ssDNA aptamer capable of specifically identifying N-cadherin, and screening method and application of ssDNA aptamer
A screening method and aptamer technology, applied in DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., to achieve the effects of easy labeling, convenient synthesis, and stable properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Screening of aptamers
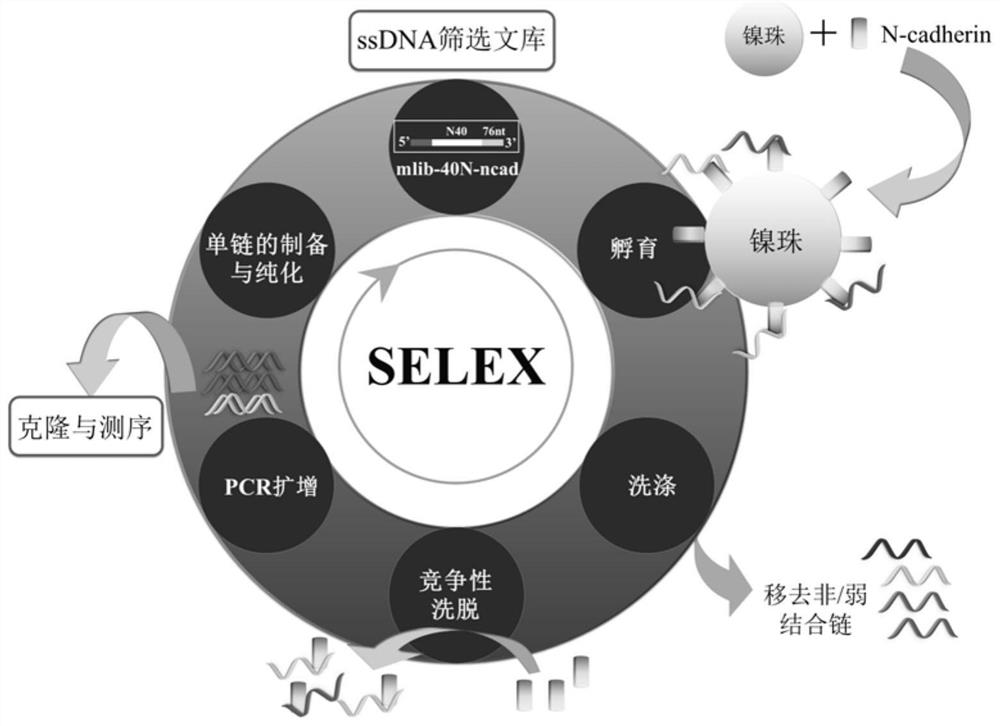
[0067] figure 1 The flow chart of using SELEX to screen an aptamer that can specifically recognize N-cadherin specifically includes the following steps:
[0068] (1) Protein immobilization: the N-cadherin protein is immobilized on the surface of nickel beads by using the specific combination between the His tag marked on the N-cadherin protein and the nickel ions on the agarose microbeads, and the hydrophilic beads filled with nickel beads are Wash the column three times to remove unbound N-cadherin protein, and react in Tris buffer (20mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4);
[0069] (2) Incubation for binding: Wash the nickel beads with the target N-cadherin and the ssDNA screening library in the screening buffer (20mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 5mM KCl, 2mM MgCl 2 ) for incubation and binding; during the incubation process, when ssDNA binds to the target, it will fold from the original single-stranded state into a three-dimensional space structur...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2: Cloning and sequencing
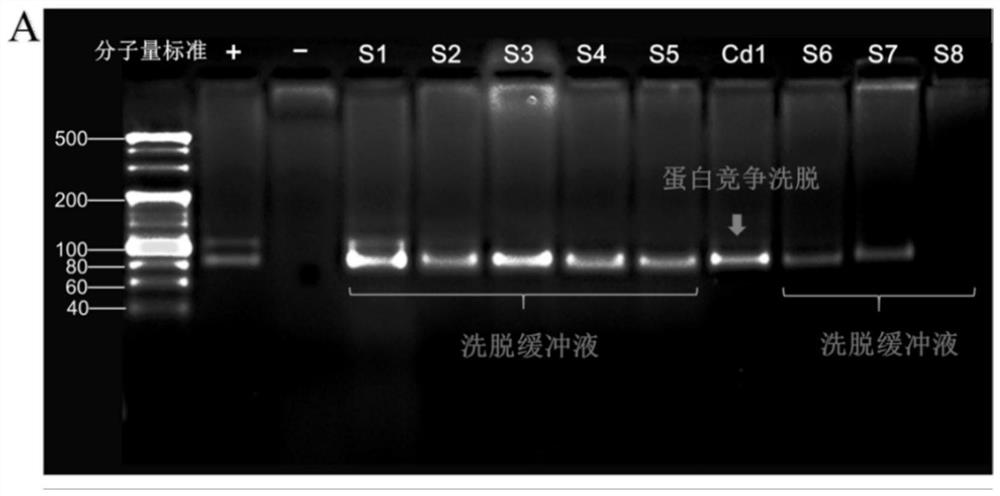
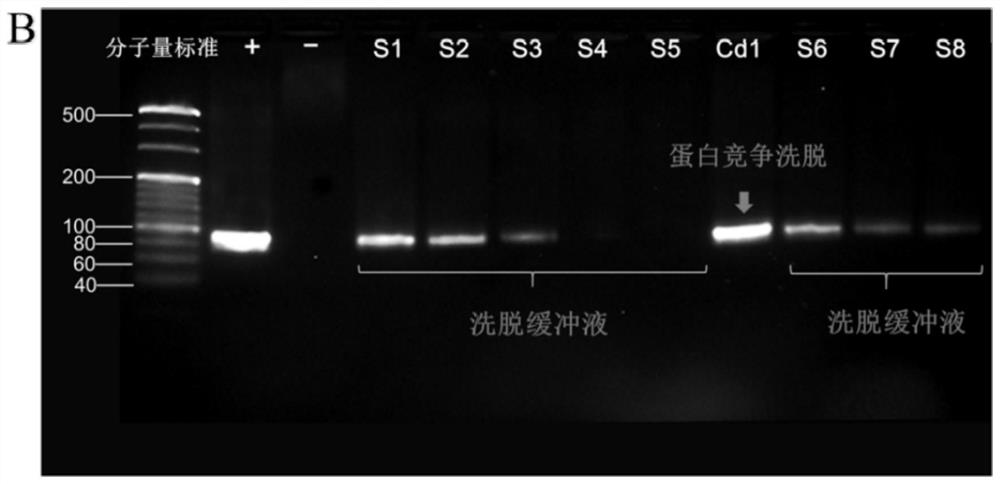
[0077]A total of 30 aptamer sequences were obtained by cloning and sequencing. Using DNAMAN, Clustal, Mega, Mfold and other software analysis, according to its primary structure, secondary structure, etc., it is divided into 5 families, and representative sequences are selected from these families, and a total of 5 candidate adaptations are selected The body was used for characteristic analysis, and the three sequences with strong fluorescence enhancement were truncated and optimized according to the ELISA results. The five full-length sequences were named Ncad1, Ncad2, Ncad3, Ncad4, and Ncad5, respectively, and the three shortened sequences were named Ncads1, Ncads2, and Ncads3, respectively. See Table 1 for detailed sequence information.
[0078] Table 1
[0079]
[0080]
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3: binding ability analysis
[0082] The above 8 candidate aptamers were synthesized, their 5' ends were labeled with fluorescein FAM, diluted with sterilized water to prepare a 2 μM solution, and stored at -20°C for use. The DNA solution was denatured at 95°C for 5 minutes before use, and immediately cooled at 0°C for 10 minutes. The binding capacity determination steps are as follows;
[0083] First, 100 μL of 30 nM N-cadherin solution was coated on a Nunc 96-well enzyme-linked plate, and coated overnight at 4 ° C. The coating solution was carbonate buffer (0.05mol / L Na 2 CO 3 / NaHCO 3 , pH 9.6), and set blank control wells at the same time; wash the plate, add 3% BSA solution to block at 25°C for 2h; wash the plate, 30μL 2μM fluorescein FAM-labeled DNA sequence was combined at 25°C for 90min, blank group Binding buffer (50mM Tris-HCl, 5mM KCl, 100mM NaCl, 1mMMgCl 2 , pH 7.4) instead of the aptamer and incubated at 25°C for 90 min. Wash the plate, add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com