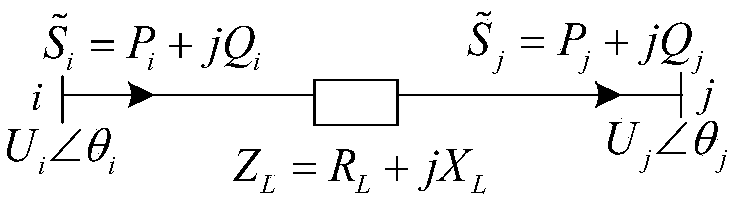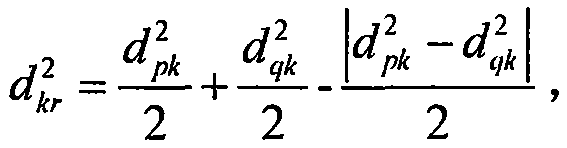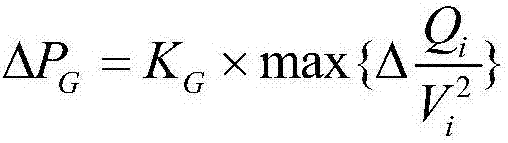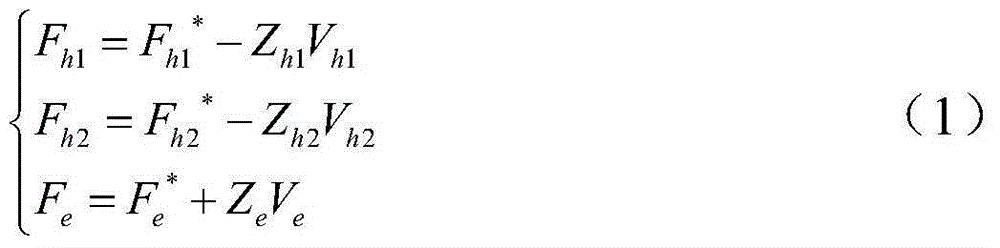Patents
Literature
37 results about "Dominant factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of Dominant factor. Dominant factor means the accident is the prevailing factor in relation to any other factors contributing to the resulting medical condition or disability.
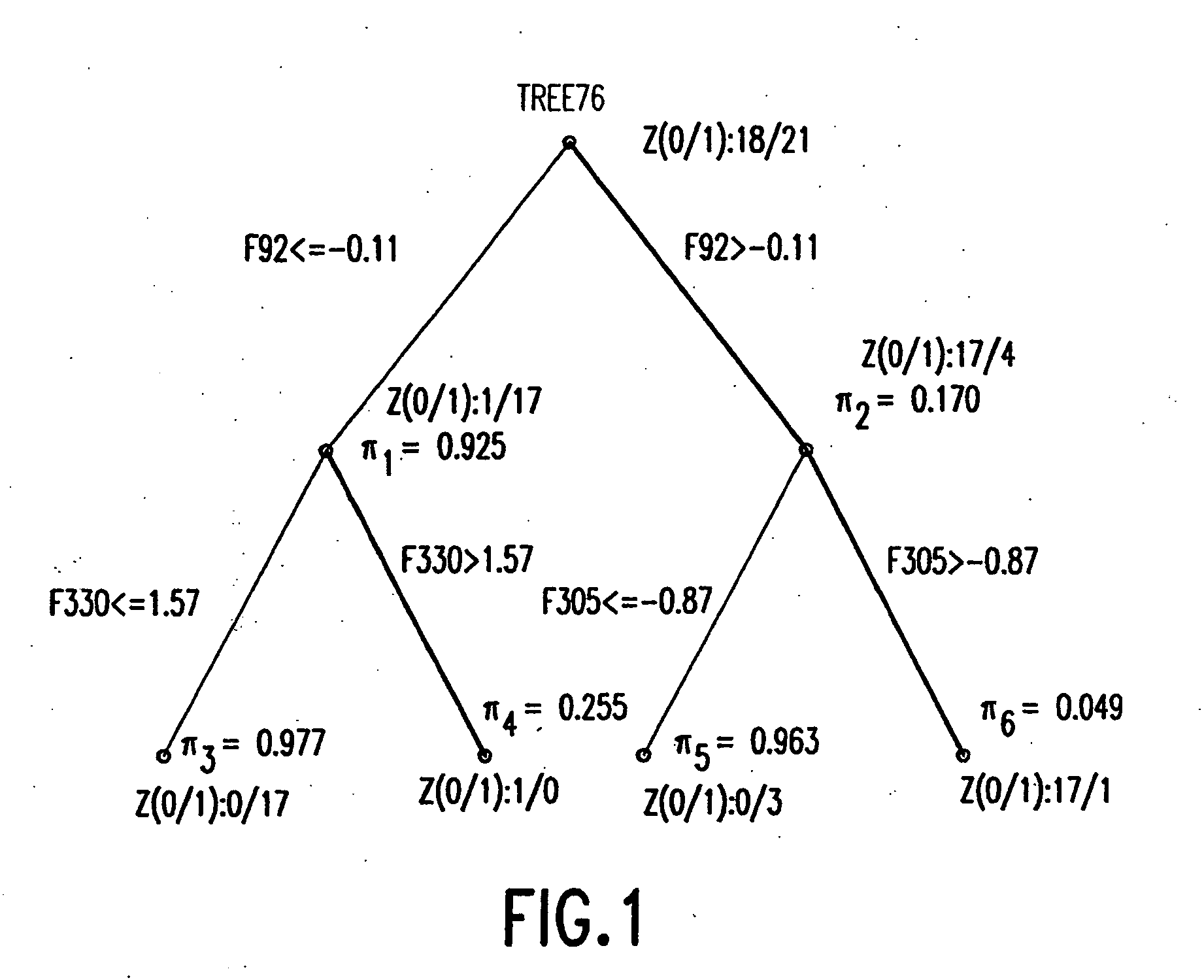
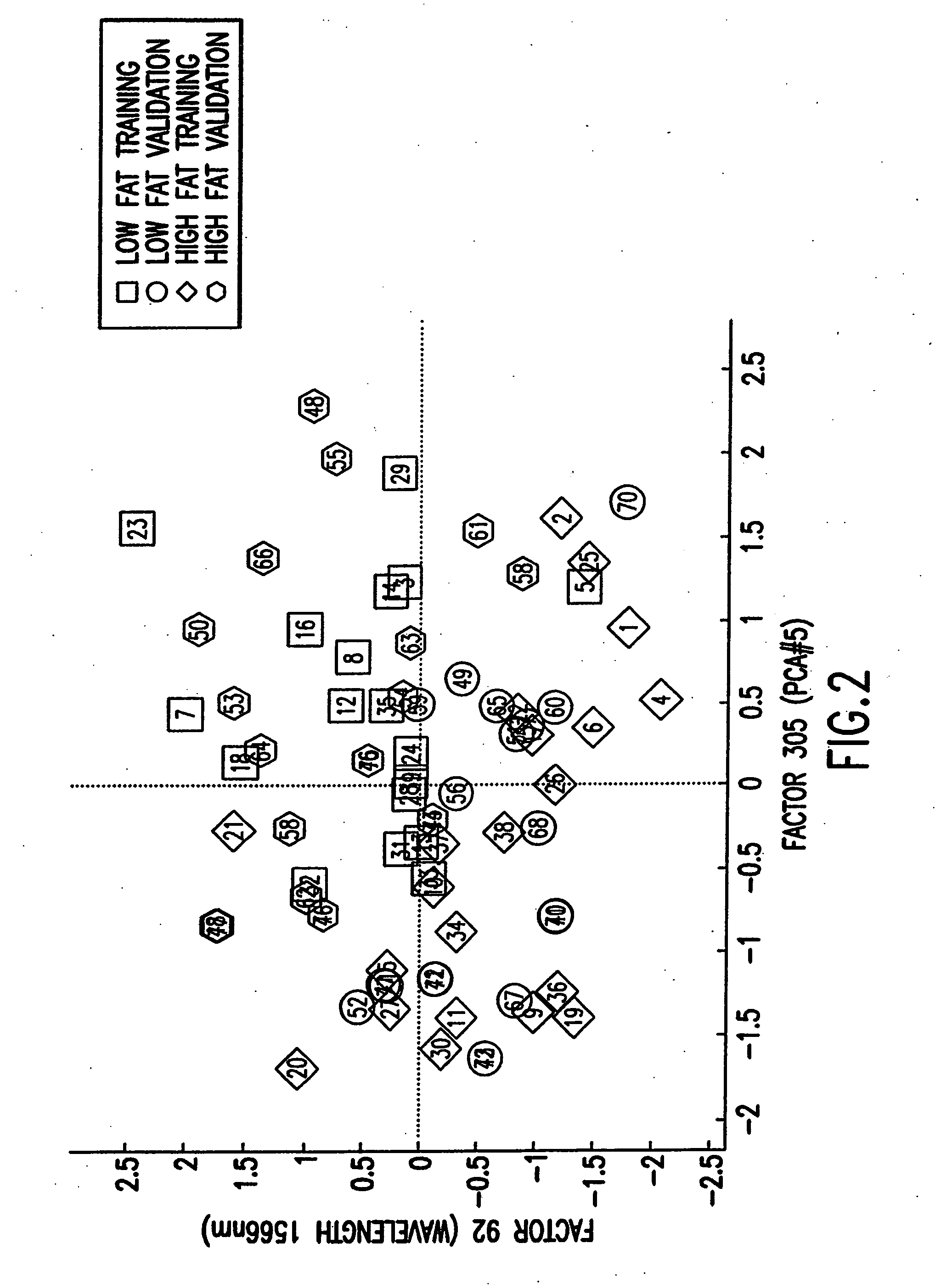
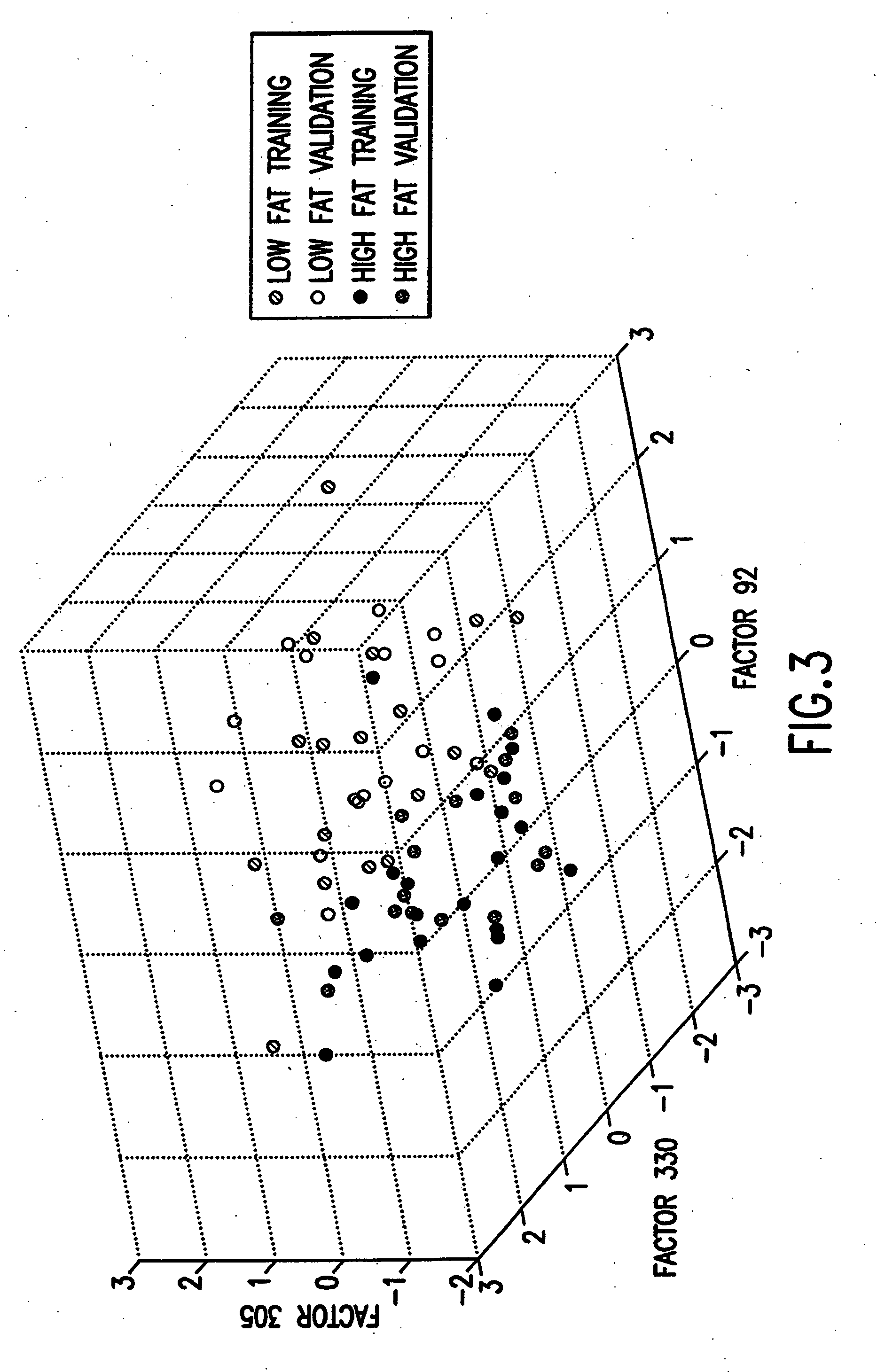
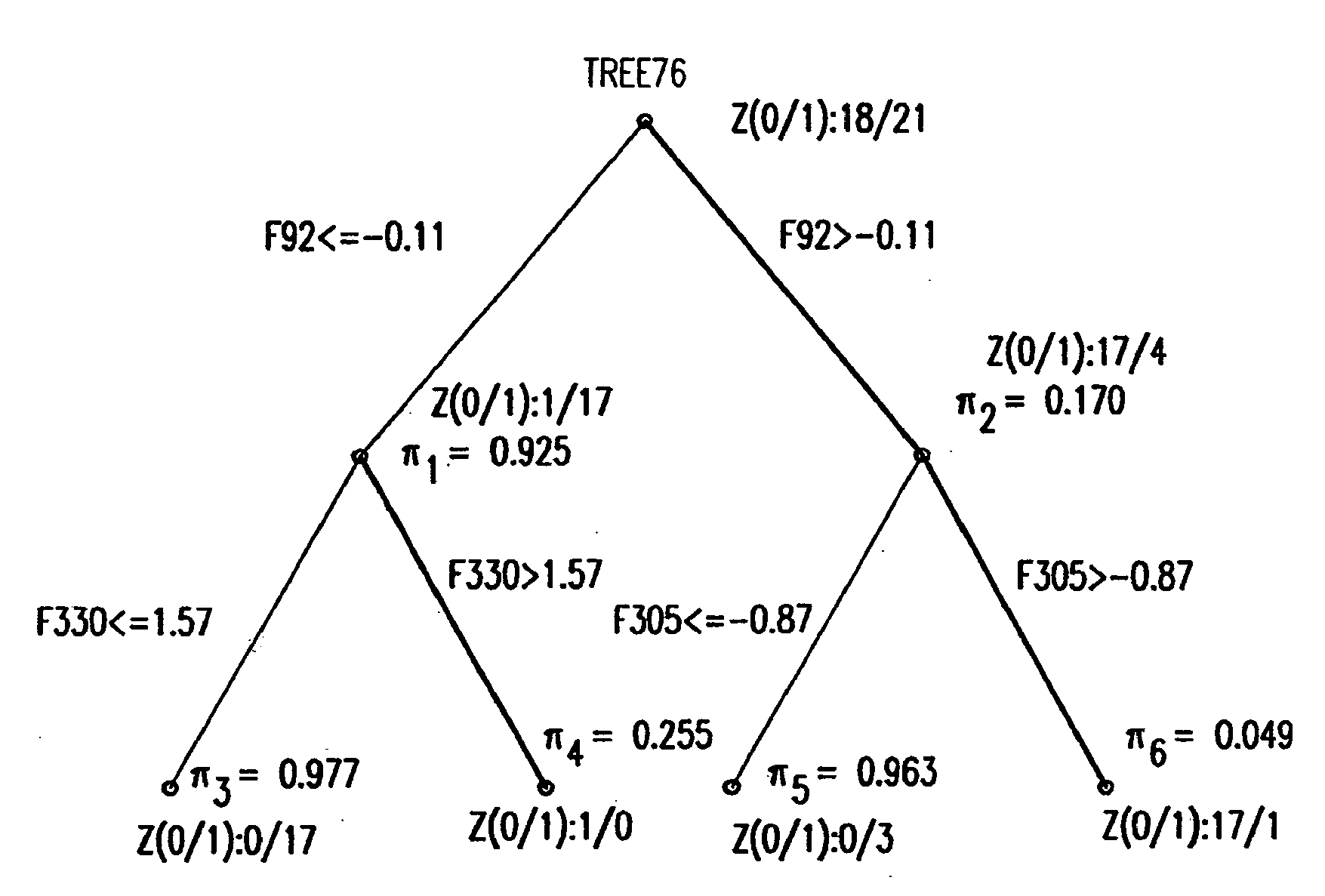
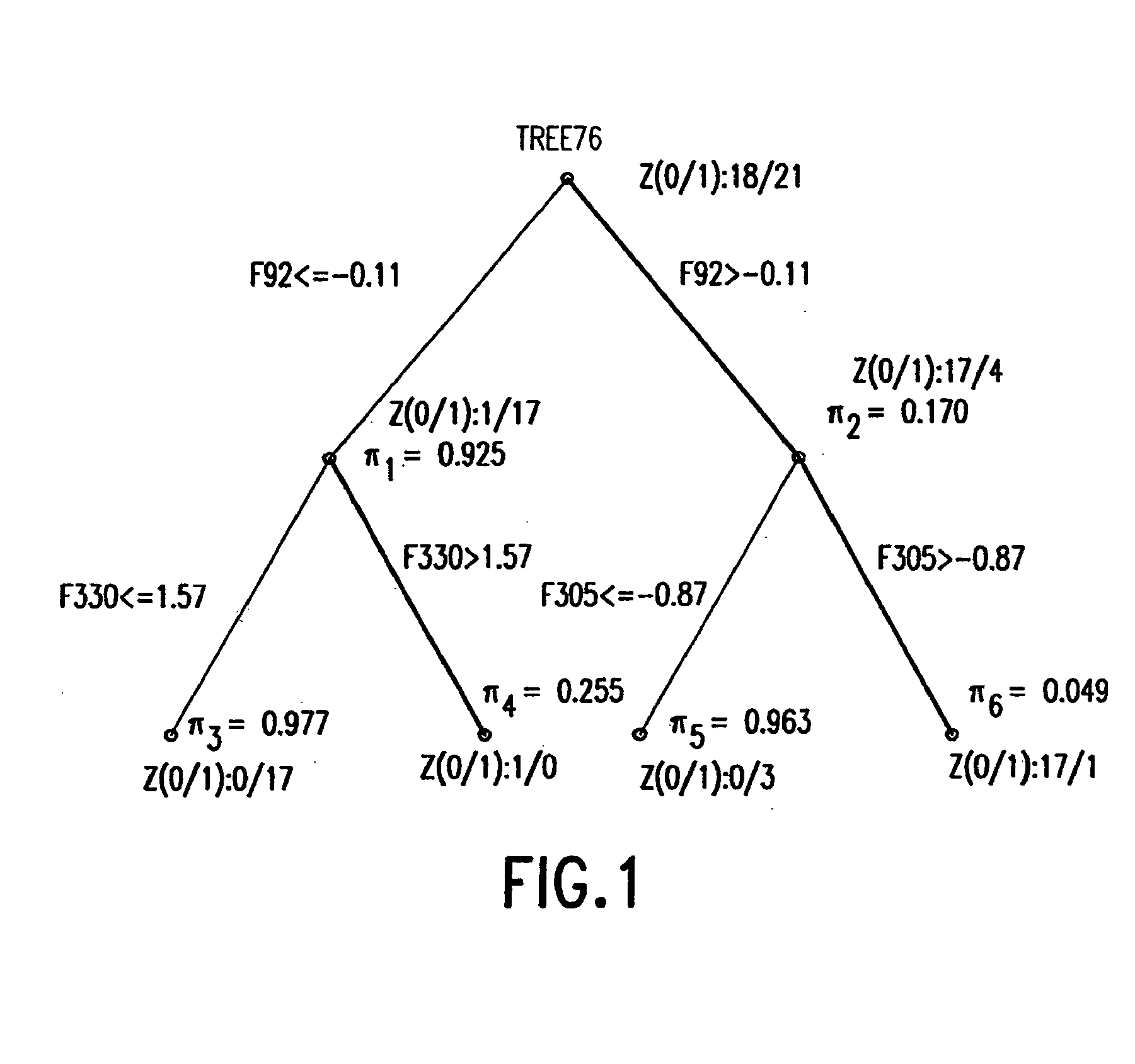
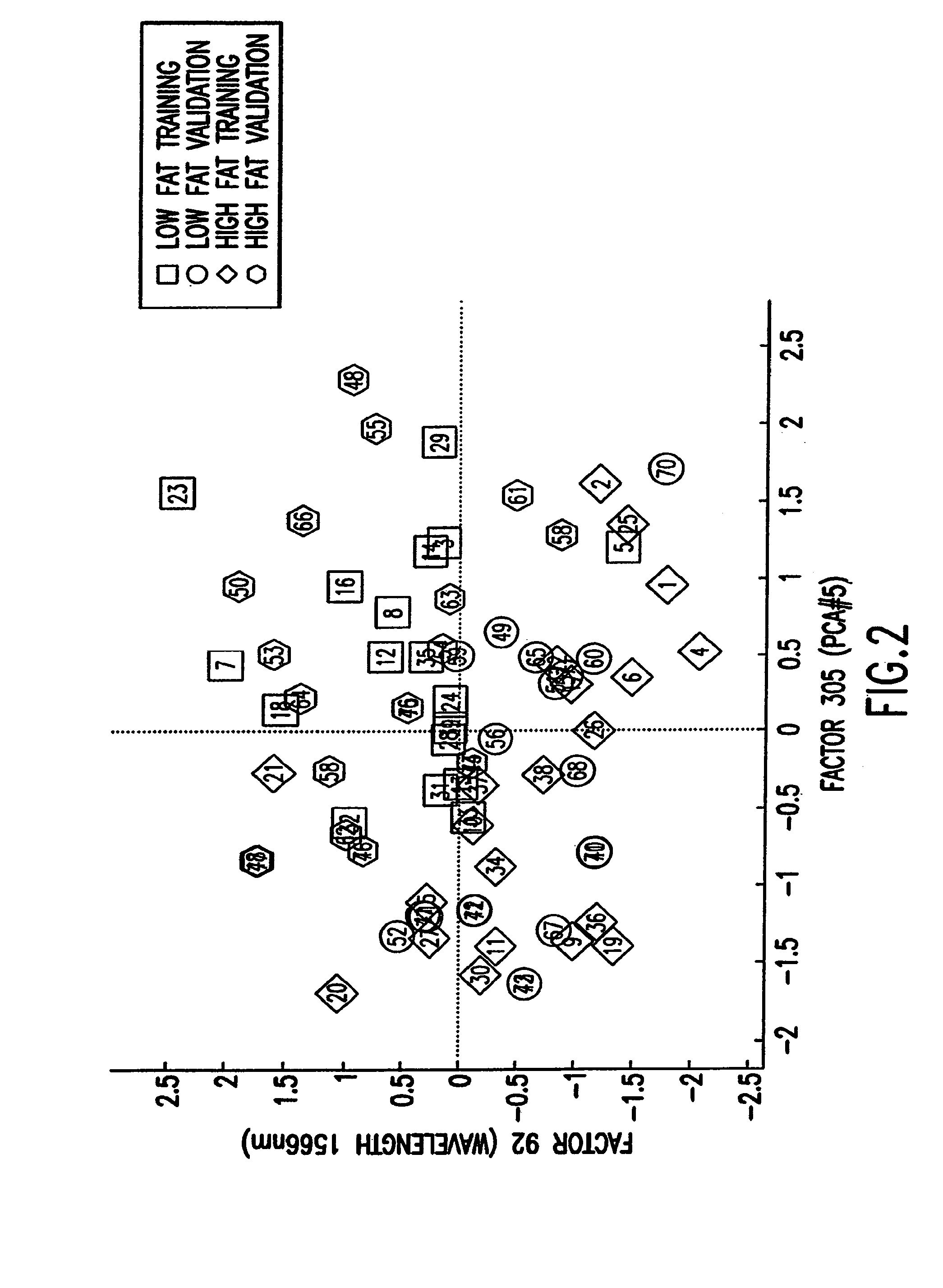
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
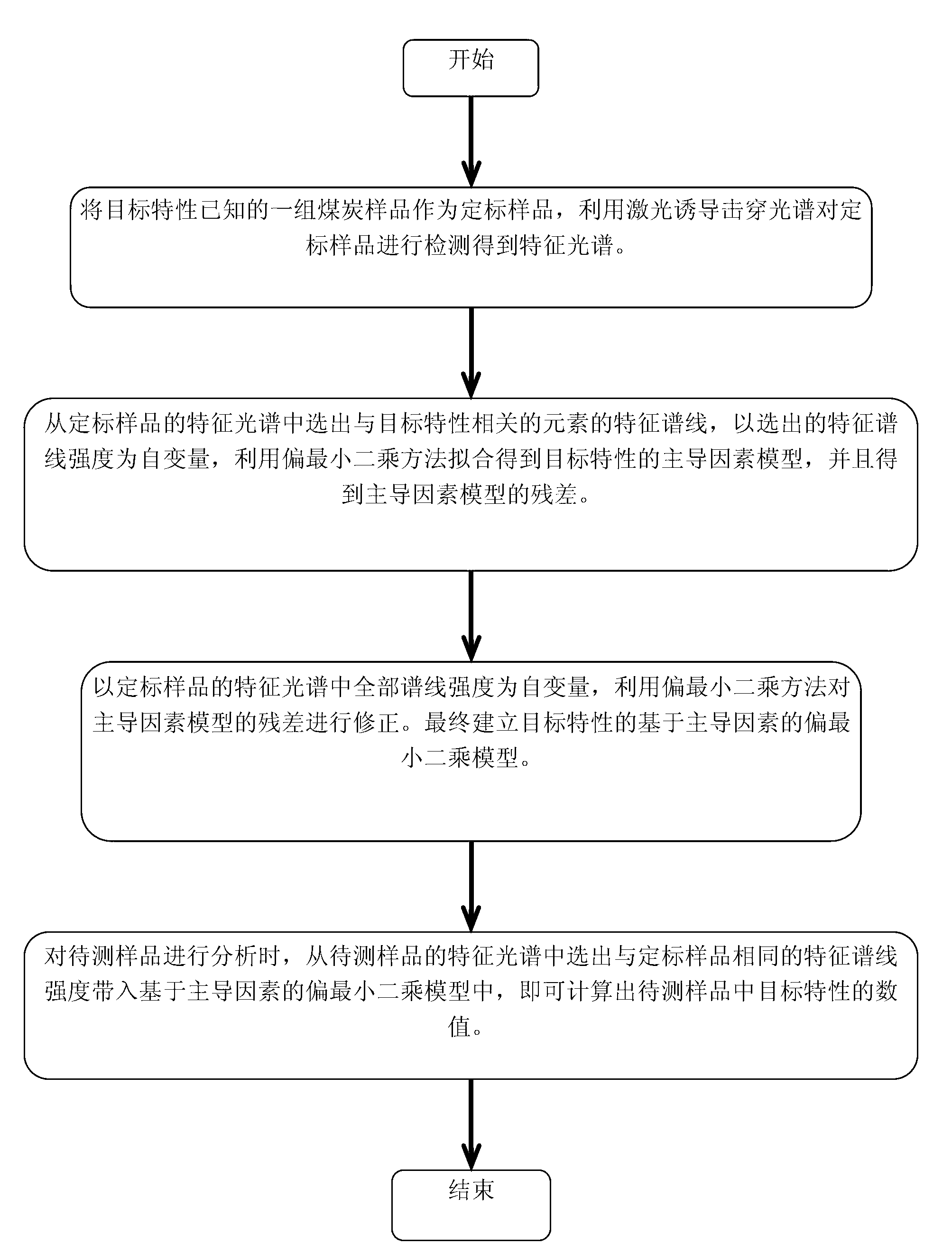
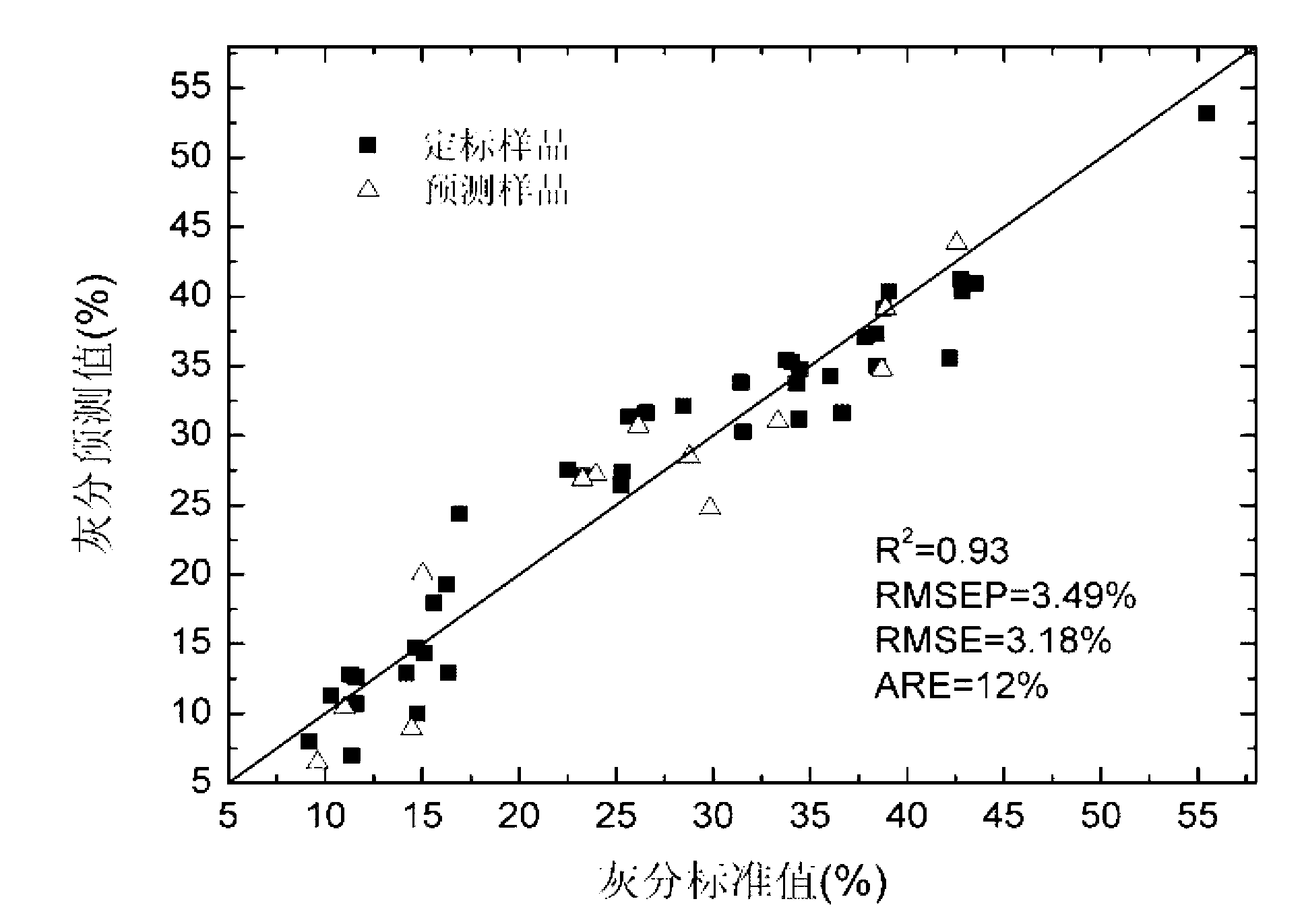
Coal quality characteristic analysis method based on combination of dominant factors and partial least square method
ActiveCN103234944ASolve the problem of online rapid analysisHigh measurement accuracyAnalysis by material excitationLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopyTwo step
The invention discloses a coal quality characteristic analysis method based on combination of dominant factors and a partial least square method, and belongs to the technical field of atomic emission spectroscopy. According to the method, modeling is carried out based on a physical background of coal quality characteristics. The method comprises two steps of partial least square fitting processes. In the first partial least square fitting process, characteristic lines in a spectrum relative to coal quality characteristics are used as inputs, and a nonlinear dominant factor model is established for describing a physical relationship between coal quality characteristics and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. In the second partial least square fitting process, dominant factor residuals are corrected by using all spectral line intensity information of the spectrum. Compared with a traditional partial least square model, with the method provided by the invention, model calibration and prediction precisions are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
InactiveUS20090319244A1Mathematical modelsAnalogue computers for chemical processesSingular value decompositionData set
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
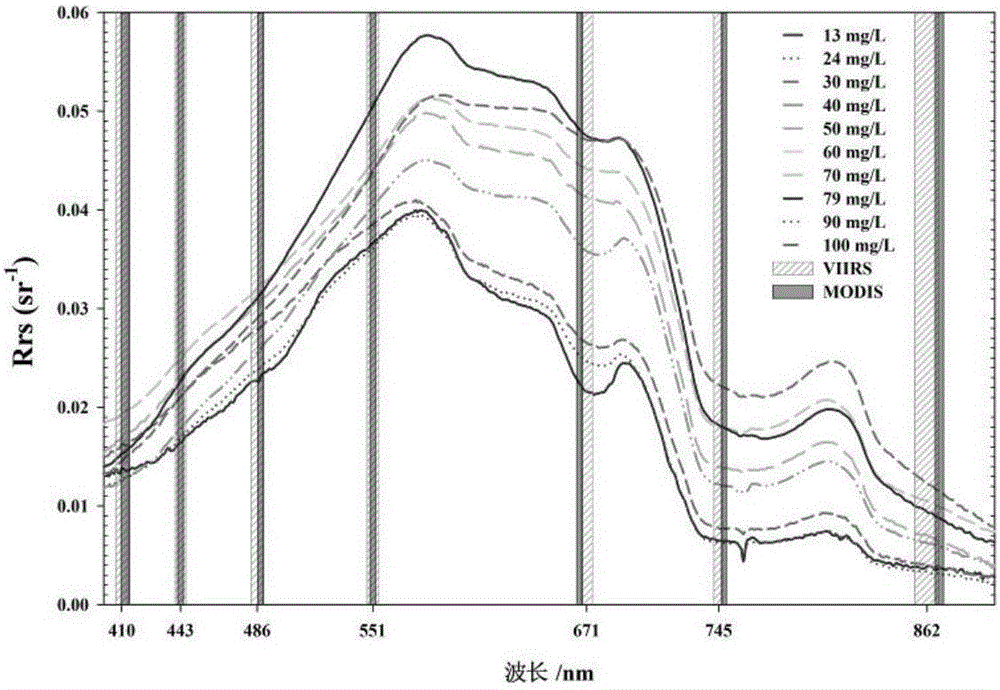
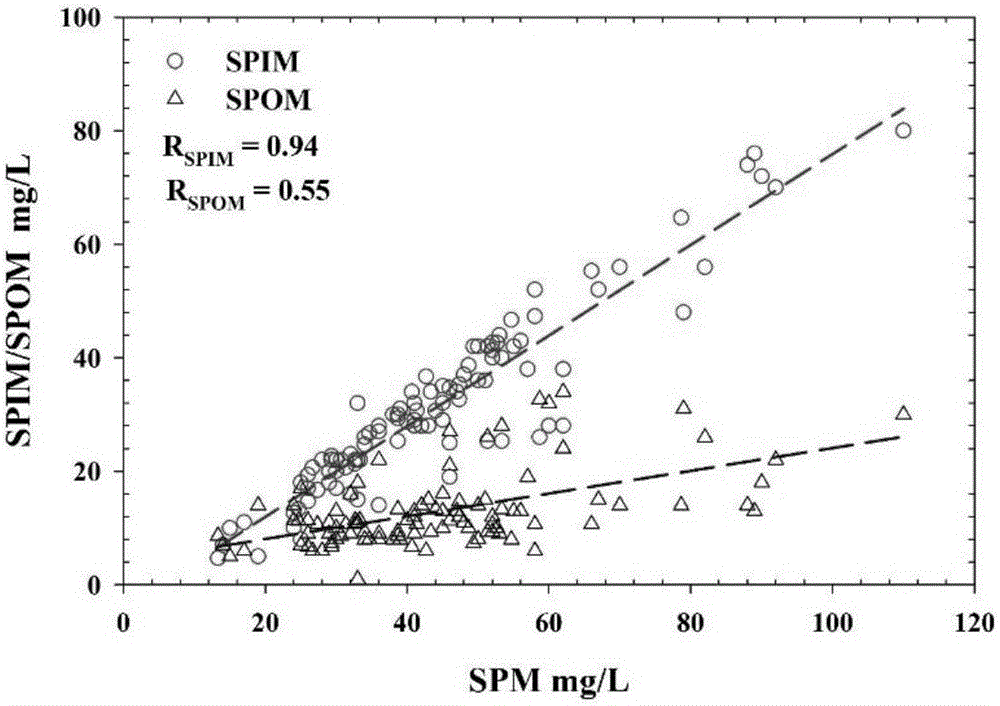
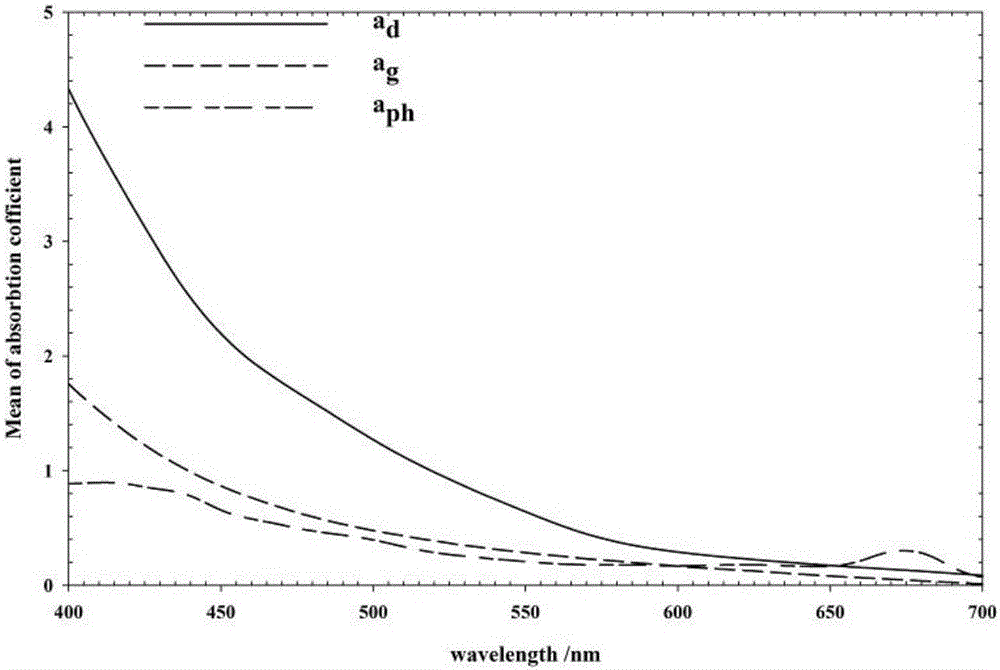
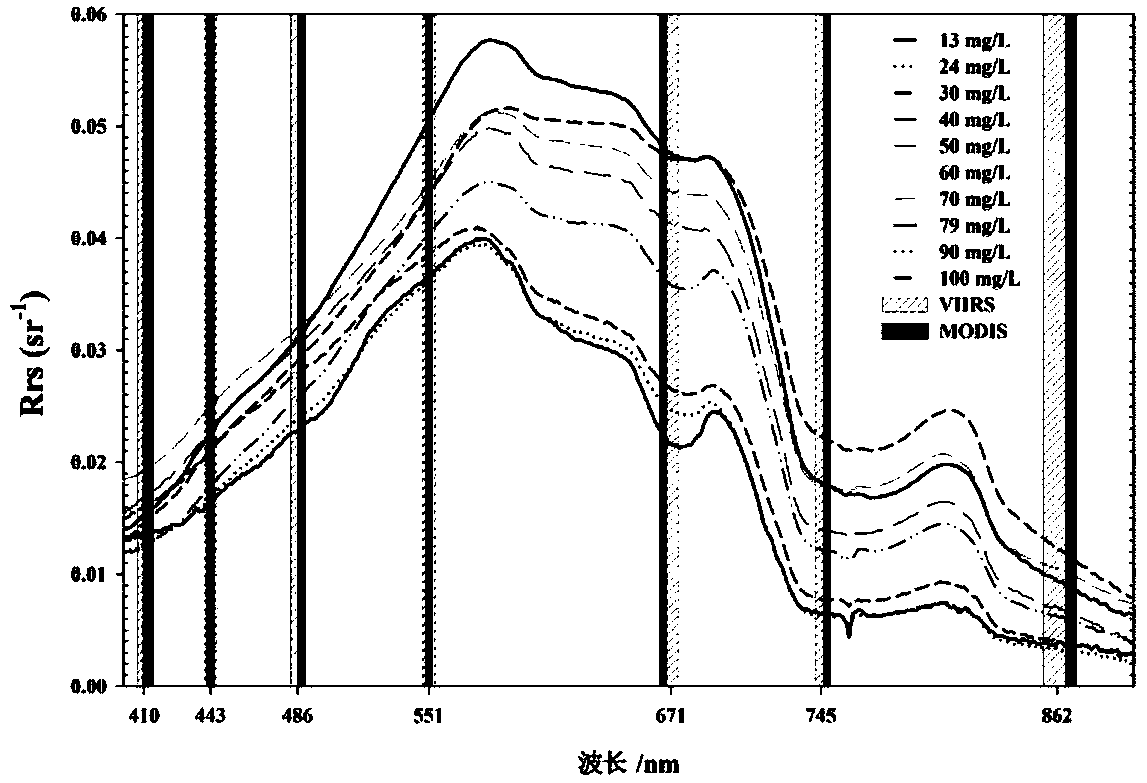
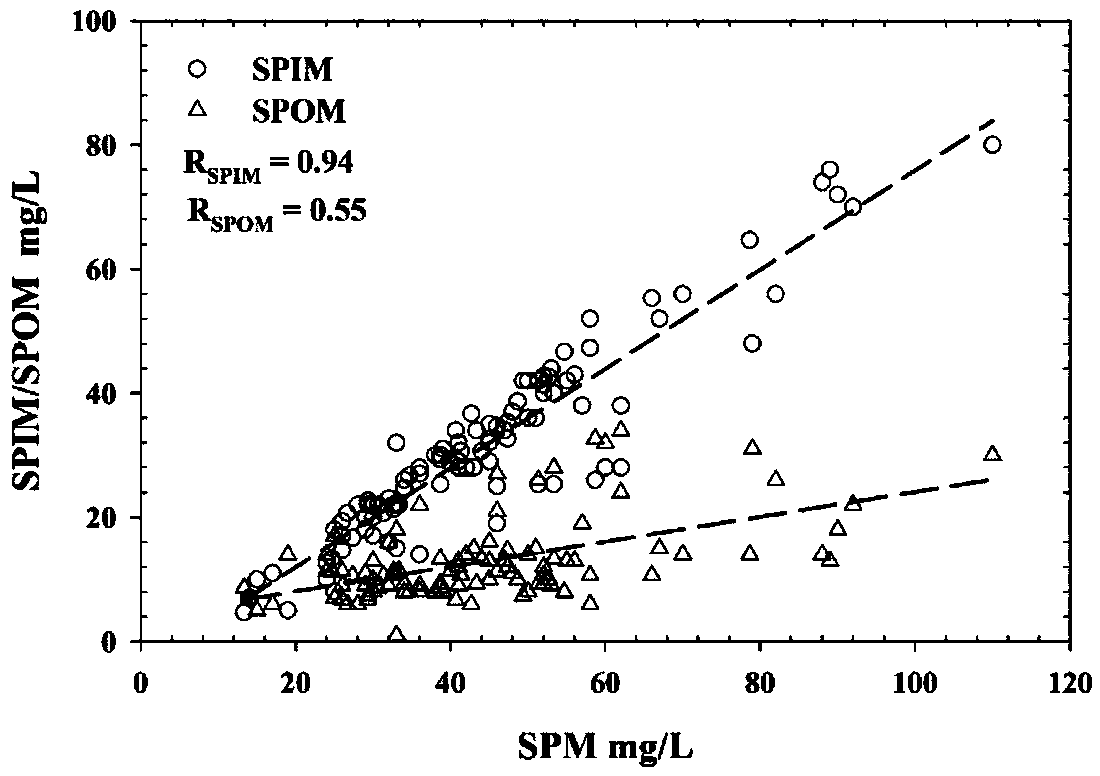
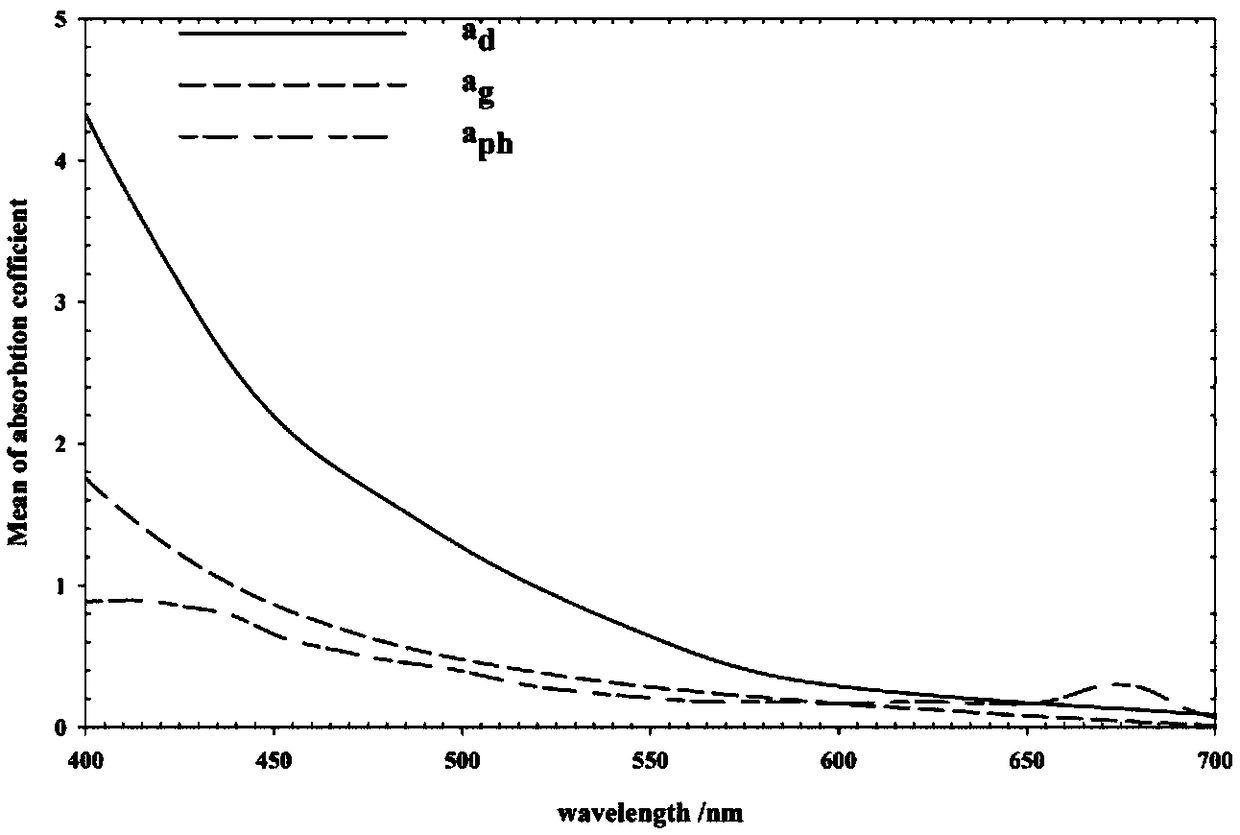
Method for estimating suspended matter concentration in turbid lake water based on VIIRS sensor
ActiveCN106126826AEffective assessmentGeneral water supply conservationDesign optimisation/simulationRayleigh scatteringEcological environment
The invention relates to a method for estimating suspended matter concentration in turbid lake water based on a VIIRS sensor. The method comprises: based on lake field measured spectrum and substance concentration data, analyzing optical properties of water body and water quality dominant factors; screening wave bands which are sensitive to suspended matter concentration variation in the turbid lake water, using curve fitting to determine an optimal model of suspended matter concentration and ground measured spectrum (Rrs); using Rrc data which is removed with water vapor and ozone absorption and corrected by Rayleigh scattering to establish a suspended matter concentration quantitative model which is suitable to be used for the VIIRS; and finally, using the established model on a VIIRS image, to accurately obtain interannual and inter-monthly variation rules and spatial distribution of the suspended matter concentration of the turbid lake water. Using the method can realize long-term high-precision monitoring of suspended matter concentration of a lake, and the method is helpful to scientifically evaluate interannual suspended matter concentration variation and development trends thereof, and effectively evaluate ecological environment changes of lake water.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Geodesic Massively Parallel Computer.
InactiveUS20120331269A1Shorten the interconnection distanceCommunication latencySingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsDigital data processing detailsSystems designProblem domain
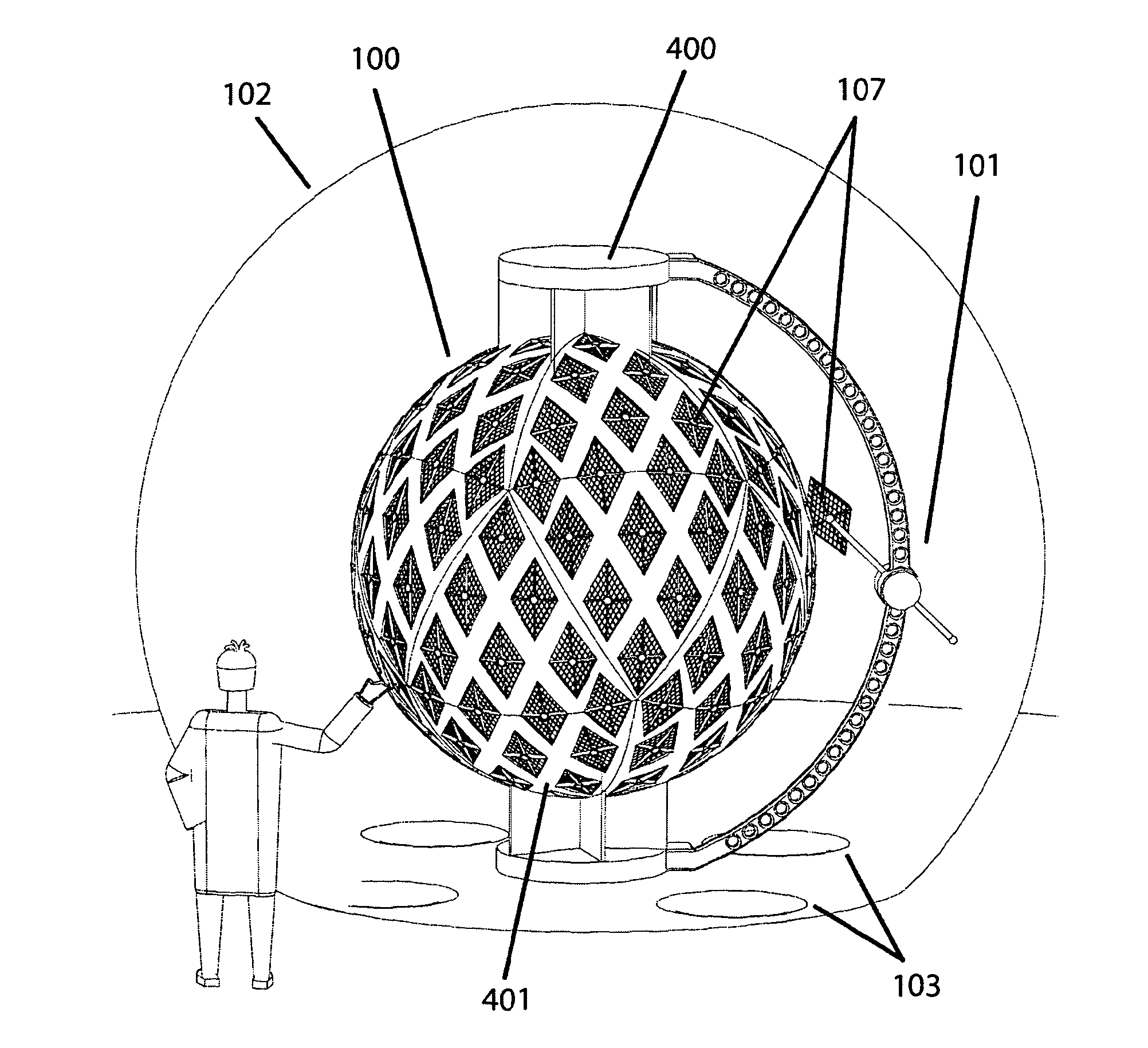
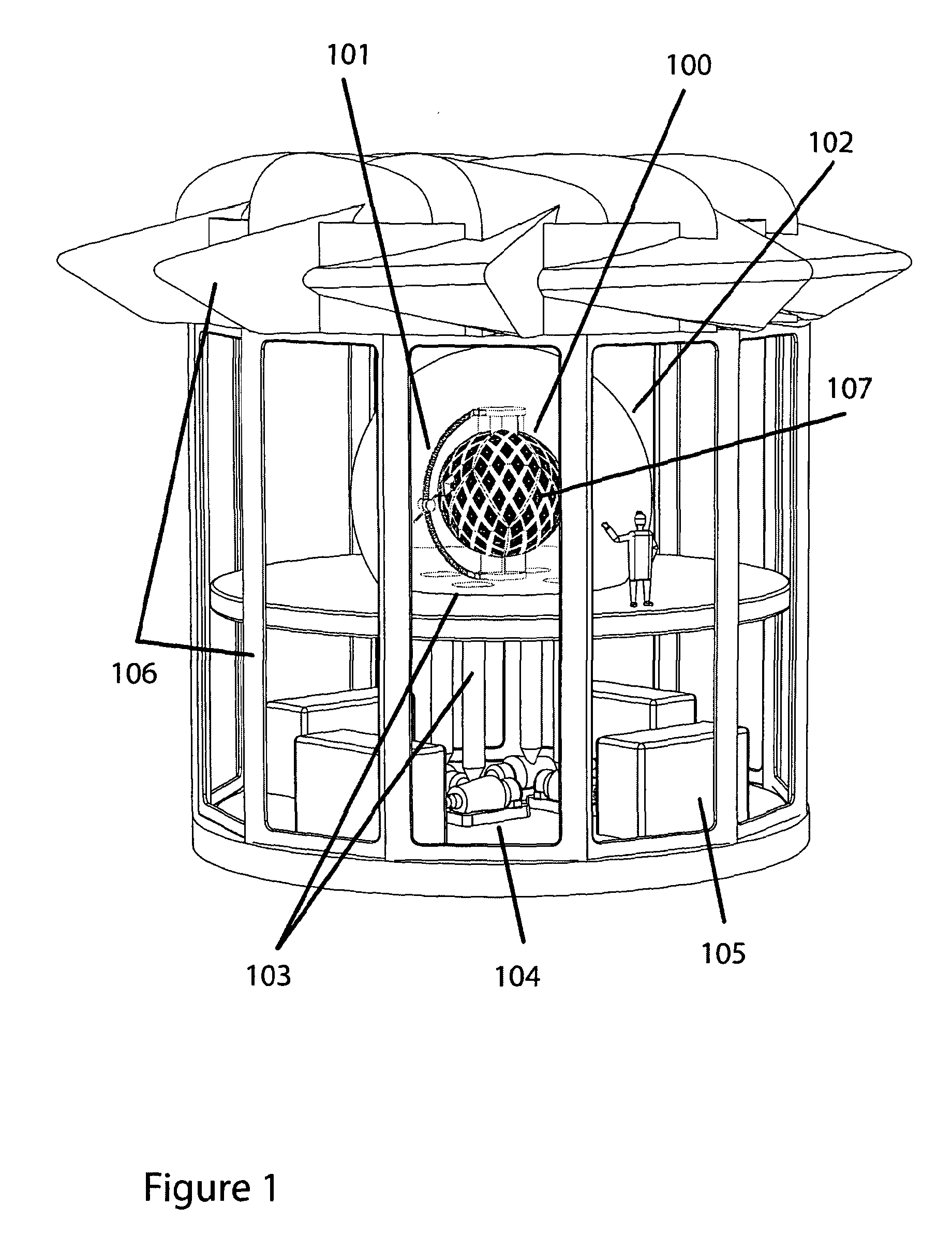
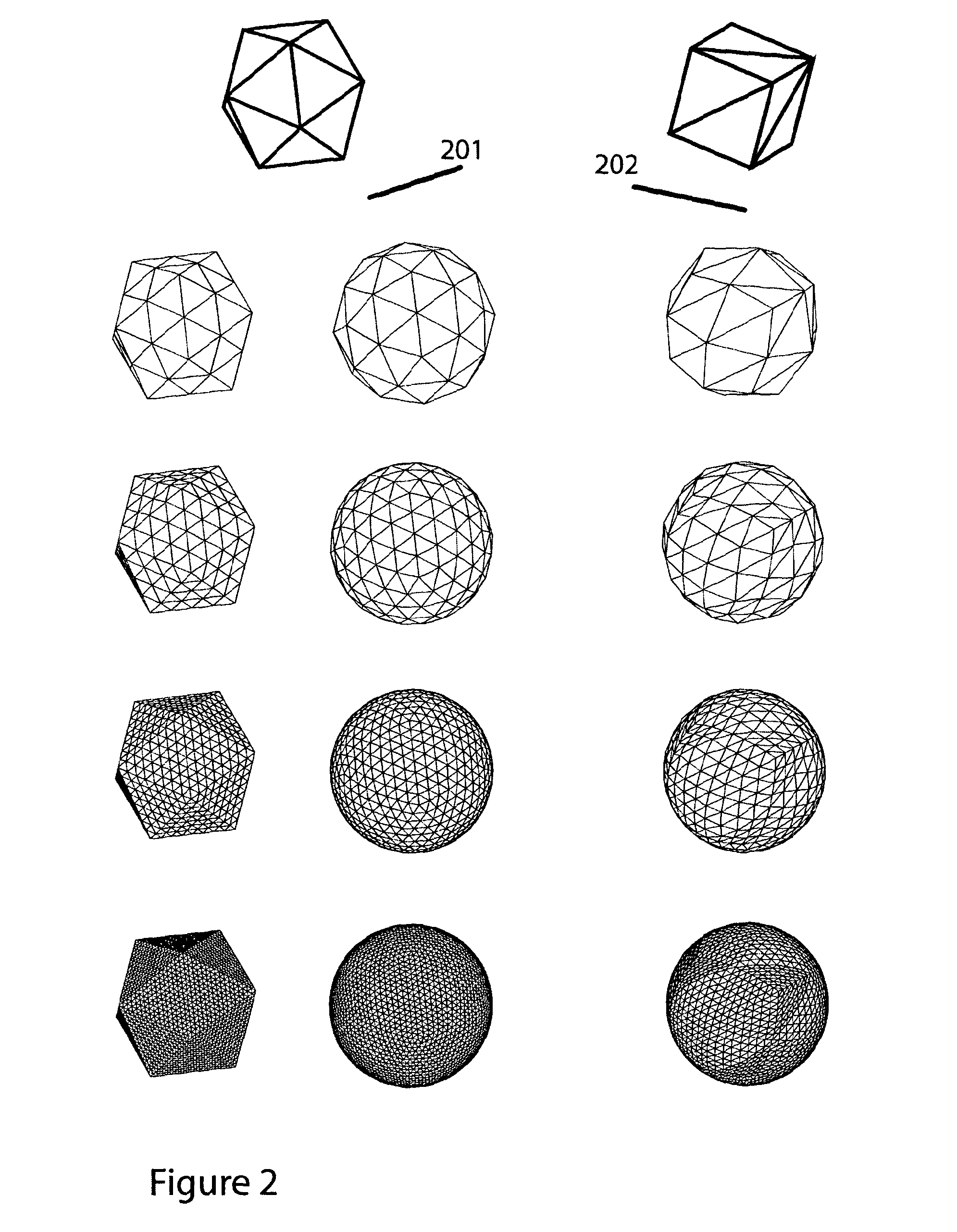
Communication latency, now a dominant factor in computer performance, makes physical size, density, and interconnect proximity crucial system design considerations. The present invention addresses consequential supercomputing hardware challenges: spatial packing, communication topology, and thermal management. A massively-parallel computer with dense, spherically framed, geodesic processor arrangement is described. As a mimic of the problem domain, it is particularly apt for climate modelling. However, the invention's methods scale well, are largely independent of processor technology, and apply to a wide range of computing tasks. The computer's interconnect features globally short, highly regular, and tightly matched distances. Communication modes supported include neighbour-to-neighbour messaging on a spherical-shell lattice, and a radial network for system-synchronous clocking, broadcast, packet-switched networking, and IO. A near-isothermal cooling system, physically divorcing heat source and sink, enables extraordinarily compact geodes with lower temperature operation, higher speed, and lower power consumption.
Owner:ARAS RICHARD JOHN EDWARD
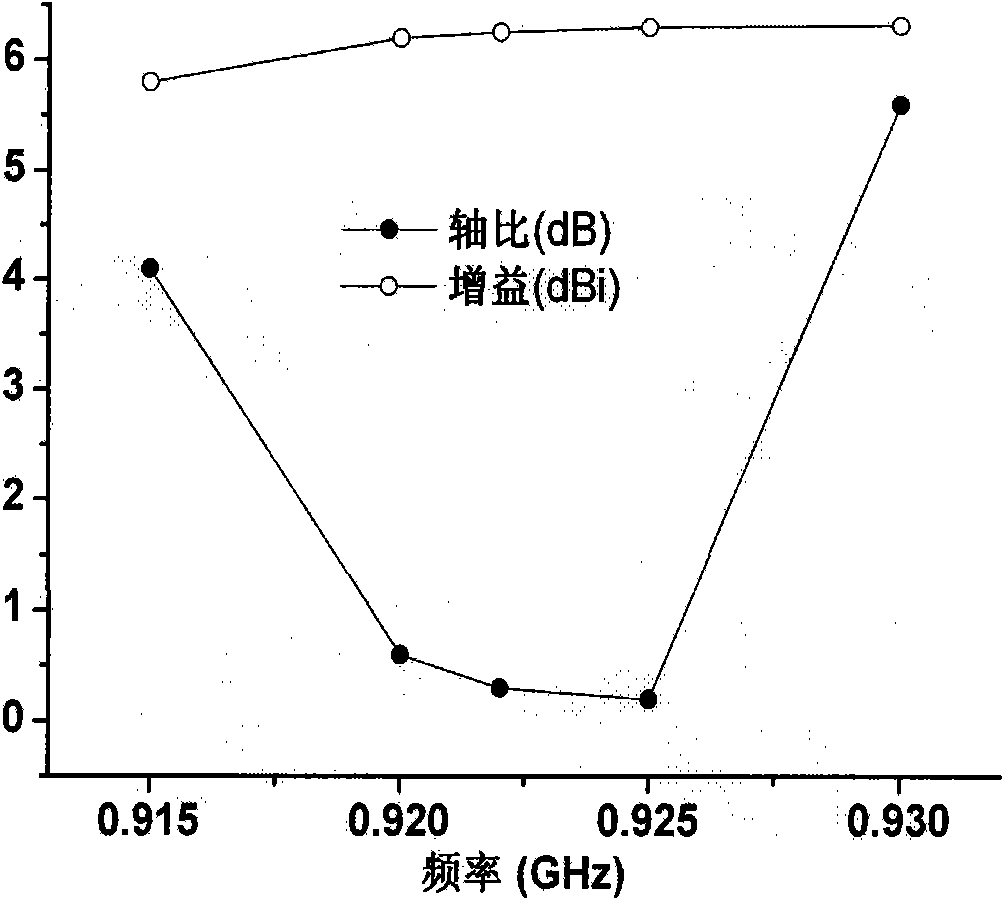
Circularly polarized array antenna for RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) vehicle management field
InactiveCN101807749ANovel structureHigh gainPolarised antenna unit combinationsRecord carriers used with machinesTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
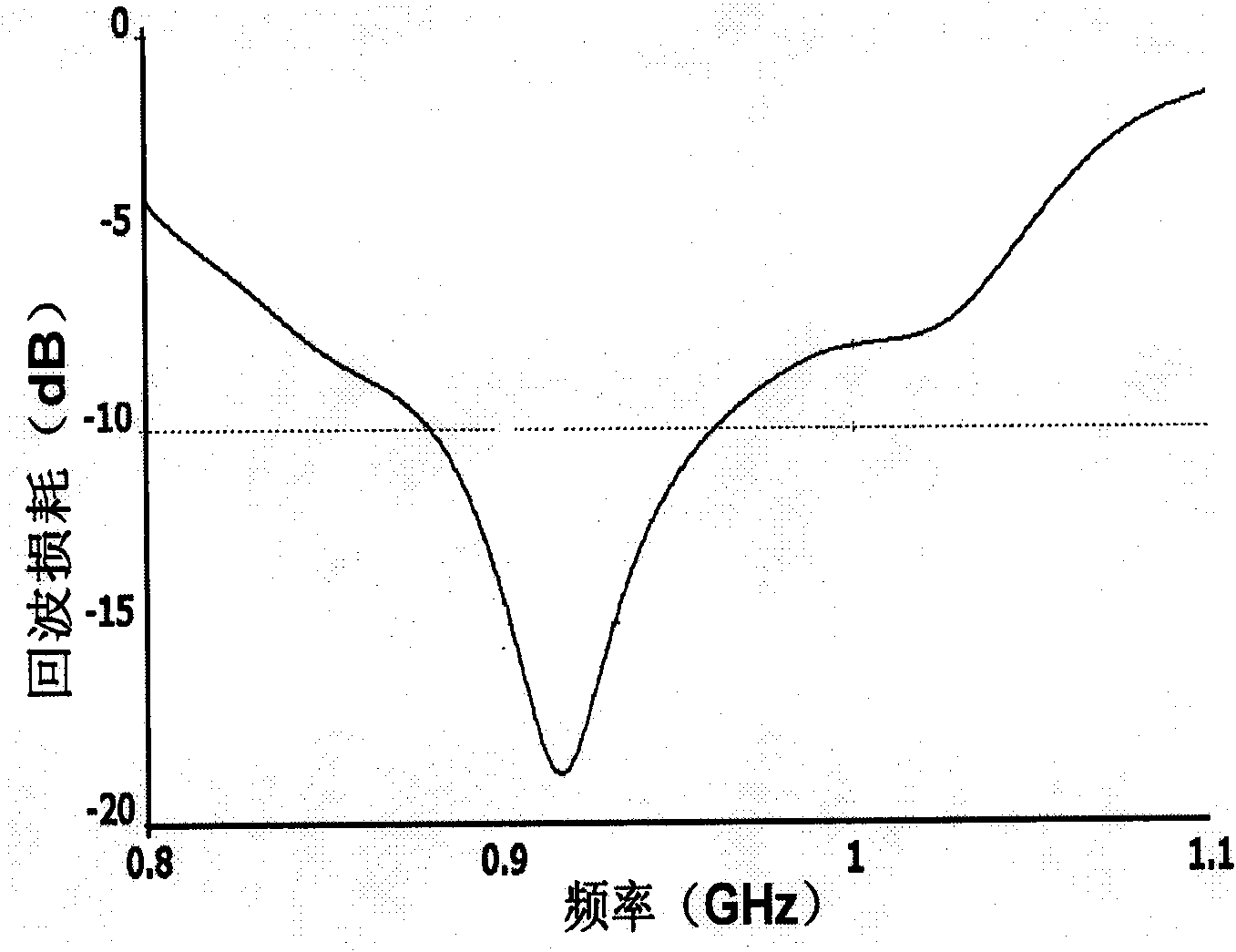
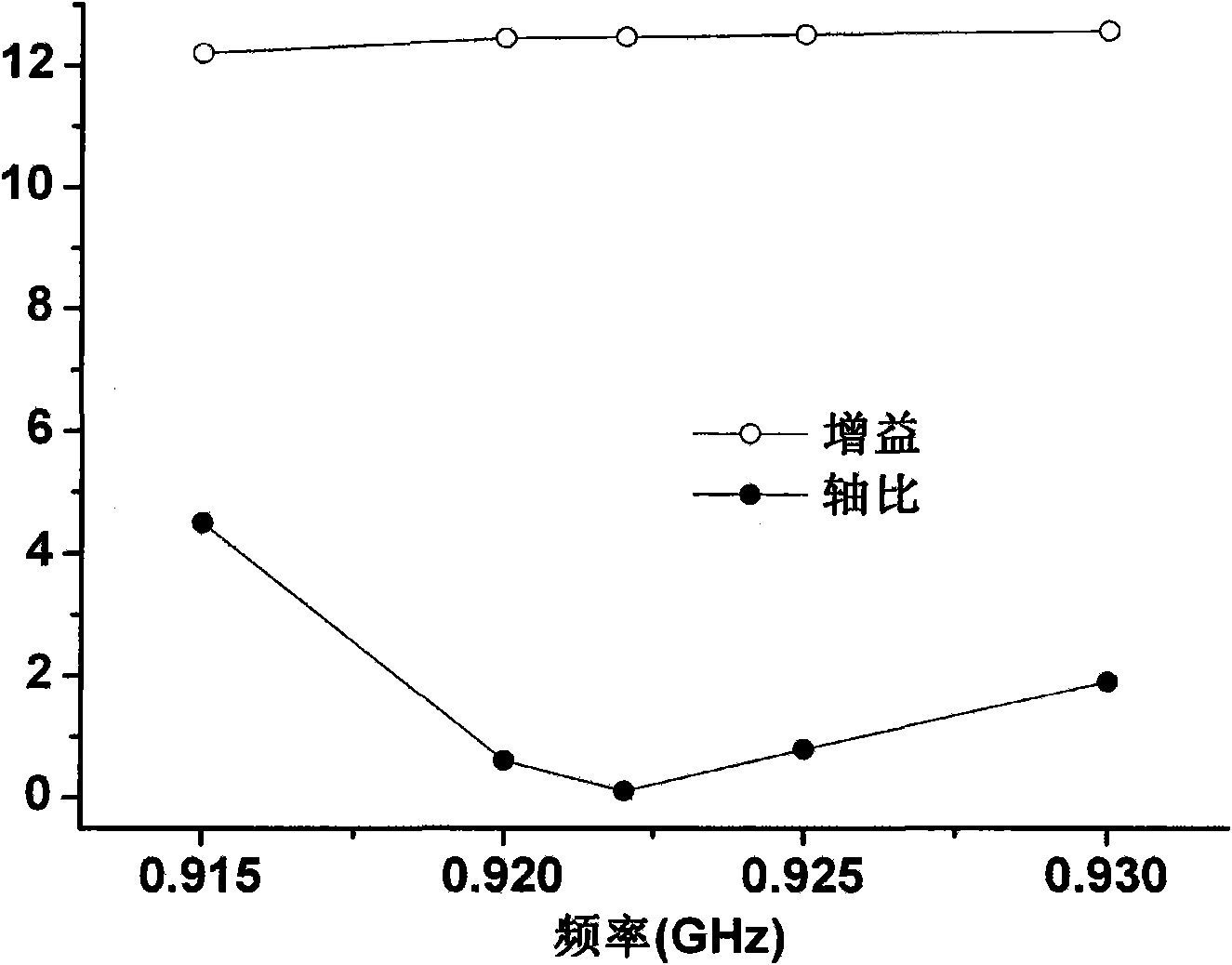
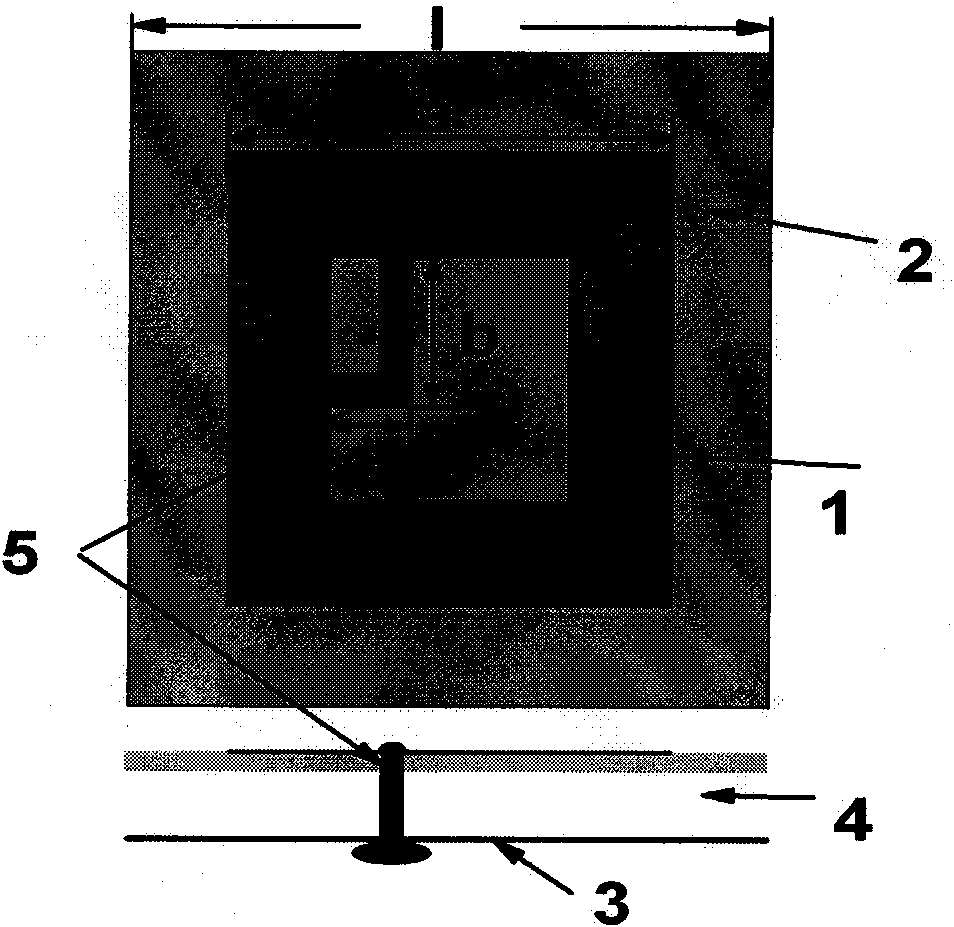
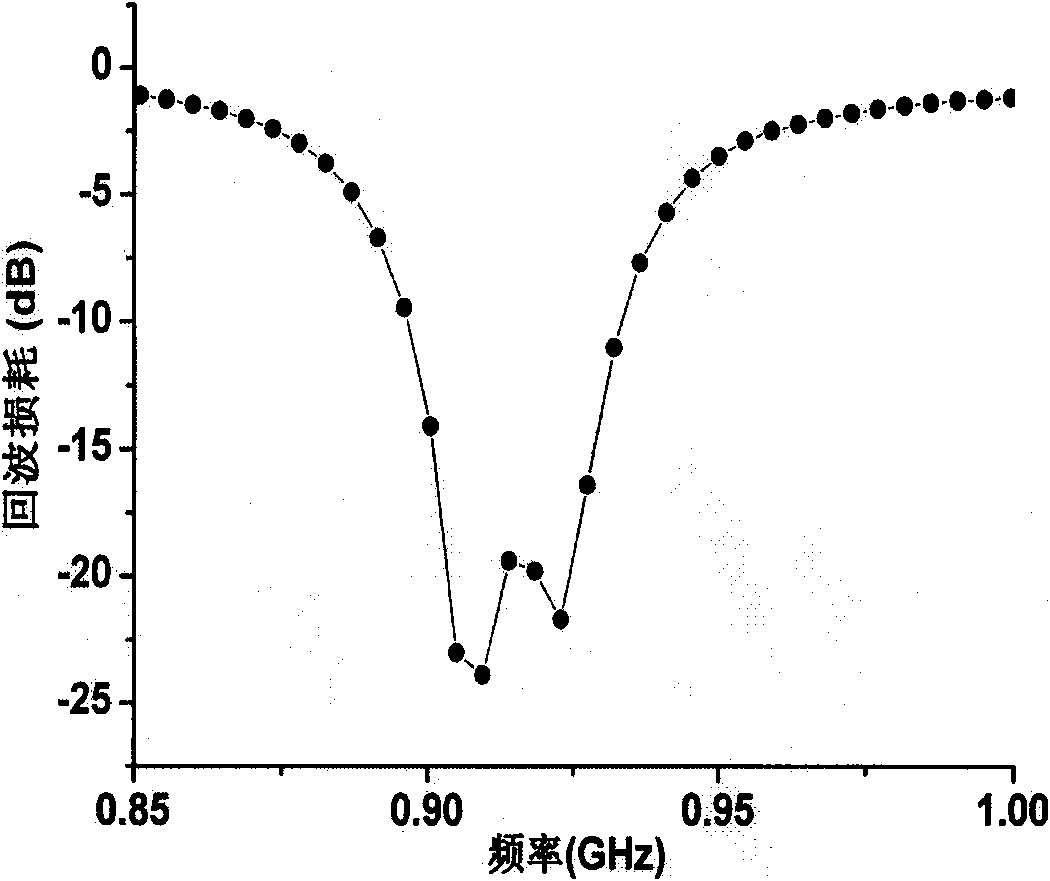
The invention belongs to the field of wireless communication, and relates to a circularly polarized array antenna for the RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) vehicle management field. When RFID is applied to identifying and managing running vehicles, requiring that the polarization matching of an RFID reader antenna and a RFID electronic license plate of a vehicle is good on the one hand, and the RFID reader antenna should have higher plus on the other hand so that effective and identifiable management can be realized for vehicles with the RFID electronic license plates. An antenna is used as receiving and transmitting terminal equipment of an RFID reader, thereby the performance indexes of the antenna are dominant factors for influencing the RFID reading-writing performance. Therefore, the circularly polarized array antenna for the RFID vehicle management is designed in the invention, and the purpose of effectively managing the vehicles with the RFID electronic license plates can be achieved by using the RFID.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Miniaturized and circularly polarized antenna for RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) management field
InactiveCN101807739ARealize no blind zone managementWith miniaturizationAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsCircularly polarized antennaTerminal equipment
The invention belongs to the field of wireless communication, in particular to a miniaturized and circularly polarized antenna for the RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) management field. When RFID is applied to managing materials in a movable container, requiring that RFID hardware devices in the container are miniaturized on the one hand, and an RFID reader has the characteristics of high efficiency and non-blind area for the read-write performance of the attached label of a managed material on the other hand. An antenna is used as receiving and transmitting terminal equipment of the RFID reader, thereby the performance indexes of the antenna are dominant factors for influencing the RFID reading-writing performance. Therefore, the miniaturized and circularly polarized antenna for the RFID material management in the movable container is designed in the invention, and the purpose of effectively managing movable material labels by an RFID system is realized.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
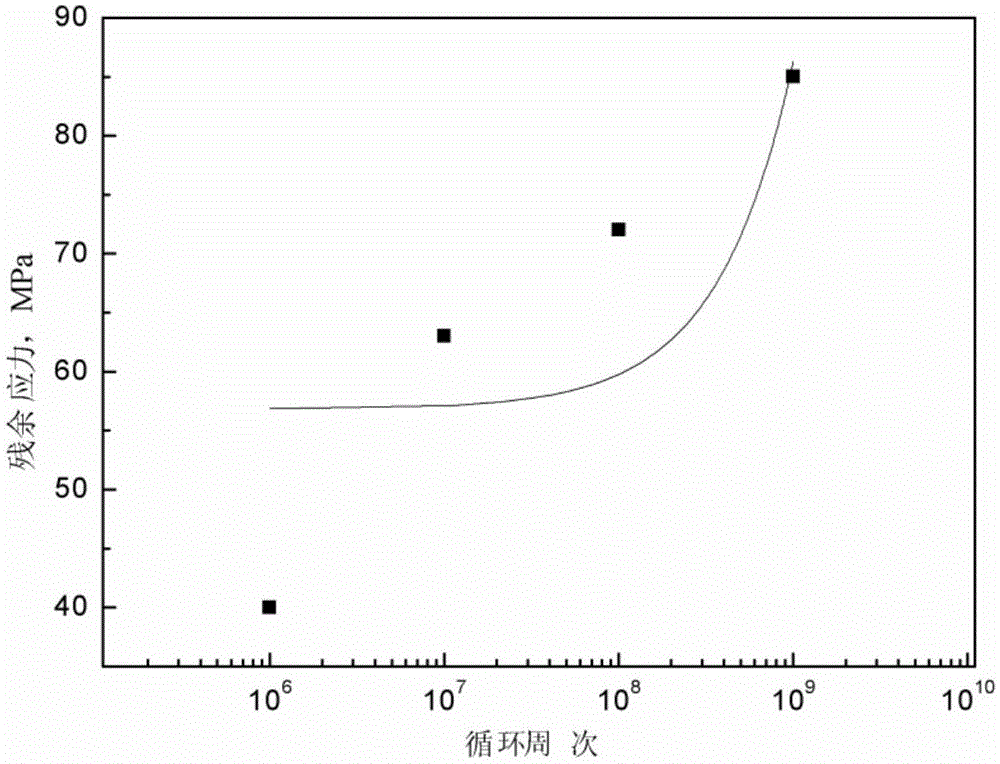
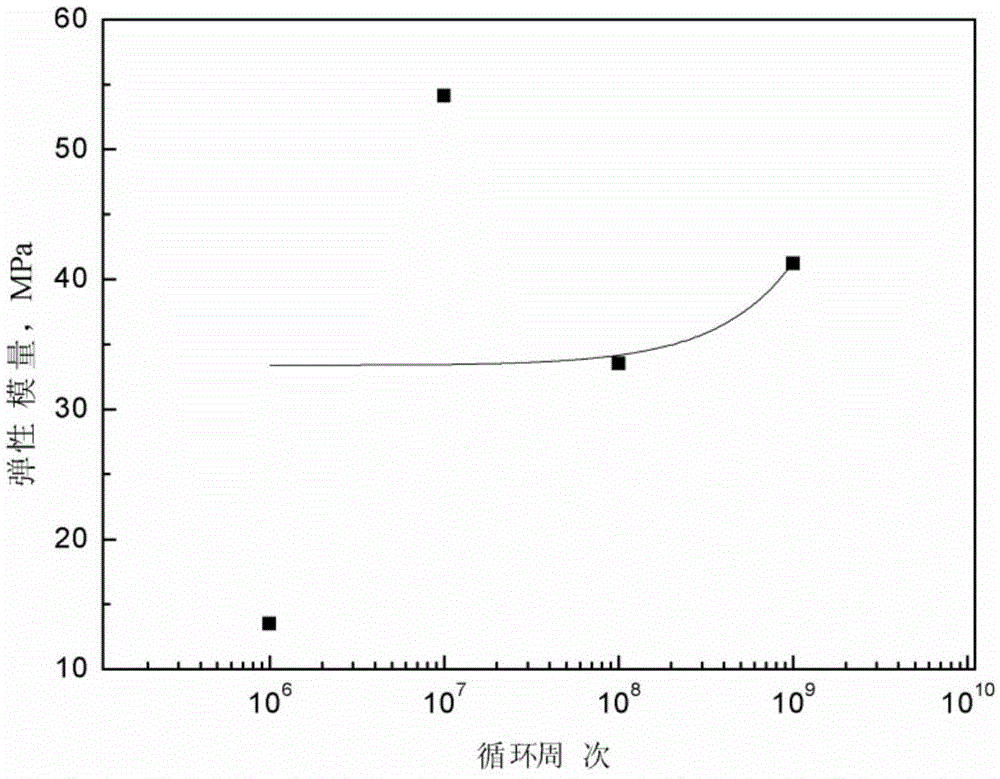
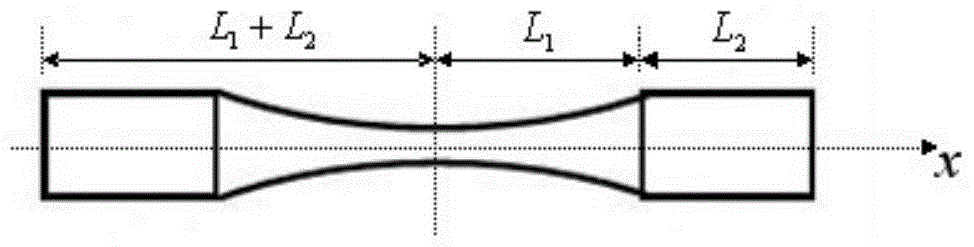
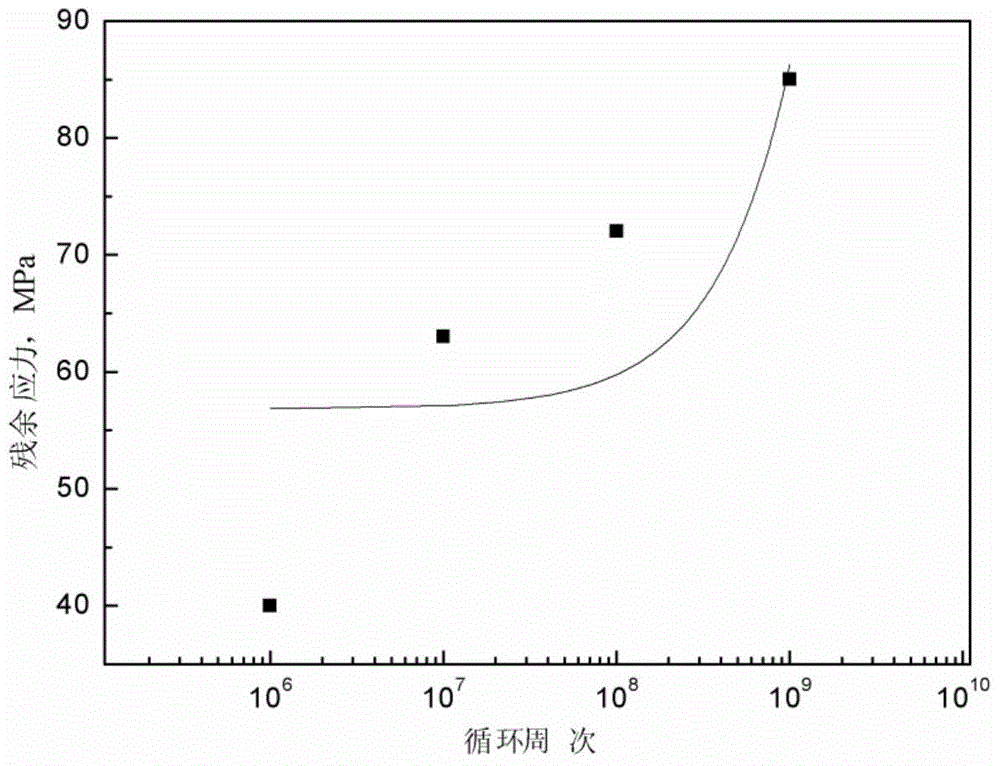
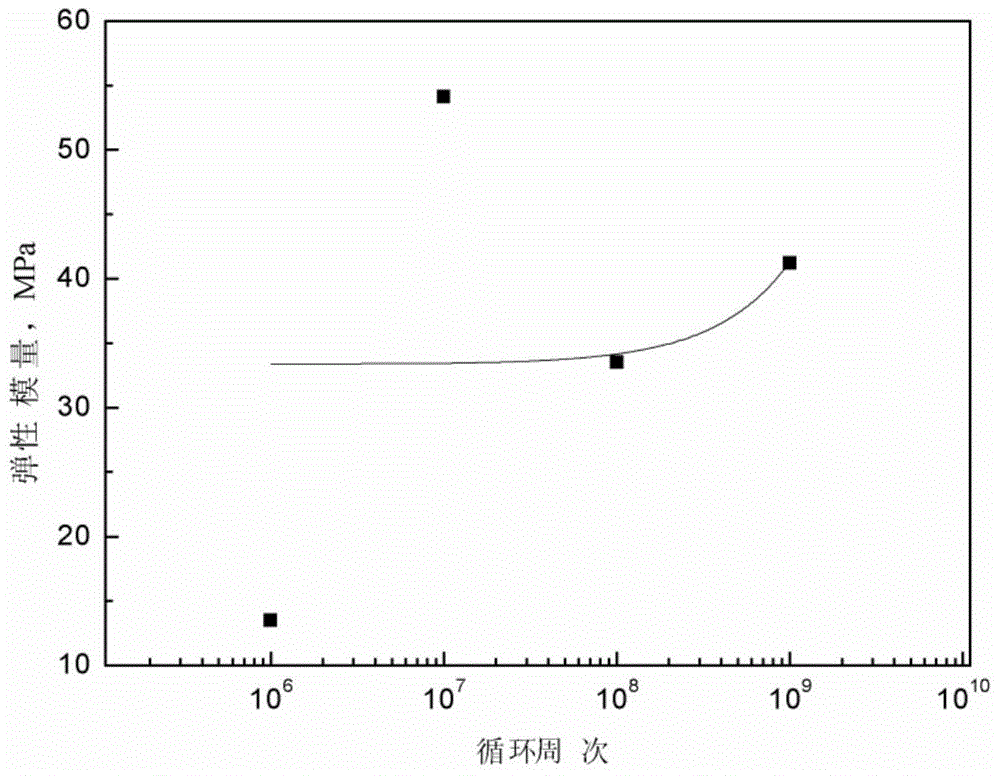
Method for simulating high temperature alloy ultra-high cycle fatigue damage
Belonging to the technical field of measuring and testing, the invention relates to ultra-high cycle fatigue of an ultrasonic fatigue test simulation material, and a high temperature alloy ultra-high cycle fatigue damage simulation method adopting a microanalysis technique for studying micromechanical properties and material deformation to conduct damage assessment. In the invention, a neutron diffraction method is employed to test high temperature alloy funnel-shaped sample surface and subsurface residual stress absolute difference, thus obtaining a relation curve of a cycle number and the residual stress absolute difference; utilizing a nanoindentor to test the elastic modulus absolute difference between dendrite arms and dendrites in the material, thus obtaining a relation curve of the cycle number and the elastic modulus absolute difference; and analyzing the crystal deformation condition by electron back scattering diffraction so as to obtain a relation curve of the cycle number and small angle subboundary crystal deformation. Through comprehensive comparison of the three curves, the dominant factors determining high temperature alloy ultra-high cycle fatigue damage can be understood clearly, and the ultra-high cycle fatigue damage condition of similar other alloys can be predicted.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for determining dominant influence factors of pollutant emission
InactiveCN101866397AImplement optimizationImplement upgradesSpecial data processing applicationsPollutant emissionsAnalysis method
The invention provides a method for determining dominant influence factors of pollutant emission. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, determining the types of pollutants and acquiring historically measured data of pollutant emission amount; secondly, selecting factors which affect the pollutant emission amount and acquiring the historically measured data of the factors; and finally, calculating grey relation degrees by using a grey relation analysis method and performing sorting according to the size of the grey relation degrees so as to determine the dominant influence factors of the pollutant emission. In the invention, the major dependency relationship between the pollutant emission and an environmental economic system can be comprehensively evaluated by a simple principle and a few data, the optimization and updating of an industrial structure can be effectively implemented and the industrial pollution can be effectively controlled after the dominant factors which affect the emission of various pollutants are determined, and thus, the task of energy conservation and emission reduction is completed and the sustainable region development is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
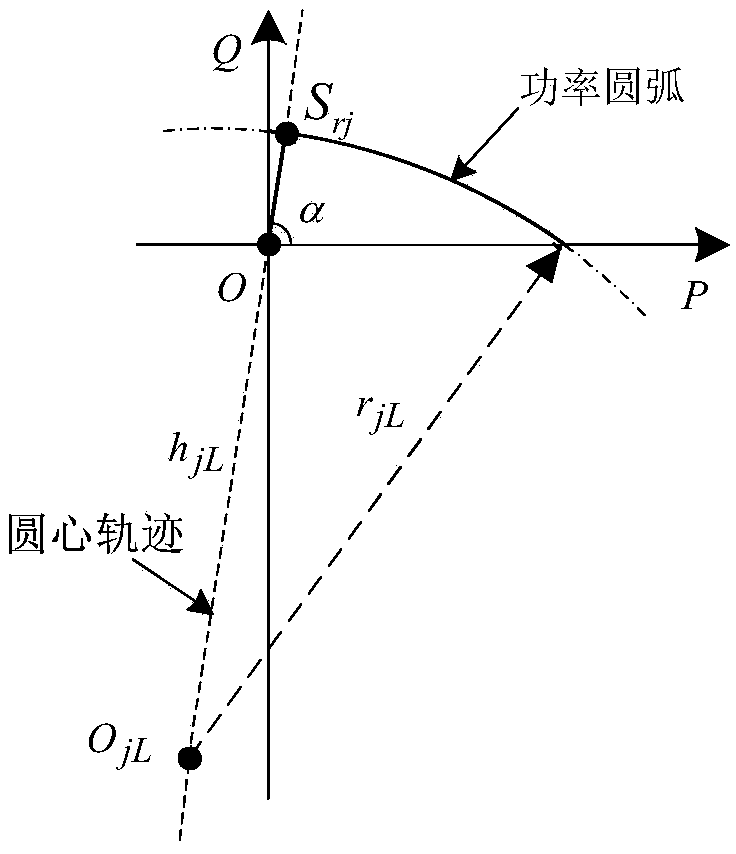
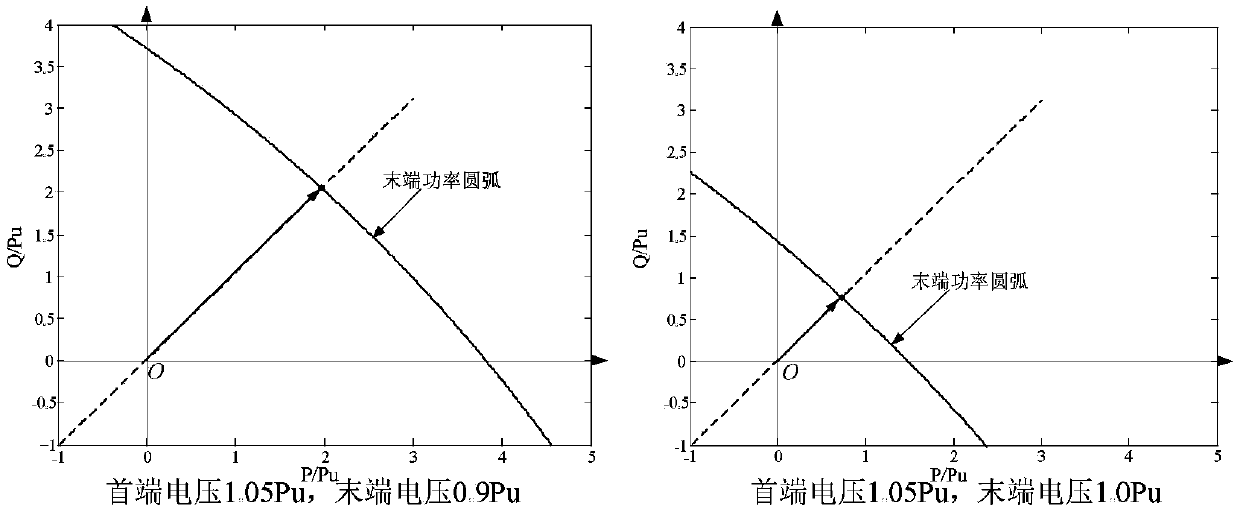
Line voltage drop torque model based 10kV line voltage quick estimation method
ActiveCN108933439ASmall amount of calculationConvenient and accurateAc network circuit arrangementsTransformerEstimation methods
The number of transformers on a 10kV line is large and the load randomness is high and line voltage quick estimation is difficult. The invention provides a line voltage drop torque model based 10kV line voltage quick estimation method. Based on analysis of correspondence of segmented line voltage drops and power arcs, a dominant factor affecting line voltage drop is obtained and a cross bar torque model for describing 10kV line voltage drop features and a torque method for voltage quick estimation are proposed. According to the invention, based on node positions of the transformers and the minimal apparent power of the load power arcs, equivalent torques of different nodes are obtained; through linear superposition of the equivalent torques of the different nodes, the voltage drop and a tail end voltage value of the line are obtained. The method is small in calculation amount; compared with an example result of a universal program PASAP, the method is good in accuracy of tail end voltage estimation. The method provided by the invention can be widely applied to operation and planning of 10kV distribution networks and is high in engineering application value.
Owner:竺炜
Method for Determining a Weight-adjusting Parameter in a Variable-weight Vulnerability Assessment Method for Water-outburst From Coal Seam Floor
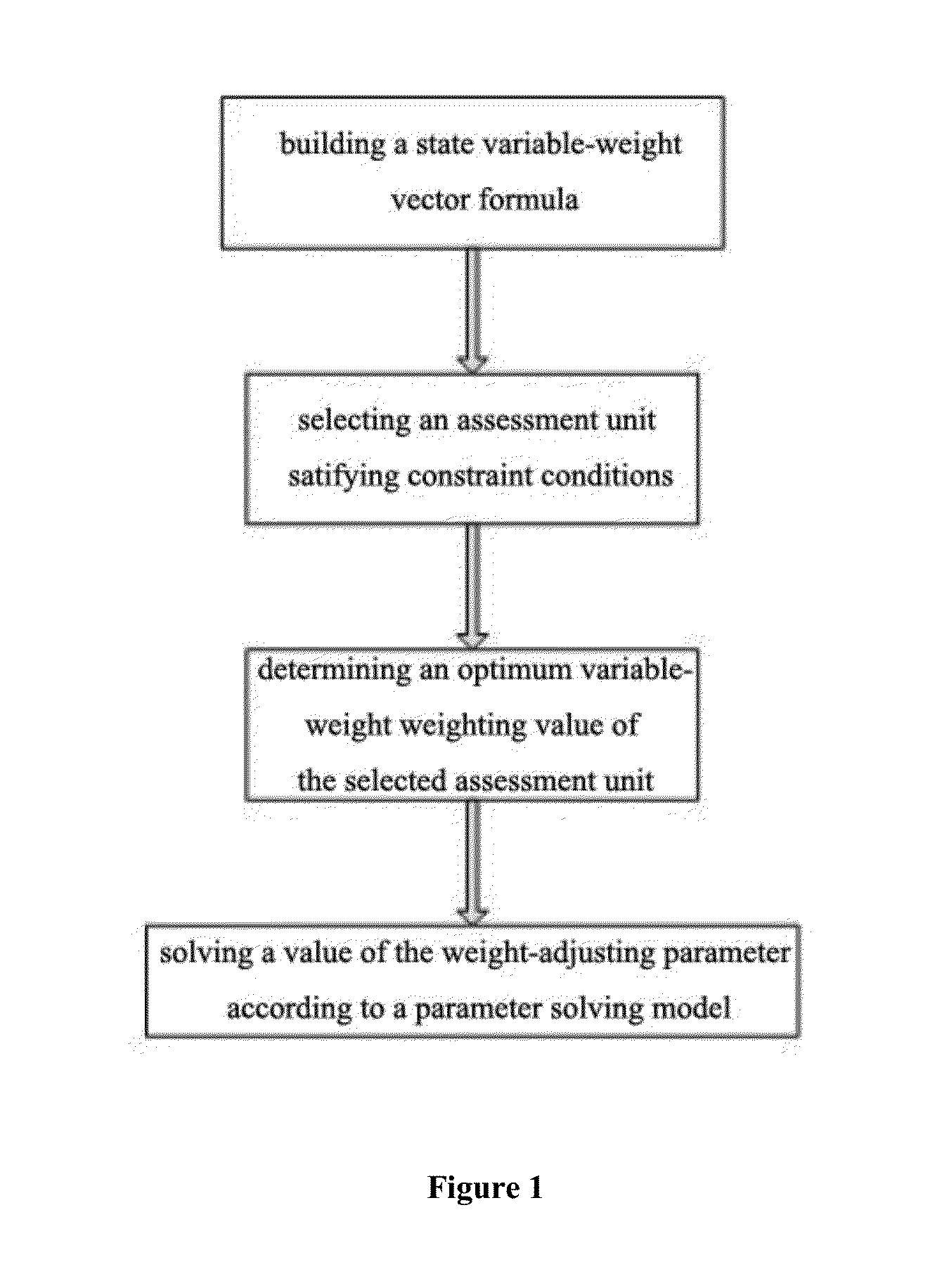
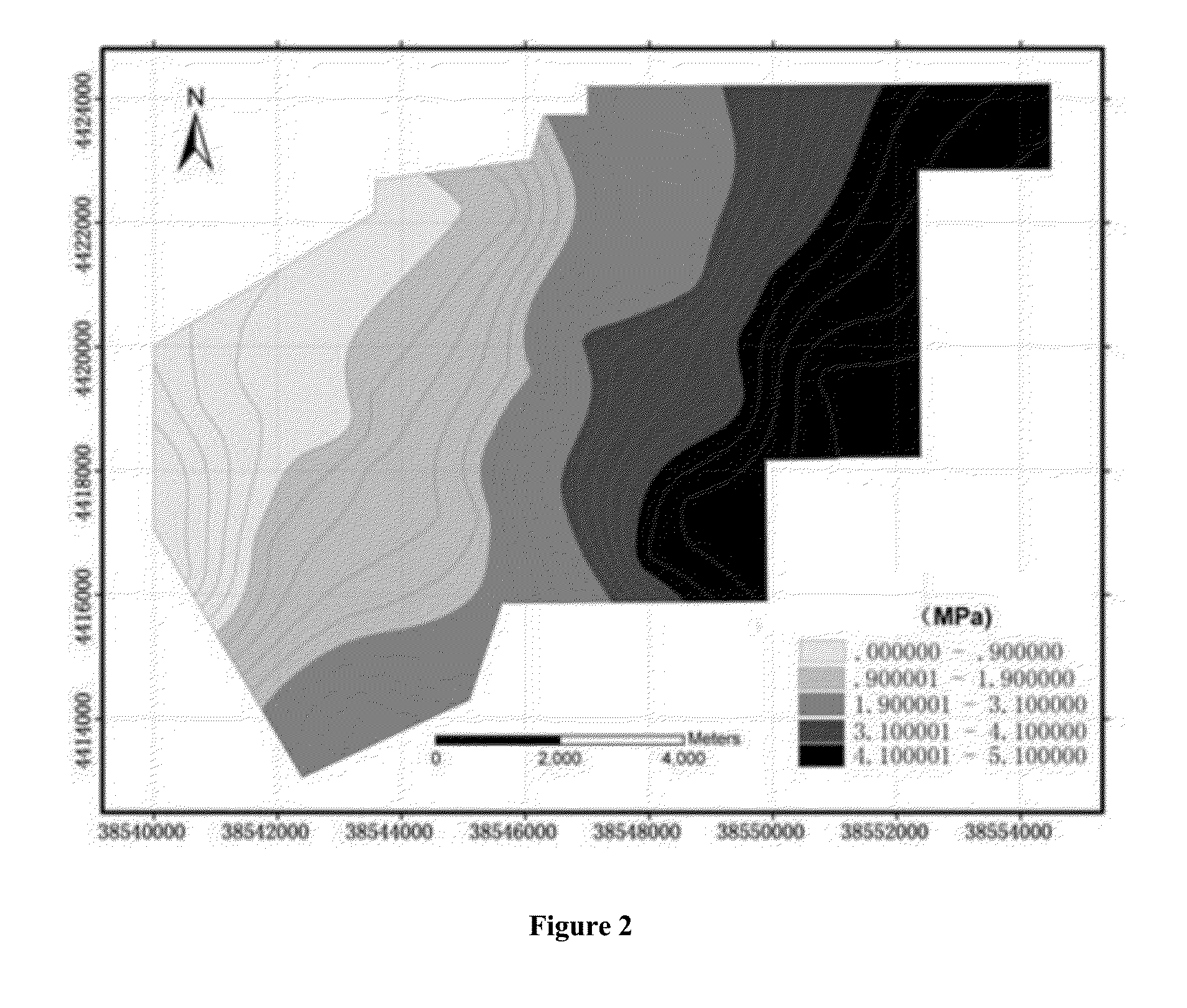
InactiveUS20150234092A1Satisfies requirementFulfil requirementsSurveySeismologyState variableVulnerability evaluation
A method for determining a weight-adjusting parameter in a variable-weight vulnerability assessment method for water-outburst from coal seam floor, comprising the steps of determining a dominant factors and a constant-weight weighting value, further comprising the following steps: 1) building a state variable-weight vector formula; 2) selecting or giving an assessment unit in accordance with constraint conditions; 3) determining an optimum variable-weight weighting value of the selected assessment unit; and 4) solving a value of the weight-adjusting parameter according to a parameter solving model. The method for determining a weight-adjusting parameter in assessment and prediction of vulnerability for water-outburst from coal seam floor by means of a variable-weight model is proposed at the first time. In this method, an optimum variable-weight weighting value of the selected assessment unit is set, and then a value of the weight-adjusting parameter is solved according to a built parameter solving model. With practical application testing, the weight-adjusting parameter determined by this method can effectively reflect the controlling effects on water-outburst of the multiple dominant factor index values in various combined states, and can effectively improve the precision of assessment and prediction of vulnerability for water-outburst from coal seam floor.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Reagent kit for fast detection of drainage oil and method for fast detection of drainage oil
InactiveCN102758025AQuality improvementEffective supervisionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA extractionPolymerase
The invention discloses a reagent kit for fast detection of drainage oil and a method for fast detection of the drainage oil. The reagent kit comprises a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction buffer, thermus aquaticus DNA (Taq DNA) polymerase, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) solution and a sample loading buffer. According to the reagent kit, on the basis of existing research, key dominant factors such as extraction reagents and reaction conditions in the whole process from extraction of drainage oil genes to PCR detection are improved and optimized, and the whole set of drainage oil detection reagent kit which is high in stability, fast and simple is produced. According to the reagent kit and the detection method, constituents of the drainage oil are identified from the point of genes, the detection of the drainage oil has the advantages of being high in specificity, high in sensitivity, good in method reproducibility, fast and simple to detect and the like, and the gap of existing detection methods is filled. The reagent kit and the detection method have important popularization and application values and are important to effective supervision of the drainage oil and protection of benefit of consumers.
Owner:GUANGZHOU QUALITY SUPERVISION & TESTING INST
Finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of soft-rock slope stability
InactiveCN107908890ASolving slope stability problemsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMechanical modelsElement analysis
The invention discloses a finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of soft-rock slope stability. The method includes the following steps: step one, obtaining rock slope failure types, slope stability influence factors and slope reinforcement support measures by induction, establishing a mechanical model of engineering geology simulation analysis under the action of the different influence factors, and analyzing a dominant factor controlling the soft-rock slope stability and a potential mode thereof; and step two, using an approximate equivalent physical model, which is formed bya plurality of mutually associated unit bodies, by a finite-element analysis method of the slope stability to replace actual structures or continua, and establishing equations, which characterize force and displacement relationships, through basic principles of structure and continuum mechanics and physical characteristics of units. The finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of thesoft-rock slope stability uses the finite-element method to analyze the stability thereof, carries out support and treatment on places where danger may further occur, and has certain guiding significance for solving slope stability problems.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
A resource block based pilot pattern design for 1/2-stream mimo ofdma systems
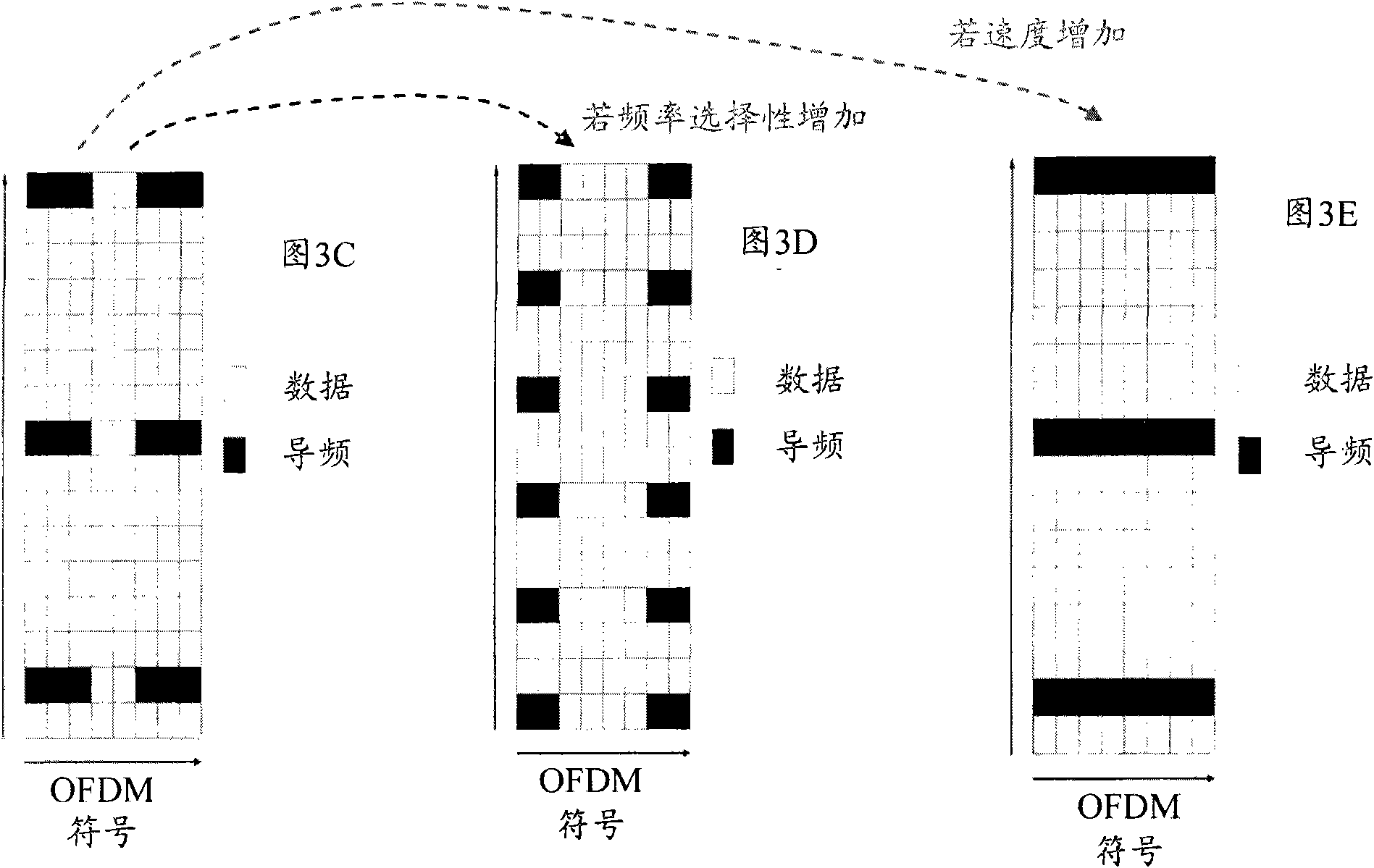
In OFDMA wireless communications systems, pilot pattern design is optimized based on predefined resource block size. The number of pilots and the spacing between pilots within a resource block is determined based on a set of system requirements. In one novel aspect, pilots are allocated within a resource block to avoid channel extrapolation in both frequency domain and time domain. First, four pilots are positioned at four corners of the resource block. Next, the remaining pilots are maximally evenly distributed within the resource block along both the frequency domain and the time domain. Finally, it is verified that an approximately equal number of pilots are evenly distributed along the time domain with respect to each data stream to minimize power fluctuation. For uplink transmission,one or more frequency tones at one or more edges of the resource block are reserved to be pilot-free to reduce mu ltiuser synchronization error effect. In another novel aspect, if resource block sizeis smaller than a predetermined number, such as three, in either frequency or time domain, then the pilots are allocated such that average pilot-to-data distance is minimized and that pilot-to-pilot distance is as large as possible. In one example, m pilots are allocated in an ixj resource block. The resource block is partitioned into n equal sub blocks, where m is a multiple of n. Within each subblock, m / n pilots are positioned such that average pilot-to-data distance is minimized. In another novel aspect, in a high-rank MIMO system, pilots are allocated within a resource block to avoid channel extrapolation in frequency domain only. Because high-rank MIMO only supports low-mobility environment, time-domain extrapolation is no longer a dominant factor.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
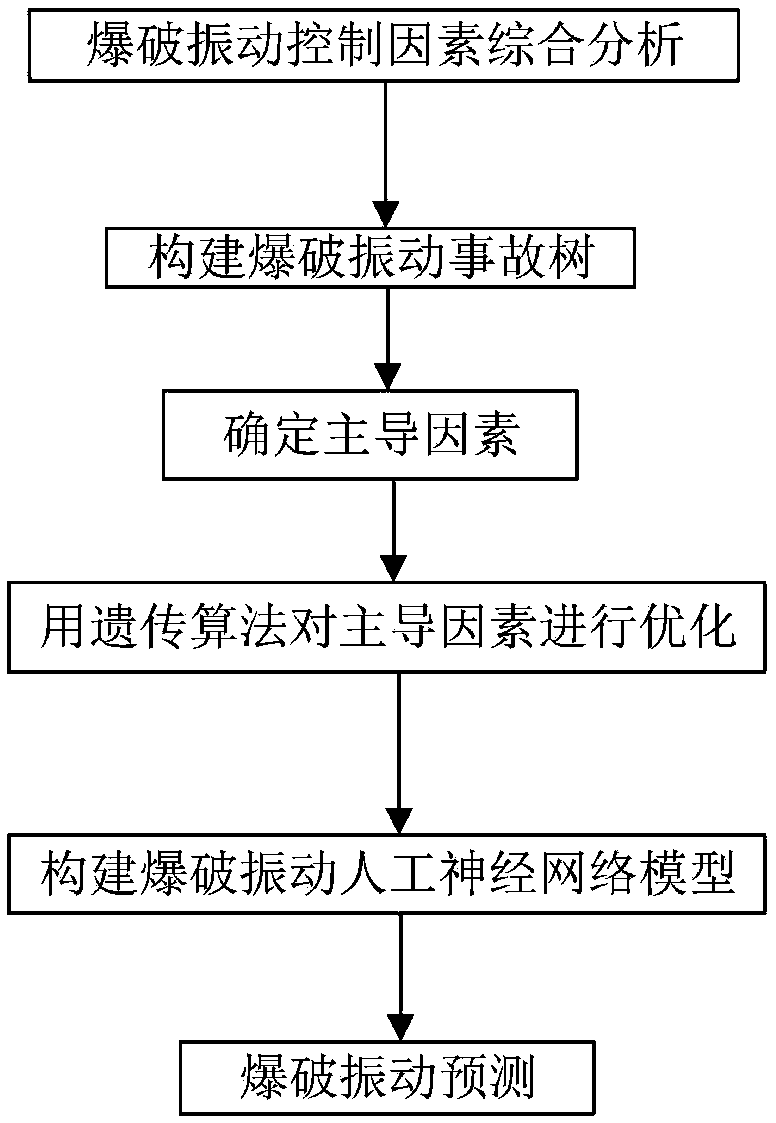
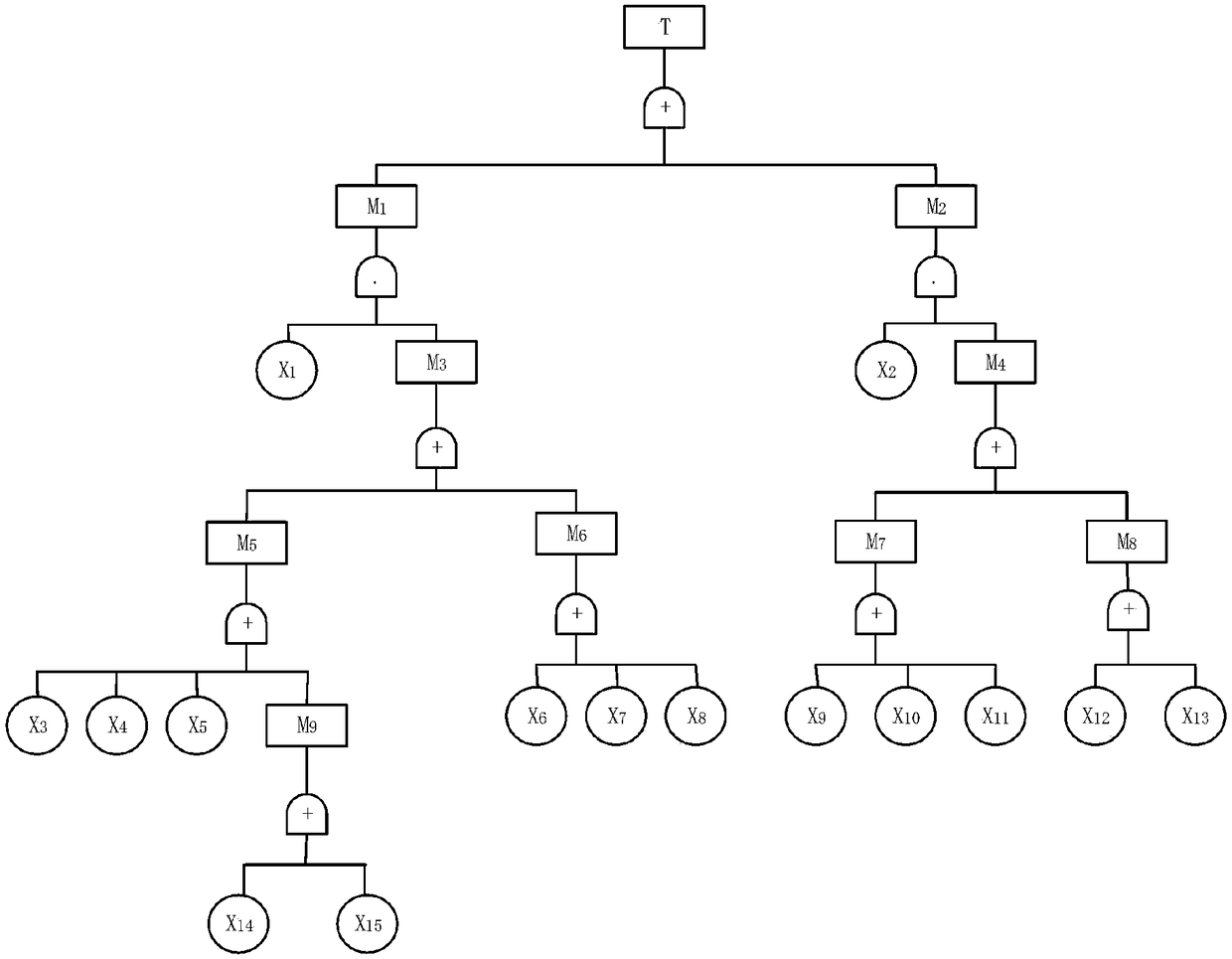
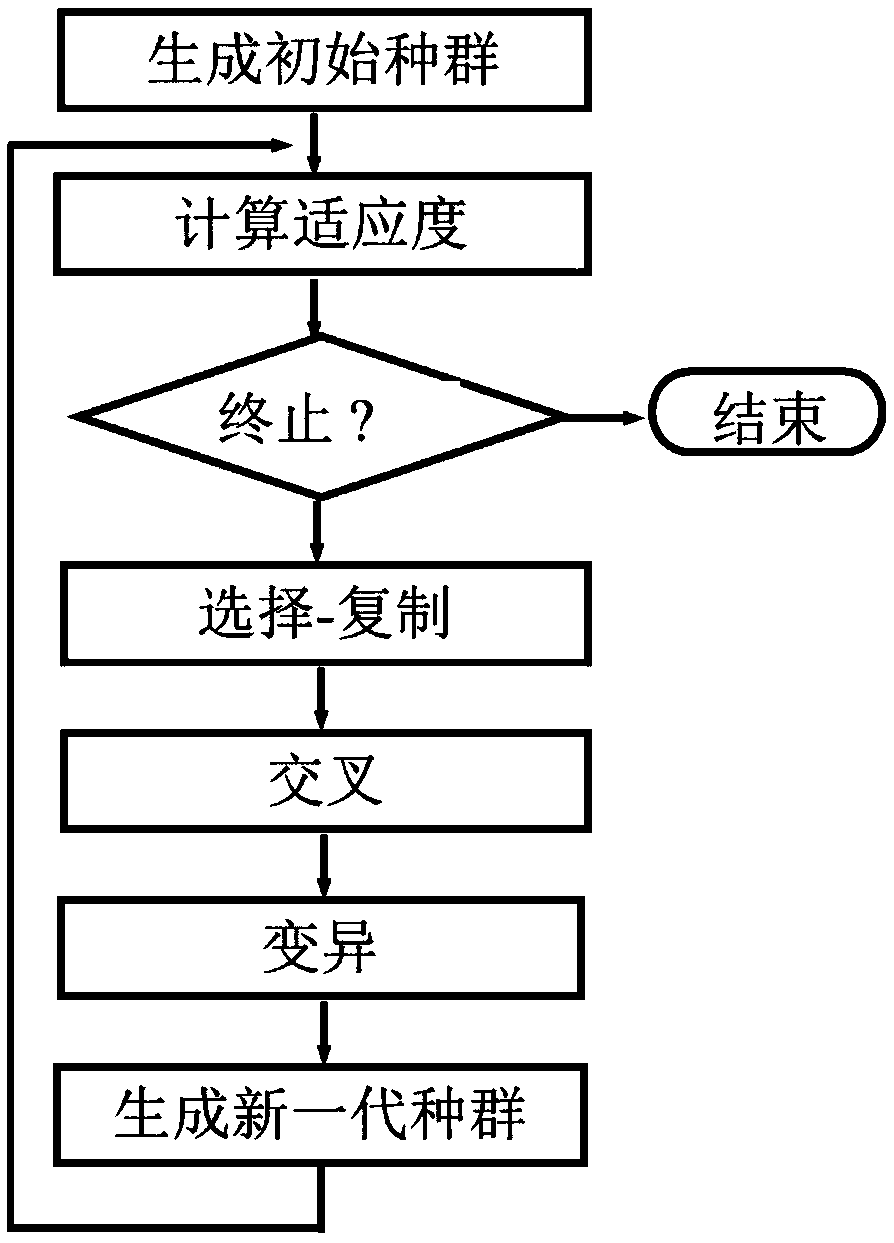
A blasting vibration control prediction method based on a fault tree and a genetic algorithm
InactiveCN109284818AImprove rationalityImprove scienceResourcesNeural architecturesAlgorithmSimulation
The invention discloses a blasting vibration control prediction method based on a fault tree and a genetic algorithm, which collects all factors influencing the blasting vibration design and construction process in the history as fault tree events and constructs a blasting vibration fault tree. Identification of dominant factors; Genetic algorithm is used to optimize the initial weights and network structure of the neural network to replace the general neural network initial weights and the random selection and blind selection of the network structure. Then the neural network algorithm is usedto fine-tune the network weights and search the optimal solution or the optimal approximate solution in the network structure; constructing a BP artificial neural network model; predicted results: within the control range (1, 0, 0, 0); reaching the critical value (0, 1, 0, 0); exceeding the control value (0, 0, 1, 0); seriously exceeds control value (0, 0, 0, 1). The invention controls the occurrence of the blasting vibration accident from the source, and effectively reduces the harmful effect caused by the blasting vibration. The rationality and scientificity of blasting design are improved.
Owner:NORTH BLASTING TECH
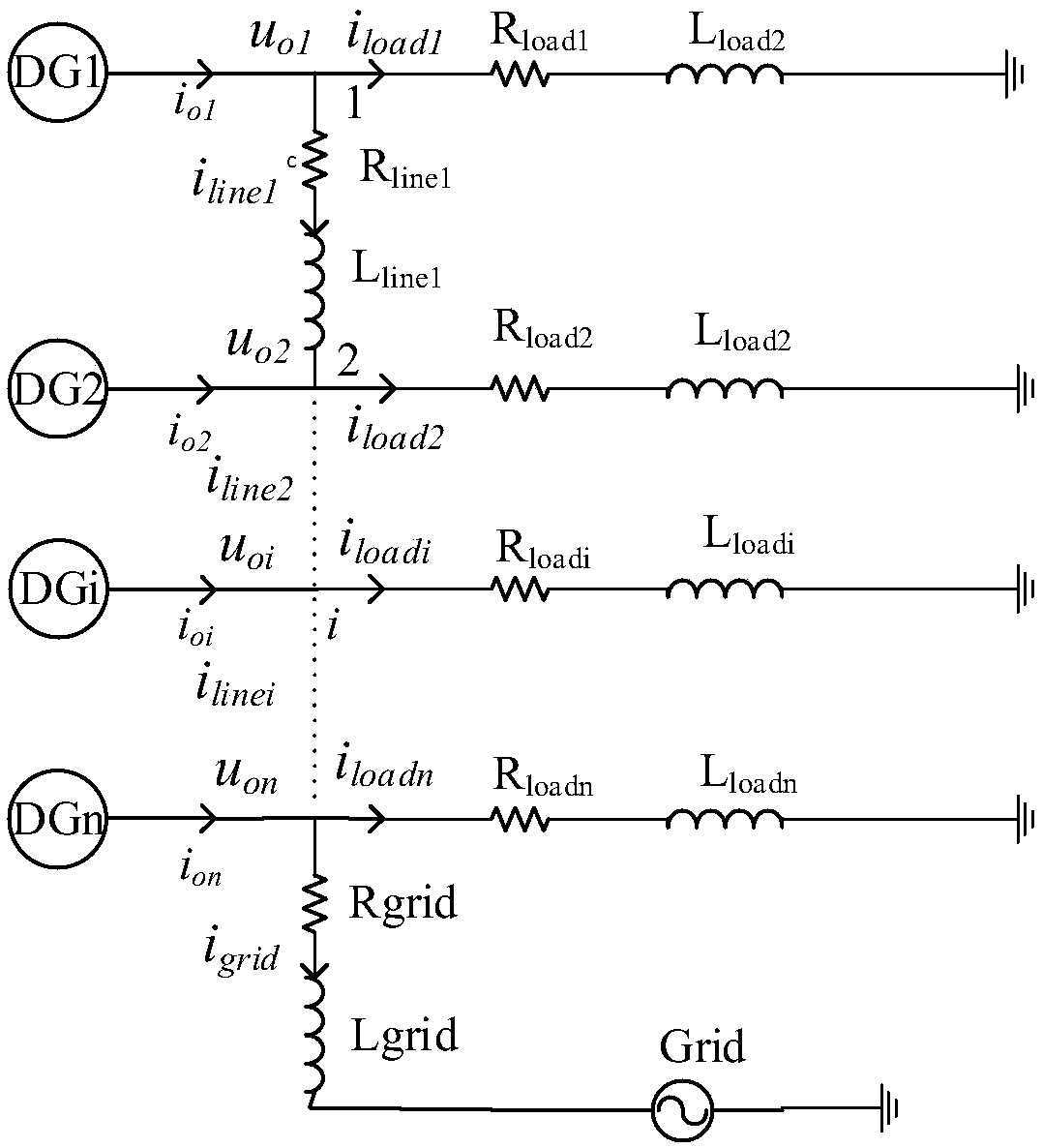
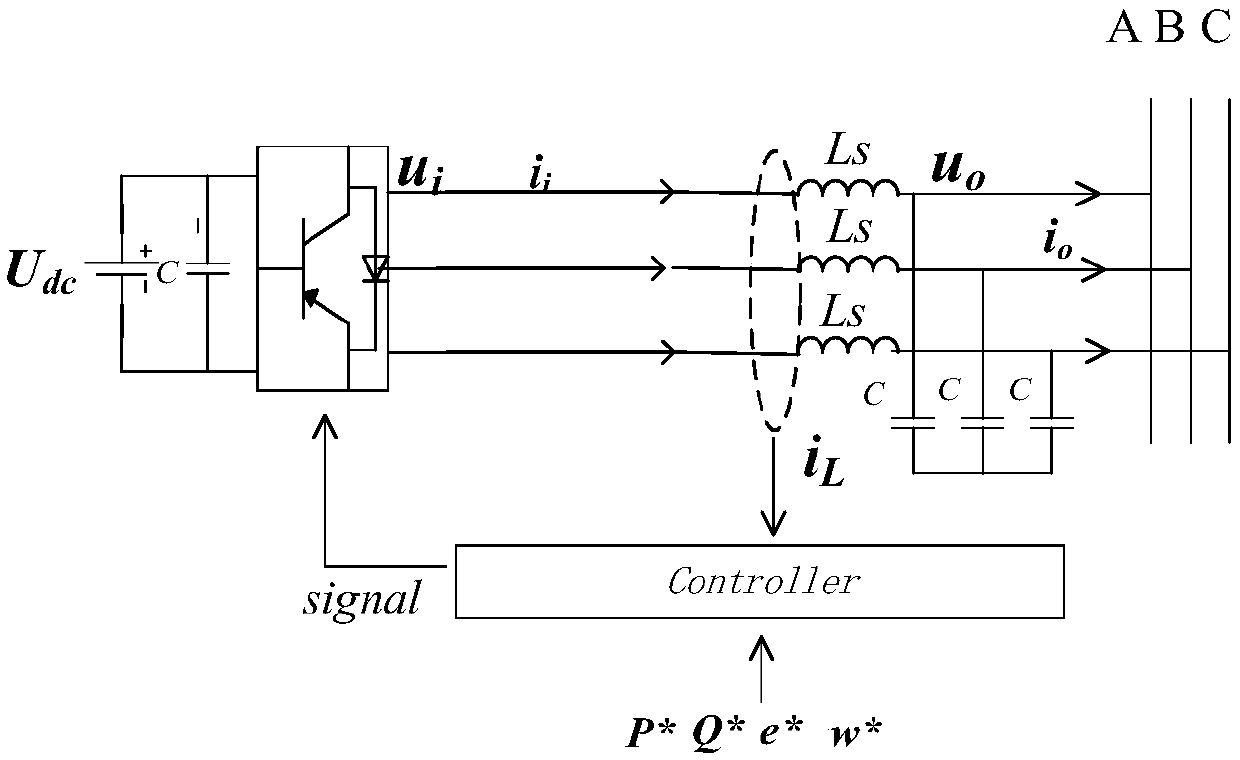
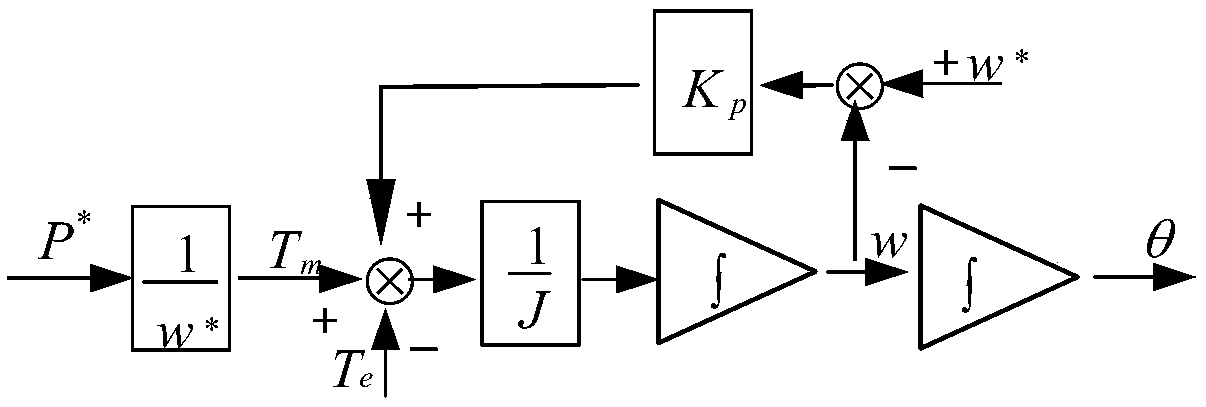
A microgrid stability control method based on bifurcation theory
InactiveCN109066784AAccurately describe dynamic characteristicsDescribe dynamic propertiesSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMicrogridState space equation
The invention discloses a microgrid stability control method based on bifurcation theory, which comprises the following steps: according to the microgrid circuit structure and the electrical relationship, respectively establishing the state equations of each distributed power source, a transmission line and a load; by Considering the frequency difference between DGs and between DGs and large powergrids, establishing a unified state space equation of micro-grid considering the output difference of DGs; Under the unified state space equation, determining the dominant factors affecting the stability of microgrid; Based on the bifurcation theory, when the dominant factors change, enabling the equilibrium solution of stable operation state of micro-grid popular, and then determining the boundary conditions of stable operation of micro-grid. The invention accurately describes the dynamic characteristics of the system, and makes up for the deficiency that the small disturbance analysis method can only be adopted in the current research. By detecting whether the bifurcation point occurs when the parameters of the system change, the condition of stable operation of the system is determined, and the limitation of stability control method in analyzing the stability of high-order system is solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +3
Forest subcompartment classification method
The invention relates to a forest subcompartment classification method. The method comprises the steps: enabling a clustering analysis idea and method to be applied in the subcompartment division research; directly comparing the qualities in dominant tree species (groups) with the consistent operation type and standing type or between samples; searching the growth dominant factors (standing conditions) of a forest subcompartment, and enabling the growth dominant factors (standing conditions) to serve as clustering factors, wherein the growth dominant factors (standing conditions) comprise the topographic conditions (slope, exposure and slope position) and soil conditions (soil thickness and humus thickness); employing the shortest distance clustering algorithm (shown in the description), wherein dkr, dpk and dqk are the distances between different clusters; taking the forest subcompartment as the classification object, and dividing all to-be-clustered forest subcompartment data in different classification modes or according to different classification numbers (two classes, three classes, four classes,..., or more classes); selecting the classification mode or classification number which enables the number of forest subcompartments in different classes are close to each other through combining with the factors that the internal difference in the same cluster is small and the difference between different clusters is remarkable; describing the features of forest subcompartments in each class, and guiding the actual production.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
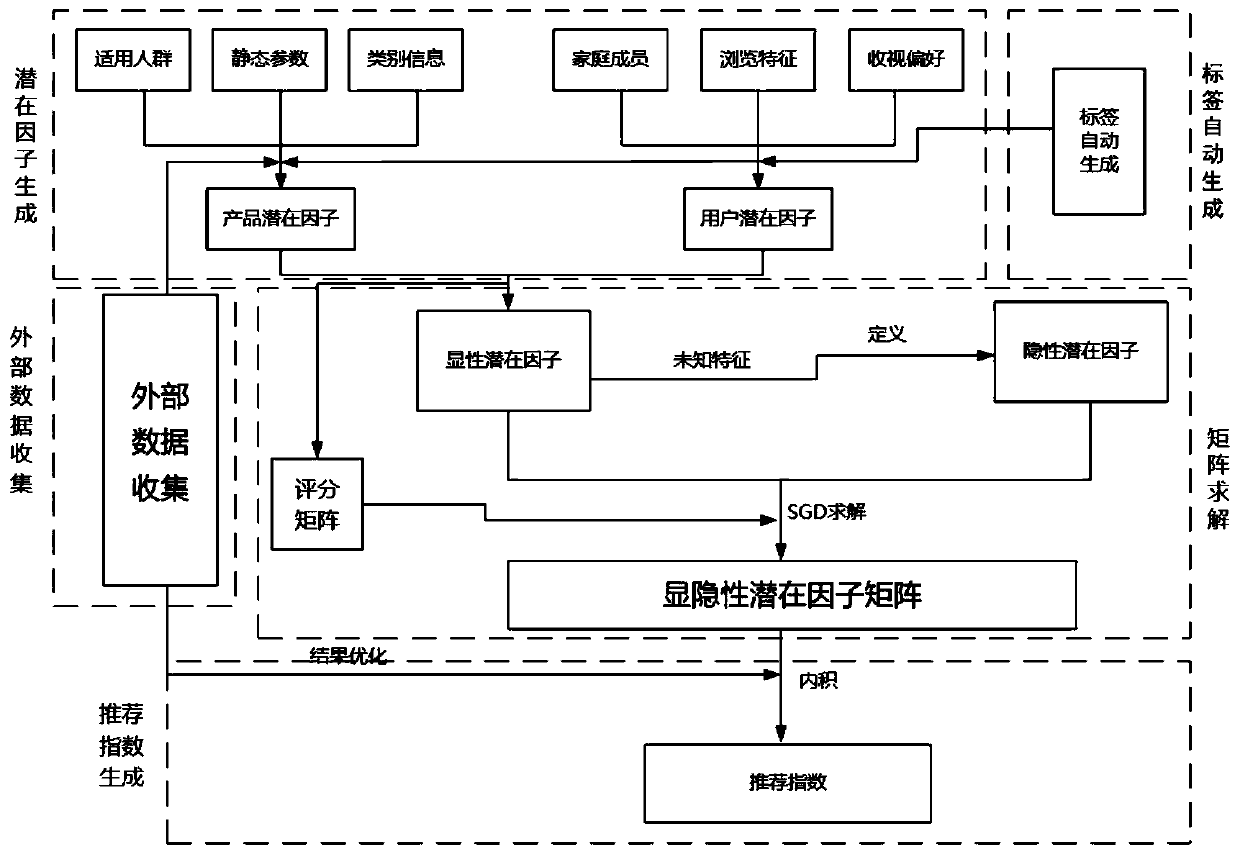
Television product accurate recommendation method and system based on explicit and implicit potential factor model
ActiveCN109963175AImplement an automatic generation mechanismThe result is obviousCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionExternal dataCrowds
The invention relates to the technical field of recommendation, and discloses a television product accurate recommendation method based on a explicit and implicit potential factor model, which comprises the following steps: processing a television product positive topic name through a regular expression, designing a crawler strategy, and crawling required external data; establishing classificationmodels aiming at the television products and the users according to different characteristics of the television products and the user groups, thereby realizing automatic label labeling of the different television products and the users in the crawled external data, and obtaining television product information after label labeling and user information after label labeling; obtaining a potential dominant factor, obtaining a potential recessive factor according to the potential dominant factor, and constructing a potential recessive factor model based on the potential dominant factor and the potential recessive factor; and recommending the television product based on the constructed explicit and implicit potential factor model. The invention also discloses a television product accurate recommendation system based on the explicit and implicit potential factor model. The recommendation accuracy is improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
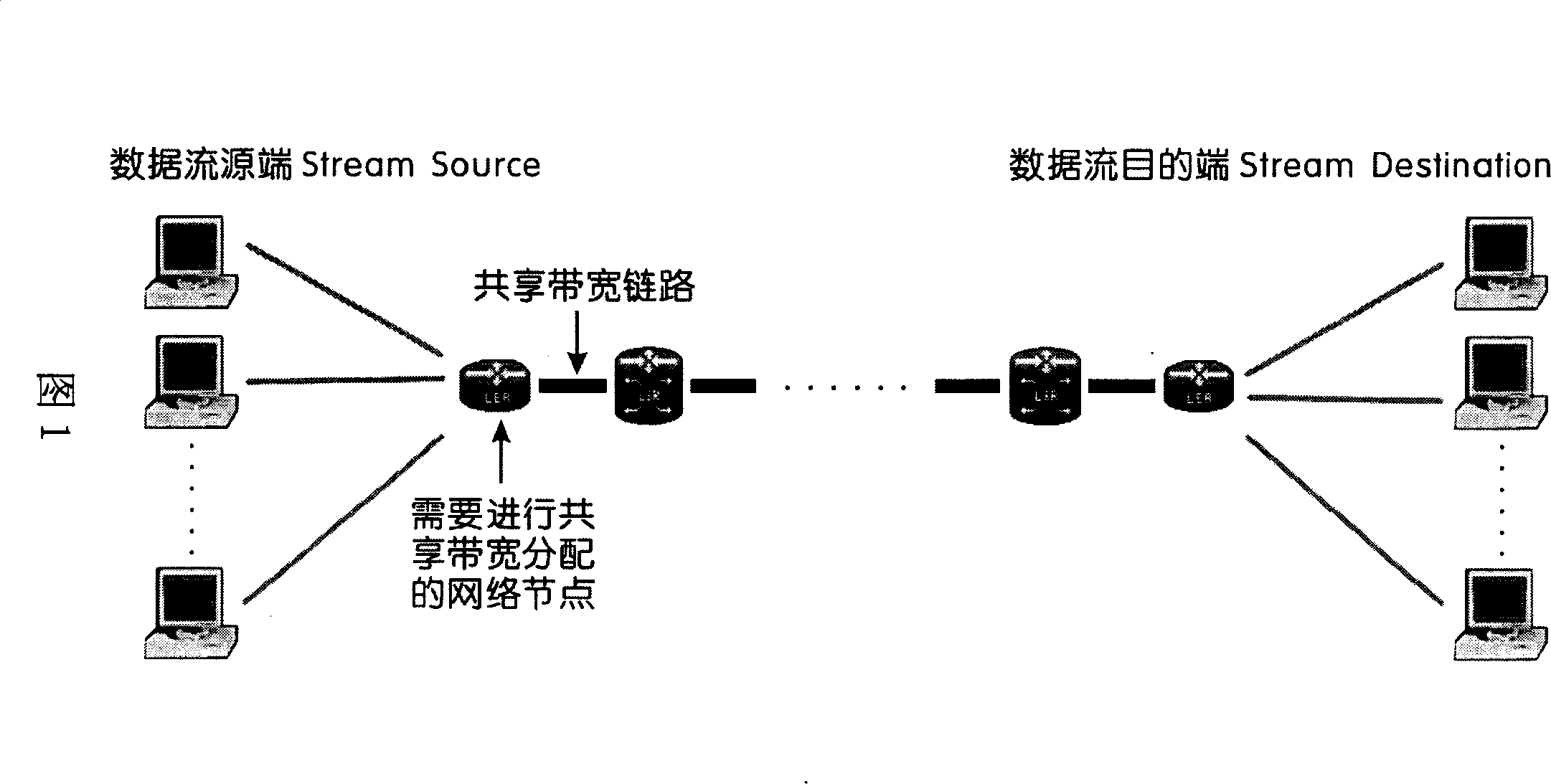
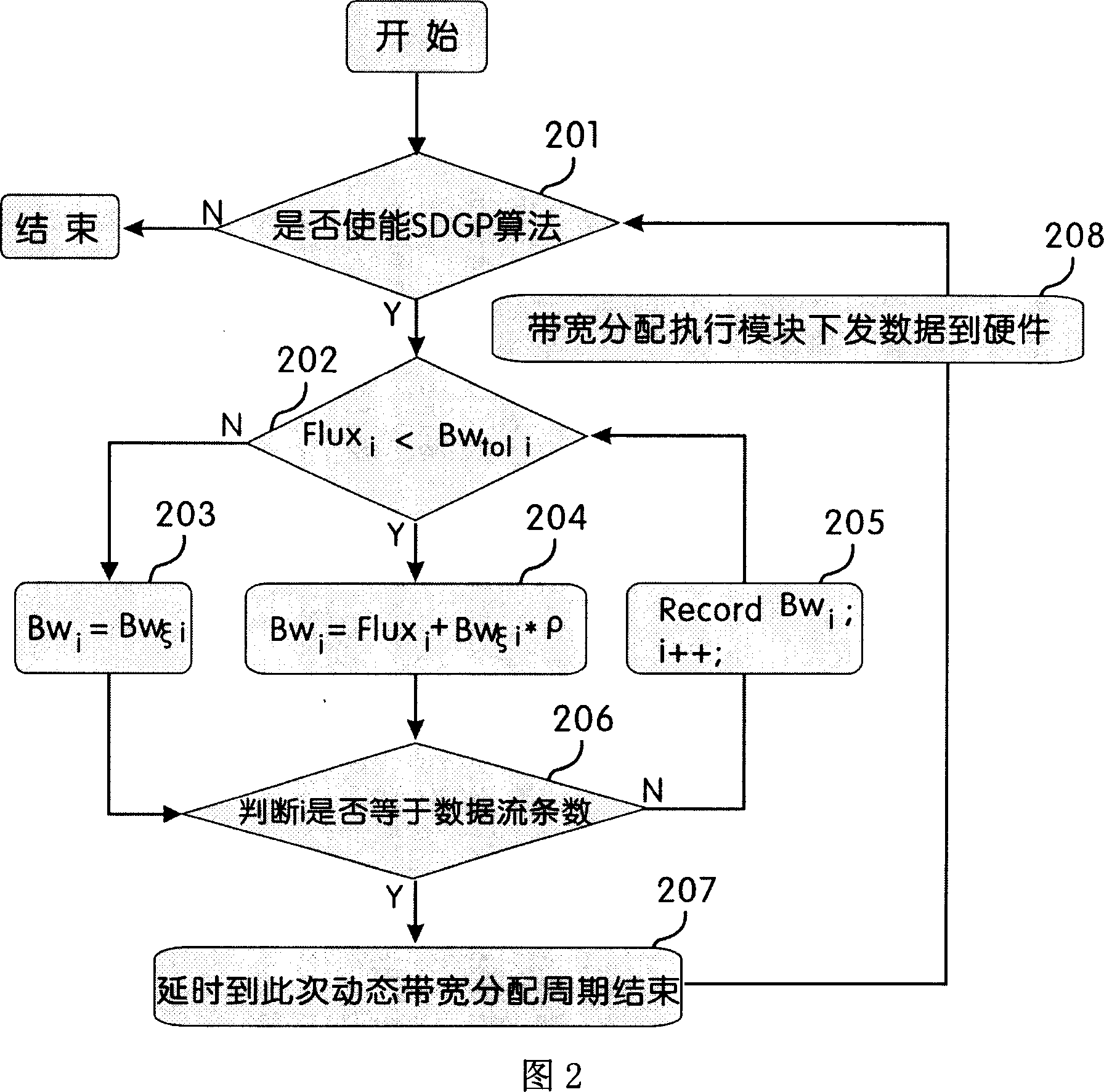
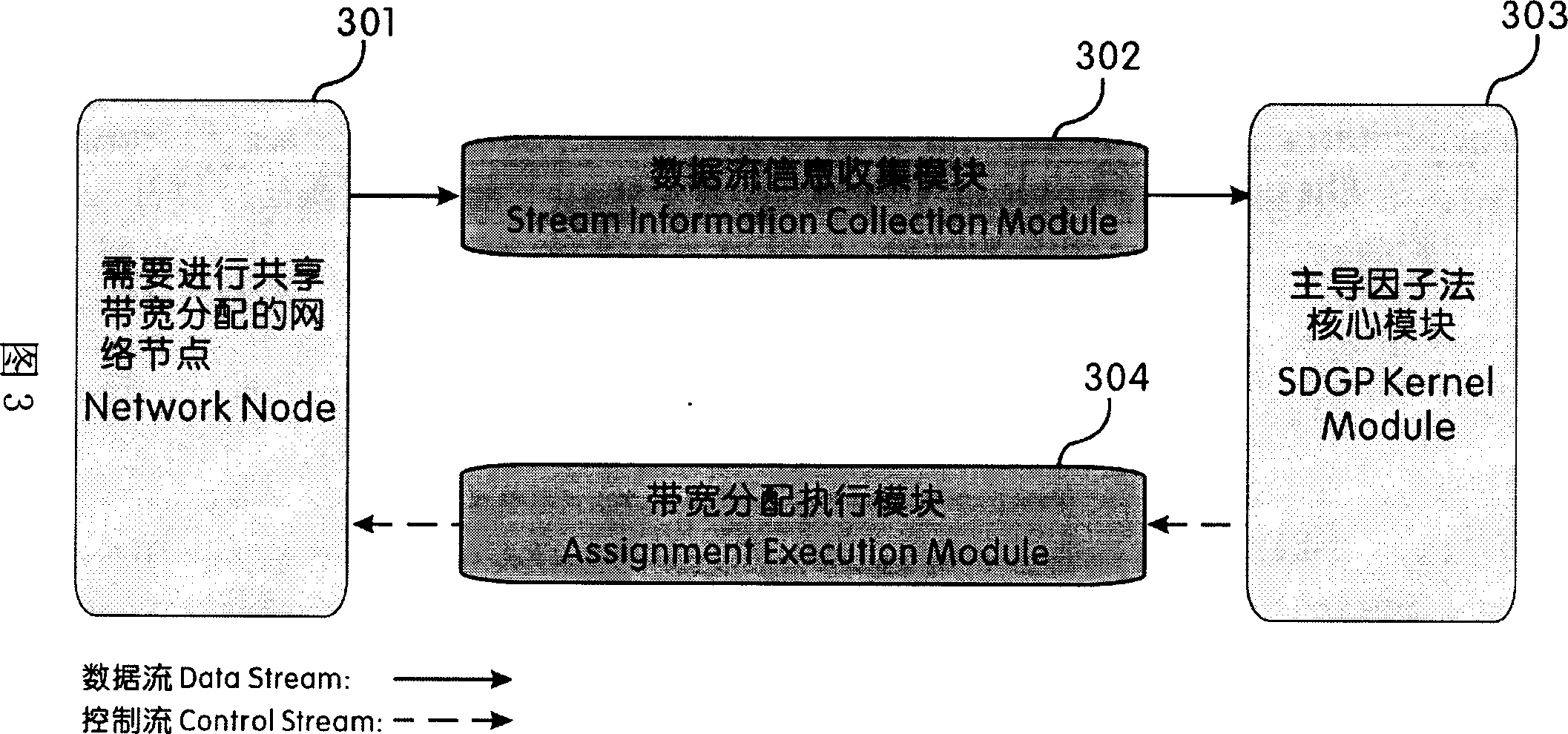
Dominant factor method based network sharing bandwidth dynamic allocation method
InactiveCN101064550AReasonable distributionFlexible allocationRadio transmissionData switching networksData streamDistributed computing
The invention relates to a network sharing bandwidth dynamic distributing method based on the dominant gene method, using the method in the invention, in the every circuit that the network nodes distributes the network sharing bandwidth dynamically, the system can make decision according to the user's requirement, the PRI of data flow and the flux and distribute the sharing bandwidth, and uses the network source rationally, that includes following processing: step 1, according to the user's requirement, the PRI of data flow and the flux, it produces a decision-making value which can effect the distribution for the bandwidth of data for the data flow with highest PRI before the distributing the bandwidth; step 2, according to the decision-making value, the system will decide the distributing strategy, and distributes the bandwidth for the data flow; step 3, using the sparing bandwidth in the system, it distributes the sharing bandwidth for the data flow with lower PRI based on the dominant gene method.
Owner:袁嘉 +1
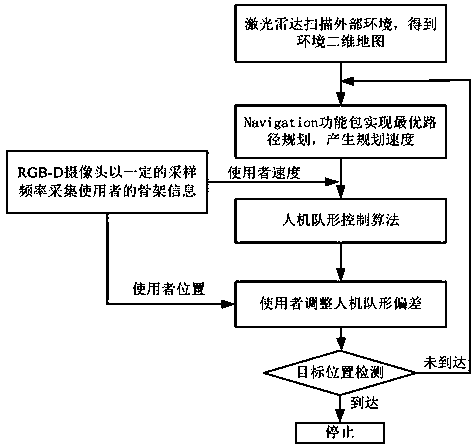
Human-robot formation control method applicable to human-aimed navigation system
ActiveCN108762253AReduce volumeEnsure safetyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesRadarNavigation system
The invention discloses a human-robot formation control method applicable to a human-aimed navigation system. The navigation system comprises a mobile robot and a portable wearable device based on vibro tactile feedback. A laser radar scans a surrounding environment, the distance information with a surrounding object is transmitted to an upper computer, and the upper computer processes the distance information to obtain a two-dimensional environment map; according to the map information, the upper computer uses software to carry out optimal path planning in real time, and a planning speed is generated; an RGB-D camera collects the skeleton information of a user at a certain sampling frequency and transmits the information to the upper computer, and after processing, the upper computer obtains the position and speed information of the user; a human-robot formation control algorithm takes the user as a dominant factor, the speed of the user and the planning speed are integrated, and theactual control speed of the robot is generated; and according to the position information of the user, the upper computer instructs the user to adjust the self position through a vibration device anda voice prompting device, a certain relative distance and a relative angle are kept between the robot and the user, and the function of human-aimed navigation is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
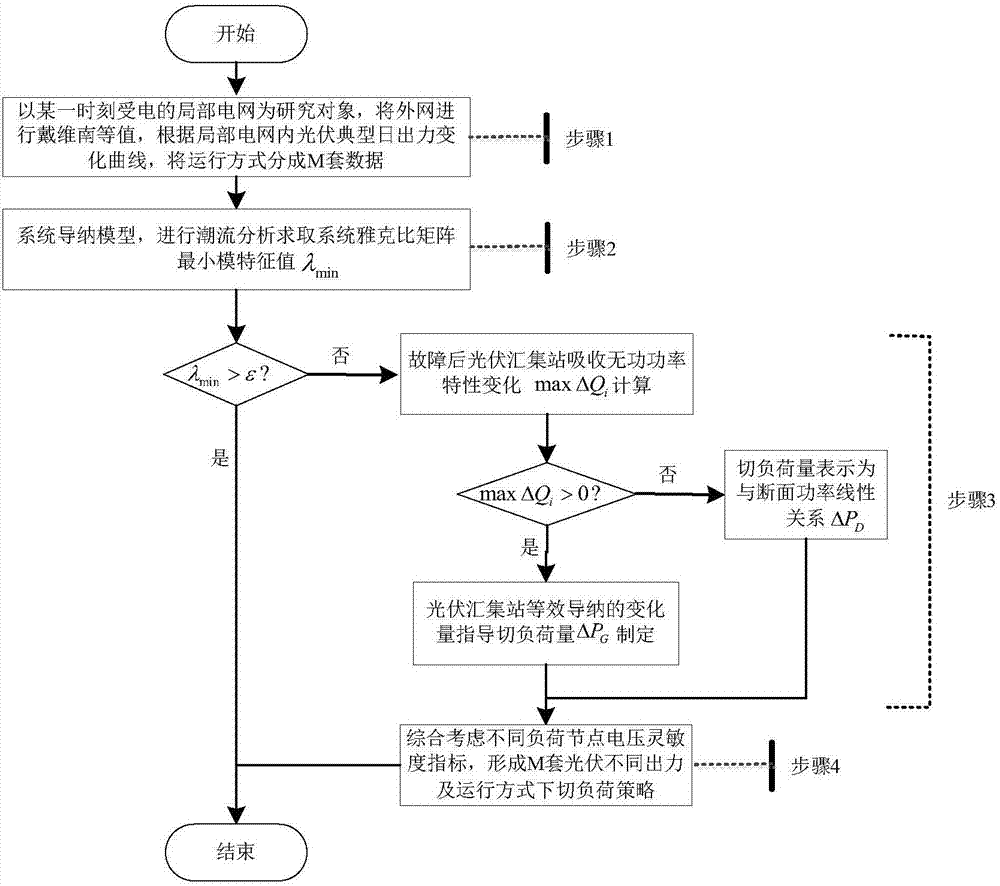
Load-shedding control method with consideration of system voltage stability after photovoltaic access
ActiveCN107359619AImprove effectivenessIncrease the level of automationPower network operation systems integrationEnergy industryPower system schedulingInstability
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of the power system and automation thereof, discloses a load-shedding control method with consideration of system voltage stability after photovoltaic access, so that the adverse influence on high-voltage grid voltage recovery after a fault by large-scale photovoltaic access to the grid is eliminated. An equivalent local grid static voltage stability index of an external network is calculated to determine a voltage instability situation; a dominant factor of voltage instability is identified based on a characteristic change of reactive power absorbing by a photovoltaic aggregation station after the fault; and then load-shedding control strategies are formulated on the condition of using a photovoltaic factor as the dominant instability factor and using a cross-section factor as the dominant instability factor, thereby realizing load-shedding control of the voltage weak node load. Therefore, the power system scheduling operation staff can obtain the inherent operation rule of the photovoltaic access system and the foundation is laid for formulating a load-shedding optimization strategy cooperatively, so that the effectiveness and automation level of secure and stable control of a large grid are improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
Method and system for optimizing primary frequency modulation, and terminal device
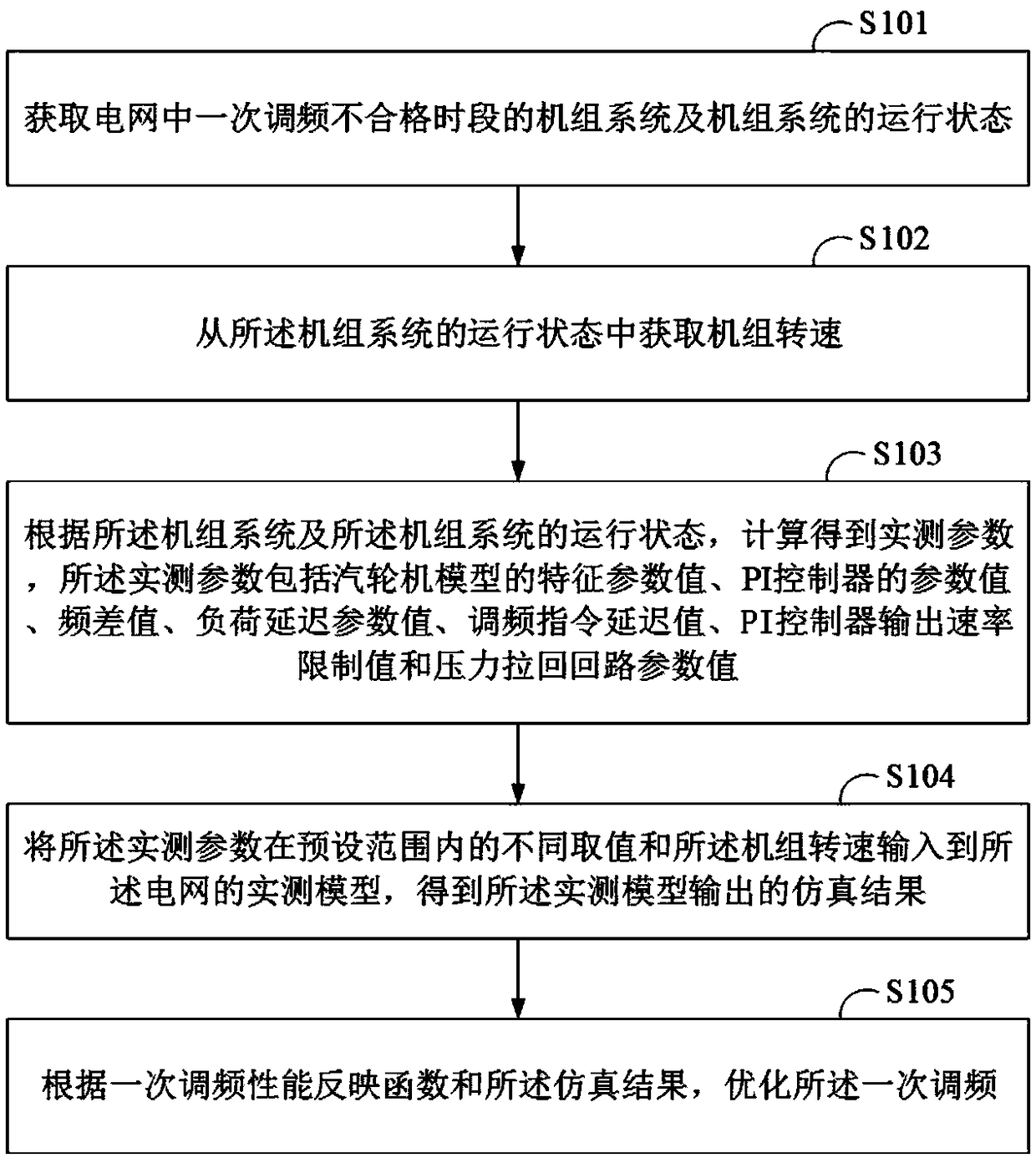
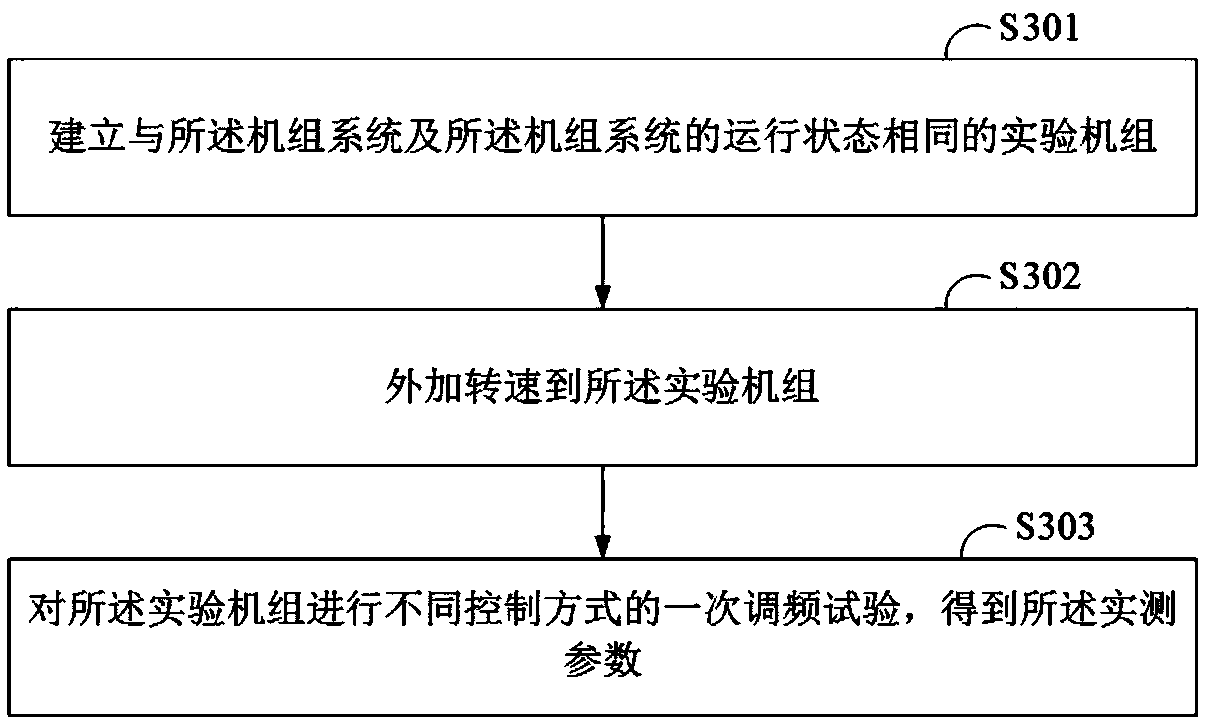
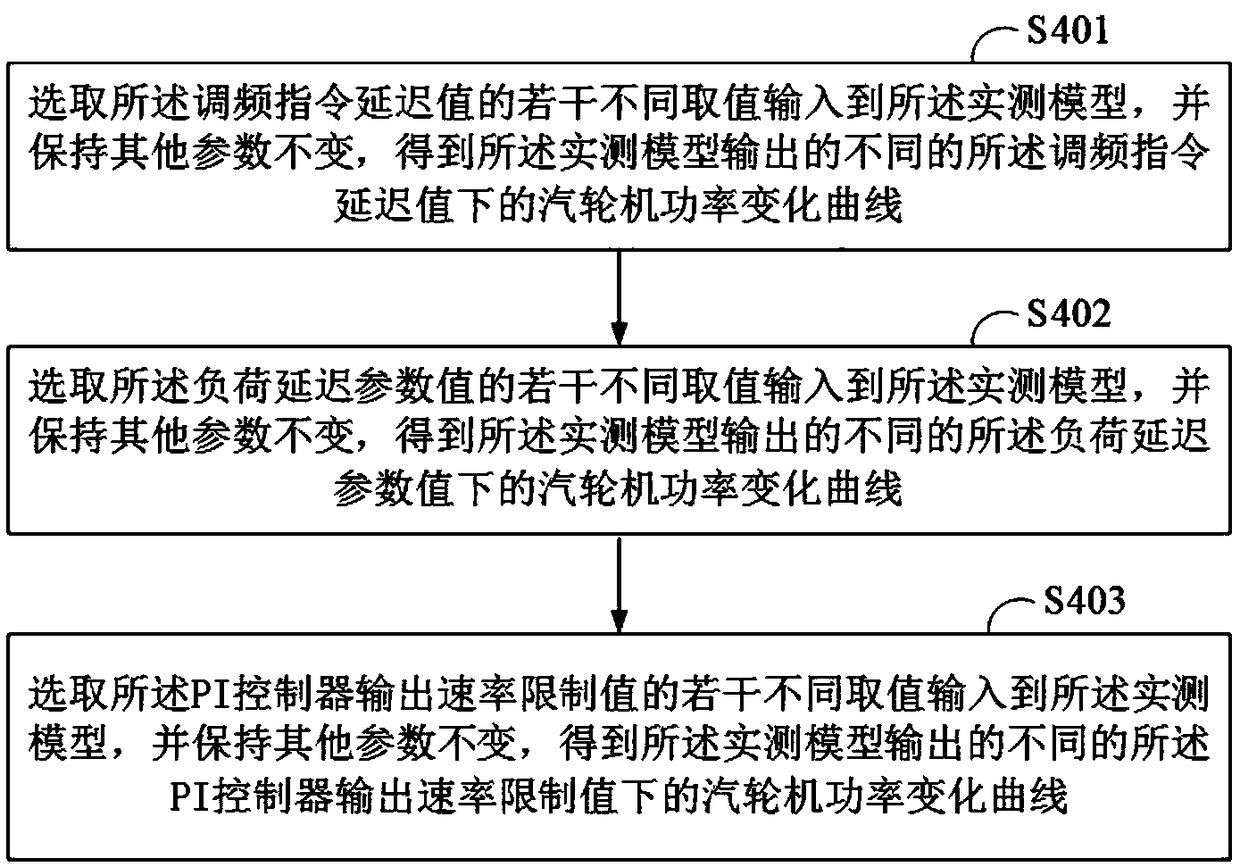
The present invention provides a method and a system for optimizing primary frequency modulation (FM), and a terminal device. The method for optimizing the primary FM comprises: obtaining a unit system of the primary frequency failure period and an operating state of the unit system; obtaining the unit speed, and the measured parameters of the measured model of the primary FM, wherein the measuredparameters comprise the characteristic parameter value of the steam turbine model, the PI controller parameter value, the rotational speed difference, the load delay parameter value, the FM instruction delay value, the PI controller output rate limit value, and the pressure pullback loop parameter value; inputting the different values of the measured parameters in the preset range and the unit speed to the measured model of the primary FM to obtain the simulation result; and optimizing the primary FM according to the primary FM performance reflection function and the simulation result. According to the technical scheme of the present invention, by using the simulation means to determine the dominant factors and optimize the control strategy, the blindness of the conventional method is avoided, the labor intensity and the test risk are reduced, the coupling influence can be solved, the key parameters can be determined, and the pertinence of the primary FM analysis optimization can be improved.
Owner:STATE GRID HEBEI ENERGY TECH SERVICE CO LTD +2
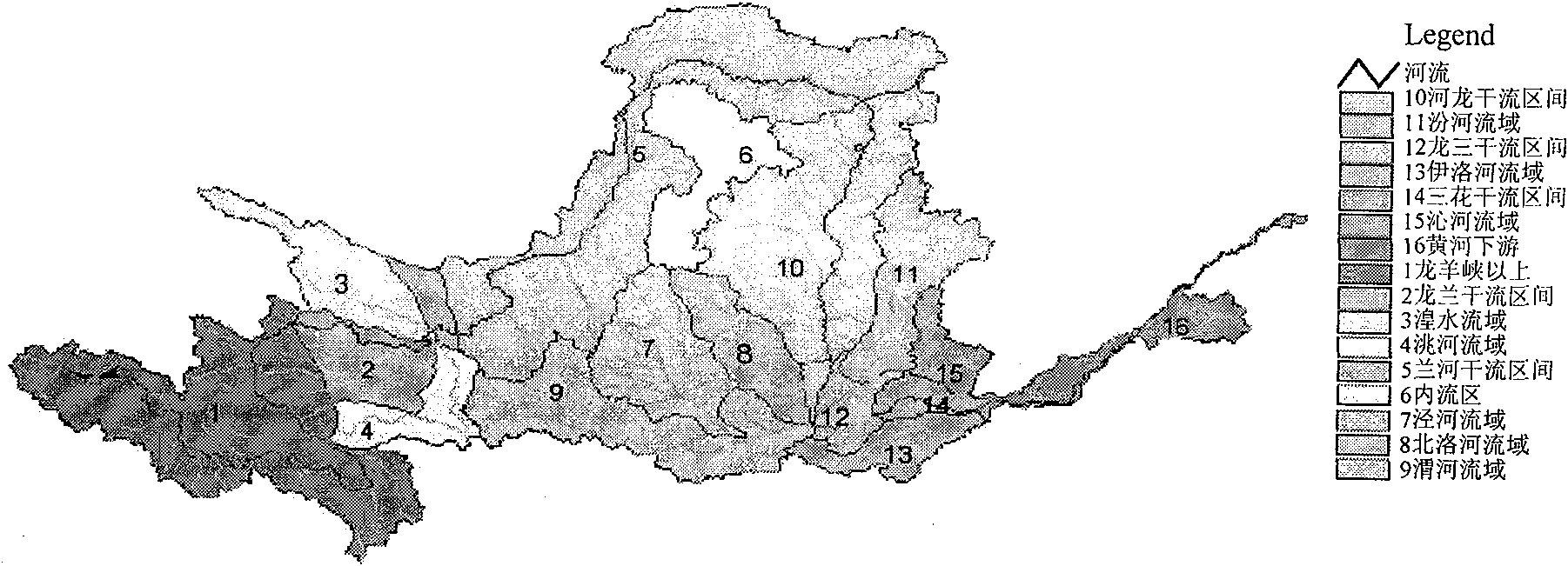
Index and method for ecological water demand zoning and classification
InactiveCN101685529AQuick calculationPartition classification results are reliableData processing applicationsEnvironmental resource managementWater source
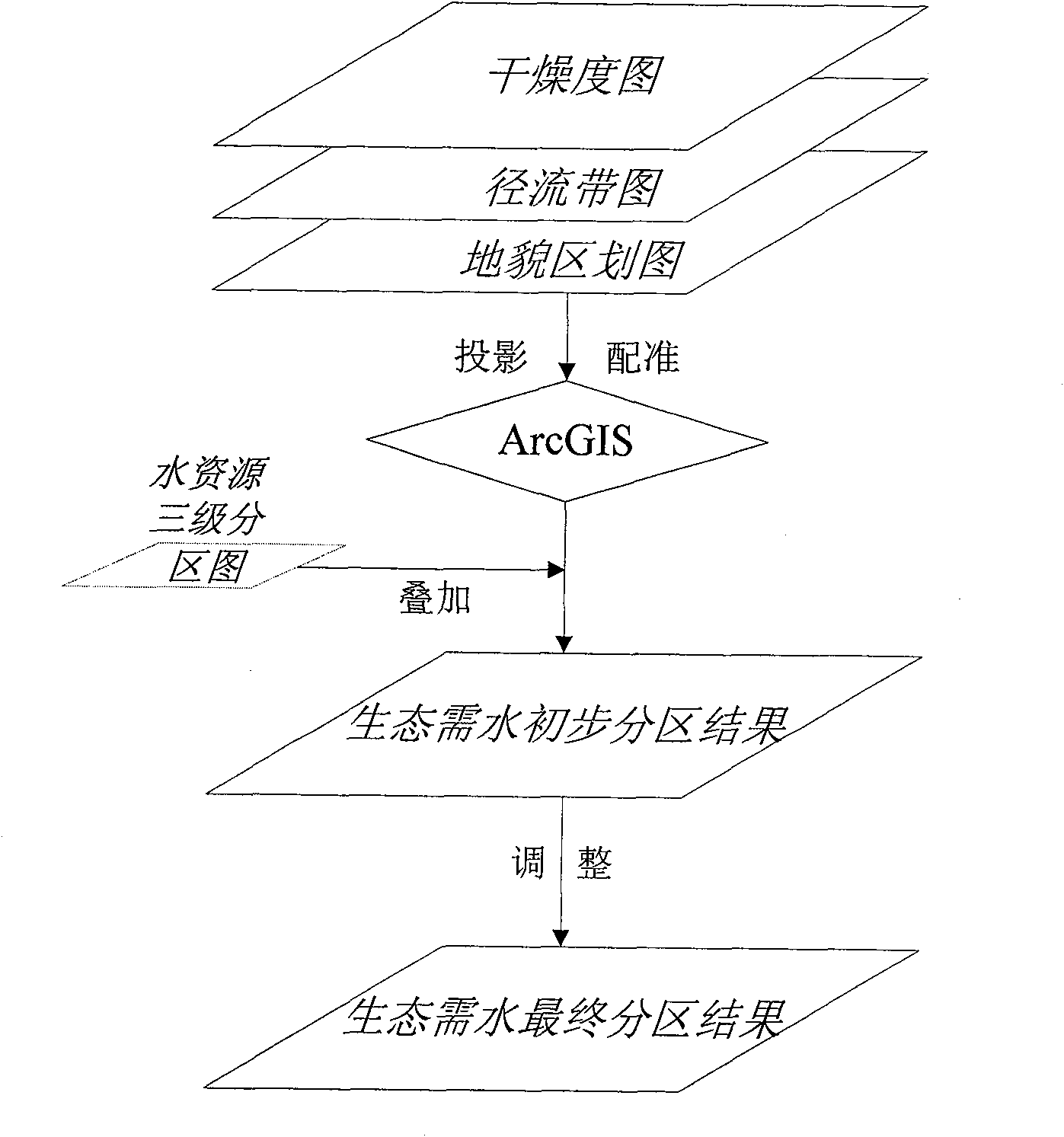
The invention discloses an index and a method for ecological water demand zoning and classification. In the method, on the basis of dominant factor prioritization and other principles, an ecological water demand zoning second-grade index system and a an ecological water demand classification second-grade classification system are created by referring to zoning and plan such as water source zoning,and a river basin or a zone can be divided into a series of relatively homogeneous and uniform units to provide a foundation for the calculation of ecological water demand. The method has the advantages that: the obtained zoning and classification results are reliable; the required documents such as a topographic map are common documents and are readily available; and powerful scientific evidences for the calculation of the ecological water demand and the reasonable configuration of water source can be provided.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
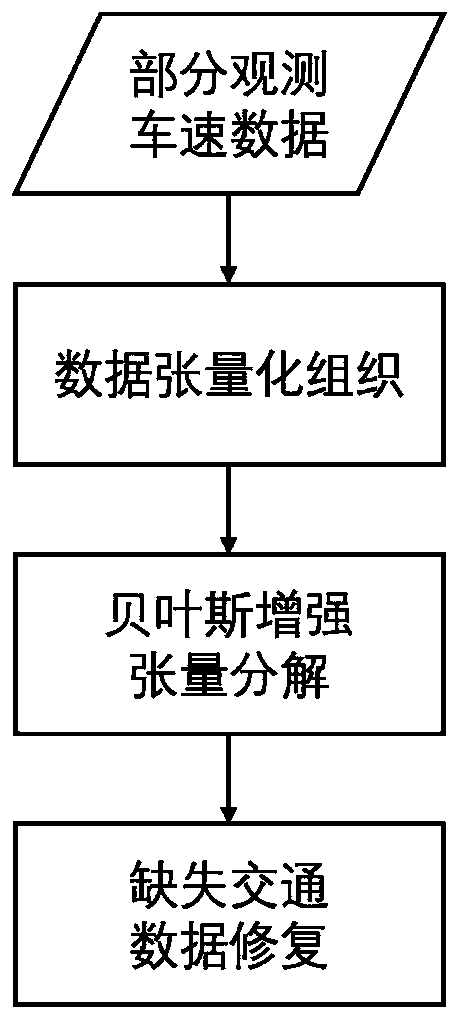
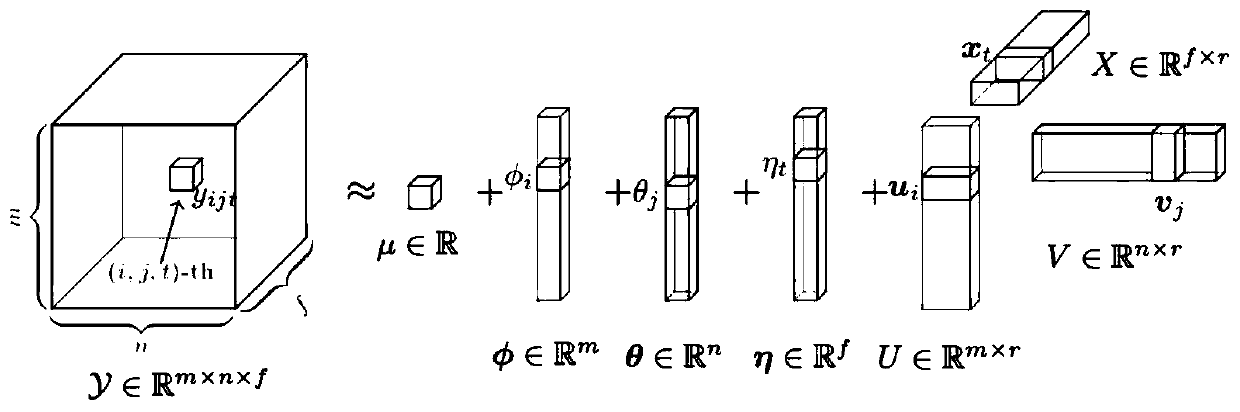
Missing traffic data repairing method based on Bayesian enhanced tensor
ActiveCN110223509AEfficient repairImprove data qualityMathematical modelsDetection of traffic movementAlgorithmTensor decomposition
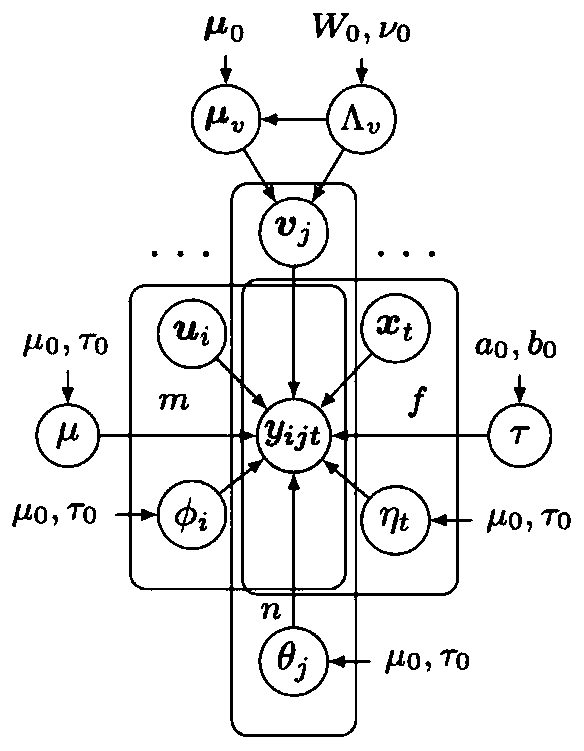
The invention discloses a missing traffic data repairing method based on Bayesian enhanced tensor decomposition. The method comprises the following steps of organizing the road network vehicle speed data into a third-order data tensor to introduce a dominant factor structure for modeling; inputting the data tensor and indicating the tensor; updating posterior distribution of a global parameter mu;updating posterior distribution of a hyper-parameter; updating posterior distribution of a bias parameter phi and posterior distribution of a factor matrix parameter U until i is equal to m; updatingposterior distribution of a bias parameter theta and posterior distribution of a factor matrix parameter V until j is equal to n; updating posterior distribution of a bias parameter eta and posteriordistribution of a factor matrix parameter X until t is equal to f; repeating the steps S5-S9 until the difference deltatau between the accuracy parameter tau and the previous parameter tau is less than epsilon, converging the model and proceeding to the next step; substituting the updated {mu, phi, theta, eta, U, V, X} parameter values into the expressions of yijt to calculate and estimate the tensor
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
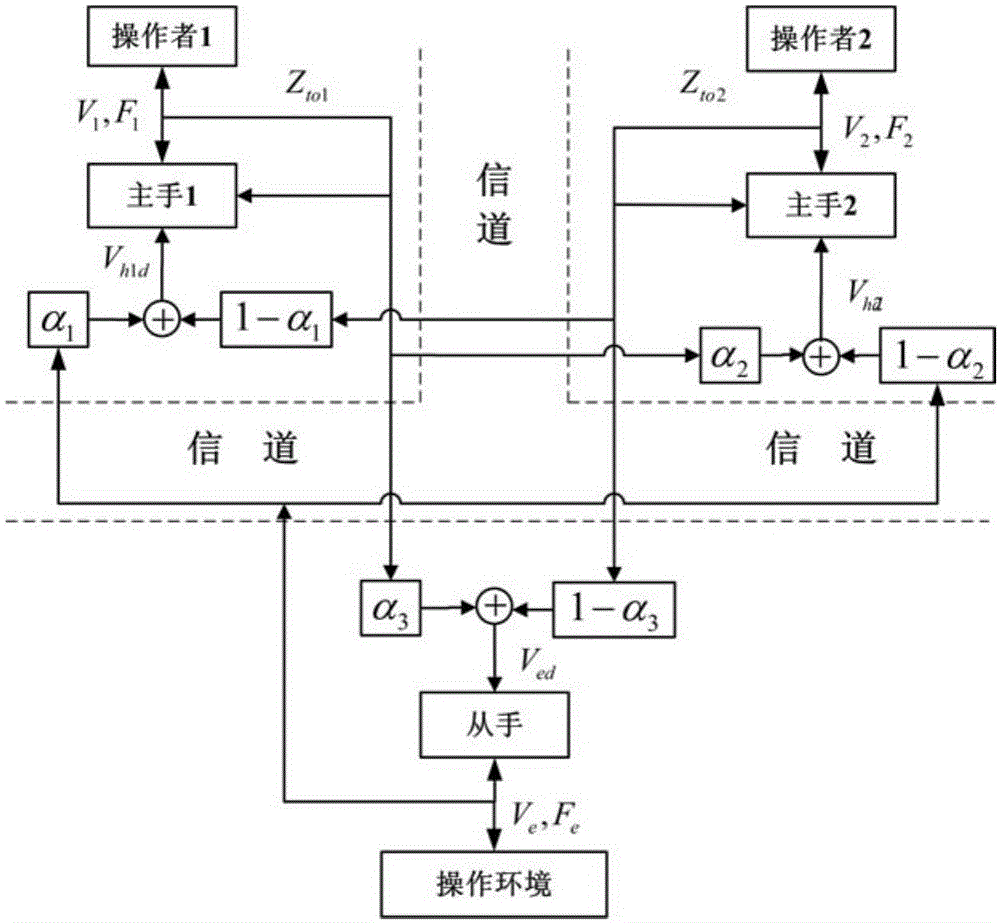
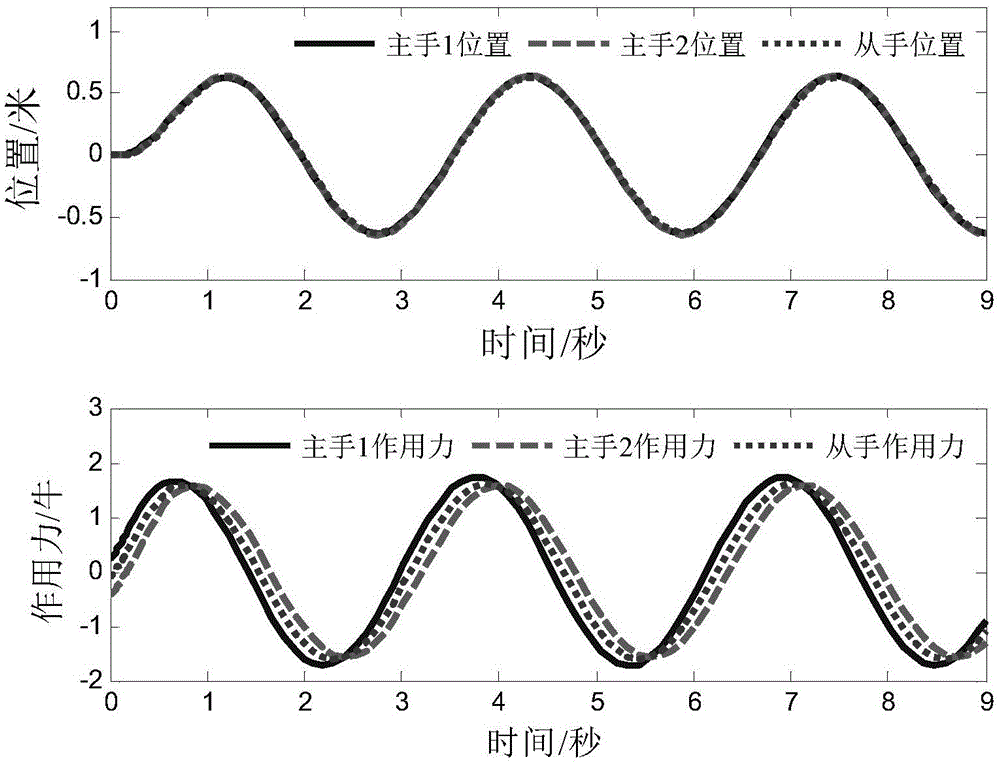
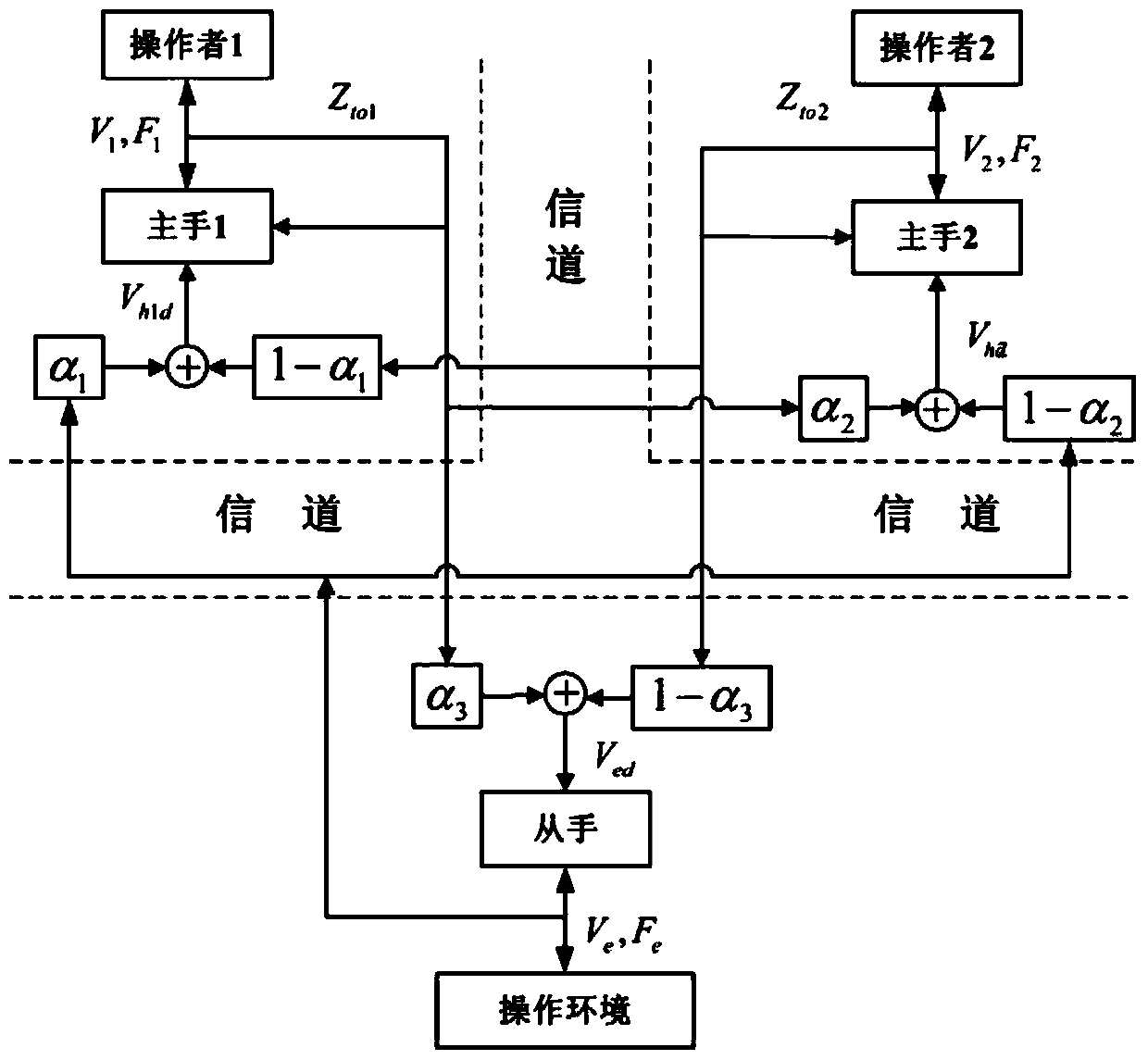
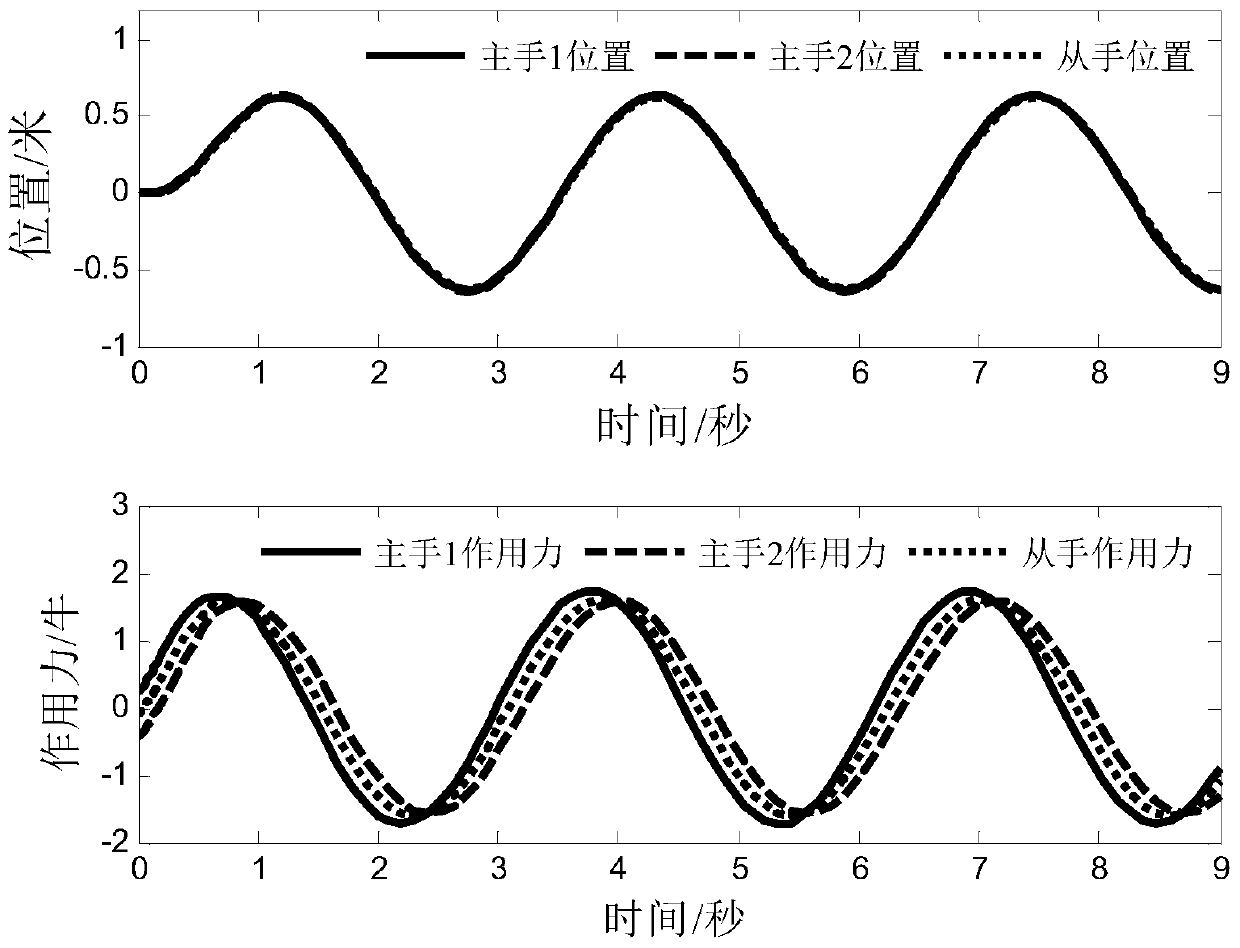
Multi-dominant-factor remote operation method shared by two persons
ActiveCN105159070ARich application modesEasy to operateAdaptive controlDominant factorSystem stability
The invention discloses a multi-dominant-factor remote operation method shared by two persons. According to the method, operation errors caused by muscle shaking, operation proficiency and mental factors of operators can be effectively reduced, and the control precision and the reliability are higher; the multiple dominant factors can be used to adjust the transparency and movement following performance of the operation system freely according to tasks, and the transparency and movement following performance in the optimal state are higher than those of traditional remote operation shared by two persons; and the system stability condition is given according to Raisbeck passive stabilization standard, parameters of the system are calculated via the stability condition, and it is ensured that the system is stable absolutely.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A method for estimating the concentration of suspended solids in turbid lake water based on viirs sensor
ActiveCN106126826BEffective assessmentGeneral water supply conservationDesign optimisation/simulationRayleigh scatteringEcological environment
The invention relates to a method for estimating suspended matter concentration in turbid lake water based on a VIIRS sensor. The method comprises: based on lake field measured spectrum and substance concentration data, analyzing optical properties of water body and water quality dominant factors; screening wave bands which are sensitive to suspended matter concentration variation in the turbid lake water, using curve fitting to determine an optimal model of suspended matter concentration and ground measured spectrum (Rrs); using Rrc data which is removed with water vapor and ozone absorption and corrected by Rayleigh scattering to establish a suspended matter concentration quantitative model which is suitable to be used for the VIIRS; and finally, using the established model on a VIIRS image, to accurately obtain interannual and inter-monthly variation rules and spatial distribution of the suspended matter concentration of the turbid lake water. Using the method can realize long-term high-precision monitoring of suspended matter concentration of a lake, and the method is helpful to scientifically evaluate interannual suspended matter concentration variation and development trends thereof, and effectively evaluate ecological environment changes of lake water.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
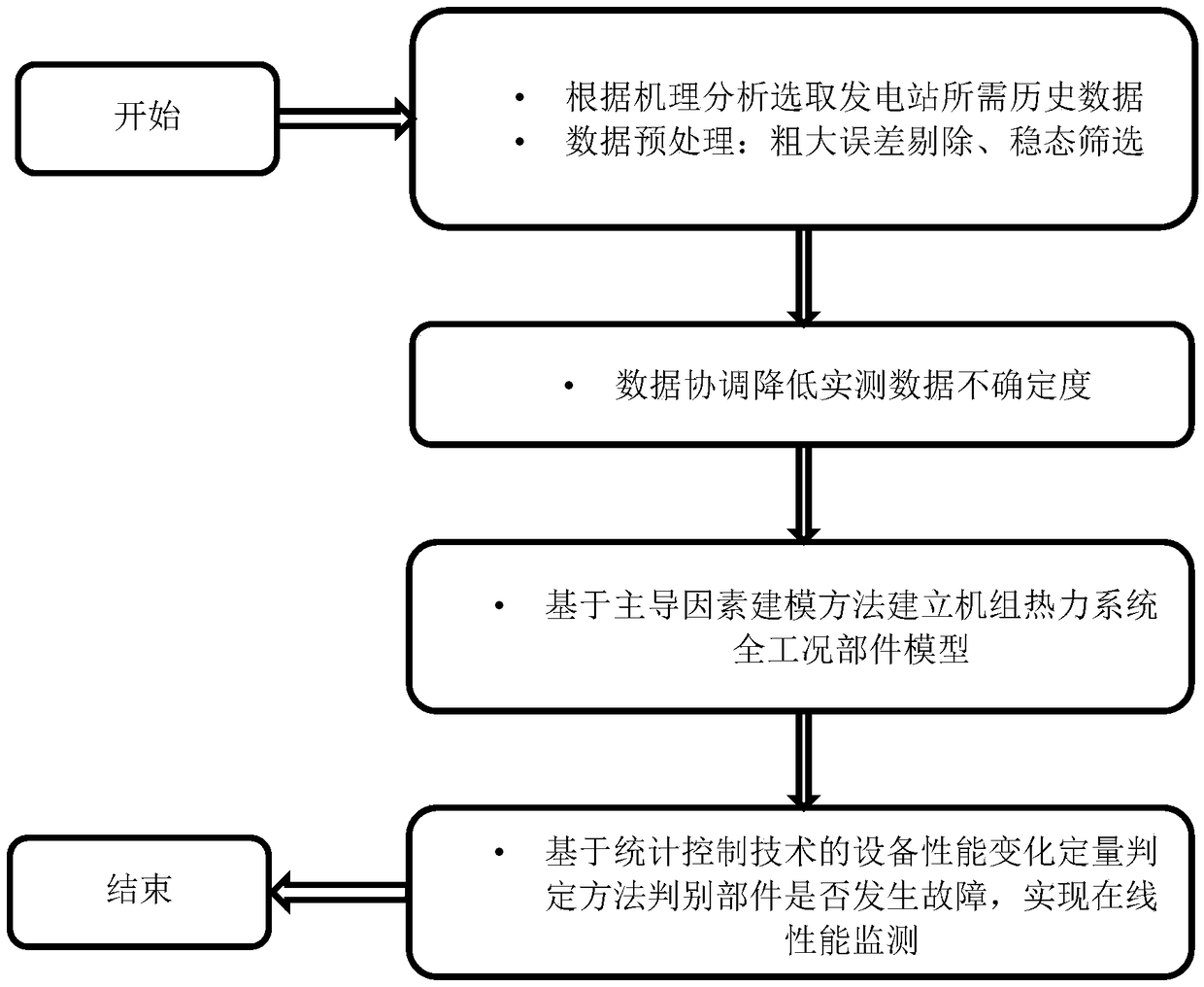
Boiler characteristic calibration method based on operating data
ActiveCN108875165AGet actual operating characteristicsAvoid uncertaintyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsData acquisitionSimulation
The invention discloses a boiler characteristic calibration method based on operating data. The method comprises construction of a steady state model of a boiler system to determine a minimum measuredvariable parameter set, data acquisition, data preprocessing, calibration calculation, and the like. Through the actual operating characteristic parameters under different operating conditions, the dominant factors of boiler operating characteristic parameters can be analyzed, and a dominant factor model of the characteristic parameters can be established. The method overcomes the uncertainty ofthe conventional calculation method based on design data, and the use of a large amount of operating data can obtain the actual operating characteristics of a boiler more precisely and describe the actual operating state and performance of the system more accurately.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A Two-Person Shared Teleoperation Method with Multi-Advantage Factors
ActiveCN105159070BRich application modesEasy to operateAdaptive controlSystem stabilityOperational approach
The invention discloses a multi-advantage factor double-person shared remote operation method, which can effectively reduce the operation error caused by the operator's muscle tremor, operational proficiency, and psychological factors through the double-person shared control method, and the control accuracy is more accurate and reliable. Sex is higher. Secondly, by designing multiple advantageous factors, the present invention can freely adjust the transparency and motion followability of the operating system, and the transparency and motion tracking effects under the optimal conditions are better than the traditional two-person shared control operation. Finally, the present invention provides system stability conditions through Raisbeck passive stability criteria, and then calculates system parameters from the stability conditions to ensure absolute stability of the system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A method for simulating ultra-high cycle fatigue damage of superalloys
Belonging to the technical field of measuring and testing, the invention relates to ultra-high cycle fatigue of an ultrasonic fatigue test simulation material, and a high temperature alloy ultra-high cycle fatigue damage simulation method adopting a microanalysis technique for studying micromechanical properties and material deformation to conduct damage assessment. In the invention, a neutron diffraction method is employed to test high temperature alloy funnel-shaped sample surface and subsurface residual stress absolute difference, thus obtaining a relation curve of a cycle number and the residual stress absolute difference; utilizing a nanoindentor to test the elastic modulus absolute difference between dendrite arms and dendrites in the material, thus obtaining a relation curve of the cycle number and the elastic modulus absolute difference; and analyzing the crystal deformation condition by electron back scattering diffraction so as to obtain a relation curve of the cycle number and small angle subboundary crystal deformation. Through comprehensive comparison of the three curves, the dominant factors determining high temperature alloy ultra-high cycle fatigue damage can be understood clearly, and the ultra-high cycle fatigue damage condition of similar other alloys can be predicted.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com