High-throughput separation culture method for crop root system microbiome
A crop root system, separation and cultivation technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, isolation of microorganisms, measurement/inspection of microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as inability to perform autonomous operations, easy contamination and loss of low-abundance bacteria, and inability to popularize laboratories
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1, rice root microbiome high-throughput isolation and culture method
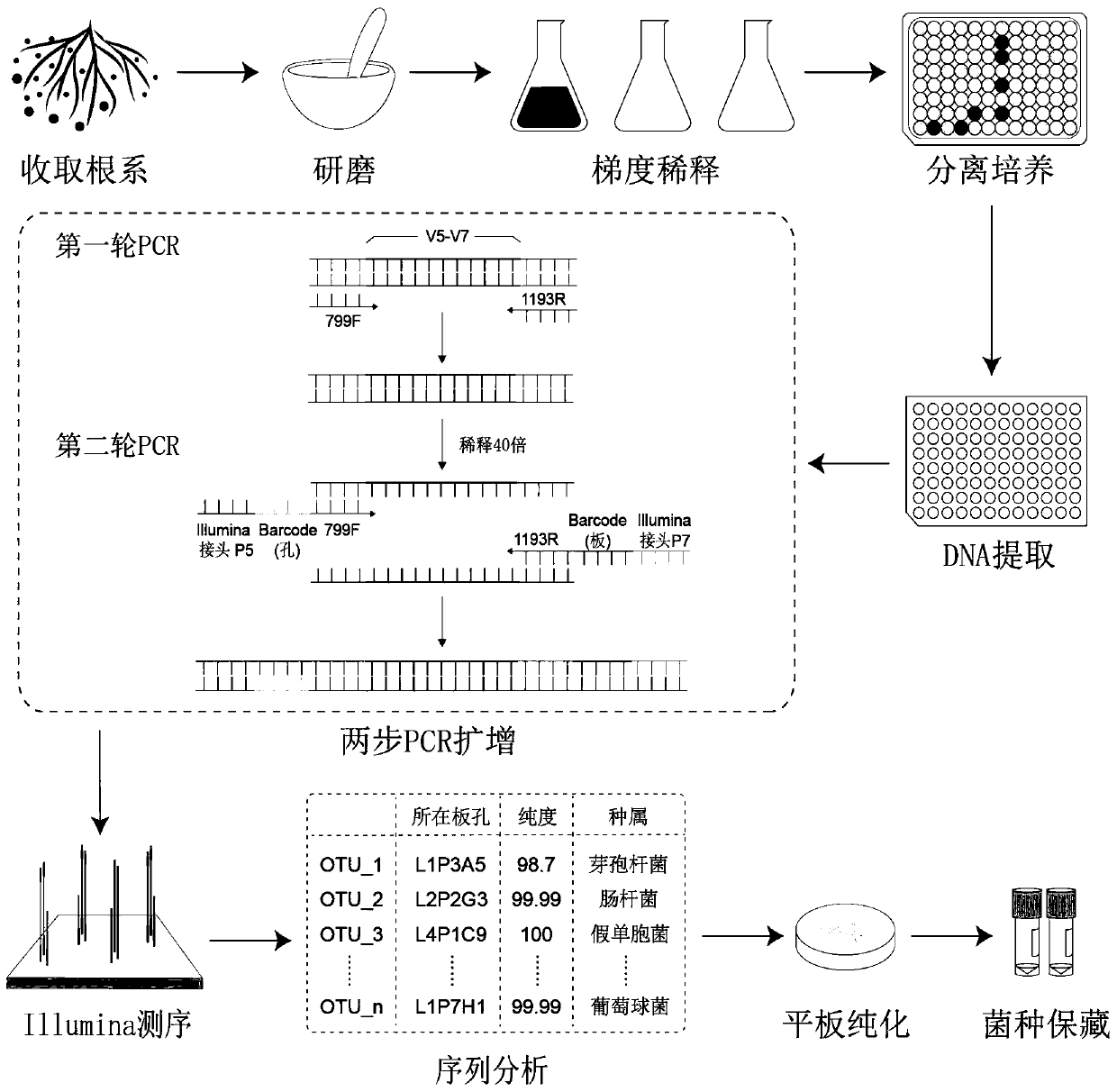
[0035] According to the flowchart ( figure 1 ) to carry out this embodiment.
[0036] In Beijing in 2016, this embodiment was carried out for rice, and the variety used was Nipponbare (belonging to japonica rice).
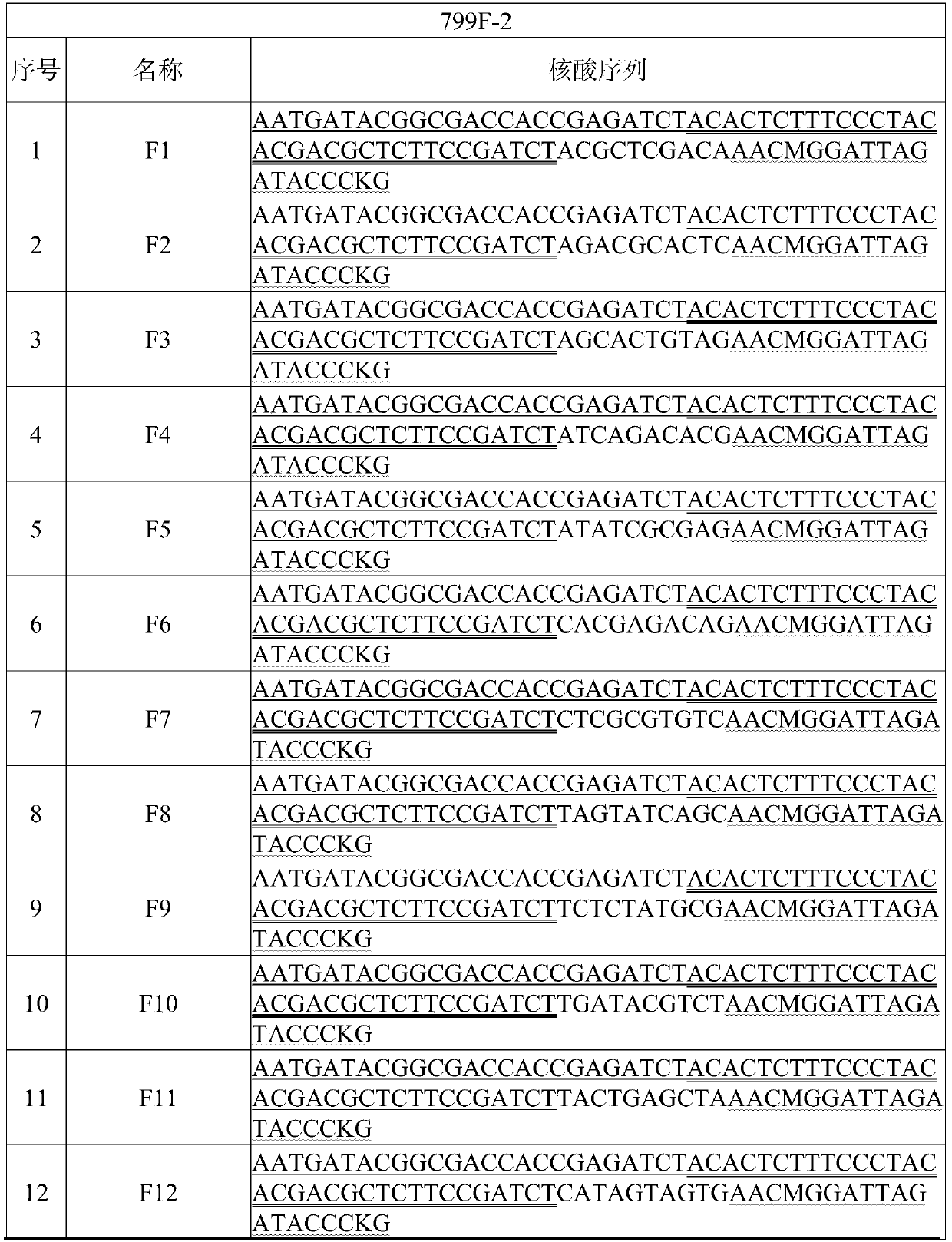
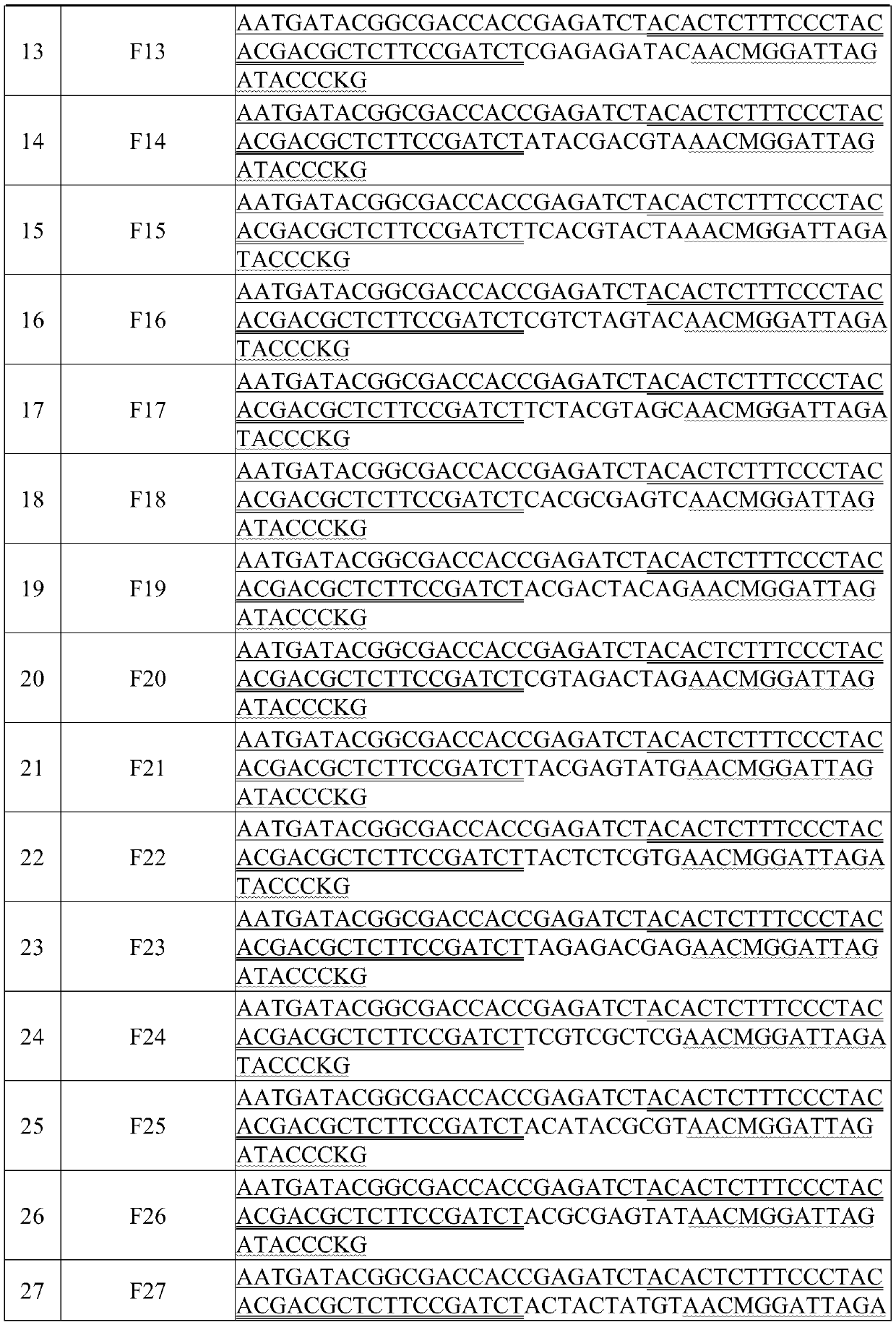
[0037] S1. Under sterile conditions, grind the rice root system to obtain a crop root homogenate, dilute the crop root homogenate by gradient dilution method to obtain multiple dilution samples, and culture each dilution sample in 45 96-hole bacterial cultures Cultivate on the plate until the number of turbid wells of all dilution samples no longer increases; the number of turbid wells accounts for 30-50% of the total number of wells inoculated with the corresponding dilution samples. The liquid in each cloudy well contains bacteria, and the liquid in each cloudy well is named cultured bacteria. Specific steps are as follows:
[0038] S1.1 Sampling and cleaning: Collect 3 r...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2, Arabidopsis root microbiome high-throughput isolation and culture method
[0105] According to the flowchart ( figure 1 ) to carry out this embodiment.
[0106] In Beijing in 2017, this example was carried out on Arabidopsis thaliana, which was grown in a greenhouse and the variety was Columbia (Colombia).
[0107] S1. Under sterile conditions, grind the root system of Arabidopsis thaliana to obtain a crop root homogenate, and use a gradient dilution method to dilute the crop root homogenate to obtain multiple dilution samples, and place each dilution sample in 45 sheets of 96 holes Cultivate on the bacterial culture plate until the number of turbid wells of all dilution samples no longer increases; the number of turbid wells accounts for 30-50% of the total number of wells inoculated with corresponding dilution samples. Well, the liquid in each turbid well contains bacteria, and the liquid in each turbid well is named as cultured bacteria. Specific ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com