Method and computer system for quantum chemical modelling of molecules under non-equilibrium conditions
A technology for calculating values and models, applied in computer-aided design, calculation, design optimization/simulation, etc., capable of solving a large number of calculation problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
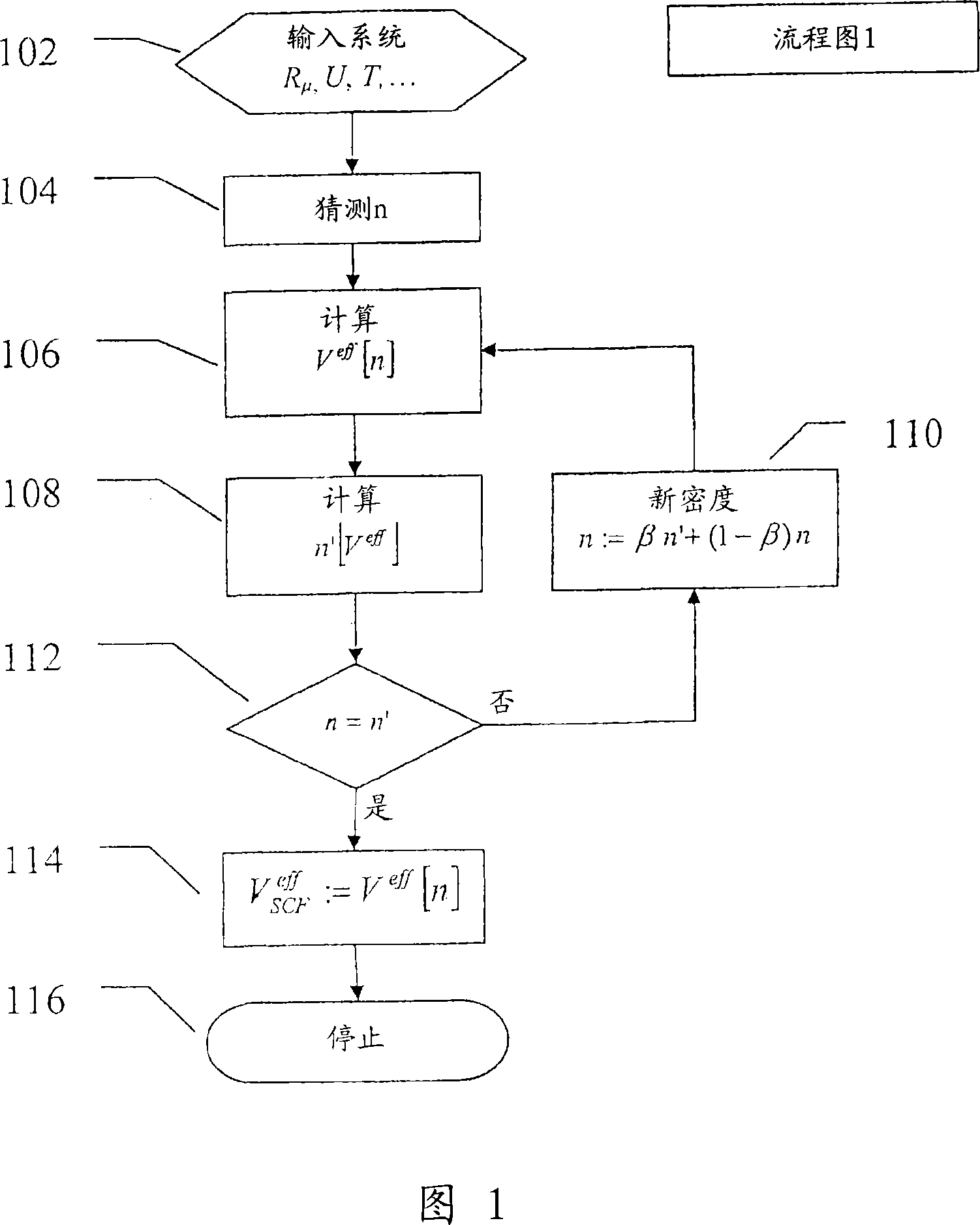
[0128] background theory
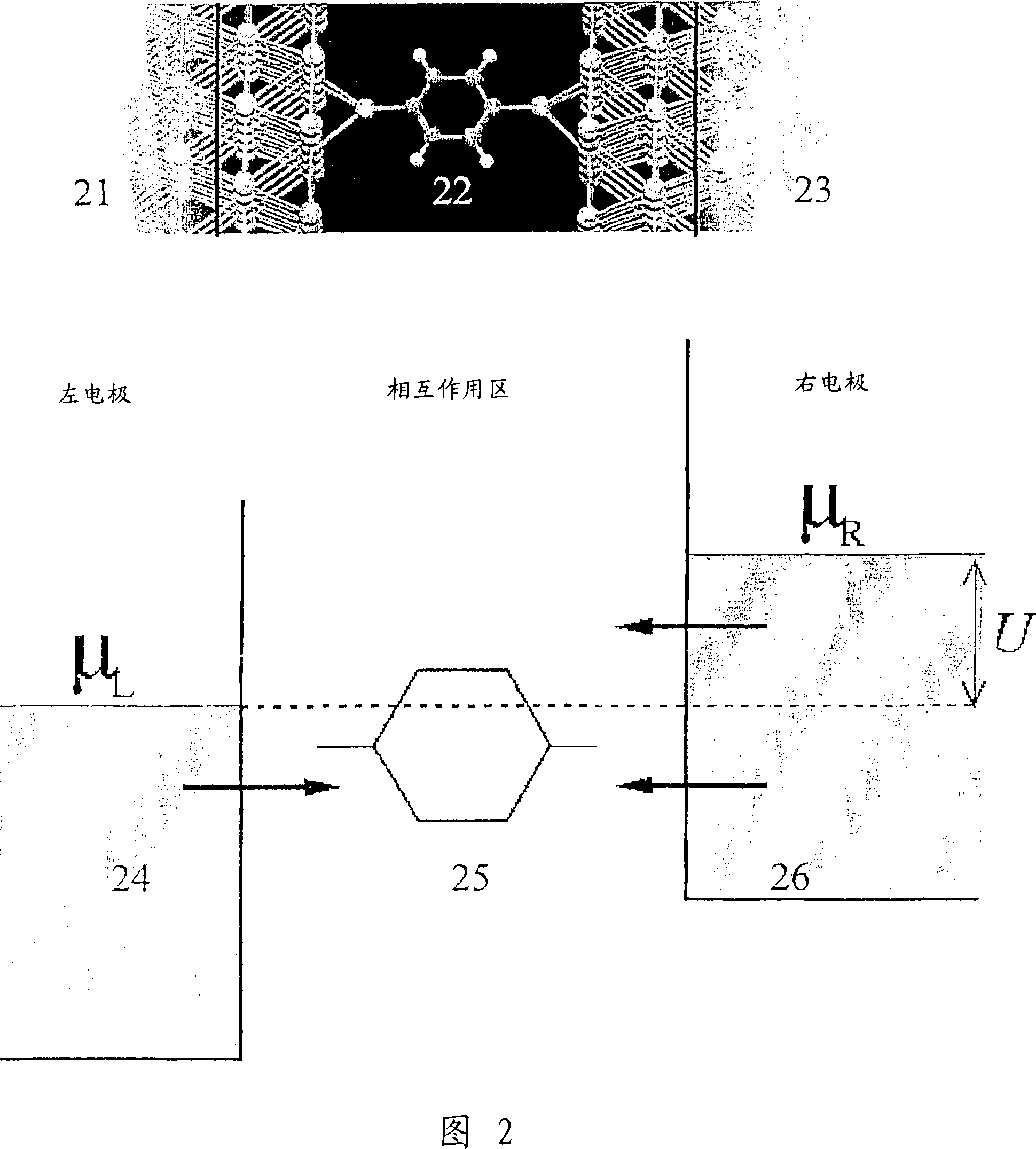
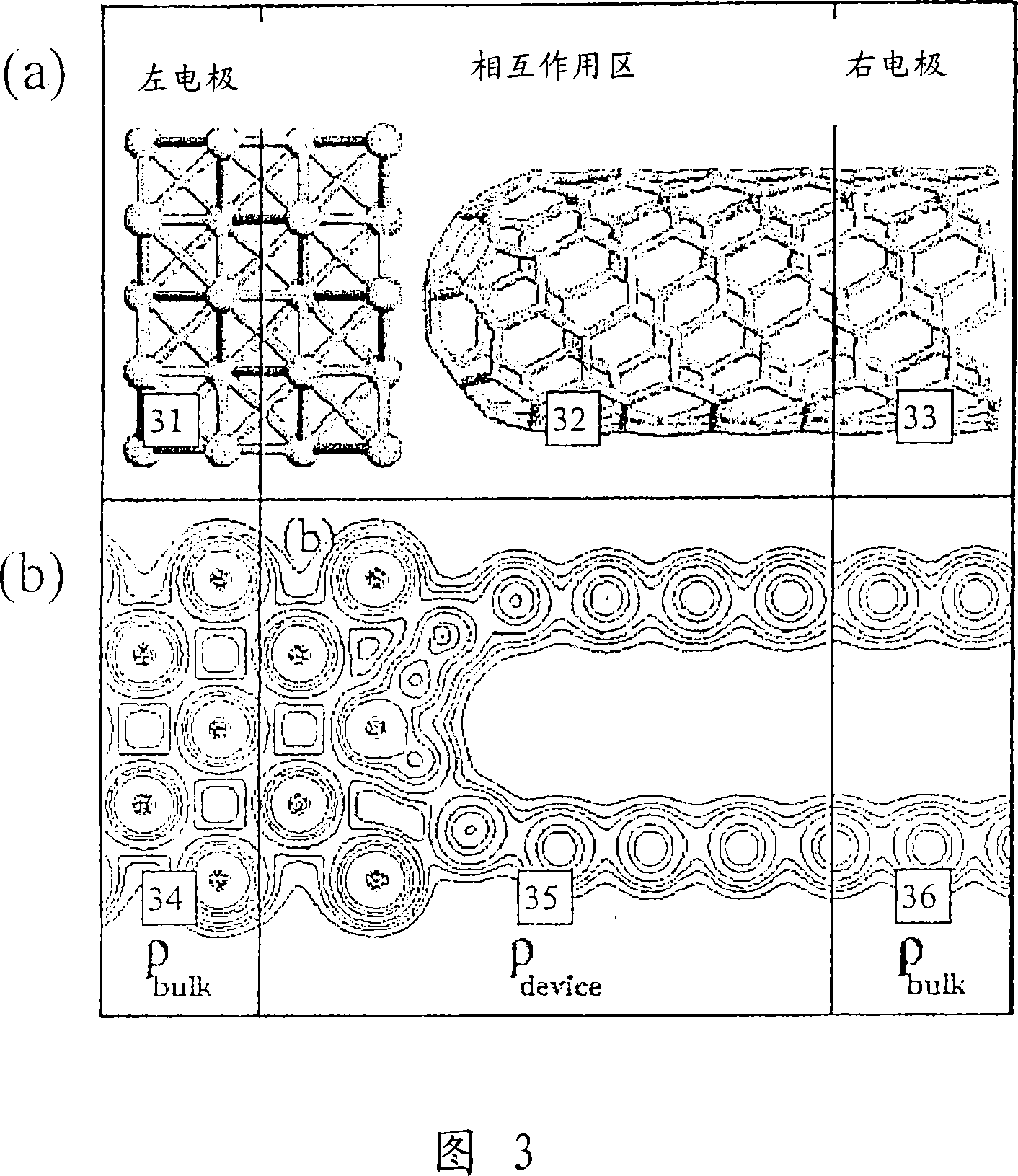
[0129] The purpose of atomic-level simulations is to calculate the properties of molecules and materials from the description of the individual atoms in the system. Atoms consist of an ion core of charge Z and an equal number of electrons that cancel this charge. we will and Z μ for the position and charge of the ions, where μ = 1, . . . , N labels the ions, and N is the number of ions. The position of the electron is given by i=1,...,n is given, n being the number of electrons.
[0130] In general, it is a good approximation to treat ions as classical particles. potential energy of ions The energy E of the electronic system depends on the following equation 0 :
[0131] V = ( R → 1 , . . . , R → ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com