Marine crustacean water ecological toxicity test method
A technology of toxicity test and water ecology, which is applied in the direction of testing water, material inspection products, measuring devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
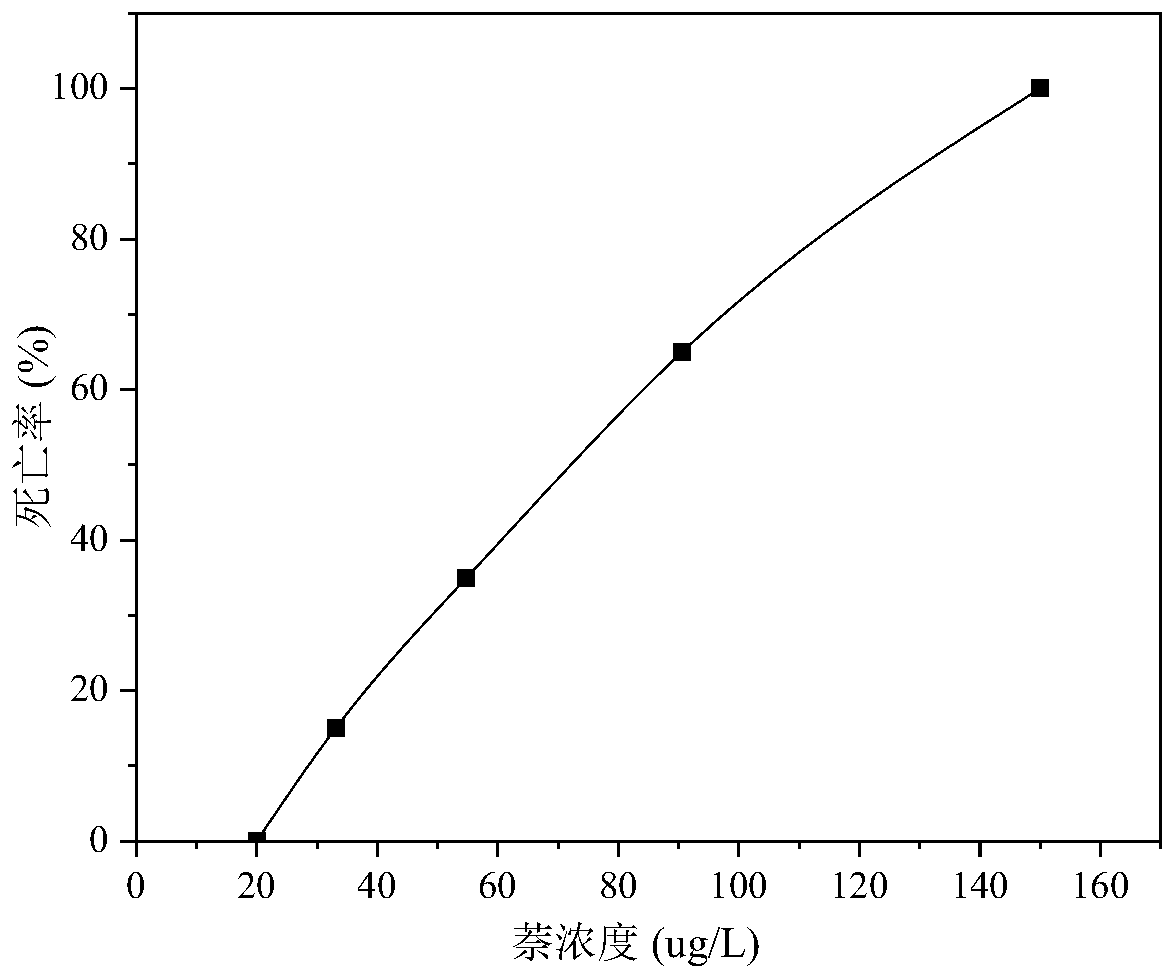
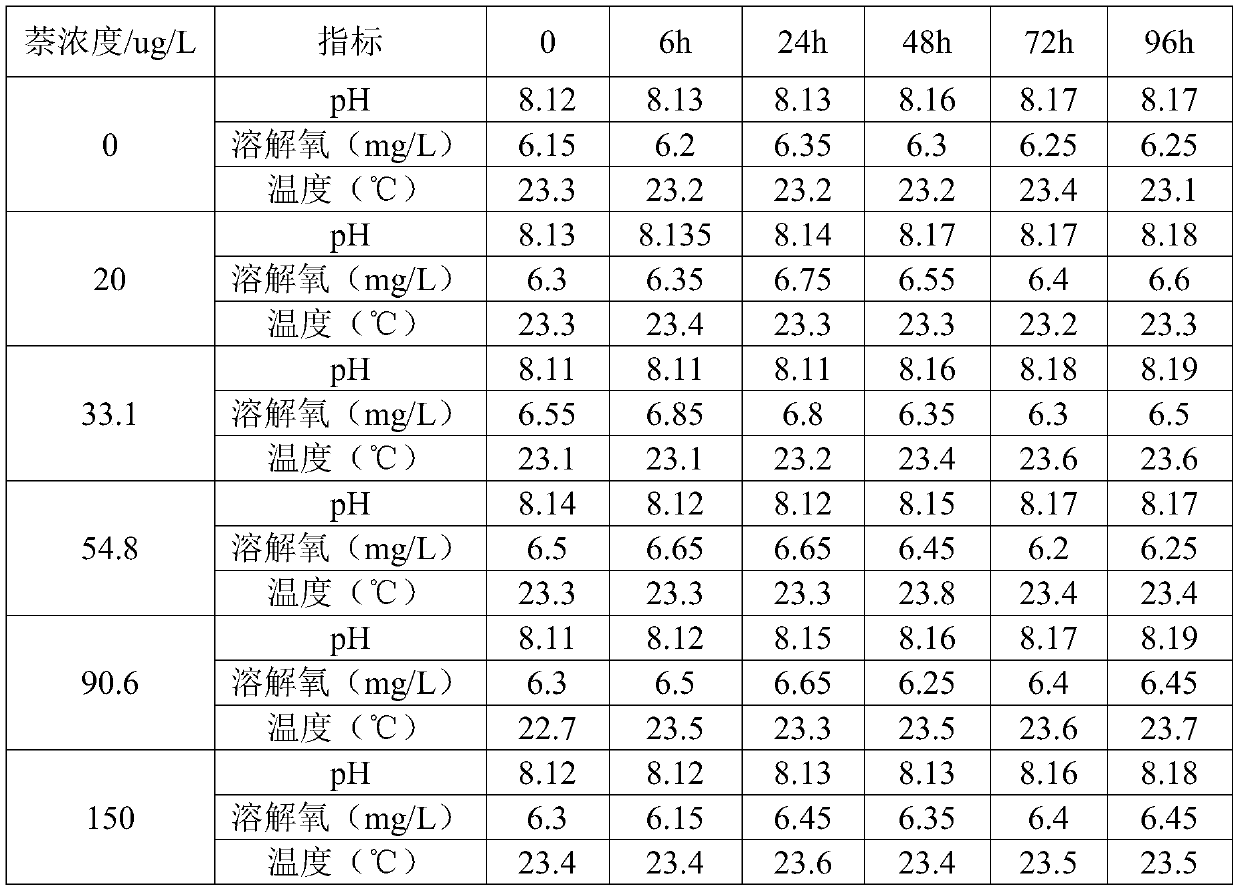
[0039] At different naphthalene concentrations: 0 μg / L, 20 μg / L, 33.1 μg / L, 54.8 μg / L, 90.6 μg / L, 150 μg / L, the changes of pH value, dissolved oxygen and temperature during the mysis acute toxicity test are shown in the table As shown in 1, the mortality rate of mysis after 96h is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0040] Table 1: Water quality parameters of naphthalene acute toxicity test on mysis
[0041]
Embodiment 2
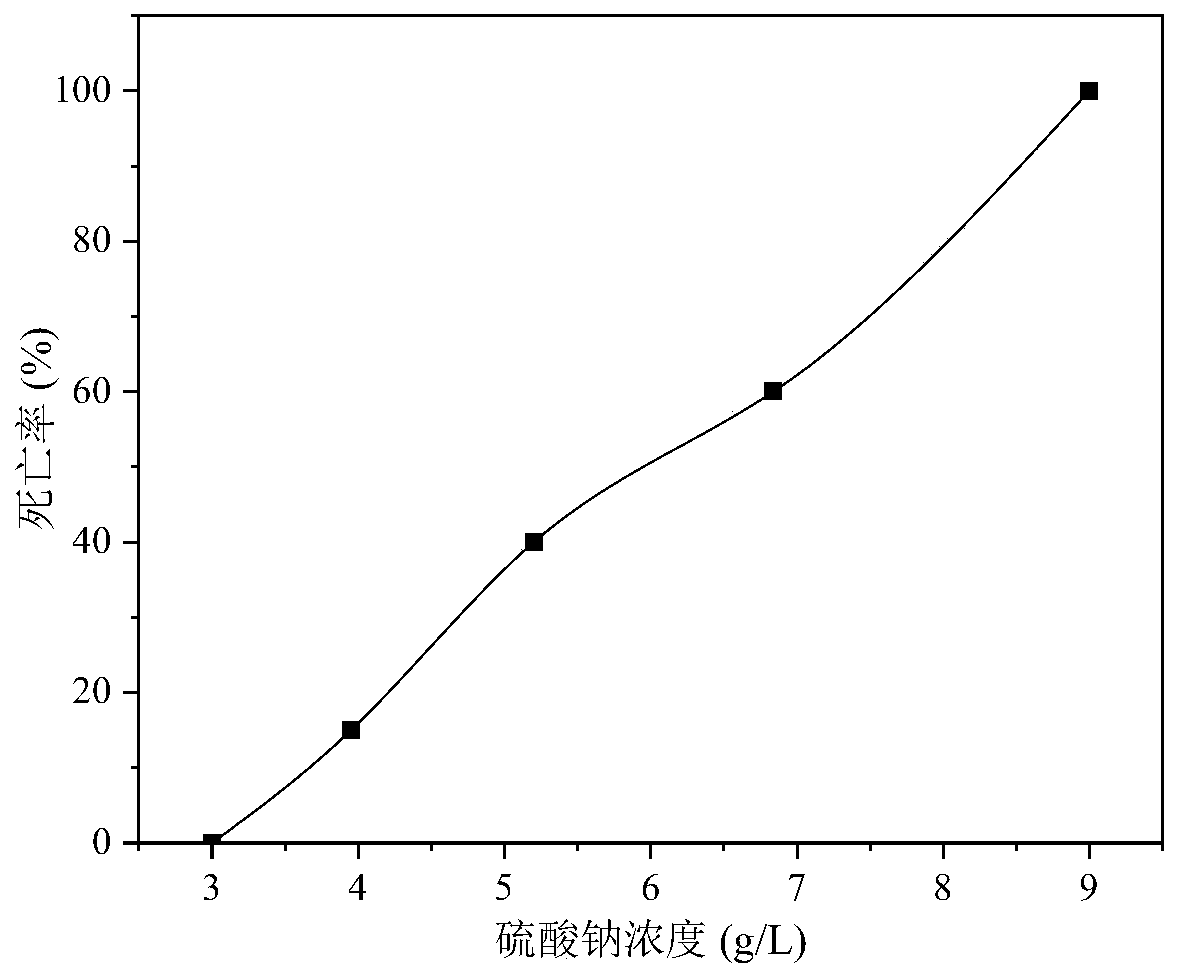
[0043] In different sodium sulfate concentrations: 0g / L, 3g / L, 3.95g / L, 5.20g / L, 6.84g / L, 9g / L, the changes of pH value, dissolved oxygen and temperature during the acute toxicity test of mysid shrimp are as follows: As shown in table 2, the mortality rate of mysis after 96h is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0044] Table 2: Water quality parameters of sodium sulfate acute toxicity test on mysis
[0045]
[0046]
[0047] According to the calculation of the mysis acute toxicity test data of embodiment 1 and 2, it can be obtained: the 96h LC of naphthalene to mysis 50 (Half lethal concentration) is 65.27μg / L, and its 95% confidence interval range is 51.42~82.85μg / L; The 96h LC of sodium sulfate to mysis 50 It was 5.73g / L, and its 95% confidence interval ranged from 5.02 to 6.54g / L. By measuring the pH value, dissolved oxygen and temperature in the test, the test data are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The pH value, dissolved oxygen and temperature fluctuate slightly within ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] After the test was carried out for 7 days, the survival number and average Changes in body weight, average body length, number of females, and average reproduction number are shown in Table 3-Table 6.
[0050] Table 3: Survival numbers of Mysis shrimp chronic toxicity test
[0051]
[0052] Table 4: Average body weight and body length of mysis chronic toxicity test
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] Table 5: Number of females in mysis chronic toxicity test
[0056] Concentration (μg / L) mean ± standard deviation Significant differences control group 2.00±1.41 none 5 2.50±1.29 P=0.97>0.05, the difference is not significant 10 2.00±0.82 P=1>0.05, the difference is not significant 20 2.25±1.26 P=0.999>0.05, the difference is not significant 50 2.75±1.71 P=0.871>0.05, the difference is not significant 70 2.25±0.96 P=0.999>0.05, the difference is not significant
[0057] Table 6: Average reproduction number of My...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average body length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average body length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com