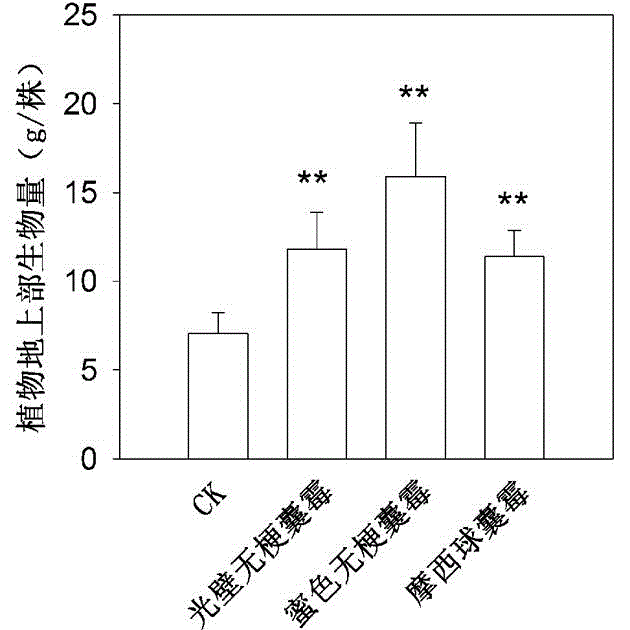
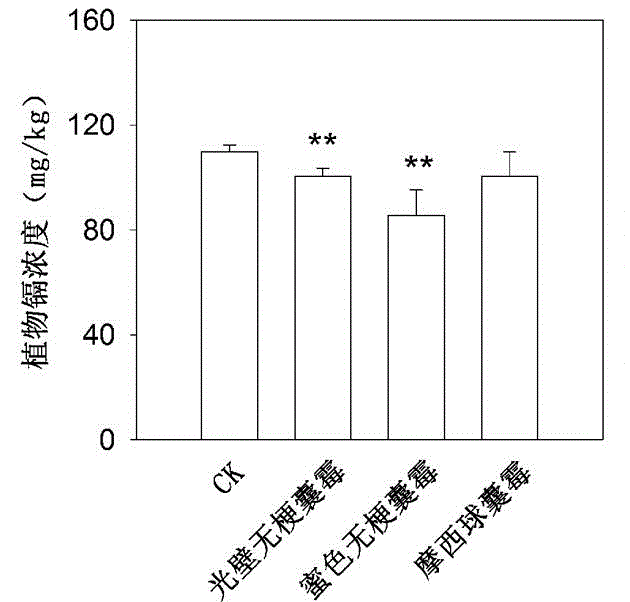
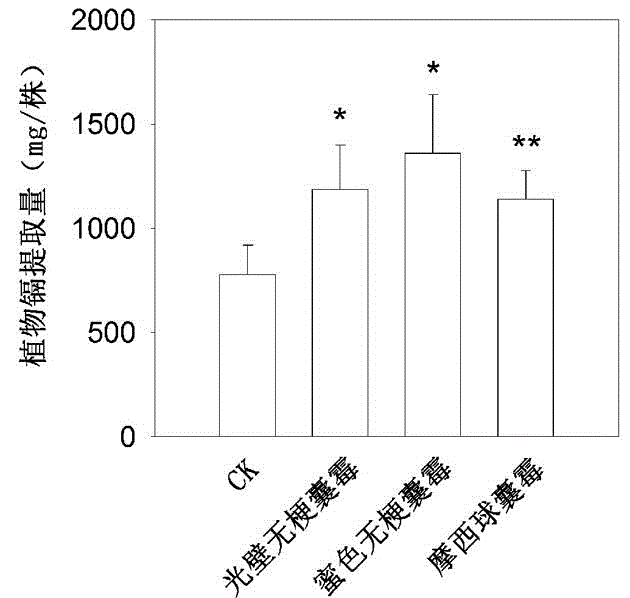
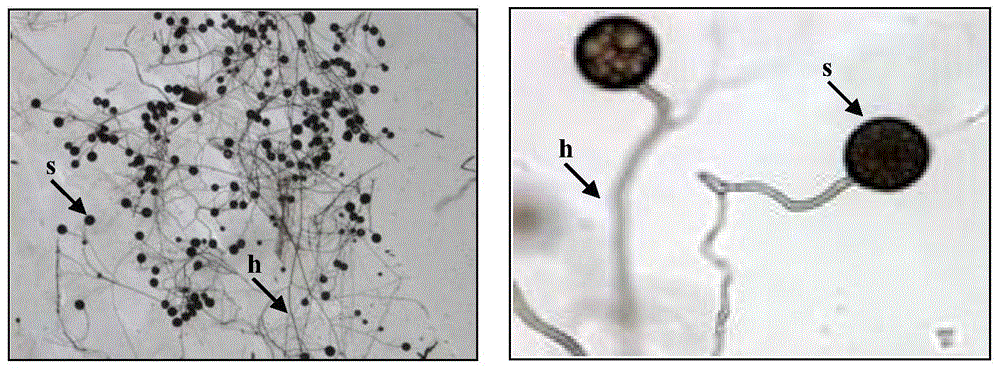
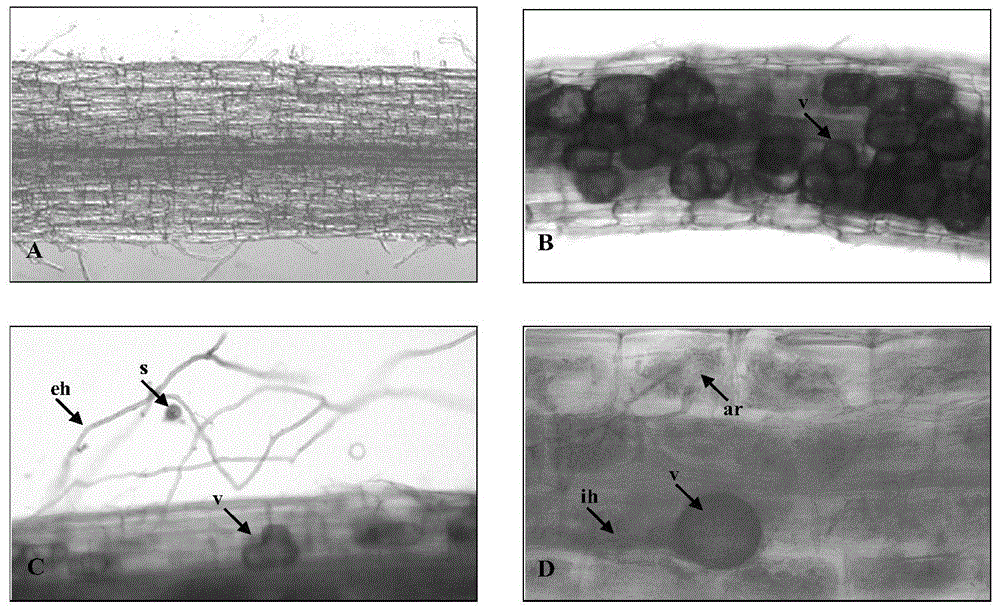
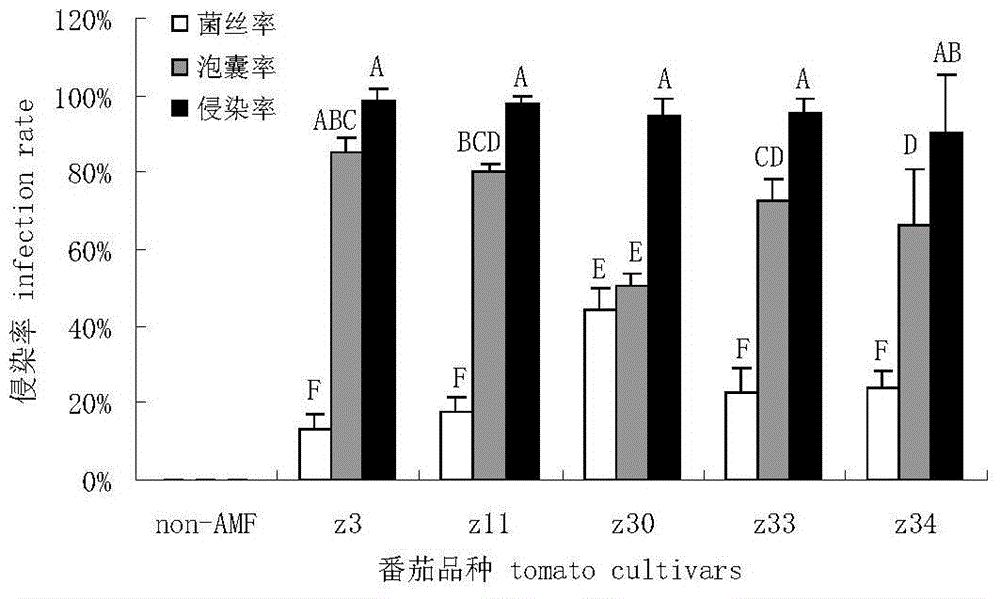
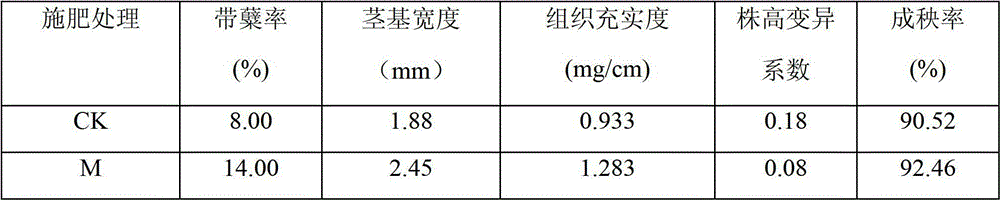
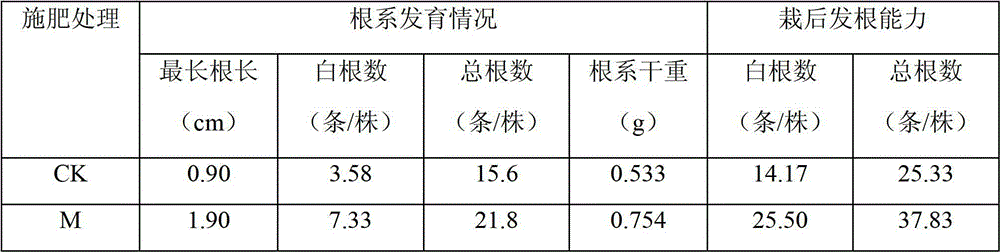
Patents
Literature
302 results about "Arbuscular mycorrhiza" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (plural mycorrhizas, a.k.a. endomycorrhiza) is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (AM fungi, or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.)
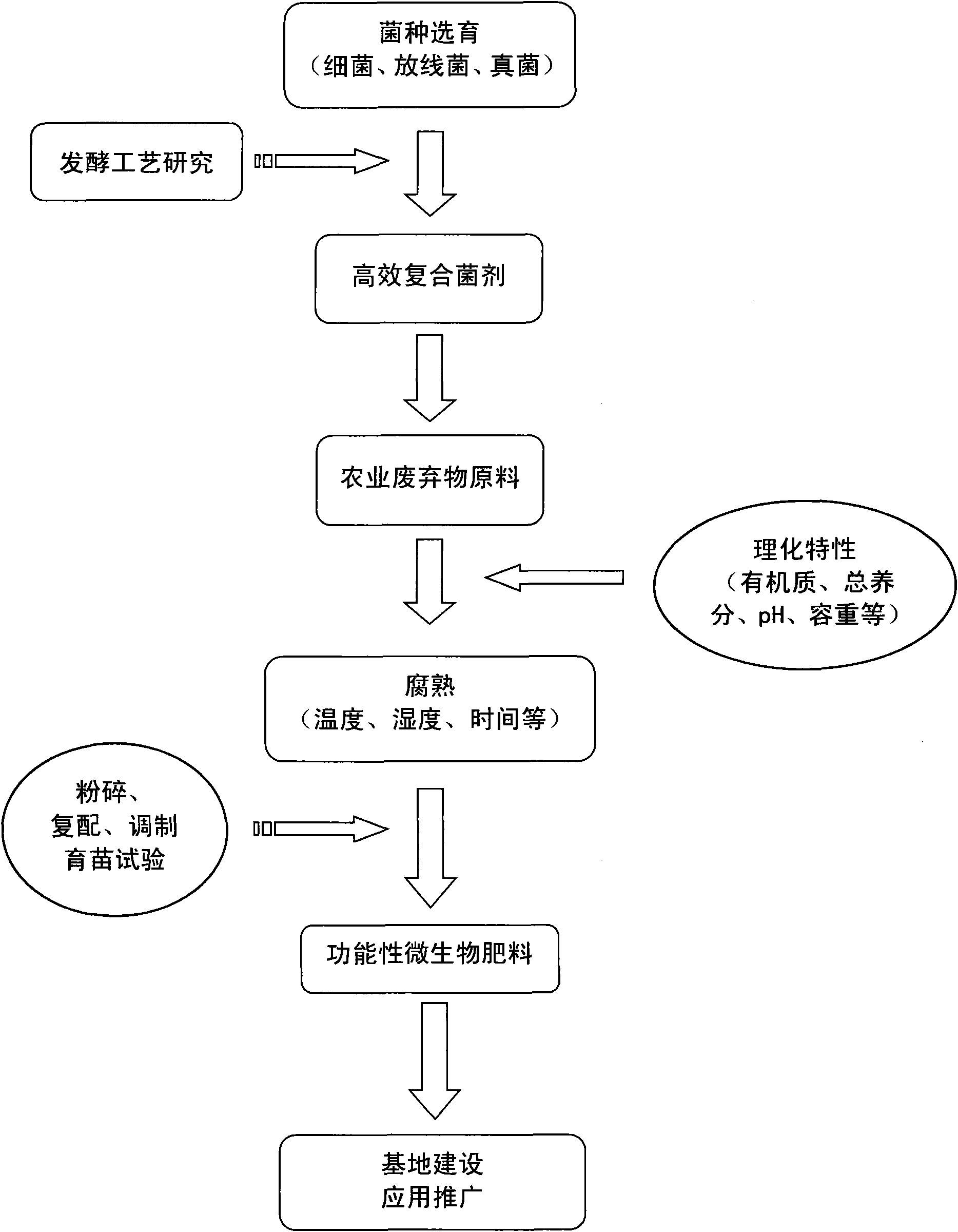
Functional microbial fertilizer production by utilizing agricultural wastes
InactiveCN101665374ASuitable physical and chemical propertiesPromote fermentation and maturityFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisBiotechnology
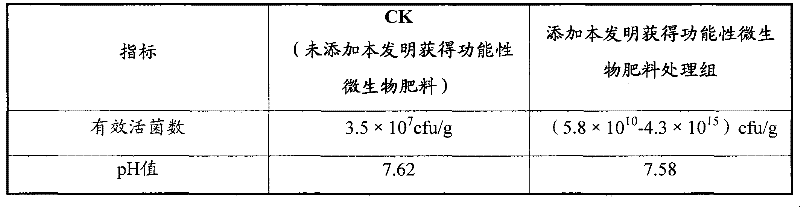
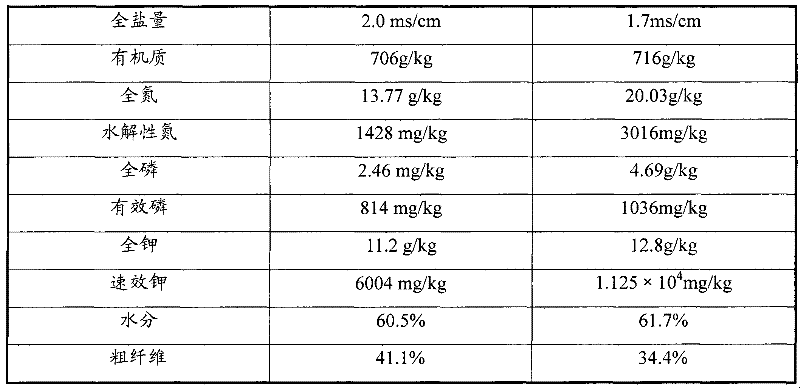
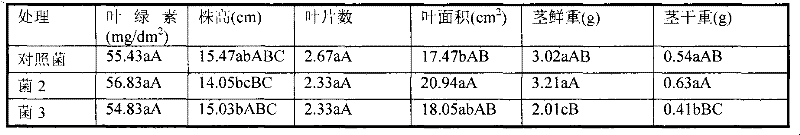
The invention discloses a functional microbial fertilizer and a production method thereof. The production method comprises the following steps: grinding 60%-70% of mushroom residue and 15%-25% of livestock manure to 2-3mm to obtain the major material by a grinder, regulating water content to be 60%-65%; adding composite fermenting agent consisting of bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, trichoderma harzianum and trichoderma viride in accordance with 50g-100g / T; stacking, fermenting and maturing for 15-30d, and turning 5-10 times during the process; evenly mixing the major material prepared from fermentation with auxiliary materials consisting of 6%-10% humic acid and 6%-10% rice hull; adding arbuscular mycorrhiza agent in accordance with 50g-100g / T; and sieving with a 3mm sieve to obtain the fertilizer. The invention provides an economic and effective technological approach for the resource recycling of agricultural wastes in China, and has important application prospect on promoting the development of green agriculture, controlling and reducing rural environmental pollution, improving rural eco-environment and other aspects.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microbial fertilizer producing by using agricultural wastes and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102515900AEasy to eliminateLight weightBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a microbial fertilizer producing by using agricultural wastes and preparation thereof. Main materials are obtained by mixing and smashing 20%-40% oil sally bean dregs, 40%-60% crop straw and 15%-25% poultry excrement, moisture content achieves 60-65%, composite leaven is added according to 150g-200g / T to pile to be cone-shaped, yellow mud is used on the outside for sealing, a plastic film is used for covering in a sealing mode, after stacking, fermentation and digesting, and the composite leaven is composed of bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, trichoderma harzianum and trichoderma viride according to the mass ratio (W / W) of 1.5:1:1:2.5:4. Auxiliary materials made of 5%-10% mushroom dregs and 6%-10% rice husk ash are evenly mixed with fermented and prepared main materials, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent are added according to 600-1000g / T for compounding, and the microbial fertilizer is prepared after passing a 3mm sieve. Good production and efficiency improvement is obtained through application, and the microbial fertilizer has good application value.
Owner:斯华四
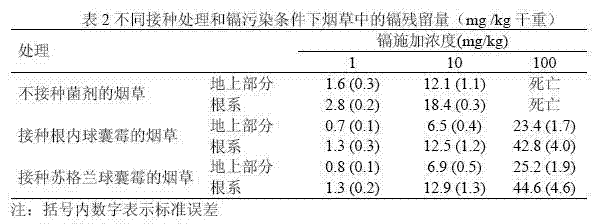
Method for reducing heavy metal residues in tobacco by use of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
InactiveCN102047808APromote growthResidue reductionFungiHorticultureBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention relates to a method for reducing heavy metal residues in tobacco by use of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The method comprises the following steps: (1) propagating preparation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; (2) culturing mycorrhizal tobacco seedlings; and (3) transplanting the obtained mycorrhizal tobacco seedlings in the field. Tests prove that the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiont of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and tobacco can improve phosphorus nutrition condition of tobacco, promote tobacco growth, reduce heavy metal absorption of tobacco, reduce the migration of heavy metal from the root system to the aboveground part of tobacco, thereby reducing the heavy metal residues in tobacco.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Continuous bioprocess for organic greenhouse agriculture
InactiveUS20150237807A1Avoid waterAvoid Fertilizer WasteSelf-acting watering devicesCultivating equipmentsMicrobial inoculationArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
A method of plant cultivation which comprises inoculating plants in a plant growing system comprising a container and an insert therefore, the microbial inoculant containing at least one species from the following group of microorganisms comprising arbuscular mycorrhizae associated bacteria, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, yeast microorganisms and substrate conditioning bacteria.
Owner:BIOPONIX TECH
Method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil
InactiveCN101947545AImprove nutritional statusPromote growthContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueBioremediation
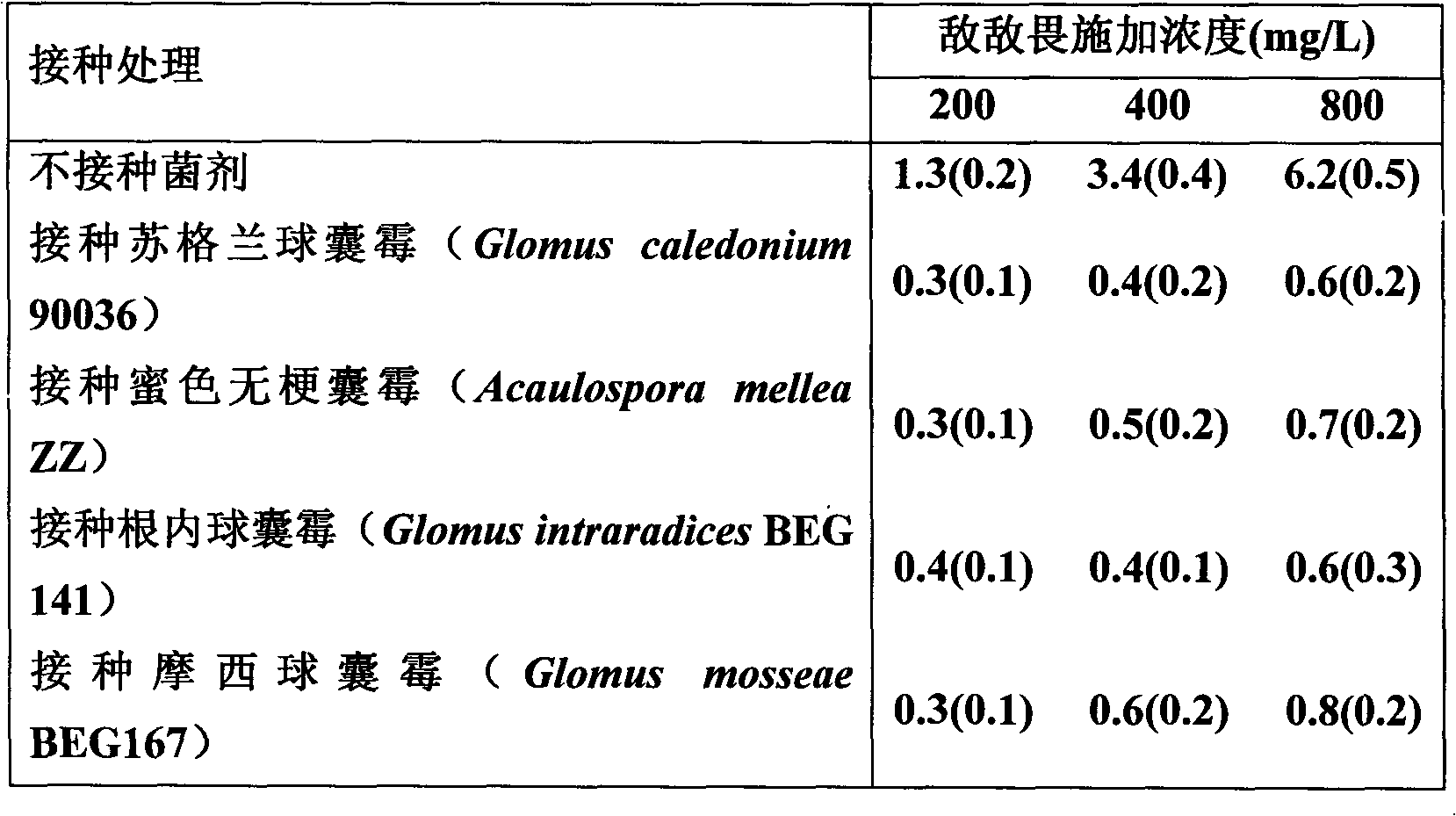
The invention discloses a method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant symbiotic system is used for accelerating the recovery of the organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent; (2) inoculating the fungi agent to the soil to be restored, and planting quick growth plants, or transplanting the plants after mycorrhizal seedling culture; and (3) managing the plants to grow 2 to 3 months. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent comprises Glomus caledonium 90036, Acaulospora mellea ZZ, Glomus mosseae BEG167 and Glomus intraradices BEG 141). The host plant is selected from quick growth plants such as Sudan grass, alfalfa, corn, broomcorn and the like. The method can reduce the pesticide residue in agricultural products, reduce environment transfer to water, atmosphere and the like and reduce harm to human health, and is simple, convenient and environment-friendly.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of enhancing cadmium absorption of black nightshade from soil by utilization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
InactiveCN103990647APromote growthPromote absorptionFungiContaminated soil reclamationArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPlant growth
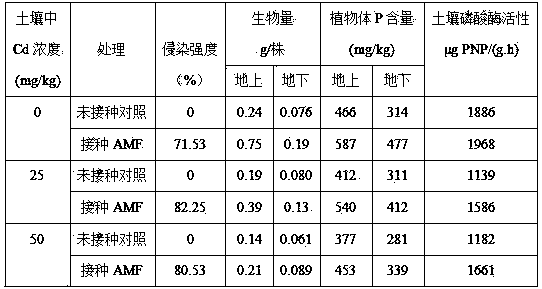
The invention provides an application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in enhancement of growth and capability of heavy metal absorption from soil of black nightshade and a method of enhancing cadmium absorption of black nightshade from soil by utilization of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. A cadmium (Cd) hyperaccumulating plant black nightshade is adopted as an experiment plant, the AMF is adopted as an Inoculant, the Cd hyperaccumulating plant black nightshade and the AMF capable of promoting plant growth are combined, and the AMF can enhance growth and capability of cadmium absorption from soil of the black nightshade, thus increasing the remediation efficiency of the black nightshade for Cd-contaminated soil. Compared with traditional chemical and agricultural measures, the method has characteristics of good treatment effects, no secondary pollution, low operation cost, and the like, and has good theoretical and application popularization value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for reducing vegetable phoxim residue by utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices
InactiveCN102057826AImprove nutritional statusPromote growthFungiHorticultureGlomus intraradicesGourd
The invention relates to a method for reducing vegetable phoxim residue by utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices. Arbuscular mycorrhiza homobium is formed by mainly utilizing glomus mosseae or glomus intraradices and a vegetable crop to reduce phoxim residue in a vegetable. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of: propagating the glomus mosseae or the glomus intraradices; using a glomus mosseae microbial inoculum or a glomus intraradices microbial inoculum on vegetables; and applying phoxim and managing the vegetable until the growth period of the vegetable crop is finished. The method of the invention is suitable for vegetable crops easy to form arbuscular mycorrhiza of a potato family, a lily family, a gourd family, a bean family, and the like. The method of the invention can reduce phoxim residue in soil and vegetables, prevent pesticide from being transferred to environments of water bodies, atmosphere, and the like and lessen harm to the health of human bodies and is simple, convenient and environment-friendly.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
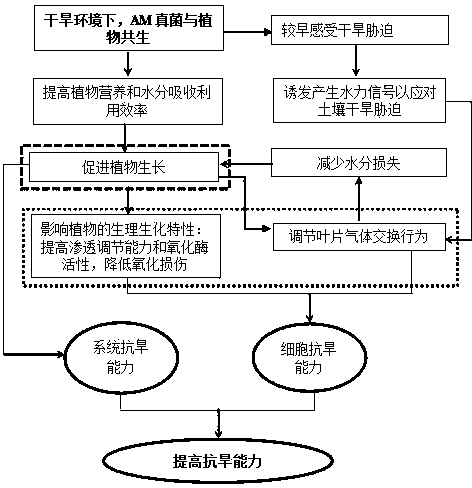
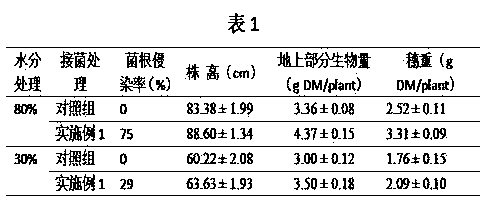
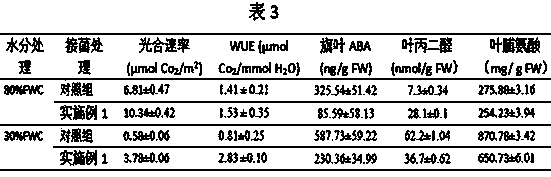
Method for inducing drought resistance of cucumber by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
InactiveCN103798052APromote absorptionMeet the needs of photosynthetic metabolismFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiNutrient solution
A method for inducing the drought resistance of cucumbers by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi comprises the following steps: carrying out individual inoculation and propagation expanding initial arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculants; cultivating cucumber seedlings through mycorrhization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculants, wherein inoculation media adopts a mixture of a Hoagland nutrient solution and perlite; inducing drought resistance: after the seedlings are grown for 3 months, transferring the seedlings in black seedling raising bags with the specification of 25 cm*25 cm, filling 3.0 kg of sterilization soil in each black seedling raising bag, applying 80 mg / kg of total phosphorus and 100 mg / kg of total nitrogen in each basin, and keeping the relative water content of the soil to be about 40% of the field capacity under moderate drought; sufficiently watering before processing to enable the seedlings to be in the natural drought, carrying out the water control processing when the natural drought reaches the preset relative water content in processing, using a weighing water supplementing method to keep the all repeated soil water content in each-time processing to be within the test required range during the water control period, setting the regulating time of the water content to be 8: 00 Am each day, and supplementing water lost on a previous day.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
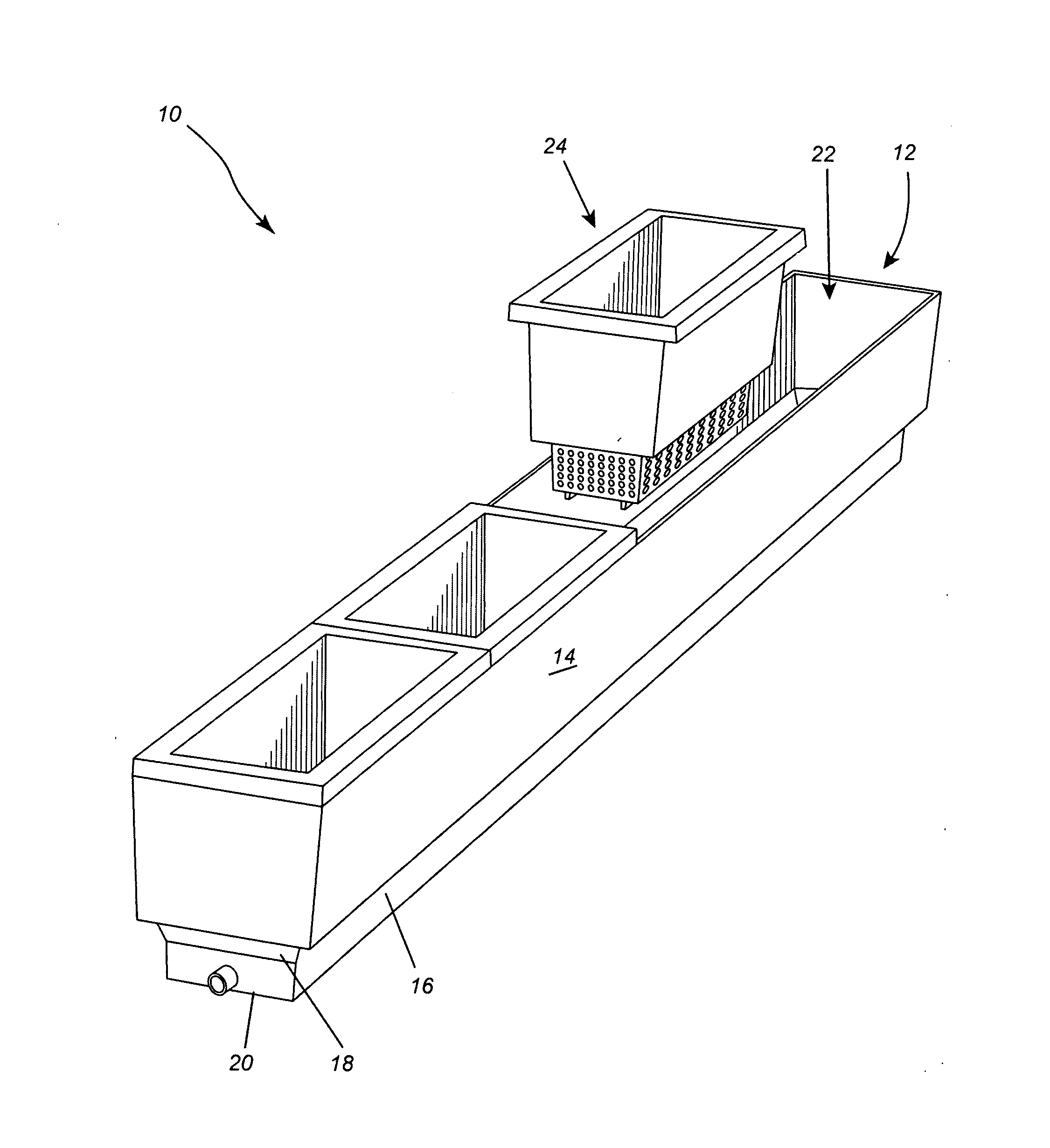
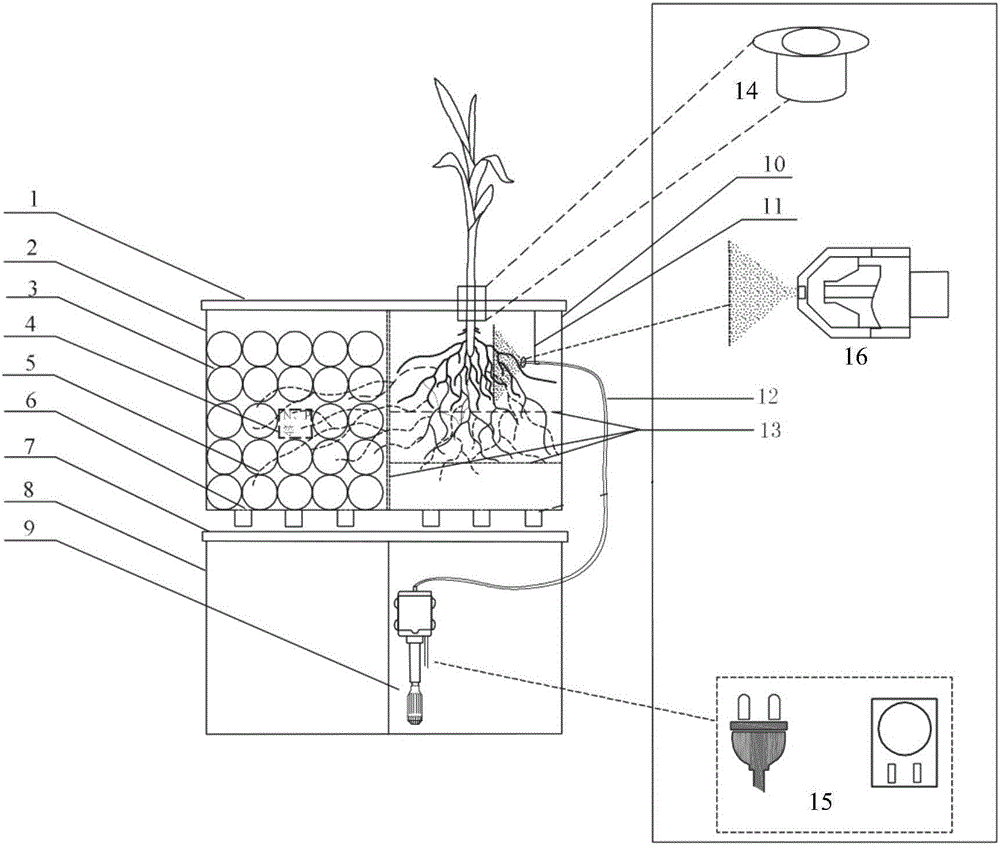
Timed and circulating AM (arbuscular mycorrhizal) fungus expanding propagation and functional experiment device and application method thereof
InactiveCN106834087AImprove cultivation efficiencySimple design and operationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiMicroorganismGrowth plant
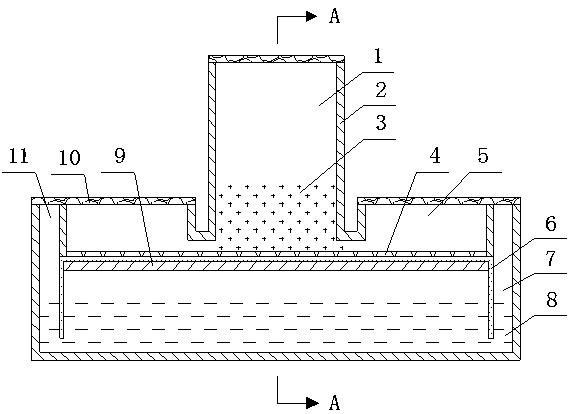
The invention provides a timed and circulating AM (arbuscular mycorrhizal) fungus expanding propagation and functional experiment device and relates to culture of soil microorganisms. The device is provided with an incubator cover, an incubator, a culture medium, a space for adding an isotope and the like, a hypha chamber, a water drainage tank cover, a water drainage tank, a filter pump, a plant growth chamber, a nozzle regulation and control hook and a nylon net, wherein the incubator cover covers the incubator, the incubator is divided into the hypha chamber and the plant growth chamber by virtue of a longitudinal net, the culture medium and the space for adding the isotope and the like are placed in the hypha chamber, and a water drainage hole is formed in the bottom of the incubator; the water drainage tank is arranged at the bottom of the incubator, the water drainage tank cover covers the water drainage tank, the filter pump is arranged in the water drainage tank, the nozzle regulation and control hook and the nylon net are arranged in the plant growth chamber, an atomizing nozzle is formed in the nozzle regulation and control hook, the atomizing nozzle and the filter pump are connected by virtue of a PVC hose, and a plant fixing device is arranged on the top of the plant growth chamber.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
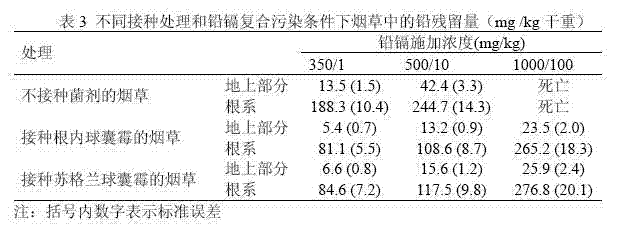
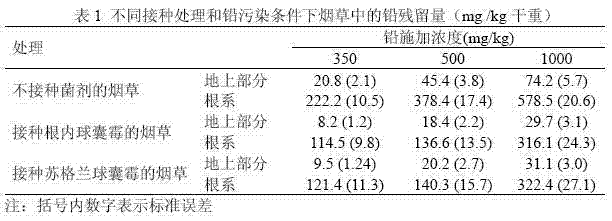
Method for using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer to reduce residue of lead and cadmium in tobacco
InactiveCN102577826AReduce poisonPromote growthHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
A method for using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer to reduce residue of lead and cadmium in tobacco includes: preparing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, culturing mycorrhizal tobacco seedlings, and transplanting and managing the mycorrhizal seedlings. Tests show that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and cow dung added to soil coordinate to promote plant growth, increase phosphorus content of vegetation, lower poison and pollution of tobacco by lead and cadmium and promote tobacco growth, thereby reducing the residue of lead and cadmium in the tobacco.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving growth and drought-resistant ability of wheat by using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
ActiveCN103828618AIncrease productionImprove infection symbiosisHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyTriticeae
The invention discloses a method for improving growth and drought-resistant ability of wheat by using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to bring the reciprocal symbiosis relation between AM fungi and host plants under drought stress into play reasonably and efficiently. According to the method, the AM fungi having a close symbiotic relation with the wheat are selectively used, and the symbiotic relation between the AM fungi and the wheat is built in a condition control mode to promote the wheat growth and improve drought adaptability. The AM fungi comprise one of glomus monosporum and acaulospora laevis, the two kinds of AM fungi are respectively propagated in an expanding mode in an expanding propagation matrix by using red clovers, and then two AM fungi inoculants and the wheat are cultured together in a symbiotic culture medium. The effective path for profitable symbiosis of the AM fungi and the host plants in adversity conditions is provided, the infection and symbiosis relation with the host plants of the AM fungi is improved in a man-made mode, and the yield of dry crops is improved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for locally culturing and producing arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus biological agent fertilizer in farmlands
InactiveCN101805216AEasy to obtainEasy to trainClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilisersArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiCulture mediums
The invention provides a method for locally culturing and producing arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus biological agent fertilizer in farmlands. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, preparing a farmland culturing pond and a culture medium; 2, transplanting and culturing arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi; 3, absorbing and converting biological fertilizer; and 4, collecting biological fertilizer. Compared with the prior art, the technique adopted in the method has the advantages that: 1, the raw materials are readily available, the culture of the raw materials is easy, and the cost is low; 2, the culture technique and the production technique are conveniently popularized in rural areas; and 3, the production technique is green and environment friendly, which facilitates the development of modern agriculture. In addition, by using the fertilizer of the invention, the used amount of the quick-acting fertilizer is reduced and the used amount of partial fertilizer is reduced, so that the pollution to soil, water resources and air is lowered, and the fertilizer is particularly suitable to be used for planting seedlings of farm crops and medicinal plants. Tests show that the yield of the farm crops cultured by using the fertilizer of the method is improved by over 50 percent compared with that of the farm crops cultured by using the common fertilizer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Fertilizer composition for improving stress resistance of land planted pear trees
ActiveCN103936500AStrong noveltyPracticalFertilizer mixturesArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPhenylacetic acid
A fertilizer composition for improving stress resistance of land planted pear trees comprises arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, betaine, salicylic acid, ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis(2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) ferric-sodium complex (EDDHA-Fe), a chelate zinc fertilizer titanium zinc ethylenediaminetetraacetate, a promoter and fertilizers containing other elements. Contained arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is capable of substantially improving stress resistance on drought, waterlogging disaster, salt and alkali, high temperature, heavy metal toxicity, toxic organics and the like of pear trees, and promoting absorption of soil mineral nutritional elements by soil. Betaine and salicylic acid are capable of inducing to improve crop resistance on adverse situations such as drought, freeze injury and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF POMOLOGY
Method for repairing farmland soil polluted by cadmium through using combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and sedum plumbizincicola
InactiveCN104604386APromote absorptionImprove repair effectSoil-working methodsArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a method for repairing farmland soil polluted by cadmium through using a combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and sedum plumbizincicola. The method comprises the steps that expanding propagation is conducted on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, and repair is conducted through inoculating the farmland soil with the inoculant to strengthen the sedum plumbizincicola. According to the method for repairing the farmland soil polluted by the cadmium through using the combination of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and the sedum plumbizincicola, it is proved in the experiment that in the mode of normal field management, the growth of the sedum plumbizincicola can be promoted through inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, repair on the cadmium of the soil by the sedum plumbizincicola is improved, and the total amount of the extraction of the cadmium can be increased by 75% to a maximum.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application method of AM (Arhusclar Mycorrhiza) fungi in cultivation of tree peony
InactiveCN102057833AIncrease productionQuality improvementCultivating equipmentsOrganic fertilisersContinuous croppingMaterials preparation
The invention belongs to the field of cultivation methods of tree peony and discloses the application method of AM (Arhusclar Mycorrhiza) fungi in the cultivation of tree peony. The application method comprises the following steps of: (1) material preparation; (2) substrate and holed plate sterilization; (3) inoculant preparation; (4) mycorrhiza seedling production; and (5) field transplanting and setting. When used in the cultivation of tree peony, the application method can improve the micro-ecological environment of tree peony rhizosphere, and especially has obvious alleviation effects on the aggravation of plant diseases and pest damages, untimely defoliation and other symptoms, which are caused by many-year continuous cropping, thereby achieving the dual purposes of improving the yield and the quantity of tree peony.
Owner:北京同仁堂安徽中药材有限公司
Formula of biological soil additives overcoming obstruction of vegetable continuous cropping
InactiveCN101200640ASimple structureIncrease vitalityAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersDiseaseContinuous cropping
The present invention belongs to the technical field of crop organic biological fertilizer, in order to solve the increasingly seriously continuous cropping obstacle of vegetable planting, lighten the occurrence of disease and improve the output and the quality of the vegetable, biological soil additive which can prevent the disease and as well as increase the production is confected, comprising two microorganisms, nonmetal mineral, fermented organic fertilizer, industrial waste residue and mineral microelement. The components comprise the weight proportion as follow: 10 percent of trichoderma functional microbial agent, 2 percent of VA arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, 6 percent of inorganic nonmetal mineral zeolite, 69 percent of fermented organic fertilizer, 4 percent of shell powder, 7 percent of calcium superphosphate and 2 percent urea. The present invention is widely applied to the vegetable planting at the protected field with seriously continuous cropping and successive cropping and has the functions of improving the soil, promoting the crop nutrient absorption, increasing the output and preventing the disease.
Owner:텐진인스티튜트오브플랜트프로텍션
Separation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as well as preparation and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide
The invention discloses separation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as well as preparation and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rhizophagus irregularis which is called arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rhizophagus irregularis CD-1 and is separated from soils; a specific sequence of verifying ribosome 28S rDNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; by utilizing the fungicide prepared by the fungi, the height of strains, the number of petioles, the overground fresh weight, the overground dry weight, the root fresh weight and the root dry weight of tomatoes can be increased, and the mycorrhizal infection rate delta gt can be obviously prompted; 80 percent of corns are high in selfing line strains and heavy in overground fresh weight and overground dry weight; the resistance to banded sclerotial blight by the corns is improved, and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi has an extremely-high genetic use value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation of compound rice dedicated bio-fertilizer based on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and application thereof
ActiveCN102718599APromote growthGood growth promoting effectRice cultivationFertilizer mixturesInfection rateArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore
ActiveCN101565689ALow costLow nutritional requirements for growthMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologyMicrobial culture technique
The invention discloses a production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism culturing, and comprises the following technical steps of: 1) culturing carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA; 2) culturing the carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA and glomus intraradices together in an improved synthetic culture medium; 3) taking a culture containing the root, hypha and spore infected by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and transplanting the culture to a special culture box for culturing; 4) collecting the spore and mycelium; and 5) storing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore. Compared with the prior art, the production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore has the advantages that: 1, the culture medium is an asepsis environment with low cost, which not only can meet the growing of a host plant, but also is suitable for the growing of AM epiphyte; 2, the nutrition requirements for the growing of the host plant are low and the host plant can grow and be cultured on the synthetic culture medium; 3, the spore cultured by the method is a non-pollution pure culture; and 4, the produced spore is stored in liquids and the activity can be maintained by above 90 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Repair method for cadmium polluted soil by arbuscular mycorrhiza-alfalfa symbiont
InactiveCN108555019ADoes not change the inherent physical and chemical propertiesImprove bindingContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiBioremediation
The invention discloses a repair method for cadmium polluted soil by an arbuscular mycorrhiza-alfalfa symbiont. The repair method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing an arbuscular mycorrhizafungi fungicide; S2, treating alfalfa seeds; and S3, inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi fungicide to the surface sol layer of the cadmium polluted soil; then planting the alfalfa seeds for field management; and after growth, harvesting plant materials, airing and transferring the plant materials, and incinerating the plant materials in a centralized manner to repair the cadmium polluted soil. By combining a microbial repair technology with a plant repair technology, the repair method solves the problem that the repair method is prevented from being popularized and applied on a large scale as a green repair technology because the microbial repair speed is slow, the responding time is long and the soil environmental requirement is high, is low in cost by plant repair, good in comprehensive ecological benefit, suitable for being popularize on a large scale and the like, and has the characteristics of being economical and convenient to repair microbially, not changing the inherentphysical and chemical properties of soil and the like. The obtained repair method is high in treatment capacity, economic, convenient and suitable for being popularized on a large scale.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving artificial breeding survival rate of populus diversifolia by inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
InactiveCN102172136ASeed and root treatmentHorticulturePopulus diversifoliaArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention relates to a method for improving artificial breeding survival rate of populus diversifolia by inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The method comprises the steps of: selecting populus diversifolia sprouts for performing pot experiment, arranging a transplanting hole in the pot, spreading sandy soils rich in glomus mosseae spores at the bottom of the hole, slowly rotating the root systems of populus diversifolia seedlings on the sandy soils of glomus mosseae spores before the transplantation, so that the sandy soils are pasted on the root systems of the populus diversifolia seedlings, transplanting the populus diversifolia seedlings into the hole in the pot, watering a dilute Hoagland nutrient solution every time, and observing the survival rate; or enabling populus diversifolia seeds to absorb water and swell and accelerating germination in an incubator, mixing the populus diversifolia seeds with the sandy soils of glomus mosseae spores, spreading the mixture on a sandy layer surface of a culture bed, and paving a layer of sandy soils rich in glomus mosseae spores under the sandy layer of the culture bed in advance, wherein the root systems are to pass through the sandy soil layer rich in glomus mosseae spores, so that the root systems can be infected. Compared with a control group, the populus diversifolia seedlings obtained by the method are obviously different from the populus diversifolia seedlings in the control group in the growing speed and survival time, particularly in survival rate.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Plant and AM (arbuscular mycorrhiza) fungus symbiotic bidirectional cultivating box
InactiveCN103875447AAchieve dual trainingReasonable designHorticultureArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPlant roots
Disclosed is a plant and AM (arbuscular mycorrhiza) fungus symbiotic bidirectional cultivating box. Nutrient solution is filled in a liquid storage tank, a support plate is connected above the liquid storage tank, imbibing paper and a hypha filter membrane are paved on the support plate, two ends of the imbibing paper are immersed in the nutrient solution, the upper portion of the support plate is provided with a plant growth chamber, mycorrhiza chambers and liquid exchange ports are respectively arranged on two sides of the plant growth chamber, cultivating matrix is disposed in the plant growth chamber and communicated with the bottom of the mycorrhiza chambers, and the top ends of the mycorrhiza chambers are sealed by breathable sealing membranes. The nutrient solution can automatically enter the mycorrhiza chambers and the plant growth chamber, so that plant roots can grow along the hypha filter membrane. Spores of the AM fungus can be inoculated to the surface of the root system after the root system enters the mycorrhiza chambers, hypha characteristics of the AM fungus and forming process of the root system symbiotic structure of host plants can be observed and plant photosynthesis and physiological and biochemical characteristics can be researched transparently and visually. The plant and AM fungus symbiotic bidirectional cultivating box realizes dual cultivation of the AM fungus and the entire plants, and provides an effective way to research the relation of the AM fungus and the plant and actions on the plant.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for restoring arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi of vegetative cover in land with discarded iron tailings of grassland ecosystem
The invention discloses a method for restoring arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi of a vegetative cover in a land with discarded iron tailings of a grassland ecosystem, and relates to the technical field of ecological restoration of vegetative covers in a land with discarded metal tailings. The method for restoring arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi comprises the following steps of: (1) covering earth on iron tailings for 3 to 7 centimeters deep; (2) inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungicides such as Glomus versiforme and the like at the place 0 to 3 centimeters far from the earth; (3) planting plants such as Elymus dahuricus Turcz and the like, harvesting the plants after 60-day to 120-day growth, using the plants which meet a relevant standard as feed, and centralizedly burning and landfilling the plants which do not meet the relevant standard. The method for restoring the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi has the following advantages that: the adopted arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi symbiose with herbs easily so that the absorption and utilization of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are promoted, the absorption or transferring of heavy metals is reduced, the thickness of covering earth is reduced, the growth situation of plants is improved, the planting and growth of plants in iron tailings covered with earth are promoted, the method for restoring the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi has high success rate of revegetation, simple process and lower cost, and is applicable to management of lands with discarded iron tailings of grassland ecosystems.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Method for promoting growth of Datian sugarcanes by using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculant
InactiveCN102986447AImprove drought resistancePromote absorptionCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationPlant rootsArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
A method for promoting growth of Datian sugarcanes by using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculant uses river sands, perlite, loam and peat soil to serve as culture substrates, uses corns as a host plant to breed arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spores, collects the culture substrates and plant root systems to serve as the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculant to be applied to production of the Datian sugarcanes after cultivating for 4-5 months. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculant produced by the method serves as an inoculum of the Datian sugarcanes, promotes absorption of nutrient and moisture in the soil of the sugarcanes, improves drought resistance of the sugarcanes, and improves production volume by more than 10%.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY RES INST GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for treating garbage, sludge or excrement by earthworms and biological organic fertilizer
The invention relates to a method for treating garbage, sludge or excrement by earthworms and a biological organic fertilizer. The method comprises the following steps: adding a microbial starter into wastes to be treated and fermenting for one time to obtain organic materials which are fermented for one time; adding vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae into the organic materials which are fermented for one time and mixing to obtain a mixture; adding young earthworms into the mixture for cultivating; and drying a mixture obtained by cultivating until the humidity is 15%-20% to obtain the biological organic fertilizer, wherein 0.08-0.12 part by weight of the vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae is added into each 100 parts by weight of the organic materials which are fermented for one time; 30000-40000 young earthworms are added into each cube of the organic materials which are fermented for one time. According to the method for treating the garbage, the sludge or the excrement by the earthworms, the high-quality and efficient biological organic fertilizer is produced and a good environment is provided for the growth of plant roots.
Owner:刘涛
Method for carrying out industrialized production on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent
ActiveCN103314676AShorten the production cycleIncrease productionSeed immunisationBiotechnologySpore
The invention discloses a method for carrying out industrialized production on an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent, and relates to a production method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The method comprises the following steps: 1. preparing and treating the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent; 2. carrying out seed treatment on hosts; 3. carrying out breeding; and 4. managing. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the implementation of production just needs eight weeks, the number of effective spores of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in each gram of the obtained arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent is 120-150, the production cycle is short, and the yield is high. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to the field of agriculture, gardens, and flowers.
Owner:黑龙江省庆东阳光农业生物科技股份有限公司
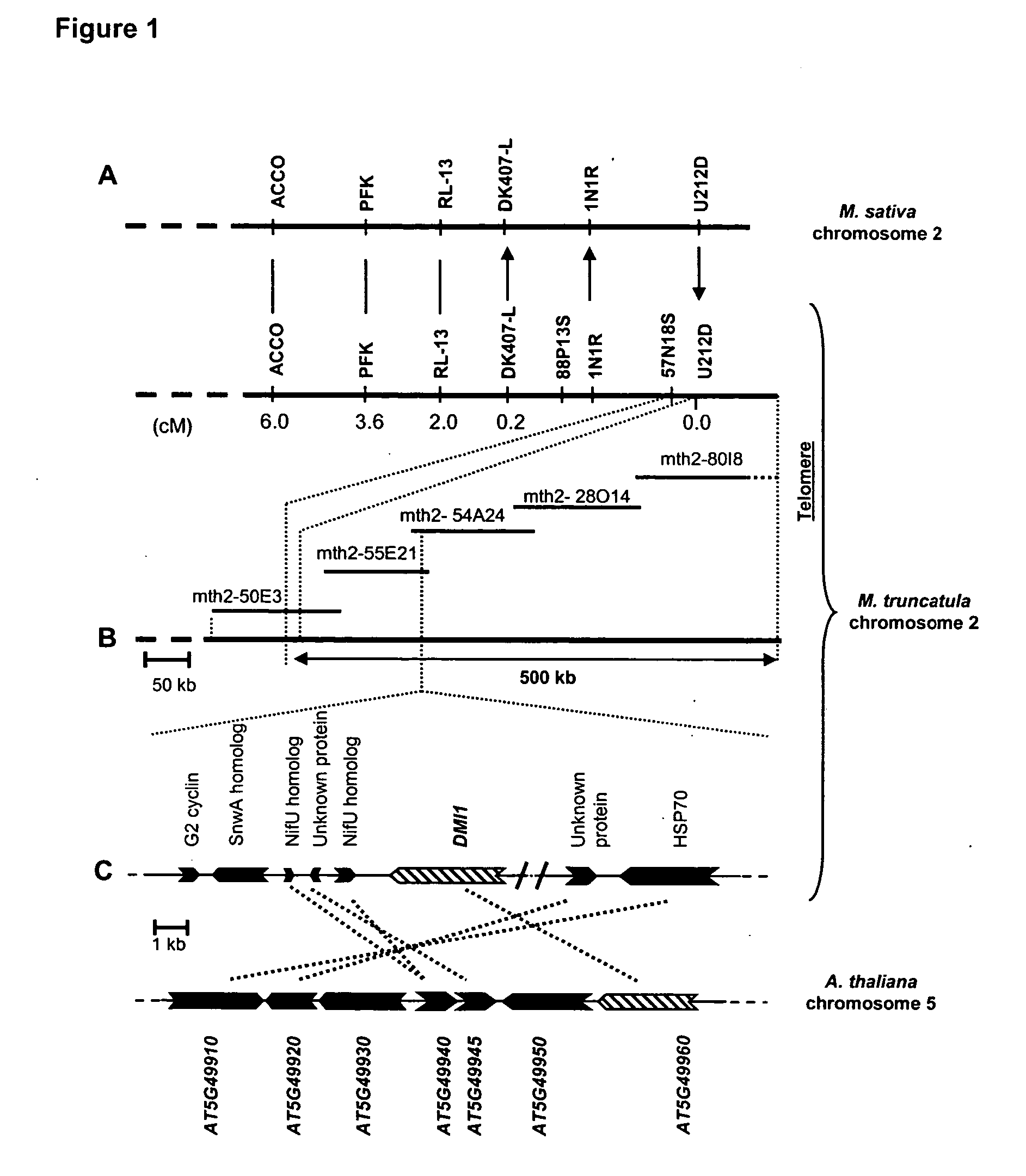
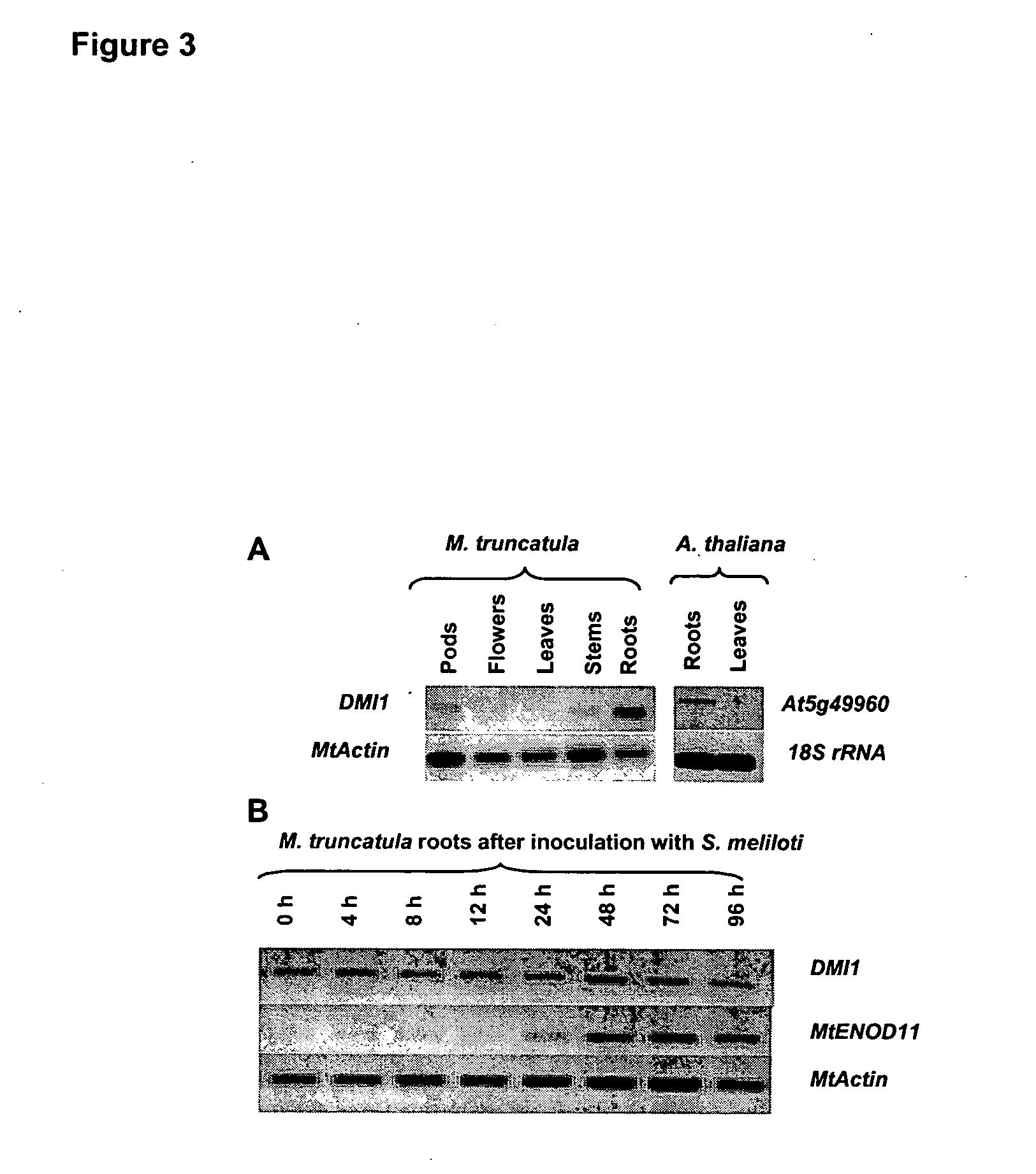
The DMI1 gene encodes a protein that is required for the early steps of bacterial and fungal symbioses
InactiveUS20050081262A1Enhanced nitrogenEnhanced phosphorous acquisitionBryophytesSugar derivativesBacteroidesPlant nodule
Mycorrhizal and rhizobial associations represent the two most important symbiotic relationships between higher plants and microorganisms, providing access to otherwise limiting supplies of phosphate and nitrogen, respectively. Although many higher plants are able to establish a symbiotic relationship with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, legumes are unusual among plants because they also form associations with nitrogen fixing soil bacteria called rhizobia. This symbiosis requires the production of bacterial signals, “Nod factors” that trigger several key developmental responses in the host plant (Dénarié et al., 1996). The DMI1 gene of the model legume M. truncatula plays a major role both in the early steps of Nod factor signaling and in the establishment of mycorrhizal symbiosis. Dmi1 mutants do not exhibit many of the early responses to Nod factors and are incapable of forming nitrogen fixing root nodules. Here we describe the cloning and preliminary characterization of DMI1. The DMI1 gene encodes a novel protein with low global similarity to ligand-gated cation channels of archaea. The protein is highly conserved in angiosperms and ancestral to land plants. Interestingly a putative A. thaliana DMI1 orthologous gene is expressed in roots. As A. thaliana is unable to establish a mycorrhizal symbiosis, this finding suggests that DMI1 may also exhibit a function that is independent of symbiotic interactions.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
Planting method for improving surviving rate of sand seedlings
ActiveCN103392459AImprove survival rateHigh infection rateHorticulture methodsArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiInfection rate
The invention discloses a sand seedling planting method. The sand seedling planting method includes the following steps of (1) soaking bare roots of seedlings to be planted in water for 6-12 hours, (2) mixing clayed soil and water according to the volume ratio of 1:3, and adding arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the mixture to form a slurry, wherein the mass ratio of the mixture and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is 100:5-10, (3) dipping the bare roots of the seedlings to be planted in the slurry of step (2) for 3-5 minutes after the bare roots are soaked in the step (1), and then planting. Experimental results show that compared with a traditional planting method, the method is used for planting the seedlings in sand soil, the infection rate of mycorrhizae can be improved by 10%, and the surviving rate of the seedlings can be improved by 20-30%. Therefore, the sand seedling water-retaining inoculation planting method has important practical significance in sand ecological restoration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Jatropha curcas mycorhiza bacterium composite fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101186542AImprove absorption rateImprove the ecological environmentSuperphosphatesAnimal corpse fertilisersEcological environmentArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention discloses a Jatropha curcas mycorrhizal fungi compound fertilizer, which comprises one or more arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi containing glomus and gigaspora that are served as the mycorrhizal fungi. The compound fertilizer consists of 20-30 percent of the mycorrhizal fungi, 1-12 percent of phosphate fertilizer, 2-18 percent of potassium fertilizer, 8-15 percent of nitrogenous fertilizer, 2-3 percent of zinc sulfate and 20-50 percent of humus soil. The compound fertilizer of the invention can improve the absorption ratio of Jatropha curcas root absorbing soil nutrition, meet the growth, development and fruit bearing of the Jatropha curcas, improve soil ecological environment and increase seed yield.
Owner:云南神宇新能源有限公司
Method for promoting growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali soil through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
ActiveCN107493896AImprove nutritional statusPromote growthFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsAlkali soilArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention relates to a method for promoting growth of sweet sorghum in saline-alkali soil through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The method includes the steps of preparing and applying an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent. When the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent is prepared, a mixture of farmland soil and organic fertilizer serves as a substrate, and the organic fertilizer and decomposed products of the organic fertilizer can be used as a fungi protecting agent to have a buffering effect on saline ions in soil around the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the early period when the fungi agent is applied to the saline-alkali soil so as to help the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to resist saline-alkali stress; the symbiotic relationship is smoothly formed between the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and the sweet sorghum, the mineral nutrition of the sweet sorghum is remarkably improved, the sweet sorghum can be helped to resist saline-alkali stress, and the growth of the sweet sorghum is promoted.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com