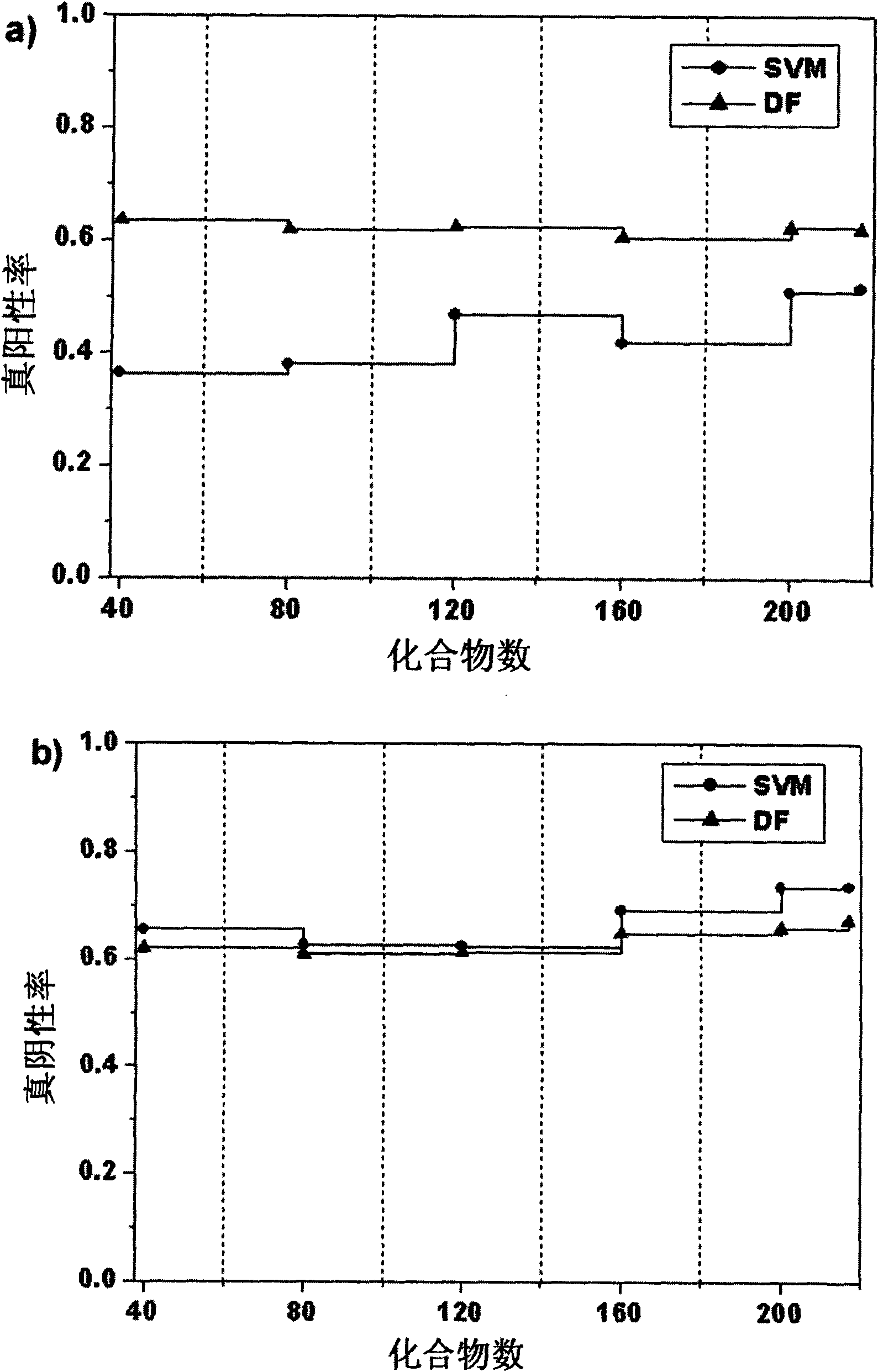
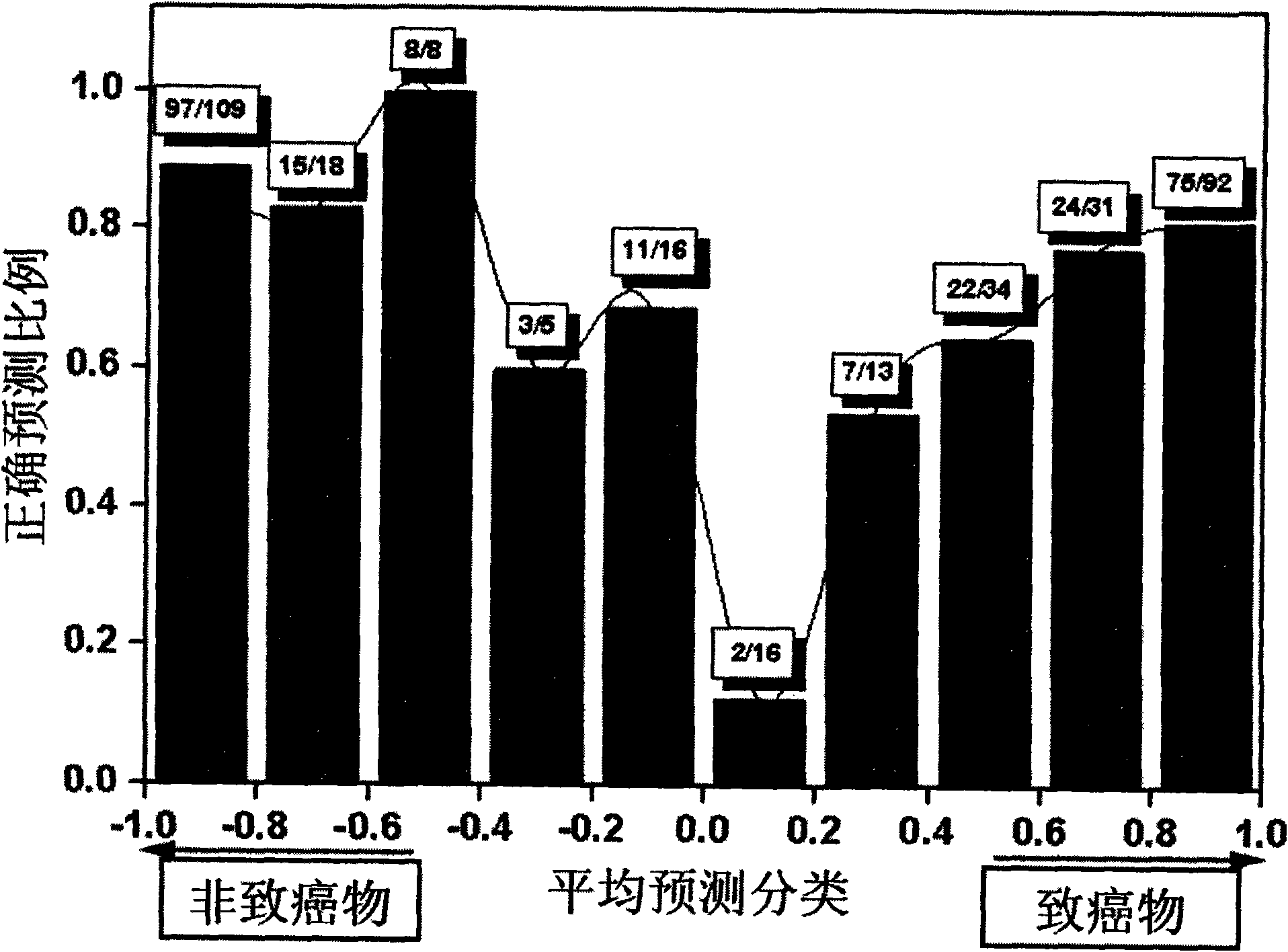
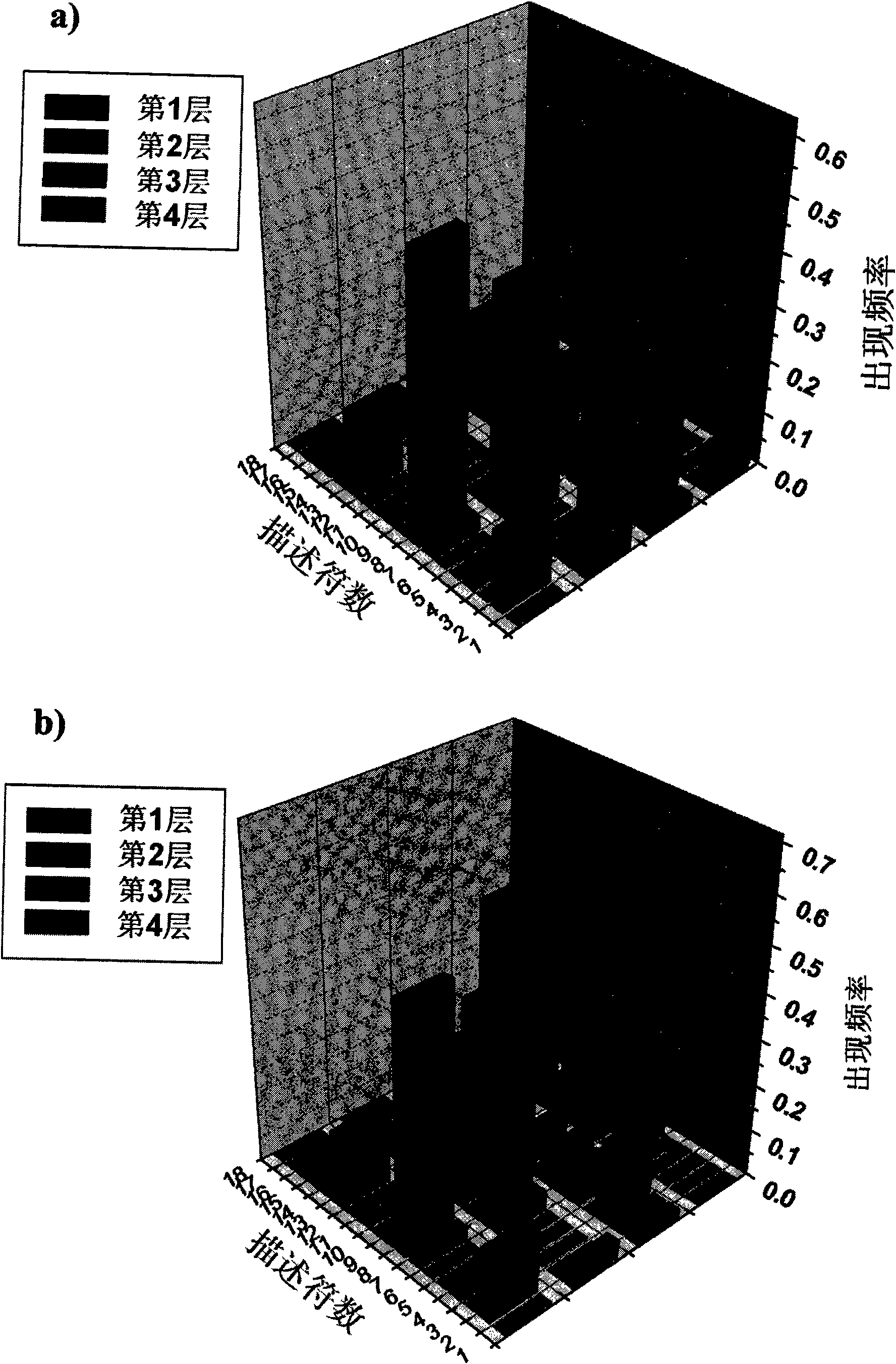
Method for predicting compound carcinogenic toxicity based on complex sampling and improved decision forest algorithm
A toxicity prediction and forest algorithm technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, random prediction, and high testing costs, and achieve balanced prediction capabilities, rapid prediction, and good application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
[0028] Among them, the establishment of a compound carcinogenic toxicity prediction model based on complex sampling and improved decision forest algorithm mainly involves five steps:
[0029] 1) Compute the atom descriptors for each atom type in the molecule:
[0030] Since carcinogenic toxicity may be related to the intrinsic properties of various compounds such as the size, shape, electronic information, polarizability, electronegativity and covalent radius of heteroatoms in the compound, we first use the following five categories of about 49 compounds that meet the above The characteristic descriptors are used to characterize the properties of compounds: a) electronic descriptors, the electronic descriptors are atomic polarization sum (Apol), dipole moment (Dipole), highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), super delocalization energy (Sr); b) space descrip...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com