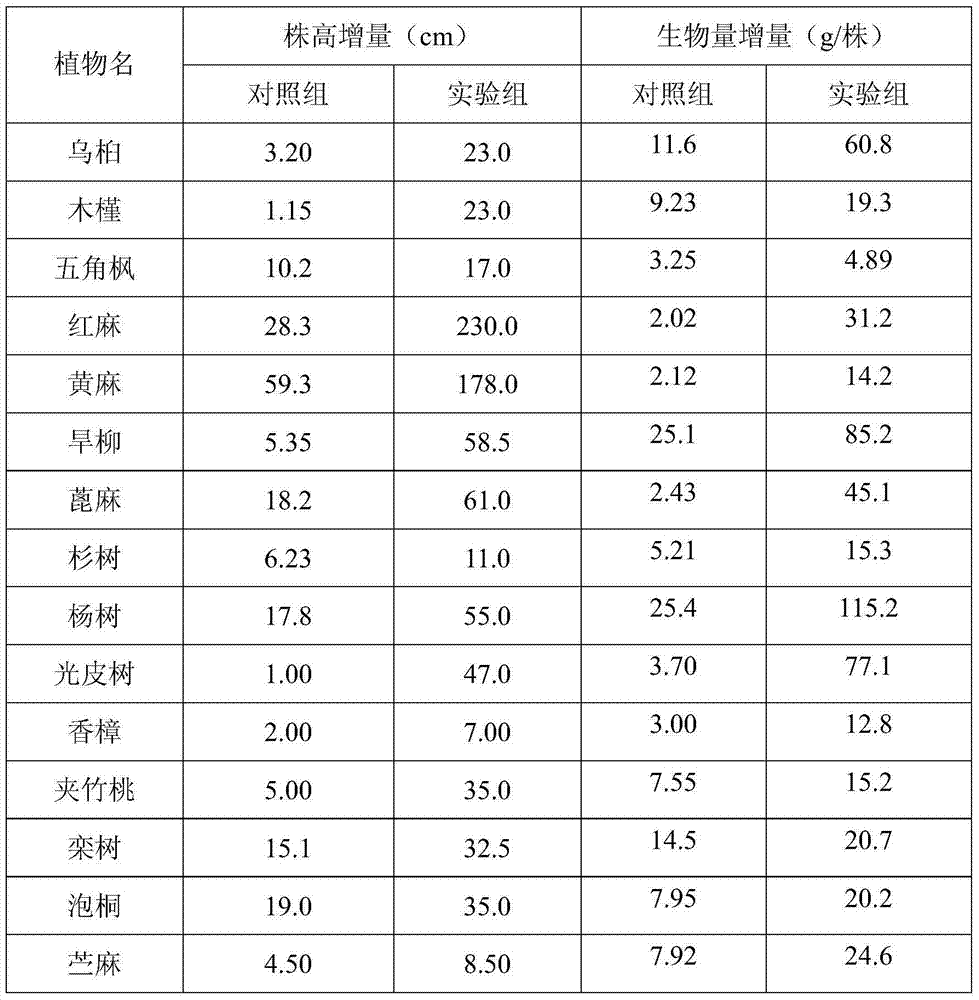
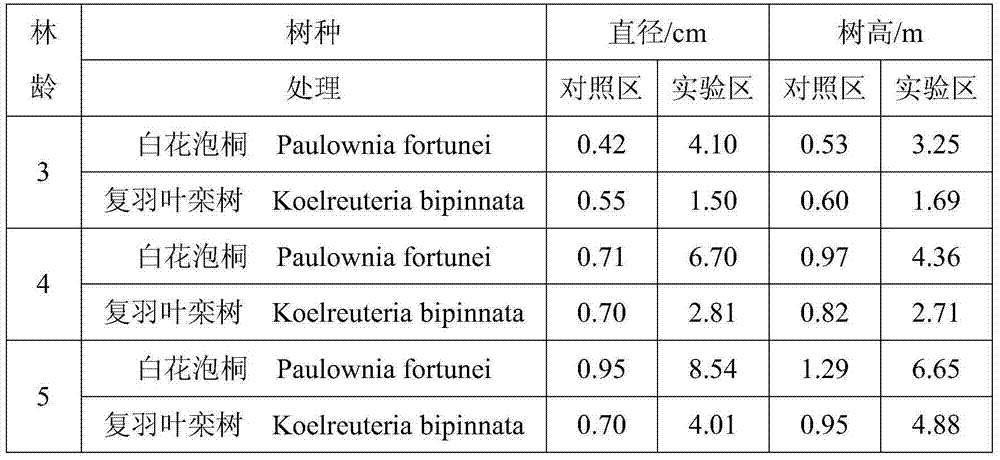
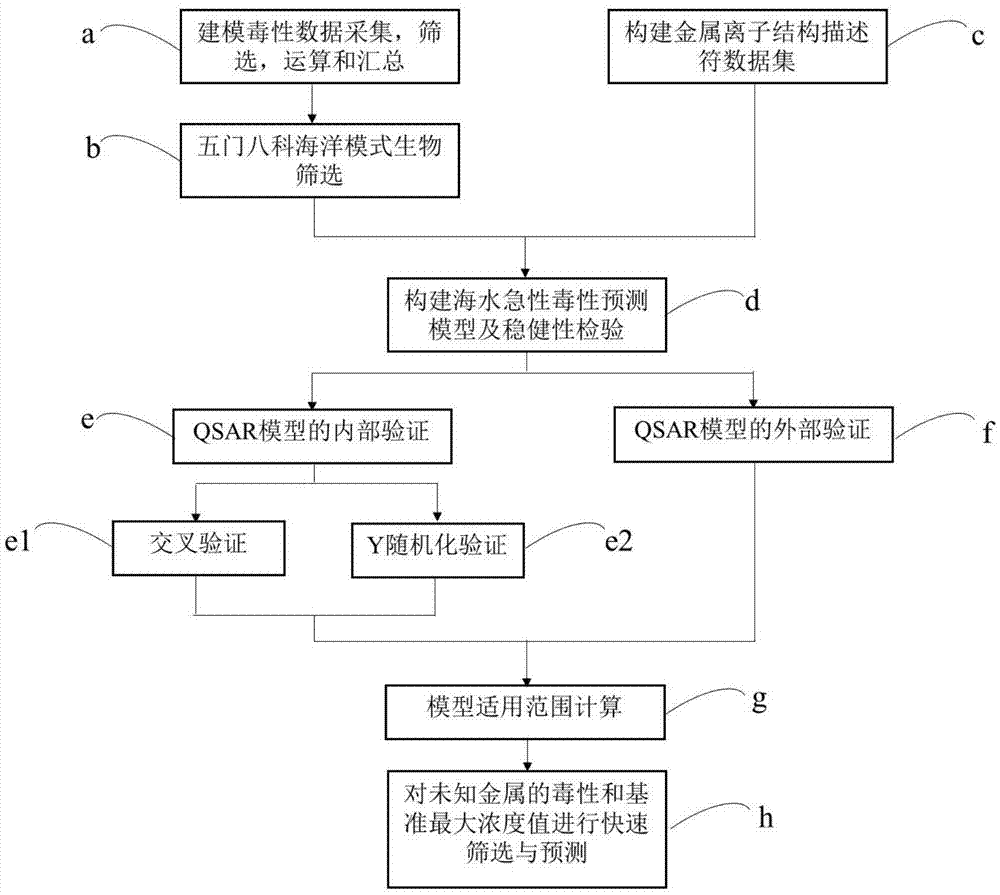
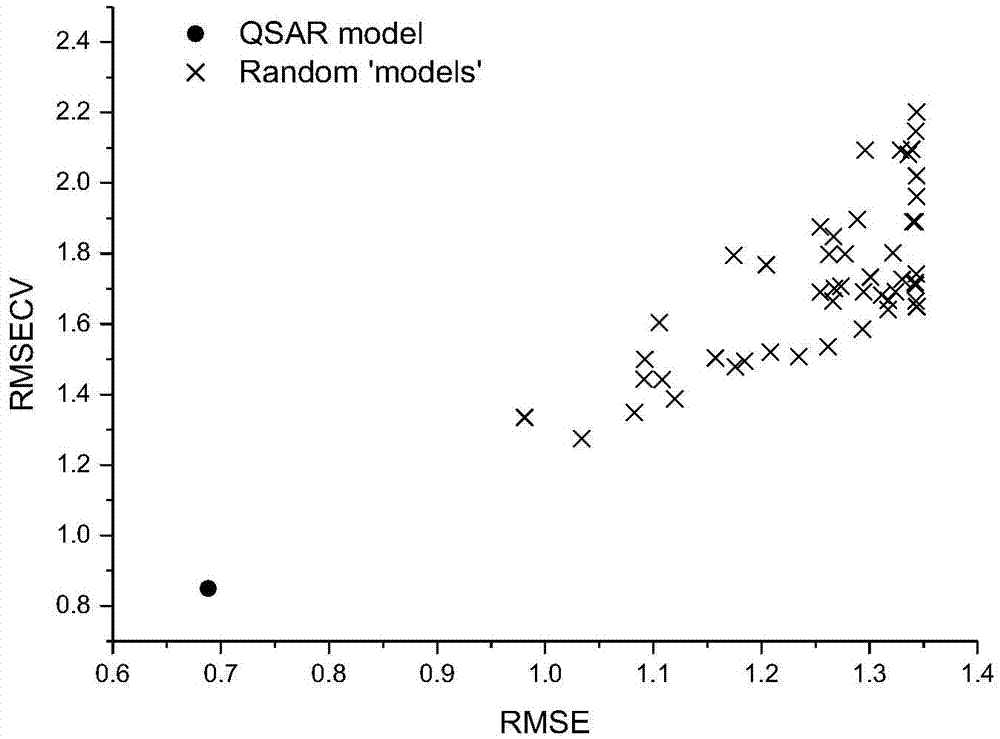
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Metal toxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metal toxicity or metal poisoning is the toxic effect of certain metals in certain forms and doses on life. Some metals are toxic when they form poisonous soluble compounds. Certain metals have no biological role, i.e. are not essential minerals, or are toxic when in a certain form. In the case of lead, any measurable amount may have negative health effects. Often heavy metals are thought as synonymous, but lighter metals may also be toxic in certain circumstances, such as beryllium and lithium. Not all heavy metals are particularly toxic, and some are essential, such as iron. The definition may also include trace elements when in abnormally high doses may be toxic. An option for treatment of metal poisoning may be chelation therapy, which is a technique which involves the administration of chelation agents to remove metals from the body.
Fertilizer composition for improving stress resistance of land planted pear trees
ActiveCN103936500AStrong noveltyPracticalFertilizer mixturesArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPhenylacetic acid
A fertilizer composition for improving stress resistance of land planted pear trees comprises arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, betaine, salicylic acid, ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis(2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) ferric-sodium complex (EDDHA-Fe), a chelate zinc fertilizer titanium zinc ethylenediaminetetraacetate, a promoter and fertilizers containing other elements. Contained arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is capable of substantially improving stress resistance on drought, waterlogging disaster, salt and alkali, high temperature, heavy metal toxicity, toxic organics and the like of pear trees, and promoting absorption of soil mineral nutritional elements by soil. Betaine and salicylic acid are capable of inducing to improve crop resistance on adverse situations such as drought, freeze injury and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF POMOLOGY
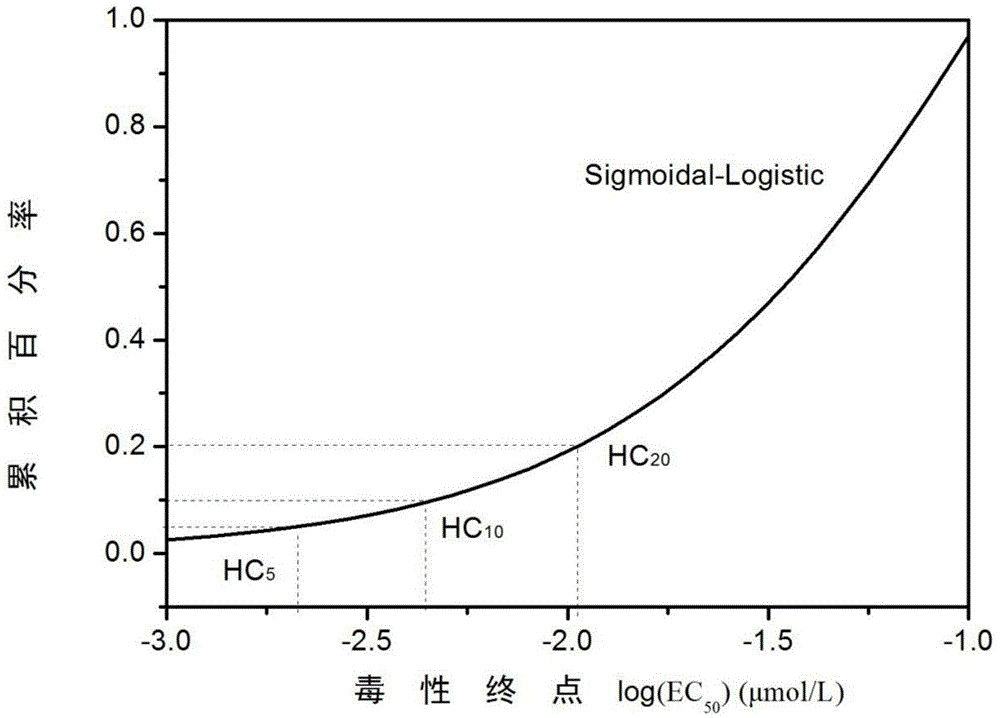
Ecological risk assessment method of heavy metal in river basin sediment based on toxicity effect
ActiveCN105608324AAccurate reflection of riskHealth-index calculationEarth material testingEcological riskNatural abundance
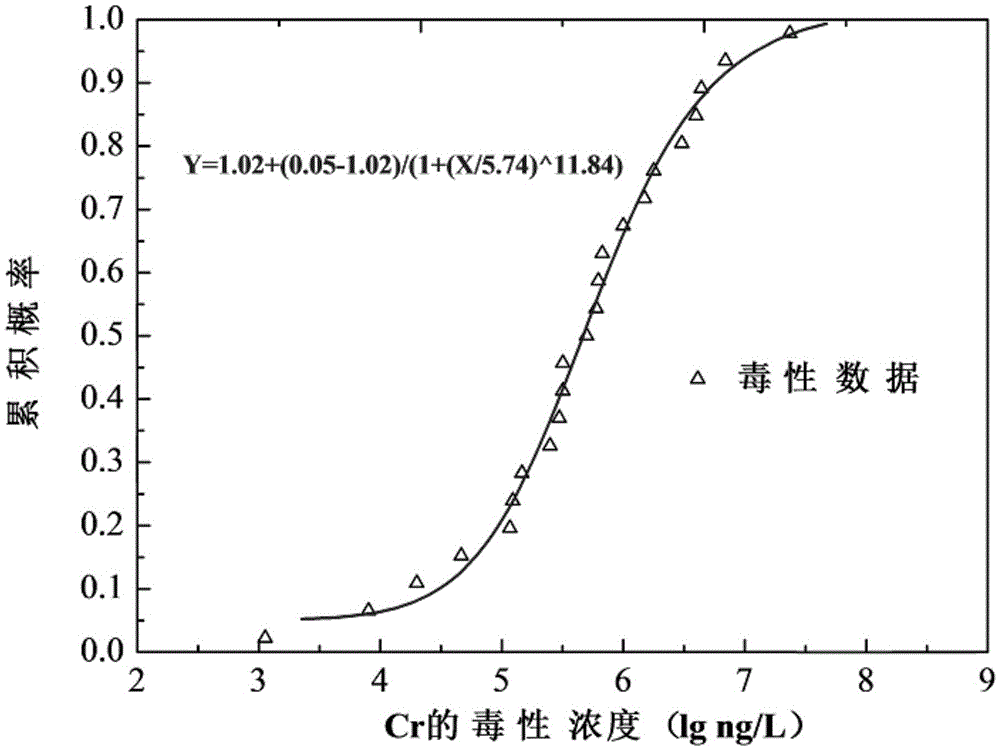
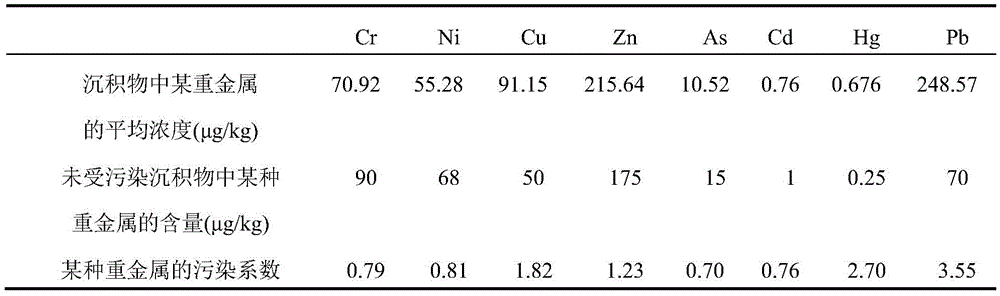
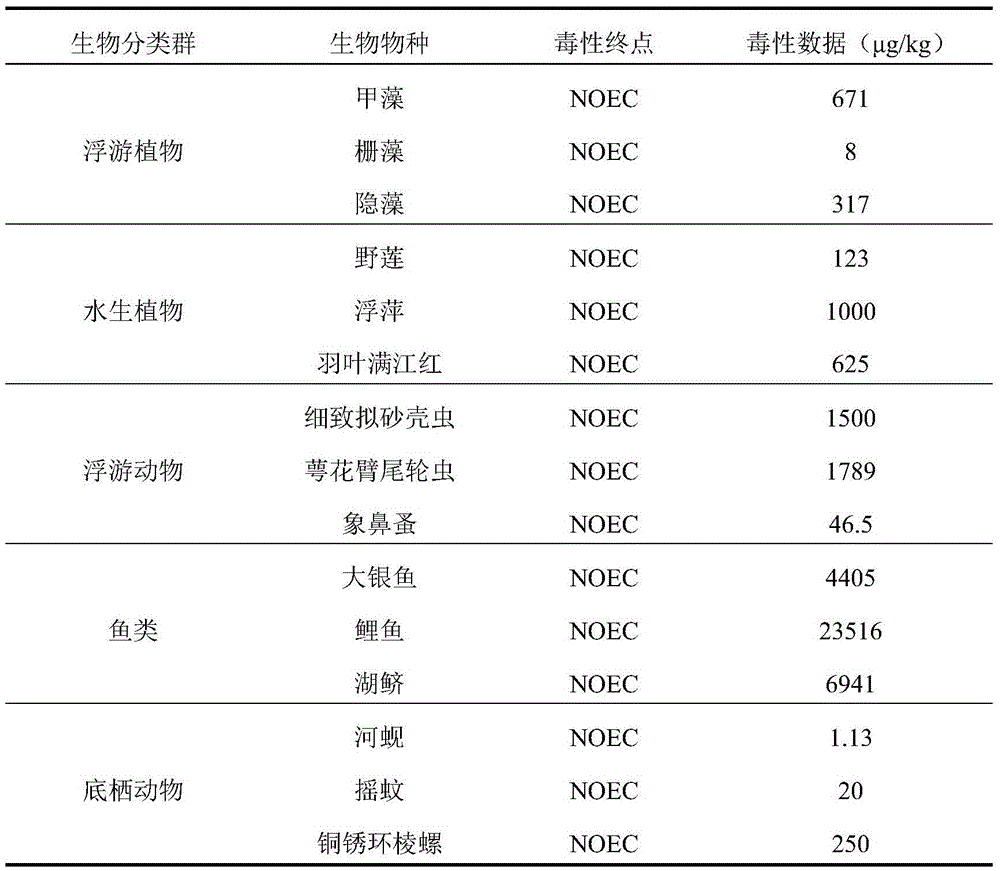
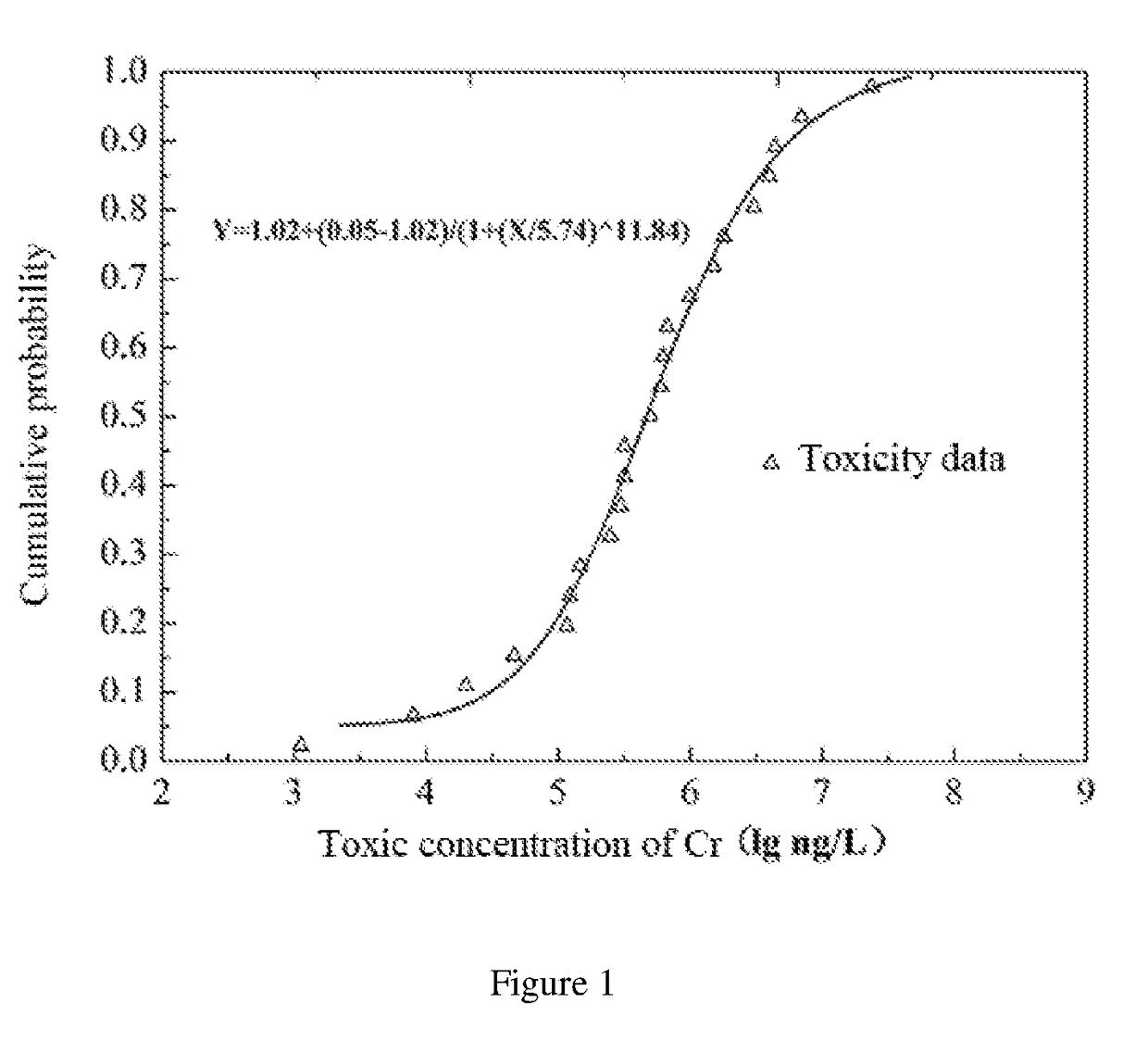
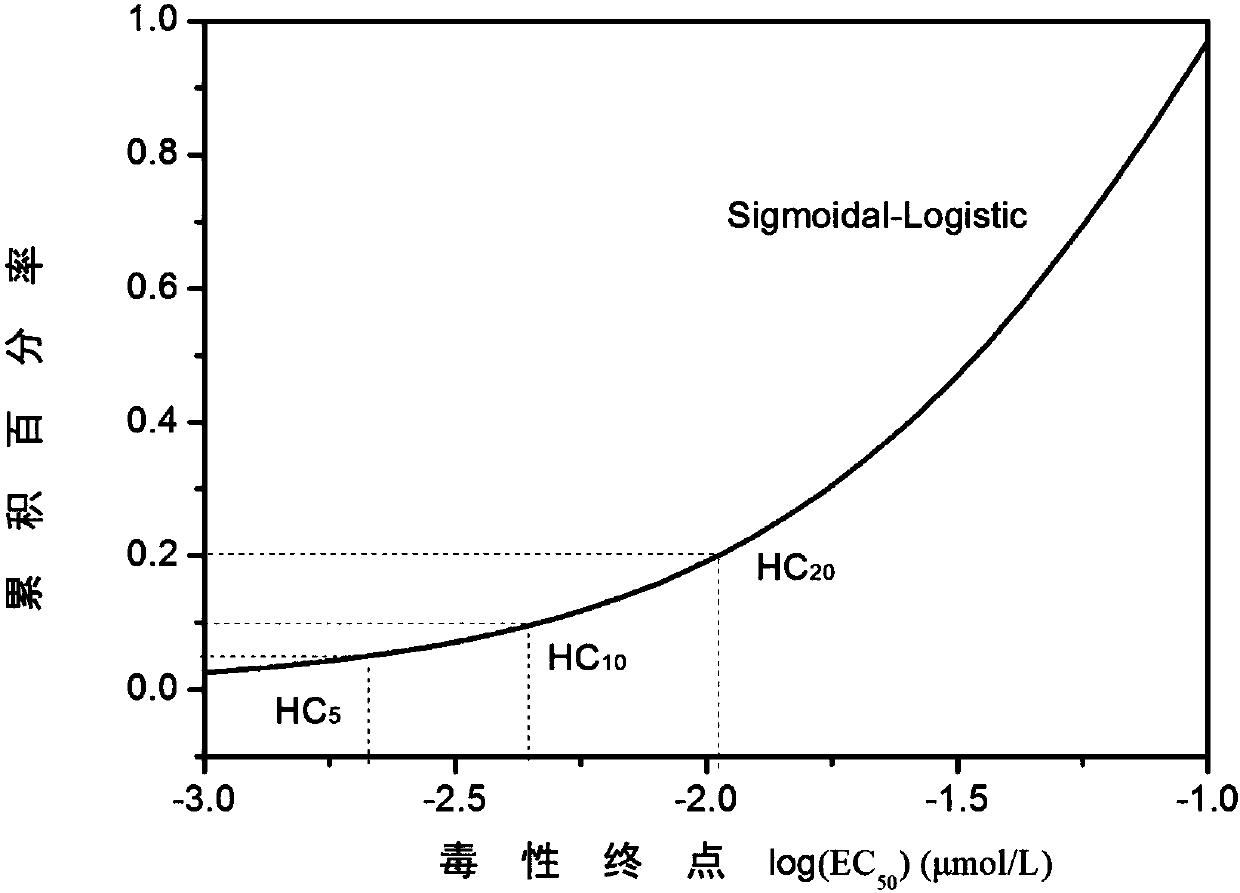
The invention relates to a method for determining ecological risks, particularly to an ecological risk assessment method of heavy metal in river basin sediment based on the toxicity effect. The assessment method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, screening main aquatic organisms in the river basin, 2, sampling sediment, and determining and detecting types of heavy metal, 3, detecting the heavy metal concentration in the sediment, 4, collecting the heavy metal release coefficient, 5, collecting heavy metal toxicity data and fitting the data, 6, determining the heavy metal HC5 value according to a fitted equation, 7, calculating the heavy metal toxicity coefficient, 8, calculating the heavy metal toxicity response coefficient, and 9, calculating the heavy metal ecological risk index, and the method can further comprise a step 10 of calculating the comprehensive ecological risk index of various types of heavy metal. Compared with the prior art that the crustal abundance is adopted to indirectly and roughly estimate the metal toxicity effect, the assessment method provided by the invention can more accurately reflect the ecological risks, caused by the heavy metal in the sediment, to the aquatic organisms in the river basin.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
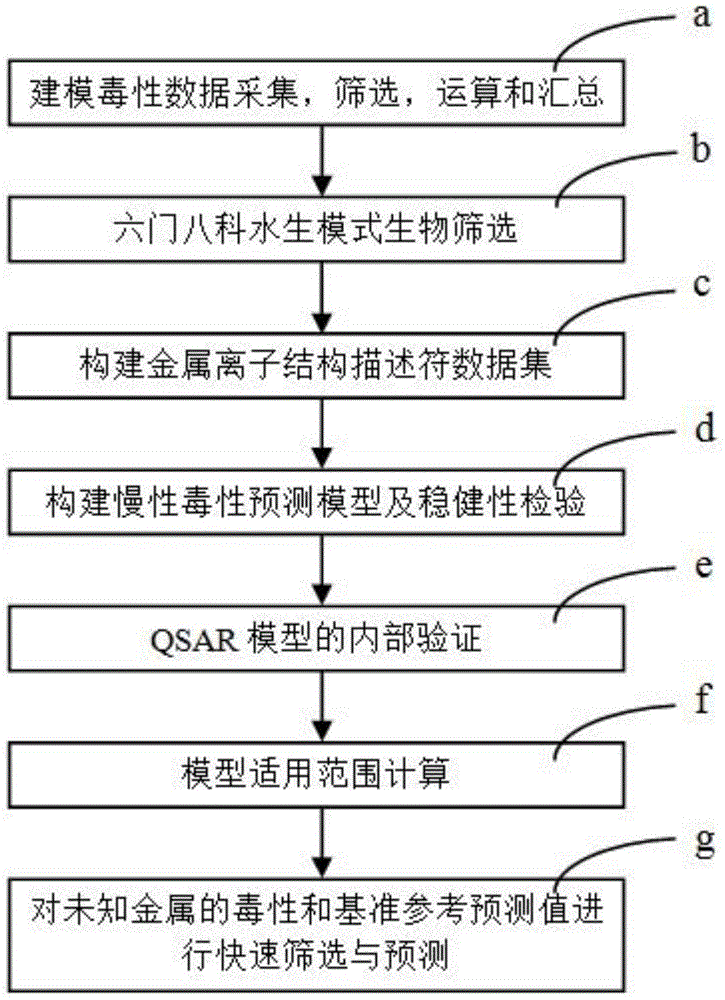
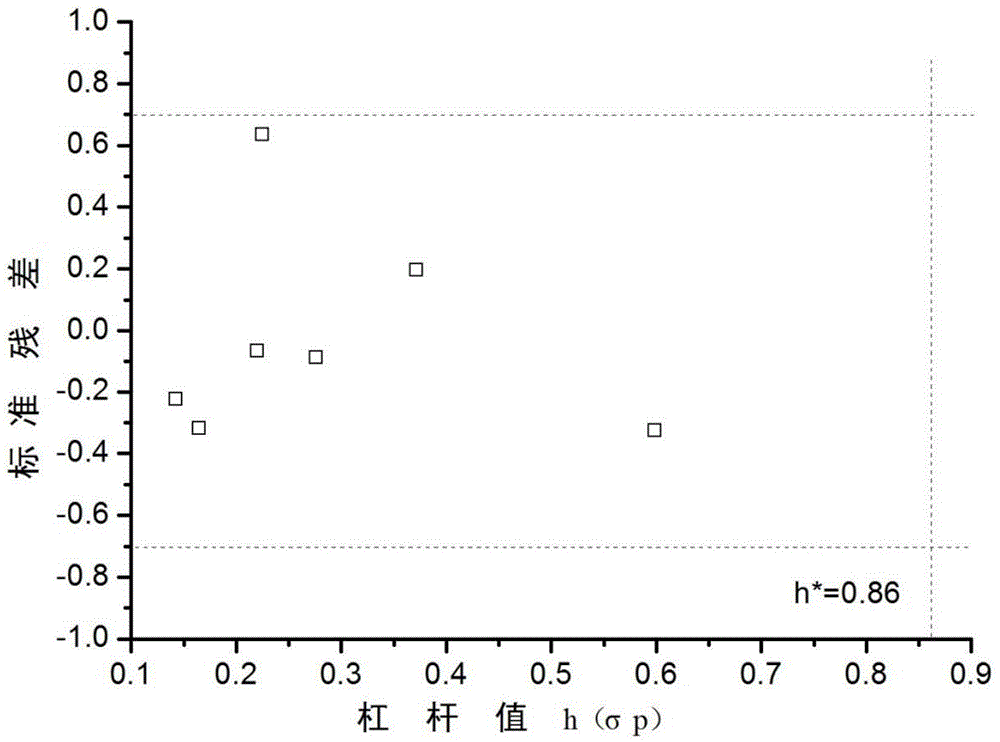
Fresh water acute criteria prediction method based on quantitative structure-activity relationship for metals
ActiveUS20170323085A1Improve precisionPredict in advanceChemical property predictionForecastingChemical structureAcute toxicity testing
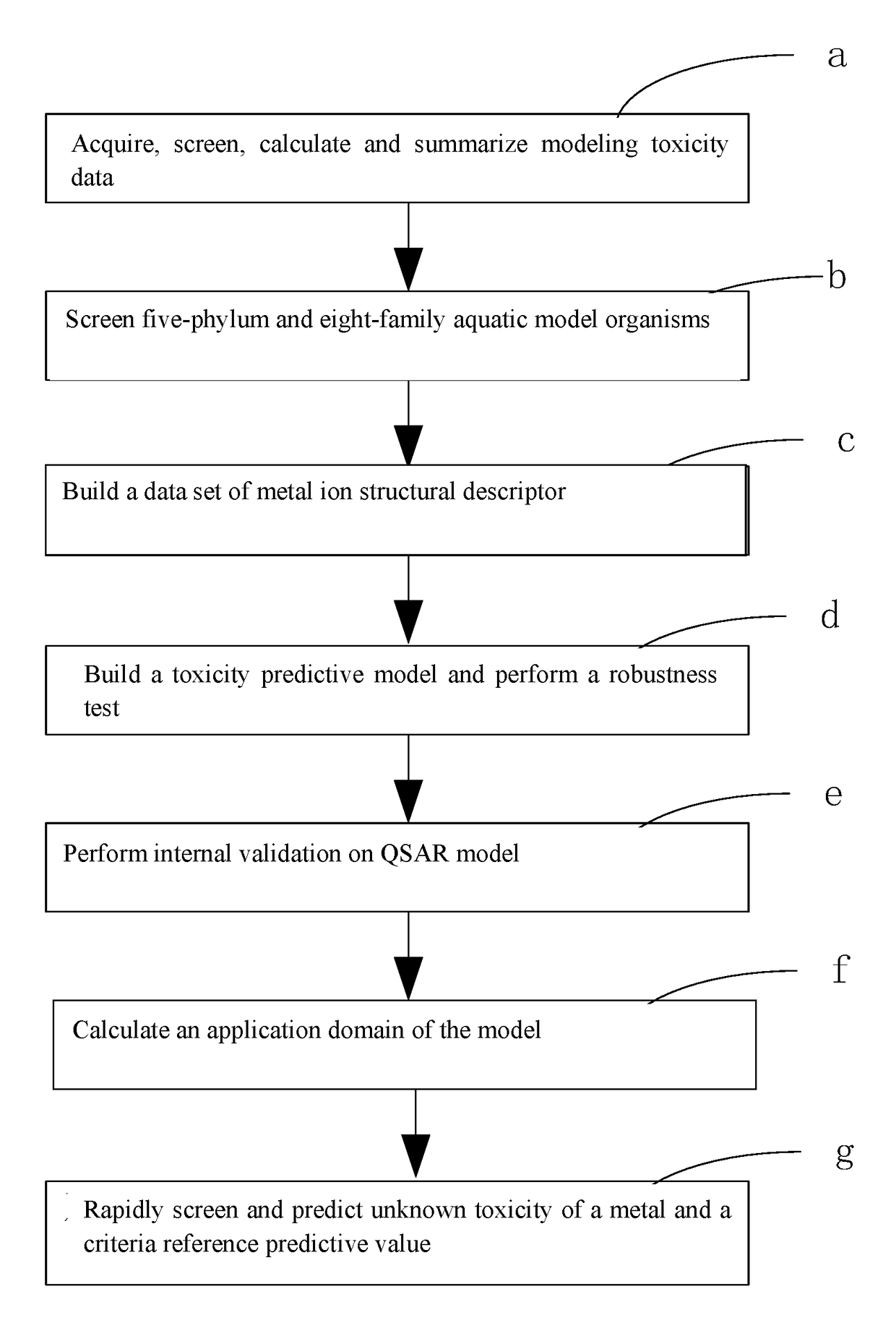
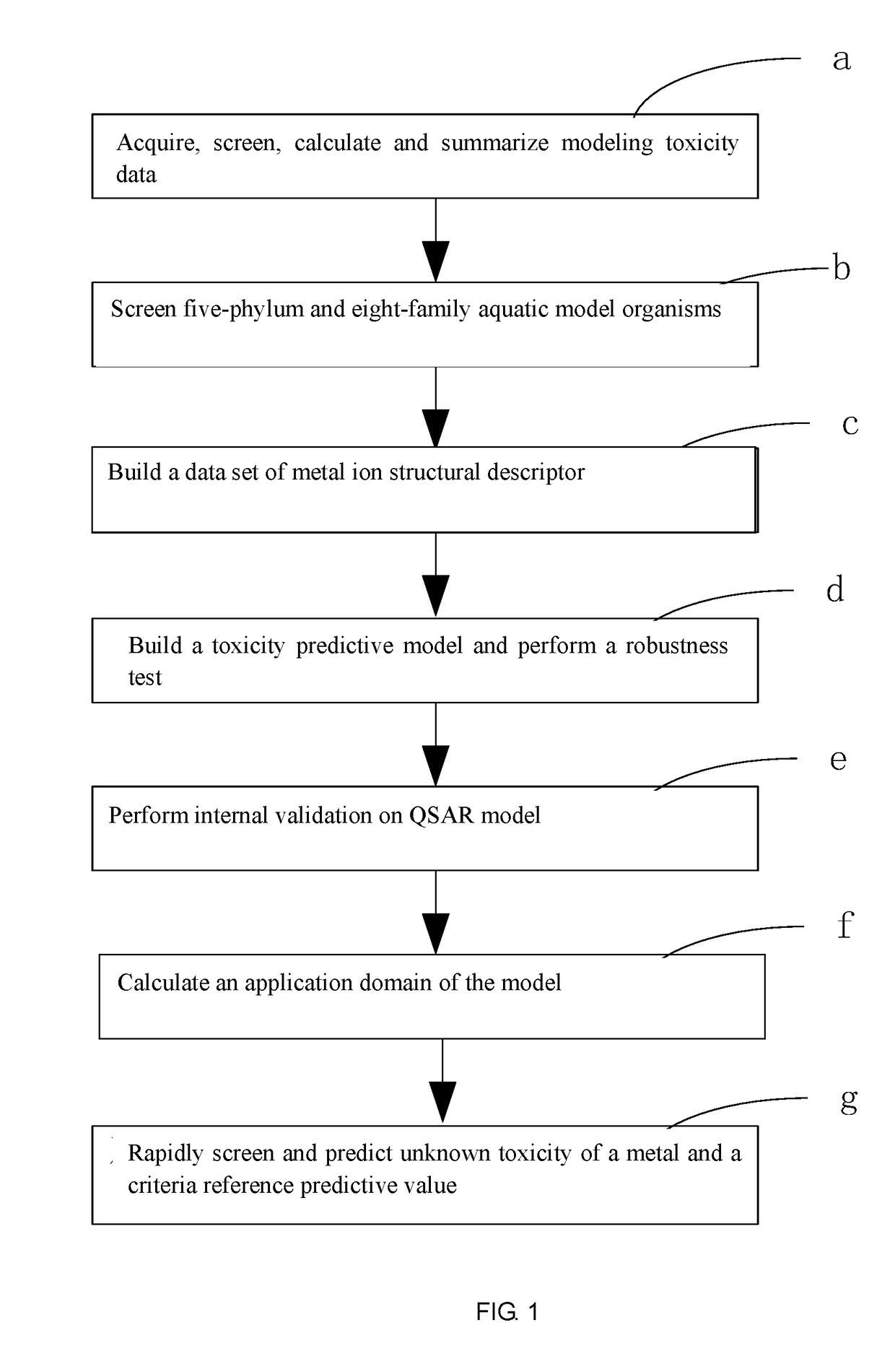
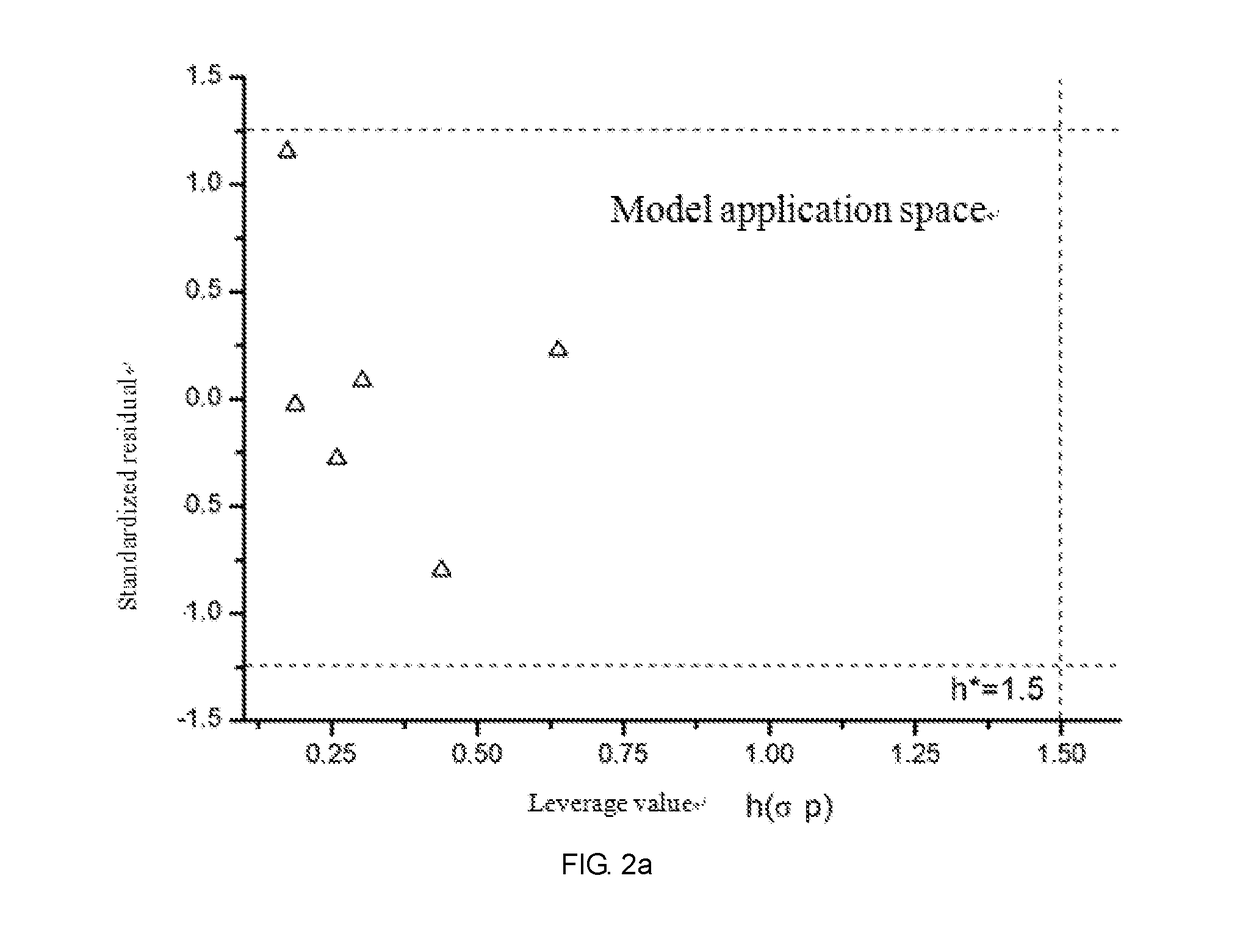
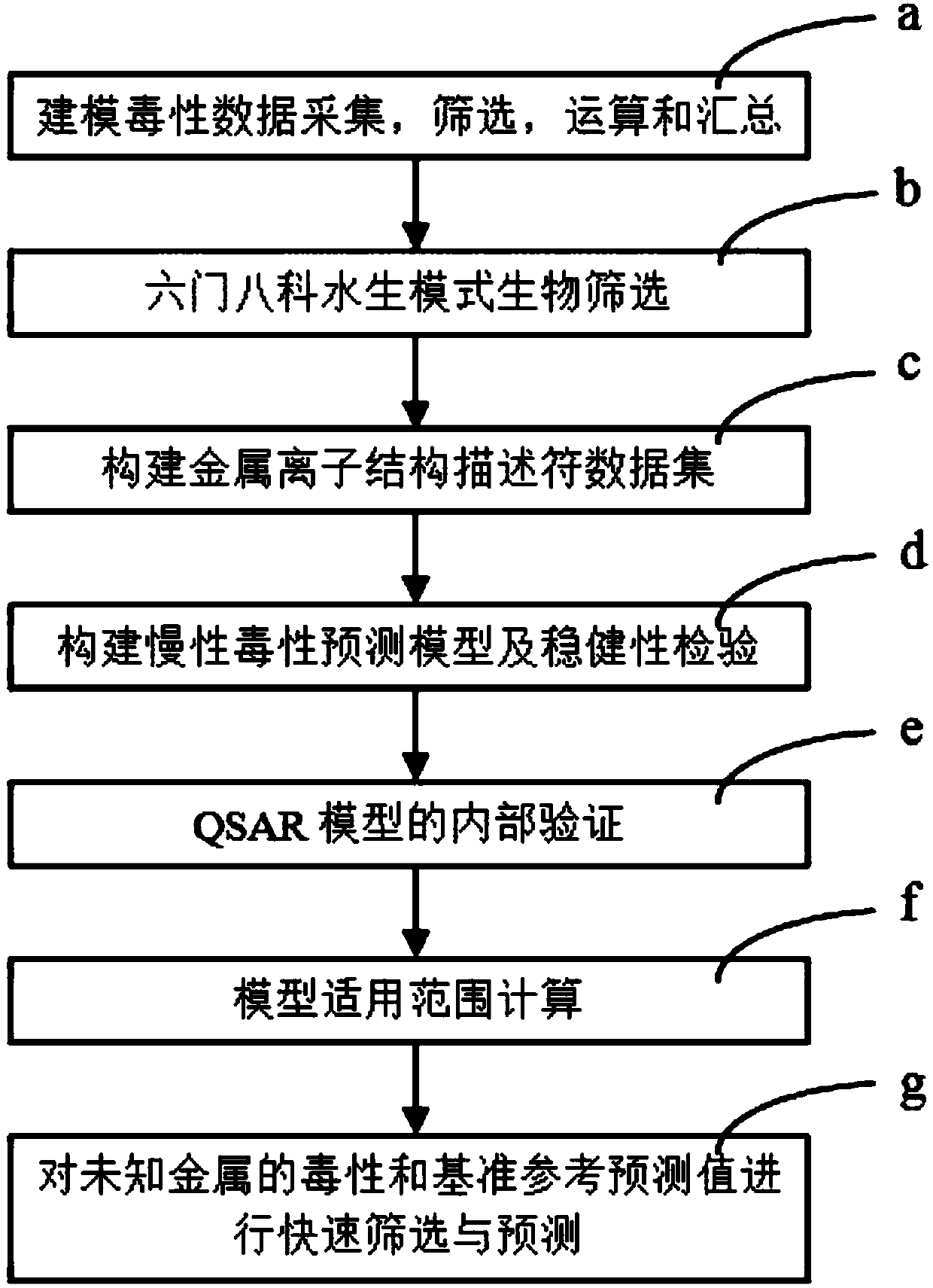
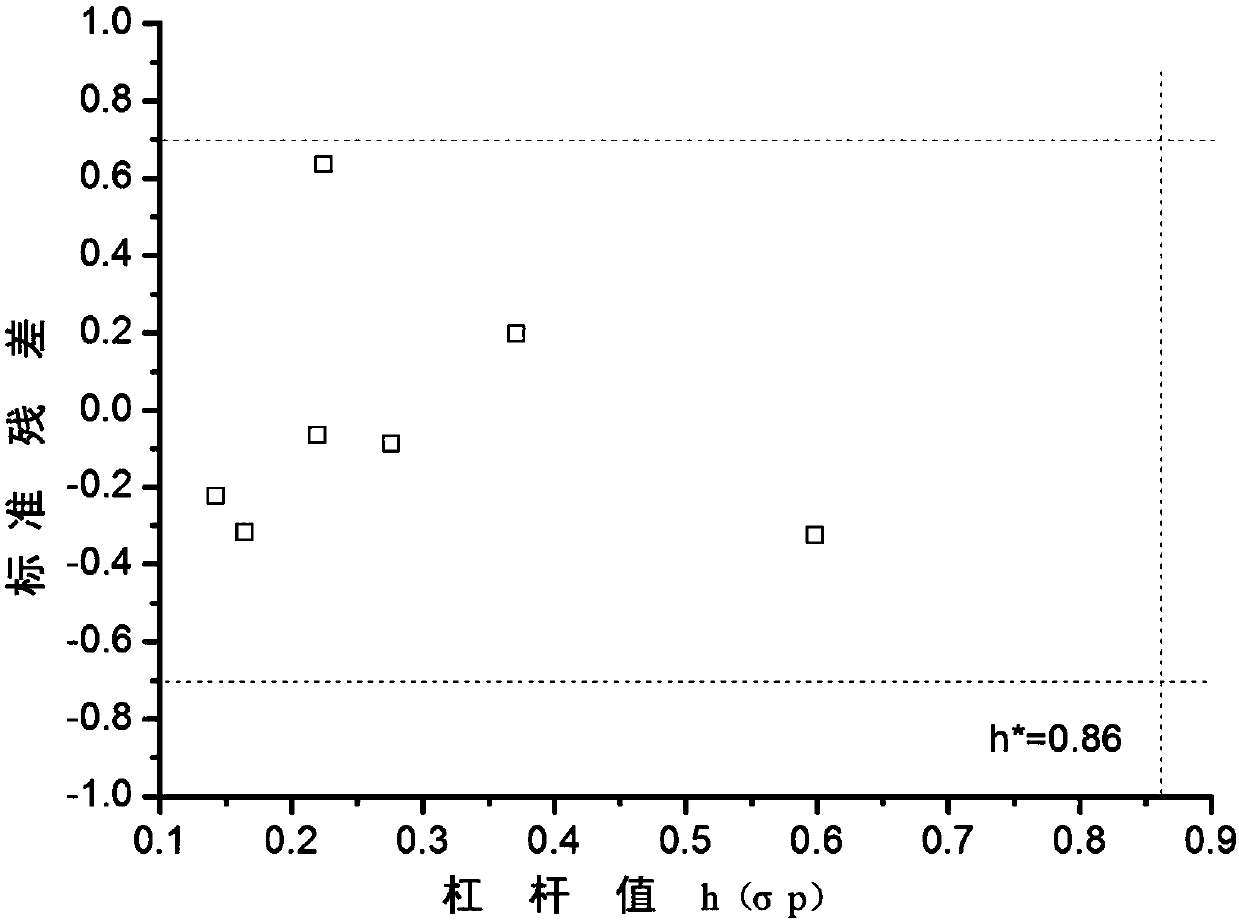
The present invention relates to a fresh water acute criteria prediction method based on a quantitative structure-activity relationship for metals. An unknown toxic endpoint of a metal is predicted according to a quantitative relationship between structural characteristics of heavy metal ions and acute toxicity effects of aquatic organisms, and hazard concentrations for protecting the aquatic organisms of different proportions are derived from sensitivity distribution analysis on different species. The fresh water acute criteria prediction method is a method for establishing a metal toxicity predictive model by integrating physicochemical structural parameters of heavy metals and toxic mechanisms of different aquatic organisms and applying the metal toxicity predictive model to prediction of an unknown criteria reference value.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in river basin sediment based on toxicity effect
ActiveUS20190004024A1Not at risk of errorHealth-index calculationEarth material testingEcological riskToxicity data
A method for determining ecological risk, particularly a method for the ecological risk assessment of a heavy metal in a river basin sediment based on a toxicity effect. The assessment method includes screening the main aquatic organisms in a river basin; sampling a sediment, and determining and detecting the heavy metal type; measuring the concentration of the heavy metal in the sediment; collecting the heavy metal release coefficient; collecting the heavy metal toxicity data and fitting the data; determining the heavy metal HCsi value according to a fitting equation; calculating the heavy metal toxicity response coefficient; calculating the ecological risk index of the heavy metal. This method can further include calculating the comprehensive ecological risk index of various types of heavy metals. The method can accurately reflect the ecological risk of a heavy metal on aquatic organisms in a river basin.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
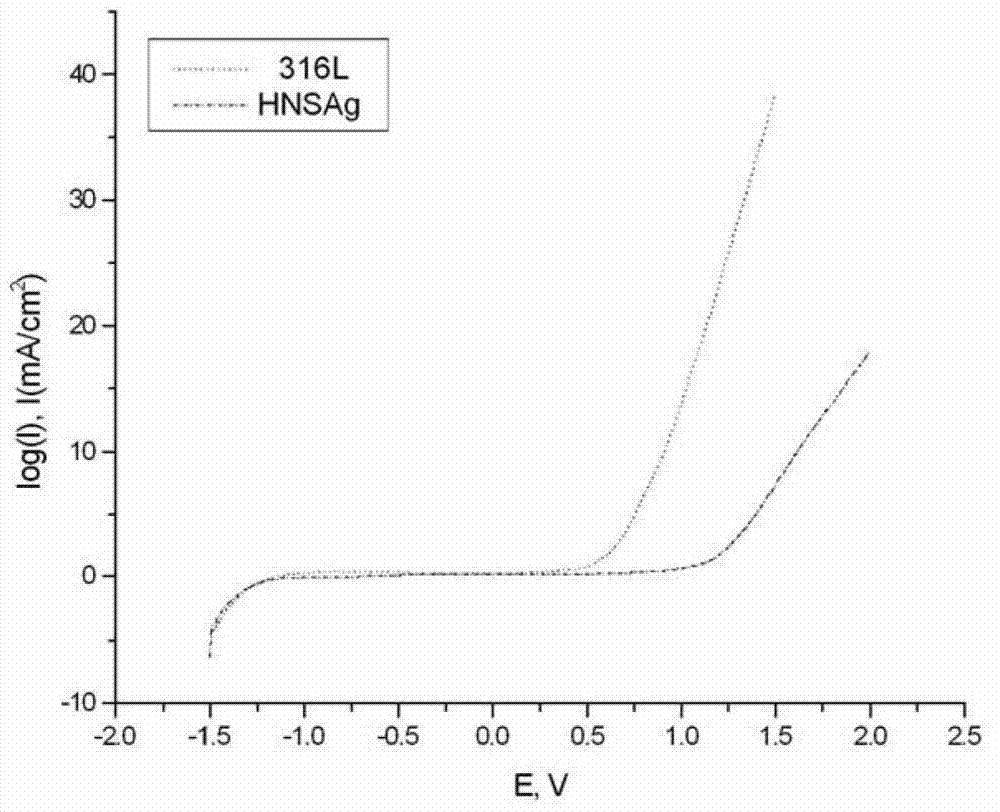
High-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103045951AImprove toughness and plasticityMeet processing requirementsChromium nickelNiobium
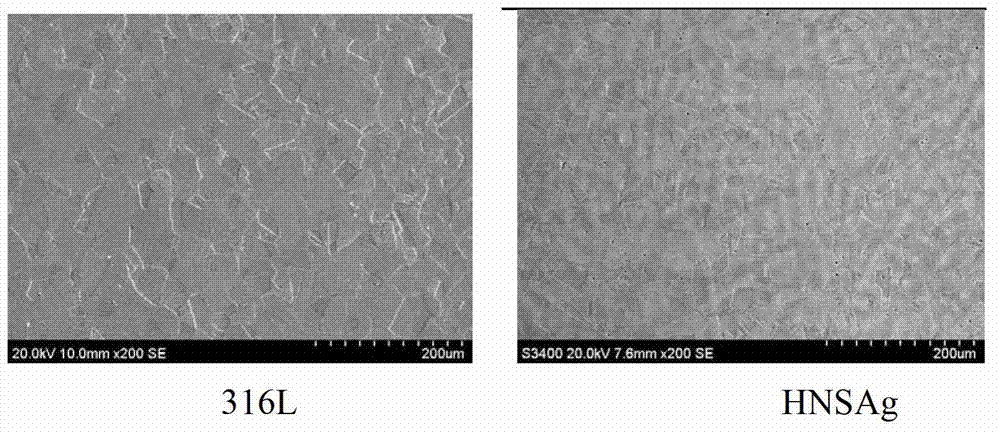
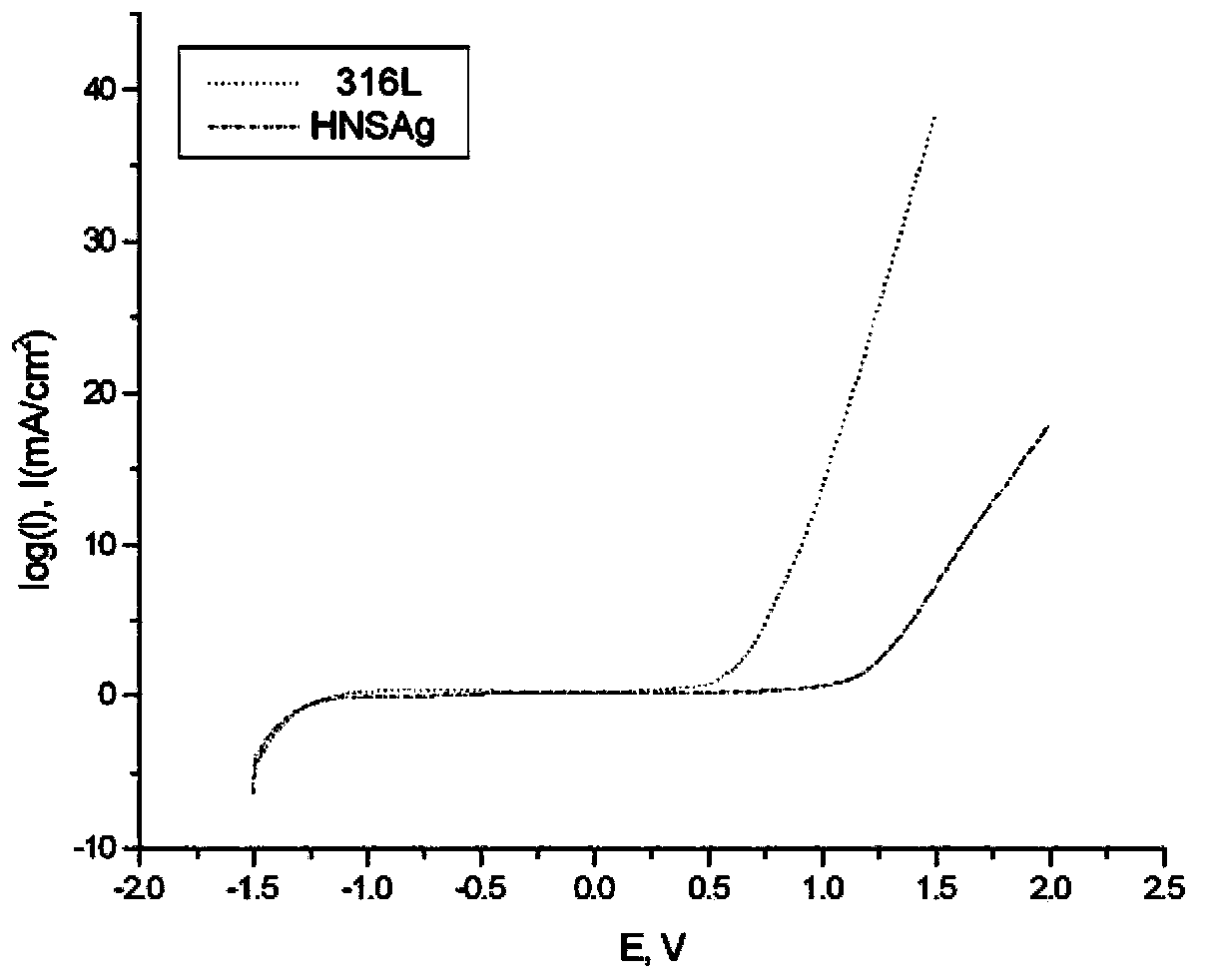
The invention discloses high-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) and a manufacturing method thereof. The stainless steel comprises carbon, silicon, manganese, chromium, molybdenum, copper, nitrogen, niobium, silver and the balance of iron by weight percent; the high-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) is of a single austenite structure after subjected to solution treatment, and is excellent in pitting corrosion resistance in a non-microorganism environment and good in bacterial resistance and microorganism corrosion resistance in a microorganism environment; the antibacterial rate of the stainless steel on staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli reaches more than 93%; the nickel release risk is inexistent; the manganese release rate in artificial saliva and sweat is much lower than the acceptable daily intake standard; the stainless steel can be used as a biomedical material; and the metal toxicity risk is inexistent. The high-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) is very good in flexibility and plasticity, can meet the processing requirements of fine parts such as jewelries and the like, and is superior to chromium-nickel austenite antibacterial stainless steel of 316 L and the like in overall performance.
Owner:郭强
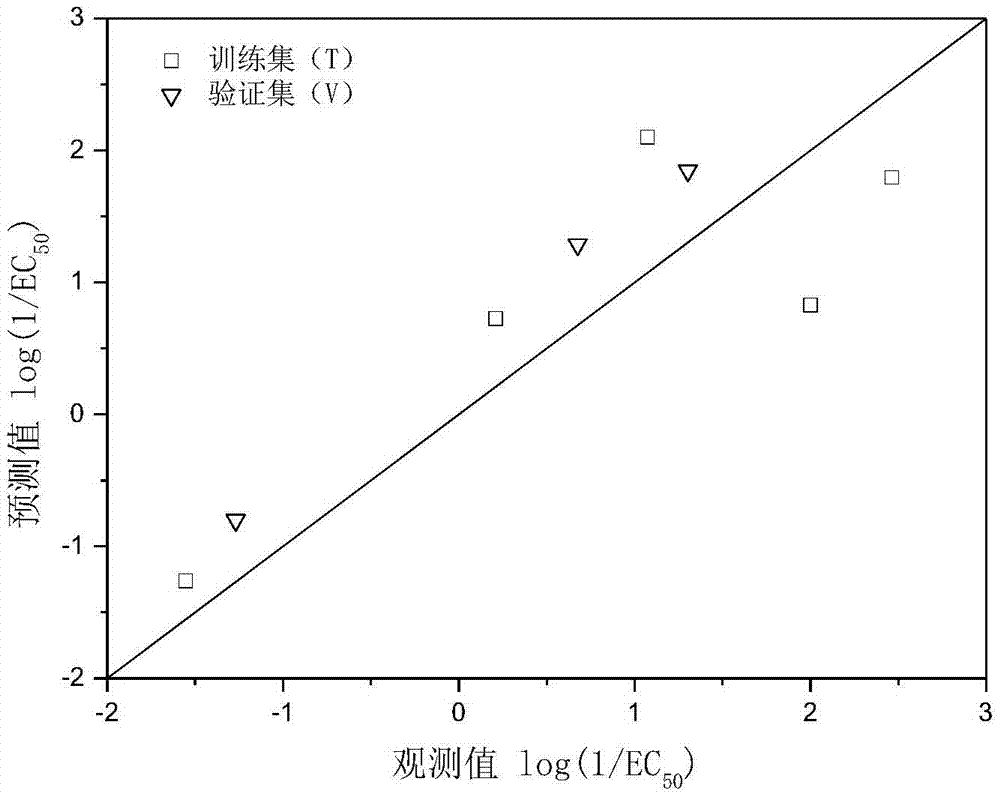
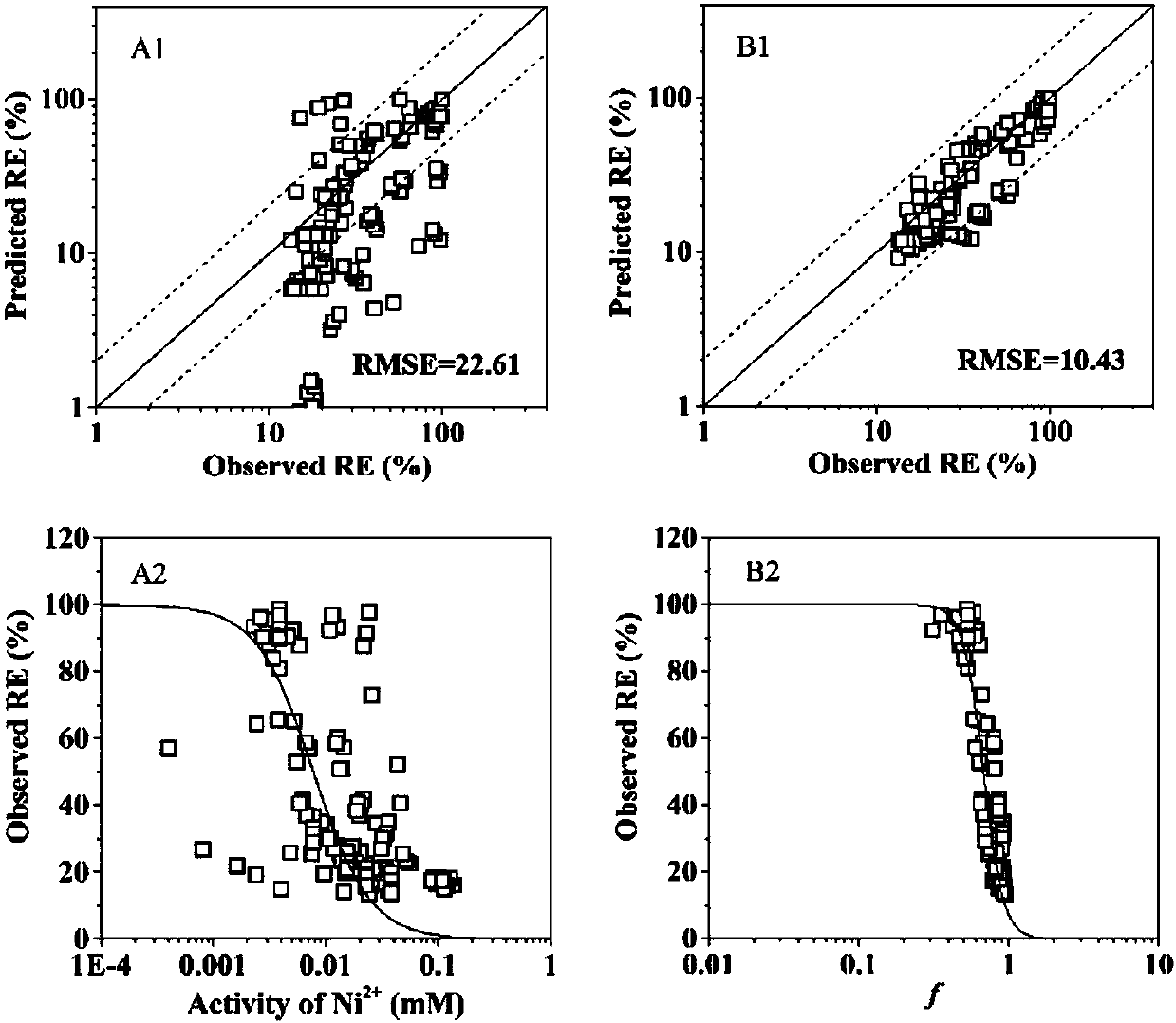
Method for predicting wheat root elongation toxicity of nickel ions in soil, and application thereof
InactiveCN106932538ASolve problems that cannot be accurately predictedValid and reliable toxicity parametersTesting plants/treesAir quality improvementSoil typeSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a method for predicting wheat root elongation toxicity of nickel ions in soil, and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of ecological heavy metal toxicity assessment. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the toxicity competitive inhibition effect of Ca<2+> and other cations on the nickel ions is considered, the influence of the osmotic pressure effect in soil conditions to the toxicity is corrected, and meanwhile the toxic effect of nickel is calculated by obtaining the activity of the nickel ions by using the visual MINTEQ program. Firstly, biological toxicity suppression parameters of the cations to the nickel ions, and the toxic effect parameters and the osmotic pressure parameters of the nickel are determined under a sand culture condition, the obtained parameters can be applied to the prediction of the wheat root toxicity of the nickel ions under different soil types, and the method is also applicable to predicting the root elongation toxicity of nickel ions to other crops and can provide reference for soil heavy mental ecological risk assessment and soil pollution abatement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Organic bacterial fertilizer for restoration of manganese ore-polluted soil, as well as preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104496724AReduce heavy metal toxicityLow toxicitySuperphosphatesExcrement fertilisersCompound organicPlant roots
The invention discloses an organic bacterial fertilizer for the restoration of manganese ore-polluted soil, as well as a preparation method thereof. The organic bacterial fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 3-5 parts of basic nutrient solution, 20-25 parts of remissive complex organic raw materials, 70-75 parts of water retention media and 3-5 parts of anti-manganese complex microbial agent. The preparation method comprises the mixing and fermentation steps. The organic bacterial fertilizer for the restoration of manganese ore-polluted soil has the effects that the soil structure is modified, the water retention and constant temperature can be achieved, the toxicity of heavy metals around roots can be reduced, the survival rate of plants can be increased, and the growth of plants can be promoted; in addition, the toxicity of manganese elements in the soil of plant roots can also be effectively relieved, the effect of the organic fertilizer can be enhanced, and the restoration capability of plants can be enhanced.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Seawater acute reference prediction method based on metal quantitative structure-activity relationship
InactiveCN105447248AHigh precisionImprove predictive performanceGeneral water supply conservationSpecial data processing applicationsChemical structurePredictive methods
The present invention relates to a seawater quality reference prediction method based on a quantitative structure-activity relationship of metal and metalloid. According to the method, the toxic endpoint of unknown metal is predicted according to a quantitative relationship between the structural feature of metallic ions and the marine life acute toxic effect, and a risk concentration for protecting different proportions of marine life is analyzed and deduced in conjunction with sensitivity distribution of different species; and a QSAR metal toxicity prediction model is established by integrating metal physical and chemical structure parameters and toxic mechanisms of different marine life and is applied to prediction of an unknown seawater quality reference maximum concentration. The seawater acute reference prediction method based on the metal quantitative structure-activity relationship is based on the ecology principle; the system screens various marine species and takes the screened marine species as smallest biological prediction sets; and single-parameter toxicity prediction models are established separately, thereby improving the model precision and prediction ability.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
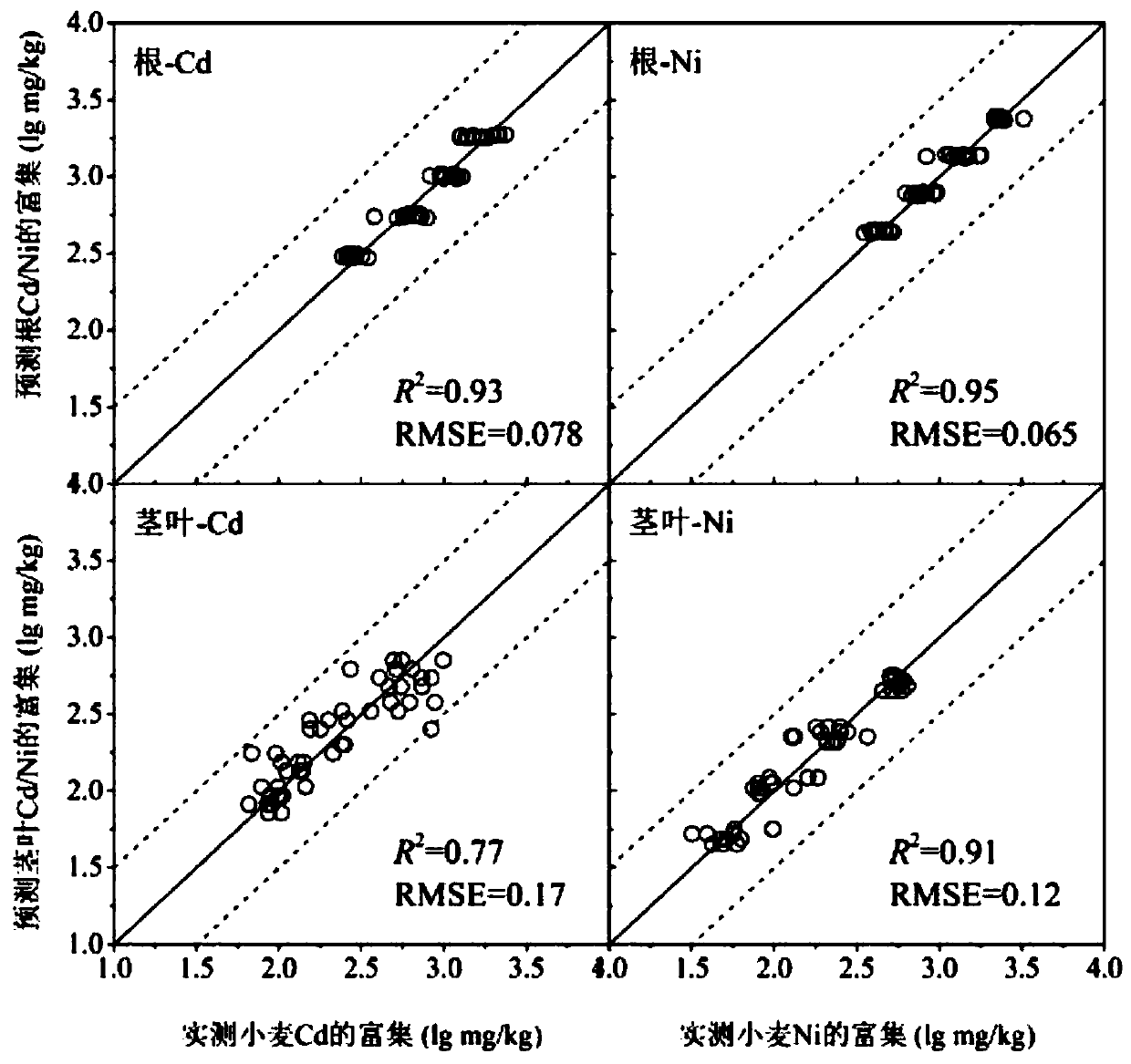
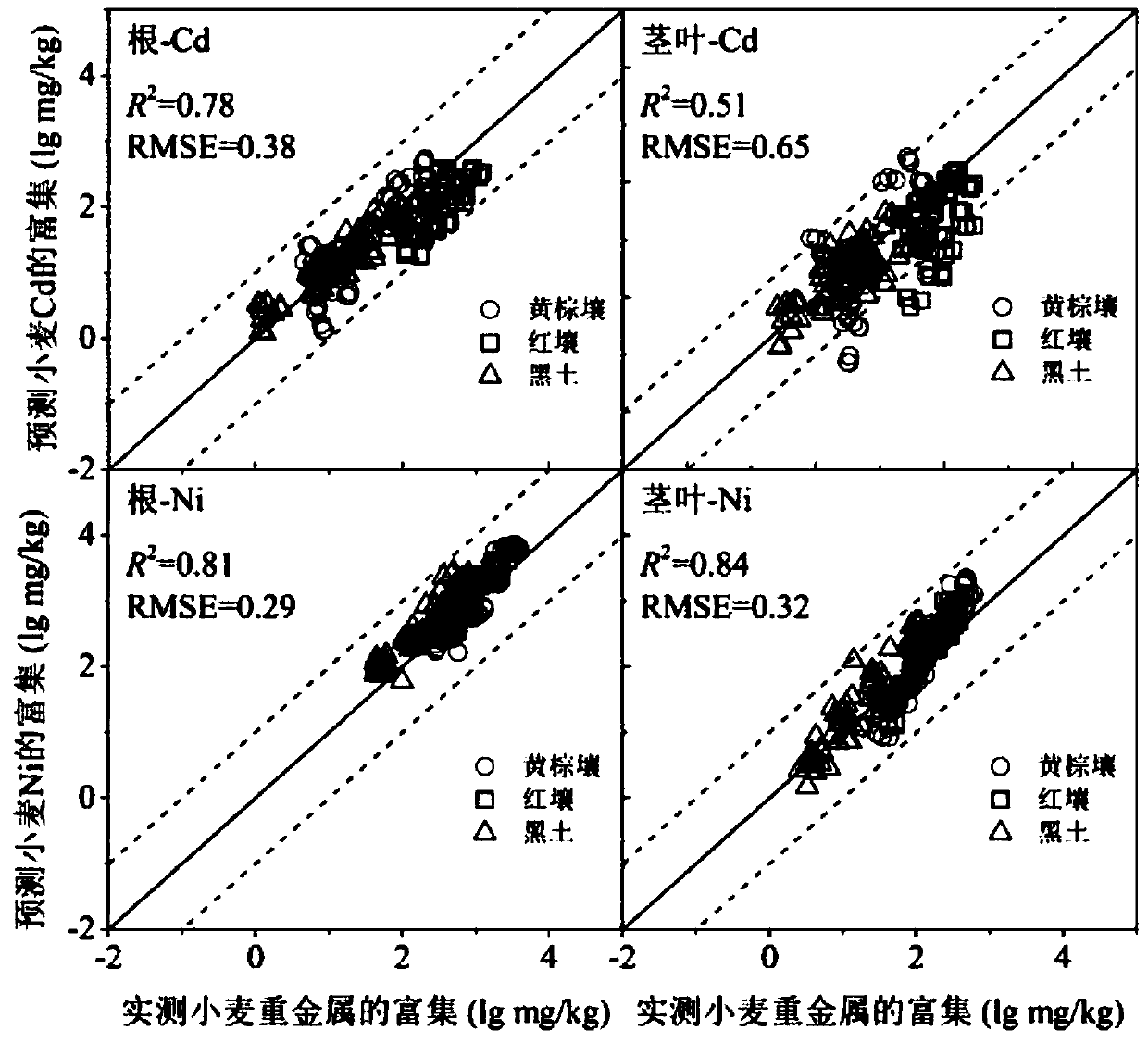
Prediction method of soil cadmium-nickel compounded wheat enrichment amount
ActiveCN110083985AGood forecastSolve the problem of direct prediction of enrichmentDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSoil heavy metalsNickel compounds
The invention discloses a prediction method of soil cadmium-nickel compounded wheat enrichment amount, and belongs to the field of ecological heavy metal toxicity assessment. According to the method,the interaction of cadmium and nickel ions in the wheat enrichment process is considered, the enrichment amount of heavy metals in roots and stems and leaves is predicted by adopting a multiple regression method, firstly, a cadmium-nickel ion composite enrichment equation is obtained by adopting a sand culture experiment, and then the biological enrichment amount of the composite heavy metals in different soils is predicted by combining with the metal concentration in actual soil pore water. The method is also suitable for predicting the biological enrichment amount of Cd-Ni recombination on heavy metals of other crops, and a new method is provided for ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals and regional soil pollution treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Protective metallothionein analog compounds, their compositions and use thereof in the treatment of pathogenic diseases
InactiveUS20160101079A1Enhancing cellular GSH levelReduce infectivityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntioxidantViral disease
Embodiments of the present invention relate generally the use of certain compositions, e.g., compositions comprising a glutathione precursor and a selenium source, in the therapy of viral diseases and / or reducing the incidence of viral diseases. Related embodiments of the present invention relate to treatment and / or reducing the incidence of respiratory ailments caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or hemorrhagic fever (EHF) caused by Ebola viruses (EBV) or Marburg virus. Yet in other embodiments, the invention relates to reducing metal toxicity in a biological system, which involves contacting the biological system with a composition comprising a glutathione precursor and a selenium source, optionally together with a chelating agent, an antioxidant, a metallothioneine protein or a fragment of metallothioneine.
Owner:CRUM ALBERT
Fresh water chronic standard prediction method based on metal quantitative structure-activity relation
InactiveCN104915563AHigh precisionImprove predictive performanceGeneral water supply conservationSpecial data processing applicationsVirulent characteristicsFresh water organism
The invention relates to the field of water quality pollution evaluation, in particular to a fresh water chronic standard prediction method based on the metal quantitative structure-activity relation. The method includes the steps of predicting the unknown metal virulence terminal point according to the quantitative relation between the structure characteristics of heavy metal ions and the choric toxicity effect of aquatic organisms, and conducting analysis and derivation to obtain the danger concentration that protects aquatic organisms of different ratios through the combination with the sensitiveness distribution of different species. According to the method, the QSAR metal toxicity prediction model is established by synthesizing heavy metal physicochemical structure parameters and toxication mechanisms of different aquatic organisms, and the model is used for predicting the unknown standard continuous concentration. On the basis of the ecology principle, six phyla and eight families of aquatic organisms are screened through a system to serve as a minimum biological prediction set, single-parameter toxicity prediction models are established, and the model accuracy and the prediction capacity are improved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
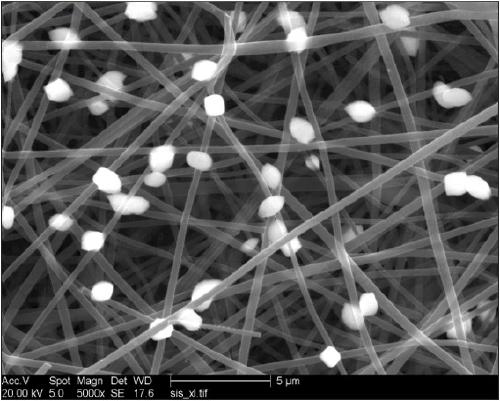
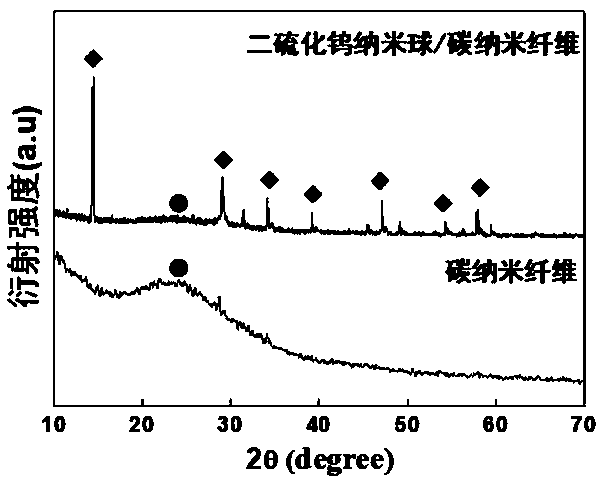
Preparation and application of tungsten disulphide nanosphere/carbon nano fibre composite material
InactiveCN109110817ASimple processLow costFibre chemical featuresMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrospinningBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to preparation of a tungsten disulphide nanosphere / carbon nano fibre composite material and application thereof in detecting dopamine in an electrochemical mode, which belongs tothe technical field of novel function material and bio-sensor detection. The preparation aims to solve the problem that an existing material is high in cost, is low in metal toxicity and sensitivityand is low in selectivity while detecting dopamine. The preparation mainly comprises the following steps: I, preparing carbon nano fibres through an electrostatic spinning method; and II, preparing the tungsten disulphide nanosphere / carbon nano fibre composite material through a hydrothermal method. The tungsten disulphide nanosphere / carbon nano fibre composite material prepared by the preparationhas the advantages of great specific surface area, high conductivity, good biocompatibility and the like, and can be used as an electrode material for detecting dopamine.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thiol-containing compounds for the removal of elements from tissues and formulations therefor
Methods and pharmaceutical formulations for ameliorating heavy metal toxicity and / or oxidative stress are disclosed, comprising administering pharmaceutically effective amounts of ligands according to the present disclosure. The ligands are of the general structure: where R1 comprises benzene, pyridine, pyridin-4-one, naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene or alkyl groups, R2 comprises hydrogen, alkyls, aryls, a carboxyl group, carboxylate esters, organic groups or biological groups, R3 comprises alkyls, aryls, a carboxyl group, carboxylate esters, organic groups or biological groups, X comprises hydrogen, lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, francium, alkyls, aryls, a carboxyl group, carboxylate esters, thiophosphate, N-acetyl cysteine, mercaptoacetic acid, mercaptopropionic acid, thiolsalicylate, organic groups or biological groups, n independently equals 1-10, m=1-6, Y comprises hydrogen, polymers, silicas or silica supported substrates, and Z comprises hydrogen, alkyls, aryls, a carboxyl group, carboxylate esters, a hydroxyl group, NH2, HSO3, halogens, a carbonyl group, organic groups, biological groups, polymers, silicas or silica supported substrates.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY RESEARCH FOUNDATION
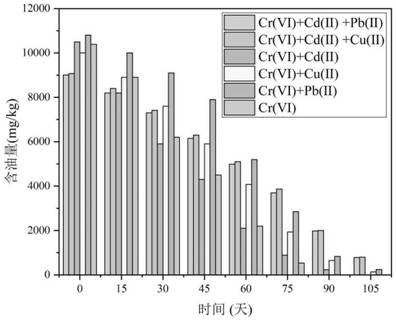
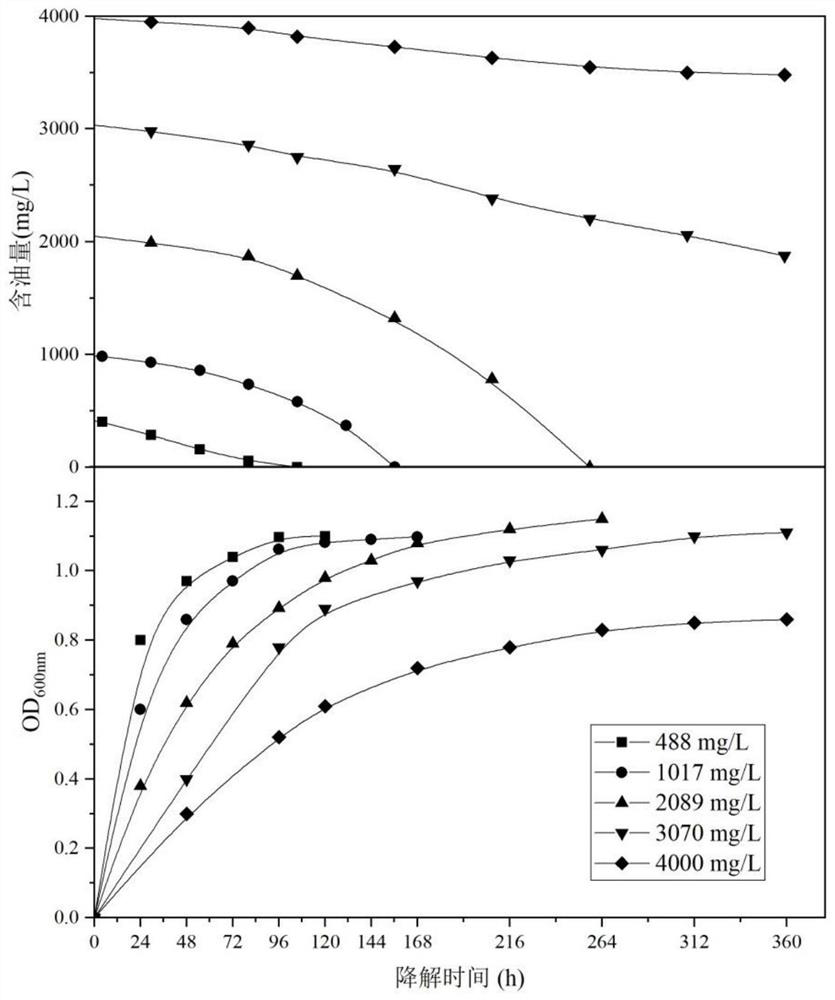
Bacillus tropicalis resistant to heavy metal degradation of waste engine oil
ActiveCN113652368AGood degreasing effectAvoid processing powerBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismEnvironmental engineering
Aiming at the defects in the prior art, the invention provides bacillus tropicalis capable of tolerating the toxicity of heavy metals and effectively degrading waste engine oil and an application of the bacillus tropicalis. The bacillus tropicalis is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on May 24, 2021, and the preservation number is GDMCC No.61680. The strain can tolerate the toxicity of high-concentration heavy metals, and meanwhile, the strain grows by taking waste engine oil as a carbon source and degrades the waste engine oil. The strain can be used for degrading waste engine oil with heavy metals in soil.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
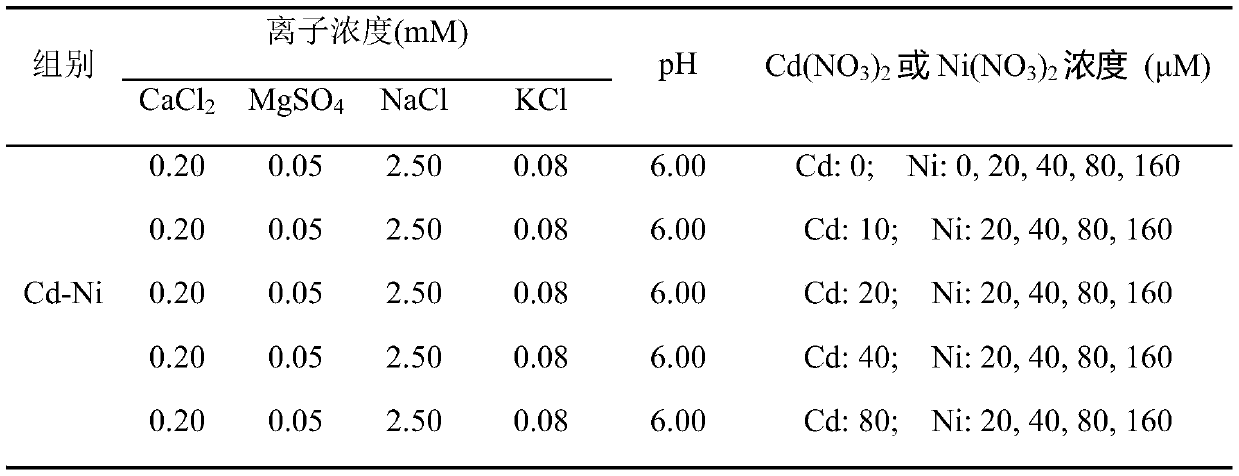
Prediction method of cadmium-nickel compound on root elongation toxicity of wheat in soil and application of prediction method
ActiveCN110018300ASolve problems that cannot be accurately predictedBiological testingTesting plants/treesNickel compoundsSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a prediction method of a cadmium-nickel compound on the root elongation toxicity of wheat in soil and application of the prediction method, and belongs to the technical field of ecological heavy metal toxicity assessment. According to the prediction method, on the basis that known competing cations of Cd<2+> and Ni<2+> are H<+> and Mg<2+>, the toxicity inhibition effect ofthe competing cations and osmotic pressure impact of a saline solution are considered, and the combined toxicity effects of Cd and Ni are calculated by adopting a single toxic concentration addition method. The prediction method includes the steps that firstly, a sand culture experiment is used for obtaining Cd-Ni compound toxicity effect parameters and osmotic pressure effect parameters of the saline solution, and then the obtained parameters are applied to prediction of the Cd-Ni compound toxicity effects in different soil. The prediction method is also applied to prediction of the Cd-Ni compound on the root elongation toxicity effects of other crops, and a new method is provided for soil heavy metal ecological risk assessment and regional soil pollution control.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
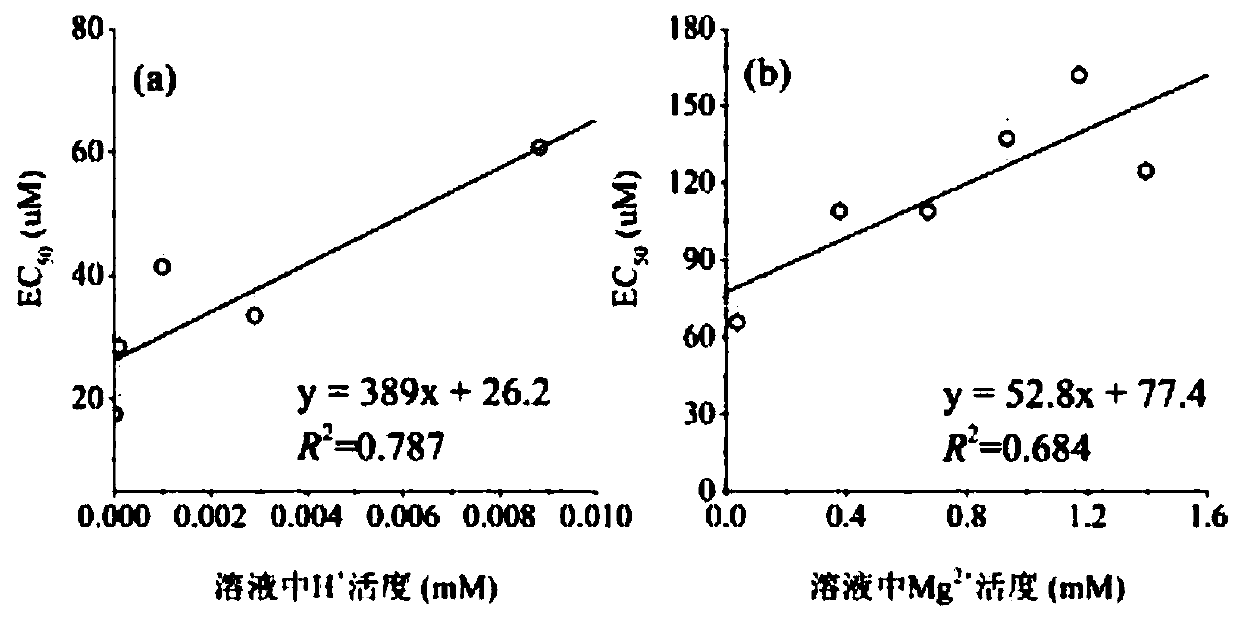
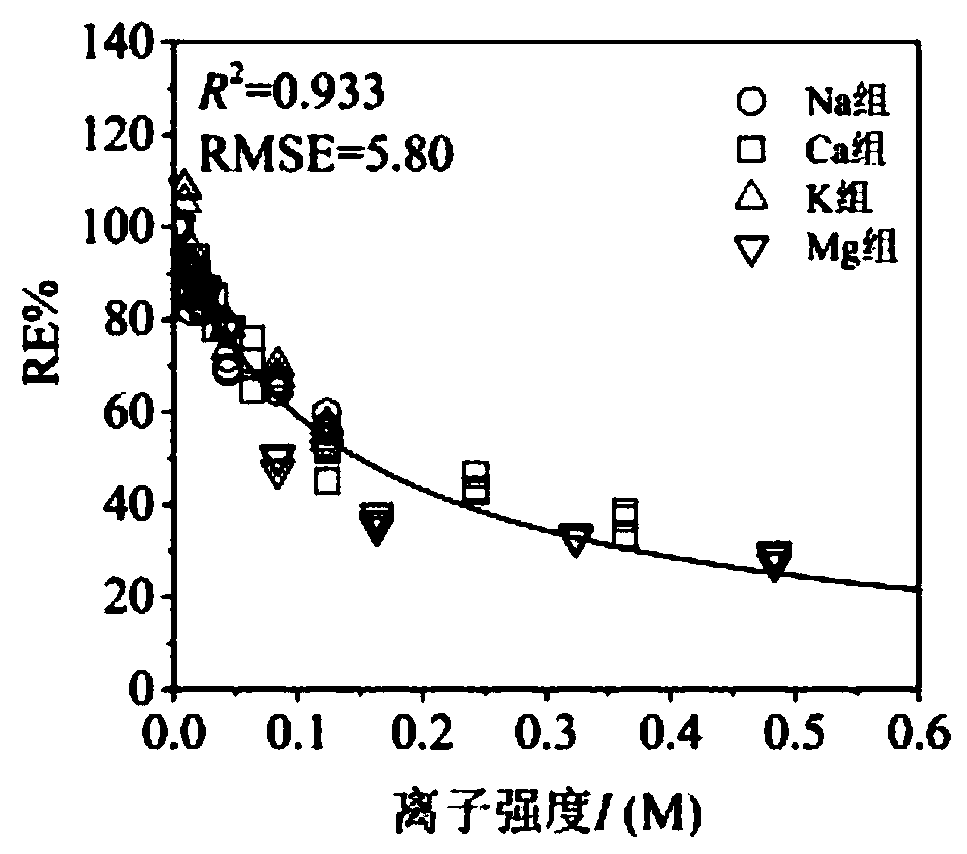
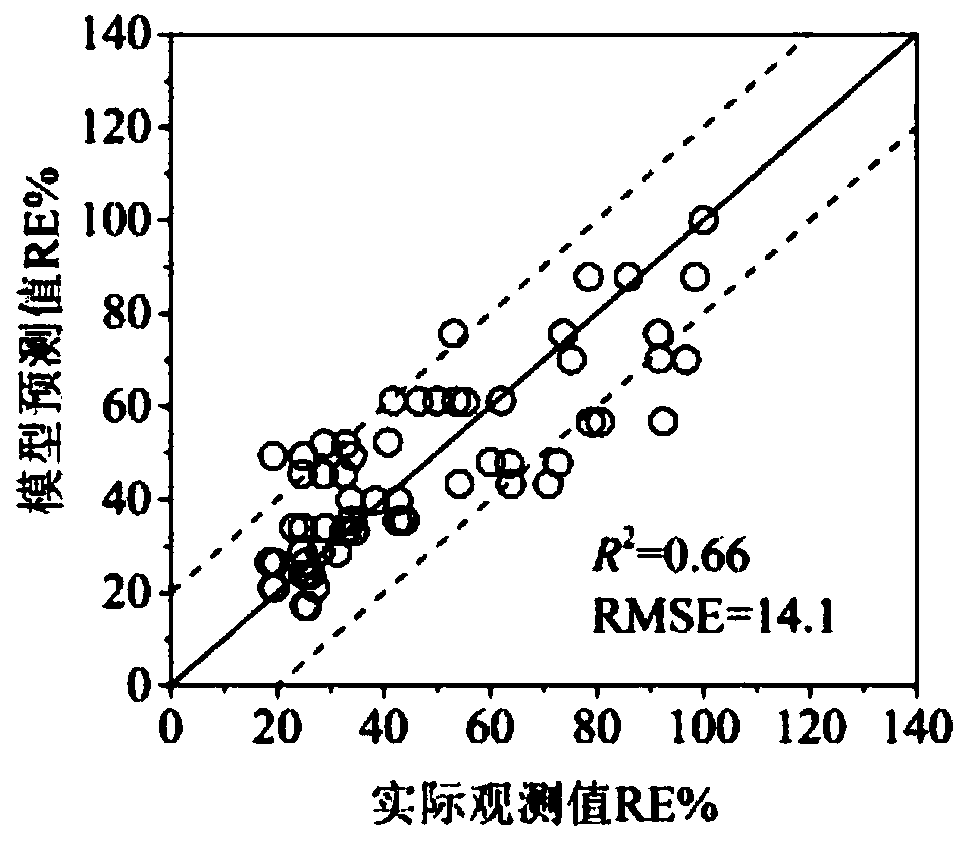
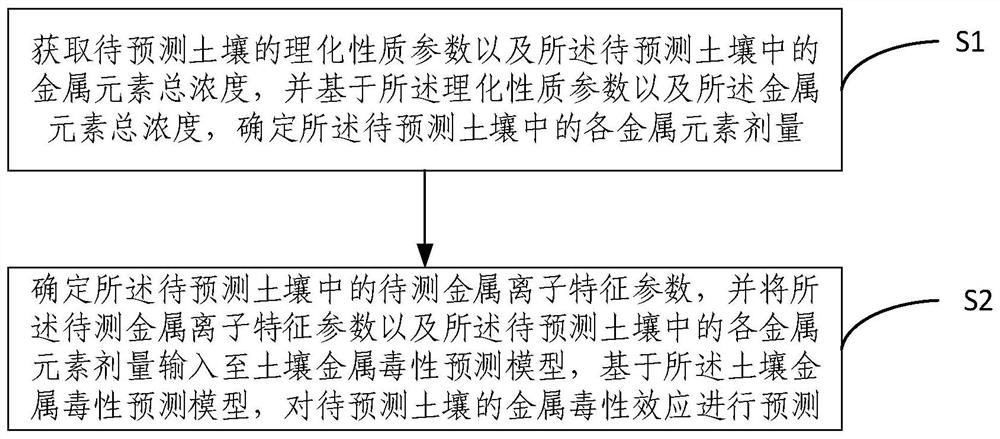
Soil metal toxicity prediction method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112750508AAccurate predictionChemical property predictionChemical machine learningSoil scienceEcological toxicology
The invention provides a soil metal toxicity prediction method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of: firstly determining the dosage of each metal element in to-be-predicted soil according to the obtained physicochemical property parameters of the to-be-predicted soil and the total concentration of the metal elements; and then determining characteristic parameters of to-be-detected metal ions in the to-be-predicted soil, and predicting the metal toxicity effect of the to-be-predicted soil through a soil metal toxicity prediction model. Due to the adoption of the soil metal toxicity prediction model, the metal toxicity effects under different soil environment conditions can be accurately predicted while geometric number-level ecological toxicology tests are avoided. Meanwhile, due to the fact that establishment of the ecological risk and the restoration standard of the metal elements is relatively slow, the soil metal toxicity prediction model can predict unknown metal toxicity data, is suitable for soil environment conditions with a wide range, provides a basis for metal ecological risk evaluation and corresponding standard formulation, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Vulcanization-promoted comprehensive protective material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a vulcanization-promoted comprehensive protective material and a preparation method thereof. The protective material is composed of an anti-aging agent RD, an anti-aging agent4020, an anti-aging agent 4030 and zinc terephthalate according to a weight part ratio of (25-30):(20-25):(20-25):(20-35). The preparation method of the protective material comprises the following steps: (1) adding an anti-aging agent RD, an anti-aging agent 4020, an anti-aging agent 4030 and an emulsifier into acetone, and stirring to obtain an emulsion system A; (2) dispersing zinc terephthalateand an emulsifier into acetone to obtain an emulsion system B; and (3) mixing the system A and the system B in a homogenizer, distilling to recover acetone, cooling the remaining substances, and granulating to obtain the target product. The protective material disclosed by the invention has excellent protective effects of thermal oxidation resistance, ozone resistance in dynamic and static states, metal toxicity resistance and the like, and can promote rubber vulcanization process.
Owner:常州市五洲化工有限公司
Broad-spectrum soil heavy metal passivation microbial inoculum as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114410527AReach the effect of passivating heavy metalsImprove toleranceAgriculture tools and machinesBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganismSoil science
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method and application of iron carbide/manganese cross-linked sodium alginate composite material
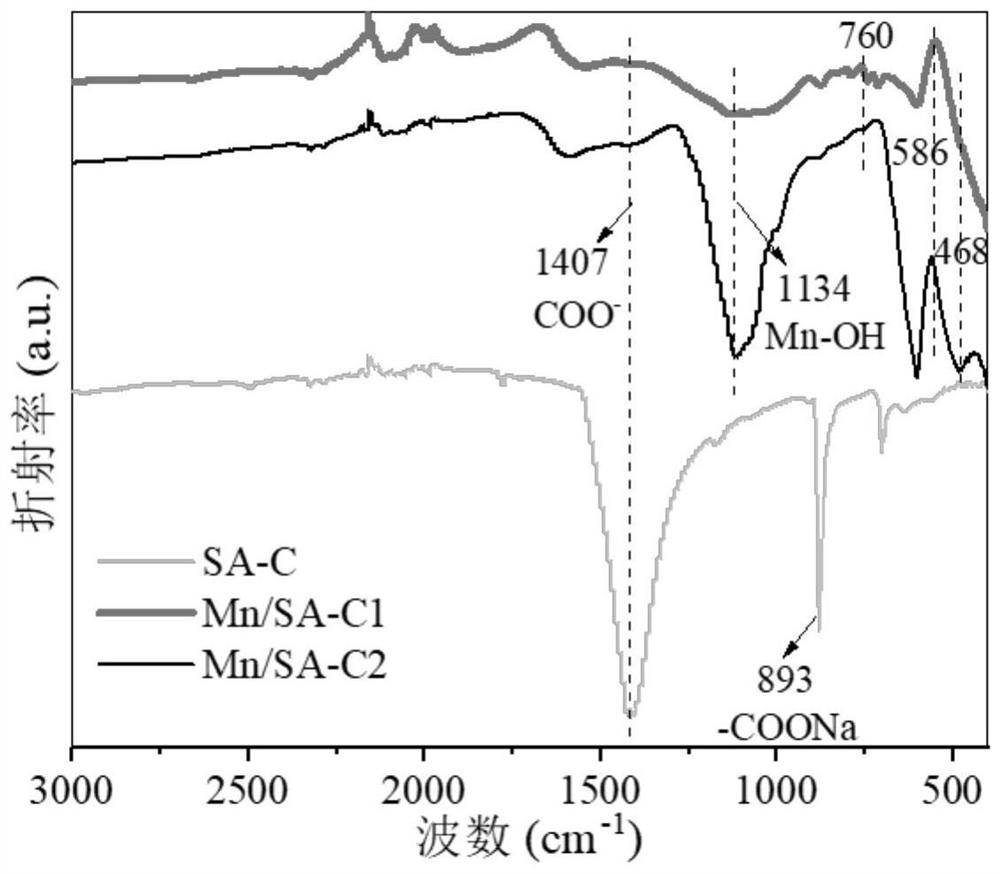
ActiveCN113398883ALarge specific surface areaHigh porosityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsManganeseCarbide
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an iron carbide / manganese cross-linked sodium alginate composite material, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: s1, dropwise adding an iron (II) salt solution and / or a manganese (II) salt solution into a 2wt% sodium alginate aqueous solution, generating iron / manganese cross-linked sodium alginate through a cross-linking reaction, washing, collecting microspherical particles, and drying; and s2, sintering and carbonizing the dried sodium alginate in the step s1 at 300-900 DEG C under protective gas for 1-4 hours, washing, drying, grinding and sieving to obtain the iron carbide / manganese cross-linked sodium alginate composite material. The iron carbide / manganese cross-linked sodium alginate composite material disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously reducing and removing the toxicity of heavy metals, retaining phosphorus and adsorbing the heavy metals by photocatalytic reduction.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
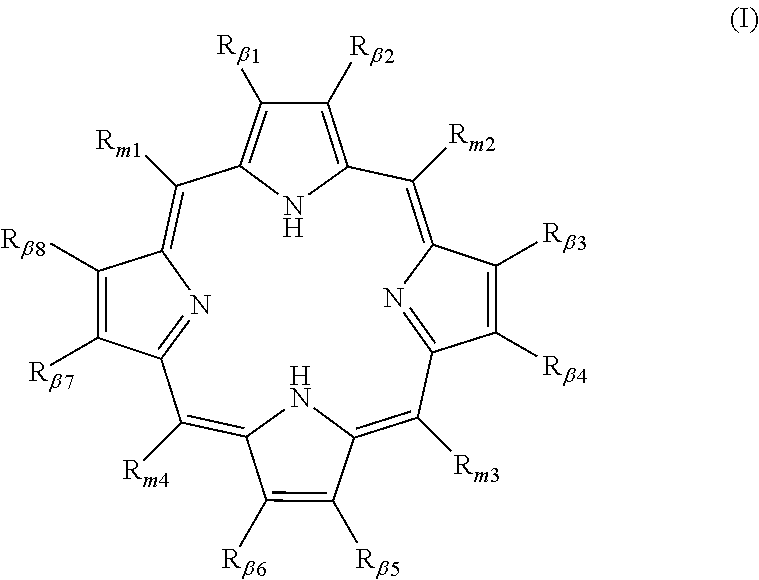
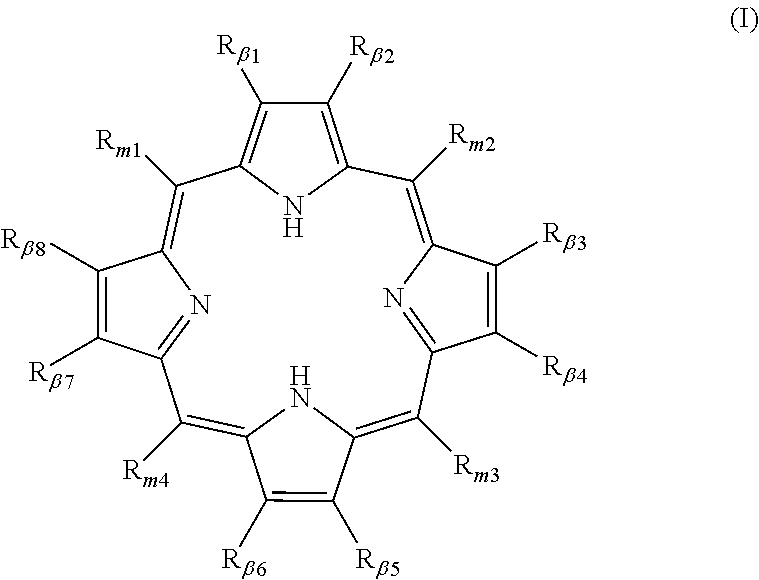
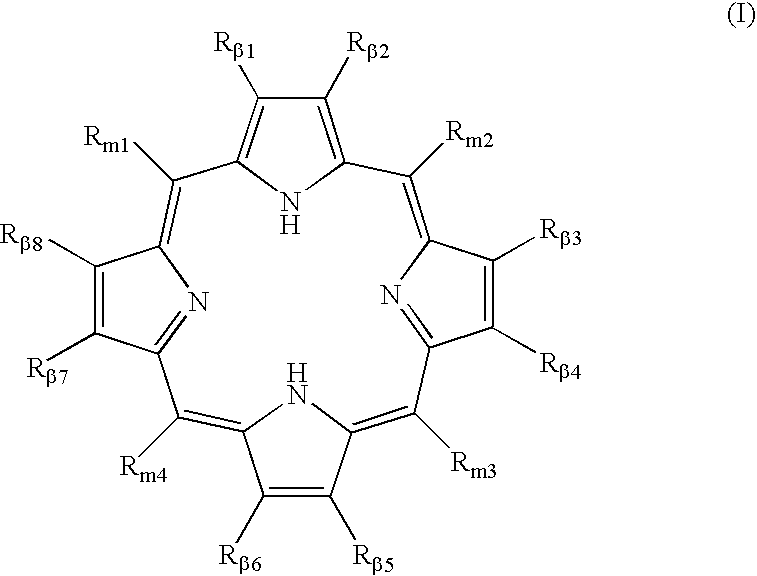
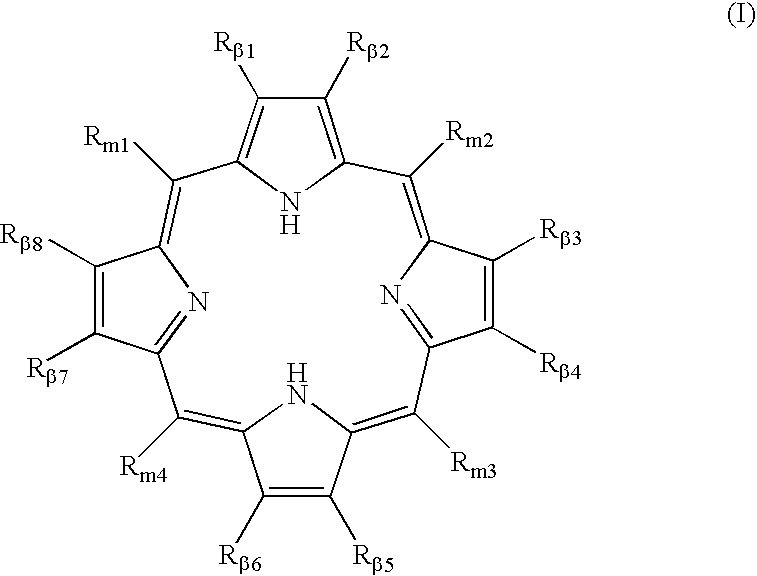
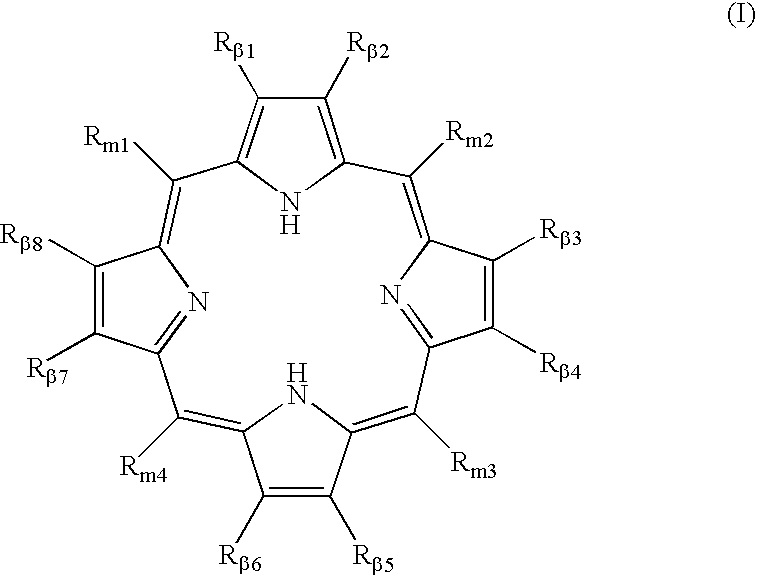
Polycarboxylated porphyrins and use thereof in treatment of metal toxicities
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Organic bacterial fertilizer for remediation of manganese ore polluted soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104496724BReduce heavy metal toxicityLow toxicitySuperphosphatesExcrement fertilisersCompound organicPlant roots
The invention discloses an organic bacterial fertilizer for the restoration of manganese ore-polluted soil, as well as a preparation method thereof. The organic bacterial fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 3-5 parts of basic nutrient solution, 20-25 parts of remissive complex organic raw materials, 70-75 parts of water retention media and 3-5 parts of anti-manganese complex microbial agent. The preparation method comprises the mixing and fermentation steps. The organic bacterial fertilizer for the restoration of manganese ore-polluted soil has the effects that the soil structure is modified, the water retention and constant temperature can be achieved, the toxicity of heavy metals around roots can be reduced, the survival rate of plants can be increased, and the growth of plants can be promoted; in addition, the toxicity of manganese elements in the soil of plant roots can also be effectively relieved, the effect of the organic fertilizer can be enhanced, and the restoration capability of plants can be enhanced.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Protective metallothionein analog compounds, their compositions and use thereof in the treatment of pathogenic diseases
InactiveUS20170079943A1Reduce in quantityEffective activityPeptide/protein ingredientsSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsAntioxidantMedicine
Embodiments of the present invention relate generally the use of certain compositions, e.g., compositions comprising a glutathione precursor and a selenium source, in the therapy of viral diseases and / or reducing the incidence of viral diseases. Related embodiments of the present invention relate to treatment and / or reducing the incidence of respiratory ailments caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or hemorrhagic fever (EHF) caused by Ebola viruses (EBV) or Marburg virus. Yet in other embodiments, the invention relates to reducing metal toxicity in a biological system, which involves contacting the biological system with a composition comprising a glutathione precursor and a selenium source, optionally together with a chelating agent, an antioxidant, a metallothioneine protein or a fragment of metallothioneine.
Owner:CRUM ALBERT
Polycarboxylated porphyrins and use thereof in treatment of metal toxicities
Metal binding polycarboxylated porphyrins, their precursors, or cofactors in the porphyrin biosynthetic pathway, are administered to individuals determined to be subject to or predisposed to a polycarboxylated porphyrin-binding metal toxicity to increase the level of the metal-binding polycarboxylated porphyrin in the individual.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Protective metallothionein analog compounds, their compositions and use thereof in the treatment of pathogenic diseases
PendingUS20170231938A1Reduce in quantityEffective activityPeptide/protein ingredientsSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsAntioxidantMedicine
Embodiments of the present invention relate generally the use of certain compositions, e.g., compositions comprising a glutathione precursor and a selenium source, in the therapy of viral diseases and / or reducing the incidence of viral diseases. Related embodiments of the present invention relate to treatment and / or reducing the incidence of respiratory ailments caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or hemorrhagic fever (EHF) caused by Ebola viruses (EBV) or Marburg virus. Yet in other embodiments, the invention relates to reducing metal toxicity in a biological system, which involves contacting the biological system with a composition comprising a glutathione precursor and a selenium source, optionally together with a chelating agent, an antioxidant, a metallothioneine protein or a fragment of metallothioneine.
Owner:THE PROIMMUNE
Freshwater Chronic Benchmark Prediction Method Based on Metal Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship
InactiveCN104915563BHigh precisionImprove predictive performanceGeneral water supply conservationForecastingVirulent characteristicsFresh water organism
The invention relates to the field of water quality pollution evaluation, in particular to a fresh water chronic standard prediction method based on the metal quantitative structure-activity relation. The method includes the steps of predicting the unknown metal virulence terminal point according to the quantitative relation between the structure characteristics of heavy metal ions and the choric toxicity effect of aquatic organisms, and conducting analysis and derivation to obtain the danger concentration that protects aquatic organisms of different ratios through the combination with the sensitiveness distribution of different species. According to the method, the QSAR metal toxicity prediction model is established by synthesizing heavy metal physicochemical structure parameters and toxication mechanisms of different aquatic organisms, and the model is used for predicting the unknown standard continuous concentration. On the basis of the ecology principle, six phyla and eight families of aquatic organisms are screened through a system to serve as a minimum biological prediction set, single-parameter toxicity prediction models are established, and the model accuracy and the prediction capacity are improved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Pharmaceutical composition for stroke treatment based on ampk inhibition
InactiveUS20190167647A1Inhibiting AMPK activityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderStroke treatmentMedicine
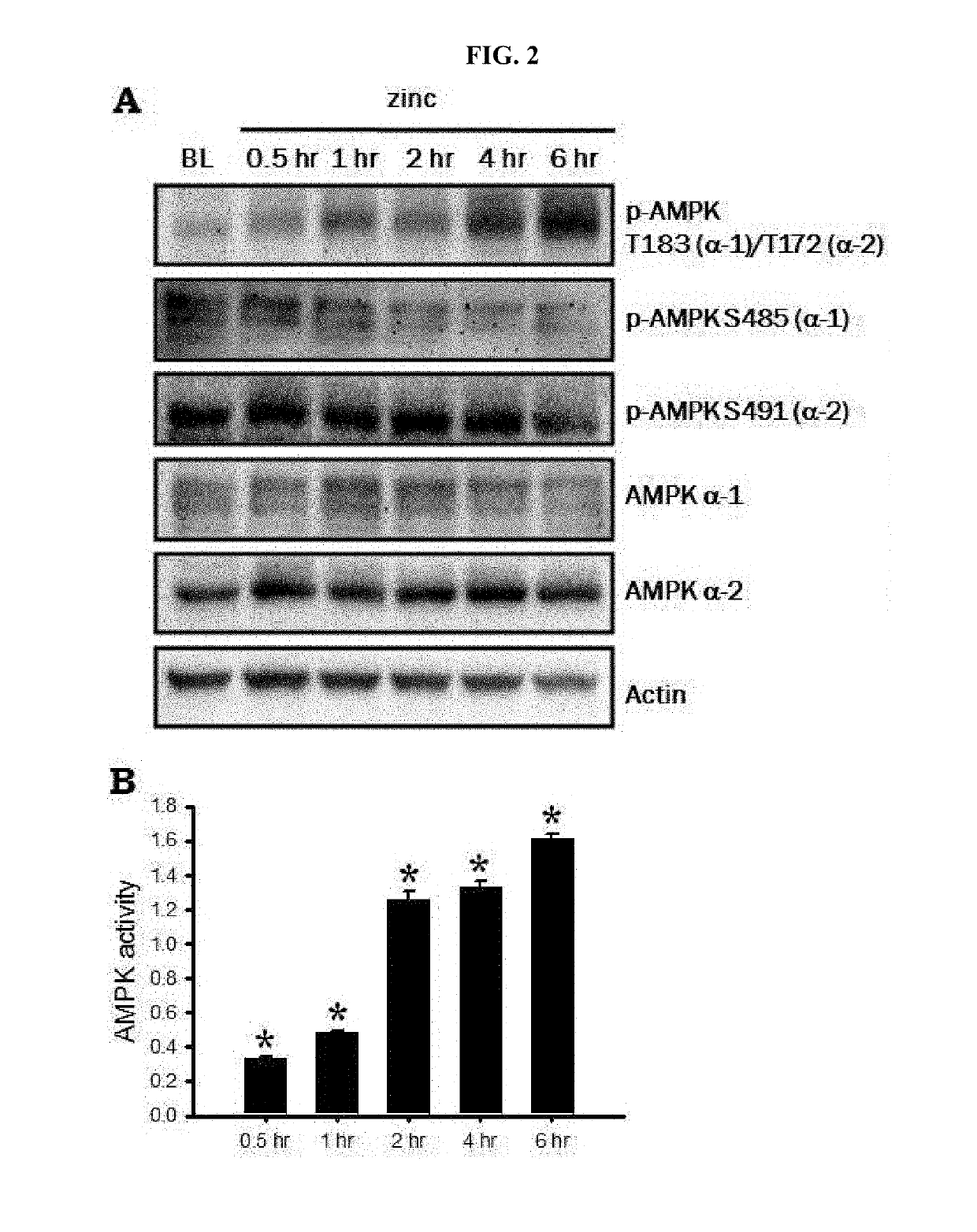
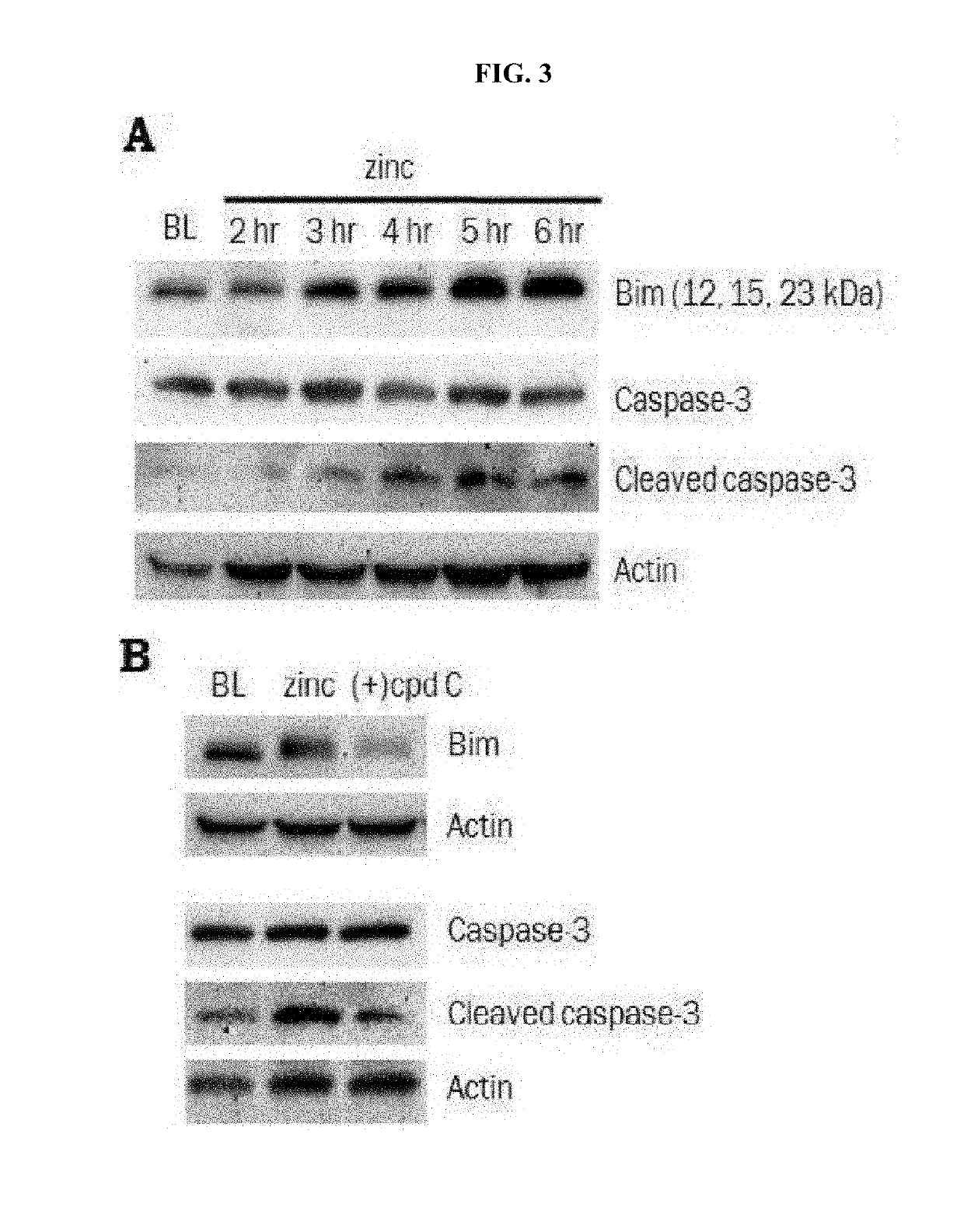
A method for treating stroke in a subject includes administering to the subject a composition that includes a compound having a structure represented by Formula 1 as an active ingredient. The composition may treat a stroke by inhibiting 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity of zinc neurotoxicity which is a main cause of strokes. The stroke may include hemorrhagic stroke, ischemic stroke or metal toxicity stroke.
Owner:ZINCURE CORP
A modification method of biochar and its application in soil remediation
InactiveCN110003912BModification process is simpleCd repair effect is remarkableContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersMeth-Polyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for modifying biochar, comprising: 1) pyrolyzing wheat straw and fresh whole cattail plants into biochar with limited oxygen and pulverizing them; 2) first soaking the prepared biochar in hydrogen peroxide, and then Soak in an aqueous solution of maleic acid and polyethylene glycol, cool and filter to obtain solid phase A; 3) disperse solid phase A in ethanol to form a suspension, add 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethylpiperidine-nitrogen-oxide, methacrylic acid to obtain solid phase B; 4) solid phase B is soaked in an aqueous solution of acetic acid, and potassium periodate is added to the solution to obtain solid phase C; 5) The solid phase C was soaked in the mixture of dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone to obtain the modified biochar. The invention optimizes the modification process of biochar, adopts wheat straw and cattail as composite biochar, and optimizes the modification on the basis of the composite biochar, so that the Cd repair effect of biochar is very significant, and after being applied to cadmium-contaminated soil , significantly reducing the toxicity of heavy metals in the soil.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
High-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103045951BImprove toughness and plasticityMeet the process requirementsChromium nickelNiobium
The invention discloses high-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) and a manufacturing method thereof. The stainless steel comprises carbon, silicon, manganese, chromium, molybdenum, copper, nitrogen, niobium, silver and the balance of iron by weight percent; the high-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) is of a single austenite structure after subjected to solution treatment, and is excellent in pitting corrosion resistance in a non-microorganism environment and good in bacterial resistance and microorganism corrosion resistance in a microorganism environment; the antibacterial rate of the stainless steel on staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli reaches more than 93%; the nickel release risk is inexistent; the manganese release rate in artificial saliva and sweat is much lower than the acceptable daily intake standard; the stainless steel can be used as a biomedical material; and the metal toxicity risk is inexistent. The high-nitrogen nickel-free austenite antibacterial stainless steel (HNSAg) is very good in flexibility and plasticity, can meet the processing requirements of fine parts such as jewelries and the like, and is superior to chromium-nickel austenite antibacterial stainless steel of 316 L and the like in overall performance.
Owner:郭强
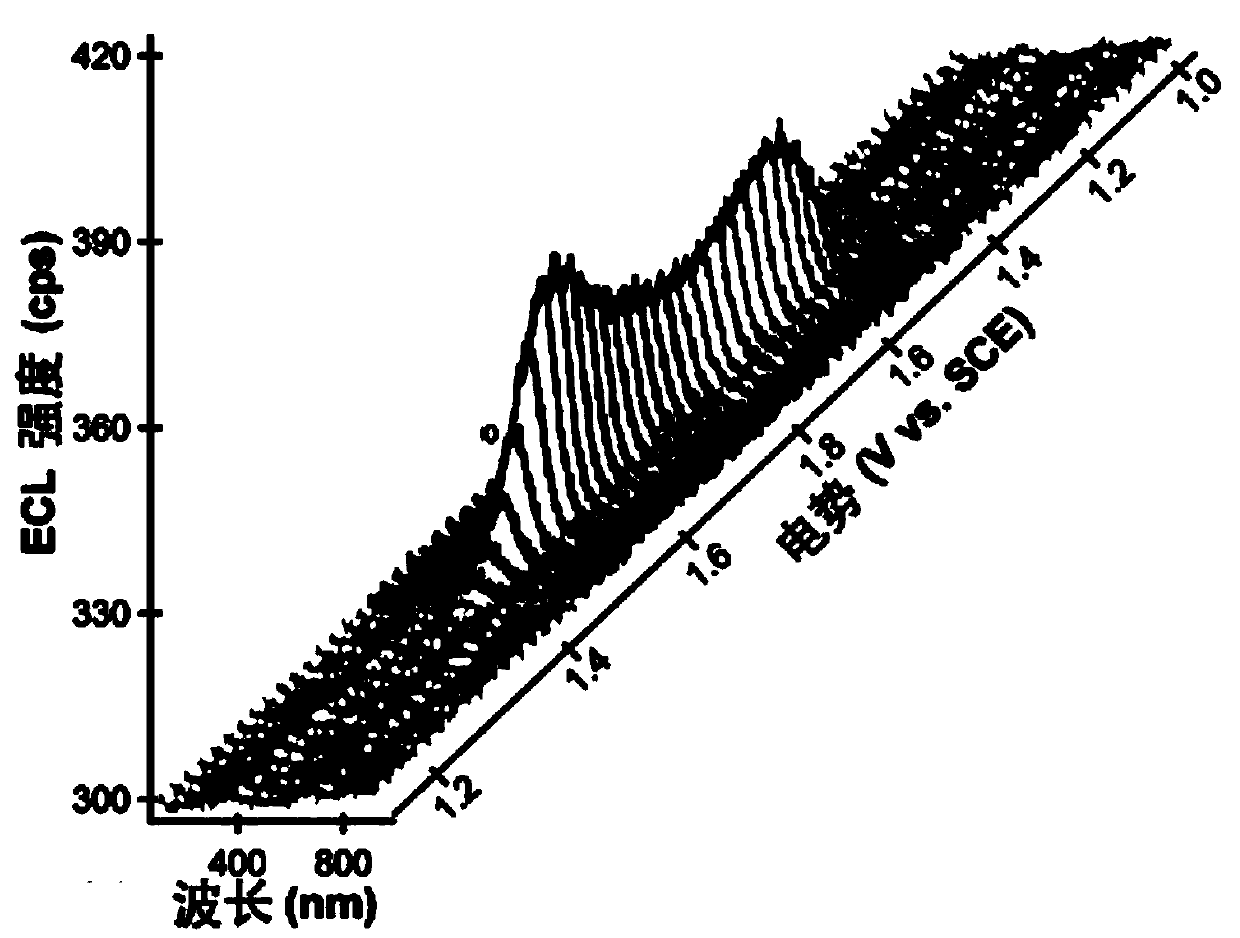
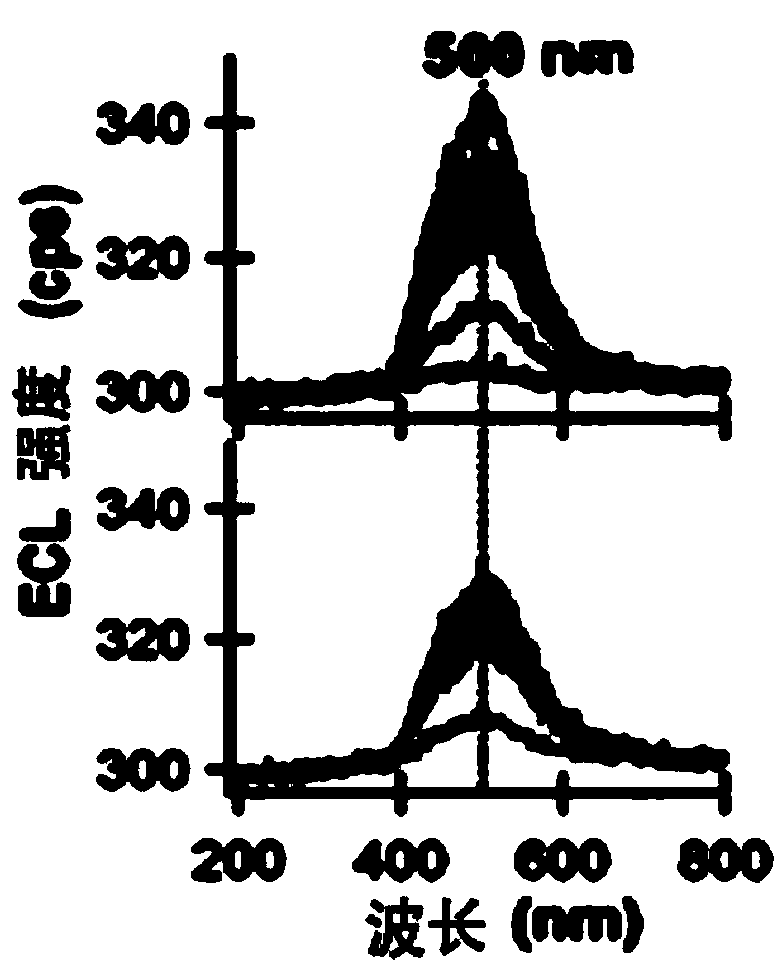
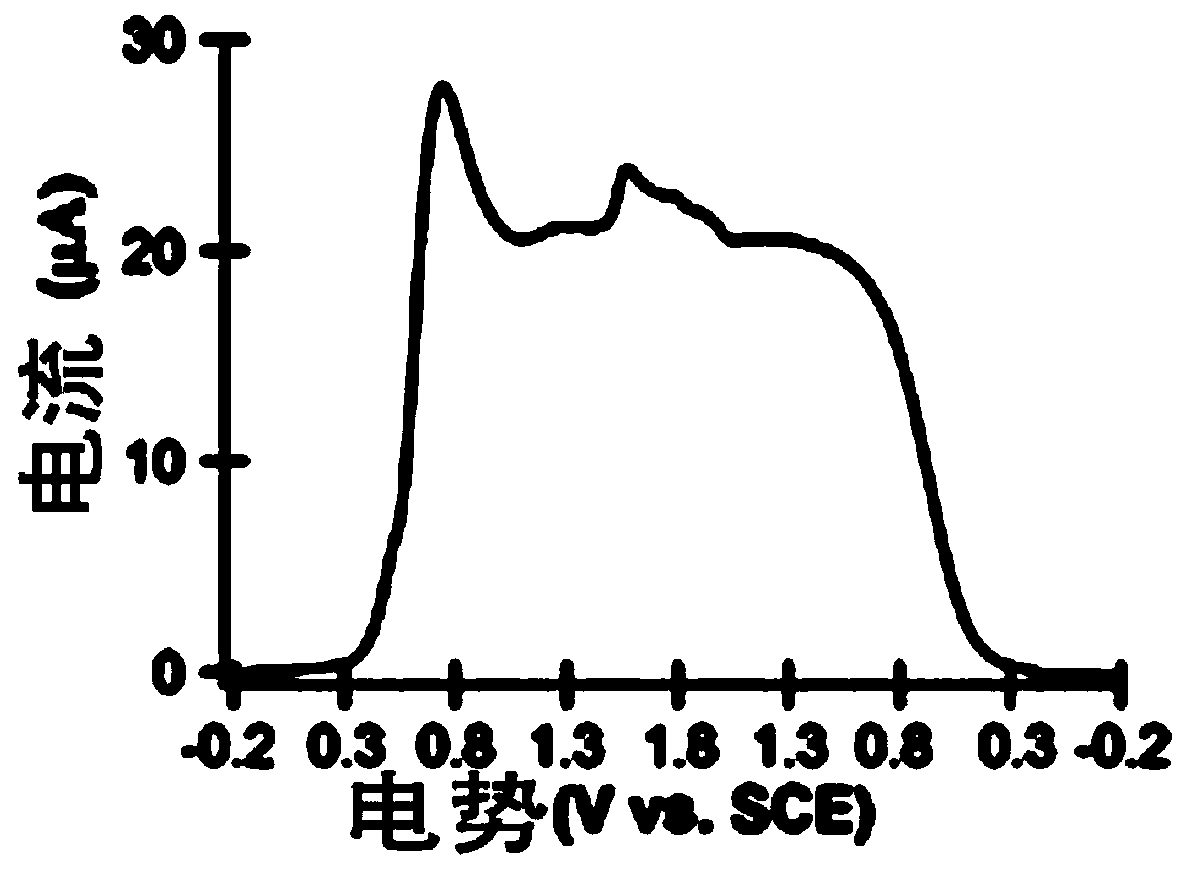
Application of a compound as an electrochemiluminescent material
ActiveCN108864085BLower synthesis costImprove luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistryAnalysis by electrical excitationEngineeringElectrochemiluminescence
The invention provides an application of a compound as an ECL material. The compound does not contain metal, has low toxicity, good biocompatibility, low cost, an environmentally friendly synthesis method and good luminous efficiency as an ECL. In the application of the compound as an ECL material, the compound has a specific structural formula that does not contain metal. Specifically, the compound is used as an ECL material, together with a co-reactant, a double electrode and a supporting electrolyte to construct an electrochemiluminescent device. The compound of the present invention can realize the construction of ECL material without metal, which greatly reduces the synthesis cost and has good biocompatibility; the compound of the present invention has good luminous efficiency as an ECL material; the compound of the present invention synthesizes The method and process are simple, water is used as the main synthesis environment in the synthesis process, and the process is green to realize environmental friendliness.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
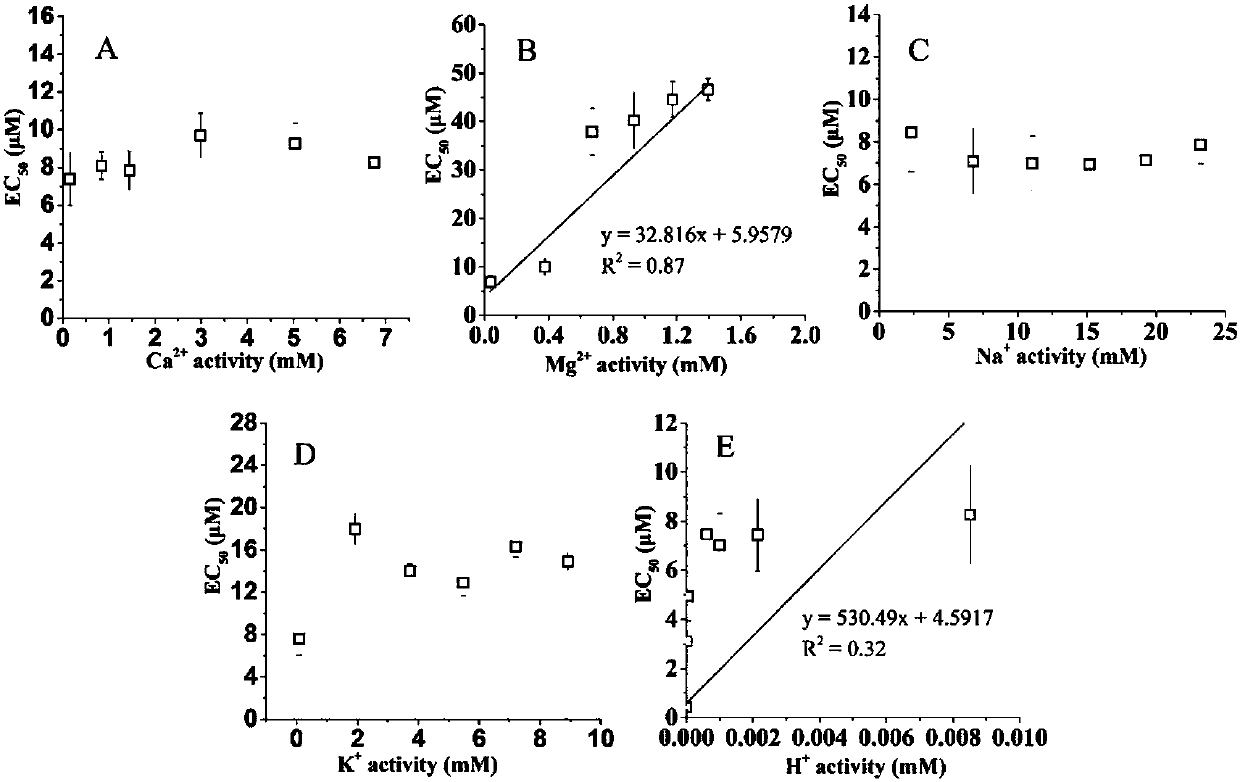
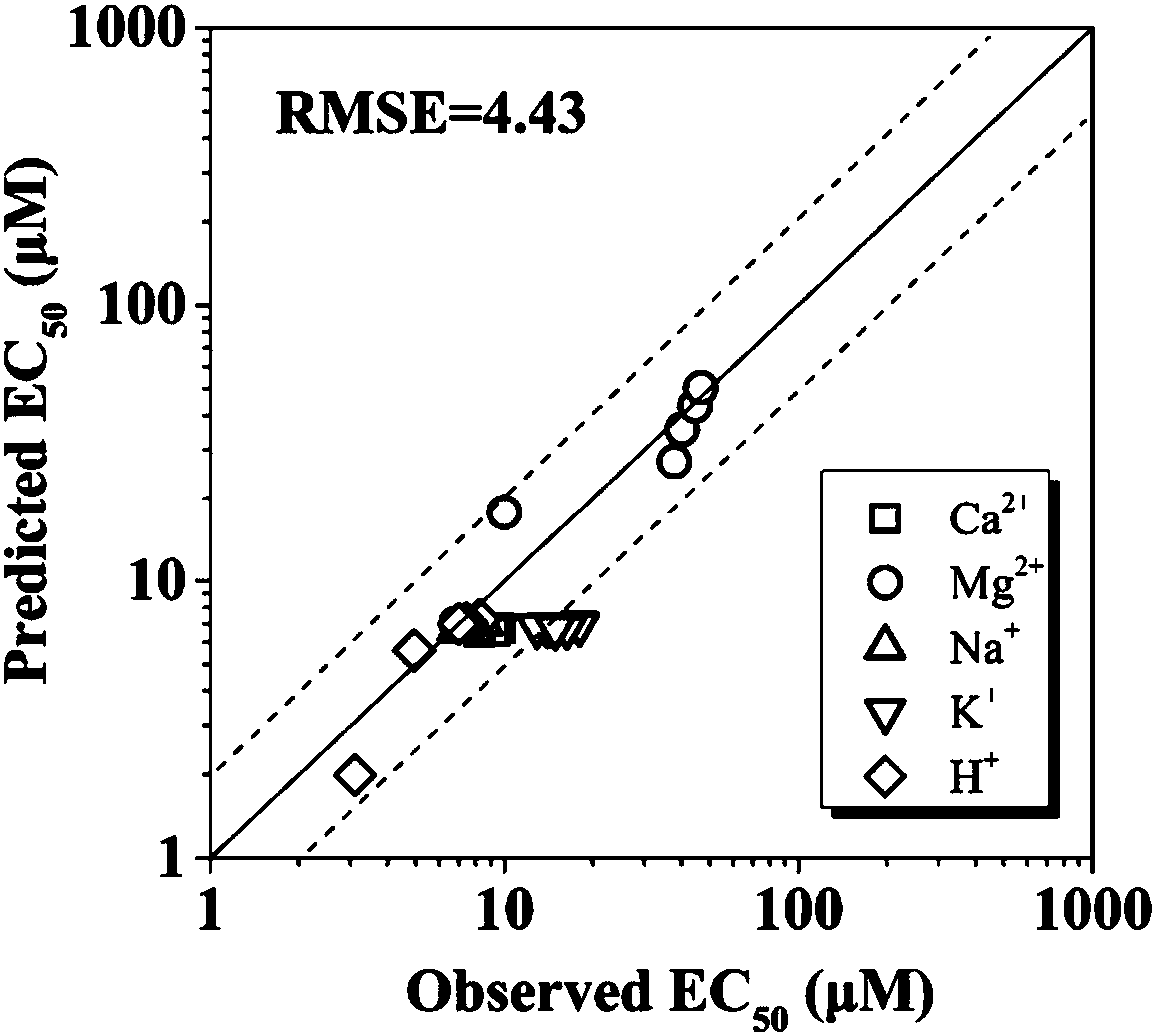
A determination method and application of nickel ion toxicity to wheat root elongation under hydroponic conditions
ActiveCN106018777BSolve the unpredictableGood predictionBiological testingTesting plants/treesSoil contaminationSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a determination method for wheat root elongation toxicity of nickel ions under a hydroponic condition and application and belongs to the field of ecological heavy metal toxicity assessment. A control variable method is adopted, concentration of positive ions is controlled and changed separately, the inhibiting effects of five types of positive ions including K<+>, Na<+>, Ca<2+>, Mg<2+> and H<+> on nickel ion toxicity are calculated out step by step, meanwhile a MINTEQ program is utilized to calculate the amount of Ni<2+> and the amount of NiHCO3<+> under all conditions so as to calculate the toxic effects of two nickel forms, biological toxicity inhibition parameters of all the positive ions on Ni and toxic effect parameters of the two Ni forms are determined, the method for determining wheat root toxicity of Ni<2+> is established under the hydroponic condition, an obtained result can be used for prediction of wheat root toxicity of the Ni<2+> under the hydroponic condition, and a reference is made to soil heavy metal ecological risk assessment and soil contamination treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com