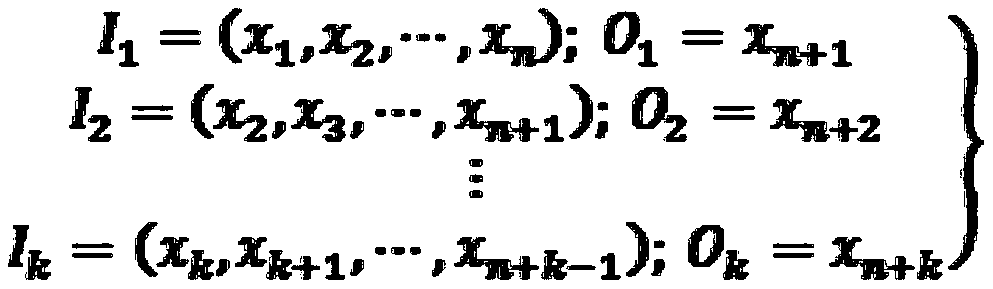Patents
Literature
184 results about "Predictive capability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
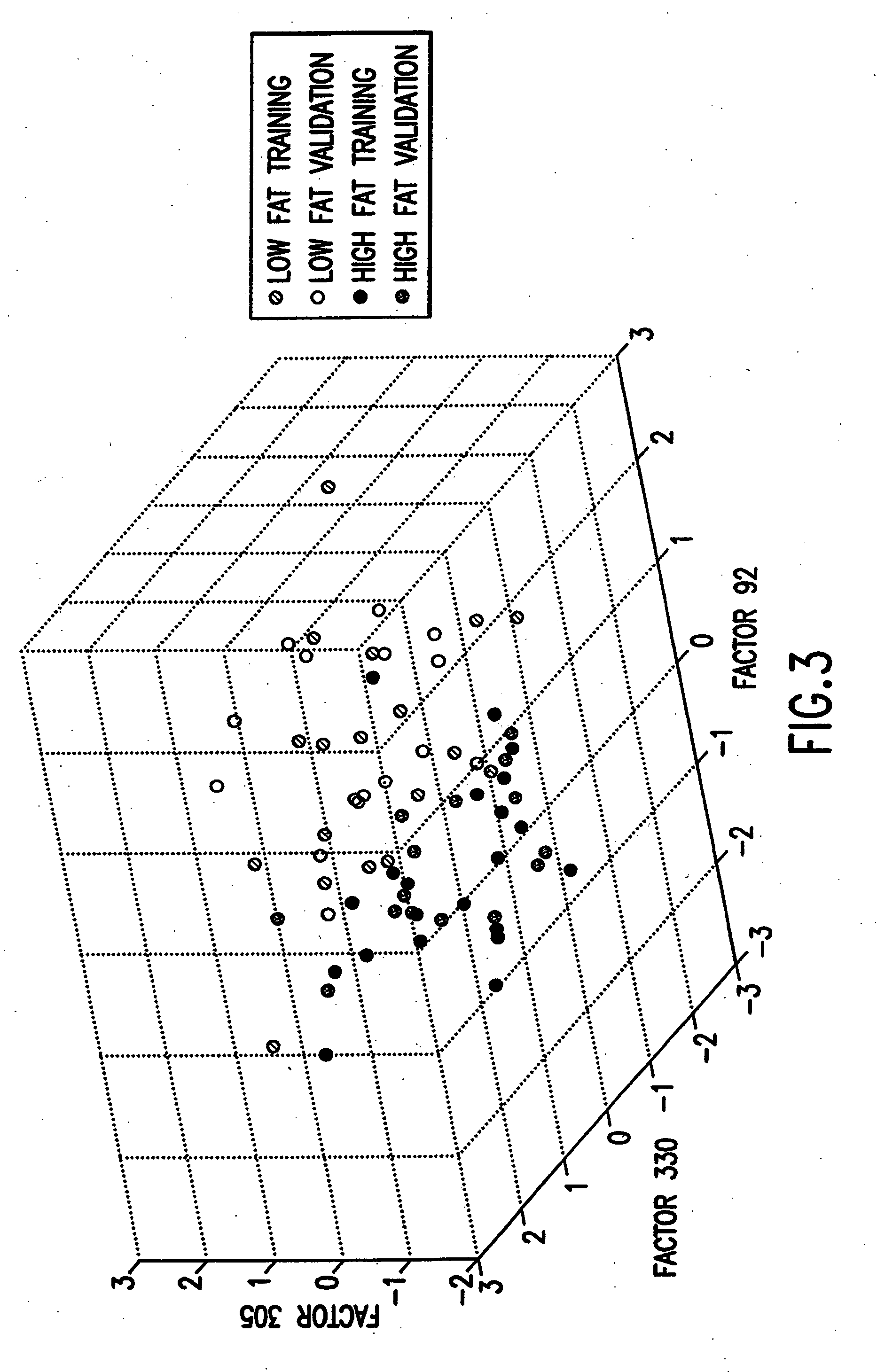
The ability of a system to predict certain ocean phenomena is the predictive capability of the system for those phenomena. It considers all sources and reductions of errors (initial and boundary conditions, model, data, etc.) and their evolution.
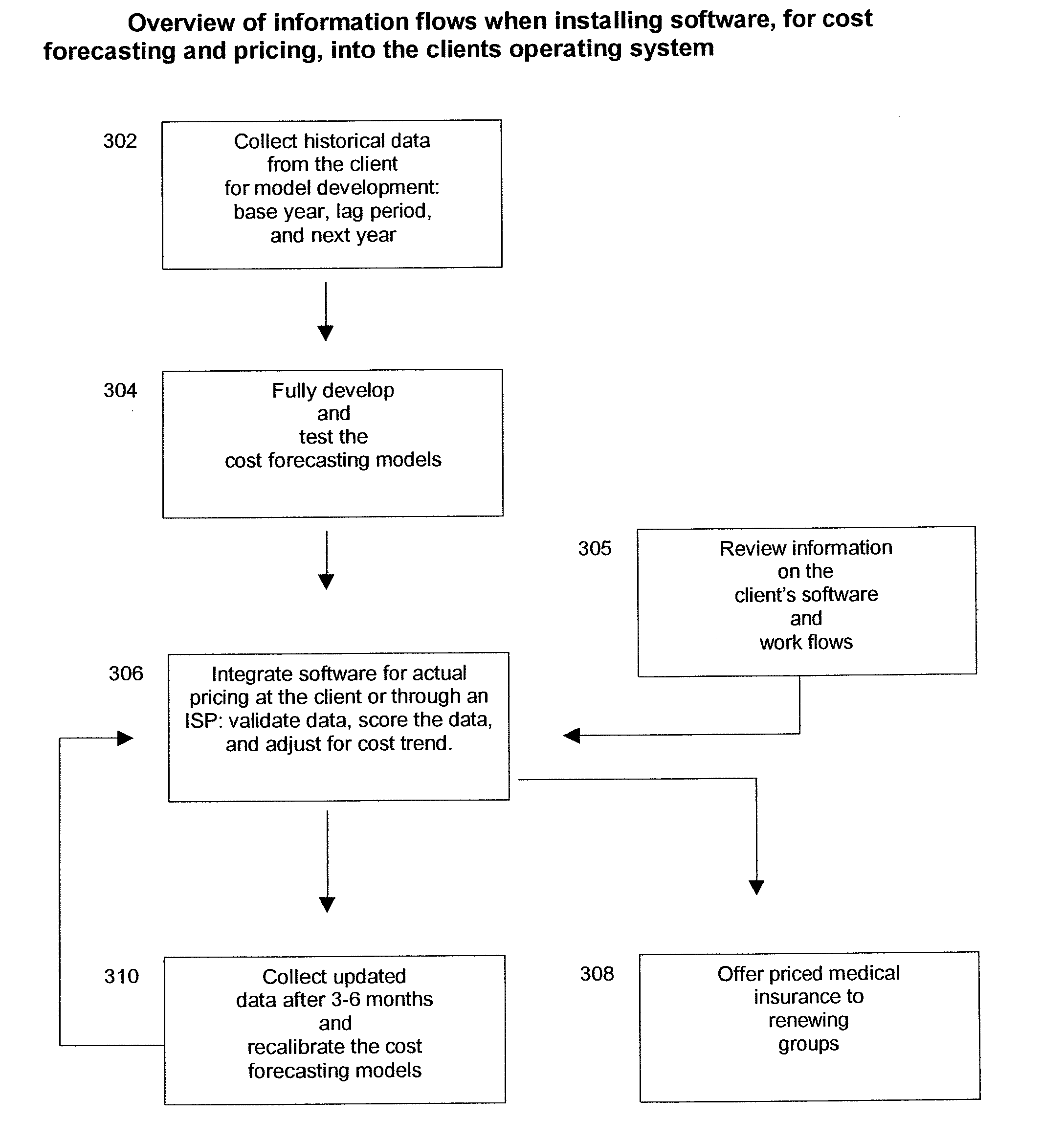
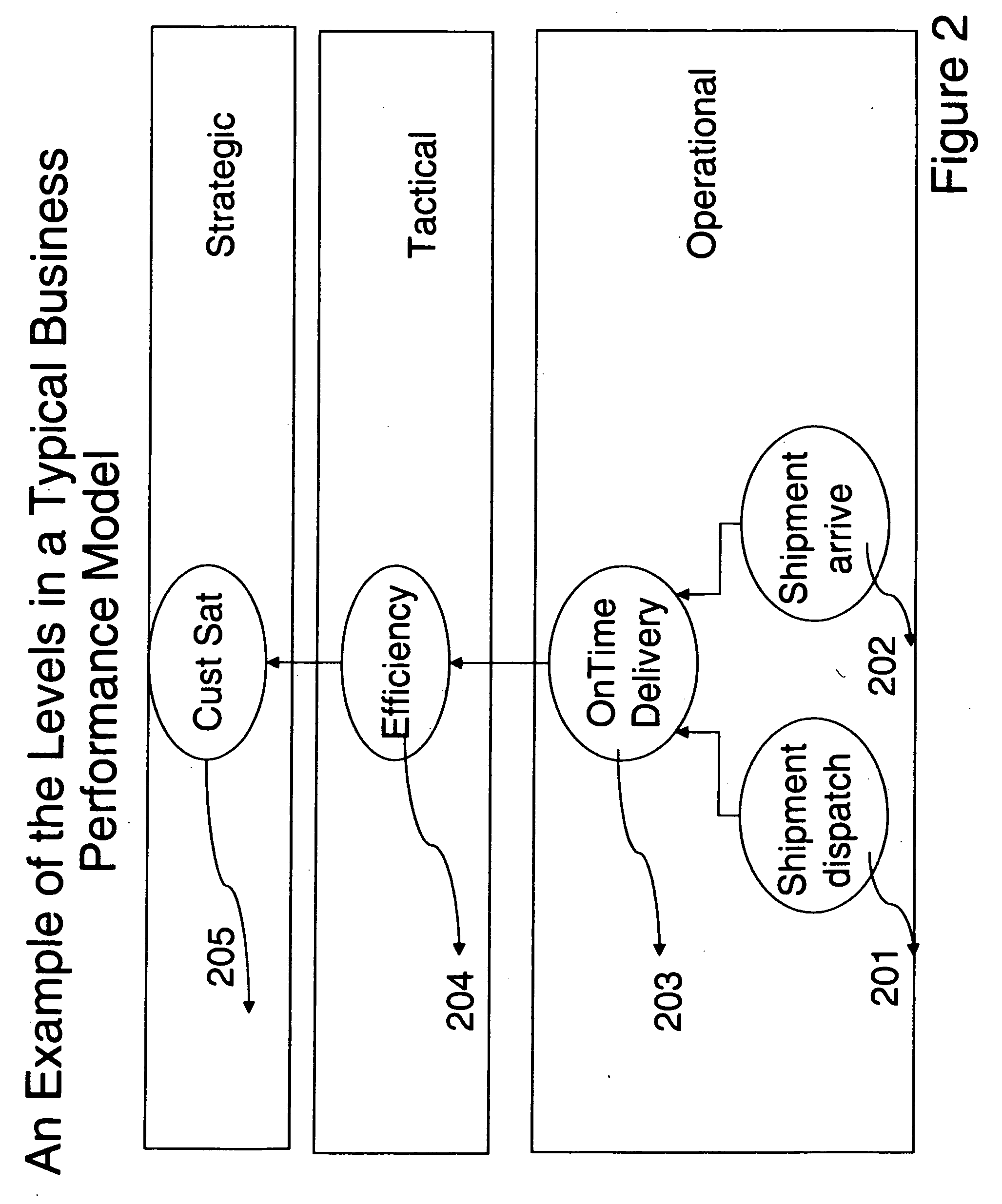
Supply Chain Performance Management Tool Having Predictive Capabilities
A method for providing a supply chain management tool may include generating a representation of a supply chain of an organization where the representation is generated responsive to identification of supply chain entities and corresponding flows therebetween. The flows may include transactional layer activities at a stock keeping unit level. The method may further include referencing the representation to determine historical data indicative of supply chain performance, and utilizing processing circuitry to employ the historical data to generate at least one prediction regarding future operating performance of the supply chain.
Owner:COMPETITIVE INSIGHTS
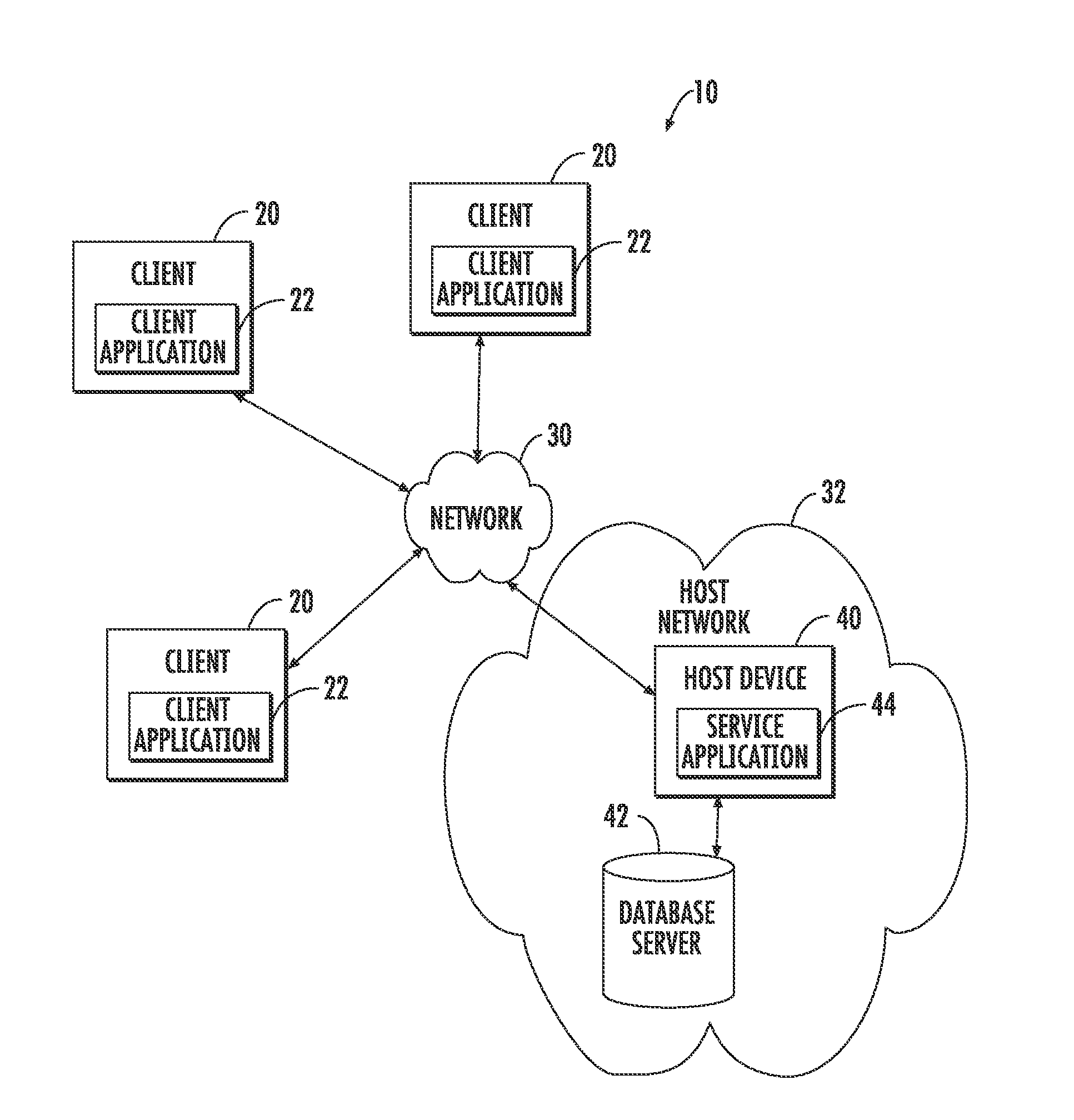
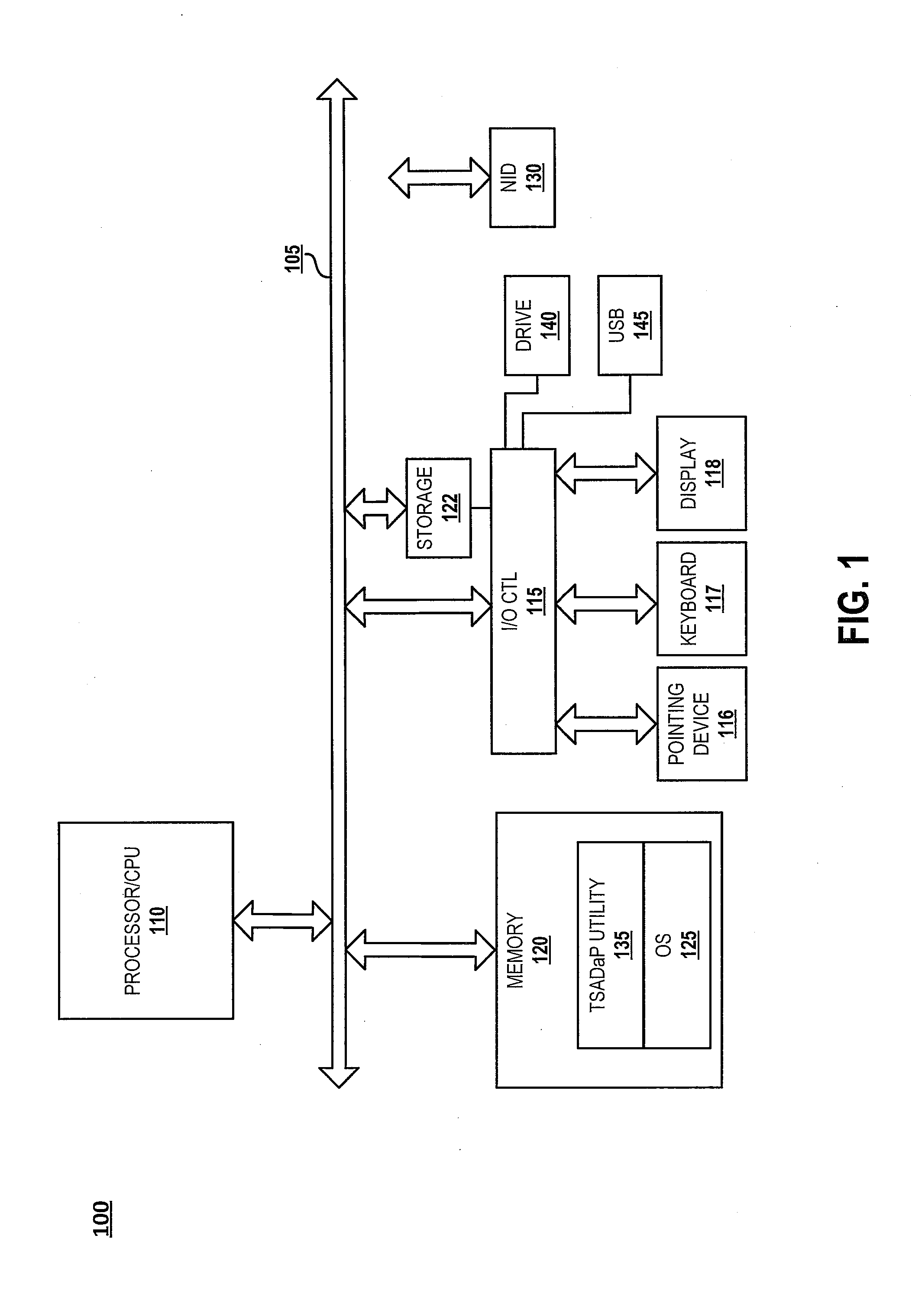
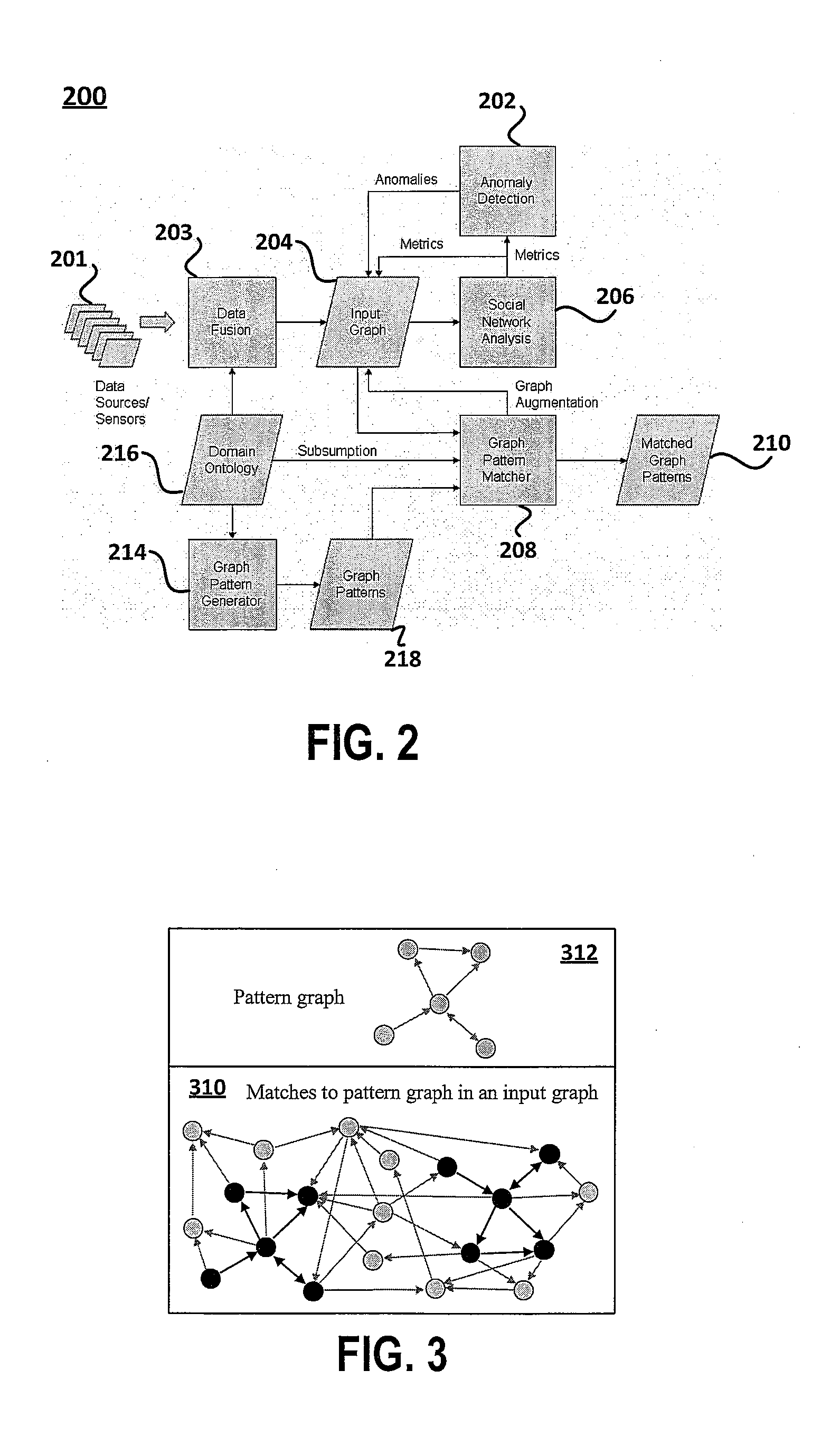
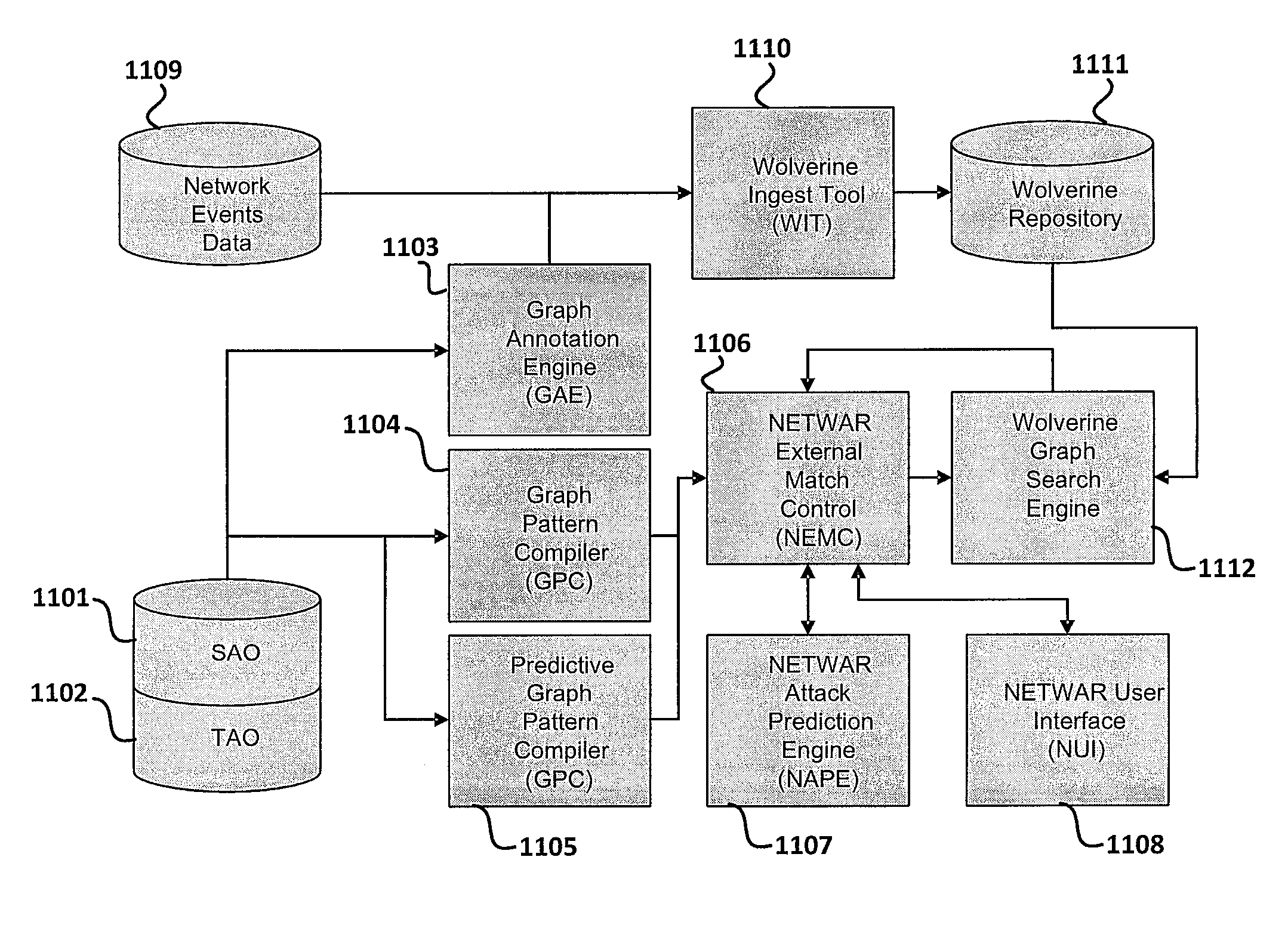
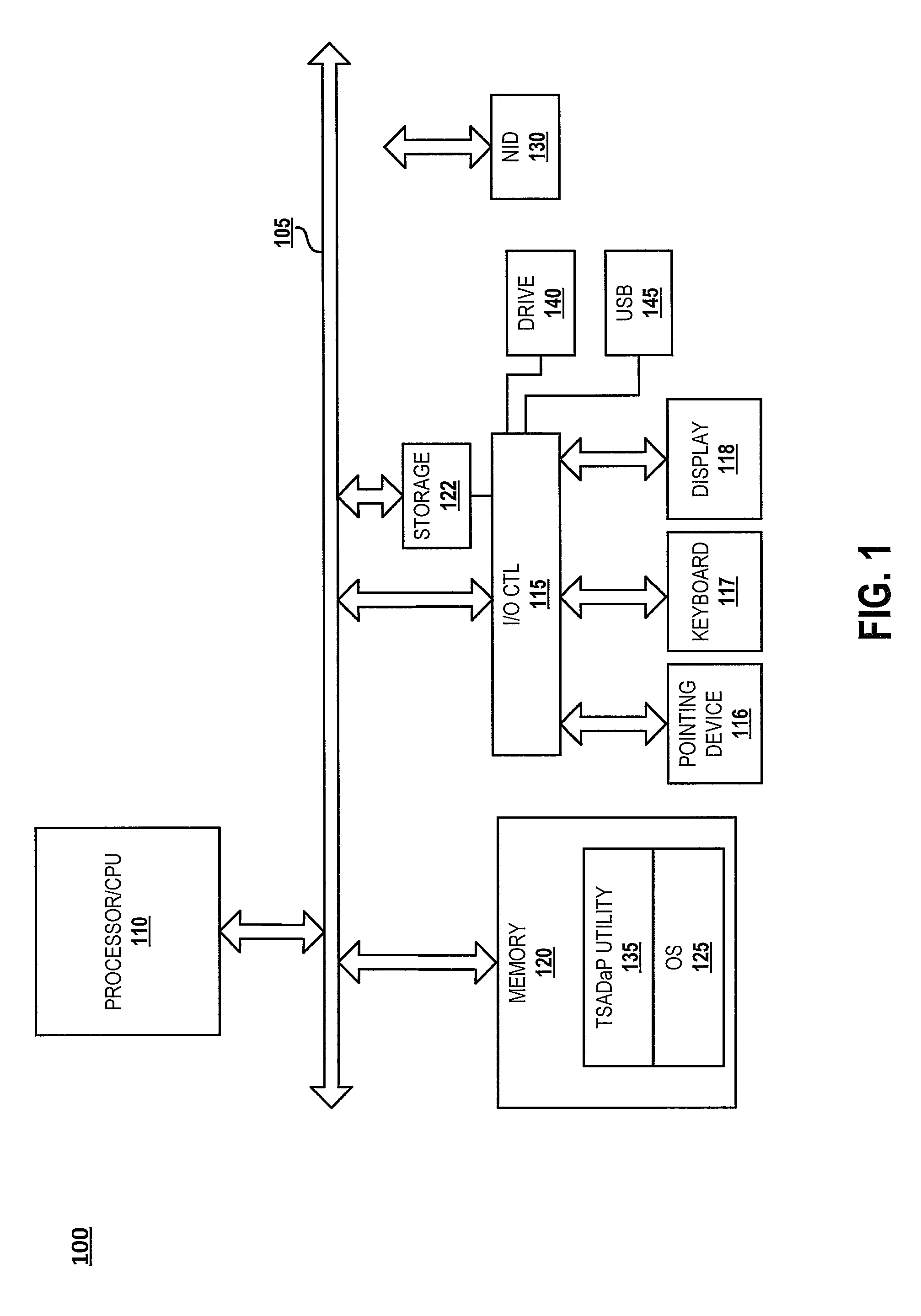
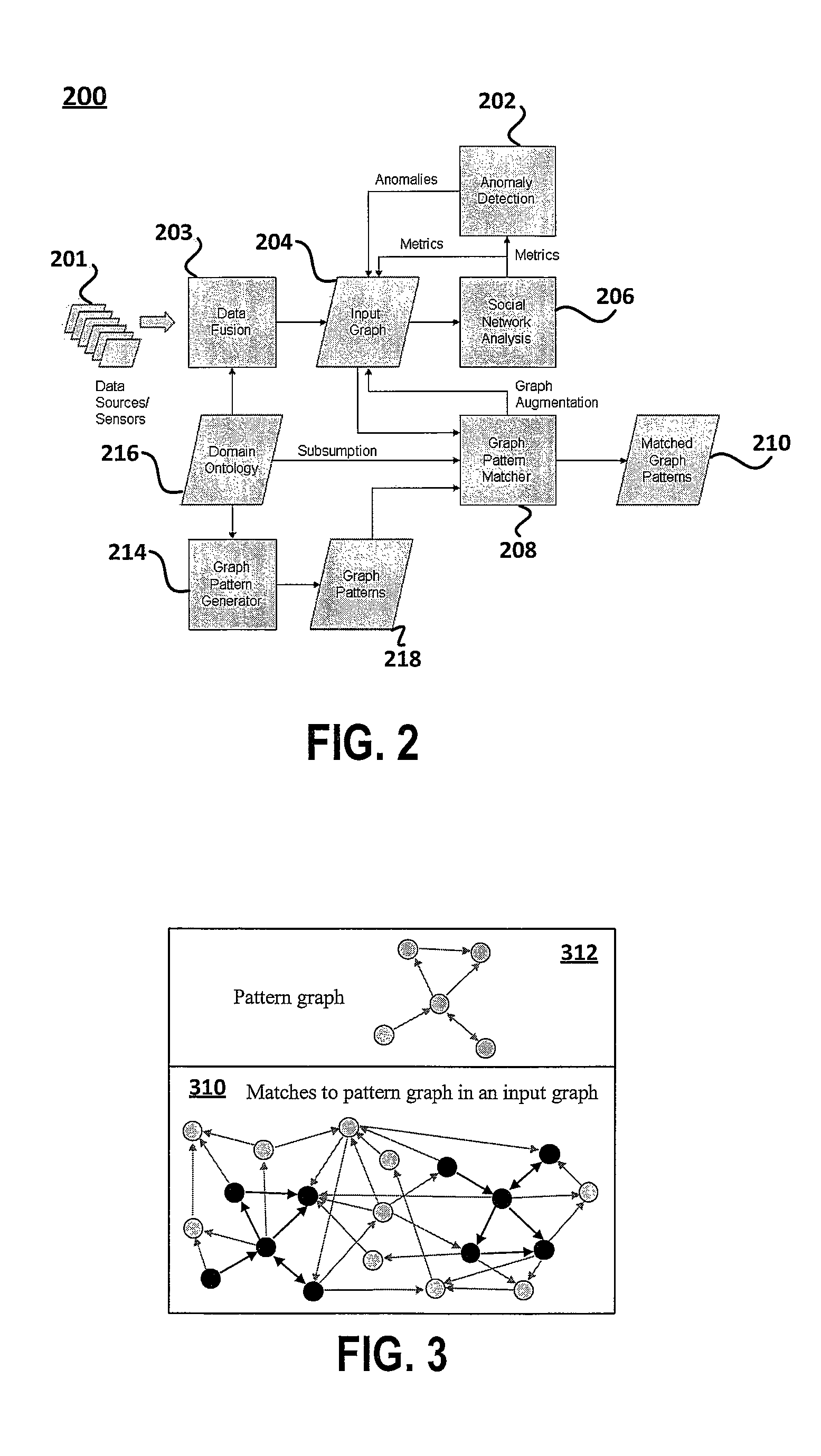
Tactical and strategic attack detection and prediction
ActiveUS20070226796A1Efficiently and effectively evaluatingShorten the timeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsSubject-matter expert
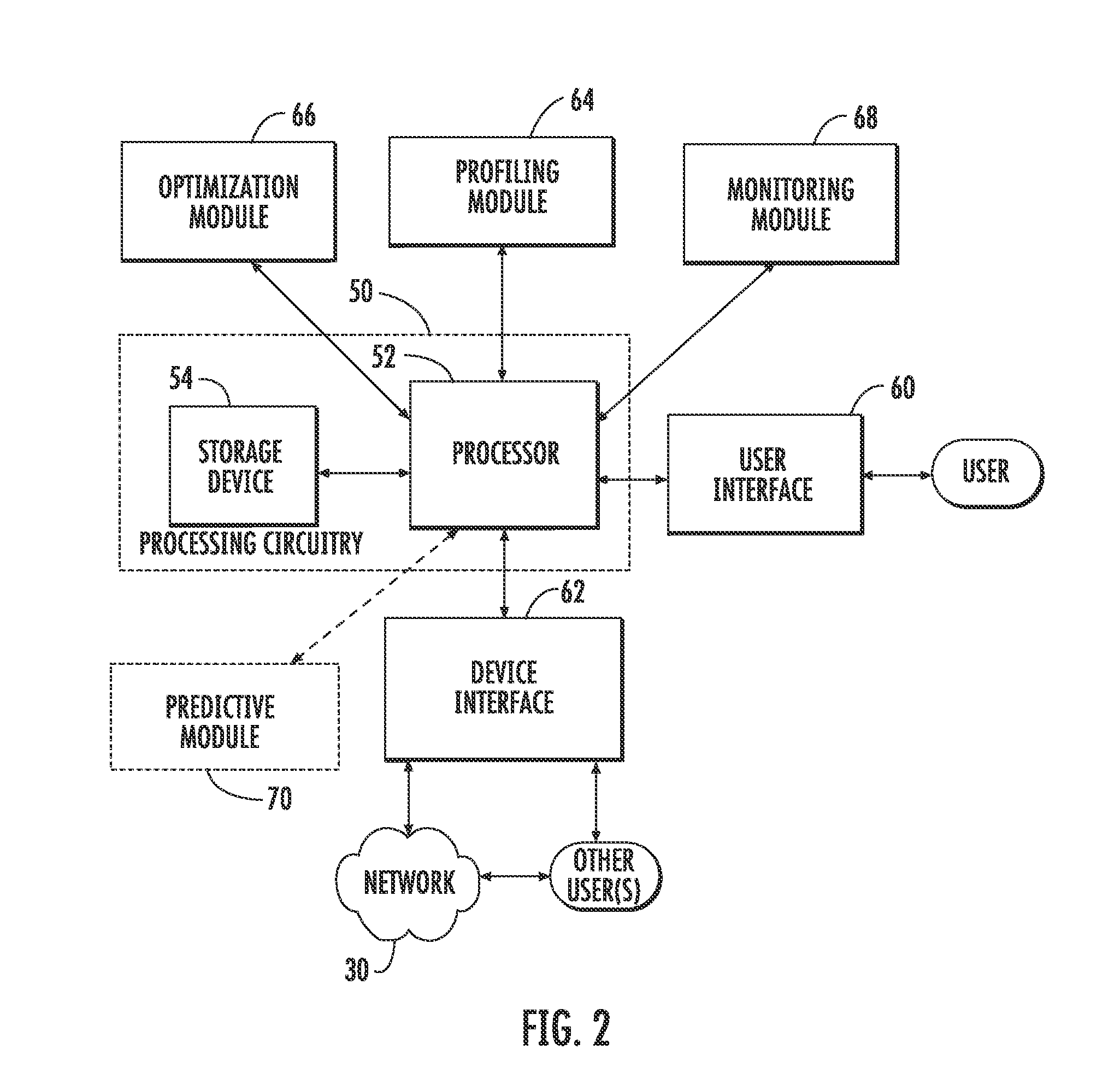
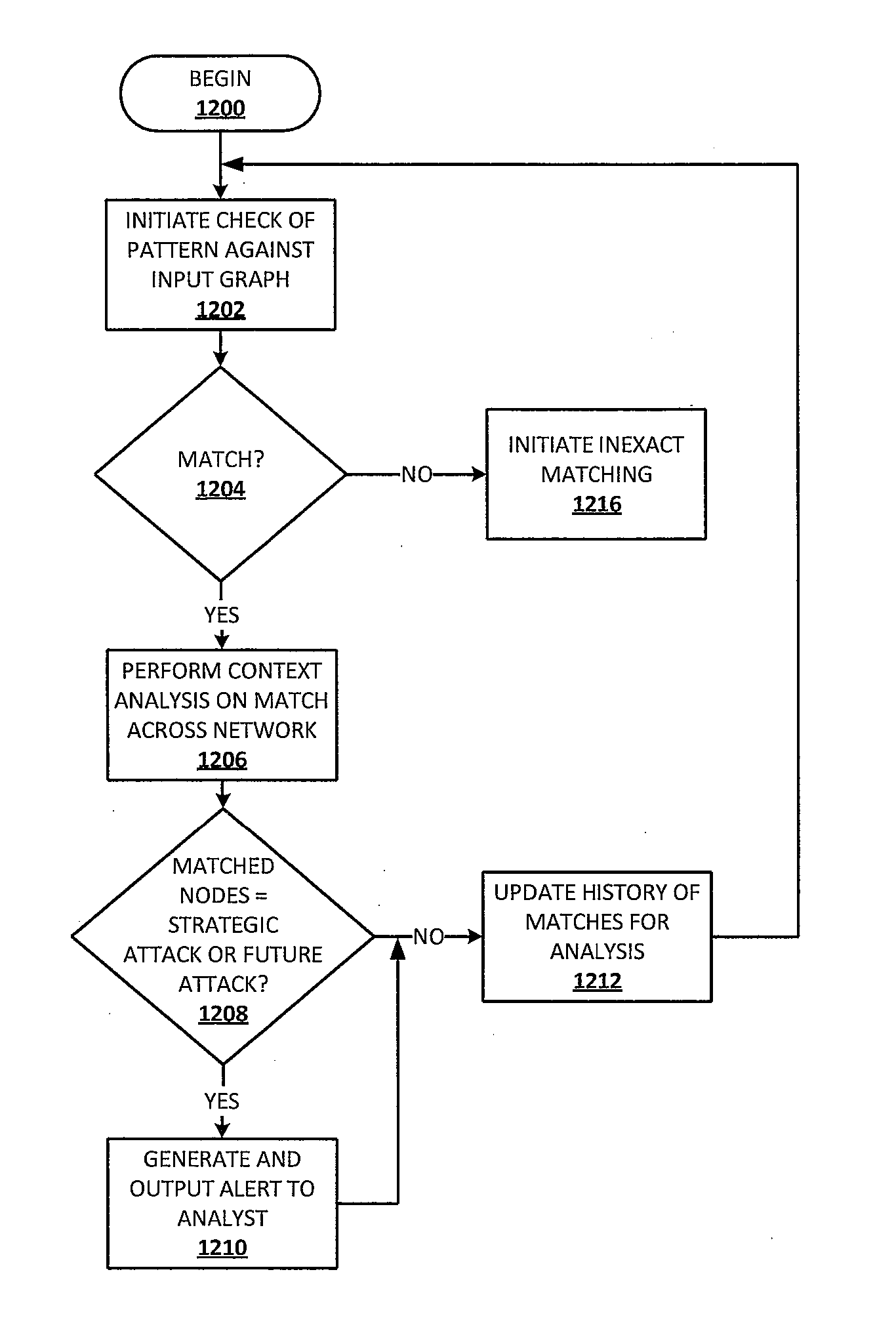
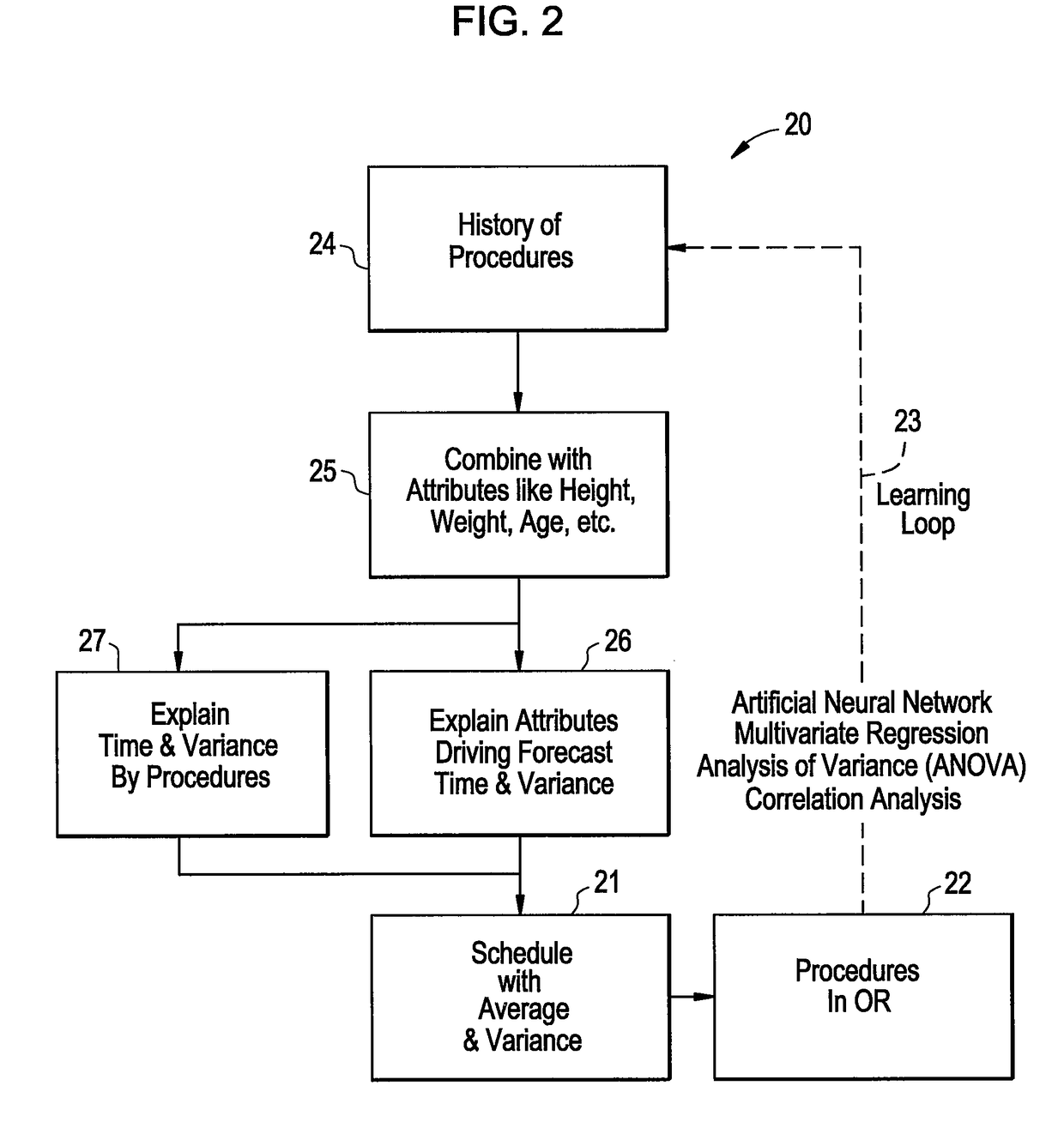
NETWAR provides a utility that enables detection of both tactical and strategic threats against an individual entity and interrelated / affiliated networks of entities. A distributed network of sensors and evaluators are utilized to detect tactical attacks against one or more entities. Events on the general network are represented as an input graph, which is searched for matches of example pattern graphs that represent tactical attacks. The search is performed using a scalable graph matching engine and an ontology that is periodically updated by a subject matter expert or analyst. NETWAR provides the functionality to determine / understand the strategic significance of the detected tactical attacks by correlating detected tactical attacks on the individual entities to identify the true motive of these attacks as a strategic attack. NETWAR also provides predictive capability to predict future entities and sub-entities that may be targeted based on evaluation of the attack data.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Tactical and strategic attack detection and prediction
ActiveUS7530105B2Efficiently and effectively evaluatingShorten the timeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionGraphicsSubject-matter expert
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
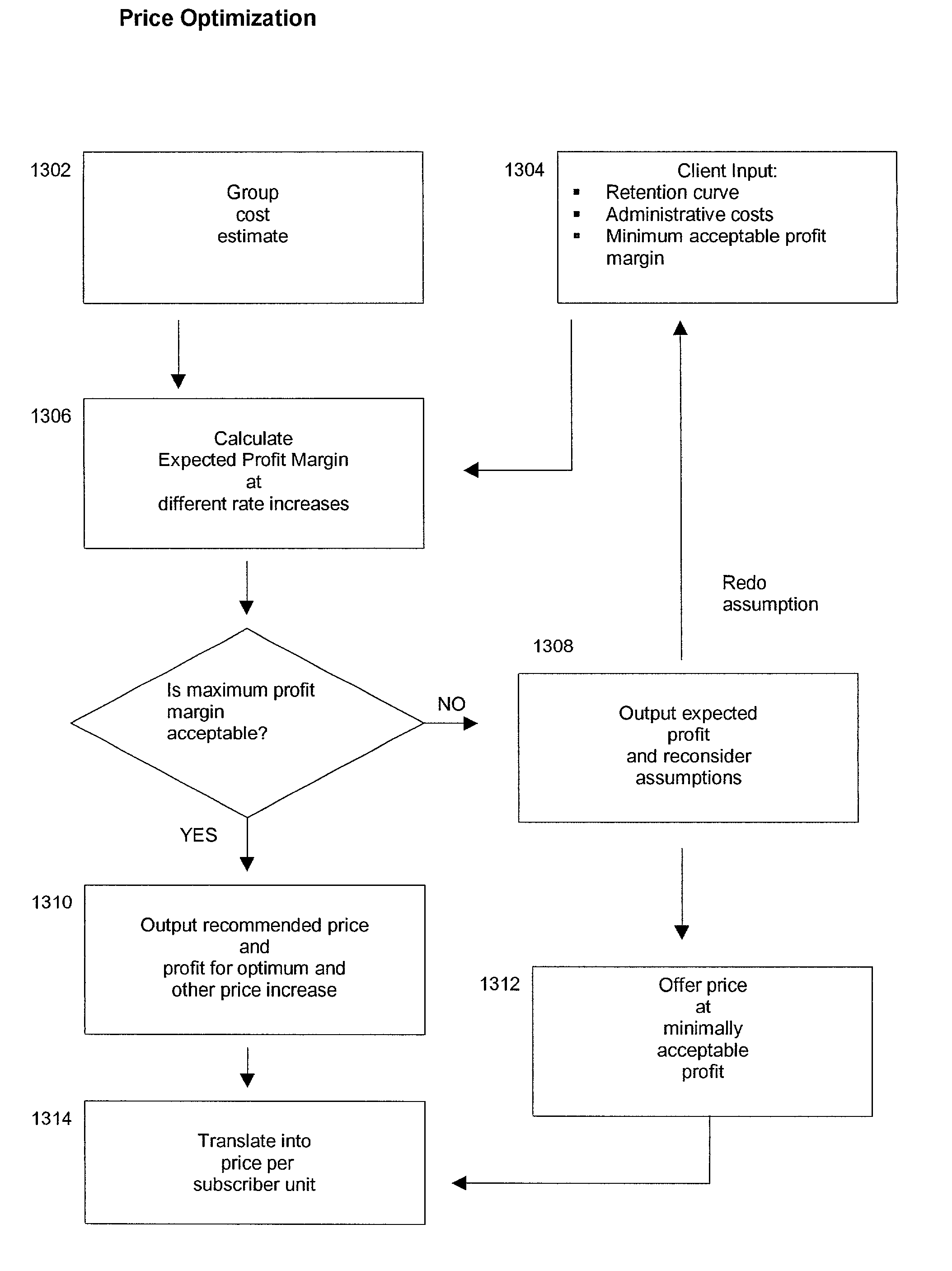
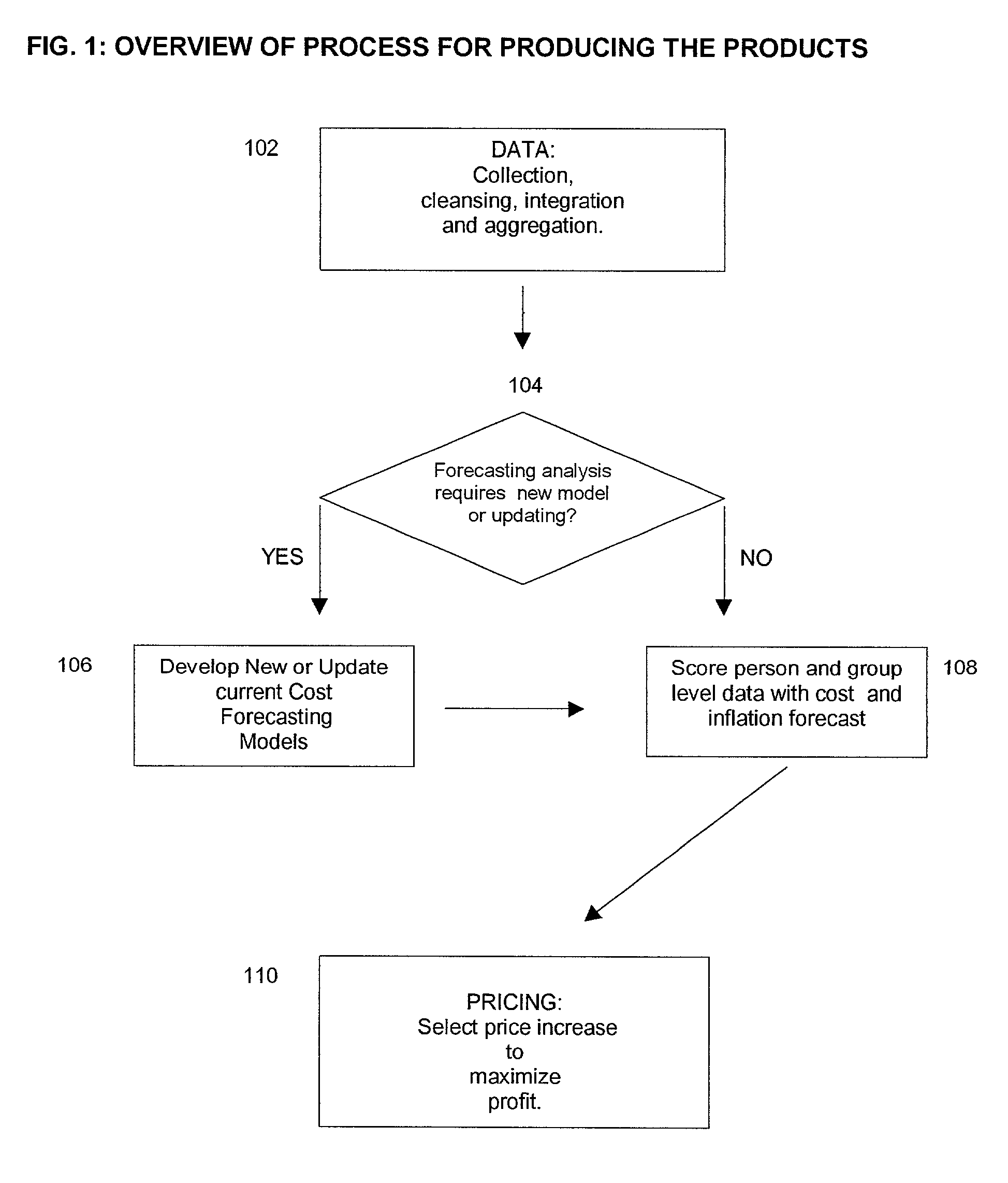
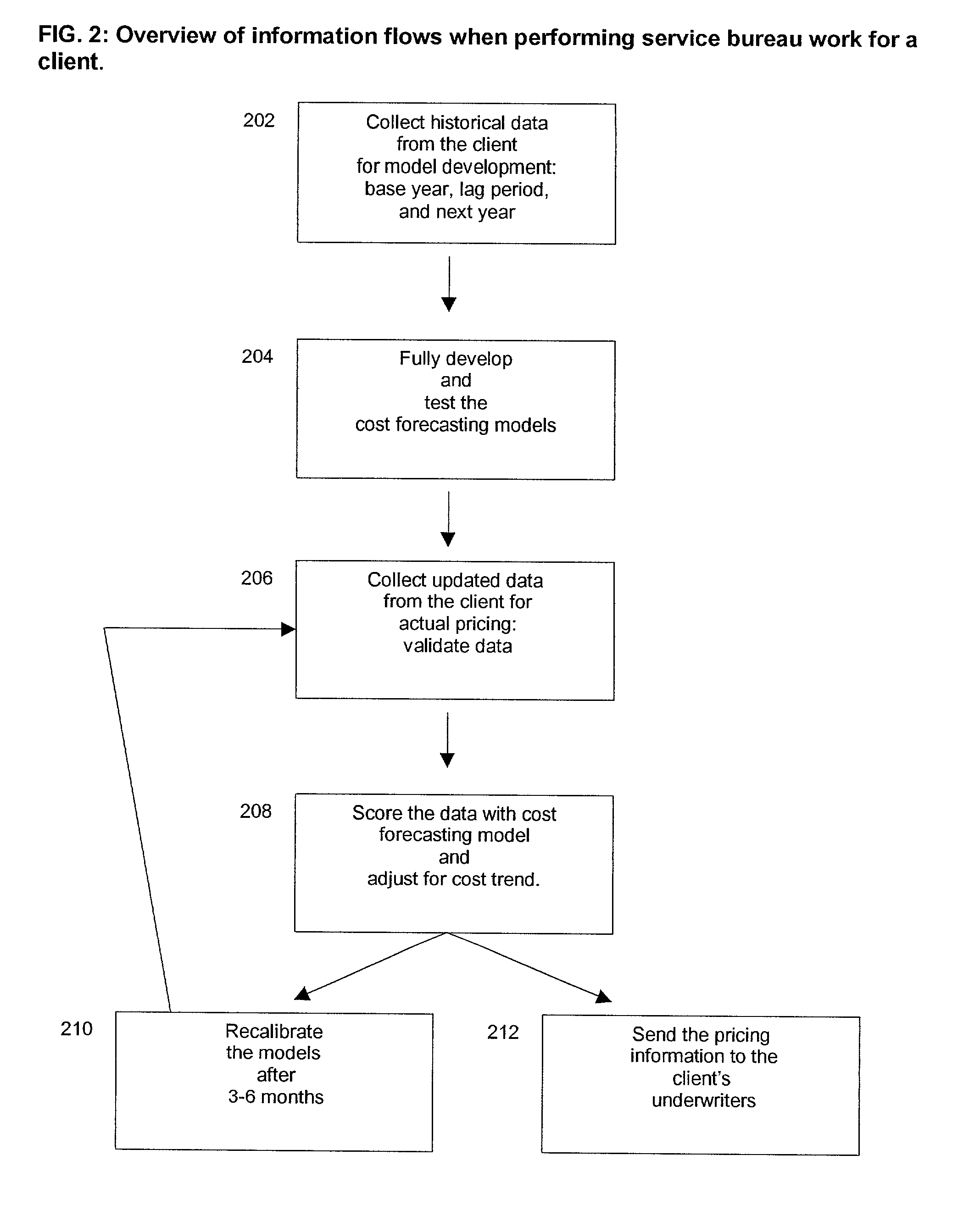
Insurance claim forecasting system
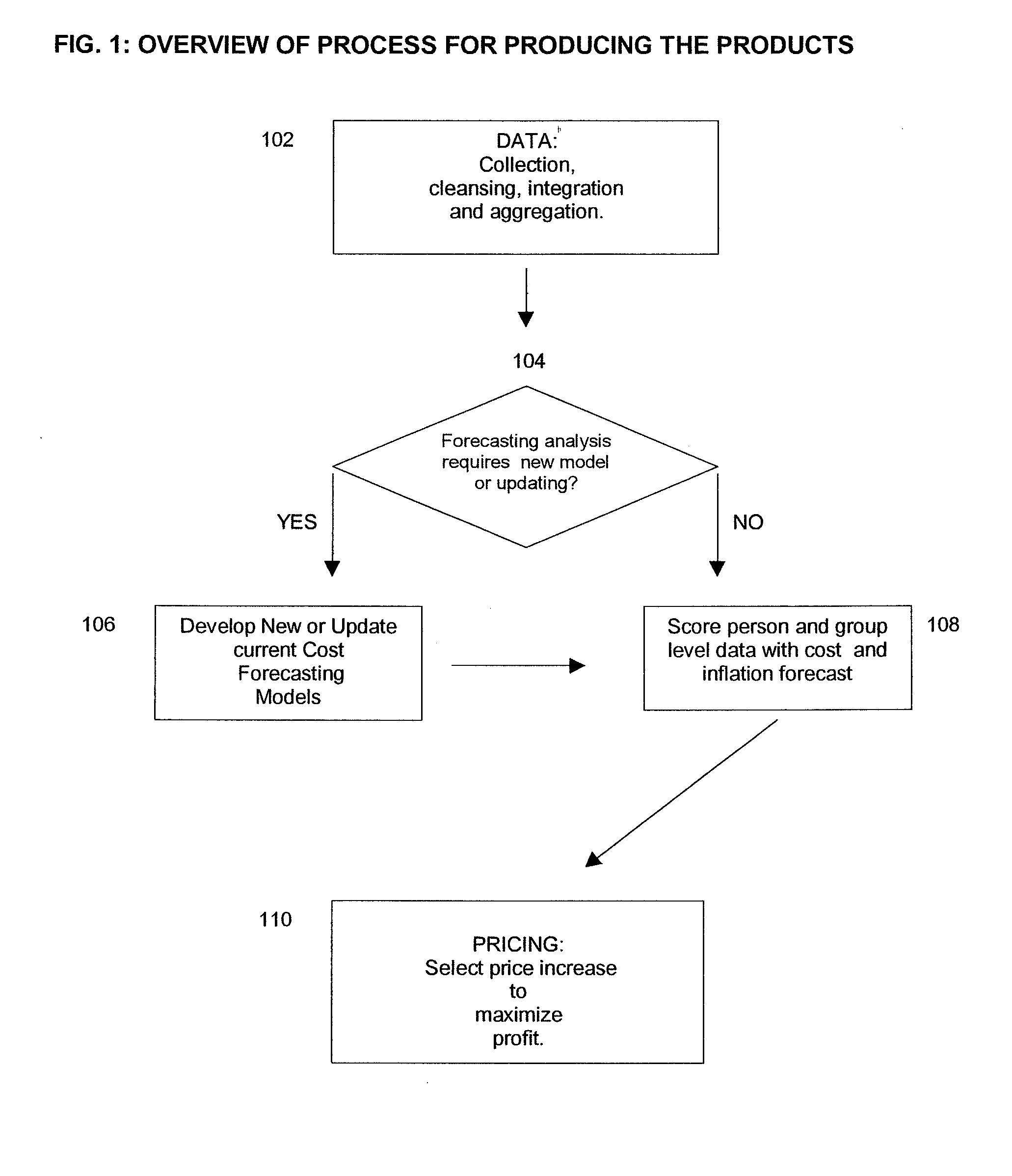
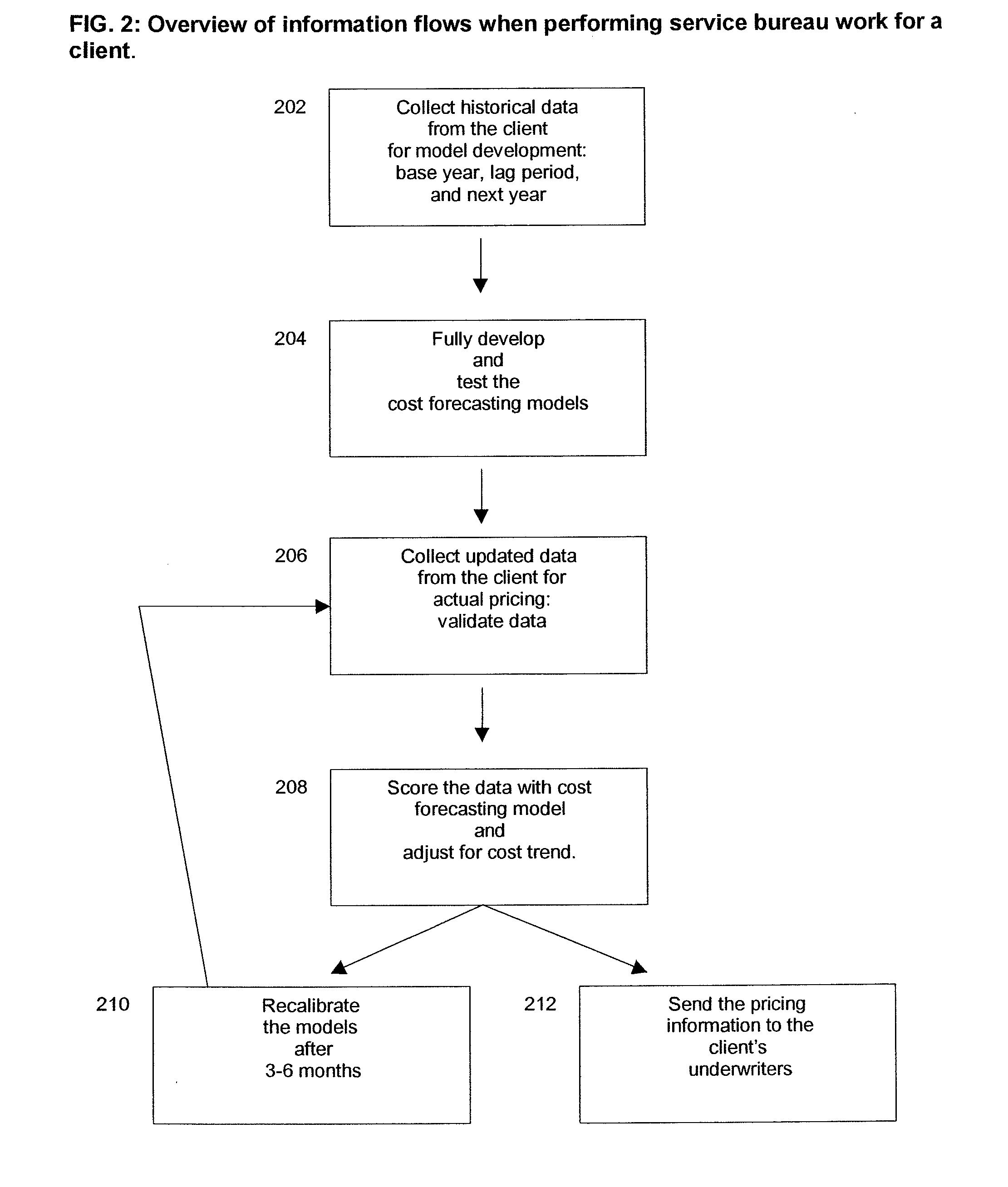
A computer-implemented process of developing a person-level cost model for forecasting future costs attributable to claims from members of a book of business, where person-level data are available for a substantial portion of the members of the book of business for an actual underwriting period, and the forecast of interest is for a policy period is disclosed. The process uses development universe data comprising person-level enrollment data, historical base period health care claims data and historical next period claim amount data for a statistically meaningful number of individuals. The process also provides at least one claim-based risk factor for each historical base period claim based on the claim code associated with the health care claim and provides at least one enrollment-based risk factor based on the enrollment data. The process also develops a cost forecasting model by capturing the predictive ability of the main effects and interactions of claim based risk factors and enrollment-based risk factors, with the development universe data through the application of an interaction capturing technique to the development universe data.
Owner:TRURISH L L C
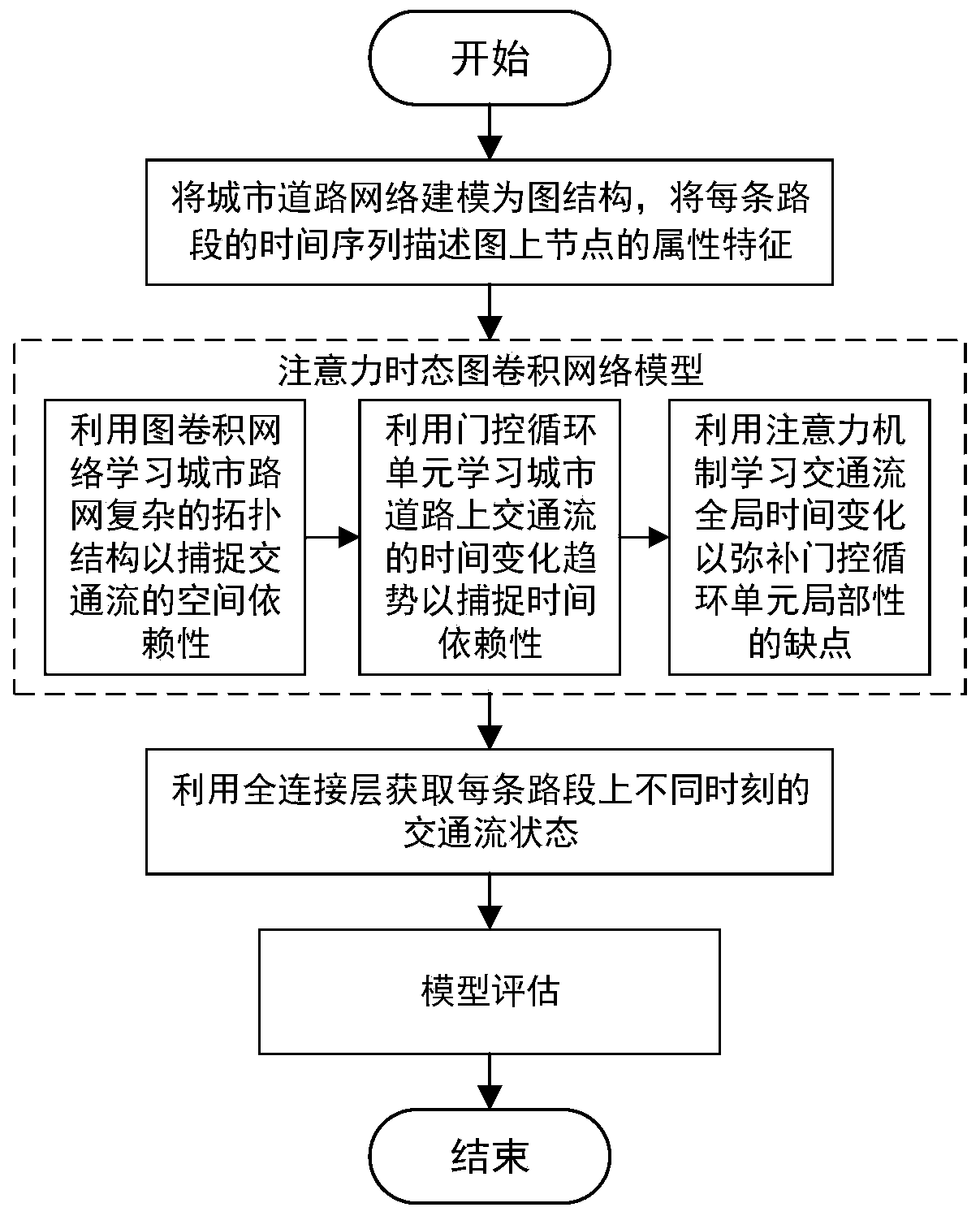
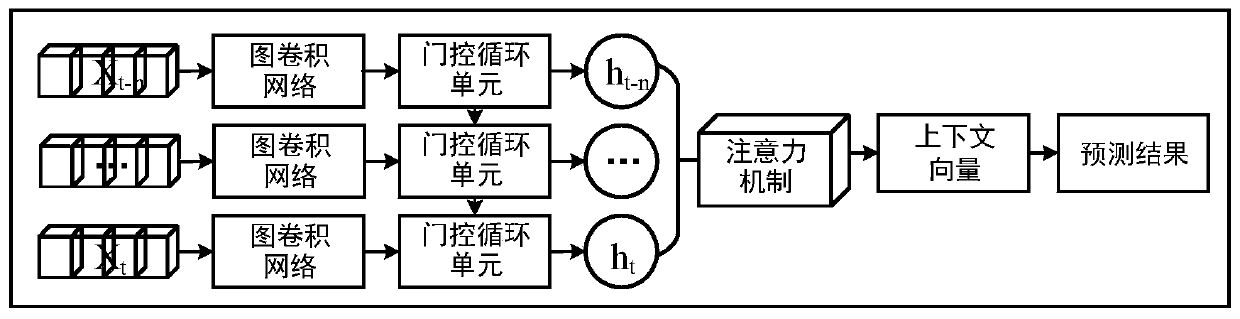
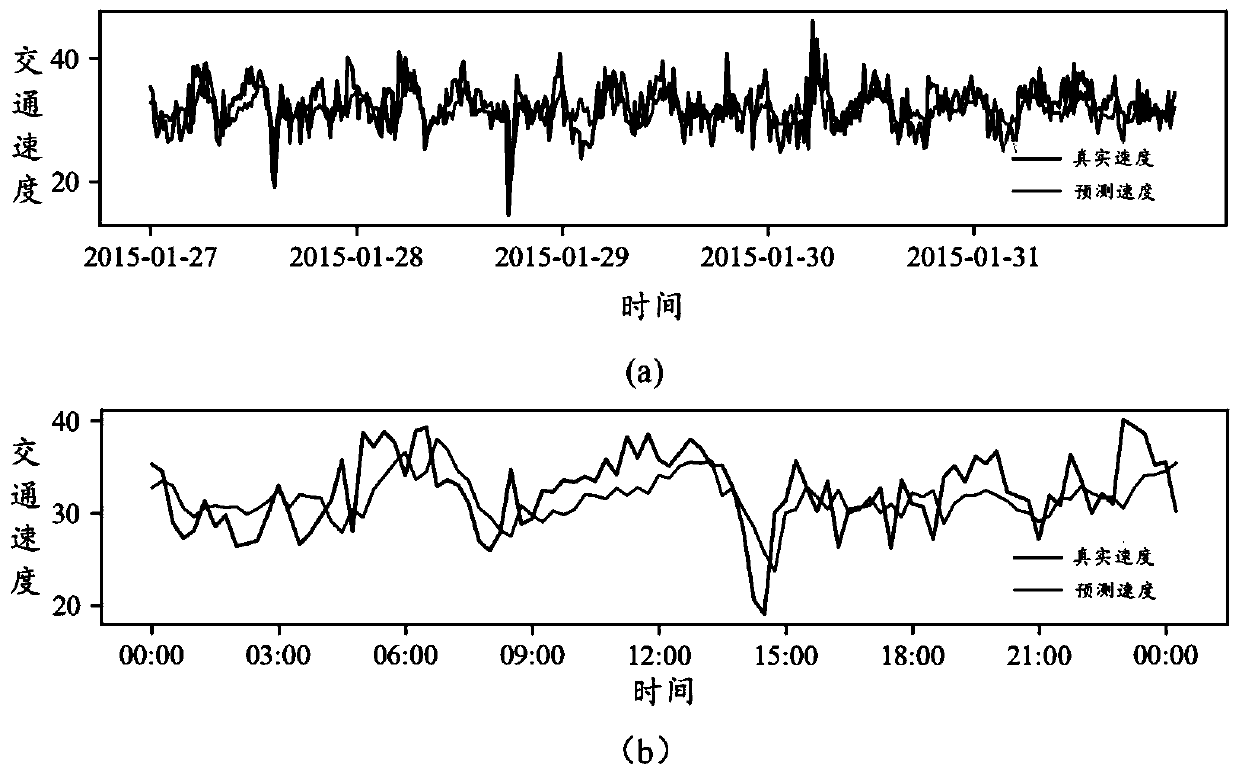
Traffic prediction method based on attention temporal graph convolutional network
ActiveCN109754605AGain spatial dependenceGood forecastDetection of traffic movementForecastingTraffic predictionNetwork model
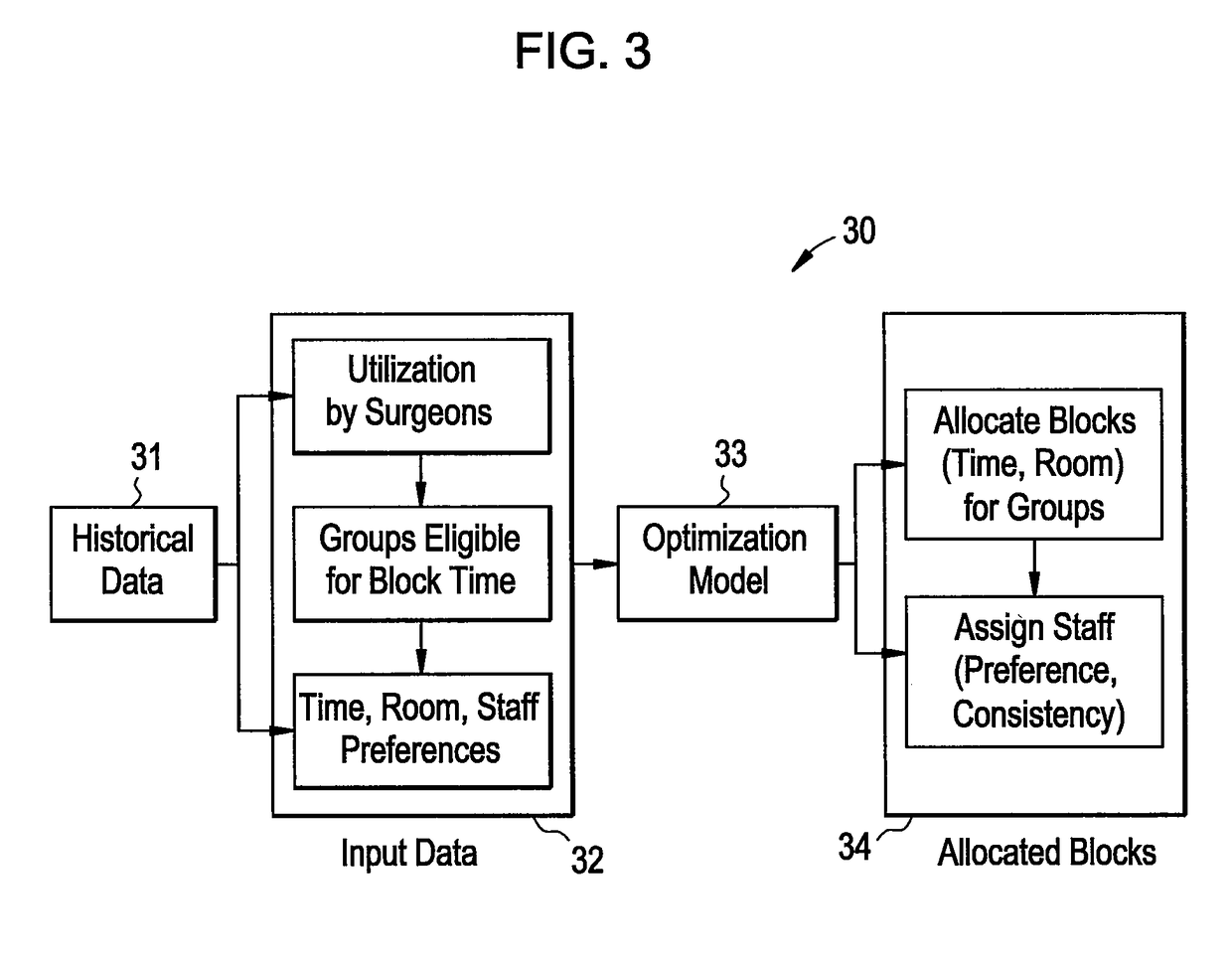
The invention belongs to the field of intelligent transportation, and discloses a traffic prediction method based on an attention temporal graph convolutional network. The method includes the following steps that: firstly, an urban road network is modeled as a graph structure, nodes of the graph represent road sections, edges are connection relationships between the road sections, and the time series of each road section is described as attribute characteristics of the nodes; secondly, the temporal and spatial characteristics of the traffic flow are captured by using an attention temporal graph convolutional network model, the temporal variation trend of the traffic flow on urban roads is learned by using gated cycle units to capture the time dependence, and the global temporal variation trend of the traffic flow is learned by using an attention mechanism; and then, the traffic flow state at different times on each road section is obtained by using a fully connected layer; and finally,different evaluation indexes are used to estimate the difference between the real value and the predicted value of the traffic flow on the urban roads and further estimate the prediction ability of the model. Experiments prove that the method provided by the invention can effectively realize tasks of predicting the traffic flow on the urban roads.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Insurance claim forecasting system
A computer-implemented process of developing a person-level cost model for forecasting future costs attributable to claims from members of a book of business, where person-level data are available for a substantial portion of the members of the book of business for an actual underwriting period, and the forecast of interest is for a policy period is disclosed. The process uses development universe data comprising person-level enrollment data, historical base period health care claims data and historical next period claim amount data for a statistically meaningful number of individuals. The process also provides at least one claim-based risk factor for each historical base period claim based on the claim code associated with the health care claim and provides at least one enrollment-based risk factor based on the enrollment data. The process also develops a cost forecasting model by capturing the predictive ability of the main effects and interactions of claim based risk factors and enrollment-based risk factors, with the development universe data through the application of an interaction capturing technique to the development universe data.
Owner:BINNS GREGORY S +1
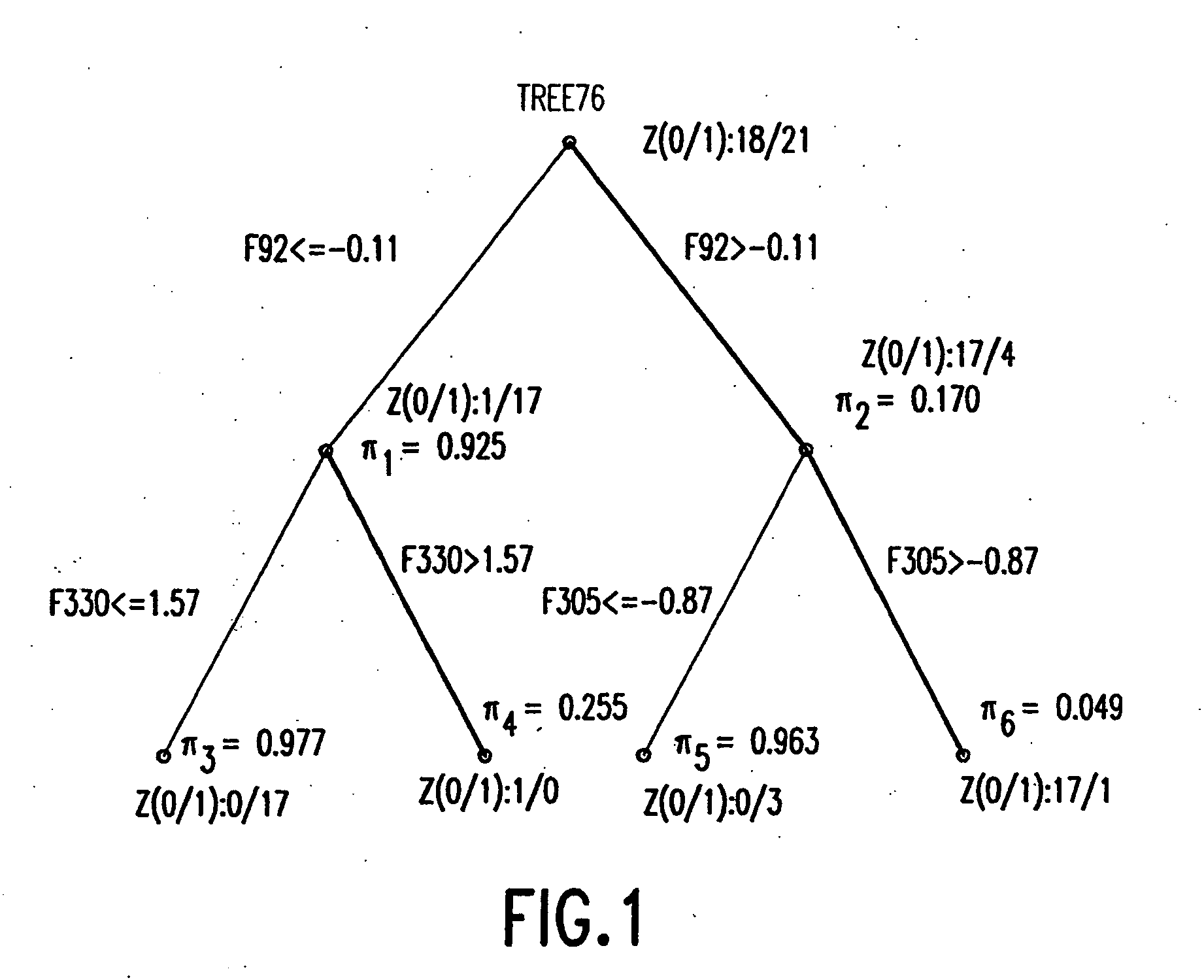
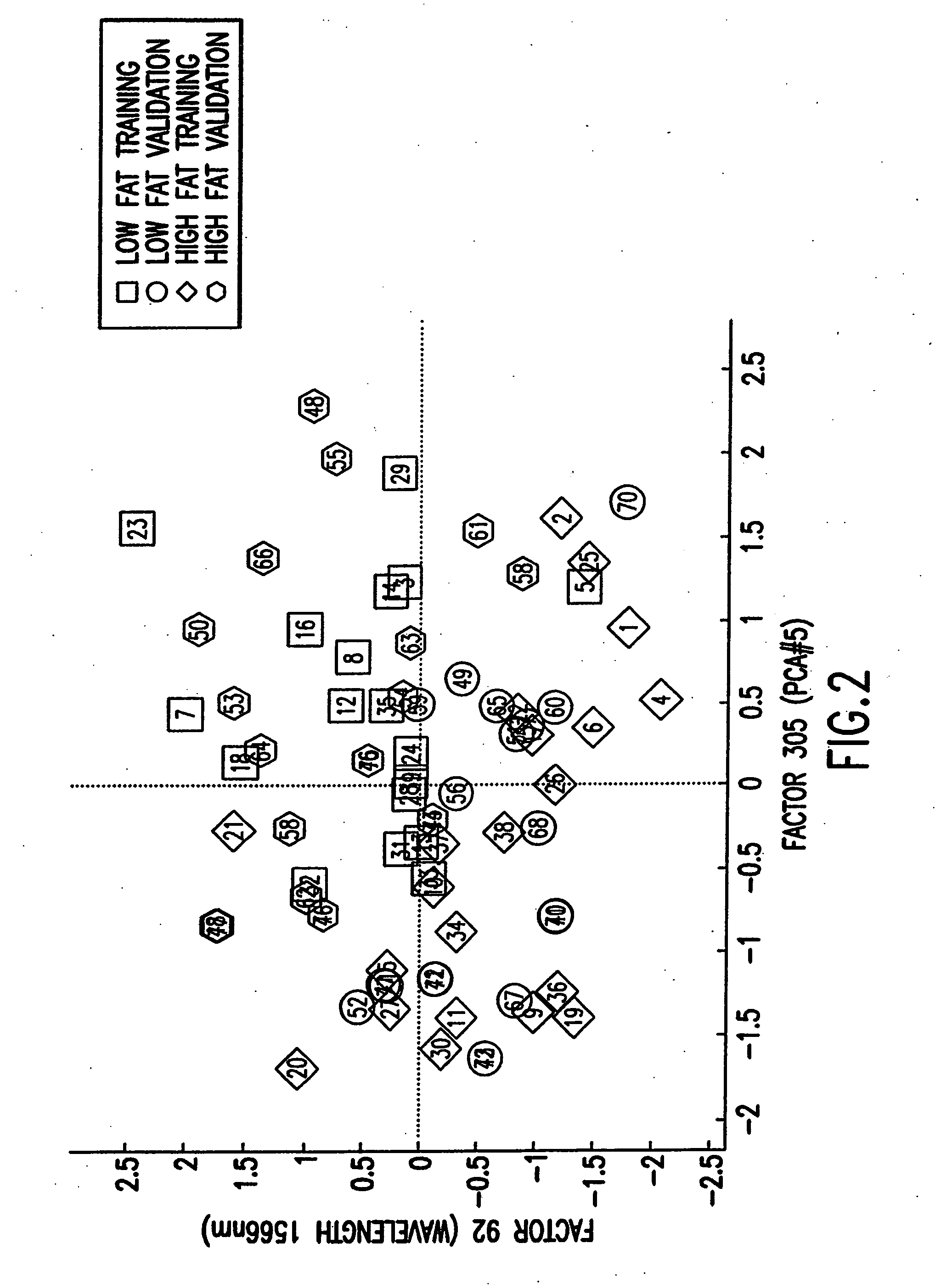
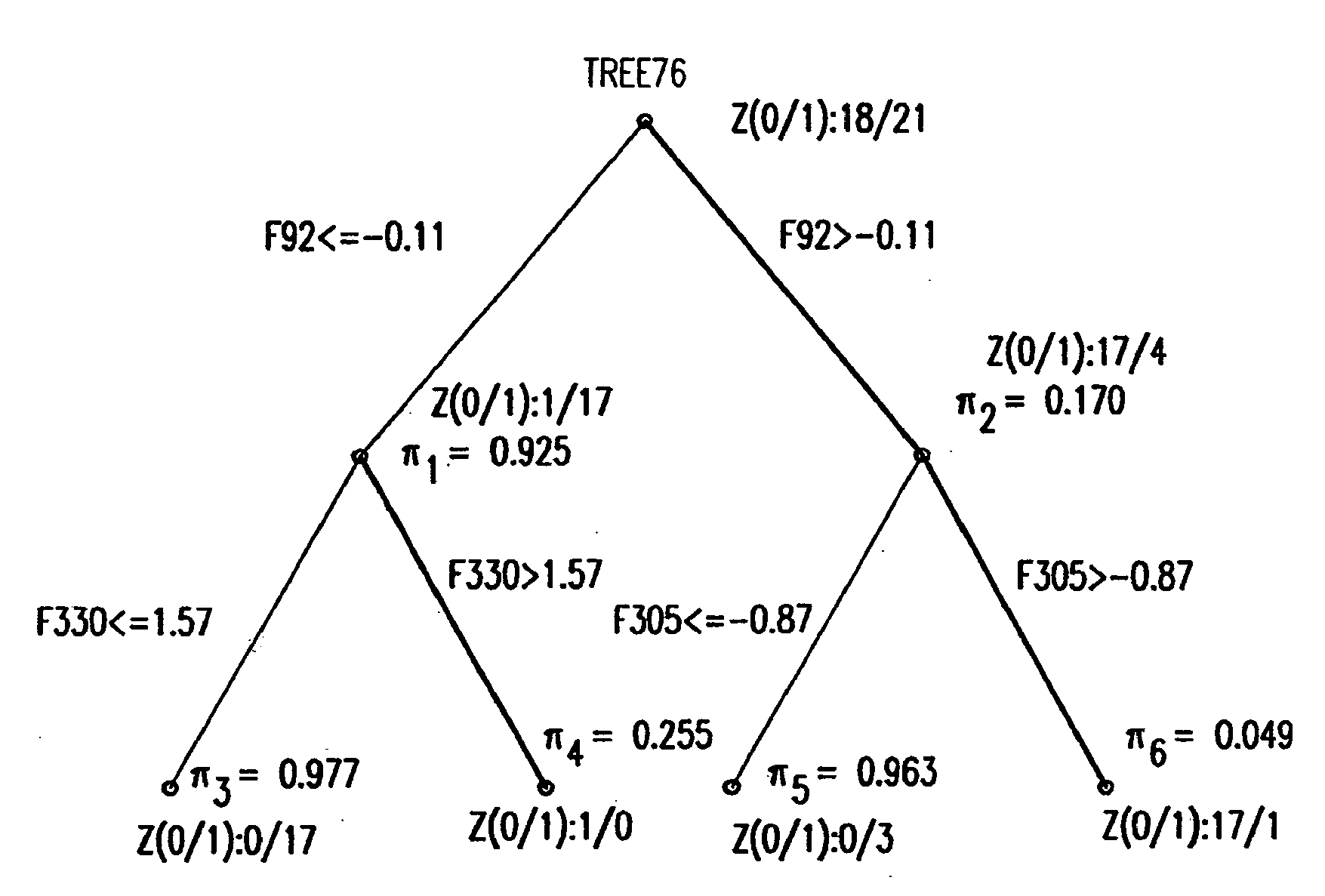
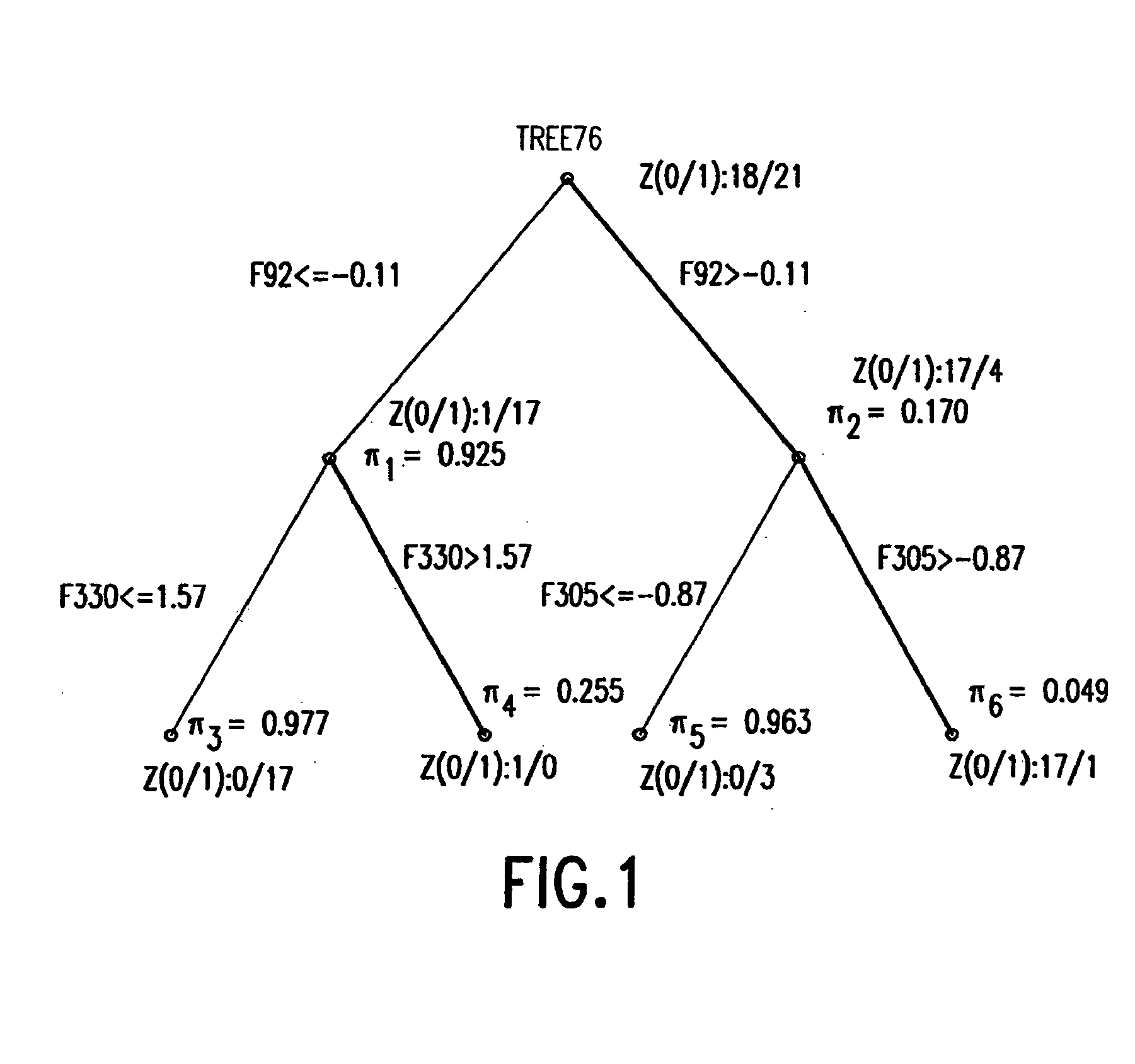
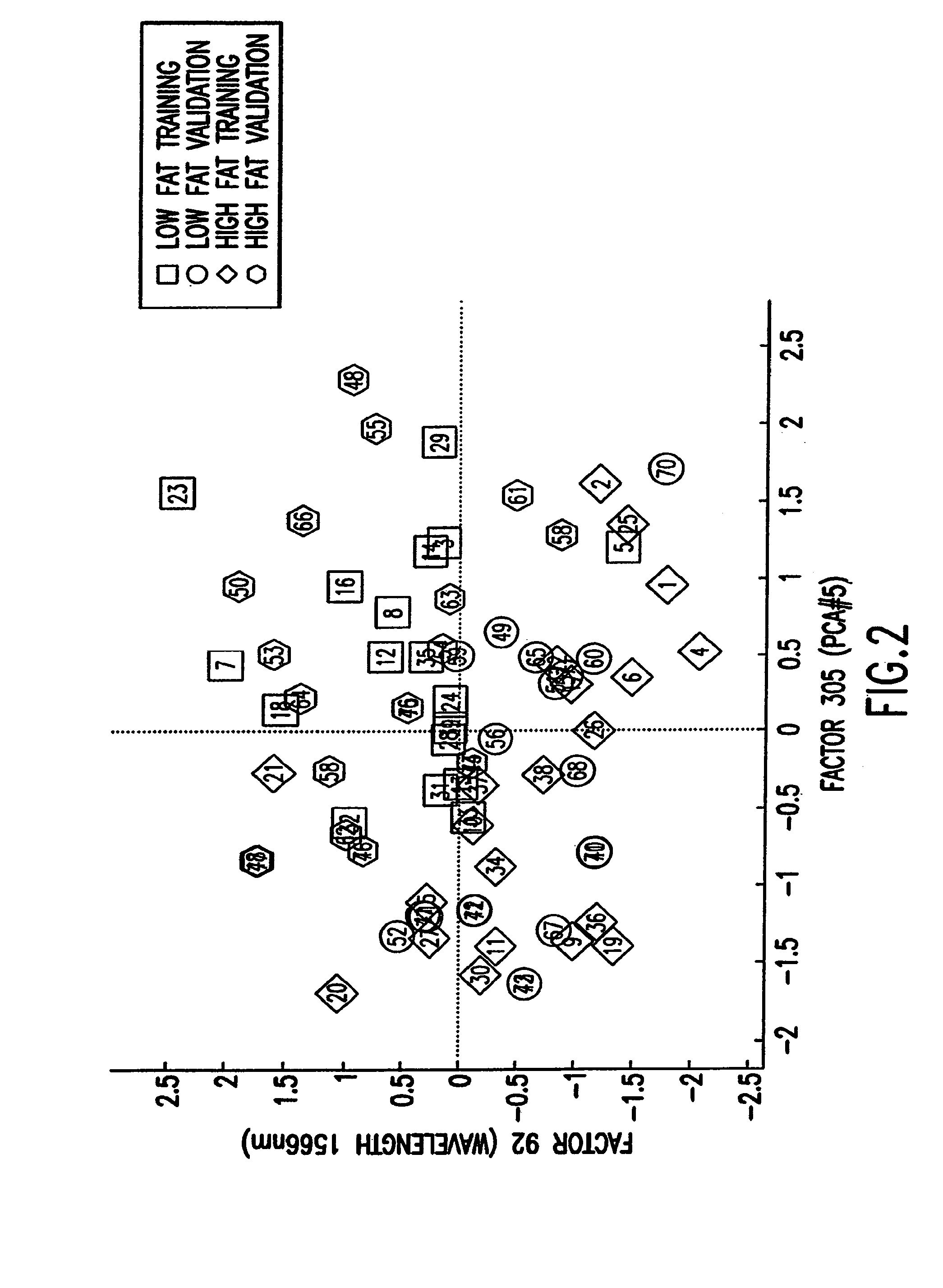
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Deep convolution neural network training method and device
InactiveCN106355248AImprove predictive performanceImprove transfer learning capabilitiesPhysical realisationNeural learning methodsData setAlgorithm
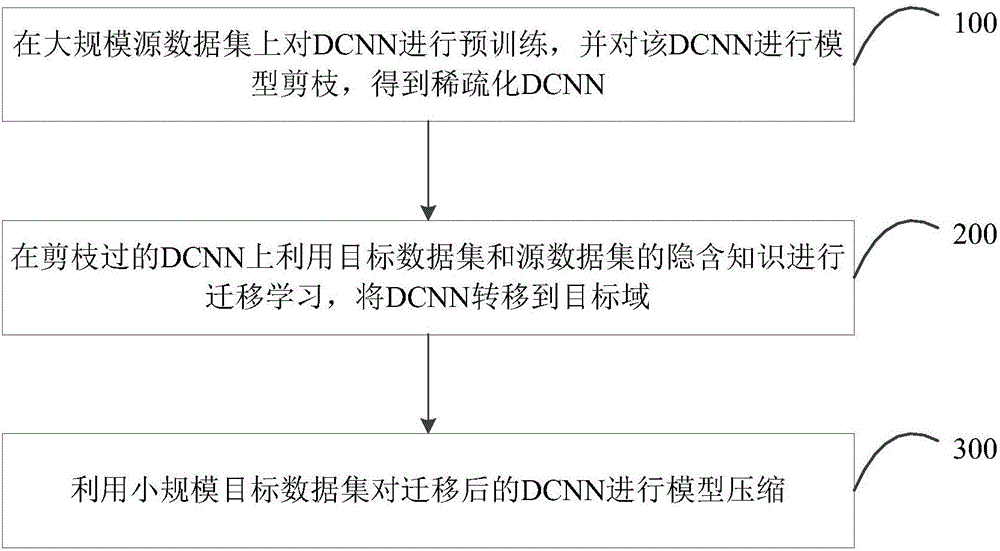
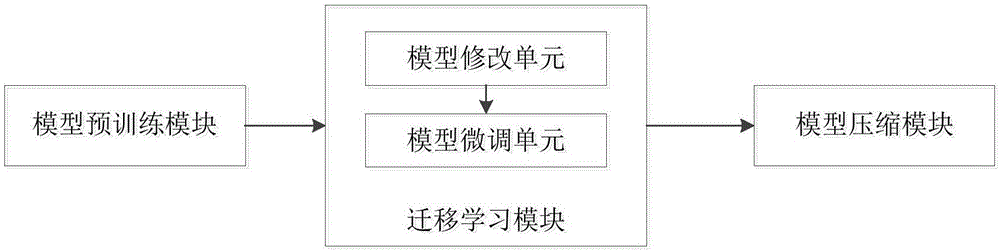
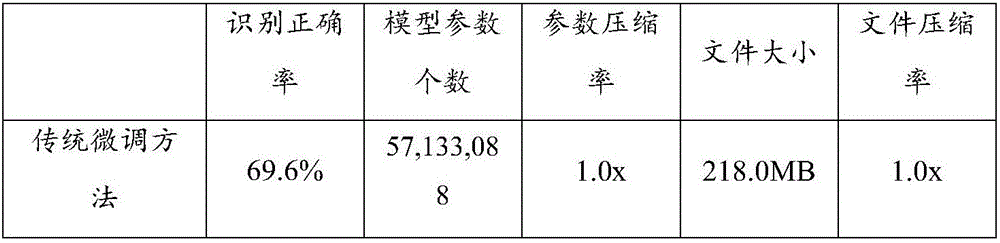
The present invention relates to the field of deep learning techniques, in particular to a deep convolution neural network training method and a device. The deep convolution neural network training method and the device comprise the steps of a, pretraining the DCNN on a large scale data set, and pruning the DCNN; b, performing the migration learning on the pruned DCNN; c, performing the model compression and the pruning on the migrated DCNN with the small-scale target data set, In the process of migrating learning of large-scale source data set to small-scale target data set, the model compression and the pruning are performed on the DCNN by the migration learning method and the advantages of model compression technology, so as to improve the migration learning ability to reduce the risk of overfitting and the deployment difficulty on the small-scale target data set and improve the prediction ability of the model on the target data set.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
System and method for many-to-many information coordination and distribution
InactiveUS20060168592A1Reduce data bandwidthImprove rendering capabilitiesMultiprogramming arrangementsOffice automationDecision takingBusiness forecasting
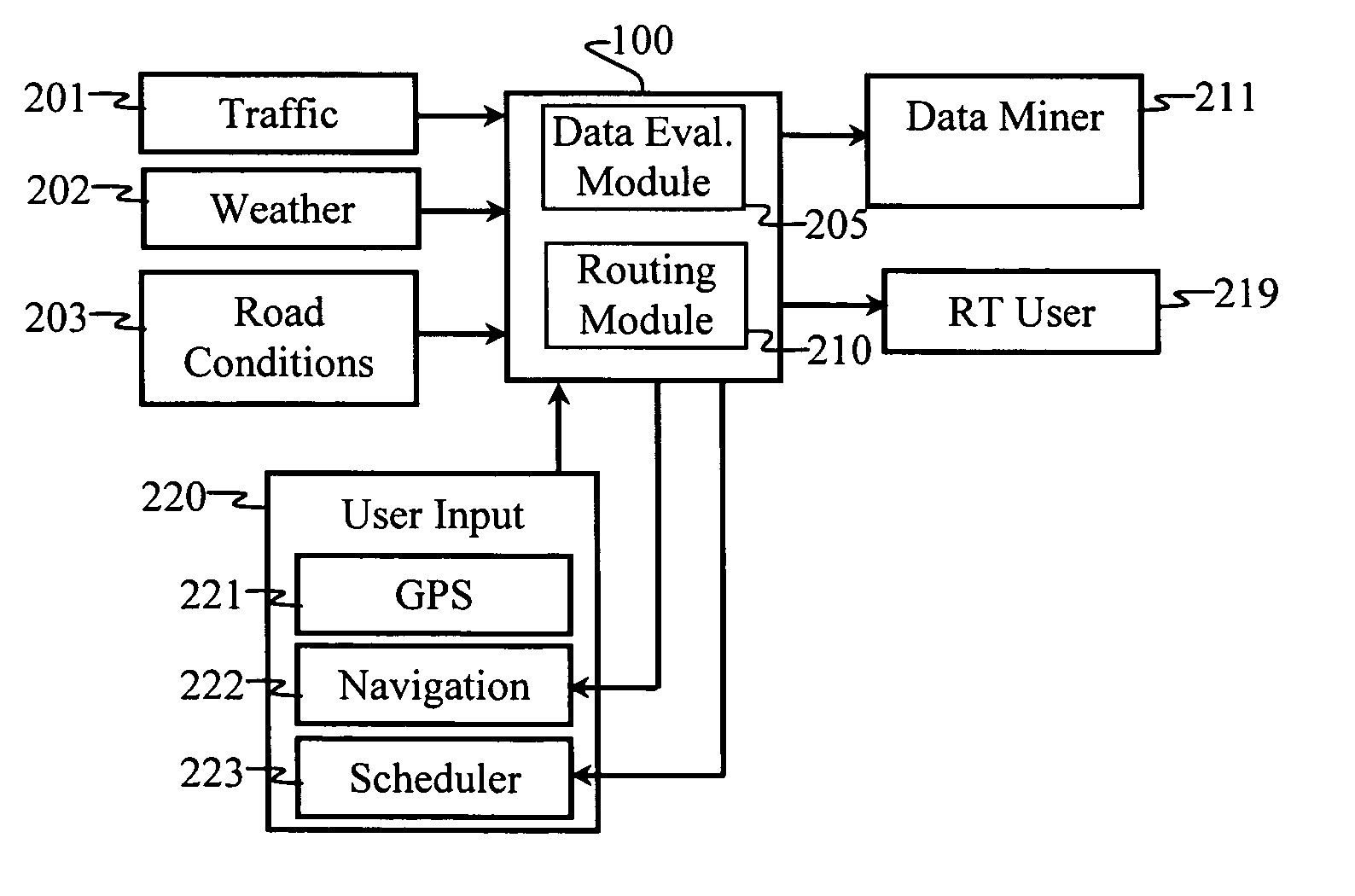
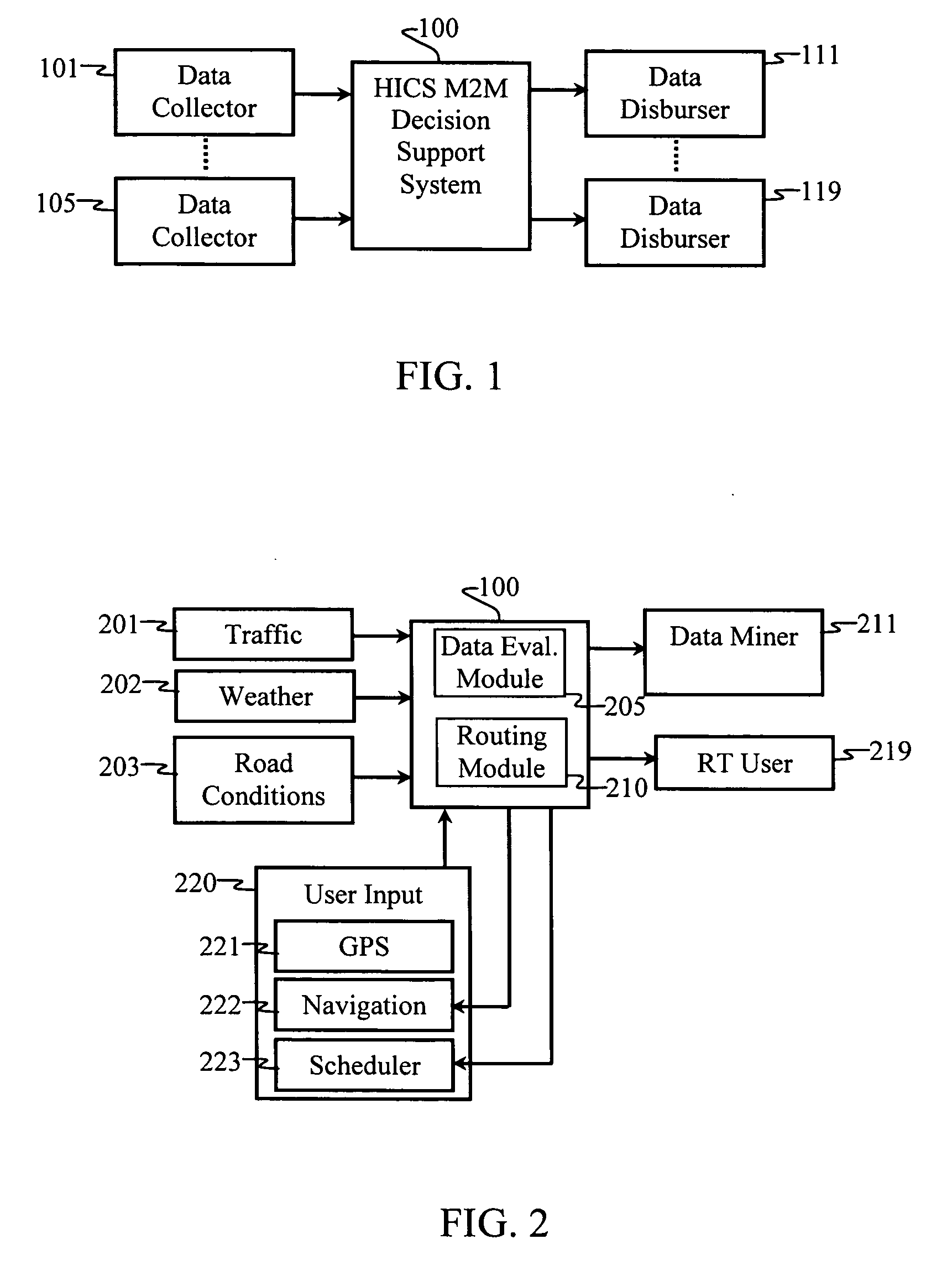
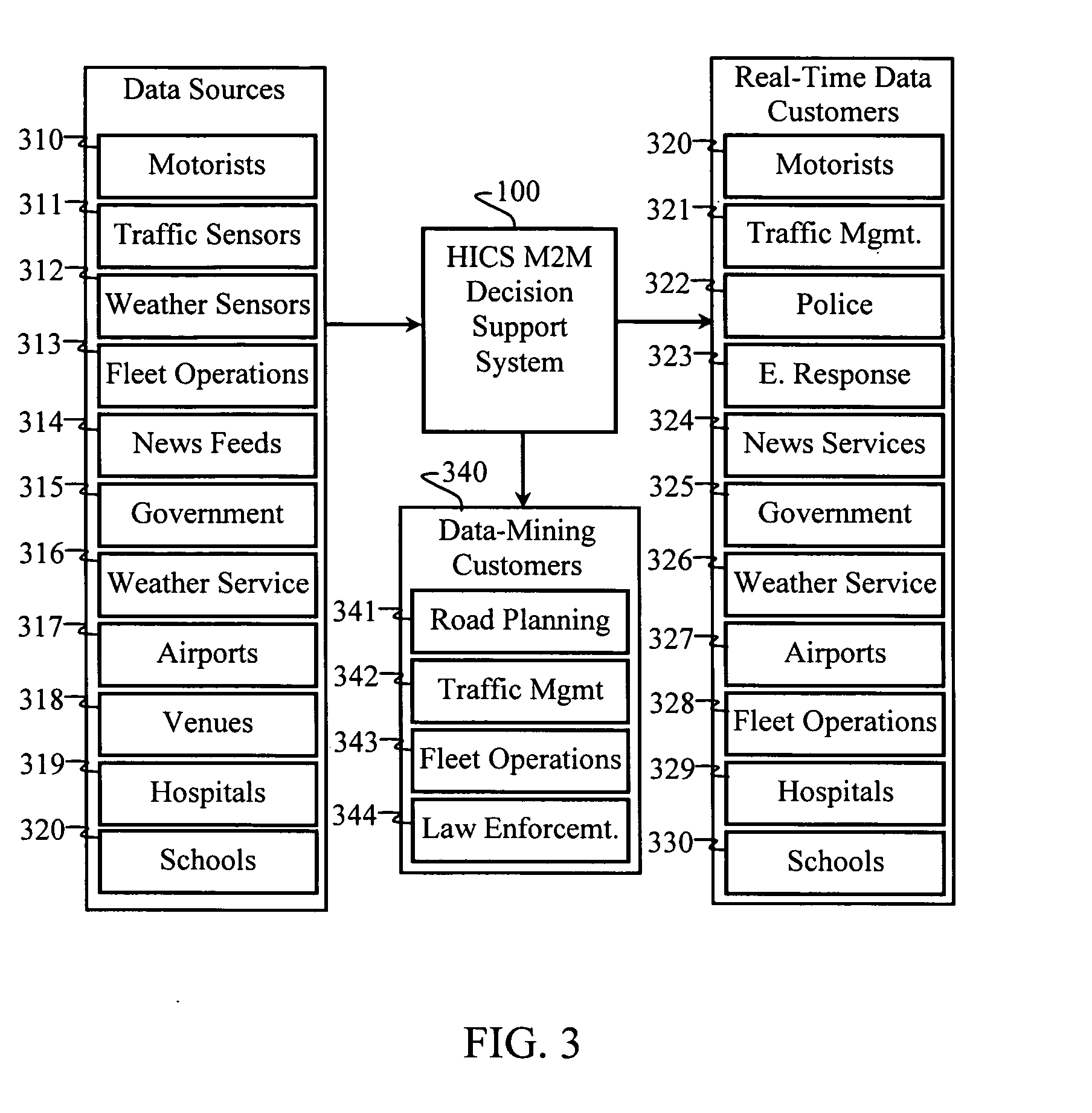
A hazard information coordination system is provided with intelligent routing to enhance the distribution of information from multiple information sources to a plurality of destinations. Routing is performed based on data values and associated intelligence that determines what data is relevant to which users. User preferences, geographical location, local environment, current activities, and planned activities help a decision support system determine what data is relevant for each user. Thus, decision support systems are preferably provided with situational awareness, context awareness, and forecasting capabilities.
Owner:WEST SAFETY SERVICES INC
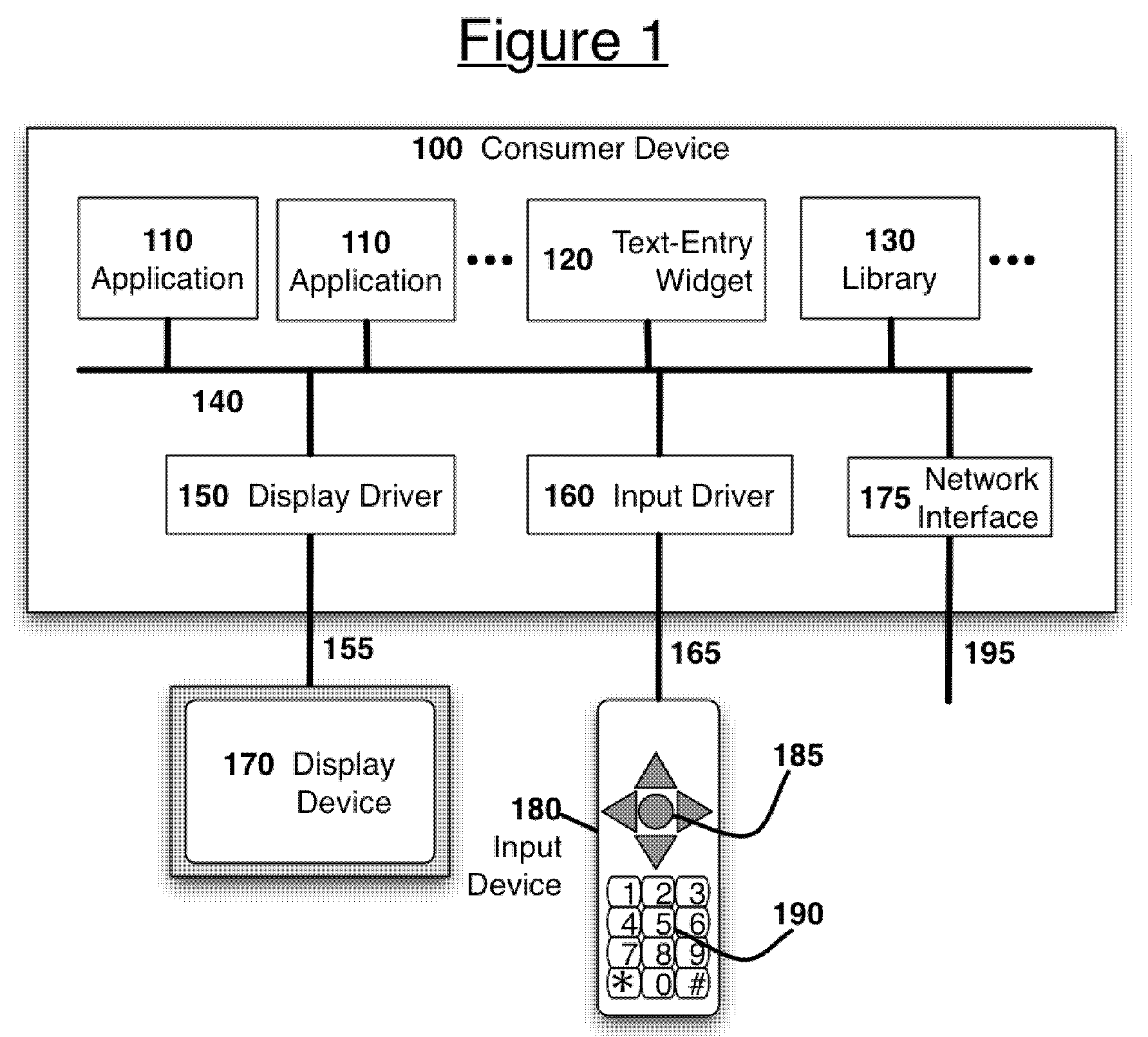
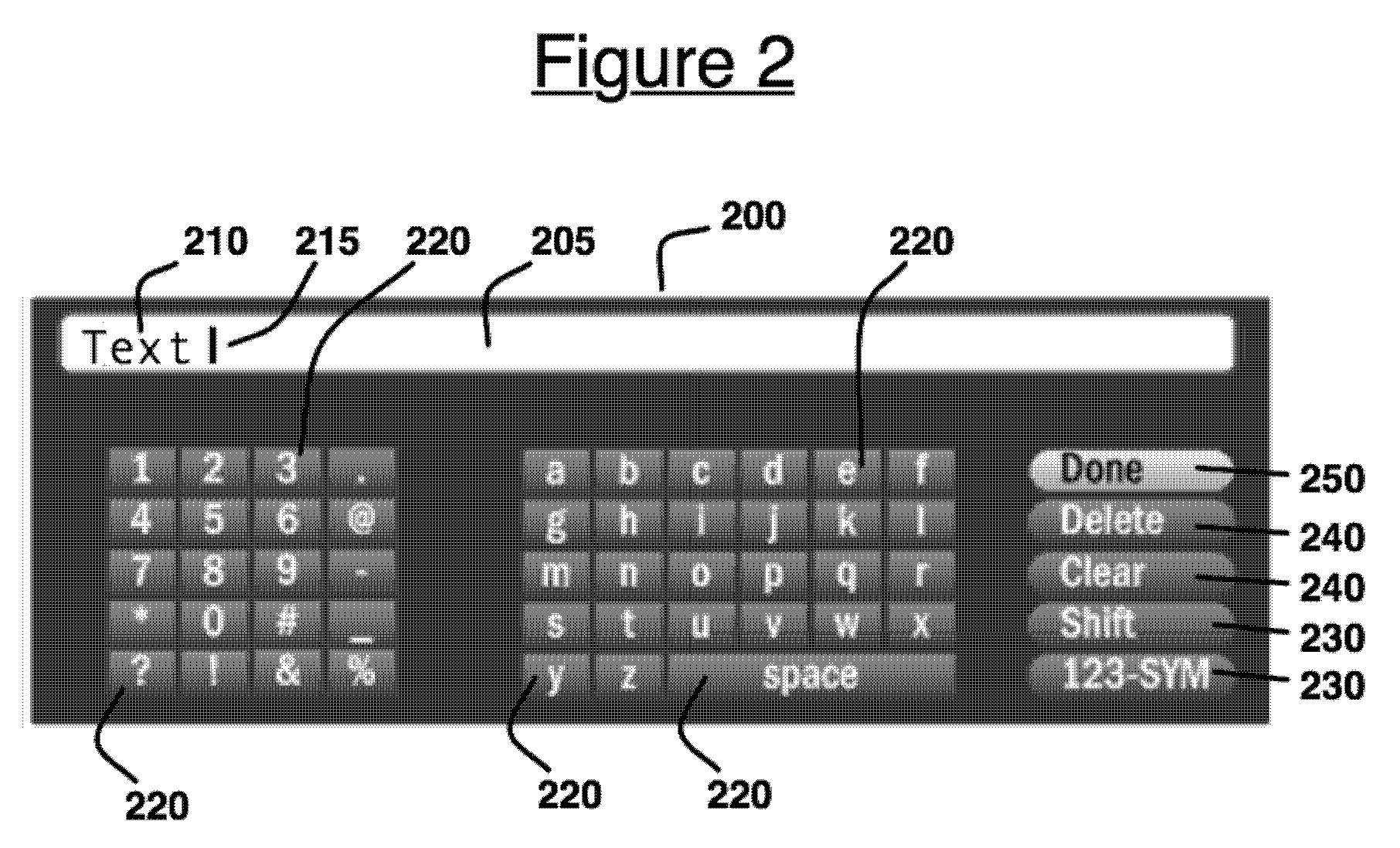
Context-dependent prediction and learning with a universal re-entrant predictive text input software component
InactiveUS20080281583A1Minimize the numberNatural language data processingWebsite content managementPrediction algorithmsText entry
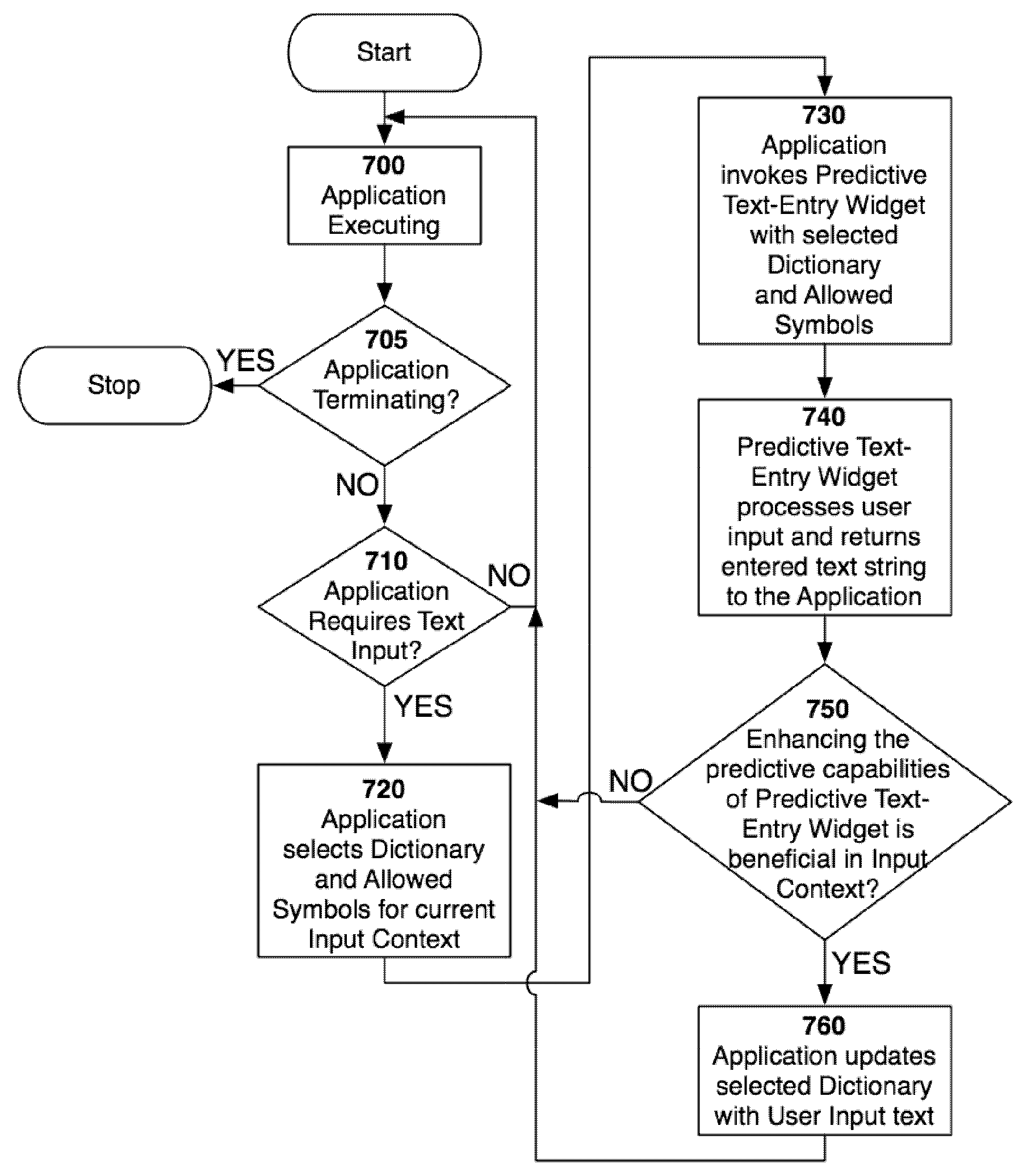
A system and method for supporting predictive text entry in software applications by sharing a common, predictive, software text-entry widget within a consumer device across multiple software applications and input contexts. The method comprises: a software application invoking an instance of a text-entry widget in a particular input context, the application optionally providing the widget a description of allowed symbols and a dictionary of expected symbol strings associated with the current context, the widget modifying a virtual keyboard display and predictive algorithm data according to the allowed symbols and dictionary, the user entering text via the widget, the widget returning the entered text to the application, and the application optionally including information derived from entered text in the associated dictionary to enhance the predictive capability of the widget on future invocations.
Owner:FOURTHWALL MEDIA
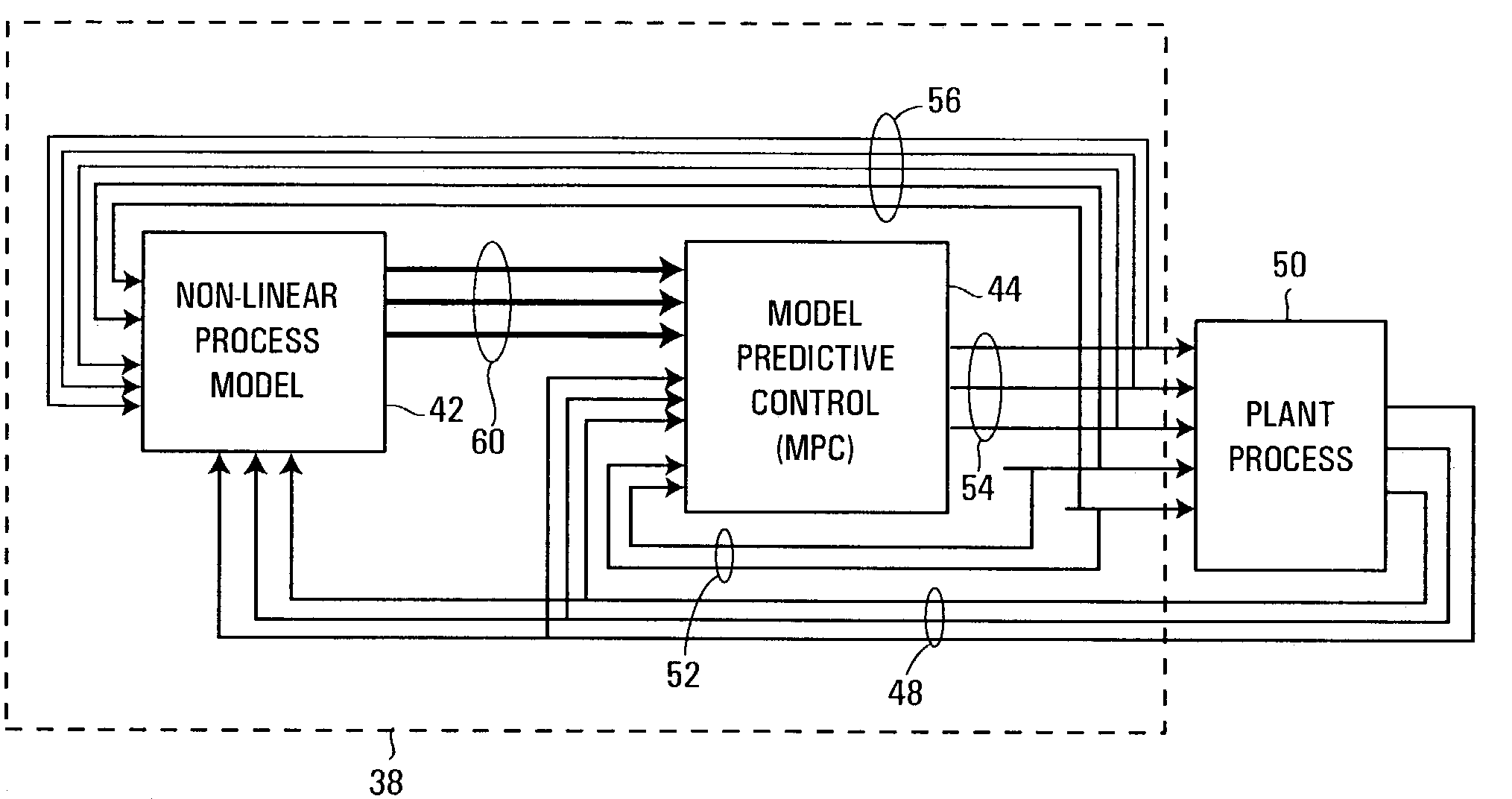
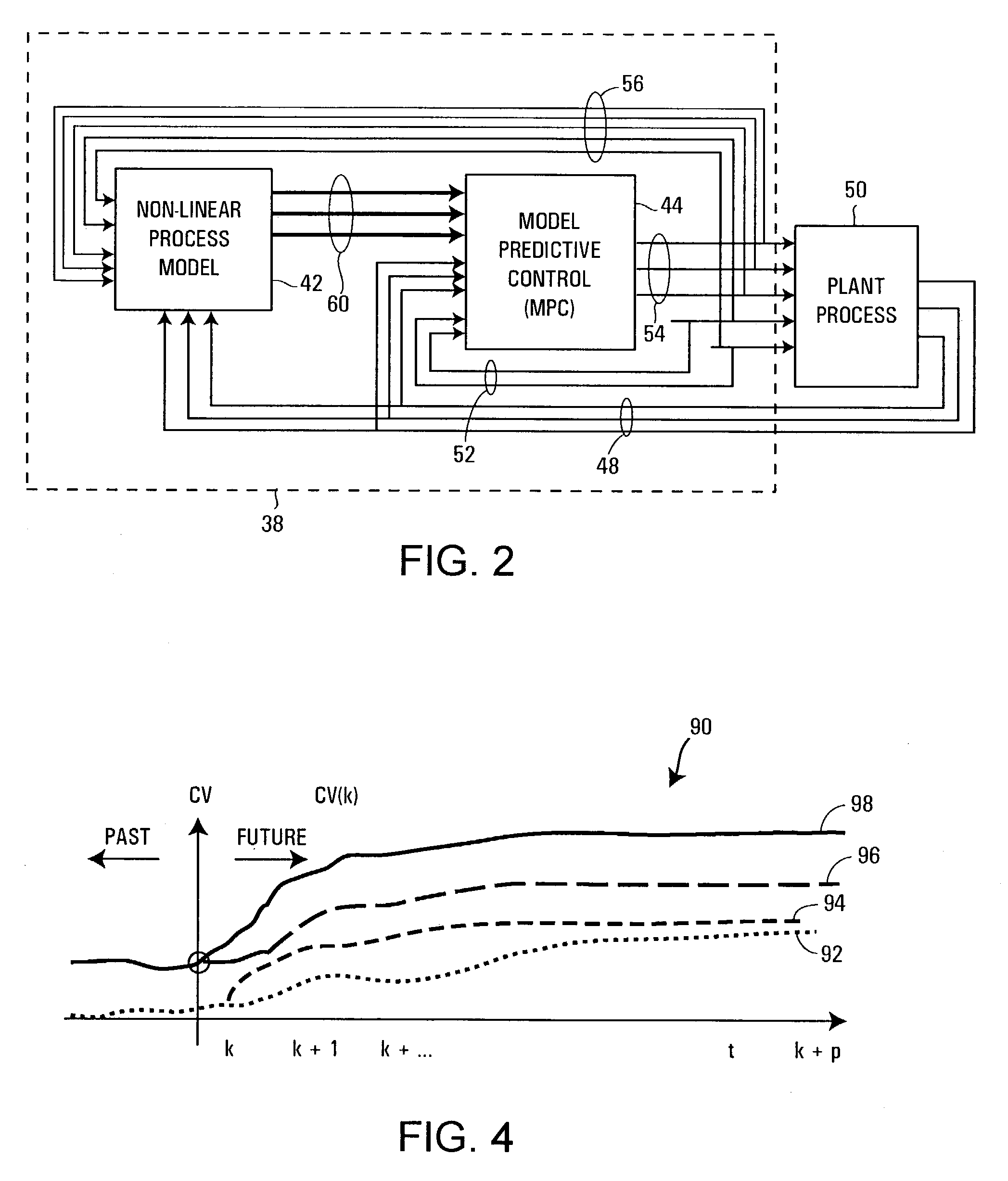
Multiple-input/multiple-output control blocks with non-linear predictive capabilities
ActiveUS7272454B2Easy to implementEasy to useComputer controlElectric testing/monitoringProcess engineeringMultiple input
A process controller that may be used to control a process having a set of process outputs effected by a set of process control input signals includes a multiple-input / multiple output controller that uses the process outputs to develop the set of process control input signals and a process model, which may be a non-linear process model, that receives the set of process control input signals to produce a prediction signal for one or more of the process outputs. The multiple-input / multiple-output control element includes another process model, which may be a standard linear process model, to develop a prediction vector for each of the process outputs and includes a correction unit that modifies the prediction vector for the one or more of the process outputs using the prediction signal for the one or more of the process outputs to thereby compensate for the non-linearities of the process.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
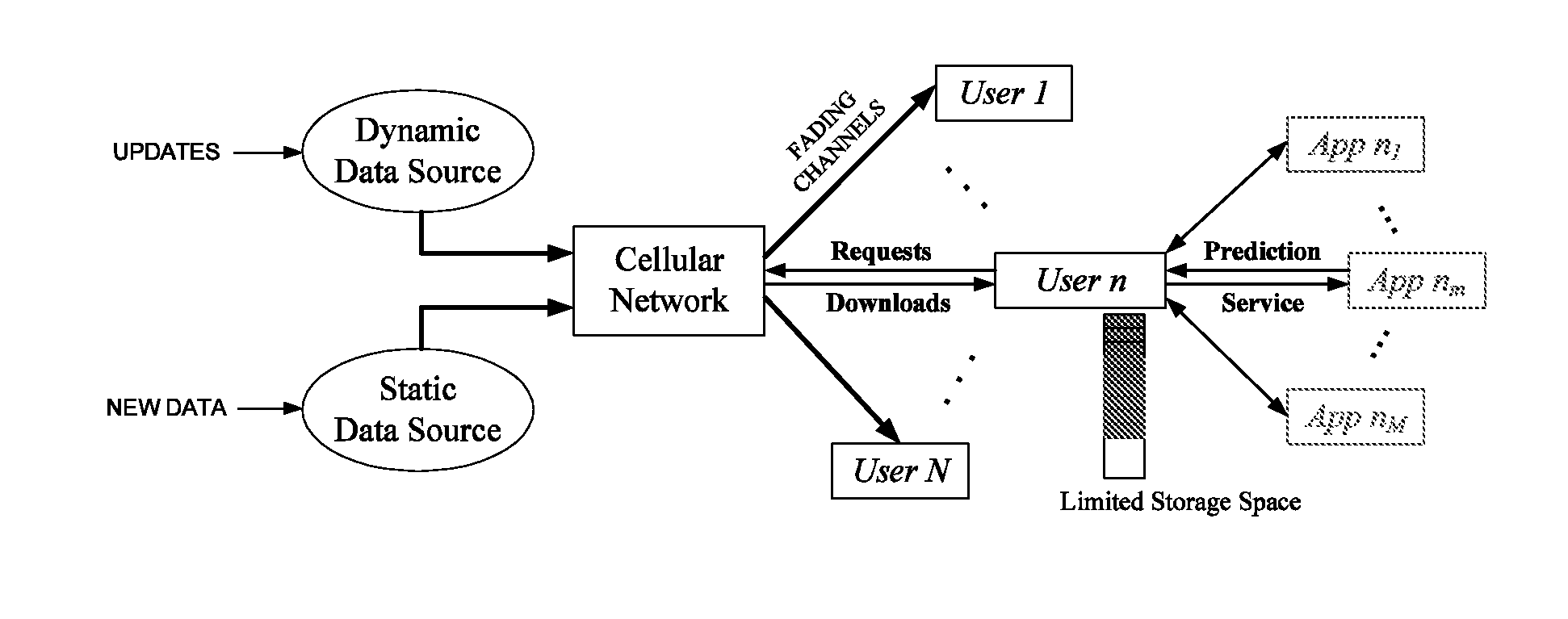
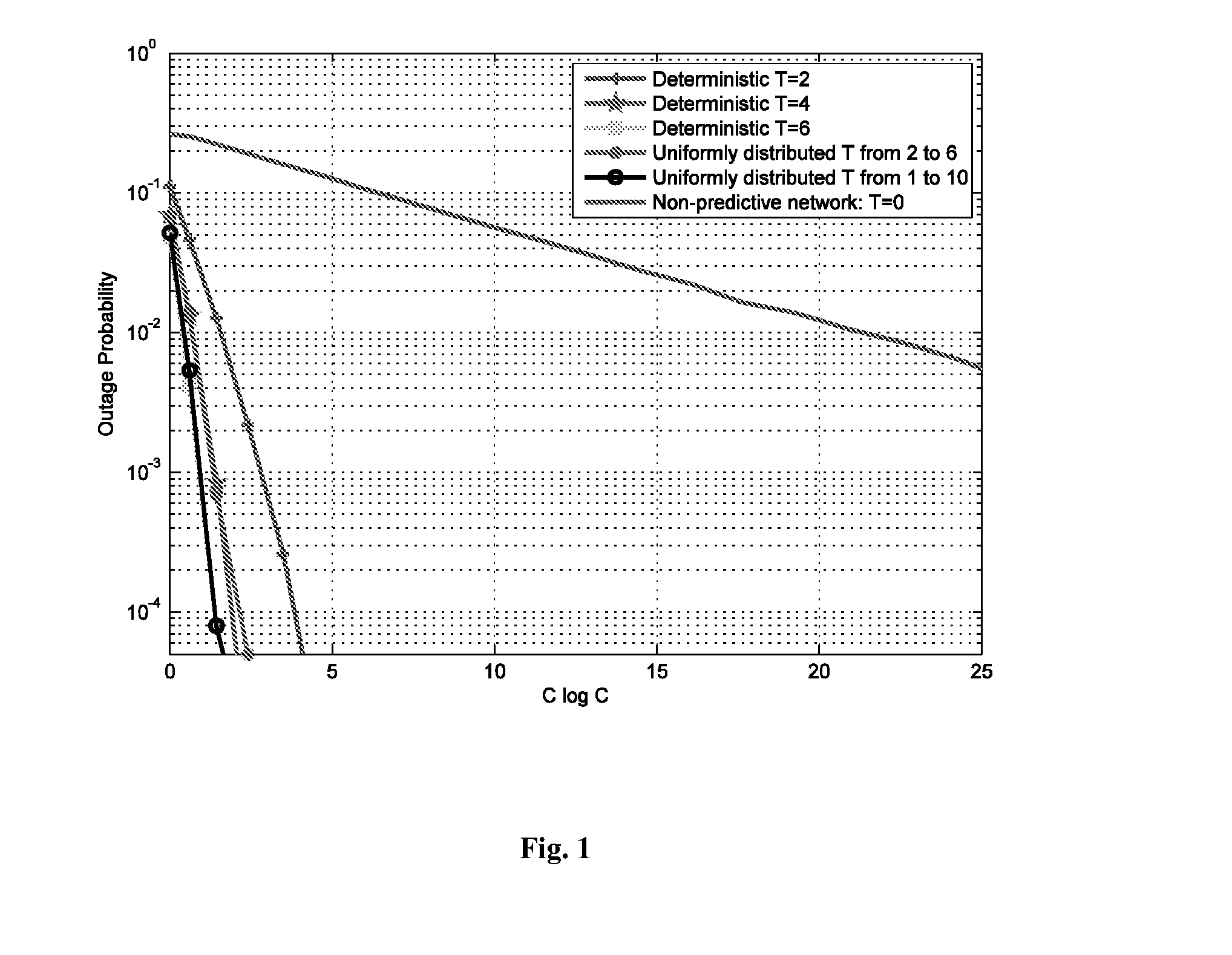
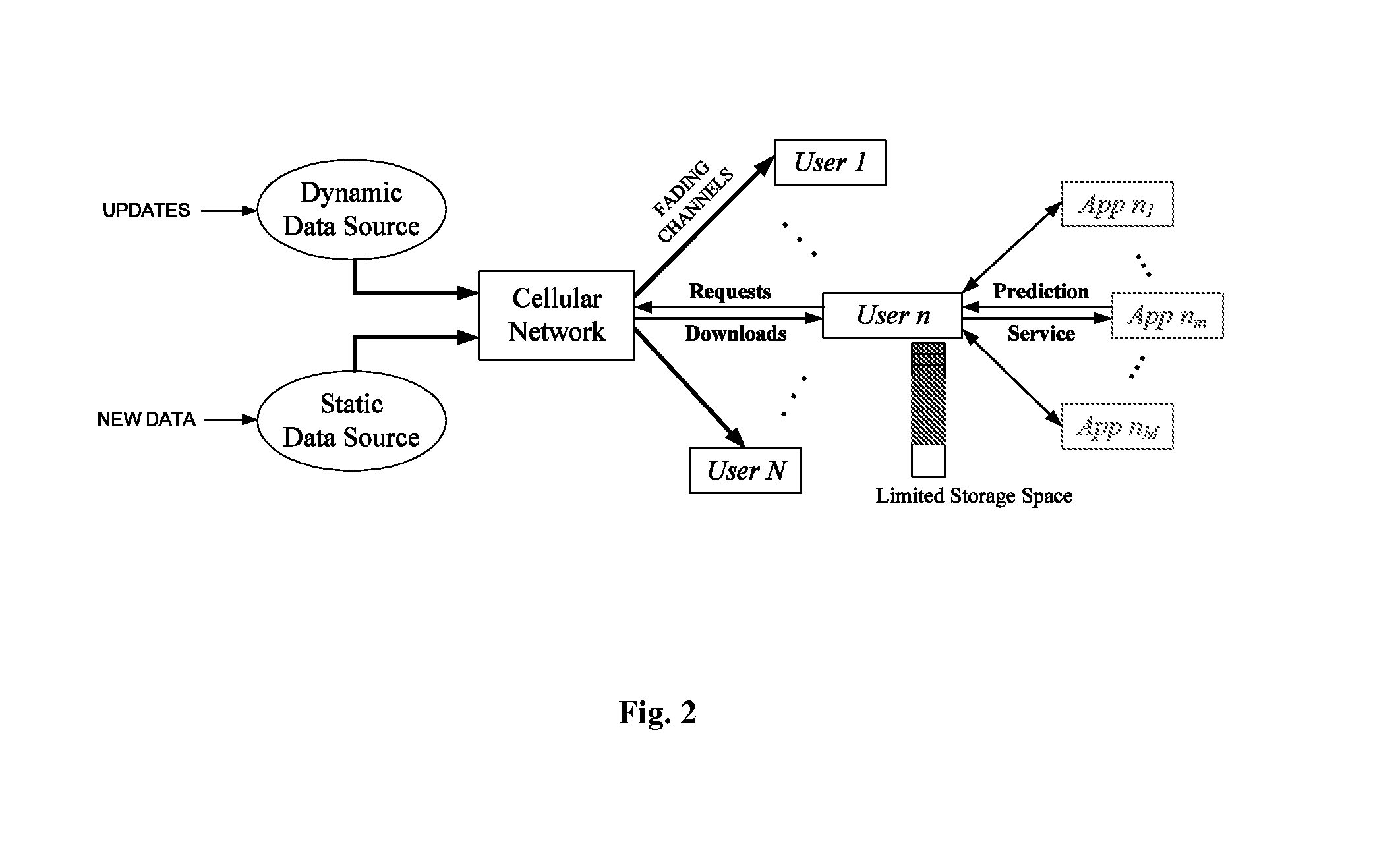
Predictive network system and method
ActiveUS20140113600A1Maximize Spectral EfficiencyReduction in peak to average demand ratioNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksCellular architectureQuality of service
A proactive networking system and method is disclosed. The network anticipates the user demands in advance and utilizes this predictive ability to reduce the peak to average ratio of the wireless traffic and yield significant savings in the required resources to guarantee certain Quality of Service (QoS) metrics. The system and method focuses on the existing cellular architecture and involves the design and analysis of learning algorithms, predictive resource allocation strategies, and incentive techniques to maximize the efficiency of proactive cellular networks. The system and method further involve proactive peer-to-peer (P2P) overlaying, which leverages the spatial and social structure of the network. Machine learning techniques are applied to find the optimal tradeoff between predictions that result in content being retrieved that the user ultimately never requests, and requests that are not anticipated in a timely manner.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Medical billing system and method
A probabilistic medical billing system and method using contextual data and inferential logic for use in screening accuracy of medical bill coding and for presenting results as probabilities or predictions of correctness. The probabilistic medical billing system and method is accomplished using the contextual information contained in a care givers' patient encounter notes, a set of rules and keywords, and an inferential, logic, engine based on Bayesian mathematics or similar disciplines. The inventive device includes an input device to capture care giver's encounter notes or other information, a lexical engine that extracts information while preserving the contextual order of the information, a relational database that contains keywords, phrases and rules and a statistical / probabilistic engine that uses Bayesian mathematics or similar disciplines to create the output. The lexical engine parses a document into words and is capable of extracting keywords or phrases as listed or defined in a master list. Further, the lexical engine would preserve the relative position of discovered keywords or phrases as the keywords or phrases and relative positions were encountered. The Bayesian engine is a mathematical algorithm that uses inferential logic to analyze historical data and shows the results as a predictive level as to the accuracy of a medical bill produced from the source documents. The inherent nature of Bayes like algorithms allows them to learn and improve their predictive capability through the use of a feedback system which is also part of the invention. Variations in algorithms and data flow can be easily made to support other predictive output related to billing or for the purposes of data mining and statistical evaluation.
Owner:COX JAMES
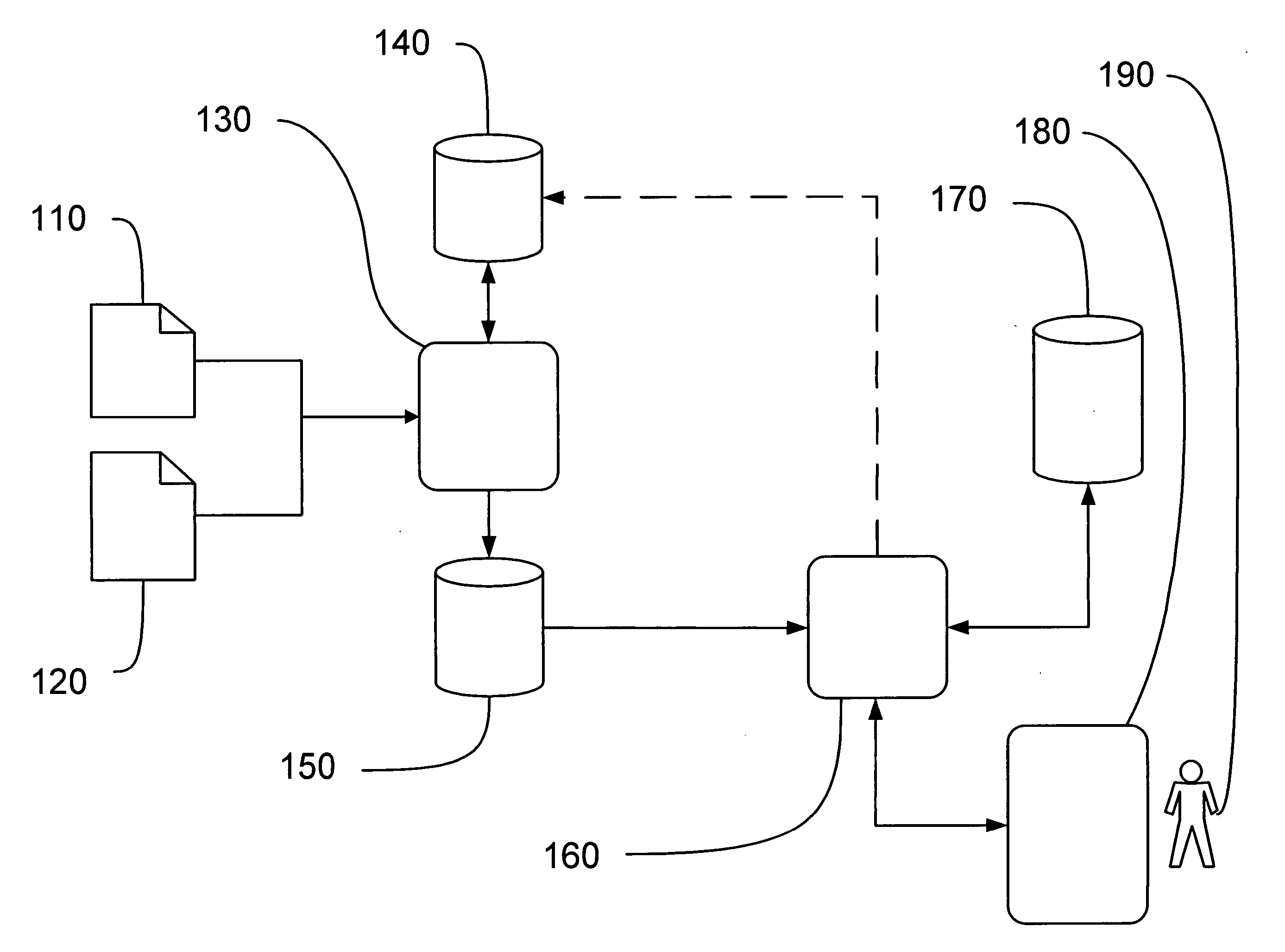
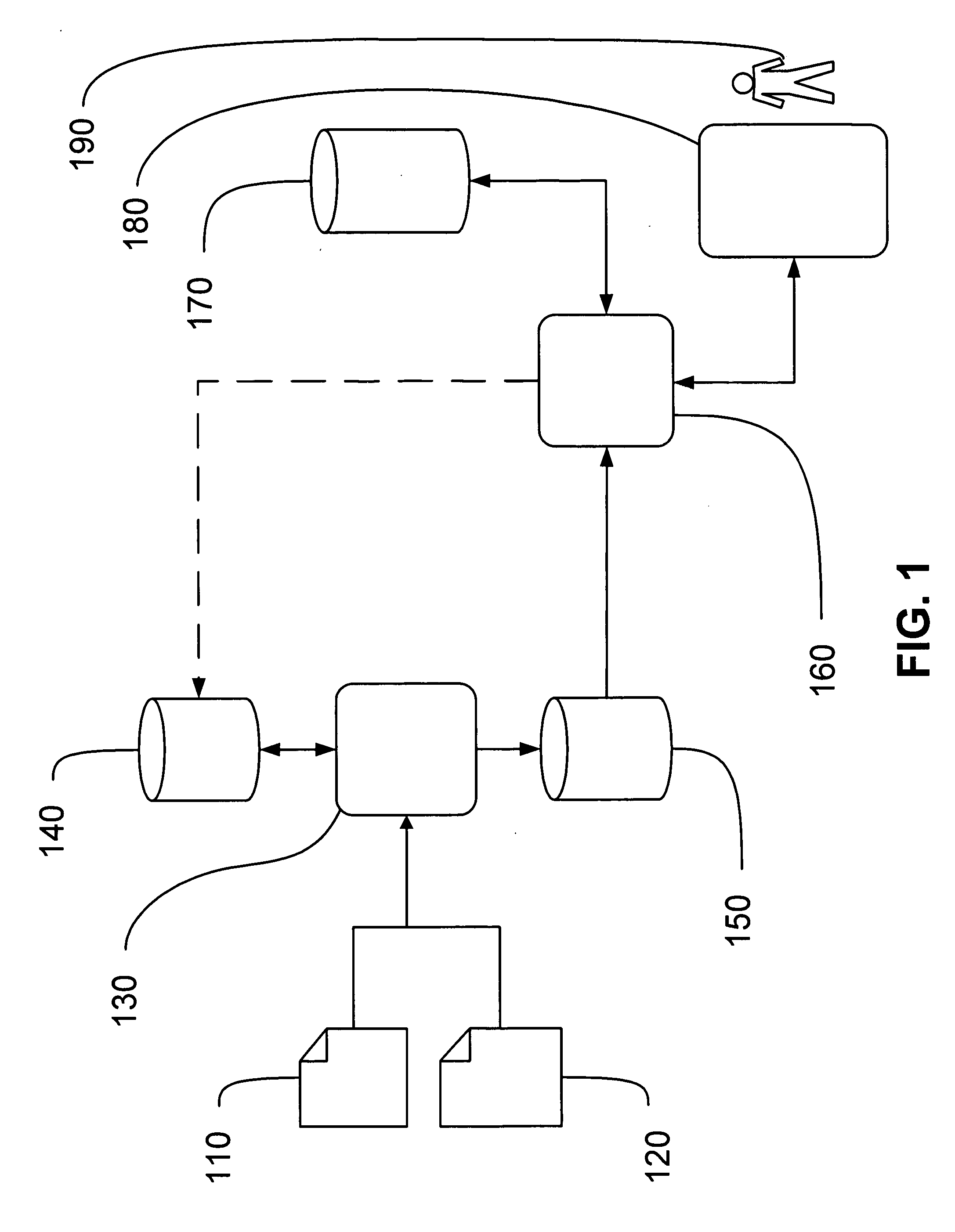
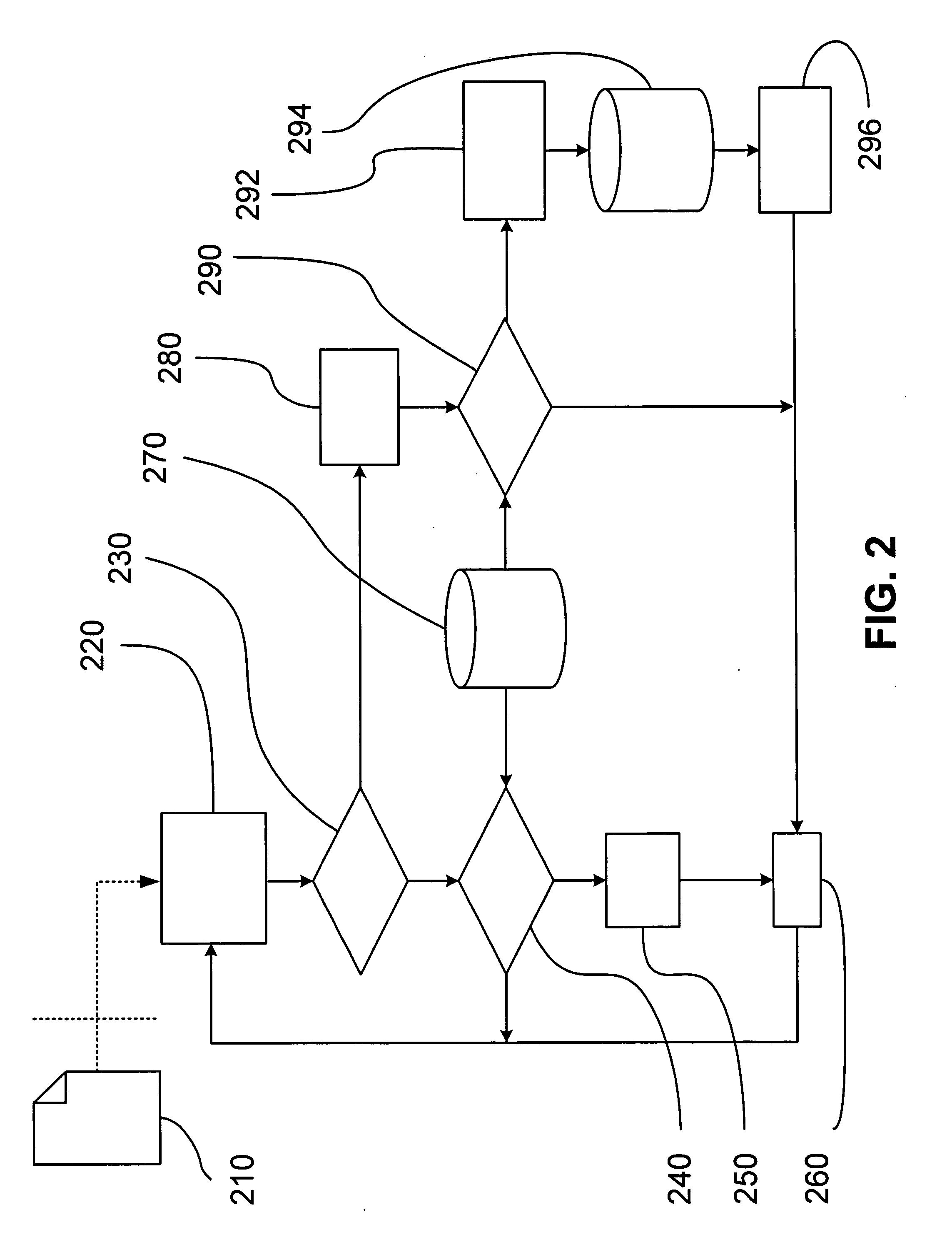
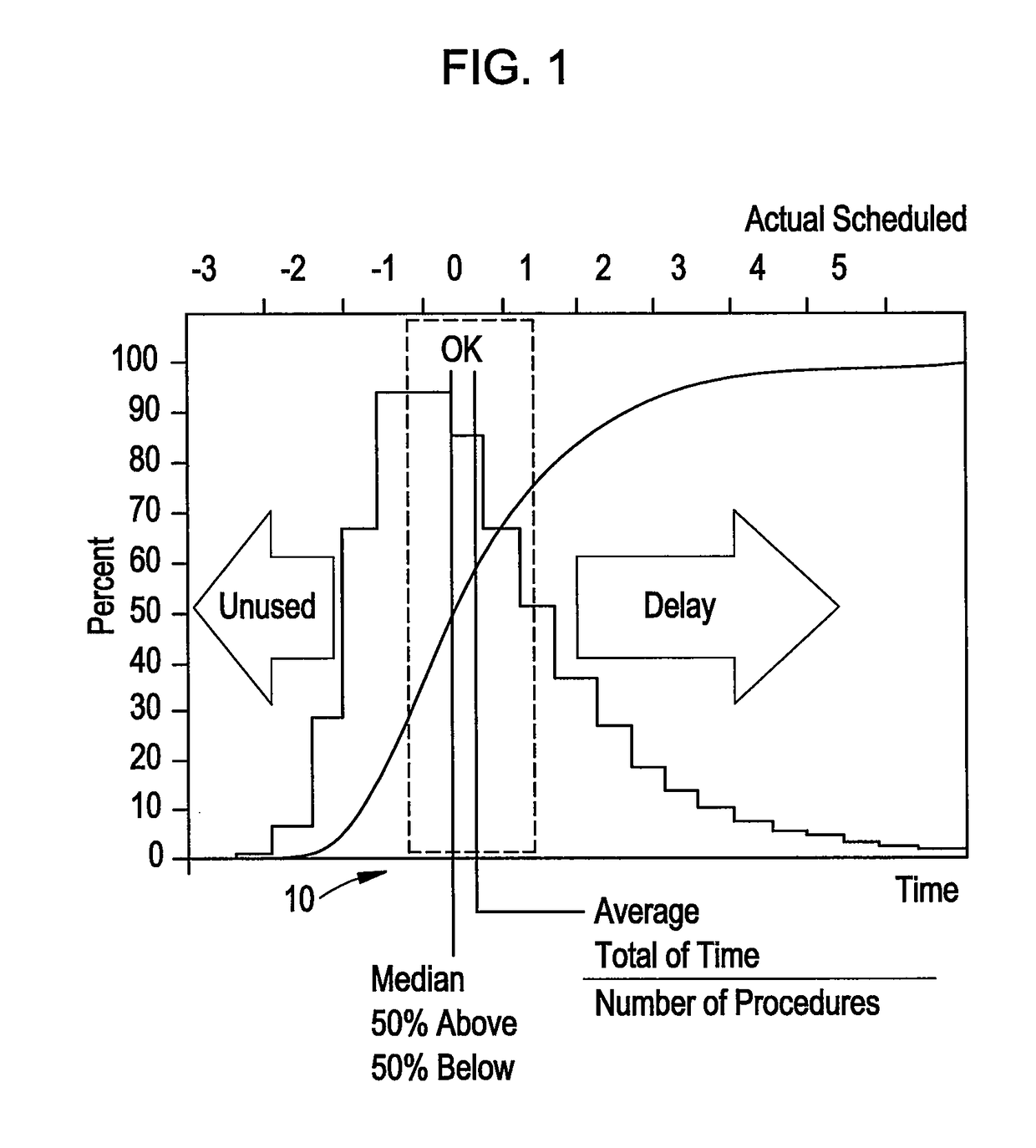
Method to view schedule interdependencies and provide proactive clinical process decision support in day view form
ActiveUS10157355B2Quick scanGreat advantageOffice automationMedical imagesProgram planningREMS Stakeholder
A system and method for use in managing and preparing for scheduled procedures that are characterized as being interdependent and variable. The disclosed method enables schedule risk management and provides a look-ahead capability along with process diagnostics to isolate specific assets and tasks that can be managed to reduce schedule risk. The method facilitates review of upcoming tasks by the process stakeholders for education as to where the schedule risks reside and in an emulation mode for review and improved scheduling going forward. Clinical workflow is integrated such that process stakeholders and assets are directed in such a way as to keep on, reduce delay risk or recover the schedule.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for applying predictive metric analysis for a business monitoring subsystem
InactiveUS20070244738A1Low costImprove healthcareData miningResourcesBusiness managementBusiness process
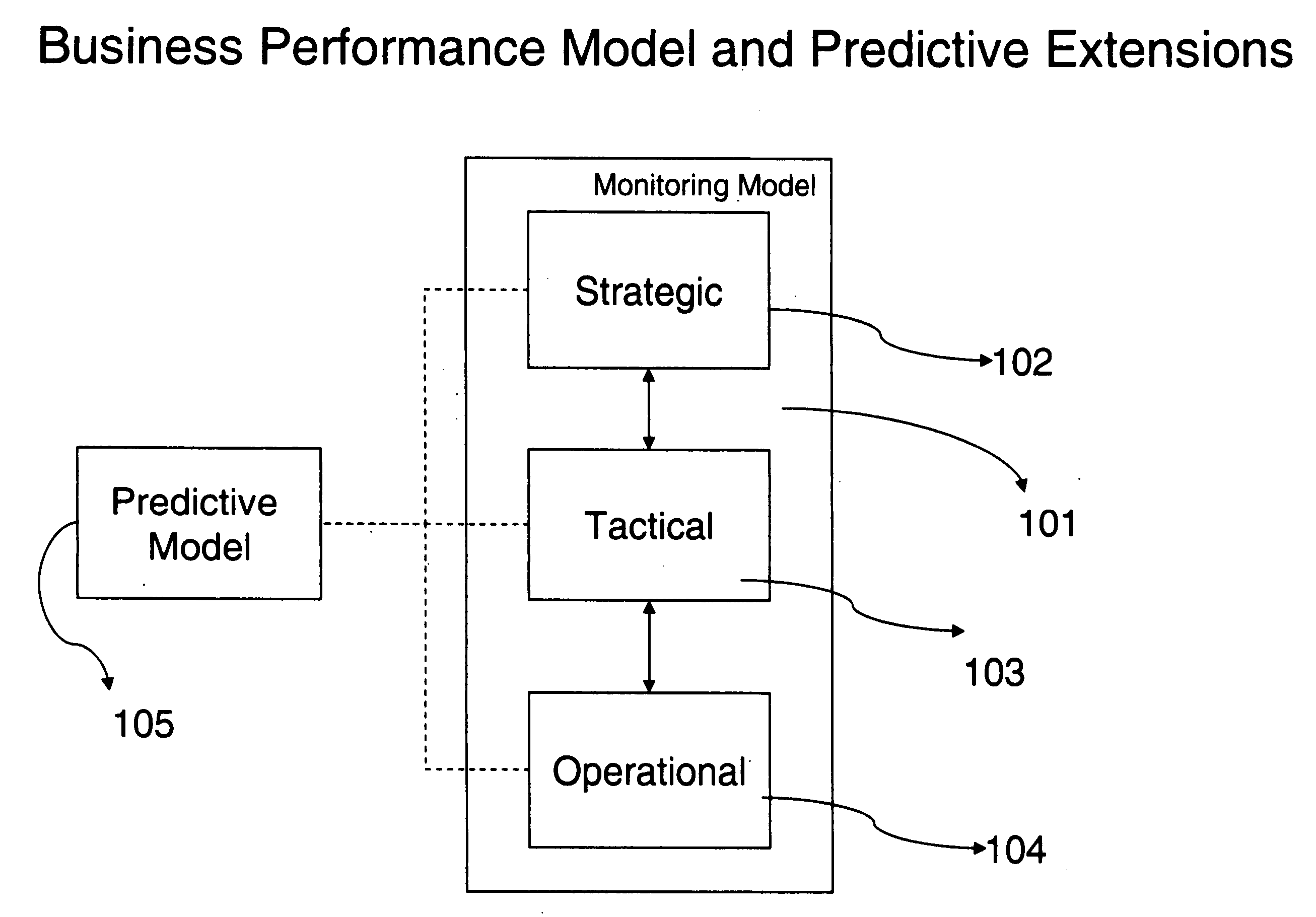
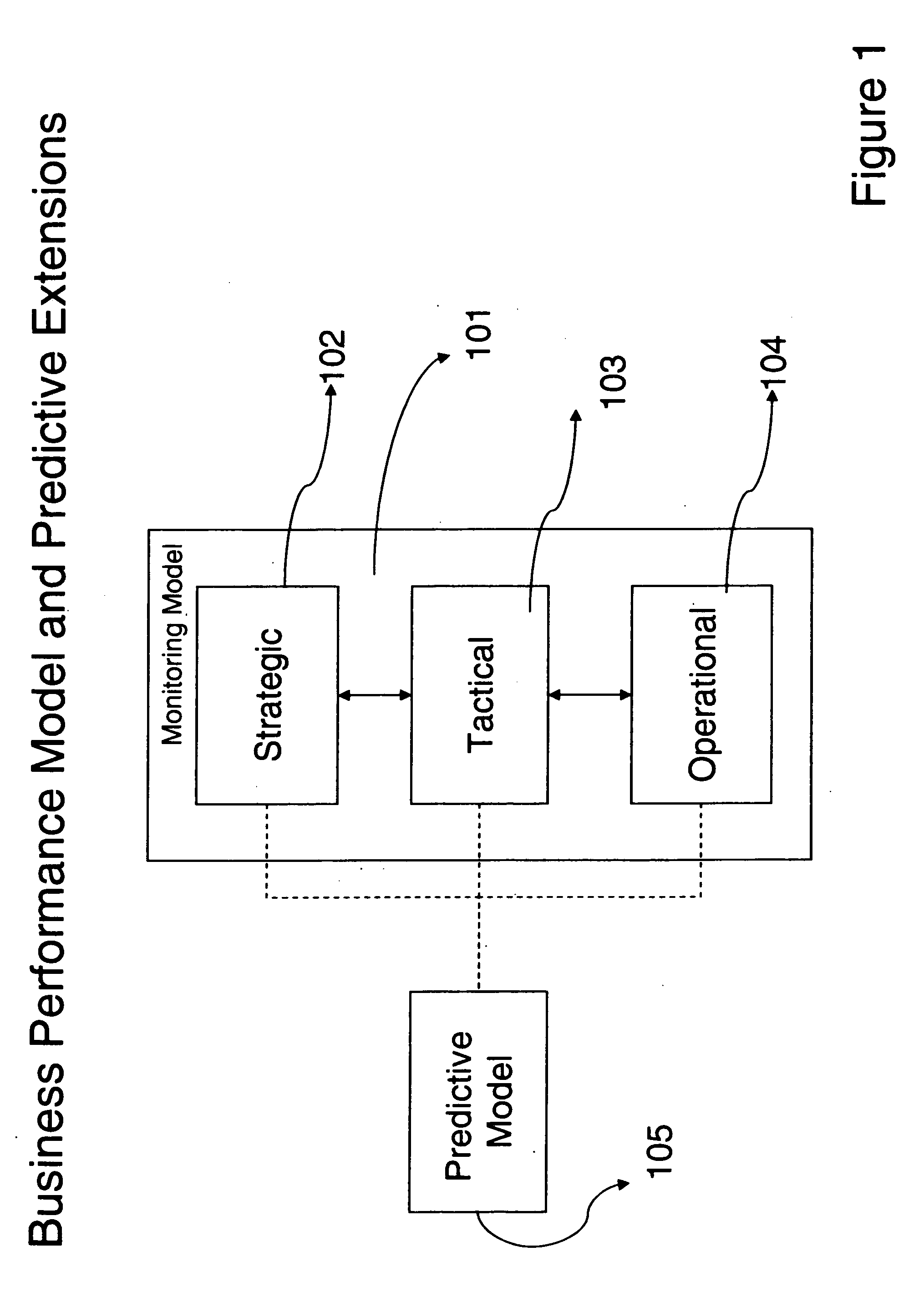
Predictive metric analysis for business management is divided into build time, corresponding to the business owner view of the enterprise, and run time, corresponding to the information technology view of the enterprise. The build time consists of a predictive model and a monitoring model. These models go through transformation processes to the components of the run time. The run time components are a Metric Value Prediction Service (MVPS), which receives as input predictive model transformation and outputs predicted metric values, and a monitoring engine, which receives as input monitoring model transformation, the predicted metric values and business events from the business process. Various analytical engines can be plugged in to provide the predictive capabilities. Input is provided to a framework from various business systems which results in predicting the value of the metrics across the future time horizons.
Owner:IBM CORP
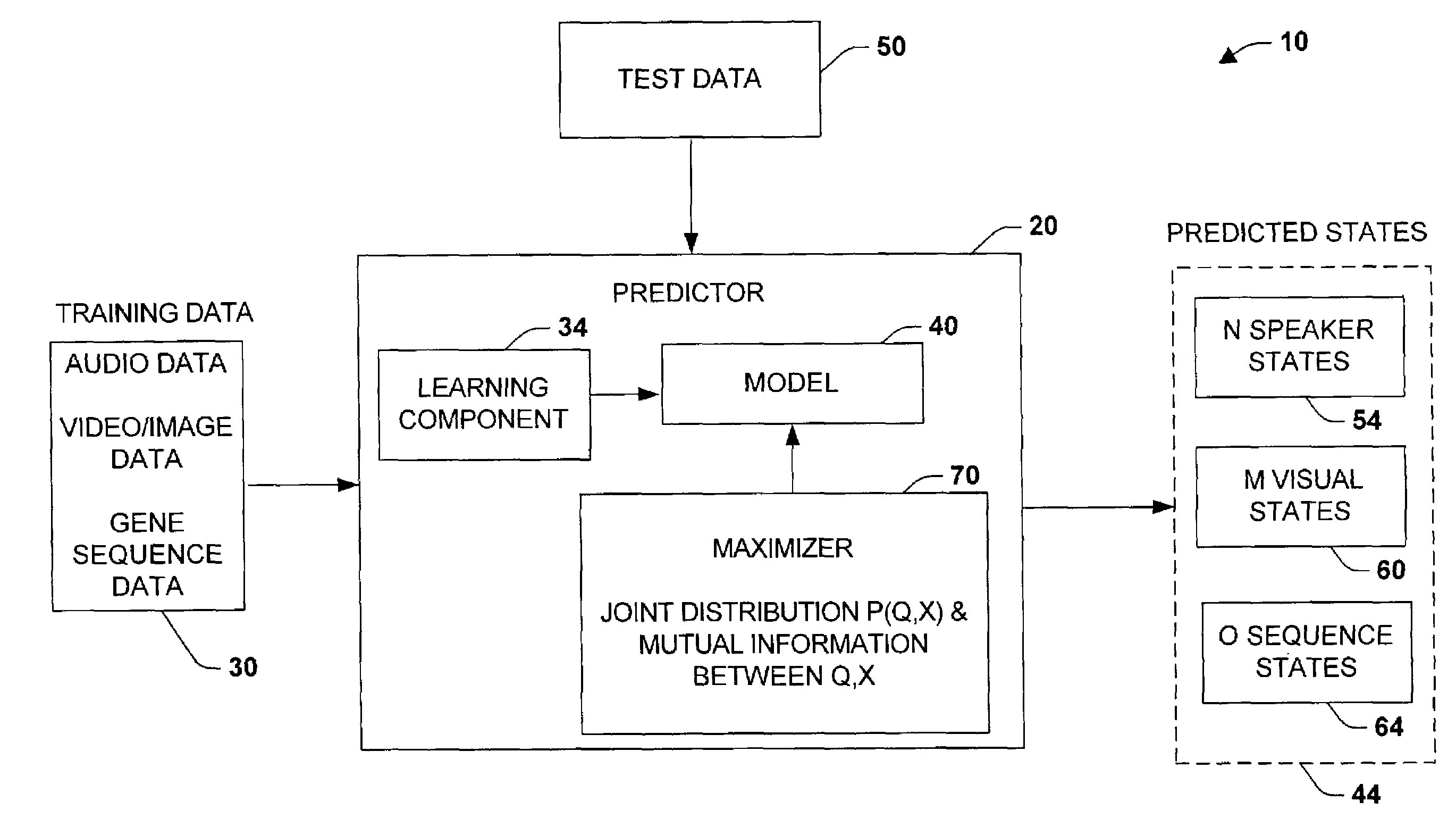
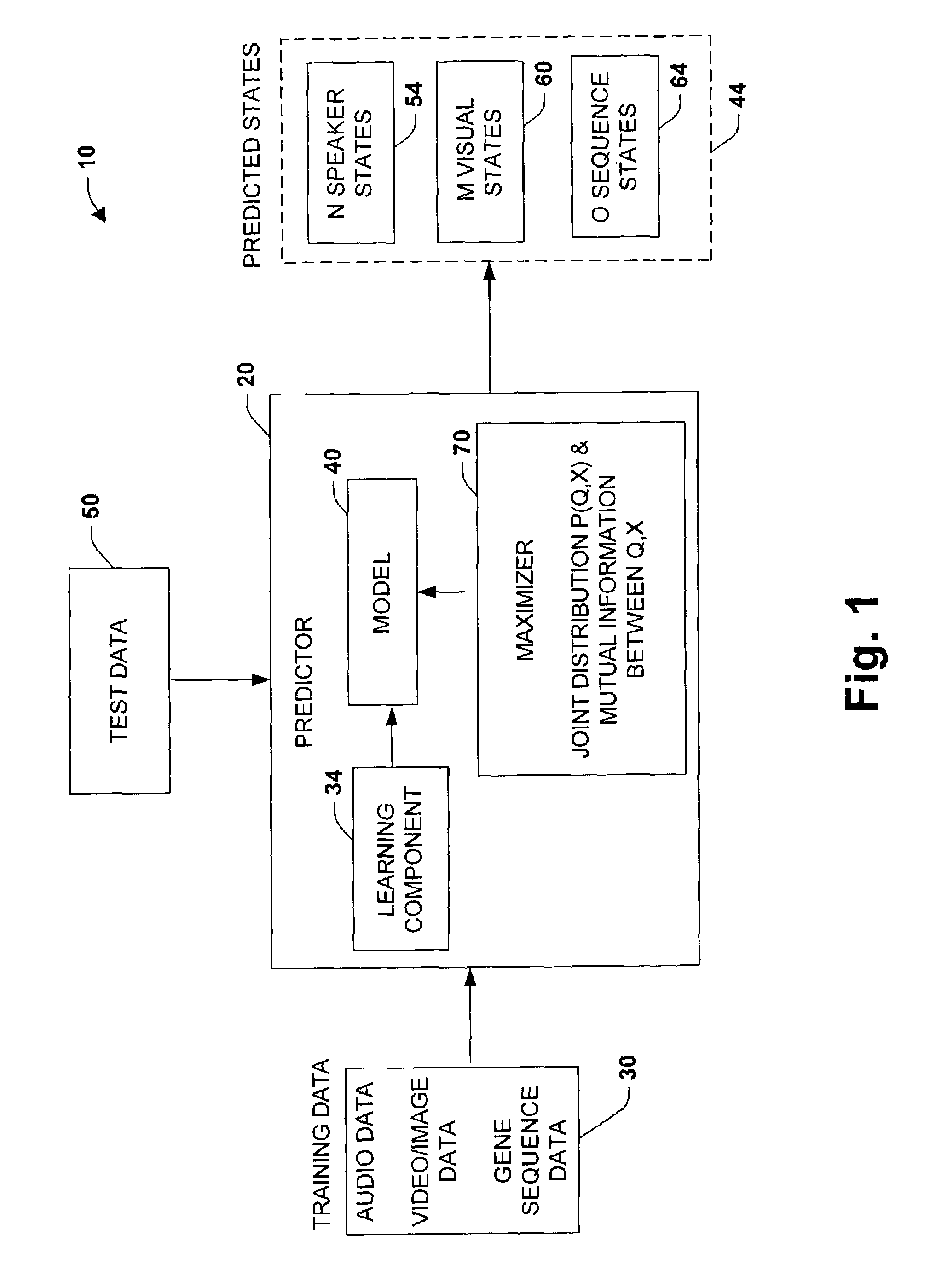
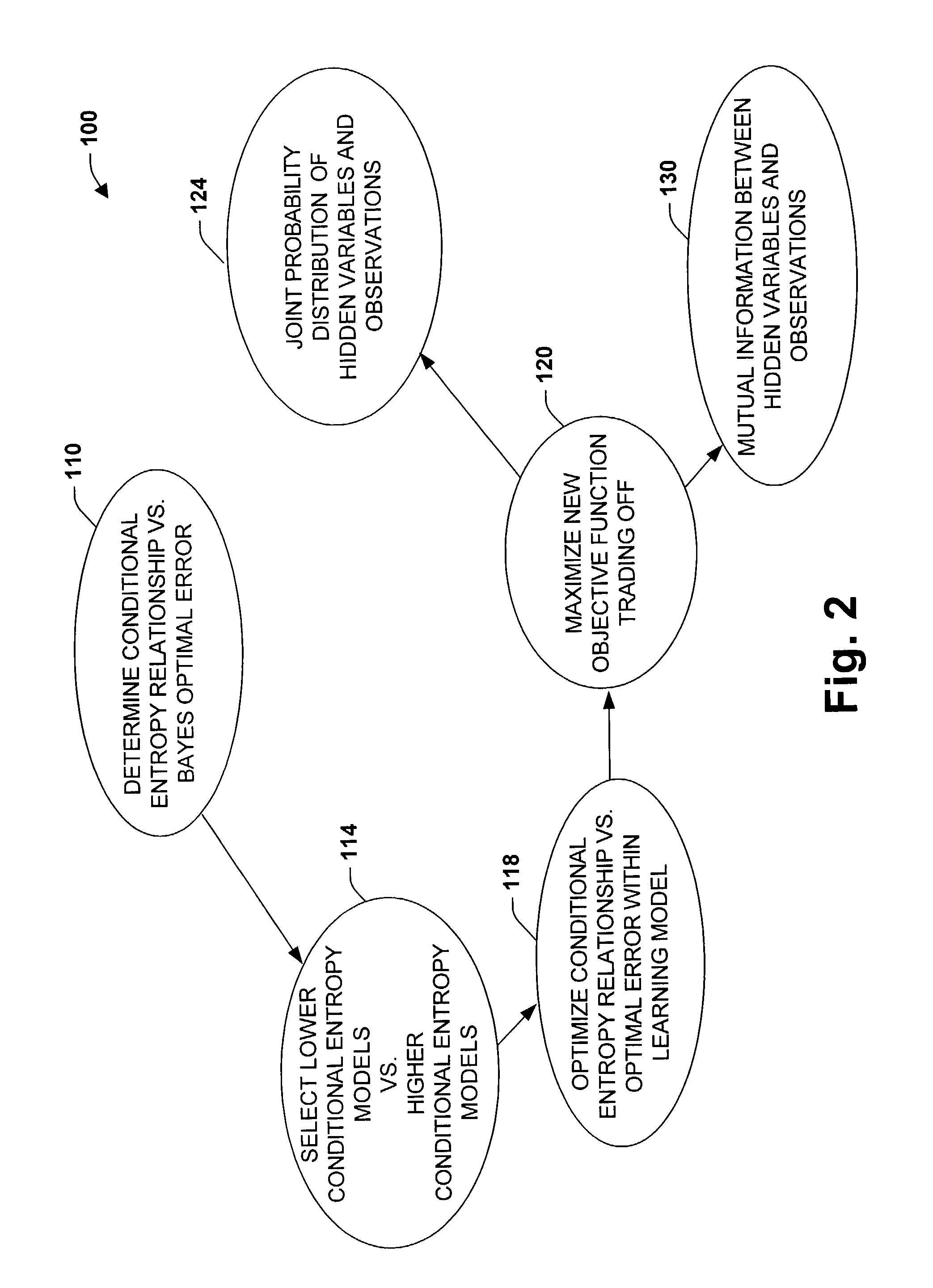
Maximizing mutual information between observations and hidden states to minimize classification errors
ActiveUS7007001B2Facilitate predicting desired informationReduce training requirementsDigital computer detailsSpeech recognitionComputational modelJoint likelihood
The present invention relates to a system and methodology to facilitate machine learning and predictive capabilities in a processing environment. In one aspect of the present invention, a Mutual Information Model is provided to facilitate predictive state determinations in accordance with signal or data analysis, and to mitigate classification error. The model parameters are computed by maximizing a convex combination of the mutual information between hidden states and the observations and the joint likelihood of states and observations in training data. Once the model parameters have been learned, new data can be accurately classified.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Modeling method for boiler combustion optimization
InactiveCN101498459AImprove forecast accuracyImprove generalization abilityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlCombustionModel method
The invention relates to a modeling method of a boiler combustion optimization. The prior method can not solve the problem of boiler combustion optimization. In the invention, segmentation is carried out according to the active parameter load of combustion of a boiler, the load working conditions of similar combustion situations are segmented into one segment, the load working conditions with large differences are separately modeled, and a modeling method which is suitable for small samples and has high generalization ability is adopted for the low load working conditions with less data or extremely low load working conditions; selections which are distributed evenly and equal in quality on a topological structure are carried out for model data before modeling, a proper pretreatment is carried out to guarantee the predictive ability and the generalization ability of models, and finally the models corresponding to the load segments are selected to be optimized according to the load segment where a real load is positioned. The invention overcomes the defects that the traditional modeling method can not carry out modeling for all loads under the conditions that combustion situations are greatly different and guarantees the prediction accuracy and the generalization ability of the models through the data selection and the pretreatment.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
InactiveUS20090319244A1Mathematical modelsAnalogue computers for chemical processesSingular value decompositionData set
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
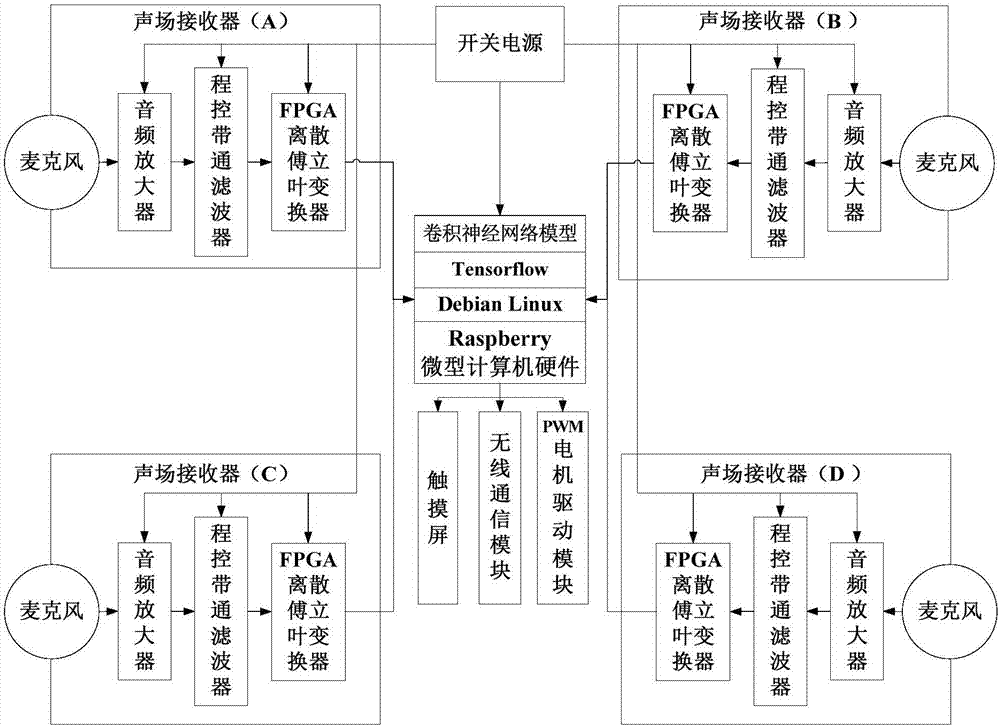
Active detection and recognition system and method for human gait behavior based on semantic folding
PendingCN107423730AEffective estimateAchieve retrievalThree-dimensional object recognitionTime informationVideo retrieval
The invention discloses an active detection and recognition system and method for a human gait behavior based on semantic folding. Embedded gait behavior detection and recognition system hardware with low power consumption is built by using a three-dimensional sound field positioning system, a sole force field positioning system, an HDMI high-definition camera, a high-definition video acquisition system, a microcomputer Raspberry and the like. Gait semantic energy diagrams with timing characteristics provided by the invention contain gait time information under different situations, and the learning and prediction ability of a gait behavior cognition system can be enhanced according to a lot of gait semantic energy diagrams with timing characteristics. Meanwhile, the active detection and recognition technology for a human gait behavior based on semantic folding has extensive application prospects in various fields which mainly comprises the fields such as long-distance identity recognition, abnormal gait behavior detection, pedestrian behavior prediction and mass video retrieval, and has excellent economical and social benefits.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
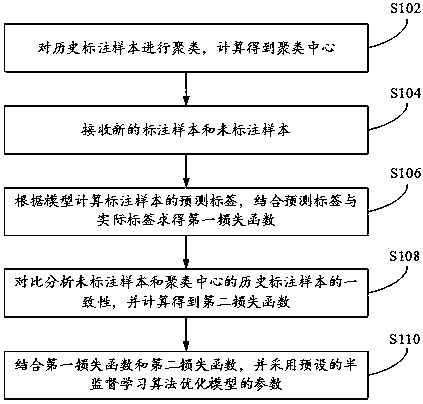
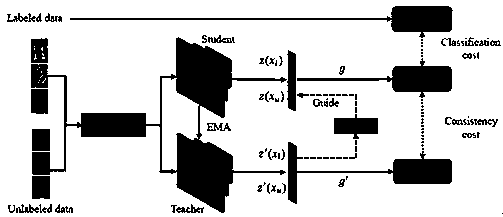
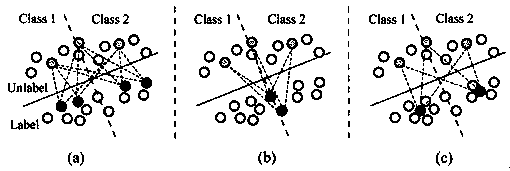
Semi-supervised learning training method and system and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN110298415AImprove predictive performanceLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmSemi-supervised learning
The invention provides a semi-supervised learning training method and system and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the clustering of historical annotation samples, and obtaining a clustering center through calculation; receiving new labeled samples and unlabeled samples; calculating a prediction label of the labeled sample according to the model,and obtaining a first loss function by combining the prediction label and an actual label; comparing and analyzing the consistency of the unlabeled samples and historical labeled samples of the clustering center, and calculating to obtain a second loss function; and optimizing parameters of the model by combining the first loss function and the second loss function and adopting a preset semi-supervised learning algorithm. As long as a small number of samples are labeled, the cost of the labeling process is greatly reduced; a small number of labeled samples are used for guiding a large number of unlabeled samples to carry out feature training, the effect of the unlabeled samples is brought into full play, the training of the model can be further assisted, and the prediction capability of the model is improved.
Owner:视睿(杭州)信息科技有限公司
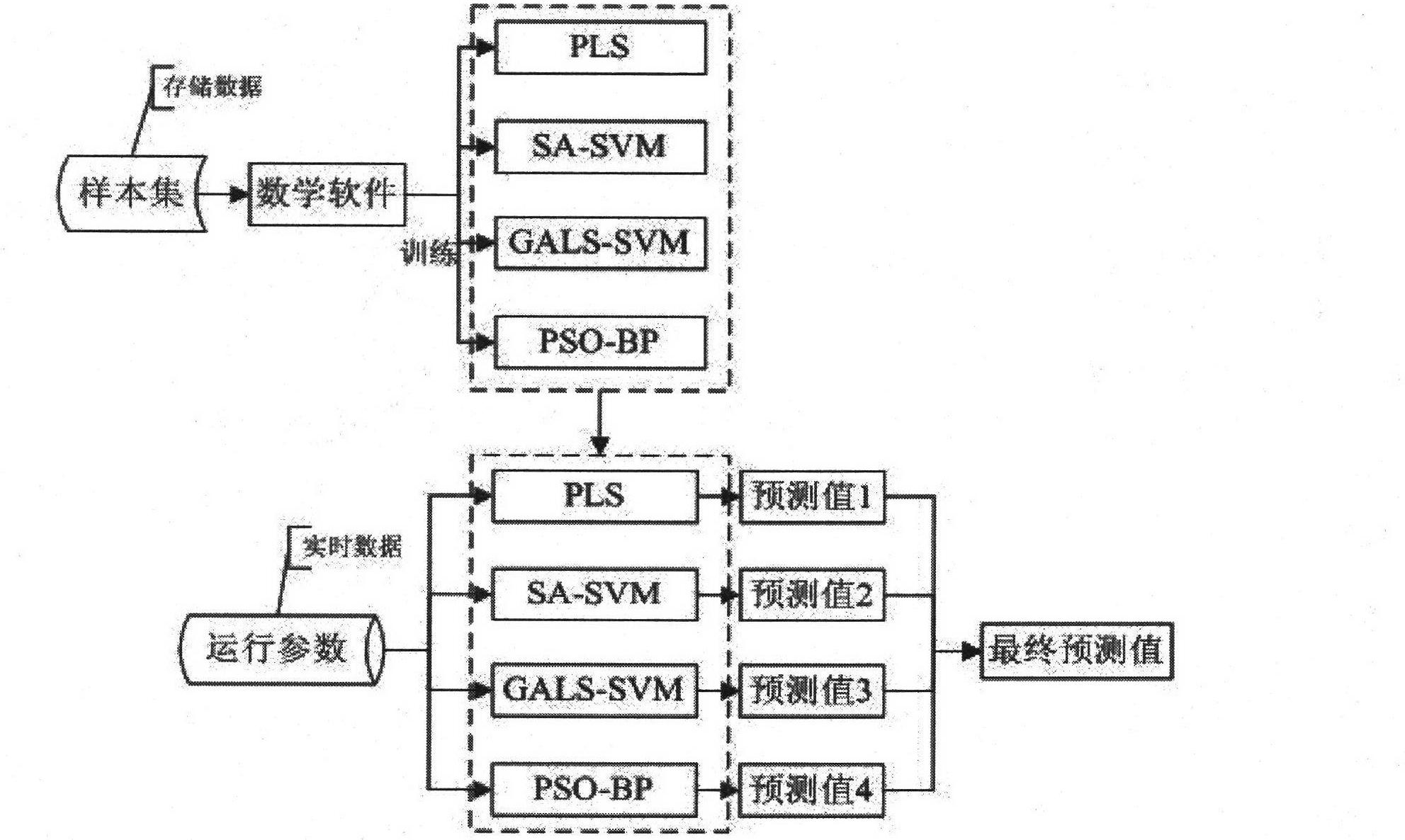
Method for predicting ammonia process flue gas desulphurization efficiency based on multiple parameters
InactiveCN102693451AReal-time monitoring of desulfurization efficiencyThe method is scientific and reasonableDispersed particle separationBiological neural network modelsPredictive methodsSlurry
The invention relates to a method for predicting ammonia process flue gas desulphurization efficiency based on multiple parameters. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: selecting four different artificial intelligent computation models and taking parameters acquired in an ammonia process desulphurization system operational process such as multiple groups of flue gas amounts, flow of a circulating pump, the flow of a concentration pump, the ammonia concentration, the concentration of absorption liquid, the liquid-gas ratio, the inlet flue gas temperature, the ammonia consumption, the density of spraying slurry, the pH value of slurry of a spraying tower and the pH value of the slurry of a pre-washing tower as input variables of the four models; respectively training each model, and establishing a non-linear function relationship between four desulphurization parameters and the desulphurization efficiency; then respectively transmitting parameters monitored in real time into the trained artificial intelligent model, and predicting the desulphurization efficiency; and taking the average value of two predicted values in the middle as a final predicted value... The method disclosed by the invention can be used for better predicting the ammonia process desulphurization efficiency and has the characteristics of higher stability and stronger prediction capability compared with single model prediction.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
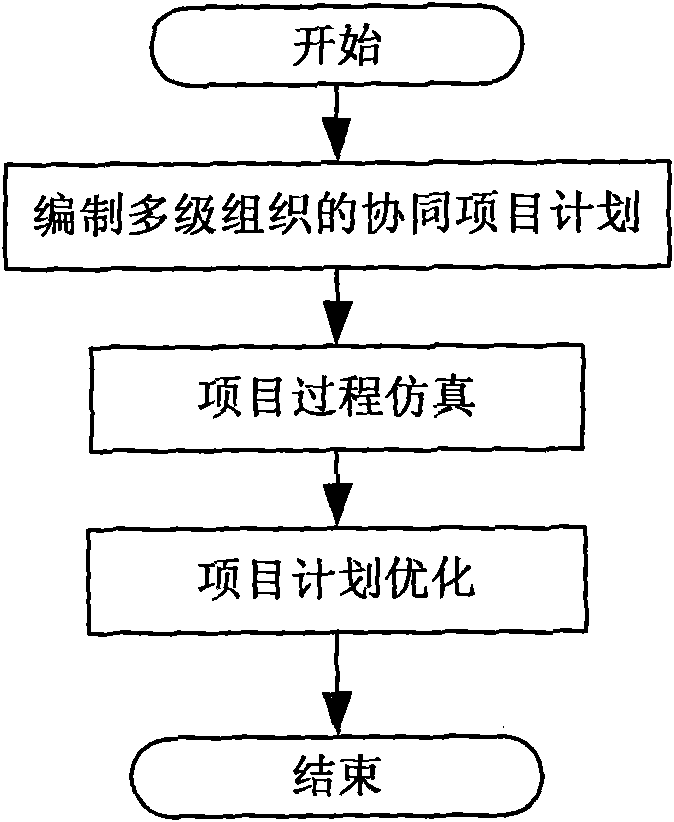
Multi-level collaborative project plan management method
The present invention discloses a multi-level collaborative project plan management method, comprising the following steps of: step 1, drawing up a multi-level organization collaborative project plan; step 2, simulating project execution processes and predicting a construction period; and step 3, optimizing the project plan. The present invention provides a method for the plan collaborative organization of the complex project, improves the organization efficiency and feasibility of the plan, enhances the predicting capability of the project execution process, decreases the regulation for the plan in the project execution process, improves the rationality of the plan formation, reduces the probability of the conflict between the resource demand and the task, and effectively shortens the total construction period of the project.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
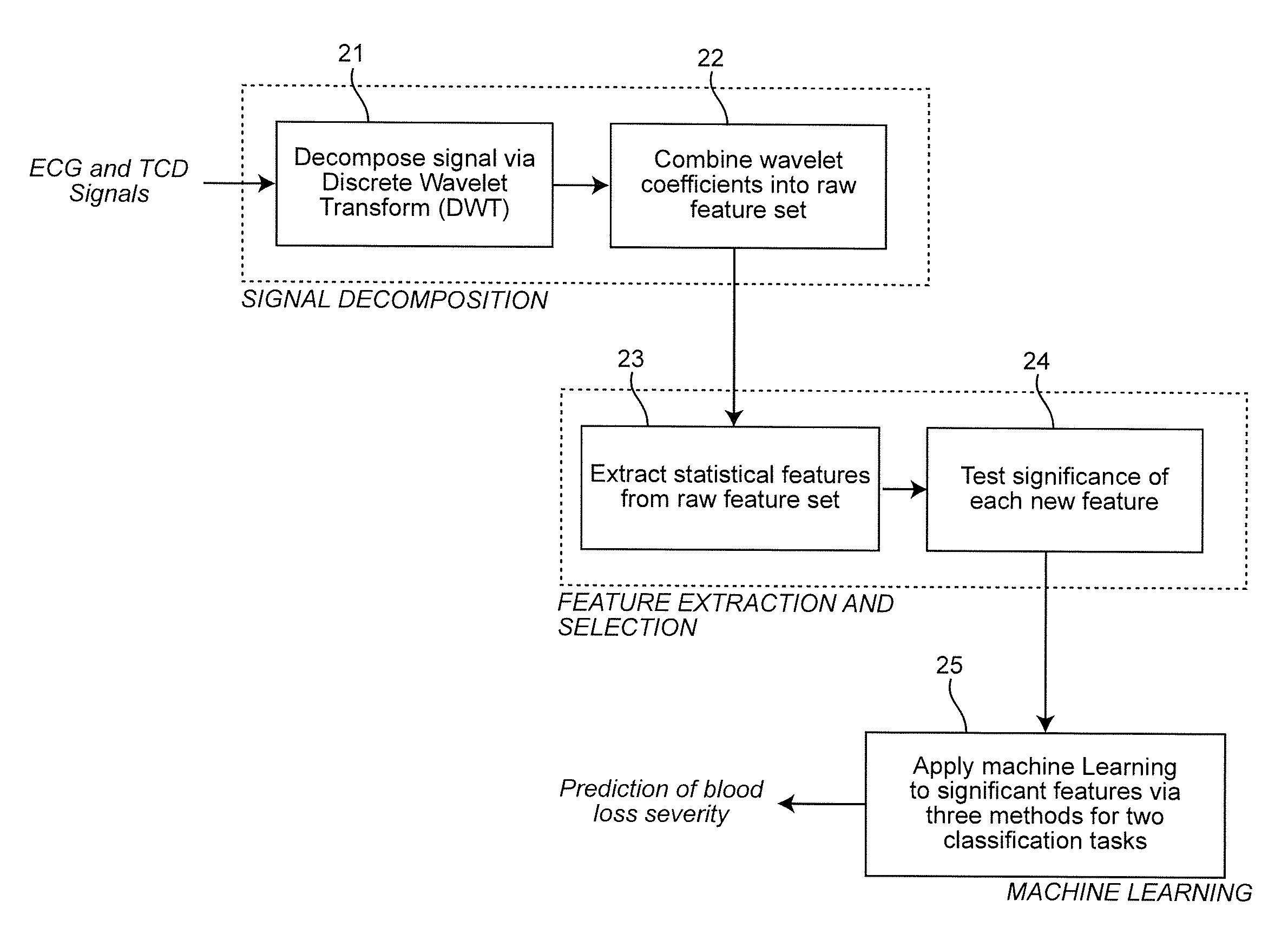
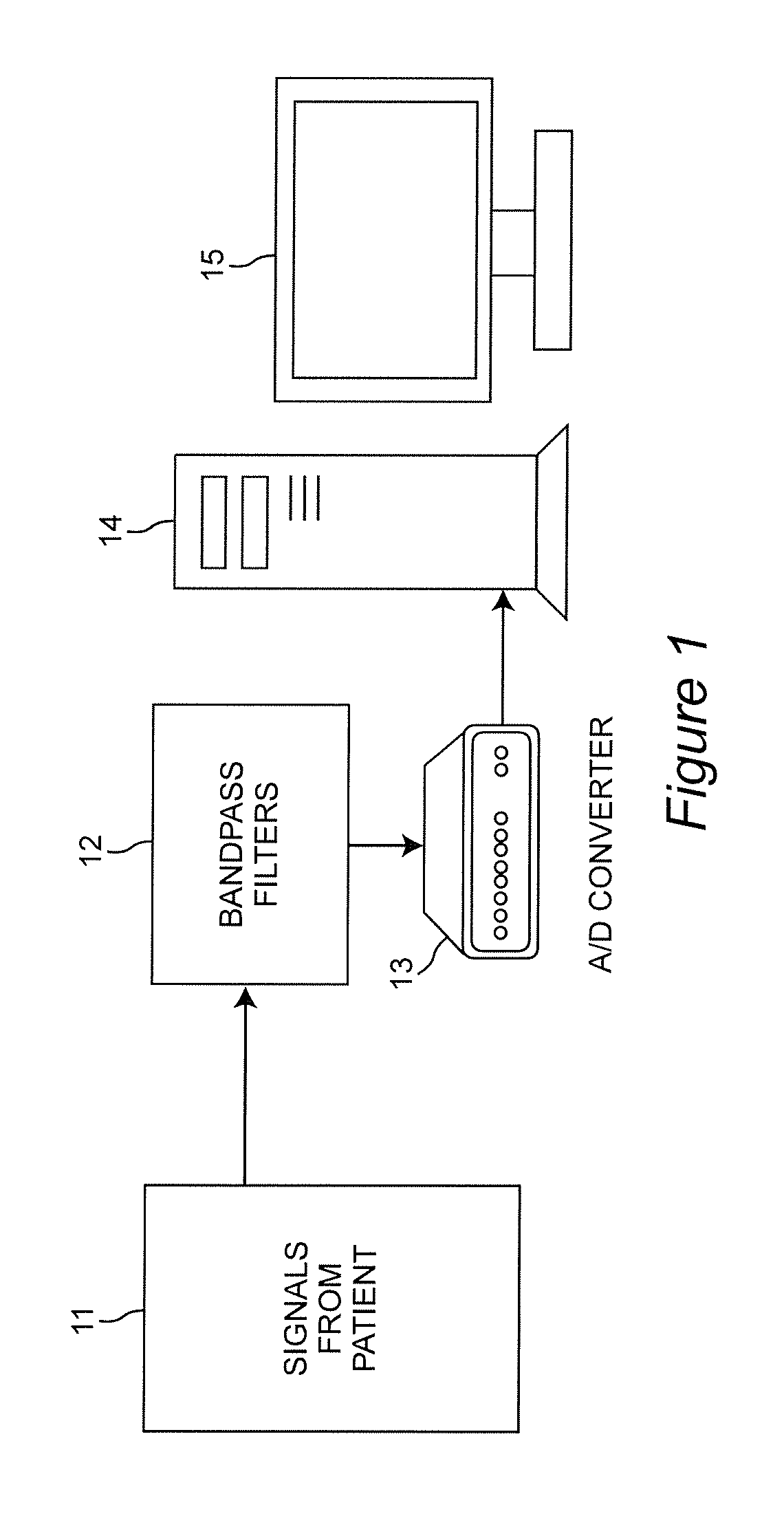
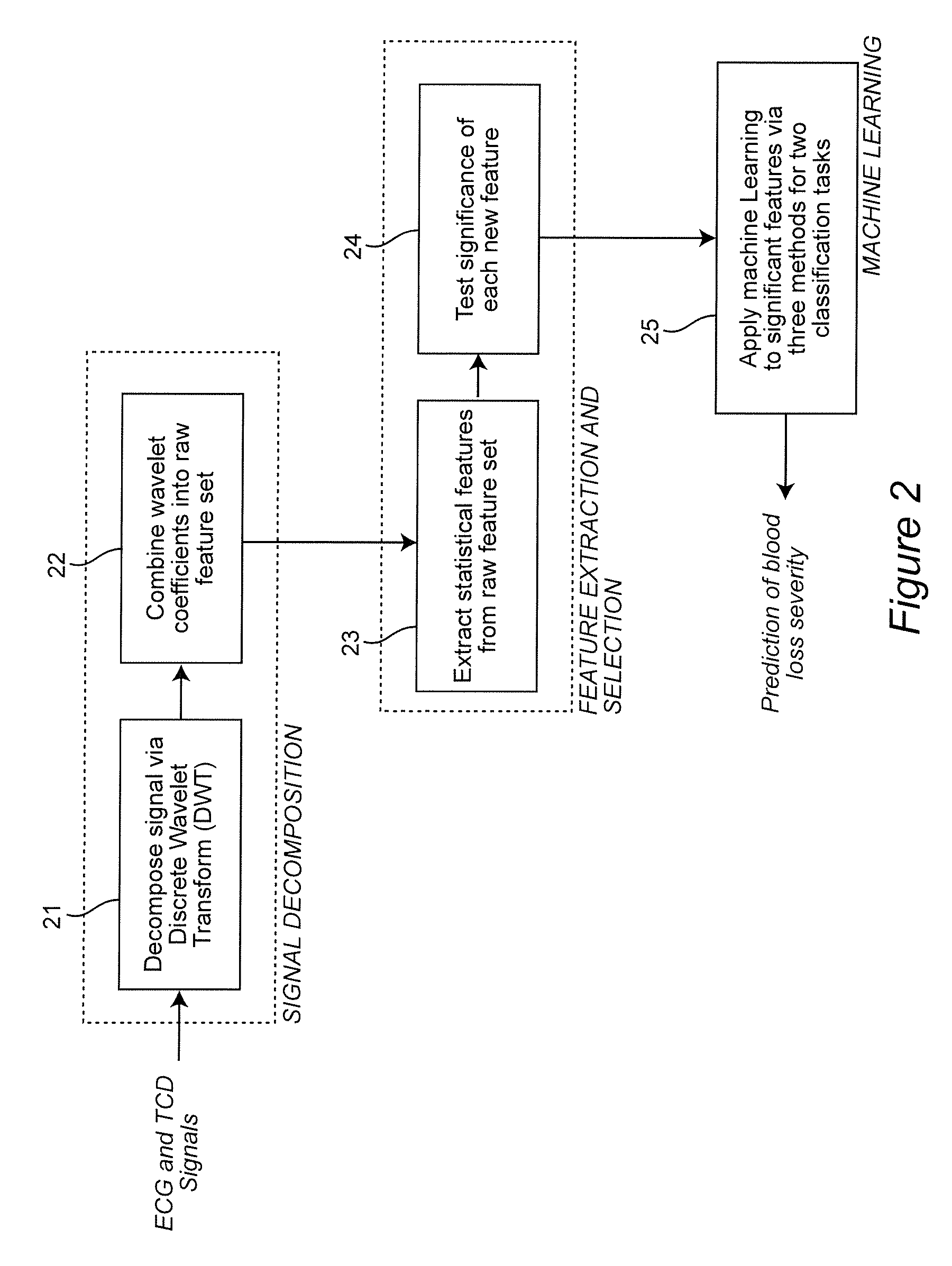
Combining predictive capabilities of Transcranial Doppler (TCD) with Electrocardiogram (ECG) to predict hemorrhagic shock
InactiveUS8762308B2Maximization of survival rateElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDecompositionHypovolemia
A real-time decision-support system predicts hemorrhagic shock of a patient by analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals and transcranial Doppler (TCD) signals from the patient. These signals are subject to signal decomposition using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to sets of wavelet coefficients and selecting significant signal features. Machine learning is applied to the significant features to evaluate and classify hypovolemia severity based on the input ECG and TCD signals from the patient. The classification of blood loss severity is displayed in real-time. An extension of the decision-support system integrates Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) signals and thoracic electrical bio-impedance (DZT) signals with the ECG and TCD signals from the patient to evaluate severity of hypovolemia.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
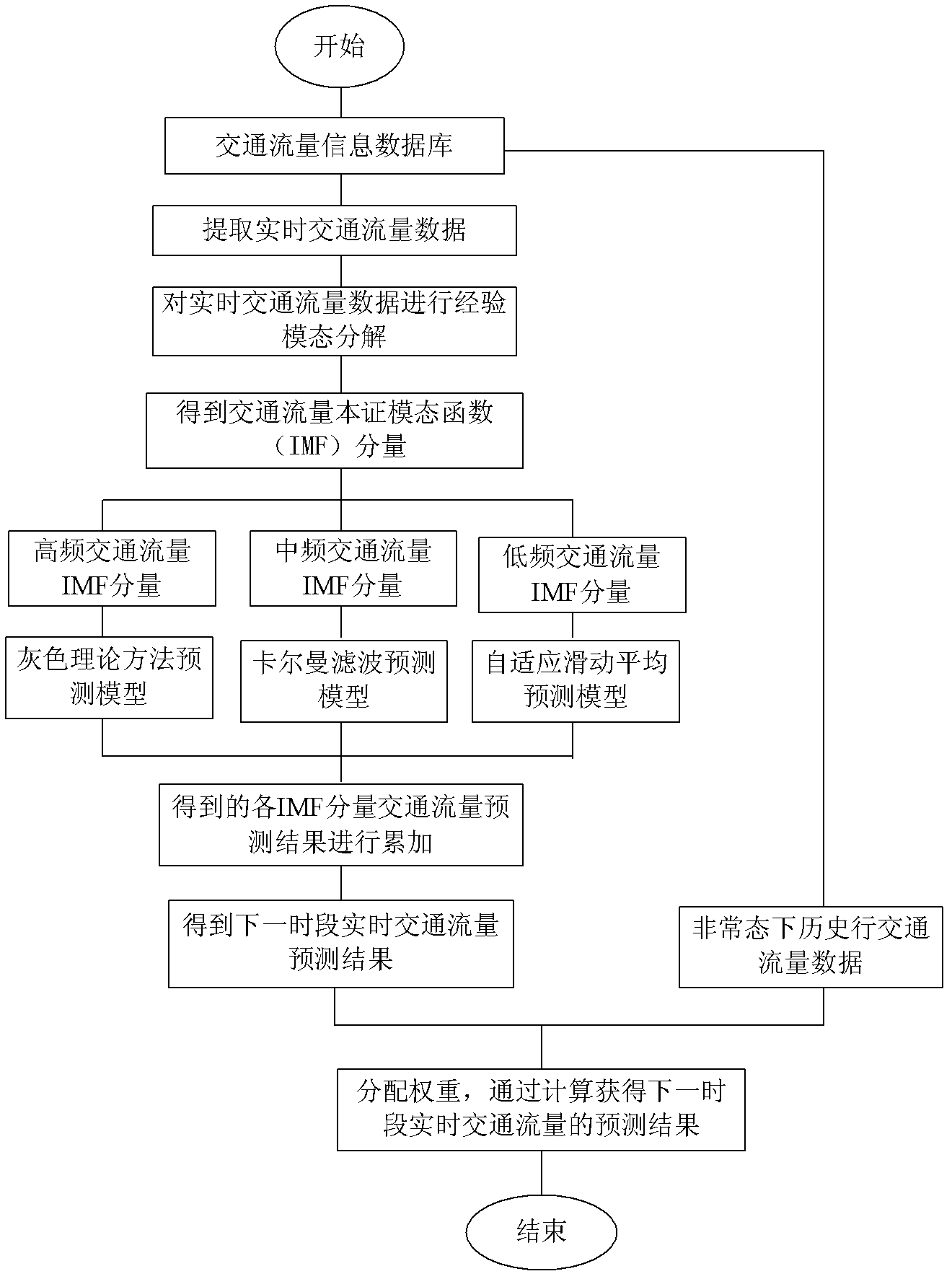
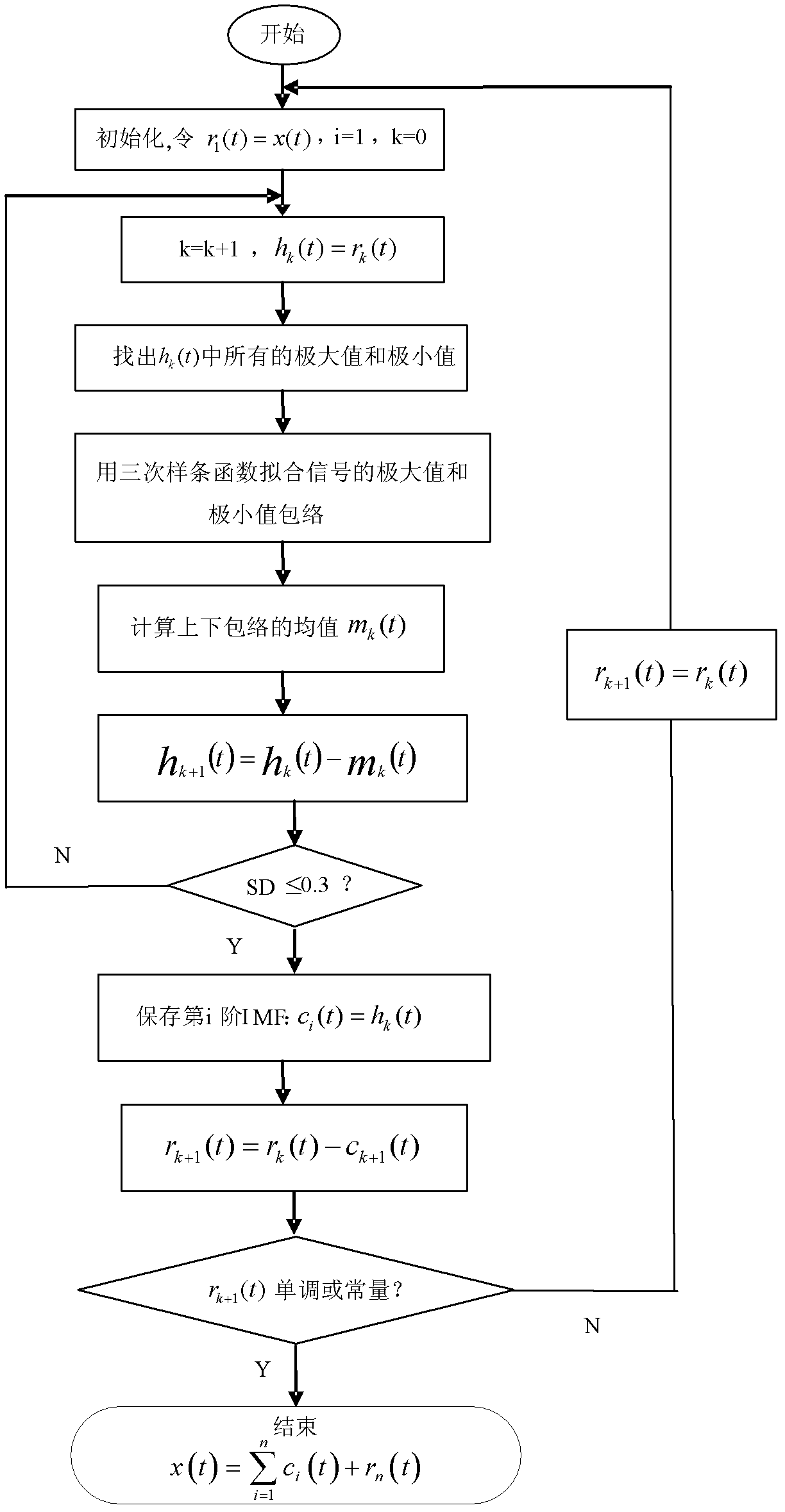
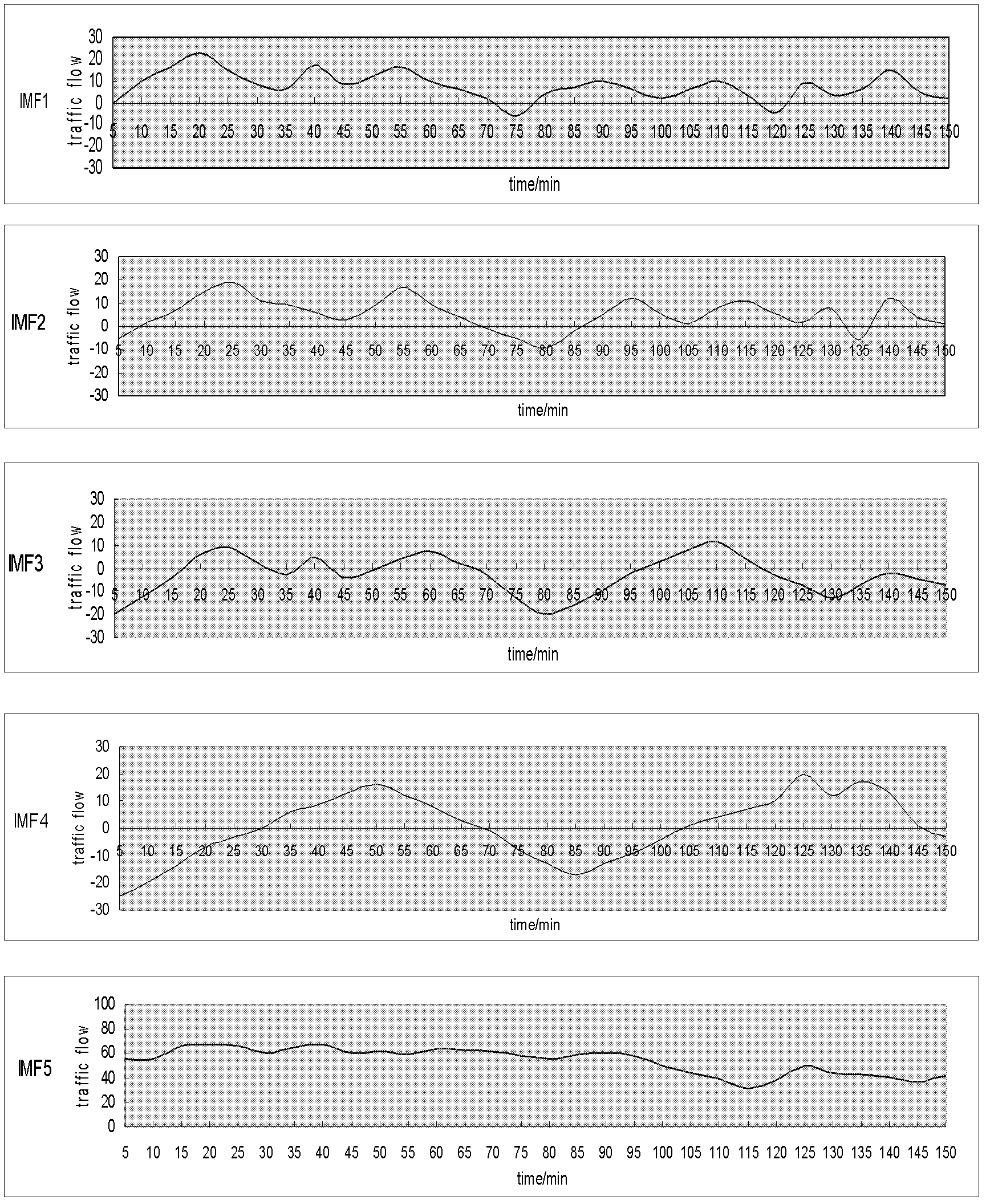
Traffic parameter short-time prediction method based on empirical mode decomposition and classification combination prediction in abnormal state
InactiveCN102568205AHigh precisionReduce distractionsDetection of traffic movementMoving averageDecomposition
A traffic parameter short-time prediction method based on empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and classification combination prediction in an abnormal state relates to the technical field of traffic information. The prediction method includes being combined with the data sequence process method of the EMD, solving unstable data sequence of traffic parameters in an abnormal state into a stable intrinsic mode function (IMF) with multi-scale features; constructing a filter bank based on EMD filtering characteristics, reorganizing the IMF into high-frequency filtering, medium-frequency filtering, and low-frequency filtering; according to different characteristics of the IMF of each group, performing predictions by using the grey theory, kalman filtering and auto regressive moving average (ARMA) model respectively; accumulating results of all the groups to generate real-time predicting results of the traffic parameters of next time interval; and according to the real-time predicting results of the traffic parameters and historical data in the abnormal state, and performing multistep prediction so as to obtain a final predicting result of the traffic parameters and a future development tendency. The traffic parameter short-time prediction method based on the EMD and the classification combination prediction in the abnormal state has a better predicting capacity on the traffic parameters in the abnormal state and a future variation tendency.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
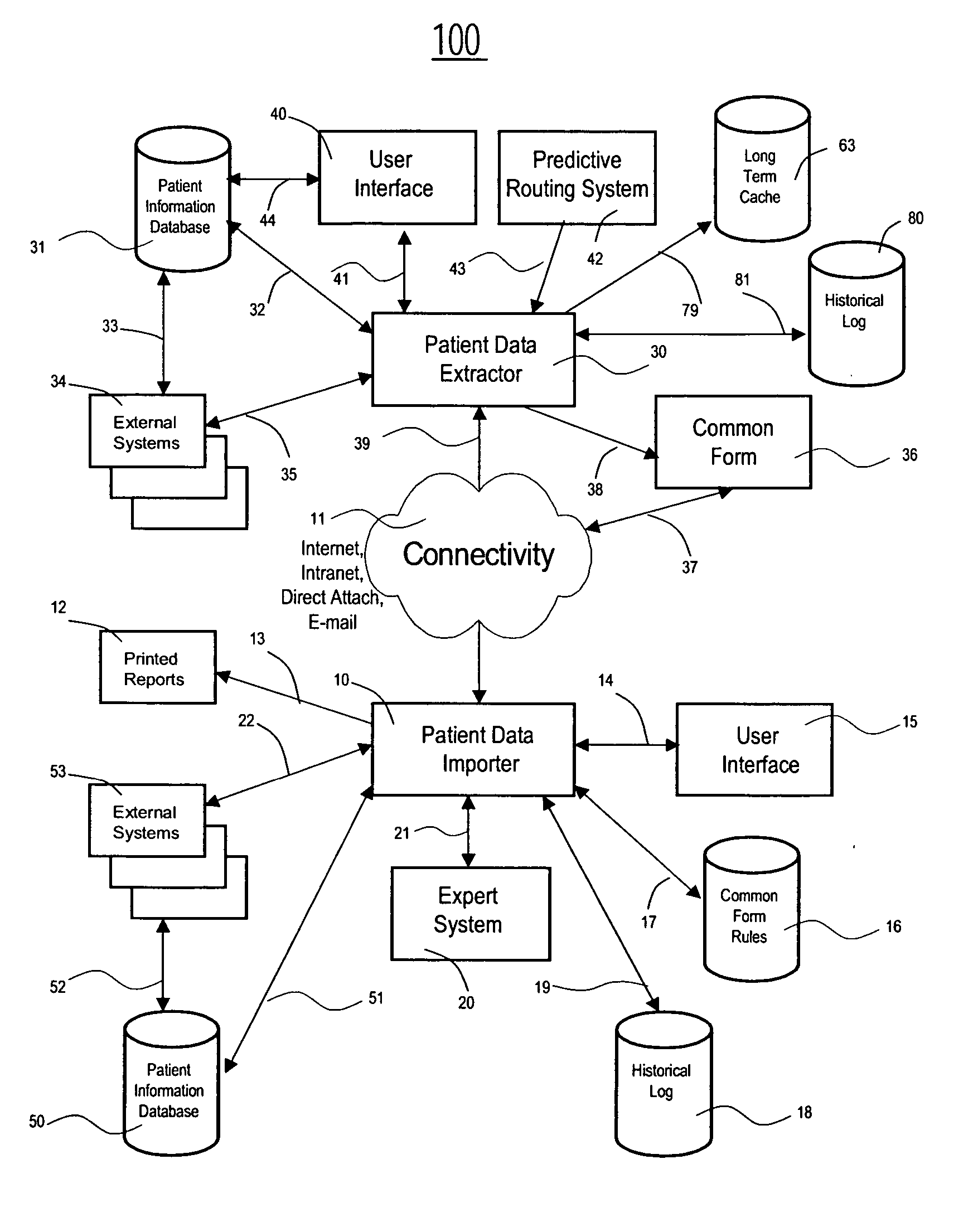
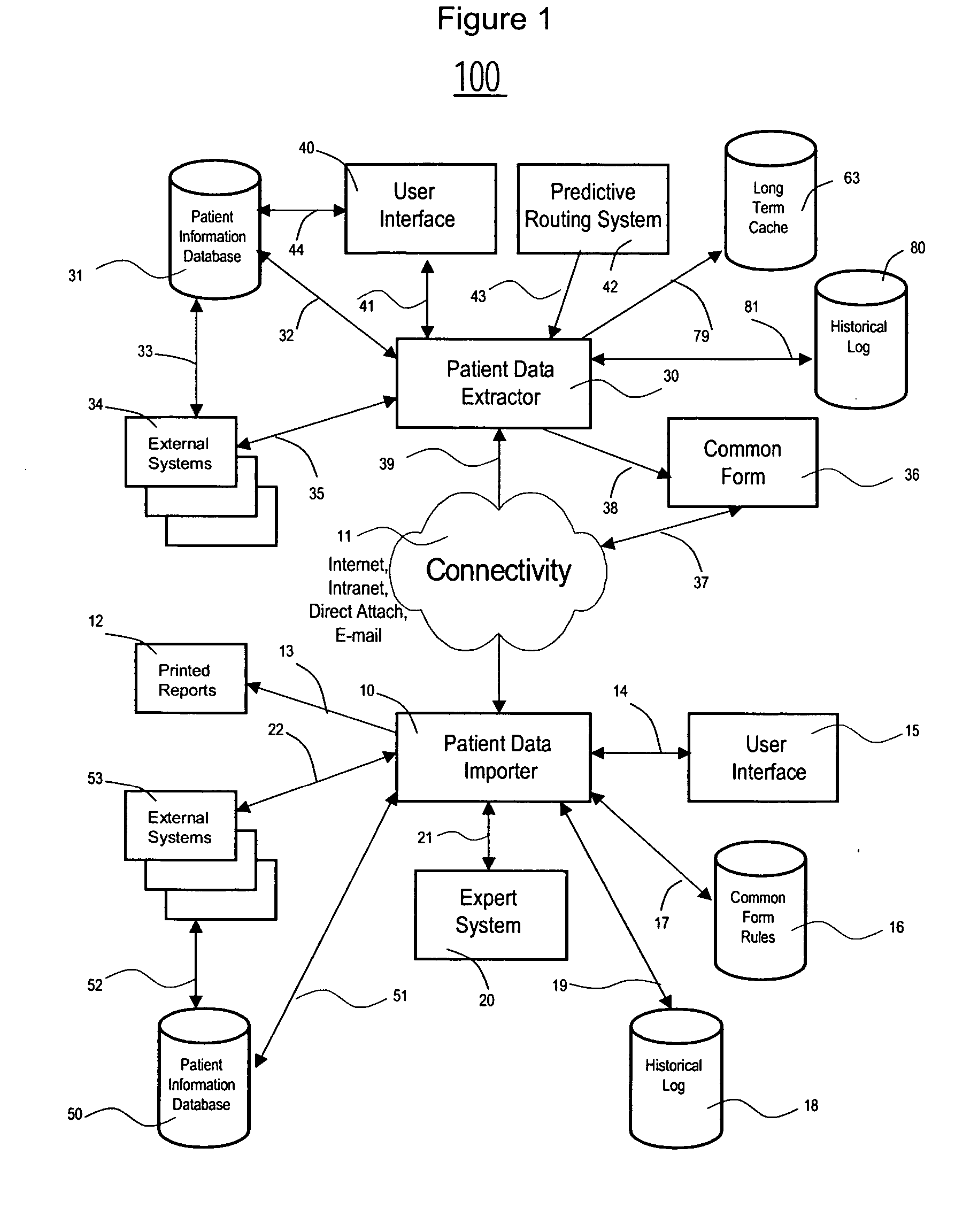
System for exchanging patient medical information between different healthcare facilities
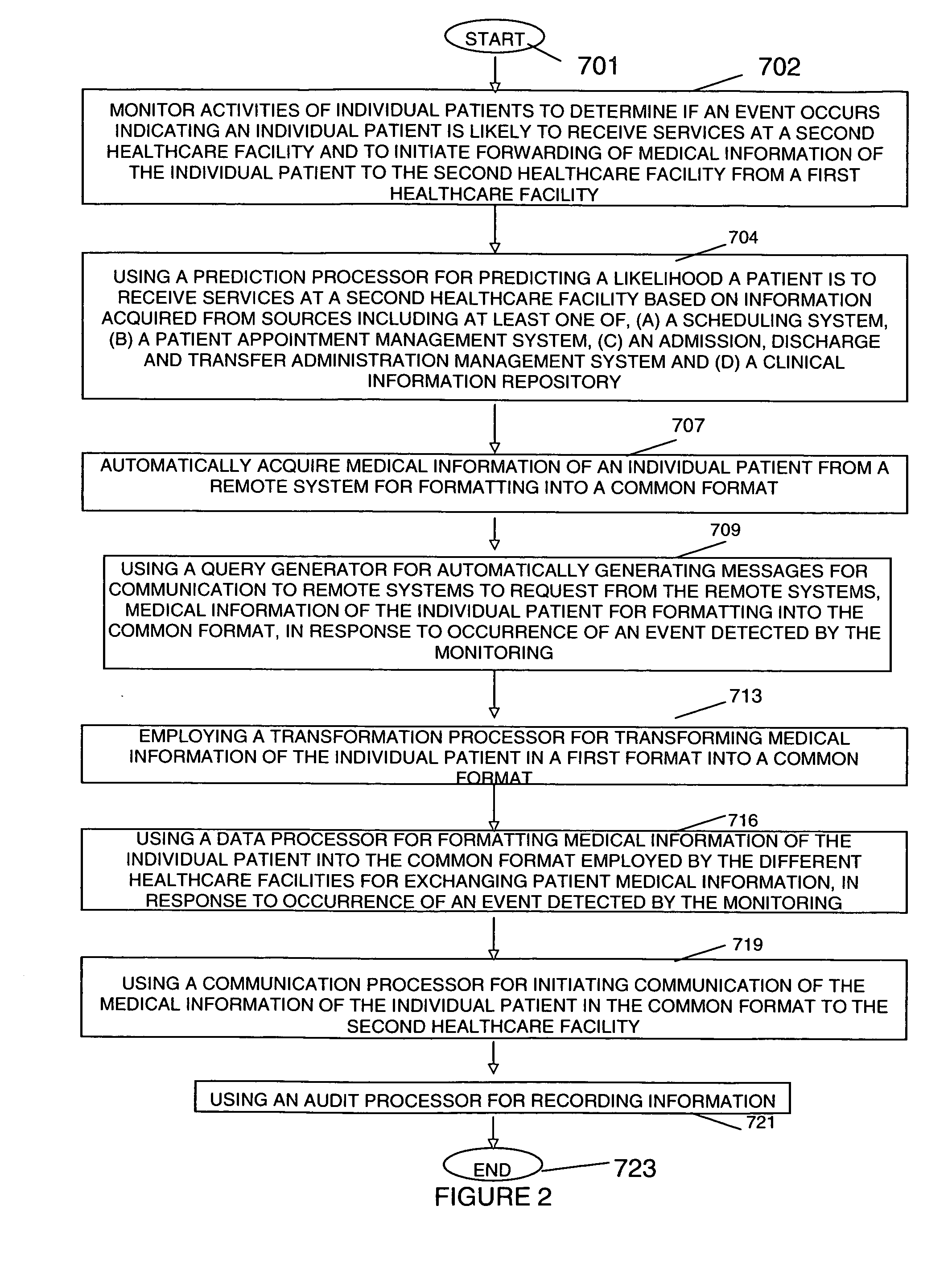
InactiveUS20070150311A1Reduce redundant dataMedical communicationOffice automationTransfer systemMedical institution
A Patient Information Sharing and Transfer System provides a system for moving patient information and clinical data between healthcare facilities using predictive capability across an enterprise or groups of patient health care facilities. A system for exchanging patient medical information between different healthcare facilities comprises a monitor for monitoring activities of individual patients to determine if an event occurs indicating an individual patient is likely to receive services at a second healthcare facility and to initiate forwarding of medical information of the individual patient to the second healthcare facility from a first healthcare facility. A data processor formats medical information of the individual patient into a common format employed by the different healthcare facilities for exchanging patient medical information, in response to occurrence of an event detected by the monitor. A communication processor initiates communication of the medical information of the individual patient in the common format to the second healthcare facility.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
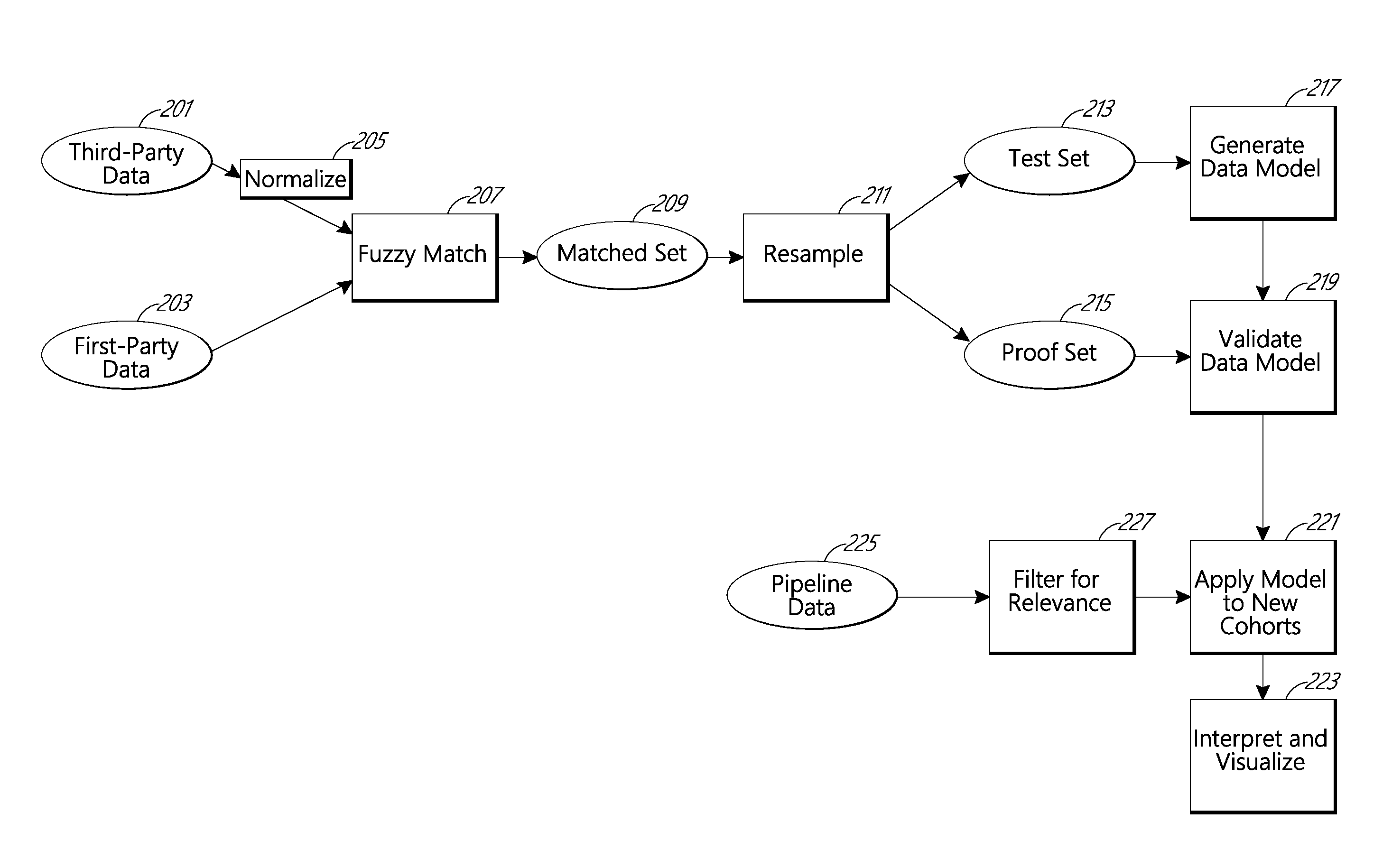
Systems and models for data analytics
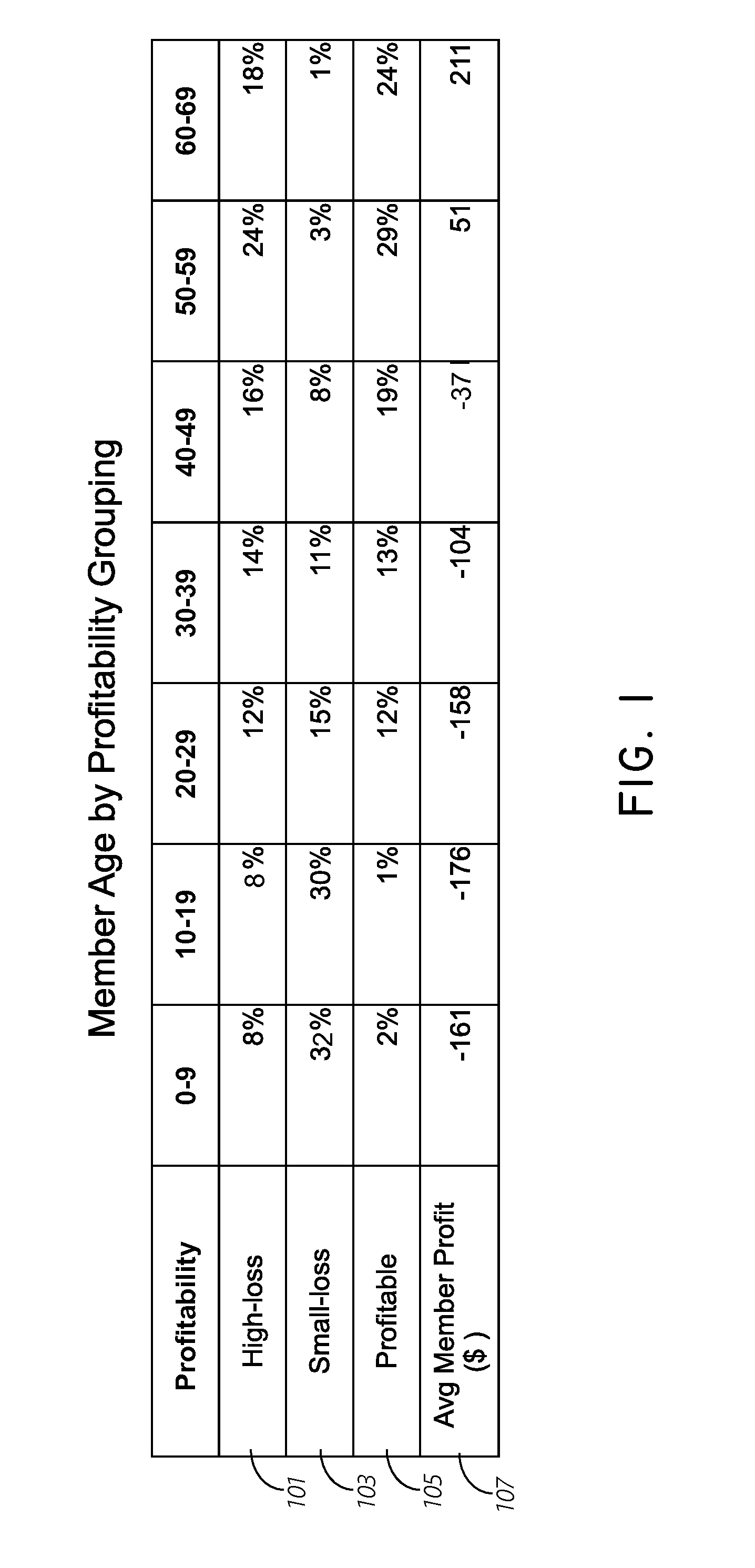
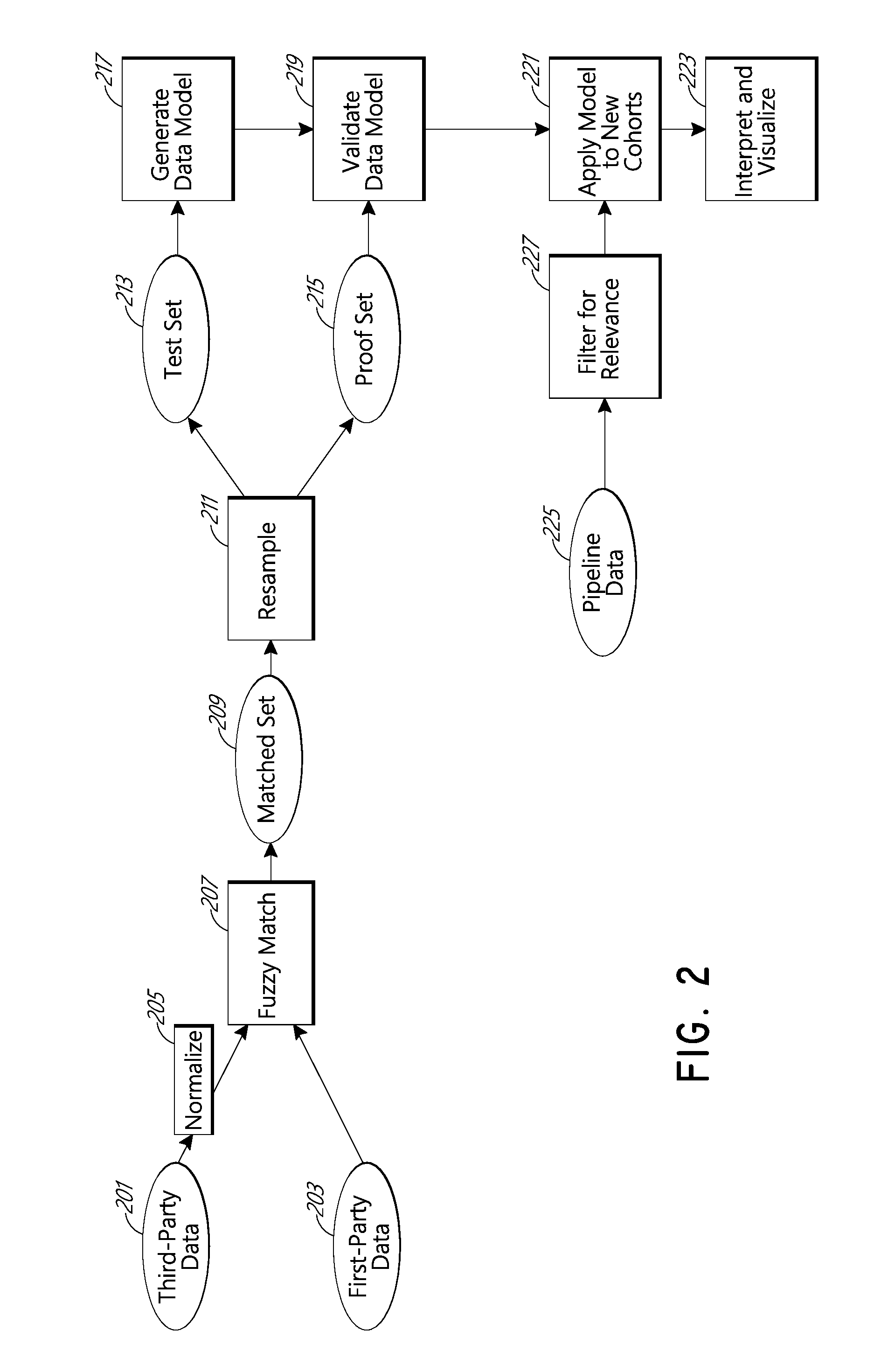
ActiveUS9418337B1Easy to interpretImprove visualizationMathematical modelsDigital data information retrievalThird partyCustomer profitability
Systems and methods are provided that allow for generating and applying an improved predictive data model that aggregates two or more models performed sequentially, for the purposes of improving the prediction of overall profitability of individuals or households in a population. The models may be generated by the processing of customer profitability data and third-party population data together. One of the two aggregated models may be an inherently probabilistic, binary model tasked with determining whether an individual is a high-loss individual and using that result to improve the predictive capability of the system.
Owner:PALANTIR TECHNOLOGIES
Sweat sensing device communication security and compliance
InactiveUS20170100035A1Effectively stimulated and analyzedEnhance predictive and alertPerson identificationInertial sensorsCommunications securityAnalyte
The invention addresses confounding difficulties involving continuous sweat analyte measurement. Specifically, the present invention provides: at least one component capable of monitoring whether a sweat sensing device is in sufficient contact with a wearer's skin to allow proper device operation; at least one component capable of monitoring whether the device is operating on a wearer's skin; at least one means of determining whether the device wearer is a target individual within a probability range; at least one component capable of generating and communicating alert messages to the device user(s) related to: wearer safety, wearer physiological condition, compliance with a requirement to wear a device, device operation; compliance with a behavior requirement, or other purposes that may be derived from sweat sensor data; and the ability to utilize aggregated sweat sensor data that may be correlated with information external to the device to enhance the predictive capabilities of the device.
Owner:UNIV OF CINCINNATI A UNIV OF THE STATE OF OHIO
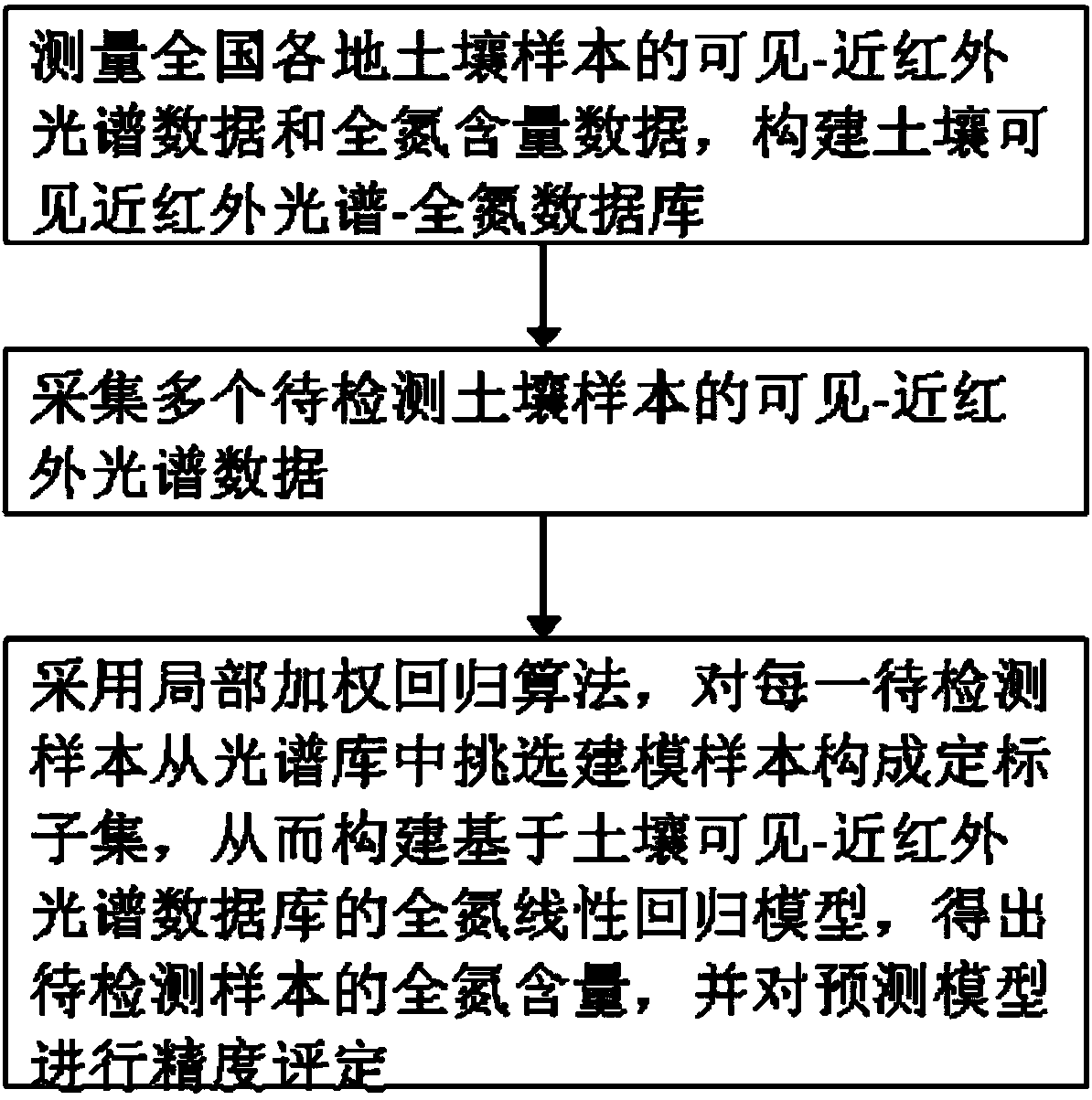
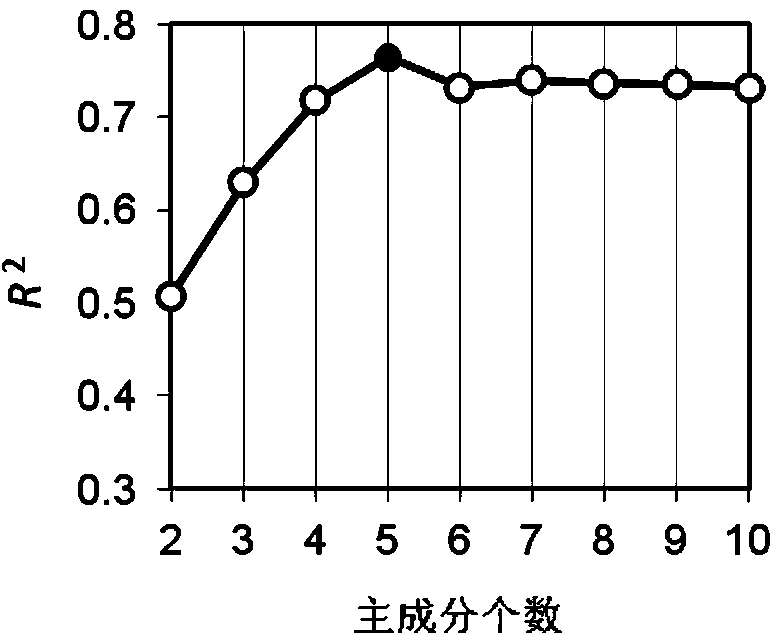
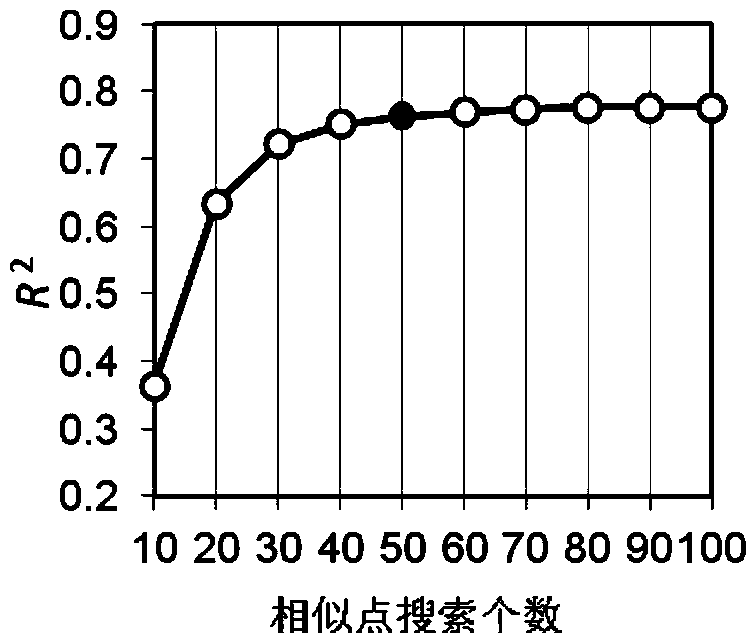
Soil total nitrogen real-time detection method based on soil visible-near infrared spectrum library
InactiveCN103884661ASolve the repeatabilitySolve the problem that the data format is not uniform and cannot be sharedColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsSoil sciencePredictive methods
The invention discloses a soil total nitrogen real-time detection method based on a soil visible-near infrared spectrum library. The soil total nitrogen real-time detection method comprises the following steps: measuring data of visible-near infrared spectrums and data of total nitrogen contents of soil samples across the country to establish a soil visible near infrared spectrum-total nitrogen database; collecting the data of the visible-near infrared spectrums of a plurality of soil samples to be detected; selecting model establishing sample from the spectrum library for each sample to be detected to form a calibration subset by using a local weighted regression algorithm to establish a total nitrogen linear regression model based on the soil visible-near infrared spectrum database to obtain the total nitrogen contents of the samples to be detected, and evaluating accuracy of a prediction model. Compared with the conventional method for establishing a prediction model by merely using all the soil sample spectrums in the region, the prediction model established by the method is excellent in stability and universality, so that the prediction capability is significantly improved and the defects that the soil spectrums are repeatedly collected, the data format is non-uniform and is incapable of being shared, and the established models are incapable of being universally used can be avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Operation information prediction method, model training method and related device
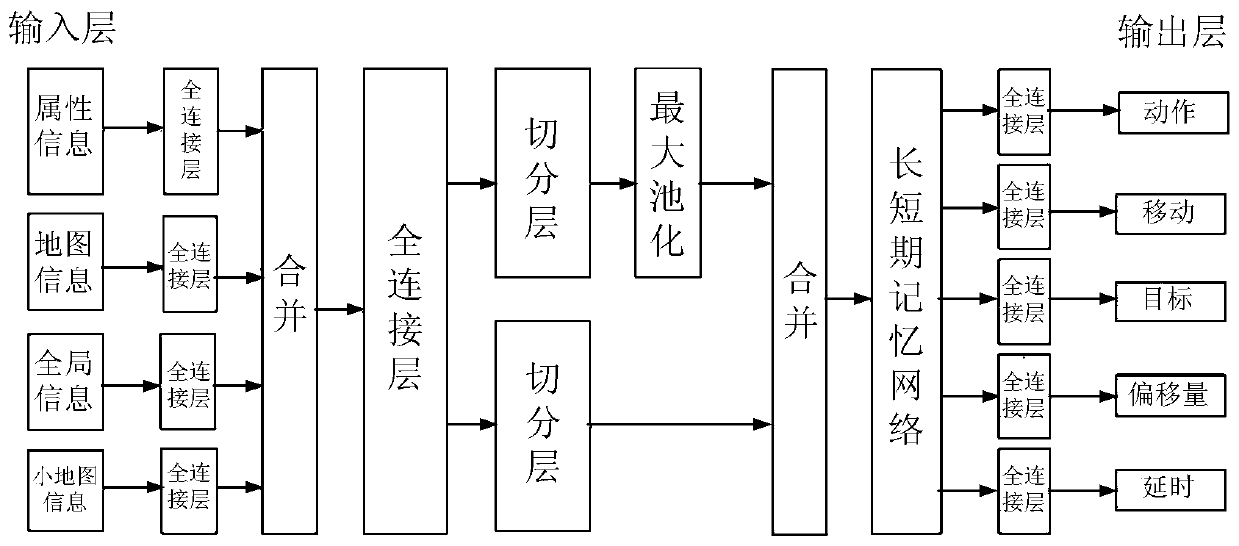
ActiveCN109893857AImprove rationalityImprove predictive performanceNeural architecturesVideo gamesMicro-operationFeature set
The invention discloses an operation information prediction method. The operation information prediction method comprises the following steps: acquiring image data to be predicted; determining N characters to be predicted in a first character set according to image data to be predicted; acquiring a feature set to be predicted of each role to be predicted in the image data to be predicted; and acquiring first operation information corresponding to each role to be predicted through a target joint model, wherein the target joint model is used for generating second operation information accordingto the feature set to be predicted, the target joint model is also used for generating first operation information according to the second operation information, the first operation information represents information related to operation contents, and the second operation information represents information related to the operation intention. The invention also discloses a model training method anda related device. According to the invention, the cooperative capability of the micro-operation level and the macro-operation level can be obtained simultaneously by utilizing the target joint model,so that the prediction capability of the model is enhanced, and the rationality of information prediction is improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Network security situation awareness model and method based on CE-RBF
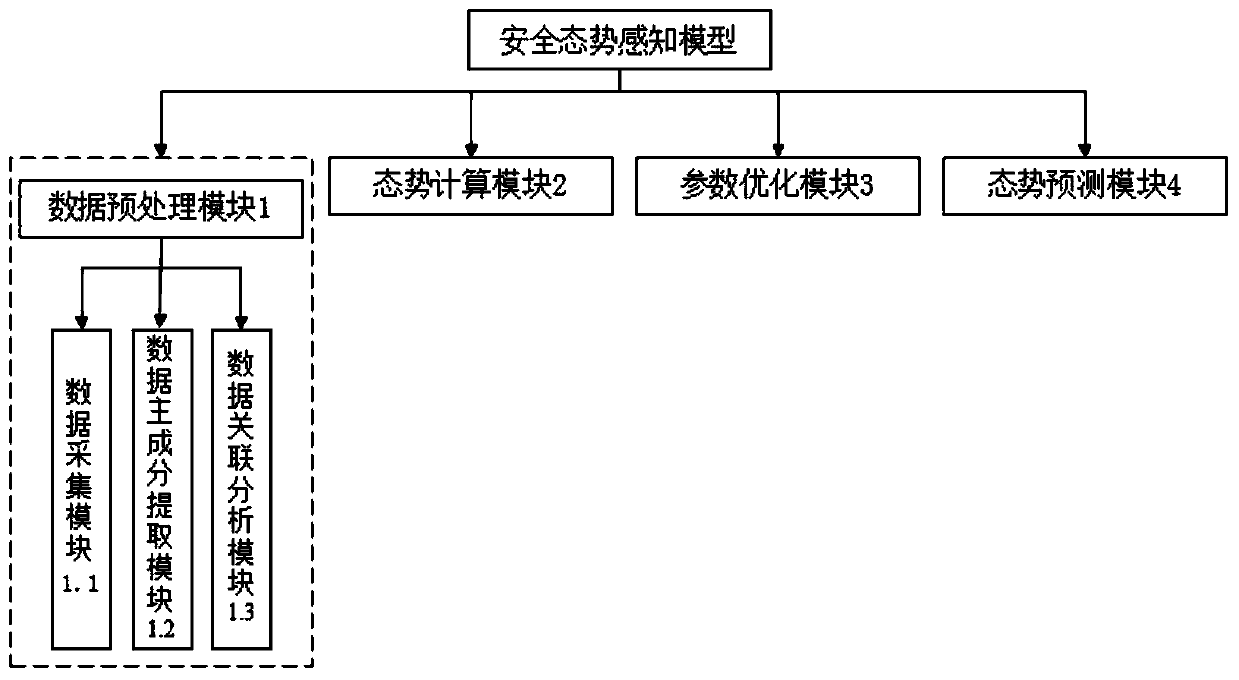
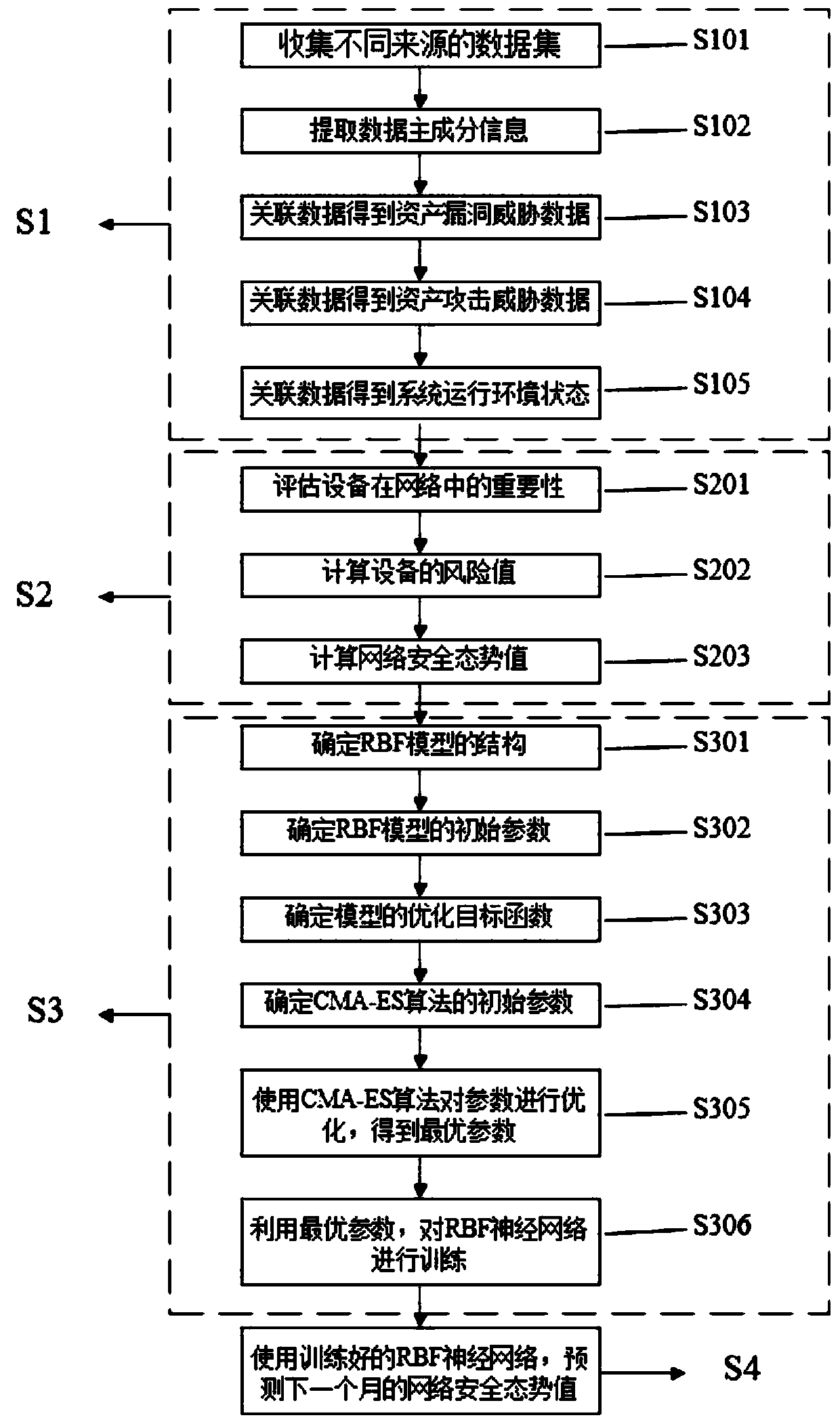
InactiveCN110392048AReasonable structureReasonable parametersNeural architecturesTransmissionData setHigh dimensional
The invention discloses a network security situation awareness model and method based on CE-RBF. The model comprises a data preprocessing module, a situation calculation module, a parameter optimization module and a situation prediction module. The method comprises the following steps: collecting data sets from different sources, and extracting principal component information for situation awareness to obtain asset attack threat data and system state data; calculating a risk value according to the asset attack threat data of the network equipment, and evaluating the security situation of the whole network; determining initial parameters of the RBF neural network, establishing an optimization objective function, optimizing the parameters in the optimization objective function by using a CEalgorithm, substituting the optimal parameter set into the RBF neural network after finding the optimal parameter set, and training by using historical network situation values as sample data; and performing situation prediction by using the trained RBF neural network. According to the method, the problem of parameter optimization in the high-dimensional model is solved by utilizing the efficientoptimization capability of CE, and the prediction capability of the neural network is improved.
Owner:湖北央中巨石信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com