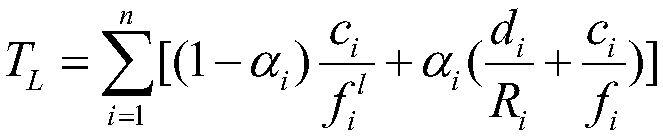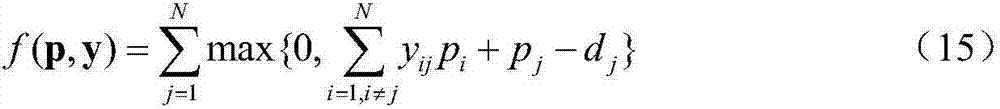Patents
Literature
122 results about "Branch and bound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
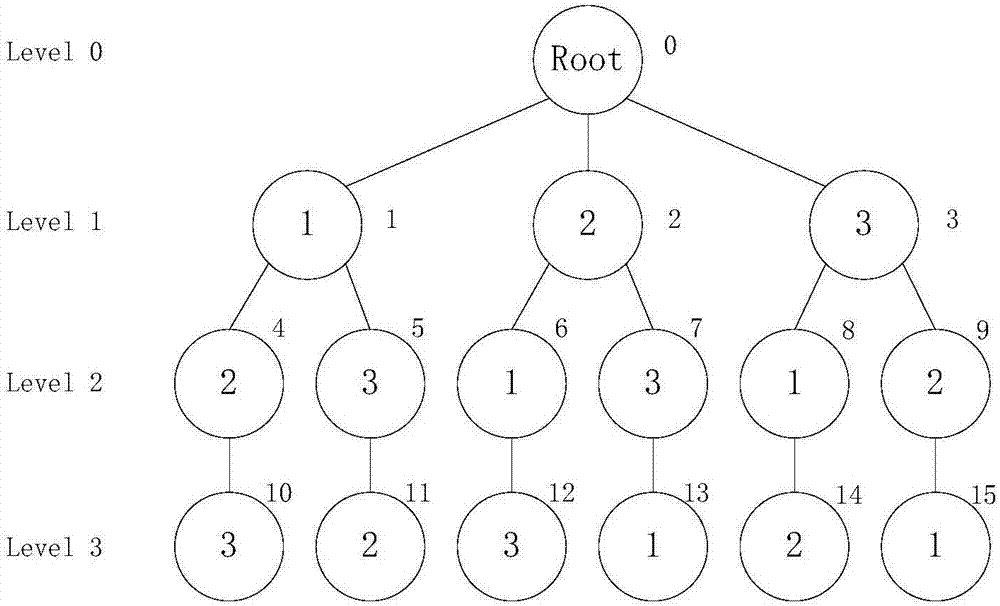
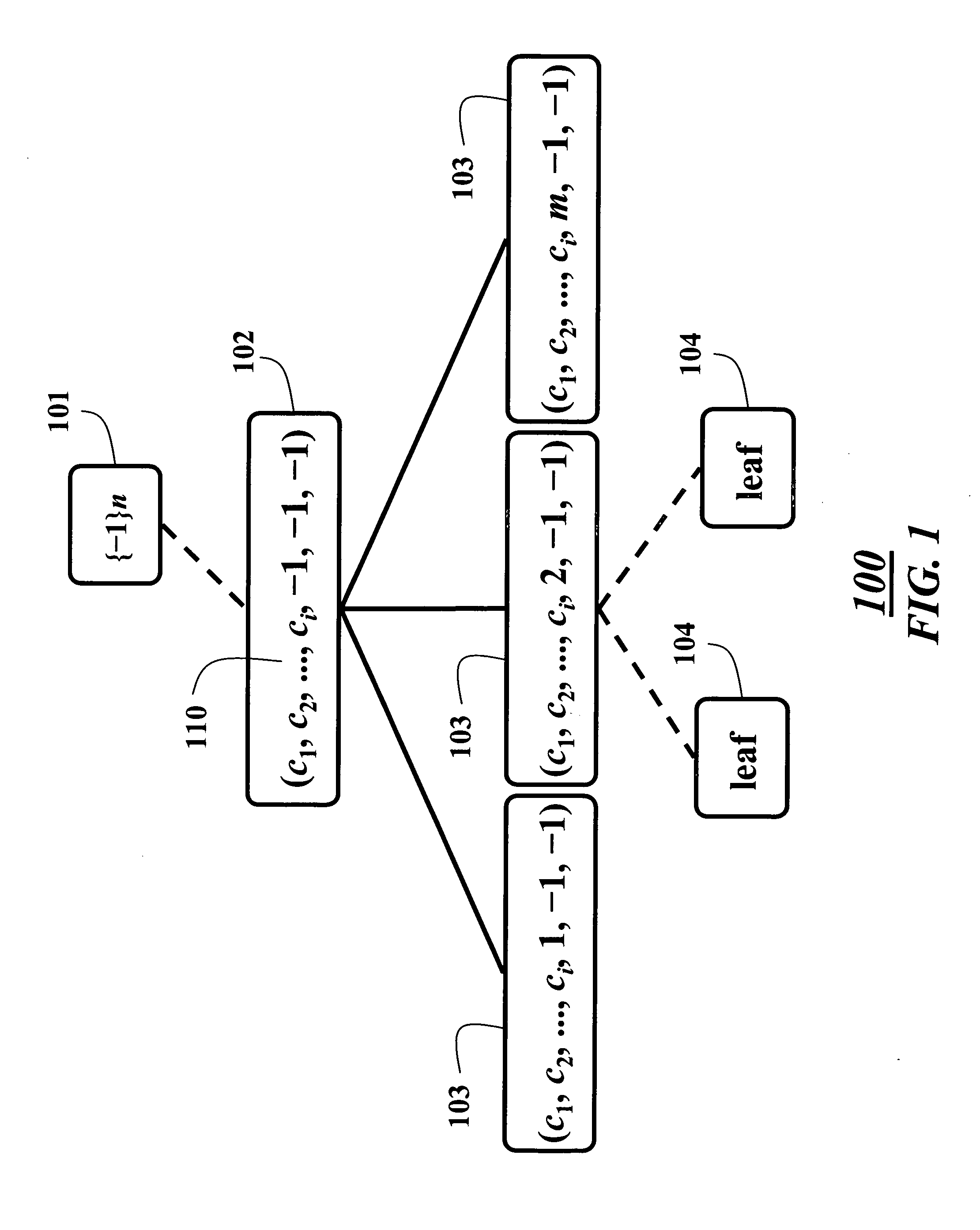
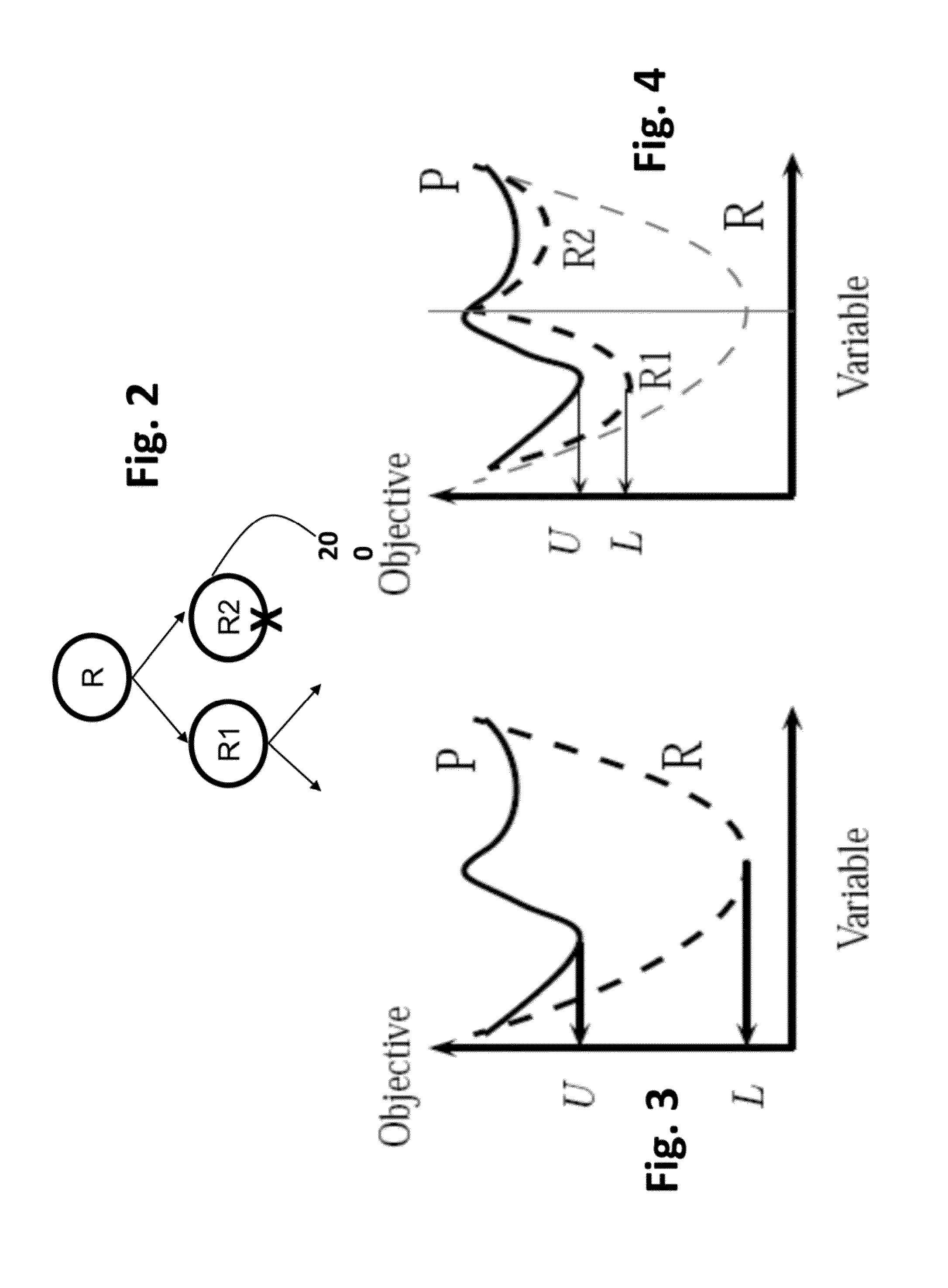
Branch and bound (BB, B&B, or BnB) is an algorithm design paradigm for discrete and combinatorial optimization problems, as well as mathematical optimization. A branch-and-bound algorithm consists of a systematic enumeration of candidate solutions by means of state space search: the set of candidate solutions is thought of as forming a rooted tree with the full set at the root. The algorithm explores branches of this tree, which represent subsets of the solution set. Before enumerating the candidate solutions of a branch, the branch is checked against upper and lower estimated bounds on the optimal solution, and is discarded if it cannot produce a better solution than the best one found so far by the algorithm.
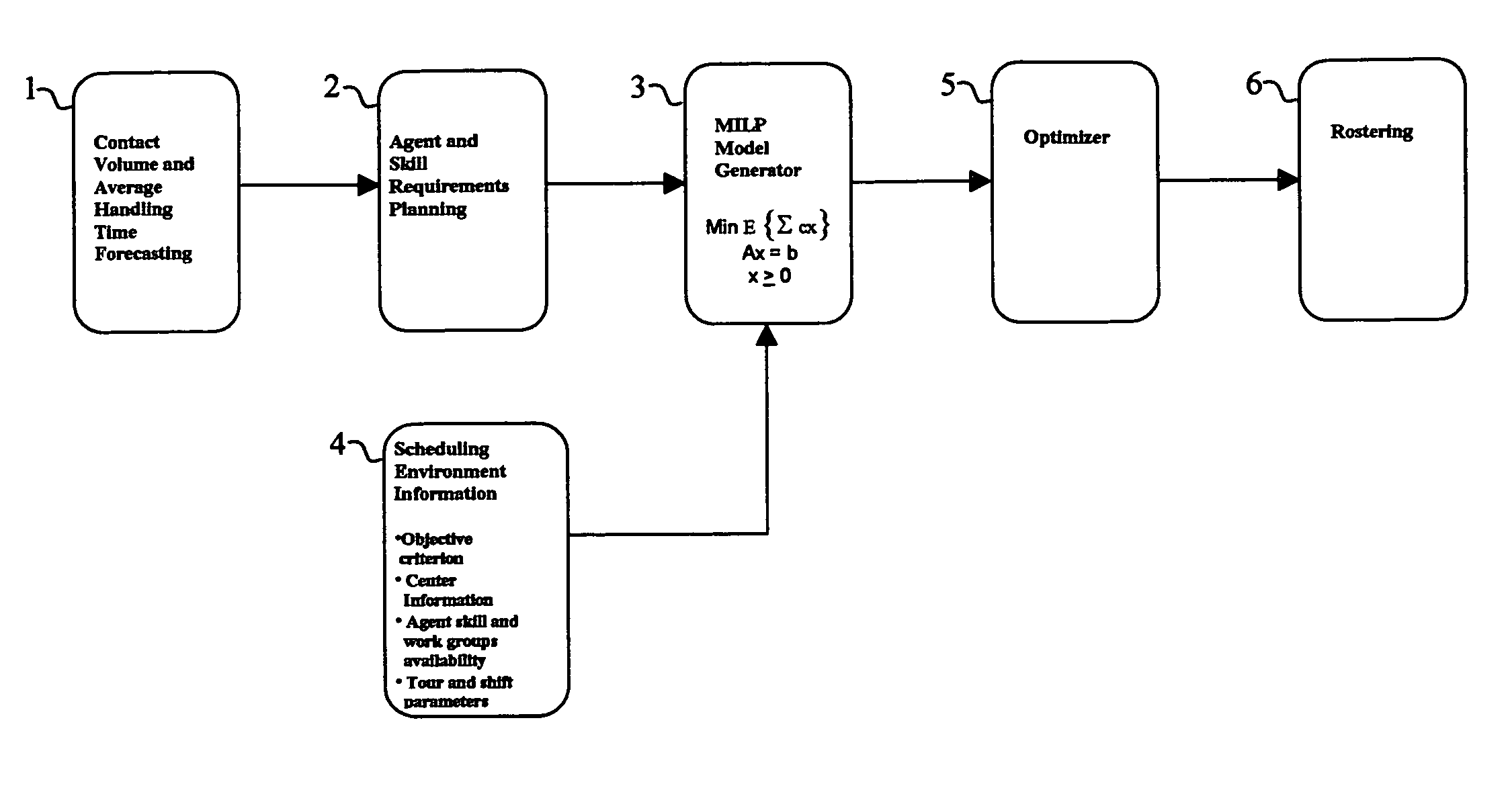
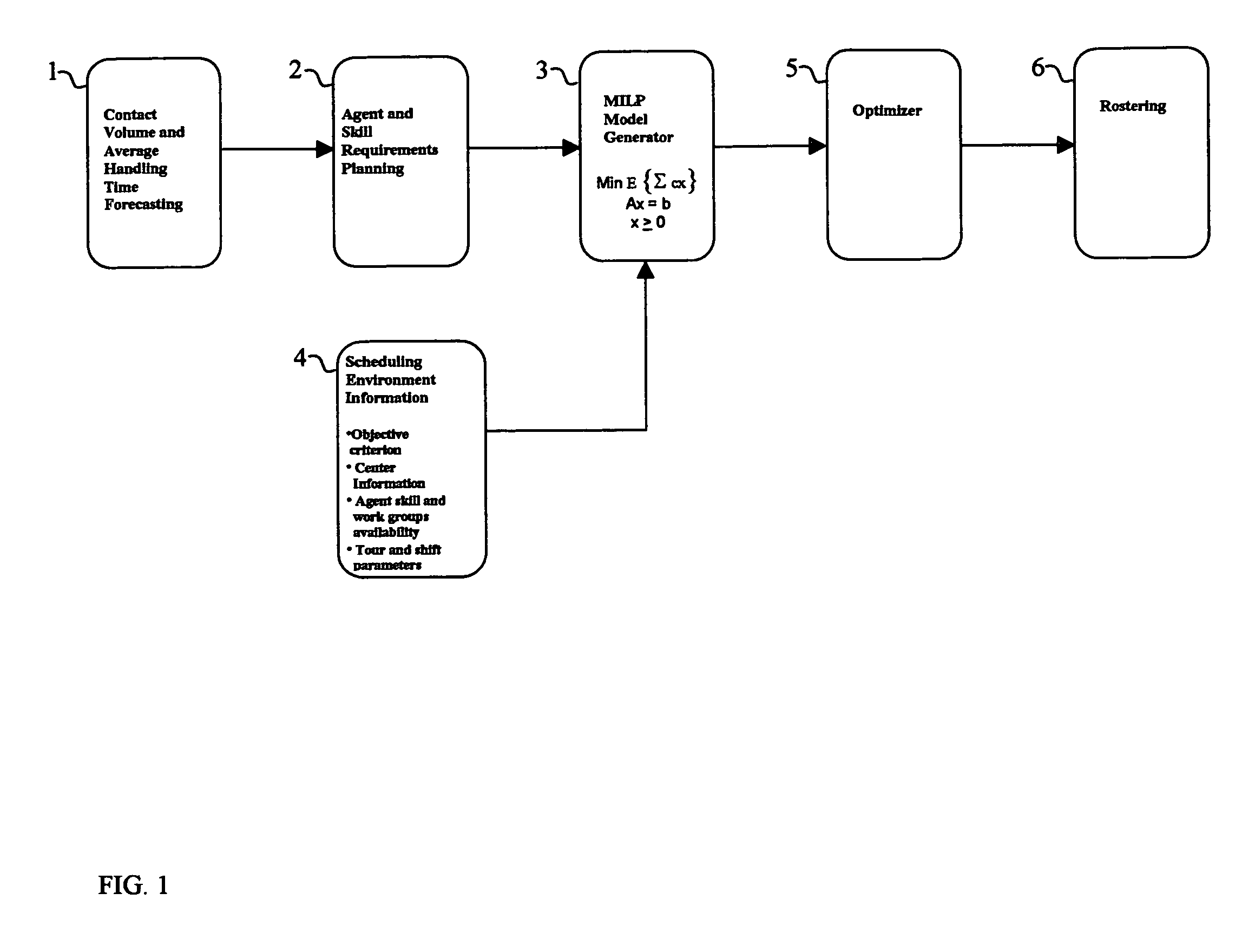
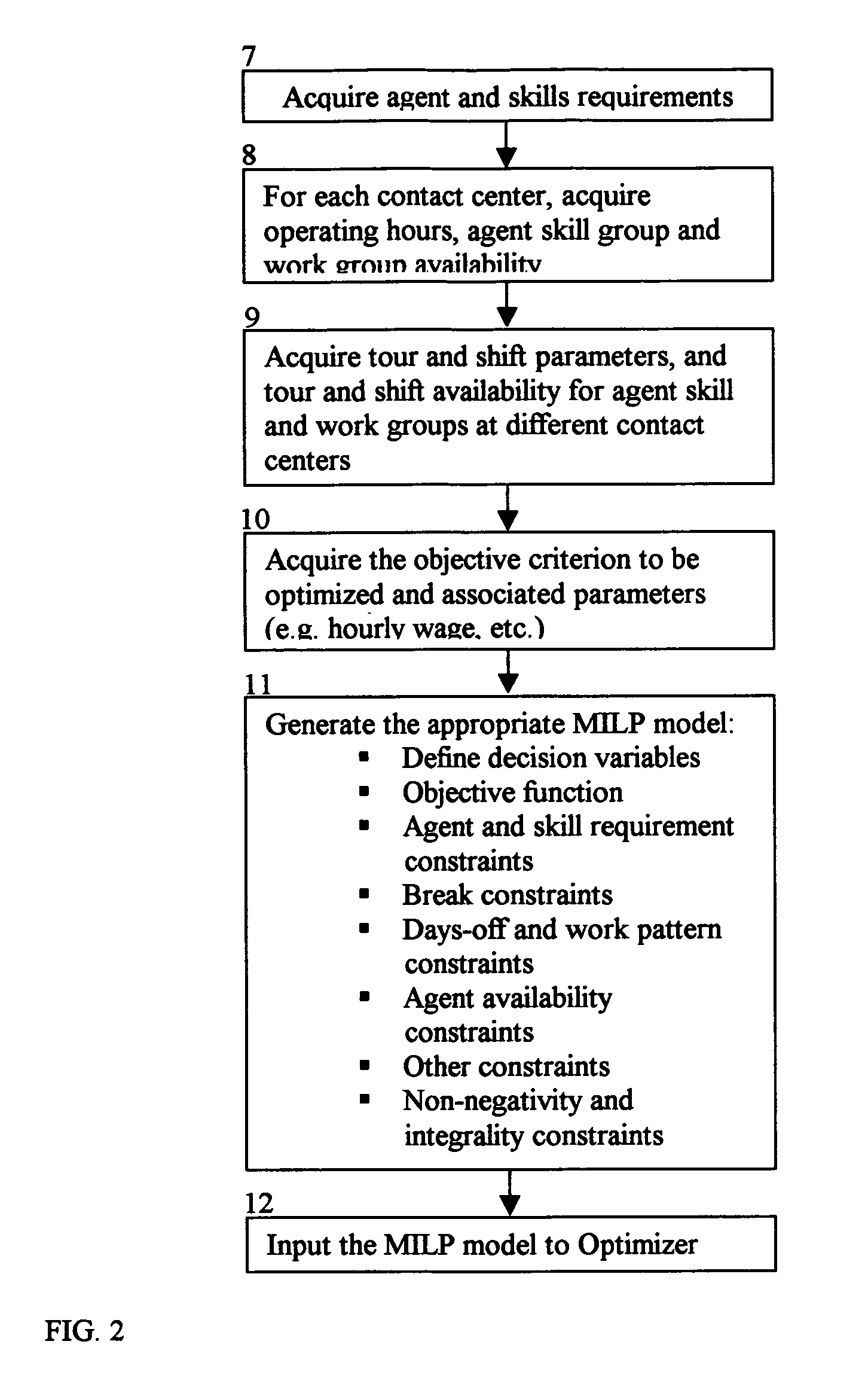
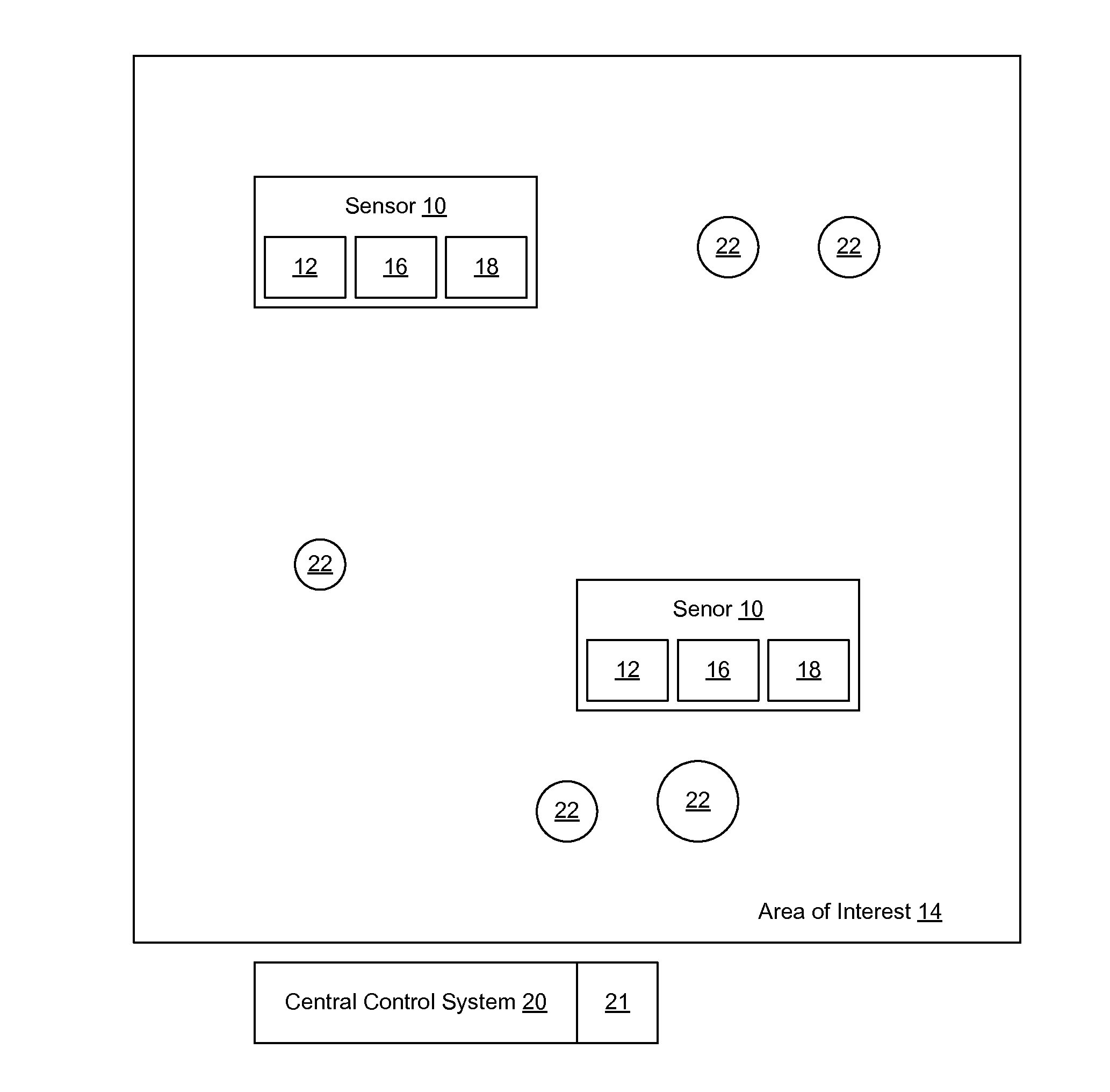
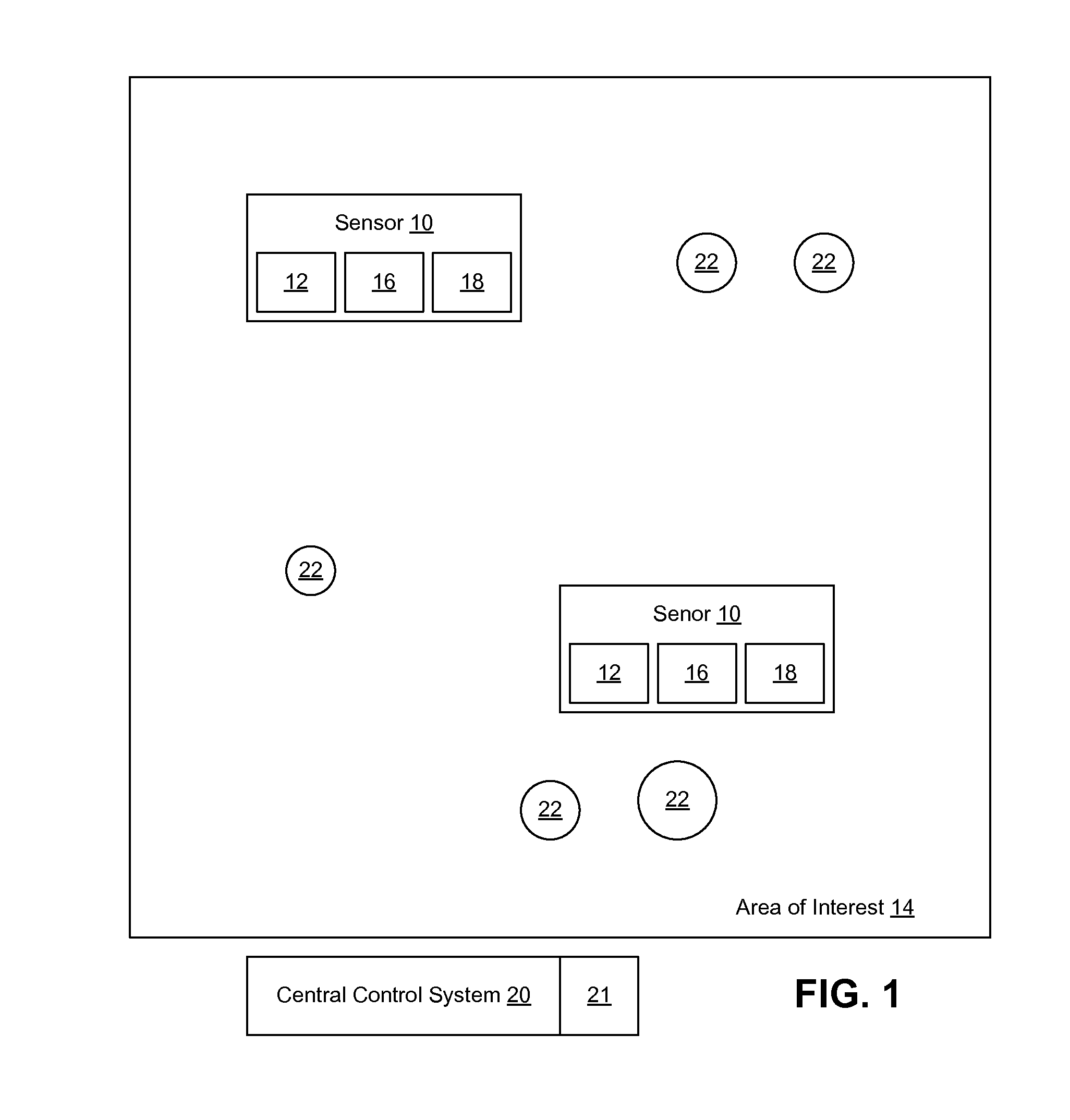
Contact center scheduling using integer programming
ActiveUS7725339B1Easy to solveFavorable objective valueOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsContact centerWorkforce scheduling
The present invention relates to a method for workforce scheduling in which workload and workload types vary during scheduling period. The method acquires agent and skill requirements for all periods and contact types; acquires the contact center information including agent skill groups, agent work groups, tour and shift scheduling rules, agent availability, objective criterion to be optimized and its parameters; develops a Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) model for the scheduling environment; applied an optimization algorithm that uses the Branch and Bound algorithm with a Rounding Algorithm to improve performance; and locates a globally optimal or near optimal workforce schedule in total cost or paid time or agent satisfaction. Detailed schedules may be developed by assigning daily shifts to work patterns, and breaks scheduled to daily shifts.
Owner:INCONTACT
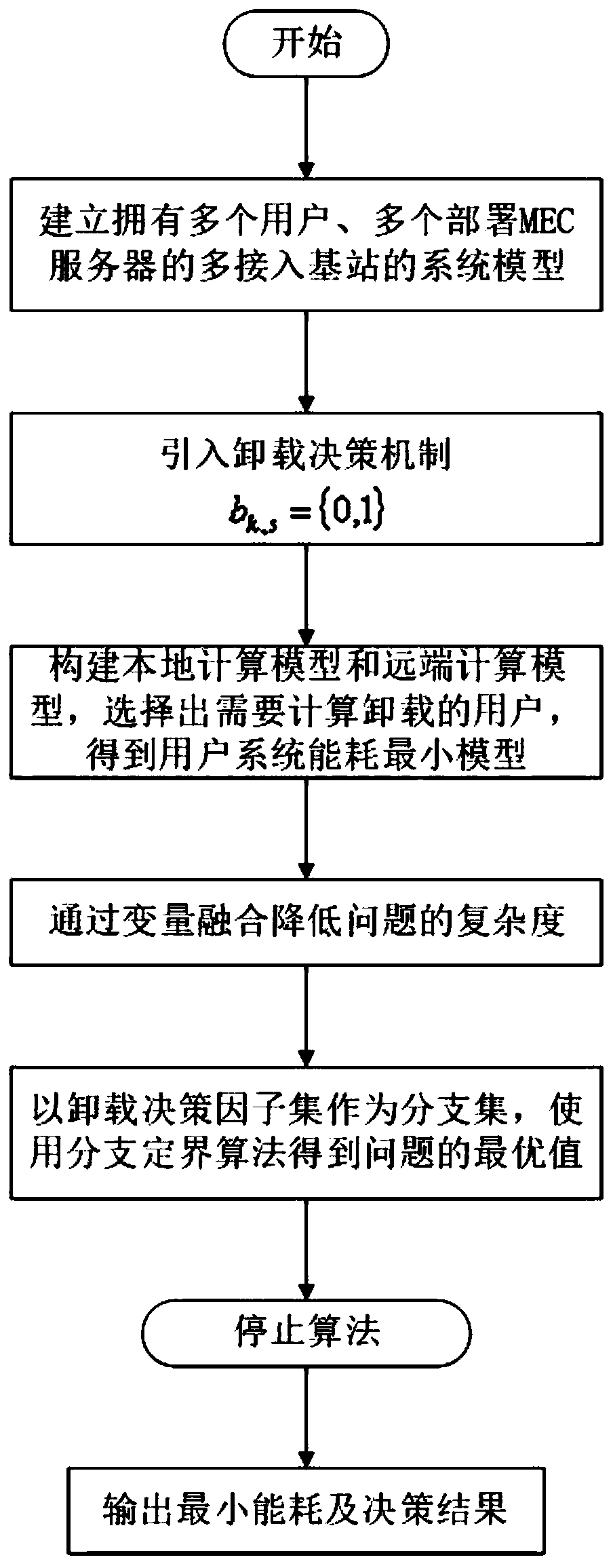
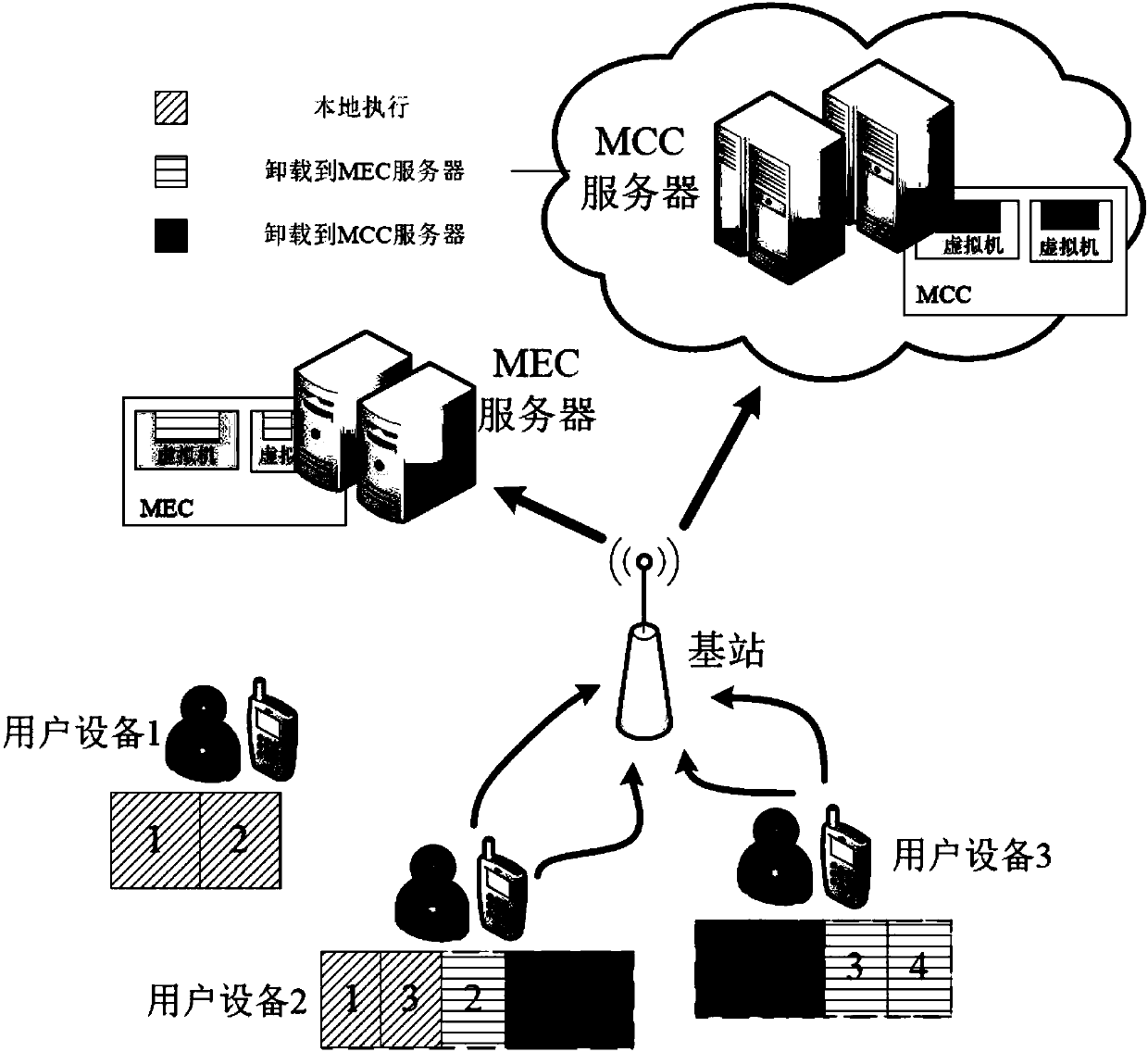
A joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network
ActiveCN109814951AFull restorationUniversalService provisioningProgram loading/initiatingDecision takingWireless resource allocation
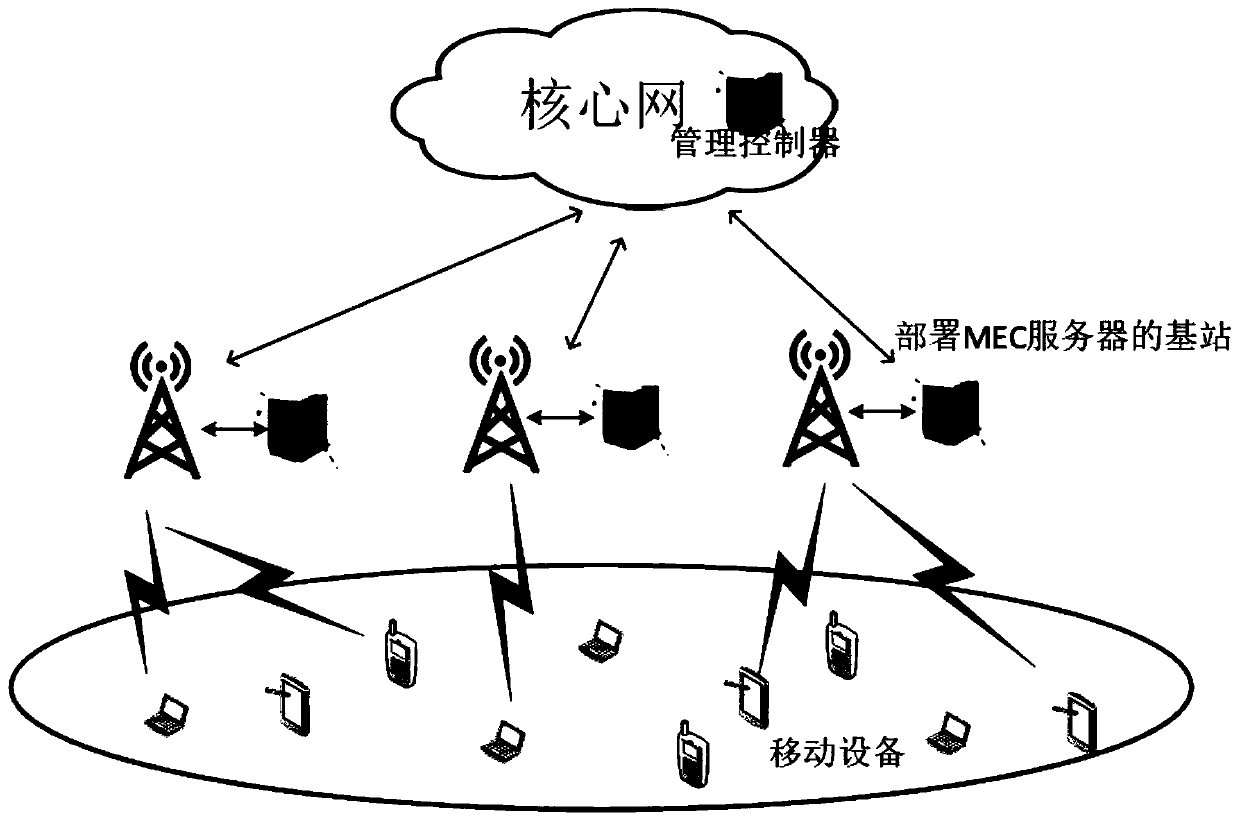
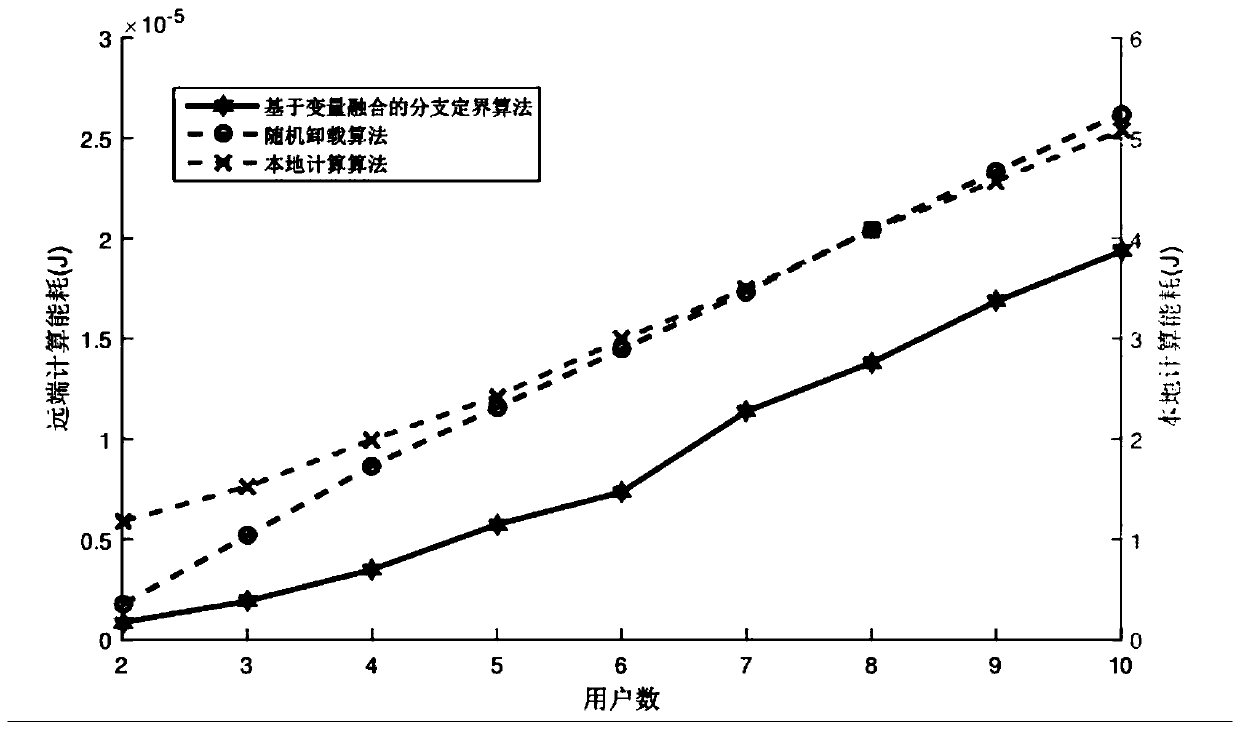
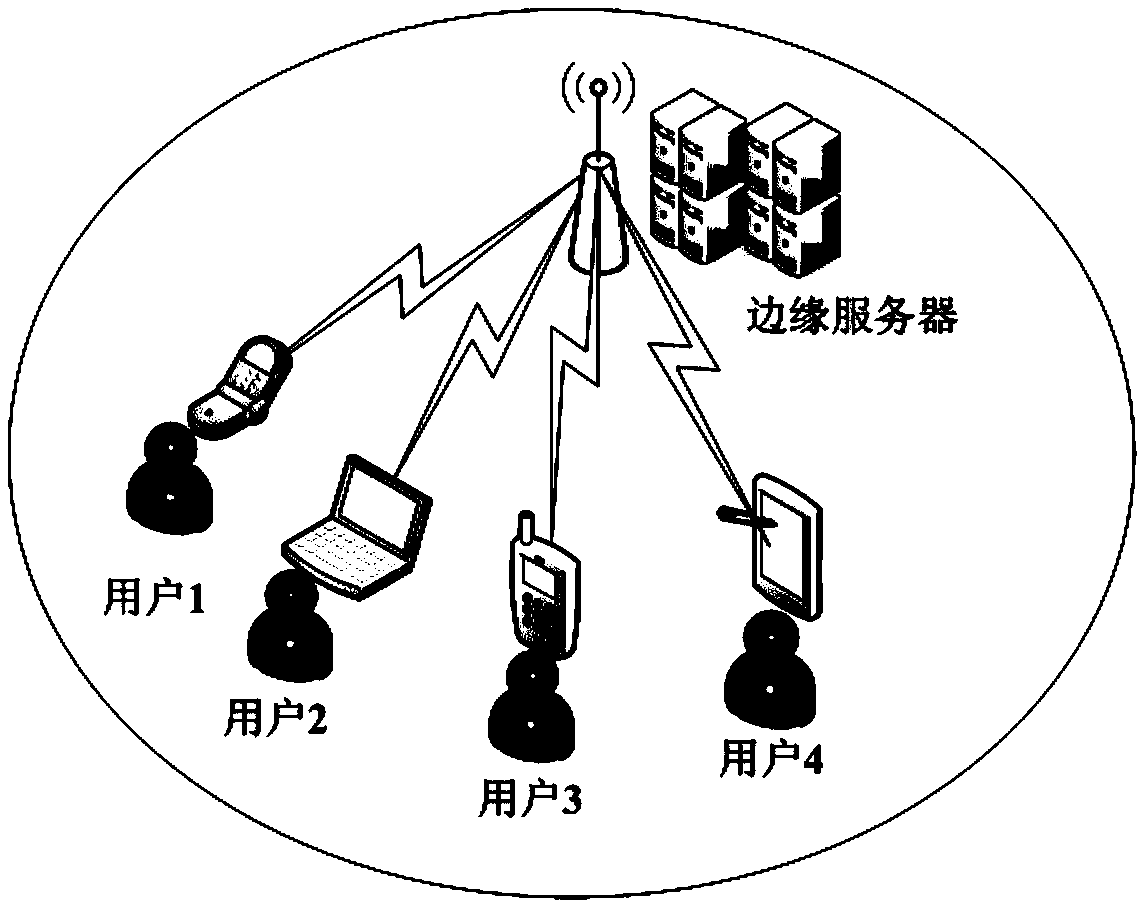
The invention discloses a joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network, which comprises the following steps of 1, establishing an OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)-based multi-MEC (Mobile Edge Computing) base station and a multi-user scene model, wherein the MEC base station supports the multi-user access; 2, introducing an unloading decision mechanism; Meanwhile, constructing a local calculation model and a remote calculation model, selecting a user needing to perform calculation unloading, and establishing a calculation task unloading and resource allocation scheme based on minimum energy consumption under the condition of meeting the time delay constraint according to the conditions; 3, carrying out variablefusion on three mutually constrained optimization variables, namely an unloading decision variable, a wireless resource distribution variable and a computing resource distribution variable, so as to simplify the problem; and 4, obtaining an unloading decision and a resource allocation result which enable the total energy consumption of the user in the MEC system to be minimum through a branch andbound algorithm. The method has the advantage that the energy consumption of the system can be effectively reduced on the premise that strict time delay limitation is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Fuzzy matching-based Chinese geo-code determination method
ActiveCN101719128AIncreased complexityImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsArray data structureFuzzy rule
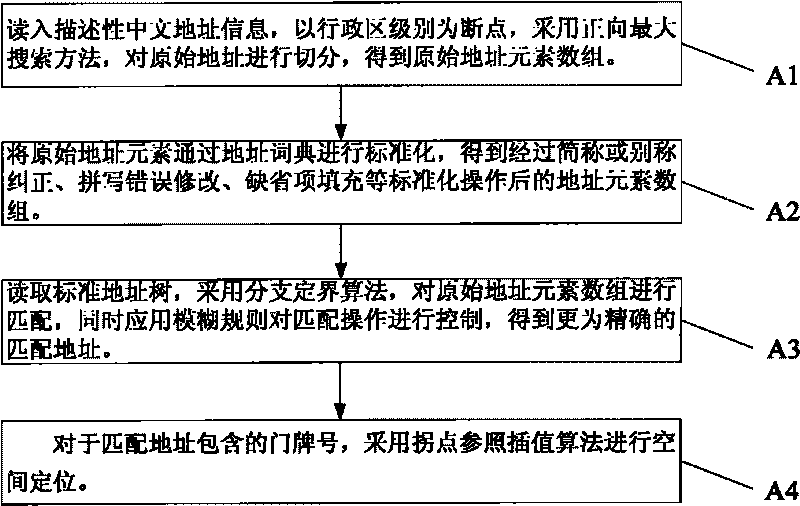
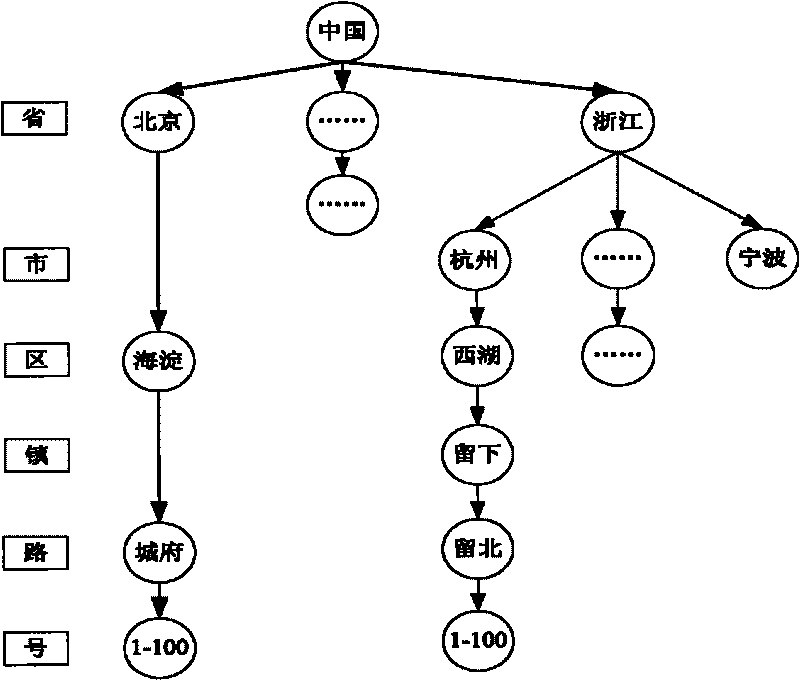
The method discloses a fuzzy matching-based Chinese geo-code determination method, which comprises the following steps: A1, reading descriptive Chinese address information in and adopting a forward maximum searching method to split an original address to obtain an original address element array in a way that the levels of administrative regions are taken as breakpoints; A2, standardizing original address elements through an address dictionary; and A3, reading a standard address tree, adopting a branch-bound algorithm to match the original address element array, simultaneously, utilizing fuzzy rules to control the matching operation, and after acquiring keywords after the original address is split, taking a matching result with the highest evaluation score as the most approximate matching result to obtain a more accurate matched address. The invention provides the fuzzy matching-based Chinese geo-code determination method, which has the advantages of rational address model, relatively higher matching rate and high speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A task unloading method based on user experience in edge computing network
ActiveCN109240818AImprove experienceReduce energy consumptionProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationService experienceEnergy expenditure
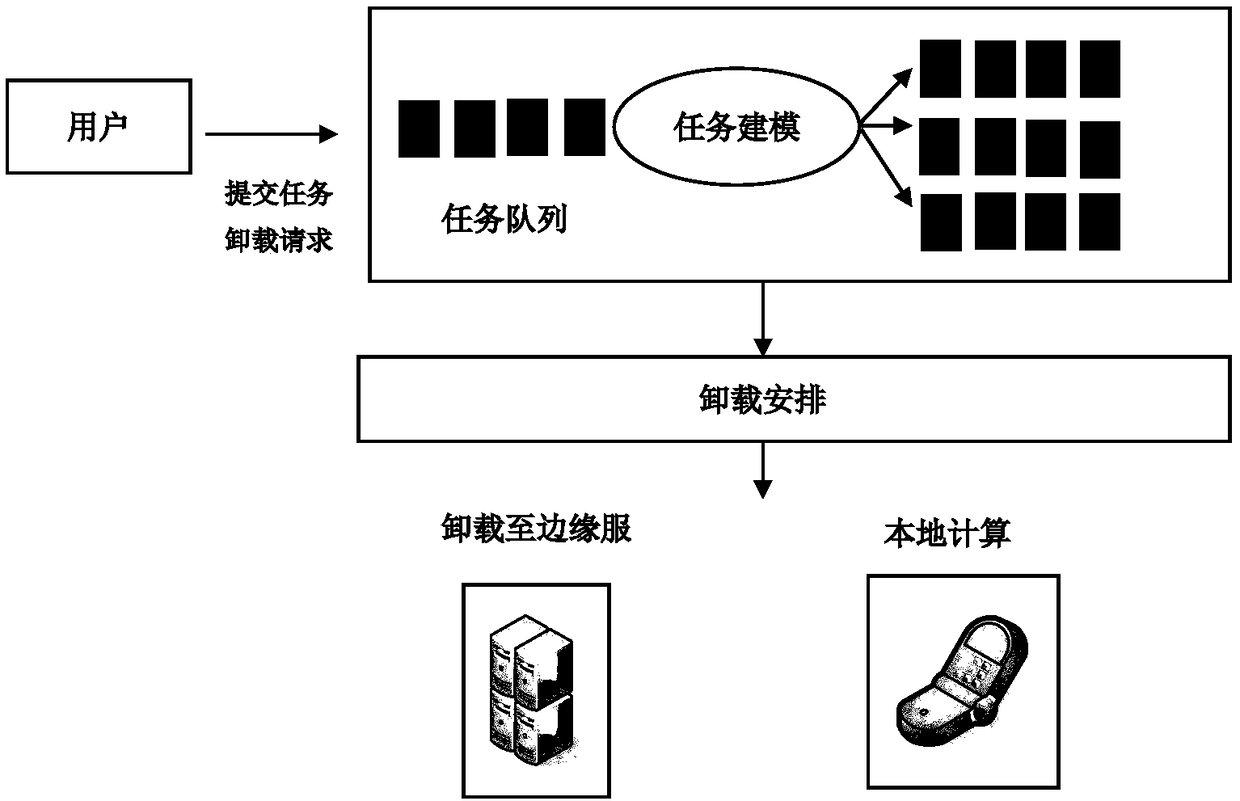
The invention discloses a task unloading method based on user experience in an edge computing network. The method comprises the following steps: a scheduler receives a task unloading request submittedby a user; a task unloading strategy model is jointly optimized based on time and energy expenditure; the model is solved and calculated based on a branch and bound algorithm of linear reconstruction; the task unloading strategy model is optimized based on time and energy expenditure. Based on the results of the calculation, the decision is made whether the task is unloaded to the edge server, and the tasks unloaded to the edge server are communicated and the computational resources are allocated. The invention combines two key indexes of optimization time delay and energy consumption, and solves the problem by branch and bound algorithm based on linear reconstruction technology, which can reduce the energy consumption of mobile intelligent device under the condition of ensuring the completion of the task, reduce the task processing time delay, and achieve the purpose of maximizing the optimization of user experience.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Remote sensing hyperspectral image band selection method based on conditional mutual information
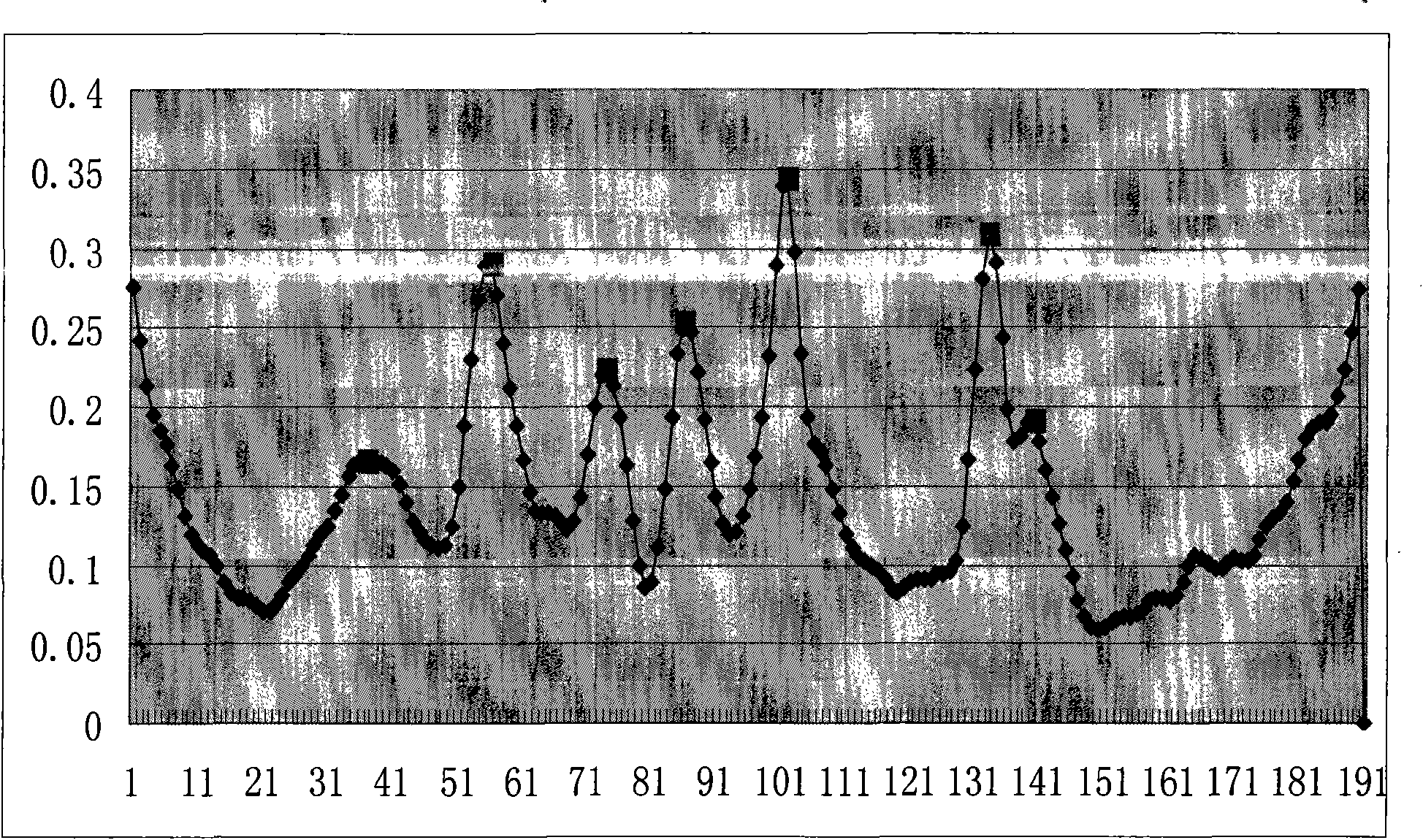
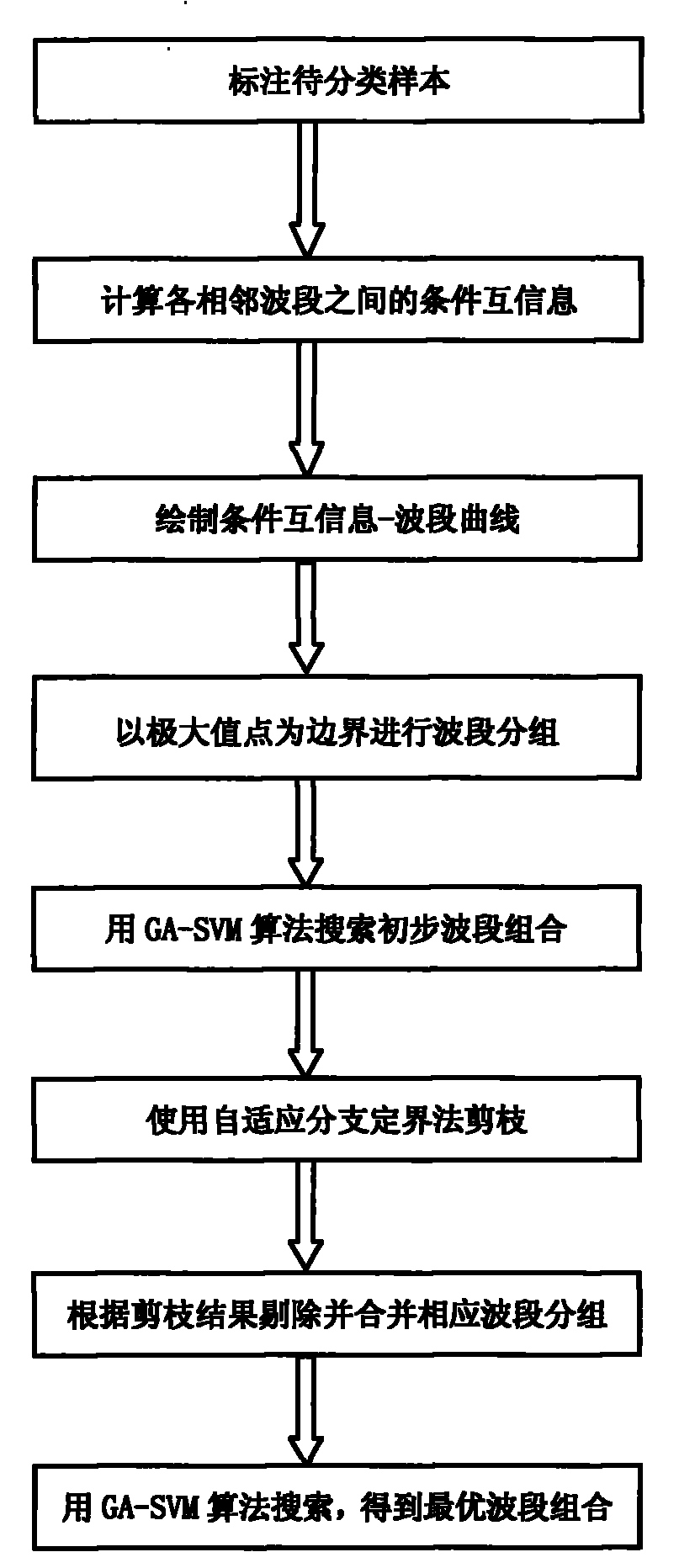
InactiveCN101853392AReduce in quantityLighten the computational burdenCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman–computer interactionBranch and bound
The invention provides a remote sensing hyperspectral image band selection method based on conditional mutual information, which comprises the following steps of: A, opening a hyperspectral remote sensing image and labeling a sample to be classified by man-machine interaction; B, grouping: carrying out band grouping by utilizing the conditional mutual information among all adjacent bands under given class condition according to the sample to be classified obtained from the step A; and C, searching: carrying out search calculation on the grouped bands obtained from the step B by utilizing a search algorithm combining a support vector machine and a genetic algorithm so as to find out an optimal band combination; and on this basis, pruning by using a self-adaptation branch and bound algorithm. Through the combinational use of the band grouping based on the conditional mutual information and the pruning based on the self-adaptation branch and bound algorithm, redundancy and noise grouping which are caused by noise perturbation are avoided, the frequency of band grouping is reduced and the classification accuracy of the band combination is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
System and method for resource allocation and management
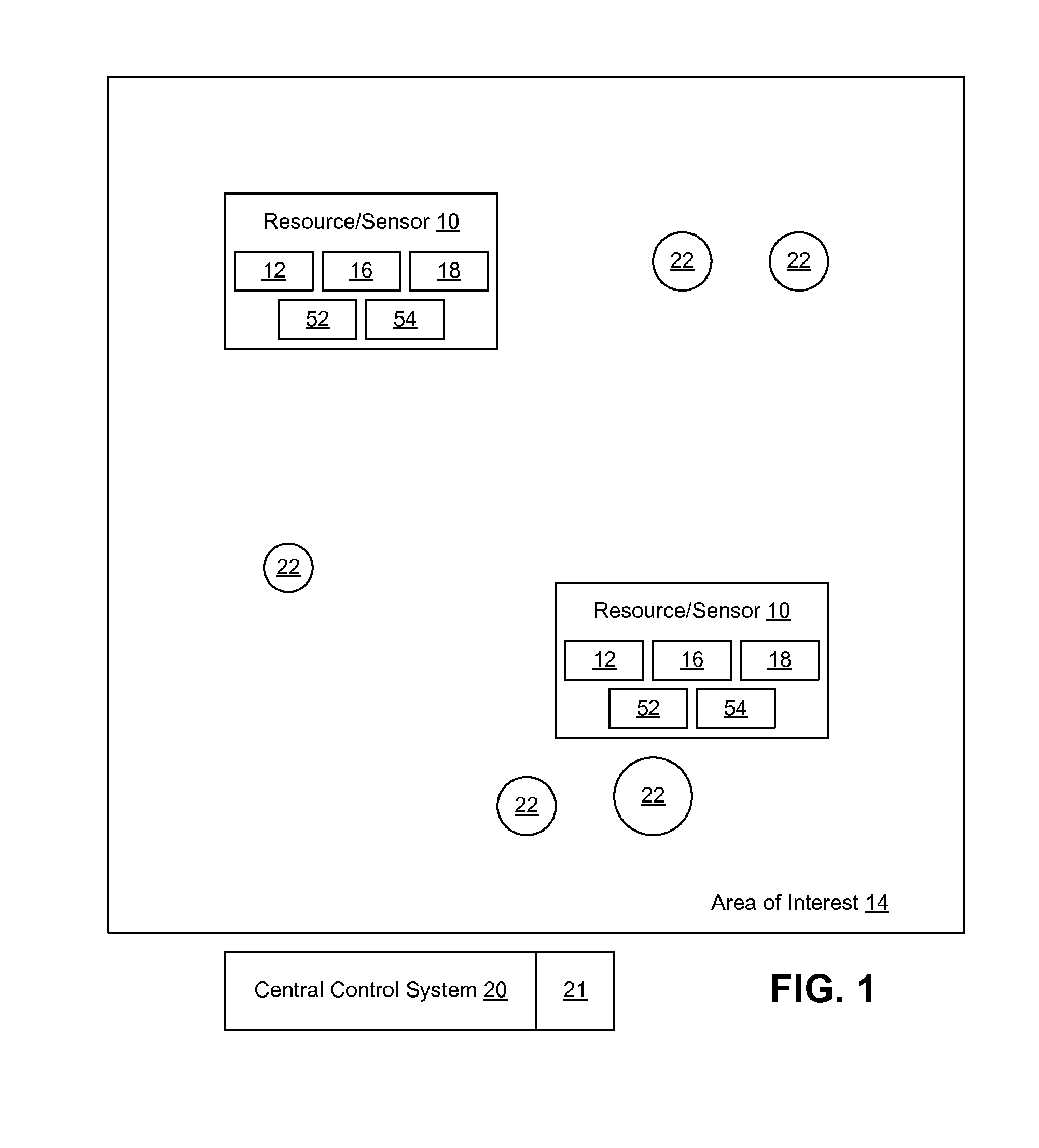
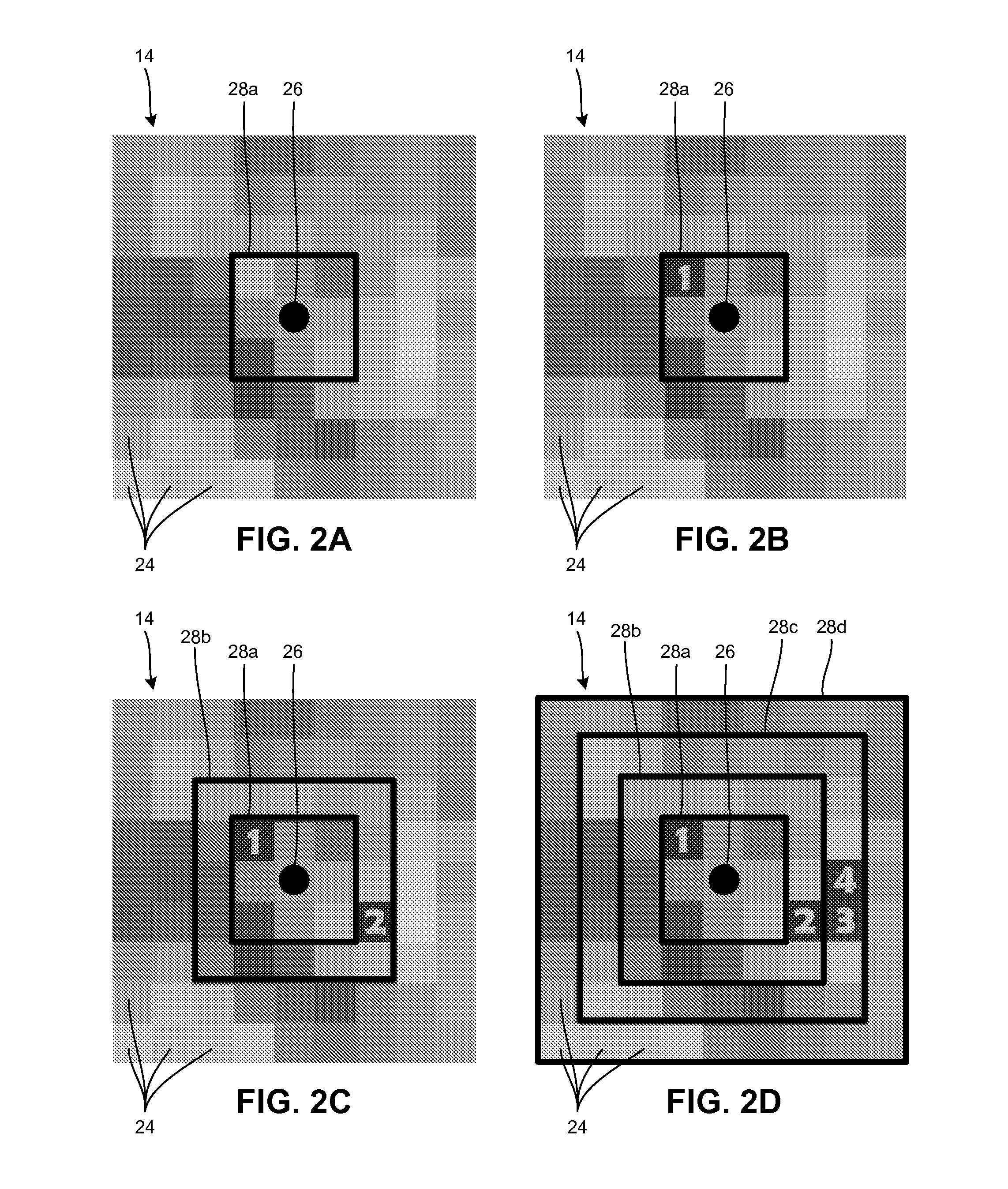
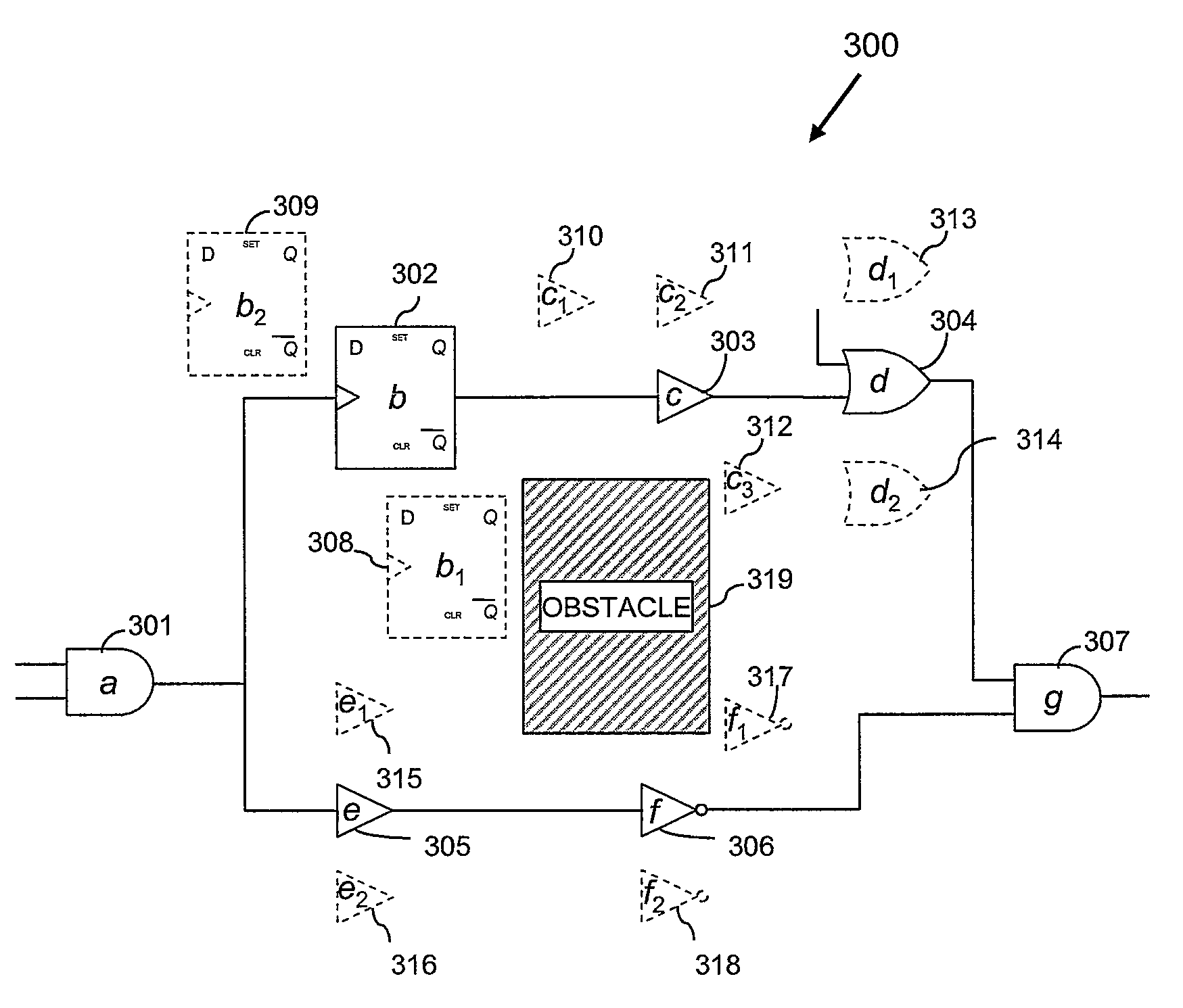
To improve the scheduling and tasking of resources, the present disclosure describes an improved planning system and method for the allocation and management of resources. The planning system uses a branch and bound approach of tasking resources using a heuristic to expedite arrival at a deterministic solution. For each possible functional mode of the resources, an upper bound is determined. The upper bounds are employed in an objective function for the branch and bound process to determine the functional mode in which to place the resources and to determine movement paths for the resources, all in an environment where a hostile force may attempt to destroy the resources.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Path planning determining method based on cladogram topological road network construction
The invention discloses a path planning determining method based on cladogram topological road network construction, which comprises the steps of: obtaining city complete road network data, constructing a road network full-connected graph G expressing original geographic information by applying an adjacent topological cladogram; classifying and dividing the road network full-connected graph G into a Y-type road network topological cladogram; obtaining the minimal branching tree comprising all target nodes; and eliminating invalid branching nodes by adopting a branching delimiting searching strategy for the minimal branching tree comprising all target nodes in a road planning problem, reducing incidence matrix dimensionality and obtaining a planning result. The invention has the advantagesof optimizing algorithm complexity of the road planning process and improving road planning efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
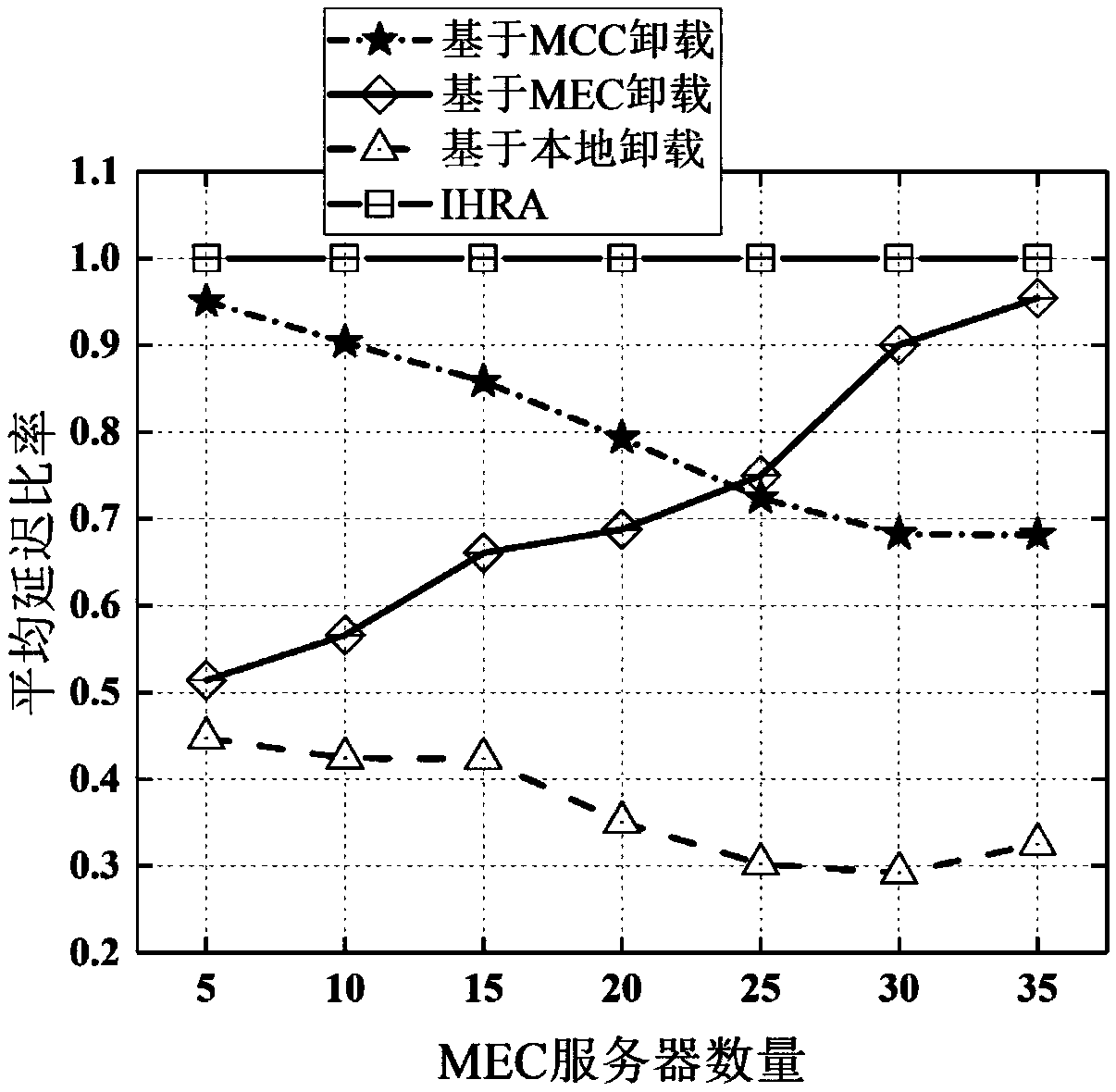
Network unloading method based on mixed cloud computation
The invention provides a network unloading method based on mixed cloud computation. The model defines transmission delay, processing delay and total delay for computing unloading computation beginningfrom the single-user unloading computation problem, and a single-user optimal solution is obtained by using a branch-bound algorithm. The boundary computing resource limitation and the transmission interference between the users are considered on this basis, the multi-user computing unloading problem is modelled as a hybrid integer linear planning MILP problem; due to the high computation complexity of the MILP problem, the model designs an iterative heuristic moving boundary computation resource allocation IHRA algorithm to solve the MILP problem and makes the unloading decision. A simulation result shows that the IHRA algorithm designed by the invention is superior to the standard algorithm in the application program running delay and unloading efficiency, and a new solution scheme is provided for the resource allocation problem of the hybrid cloud computation network unloading model.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Spectral method for sparse principal component analysis
InactiveUS20070156471A1Improve approximate candidate solutionEasy to solveFinanceCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorRenormalization
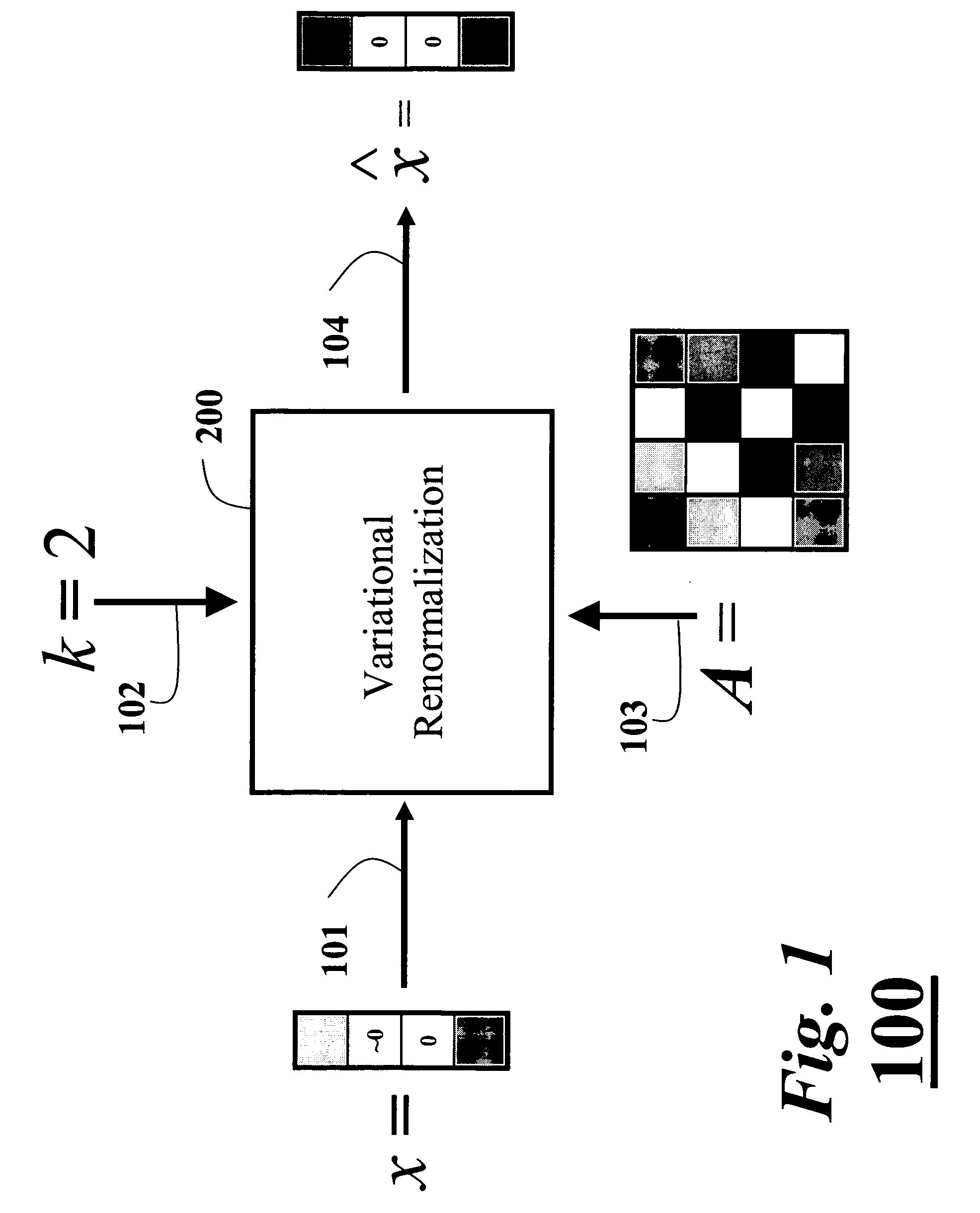
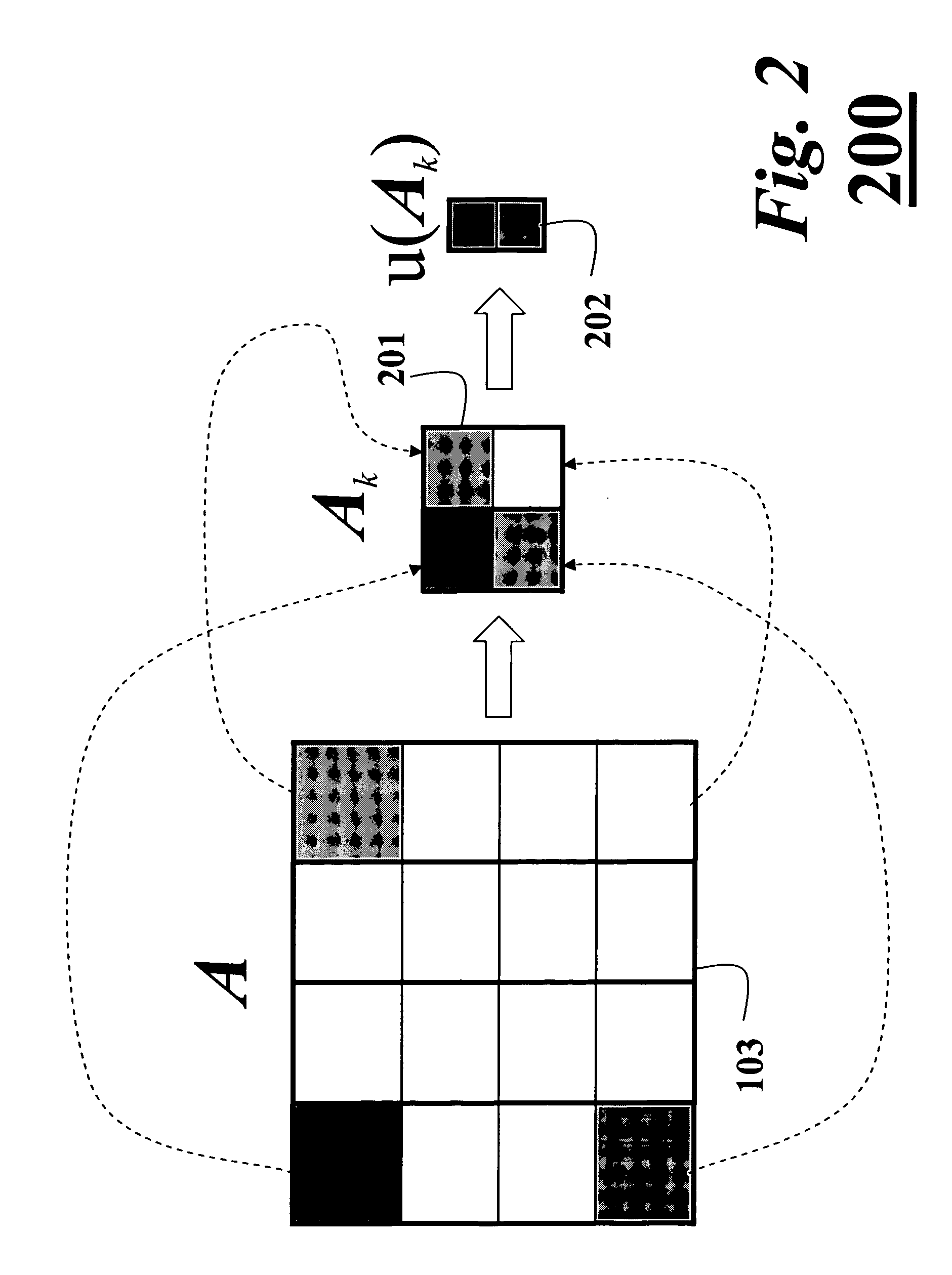
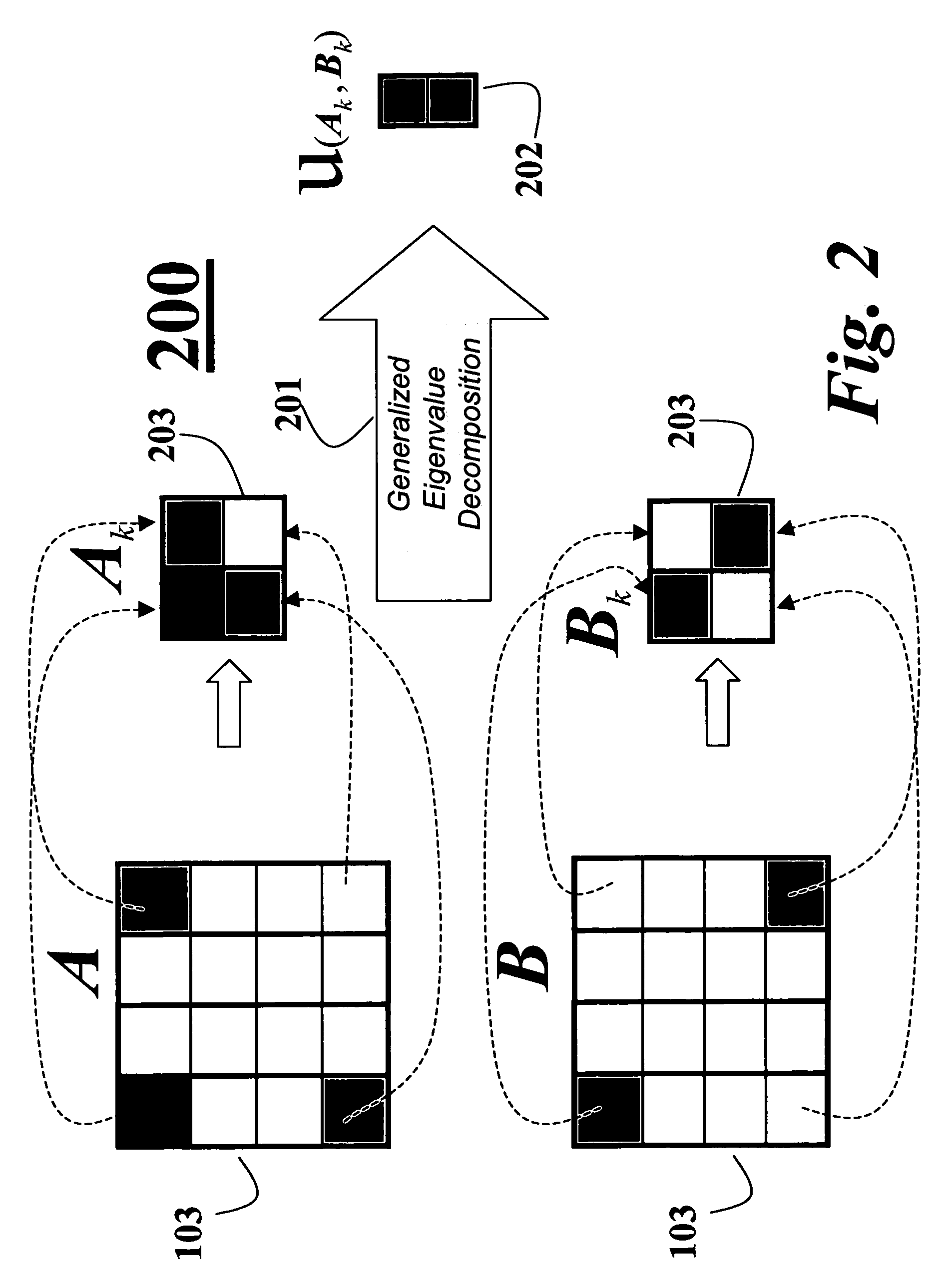
A method maximizes a candidate solution to a cardinality-constrained combinatorial optimization problem of sparse principal component analysis. An approximate method has as input a covariance matrix A, a candidate solution, and a sparsity parameter k. A variational renormalization for the candidate solution vector x with regards to the eigenvalue structure of the covariance matrix A and the sparsity parameter k is then performed by means of a sub-matrix eigenvalue decomposition of A to obtain a variance maximized k-sparse eigenvector x that is the best possible solution. Another method solves the problem by means of a nested greedy search technique that includes a forward and backward pass. An exact solution to the problem initializes a branch-and-bound search with an output of a greedy solution.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Spectral method for sparse linear discriminant analysis
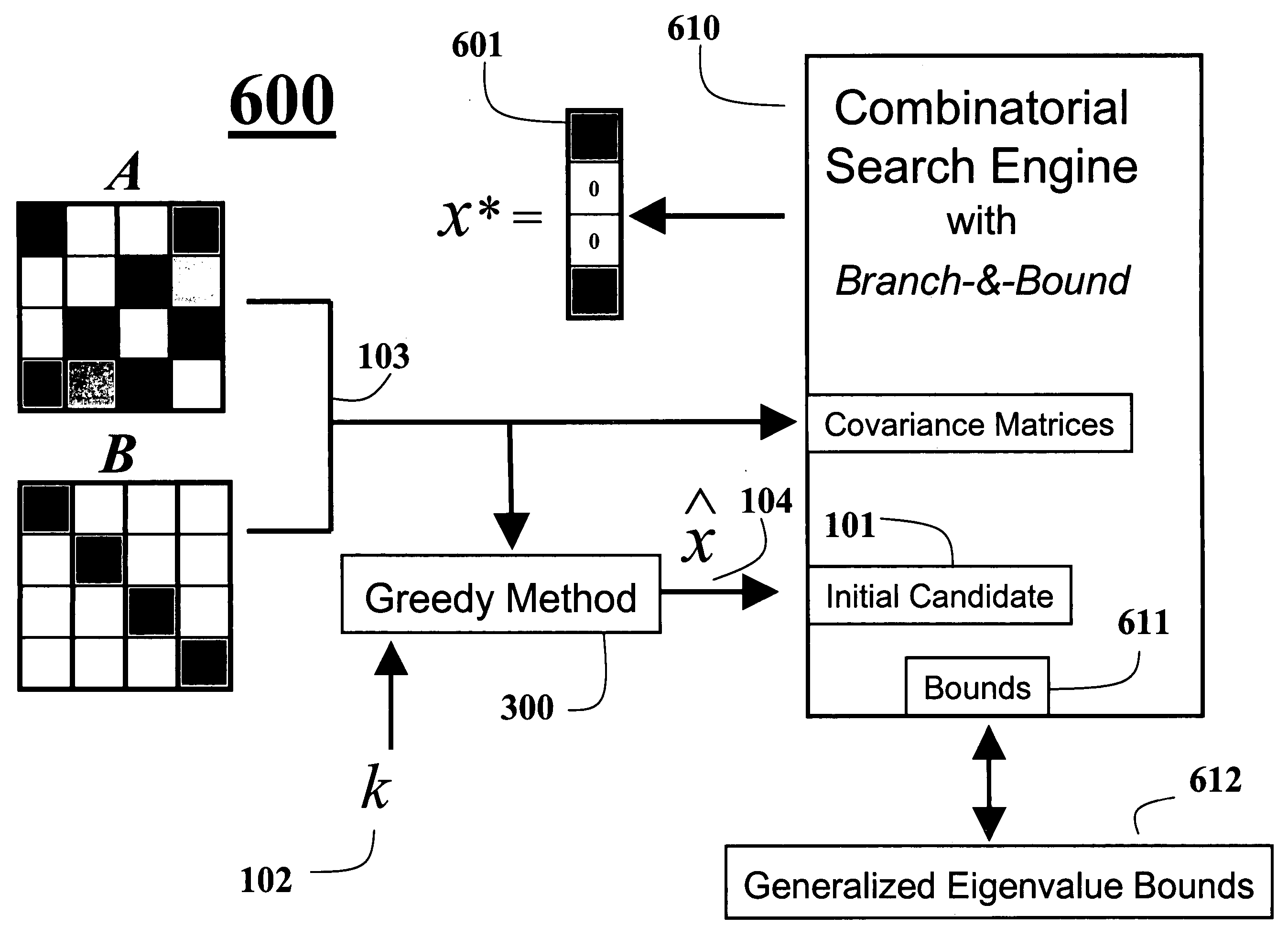
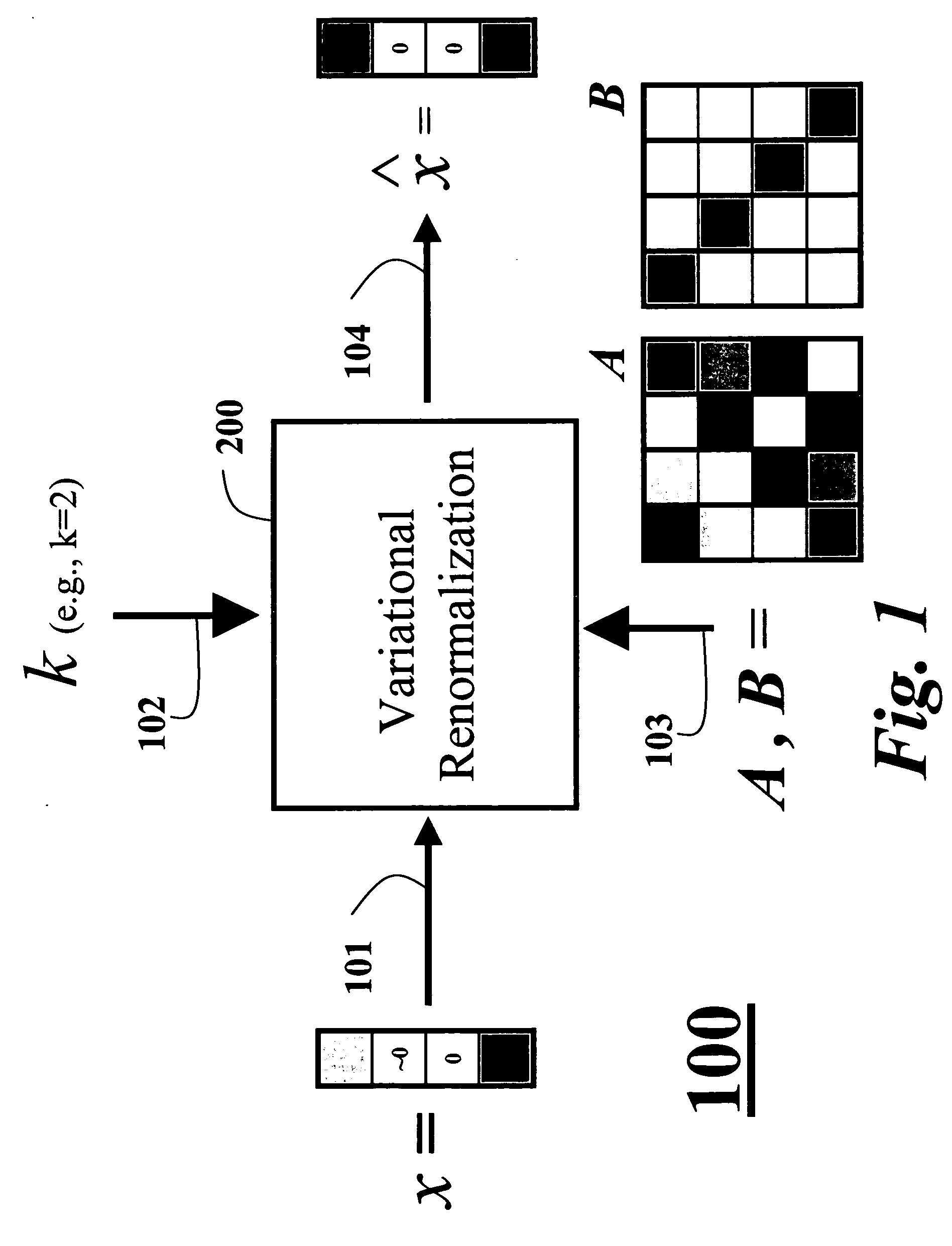
A computer implemented method maximizes candidate solutions to a cardinality-constrained combinatorial optimization problem of sparse linear discriminant analysis. A candidate sparse solution vector x with k non-zero elements is inputted, along with a pair of covariance matrices A, B measuring between-class and within-class covariance of binary input data to be classified, the sparsity parameter k denoting a desired cardinality of a final solution vector. A variational renormalization of the candidate solution vector x is performed with regards to the pair of covariance matrices A, B and the sparsity parameter k to obtain a variance maximized discriminant eigenvector {circumflex over (x)} with cardinality k that is locally optimal for the sparsity parameter k and zero-pattern of the candidate sparse solution vector x, and is the final solution vector for the sparse linear discriminant analysis optimization problem. Another method solves the initial problem of finding a candidate sparse solution by means of a nested greedy search technique that includes a forward and backward pass. Another method, finds an exact and optimal solution to the general combinatorial problem by first finding a candidate by means of the previous nested greedy search technique and then using this candidate to initialize a branch-and-bound algorithm which gives the optimal solution.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
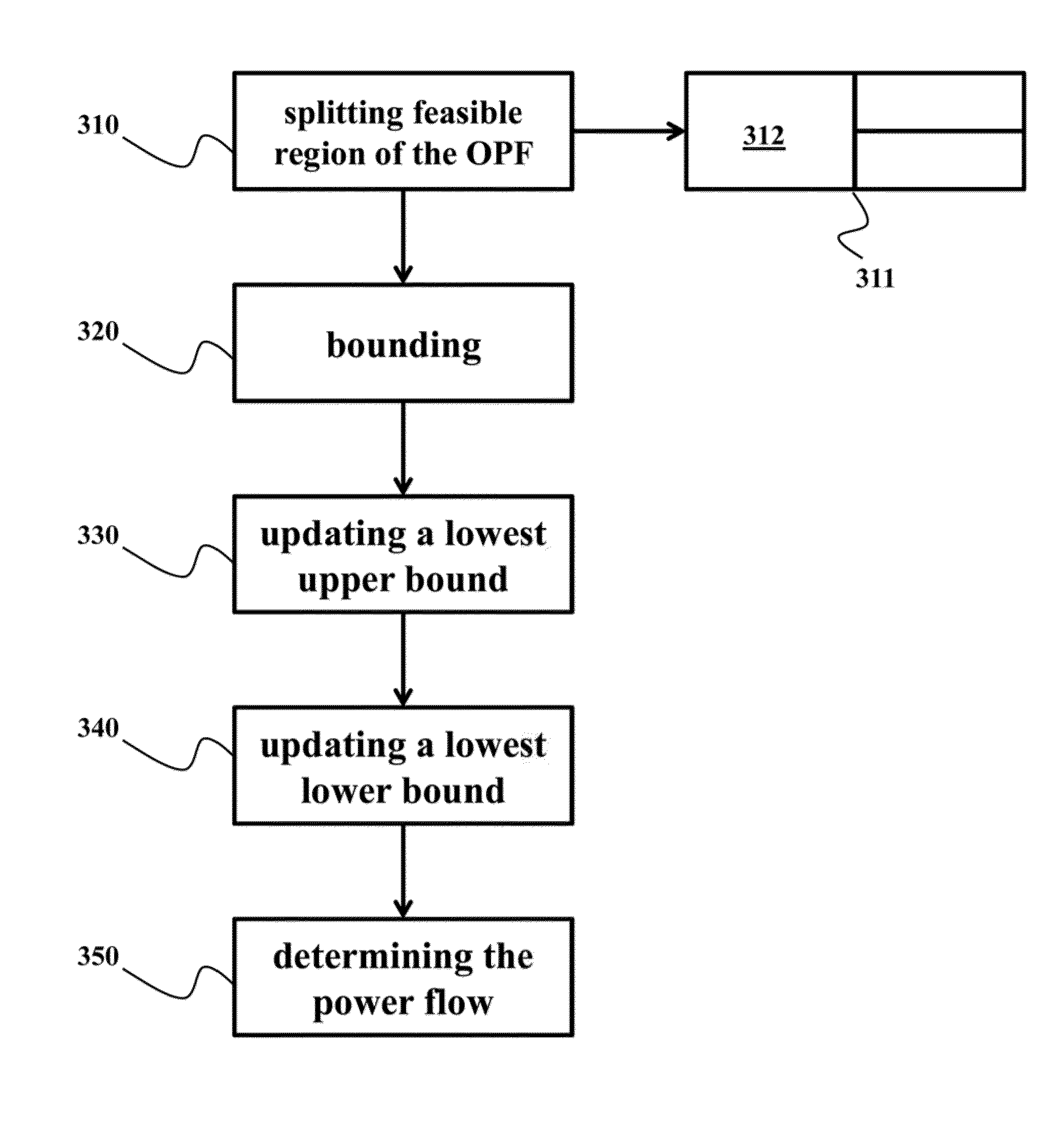
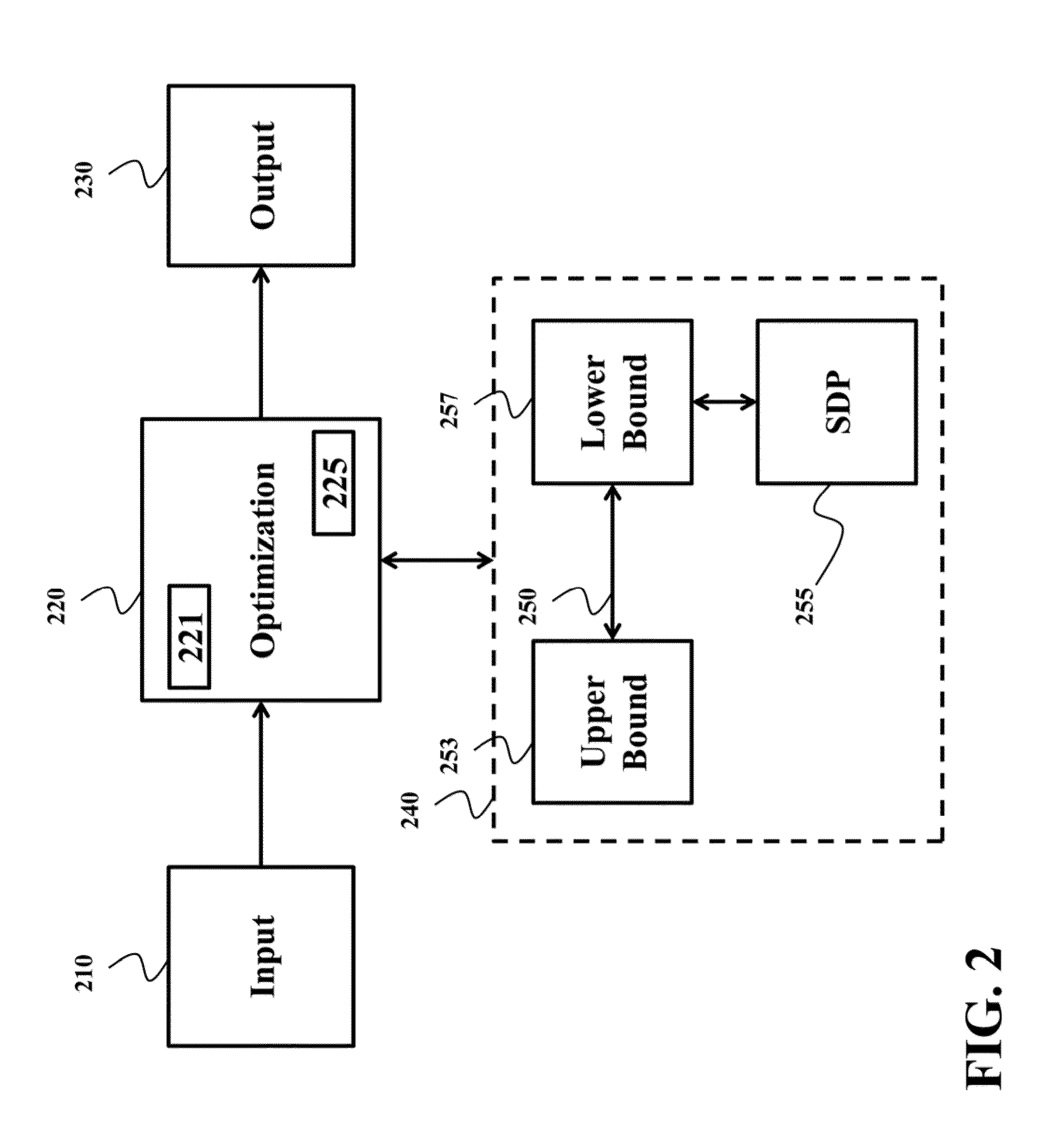
Method for Globally Optimizing Power Flows in Electric Networks
ActiveUS20140052301A1Convergence can be speededEasy to solveMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlLower limitPower flow
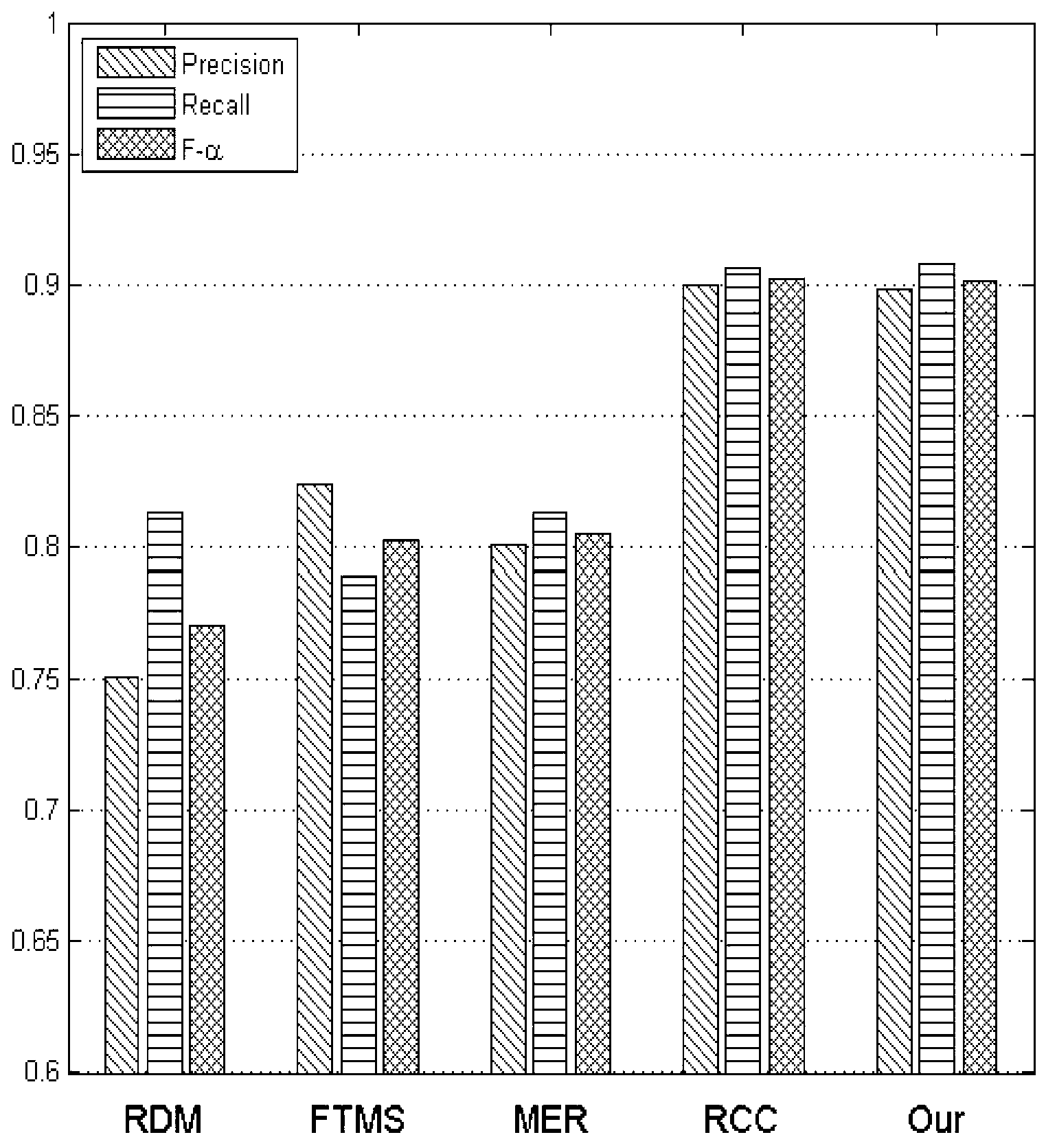
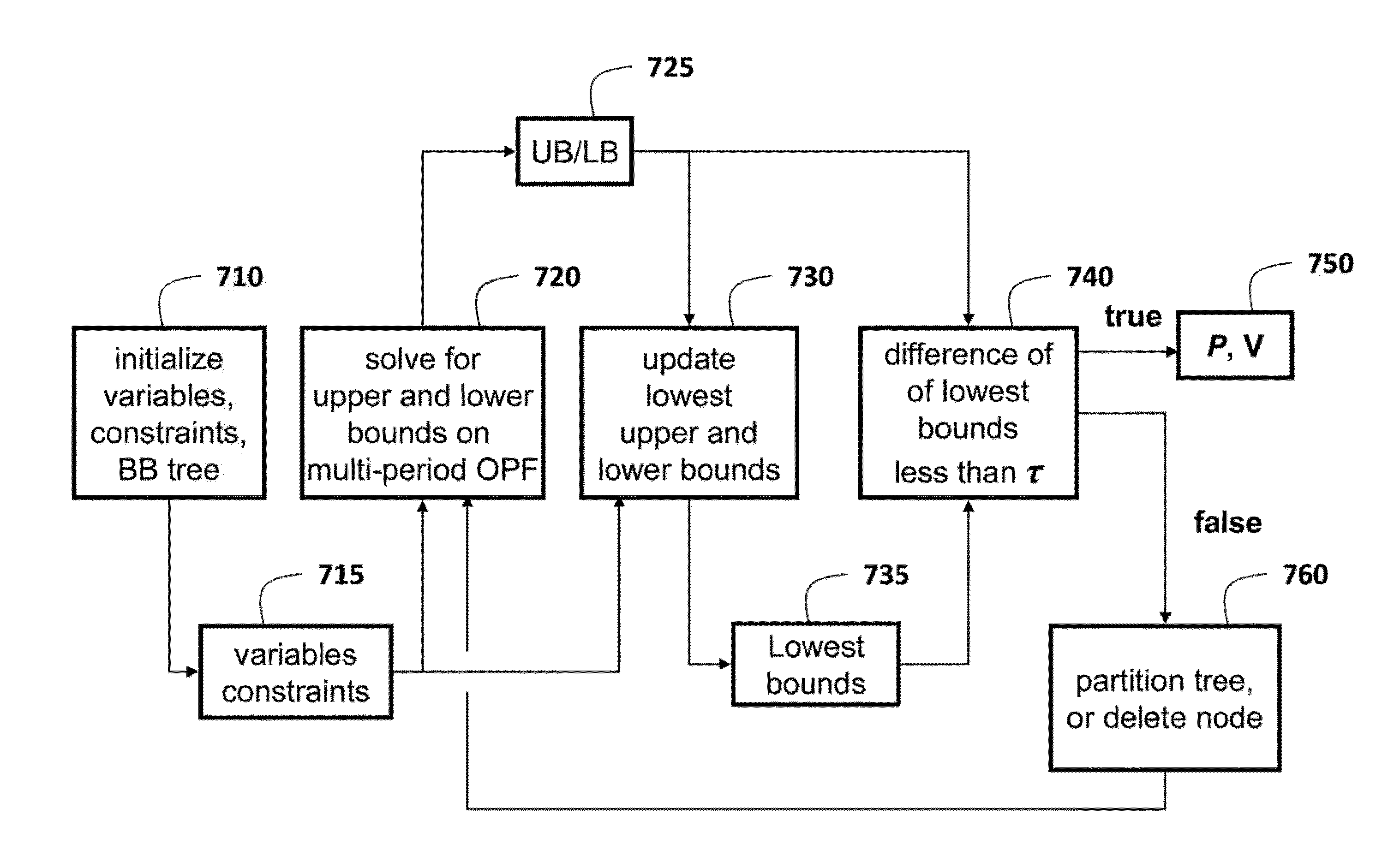
A power flow problem (OPF) in an electric power network is globally optimized using a branch and bound tree of nodes connected by edges. The BB initially includes at least a root node, and each node represents a feasible region of limits on voltages and powers. An upper bound on the OPF problem is solved for selected nodes using nonlinear programming, while a lower bound is solved using a convex relaxation. The lowest upper and lower bounds are updated using the current upper and lower bound. If a difference between the lowest upper and lowest lower bound is less than a threshold, then outputting the voltages and the powers for the electric power network as represented by the feasibility region for the selected node. Otherwise, the feasible region of the node is partitioned to replace the node. The process is repeated until the tree is empty.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System and method for resource allocation and management
ActiveUS20110046837A1Vehicle position/course/altitude controlDistance measurementGlobal planningSystem usage
To improve the scheduling and tasking of sensors, the present disclosure describes an improved planning system and method for the allocation and management of sensors. In one embodiment, the planning system uses a branch and bound approach of tasking sensors using a heuristic to expedite arrival at a deterministic solution. In another embodiment, a progressive lower bound is applied to the branch and bound approach. Also, in another embodiment, a hybrid branch and bound approach is used where both local and global planning are employed in a tiered fashion.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
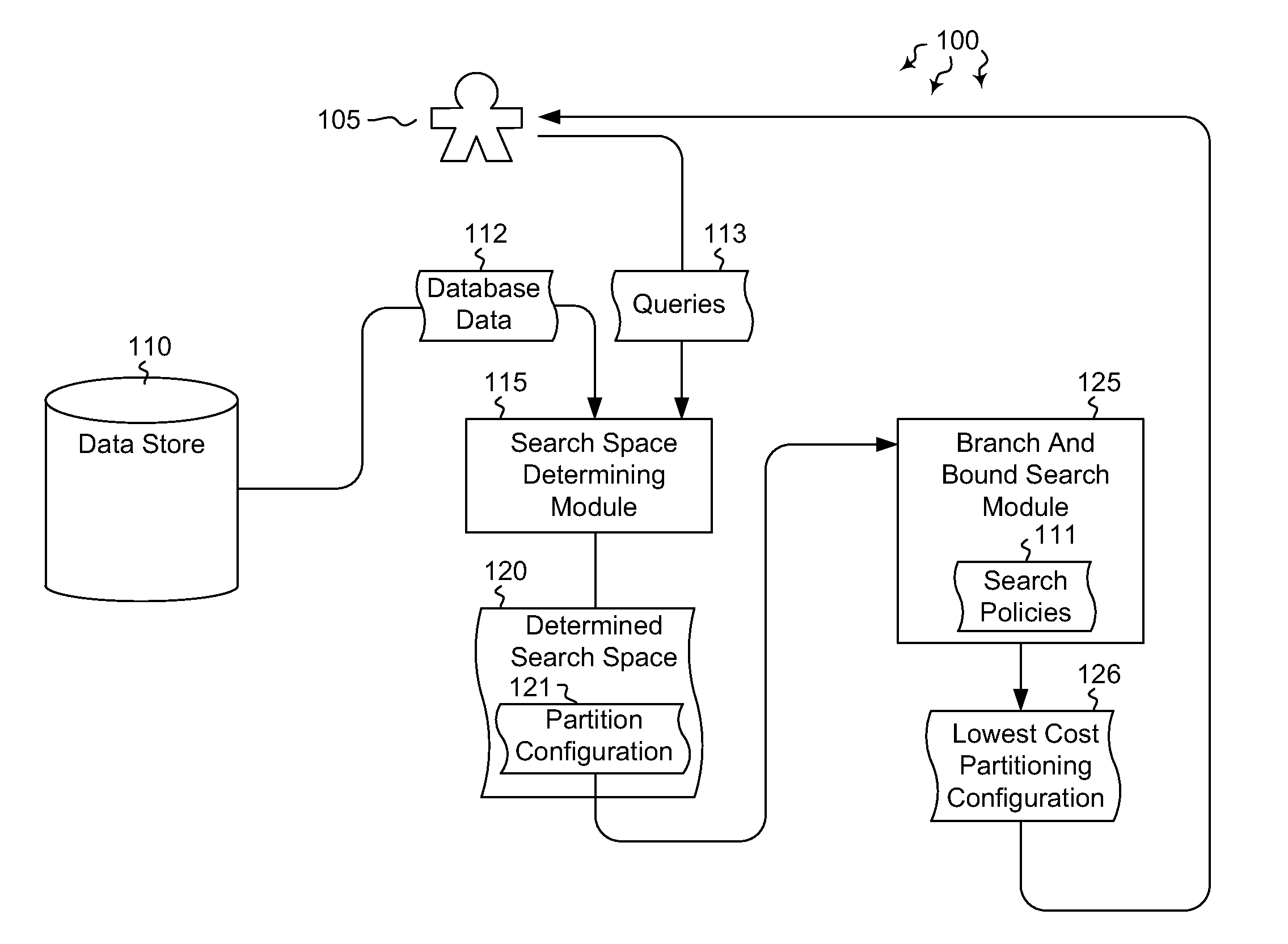
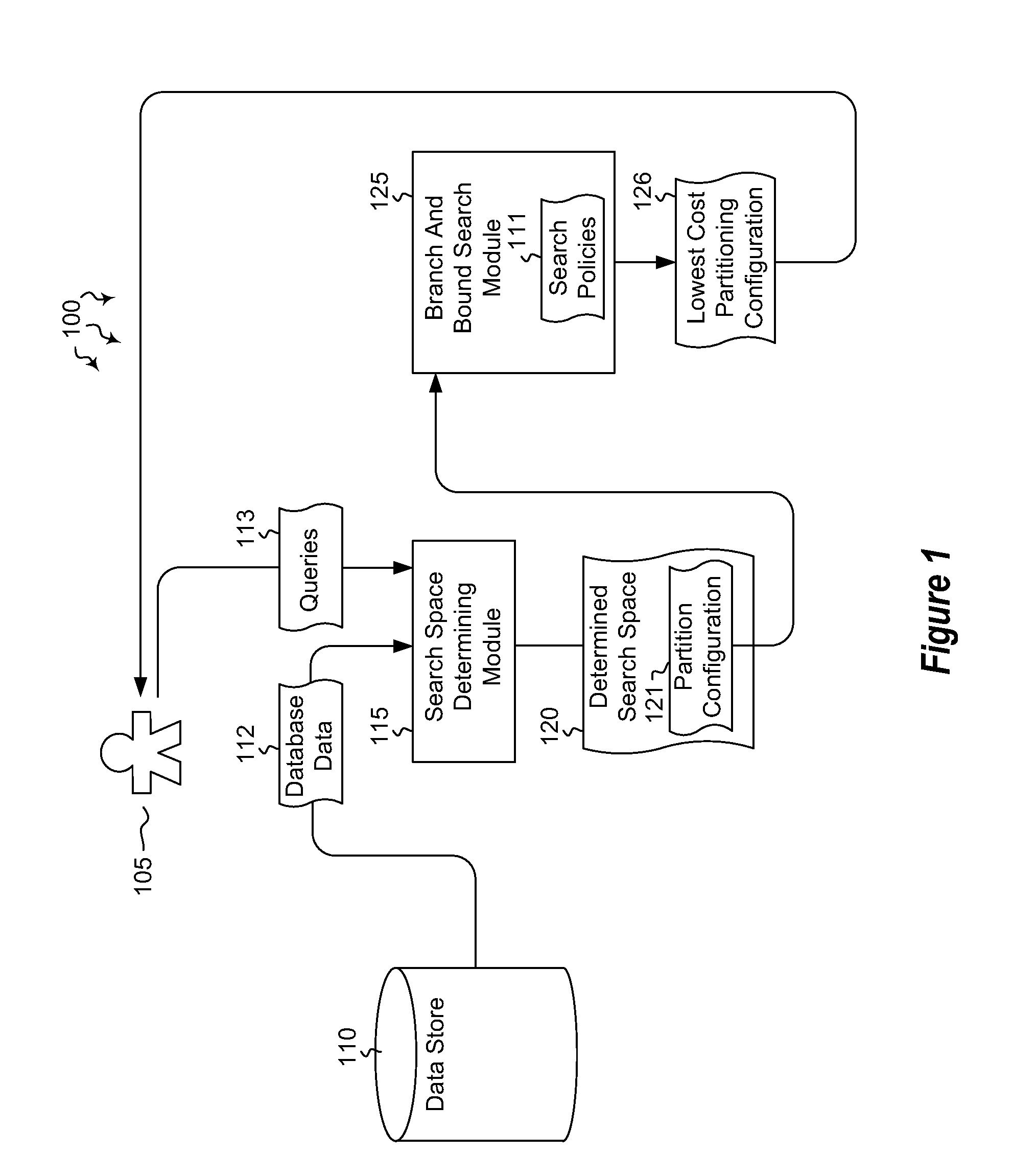
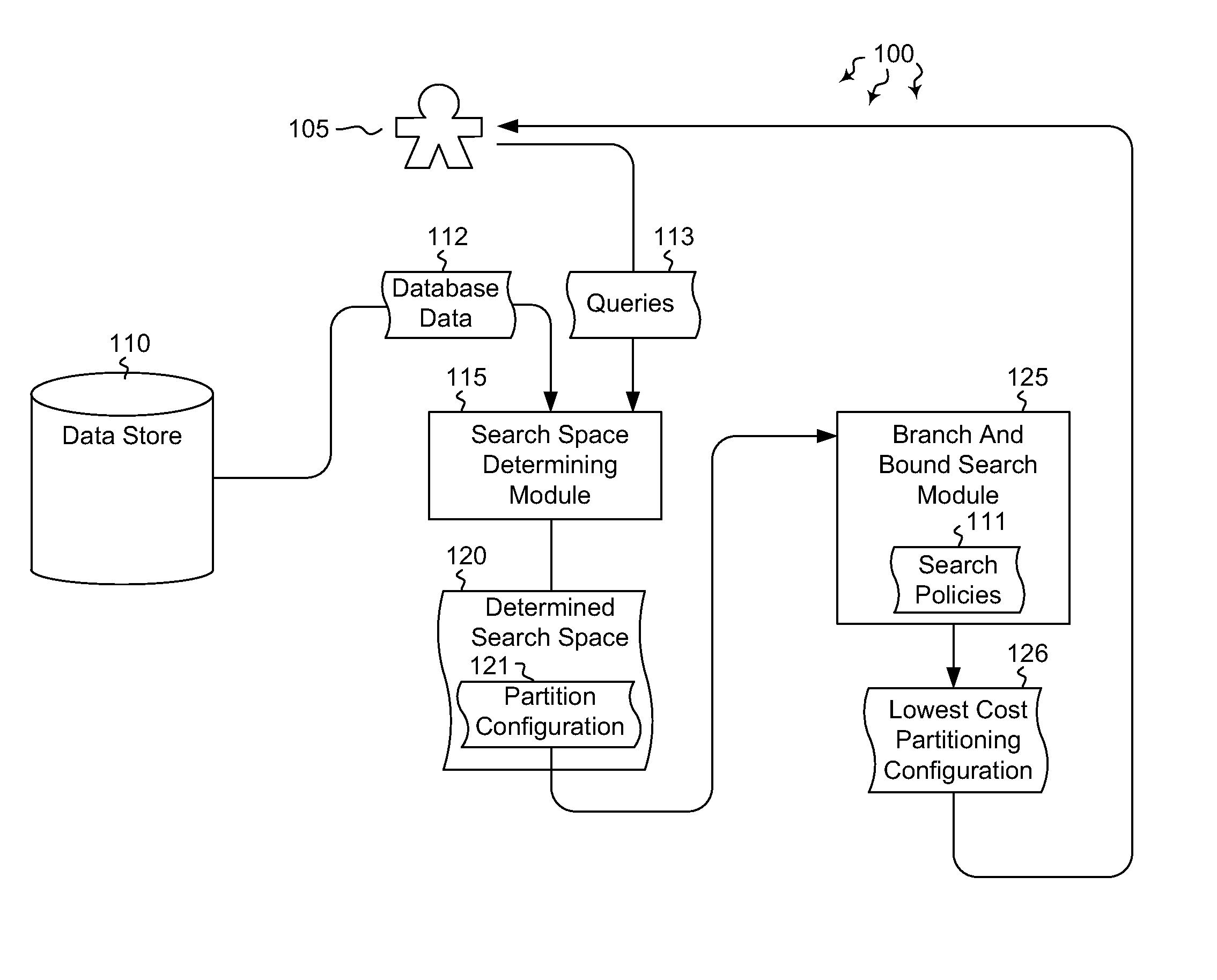
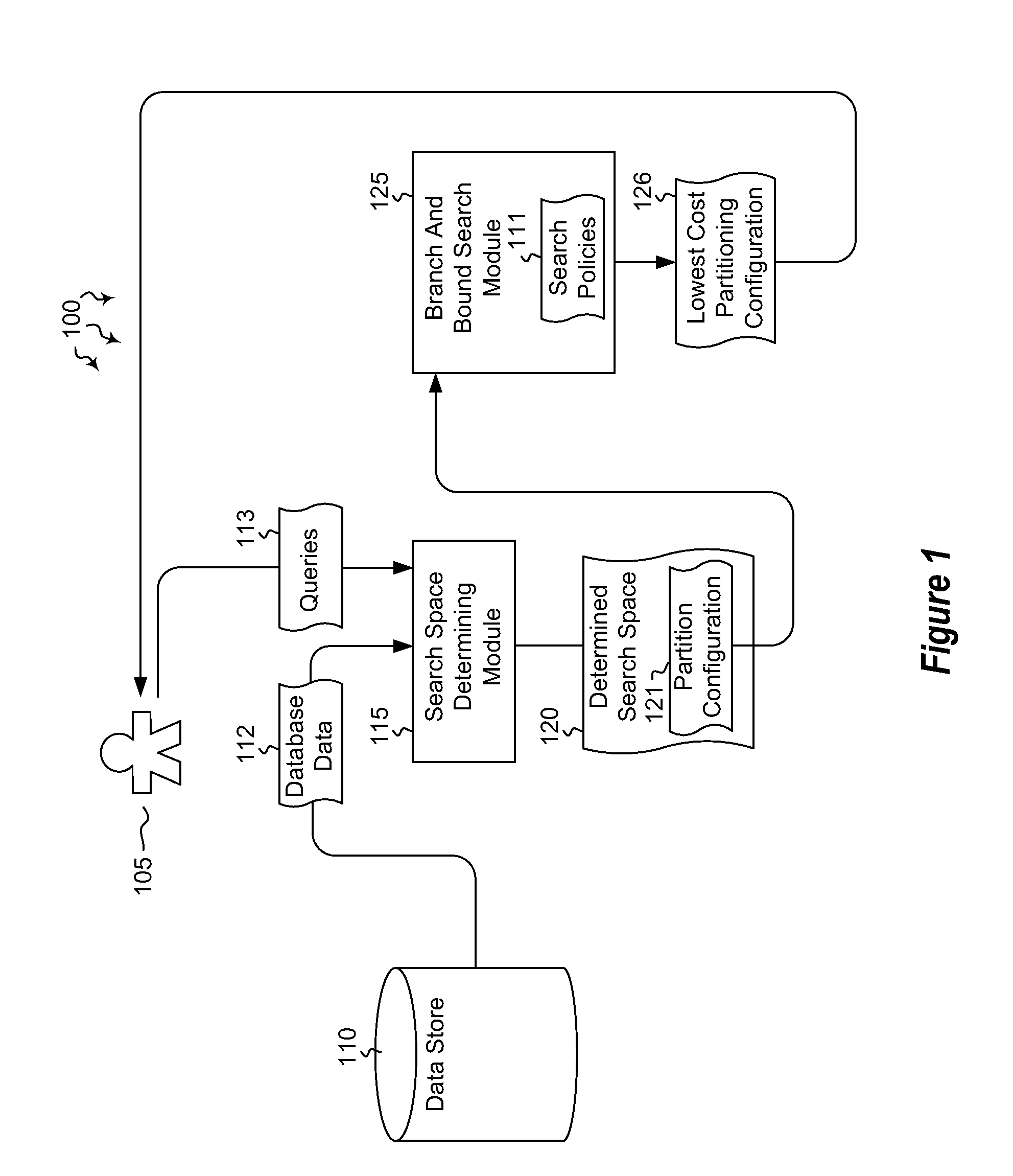
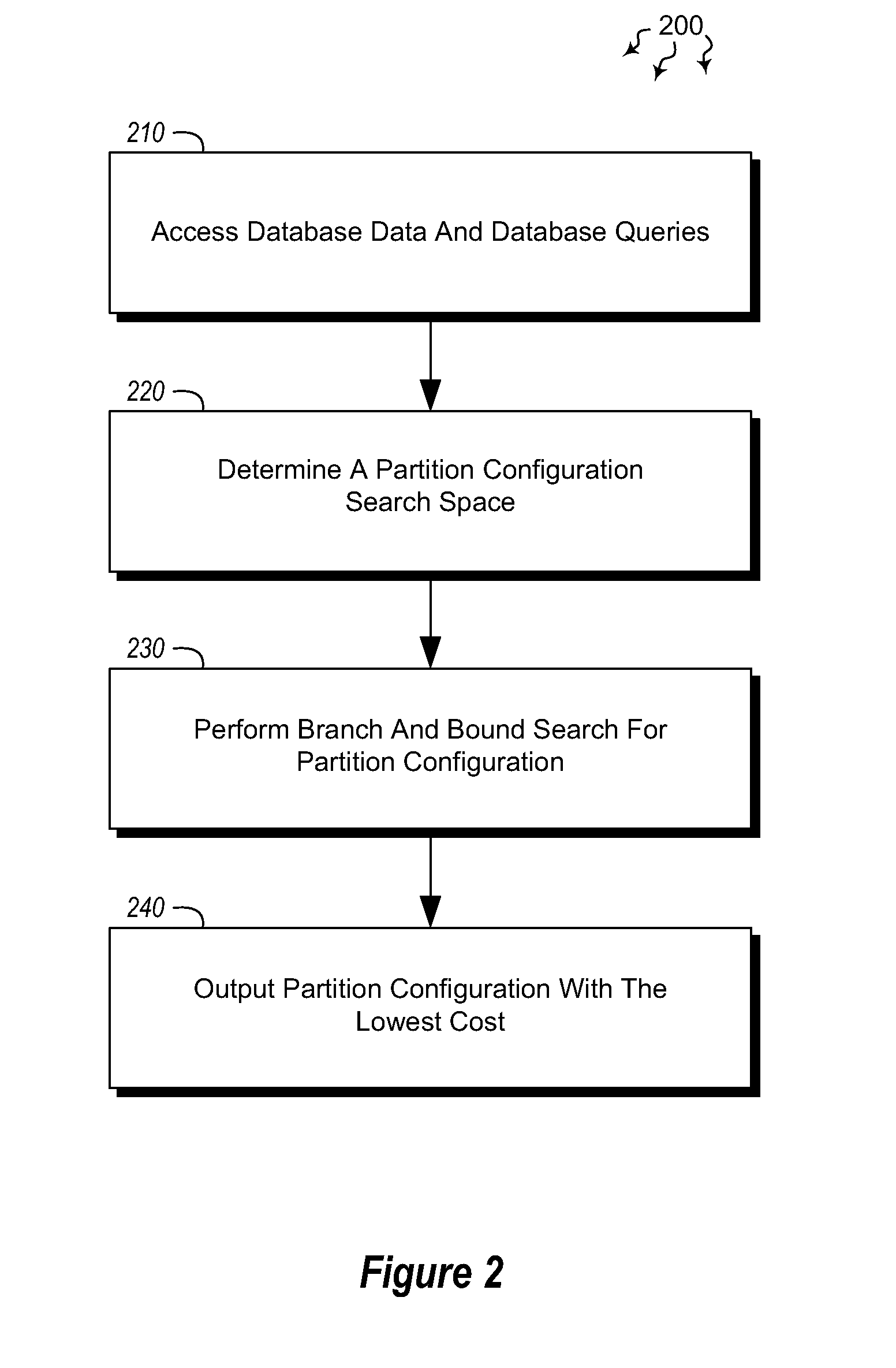
Automated partitioning in parallel database systems
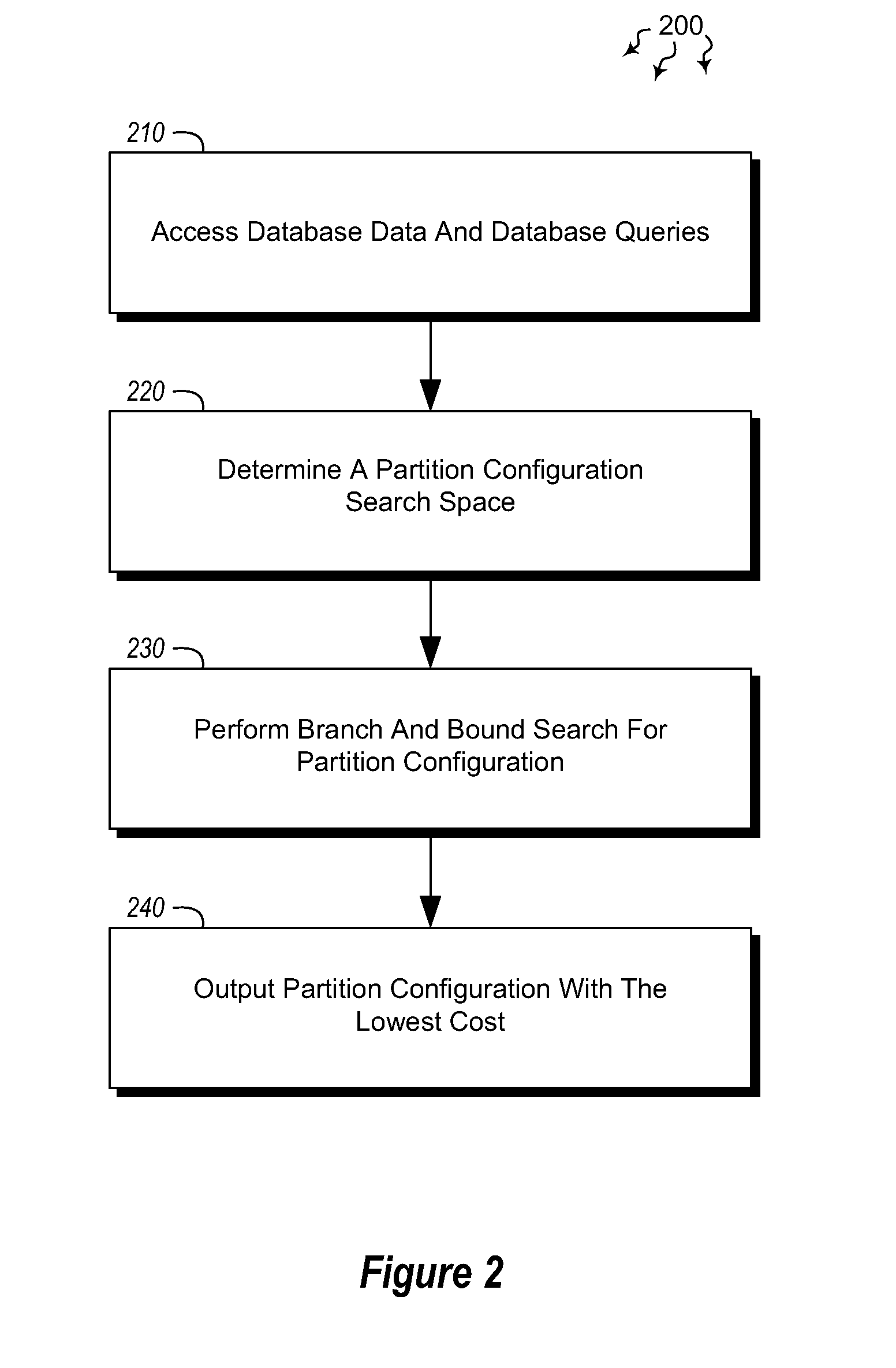
InactiveUS20120117065A1Improve partition configuration cost determination efficiencyReduce the cost of determiningDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsQuery optimizationWorkload
Embodiments are directed to determining optimal partition configurations for distributed database data and to implementing parallel query optimization memo data structure to improve partition configuration cost estimation efficiency. In an embodiment, a computer system accesses a portion of database data and various database queries for a given database. The computer system determines, based on the accessed database data and database queries, a partition configuration search space which includes multiple feasible partition configurations for the database data and a workload of queries expected to be executed on that data. The computer system performs a branch and bound search in the partition configuration search space to determine which data partitioning path has the lowest partitioning cost. The branch and bound search is performed according to branch and bound search policies. The computer system also outputs the partition configuration with the determined lowest partitioning cost.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automated partitioning in parallel database systems
InactiveUS8326825B2Reduce the cost of determiningImprove partition configuration cost determination efficiencyDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsQuery optimizationWorkload
Embodiments are directed to determining optimal partition configurations for distributed database data and to implementing parallel query optimization memo data structure to improve partition configuration cost estimation efficiency. In an embodiment, a computer system accesses a portion of database data and various database queries for a given database. The computer system determines, based on the accessed database data and database queries, a partition configuration search space which includes multiple feasible partition configurations for the database data and a workload of queries expected to be executed on that data. The computer system performs a branch and bound search in the partition configuration search space to determine which data partitioning path has the lowest partitioning cost. The branch and bound search is performed according to branch and bound search policies. The computer system also outputs the partition configuration with the determined lowest partitioning cost.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and Method for Optimal Power Flow Analysis
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
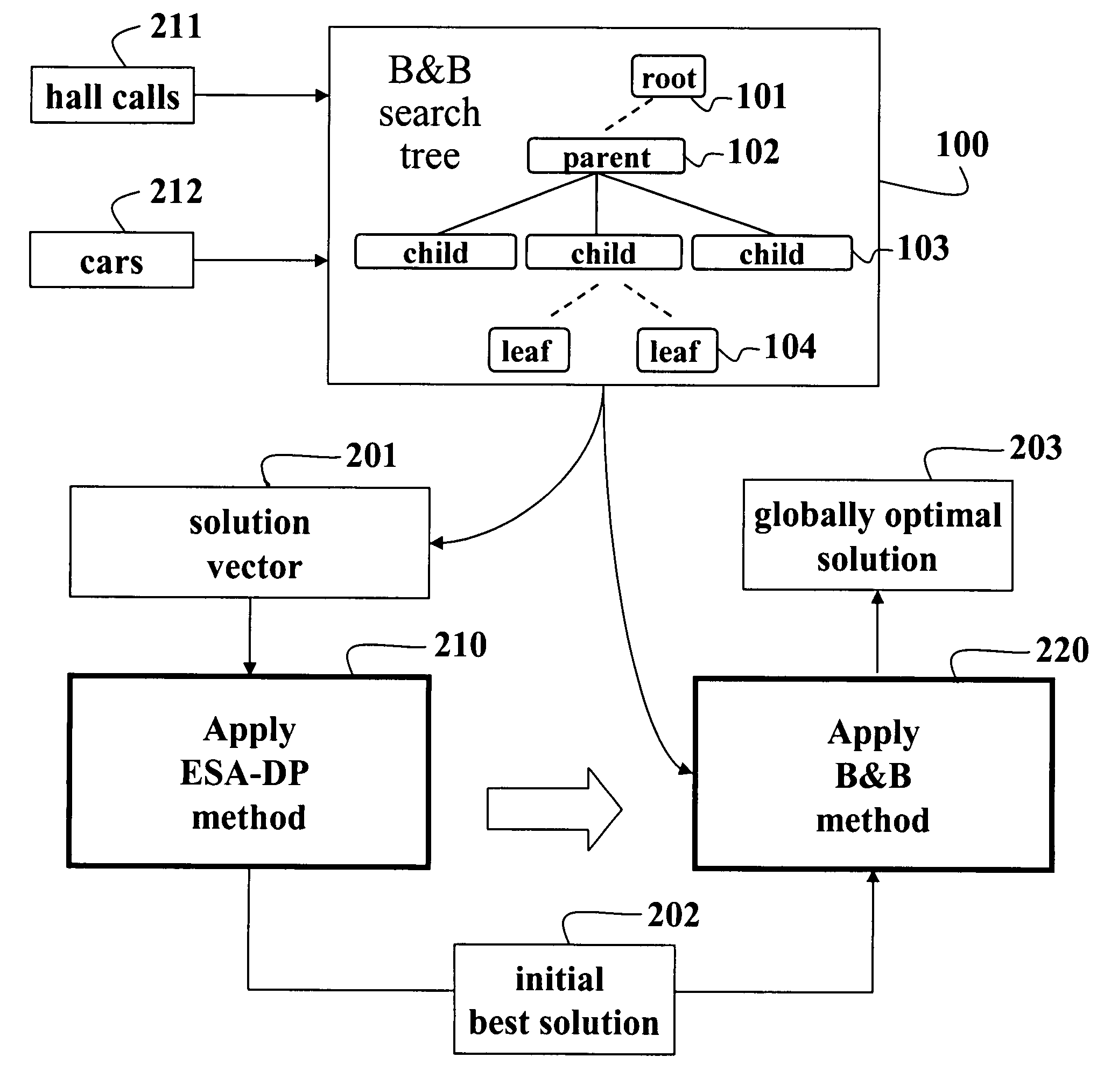
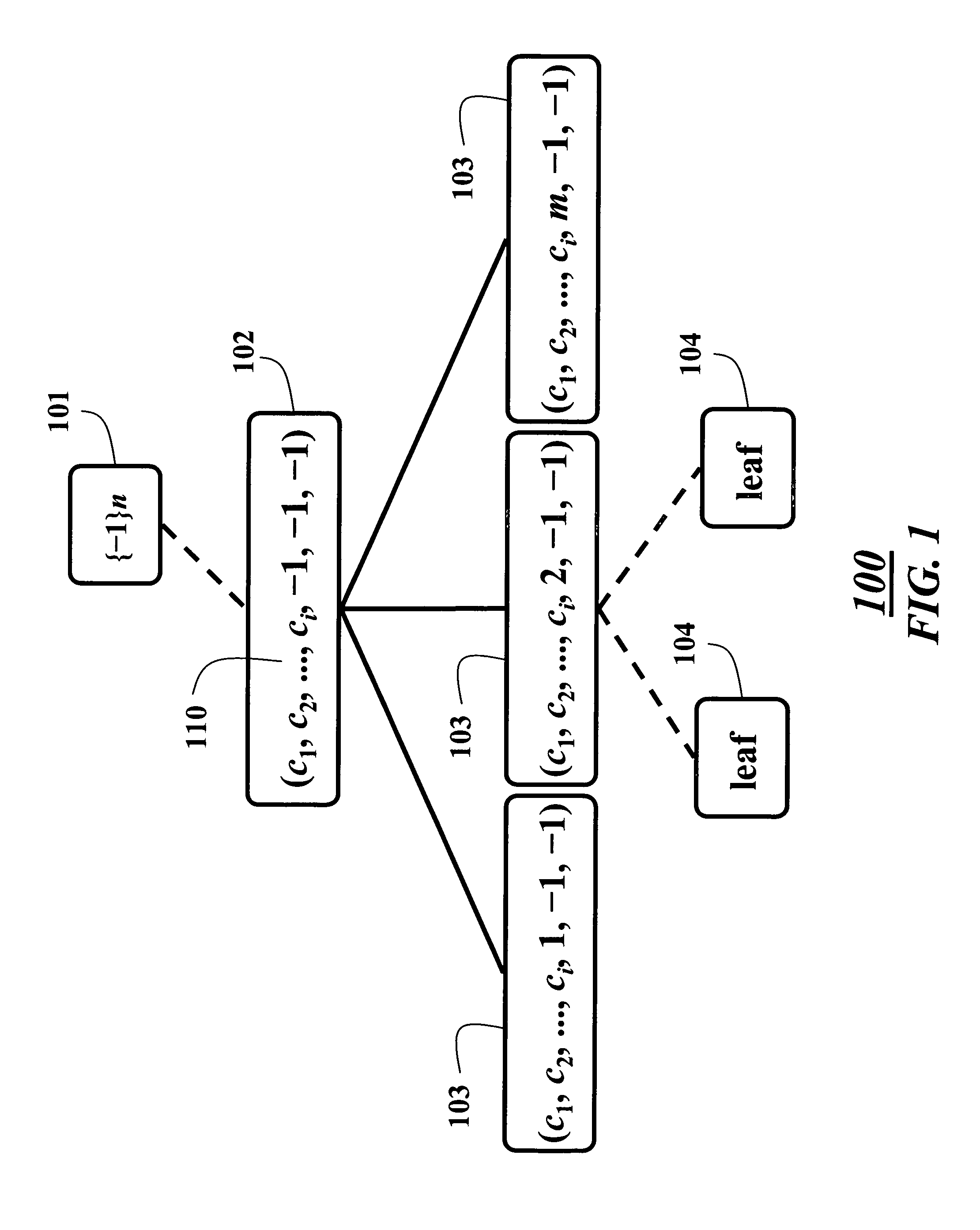
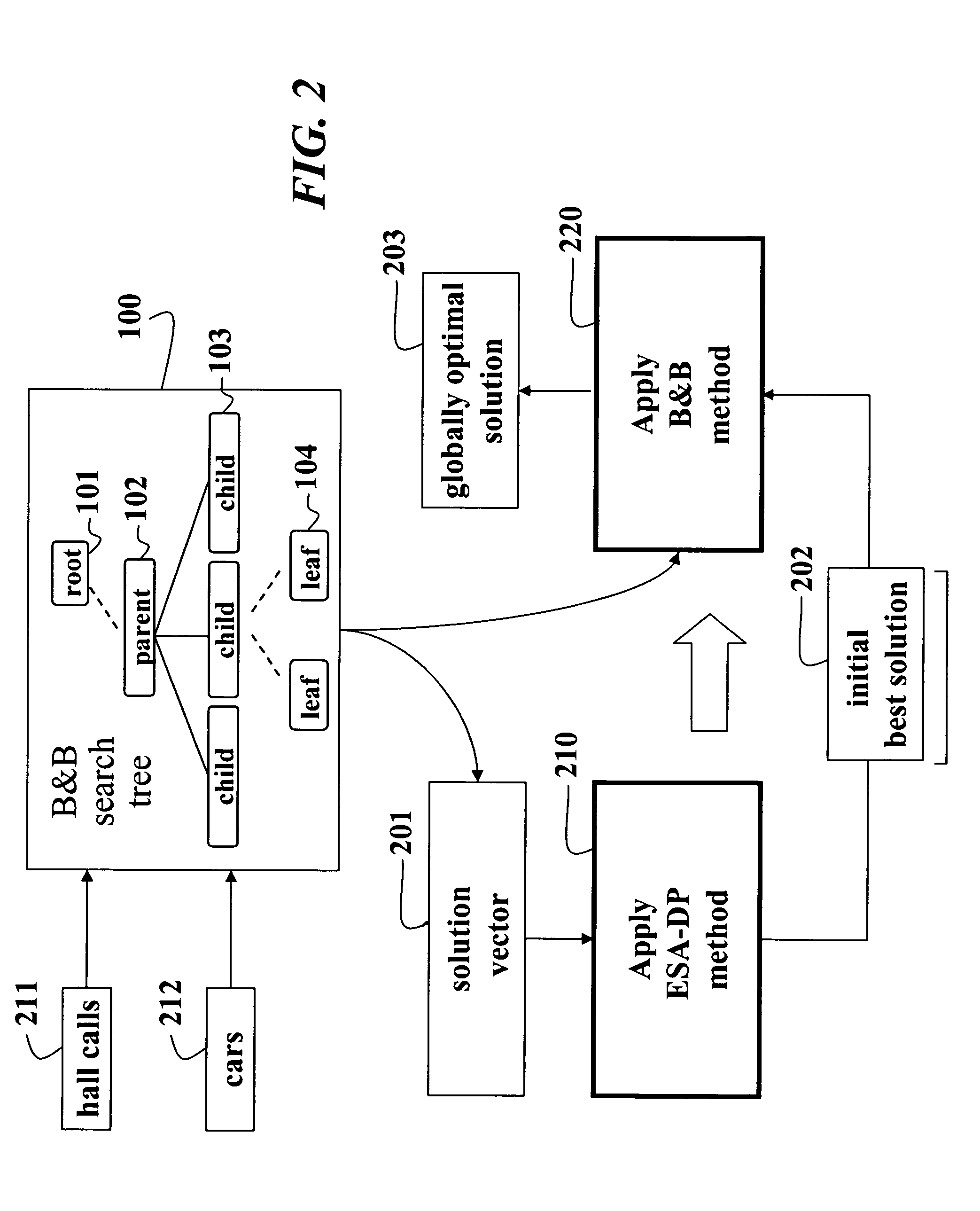
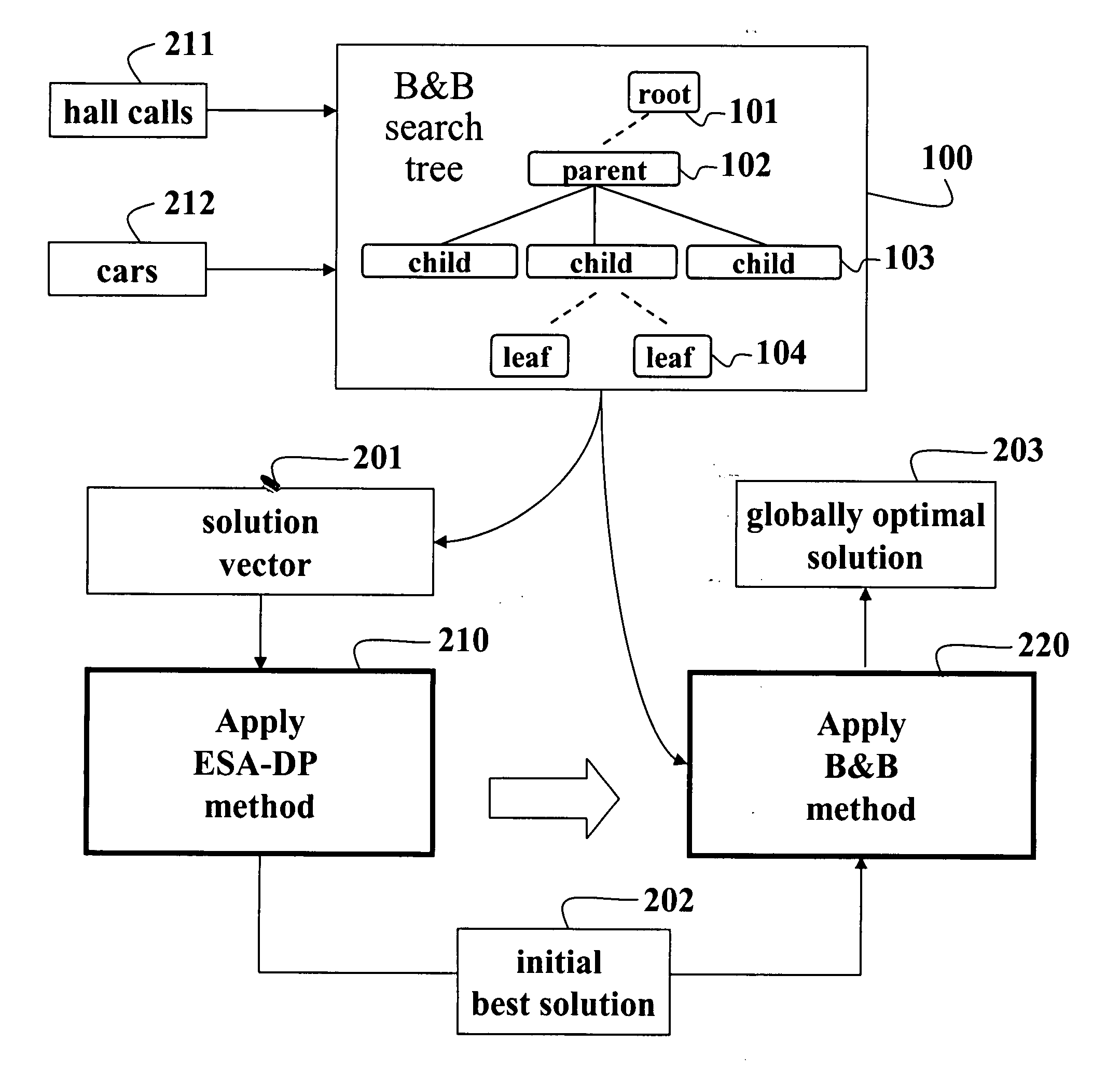
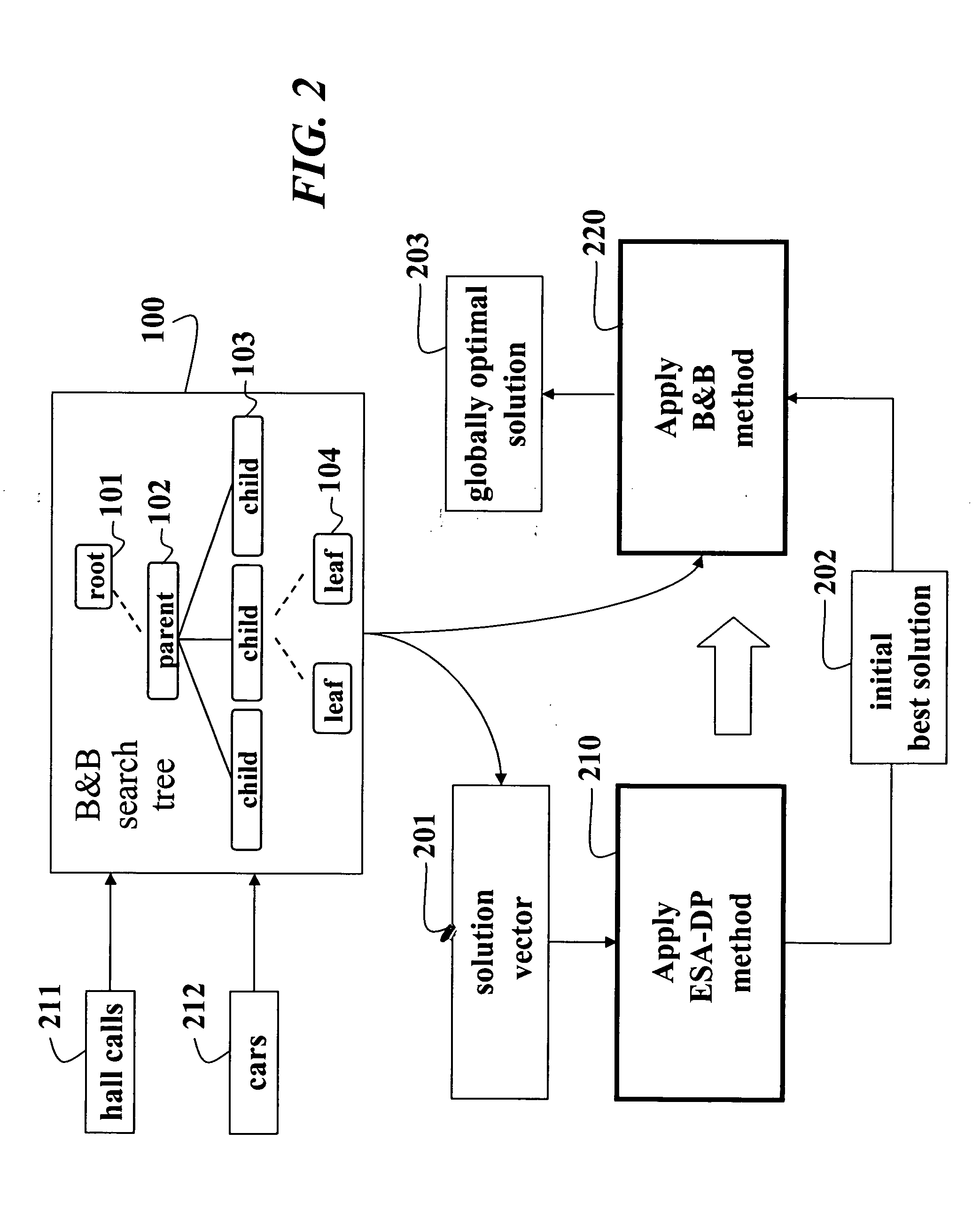
System and method for scheduling elevator cars using branch-and-bound
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
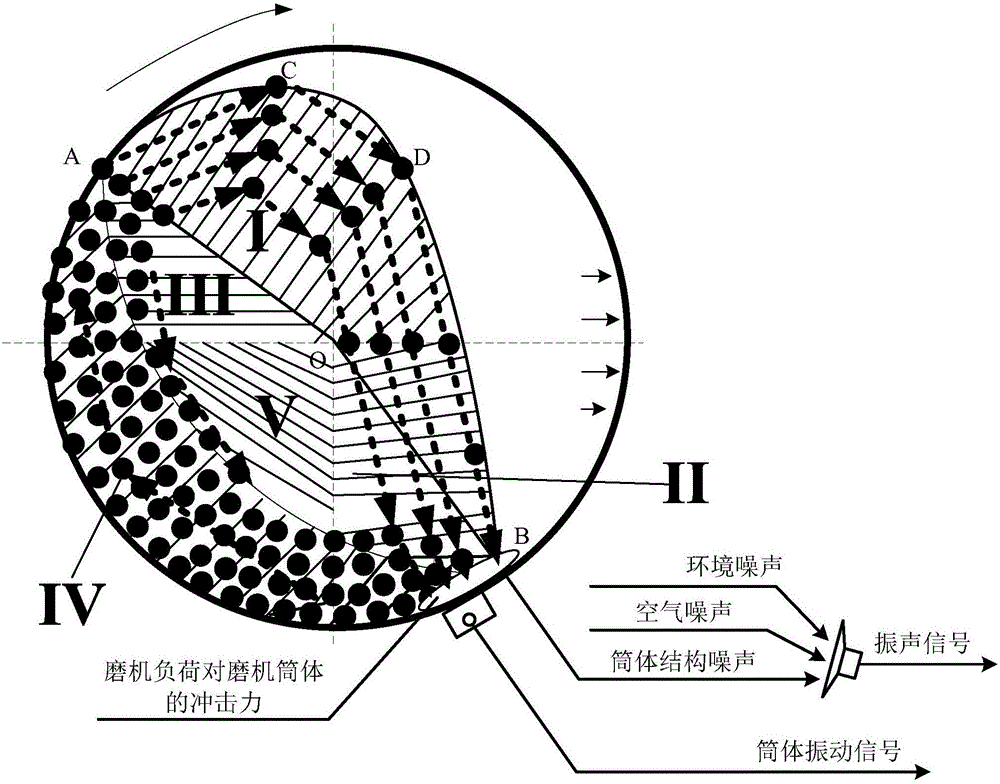
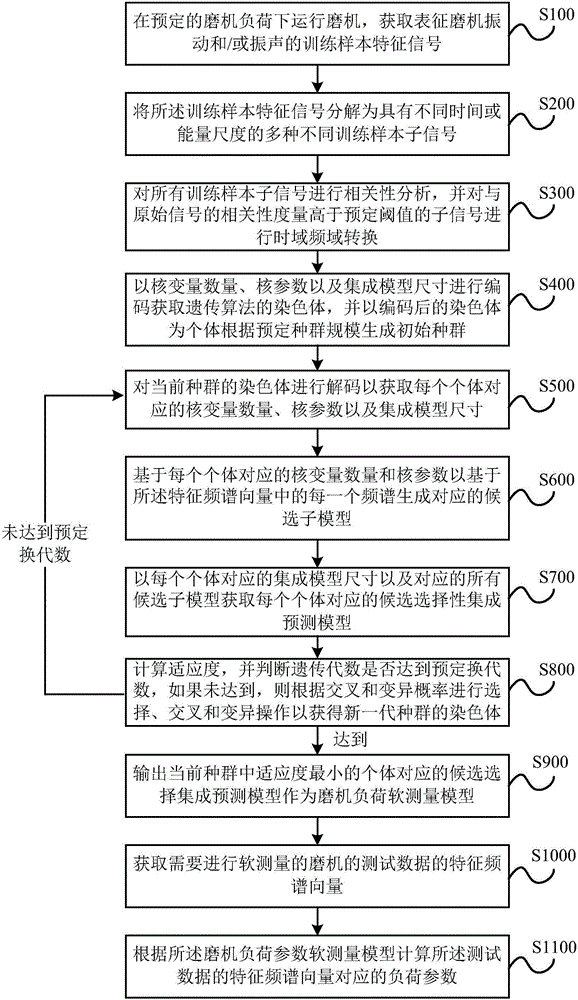
Soft measurement method for load parameters of mill
InactiveCN105787255AHigh precisionEffective selective fusionInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumDecomposition
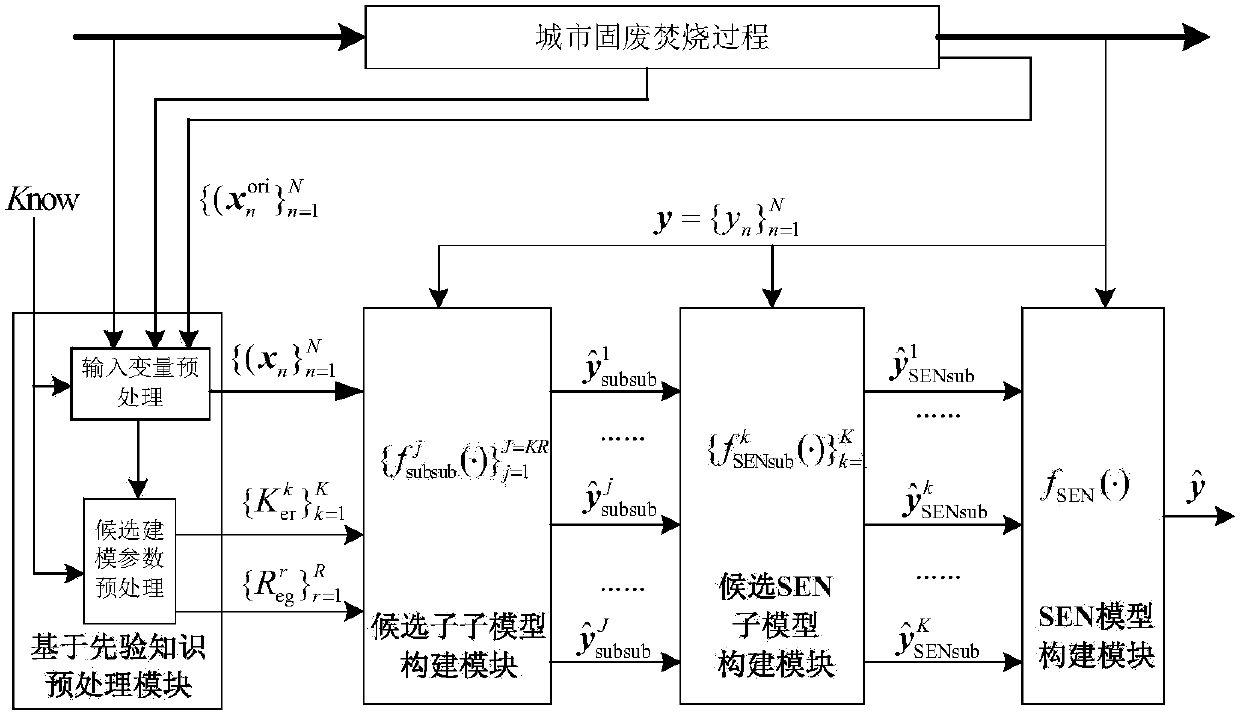
The invention discloses a soft measurement method for load parameters of a mill. The method adopts various different signal decomposition technologies to decompose the original cylinder vibration signal and vibration-sound signals into a series of sub-signals based on different perspectives for multi-scale and unsteady characteristics of the cylinder vibration and vibration-sound signals. The selected sub-signal spectrum and the original signal spectrum are taken as multisource multi-scale information to construct a soft measurement model for the load parameters of the mill. A global optimization selective ensemble kernel partial least squares (GOSENKPLS) based on an adaptive genetic algorithm (AGA) and a branch-and-bound (BB) algorithm is adopted to carry out optimization selection on structural parameters and learning parameters of candidate sub-models and a selective ensemble model (SEN model), so that the effectively selective fusion of the multisource multi-scale signals is realized. According to the method, the accuracy for soft measurement of the load parameters of the mill can be improved.
Owner:中国人民解放军61599部队计算所 +1
Dioxin soft measurement system based on selective ensemble and least squares support vector machine
ActiveCN107944173ACharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationAdaptive weightingLeast squares support vector machine
The invention discloses a dioxin soft measurement system based on a selective ensemble and least squares support vector machine. First, a candidate kernel parameter set having the number of K and a candidate penalty parameter set having the number of R are given based on prior knowledge; second, an LSSVM (least squares support vector machine) algorithm is used to construct a candidate sub-model set having the number of K*R based on these candidate kernel parameters and candidate penalty parameters; third, an SEN(BBSEN-AWF) algorithm based on BB (brand and bound) and AWF (adaptive weighted fusion) is used to select and merge candidate sub-models having same kernel parameter and different penalty parameters so as to obtain a candidate SEN sub-model set having the number K; fourth, subjectingthe candidate SEN sub-model set having the number of K to the BBSEN-AWF algorithm again so as to obtain an SEN-LSSVM DXN (dioxin) soft measurement model.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Incremental timing-driven, physical-synthesis using discrete optimization
ActiveUS7707530B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designData processing systemSelection criterion
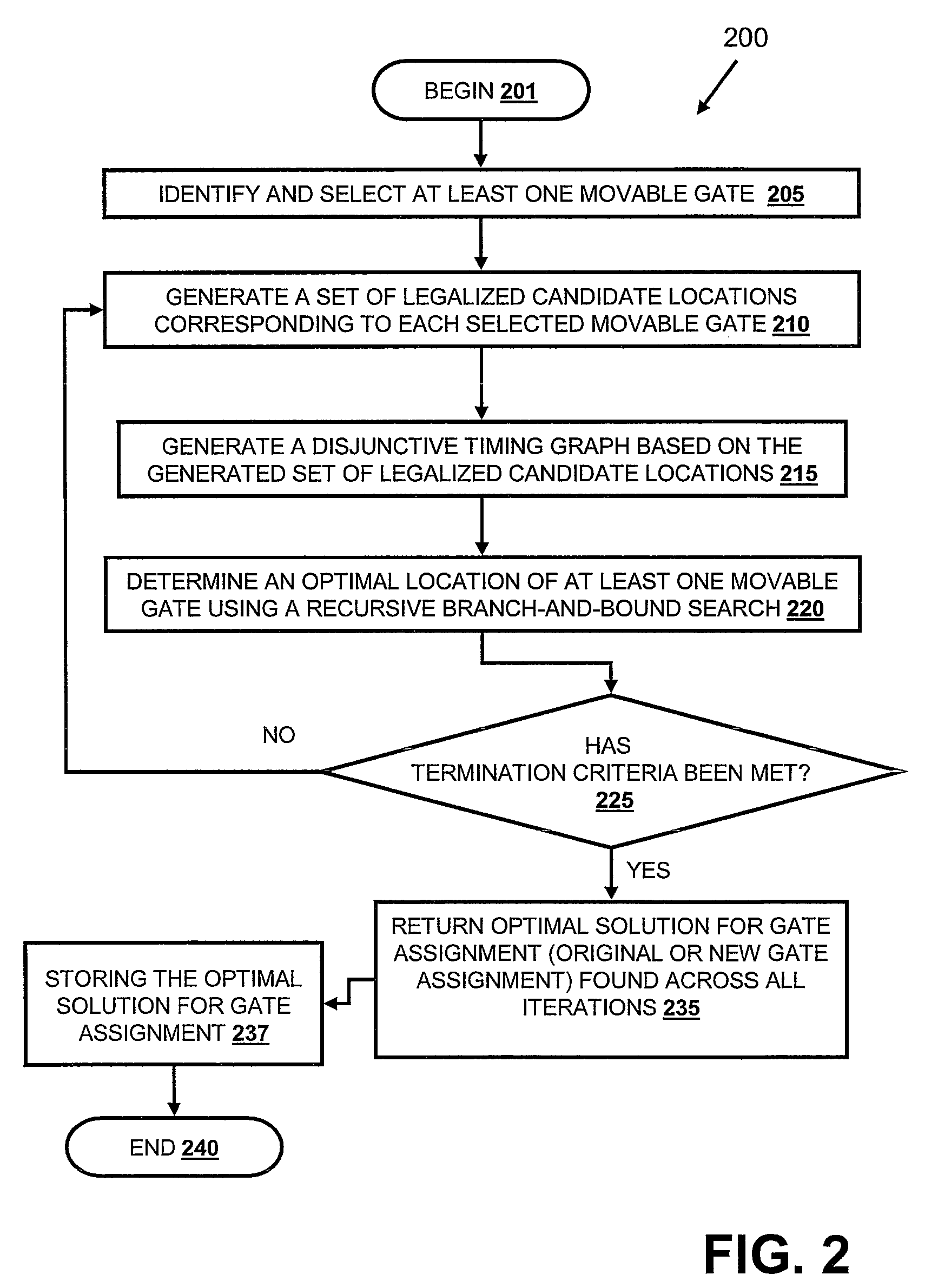
A method, data processing system and computer program product for optimizing the placement of logic gates of a subcircuit in a physical synthesis flow. A Path Smoothing utility identifies one or more movable gates based on at least one selection criteria. A set of legalized candidate locations corresponding to one or more identified movable gates is generated. A disjunctive timing graph based on the generated set of legalized candidate locations is then generated. An optimal location of one or more movable gate(s) is determined using a recursive branch-and-bound search and stored in the computing device.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
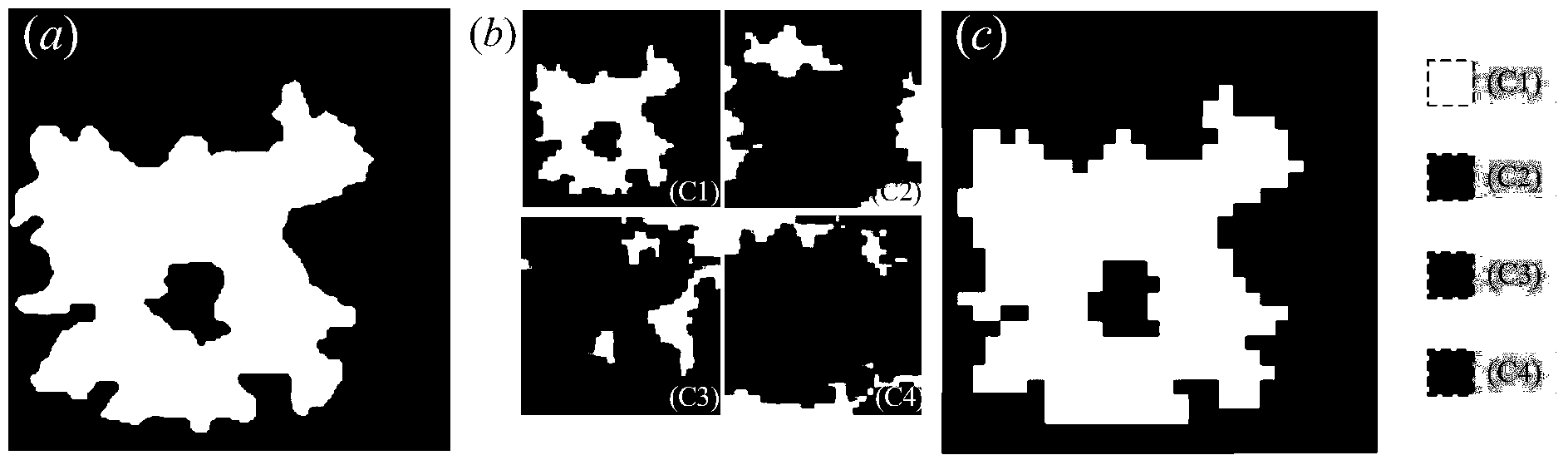
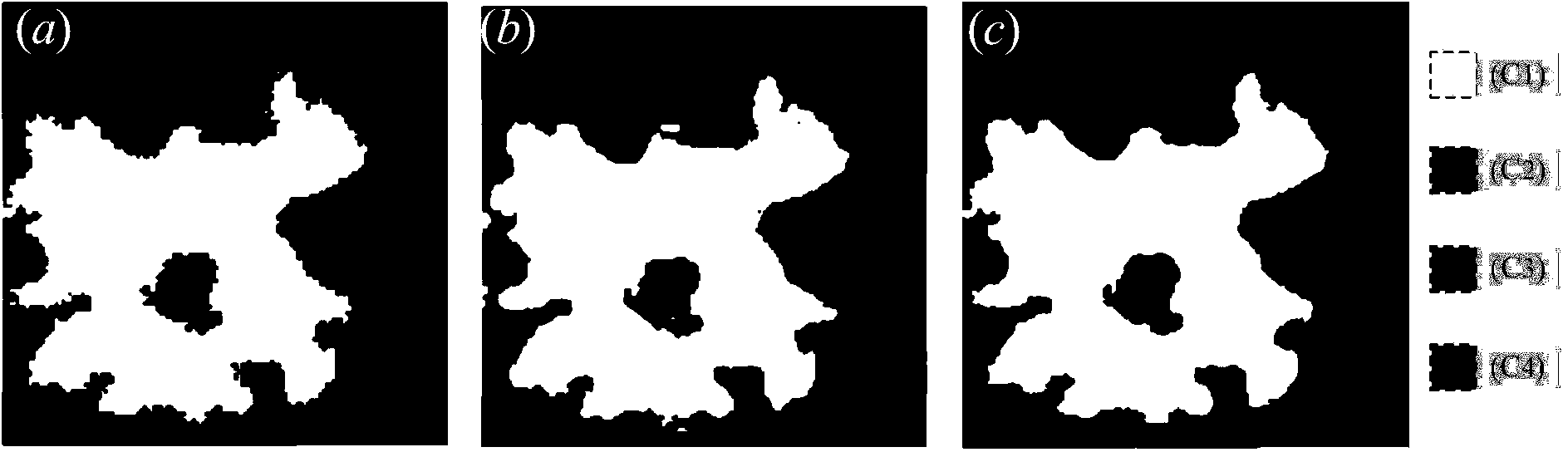
Remote sensing sub-pixel map-making method based on integrated pixel level and sub-pixel level spatial correlation characteristics
InactiveCN104268581AImprove efficiencySimple calculation2D-image generationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSpatial correlation
The invention discloses a remote sensing sub-pixel map-making method based on integrated pixel level and sub-pixel level spatial correlation characteristics. The method includes the steps that firstly, a frequently-used pixel level spatial correlation characteristic description method (a spatial attraction model) is utilized for extracting pixel level spatial correlation characteristics from soft classification information (category proportions) of a neighborhood pixel easily and rapidly without iteration; secondly, a widely-used sub-pixel level spatial correlation characteristic description method (an exponential decay model) is utilized for extracting sub-pixel level spatial correlation characteristics from a sub-pixel map-making iteration result; then, the spatial correlation characteristics of the pixel level and the sub-pixel level are normalized and fused to obtain the integrated spatial correlation characteristic value used for determining the sub-pixel categorical attribute; finally, the optimal spatial layout of the sub-pixel with the largest sum of all the category spatial correlation characteristic values in mixed pixels is obtained according to the integrated spatial correlation characteristic value through a classical binary branching-bounding integer programming algorithm. The remote sensing sub-pixel map-making method is high in calculation speed and simulation precision.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
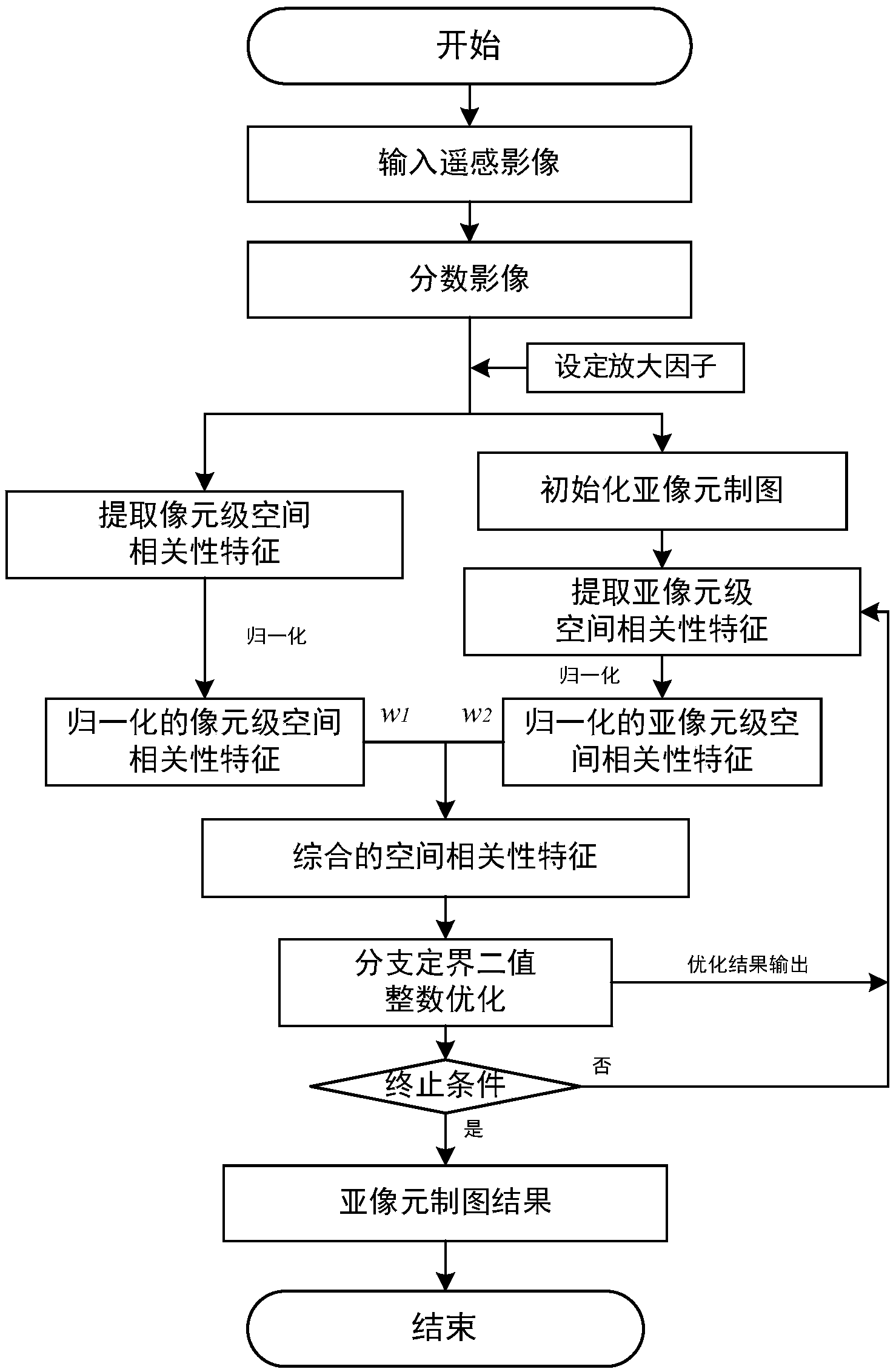
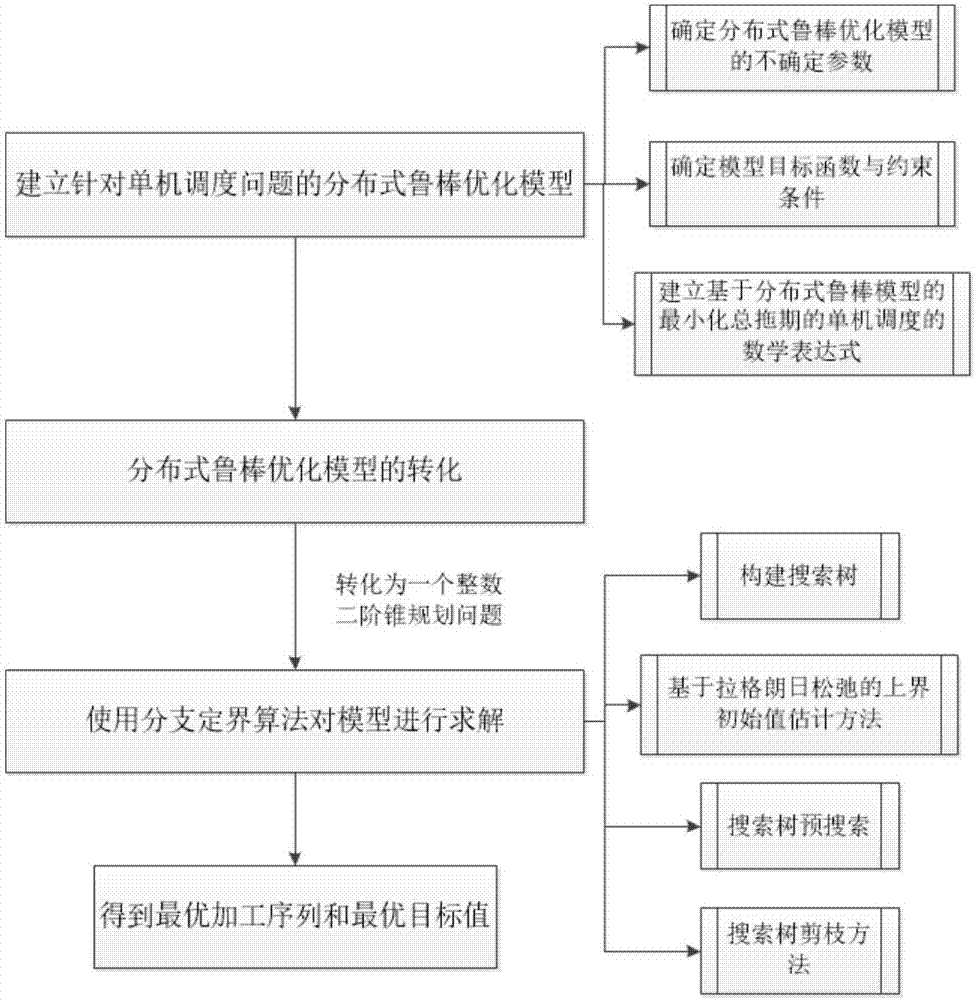
Single-machine minimized total tardiness scheduling method based on distributed robust model
ActiveCN107544251AReduce conservatismEffectiveAdaptive controlSingle-machine schedulingBranch and bound
The invention provides a single-machine minimized total tardiness scheduling method based on a distributed robust model and belongs to the technical field of production scheduling and internal and external production resource optimization. The method comprises the steps that a distributed robust optimization model for solving the single-machine scheduling problem is established firstly to obtain atarget function expression of the model; then, the distributed robust optimization model is converted into an integer second-order cone programming model; the converted model is solved, arrangement combinations of all workpiece machining sequences are expressed in a search tree in an enumeration way, the search tree is pruned through a branch-and-bound algorithm, and finally an optimal single-machine scheduling scheme of the minimized total tardiness is obtained. The method gives consideration to uncertain factors of a production environment, so that the model is a determined single-machine model more conforming to the actual production situation compared with an assumed production environment, and the obtained scheduling scheme can be better applied to actual production.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
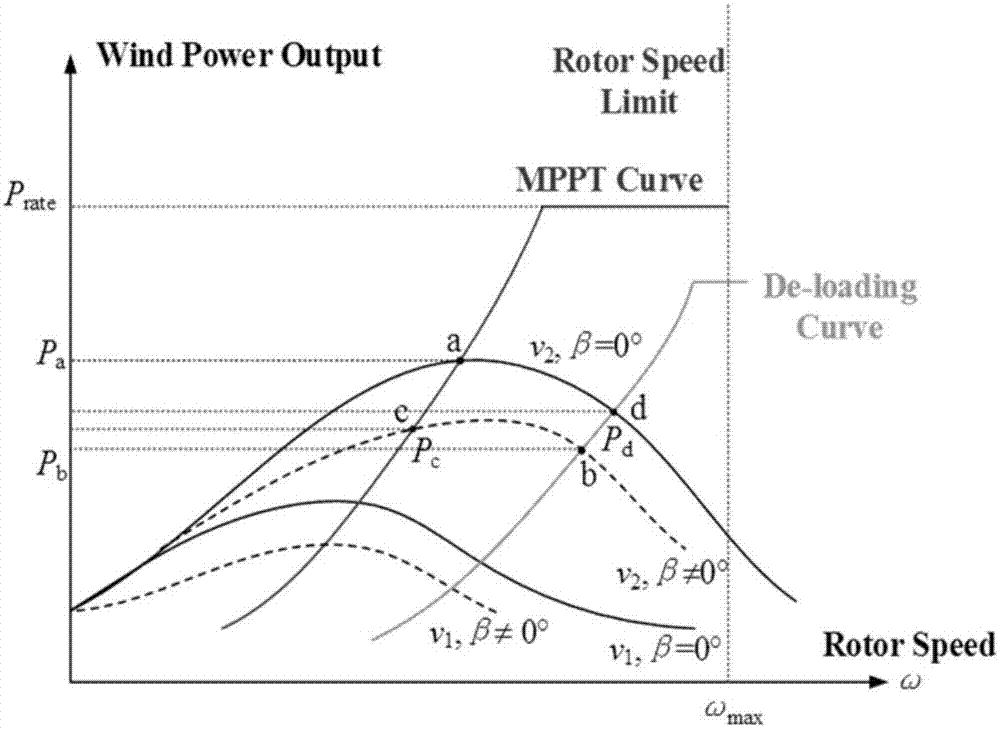
Wind power load reduction considering power system robust reserve optimization method
InactiveCN108011394ARelieve pressureSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectric power systemEngineering
The invention discloses a wind power load reduction considering power system robust reserve optimization method. The method comprises the steps of firstly quantitatively measuring the reserve capacityof each wind power farm by using a load reduction ratio; further building a wind power load reduction considering system robust reserve scheduling optimization model; then obtaining a relaxed robustoptimization model by using a linear relaxation technology; then converting the linear robust optimization model into an equivalent deterministic linear programming model by using a duality principle;and finally solving the wind power load reduction considering system robust reserve scheduling optimization problem by using a space branch-and-bound solving model. The uncertainty of wind power output is processed by using distribution information independent robust optimization by combining active control assistant frequency modulation services of the wind power farms in allusion to a reserve problem brought about by operations of a large-scale wind power access system. Compared with the traditional system reserve scheduling method, the method disclosed by the invention can adjust the robustness and economy of a reserve scheme. In addition, compared with an MPPT mode, the wind power load reduction considering control can reduce the pressure of the traditional reserve.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
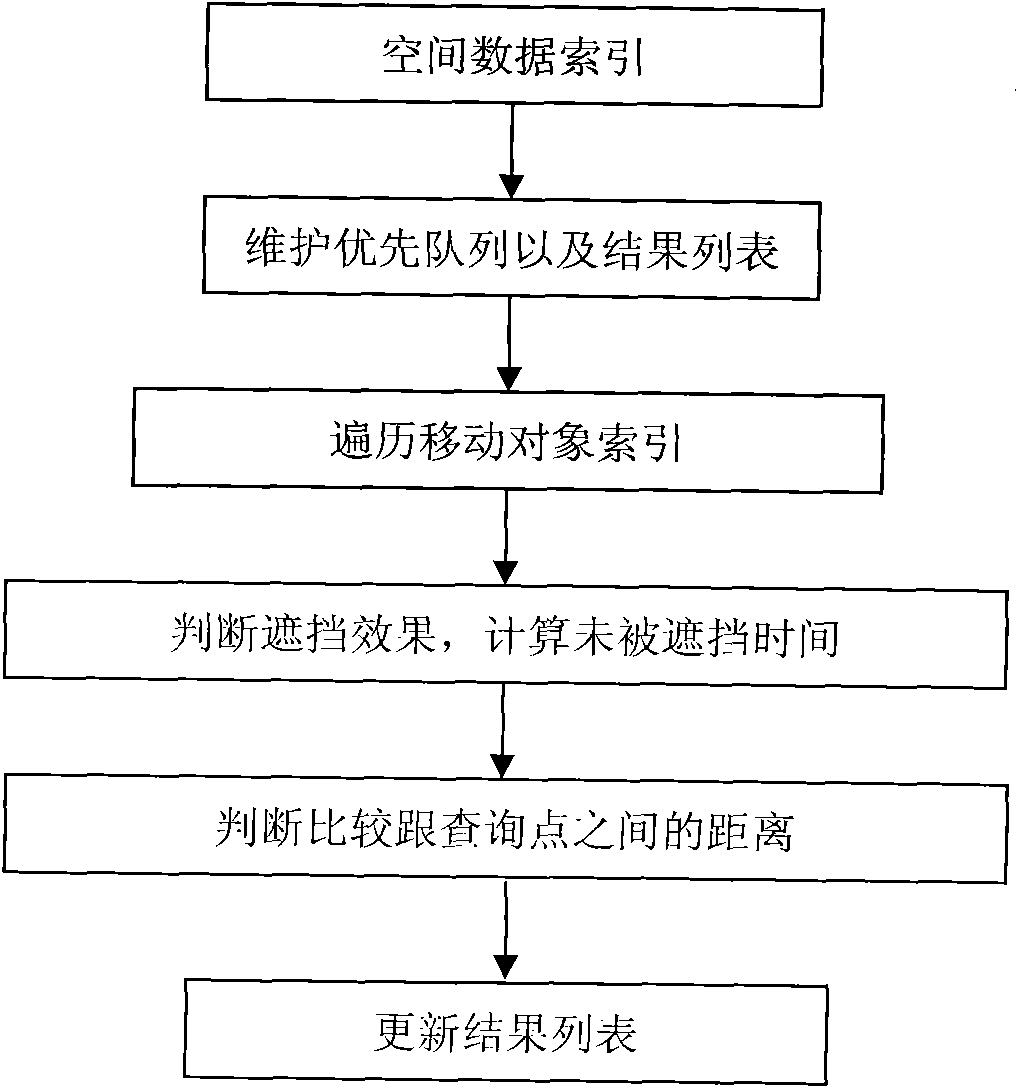
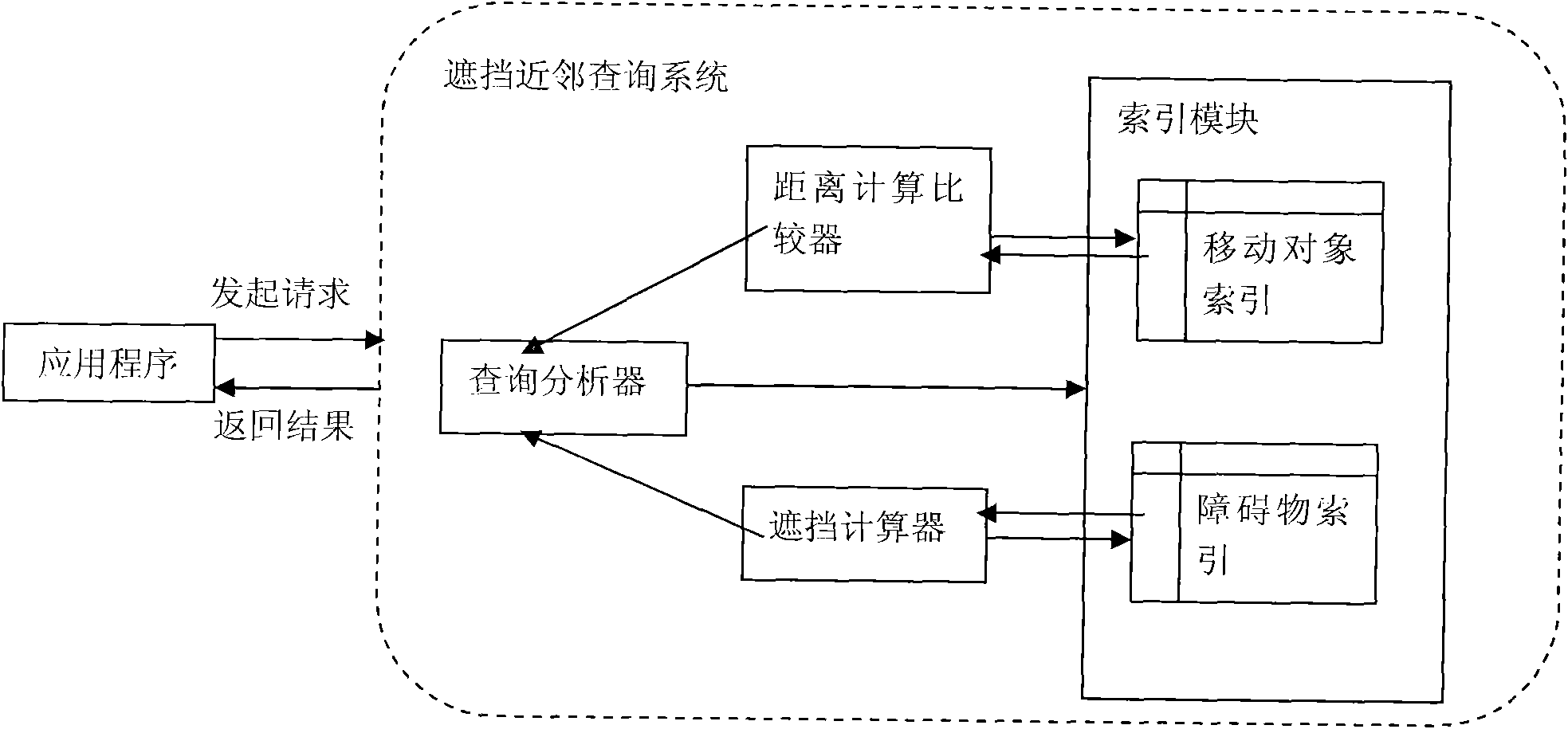
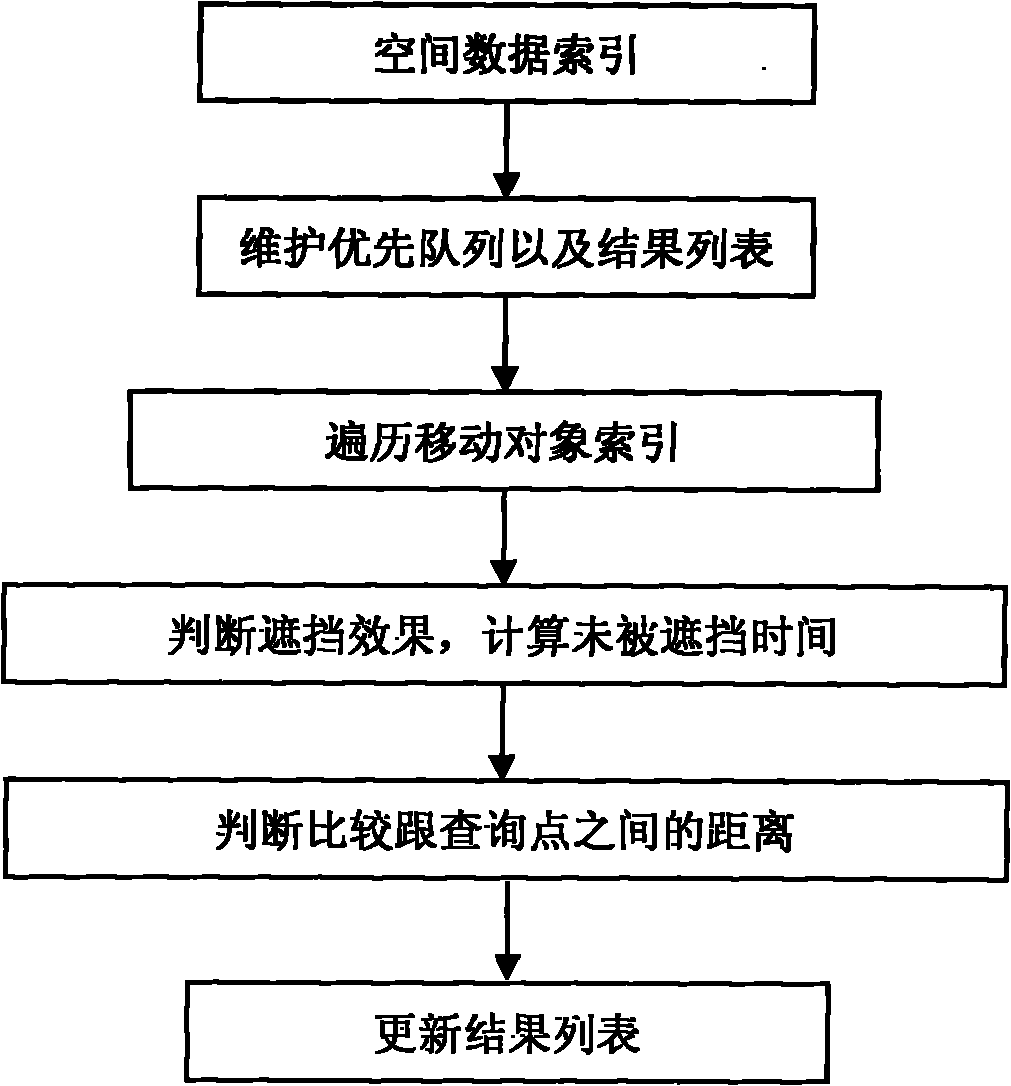
Method for inquiring visible neighbours of moving objects in environment with barriers
The invention discloses a method for inquiring visible neighbours of moving objects in the environment with barriers. The neighbour inquiry technology of the moving objects in a spatial database is utilized and the existing branch and bound algorithm is utilized to inquire the neighbours which are not blocked in the environment with barriers. In the spatial data, R-tree index is utilized for the barriers, TPR-tree index is utilized for the moving objects, the branch and bound algorithm is utilized to traverse the indexes, and meanwhile inquiry is realized by combining calculation of the blocking time of the moving objects. The method has the following beneficial effects: utilizing the existing indexing technology and the moving object neighbour inquiry technology in the spatial database and researches and achievements in the environment with barriers, providing the method of inquiring the moving objects which are not blocked in certain period in the environment with barriers, ensuring that the users can select the optimum inquiry time interval according to the application requirements and providing best performances.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method for scheduling elevator cars using branch-and-bound
A method schedules cars of an elevator system. Each possible assignment of a set of hall calls to a set of cars is represented by a solution vector maintained as a node in a search tree. Each solution vector is evaluated using an ESA-DP process according to an immediate policy to determine initially a best solution. A branch-and-bound process is applied to each solution vector using the initial best solution and the search tree to determine a globally optimal solution for scheduling the cars according to a reassignment policy.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
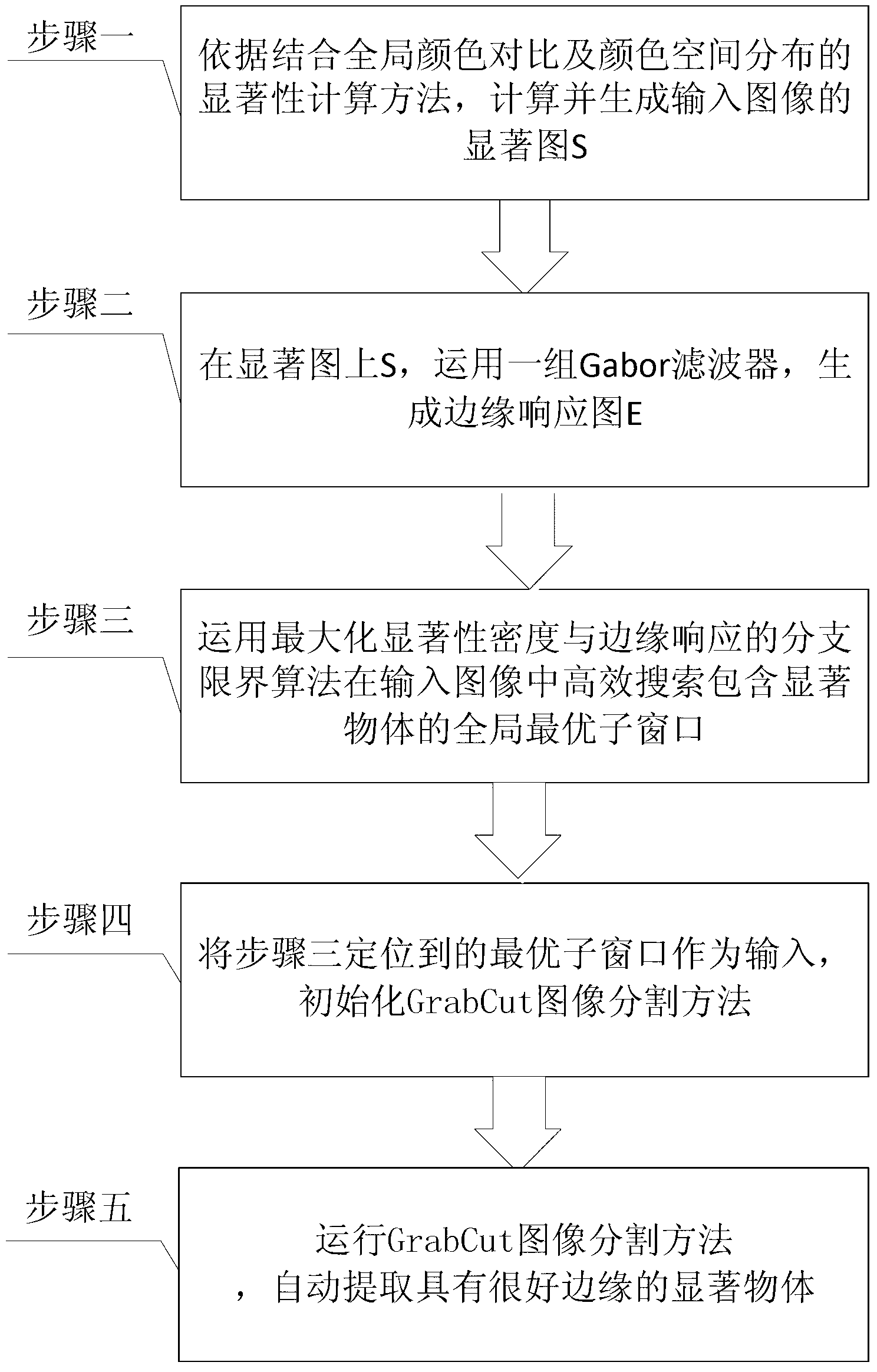
Automatic detection method of salient object based on salience density and edge response
ActiveCN103198489AImplement automatic detectionImprove accuracyImage analysisImaging processingSalient objects
The invention provides an automatic detection method of a salient object based on salience density and edge response, and relates to a method for automatically detecting the salient object, solving the problems of the convectional salient object detection method that only one attribute that is the salience is utilized, but the edge attribute of the salient object is not taken into account, therefore, the detection accuracy of the salient object is relatively low. The automatic detection method of the salient object based on the salience density and the edge response comprises the following steps of: calculating and generating a salient map S of an input map according to the regional salience calculation method in combination of the global color comparison and the color space distribution; generating an edge response map E on the salient map S by utilizing a group of Gabor filters; efficiently searching a global optimal sub-window containing the salient object in the input map by utilizing the maximized branch-and-bound algorithm of the salience density and the edge response; adopting the obtained optimal sub-window as the input; initializing the GrabCut graphic cutting method; carrying out the GrabCut graphic cutting method; and automatically extracting the salient object with a good edge. The automatic detection method is applicable to the image processing field.
Owner:中数(深圳)时代科技有限公司
Method for Optimizing Power Flows in Electric Power Networks
Power flow in an electric power network is optimized during multiple time periods of operation of the electric power network by solving an optimization problem represented by an objective function by first initializing variables and constraints of a branch and bound (BB) tree, wherein nodes in the BB tree represent feasible regions of the optimization problem. Upper and lower bounds on the objective function are solved using the BB tree. A lowest upper bound and a lowest upper bound are updated. If difference between the lowest lower bound and the lowest upper bound is less than a threshold, the power flow is outputted based on the lowest lower bound and the lowest upper bound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for scheduling multiple types of tasks in spatial crowdsourcing
ActiveCN107317872AExact Execution Path SolutionImprove operational efficiencyResourcesTransmissionTask completionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for scheduling multiple types of tasks in spatial crowdsourcing. For a task allocated to each worker, a task execution path is planned, a scheduling algorithm based on branch-and-bound idea is adopted in combination with expertise matching scores of the multiple types of tasks, but when the task scale is large, the operation speed of the scheduling algorithm is low, two similar scheduling algorithms, that is, a most promising branch heuristic algorithm and a search heuristic algorithm based on width k, can be adopted, and the k value is adjusted to obtain the balance of the operation speed and the accuracy. By adoption of the method, the quality and the quantity of the accomplished tasks can be improved, and the operation speed and the accuracy are good.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
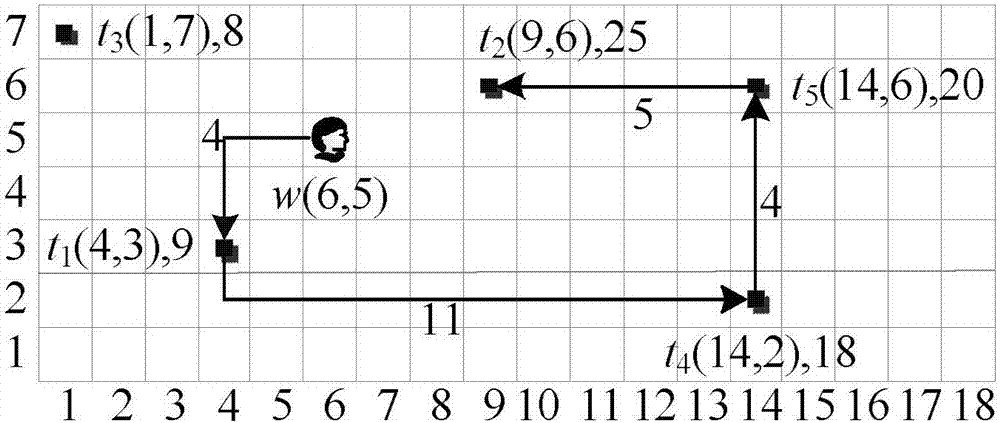
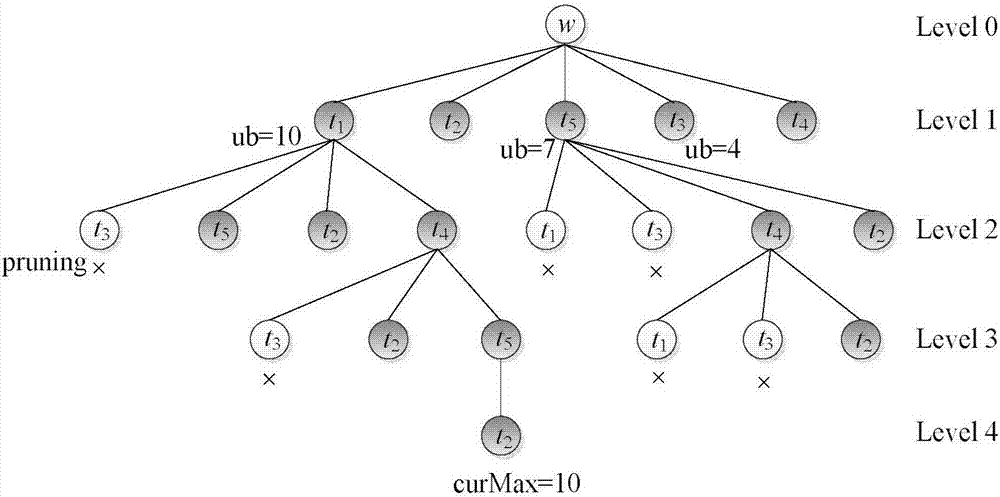
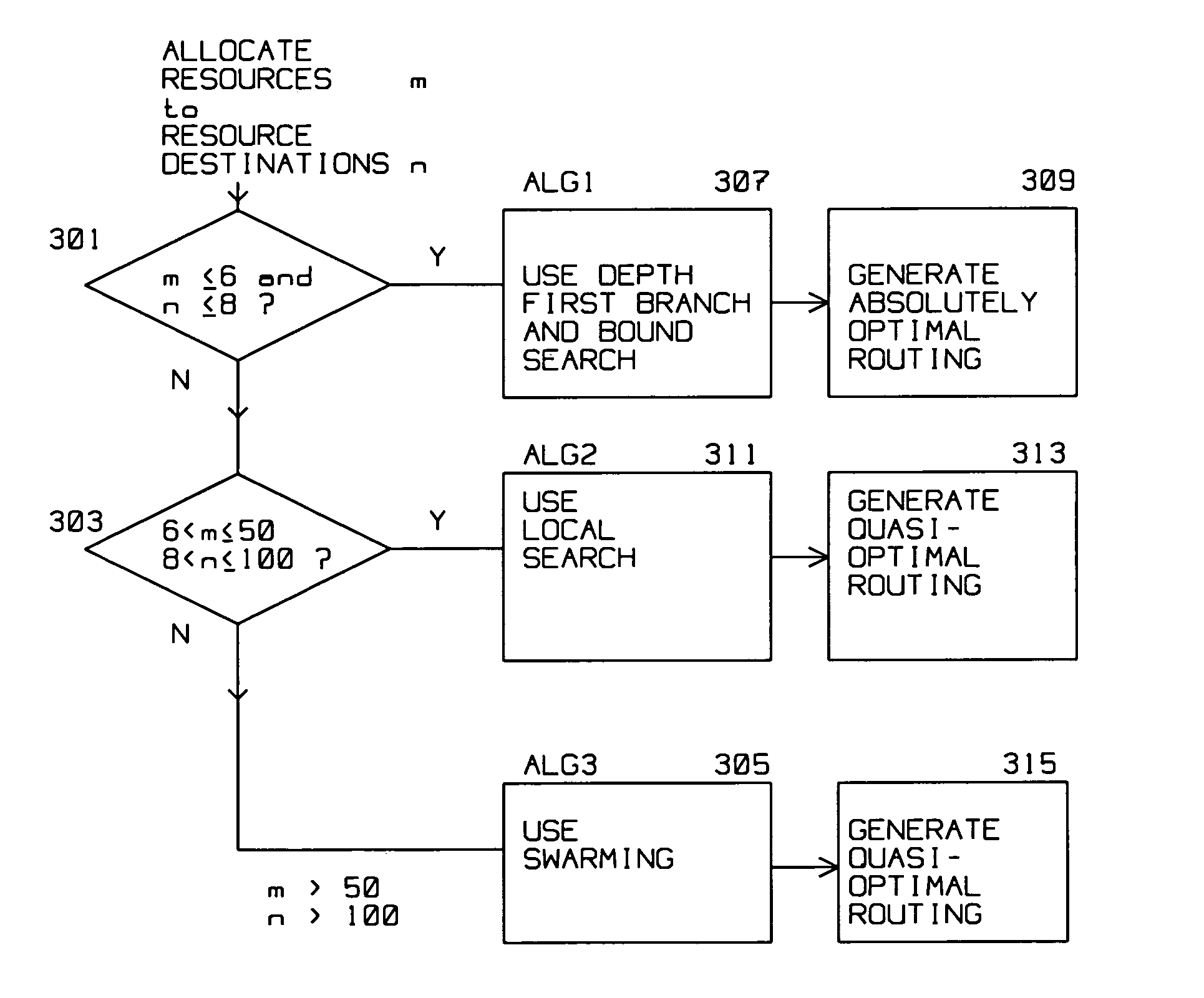
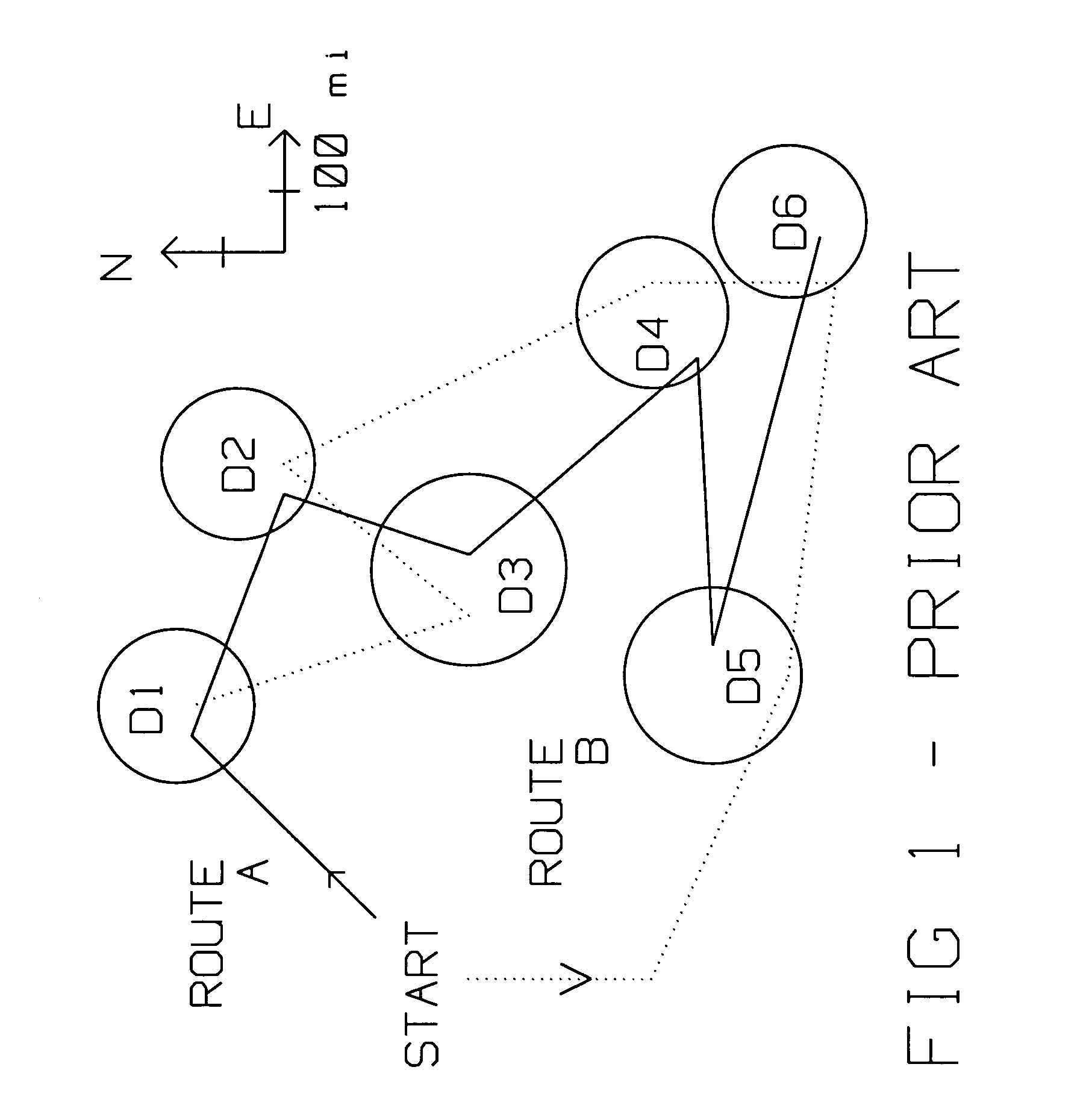
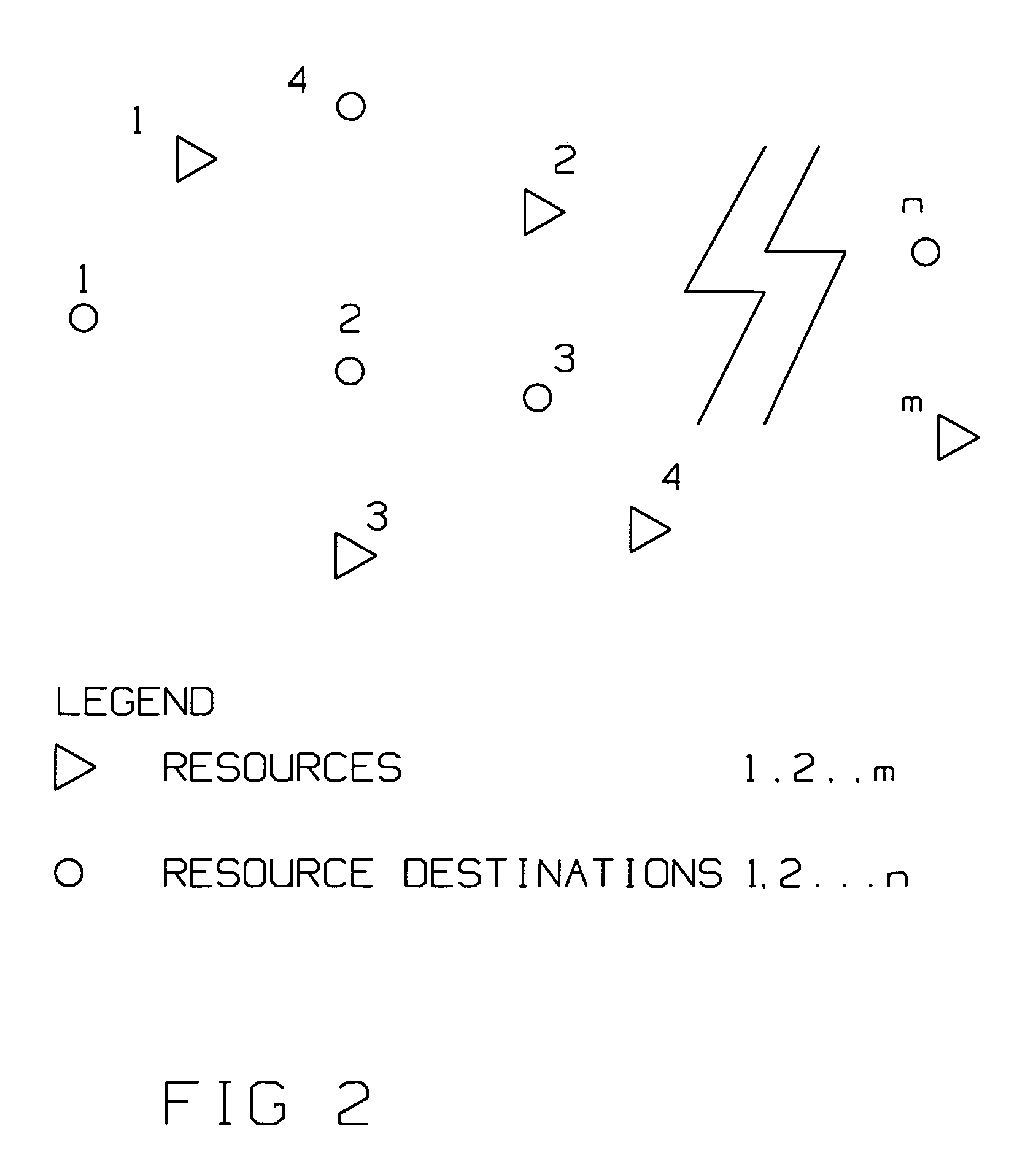
Method for realtime scaling of the vehicle routing problem
ActiveUS7756631B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlBranch and boundOptimal route
An absolutely optimal routing or a quasi-optimal routing is computed for a first plurality of resources m to be routed to a second plurality of resource destinations n, depending on a count of m and n. Three different algorithms are used. For the case where the count is m≦̸6 and n≦̸8, a first algorithm is used to arrive at an absolutely optimal routing. An example of the first algorithm is Depth First Branch and Bound Search. For a second count, where the value of the count is more numerous than the first count, m is greater than six, but equal to, or less than or equal to fifty, 6<m≦̸50, and n is greater than 8, but less than or equal to one hundred, 8<n≦̸100, a second algorithm, is used to compute a quasi-optimal routing. An example of this second algorithm is Local Search. For a third count, where the count exceeds those above, a third algorithm is used for computing a quasi-optimal routing. Typically this third algorithm applies where m>50, and n>100. An example of this third algorithm is Swarming.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
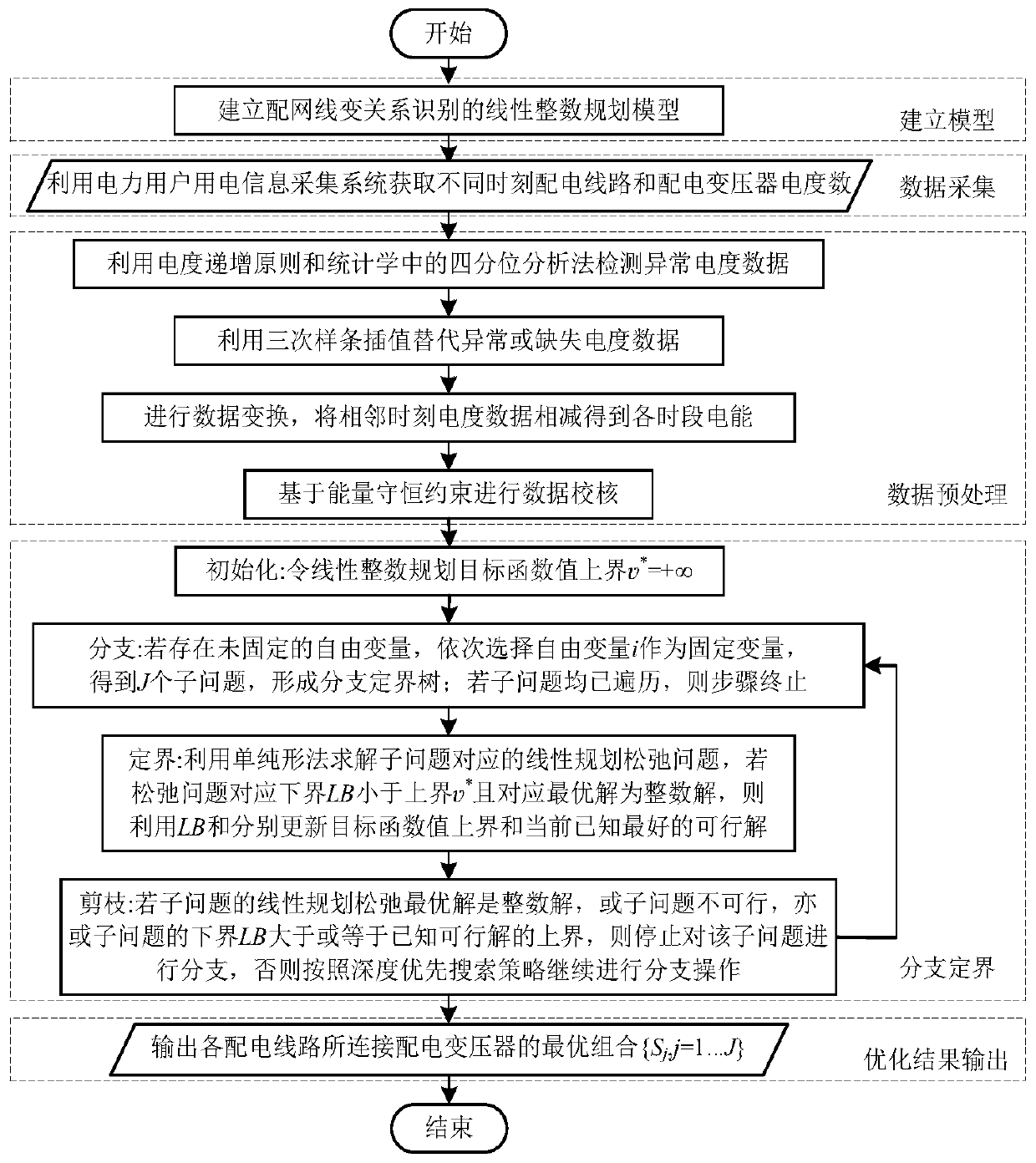
Distribution network cable variable relationship identification method based on linear integer programming
ActiveCN110555556AImprove management levelAchieving identifiabilityForecastingSystems intergating technologiesBranch and boundElectric power
The invention discloses a distribution network cable variable relationship identification method based on linear integer programming, which relates to the technical field of electric power, and comprises the steps of establishing a linear integer programming model based on energy conservation constraints and topological constraints of an electric power distribution network, and setting an objective function of the model as the sum of line loss rates of all distribution lines in the distribution network; acquiring electric degree data of a distribution line and a distribution transformer in each time period in the power distribution network; carrying out abnormal value detection, abnormal value and missing value processing, data conversion and data check preprocessing on the electrical degree data of the distribution line and the distribution transformer to obtain input data of the model; optimizing and solving the linear integer programming model by adopting a branch and bound algorithm based on the input data; and based on the optimal solution of the model, outputting an optimal combination of the variable relationship of the distribution network cable. According to the invention,the high-quality distribution network line transformation relationship can be rapidly obtained, the line loss rate is effectively reduced, and the power grid operation management level is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER +1
Method for making optimal task unloading decision in large-scale cloud and mist computing environment
PendingCN110058934AFast solutionFlexible tuningProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationTime delaysDecision taking
The invention aims to provide a method for obtaining an optimal task unloading decision in a cloud and mist computing environment. Meanwhile, the time delay and the energy consumption are considered,so that the system overhead is reduced to the minimum. The method for obtaining an optimal task unloading decision in a cloud and mist computing environment mainly comprises the following three steps:A, performing mathematical modeling on a system; b, mixing a problem formalized text with an integer programming problem; C, using a branch and bound algorithm for solving. According to the method, the scene that the cloud node and the mist node exist at the same time is considered, the scene that unloading decisions need to be made for multiple tasks is solved, energy consumption and time delayare comprehensively considered, and therefore expenditure of the mobile terminal is reduced to the minimum.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com