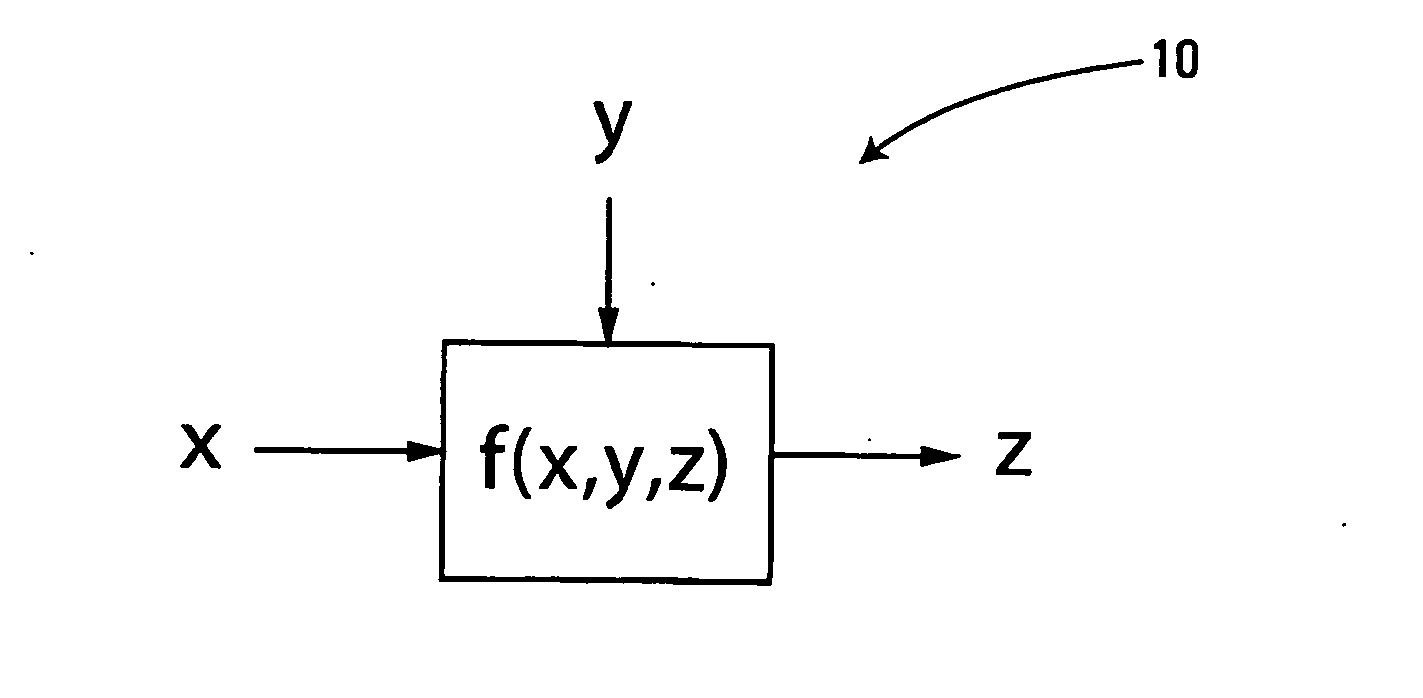Patents
Literature
47 results about "Renormalization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Renormalization is a collection of techniques in quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, that are used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities by altering values of quantities to compensate for effects of their self-interactions. But even if it were the case that no infinities arose in loop diagrams in quantum field theory, it could be shown that renormalization of mass and fields appearing in the original Lagrangian is necessary.
Evaluating and optimizing error-correcting codes using a renormalization group transformation
InactiveUS6857097B2Improve performanceCorrect operation testingOther decoding techniquesRenormalizationParity-check matrix
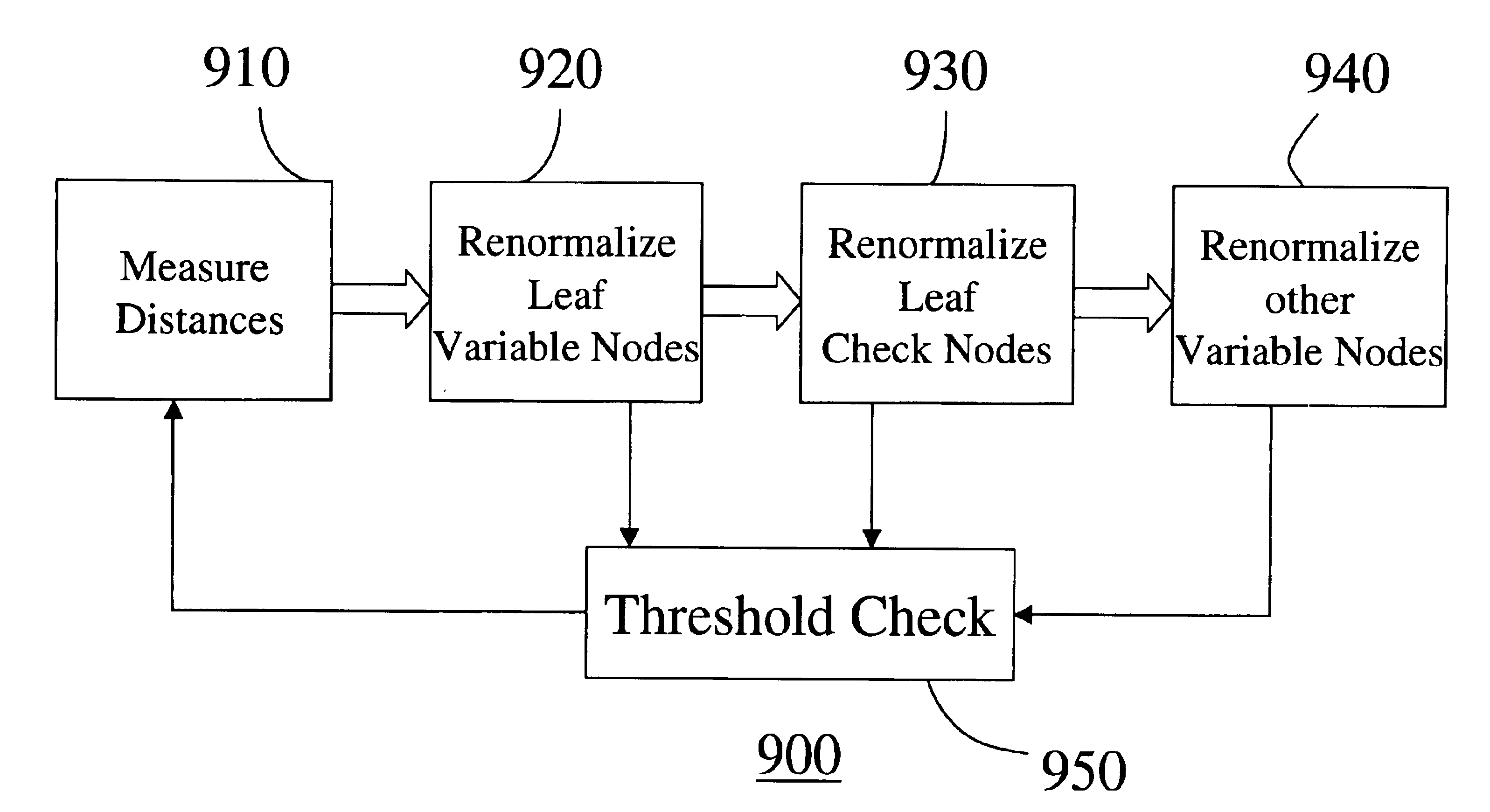
A method evaluates an error-correcting code for a data block of a finite size. An error-correcting code is defined by a parity check matrix, wherein columns represent variable bits and rows represent parity bits. The parity check matrix is represented as a bipartite graph. A single node in the bipartite graph is iteratively renormalized until the number of nodes in the bipartite graph is less than a predetermine threshold. During the iterative renormalization, a particular variable node is selected as a target node, and a distance between the target node and every other node in the bipartite graph is measured. Then, if there is at least one leaf variable node, renormalize the leaf variable node farthest from the target node, otherwise, renormalize a leaf check node farthest from the target node, and otherwise renormalize a variable node farthest from the target node and having fewest directly connected check nodes. By evaluating many error-correcting codes according to the method, an optimal code according to selected criteria can be obtained.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Spectral method for sparse principal component analysis
InactiveUS20070156471A1Improve approximate candidate solutionEasy to solveFinanceCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorRenormalization
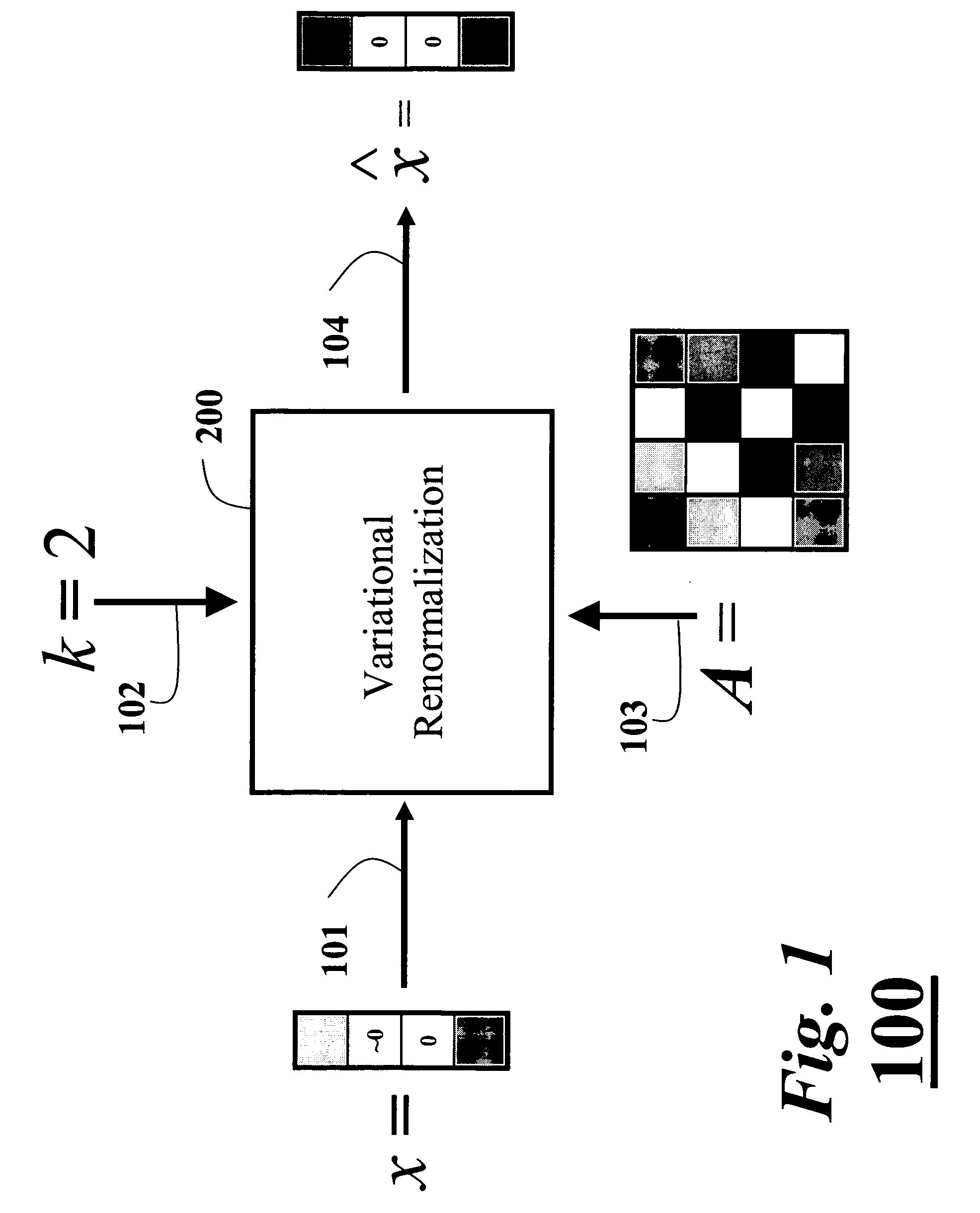
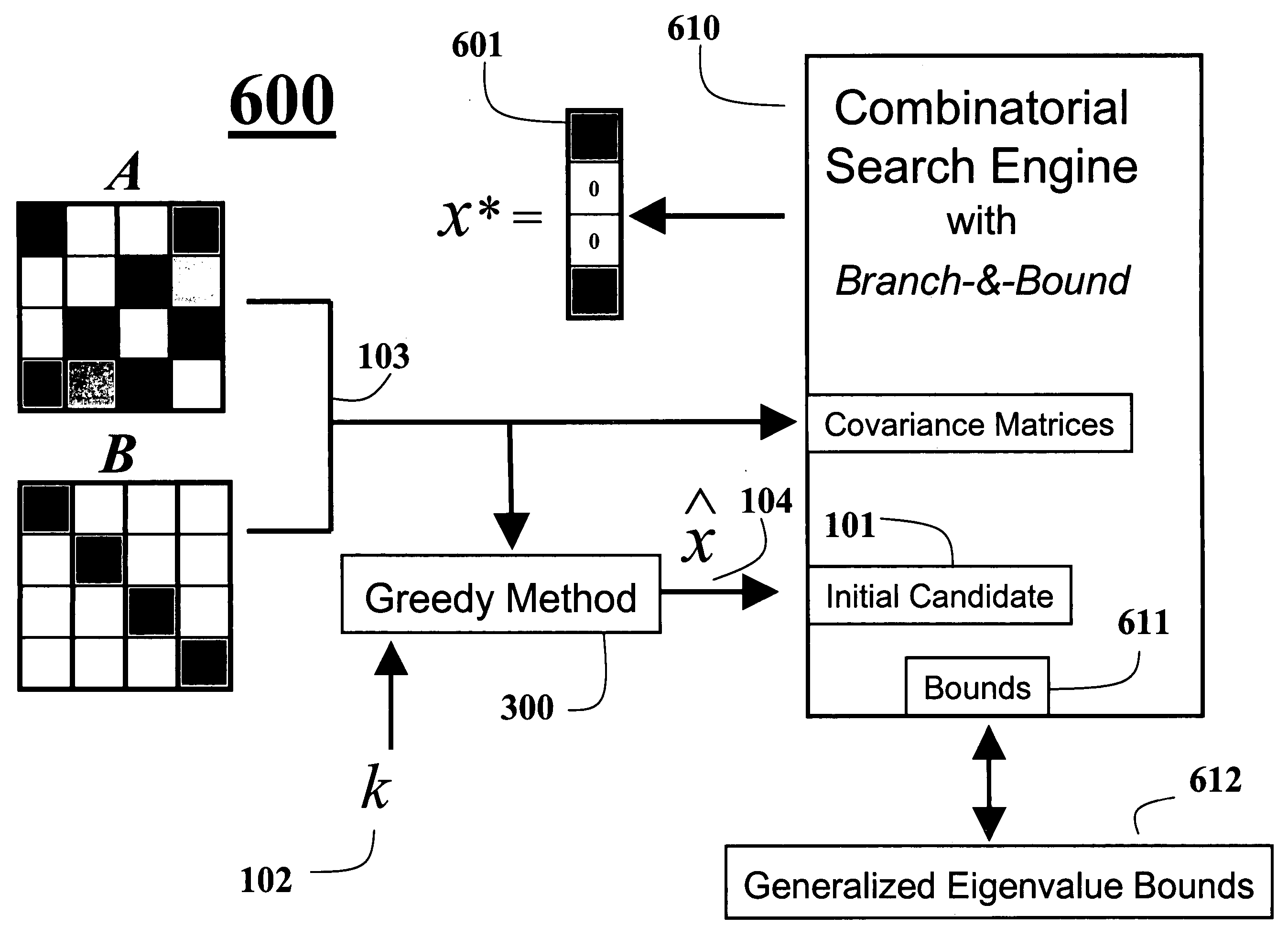
A method maximizes a candidate solution to a cardinality-constrained combinatorial optimization problem of sparse principal component analysis. An approximate method has as input a covariance matrix A, a candidate solution, and a sparsity parameter k. A variational renormalization for the candidate solution vector x with regards to the eigenvalue structure of the covariance matrix A and the sparsity parameter k is then performed by means of a sub-matrix eigenvalue decomposition of A to obtain a variance maximized k-sparse eigenvector x that is the best possible solution. Another method solves the problem by means of a nested greedy search technique that includes a forward and backward pass. An exact solution to the problem initializes a branch-and-bound search with an output of a greedy solution.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
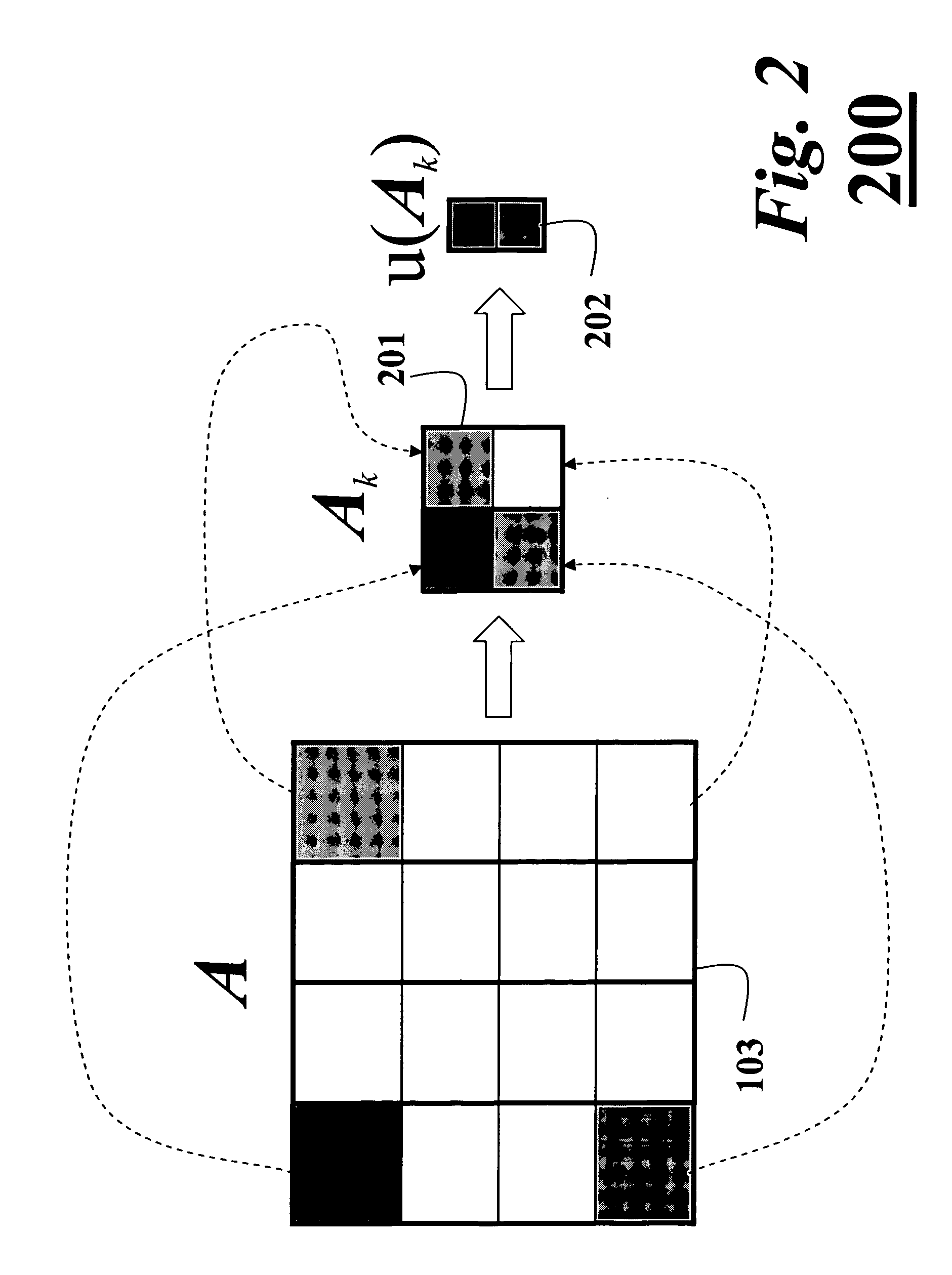
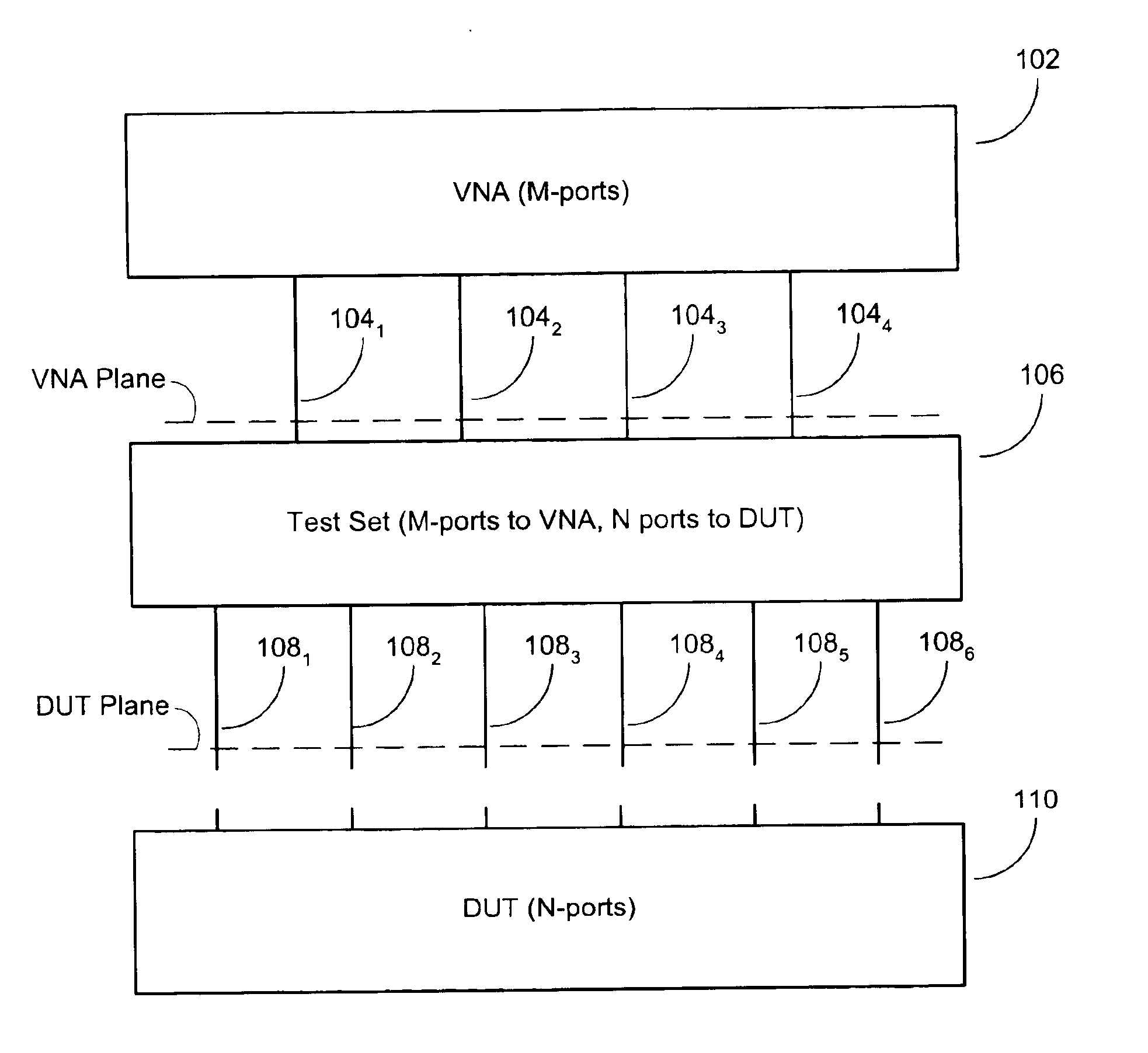
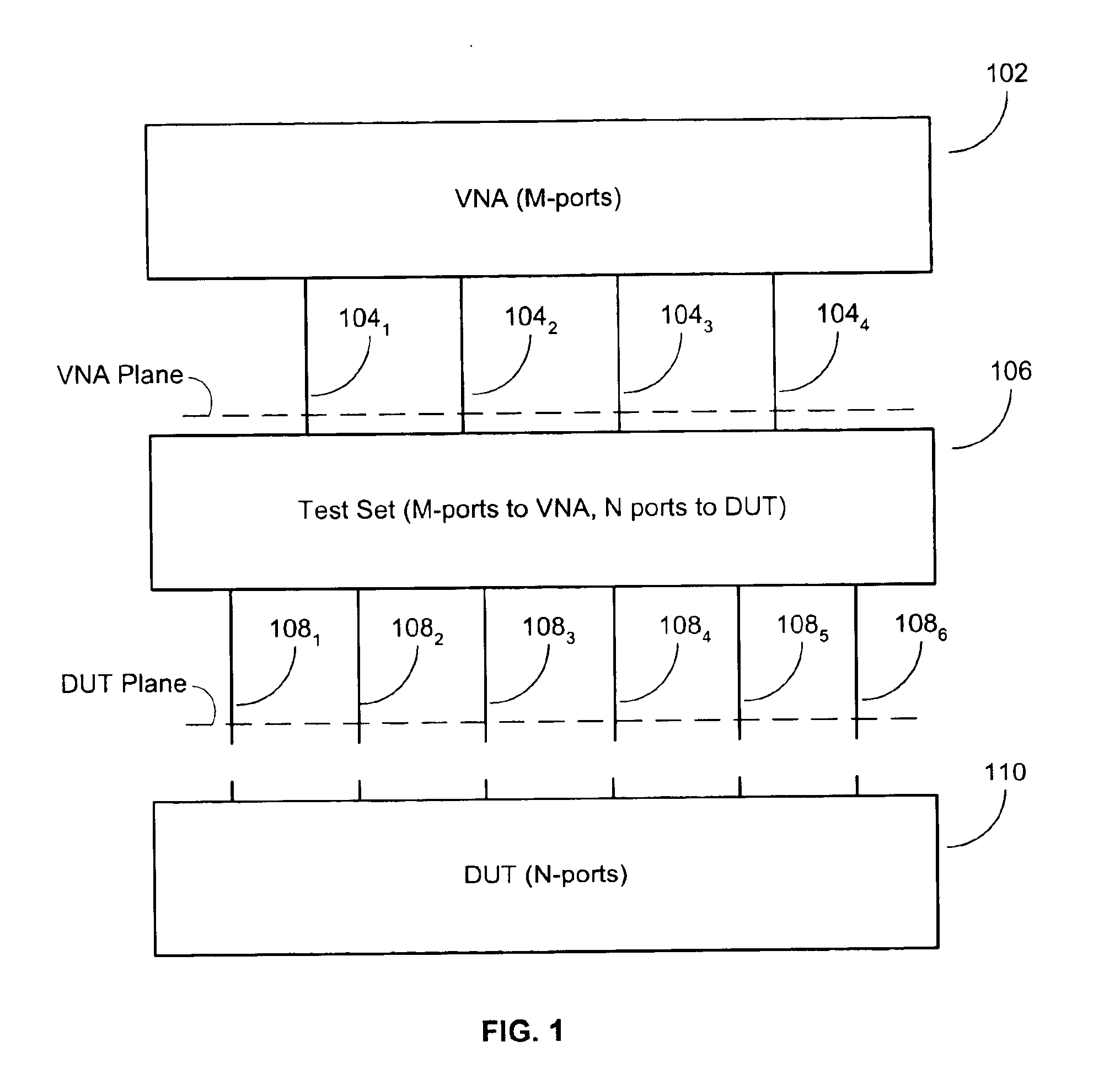
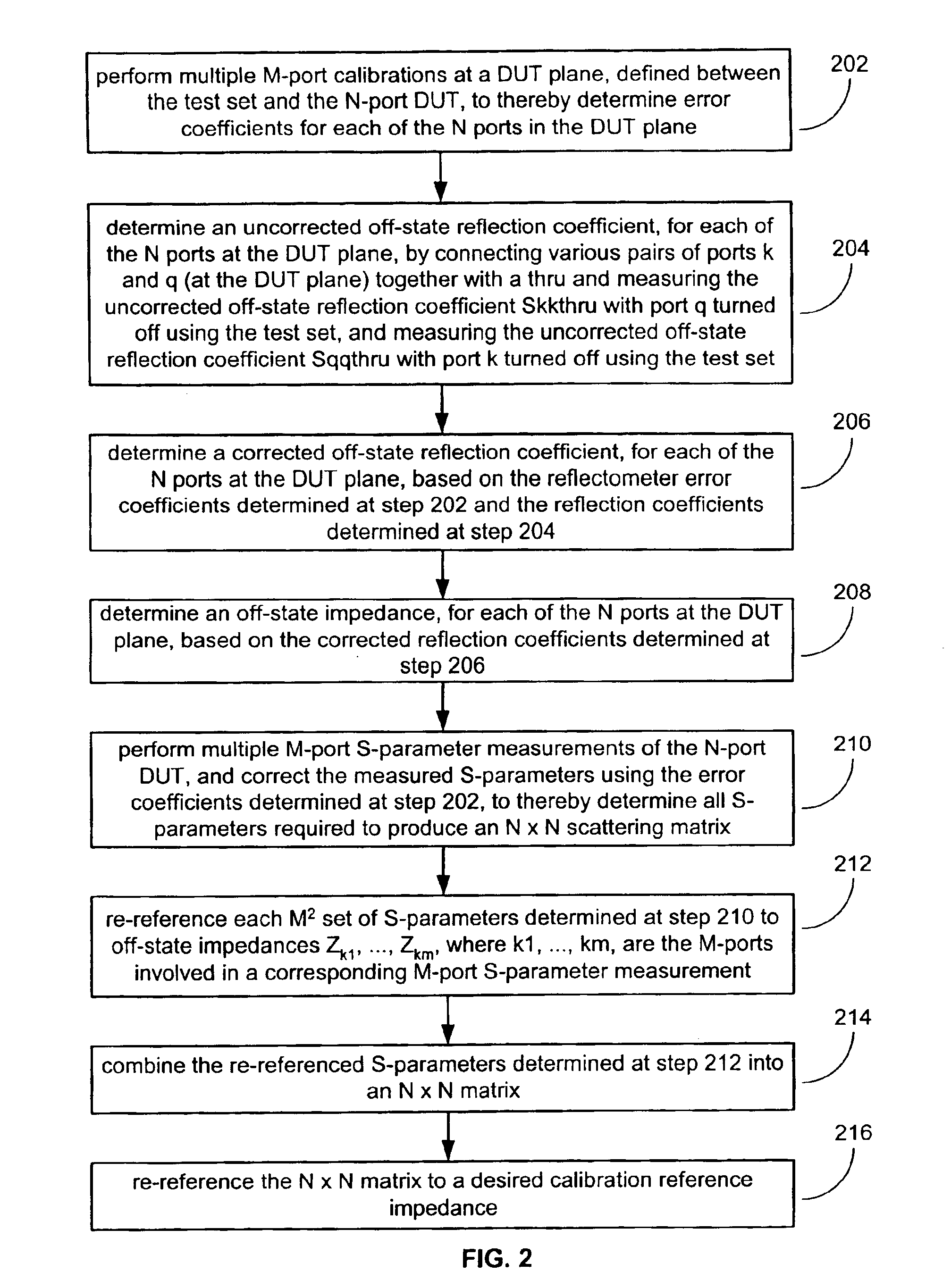
Methods and computer program products for full N-port vector network analyzer calibrations
InactiveUS6882160B2Efficient yet accurateElectronic circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceRenormalizationParallel computing
Techniques are provided for performing full N-port calibrations in an environment in which a test set is used to connect an N-port DUT to an M-port VNA, where N>M. Techniques for incorporating port impedances as part of a calibration sequence are provided. Also provided are techniques for using sequential characterization and de-embedding to generate virtual calibrations that are then used in a renormalization process.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Spectral method for sparse linear discriminant analysis
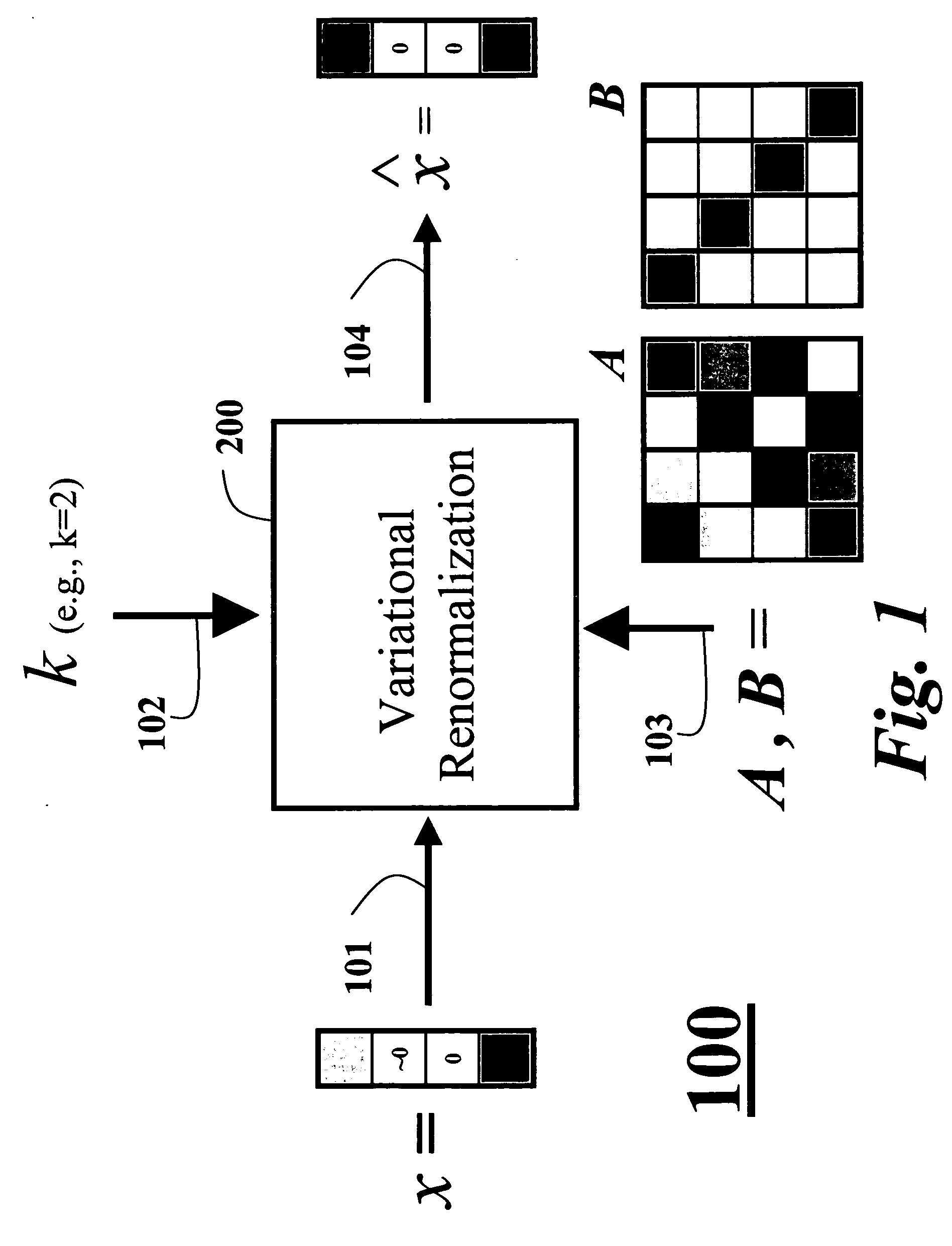
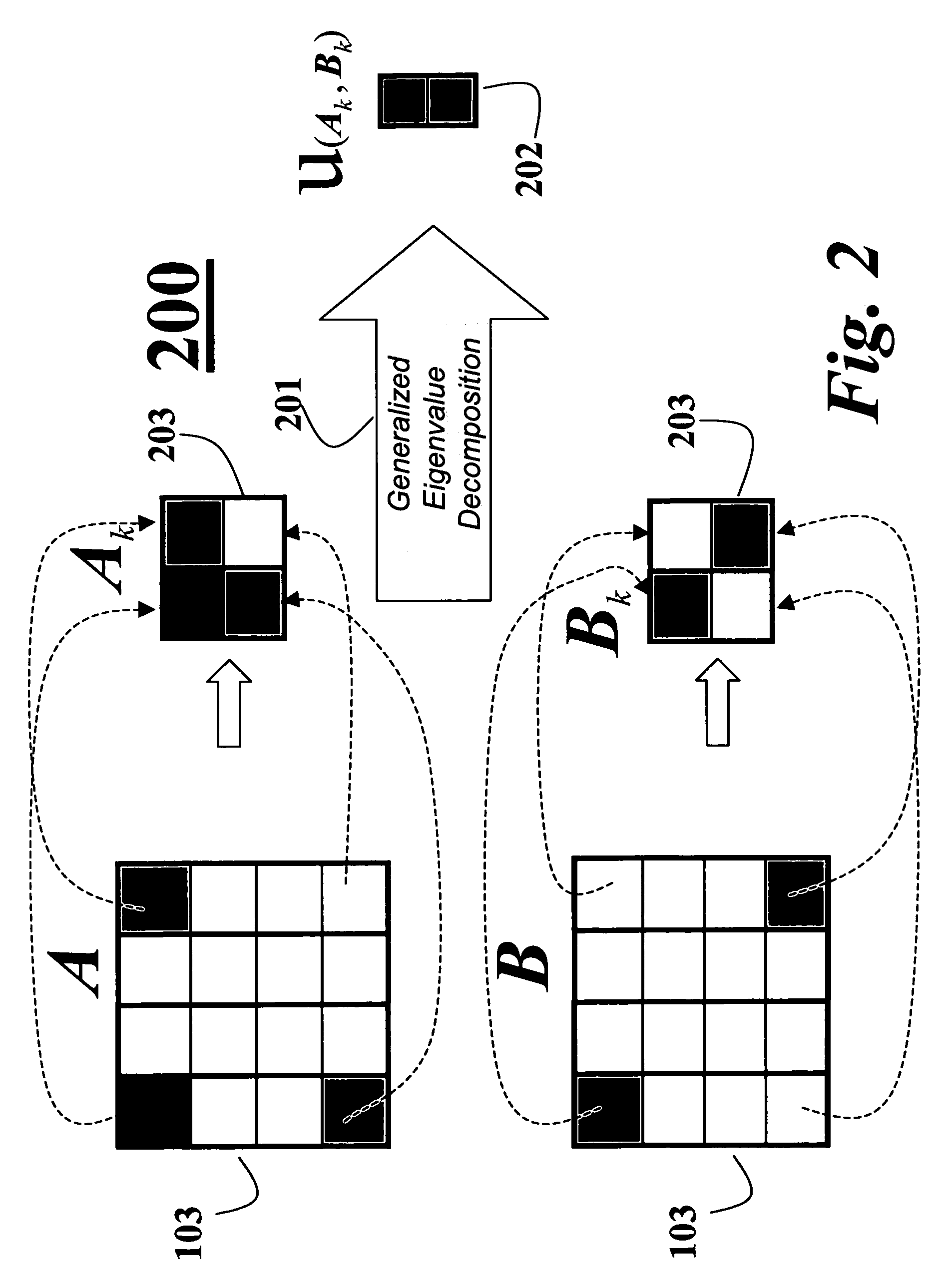
A computer implemented method maximizes candidate solutions to a cardinality-constrained combinatorial optimization problem of sparse linear discriminant analysis. A candidate sparse solution vector x with k non-zero elements is inputted, along with a pair of covariance matrices A, B measuring between-class and within-class covariance of binary input data to be classified, the sparsity parameter k denoting a desired cardinality of a final solution vector. A variational renormalization of the candidate solution vector x is performed with regards to the pair of covariance matrices A, B and the sparsity parameter k to obtain a variance maximized discriminant eigenvector {circumflex over (x)} with cardinality k that is locally optimal for the sparsity parameter k and zero-pattern of the candidate sparse solution vector x, and is the final solution vector for the sparse linear discriminant analysis optimization problem. Another method solves the initial problem of finding a candidate sparse solution by means of a nested greedy search technique that includes a forward and backward pass. Another method, finds an exact and optimal solution to the general combinatorial problem by first finding a candidate by means of the previous nested greedy search technique and then using this candidate to initialize a branch-and-bound algorithm which gives the optimal solution.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
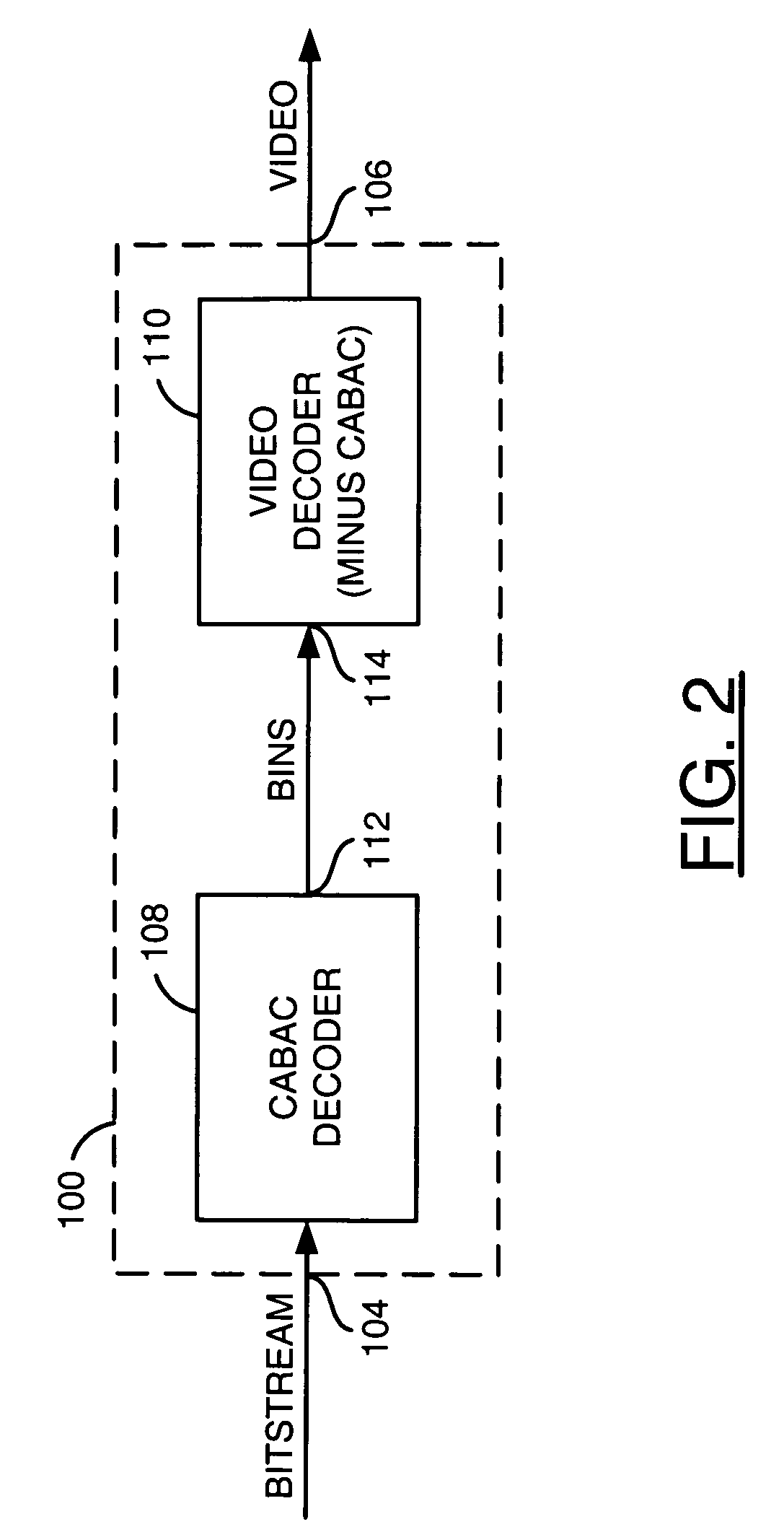
Video coding with CABAC
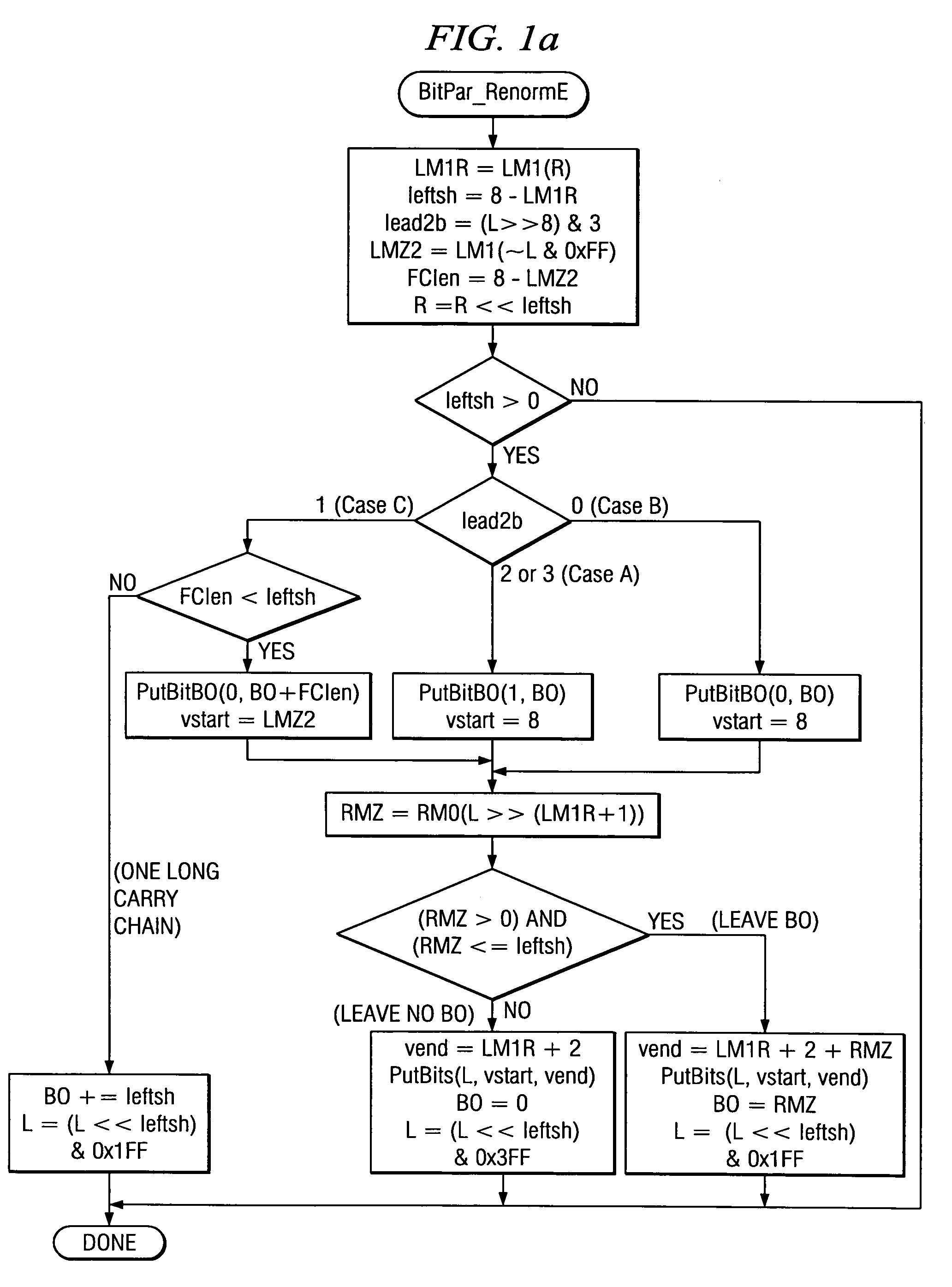
Context-based adapative binary arithmetic coding (CABAC), as used in video standards such as H.264 / AVC, with a renormalization of the interval low value plus range that includes partitioning of the bits of the low value to provide output bits plus low value update without bit-level iterations or aggregation of output bits until a full byte can be output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Optimized CABAC decoder
InactiveCN101809871ACode conversionDigital video signal modificationRenormalizationProcessor register
A device employing techniques to optimize Context-based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) for the H.264 video decoding is provided. The device includes a processing circuit operative to implement a set of instructions to decode multiple bins simultaneously and renormalize an offset register and a range register after the multiple bins are decoded. The range register and offset registers may be 32 or 64 bits. The use of a larger range register allows renormalization to be skipped when enough bits are still in the range register.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
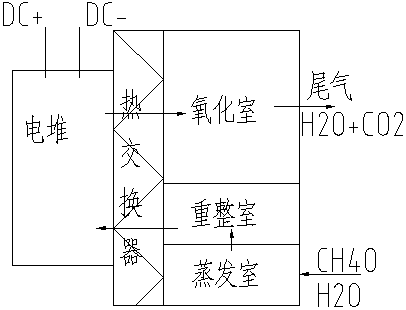
Fuel cell prepared based on methanol and water renormalization
ActiveCN108206289AImplement extractionRealize comprehensive utilizationFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlFuel cellsRenormalization
The invention discloses a fuel cell prepared based on methanol and water renormalization. The fuel cell comprises an evaporation chamber; an evaporator is arranged in the evaporating chamber; the evaporating chamber is connected with a renormalization chamber; the renormalization chamber is connected with a high temperature fuel cell stack through a micro channel; an anode and a cathode are arranged in the high temperature fuel cell stack; a proton membrane is arranged between the anode and the cathode; and the anode is provided with a catalyst. The advantages are that: hydrogen energy carriedby methanol is converted into electric energy, hydrogen energy carried by water is converted into electric energy, extraction and utilization of energy in water is realized, waste of heat utility isavoided; cycle utilization can be realized; and hydrogen production efficiency and methanol conversion rate are increased.
Owner:CHINA HYDROGEN NEW ENERGY TECH CO
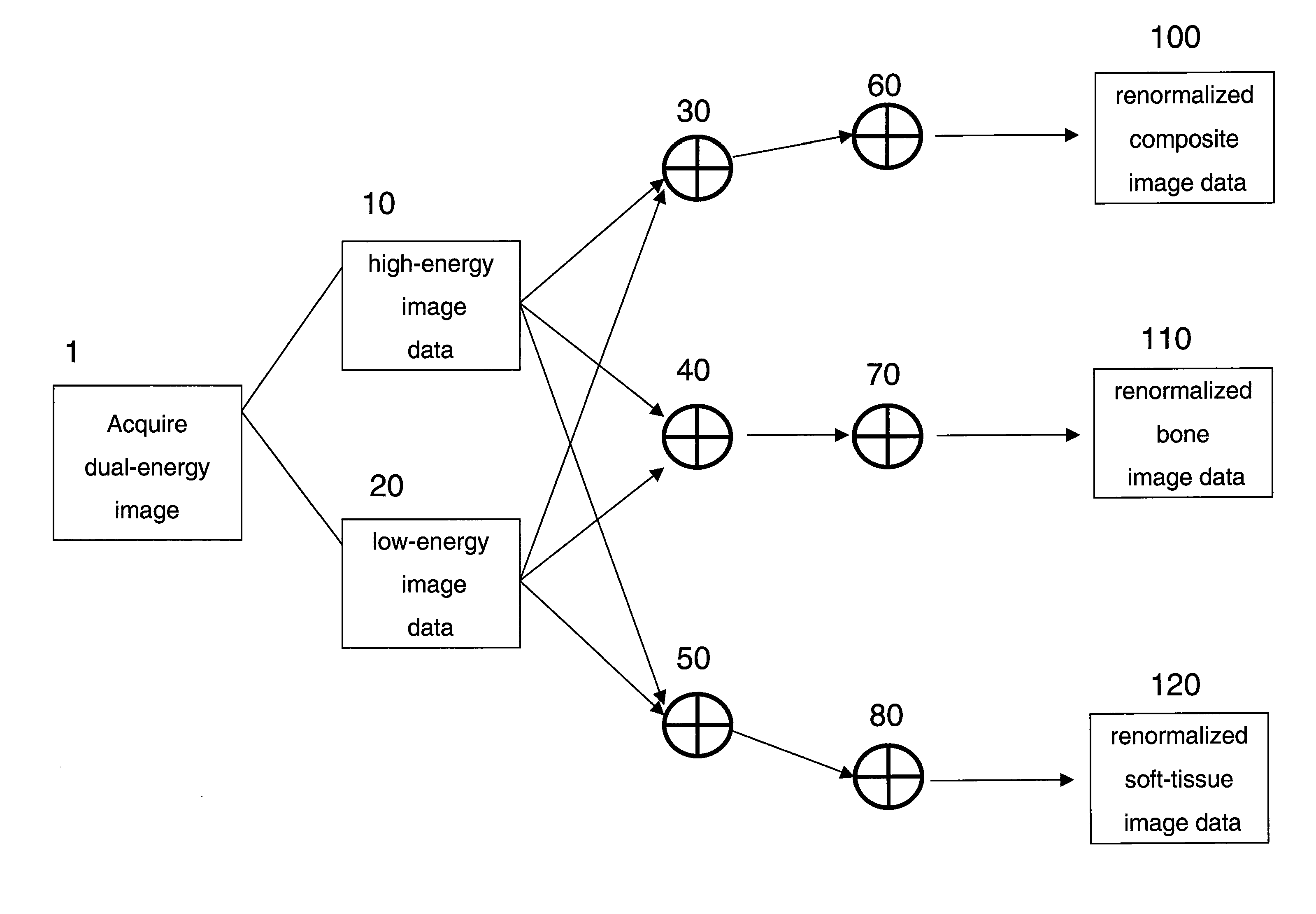
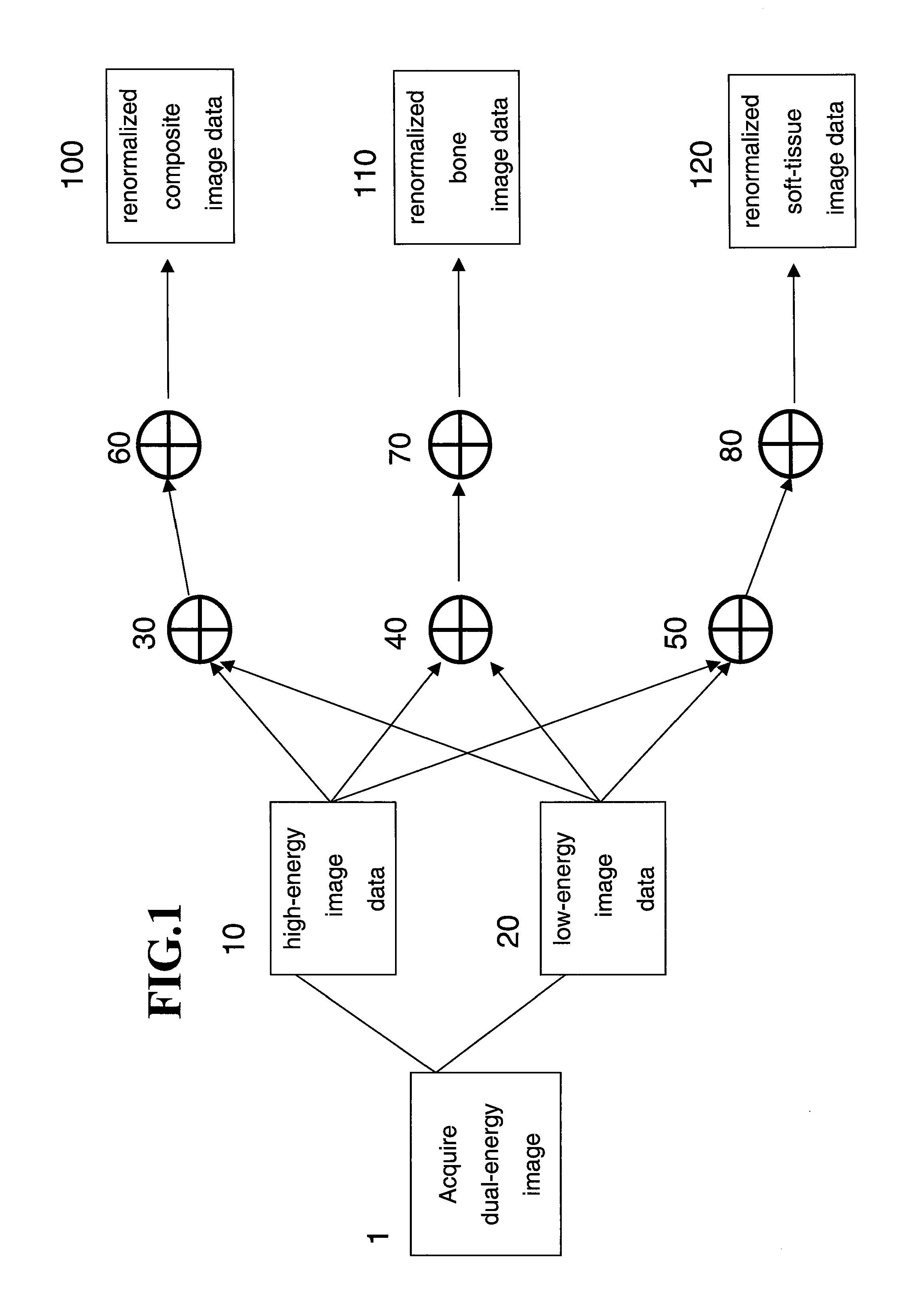
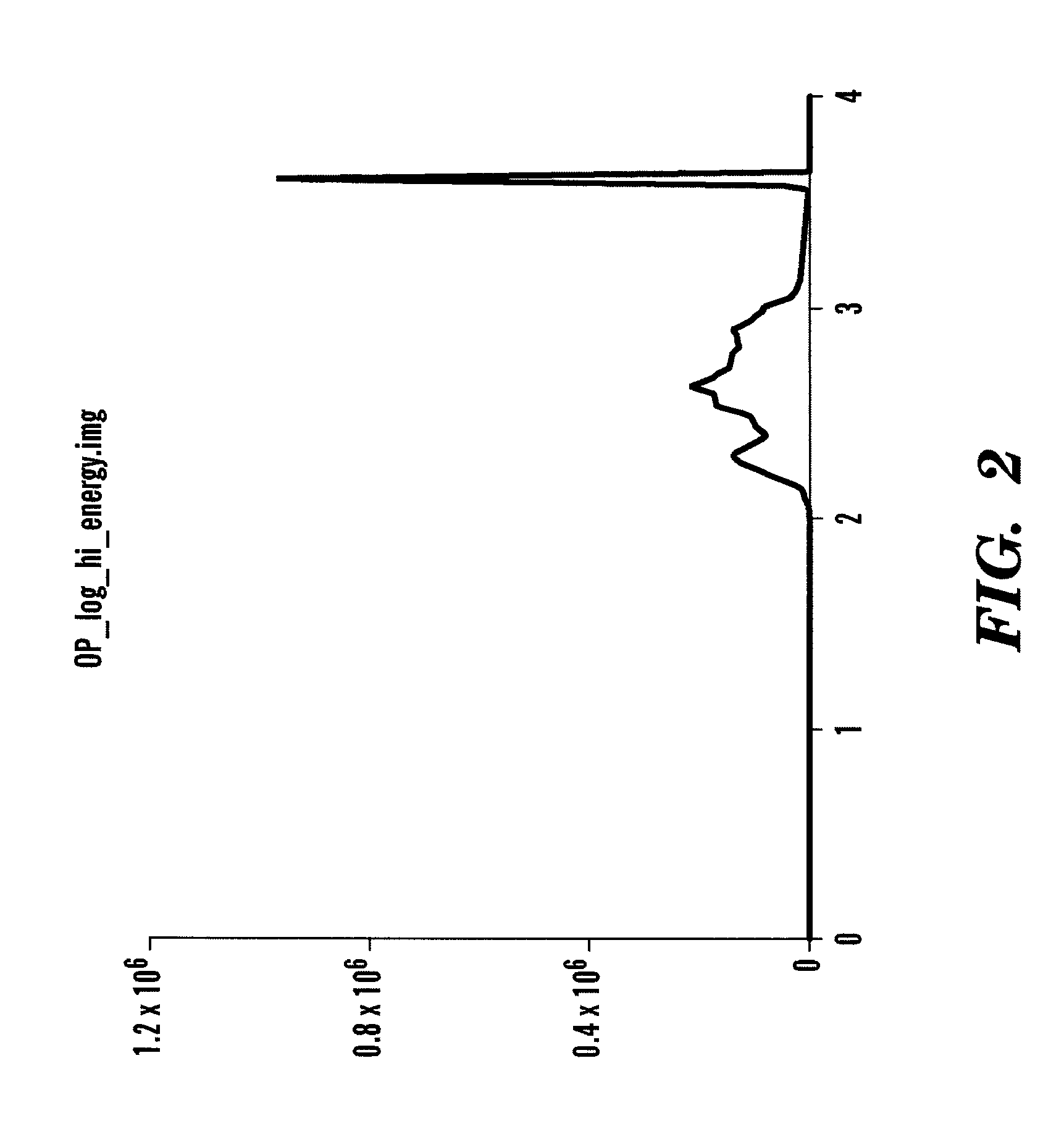
Renormalization of dual-energy images
ActiveUS20080192898A1Easy to useReconstruction from projectionX-ray apparatusRenormalizationHigh energy
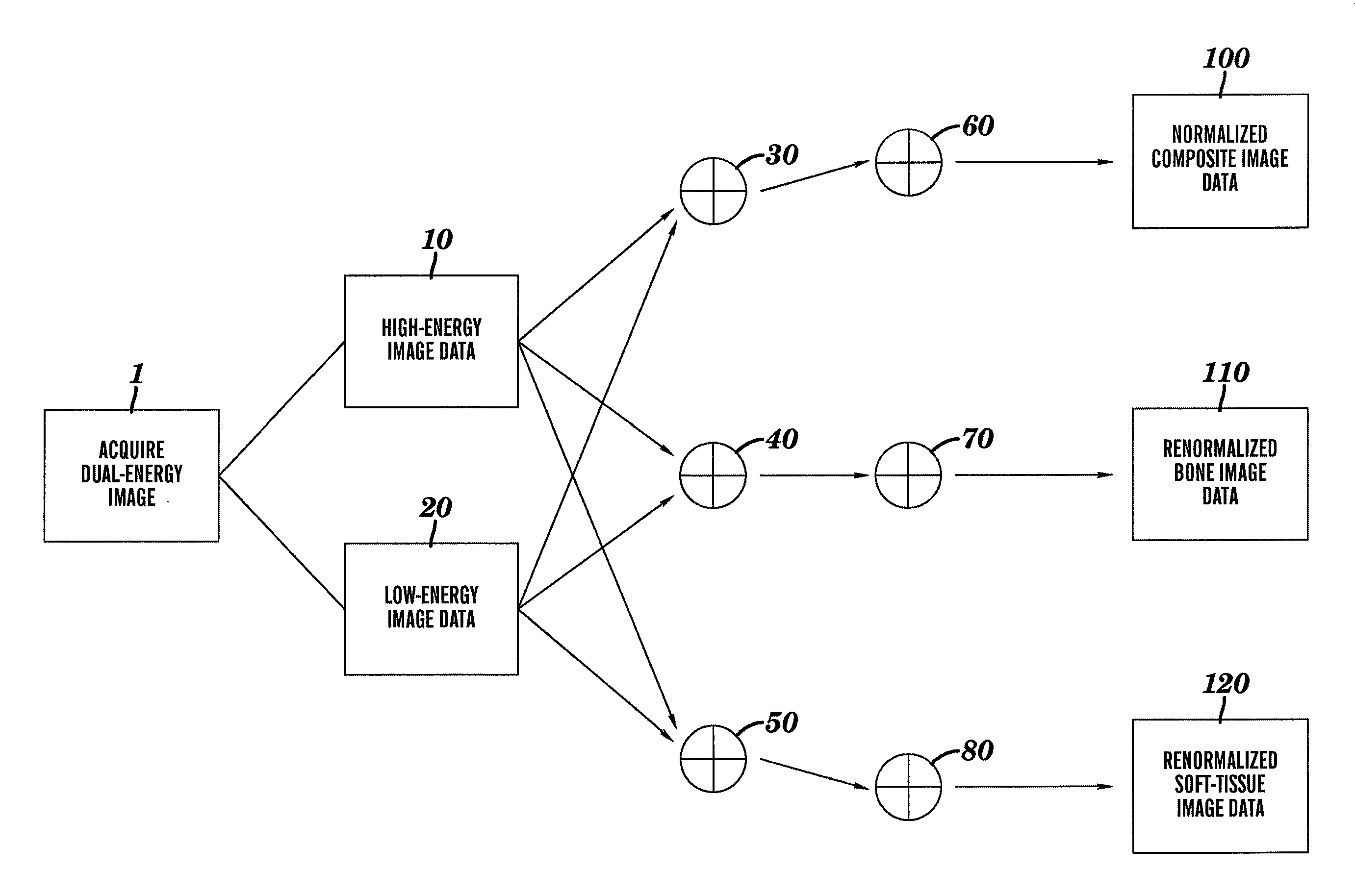
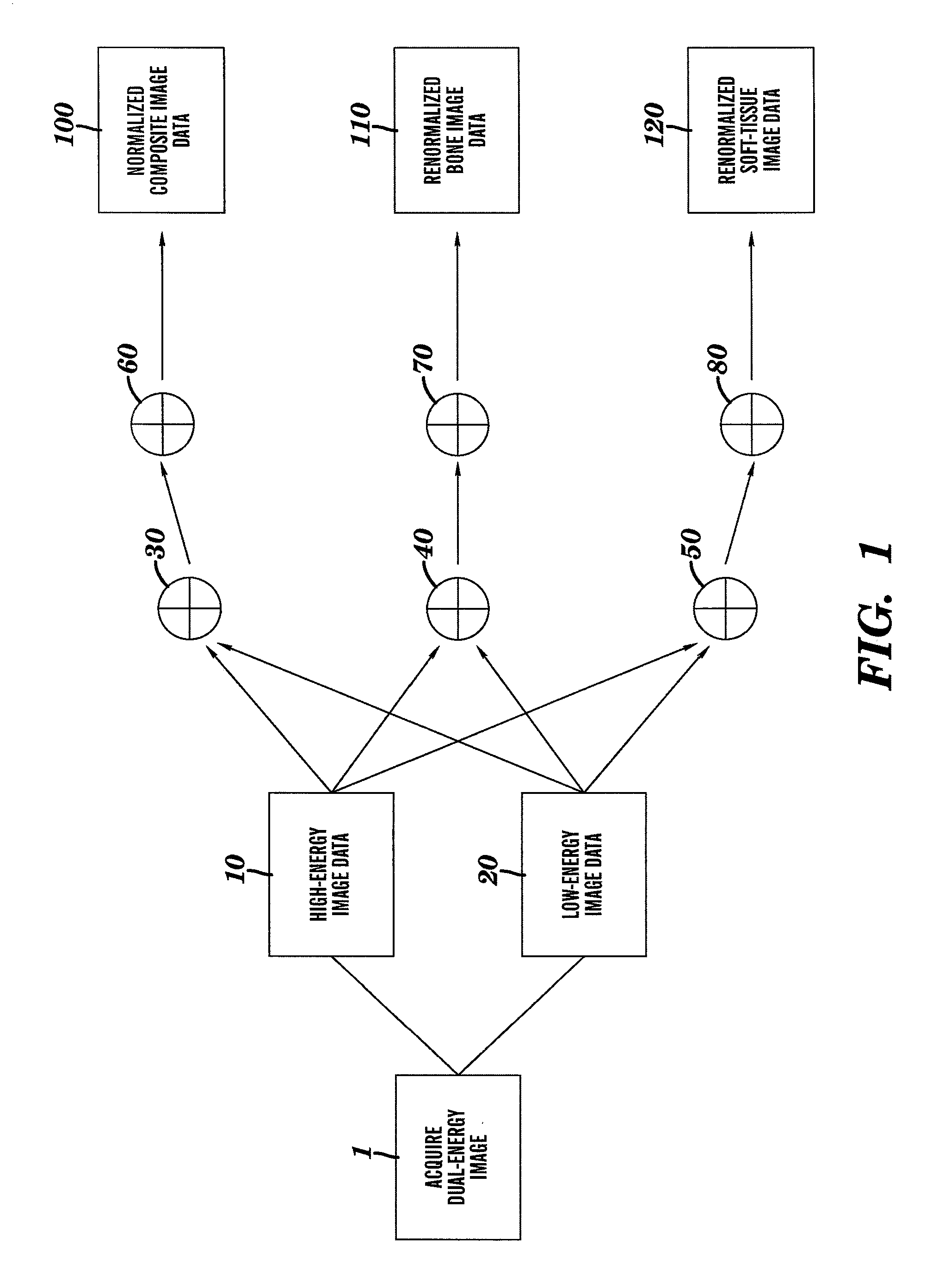
A method is disclosed for generating a composite image from dual-energy projection radiographic image data and renormalizing the composite image such that the pixel values for the composite image have the same relationship to the detected x-ray energy as the original high- and low-energy images. The method disclosed further provides for renormalization of material specific decomposition images formed form dual energy projection radiographic image data such that the decomposition images are on a common scale with either the high-energy, low-energy or composite image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
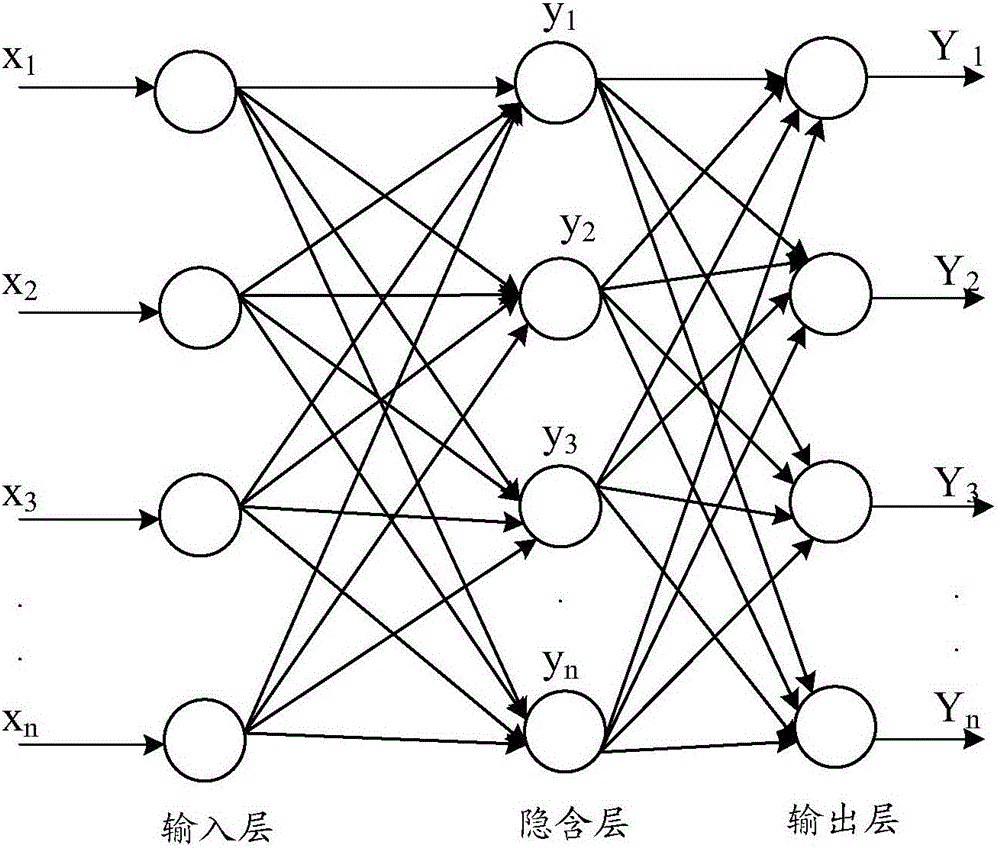
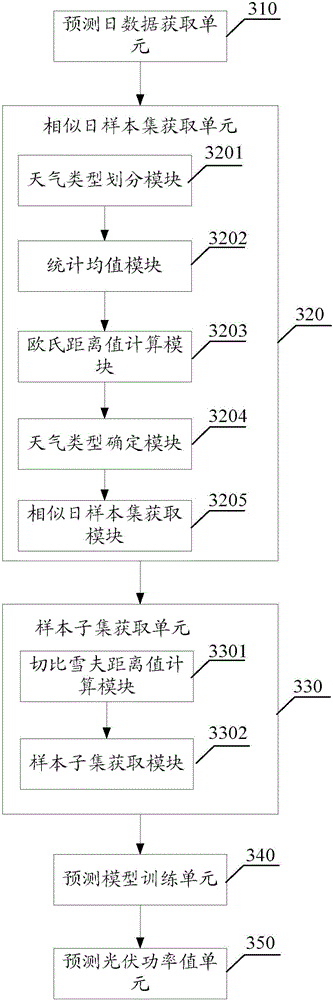
Method and system for predicting photovoltaic power based on dynamic neural network
The invention provides a method for predicting photovoltaic power based on a dynamic neural network. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining values which are respectively corresponding to weather characteristic parameters of a predicting daily in each time bucket in a set time bucket; dividing a weather type, identifying the weather type of the predicting daily based on the values obtained by the predicting daily through weighted Euclidean distance calculation, and constructing a similar day sample set of the predicting daily in history weather data according to the identified weather type; counting a number of days of the similar day sample set and solving a Chebyshev distance value thereof with the predicting daily for every day, and constructing a sample subset meeting a predetermined condition; carrying out normalization processing on the sample subset and training in a dynamic neural network prediction model; and after completing training, importing the values obtained by the predicting daily and carrying out renormalization processing to obtain photovoltaic power predicted values which are respectively corresponding the predicting daily in each time bucket of the set time bucket. By applying the embodiments of the invention, the predicting accuracy and the predicting speed can be simultaneously improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU +1
Low-voltage CMOS circuits for analog decoders
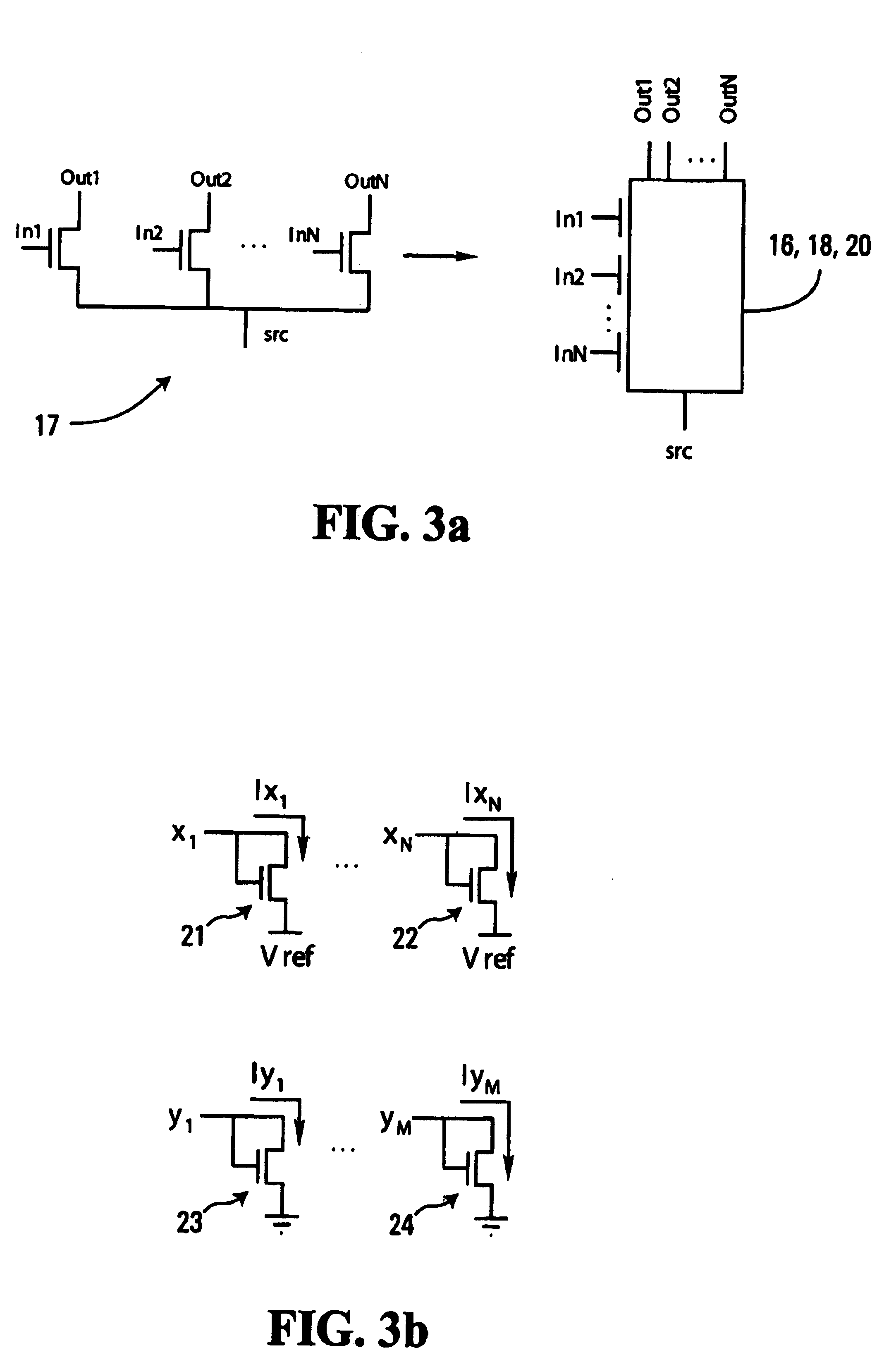
InactiveUS20060004901A1Computation using non-contact making devicesCode conversionRenormalizationBinary multiplier
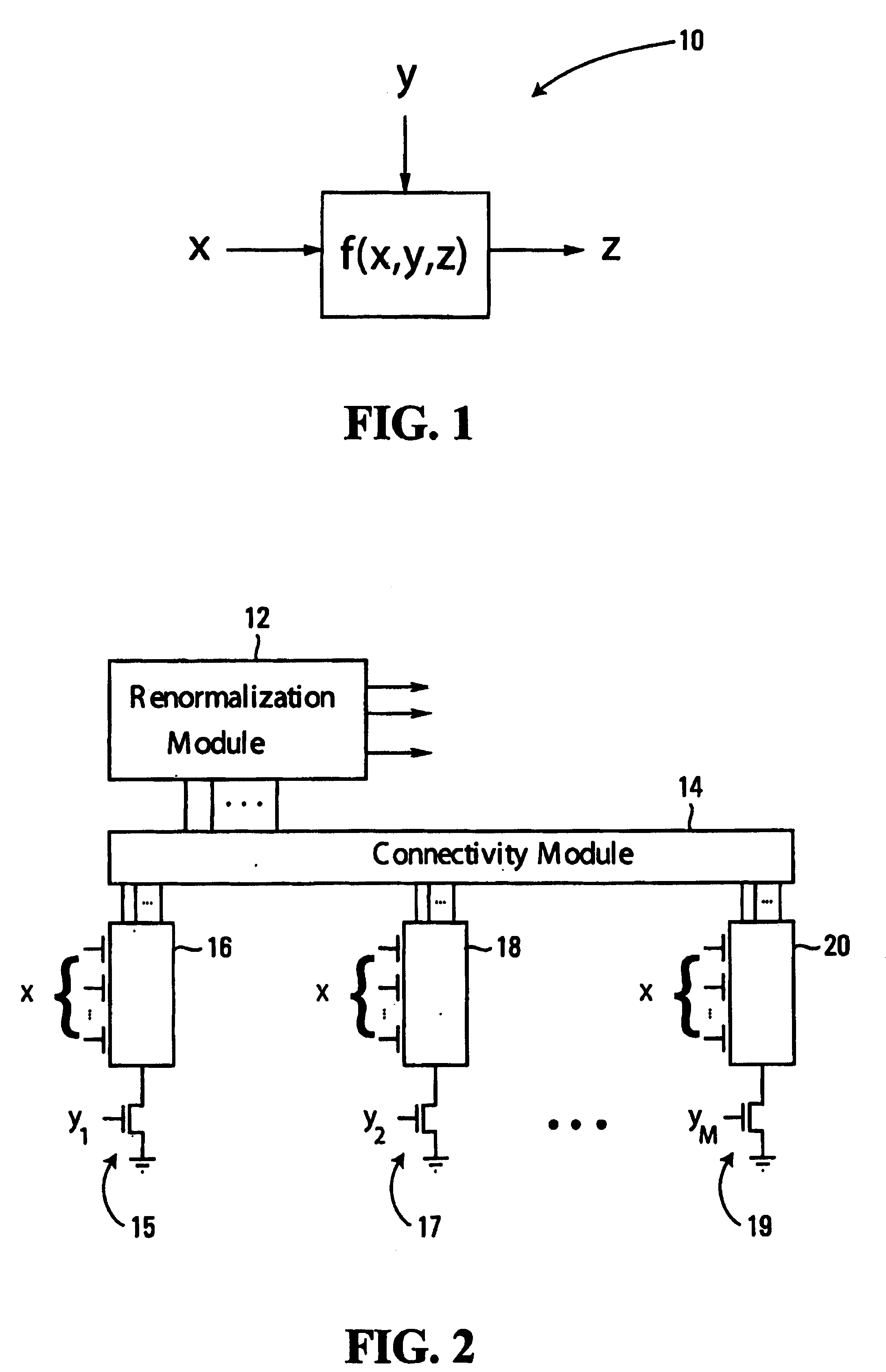
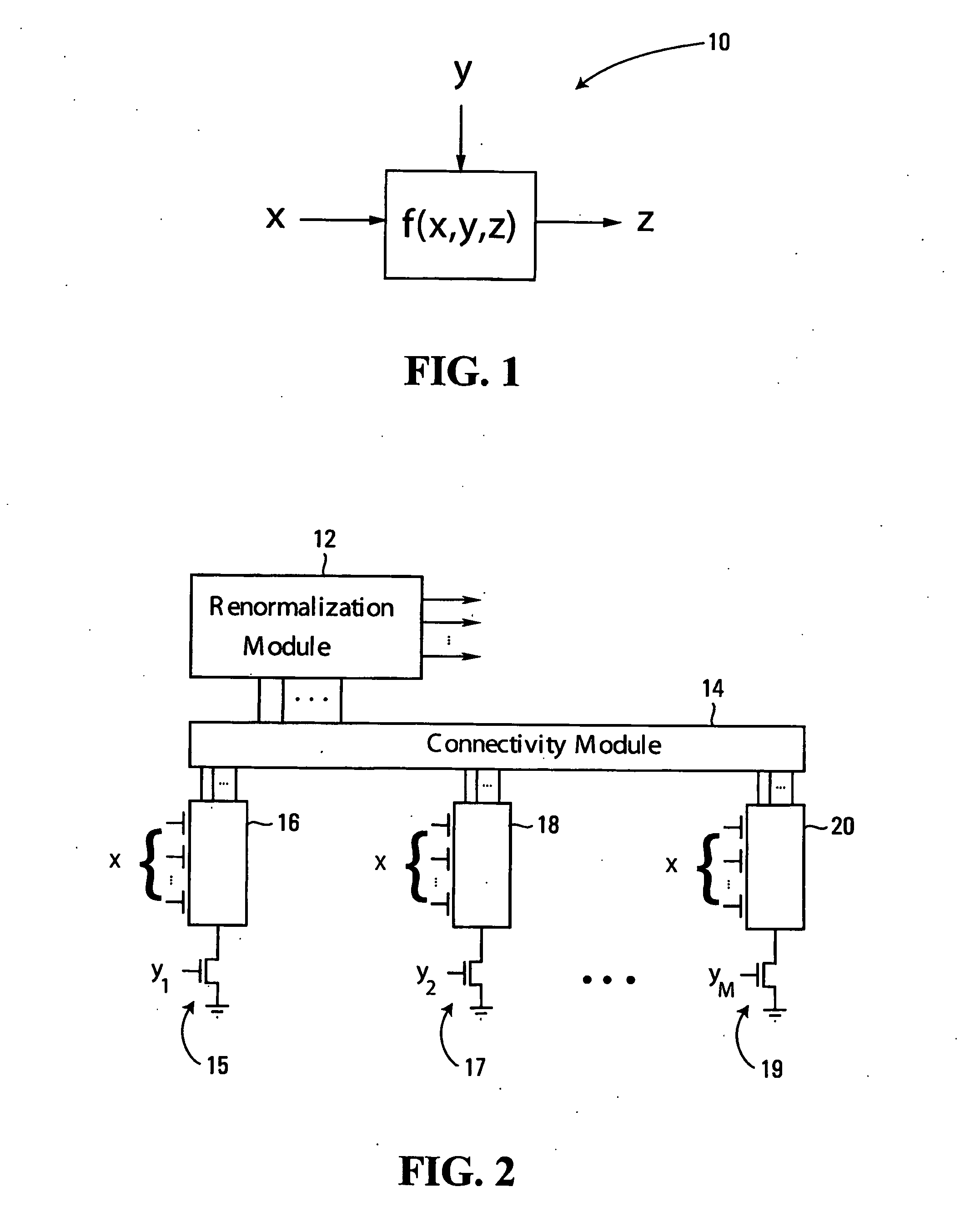
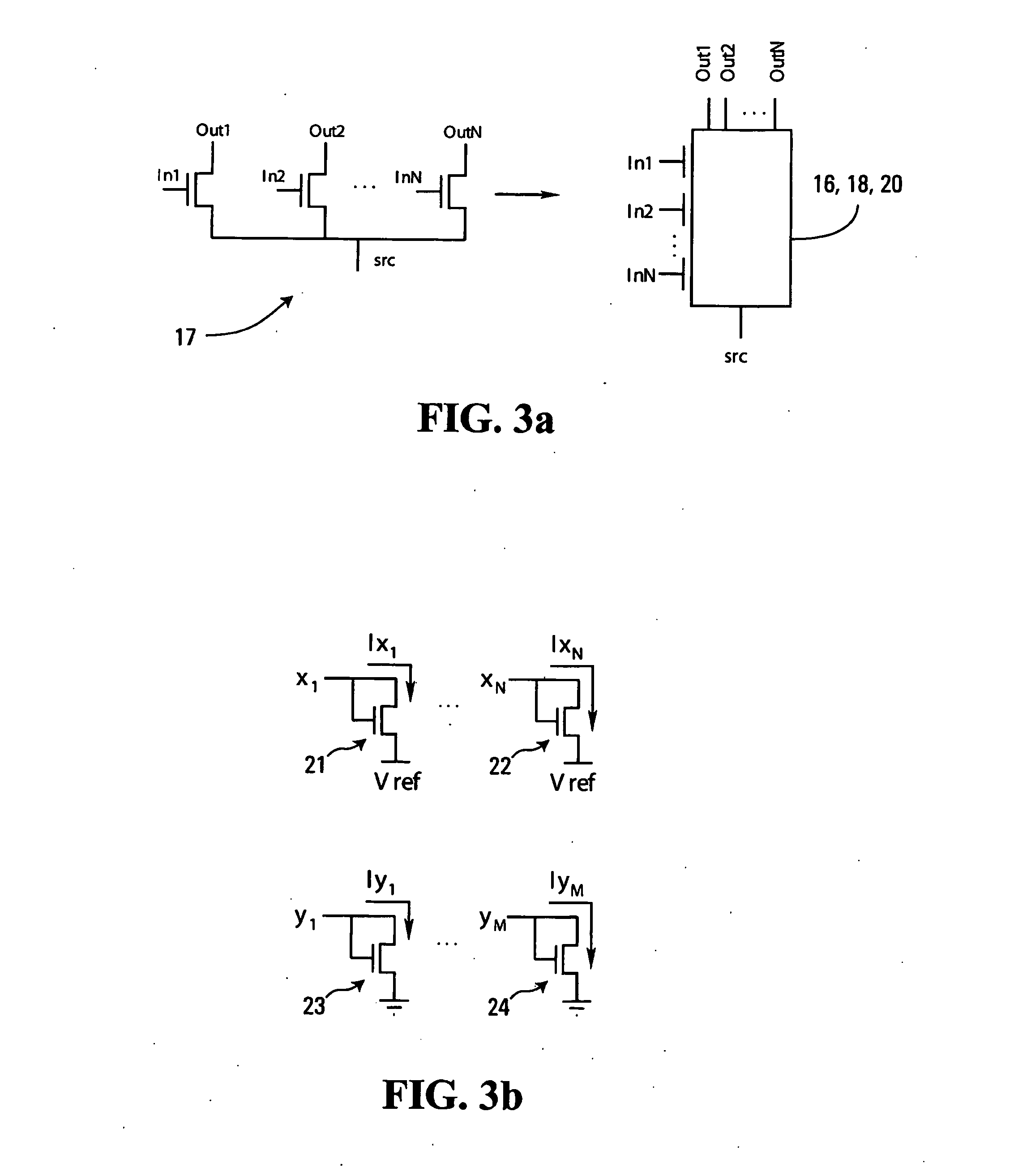
Low-voltage CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) circuits, suitable for analog decoders, for example, are provided. The circuits include multiplier modules that receive first input signals and respective ones of a plurality of second input signals. Each multiplier module generates as output signals products of the first input signals and its respective second input signals. Dummy multiplier modules that respectively correspond to the multiplier modules receive the second input signals, and each dummy multiplier module forms products of the second input signal of its corresponding multiplier module and the other second input signals. The dummy multiplier modules reduce the overall voltage requirements of the circuit, thereby providing for low-voltage operation. In some embodiments, a connectivity module receives output signals from the multiplier modules and generates as output signals sums of predetermined ones of the output signals, and a renormalization module receives and normalizes the output signals from the connectivity module to generate output signals that sum to a predetermined unit value.
Owner:ALBERTA UNIV OF
Method of compressing and decompressing images
InactiveUS7218786B2Improve codec speedImprove processing speedCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationRenormalizationWork cycle
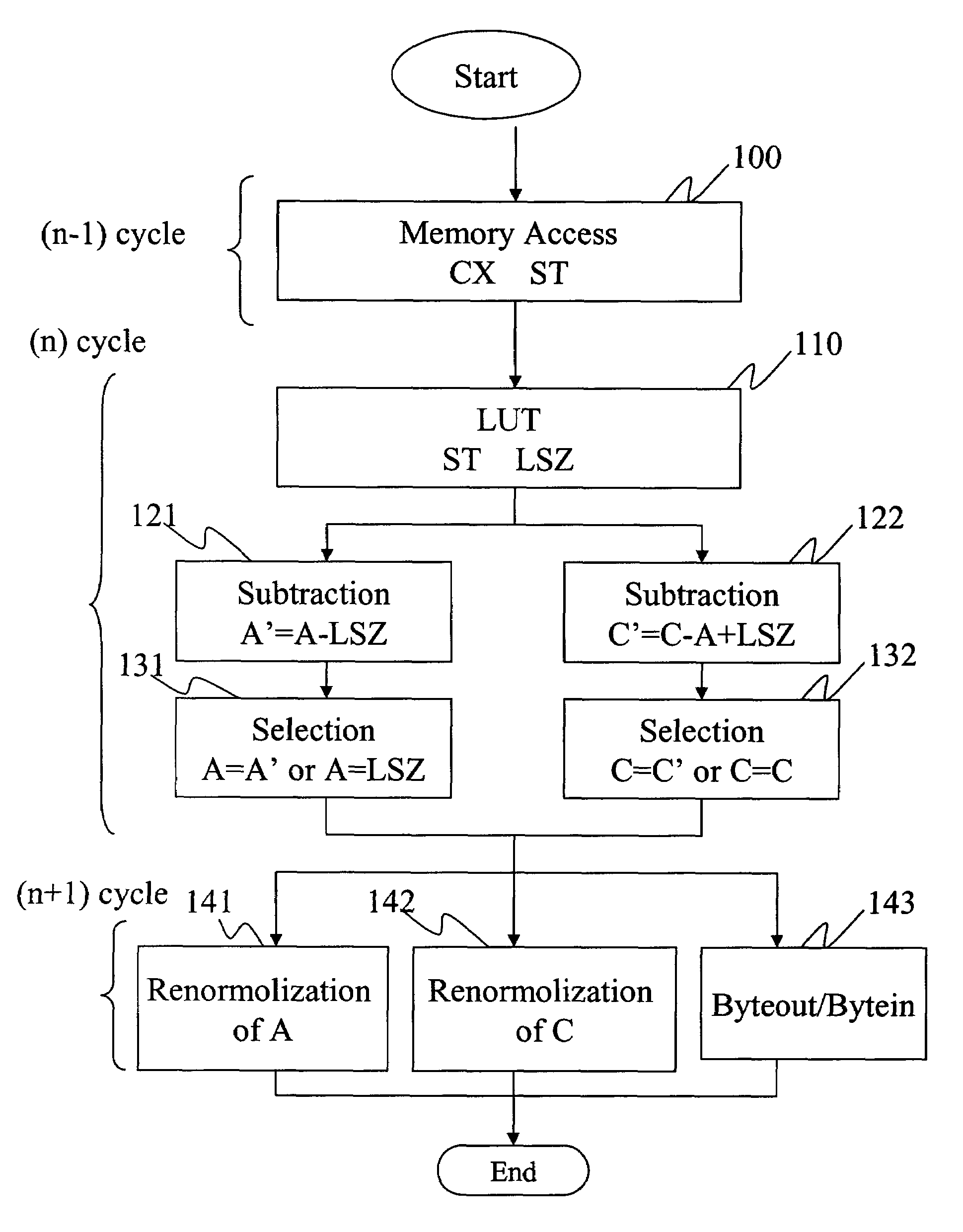
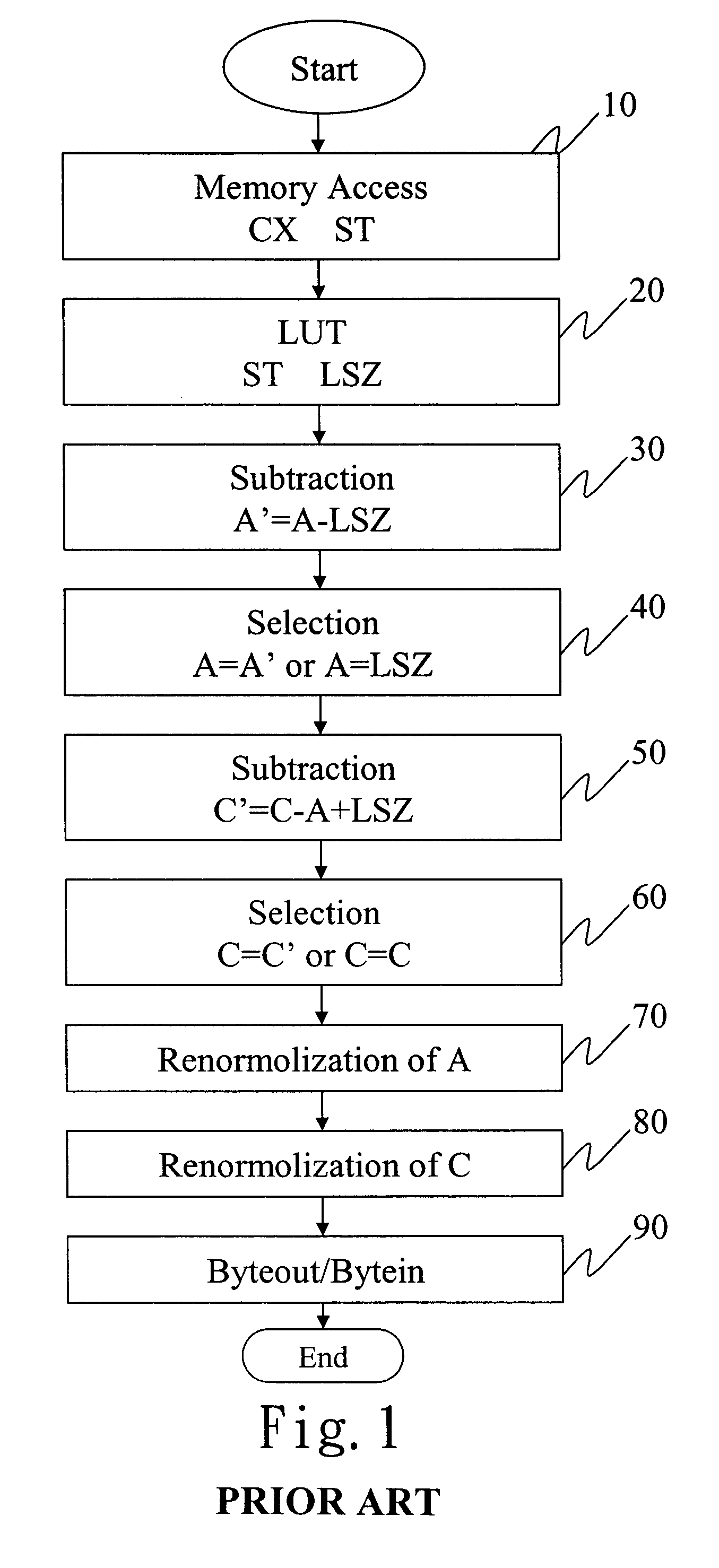
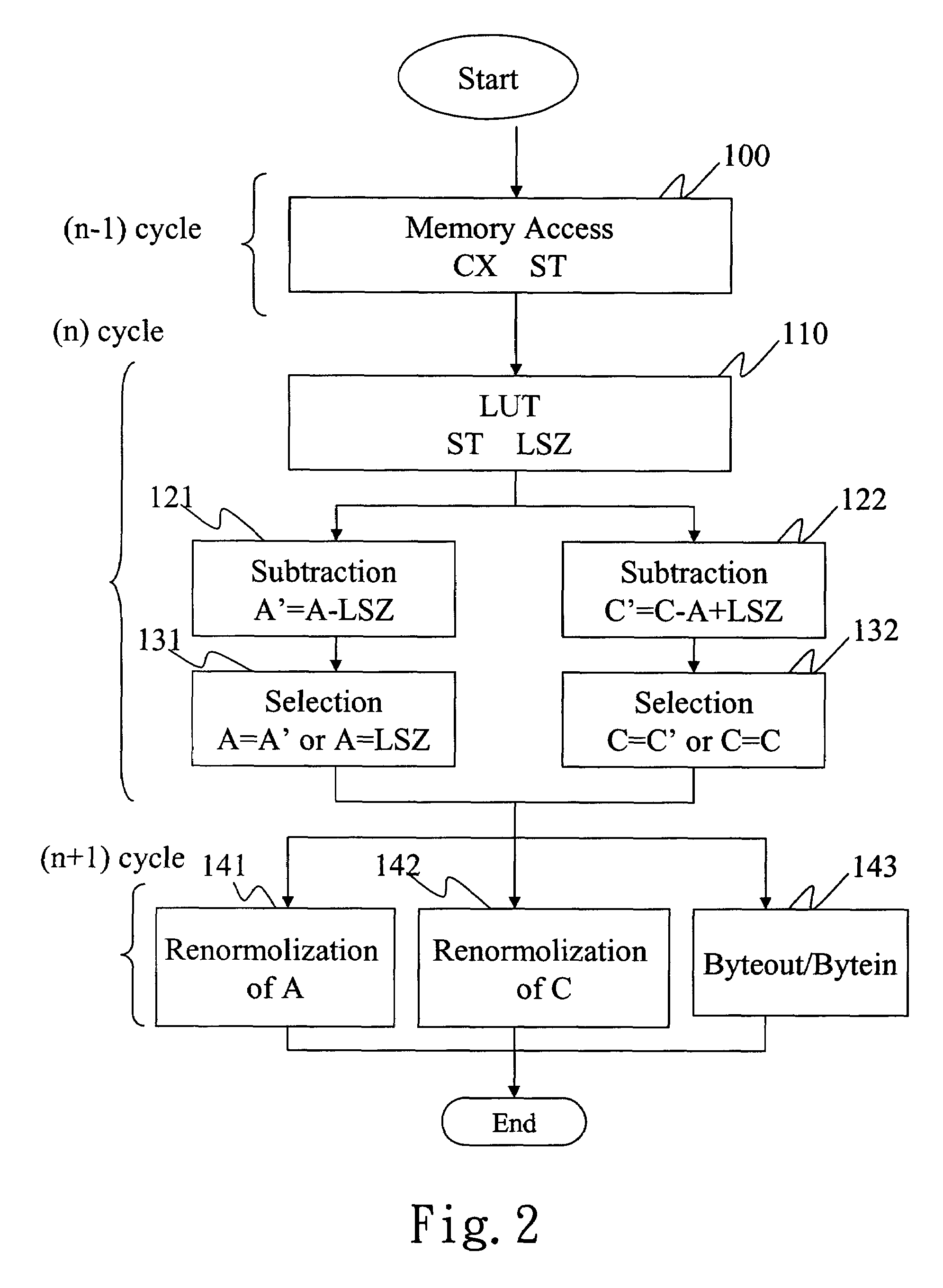
A method of compressing and decompressing images is disclosed for applications in compression and decompression chips with the JBIG standard. The pipeline of computing a pixel is divided into three parts: memory access, numerical operations, renormalization and byteout / bytein. Each steps takes a work cycle; therefore, three pixels are processed in parallel at the same time. In comparison, the work cycle of the prior art without pipeline improvement is longer. This method can effectively shorten the work cycle of each image data process, increasing the speed of compressing and decompressing image data.
Owner:PRIMAX ELECTRONICS LTD
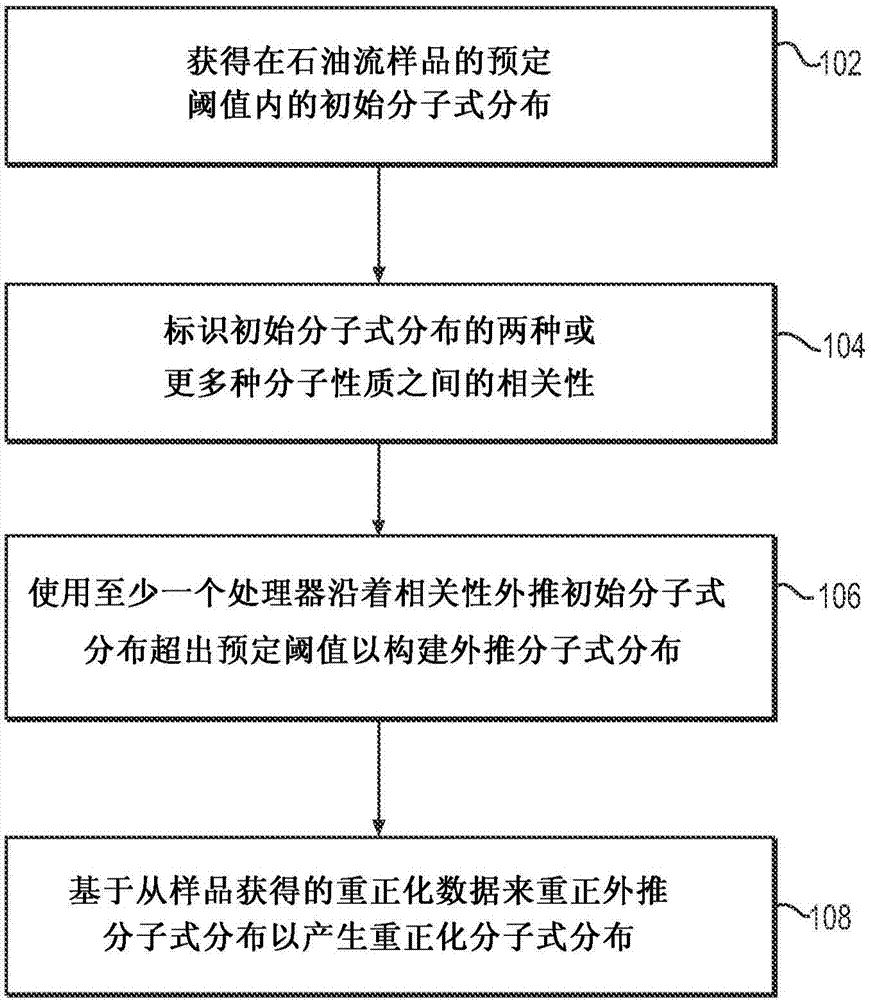
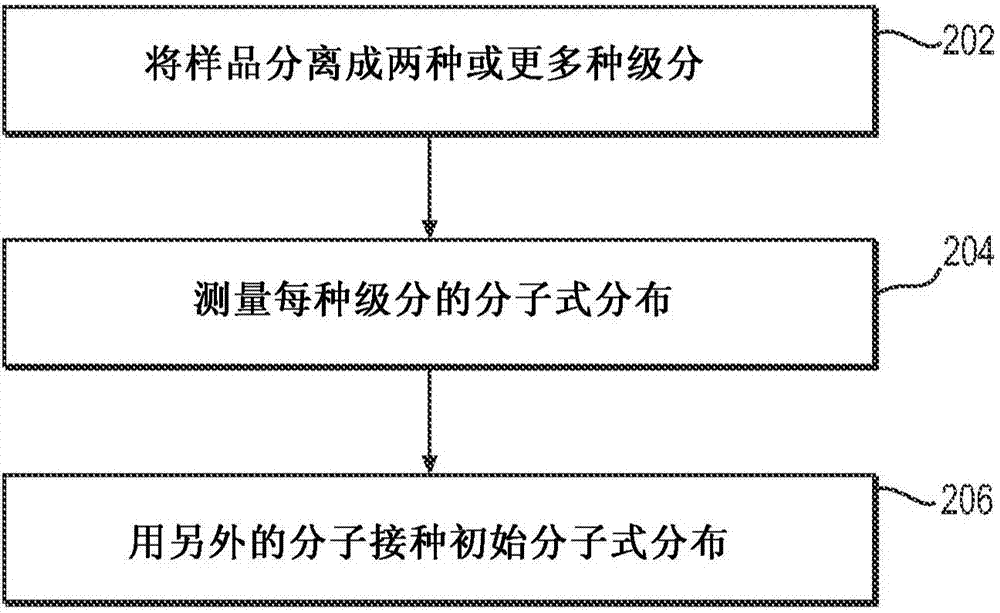
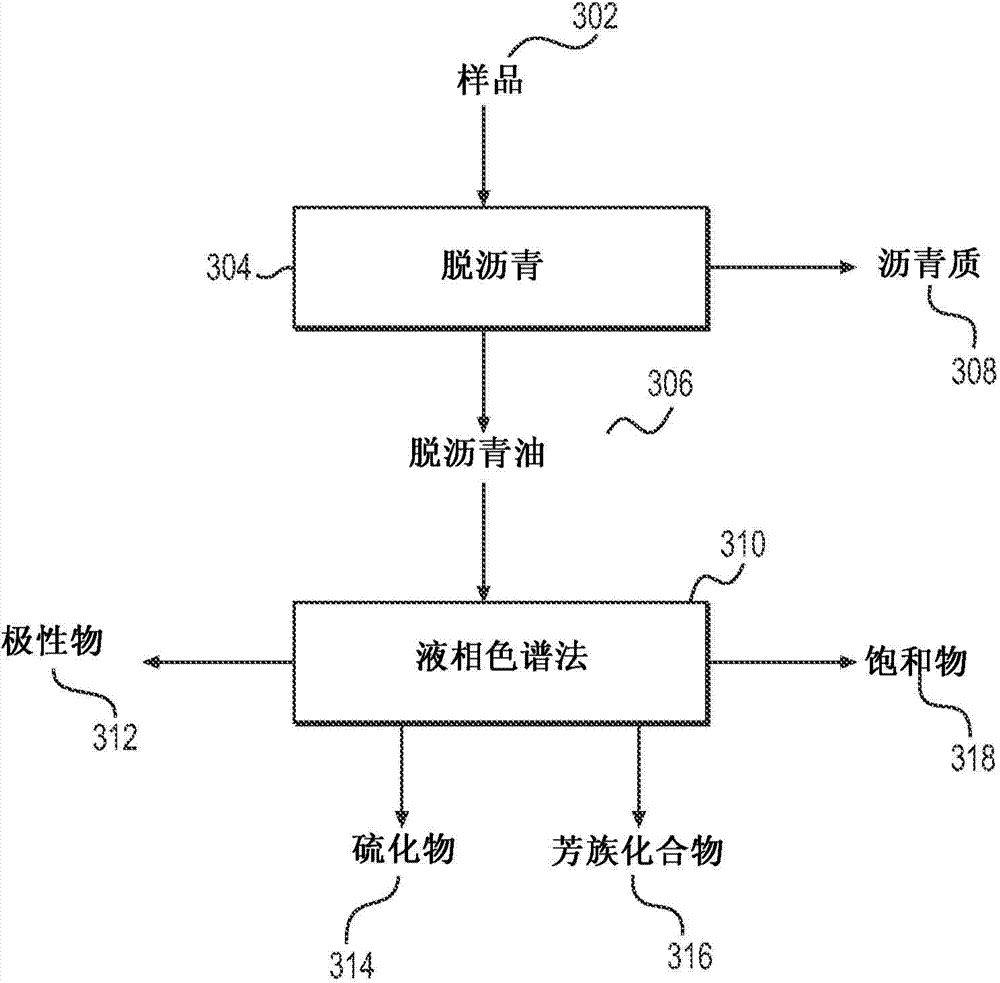
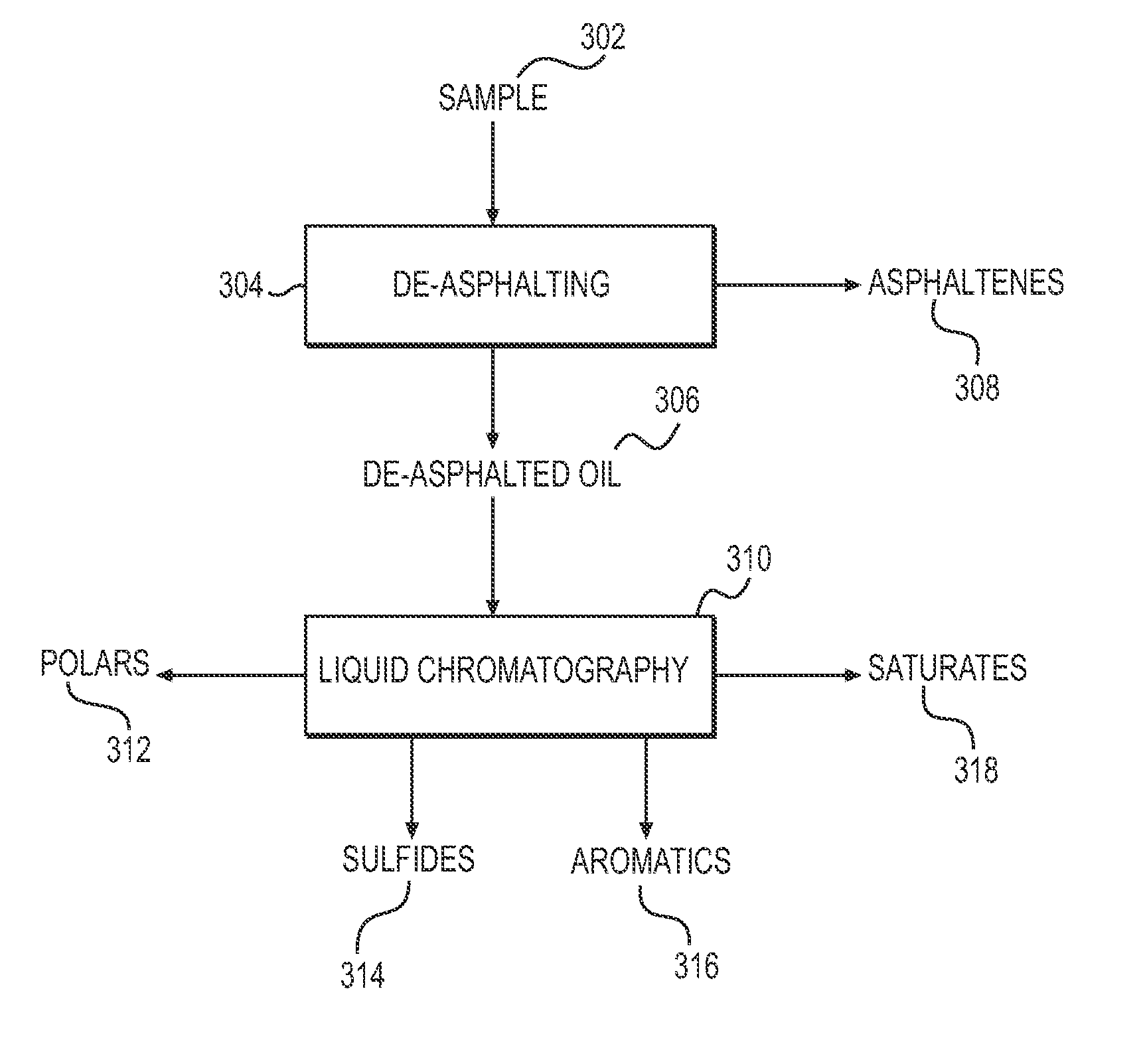
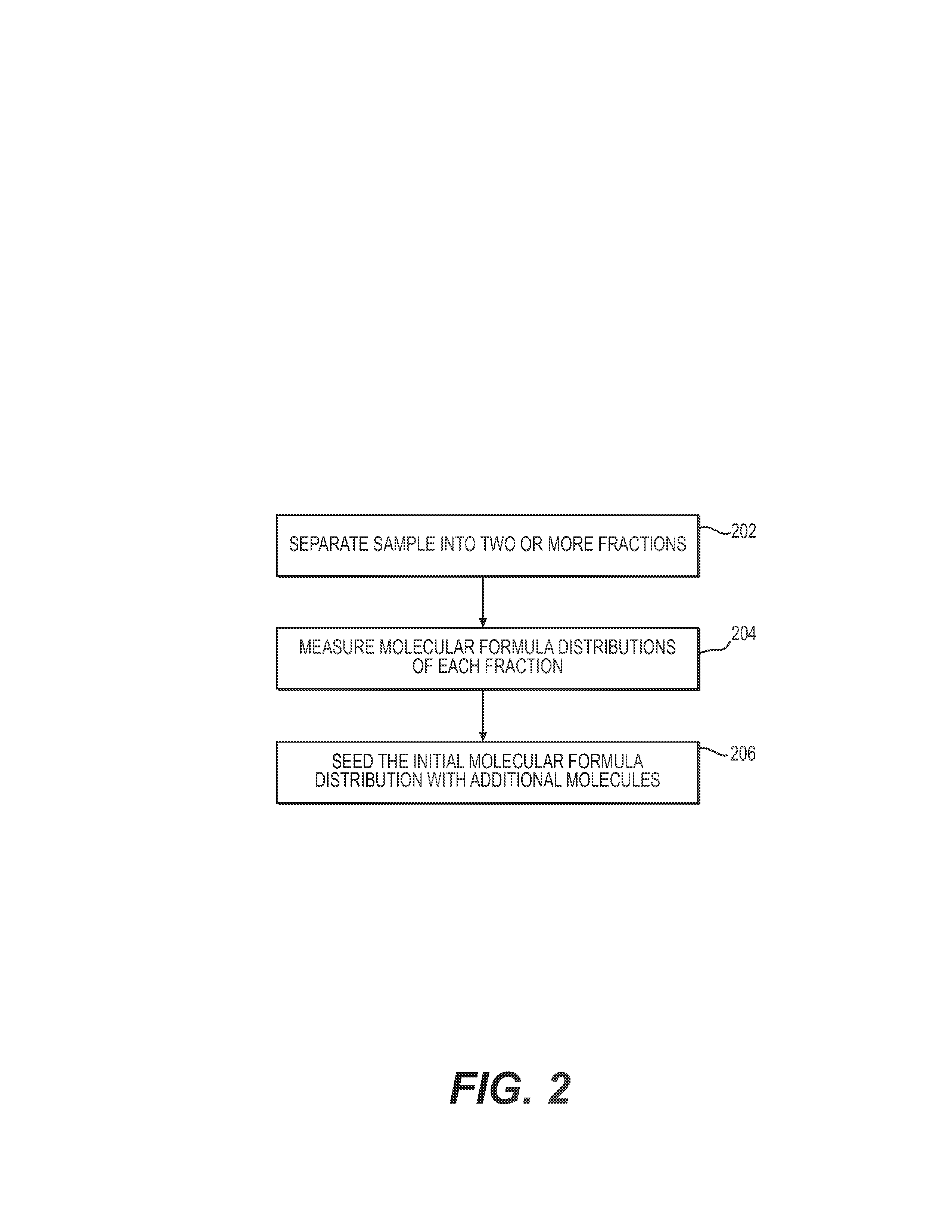
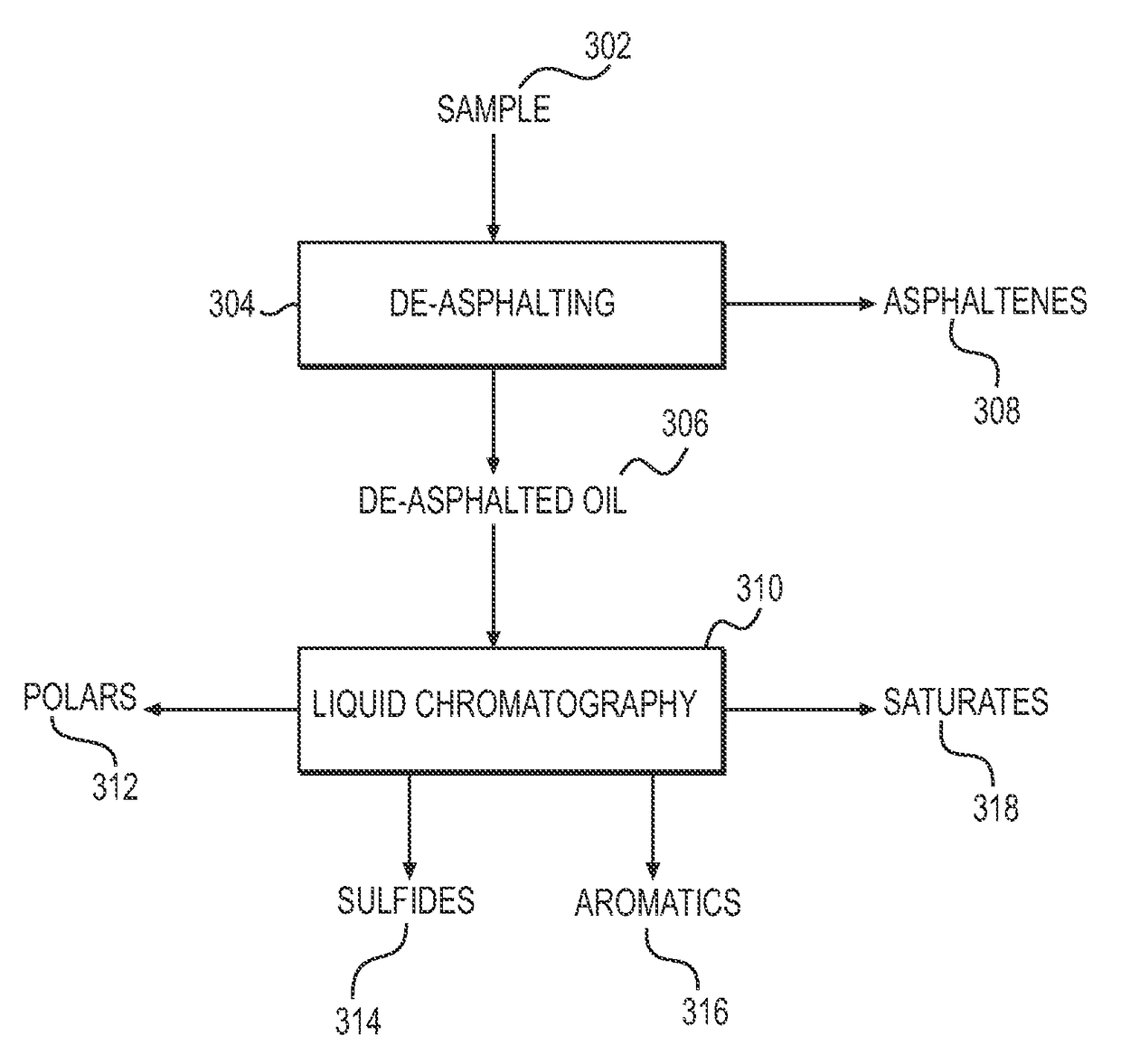
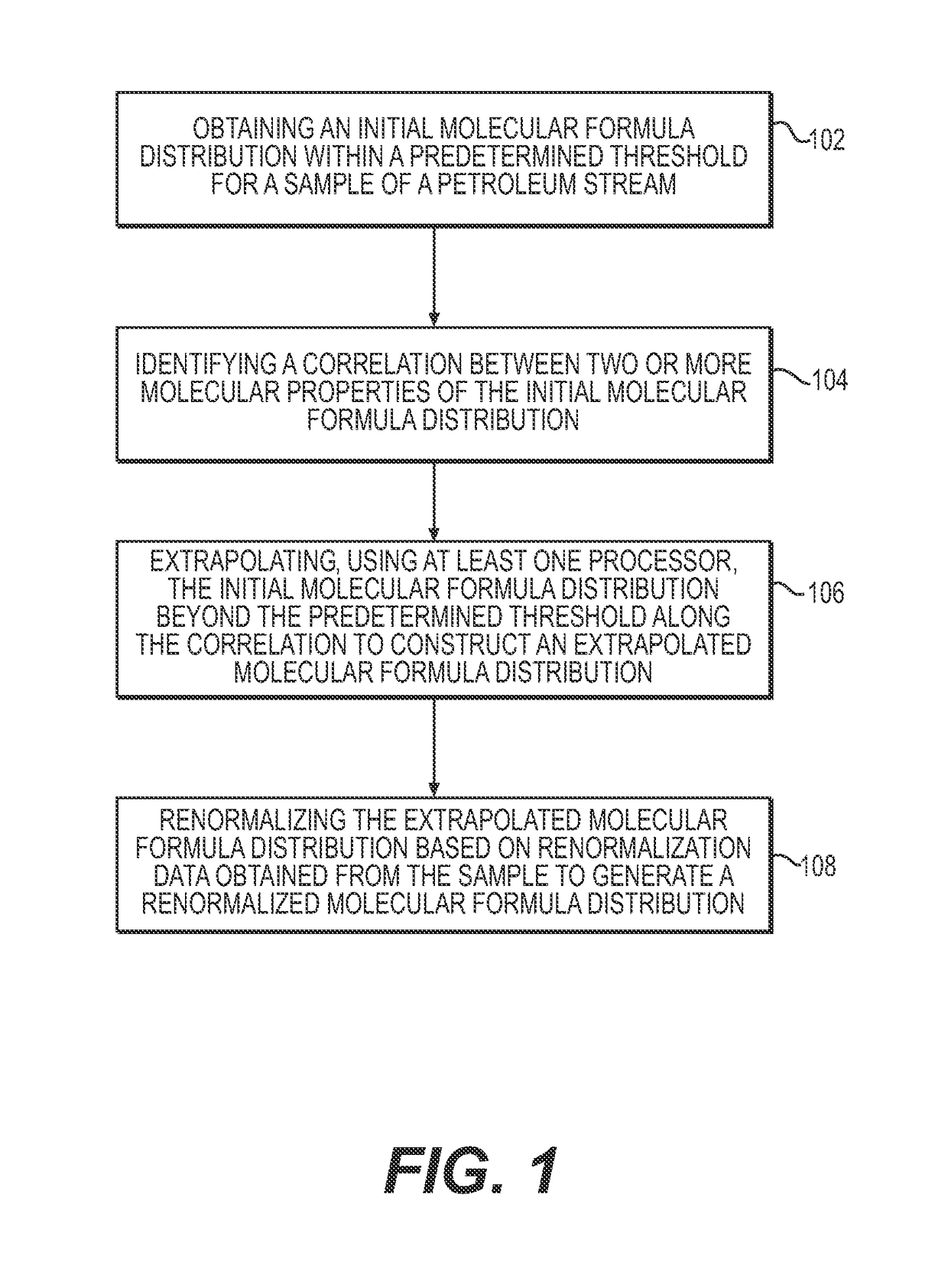
System and method to generate molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream
InactiveCN104335210AChemical property predictionMaterial testing goodsMolecular compositionRenormalization
Methods for generating molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream are disclosed. An initial molecular formula distribution within a predetermined threshold is obtained for a petroleum stream. A correlation between two or more molecular properties of the initial molecular formula distribution is identified, and the initial molecular formula distribution is extrapolated beyond the predetermined threshold along the correlation. The extrapolated molecular formula is renormalized based on renormalized based on renormalization data obtained from the sample. The renormalized molecular formula distribution can then be blended with the initial molecular formula distribution, reconciled to secondary analytical measurements, and / or used to create a model of composition and / or a molecular composition-based model of a resid upgrading process. Systems for implementing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
System and method to generate moledular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream
ActiveUS20130325418A1Chemical property predictionComputation using non-denominational number representationMolecular compositionRenormalization
Methods for generating molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream are disclosed. An initial molecular formula distribution within a predetermined threshold is obtained for a petroleum stream. A correlation between two or more molecular properties of the initial molecular formula distribution is identified, and the initial molecular formula distribution is extrapolated beyond the predetermined threshold along the correlation. The extrapolated molecular formula is renormalized based on renormalized based on renormalization data obtained from the sample. The renormalized molecular formula distribution can then be blended with the initial molecular formula distribution, reconciled to secondary analytical measurements, and / or used to create a model of composition and / or a molecular composition-based model of a resid upgrading process. Systems for implementing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
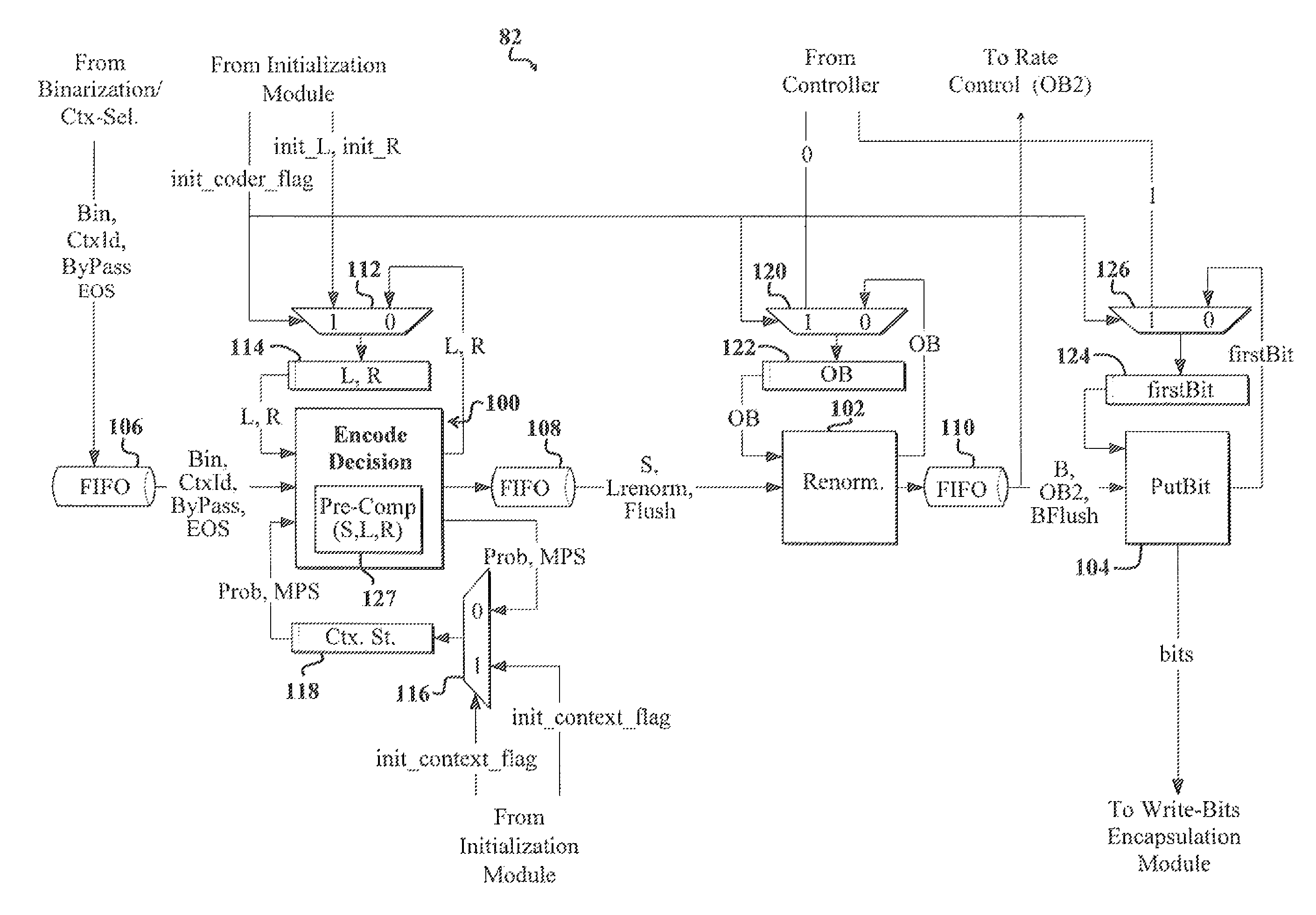
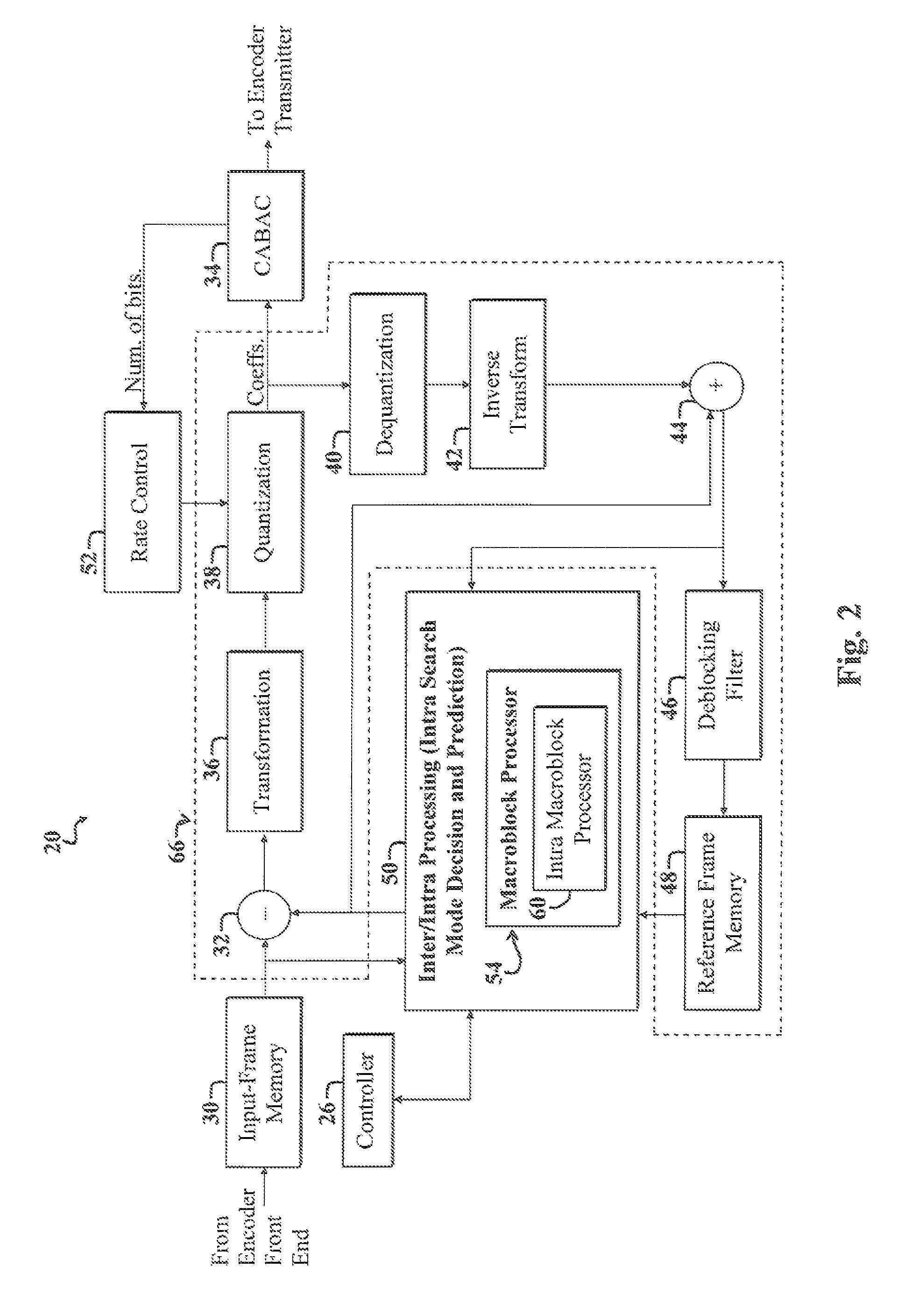
Entropy coding for video processing applications
ActiveUS8422552B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRenormalizationVideo processing
An entropy coding apparatus. In a specific embodiment, the entropy coding apparatus includes a renormalization process and an encode-decision process that communicates with the renormalization process. The encode-decision process is adapted to run in parallel with the renormalization process without the renormalization process being nested therein. In a more specific embodiment, the entropy coding apparatus includes an entropy encoder that is H.264 compliant. The encode-decision process includes a first mechanism for pre-computing certain parameters to eliminate the need to nest the renormalization process within the encode-decision process. The renormalization process and the encode-decision process are components of a Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) module.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Low-voltage CMOS circuits for analog decoders
InactiveUS20070276895A9Computation using non-contact making devicesCode conversionRenormalizationBinary multiplier
Low-voltage CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) circuits, suitable for analog decoders, for example, are provided. The circuits include multiplier modules that receive first input signals and respective ones of a plurality of second input signals. Each multiplier module generates as output signals products of the first input signals and its respective second input signals. Dummy multiplier modules that respectively correspond to the multiplier modules receive the second input signals, and each dummy multiplier module forms products of the second input signal of its corresponding multiplier module and the other second input signals. The dummy multiplier modules reduce the overall voltage requirements of the circuit, thereby providing for low-voltage operation. In some embodiments, a connectivity module receives output signals from the multiplier modules and generates as output signals sums of predetermined ones of the output signals, and a renormalization module receives and normalizes the output signals from the connectivity module to generate output signals that sum to a predetermined unit value.
Owner:ALBERTA UNIV OF
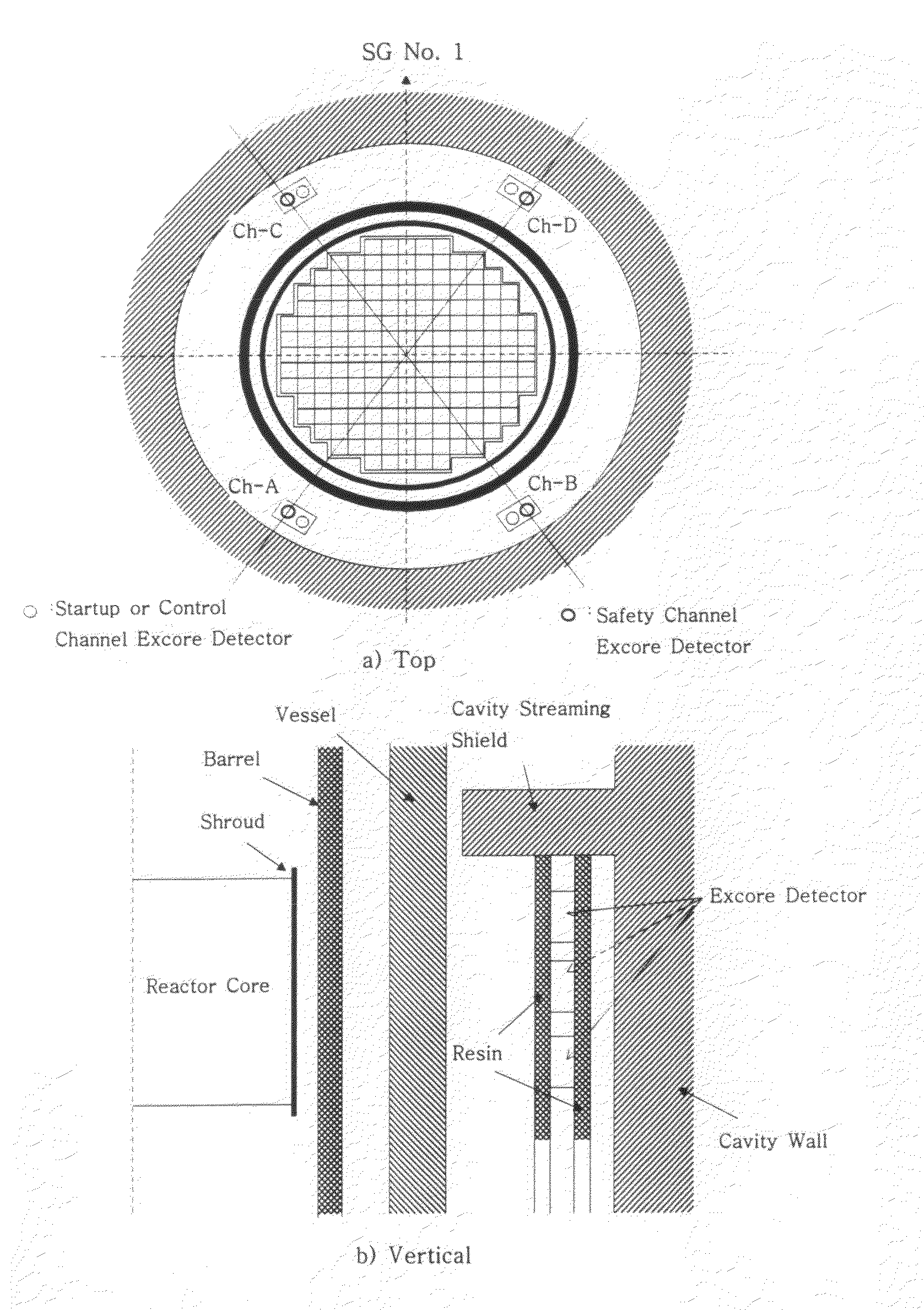
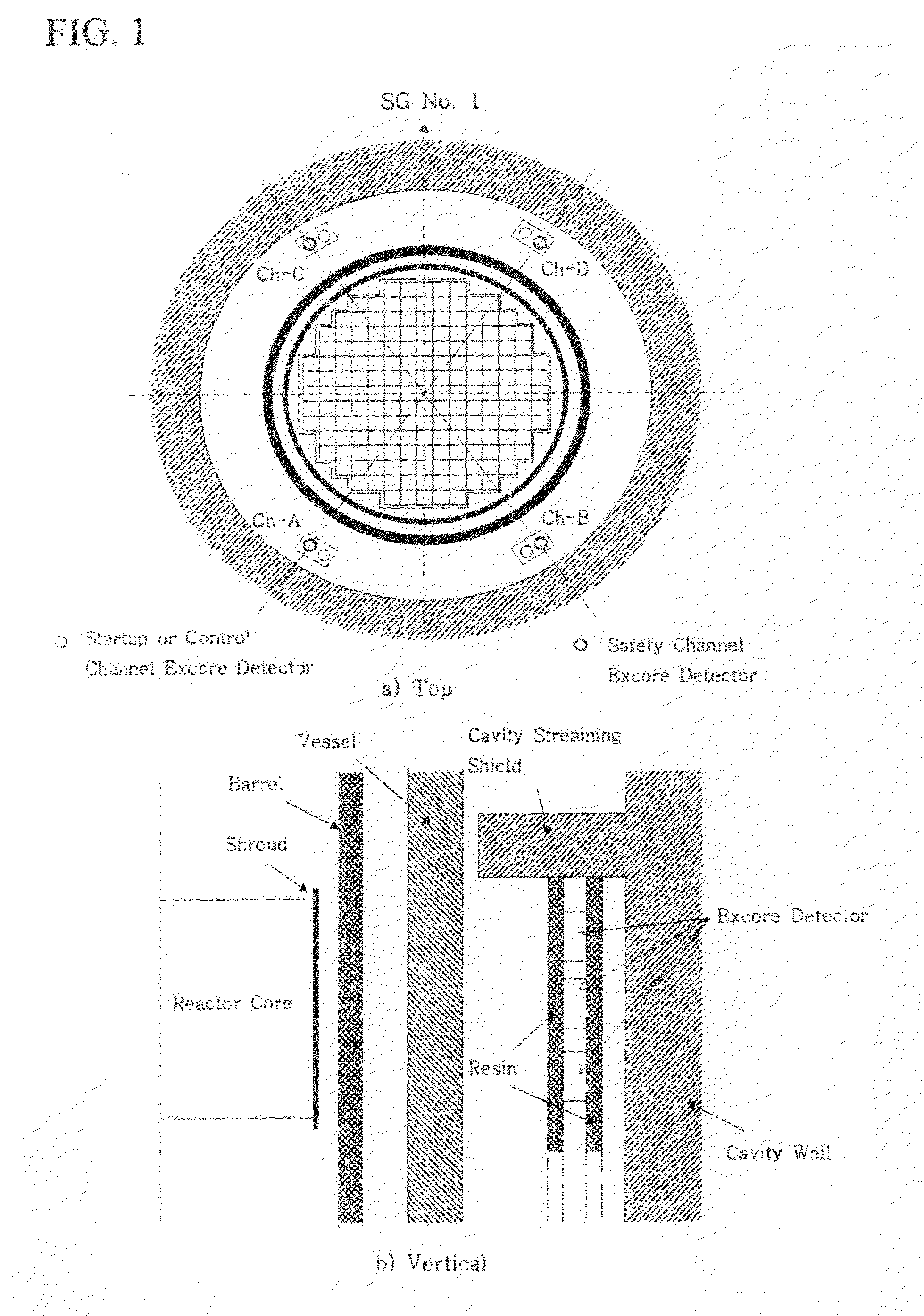
Renormalization method of excore detector
InactiveUS20100104059A1Preventing unnecessary tripAccurate predictionNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringRenormalizationNuclear power
Disclosed is a calibration method of an excore detector used in core power monitoring of a nuclear power plant, in which a spatial weighting function (SWF), used to theoretically predict a signal of the excore detector is multiplied by a designated calibration factor to reflect characteristics of the excore detector in a calibration process. It is assumed that the SWF is the multiplication of a one-dimensional shape annealing function (SAF) and a two-dimensional SWF, and the SAF is multiplied by the calibration factor. Since the SAF is calculated in a normalized form, the multiplication of the SAF by the calibration factor to reflect characteristics of the excore detector corresponds to new normalization and thus the calibration of the SAF is referred to as renormalization The signal of the excore detector is considerably accurately predicted by multiplying the theoretically calculated SAF by the renormalization factor, and the multiplication is equally applied although the characteristics of the excore detector are highly changed. An increase in the accuracy of the excore detector in the nuclear power plant prevents unnecessary reactor trips and allows a reactor to be operated at a stable power, thus obtaining the safety of a core and raising economical efficiency.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
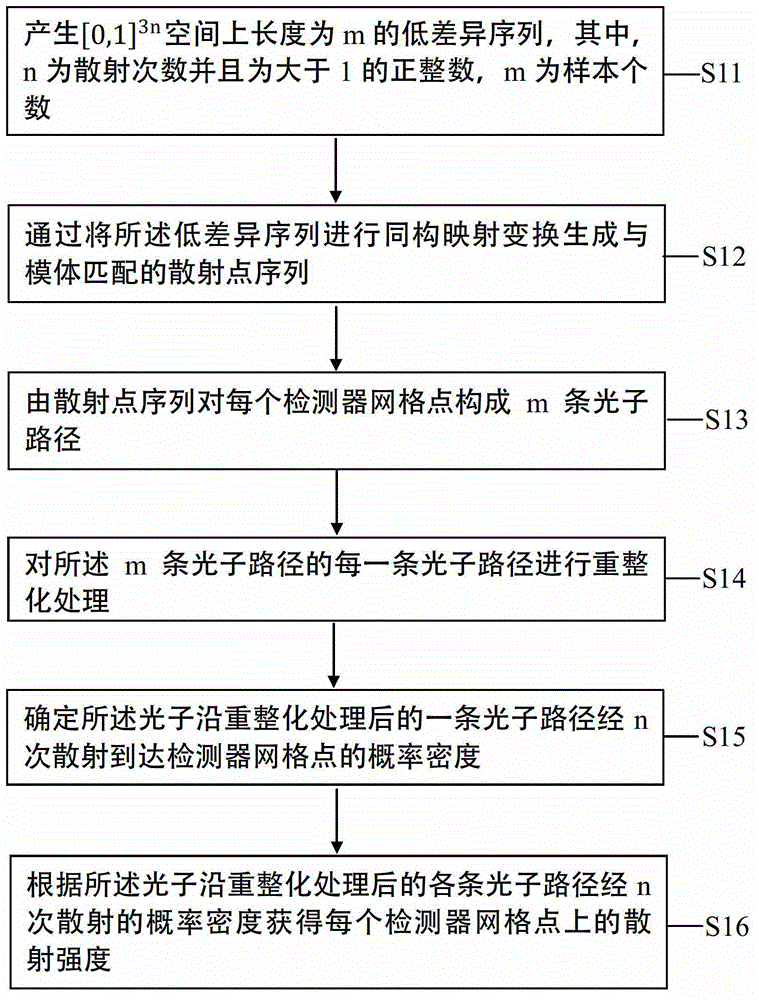
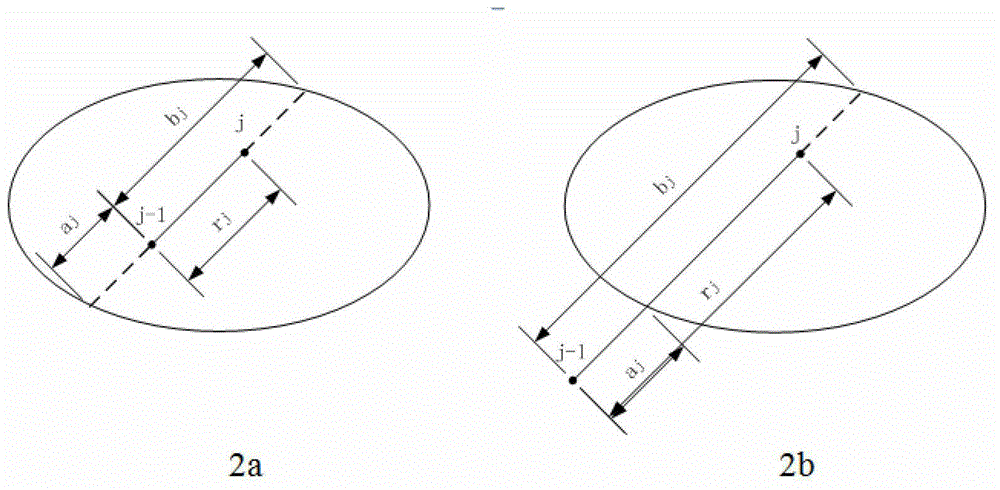
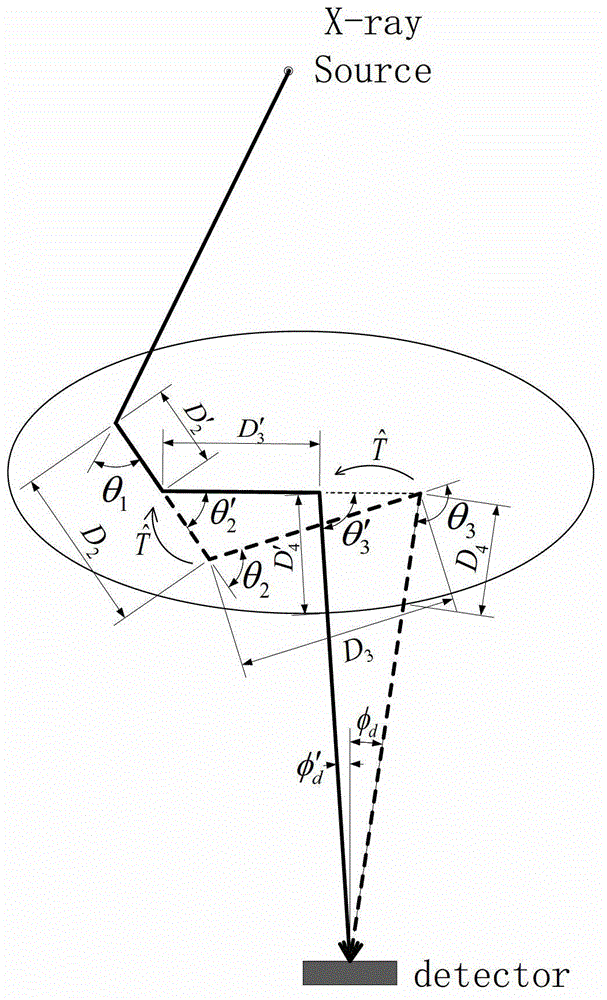
Method for renormalization of X-ray multiple scattering simulation
ActiveCN104027121AEliminate errorsSmall amount of calculationRadiation diagnosticsSoft x rayRenormalization
The invention provides a method for renormalization of X-ray multiple scattering simulation. The method comprises a first step of generating a low-difference sequence with the length of m in [0,1]<3n> space, enabling n to be scattering times and be a positive integer larger than 1, and enabling m to be the sample number; a second step of generating a scattering point sequence matched with the geometrical shape of a die body by performing isomorphic mapping transformation on the low-difference sequence; a third step of forming m photon paths for each detector grid point through the scattering point sequence; a fourth step of performing renormalization processing on each photon path among the m photon paths; a fifth step of determining the probability density of photons reaching the detector grid points through n-time scattering along each photon path after renormalization processing; and a sixth step of obtaining scattering intensity of each detector grid point according to the probability density of the photons through n-time scattering along each photon path after renormalization processing. The method can improve multiple scattering simulation efficiency and eliminate errors caused by die body edge incontinuity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Complex network community detection method based on fractal feature
A complex network community detection method based on a fractal feature includes two phases of offline static complex network community detection processing and online dynamic complex network community detection processing. Multi-scale features of a complex network are fully utilized, a renormalization process is used as a bridge for connecting different scales, the purpose of using previous community structure information to detect a new community structure is achieved, incremental community detection is achieved, new attempts for researching dynamic complex network community structures are conducted, and satisfying results are obtained.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
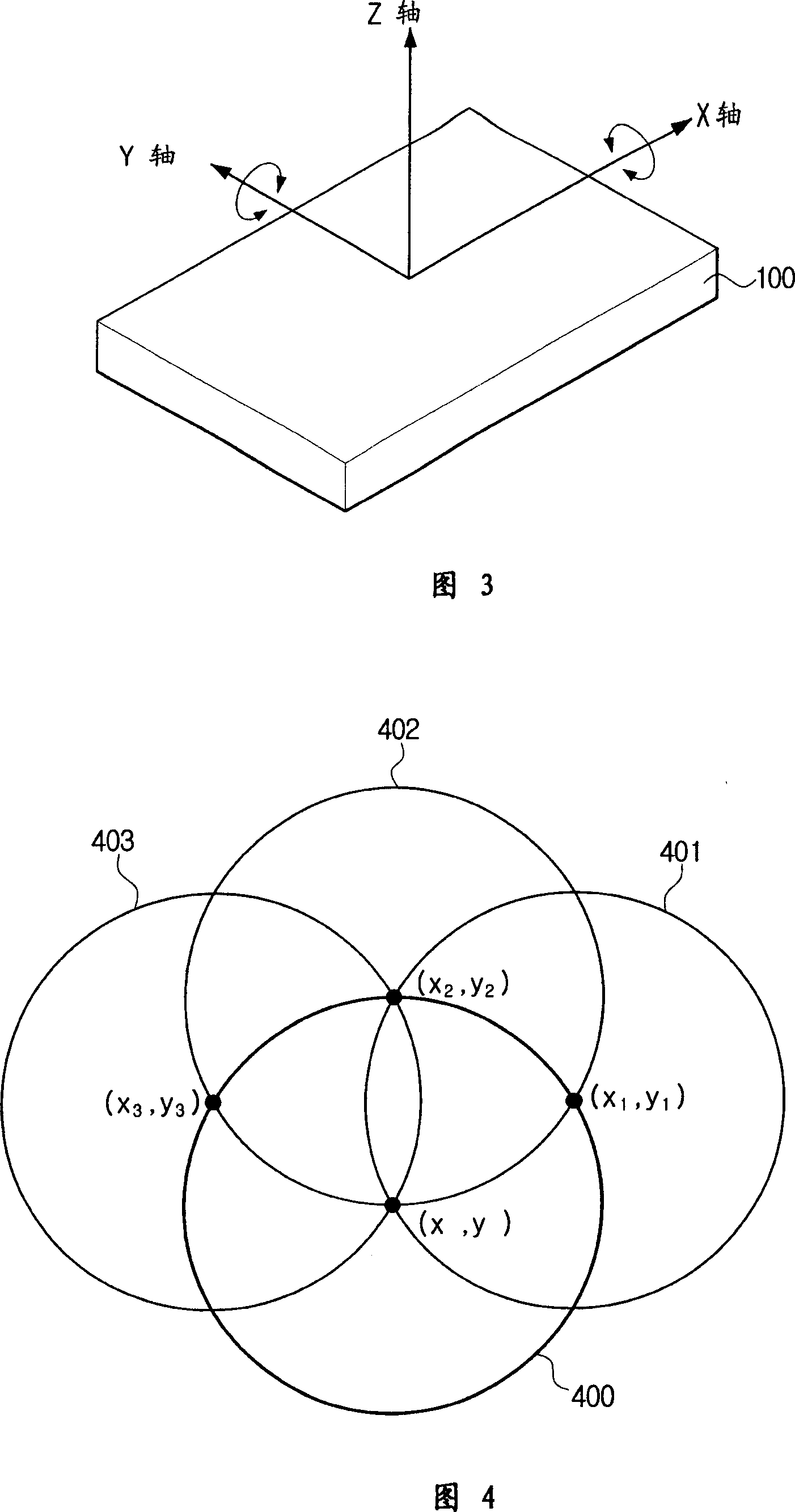
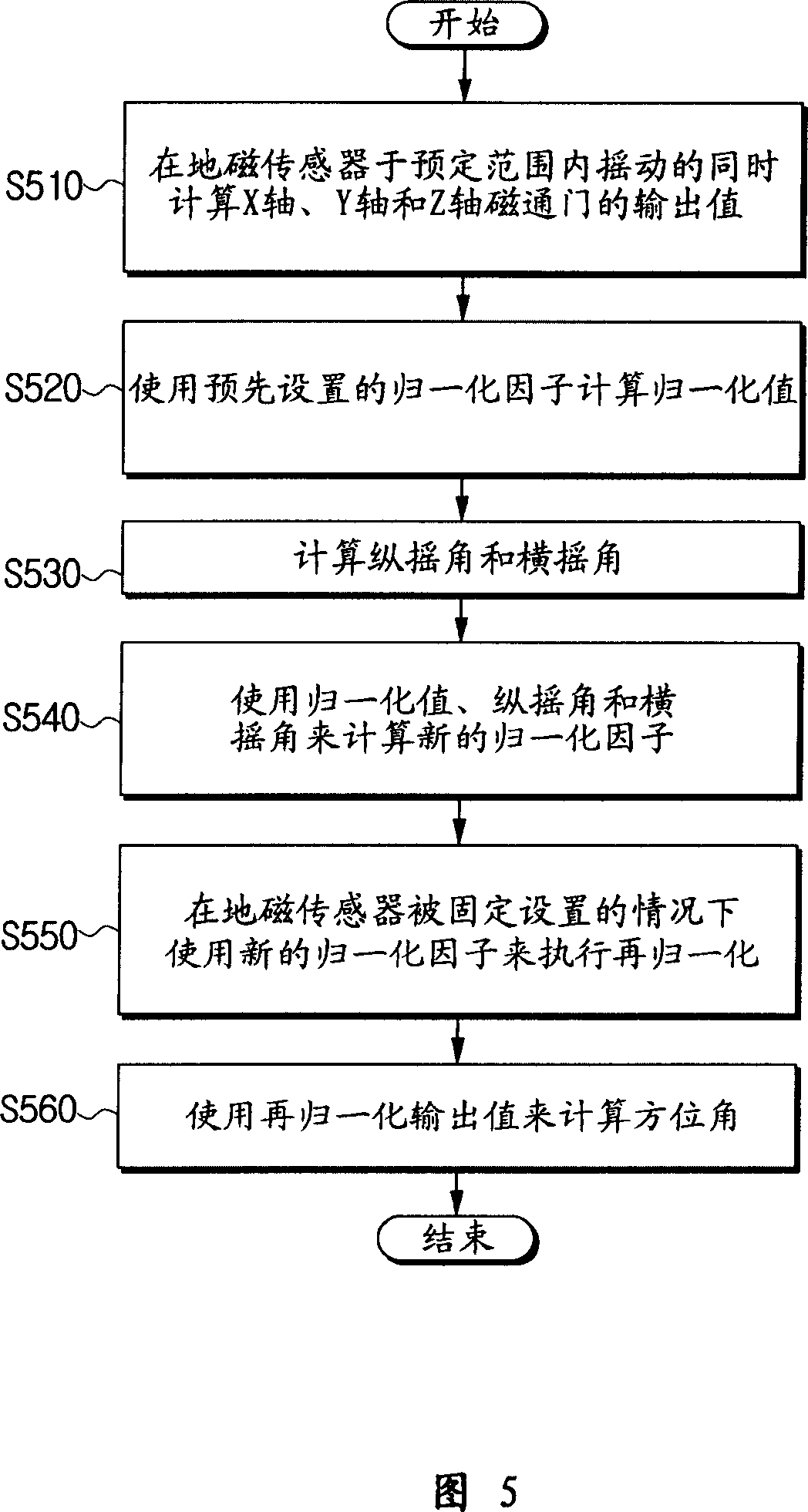
Geomagnetic sensor for computing azimuth and method thereof
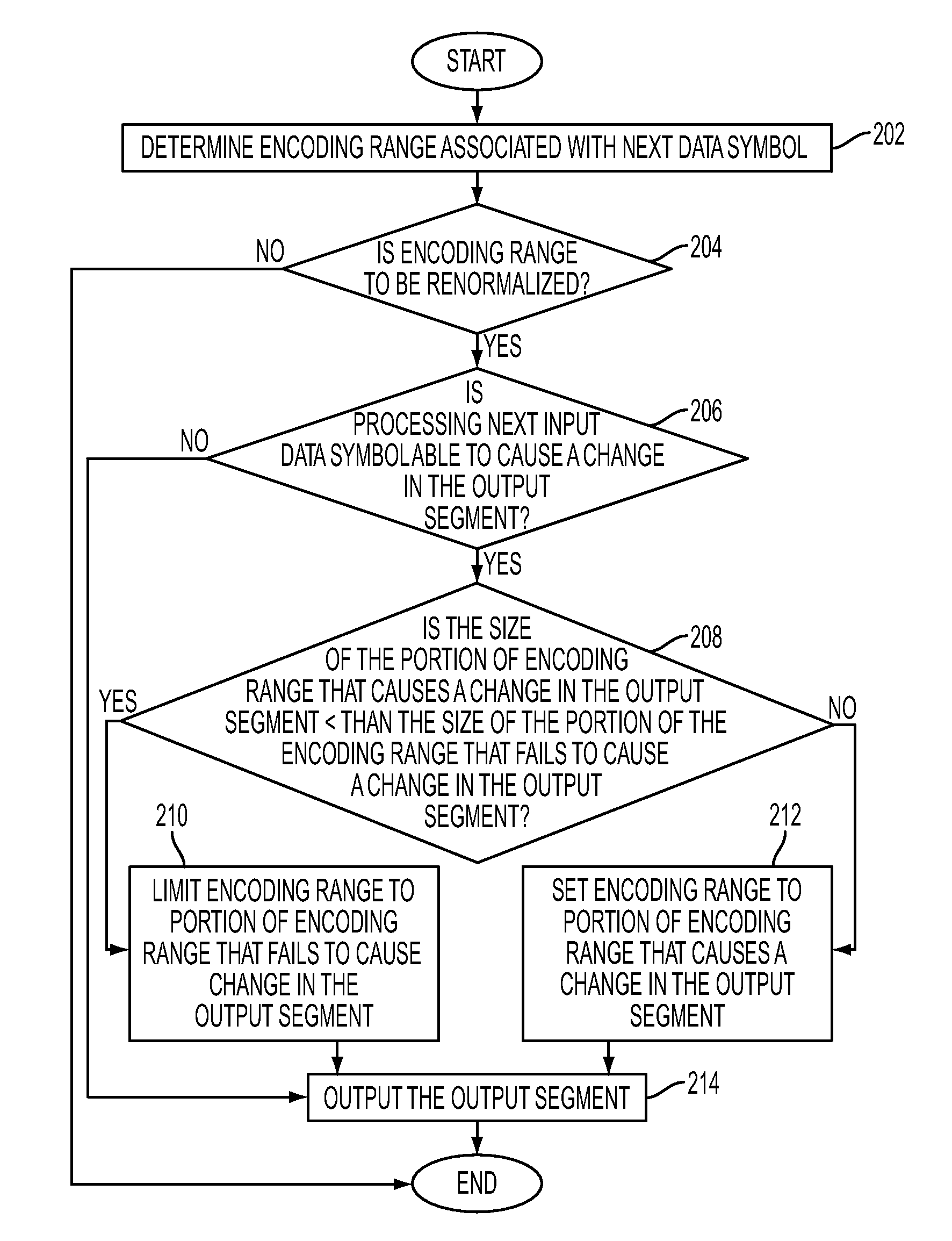
InactiveUS7389590B2Good compensationEasy to operateMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesRenormalizationComputer science
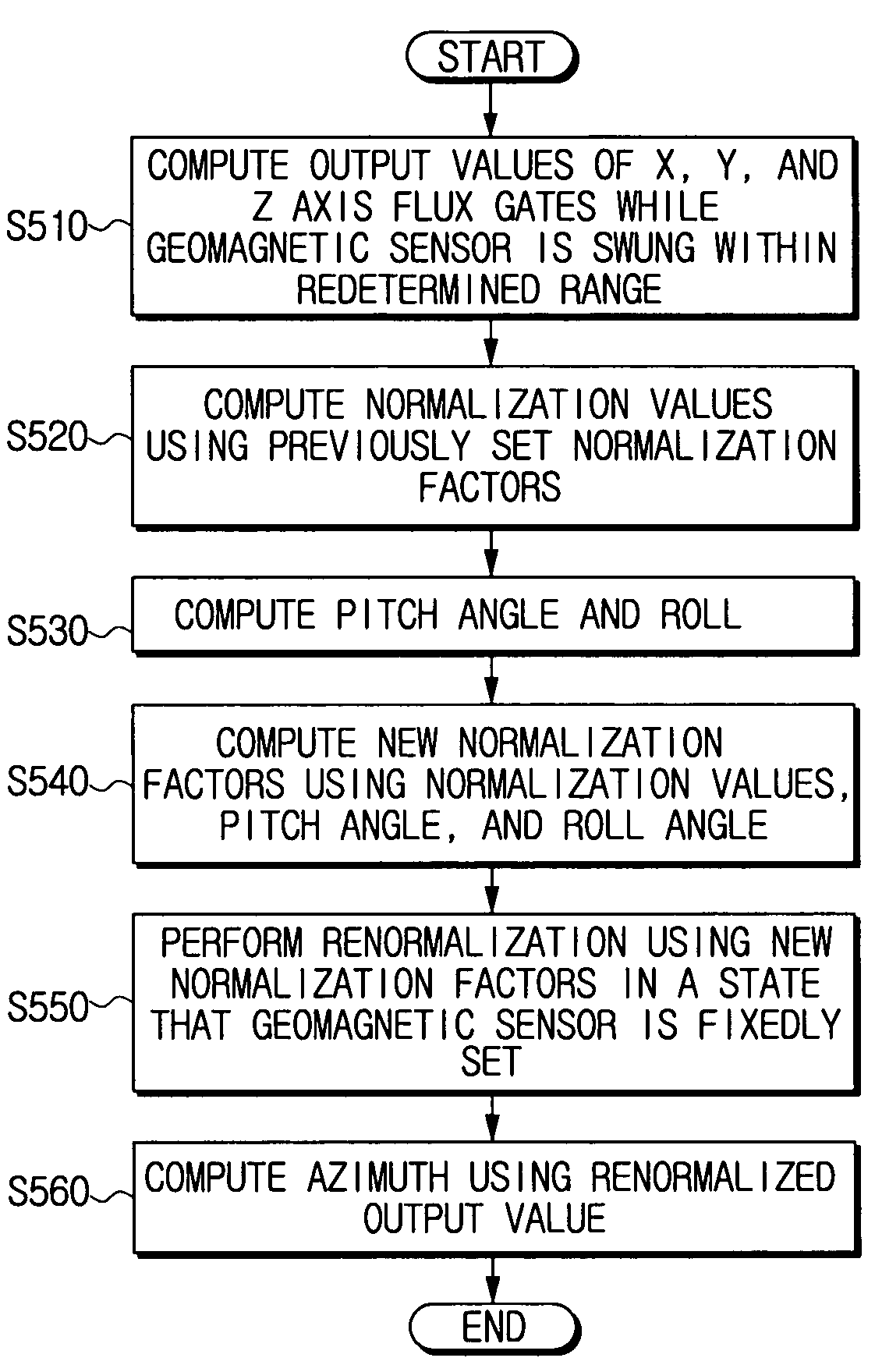
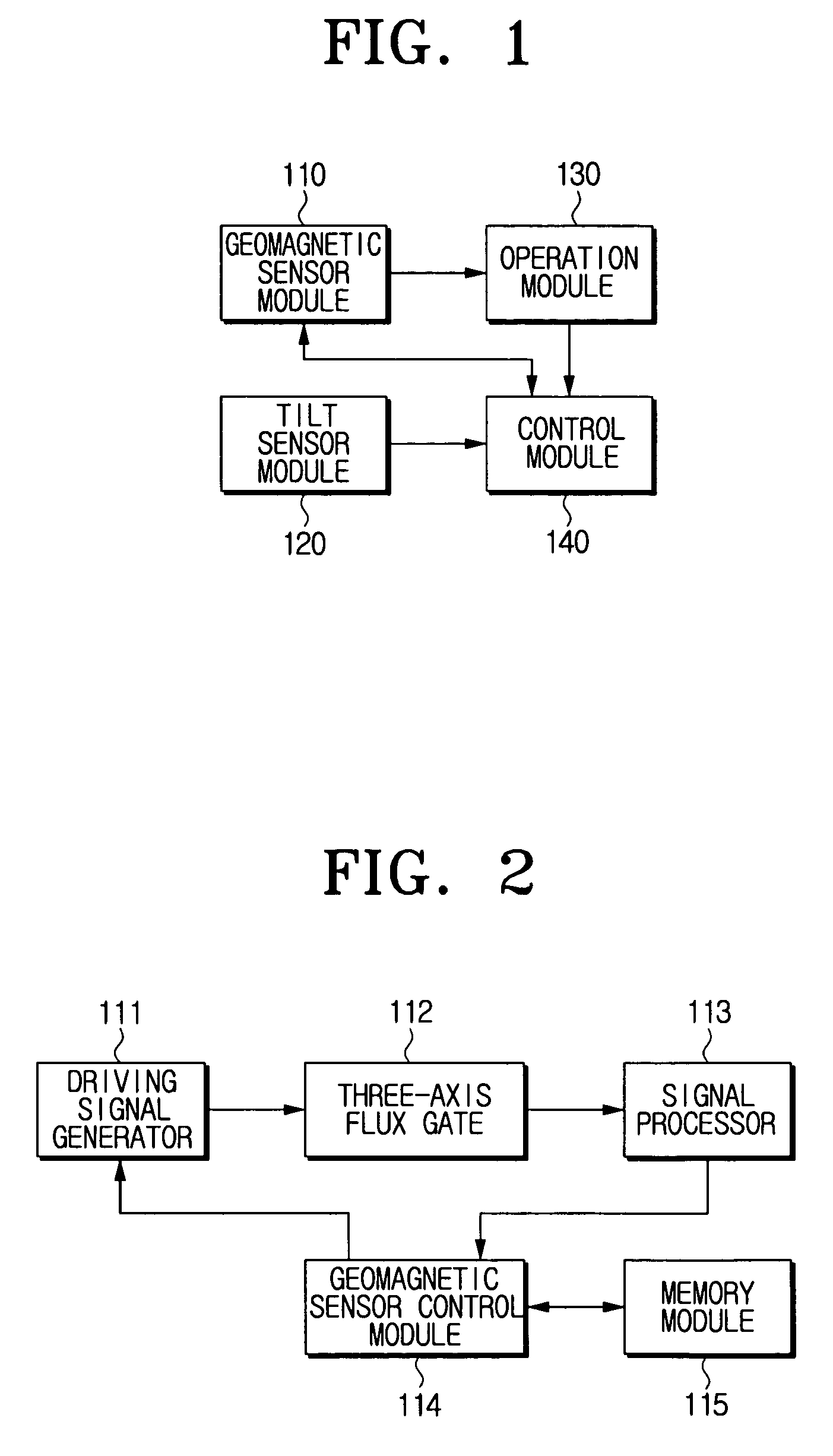
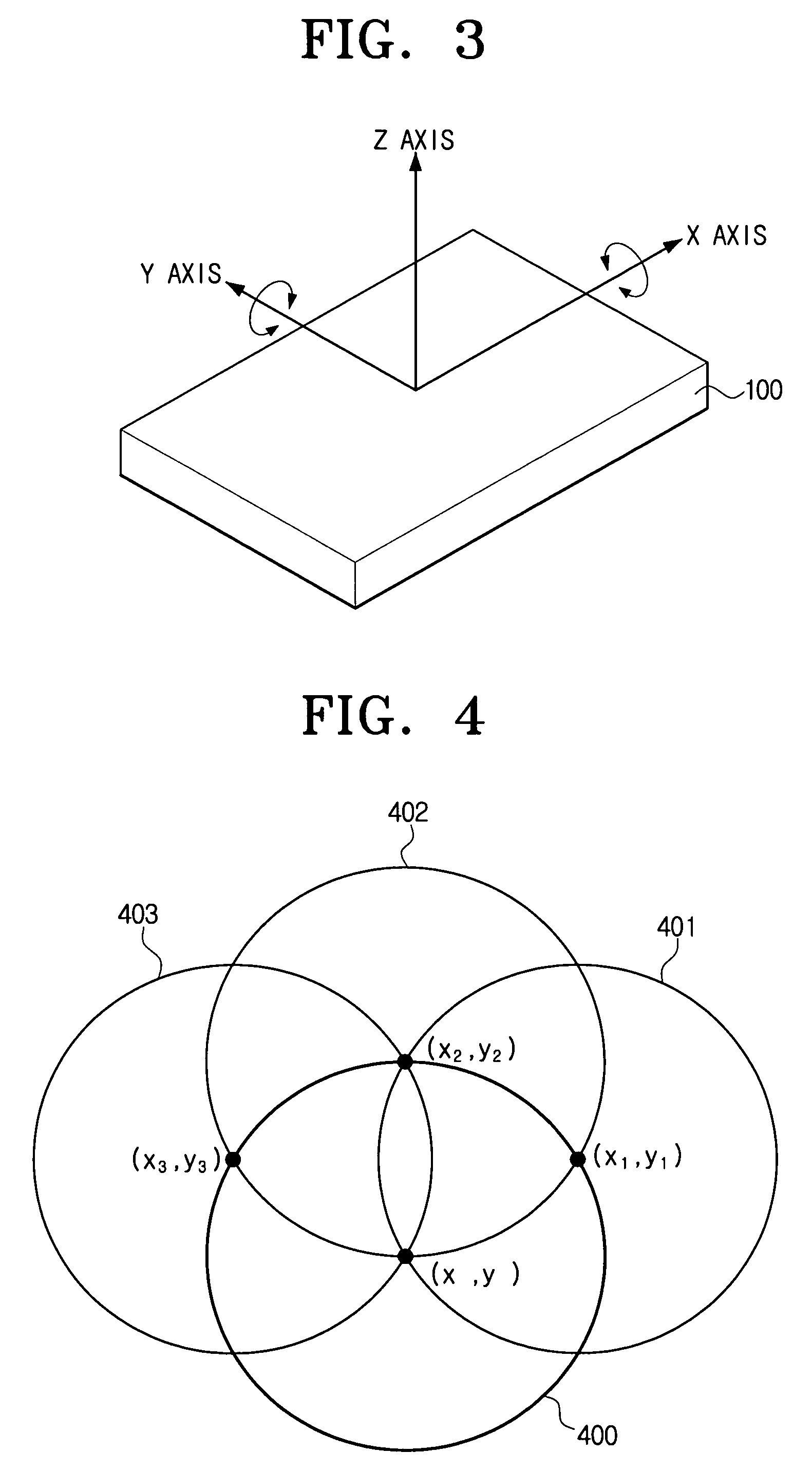
A geomagnetic sensor for computing an azimuth and a method thereof. The geomagnetic sensor includes a geomagnetic sensor module, including X, Y and Z axis fluxgates orthogonal to one another, for performing normalization for mapping output values of the X, Y and Z axis fluxgates onto a previously set normalization range using previously set normalization factors, an operation module for performing operation of new normalization factors based on a plurality of normalization values output from the geomagnetic sensor module when the geomagnetic sensor is swung within a previously set range, a tilt sensor module for computing a pitch angle and a roll angle, and a control module for providing the new normalization factors to the geomagnetic sensor module to allow the geomagnetic sensor module to perform renormalization and computing an azimuth using the output values renormalized by the geomagnetic sensor module and the pitch and roll angles computed during the renormalization. Therefore, it is possible to easily compute the normalization factors used for azimuth compensation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Geomagnetic sensor for computing azimuth and method thereof
InactiveCN1971310AGood compensationMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleElectric/magnetic detectionRenormalizationComputer science
A geomagnetic sensor for computing an azimuth and a method thereof. The geomagnetic sensor includes a geomagnetic sensor module, including X, Y and Z axis fluxgates orthogonal to one another, for performing normalization for mapping output values of the X, Y and Z axis fluxgates onto a previously set normalization range using previously set normalization factors, an operation module for performing operation of new normalization factors based on a plurality of normalization values output from the geomagnetic sensor module when the geomagnetic sensor is swung within a previously set range, a tilt sensor module for computing a pitch angle and a roll angle, and a control module for providing the new normalization factors to the geomagnetic sensor module to allow the geomagnetic sensor module to perform renormalization and computing an azimuth using the output values renormalized by the geomagnetic sensor module and the pitch and roll angles computed during the renormalization. Thereby, the azimuth compensatory normalization factors can be calculate easily.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
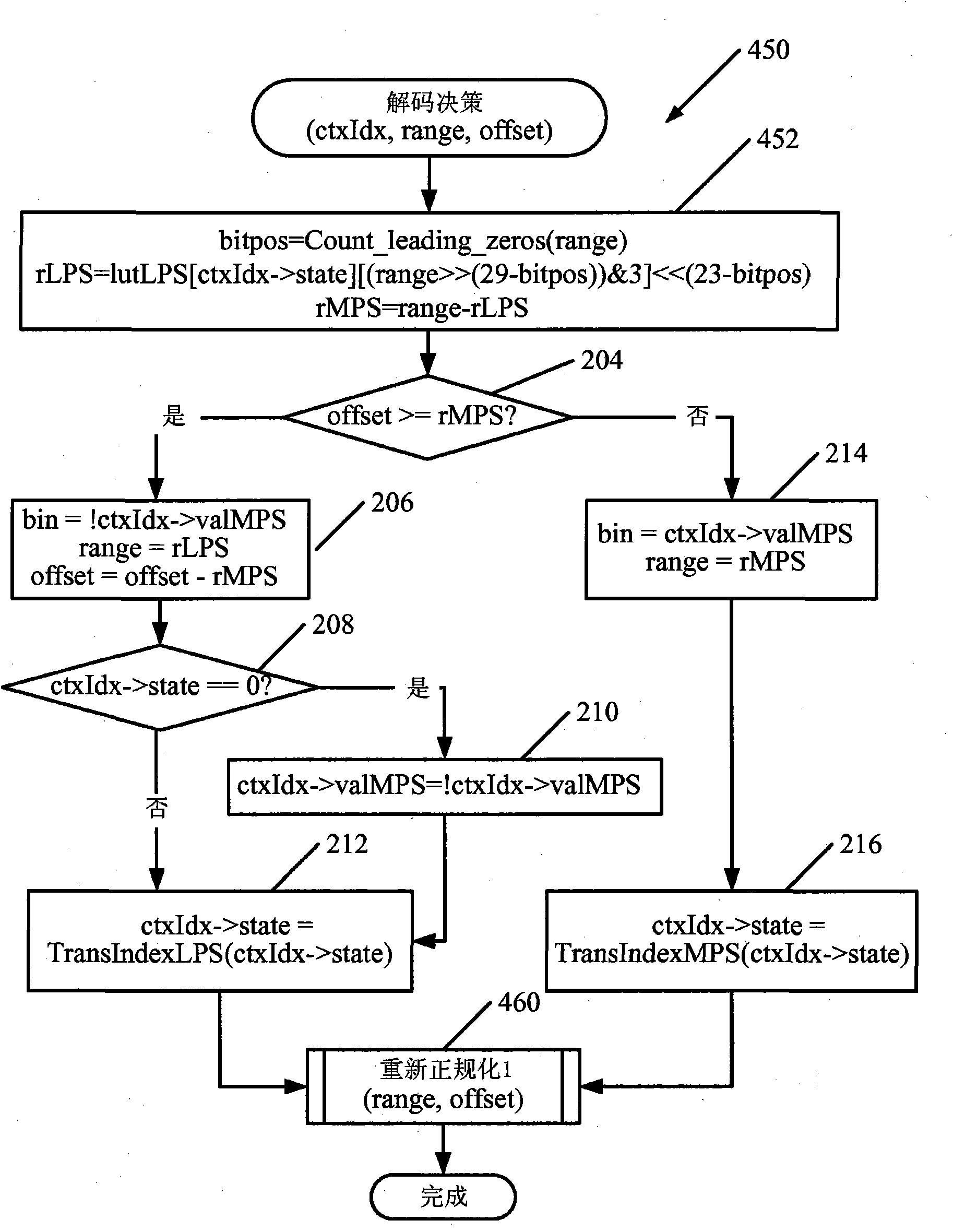
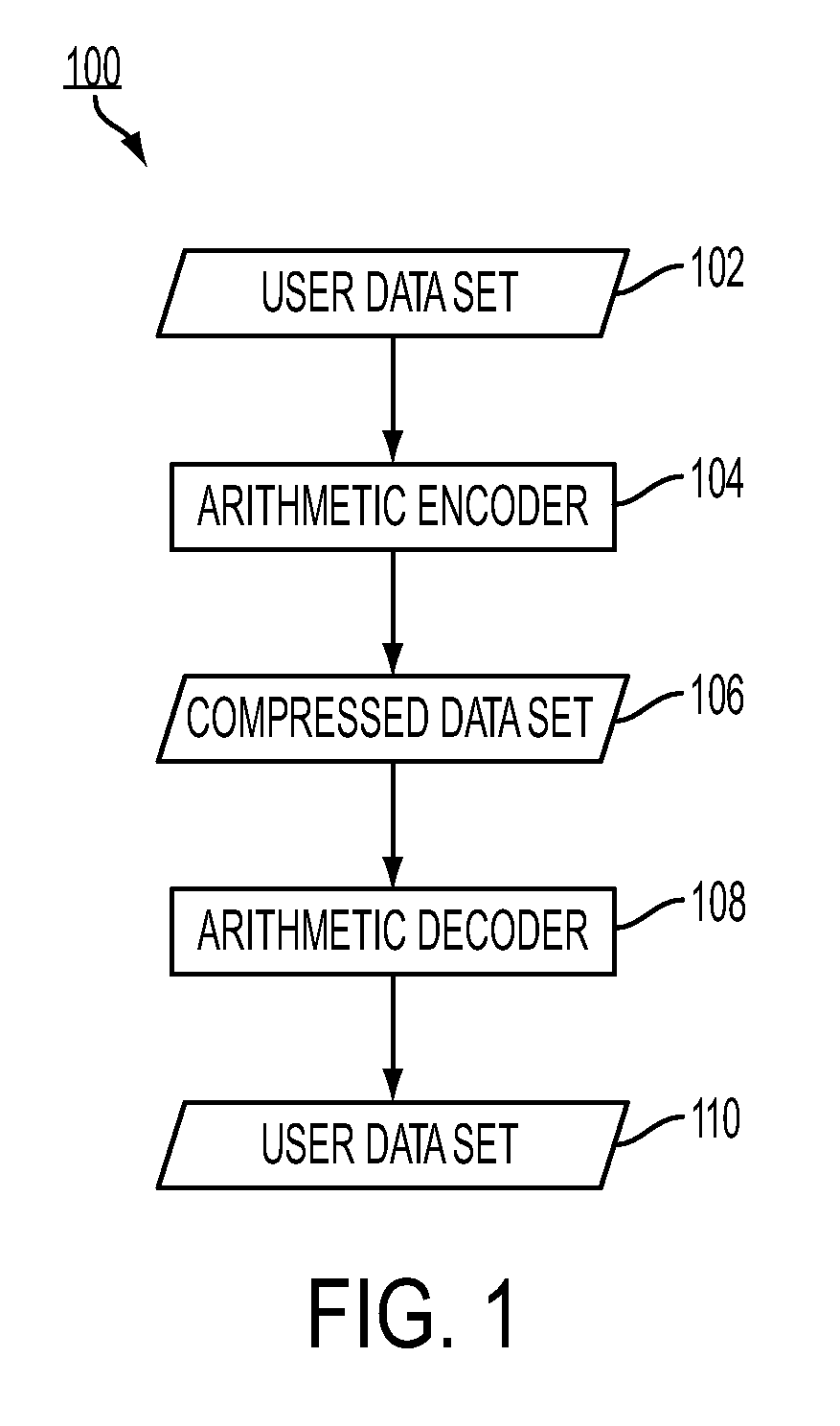
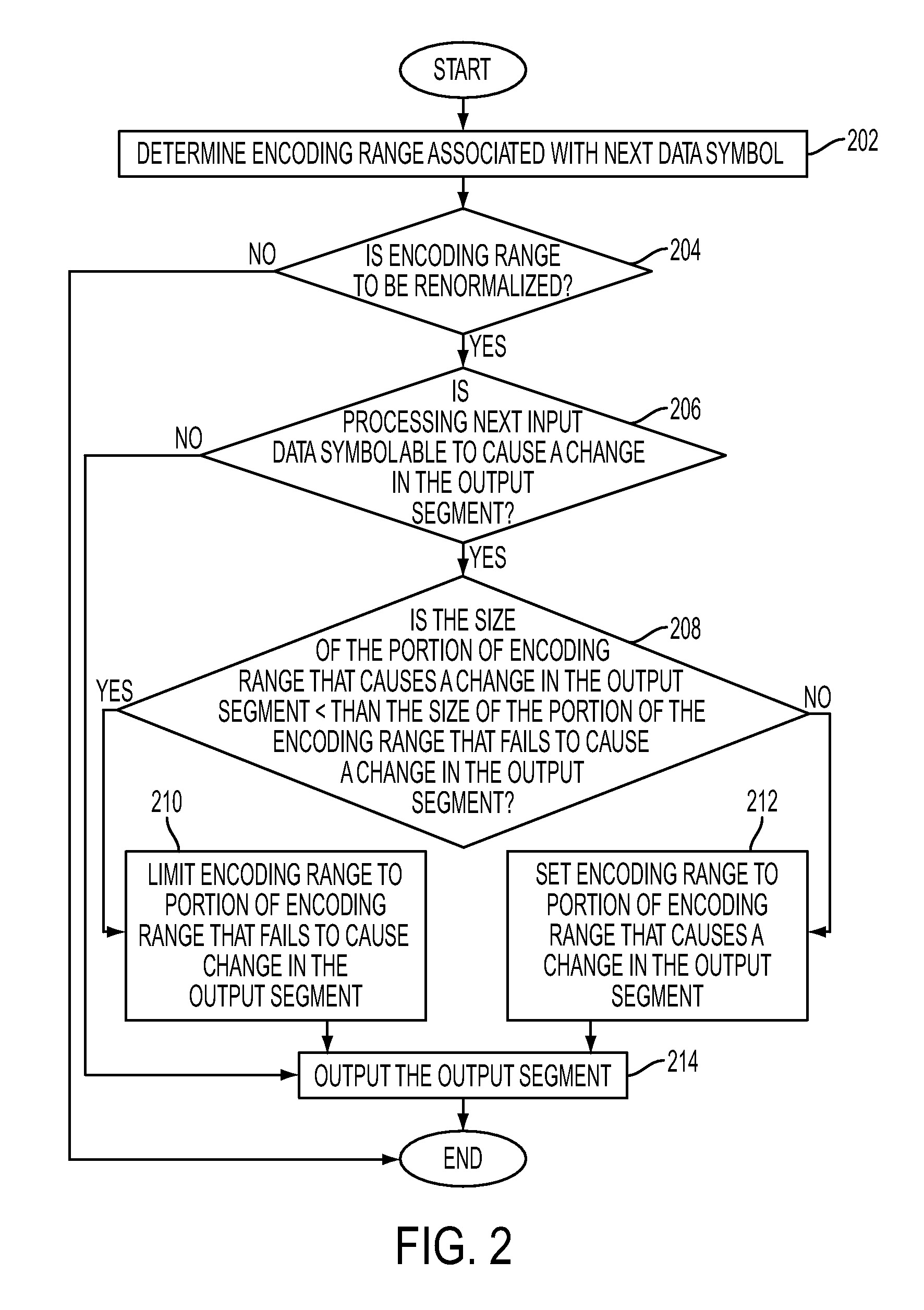
Range normalization for entropy reduction arithmetic encoding/decoding
InactiveUS7652599B1Reduce the amount of processingEfficiently determinedCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionEntropy reductionRenormalization
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for performing renormalization in a data entropy reduction process of an image in a compression path. An accumulator is used for one of arithmetic encoding and decoding according to an arithmetic coding process and a number of most significant bits of the accumulator represents an output segment. If processing an input data symbol is determined to be able to cause a change in a value of the output segment, the encoding range is changed. If the size of the encoding range portion that can cause the output segment value to change is less than the size of the portion of the encoding range that fails to cause the change, the encoding range is limited to the size that can cause the change. Otherwise, the encoding range is set to the size that fails to cause the change.
Owner:XEROX CORP
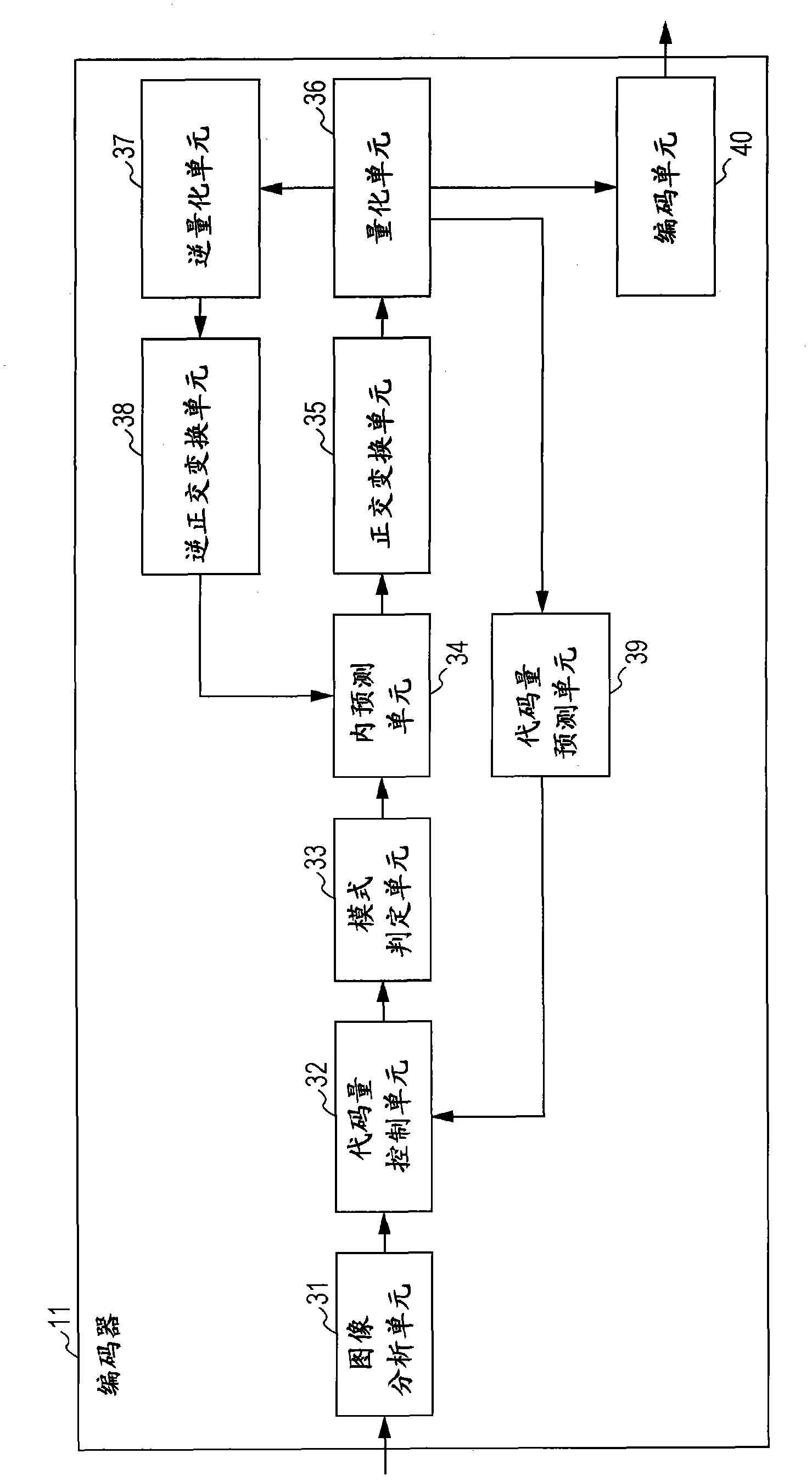
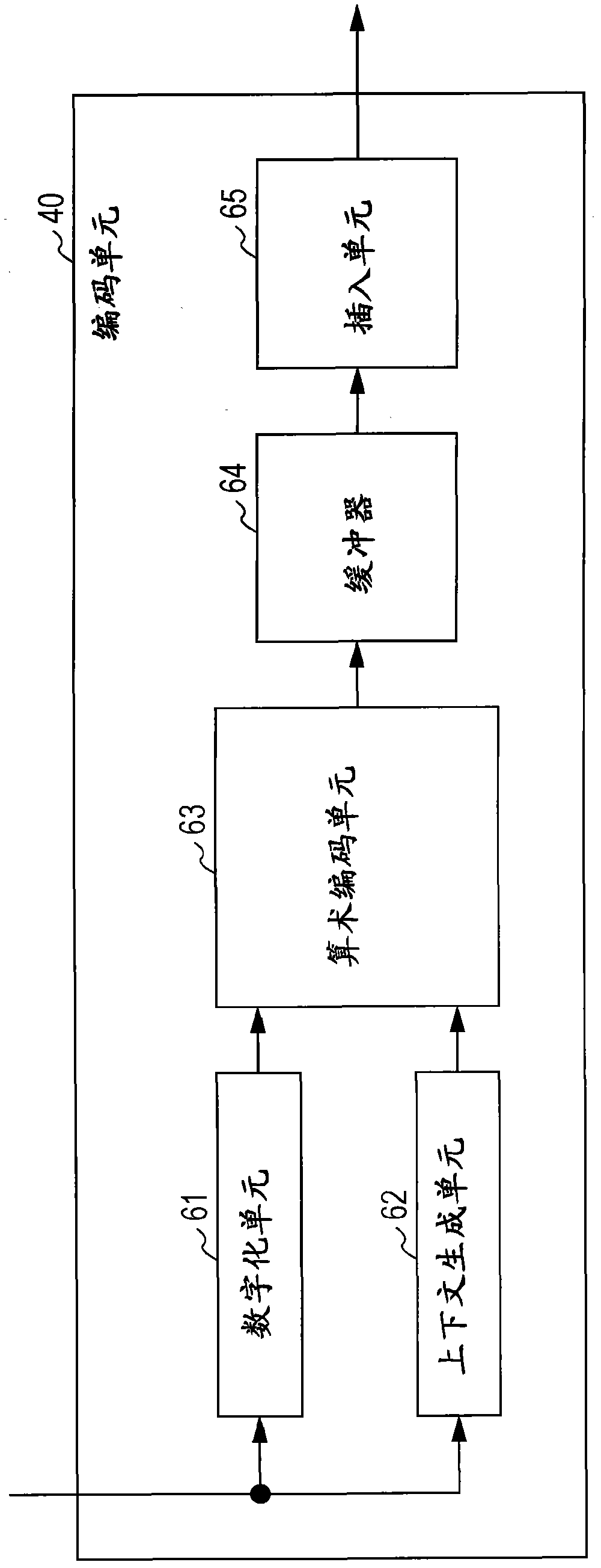
Encoder, encoding method and program
InactiveCN102457729AFast predictionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationRenormalizationTheoretical computer science
An encoder including a code amount prediction unit predicting the amount of code of data to be encoded, the code amount prediction unit including a conversion unit converting input syntax elements to symbol data, and a measurement unit measuring the predicted amount of code of the data to be encoded on the basis of the number of times of renormalization processing performed on each bit in an arithmetic encoding process applied to the symbol data.
Owner:SONY CORP
System and method to generate molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream
ActiveUS9665693B2Chemical property predictionComputation using non-denominational number representationMolecular compositionRenormalization
Methods for generating molecular formula distributions beyond a predetermined threshold for a petroleum stream are disclosed. An initial molecular formula distribution within a predetermined threshold is obtained for a petroleum stream. A correlation between two or more molecular properties of the initial molecular formula distribution is identified, and the initial molecular formula distribution is extrapolated beyond the predetermined threshold along the correlation. The extrapolated molecular formula is renormalized based on renormalization data obtained from the sample. The renormalized molecular formula distribution can then be blended with the initial molecular formula distribution, reconciled to secondary analytical measurements, and / or used to create a model of composition and / or a molecular composition-based model of a resid upgrading process. Systems for implementing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
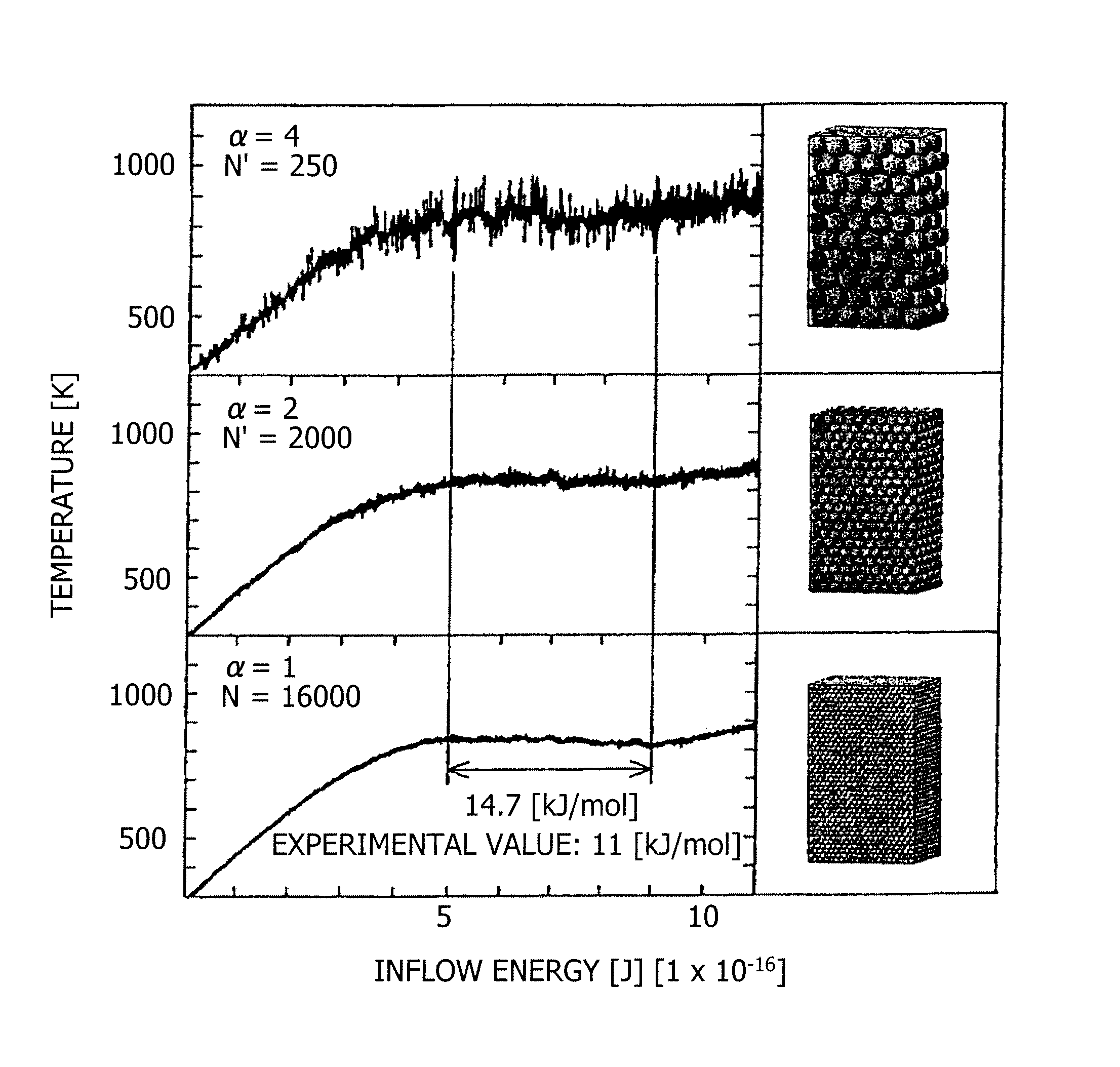
Simulation method
InactiveUS8781799B2Analogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationRenormalizationParticle interaction
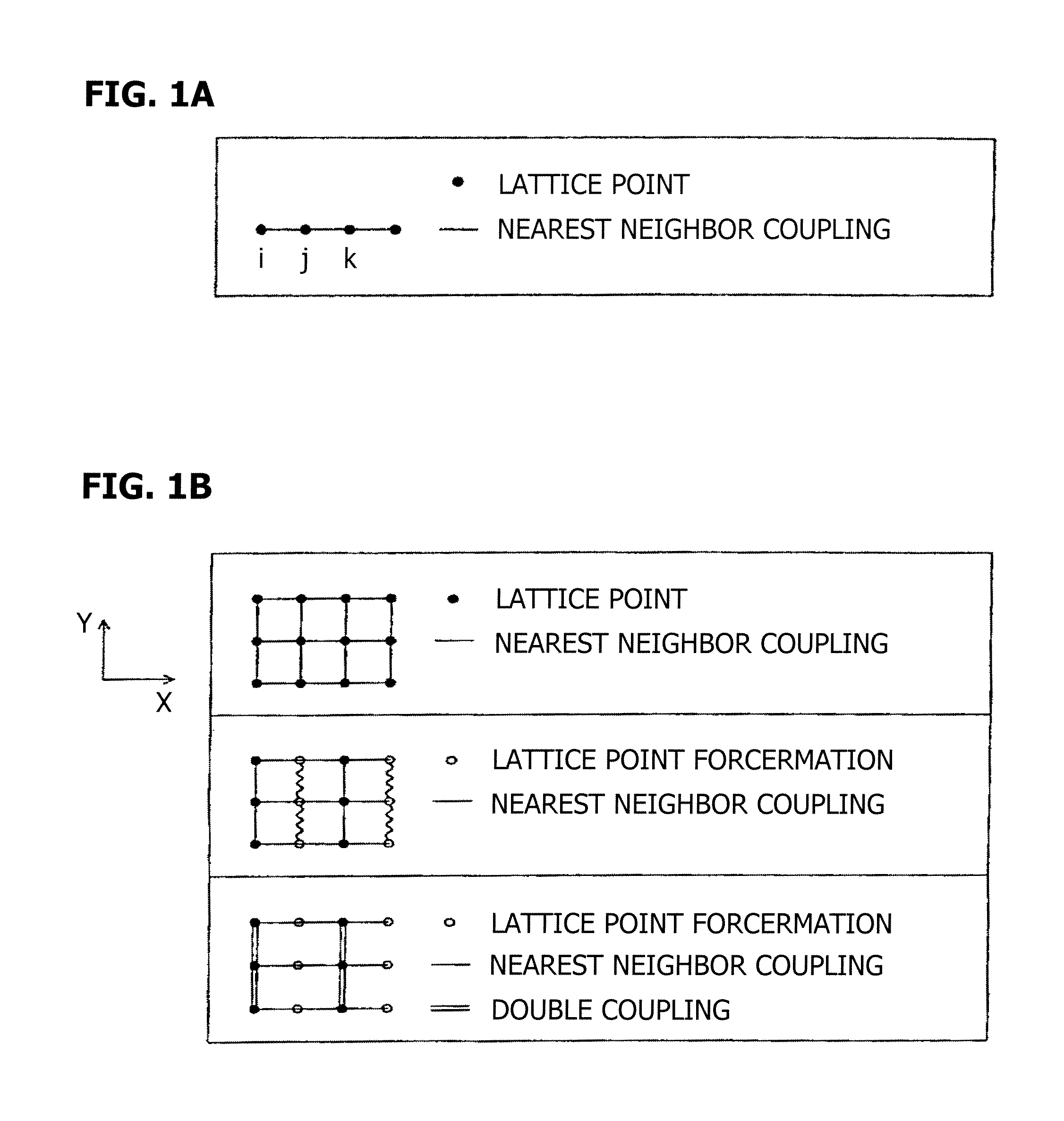
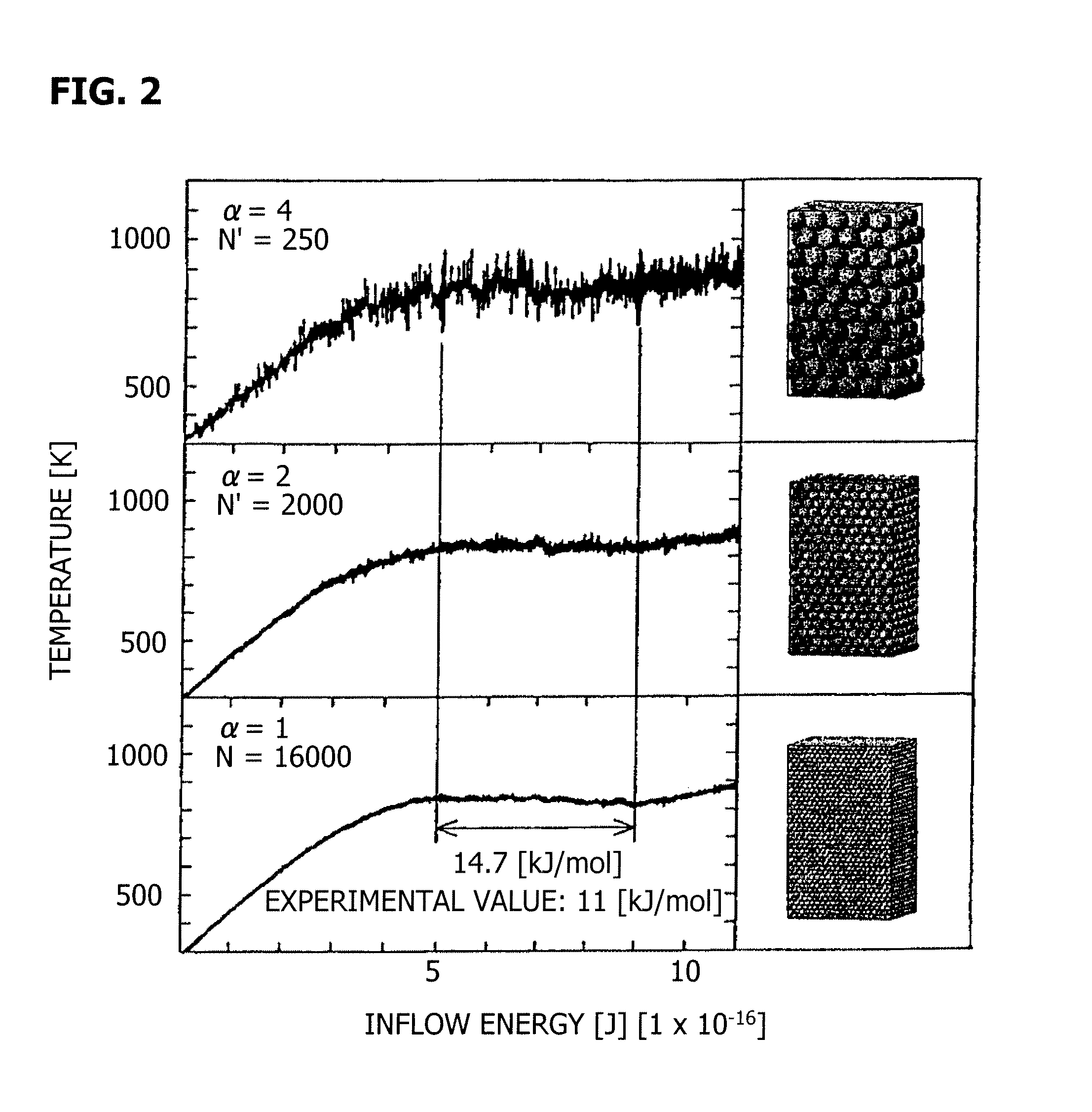
(a) Regarding a particle system S in which the number of particles is N, the mass of each particle is m, and inter-particle interaction potential energy can be expressed by εf, α greater than 1, γ equal to or greater than 0 and equal to or smaller than d, and δ equal to or greater than 0 are determined using a dimension number d of a space where the particle system S is arranged to obtain the number N′ of renormalized particles by N′=N / αd, to obtain the mass m′ of each of the renormalized particles by m′=mαδ / αγ, and to obtain a renormalized interaction coefficient ε′ by ε′=εαγ. (b) Molecular dynamics calculation is carried out on a particle system S′ in which the number of renormalized particles is N′, the mass of each particle is the mass m′ of each renormalized particle, and inter-particle interaction potential energy is expressed by ε′f.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Quantum chip
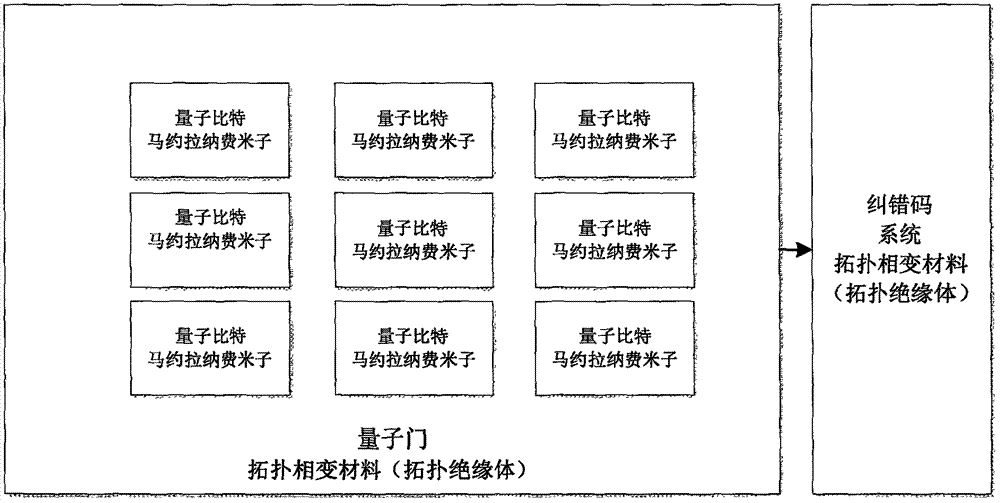
InactiveCN107038141AEnergy efficient computingArchitecture with single central processing unitRenormalizationQuantum gate
In order to solve the problems of high electronic chip power consumption of a computer and an electronic product and low operation speed and operation speed and the like since the computer and the electronic product generate heat due to mutual collision among electrons in a chip, the invention puts forward a quantum chip which is made of a material with topological phase change. The quantum chip comprises a quantum bit, a quantum gate and an error correcting code system and adopts a topological quantum calculation mode, wherein topological quantum calculation comprises a quantum compiling algorithm of a renormalization group. The operation of the quantum gate is expressed by a 2kx2k unitary matrix. Through the quantum chip, the calculation process of the computer is reversible, the motion and the information transfer of particles used for preparing the chip do not mutually interfere through quantum properties including electron self rotation and the like, the computer and the electronic product do not generate heat in a use process, and the operation speed and the communication speed of the computer can realize geometric increase so as to push the integral property of the computer and electronic industries to leap on the aspects of technologies and economic benefits.
Owner:章美前
Self-adaptive finite state entropy coding method
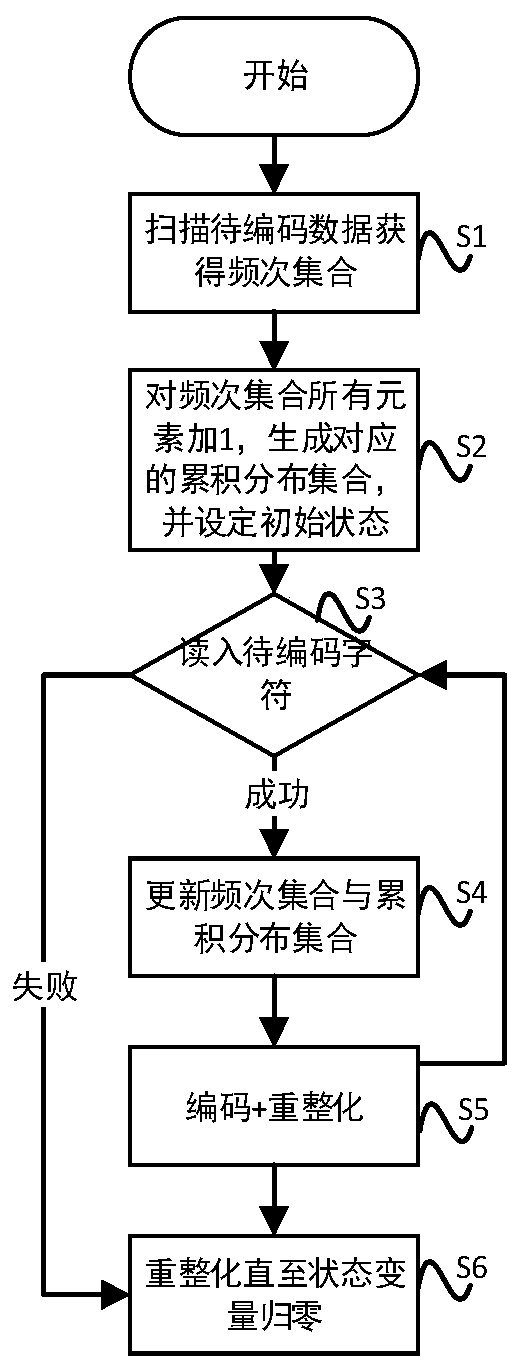
ActiveCN110602498AStable and reliable compression rateFast encodingDigital video signal modificationData compressionRenormalization
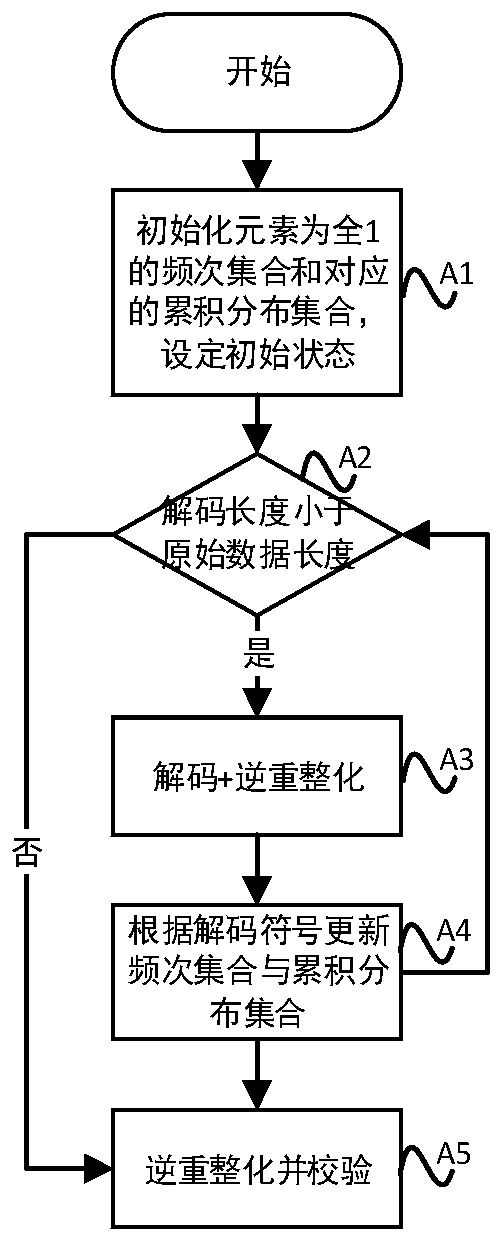
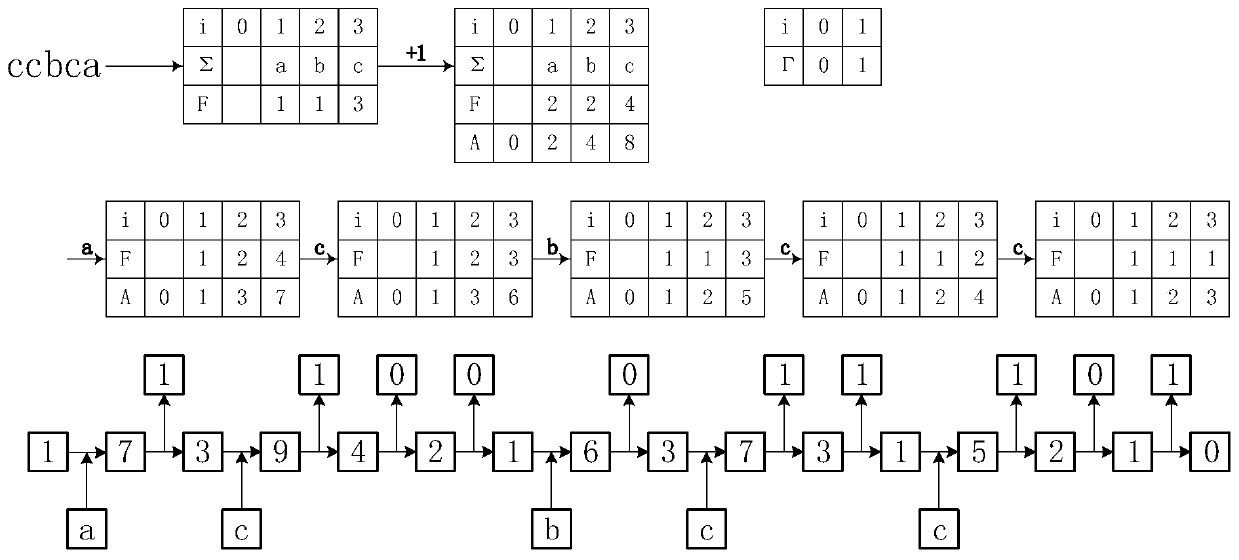
The invention discloses a self-adaptive finite state entropy coding method, and relates to the field of data compression. The method comprises the steps of scanning to-be-coded data to obtain a frequency set of symbols, preprocessing the frequency set, dynamically maintaining and updating the frequency set and an accumulated distribution set, and performing adaptive coding based on a coding rule in combination with reforming processing to obtain coded output data; establishing an initial frequency set of which the elements are all 1, reading in to-be-decoded data, performing self-adaptive decoding based on a decoding rule and in combination with inverse reforming processing, dynamically maintaining and updating the frequency set and the cumulative distribution set, and obtaining decoded output data; and converting the alphabet set of the to-be-coded data and the alphabet set of the coded output data, and performing adaptive finite state entropy coding on the to-be-coded data to obtainencrypted data. According to the invention, on the premise of ensuring the coding precision, the coding steps are simplified, the coding speed is improved, and the coding requirements at the present stage can be better met.
Owner:唐驰鹏
Renormalization of dual-energy images
ActiveUS8184877B2Easy to useReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionRenormalizationDecomposition
A method is disclosed for generating a composite image from dual-energy projection radiographic image data and renormalizing the composite image such that the pixel values for the composite image have the same relationship to the detected x-ray energy as the original high- and low-energy images. The method disclosed further provides for renormalization of material specific decomposition images formed form dual energy projection radiographic image data such that the decomposition images are on a common scale with either the high-energy, low-energy or composite image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
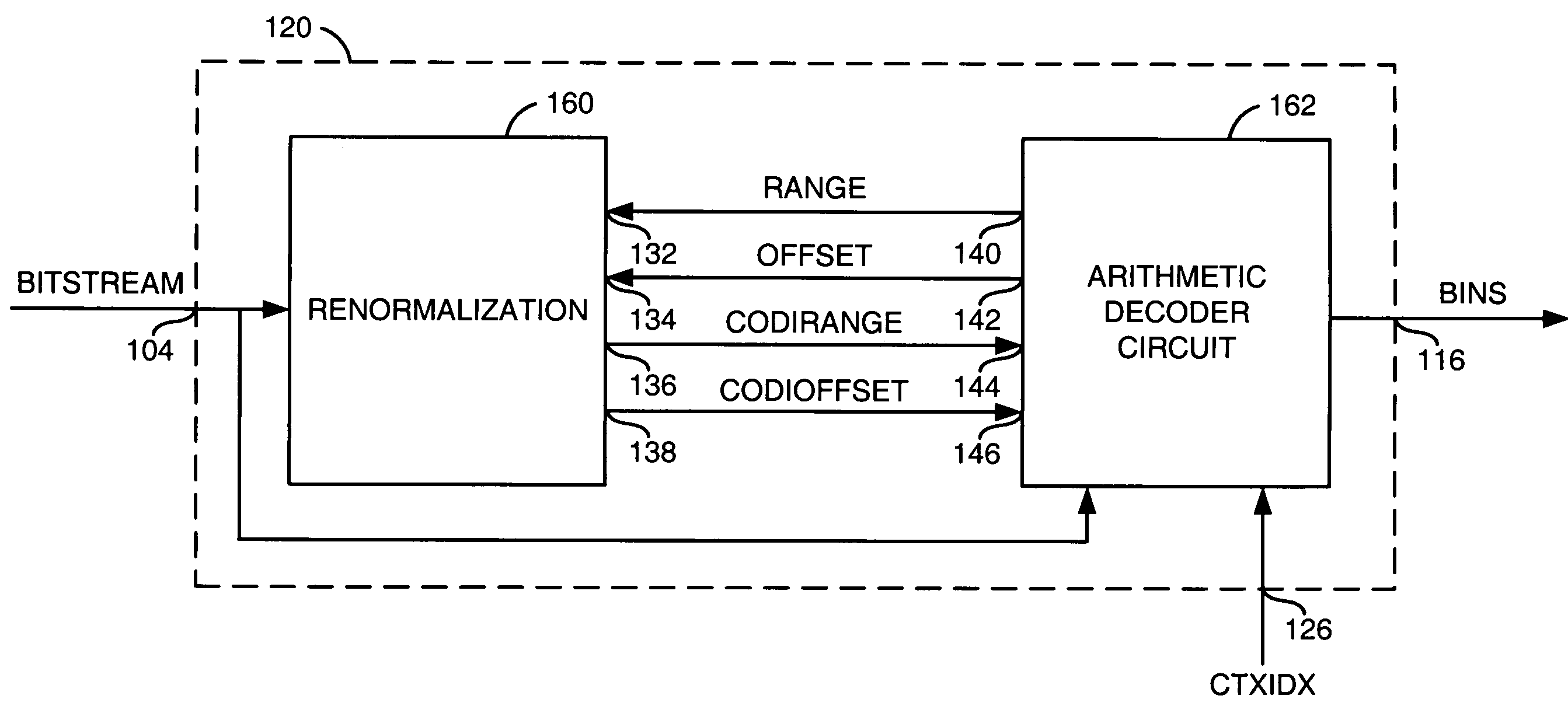
Arithmetic decode without renormalization costs
ActiveUS7397401B2Without renormalizationLow implementation costCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionRenormalizationSingle cycle
An apparatus comprising a first circuit and a second circuit. The first circuit may be configured to generate context information in response to one or more bins on a binary signal. The second circuit may be configured to generate the binary signal in response to (i) one or more input bits on a bitstream signal, and (ii) simultaneously performing in a single cycle (a) an arithmetic decode of the context information and (b) a renormalization of the context information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
An interferometric IQ-mixer/DAC solution for active, high speed vector network analyser impedance renormalization
InactiveUS20190391193A1Avoid deformationGuaranteed uptimeDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceAudio power amplifierRenormalization
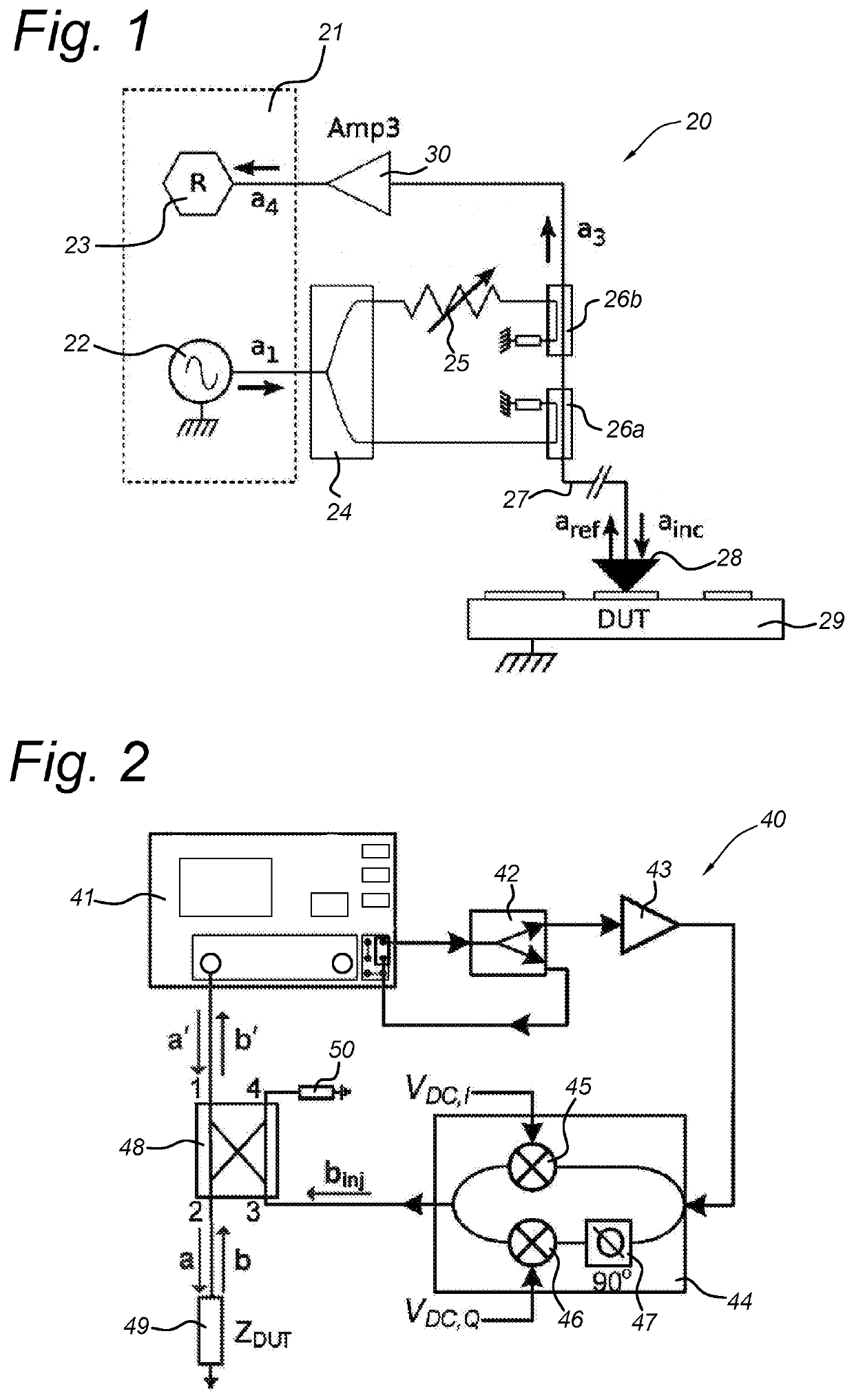
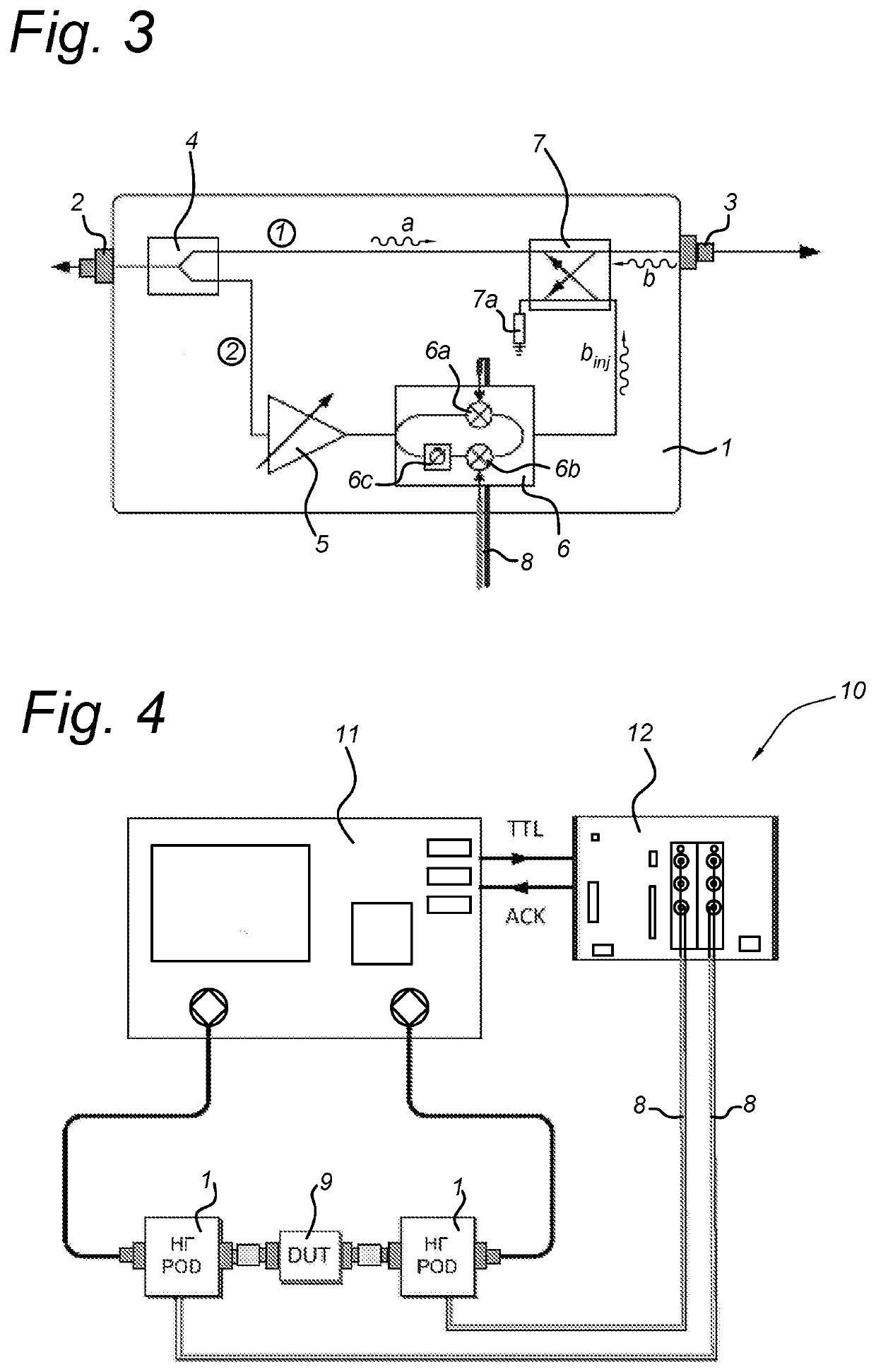
Device under test (DUT) interface device for use in a system for executing measurements on a device under test (9) with a vector network analyser (11).The DUT interface device comprises a divider / coupler component (4), a variable gain amplifier (5), an I / Q mixer (6) and a bridge / coupler component (7) and provides a test signal (a) to the DUT terminal (3).The system further comprises a control unit (12) connected to the vector network analyser (11) and to control input terminals (8) of associated ones of the at least one DUT interface device (1). The control unit (12) provides quadrature control signals (VI, VQ) for the associated at least one DUT interface device (1), which are connected directly to the device under test (9). The present invention further relates to proper calibration and measurement methods.
Owner:VERTIGO TECH BV
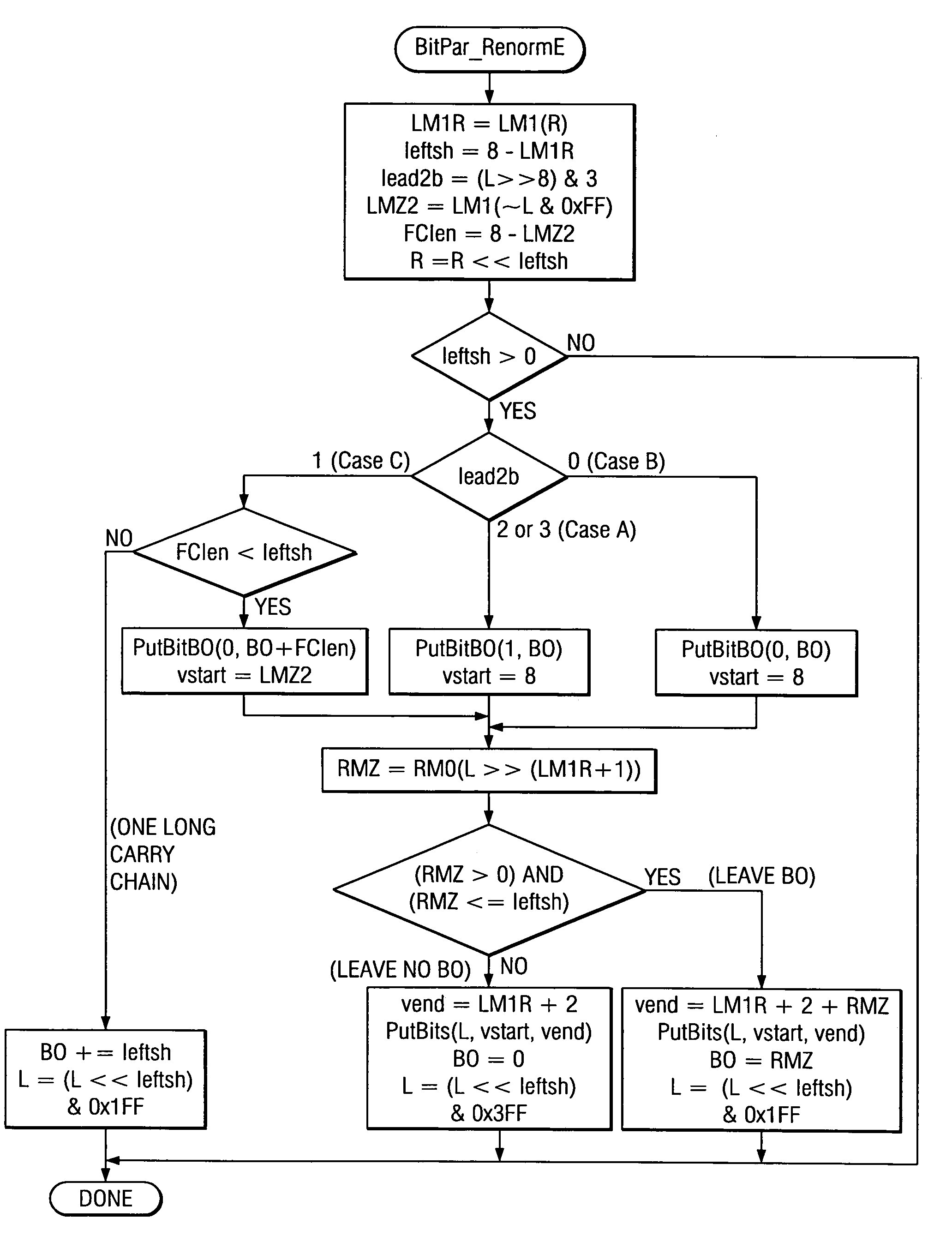
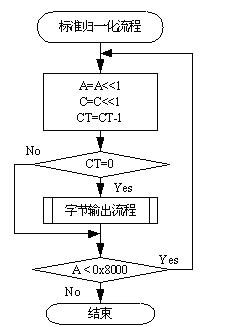
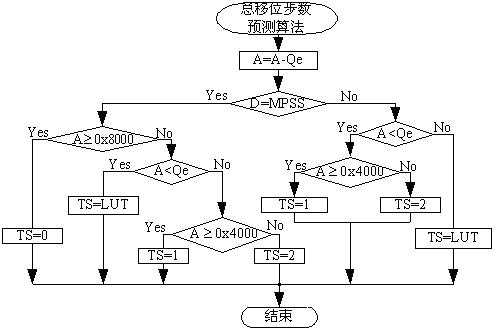
Arithmetic encoder sequence renormalization method used for image compression
InactiveCN102438140AGuaranteed to be correctSuitable for realizationTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationRenormalizationJPEG
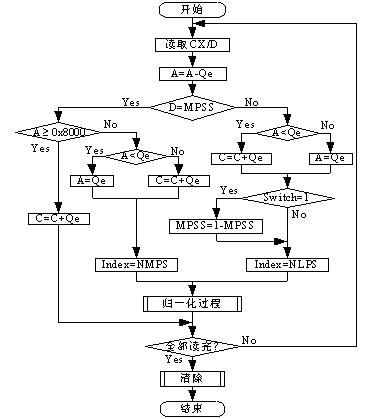
The invention provides an arithmetic encoder sequence renormalization method used for image compression in a joint photographic experts group (JPEG) 2000 image compression standard. The method is characterized in that: an independent total shift step number prediction rule is added to obtain a total shift step number of a probability interval A, probability interval lower boundary C is shifted successively under three conditions of without byte output, single byte output and double bytes output, thus parameter calculation can be completed sequentially in one time after reading each pair of a context CX and a code value D, and iteration loop calculation is not needed. The arithmetic encoder renormalization process method of the present invention can substitute an original part seamlessly, and other links of an arithmetic coding algorithm are not needed to be changed; no interweaving determination exists between logic branches; computation burden is reduced, data reading efficiency is effectively raised, and hardware realization is facilitated.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com