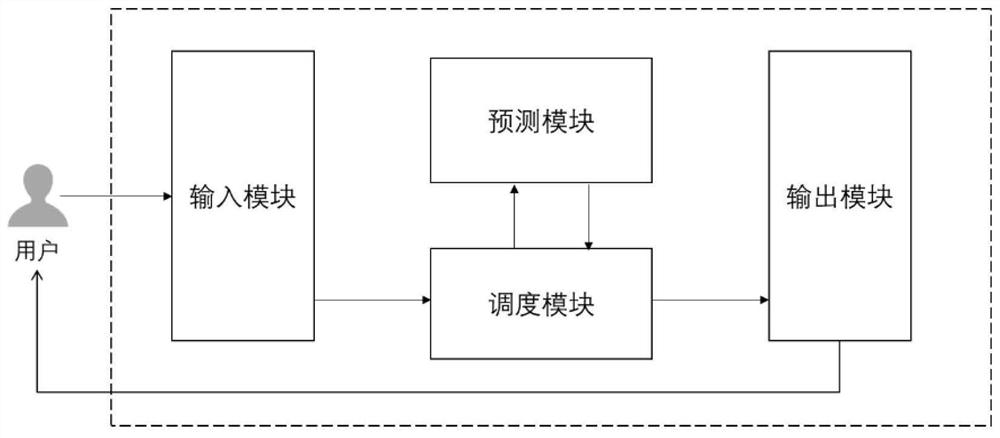
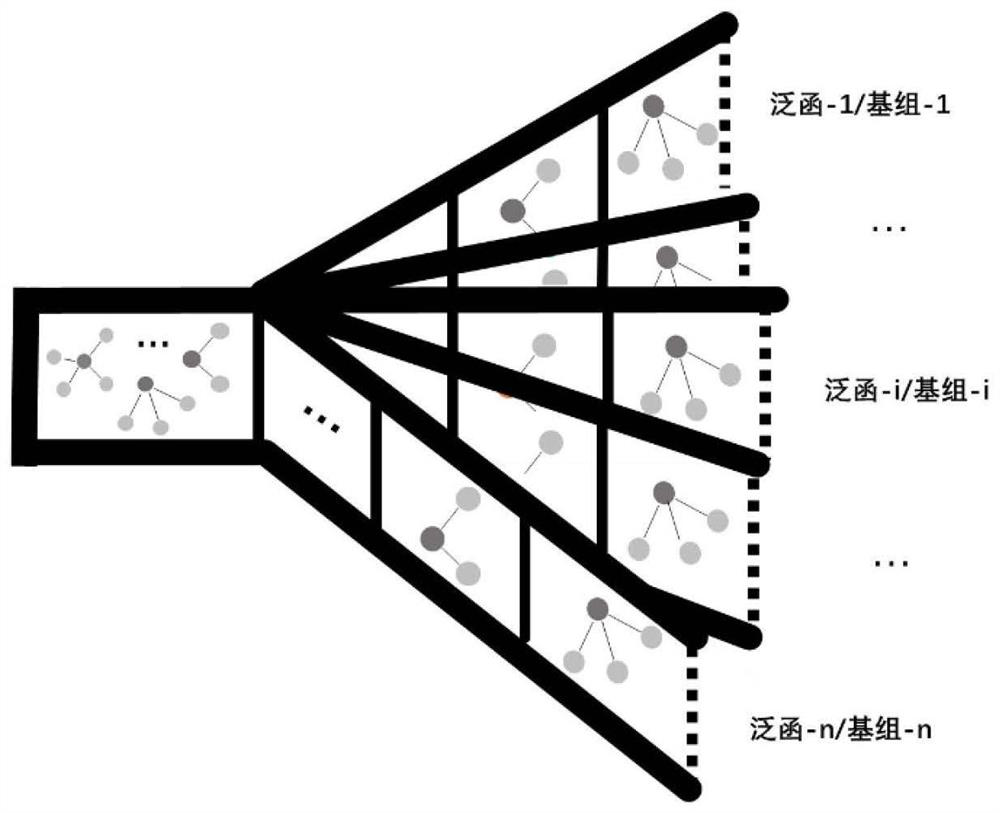
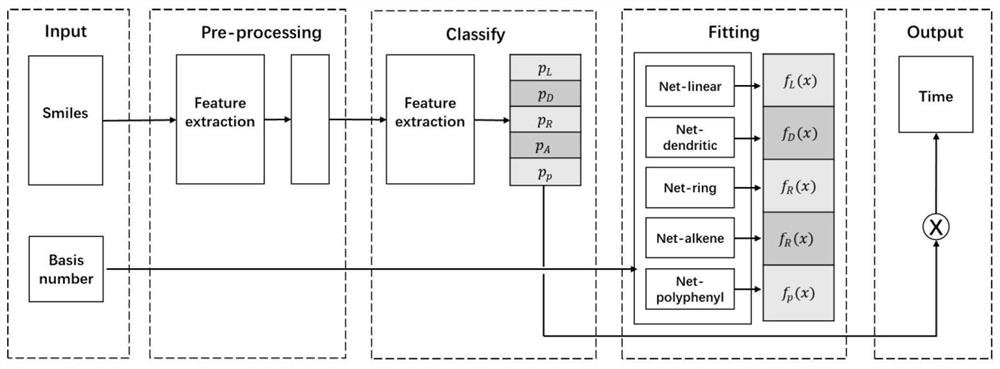
Molecular property prediction method and system
ActiveCN111710375AThe regression analysis method is accurateChemical property predictionChemical machine learningCheminformaticsQuantum chemistry
The invention provides a molecular property prediction method and system, and relates to the fields of quantum chemistry / computational chemistry, chemical informatics and machine learning / artificial intelligence. Under the framework of chemical multi-world explanation, a density functional theory, chemical informatics and machine learning / artificial intelligence means are used, information such asa molecular structure, a base group, a functional and the like is used as input, and a prediction result of molecular property is output through a machine learning model. According to the method, anytype of molecular structure and any calculation strategy can be predicted, and the method is more accurate than a common experience method and a regression analysis method.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
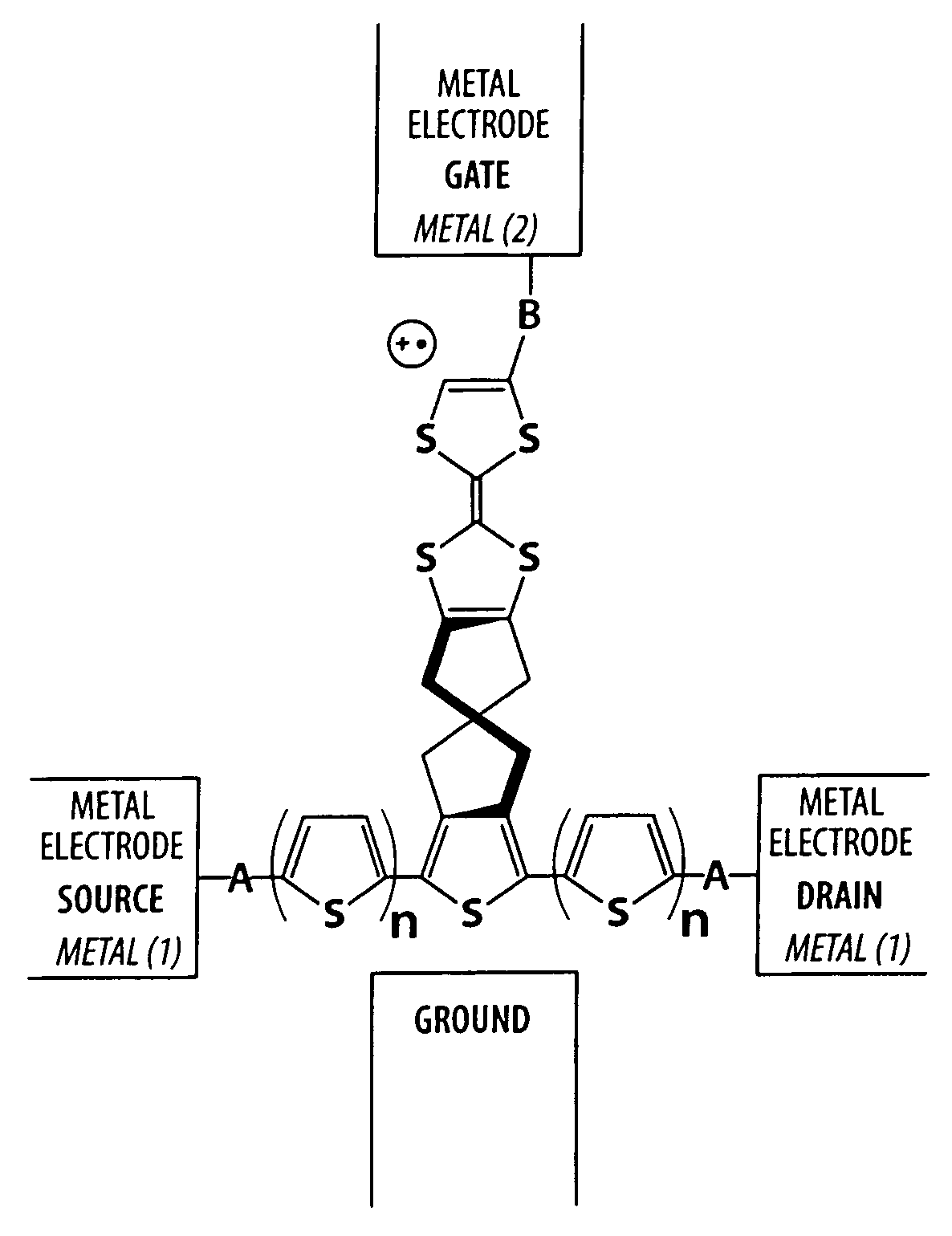
Electrical contacts for molecular electronic transistors
ActiveUS6989290B2Rapid and reliable meanHighly cost-effectiveNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectricityMolecular transistor
Electronic circuits based on molecular transistors, generally used in place of semiconductors. More particularly, the invention relates to a unique method of wiring of a three-terminal molecule (or an aggregate thereof) to serve as an electronic transistor, containing a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode. The source electrode and drain electrode are fabricated from one metal and the gate electrode is fabricated from another metal. The usage of molecular properties in this context provides significant advantages over the fabrication methods of the prior art.
Owner:AVIRAM ARI
Method for predicting enzyme-catalyzed reactions
InactiveUS20080177478A1Chemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designSupport vector machineMetabolite
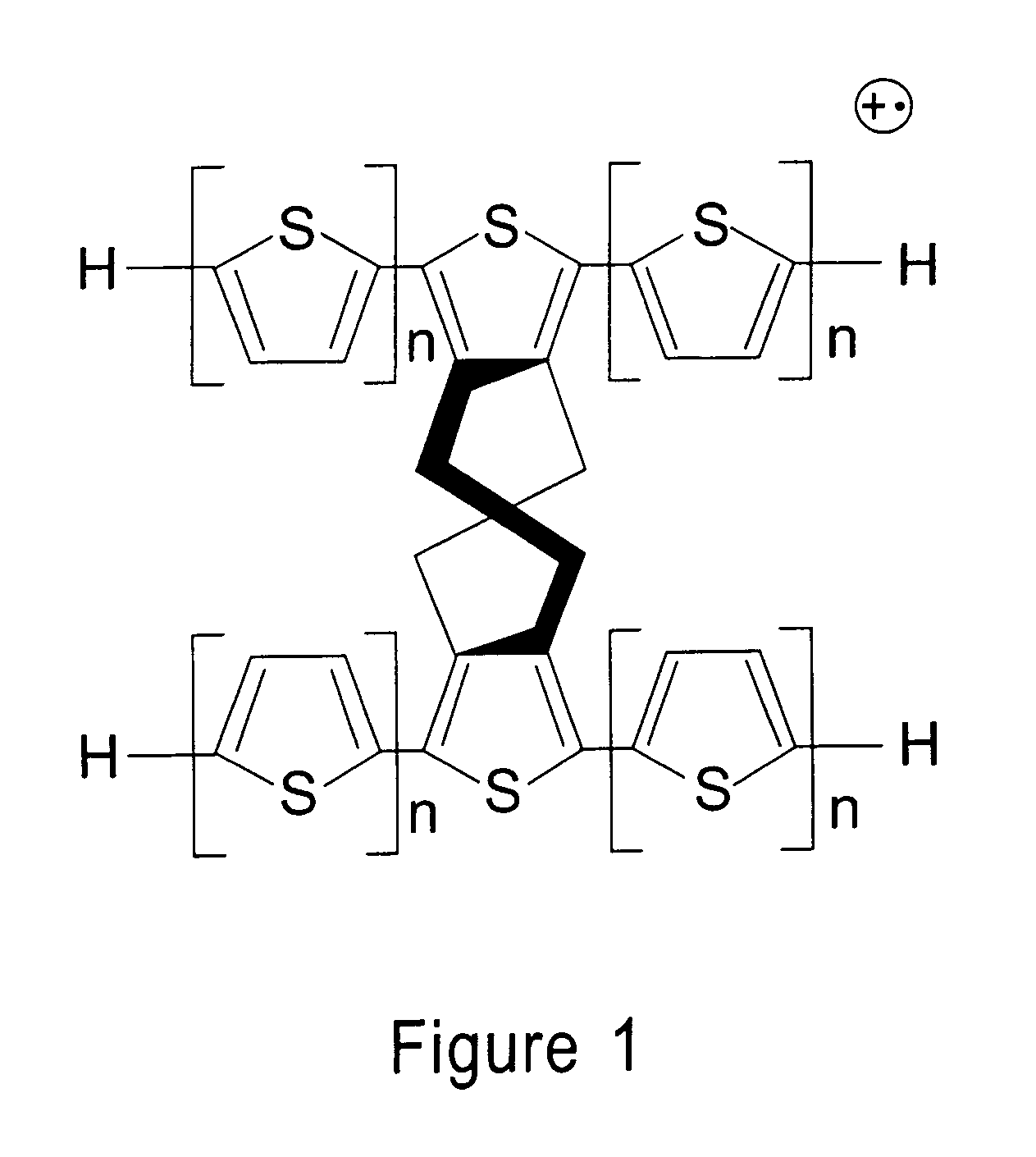
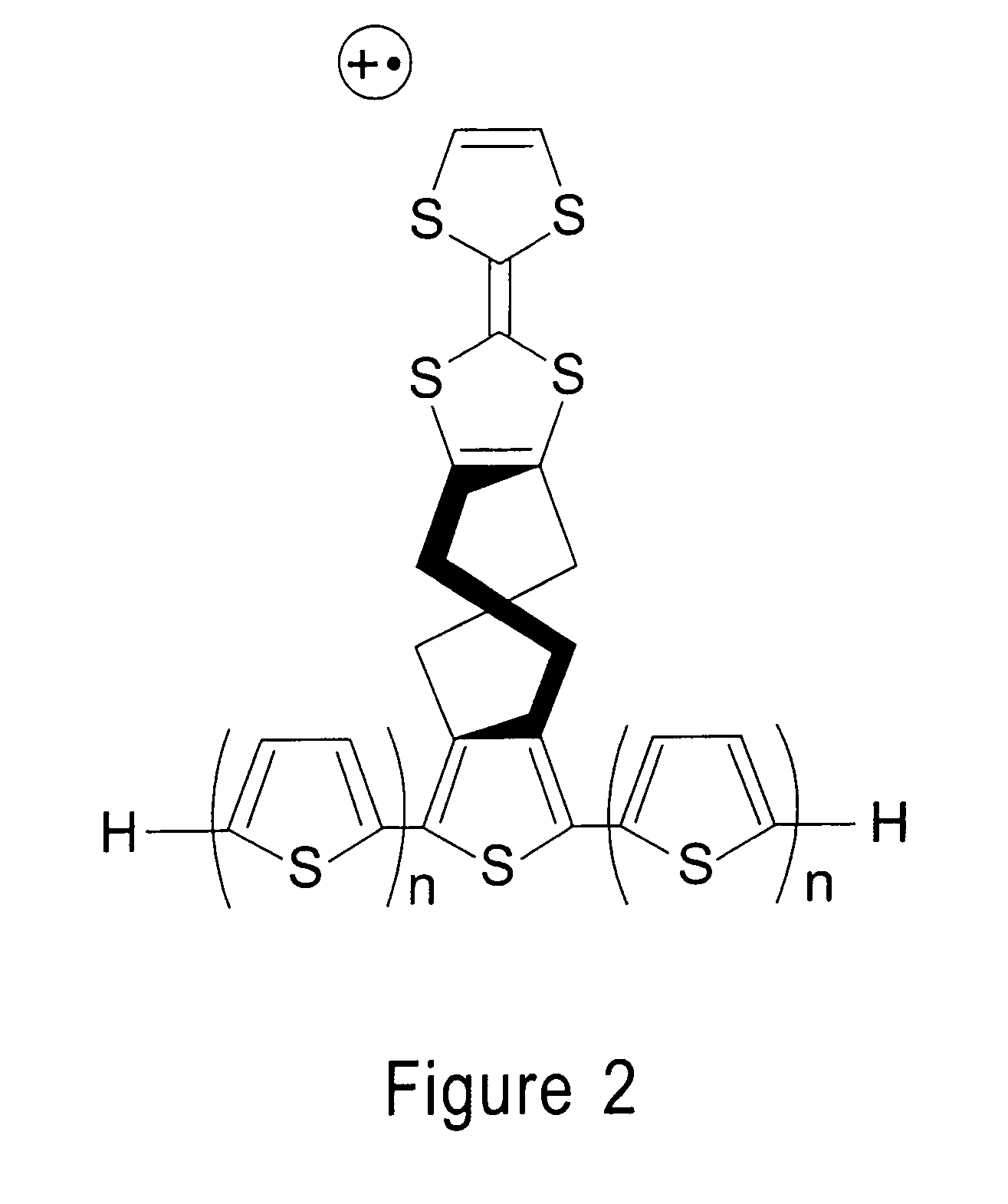
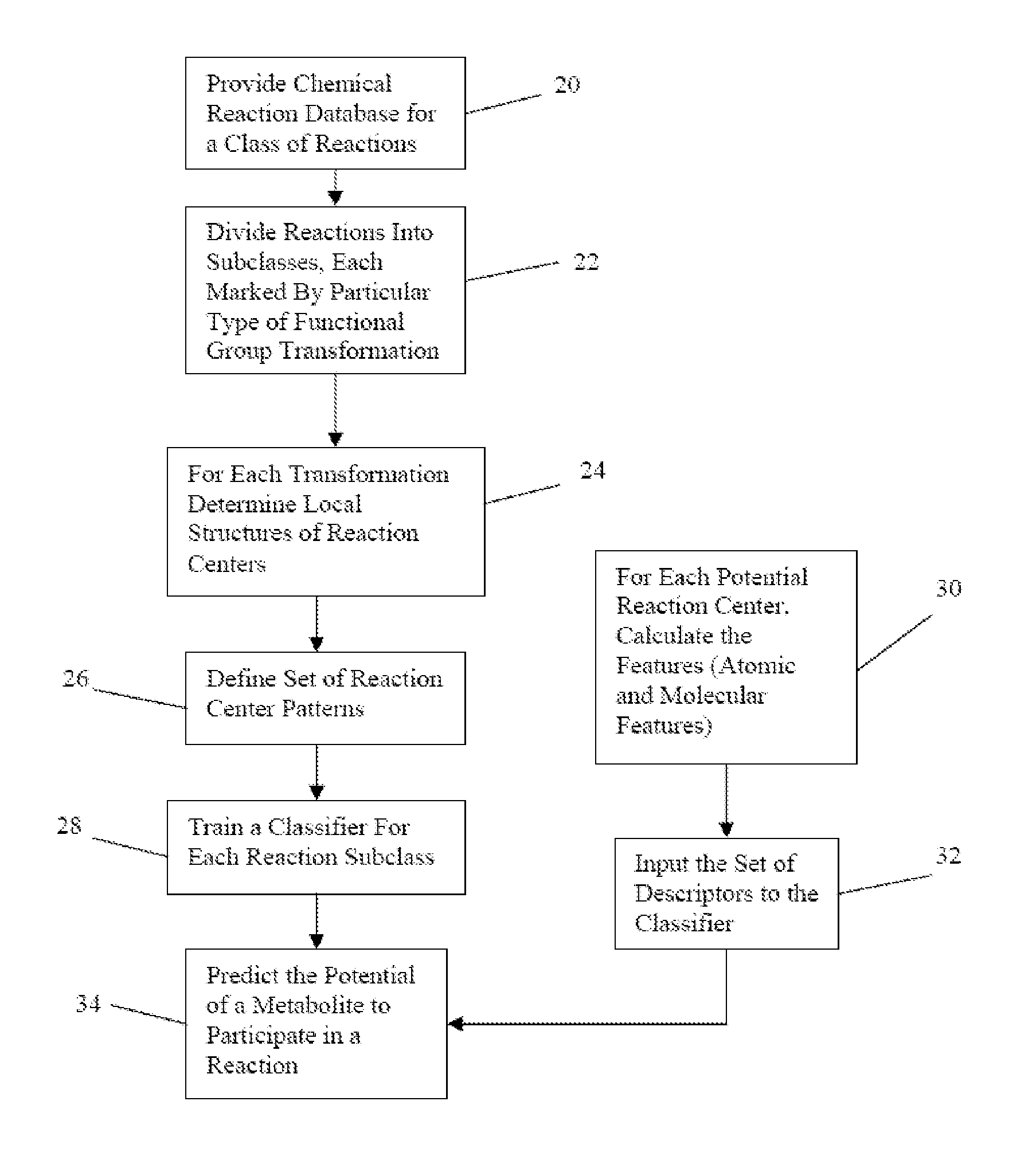
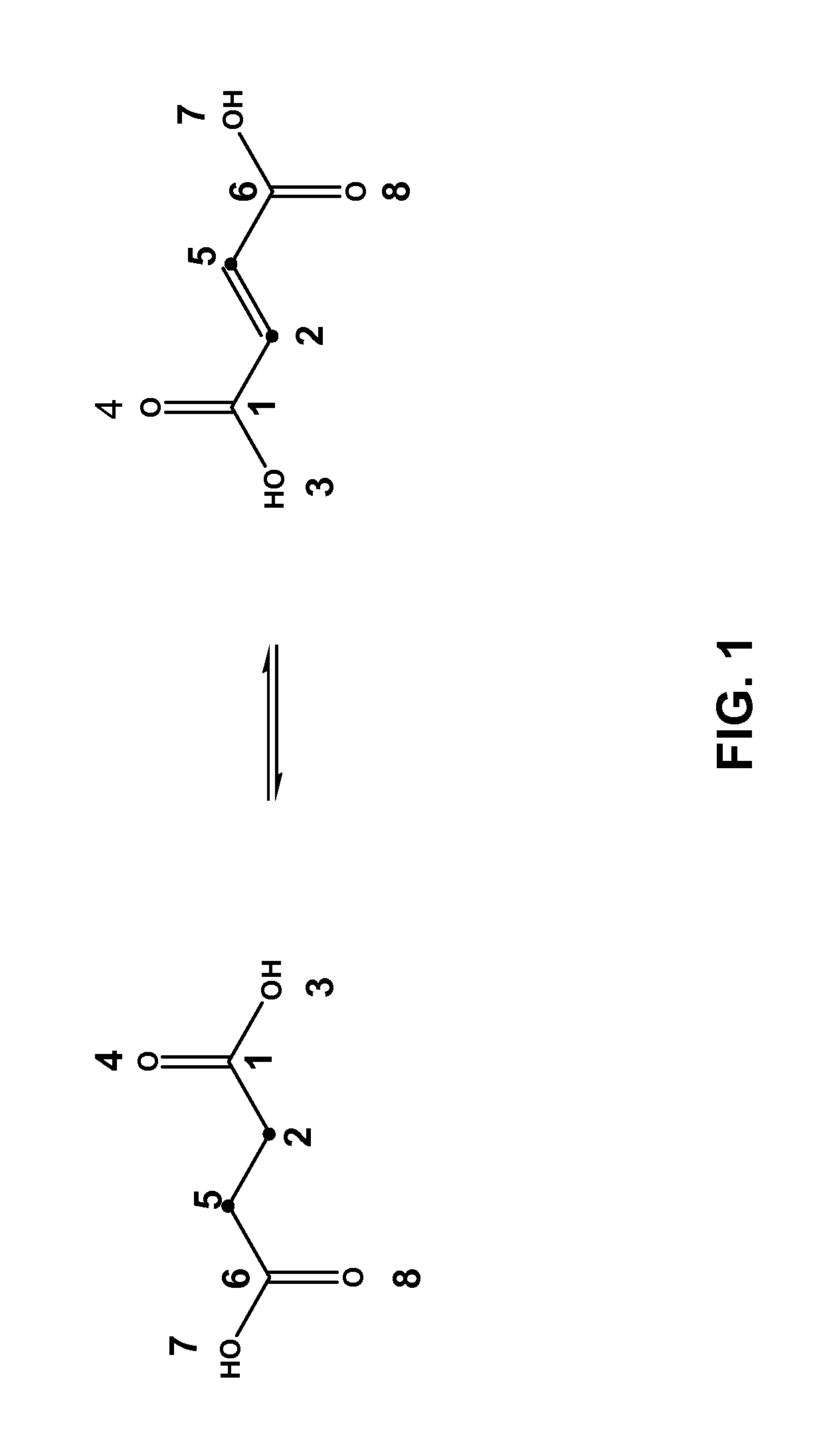
The reactivity of given metabolites is assessed using selected empirical atomic properties in the potential reaction center. Metabolic reactions are represented as biotransformation rules. These rules are generalized from the patterns in reactions. These patterns are not unique to reactants but are widely distributed among metabolites. Using a metabolite database, potential substructures are identified in the metabolites for a given biotransformation. These substructures are divided into reactants or non-reactants, depending on whether they participate in the biotransformation or not. Each potential substructure is then modeled using descriptors of the topological and electronic properties of atoms in the potential reaction center; molecular properties can also be used. A Support Vector Machine (SVM) or classifier is trained to classify a potential reactant as a true or false reactant using these properties.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Estimating the accuracy of molecular property models and predictions
ActiveUS7194359B2Chemical property predictionPreparing sample for investigationData setComputer science
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for evaluating the accuracy of a molecular model properties model (or predictions generated using a molecular properties model). The accuracy of a molecular properties model may be evaluated using three general approaches, (i) by using the same data set to both train the model and to estimate the accuracy of the model, (ii) by using distinct data sets to train and subsequently test a model, and (iii) by using multiple models (or sets of predictions).
Owner:VALO HEALTH INC
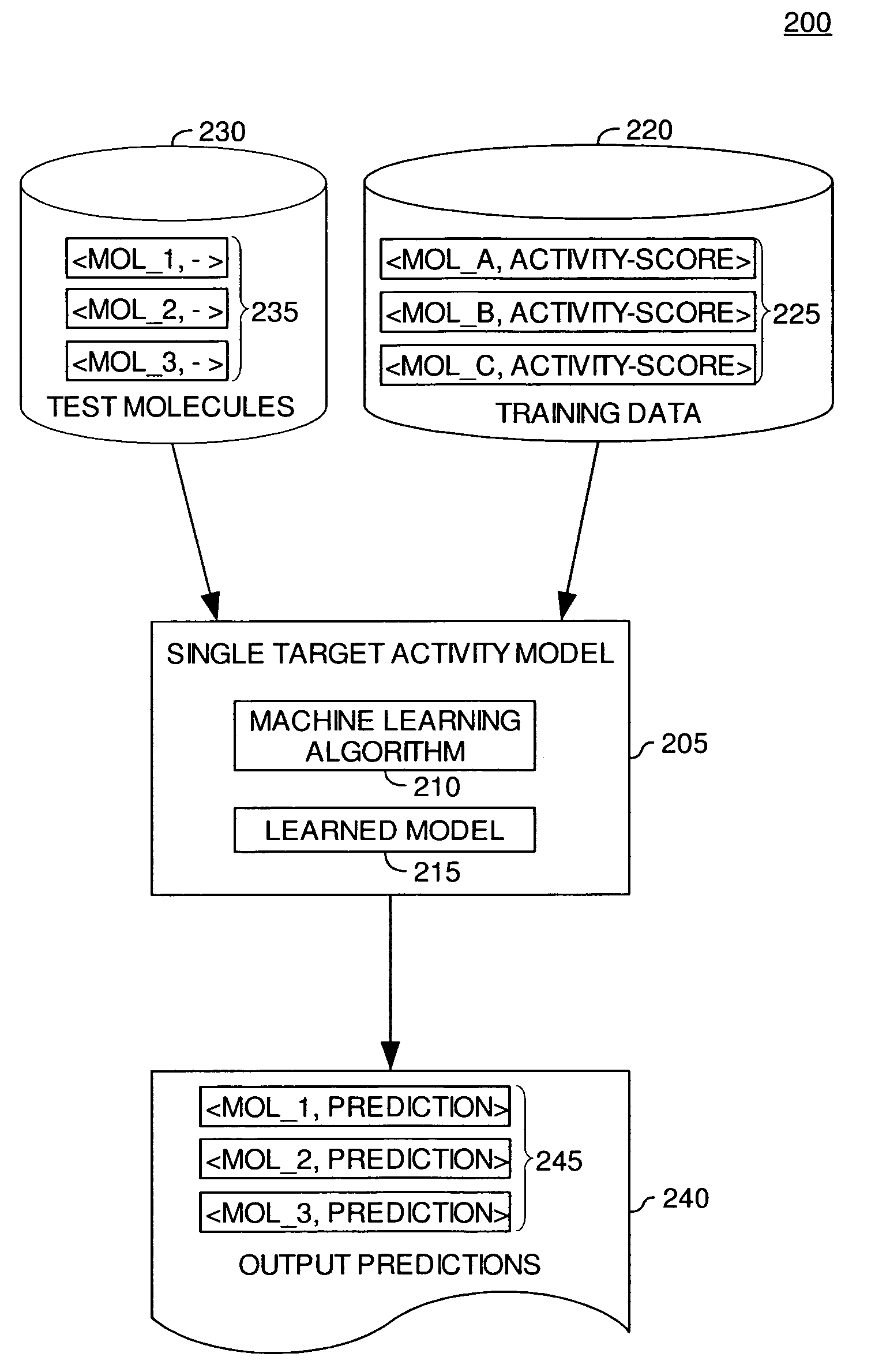
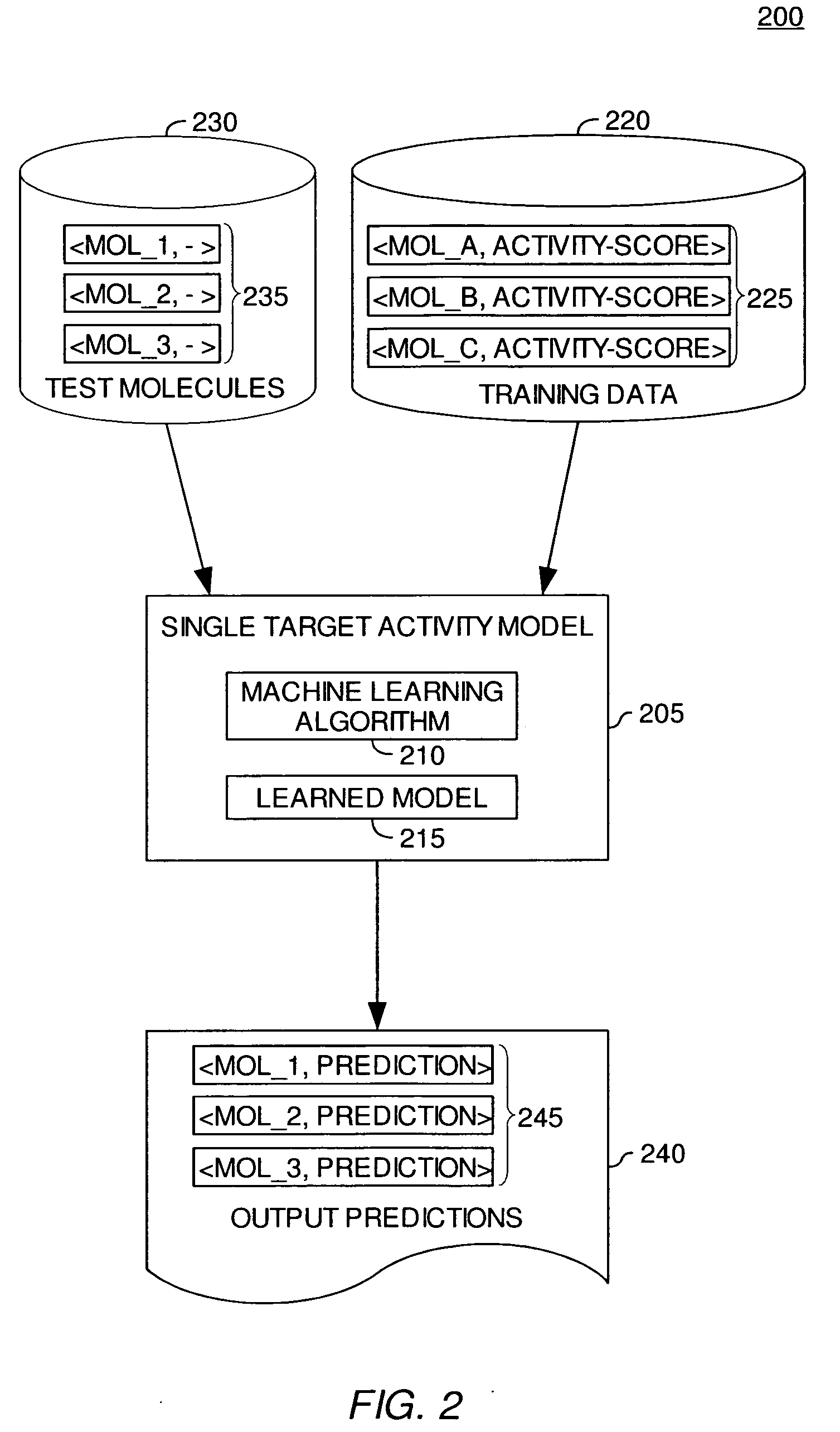
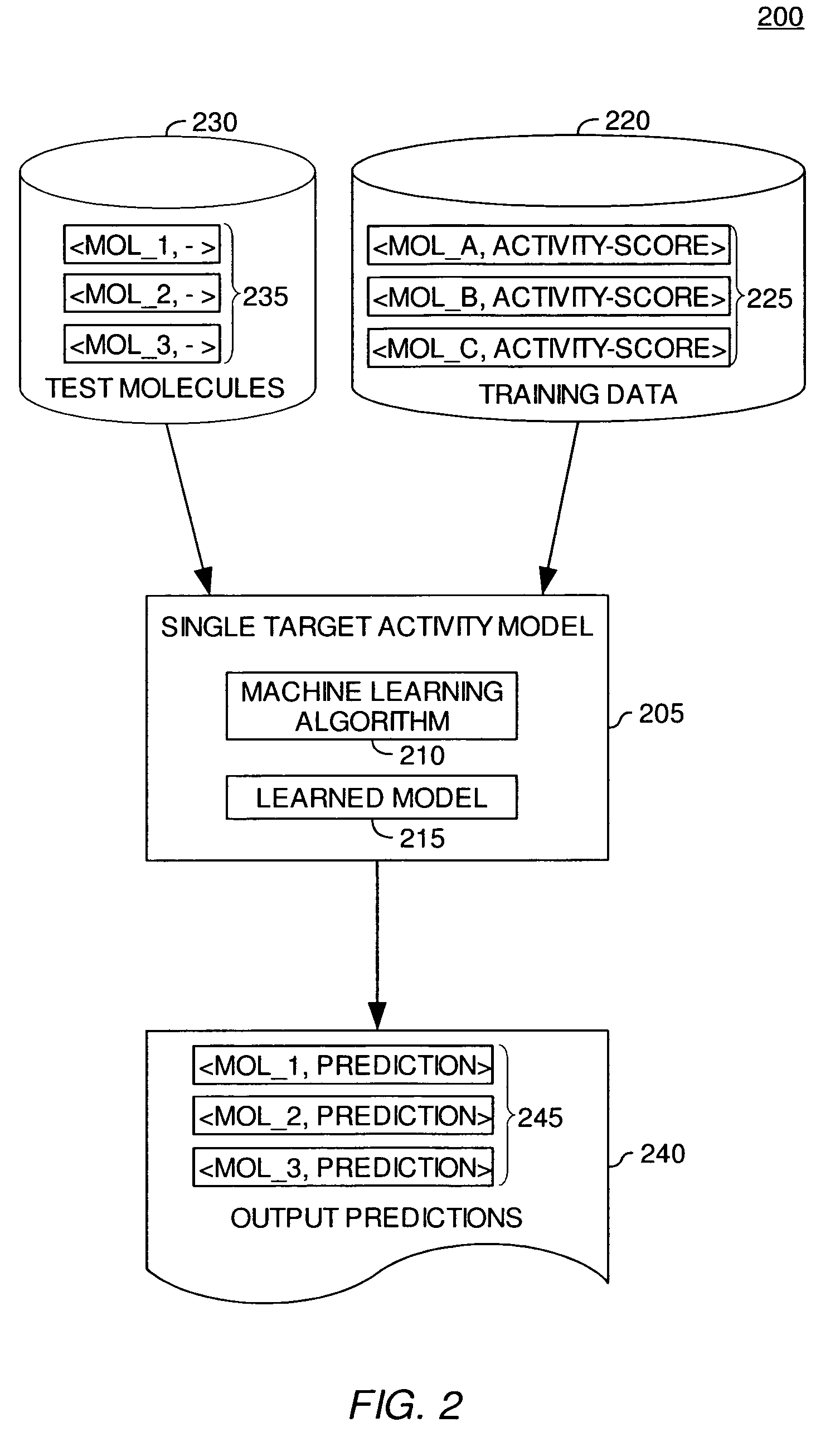
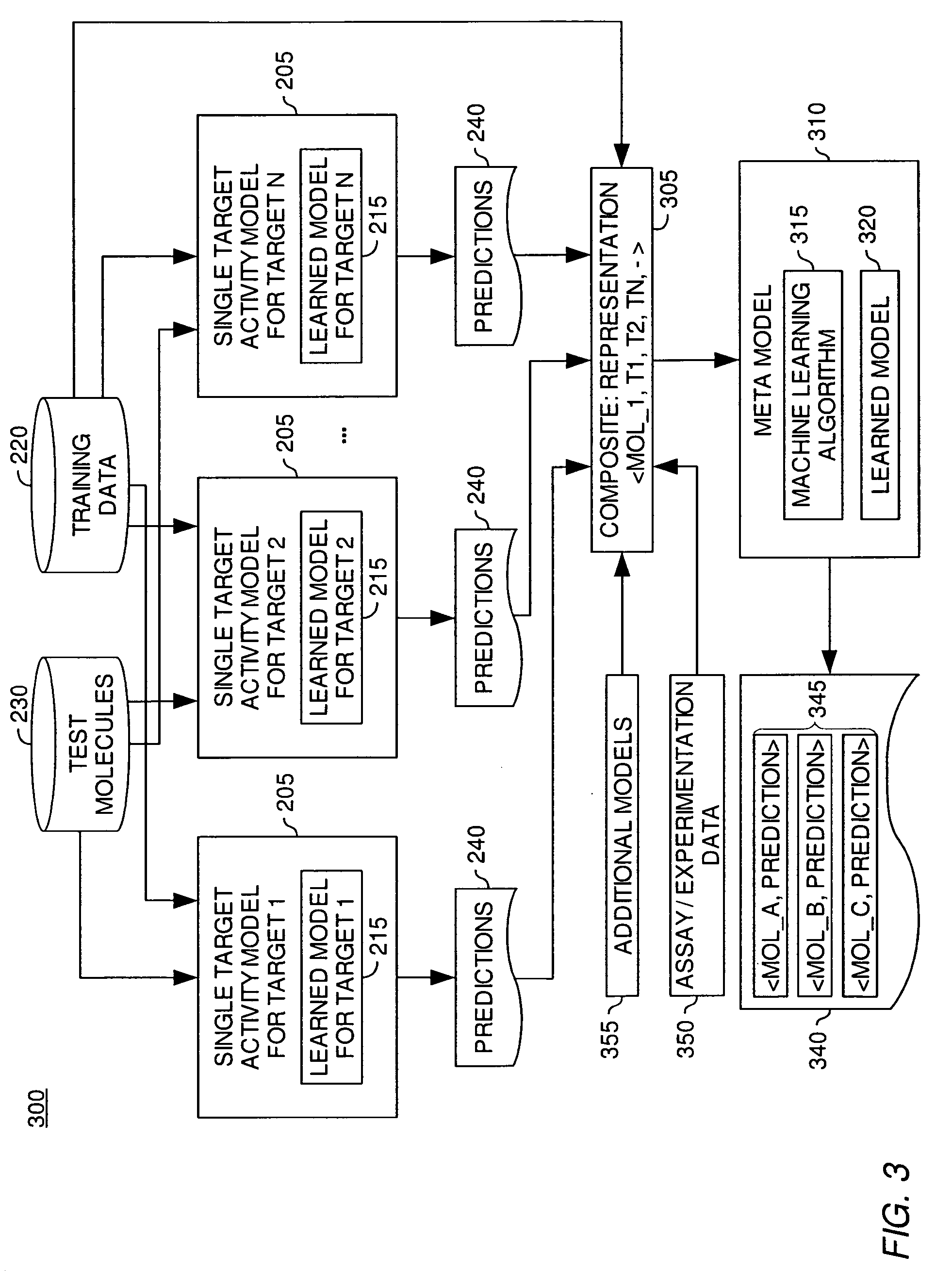
Modeling biological effects of molecules using molecular property models
ActiveUS20060161407A1Analogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsModel methodBiological property
Method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for modeling the biological effects of a molecule are disclosed. A machine learning application may be configured to process a set of training examples regarding a biological property of interest. Once trained, the machine learning application may be configured to generate a prediction regarding a property of interest for a test molecule. Embodiments of the invention provide a meta-model configured to generate a biological effect prediction for a molecule based on the predictions generated for the test molecule by a plurality of molecular property models.
Owner:VALO HEALTH INC
Modeling biological effects of molecules using molecular property models
ActiveUS7856321B2Analogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsModel methodBiological property
Owner:VALO HEALTH INC
Continuous biomolecule separation in a nanofilter
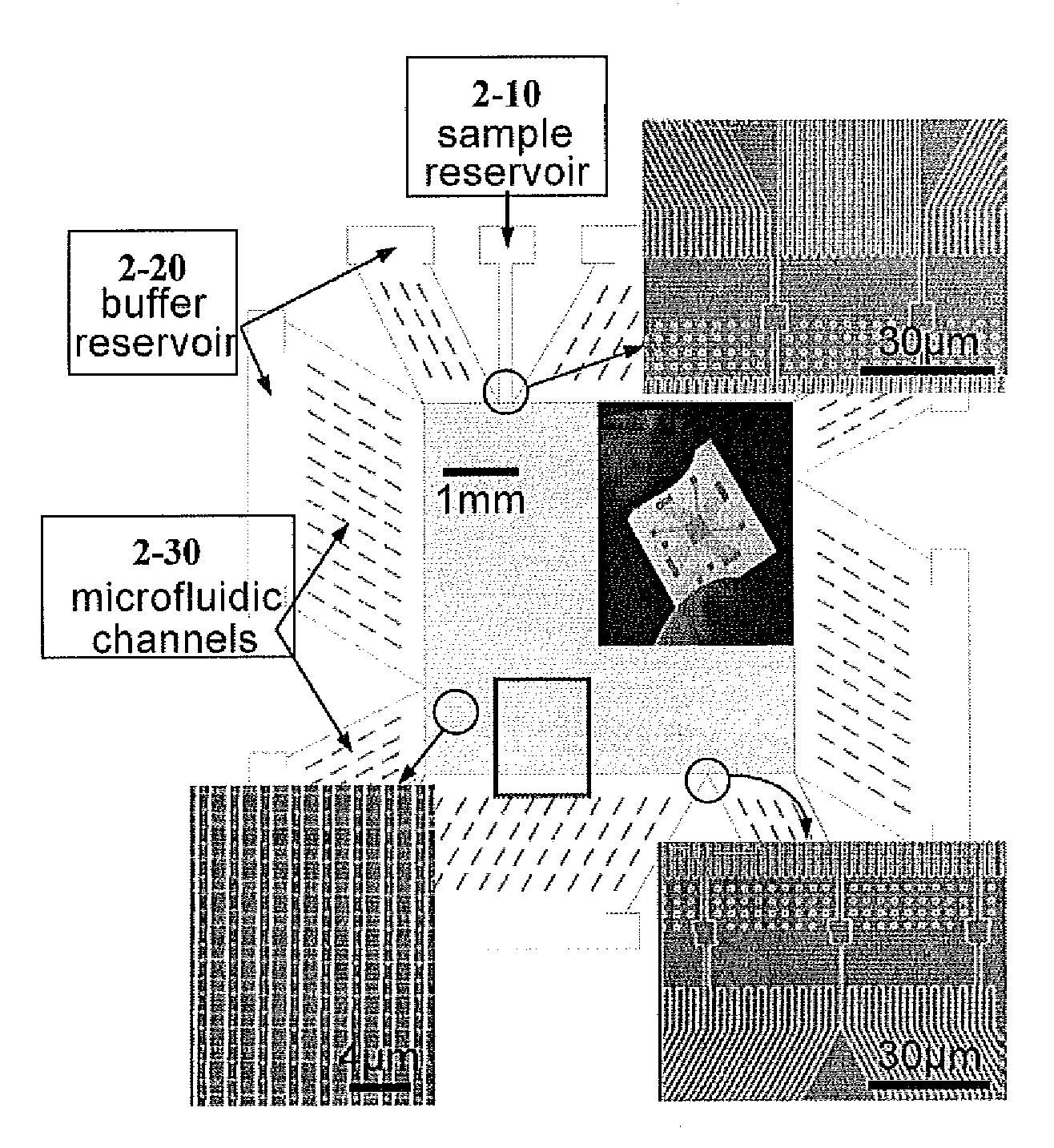
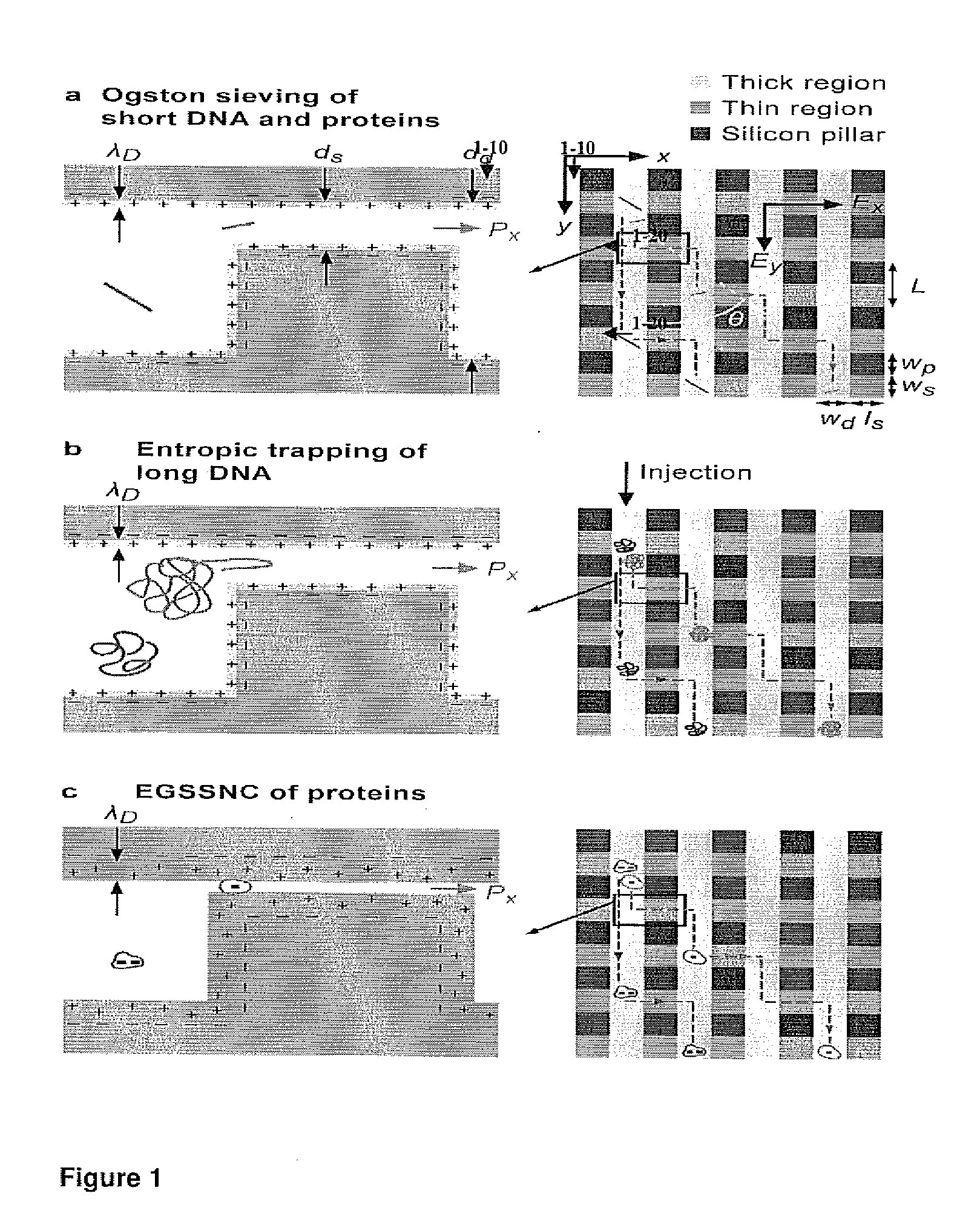
InactiveUS20110114486A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementContinuous flowElectrostatic interaction
This invention provides a method and an apparatus for quickly continuously fractionating biomolecules, such as DNAs, proteins and carbohydrates by taking advantage of differential bidirectional transport of biomolecules with varying physico-chemical characteristics, for example size, charge, hydrophobicity, or combinations thereof, through periodic arrays of microfabricated nanofilters. The passage of biomolecules through the nanofilter is a function of both steric and electrostatic interactions between charged macromolecules and charged nanofilter walls, Continuous-flow separation through the devices of this invention are applicable for molecules varying in terms of any molecular properties (e.g., size, charge density or hydrophobicity) that can lead to differential transport across the nanofilters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Novel coal mine foam dedusting agent
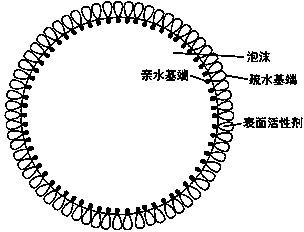
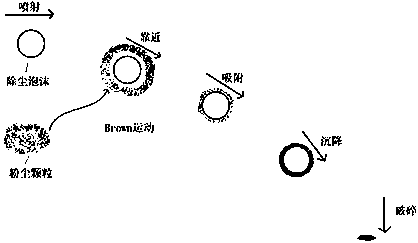
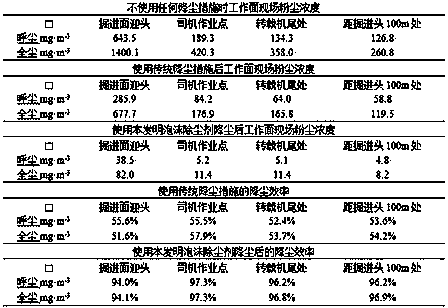
PendingCN108285774AGood water solubilityImprove downhole operating environmentOther chemical processesCelluloseFoaming agent
The invention discloses a novel coal mine foam dedusting agent. The agent is prepared from, by weight, 0.45-0.80% of foaming agent, 0.01-0.03% of foam stabilizer, 0.20-0.85% of wetting agent and 98.79-98.99% of water. Lauryl glucoside, polyanionic cellulose, alkylphenol polyoxyethylene ether and fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether glucoside are fully mixed with water, then the liquid mixture is put into a foam dedusting foamer for mining to generate foam, the foam is conveyed to a dust source to cover the dust source, correspondingly dust generated by the dust source is caught and sedimented,and finally, a great operation environment under a coal mine well is ensured. Hydrophobic groups (also named as lipophilic groups), adsorbed to a water source layer, of wetting agent molecules are thefirst ones in contact with coal dust and are composed of long organic carbon chains; the molecular property of the hydrophobic groups is similar to that of the surface of the coal dust, and comparedwith water molecules, the hydrophobic groups can achieve adsorption more easily, so that the dust catching efficiency of the foam is improved, the dustfall rate is increased to 97% or above, and the dustfall efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Electrical contacts for molecular electronic transistors
ActiveUS20050106804A1Highly cost-effectiveLarge storage capacityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectricityMolecular transistor
Electronic circuits based on molecular transistors, generally used in place of semiconductors. More particularly, the invention relates to a unique method of wiring of a three-terminal molecule (or an aggregate thereof) to serve as an electronic transistor, containing a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode. The source electrode and drain electrode are fabricated from one metal and the gate electrode is fabricated from another metal. The usage of molecular properties in this context provides significant advantages over the fabrication methods of the prior art.
Owner:AVIRAM ARI
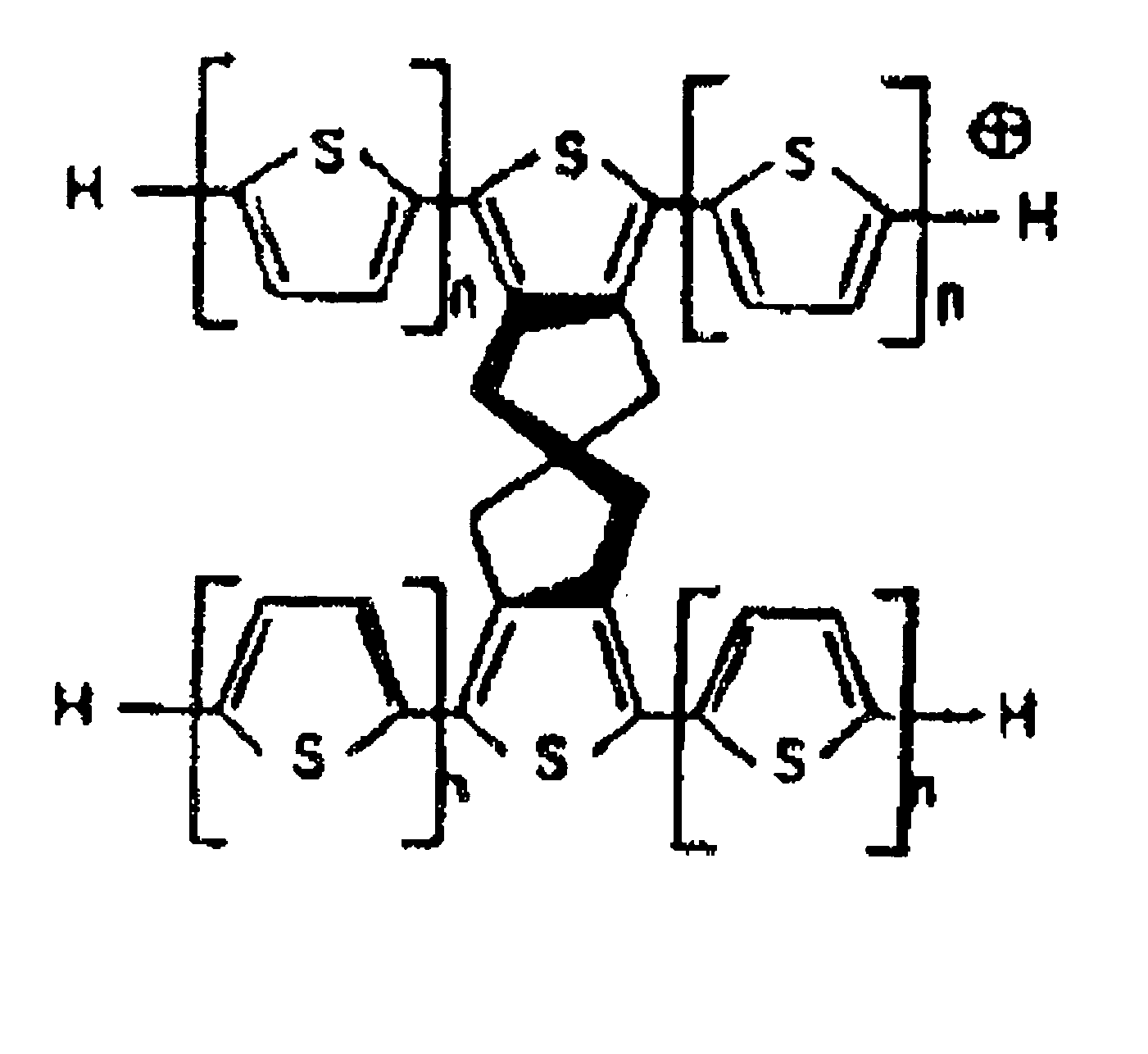
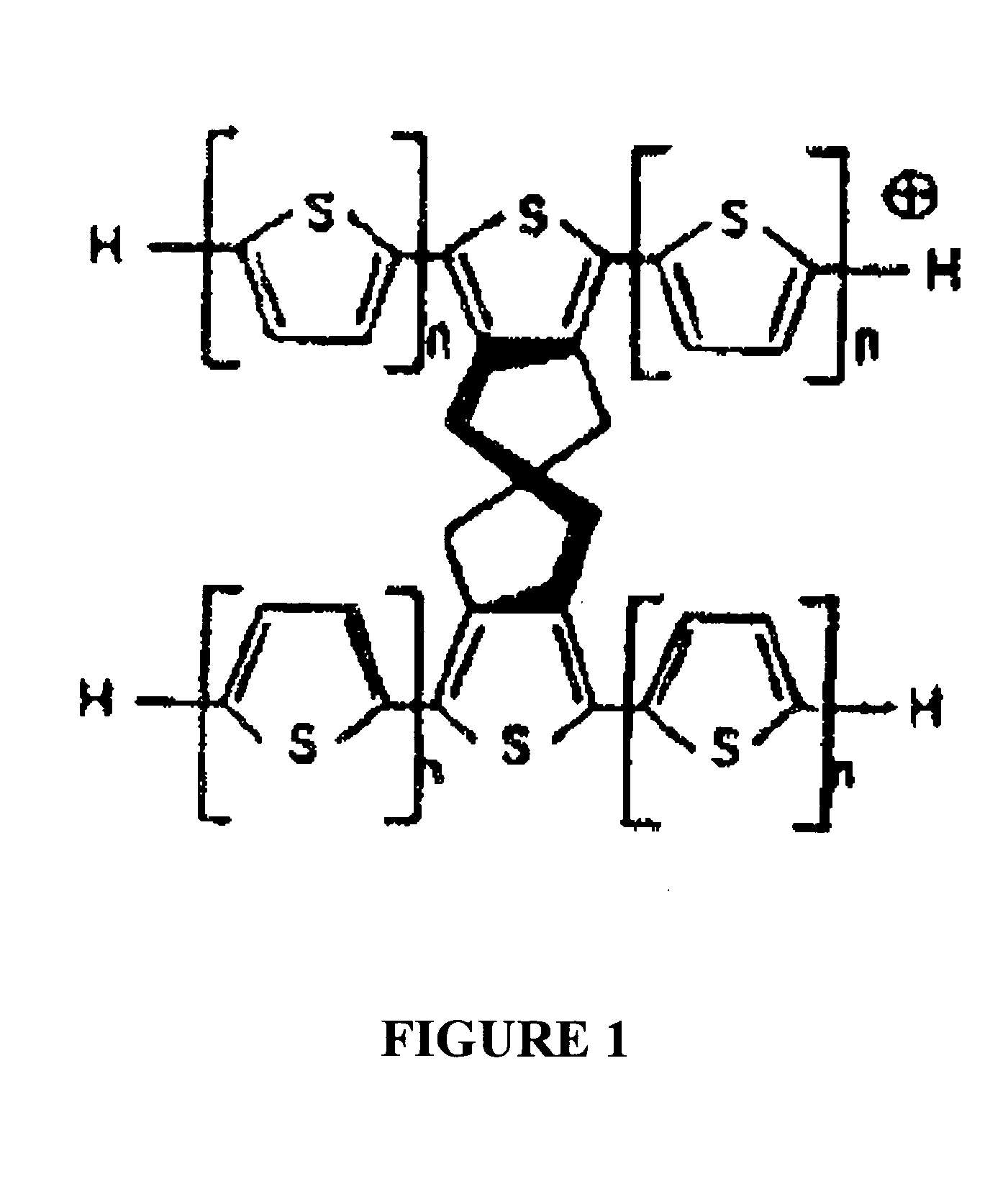
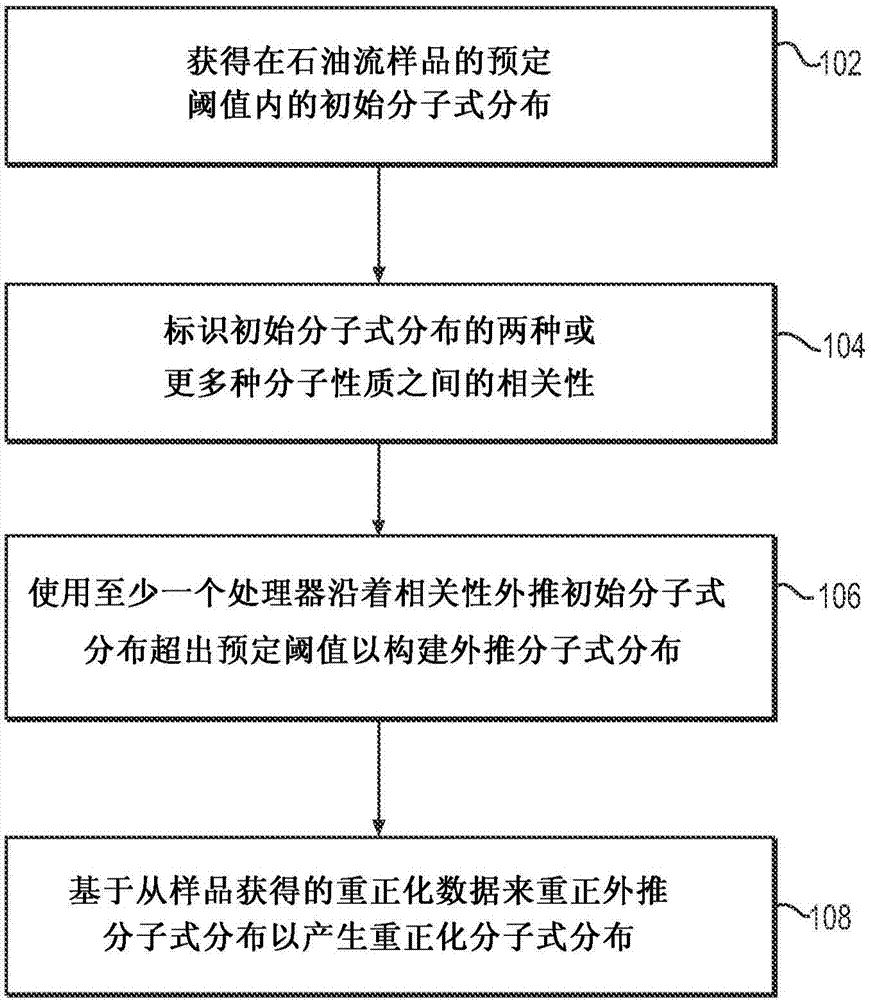
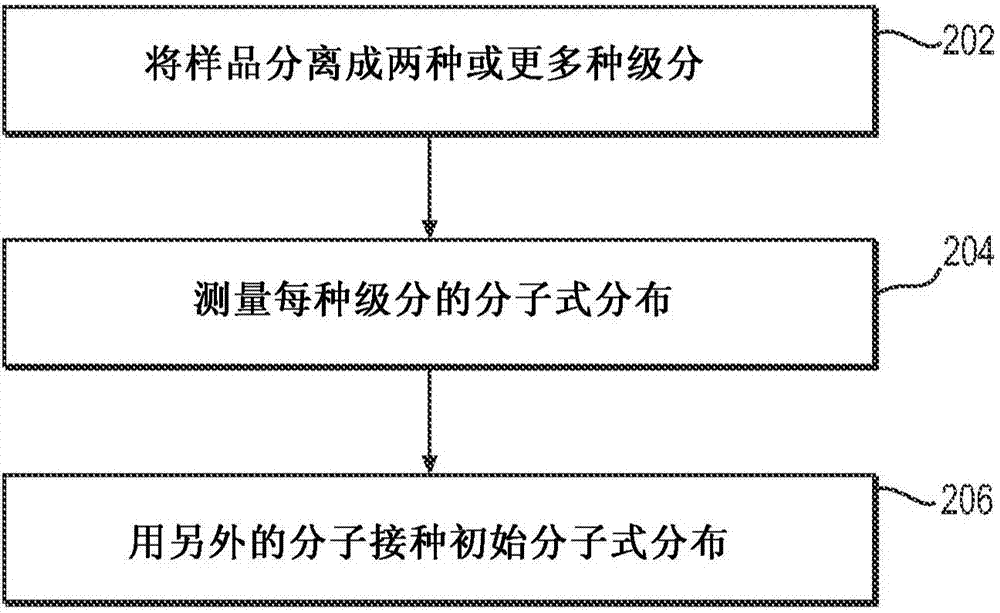
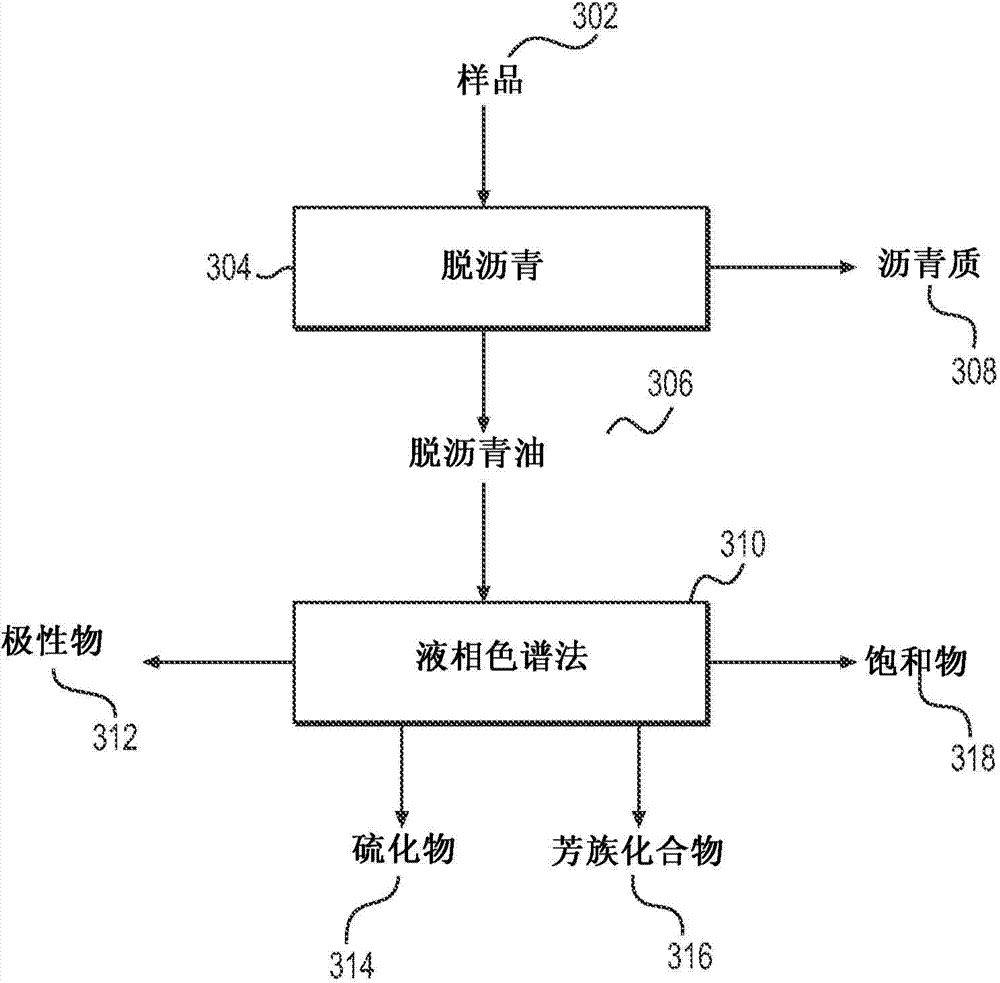
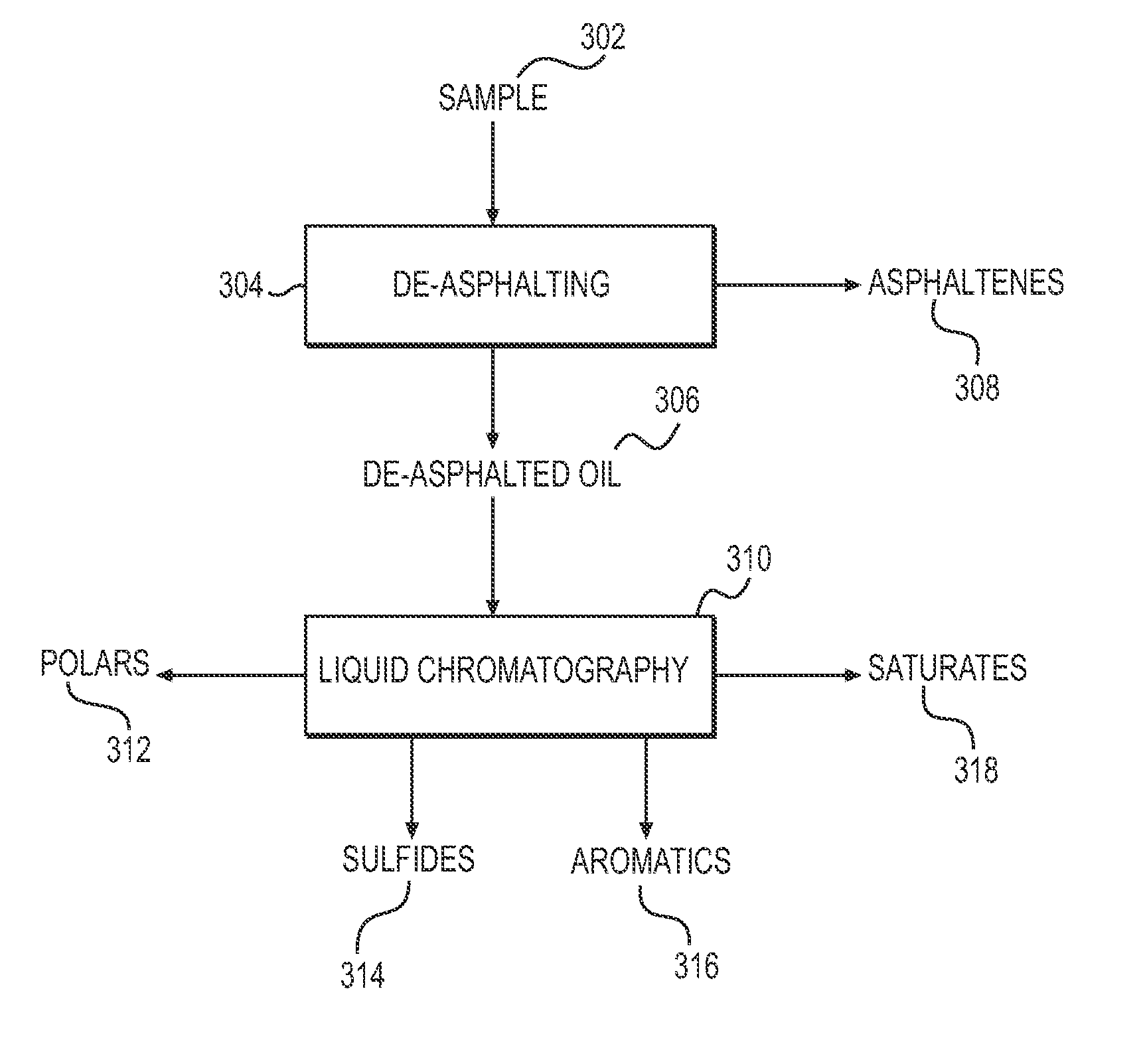
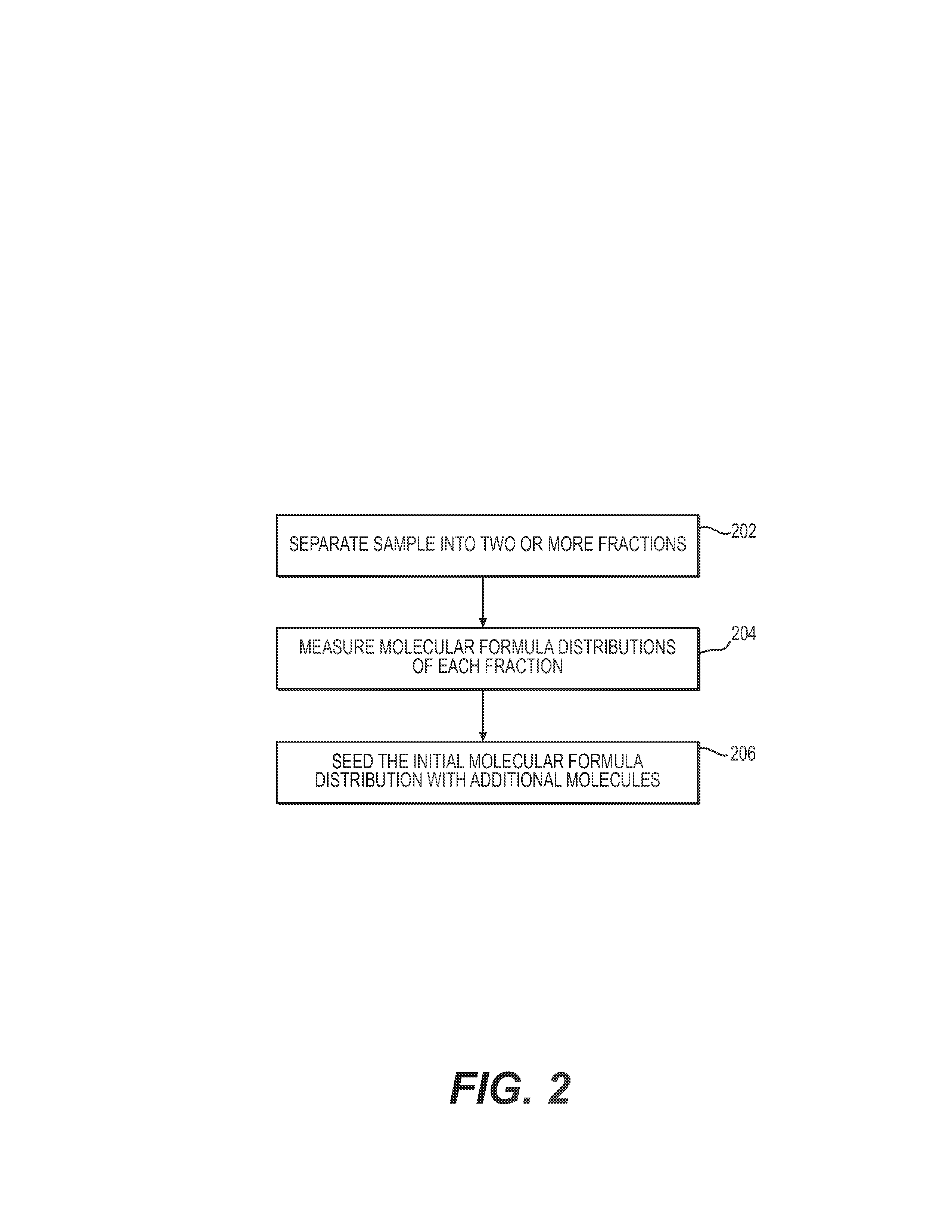
System and method to generate molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream
InactiveCN104335210AChemical property predictionMaterial testing goodsMolecular compositionRenormalization
Methods for generating molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream are disclosed. An initial molecular formula distribution within a predetermined threshold is obtained for a petroleum stream. A correlation between two or more molecular properties of the initial molecular formula distribution is identified, and the initial molecular formula distribution is extrapolated beyond the predetermined threshold along the correlation. The extrapolated molecular formula is renormalized based on renormalized based on renormalization data obtained from the sample. The renormalized molecular formula distribution can then be blended with the initial molecular formula distribution, reconciled to secondary analytical measurements, and / or used to create a model of composition and / or a molecular composition-based model of a resid upgrading process. Systems for implementing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Dust settling agent for coal mine and using method thereof
InactiveCN101979834AReduce water consumptionReduce surface tensionOther chemical processesDust removalBetaineCarbon chain
The invention discloses a dust settling agent for a coal mine and a using method thereof. 0.04 to 0.06 weight percent of octylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, 0.04 to 0.06 percent of dodecyl betaine, 99.547 to 99.91 percent of water and 0.111 to 0.333 percent of calcium chloride are mixed fully; and the mixture is pressed into a spraying and dust settling system on the working surface of the coal mine for spraying. The octylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, the dodecyl betaine, the water and the calcium chloride are mixed fully, both the octylphenol polyoxyethylene ether and the dodecyl betaine are surface active substances of which each molecule consists of a hydrophilic group and a hydrophobic group, and the hydrophobic group generally consists of a longer organic carbon chain, has a surface molecular property similar to that of coal dust and is easier to adsorb than moisture, so that the dust catching efficiency of water is improved, dust settling efficiency is over 90 percent and dust settling water consumption is saved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
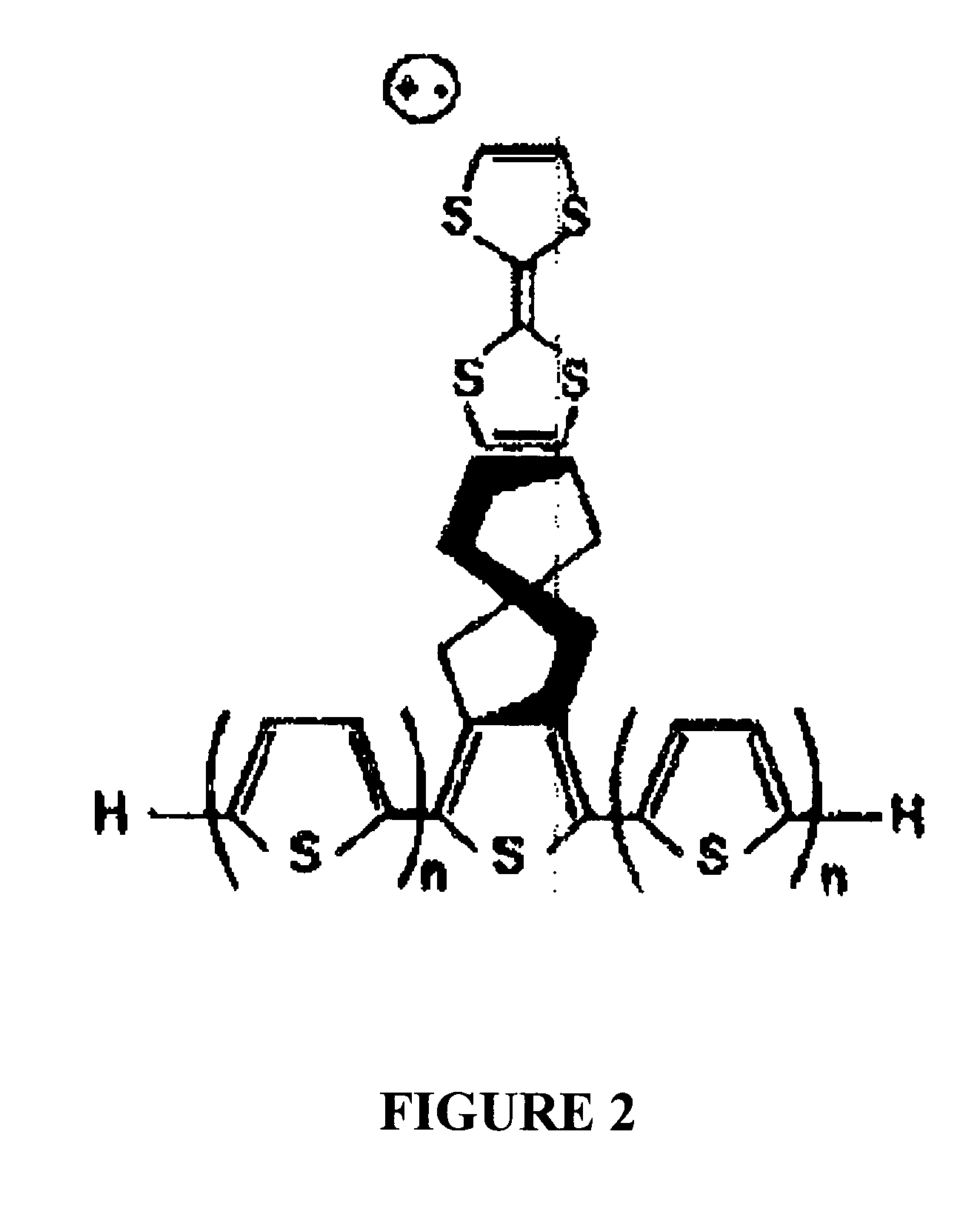
System and method to generate moledular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream
ActiveUS20130325418A1Chemical property predictionComputation using non-denominational number representationMolecular compositionRenormalization
Methods for generating molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream are disclosed. An initial molecular formula distribution within a predetermined threshold is obtained for a petroleum stream. A correlation between two or more molecular properties of the initial molecular formula distribution is identified, and the initial molecular formula distribution is extrapolated beyond the predetermined threshold along the correlation. The extrapolated molecular formula is renormalized based on renormalized based on renormalization data obtained from the sample. The renormalized molecular formula distribution can then be blended with the initial molecular formula distribution, reconciled to secondary analytical measurements, and / or used to create a model of composition and / or a molecular composition-based model of a resid upgrading process. Systems for implementing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Hyperbranched polysiloxane and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a phosphaphenanthrene structure and vinyl containing-hyperbranched polysiloxane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of evenly mixing distilled water with vinyl-containing trialkoxysilane, dropwise adding catalyst slowly under the stirring condition, and increasing temperature to 50-60 DEG C, thus obtaining vinyl-containing hyperbranched polysiloxane; and mixing the vinyl-containing hyperbranched polysiloxane with 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide, adding initiator and alcohol solvent, increasing temperature to 95-100 DEG C, and carrying out purification, filtering, reduced pressure distillation and vacuum drying after reaction is finished, thus obtaining phosphaphenanthrene structure and vinyl containing-hyperbranched polysiloxane. The phosphaphenanthrene structure and vinyl containing-hyperbranched polysiloxane integrates molecular properties of hyperbranched polysiloxane, 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide and vinyl, thus having wide application prospects on polymer modification aspect. The preparation method adopted has the advantages of wide applicability and simple operation process.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Direct adsorption scintillation assay for measuring enzyme activity and assaying biochemical processes
InactiveUS6977141B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAssay
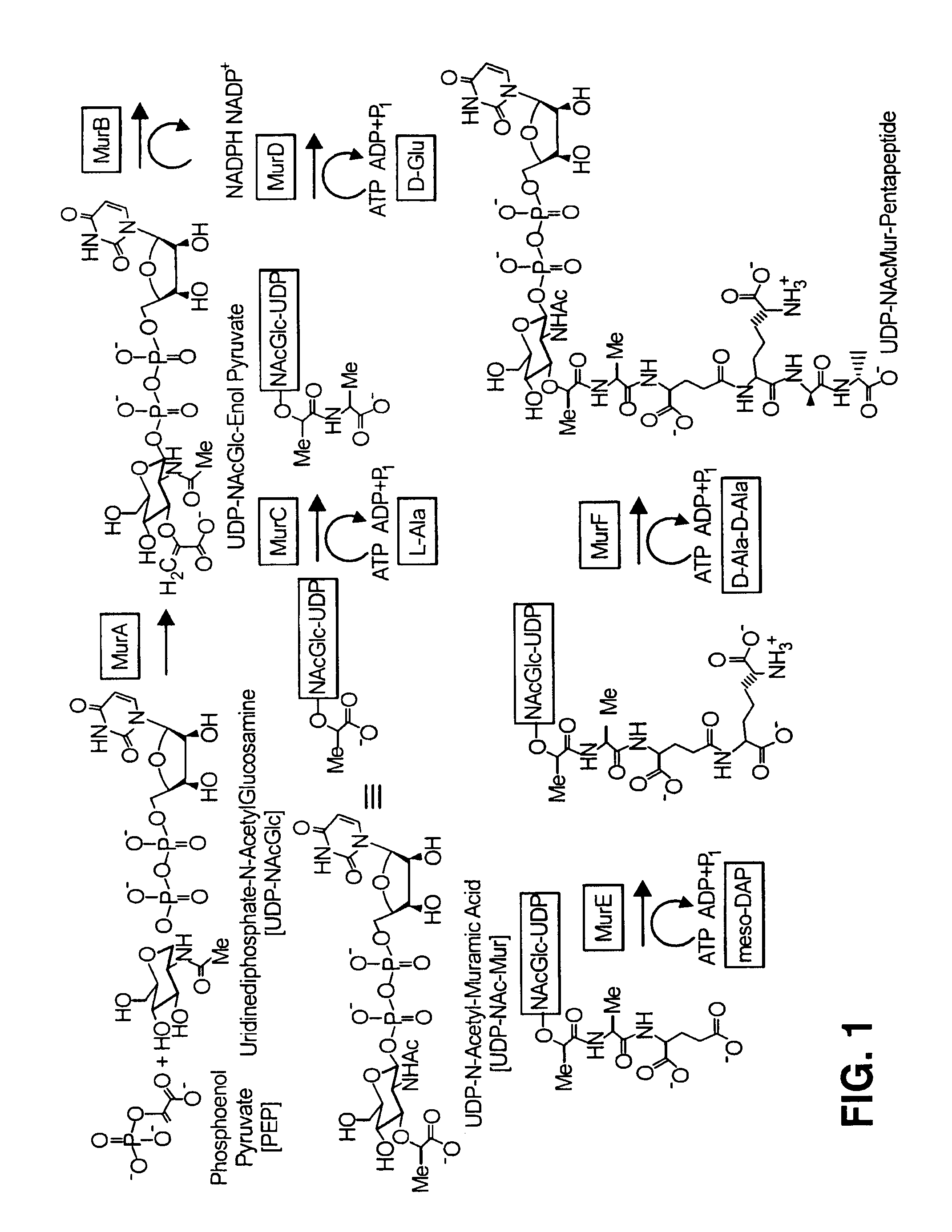
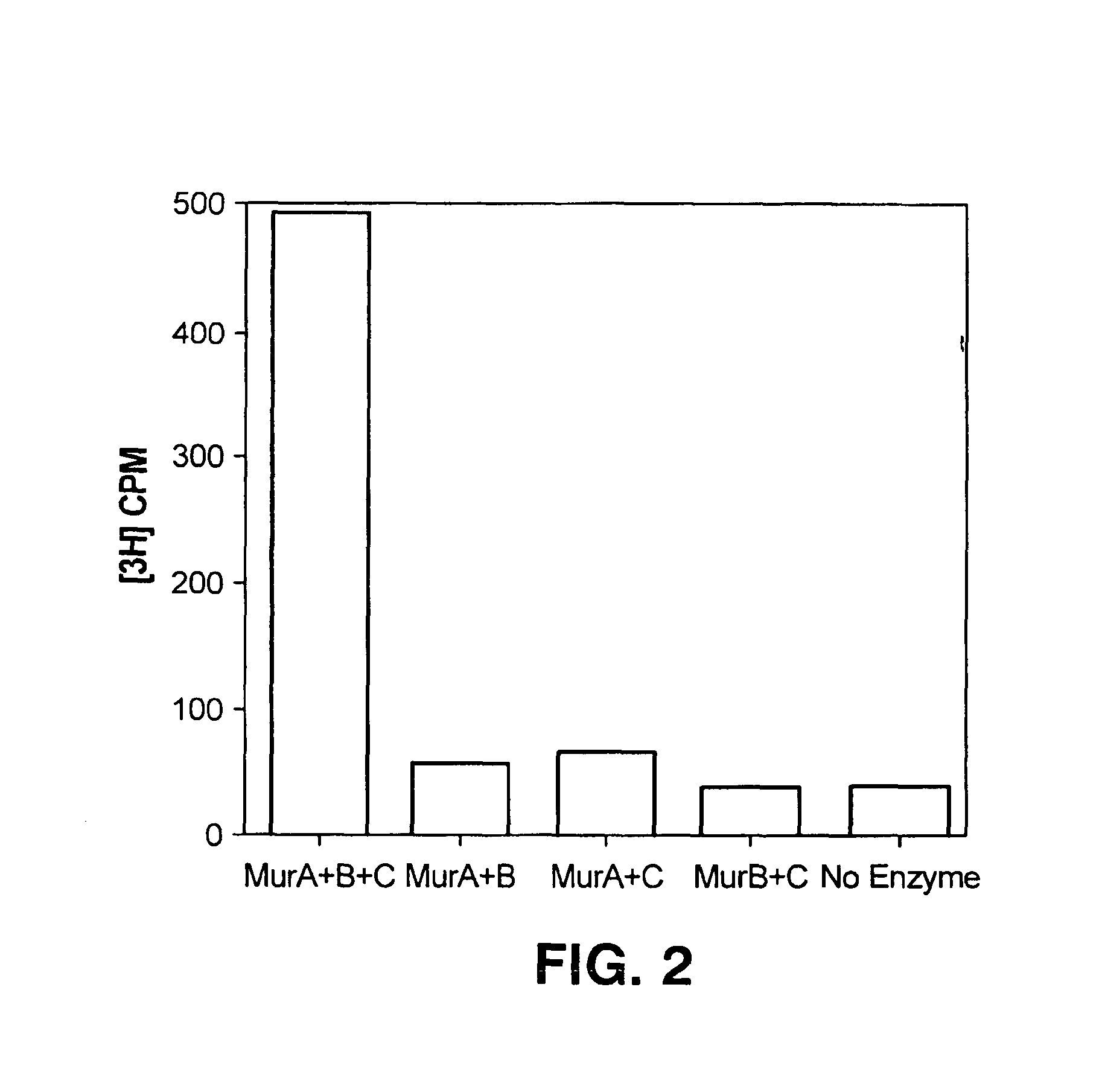
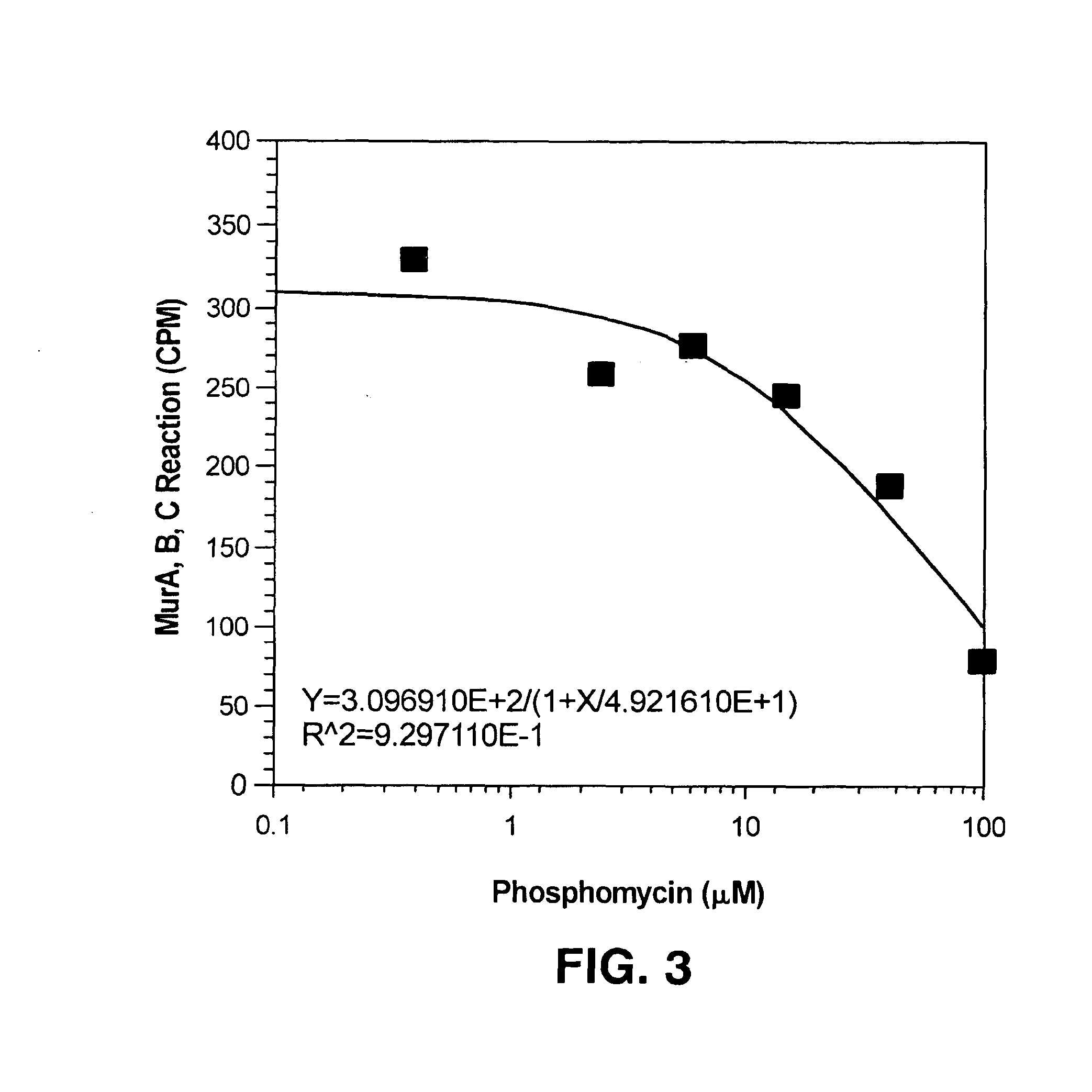
Methods and materials for scintillation assays are disclosed. The scintillation assays rely on differences in general molecular property-based binding interactions, such as charge or hydrophobicity, to localize a radioactive substance near a scintillating material, stimulating scintillation. They are thus described as a direct adsorption scintillation assay (DASA) to distinguish them from the scintillation proximity assay (SPA). The assays are more convenient and inexpensive to implement than SPAs, which rely on specific binding of ligand-receptor pairs, antibody-antigen pairs, or other binding partners which rely on the precise and specific structural complementarity of the partners. The assays can be employed for studying enzymatic reactions, such as those involved in the synthesis of Mur-pentapeptide. The assays are readily adaptable to high throughput screening for use in conjunction with combinatorial libraries of compounds.
Owner:VICURON PHARM INC
Methods for measuring the distribution, metabolism and clearance of traceable small molecule compounds in the brain
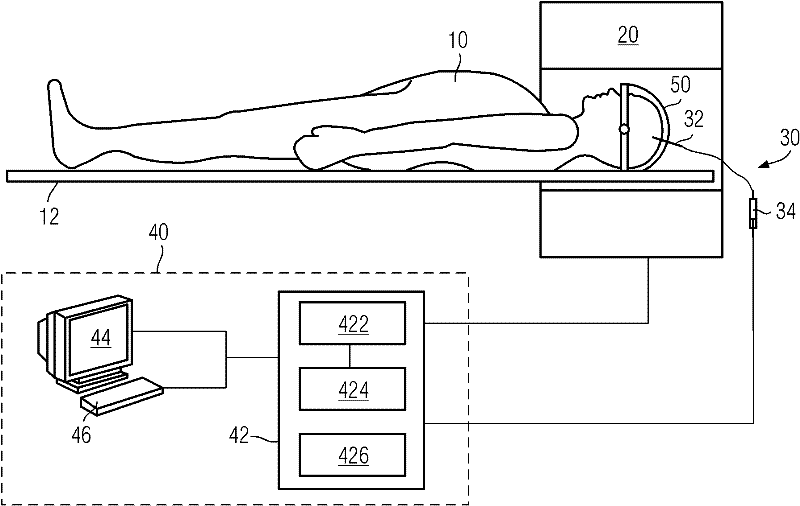
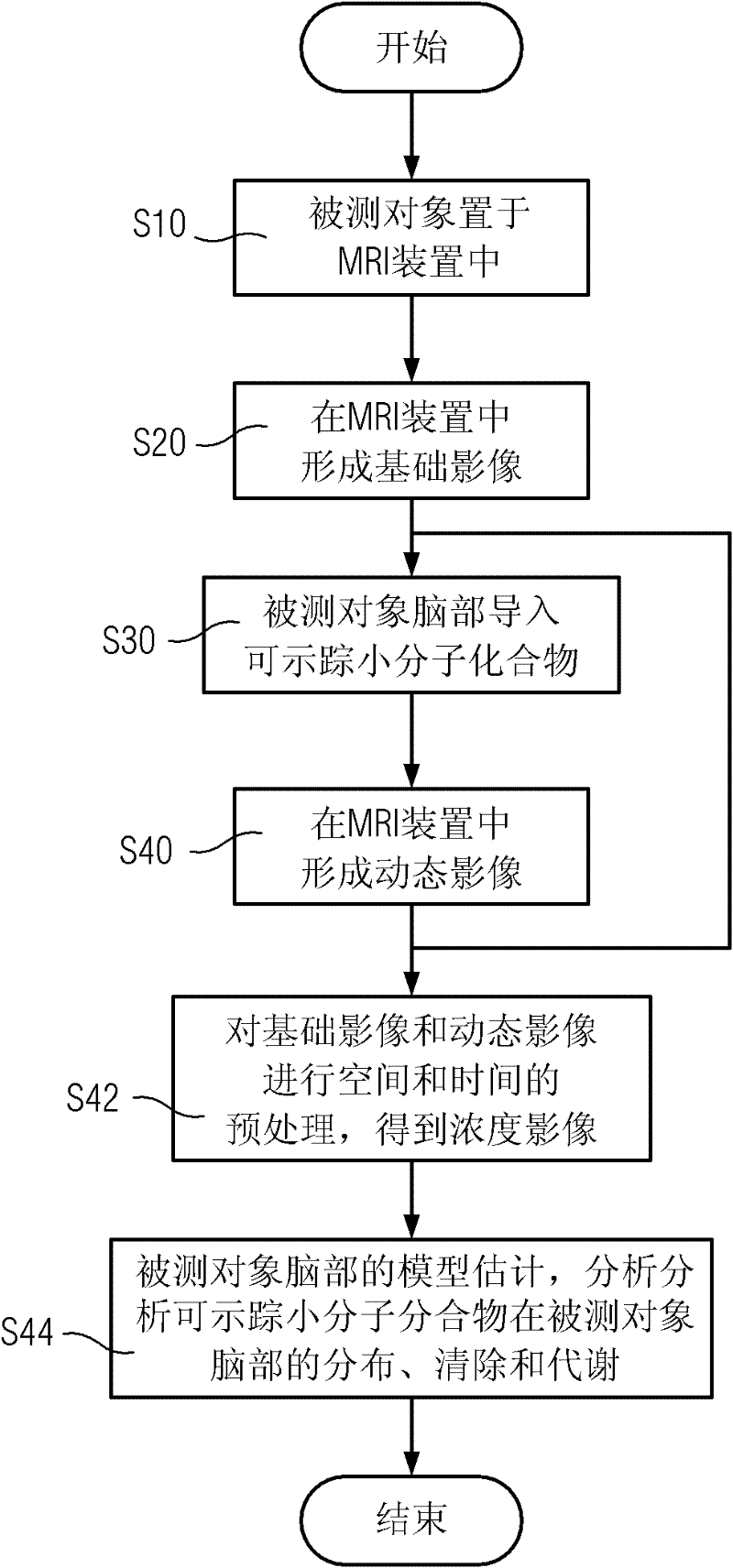
InactiveCN102293634AThe calculation method is accurateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTissue fluidMolecular property
The invention provides a method for measuring the distribution, metabolism and clearance of traceable small molecule compounds in the brain, the method comprising: placing the brain of the subject under test in an imaging device; using the imaging device to form the basis of the brain of the subject under test Imaging; introduce the compound into the interstitial fluid of the brain of the subject; use the imaging device to form a dynamic image of the brain of the subject; perform temporal and spatial preprocessing on the dynamic image and the basic image to obtain the net concentration image of the compound in the brain; Model estimation and analysis are performed on the net concentration images to obtain information on the distribution, metabolism and clearance process of compounds in the brain after they diffuse in the interstitial fluid of the brain. The present invention introduces a traceable small molecule compound of a corresponding size, dynamically displays and quantitatively measures the process of distribution, metabolism and clearance of the molecule and small molecules with similar molecular weight and properties in the brain through the brain tissue fluid in the living body.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Ion mobility based separation methods and apparatus
ActiveUS8063361B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotope separationProduct gasSpectrometer
The present invention describes separating components in a sample in an ion mobility based spectrometer using at least one matching property of the components other than the molecular properties in conventional ion mobility measurements in noble drift gases to enhance separation and resolution of the sample. Separation based on the matching property is realized by altering the drift media of the IMS. Besides altering drift media, energy level of ions and / or drift media are also controlled during the separation process. This invention describes an ion mobility apparatus wherein an energy source is added to the IMS that provides additional energy to the ions and / or drift media and tuning methods that involve selecting drift media and optimizing the energy level in order to achieve optimal performance.
Owner:EXCELLIMS CORP
Method for predicting enzyme-catalyzed reactions
InactiveUS8401797B2Chemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designSupport vector machineMetabolite
The reactivity of given metabolites is assessed using selected empirical atomic properties in the potential reaction center. Metabolic reactions are represented as biotransformation rules. These rules are generalized from the patterns in reactions. These patterns are not unique to reactants but are widely distributed among metabolites. Using a metabolite database, potential substructures are identified in the metabolites for a given biotransformation. These substructures are divided into reactants or non-reactants, depending on whether they participate in the biotransformation or not. Each potential substructure is then modeled using descriptors of the topological and electronic properties of atoms in the potential reaction center; molecular properties can also be used. A Support Vector Machine (SVM) or classifier is trained to classify a potential reactant as a true or false reactant using these properties.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
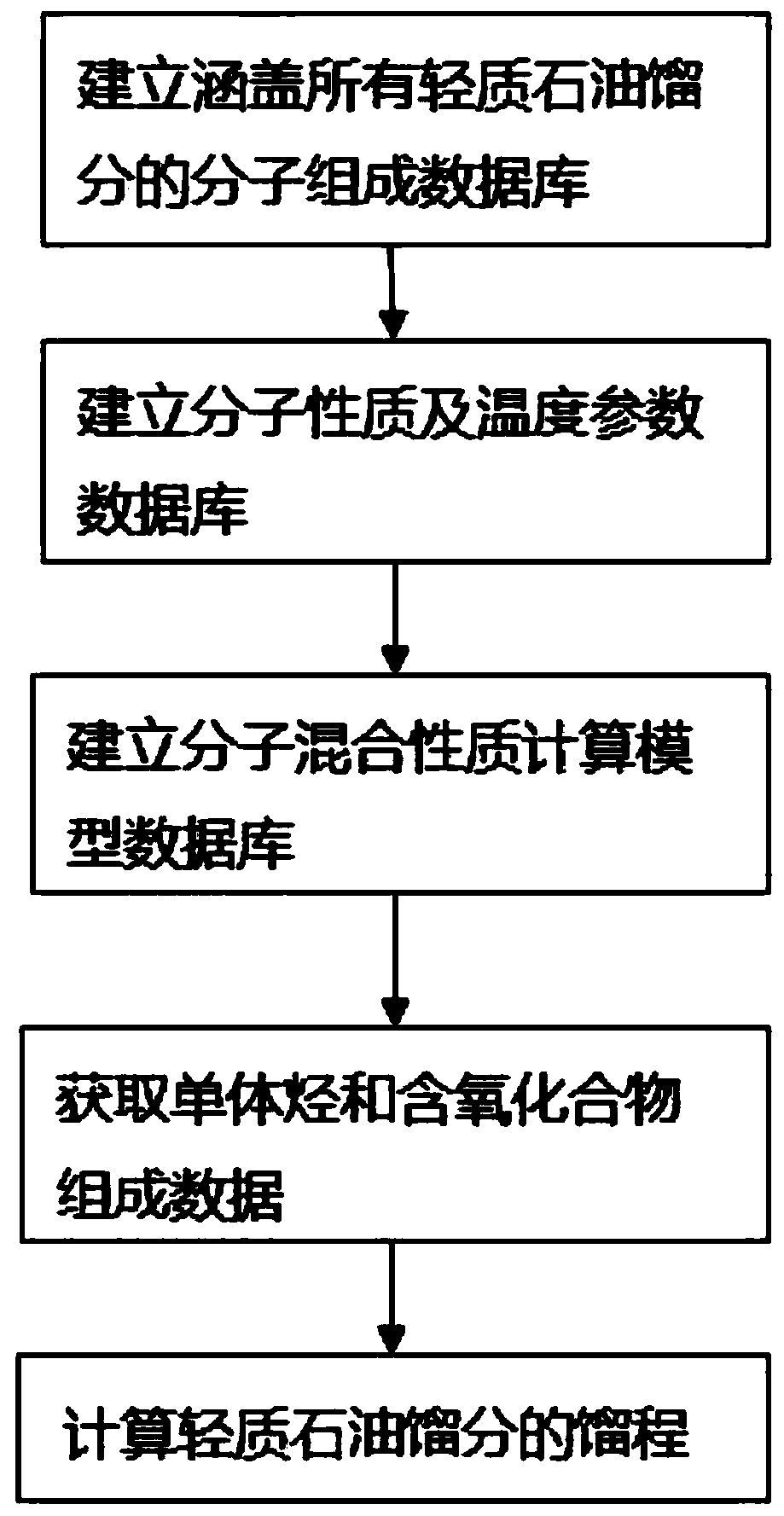
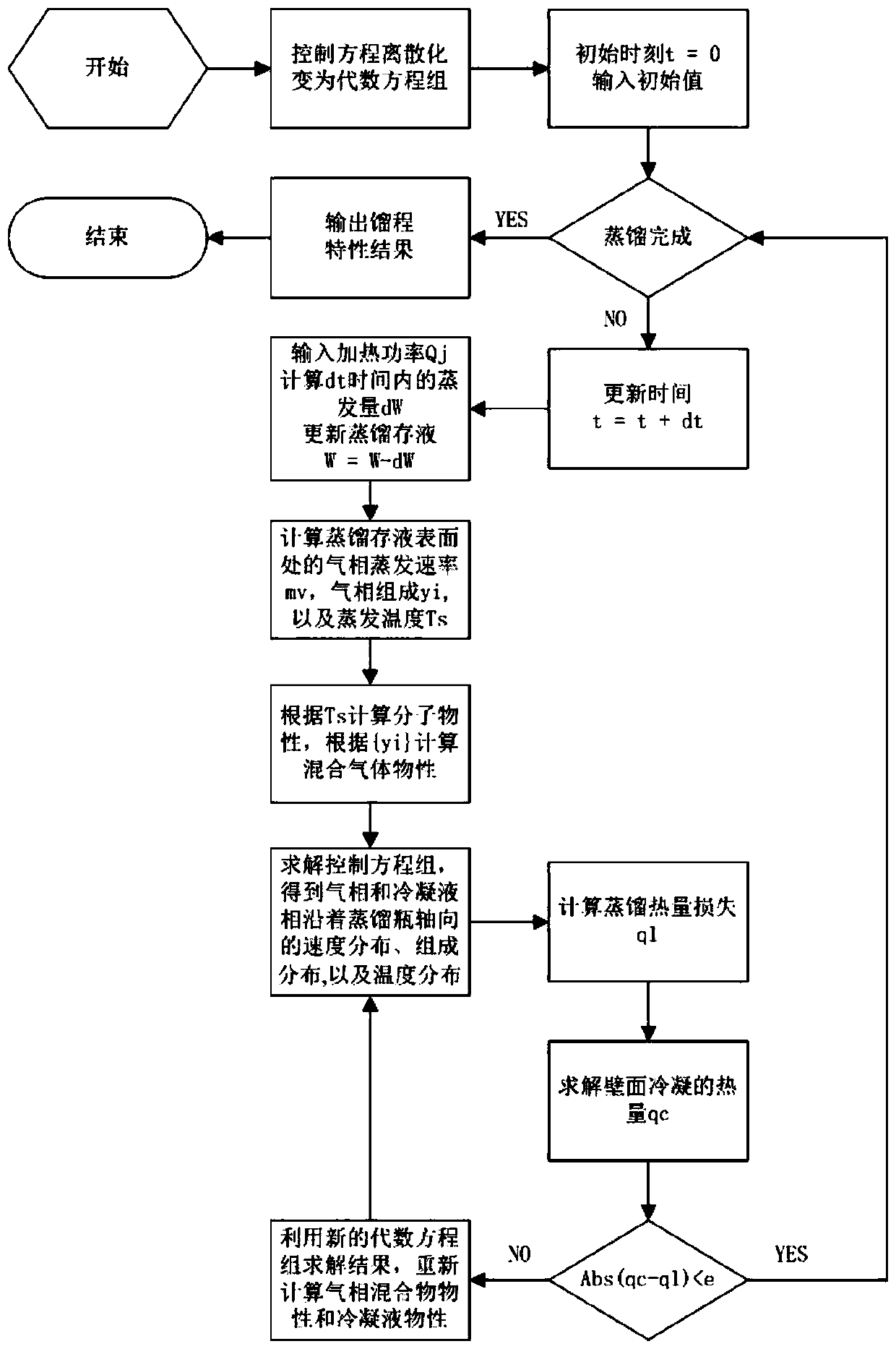
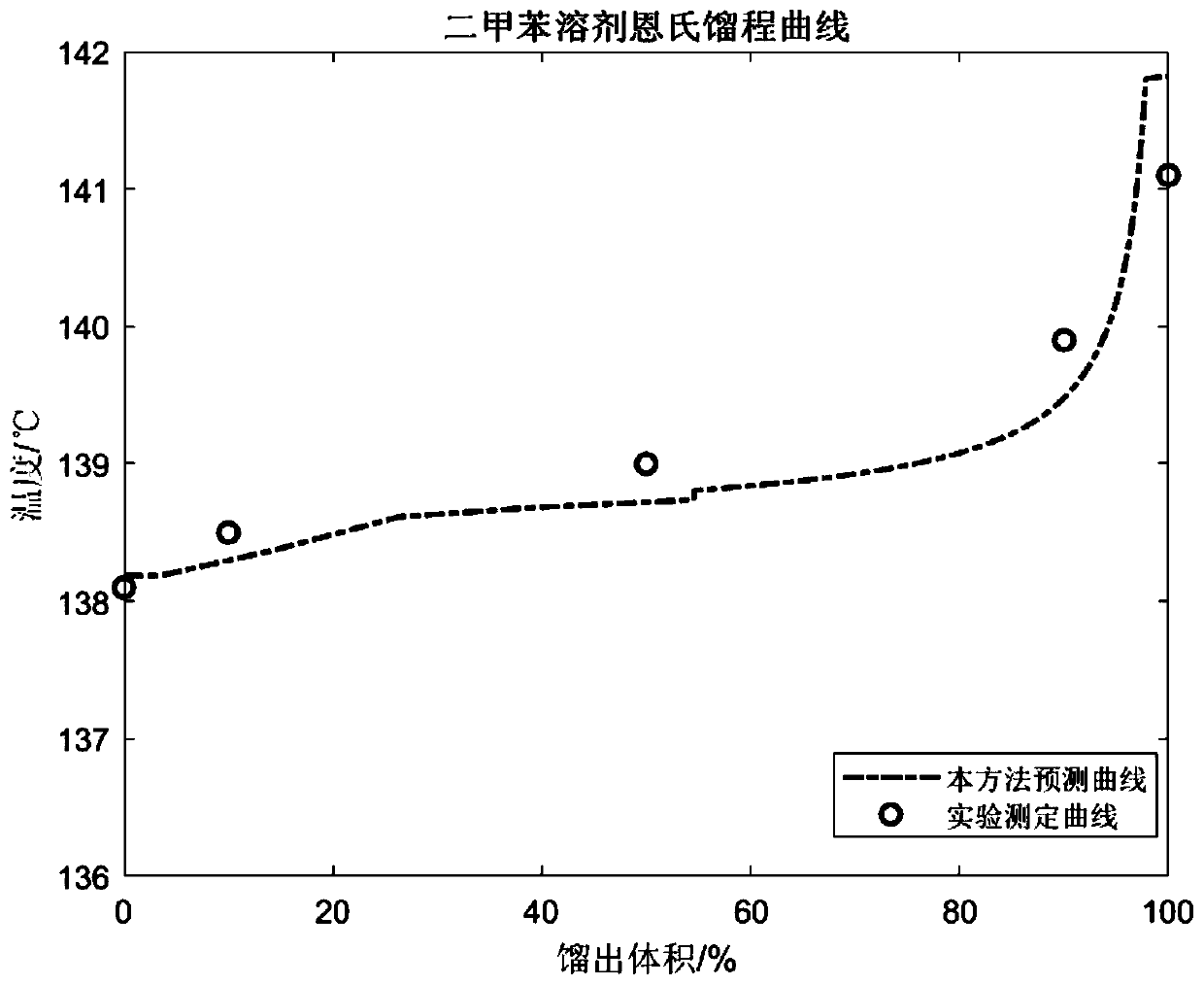
Method for calculating light petroleum fraction distillation range according to molecular composition
ActiveCN109839495AImprove versatilityImprove accuracyMaterial testing goodsMolecular compositionMathematical model
The invention relates to a method for calculating a light petroleum fraction distillation range according to a molecular composition. The method comprises the following steps of (1) converging molecular types of all light fractions in petroleum production, and establishing a molecular composition database covering light petroleum fractions and products; (2) establishing a molecular property and temperature parameter database based on the molecular composition database; (3) establishing a molecular hybrid property calculation model database based on the molecular composition database; (4) obtaining real monomer hydrocarbon of detected oil and oxygen-containing compound composition data, wherein the data can be obtained by laboratory analysis or by mathematical model prediction; and (5) based on the monomer hydrocarbon and an oxygen-containing compound obtained in the step (4), calculating and acquiring the distillation range of the light petroleum fraction. The method has good versatility and is suitable for distillation range calculation of the light petroleum fractions and the products and accuracy is high; and problems that an existing chromatographic simulation distillation andEngler distillation association conversion error is large and difficulty is large too are solved.
Owner:SYSPETRO TECH CO LTD
Method for determining average properties of molecules in solution by injection into a flowing solvent
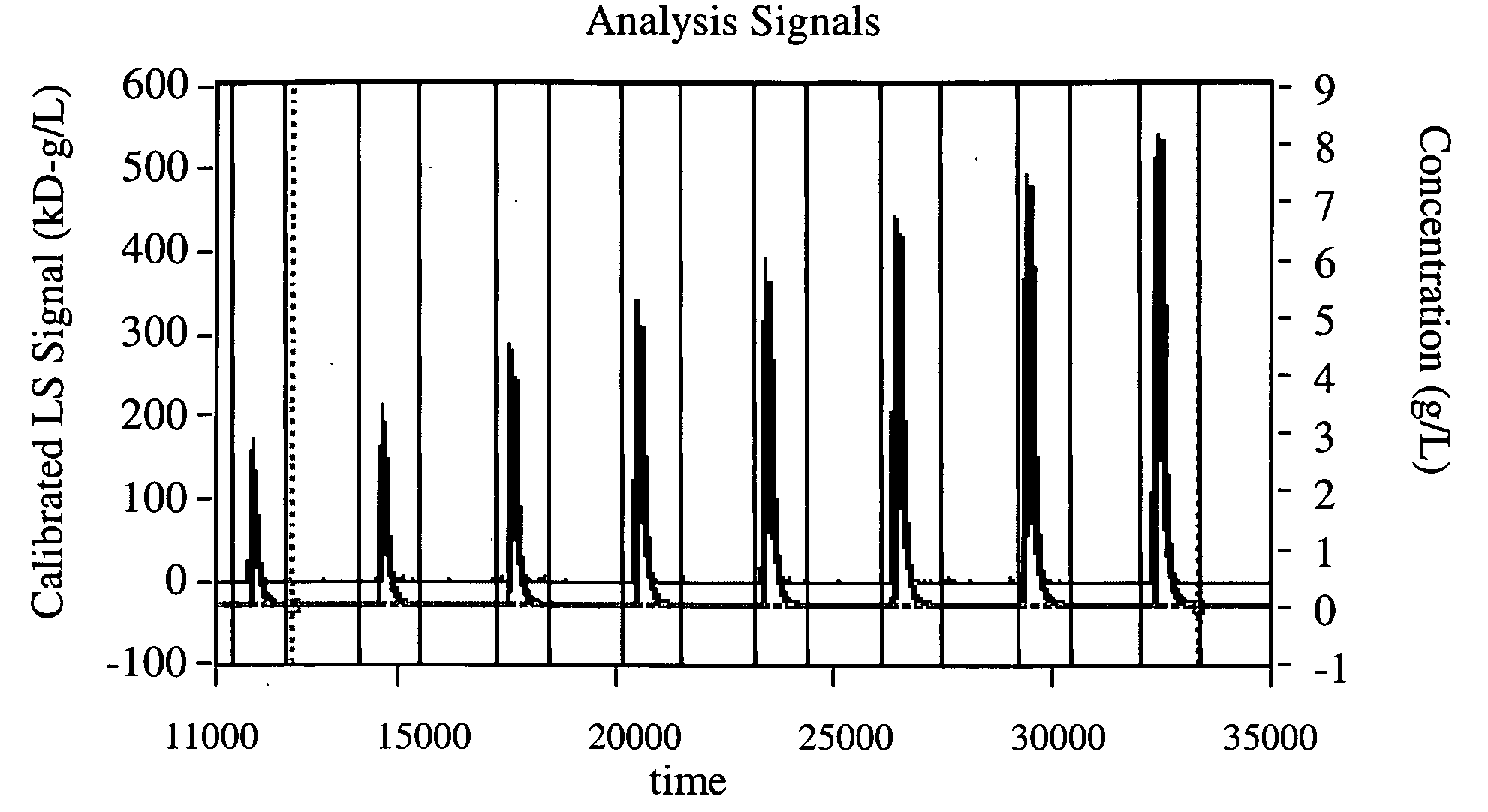
ActiveUS20090222219A1Improve automationImprove accuracyIon-exchange process apparatusAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMean squareSolvent
A new method is presented for measuring the molecular properties of an unfractionated solution of macromolecules. Sample aliquots spanning a range of concentrations are injected sequentially into a stream of solution and flow towards the detectors. Each aliquot produces, thereby, an effective “peak” whose elements correspond to different concentrations of the diluted aliquot. The weight averaged molar mass, the mean square radius, and the second virial coefficient of the macromolecules in solution are derived from an analysis of the angular and concentration dependence of the scattering signals throughout the corresponding peaks. In contrast to earlier on-line methods, better accuracy is achieved, while using a smaller quantity of sample. A similar method for determining cross virial coefficients between two distinct species of macromolecules is also presented.
Owner:WYATT TECH
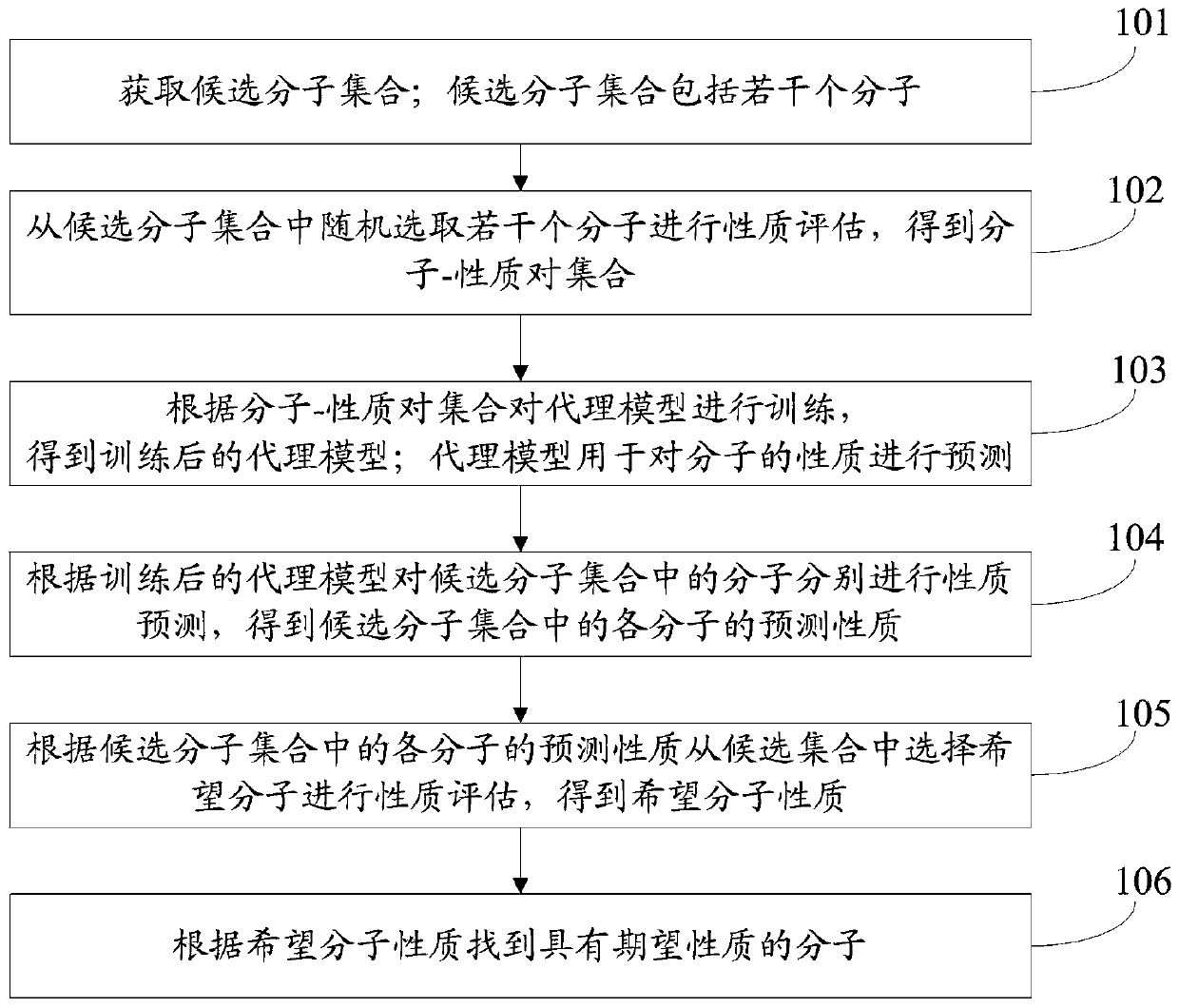
Molecule discovery method based on graph Bayesian optimization
ActiveCN111063398AReduce the number of evaluationsCutting costsComputational theoretical chemistryChemical machine learningData miningComputer science
The invention relates to a molecule discovery method based on graph Bayesian optimization. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a candidate molecule set; randomly selecting a plurality of molecules from the candidate molecule set for property evaluation to obtain a molecule-property pair set; training an agent model according to the molecule-property pair set to obtain a trained agent model; performing property prediction on molecules in the candidate molecule set according to the trained agent model, and selecting desired molecules from the candidate set to perform property evaluationto obtain desired molecule properties; and finding molecules having desired properties according to the desired molecular properties. According to the molecule discovery method based on graph Bayesianoptimization, the molecules in the candidate set are predicted, then the molecules are selected according to the prediction result for evaluation to obtain the actual properties of the molecules, themolecules are selected accordingly for evaluation, the evaluation frequency of the molecules is reduced, and thus the analysis and evaluation cost is reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for standardization of chemical and therapeutic values of foods and medicines using animated chromatographic fingerprinting
InactiveUS20110040486A1Quick identificationFacilitates chemical therapeutic standardizationComponent separationBiological testingDrug profilingChemical reaction
The present invention provides a method of standardization of chemical and therapeutic properties and quality of foods and medicines. The present invention provides a method of chromatographic finger printing facilitating correlation of traditional methods used for chemical and therapeutic standardization of medicines and humors in the living things with physico chemical properties of the medicines and their constituents. The method is used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the energy involved in the medicines and living things and to understand various bio chemical reactions in living things using an energy system. It provides a rational basis to understand the traditional methods of assessment of chemical and therapeutic qualities of materials used for the said purpose. The present invention also provides the influence, of factors like pH, temperature, viscosity and ionic nature of the media along with atomic and molecular properties indicating the chemical and therapeutic values of the foods and medicines of natural and synthetic nature. The analysis of biological samples like blood indicated the utility of the method for the assessment of clinical pathological conditions of healthy and diseased. This facilitates for a better drug discovery, drug monitoring, drug targeting and drug profiling using different features of 3-D animated energy box created after analyzing the sample by different analysis, separation and detection methods.
Owner:DADALA VIJAYA KUMAR +1
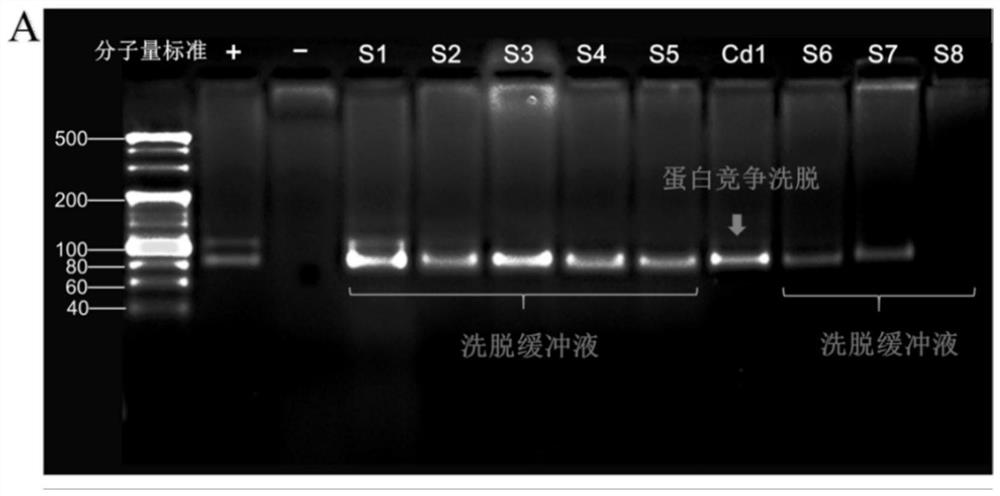
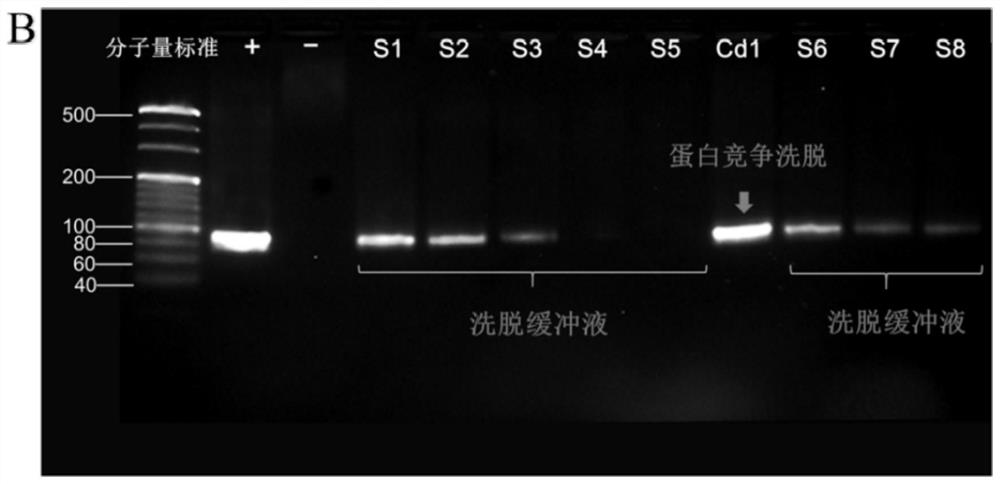
ssDNA aptamer capable of specifically identifying N-cadherin, and screening method and application of ssDNA aptamer
ActiveCN112143732AEasy to markShort screening cycleLibrary screeningBiological material analysisAptamerNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses an ssDNA aptamer capable of specifically identifying N-cadherin, and a screening method and application of the ssDNA aptamer. The aptamer has a nucleotide sequence disclosed byany one of SEQ ID No.1-8. Preferably, the nucleotide sequence of the aptamer is disclosed by SEQ ID No.6. The ssDNA aptamer disclosed by the invention can be subjected to in vitro screening, has a short screening period, can be conveniently synthesized, can easily mark various functional groups and reporter molecules, has stable properties and can be stored and utilized for a long time. The ssDNAaptamer disclosed by the invention is especially suitable for detecting N-cadherin protein.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com