Dominant factor method based network sharing bandwidth dynamic allocation method
A leading factor, dynamic allocation technology, applied in data exchange networks, radio transmission systems, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as low update rate, not an ideal research direction, unreasonable, etc., to achieve the effect of timely allocation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
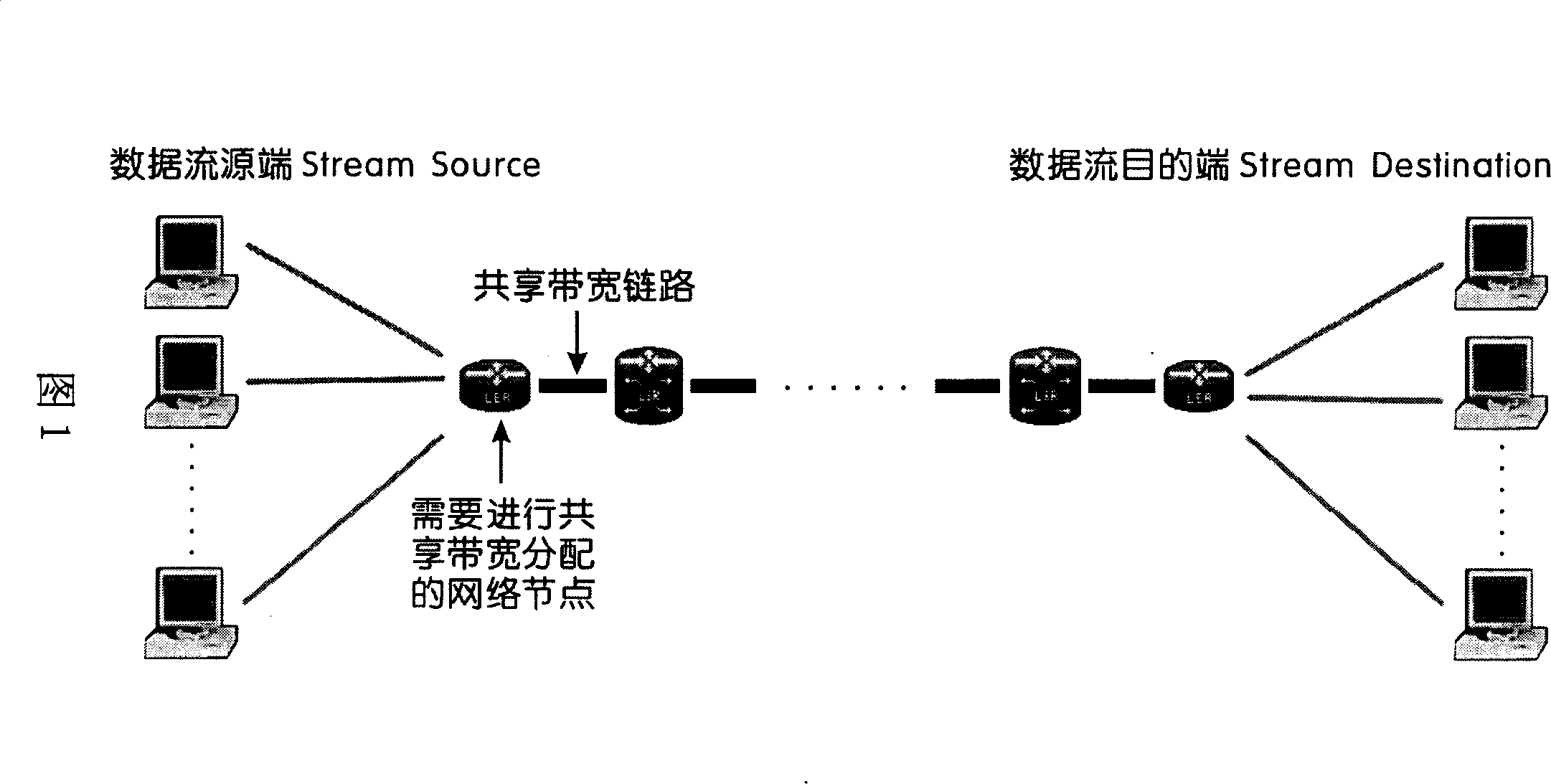
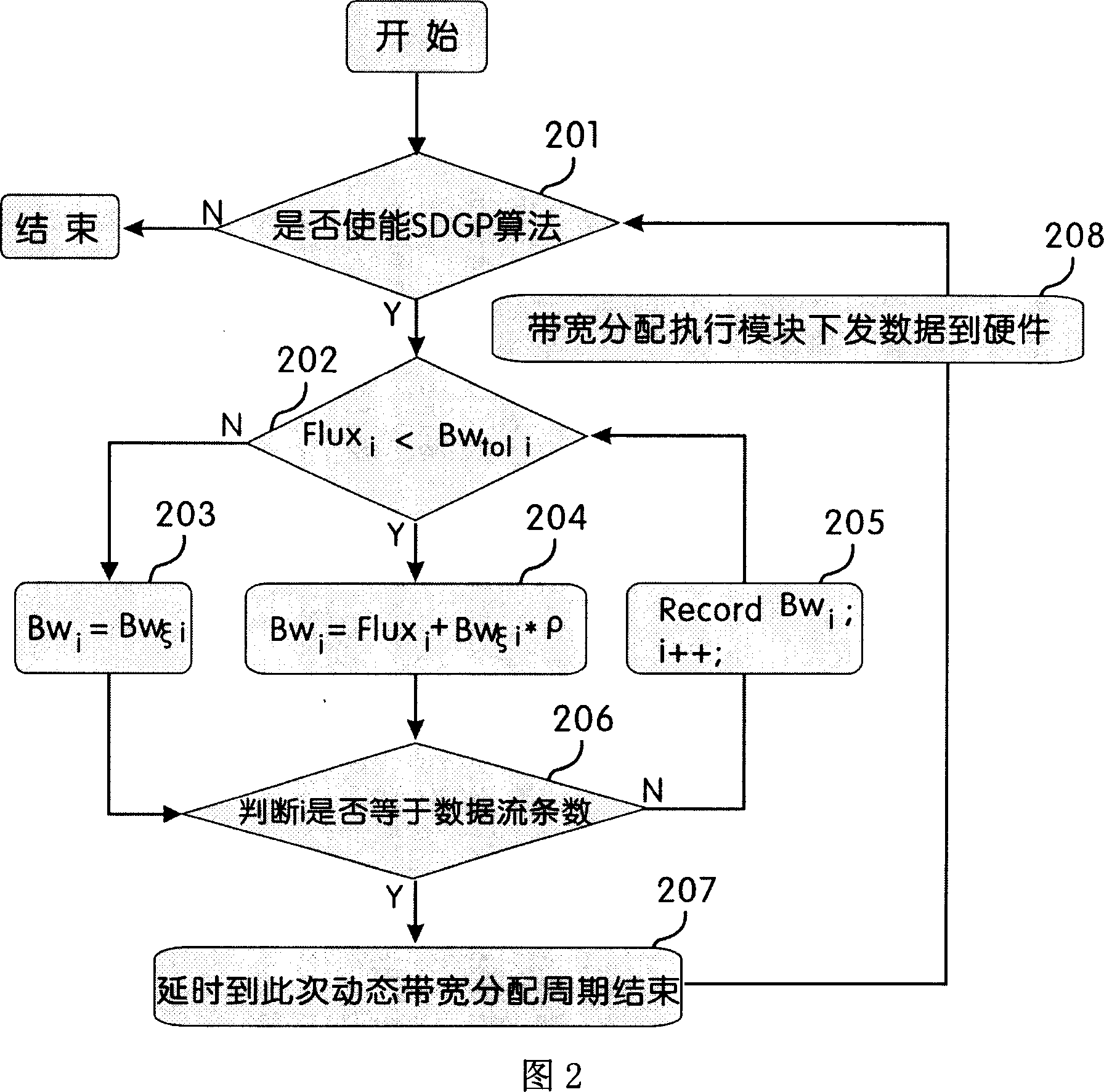
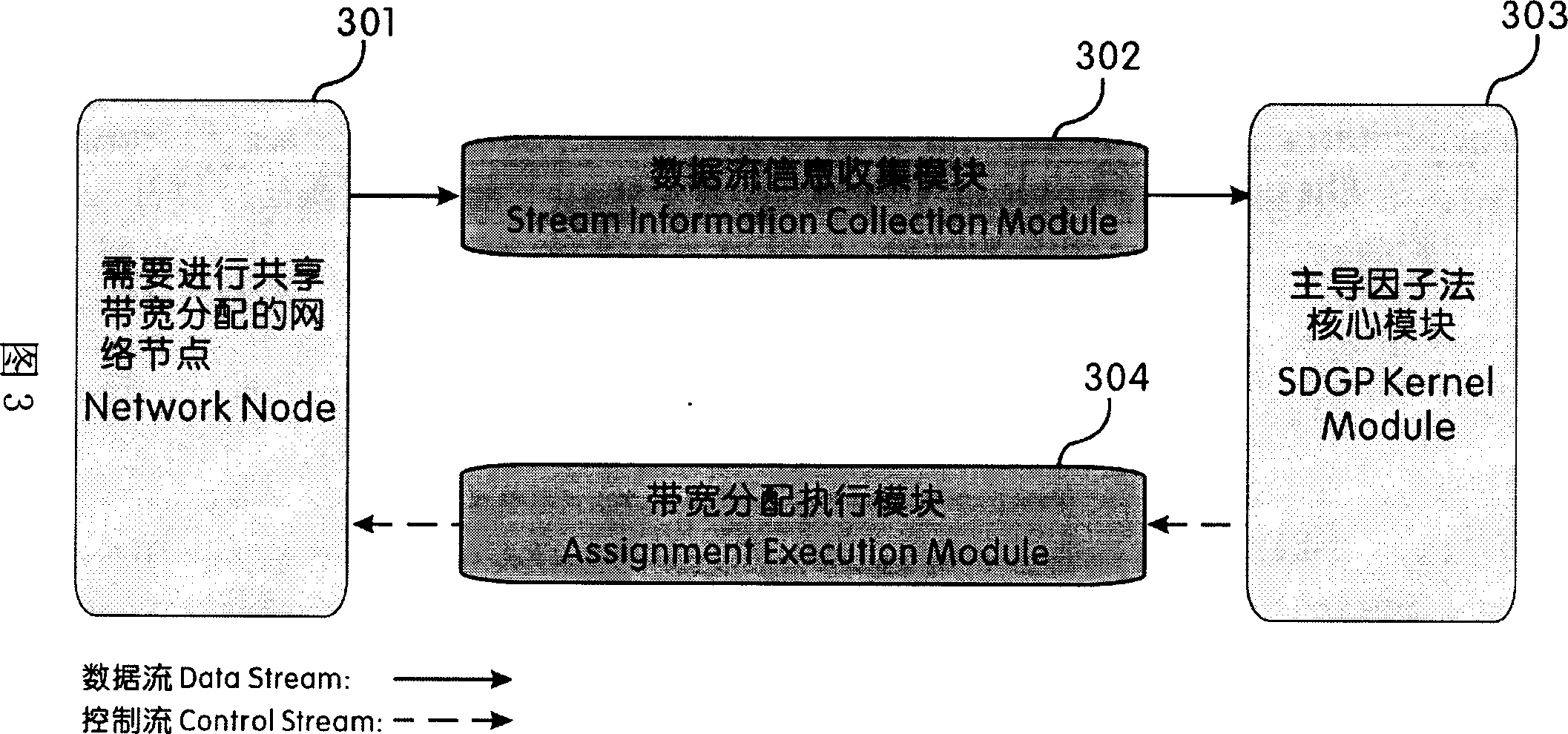
[0021] Fig. 2 is a schematic flowchart of the method of the present invention. In a network with shared bandwidth links, the total shared bandwidth of a link is Bw max . At a certain moment, the link has N priorities from Pri 0 to Pri N-1 (Pri i =Pri i+1 or Pri i =Pri i+1 -1, 0≤i≤N-2) data flow, the smaller the priority value, the higher the priority, so Pri 0 =0 The priority is the highest, and there is no priority jump. From Priority Pri 0 to Pri N-1 , the number of data streams with the same priority is expressed as e 0 、e 1 、e 2 ...... e k (0≤k≤N-1), where k indicates that there are k different priority levels in N data streams, and e m (0≤m≤k) has the following relationship with N:
[0022] Σ m = 0 k e m = N (where 0≤k≤N-1)
[0023] In step 201, when the dominant factor method is enabled, the system ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com