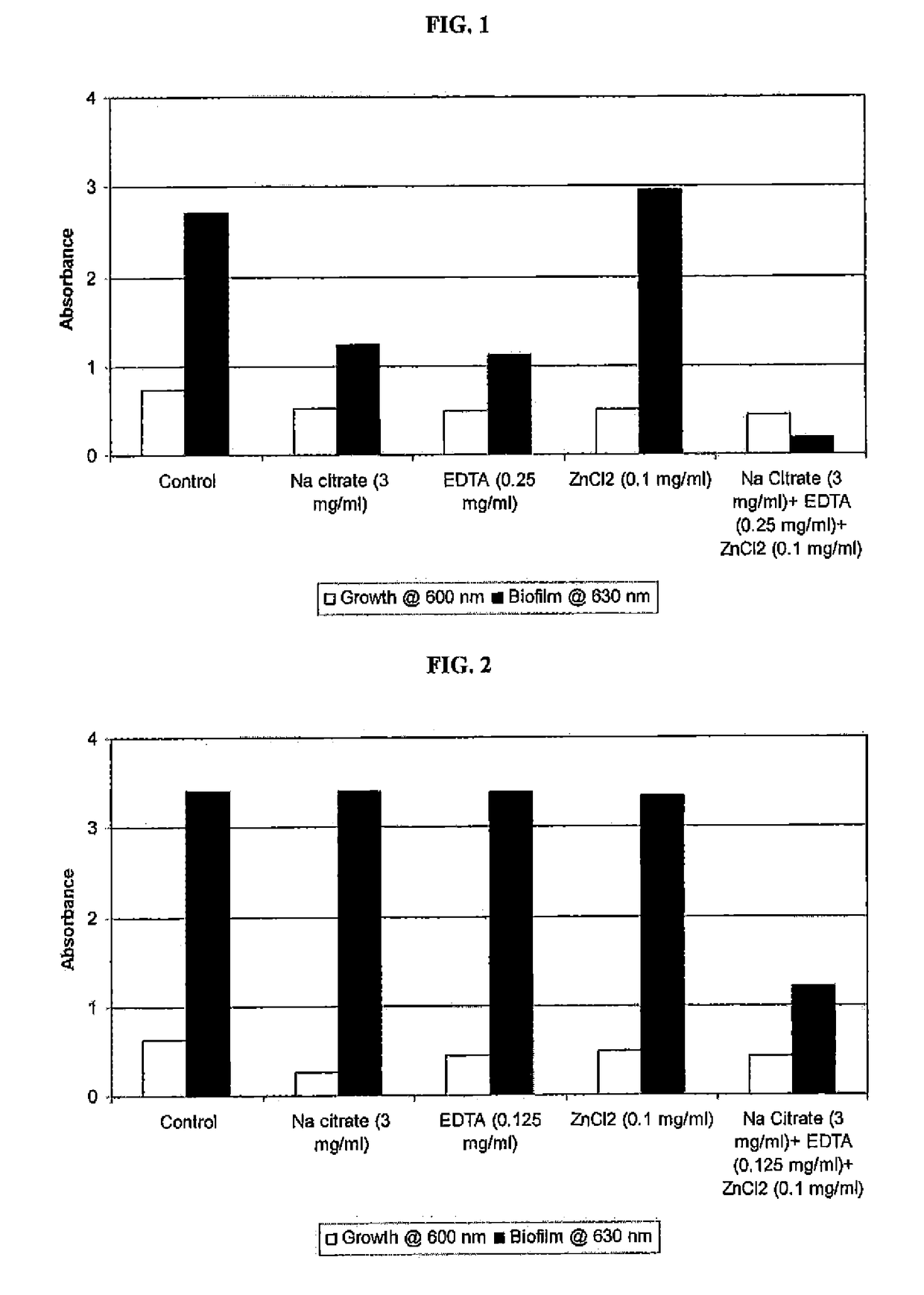
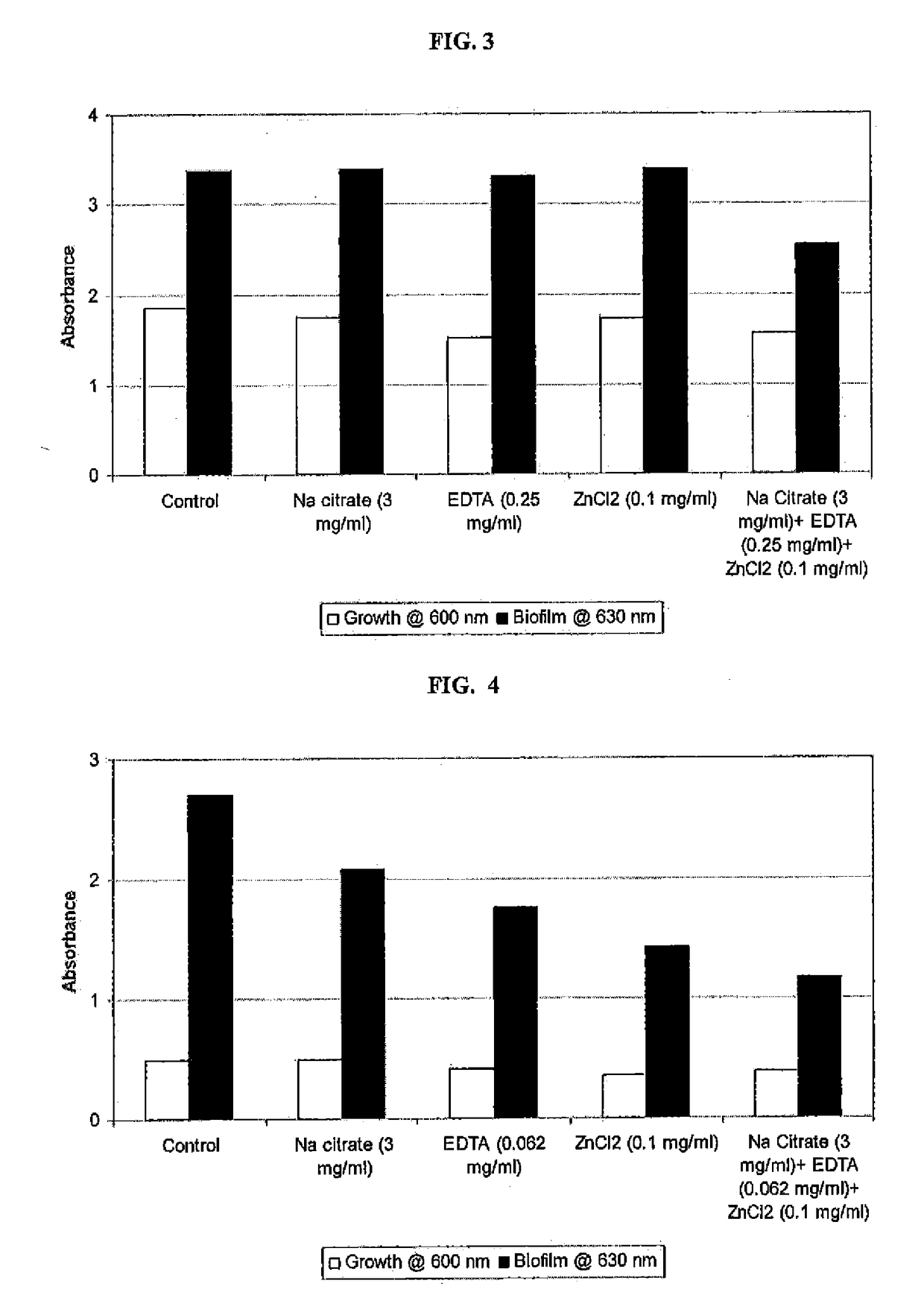
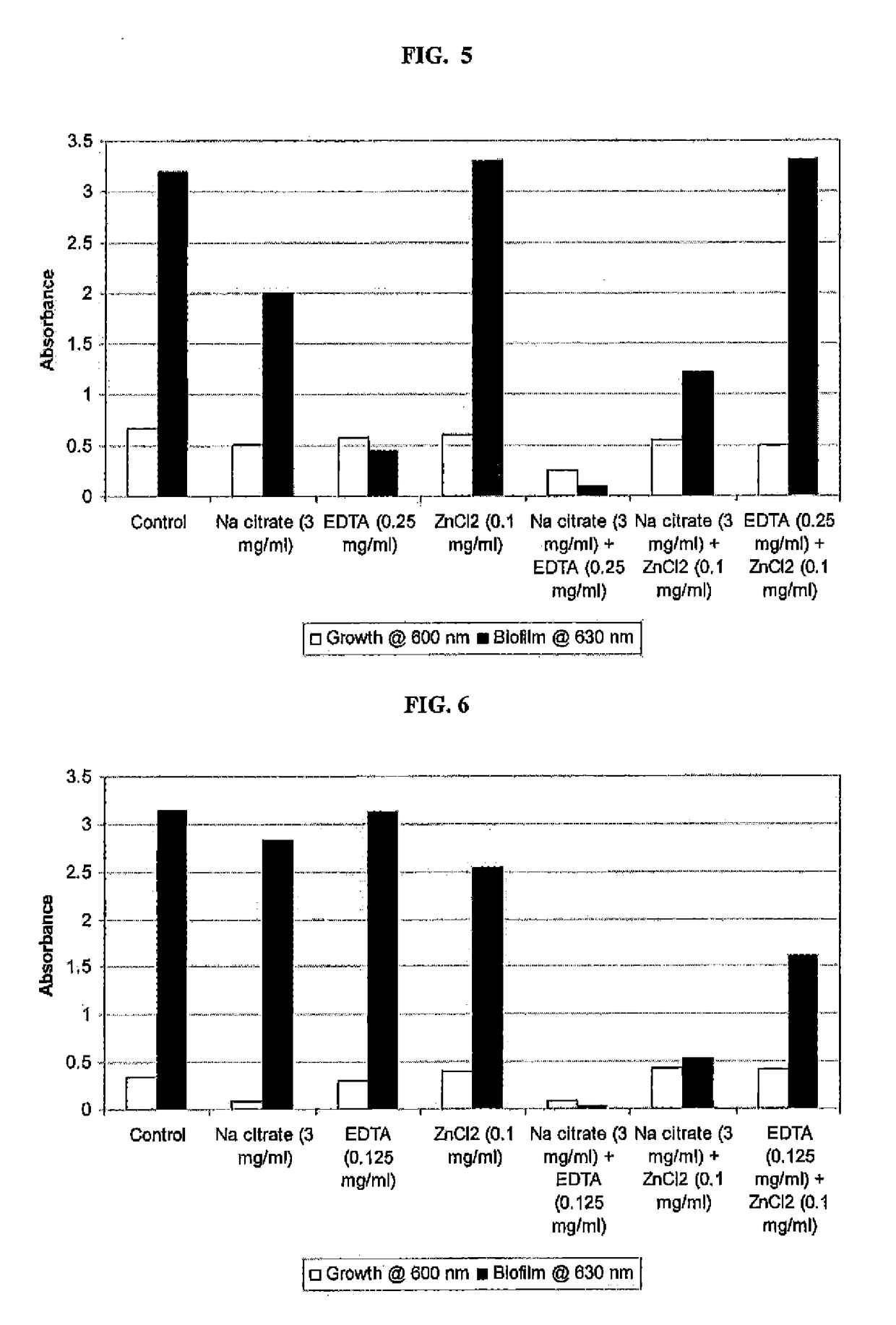
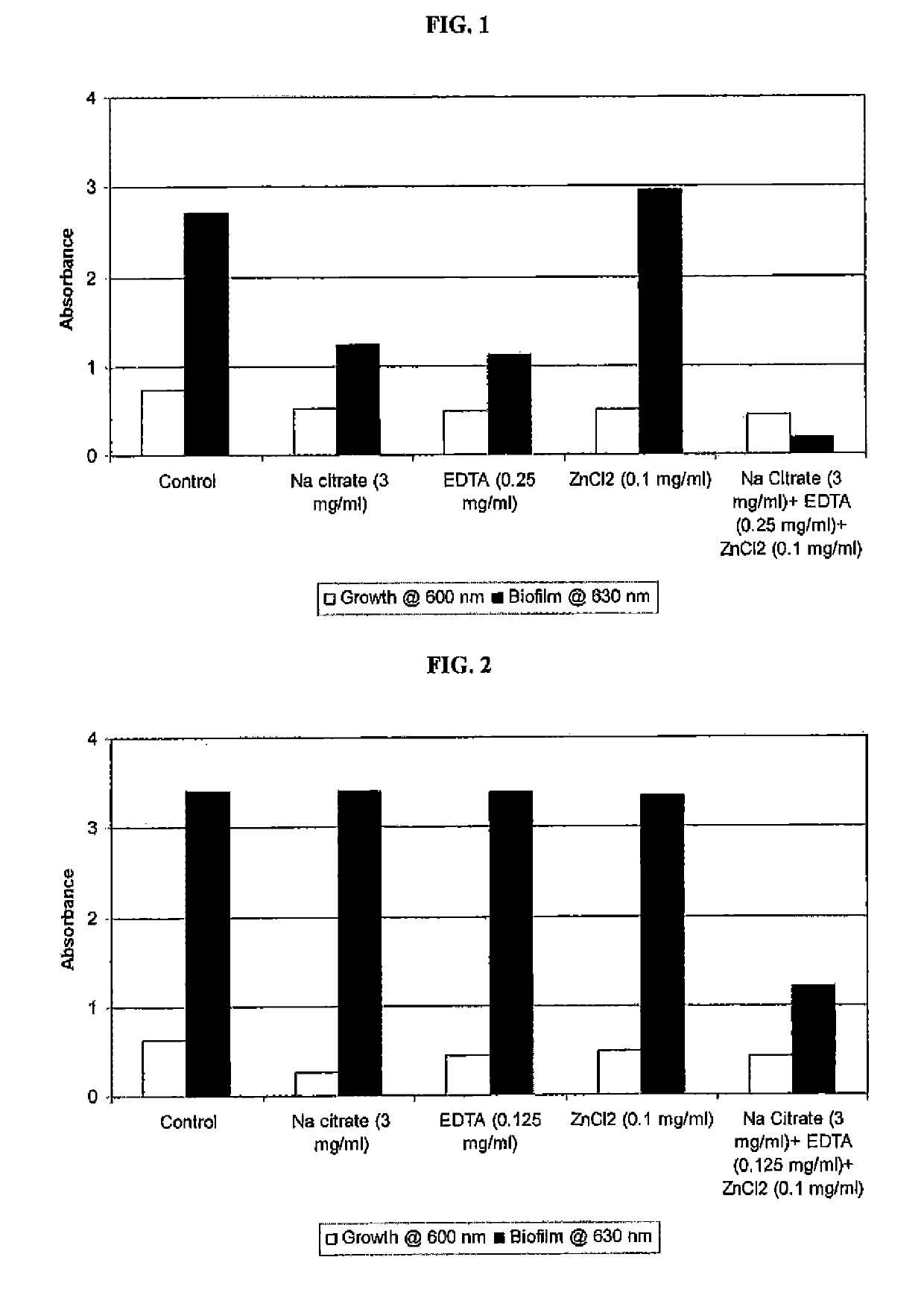
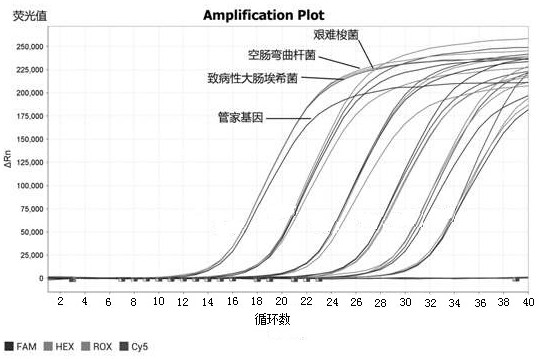
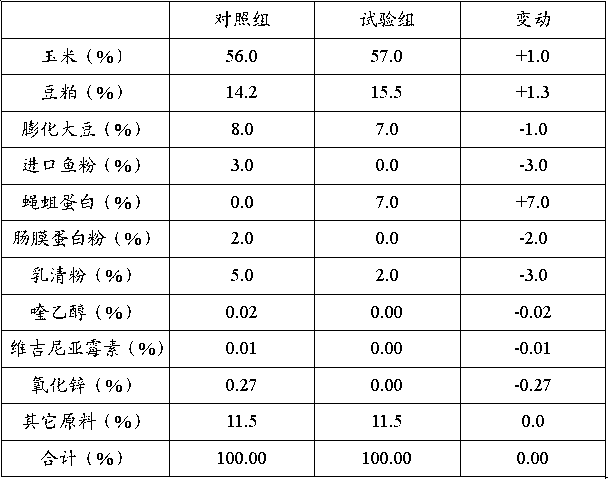
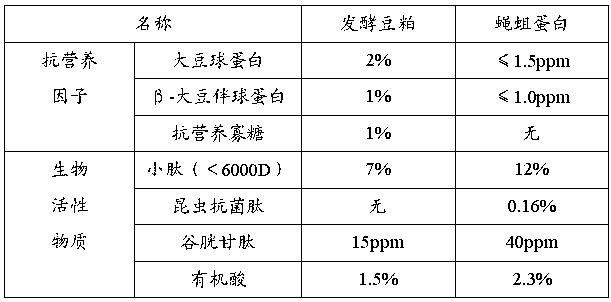
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Associated bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
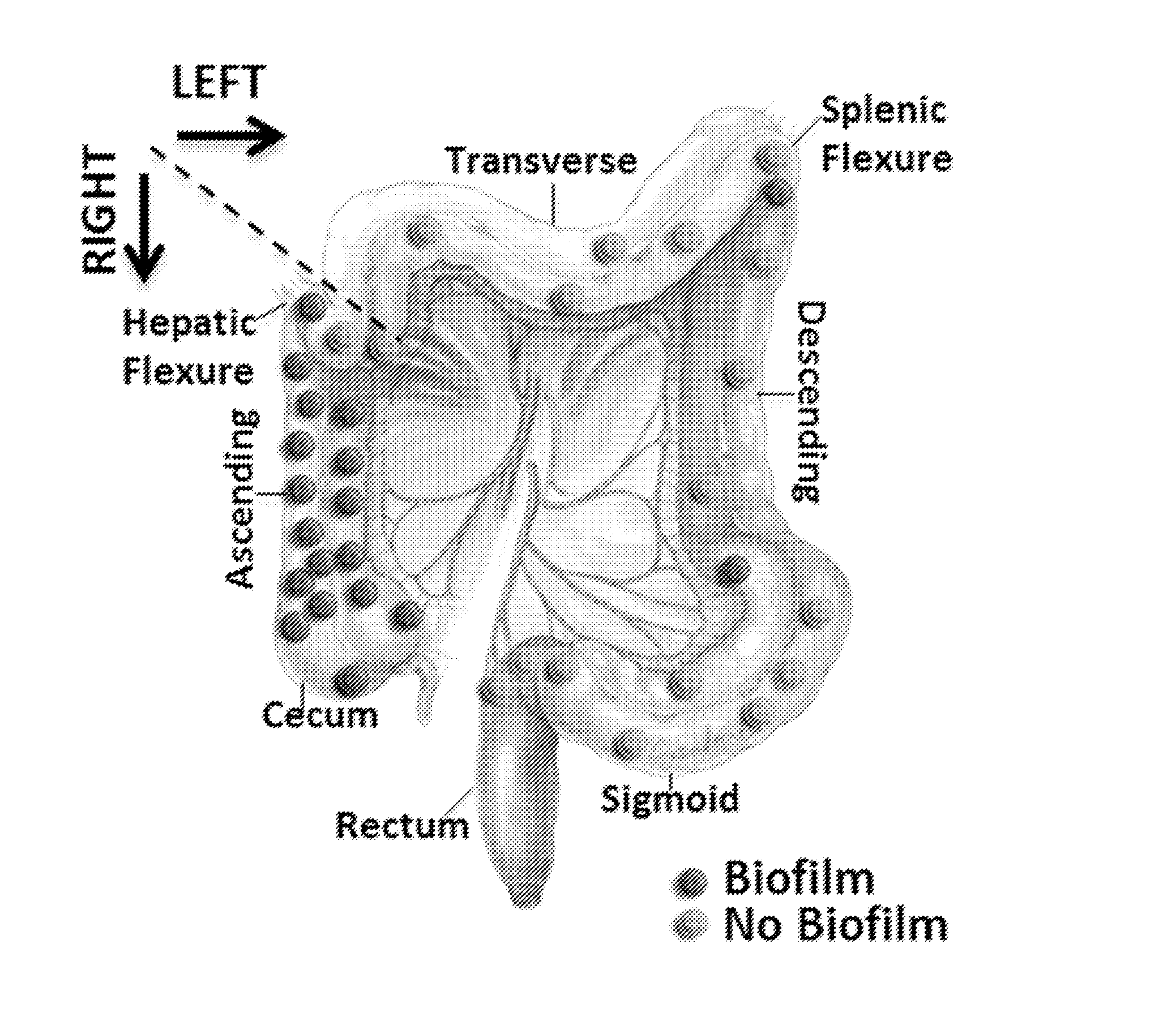
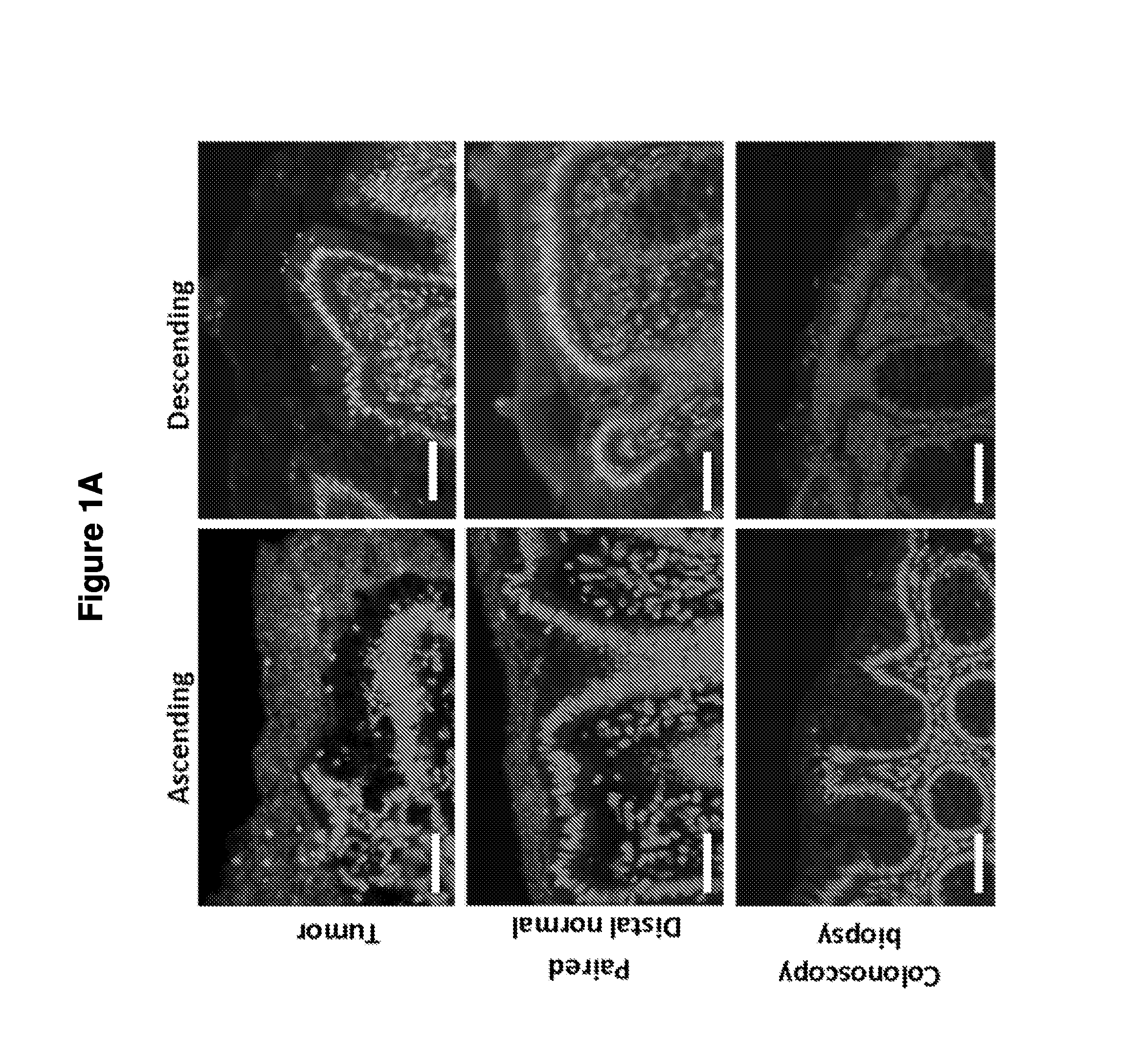
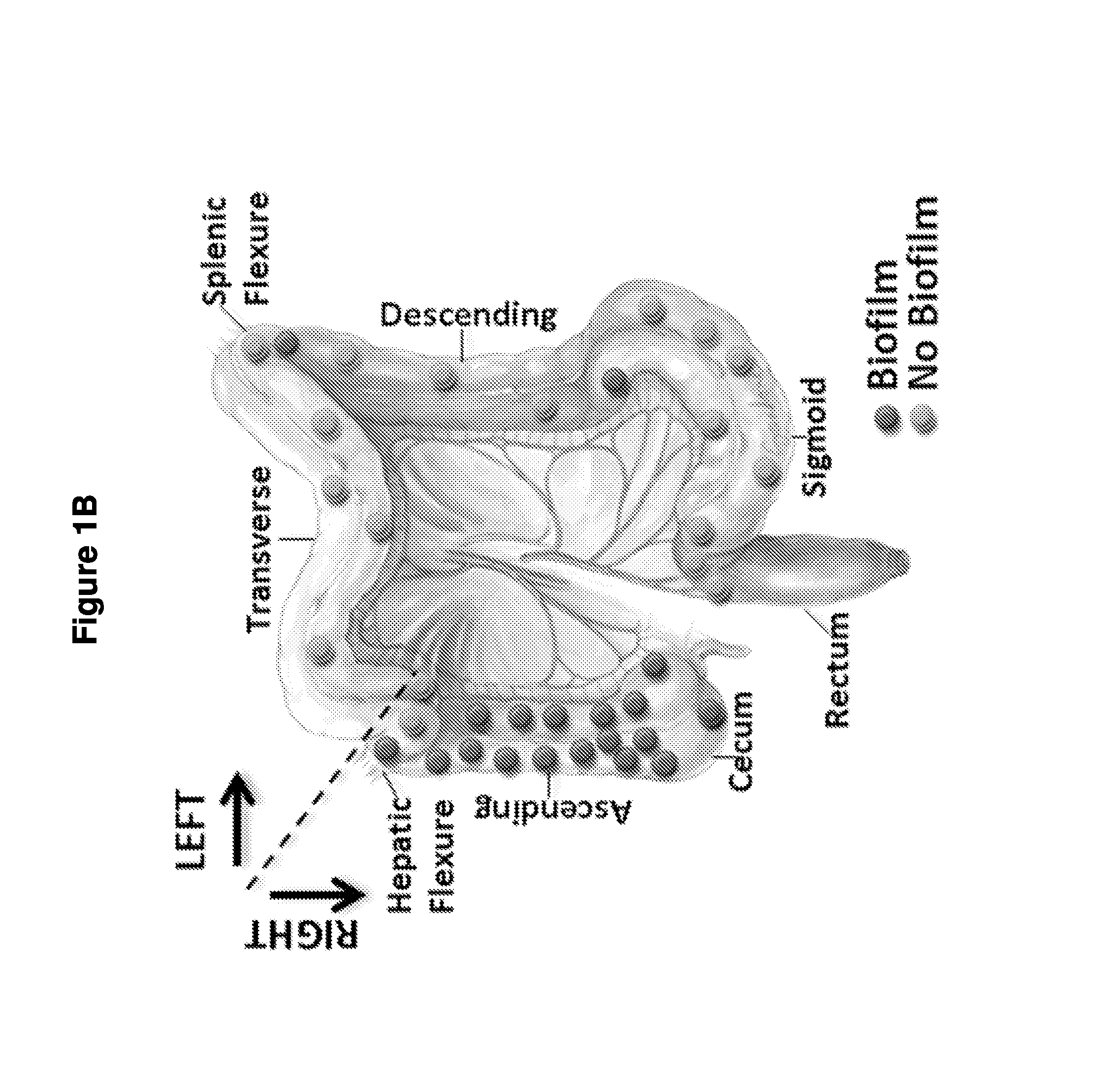
Biofilm formation to define risk for colon cancer
ActiveUS20160223553A1Preventing and diminishing developmentIncreased proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementUnknown materialsFecesIncreased risk
Methods of identifying subjects at increased risk of cancer, based upon detection of biofilms and / or biofilm-associated microbes within a subject, are disclosed. Therapies designed to prevent formation and / or reduce the size of biofilms in a subject identified to be at increased risk of cancer based upon detection of biofilms and / or biofilm-associated microbes are disclosed. In particular embodiments, the invention provides for identification of a subject at elevated risk of developing or having colorectal cancer and / or a colorectal adenoma, based upon detection of a biofilm and / or biofilm-associated bacteria within the gastrointestinal tract of the subject (optionally, within a biopsy specimen and / or stool sample of such subject). Therapies involving administration of an antibiotic agent and / or a probiotic agent to a subject, to prevent or reduce biofilm formation within the gastrointestinal tract of the subject, optionally provided in combination with additional cancer therapy, are also disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
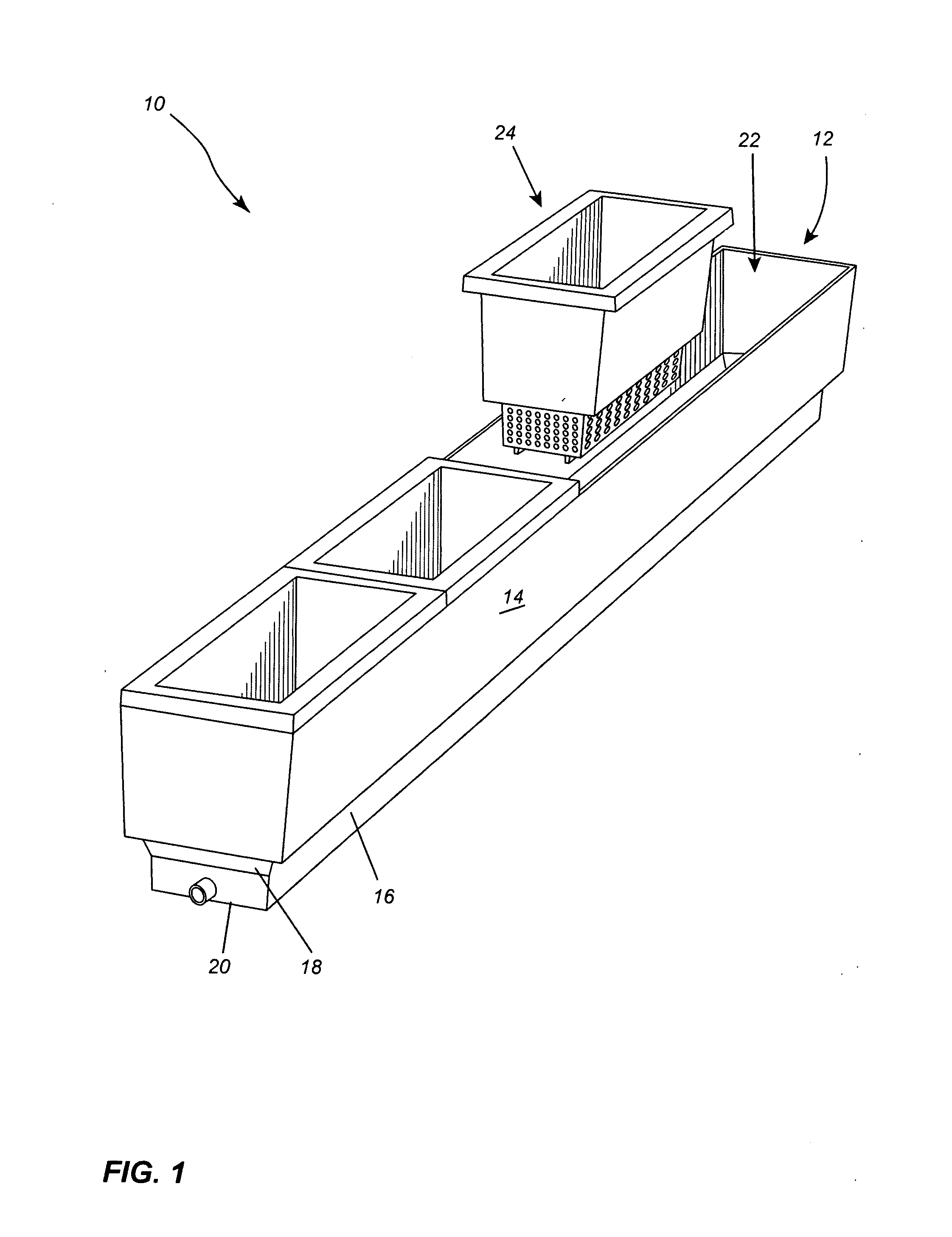
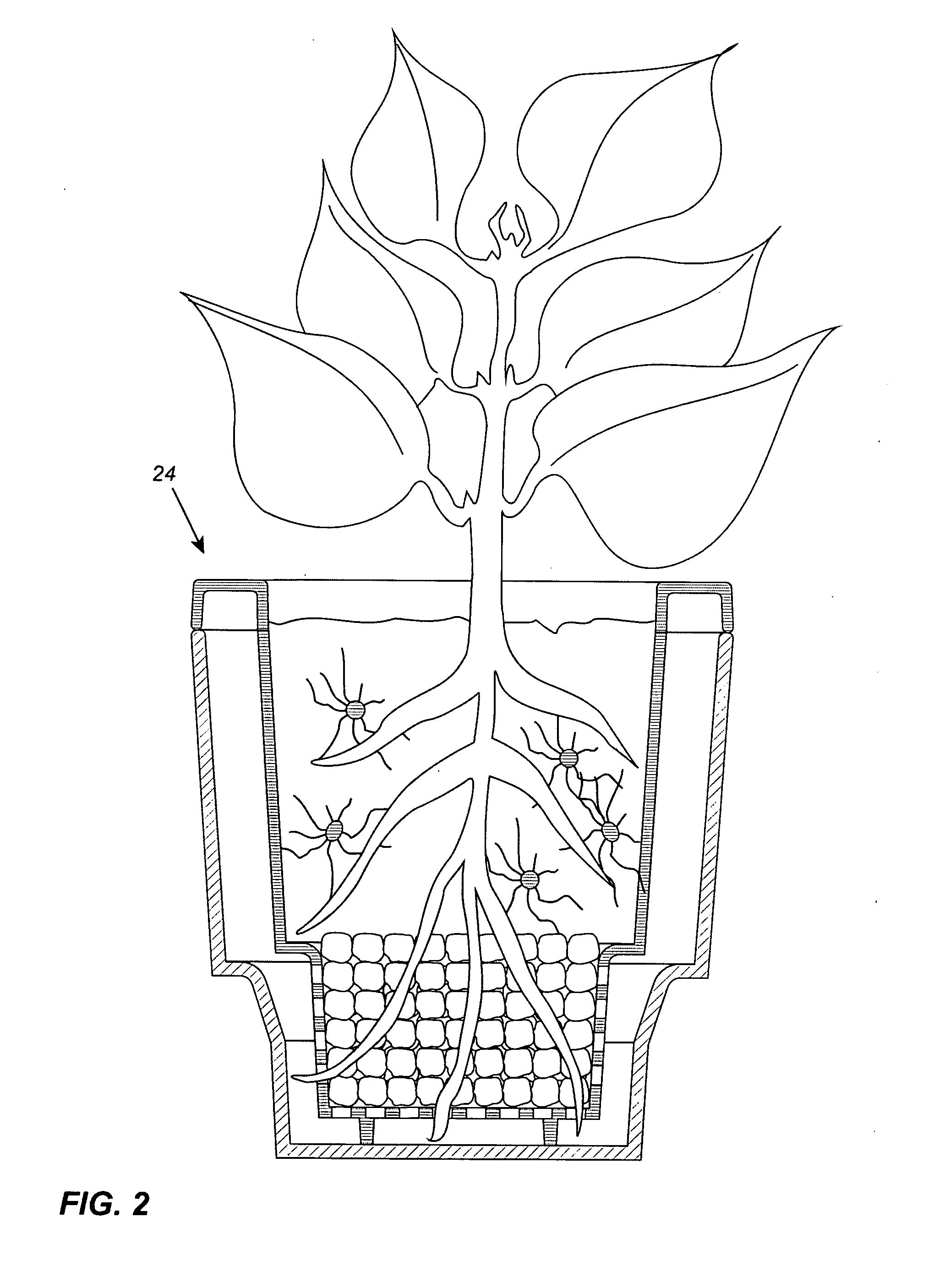
Continuous bioprocess for organic greenhouse agriculture
InactiveUS20150237807A1Avoid waterAvoid Fertilizer WasteSelf-acting watering devicesCultivating equipmentsMicrobial inoculationArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
A method of plant cultivation which comprises inoculating plants in a plant growing system comprising a container and an insert therefore, the microbial inoculant containing at least one species from the following group of microorganisms comprising arbuscular mycorrhizae associated bacteria, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, yeast microorganisms and substrate conditioning bacteria.
Owner:BIOPONIX TECH
Method for specific fast detection of relevant bacteria in drinking water
InactiveUS20050064444A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacteria in drinking water and surface water, especially a method for simultaneous specific detection of bacteria from the Legionella species and the Legionella pneumophila species by in situ hybridization. The invention also relates to a method for specific detection of faecal streptococci by in situ-hybridization and a method for simultaneous specific detection of coliform bacteria and bacteria of the Escherichia coli species, in addition to corresponding oligonucleotide probes and kits enabling said inventive method to be carried out.
Owner:VERMICON
Rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial bacterium manure
ActiveCN104844284AImprove physical and chemical propertiesPromote decompositionFungiBacteriaBacillus cereusGrowth promoting
The invention discloses rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial bacterium manure. The rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial bacterium manure is prepared from culture obtained by carrying out aerobic mixed fermentation on bacillus cereus GF-1, streptococcus thermophilus BLST, bacillus mucilaginosus G3, bacillus subtilis B7348, bacillus subtilis N9-1-35, lactobacillus plantarum LP and candida utilis CUM on a universal culture medium, wherein the total number of biological living bacteria in the microbial bacterium manure is greater than or equal to 2*10<10> CFU / g. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial bacterium manure. The microbial bacterium manure disclosed by the invention utilizes exogenous plant growth-promoting bacteria and associated bacteria to improve the micro-environment of root soil, and the prepared microbial bacterium manure is applied into the soil, the soil environment can be effectively improved, the growth of plants is promoted, and the resistances of the plants are improved.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司 +1
Signal peptides, nucleic acid molecules and methods for treatment of caries
InactiveUS20060067951A1Inhibits transcriptionInhibits exportCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiofilmMicroorganism
Peptide analogues of S. mutans CSP peptide which inhibit biofilm formation, uses thereof in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions, antimicrobial compositions and uses thereof in the treatment and prevention of infections caused by biofilm forming bacteria, dental plaque formation, and conditions caused by dental plaque associated bacteria are provided.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO +1
Gluconobacter oxydans gene engineering bacteria for producing 2-KLG and its application
InactiveCN103484418AEliminate dependenciesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesVitamin CD-Sorbitol
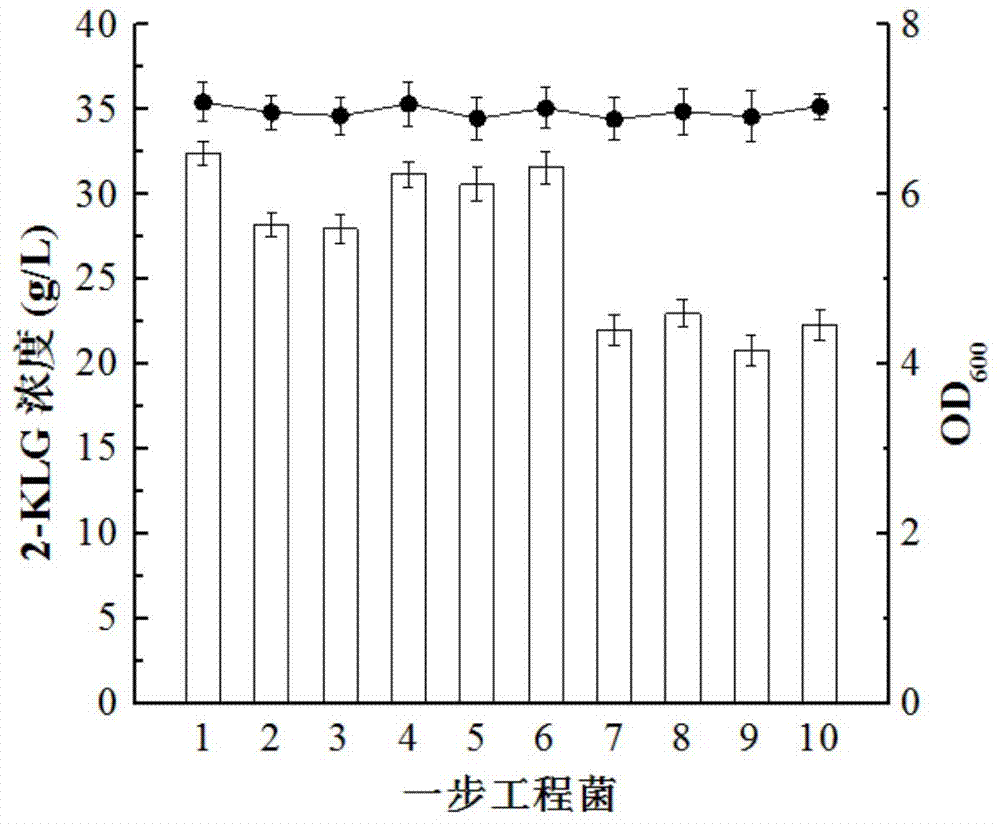
The invention discloses a Gluconobacter oxydans gene engineering bacteria for producing 2-KLG and its application. According to the invention, by means of a genetic engineering technology, sorbose dehydrogenase (SDH) and sorbosone dehydrogenase (SNDH) genes derived from Ketogulonigenium vulgare are connected by a connecting peptide and then expressed in Gluconobacter oxydans so as to obtain G. oxydans engineering bacteria for high efficiency production of 2-KLG. The G. oxydans is a strain commonly used in a first step fermentation process during two-step fermentation production of 2-KLG. The expression of sdh and sndh genes in G.oxydans can dissolve the dependence problem of small bacteria on associated bacteria, thus realizing direct conversion from D-sorbitol to 2-KLG, and simplifying the vitamin C production process. With a 2-KLG yield of 32.4g / L, the Gluconobacter oxydans gene engineering bacteria has very good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Antimicrobial-antibiofilm compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20160015047A1Improve stabilityImprove efficacyAntibacterial agentsBiocideFood borneMicrobial agent
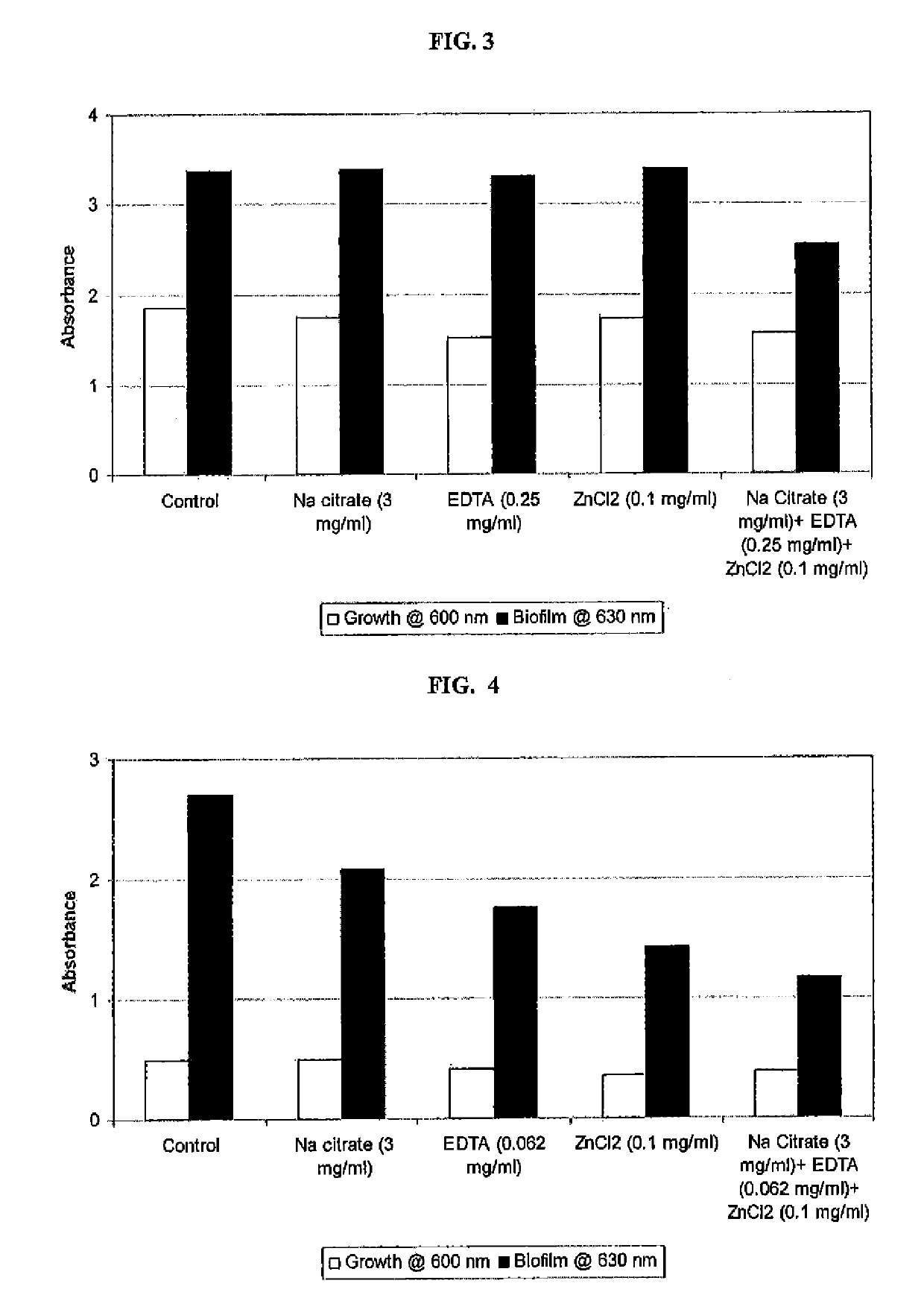
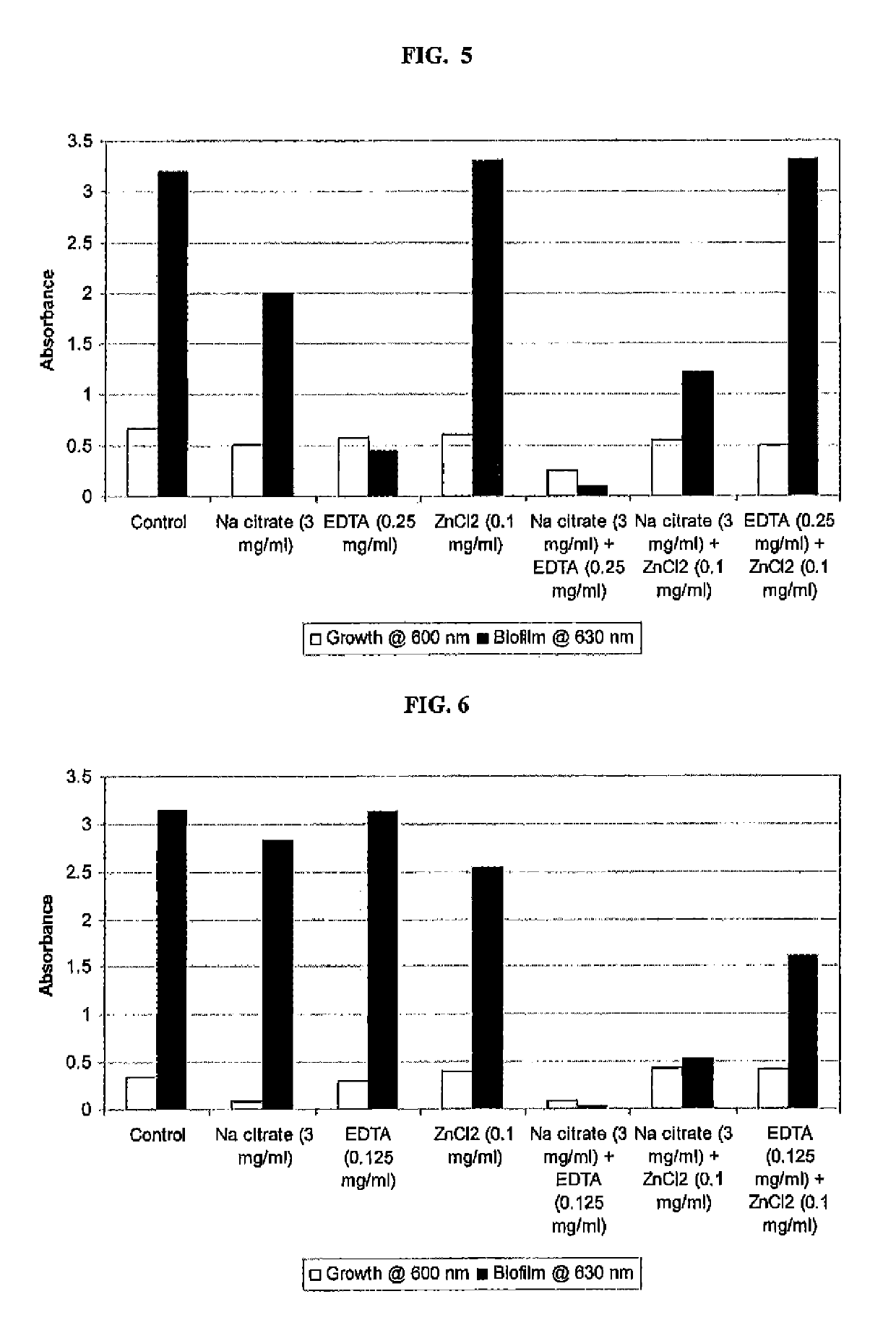
Compositions comprising chelating agents, metal ion salts, gelling agents or a buffer, antimicrobials, antibiofilm agents and a pH adjuster or a buffer for the prevention and treatment of wound infections and food-borne diseases involving bacterial biofilms are disclosed. The anti-infective properties of a composition include reduction or killing of anaerobic / aerobic / facultative gram-negative and gram-positive wound infection associated bacteria occurring in polymicrobial biofilms. The composition may be in the form of lotion, cream, ointment, dressing, bandage, rinse, soak, gel, spray, or other suitable forms, including certain devices. Additionally, the invention offers an efficient method of delivering the formulated composition containing one or two chelating agents or chelating agents alone or in combination with a metal ion salt using either a nanoparticle or other efficient delivery systems.
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Signal peptides, nucleic acid molecules and methods for treatment of caries
Peptide analogues of S. mutans CSP peptide which inhibit biofilm formation, uses thereof in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions, antimicrobial compositions and uses thereof in the treatment and prevention of infections caused by biofilm forming bacteria, dental plaque formation, and conditions caused by dental plaque associated bacteria are provided.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO +1
Antimicrobial-antibiofilm compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9980497B2Enhance stability and efficacyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFood bornePolymicrobial biofilms
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Antimicrobial-antibiofilm compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20180015061A1Improve stabilityImprove efficacyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFood bornePolymicrobial biofilms
Compositions comprising chelating agents, metal ion salts, gelling agents or a buffer, antimicrobials, antibiofilm agents and a pH adjuster or a buffer for the prevention and treatment of wound infections and food-borne diseases involving bacterial biofilms are disclosed. The anti-infective properties of a composition include reduction or killing of anaerobic / aerobic / facultative gram-negative and gram-positive wound infection associated bacteria occurring in polymicrobial biofilms. The composition may be in the form of lotion, cream, ointment, dressing, bandage, rinse, soak, gel, spray, or other suitable forms, including certain devices. Additionally, the invention offers an efficient method of delivering the formulated composition containing one or two chelating agents or chelating agents alone or in combination with a metal ion salt using either a nanoparticle or other efficient delivery systems.
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Antimicrobial-antibiofilm compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10357470B2Enhance stability and efficacyAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsFood borneMicrobial agent
Compositions comprising chelating agents, metal ion salts, gelling agents or a buffer, antimicrobials, antibiofilm agents and a pH adjuster or a buffer for the prevention and treatment of wound infections and food-borne diseases involving bacterial biofilms are disclosed. The anti-infective properties of a composition include reduction or killing of anaerobic / aerobic / facultative gram-negative and gram-positive wound infection associated bacteria occurring in polymicrobial biofilms. The composition may be in the form of lotion, cream, ointment, dressing, bandage, rinse, soak, gel, spray, or other suitable forms, including certain devices. Additionally, the invention offers an efficient method of delivering the formulated composition containing one or two chelating agents or chelating agents alone or in combination with a metal ion salt using either a nanoparticle or other efficient delivery systems.
Owner:KANE BIOTECH
Chrysophaentin analogs that inhibit FtsZ protein
InactiveCN103649028AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationBiochemistryResistant strain
Embodiments of antimicrobial chrysophaentin compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including the chrysophaentin compounds, methods for using the chrysophaentin compounds, and methods for synthesizing the chrysophaentin compounds are disclosed. Certain embodiments of the chrysophaentin compounds inhibit FtsZ protein, thereby inhibiting the growth of clinically relevant bacteria, including drug-resistant strains.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Compositions and methods for detecting bv-associated bacterial nucleic acid
ActiveUS20140065617A1Opens up structureStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacterial vaginosisOligomer
Disclosed are nucleic acid oligomers, including amplification oligomers, capture probes, and detection probes, for detection of a 16S rRNA or its encoding gene from bacterial species associated with bacterial vaginosis. Also disclosed are methods of specific nucleic acid amplification and detection using the disclosed oligomers, as well as corresponding reaction mixtures and kits.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Field separation method for tomicus piniperda-associated bacteria
The invention discloses a field separation method for tomicus piniperda-associated bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: determining a tomicus piniperda invasion hole on a suffered pine tree in a forest, peeling off the surface bark of the mother gallery of tomicus piniperda pests along the direction of the mother gallery of the tomicus piniperda pests by taking the invasion hole as an origin, so as to expose the phloem tissues of the eaten mother gallery of the tomicus piniperda, if larvae galleries are already formed at the both sides of the mother gallery, exposing the larvae galleries, inspecting and confirming whether the spores, hyphae, perithecia and blue-stain phloem tissues of tomicus piniperda-associated bacteria exist in the various eaten galleries of the tomicus piniperda, and adopting corresponding separation measures for the tomicus piniperda-associated bacteria according to the growth and development progresses and the blue-stain phloem tissue conditions of the tomicus piniperda-associated bacteria. The method disclosed by the invention integrates field sampling with laboratory strain separation, and is simple in steps and convenient to operate; the separation obtaining success rate of the tomicus piniperda-associated bacteria is high; the many links of bringing the wood blocks infected by the associated bacteria or the phloems with galleries, and the blue-stain tissues back to a laboratory at first, and then separating are effectively simplified, the separation time for the associated bacteria is saved, the separation is accurate, and the separation efficiency is increased.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
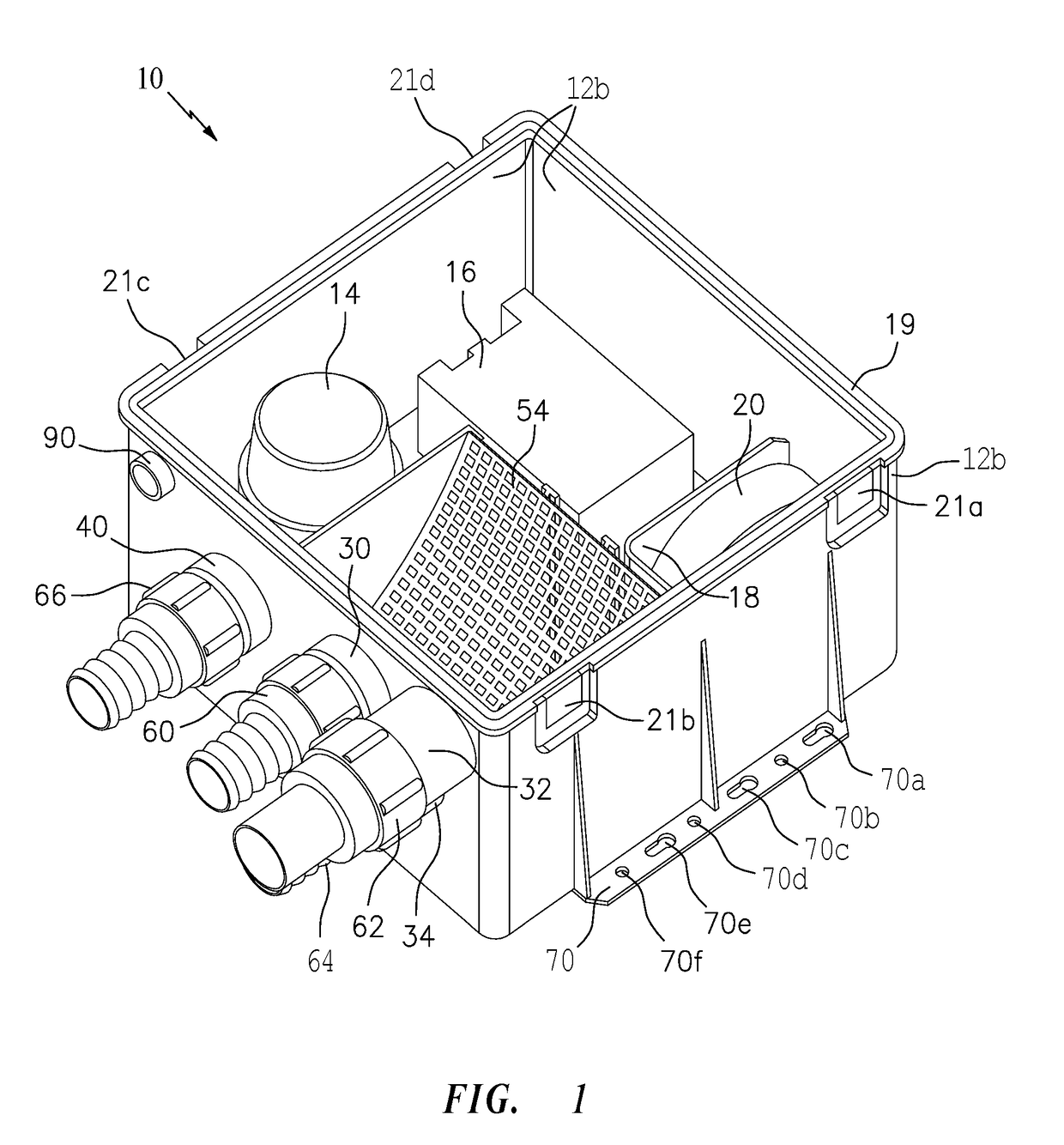
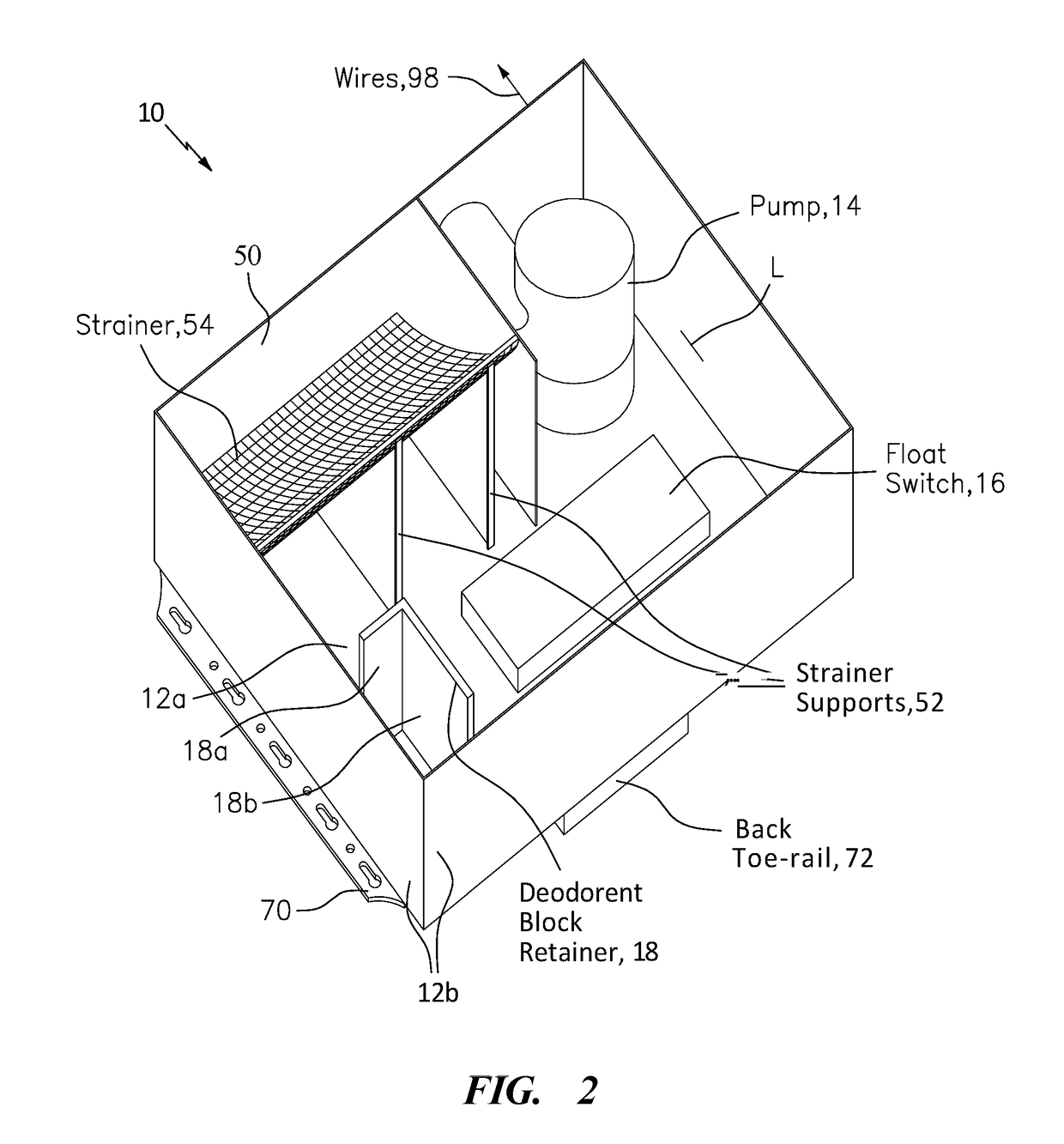
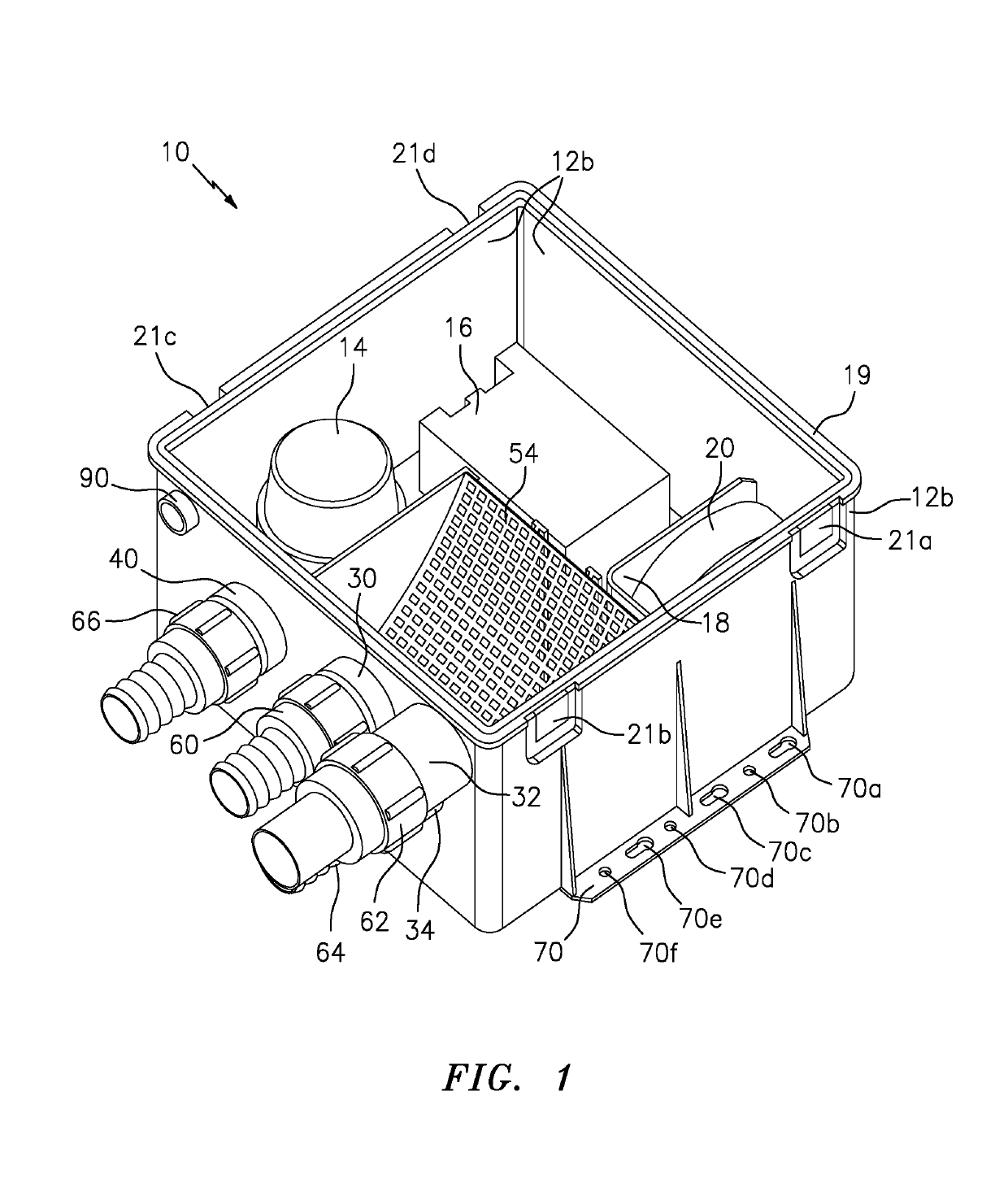
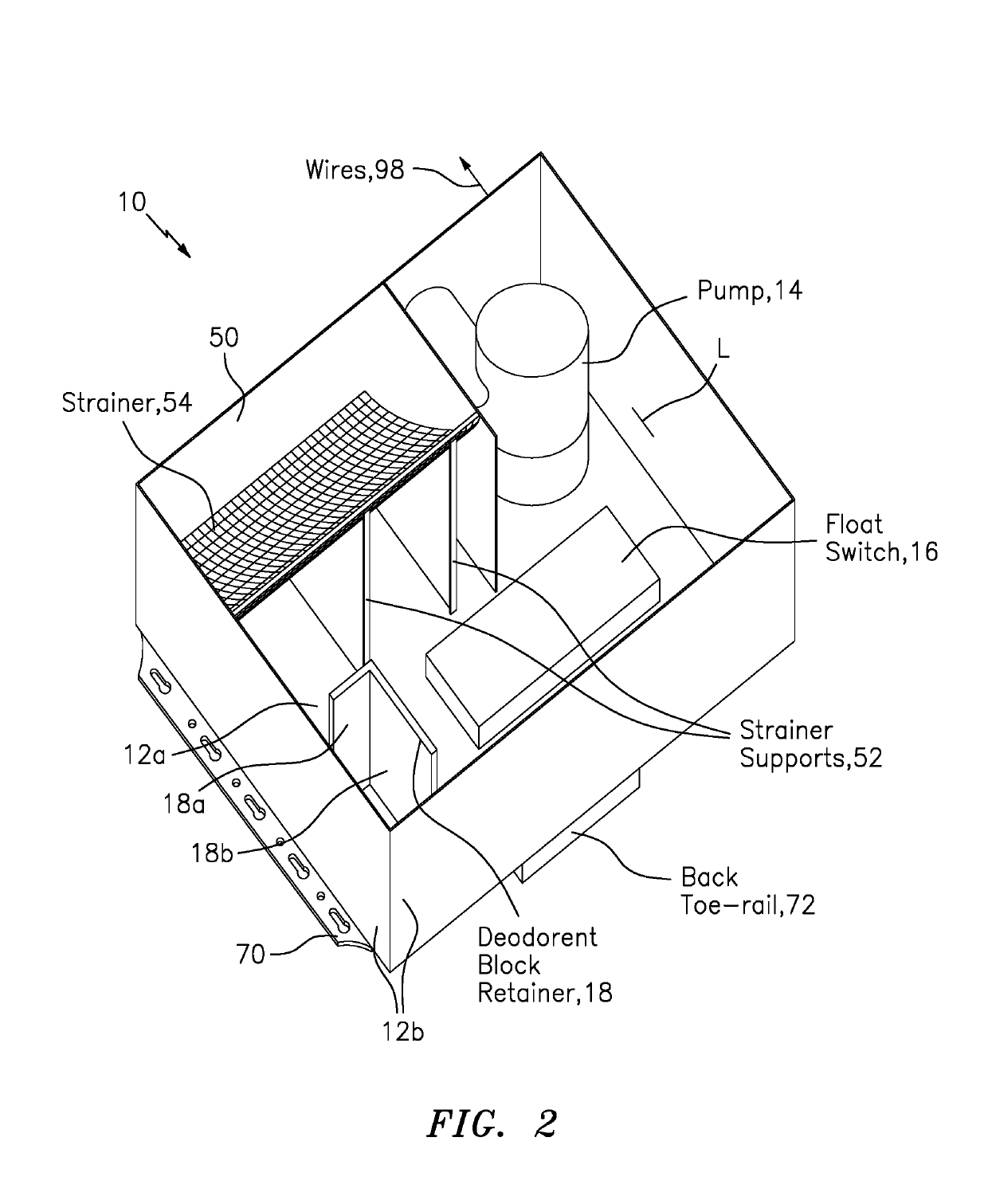
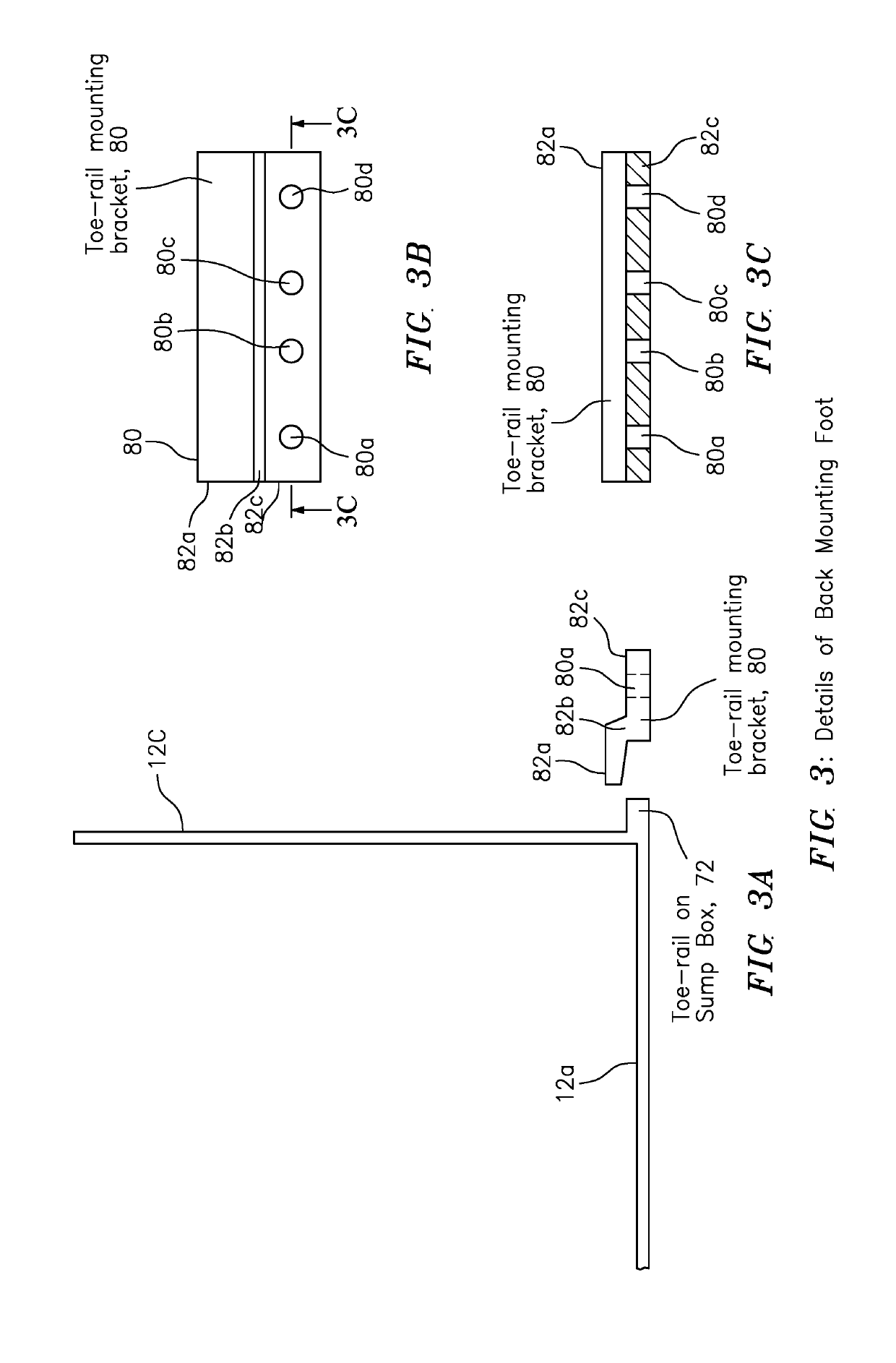
Shower Drain Box
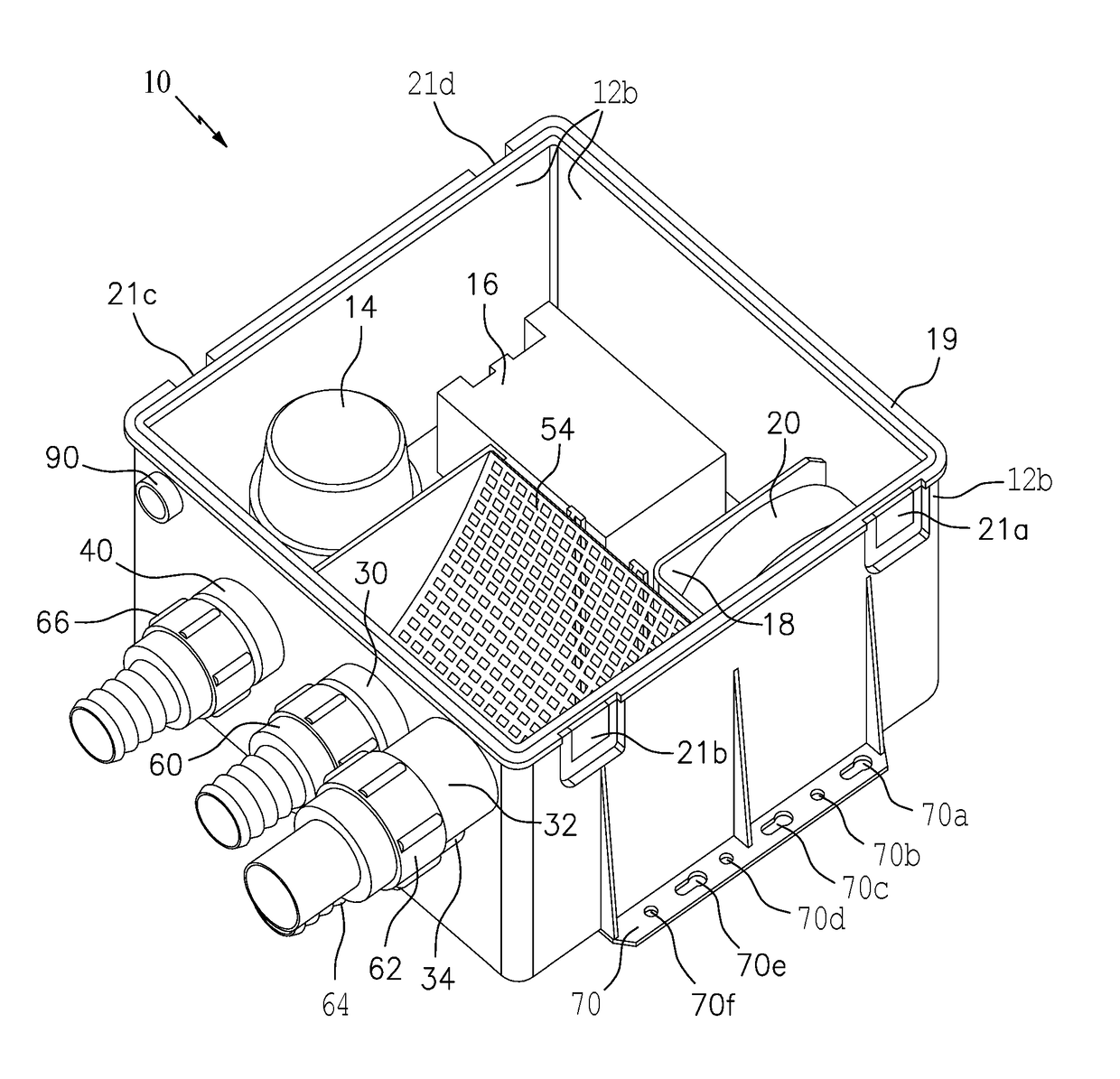
A drain or sump box features a combination of a housing, a pump, a float switch and a deodorant bar retainer. The housing may include a housing floor and a wall structure attached thereto and configured to receive and contain waste water. The pump is arranged in the housing to respond to signaling for pumping the waste water from the housing. The float switch is arranged in the housing to sense the level of the waste water and provide the signaling to turn the pump on when the waste water exceeds a certain level. The deodorant bar retainer is arranged in the housing in the housing to receive and retain a deodorant bar for preventing, reducing or masking waste water odor and associated bacteria causing the waste water odor.
Owner:FLOW CONTROL LLC
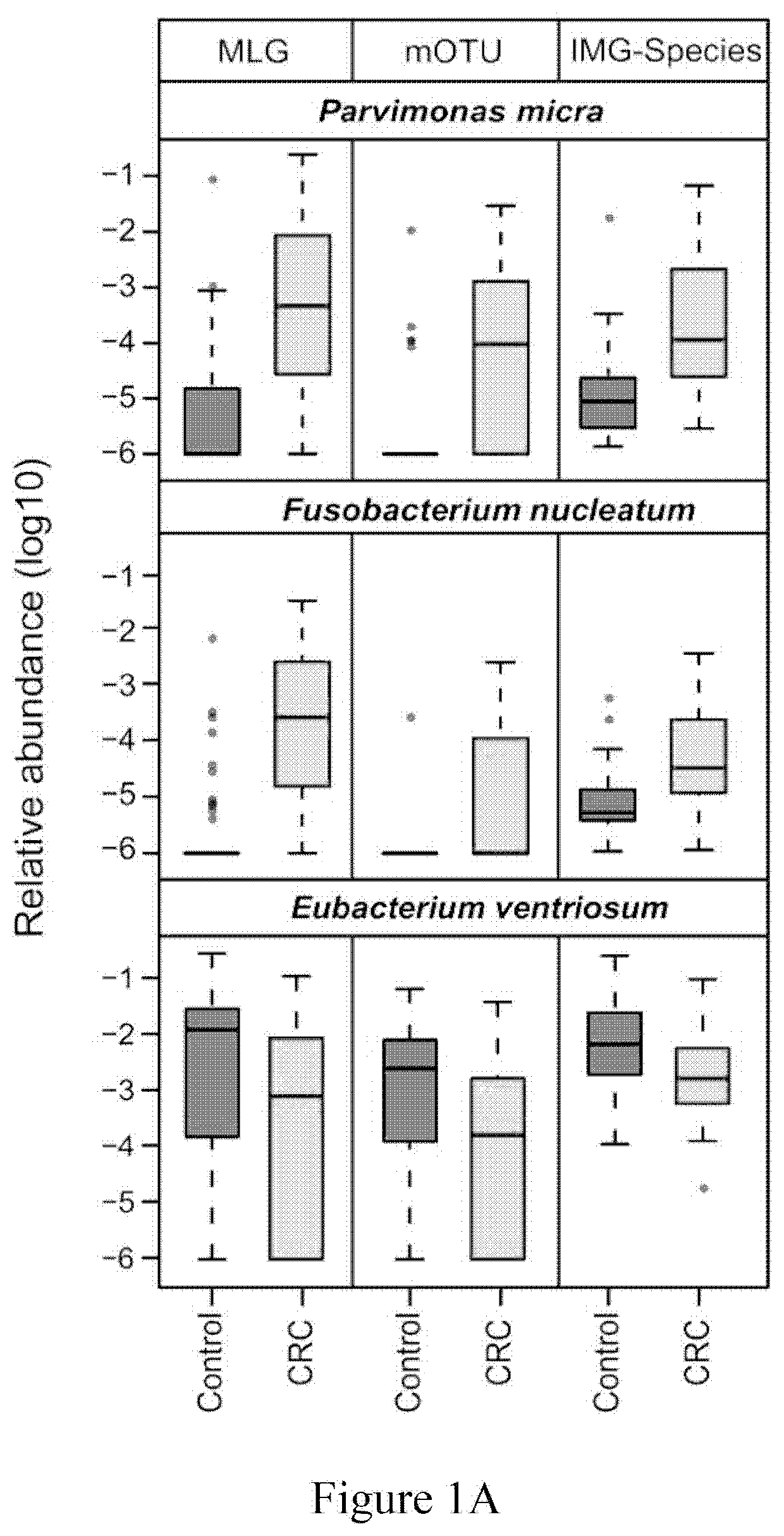
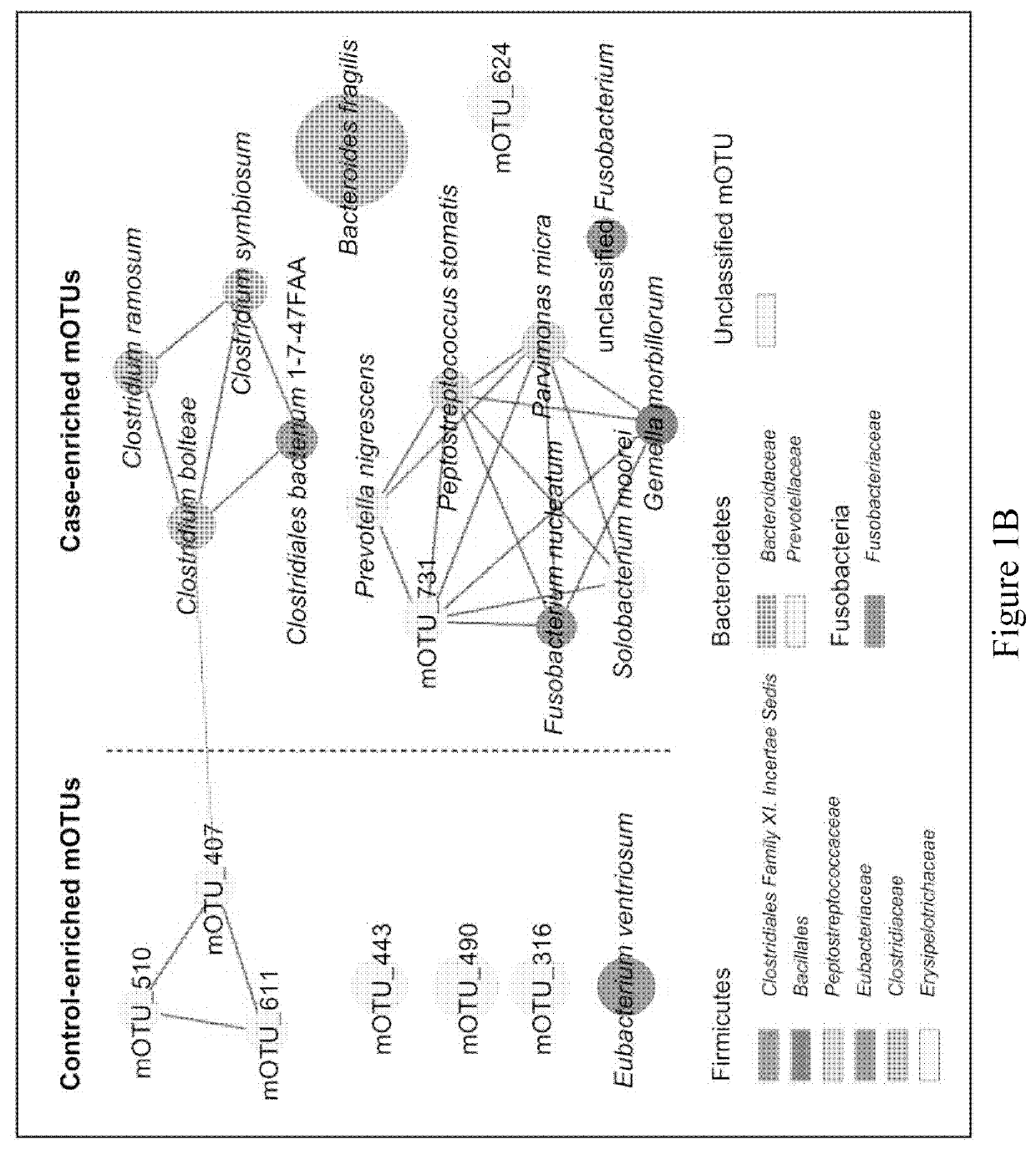
Fecal bacterial markers for colorectal cancer
ActiveUS20200002769A1Reduce development riskIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisColon rectal cancerFaecal bacteria
Provided is a non-invasive method for diagnosing colorectal cancer in a subject by detecting enrichment or reduction of certain bacterial species. A kit and device useful for such methods are also provided. In addition, a method for reducing the risk of colon cancer by regulating the pertinent bacterial species in human colon is also provided.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Compositions and methods for detecting BV-associated bacterial nucleic acid
ActiveUS9663829B2Opens up structureStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsBacterial vaginosisOligomer
Disclosed are nucleic acid oligomers, including amplification oligomers, capture probes, and detection probes, for detection of a 16S rRNA or its encoding gene from bacterial species associated with bacterial vaginosis. Also disclosed are methods of specific nucleic acid amplification and detection using the disclosed oligomers, as well as corresponding reaction mixtures and kits.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Hydrophobic self-cleaning resin slurry, hydrophobic self-cleaning resin dental material and application of resin slurry and resin dental material
ActiveCN113773442AGood biocompatibilityAvoid stickingImpression capsDentistry preparationsPolymer scienceMeth-
The invention provides hydrophobic self-cleaning resin slurry, a hydrophobic self-cleaning resin dental material and application of the resin slurry and resin dental material, and relates to the technical field of oral materials. The hydrophobic self-cleaning resin slurry provided by the invention is prepared from the following raw materials: a dimethacrylate monomer, triethylene glycol dimethacrylate, perfluoroalkyl acrylate, a diluent, nano silicon dioxide, gamma-methacryloyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane, camphorquinone and a light curing accelerator. The perfluoroalkyl acrylate is added, so that the surface energy of the material is reduced. By introducing nano silicon dioxide, the mechanical property of the resin is improved, the microscopic roughness of the resin is increased, a lotus-leaf-like hydrophobic micro-nano hierarchical structure is constructed, the hydrophobic surface of the micro-nano structure can retain air, an air layer is formed on the surface of the material, and the contact area with protein and bacteria is reduced. Therefore, the adhesion of related bacteria in the oral cavity and the formation of bacterial biofilms are inhibited, and the material has excellent self-cleaning biological decontamination performance.
Owner:陕西龙麟纳纤材料科技有限公司
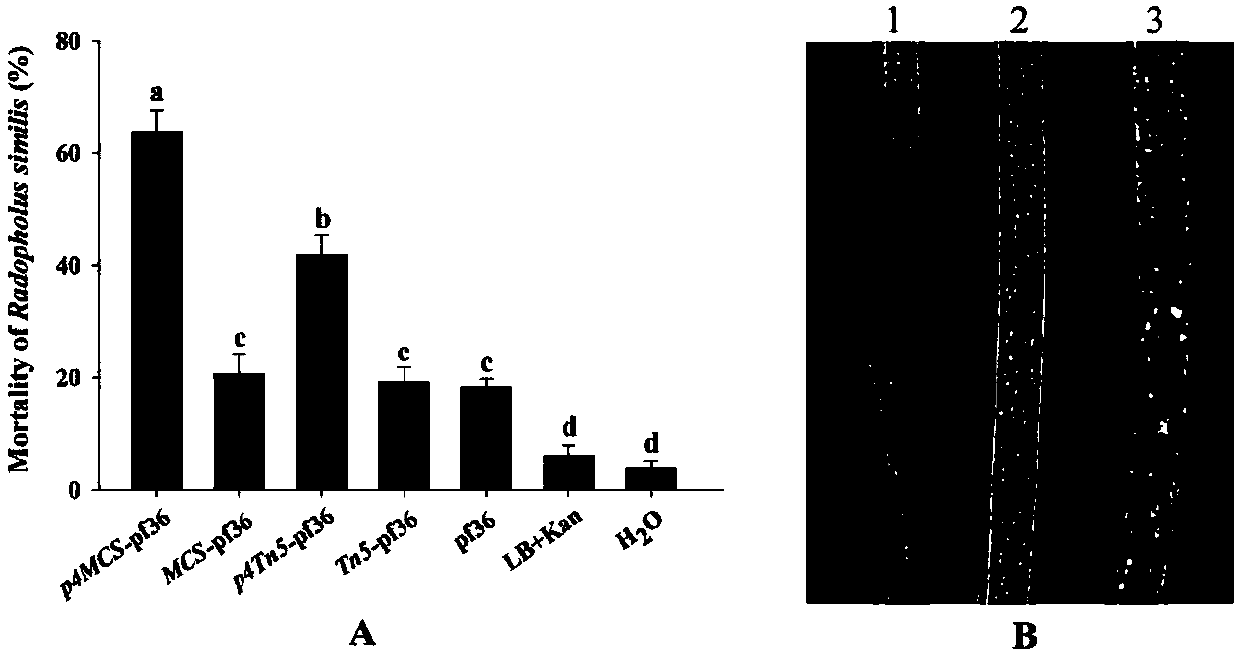
Radopholus-similis control method through mediation of radopholus-similis associated bacteria
ActiveCN108018305AGood genetic stabilityGood prevention and control effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesPlant nematode
The invention discloses a radopholus-similis control method through mediation of radopholus-similis associated bacteria. A method for establishing radopholus-similis biocontrol engineering bacteria mediated by the associated bacteria is provided, wherein coding genes of biological enzyme with the nematocidal activity are transformed into the radopholus-similis associated bacteria, and the engineering bacteria are obtained after establishing; then radopholus similis is controlled through the engineering bacteria, and the aim that the nematocidal protease is mediated and expressed through the associated bacteria to control the radopholus similis is achieved. The genetic-modification pseudomonas fluorescens engineering bacteria obtained with the radopholus-similis control method are good in genetic stability, remarkable in control effect of the radopholus similis and low in commercialized production difficulty; two biocontrol factors of living bacteria and thallus secondary metabolites are effectively combined, the continuous self-propagation expanding and automatic diffusion characteristics of the living bacteria and the activities when the radopholus similis is efficiently killed through metabolites are fully developed, and the radopholus-similis control method is a new method and a new path which is safe, efficient, stable and capable of sustainably controlling plant nematode parasites.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Multiplex detection of vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis
Methods and compositions for detection of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis (BV) are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, the presence or absence of VVC-associated Candida, Trichomonas vaginalis, and a plurality of BV-related bacteria in a sample is determined using multiplex nucleic acid-based testing methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Shower drain box
A drain or sump box features a combination of a housing, a pump, a float switch and a deodorant bar retainer. The housing may include a housing floor and a wall structure attached thereto and configured to receive and contain waste water. The pump is arranged in the housing to respond to signaling for pumping the waste water from the housing. The float switch is arranged in the housing to sense the level of the waste water and provide the signaling to turn the pump on when the waste water exceeds a certain level. The deodorant bar retainer is arranged in the housing in the housing to receive and retain a deodorant bar for preventing, reducing or masking waste water odor and associated bacteria causing the waste water odor.
Owner:FLOW CONTROL LLC
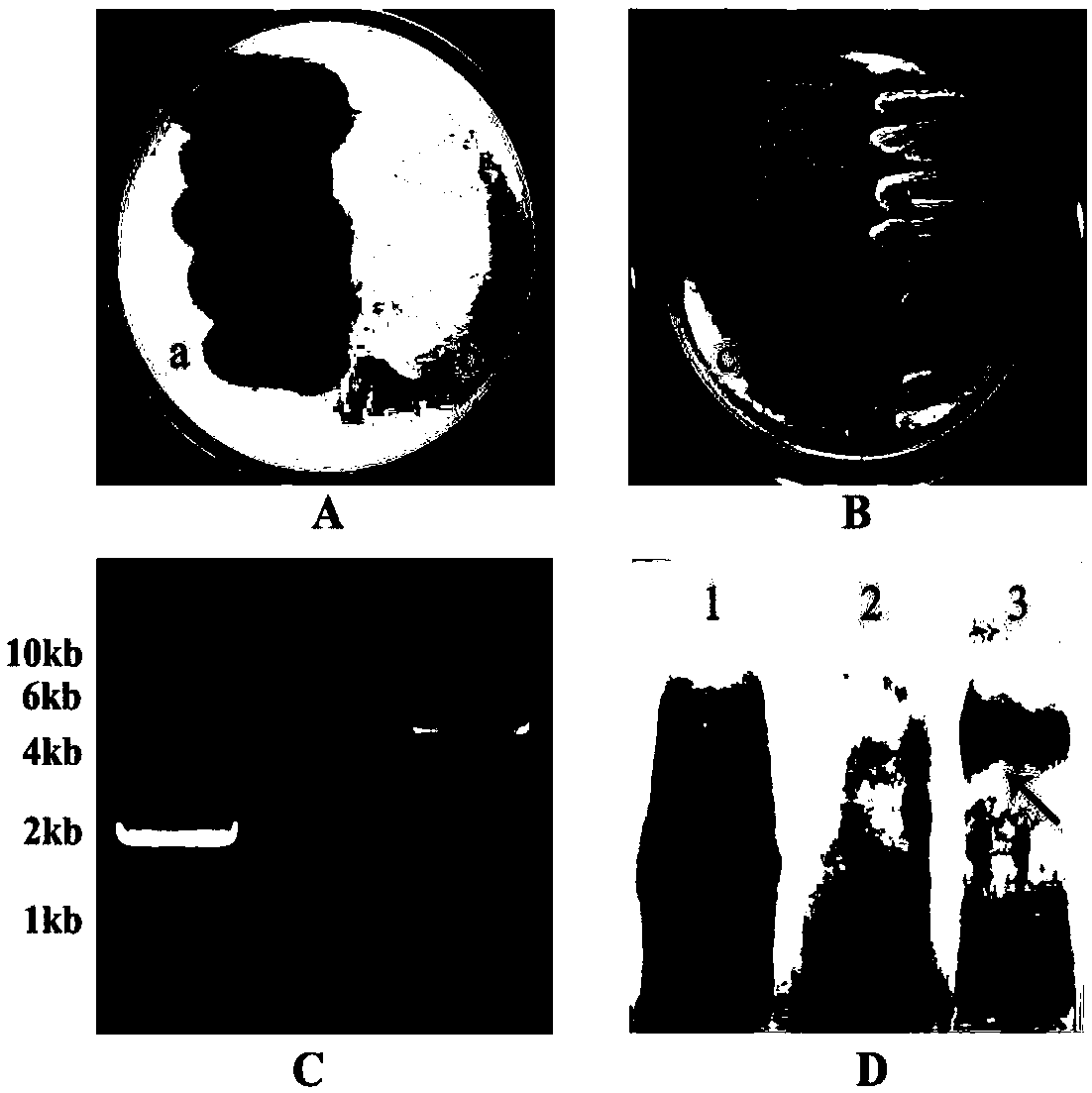
Radopholus similis associated bacteria with potential of genetic transformation
ActiveCN108018232AStable companionshipStrong companionshipBiocideBacteriaPlant nematodeRadopholus similis
The invention discloses radopholus similis associated bacteria with the potential of genetic transformation. The associated bacteria are Pseudomonas fluorescens (pf36), and are preserved in GuangdongMicrobial Culture Collection Center on November 8, 2017, and the preservation number is GDMCC No:60278. One dominant associated bacterium is separated and screened from multiple populations of radopholus similis, and the dominant associated bacterium is the Pseudomonas fluorescens (pf36) which has the very stable associated relationship with the radopholus similis, a genetically modified target bacterium is provided for mediated expression of nematicidal protease genes, and due to the fact that the associated relationship of the target bacterium and the radopholus similis is improved to express the nematicidal protease genes, the target bacterium can be used for biological control over the radopholus similis, and the associated bacteria are safe to crops. Accordingly, a new idea and methodare provided for control over the plant nematode, that is to say, biological control over nematode is achieved by means of nematode associated bacterium mediated nematicidal protease genes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Primer and probe combination and kit for detecting 12 kinds of children digestive tract infection related bacteria
ActiveCN112501330AAlleviating Technical Problems of Inadequate Diagnostic ResearchHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidalesMicrobiology
The invention relates to a primer group, a probe group and a kit containing the primer group and the probe group, which are used for synchronously detecting various common digestive tract infection related bacteria of children and can be used for simultaneously detecting various common bacteria causing digestive system infection by one-time reaction. The kit is the most comprehensive children digestive tract bacterial infection detection method at present, is high in efficiency and specificity, and provides an auxiliary diagnosis basis for clinical examination. According to the technical scheme, the technical problem that in the prior art, diagnosis and research on bacterial pathogenic bacteria related to children digestive tract infection are still insufficient can be solved.
Owner:爱科睿特生物医疗科技(南京)有限公司
Antibacterial fly maggot protein and preparing method thereof
PendingCN109874939AConsiderable enzymolysisEnhance synergistic symbiosisFood processingAnimal feeding stuffMaggotMixed materials
The invention discloses an antibacterial fly maggot protein and a preparing method thereof. The preparing method comprises the following steps of mixing a mixed bacterial liquid and a culture base material to obtain a mixed material; putting young project fly maggots into the mixed material, and conducting first-stage fermentation, second-stage fermentation and third-stage fermentation. By means of the technology, the powerful degradation capability of external digestion of the fly maggots can be fully utilized; meanwhile, the coordinated symbiosis effect of the fly maggots and associated bacteria thereof is also enhanced, so that the enzymolysis effect of a double-fermentation device on the material is more considerable. The antibacterial fly maggot protein can be used as a conventional raw protein feed material in porcine complete feeds. The antibacterial fly maggot protein can provide protein nutrients, can effectively control the diarrhea rate of piglets and can also be used for replacing zinc oxide in the porcine feeds.
Owner:JIANGMEN XINTAI BIOLOGICAL PROTEINS
Nutrition-enhanced culture medium for preparing 2-KGA through fermentation and method thereof for preparing 2-KGA
InactiveCN101845475BPromote growthMeet or exceed concomitant effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention relates to a culture medium in the technical fields of fermentation engineering and biology, in particular to a nutrition-enhanced culture medium for preparing 2-KGA through fermentation, and the nutrition-enhanced culture medium comprises a conventional culture medium and a nutrition enhancer, wherein sorbitol or sorbose is used as a substrate of the conventional culture medium. Meanwhile, the invention also relates to a method for preparing the 2-KGA by applying the enhanced culture medium. The nutrition-enhanced culture medium can promote the growth of small bacteria, enablesthe small bacteria to be disengaged from the dependence on associated bacteria, establishes independent growth and provides a foundation for the improvement of a 2-KGA fermentation process.
Owner:仪宏
An associated bacterium of the banana borer nematode with potential for genetic modification
ActiveCN108018232BStable companionshipStrong companionshipBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPlant nematode
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Christine analogues that inhibit the FTSZ protein
InactiveCN103649028BOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationPharmaceutical drugMicrobiology
Embodiments of antimicrobial chrysophaentin compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including the chrysophaentin compounds, methods for using the chrysophaentin compounds, and methods for synthesizing the chrysophaentin compounds are disclosed. Certain embodiments of the chrysophaentin compounds inhibit FtsZ protein, thereby inhibiting the growth of clinically relevant bacteria, including drug-resistant strains.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Production method for collaborative increase and stabilization of multiple active substances of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN111587735AIncrease contentStable productionCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologySporocarp (fungi)
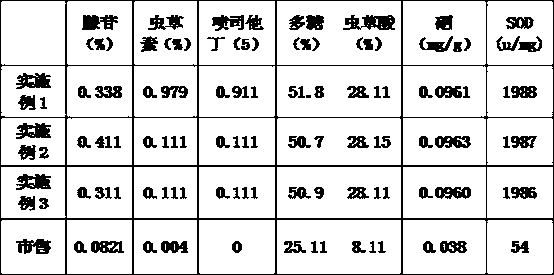
The invention discloses a production method for collaborative increase and stabilization of multiple active substances of cordyceps militaris and belongs to the technical field of production of fruiting bodies of edible medicinal fungi. The method comprises: (1) smashing and uniformly mixing rice, wheat and soybean meal, adding a nutrient solution and preparing a growth culture medium; (2) takingcordyceps militaris mother strains which have a conidial fructification structure of both an imbricate paecilomyces type and a capitate-gathering verticillium type on a same hypha as effective motherstrains, taking streptomycete mother strains as associated bacteria, performing inoculation in a liquid culture medium and obtaining effective composite liquid stains; (3) diluting and effective composite liquid strains and inoculating the strains in the growth culture medium for culture of 40-60 days; and (4) collecting fruiting bodies, spraying white liquor soaked with dry pine needles on surfaces of the fruiting bodies and performing drying. The method can promote collaborative increase of contents of the multiple active substances and stabilize production; in particular, contents of anti-cancer substances such as Pentostatin, polysaccharide, cordycepic acid and SOD enzyme can be increased obviously; and the method is applied to industrial generalization and application.
Owner:SHANXI WANHAIAO BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for improving production capacity of acid producing bacteria by adopting Vc two-step fermentation
InactiveCN106636231AImprove controllabilityIncrease productivityFermentationEnd stagesActive protein
The invention relates to the field of industrial biological fermentation, in particular to a method for improving production capacity of acid producing bacteria by adopting Vc two-step fermentation. The method comprises the steps as follows: associated bacteria are cultured independently in a seed culture medium to a stable end stage, and an active protein solution is prepared from an obtained culture solution through cell disruption; the fermentation medium containing the active protein solution is inoculated with a bacterial suspension of the acid producing bacteria, and a fermentation seed liquid is obtained through fermentation; the fermentation medium containing the active protein solution is inoculated with the fermentation seed liquid, the acid producing bacteria perform fermentation, biosynthesis of the sorbose is performed, and gulonic acid is obtained after fermentation. The method is easy to operate, high in stability, short in fermentation cycle, high in recovery rate, good in product quality, low in cost, green and environment-friendly.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial fertilizer
ActiveCN104844284BImprove physical and chemical propertiesPromote decompositionFungiBacteriaBacillus cereusGrowth promoting
The invention discloses a rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial fertilizer, which is composed of Bacillus cereus GF-1, Streptococcus thermophilus BLST, Bacillus jelly-like G3, Bacillus subtilis B7348, Bacillus subtilis N9- 1‑35, Lactobacillus plantarum LP and Candida utilis CUM, made from the culture obtained by aerobic mixed fermentation on the universal medium; the total number of living bacteria in the microbial fertilizer is greater than or equal to 2×1010CFU / g. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the rhizosphere growth-promoting water-soluble microbial fertilizer. The microbial fertilizer of the present invention improves the microenvironment of the root soil by adding plant growth-promoting bacteria and associated bacteria from external sources, and makes microbial fertilizer and applies it to the soil, which can effectively improve the soil environment, promote plant growth, and increase plant resistance .
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com