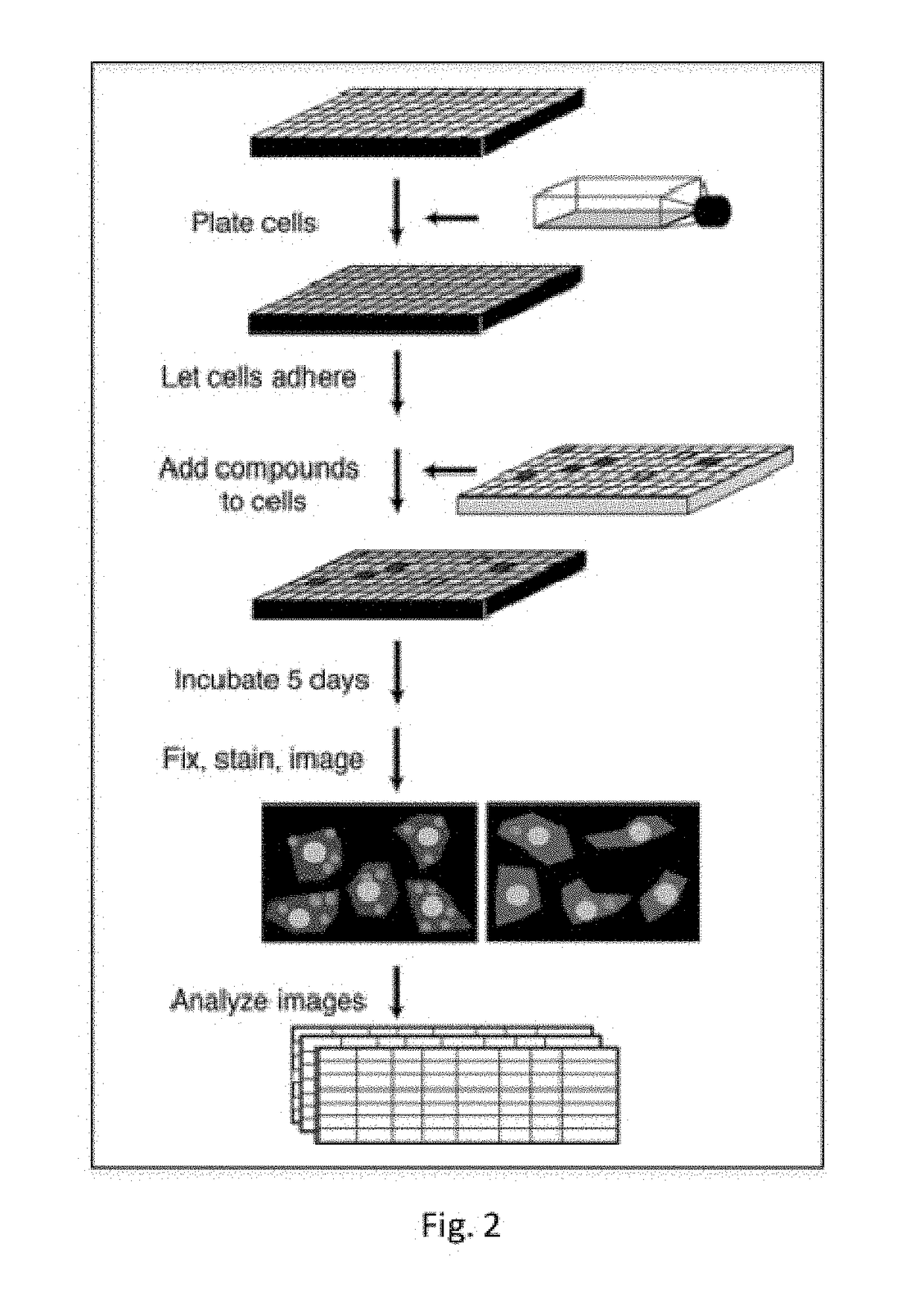
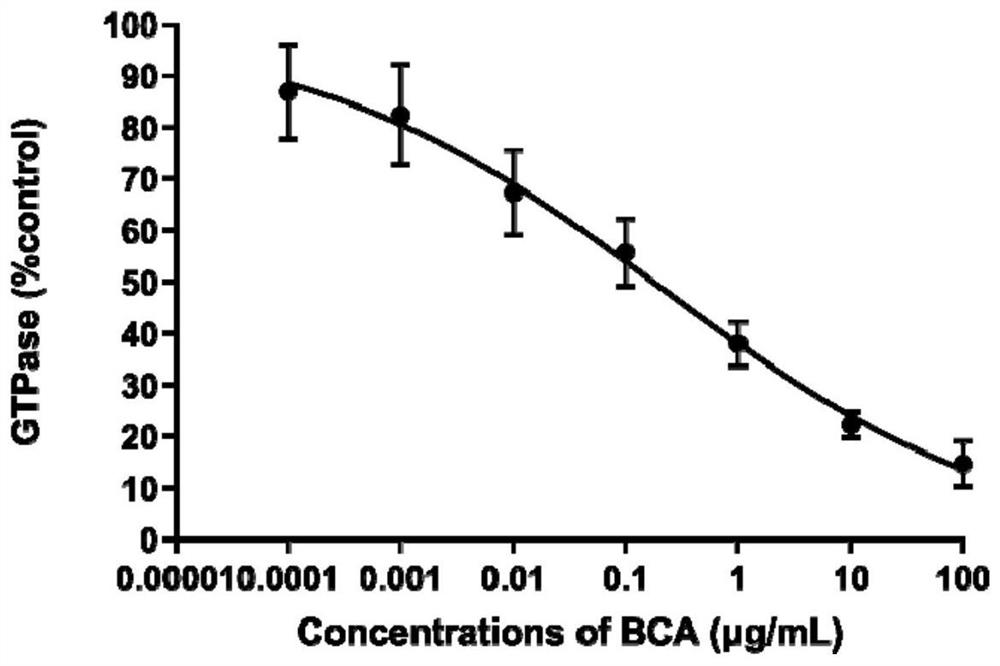
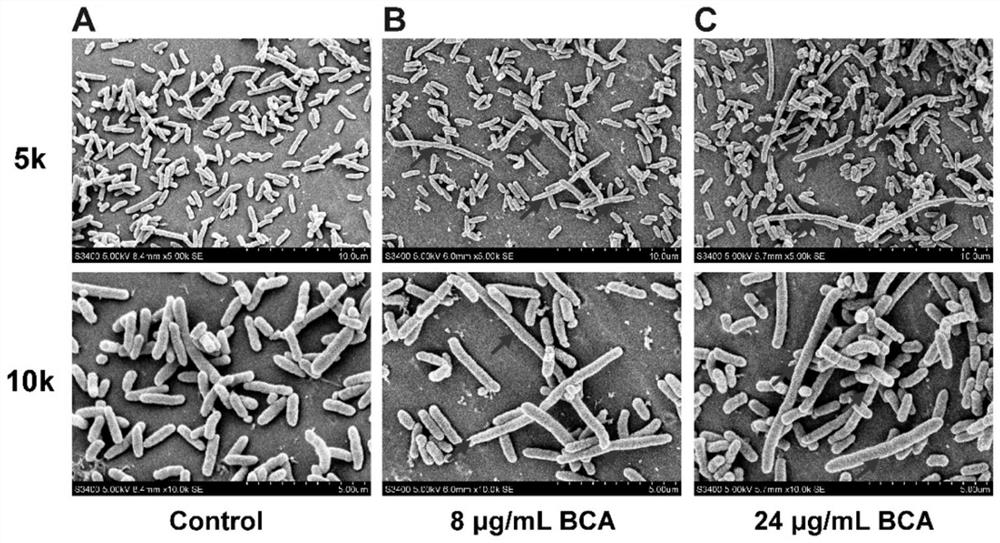
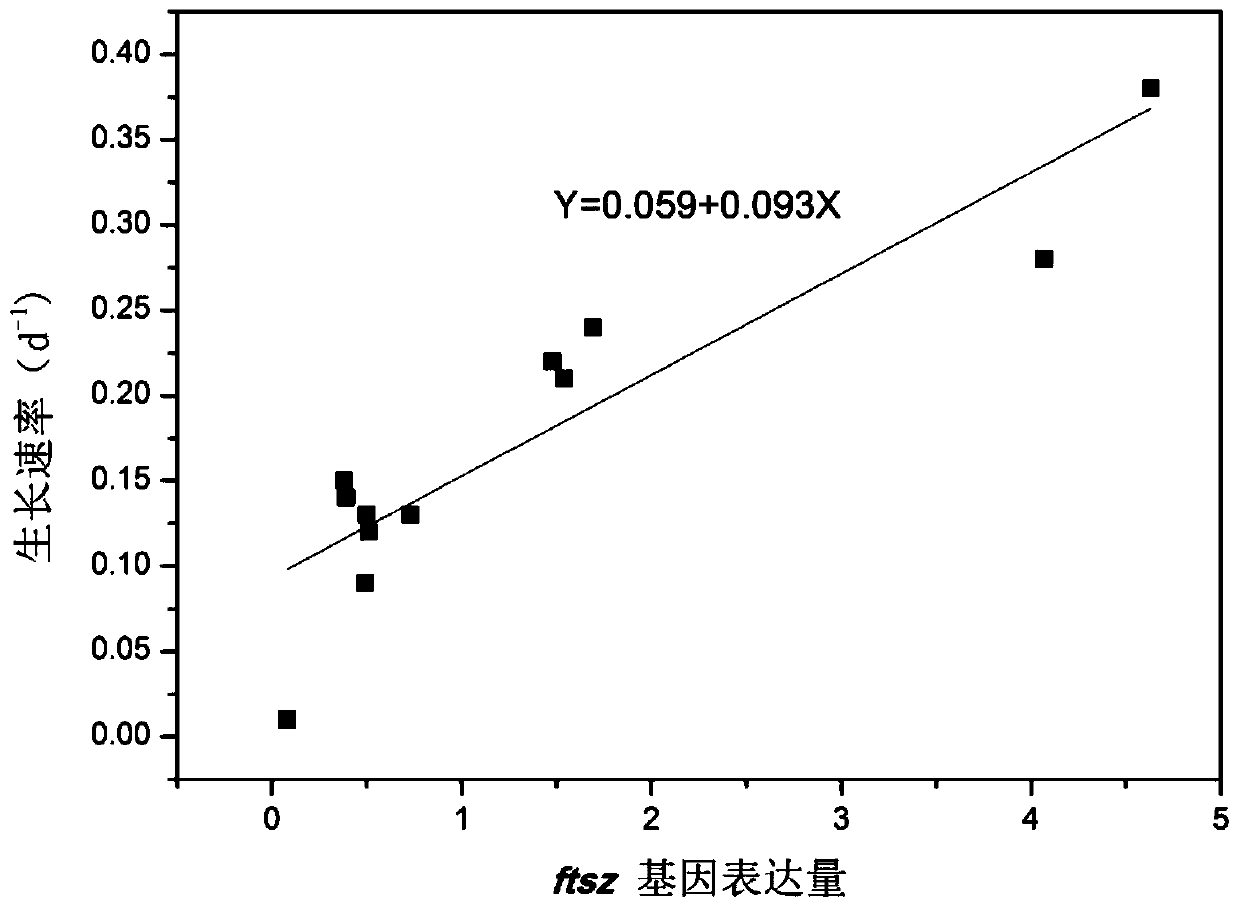
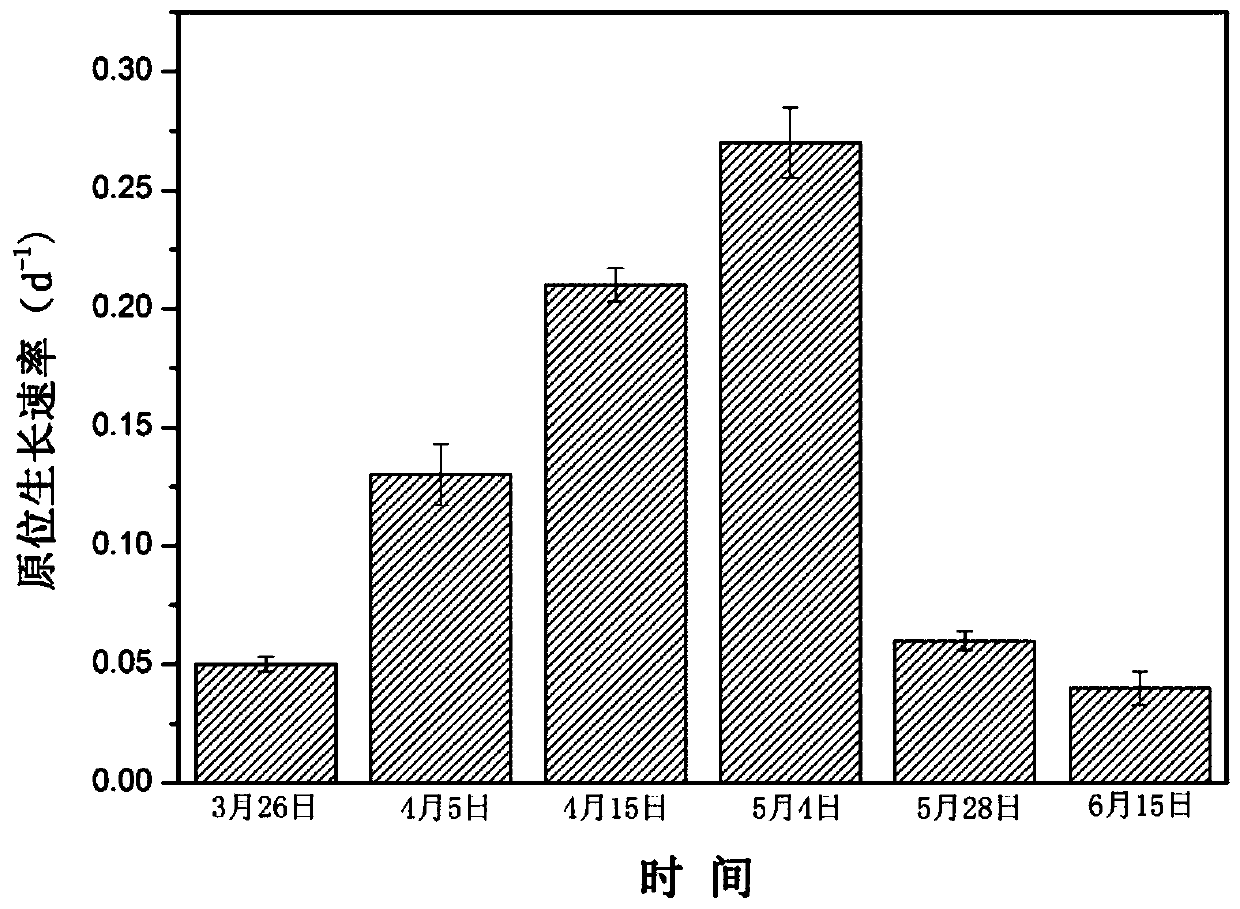
Patents
Literature
38 results about "FtsZ" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
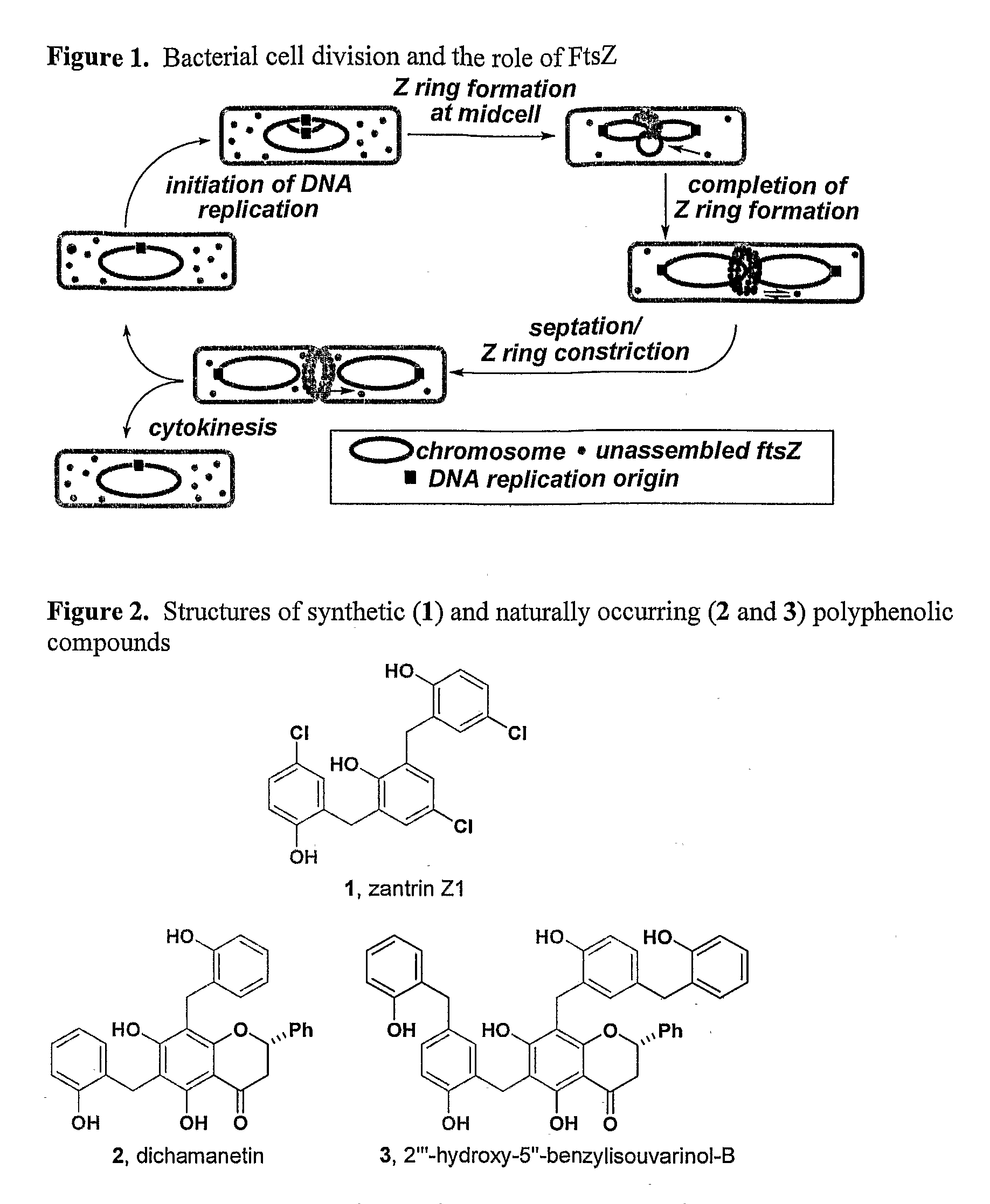
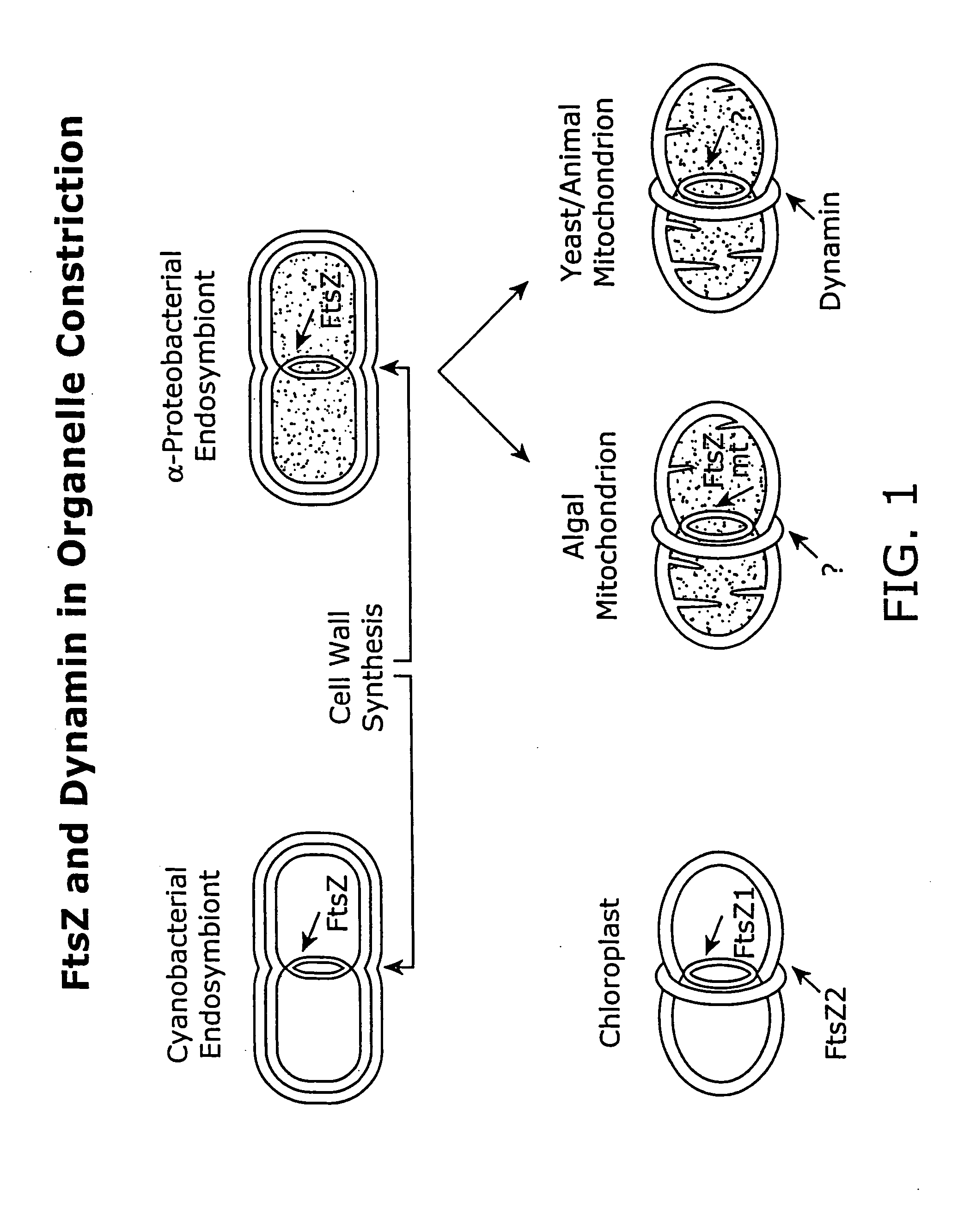
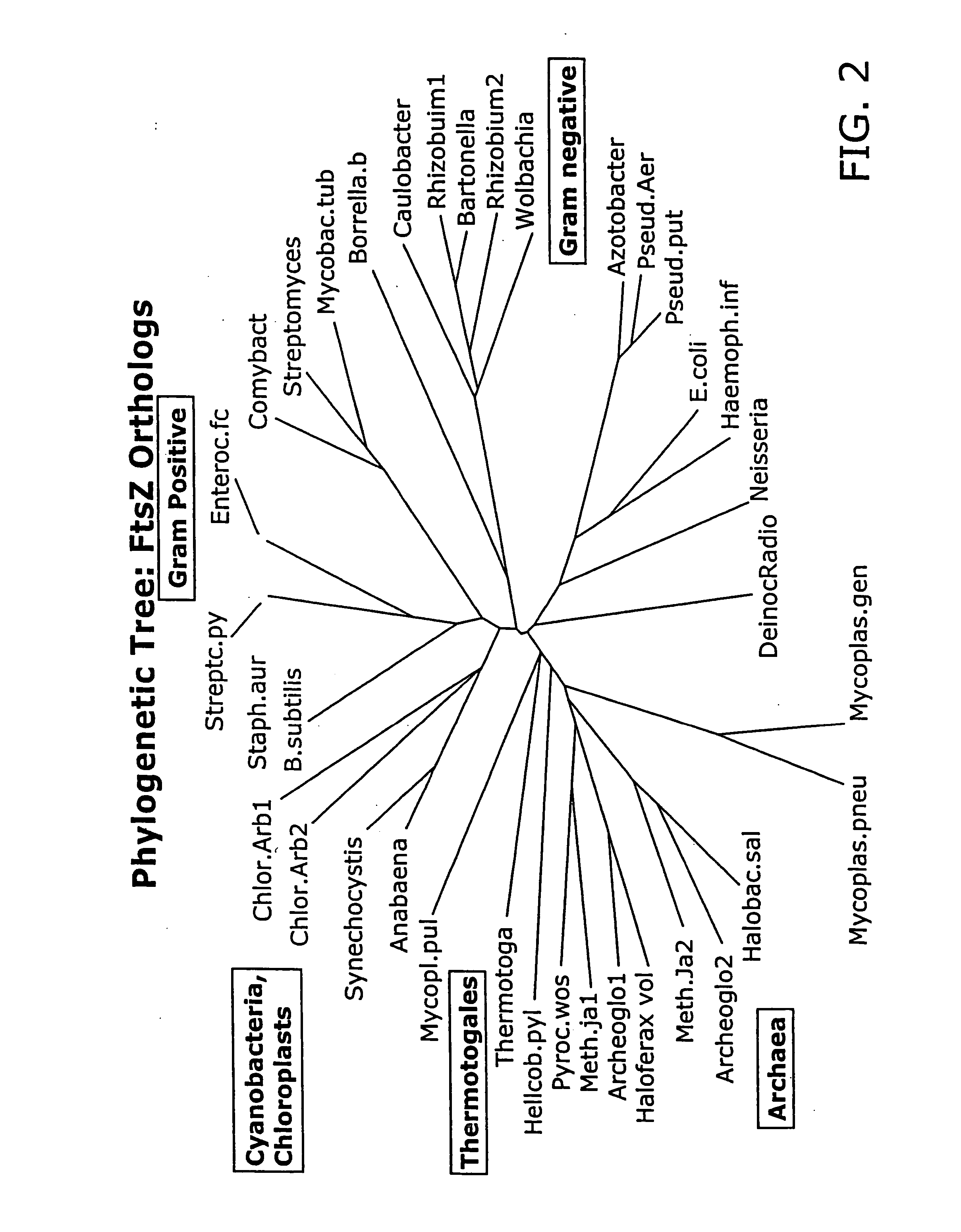
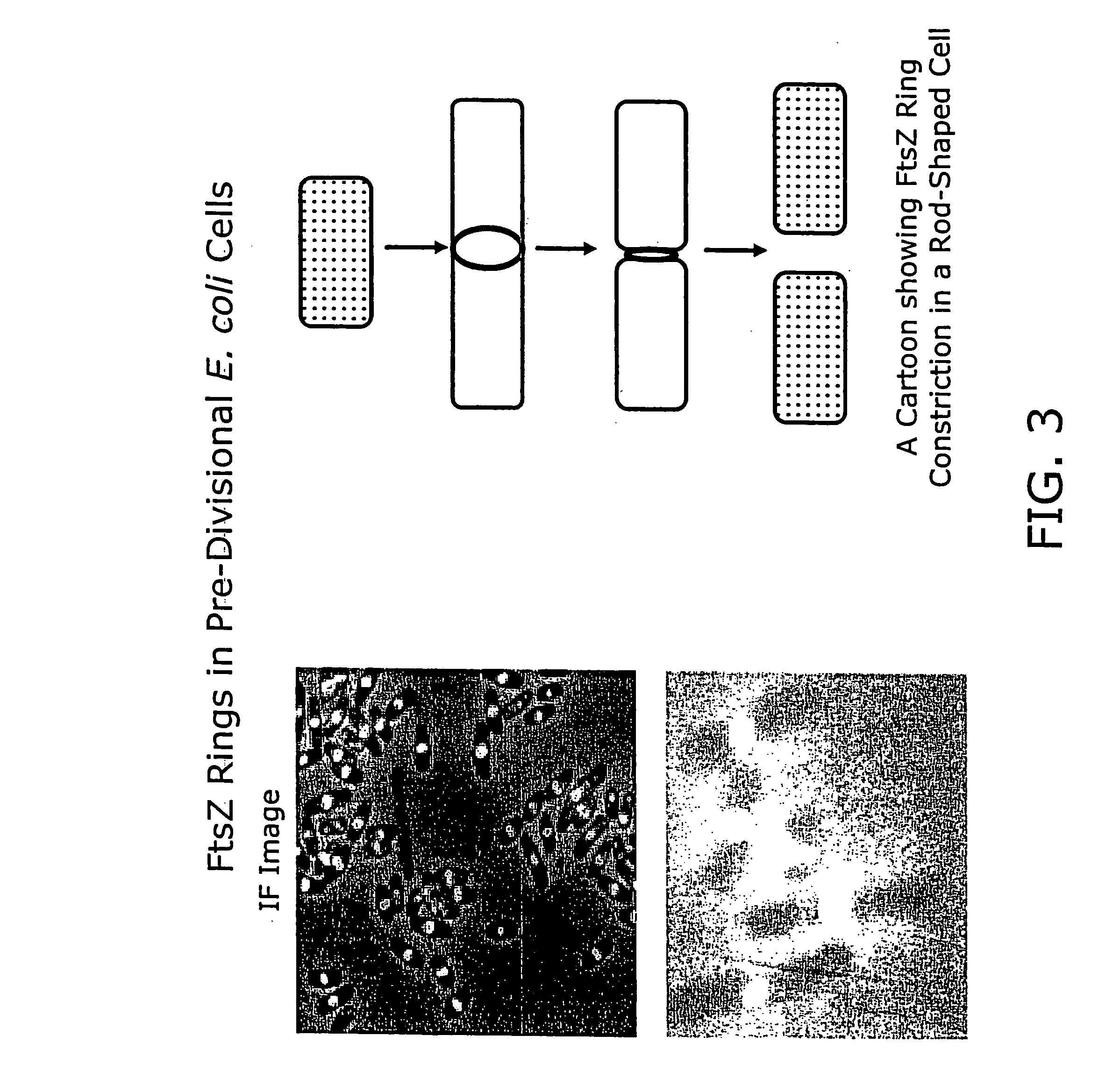
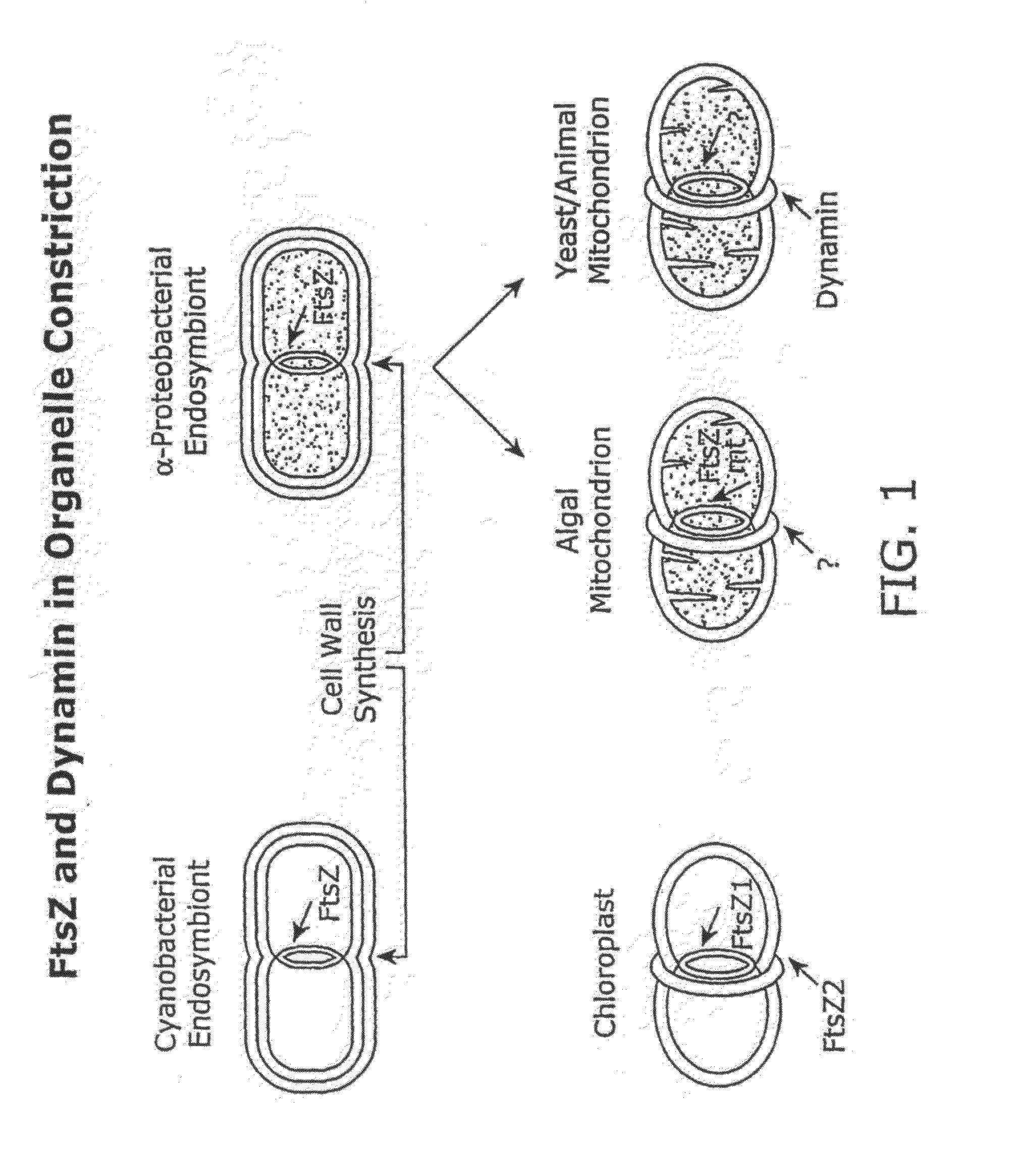
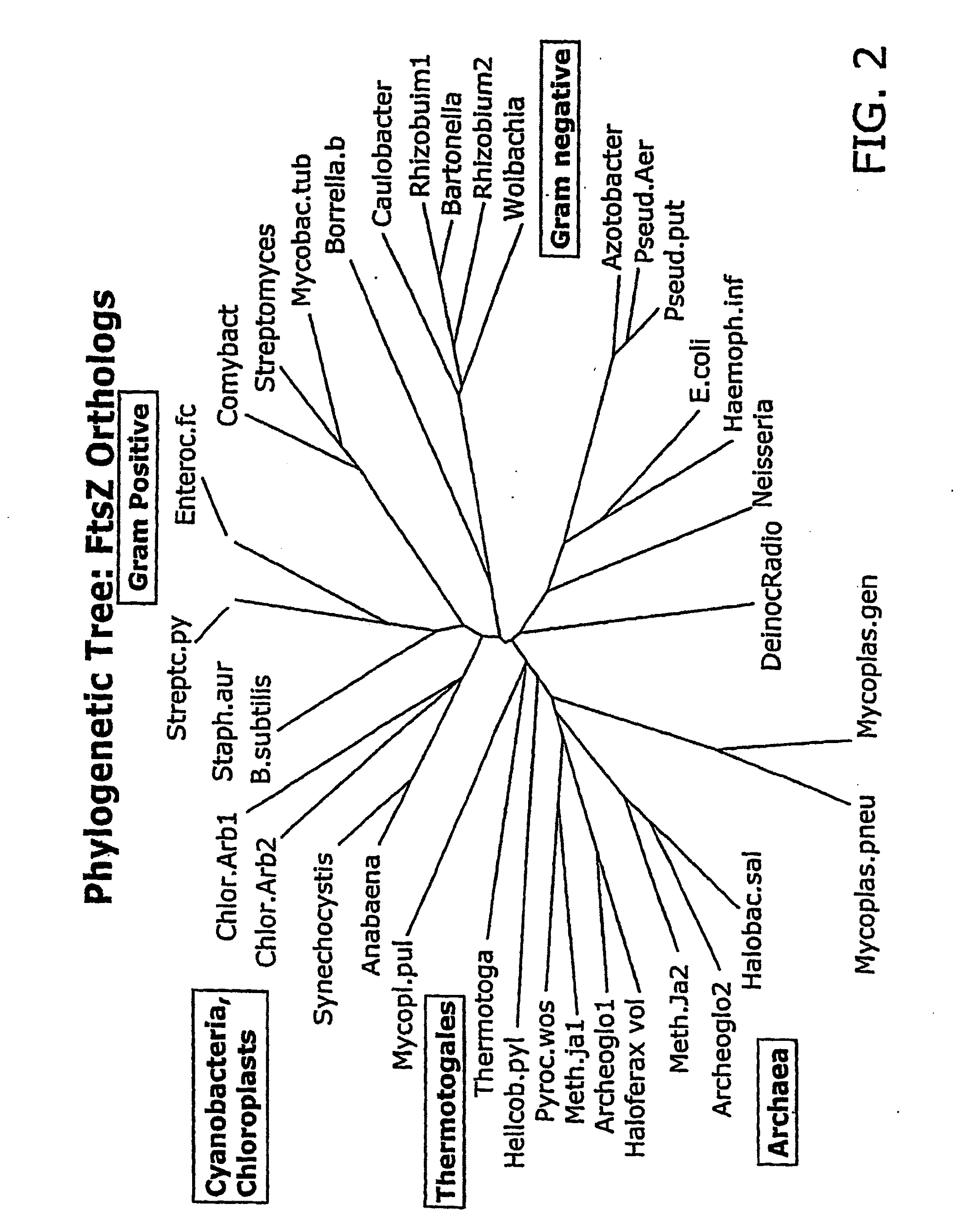
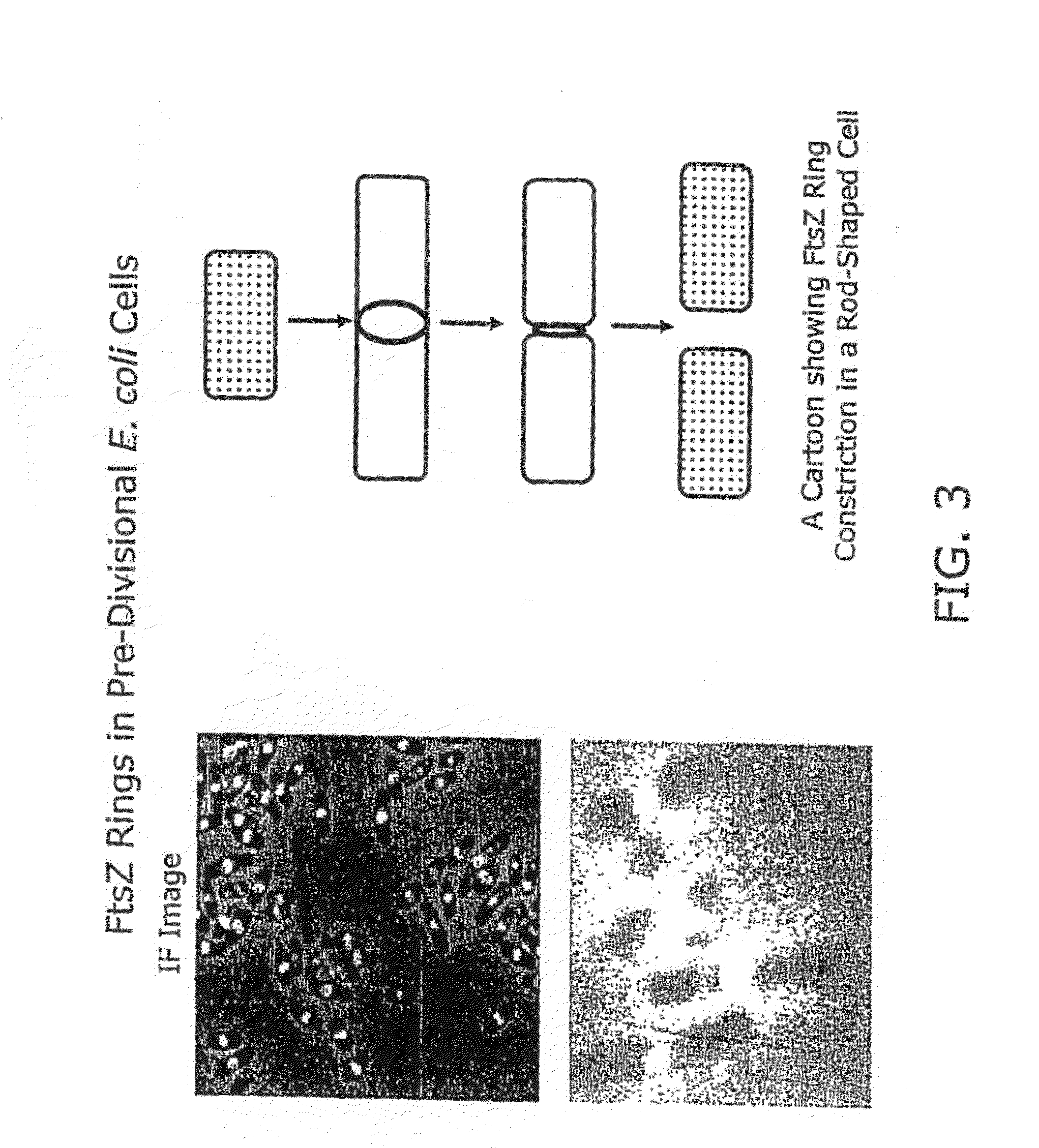
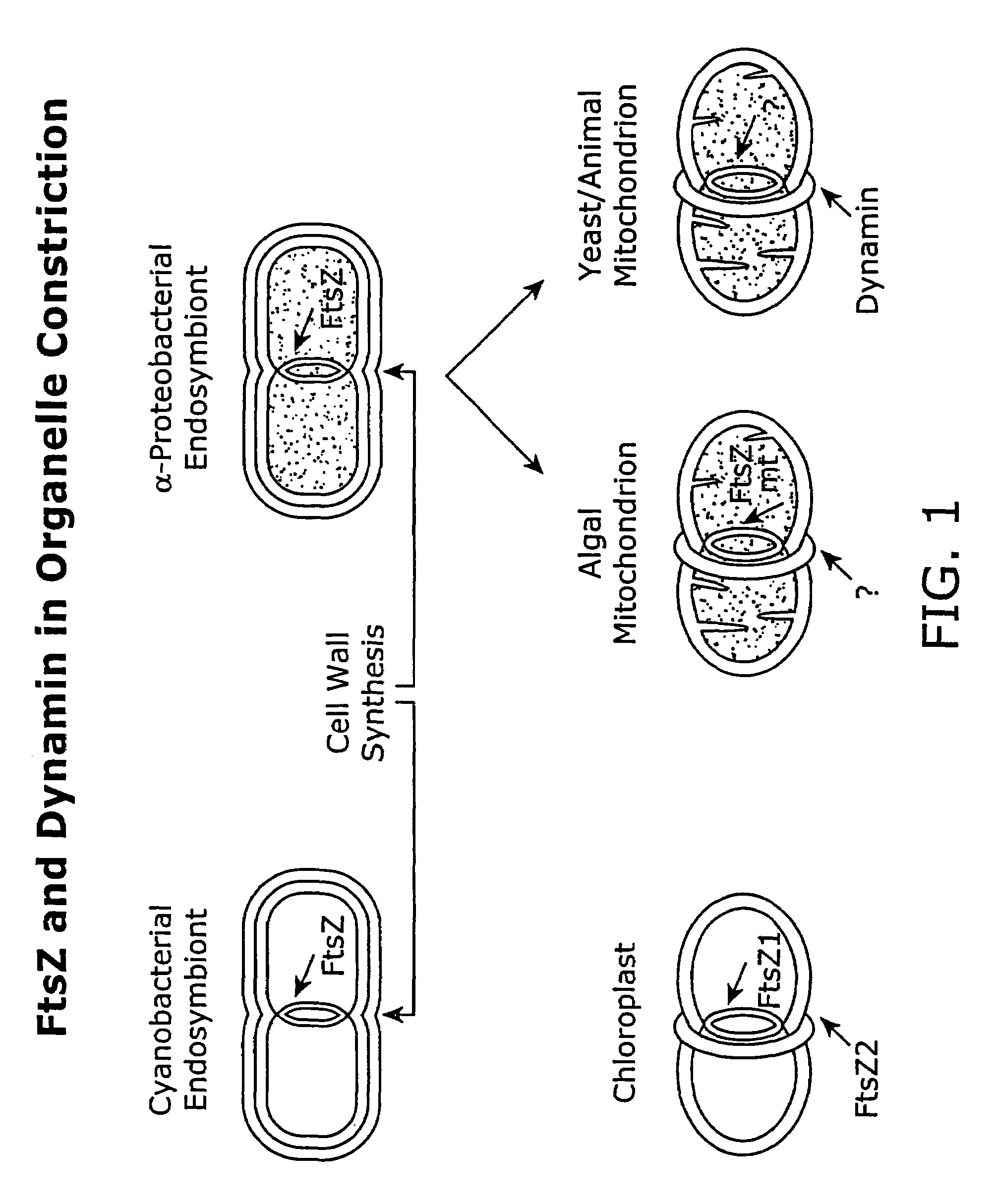
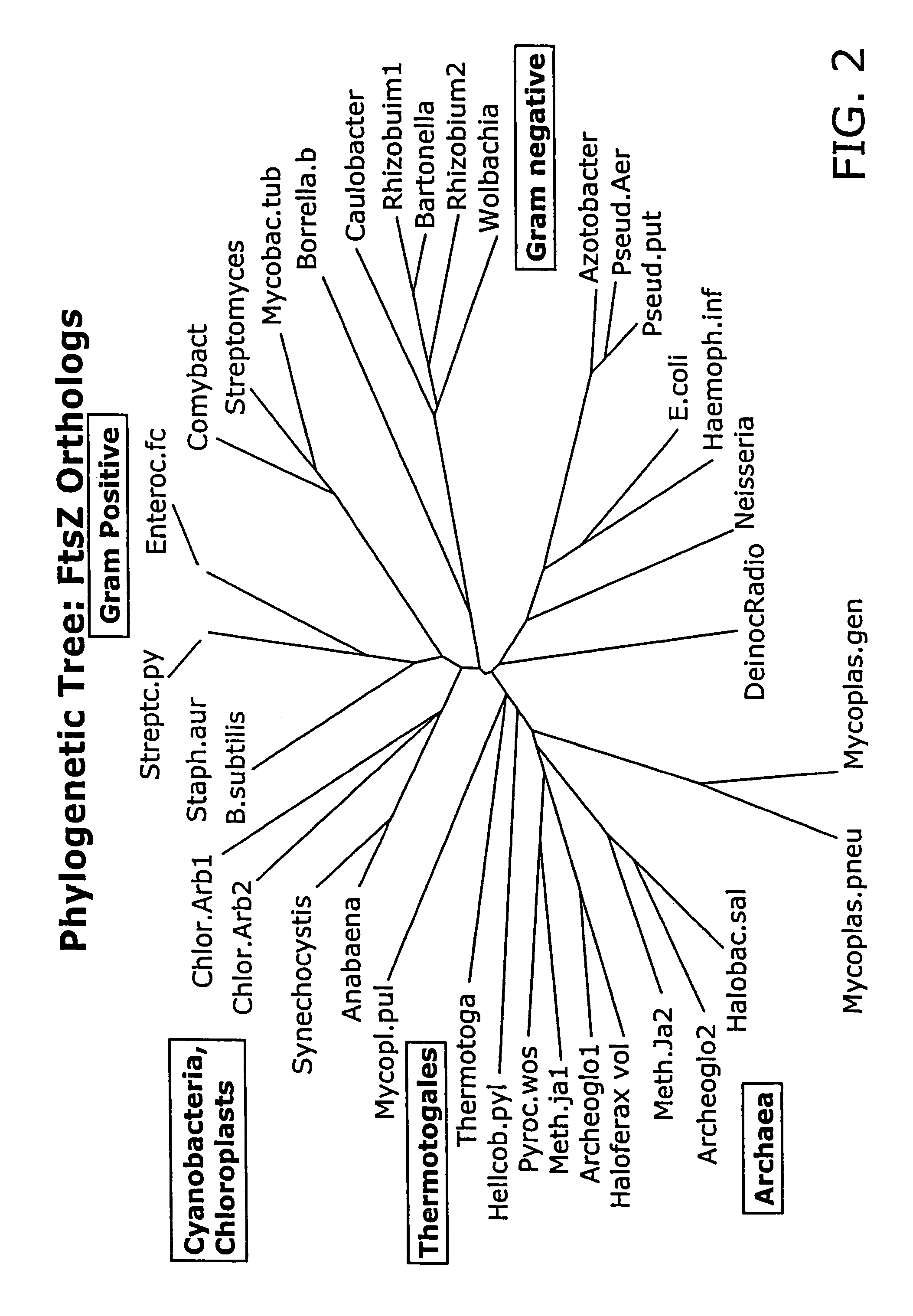
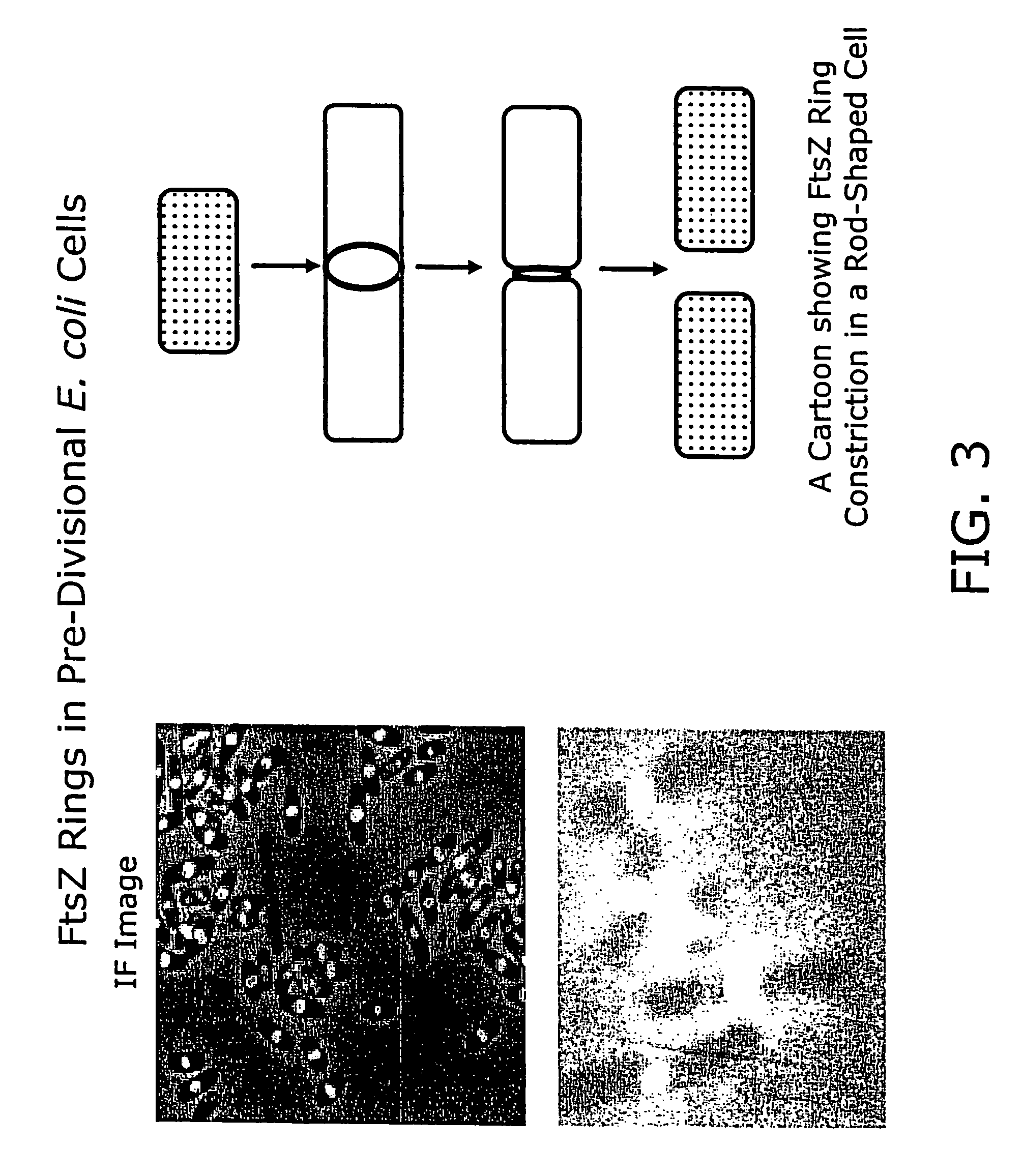
FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ftsZ gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of bacterial cell division. FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of the eukaryotic protein tubulin. The initials FtsZ mean "Filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z". The hypothesis was that cell division mutants of E. coli would grow as filaments due to the inability of the daughter cells to separate from one another. FtsZ is found in almost all bacteria, many archaea, all chloroplasts and some mitochondria, where it is essential for cell division. FtsZ assembles the cytoskeletal scaffold of the Z ring that, along with additional proteins, constricts to divide the cell in two.
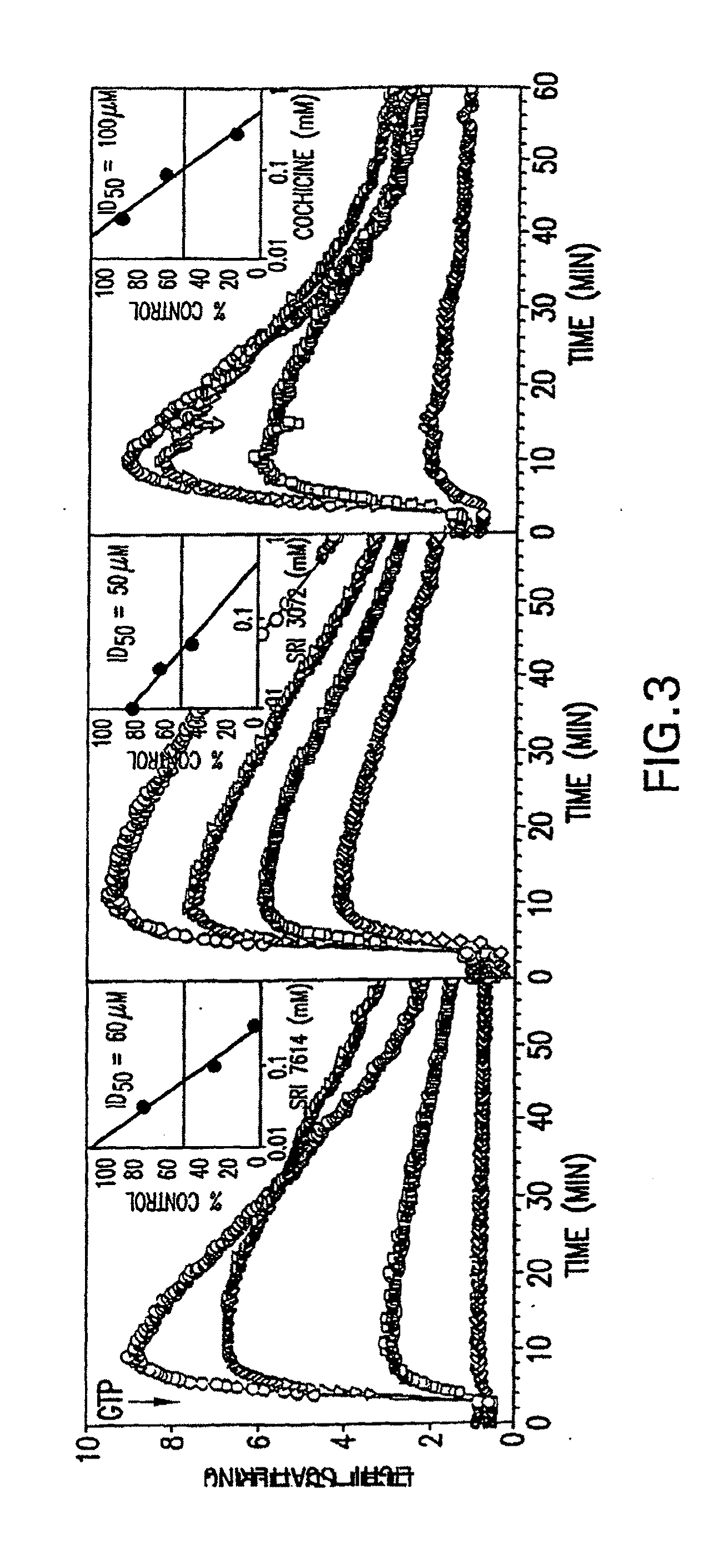
Synthesis of Inhibitors of FtsZ
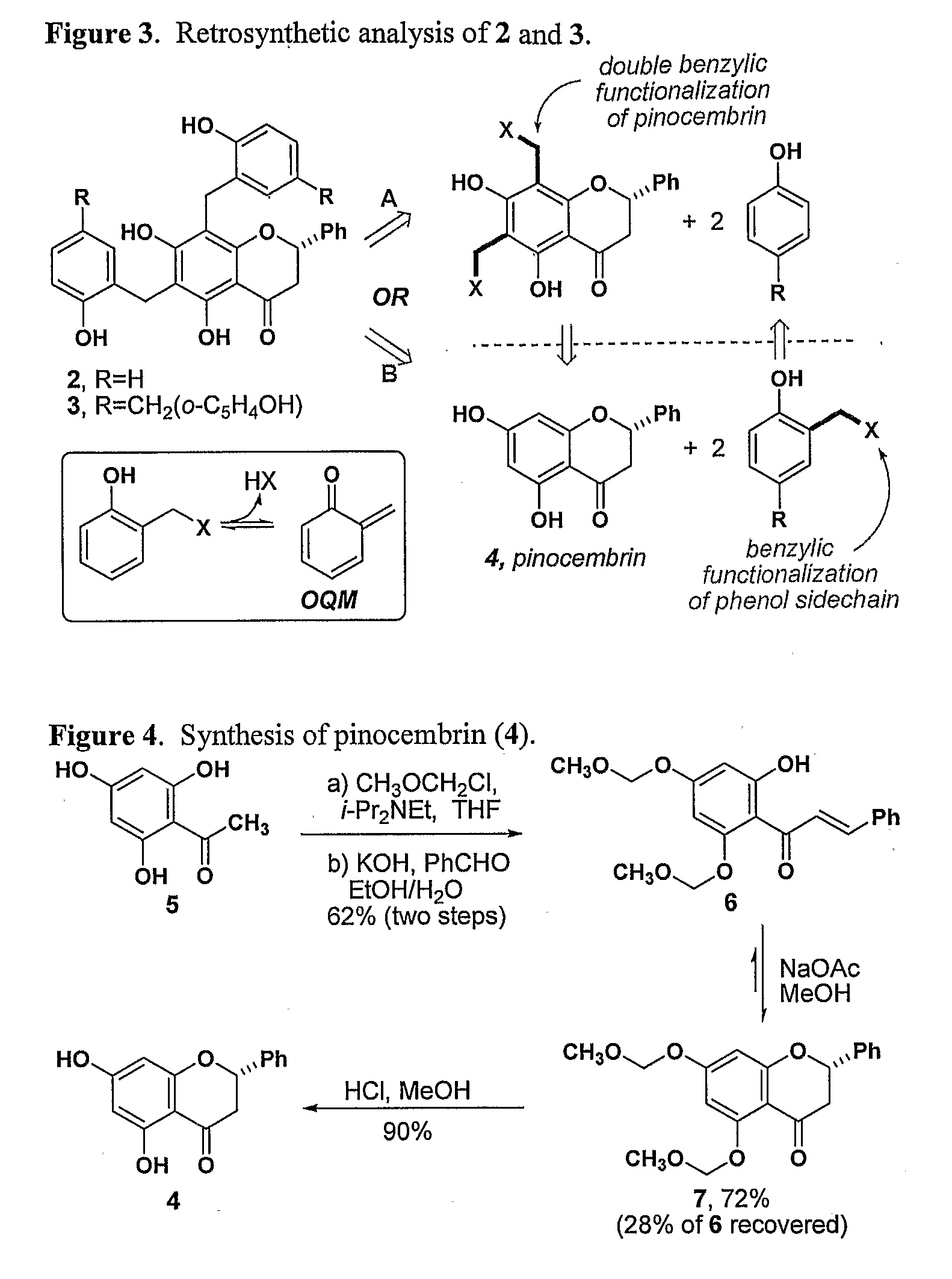
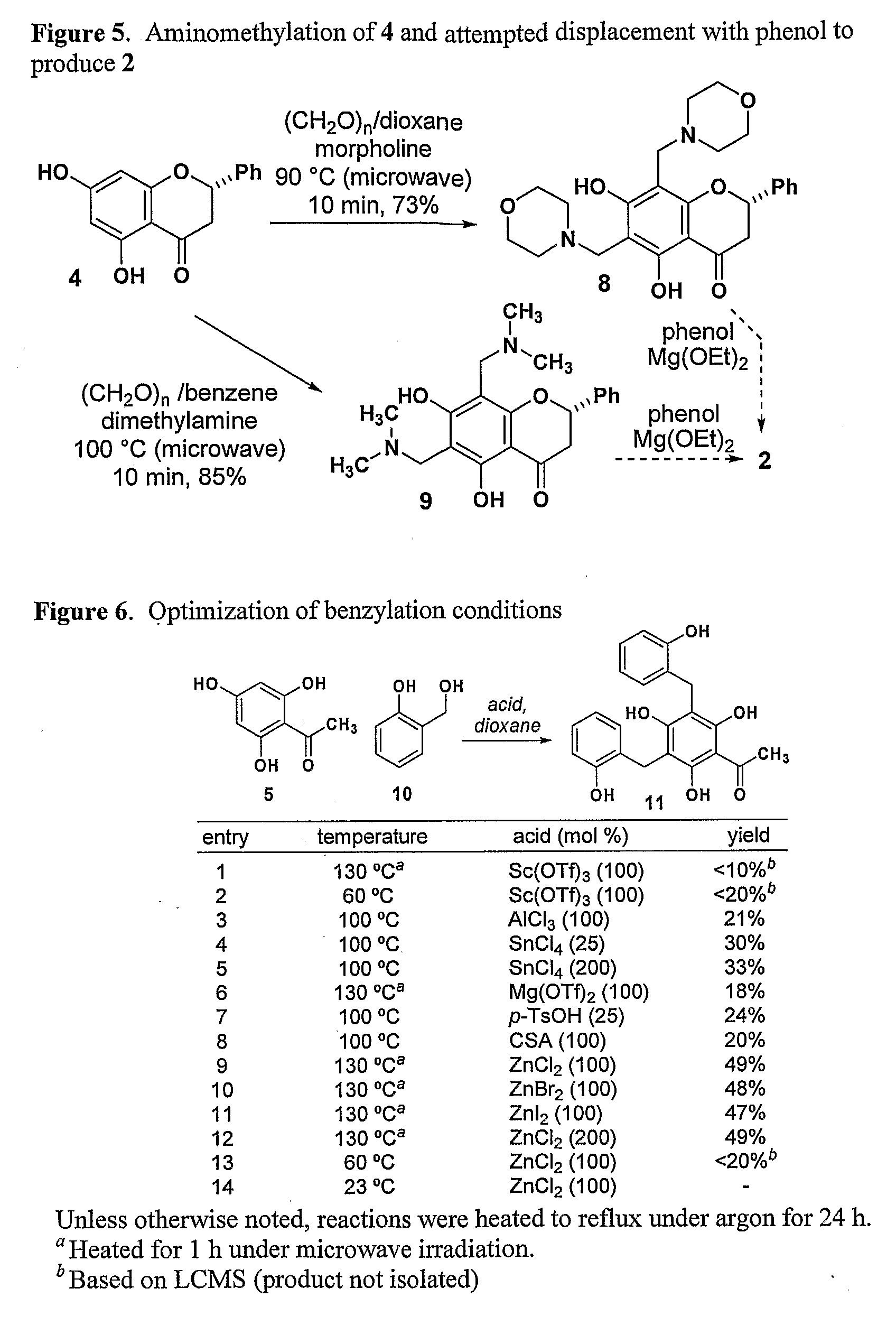
FtsZ, the bacterial analog of tubulin, is a promising new target for developing new antibiotics. It has been shown that polyphenols inhibit the GTPase activity of FtsZ, thereby inhibiting Z-ring formation during mitosis. The present invention provides novel polyphenols compounds, which can be accessed by the synthesis of dichamametin and 2′″-hydroxy-5″-benzylisouvarinol-B as described herein. These novel compounds are useful in treating infections, particularly infections caused by gram-positive organisms. Methods of preparing the inventive compounds are also provided. The compounds are prepared by the benzylation of pinocembrin or chrysin core structure. Pharmaceutical compositions and method of using the compounds to treat disease are also provided. These compounds may be screened for antimicrobial activity as well as other biological activities such as anti-neoplastic, anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, and cytotoxic activity.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV +2
Internal reference genes of fluorescence quantitative analysis of candidatus liberibacter asiaticus and application thereof
ActiveCN109706255AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesFluorescence
The present invention discloses internal reference genes of fluorescence quantitative analysis of candidatus liberibacter asiaticus and an application thereof. The internal reference genes are gyrA and ftsZ, and nucleotide sequences thereof are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO.9 and SEQ ID NO.10. An internal reference gene combination of the gyrA and ftsZ is firstly screened to be suitable for geneexpression analysis of candidatus liberibacter asiaticus infected with different hosts and after infected with the hosts in different periods, specific primers are further provided, and the internalreference gene combination provides a reliable guarantee for accurate and quantitative detection of the candidatus liberibacter asiaticus gene, and at the same time can be used to detect whether samples are infected with the candidatus liberibacter asiaticus. The selected internal reference gene combination of the gyrA and ftsZ has advantages of high reliability, good stability and wide applicability. A detection method and a detection kit for the candidatus liberibacter asiaticus constructed by using the internal reference gene combination have great advantages compared with single or traditional internal reference genes, and are worthy of promotion and application in a large area.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Inhibitors of ftsz and uses thereof
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP
Chrysophaentin analogs that inhibit FtsZ protein
InactiveCN103649028AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationBiochemistryResistant strain
Embodiments of antimicrobial chrysophaentin compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including the chrysophaentin compounds, methods for using the chrysophaentin compounds, and methods for synthesizing the chrysophaentin compounds are disclosed. Certain embodiments of the chrysophaentin compounds inhibit FtsZ protein, thereby inhibiting the growth of clinically relevant bacteria, including drug-resistant strains.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Compound, pharmaceutical composition, medicine and application of compound, pharmaceutical composition and medicine in preparation of antibacterial products
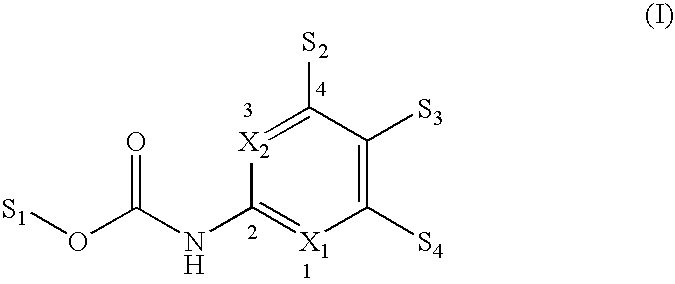
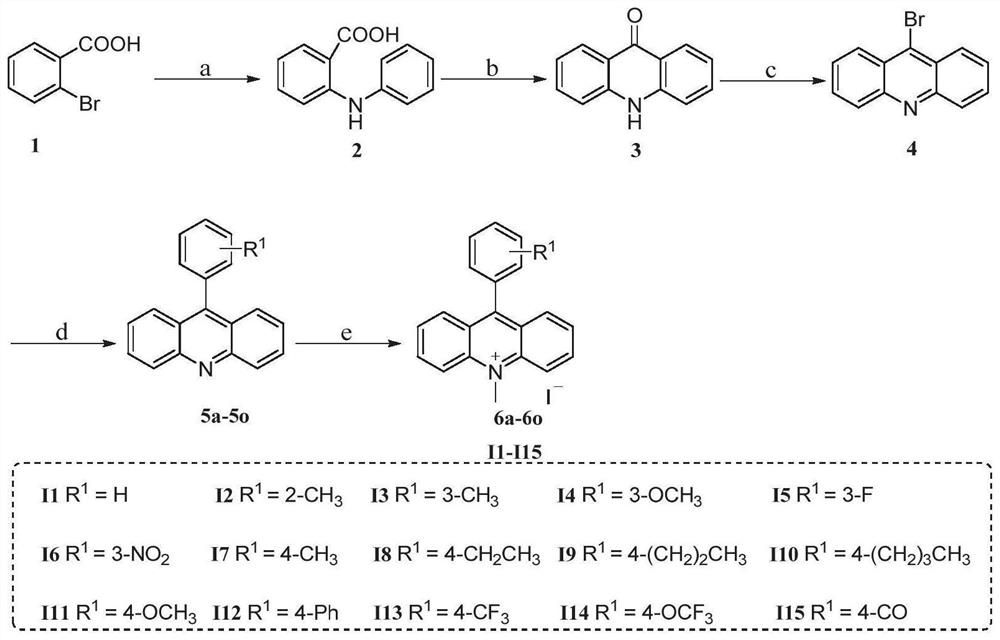
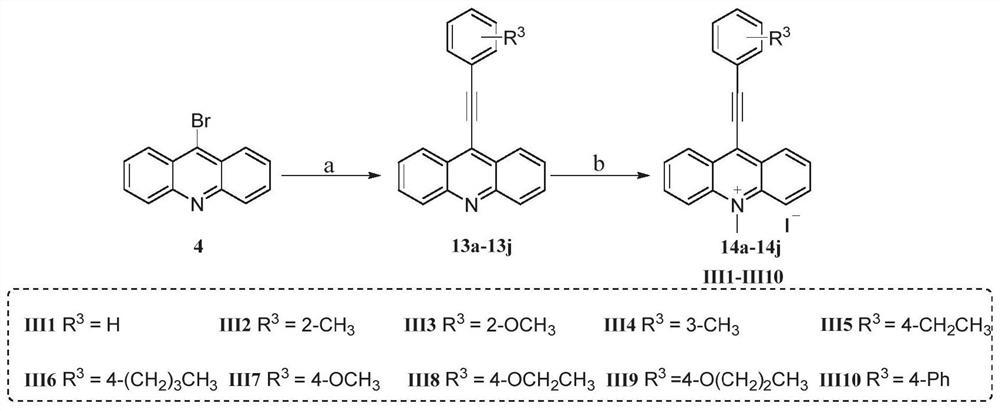
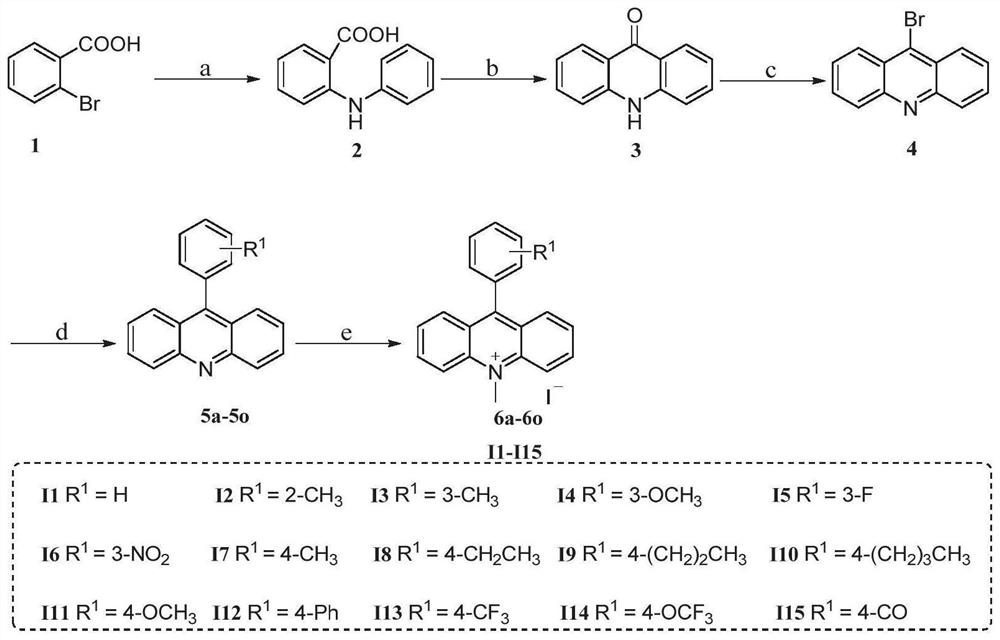
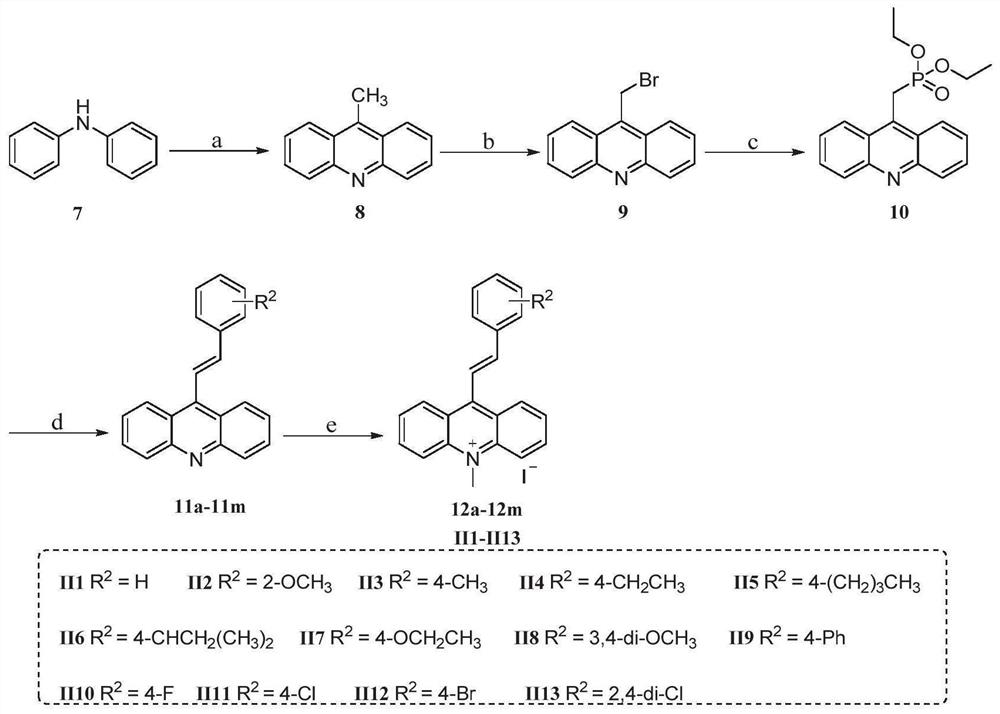
The invention particularly relates to a compound, a pharmaceutical composition, a medicine and application of the compound, the pharmaceutical composition and the medicine in preparation of antibacterial products. The seeking of a novel antibacterial target and the development of a novel chemical entity have important significance for solving the increasingly severe bacterial drug resistance problem at present, and the design of a compound entity acting on the FtsZ target is expected to be developed to obtain an antibacterial drug which has no influence on a host. The invention provides a 9-aralkyl-10-methylacridine quaternary ammonium salt derivative and a preparation method thereof, and the compound has significant bactericidal and / or bacteriostatic activity on gram-positive bacteria, has a good effect of inhibiting bacterial division protein FtsZ, and can be used for preparing antibacterial products.
Screening and application of burkholderia gladioli real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reference genes and primers thereof
ActiveCN111705149AImprove stabilityWide adaptabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReference genesCandidate Gene Association Study
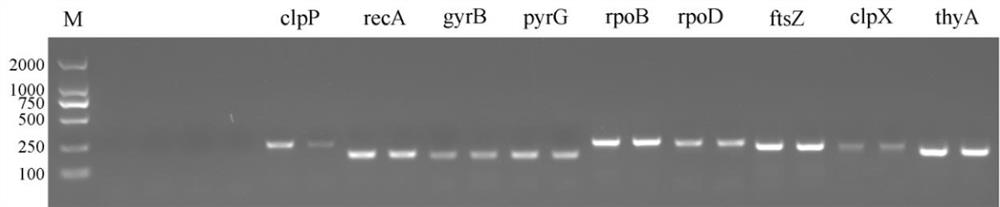
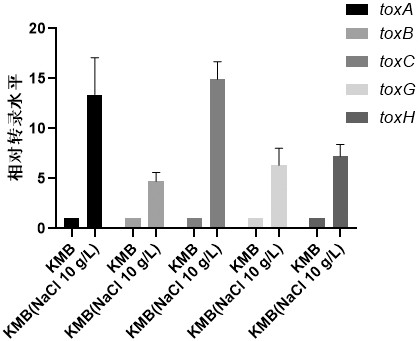
The invention discloses screening and application of burkholderia gladioli real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) reference genes and primers thereof. According to obtained transcriptome analysis results and reported reference genes, 12 candidate reference genes with relatively stable expression are preliminarily screened, and gene names are shown as follows: atpD, clpP, clpX,ftsZ, gyrB, lpxC, pyrG, recA, rpoB , rpoD, thyA and 16S; for the candidate genes, amplification primers are designed; reference genes under different culture conditions (temperature, initial pH valueof medium, culture time, treatment with NaCl different in concentration) of burkholderia gladioli are screened; geNorm, NormFinder and Bestkeeper software is employed to analyze qRT-PCR results; and finally, the reference genes with most stable expression under different culture conditions and NaCl treatment condition are obtained by screening. The invention is beneficial to the stability and reliability of analysis and study of gene expression of the burkholderia gladioli under different conditions.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Compound combinations for inhibiting cell division and methods for their identification and use
InactiveUS20060252114A1Wide range of activitiesImprove bioavailabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCell survivalCell growth
The present invention provides in vitro assays, e.g., FtsZ GTPase assays, and / or in vivo assays and methods of use thereof to identify particular compounds and combinations of compounds that affect microbial cell division. The invention further provides such compounds and compound combinations, including combinations that result in inhibition of cell survival or growth when present together at concentrations below their individual MICs. Certain of the compound combinations display synergism. Certain of the combinations include a compound that inhibits FtsZ GTPase activity and a compound that inhibits cell growth by a mechanism other than inhibition of FtsZ GTPase activity. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions that have anti-microbial activity and methods of treating microbial infections.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV +1
Method of Screening Antibacterial Drug Compounds
InactiveUS20100137146A1Increased toxicityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesAntimicrobial drug
Compounds are identified simultaneously as having antibiotic activity targeting a specific microbial protein and having no or limited toxicity against eukaryotic cells by expressing the microbial protein in eukaryotic cells by expressing the microbial protein in eukaryotic cells which then are used to screen candidate antibiotic compounds. Preferably, yeast cells such as Schizosaccharomyces pombe are transfected with and express a target bacterial protein such as FtsZ or MreB, optionally as a fusion with a reporter protein, and these transfected cells are used to screen libraries of compounds simultaneously for activity against the bacterial protein and lack of toxicity against the yeast cell.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Inhibitors of ftsz and uses thereof
Owner:WHITE E LUCILE +2
Application of 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic ethylene derivative to preparation of drugs for resisting drug-resistant bacteria
ActiveCN111870601AHigh antibacterial activityReduce doseAntibacterial agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsQuinolinePharmaceutical medicine
The invention belongs to the technical field of drugs, and particularly relates to an application of a 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic ethylene derivative to preparation of drugs for resisting drug-resistant bacteria. The 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic ethylene derivative is a compound shown as a formula I or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a solvent compound, an enantiomer, a diastereoisomer and a tautomer of the compound shown as the formula I or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a mixture of the solvent compound, the enantiomer, the diastereoisomer and the tautomer in any proportion, and comprises a racemic mixture. The 6-dimethylamino quinoline aromatic ethylene derivative can be used as an FtsZ inhibitor, has a remarkable antibacterial effect on gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria and an effect of inhibiting bacterial division protein FtsZ, and can be used for preparing the drugs for resisting drug-resistant bacteria.(As shown in the descriptions).
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Manipulation of starch granule size and number
InactiveUS20030177532A1Increase and decrease viscositySize can be alteredSugar derivativesHydrolasesBiotechnologyStarch granule
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids which encompass FtsZ nucleic acid molecules, FtsZ protein products (including, but not limited to, transcriptional products such as mRNAs, antisense and ribozyme molecules, and translational products such as FtsZ proteins, polypeptides, peptides and fusion proteins related thereto), antibodies to FtsZ protein products, vectors and expression vectors with FtsZ nucleic acids, cells, plants and plant parts with FtsZ nucleic acids, modified starch and starch granules from such plants and the use of the foregoing to improve agronomically valuable plants, including but not limited to maize, wheat, barley and potato.
Owner:GEMSTAR CAMBRIDGE
Compound combinations for inhibiting cell division and methods for their identification and use
InactiveUS20100311770A1Wide range of activitiesImprove bioavailabilityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCell survivalCell growth
The present invention provides in vitro assays, e.g., FtsZ GTPase assays, and / or in vivo assays and methods of use thereof to identify particular compounds and combinations of compounds that affect microbial cell division. The invention further provides such compounds and compound combinations, including combinations that result in inhibition of cell survival or growth when present together at concentrations below their individual MICs. Certain of the compound combinations display synergism. Certain of the combinations include a compound that inhibits FtsZ GTPase activity and a compound that inhibits cell growth by a mechanism other than inhibition of FtsZ GTPase activity. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions that have anti-microbial activity and methods of treating microbial infections.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
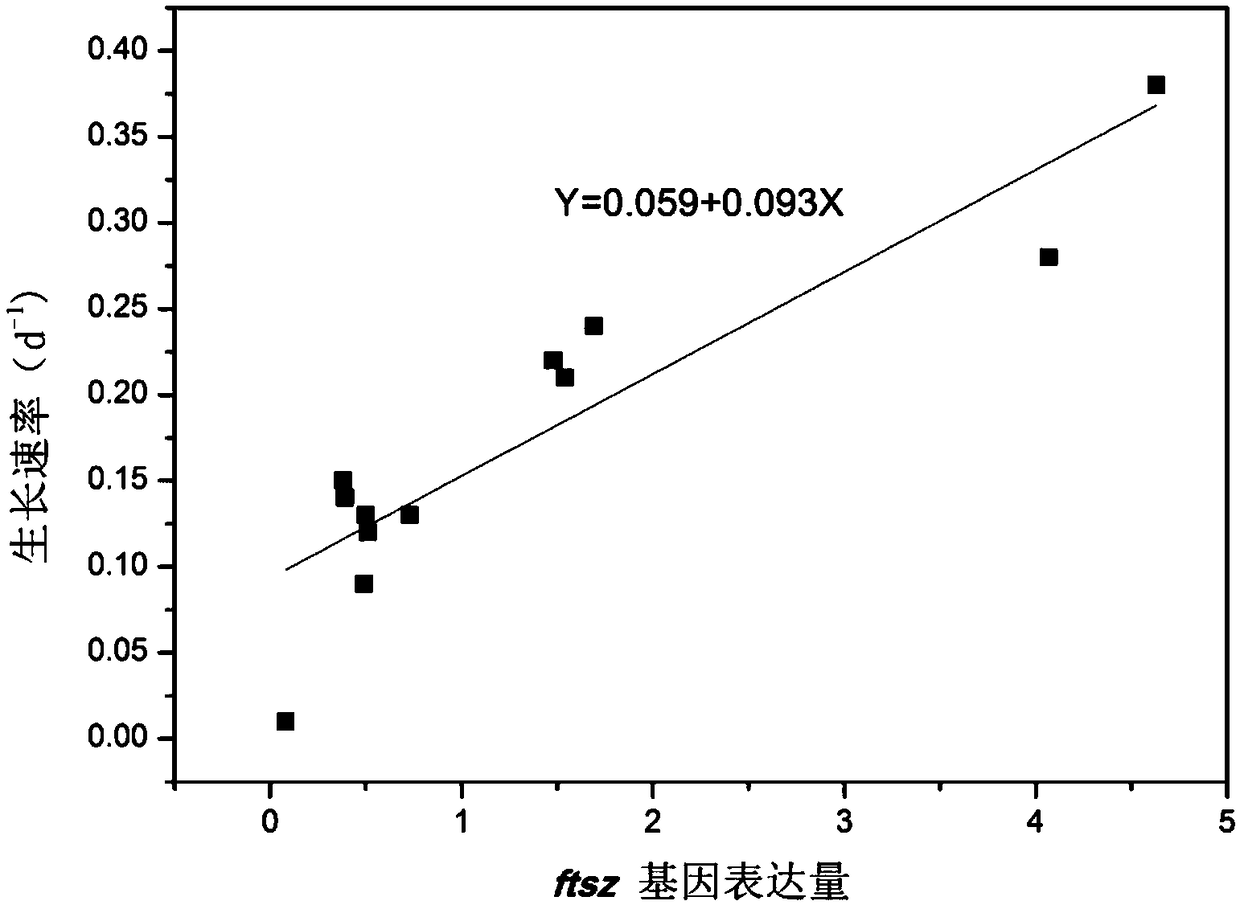
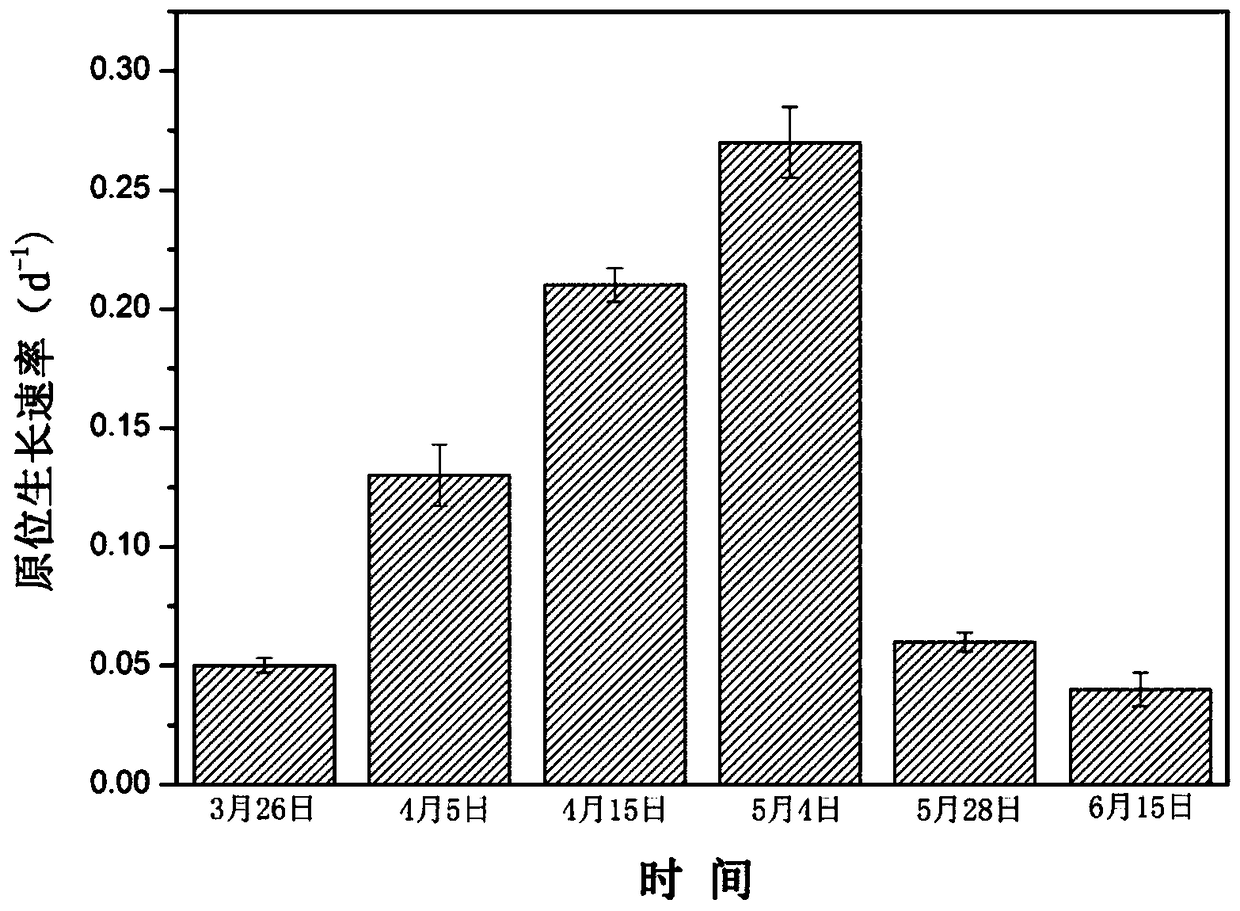
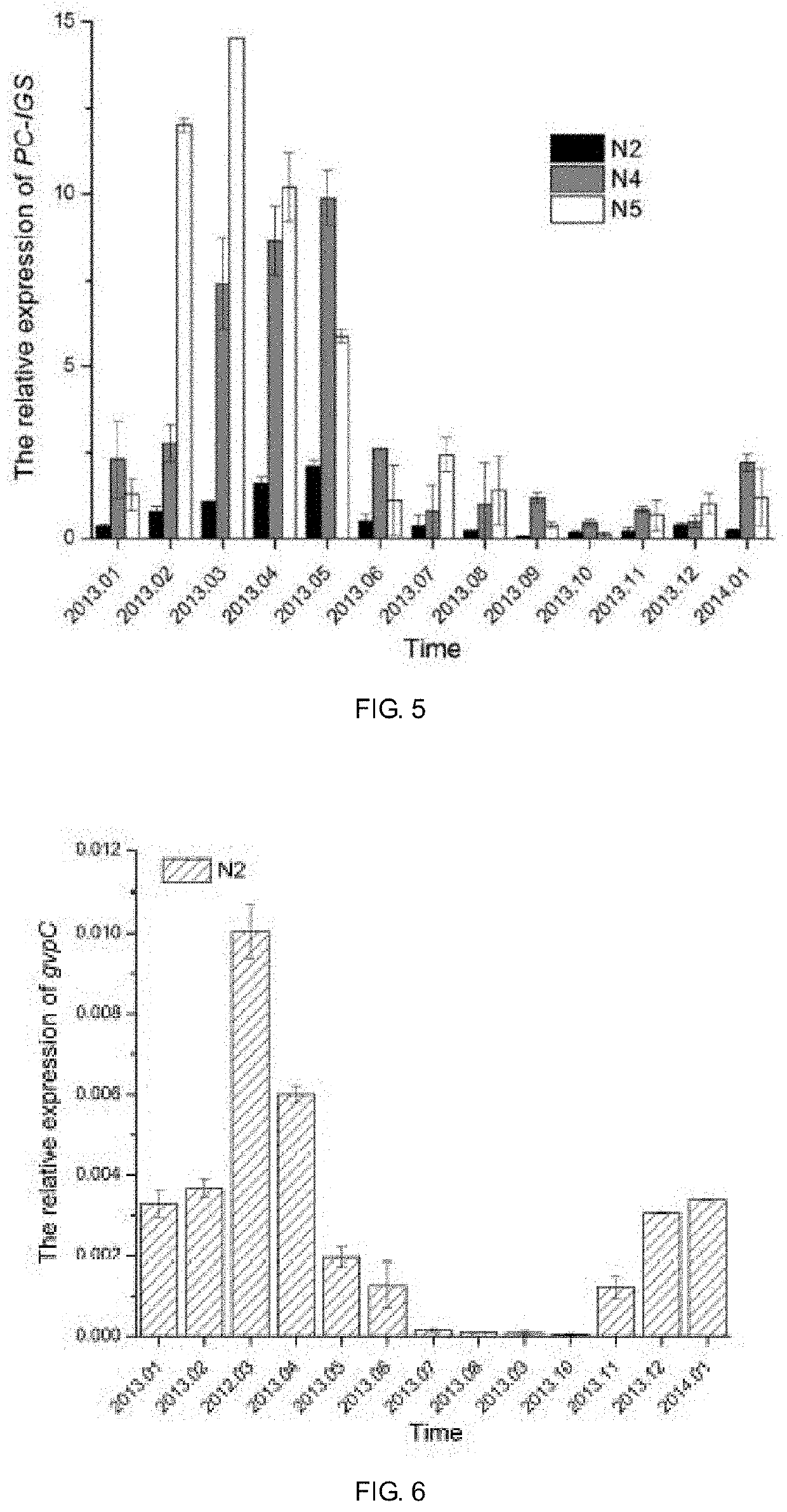
Method of judging rapid growth period of cyanobacteria based on cell division ftsZ gene expression quantity
ActiveCN108660190AAccurately distinguish the rapid growth periodRapid high-throughput detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPhylum CyanobacteriaRNA extraction
The invention provides a method of judging rapid growth period of cyanobacteria based on cell division ftsZ gene expression quantity. In-situ sampling is performed on a lake; samples are subjected toRNA extraction before reverse transcription; ftsZ and 16SrRNA are subjected to primer amplification before reverse transcription is performed to obtain microcystis cDNA; fluorescence quantitative PCR(polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on ftsZ and 16SrRNA genes of each sample; with 16SrRNA as a housekeeping gene and ftsZ as a target gene, relative expression quantity of ftsZ gene in unit cells is deducted; microcystis separated in situ from the lake are subjected to indoor culture experiment, a regression equation of microcystis growth rate mu and ftsZ gene relative expression quantity is established; rapid growth period of microcystis is determined; meanwhile, the ftsZ gene relative expression quantity is used as a threshold of window for the rapid growth period of cyanobacteria; the period greater than the threshold is determined as the rapid growth period of lake cyanobacteria. The method herein can provide rapid high-throughput detection, detection results of multiple samples are attained within hours, and the rapid growth period of cyanobacteria can be judged accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Method for defining stages of development of cyanobacterial bloom
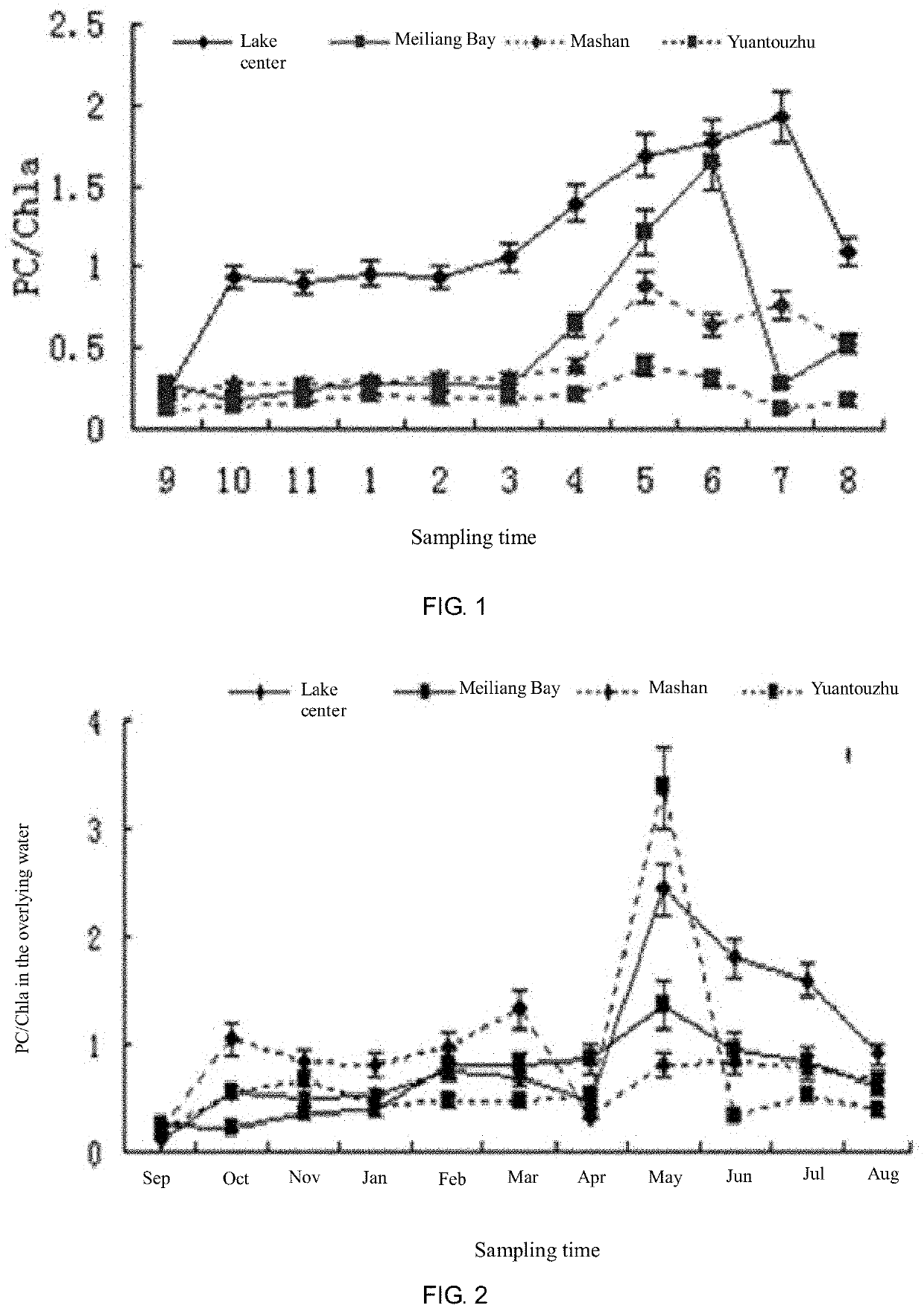
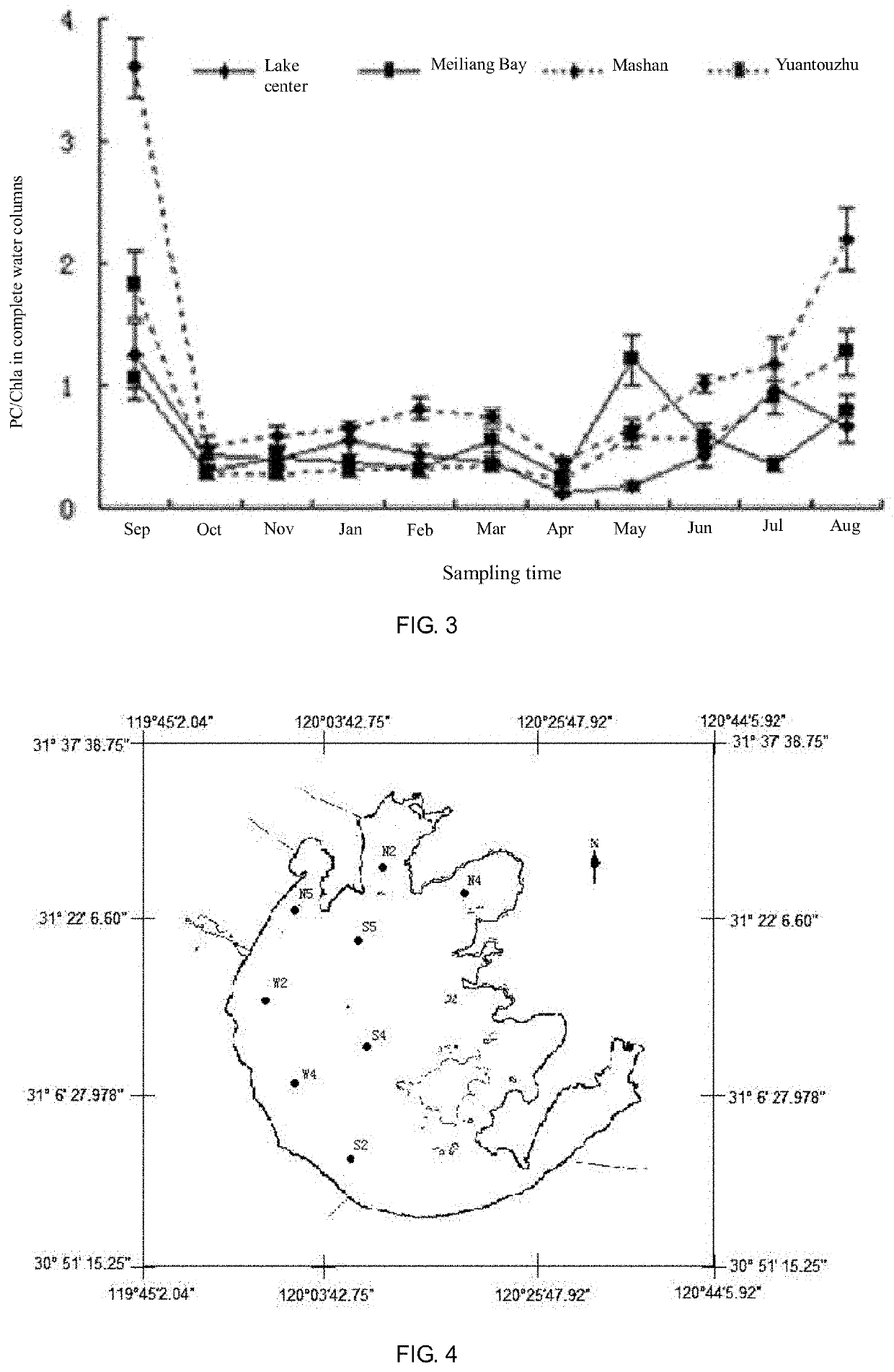
PendingUS20210348211A1Microbiological testing/measurementTesting plants/treesToxin synthesisPhycocyanin
Disclosed is a method for defining the stages of development of a cyanobacterial bloom, wherein the development of a cyanobacterial bloom is divided into five stages: a cyanobacteria wintering period, a resuscitation period, a rapid growth period, an outbreak period and a cyanobacteria decline period; the wintering period is defined based on the concentration / content ratio of algocyan / chlorophyll a; the resuscitation period is defined based on the relative expression levels of the phycocyanin synthesis gene PC-IGS, the algal toxin synthesis gene mcyA and the gas vesicle synthesis gene gvpC in the surface sediment; the cyanobacteria rapid growth period is defined based on the relative expression level of the ftsZ gene; the cyanobacteria outbreak period is defined based on the wind speed; and the cyanobacteria decline period is defined based on the relative expression level of the nblA gene and the ratio of glucose to neutral polysaccharides in dissolved organic matter.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
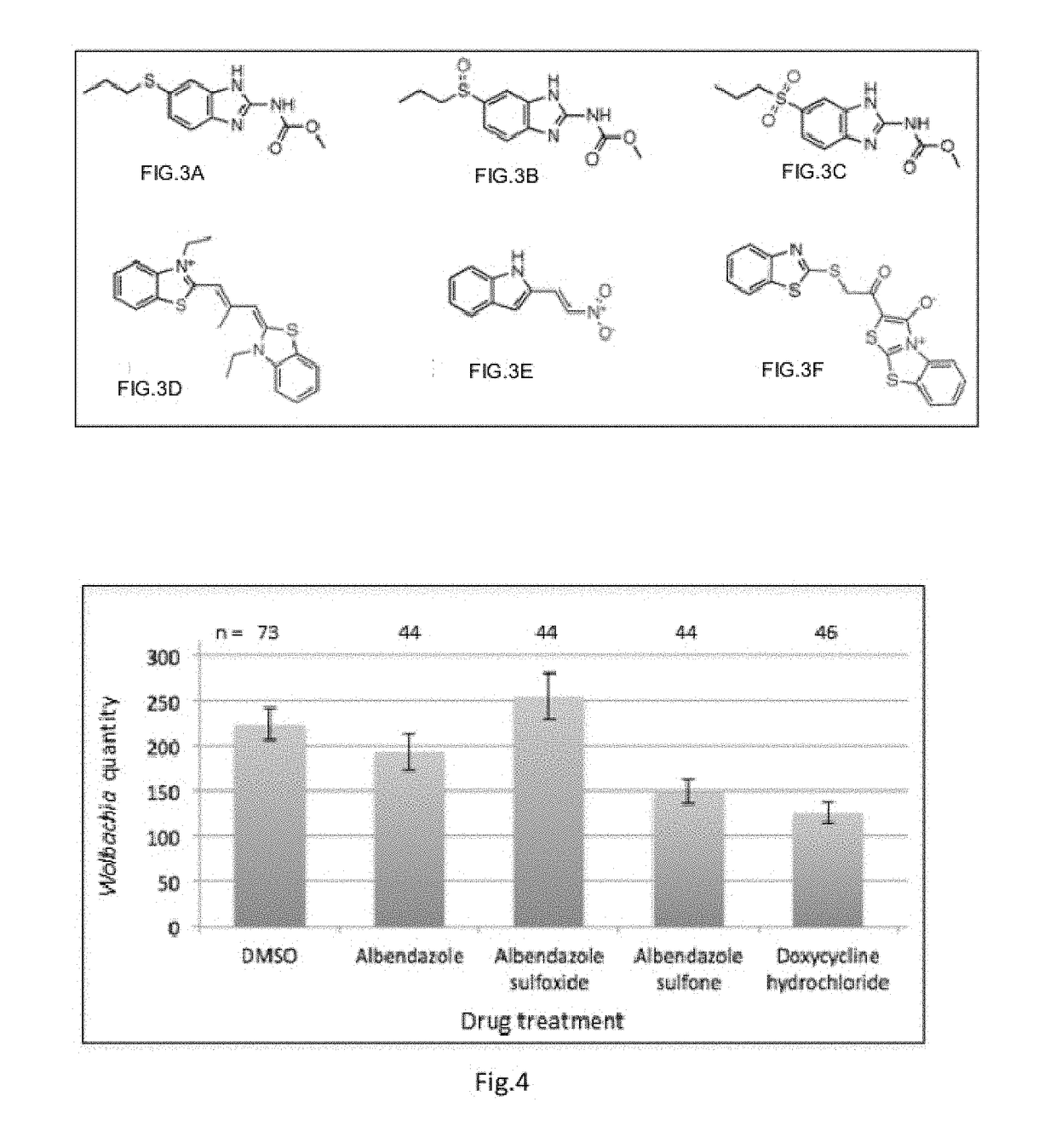
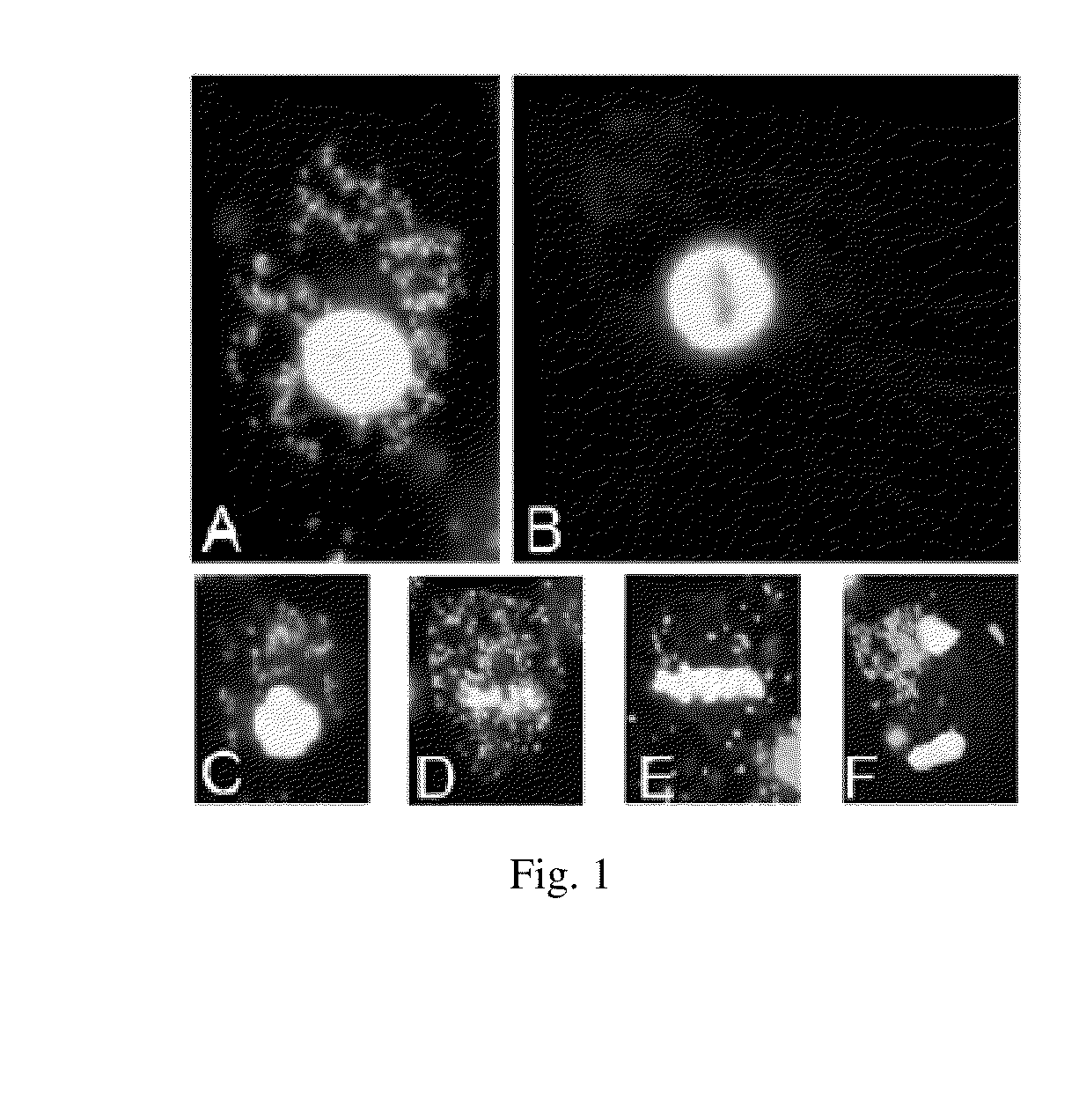
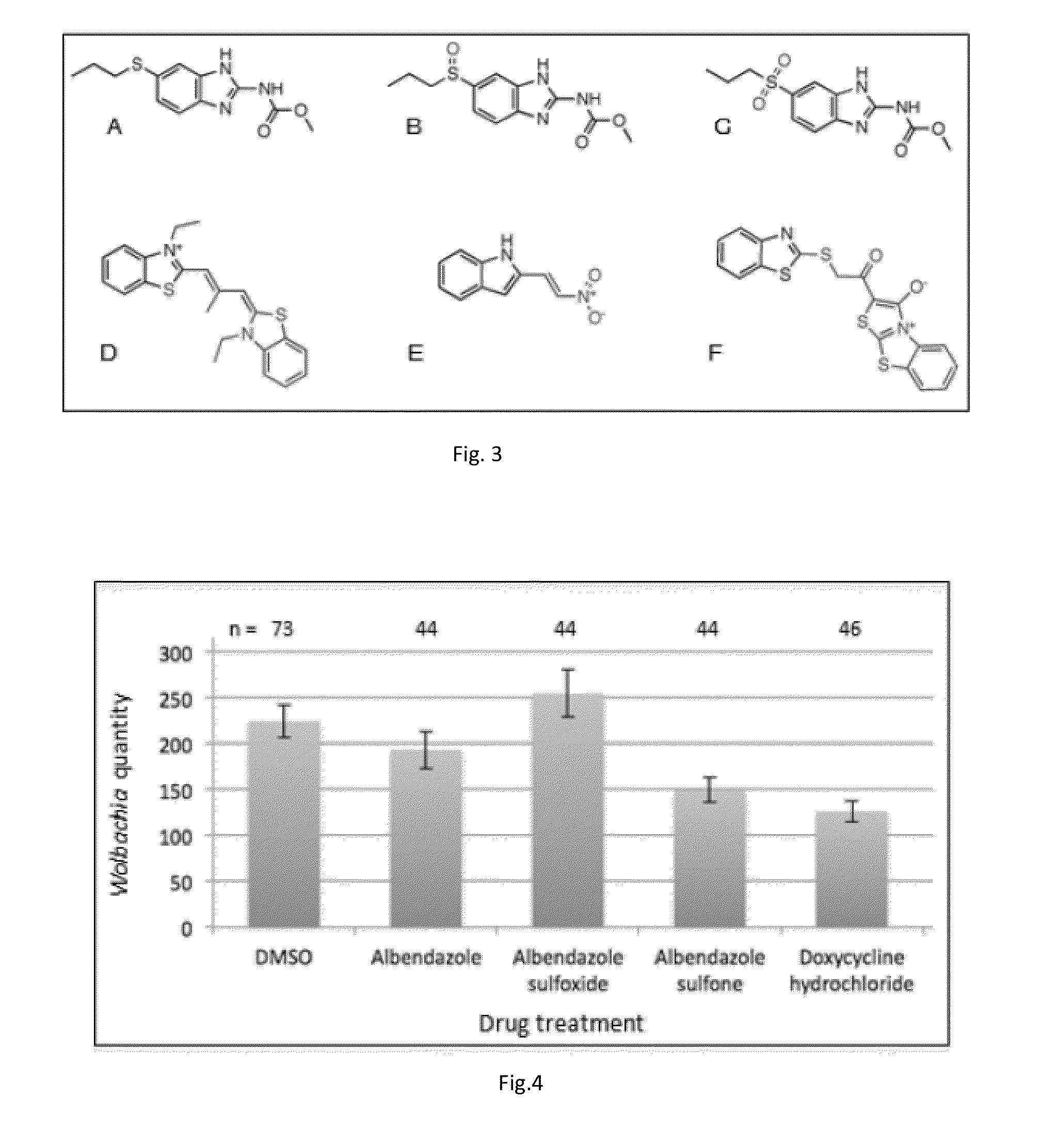
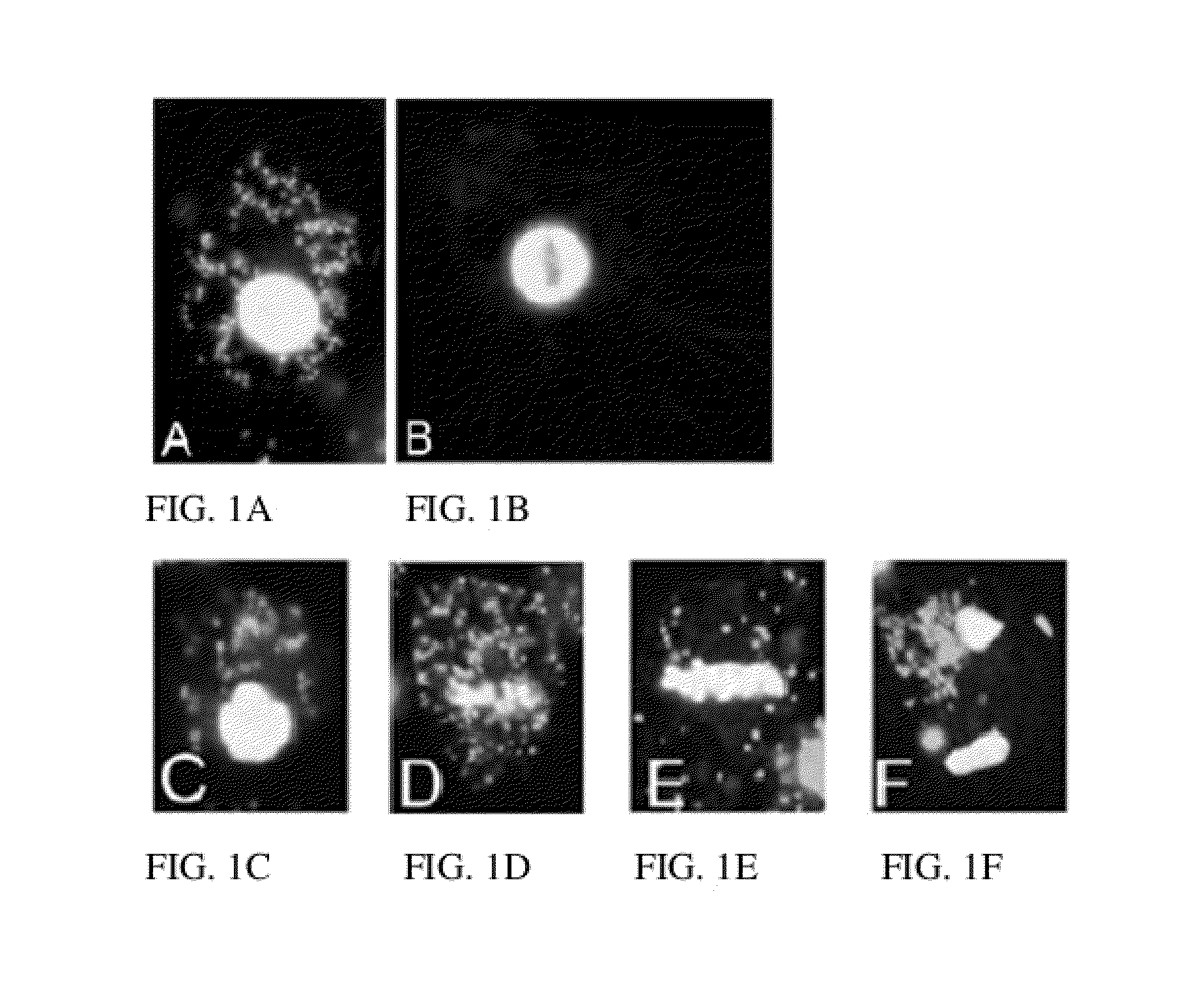
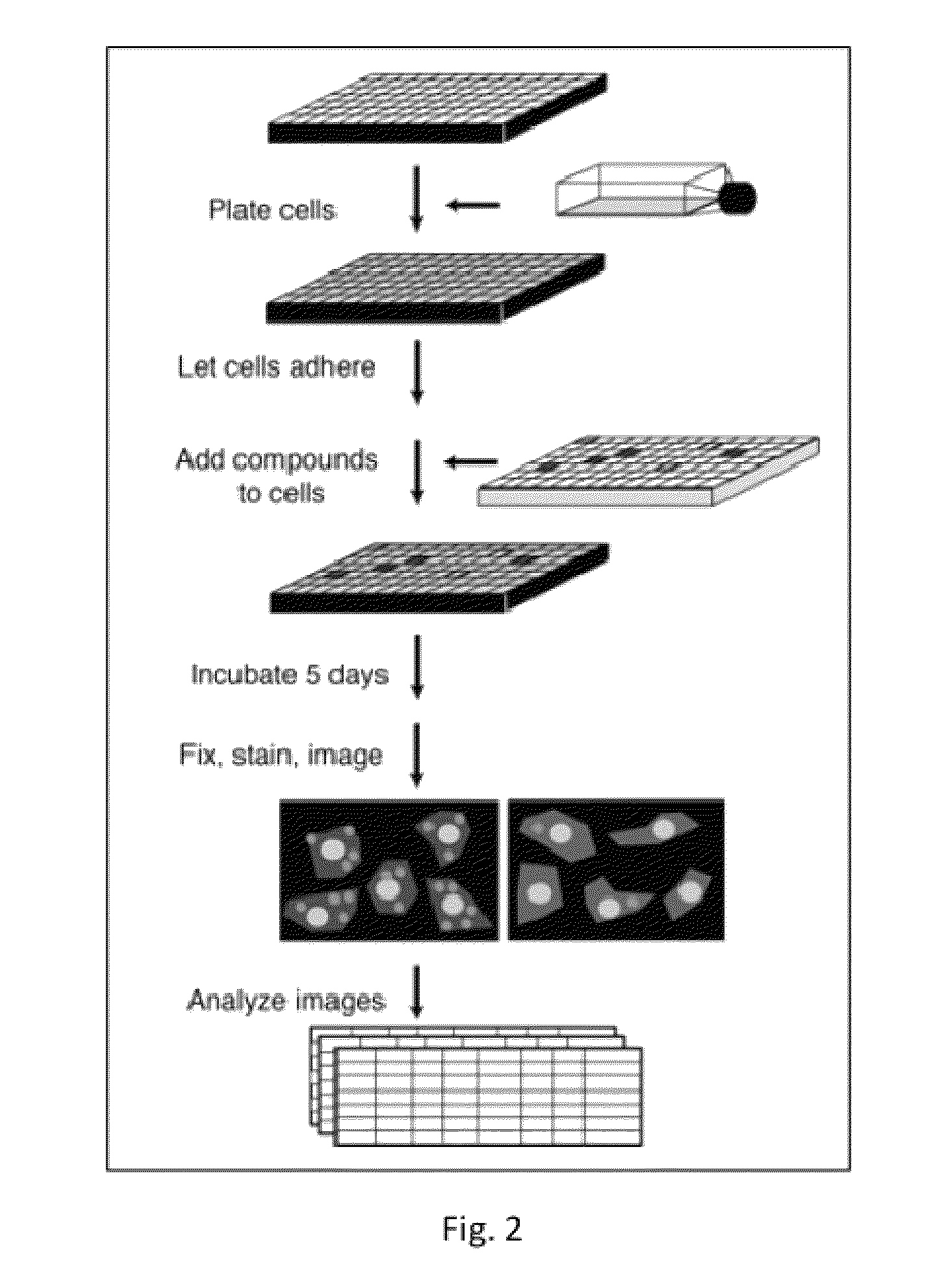
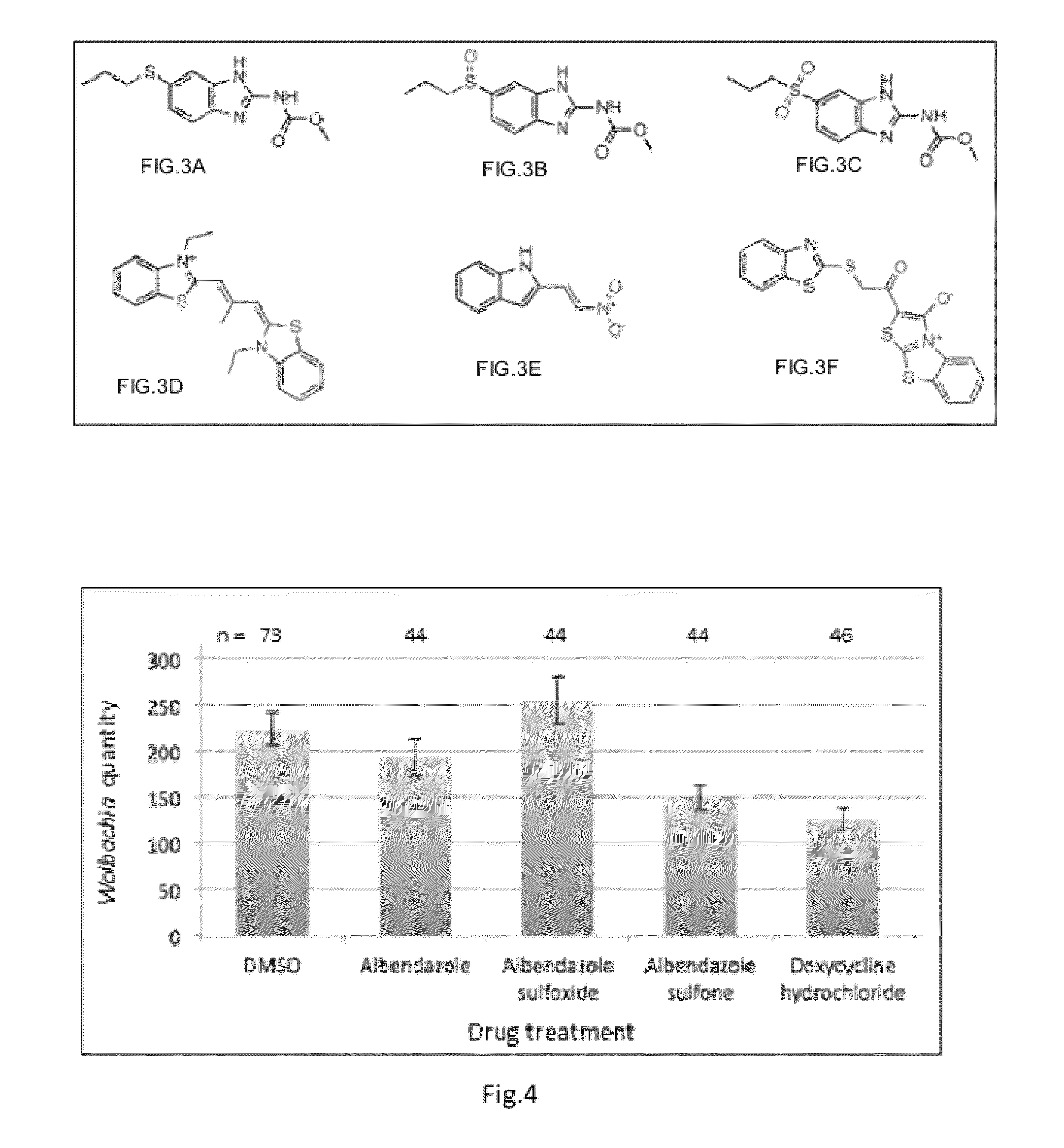
Compositions and Methods employing Wolbachia FtsZ as a target for Albendazole sulfone
InactiveUS20180042900A1Tetracycline active ingredientsAgainst vector-borne diseasesCancer researchFtsZ
Compositions and Methods are described in which Albendazole sulfone binds to Wolbachia FtsZ providing anti filarial activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
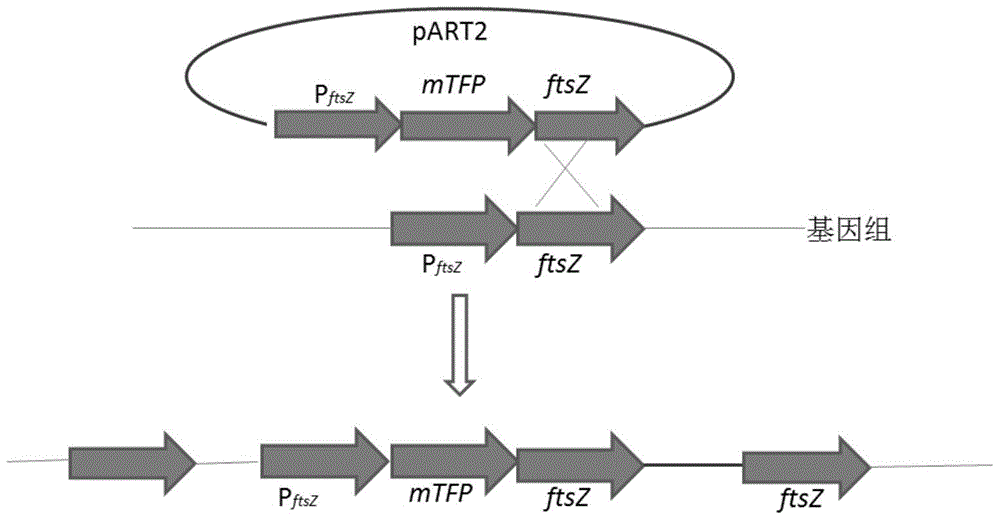
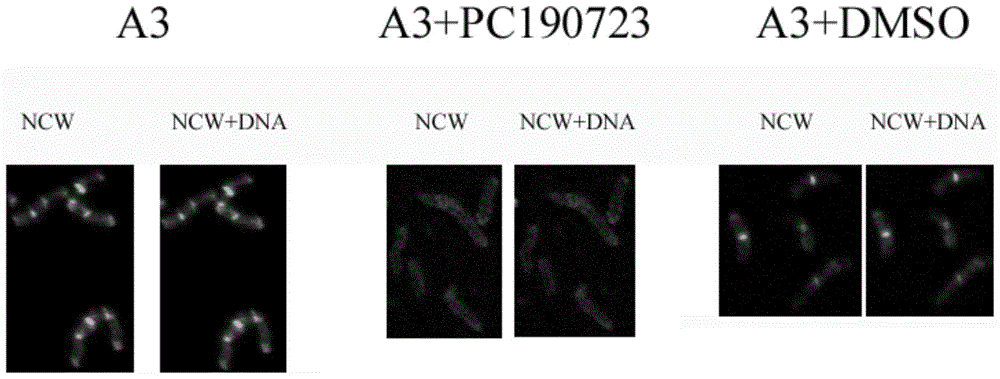
A kind of recombinant bacteria and its application
InactiveCN103540560BEasy to operateImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArthrobacterAntibiotic Y
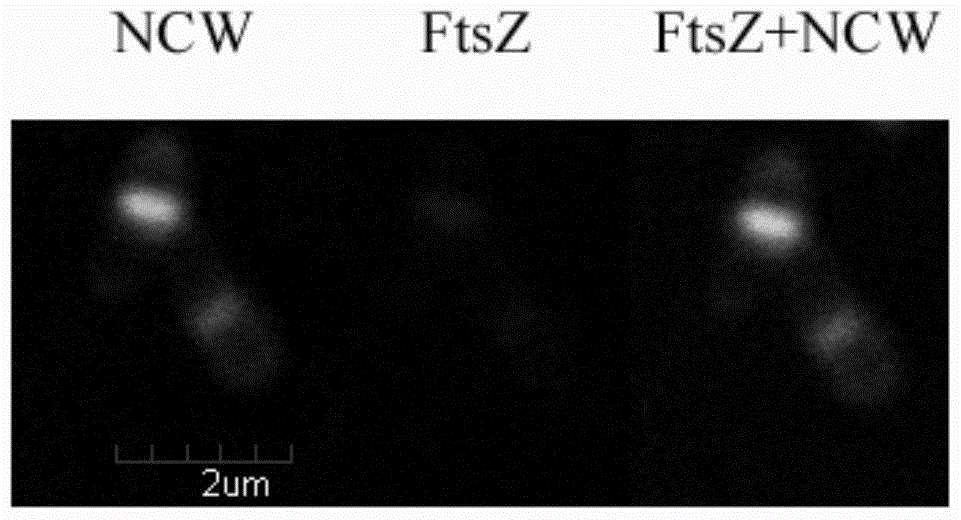
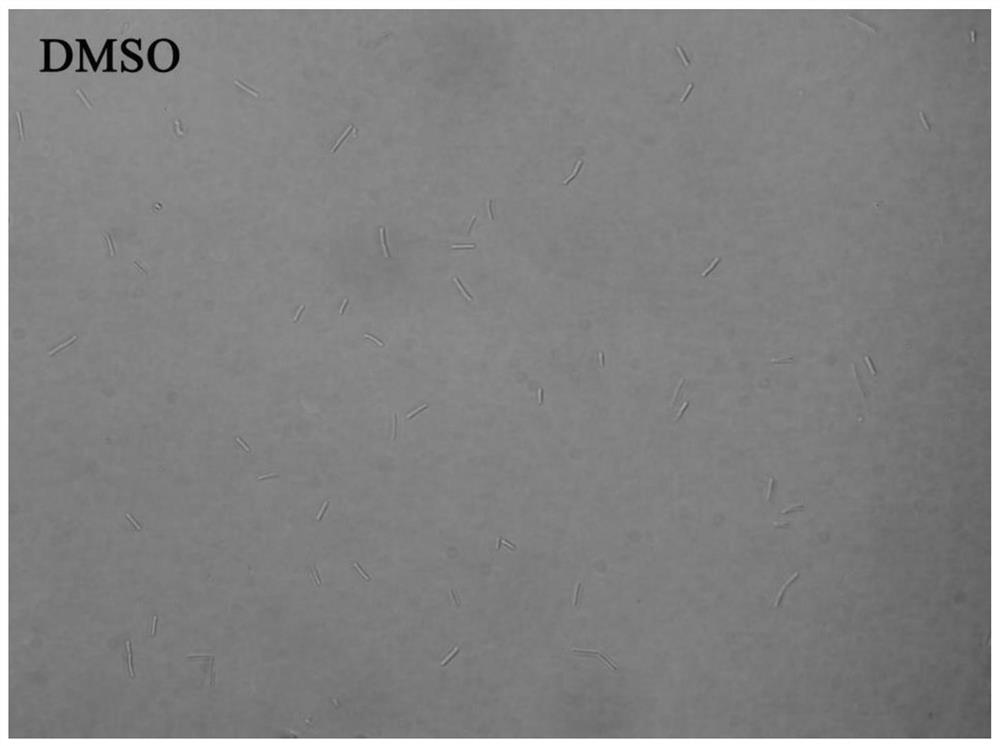
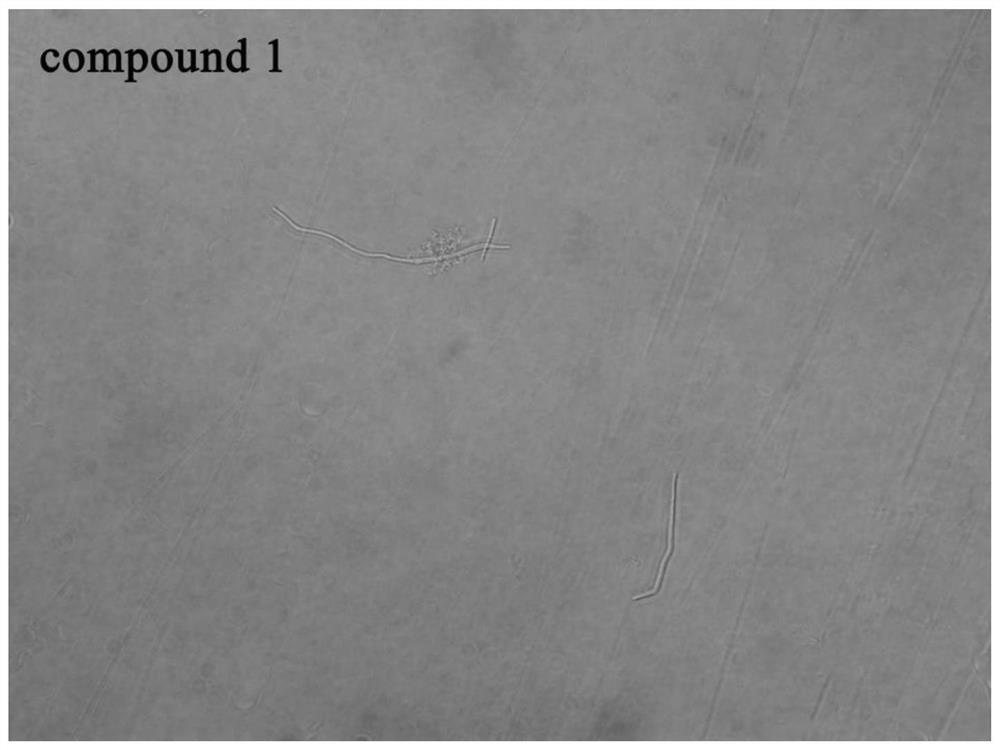
The invention provides a recombinant bacterium containing mTFP‑ftsZ recombinant Arthrobacter Arthrobacter sp .A3, mTFP‑ftsZ The gene sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence listing. The present invention also provides a method for rapidly detecting and inhibiting antibiotics related to FtsZ, which is to insert the compound to be tested into Arthrobacter, cultivate to the early and middle logarithmic growth phase, and then fluorescently label the new cell wall, compare it with a blank control, and observe The location and ratio of the new cell wall ring, if the formation or ratio of the new cell wall ring changes, the compound to be tested has the ability to inhibit FtsZ-related antibiotics. The method provided by the invention can detect whether there is an ftsZ-inhibiting active substance in a fermentation product or a variety of chemical derivatives at a time, and has the advantages of simple operation and high efficiency, and a definite result can be obtained in only 2 hours, and has good popularization and use value.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
Method for judging whether spirulina strains can be applied in large-scale aquaculture production
InactiveCN102329868BClear standardLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh-throughput screening
The invention belongs to a technology for development and application of spirulina, and aims at providing a method for judging whether spirulina strains can be applied in large-scale aquaculture production. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out sequencing on ftsZ genes of the identified spirulina strains, and carrying out variance analysis on site numbers and phylogenetic treeconstruction on the basis of a ftsZ gene sequence together with the known spirulina platensis; and if the identified spirulina strains and the ftsZ gene sequence of the known spirulina platensis strains are gathered into one type, showing that the production traits of the identified spirulina strains are good, and the identified spirulina strains can be applied in large-scale aquaculture production. Compared with the conventional method, the new method for identifying the good and bad production traits of the spirulina strains by applying the ftsZ gene sequence not only is simple, fast, standard and accurate, but also is low in cost, and is suitable for large-scale and high-throughput screening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compositions and Methods employing Wolbachia FtsZ as a target for Albendazole sulfone
InactiveUS20180177765A9Tetracycline active ingredientsAgainst vector-borne diseasesCancer researchFtsZ
Compositions and Methods are described in which Albendazole sulfone binds to Wolbachia FtsZ providing anti filarial activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for judging whether spirulina strains can be applied in large-scale aquaculture production
InactiveCN102329868AClear standardLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh-throughput screening
The invention belongs to a technology for development and application of spirulina, and aims at providing a method for judging whether spirulina strains can be applied in large-scale aquaculture production. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out sequencing on ftsZ genes of the identified spirulina strains, and carrying out variance analysis on site numbers and phylogenetic treeconstruction on the basis of a ftsZ gene sequence together with the known spirulina platensis; and if the identified spirulina strains and the ftsZ gene sequence of the known spirulina platensis strains are gathered into one type, showing that the production traits of the identified spirulina strains are good, and the identified spirulina strains can be applied in large-scale aquaculture production. Compared with the conventional method, the new method for identifying the good and bad production traits of the spirulina strains by applying the ftsZ gene sequence not only is simple, fast, standard and accurate, but also is low in cost, and is suitable for large-scale and high-throughput screening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Christine analogues that inhibit the FTSZ protein
InactiveCN103649028BOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationPharmaceutical drugMicrobiology
Embodiments of antimicrobial chrysophaentin compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including the chrysophaentin compounds, methods for using the chrysophaentin compounds, and methods for synthesizing the chrysophaentin compounds are disclosed. Certain embodiments of the chrysophaentin compounds inhibit FtsZ protein, thereby inhibiting the growth of clinically relevant bacteria, including drug-resistant strains.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
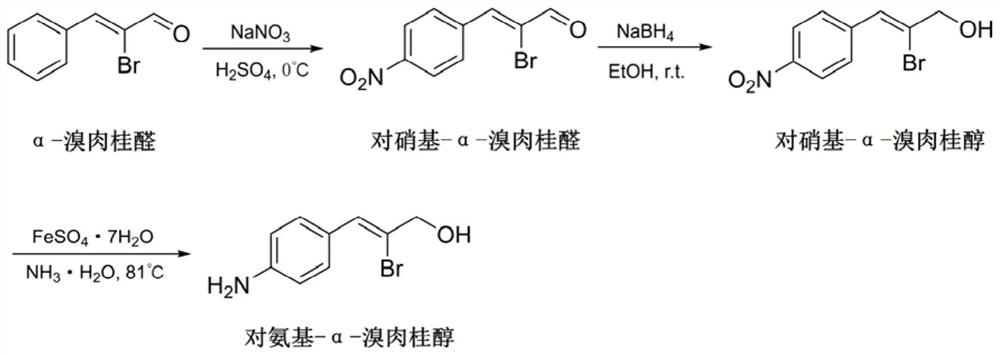
Application of alpha-bromocinnamyl aldehyde in prevention and treatment of bacterial infectious diseases
InactiveCN112791073AInterfere with normal divisionEffective protectionAntibacterial agentsAldehyde active ingredientsProtein polymerizationAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses an application of alpha-bromocinnamyl aldehyde in prevention and treatment of bacterial infectious diseases, the alpha-bromocinnamyl aldehyde can inhibit FtsZ protein polymerization and interfere normal division of bacteria, and the alpha-bromocinnamyl aldehyde shows broad-spectrum antibacterial activity to gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. In a mouse multidrug resistance bacteria abdominal cavity infection model, the alpha-bromocinnamyl aldehyde can significantly improve the survival rate of infected animals, and has the characteristics of safety and low toxicity, which indicates that the alpha-bromocinnamyl aldehyde has good antibacterial activity, and can be used as a leading drug for treating bacterial infectious diseases.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Discrimination method of rapid growth period of cyanobacteria based on cell division ftsz gene expression
ActiveCN108660190BAccurately distinguish the rapid growth periodRapid high-throughput detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHousekeeping geneMicrobiology
The invention provides a method of judging rapid growth period of cyanobacteria based on cell division ftsZ gene expression quantity. In-situ sampling is performed on a lake; samples are subjected toRNA extraction before reverse transcription; ftsZ and 16SrRNA are subjected to primer amplification before reverse transcription is performed to obtain microcystis cDNA; fluorescence quantitative PCR(polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on ftsZ and 16SrRNA genes of each sample; with 16SrRNA as a housekeeping gene and ftsZ as a target gene, relative expression quantity of ftsZ gene in unit cells is deducted; microcystis separated in situ from the lake are subjected to indoor culture experiment, a regression equation of microcystis growth rate mu and ftsZ gene relative expression quantity is established; rapid growth period of microcystis is determined; meanwhile, the ftsZ gene relative expression quantity is used as a threshold of window for the rapid growth period of cyanobacteria; the period greater than the threshold is determined as the rapid growth period of lake cyanobacteria. The method herein can provide rapid high-throughput detection, detection results of multiple samples are attained within hours, and the rapid growth period of cyanobacteria can be judged accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
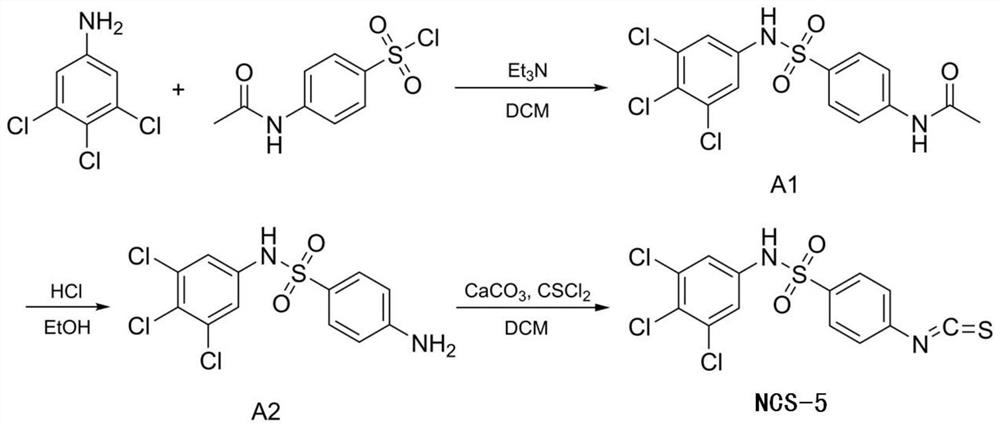
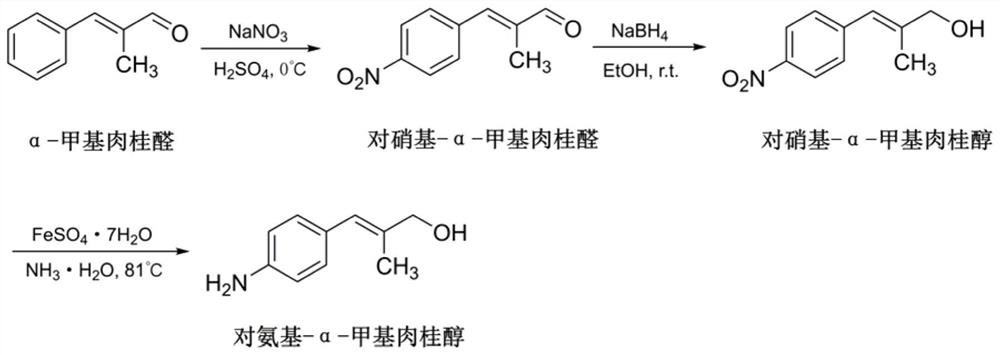
FtsZ and QseC double-target antibacterial molecule as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112851559AEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationPharmaceutical drugAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses an FtsZ and QseC double-target antibacterial molecule as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the antibacterial molecule is shown as a formula 1 defined in the description, wherein R1 is H, F, Cl, Br or I; and R2 is CH2OH and CHO. According to the invention, the bacterial infection resistance effect of the antibacterial molecule is evaluated through the in vitro antibacterial activity experiment, and the result shows that the antibacterial molecule can effectively kill Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria, can reduce the toxicity of Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria, and can be used for preparing bacterial infection resistance and other related drugs.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Application of a 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic vinyl derivative in the preparation of anti-drug resistant bacteria
ActiveCN111870601BHigh antibacterial activityInhibition of growth and reproductionAntibacterial agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsQuinolinePharmaceutical medicine
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and in particular relates to the application of a 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic vinyl derivative in the preparation of anti-drug resistance medicines. Described 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic vinyl derivative is formula I compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, and the solvate, enantiomer of described formula I compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt isomers, diastereomers, tautomers or mixtures thereof in any ratio, including racemic mixtures; this 6-dimethylaminoquinoline aromatic vinyl derivative can be used as an FtsZ inhibitor, which is gram-positive Bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria have significant bacteriostatic effect and the effect of inhibiting bacterial division protein FtsZ, and can be used to prepare anti-drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Compound combinations for inhibiting cell division and methods for their identification and use
InactiveUS7575889B2Wide range of activitiesImprove bioavailabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCell survivalCell growth
The present invention provides in vitro assays, e.g., FtsZ GTPase assays, and / or in vivo assays and methods of use thereof to identify particular compounds and combinations of compounds that affect microbial cell division. The invention further provides such compounds and compound combinations, including combinations that result in inhibition of cell survival or growth when present together at concentrations below their individual MICs. Certain of the compound combinations display synergism. Certain of the combinations include a compound that inhibits FtsZ GTPase activity and a compound that inhibits cell growth by a mechanism other than inhibition of FtsZ GTPase activity. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions that have anti-microbial activity and methods of treating microbial infections.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE +1
Pyrimidines for treatment of bacterial infections
ActiveUS20170291887A1Excellent antimicrobial activityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryCell phenotypeLethal dose
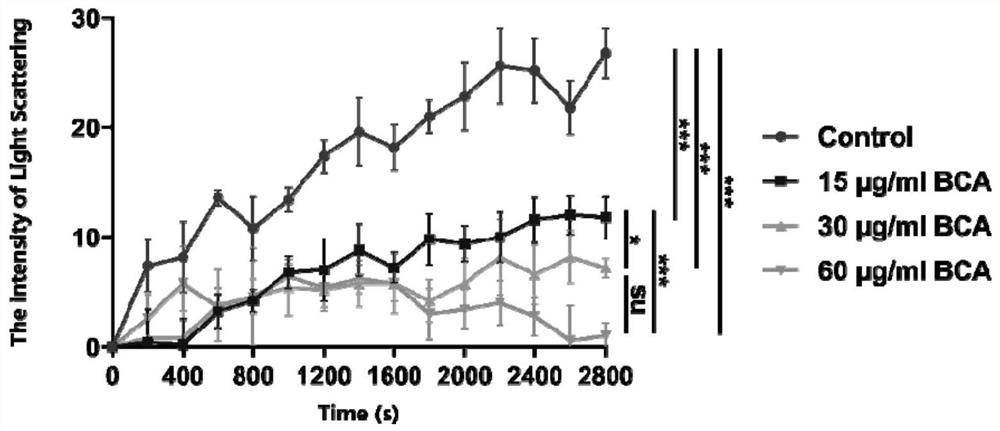
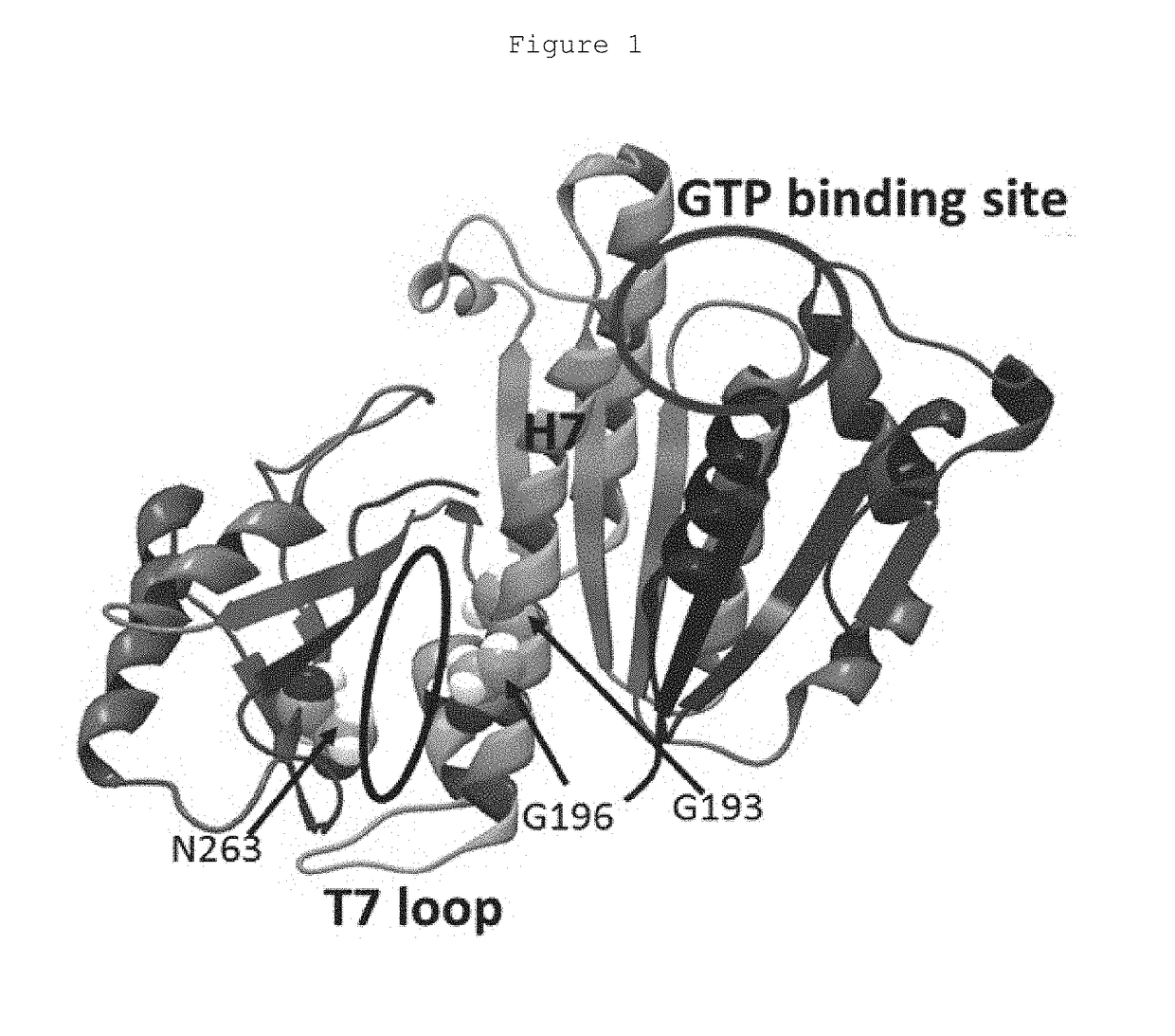
Filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z (FtsZ) protein plays a crucial role in the bacterial cell division machinery and is a validated drug target for antibacterial agents. The present invention relates to FtsZ-interacting compounds that possess a 2,4,6-trisubstituted pyrimidine scaffold. Some of these compounds possess potent anti-staphylococcal properties and potent antibacterial activities against clinically isolated MRSA strains. Compounds have been identified to exhibit low spontaneous frequency of resistance, low toxicity as well as the ability to rescue G. mellonella larvae infected with lethal dose of the MRSA ATCC 43300 strain. Characterization by saturation transfer difference NMR, light scattering assay and GTPase hydrolysis assay with purified S. aureus FtsZ protein verified the interaction of 2,4,6-trisubstituted pyrimidine with the FtsZ protein, further confirmed by observations of iconic filamentous cell phenotype and mislocalization of the Z-ring formation. Taken together, these pyrimidine derivatives have the potential as effective treatment of staphylococcal infections.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
Compositions and Methods employing Wolbachia FtsZ as a target for Albendazole sulfone
Compositions and Methods are described in which Albendazole sulfone binds to Wolbachia FtsZ providing anti filarial activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods employing wolbachia FtsZ as a target for albendazole sulfone
ActiveUS9439889B2Tetracycline active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCancer researchFtsZ
Compositions and Methods are described in which Albendazole sulfone binds to Wolbachia FtsZ providing anti filarial activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
A compound, pharmaceutical composition, medicine and its application in the preparation of antibacterial products
ActiveCN113121439BAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial drugPharmaceutical Substances
The invention specifically relates to a compound, a pharmaceutical composition, a medicine and an application thereof in preparing antibacterial products. The search for new antibacterial targets and the development of new chemical entities are of great significance to solve the increasingly serious problem of bacterial drug resistance. Compound entities designed to act on the FtsZ target are expected to be developed to produce antibacterial drugs that have no effect on the host. The invention provides a 9-arylalkyl-10-methylacridine quaternary ammonium salt derivative and a preparation method thereof. The compound has significant bactericidal and / or bacteriostatic activity against Gram-positive bacteria, and has The invention has a good effect of inhibiting the bacterial division protein FtsZ and can be used to prepare antibacterial products.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
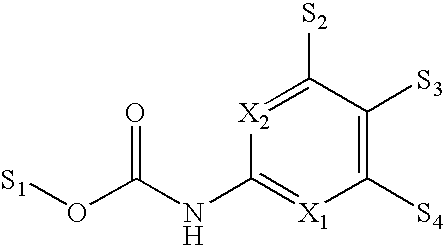
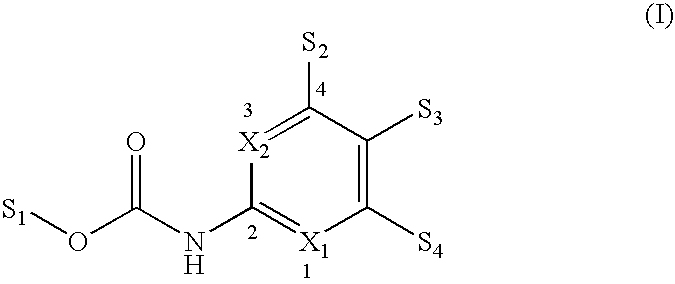
Application of styrene quinoline derivatives in the preparation of anti-drug-resistant bacteria drugs and anti-drug-resistant bacteria drugs
ActiveCN110302201BEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsQuinolinePharmaceutical Substances
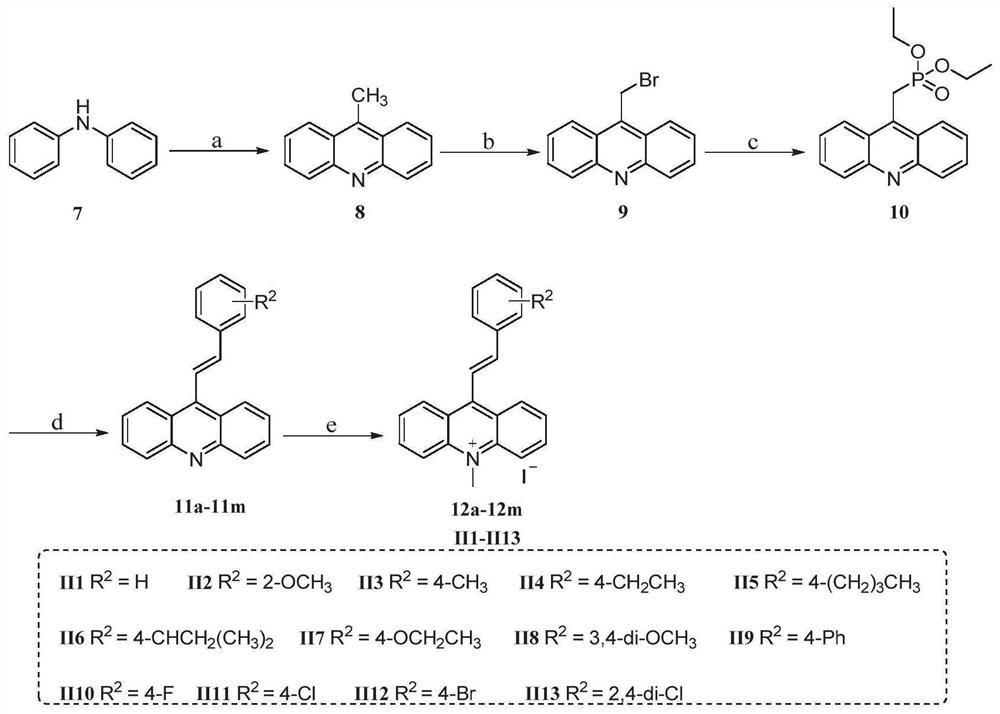
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and in particular relates to the application of styrene quinoline derivatives in the preparation of anti-drug-resistant bacteria medicines and the anti-drug-resistant bacteria medicines. The invention provides the application of the styrene quinoline derivatives with the structure shown in formula (I) in the preparation of drugs against drug-resistant bacteria. Positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus have obvious inhibitory effect, and it also has a certain effect on negative bacteria. Through the experiment on the bacterial morphology under the action of the styrene quinoline derivative of the present invention, it can be preliminarily judged that the target of the styrene quinoline derivative of the present invention is the split protein FtsZ ubiquitous in bacteria.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com