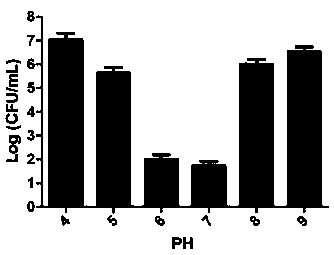
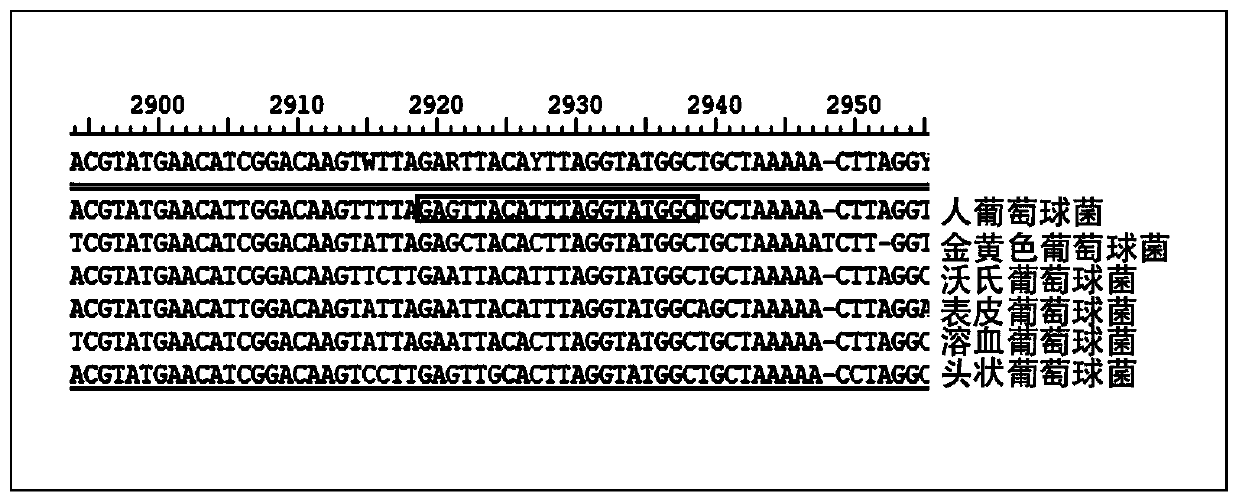
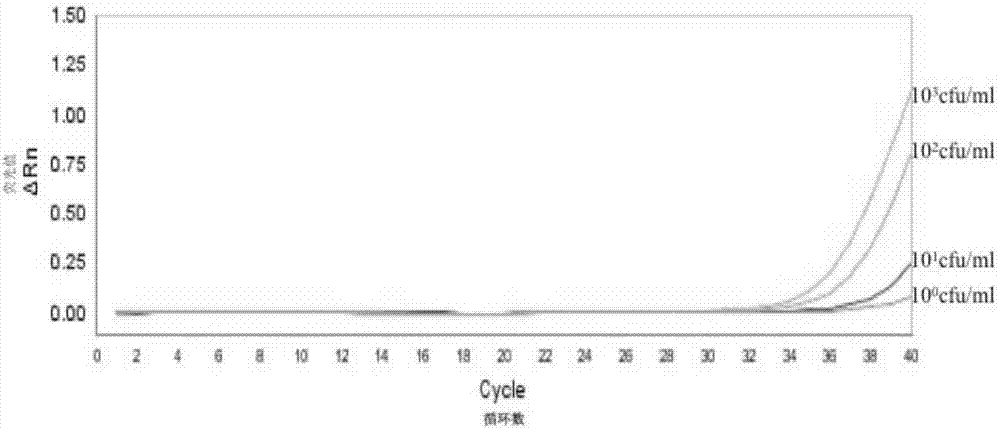
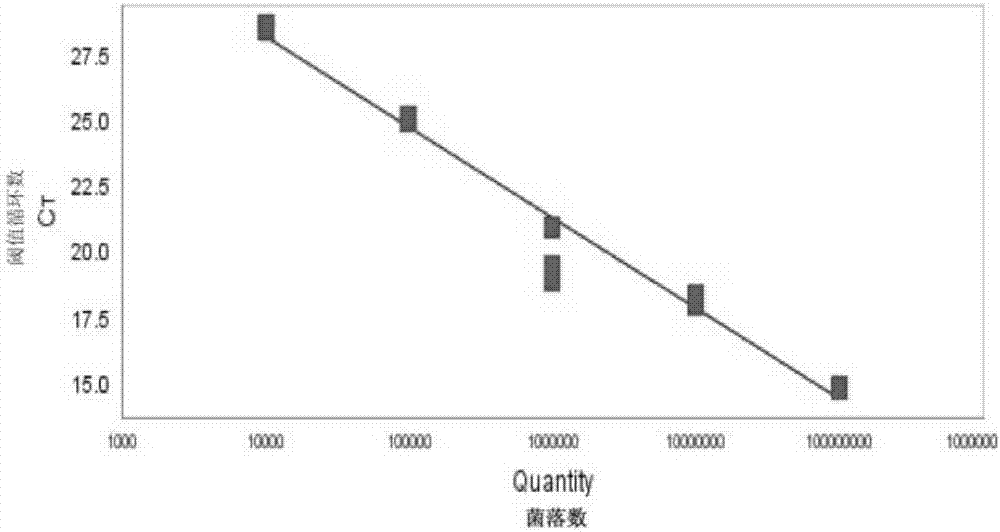
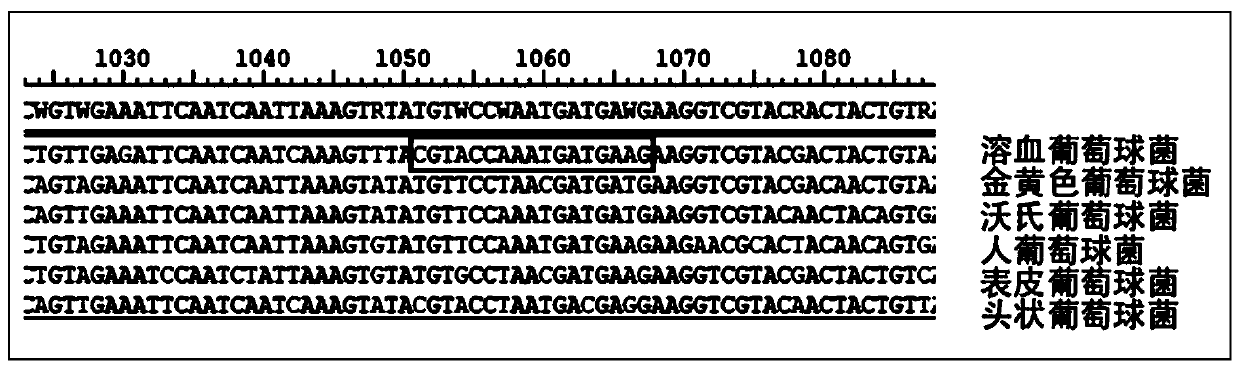
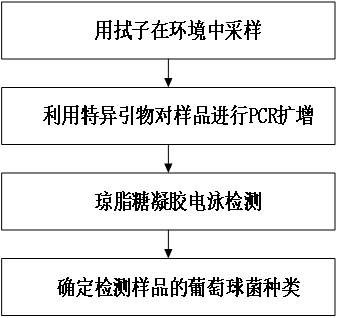
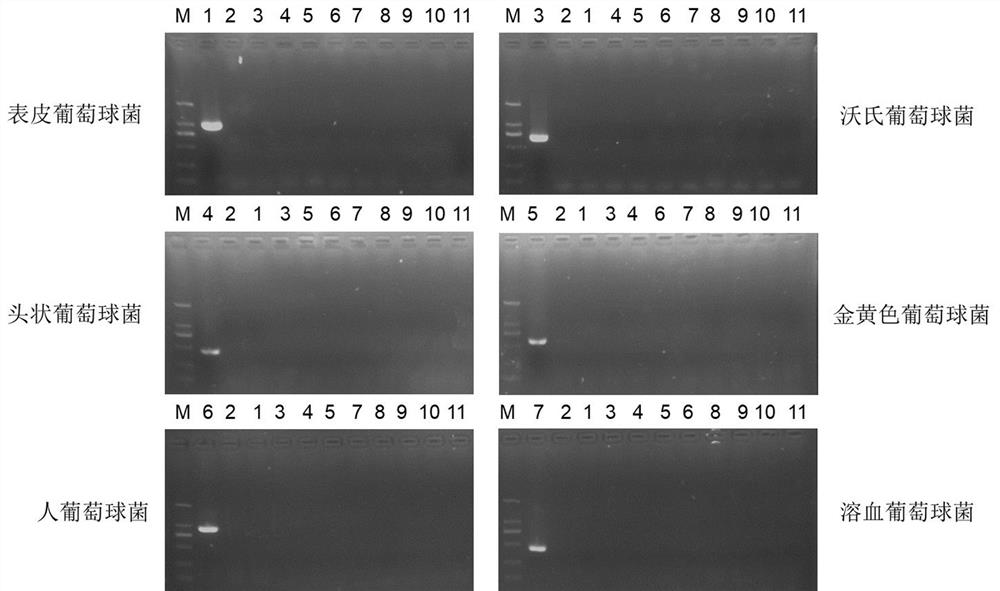
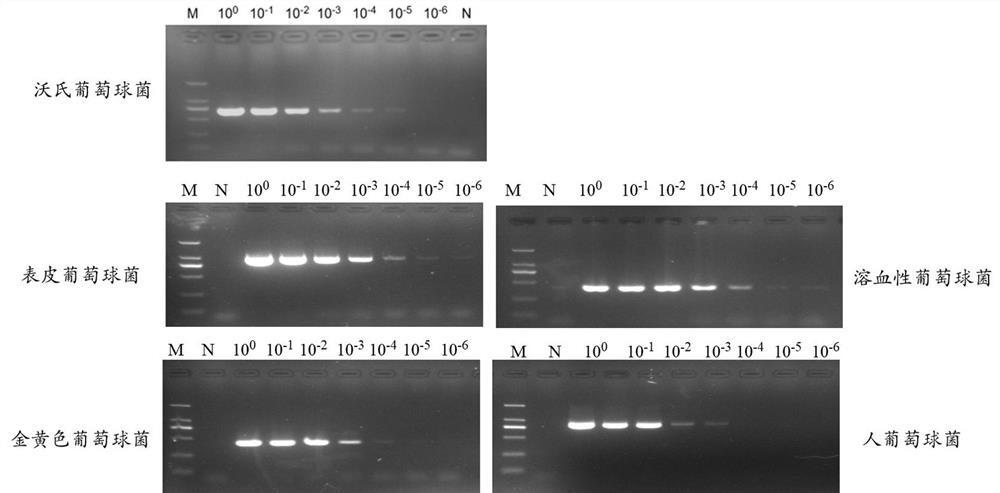
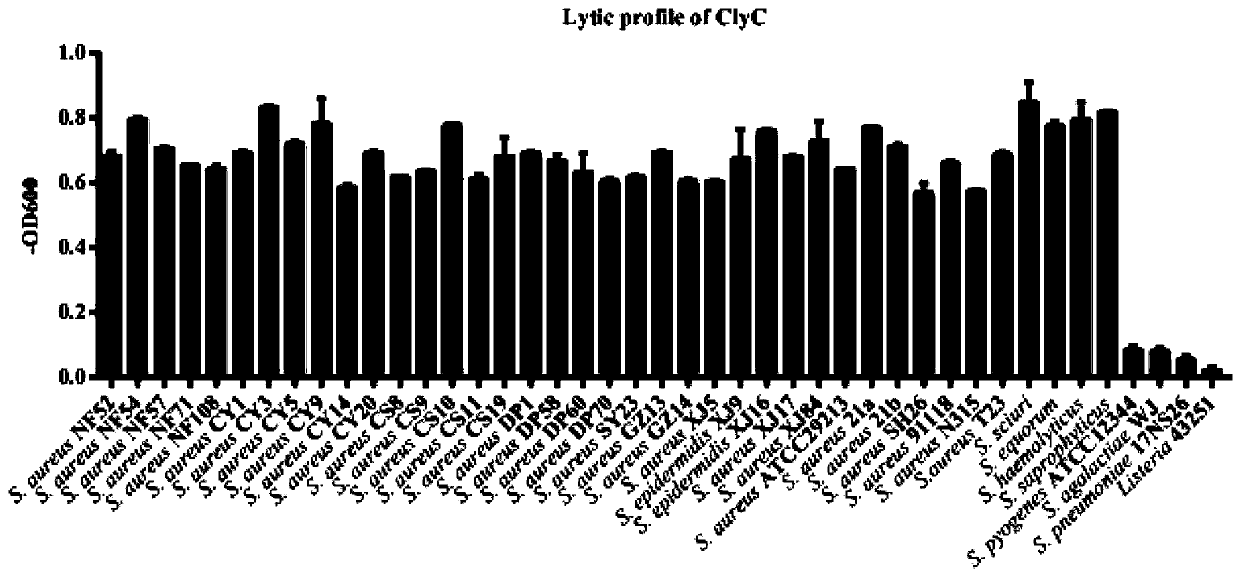
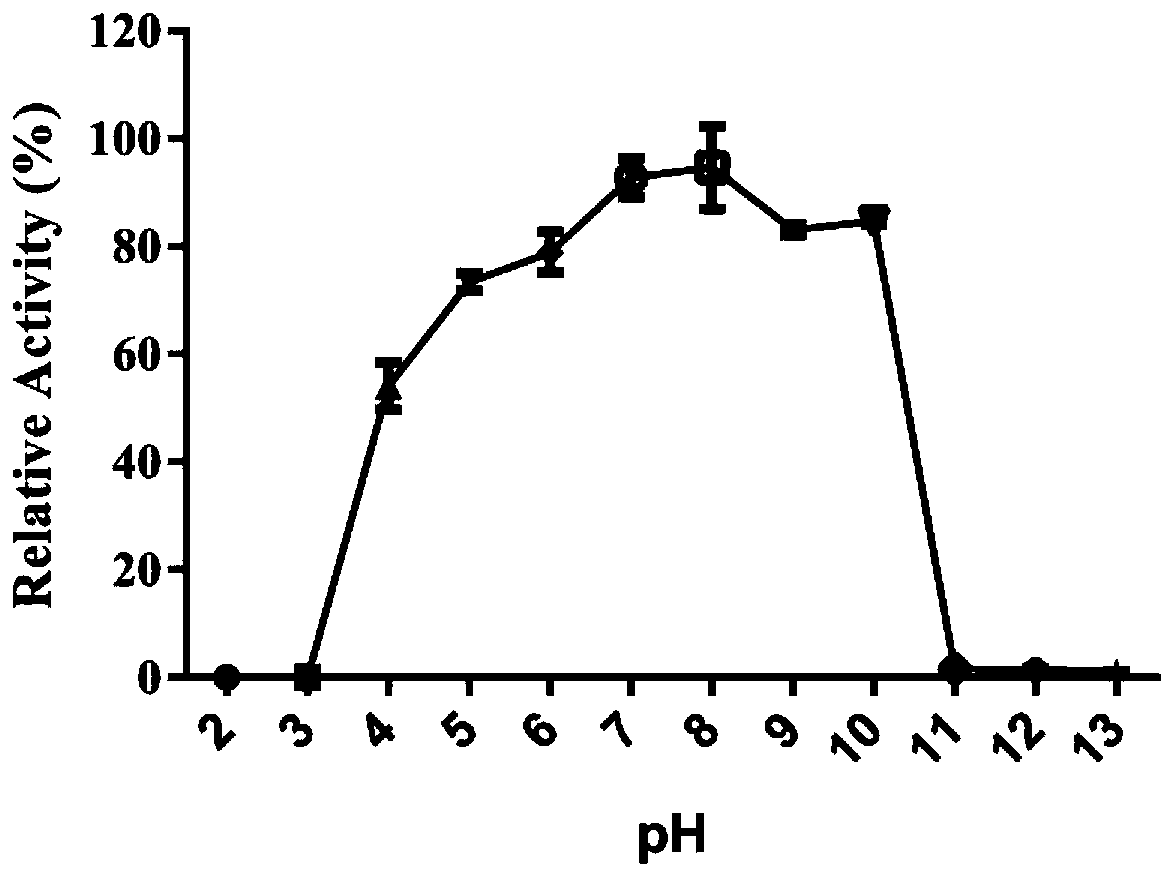
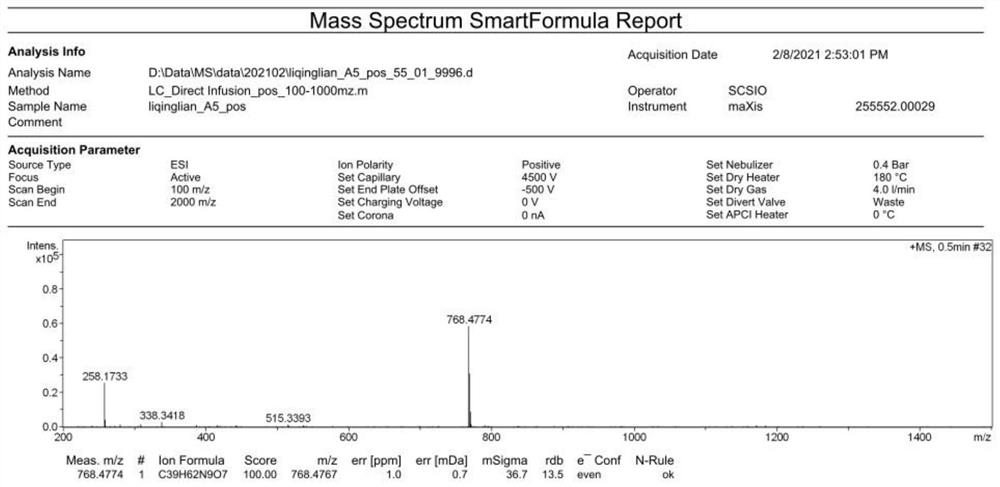
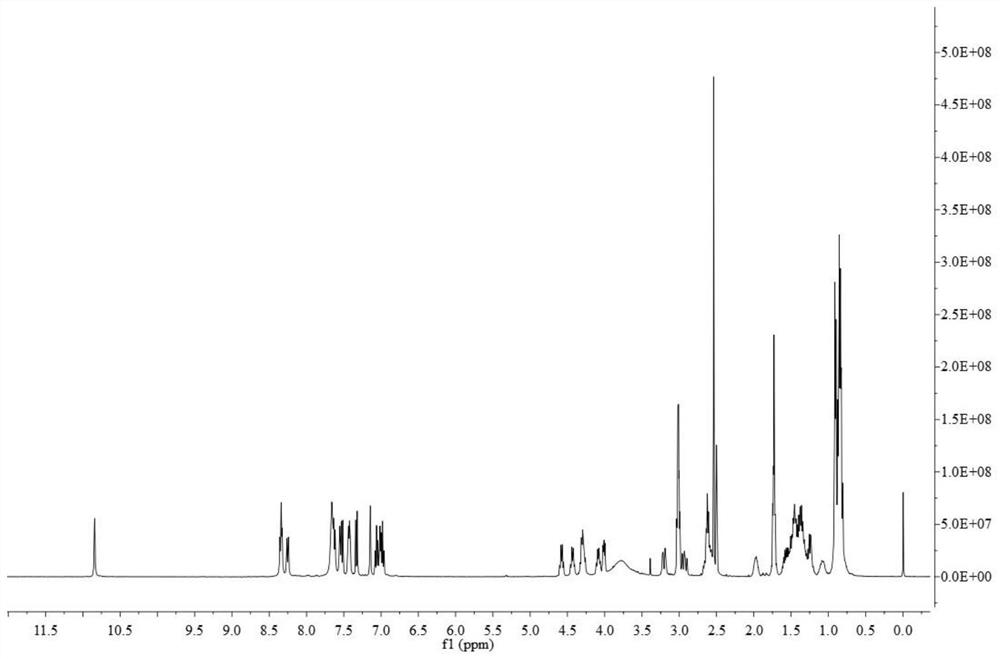
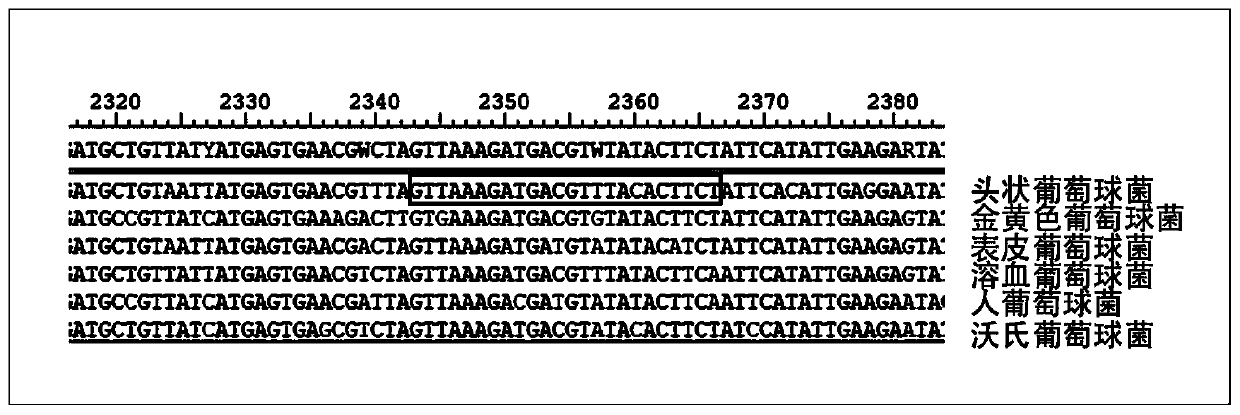
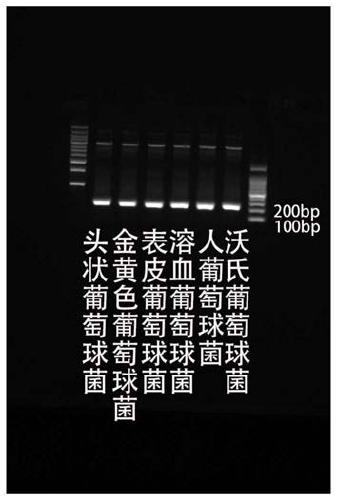
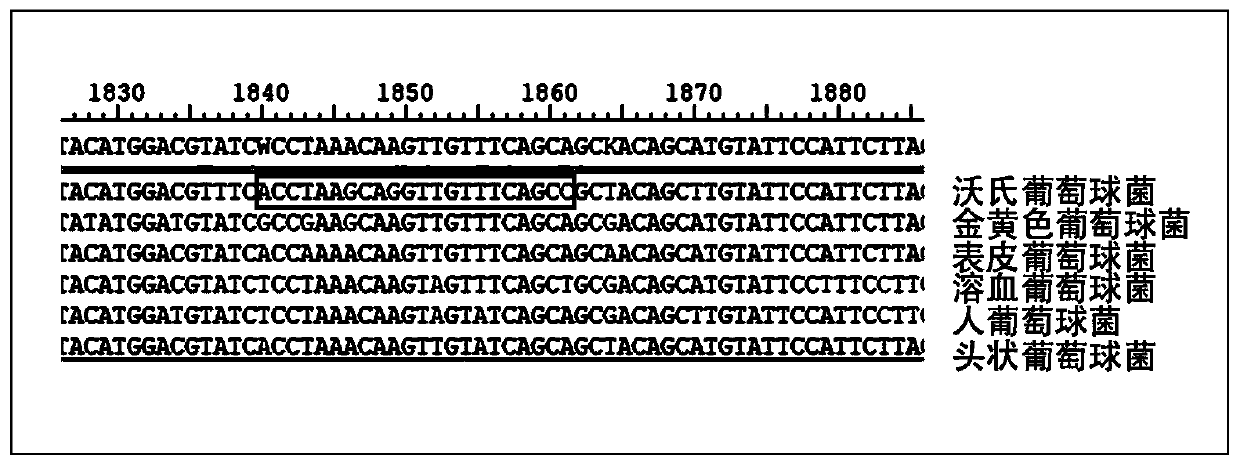
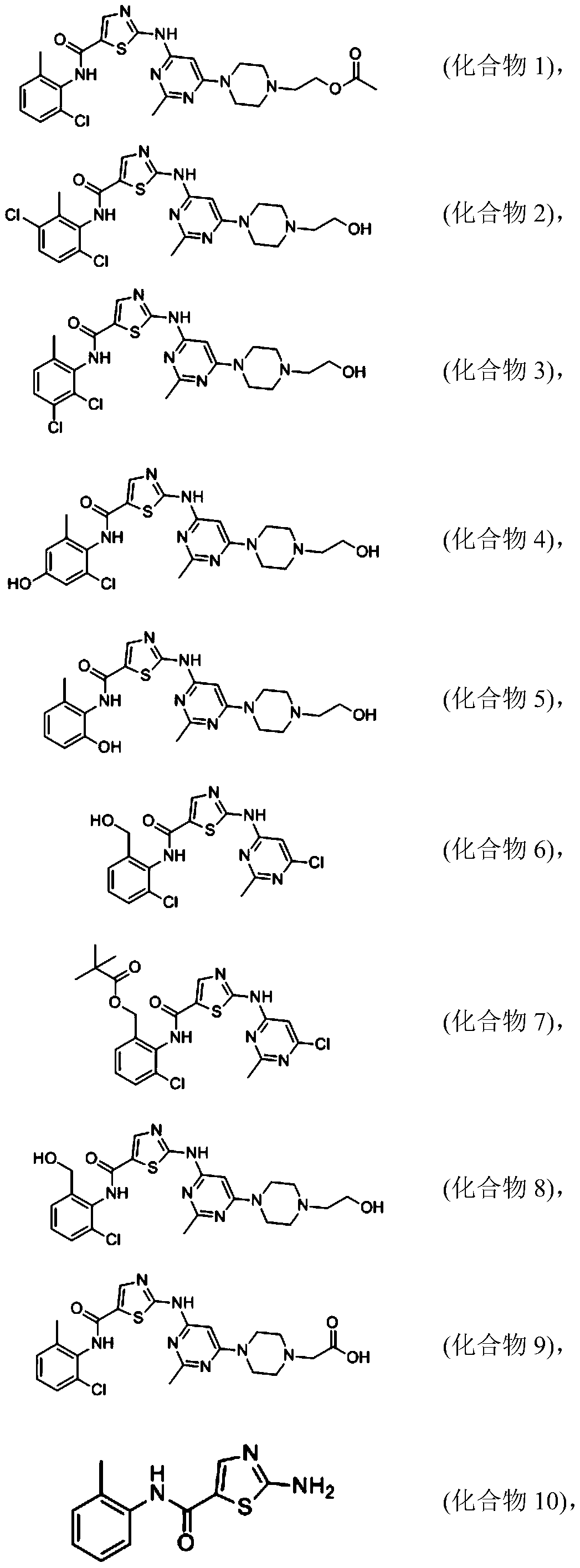
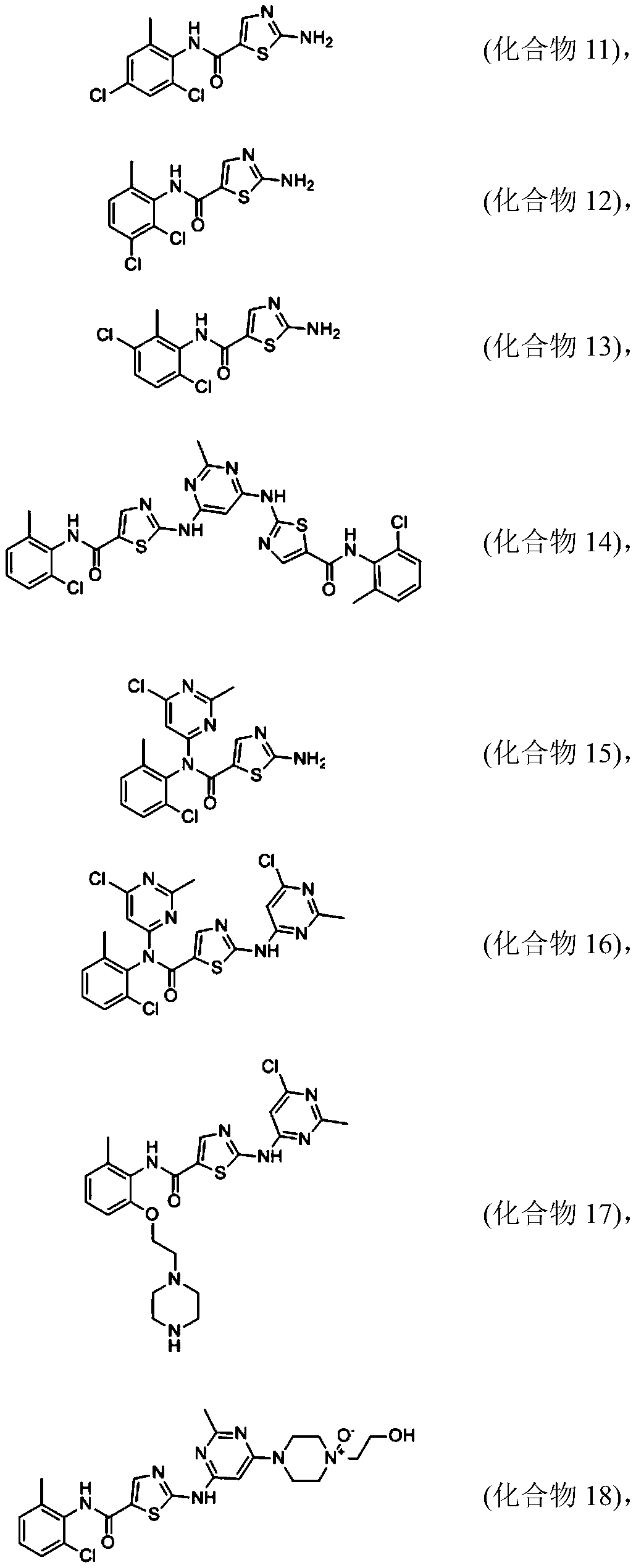
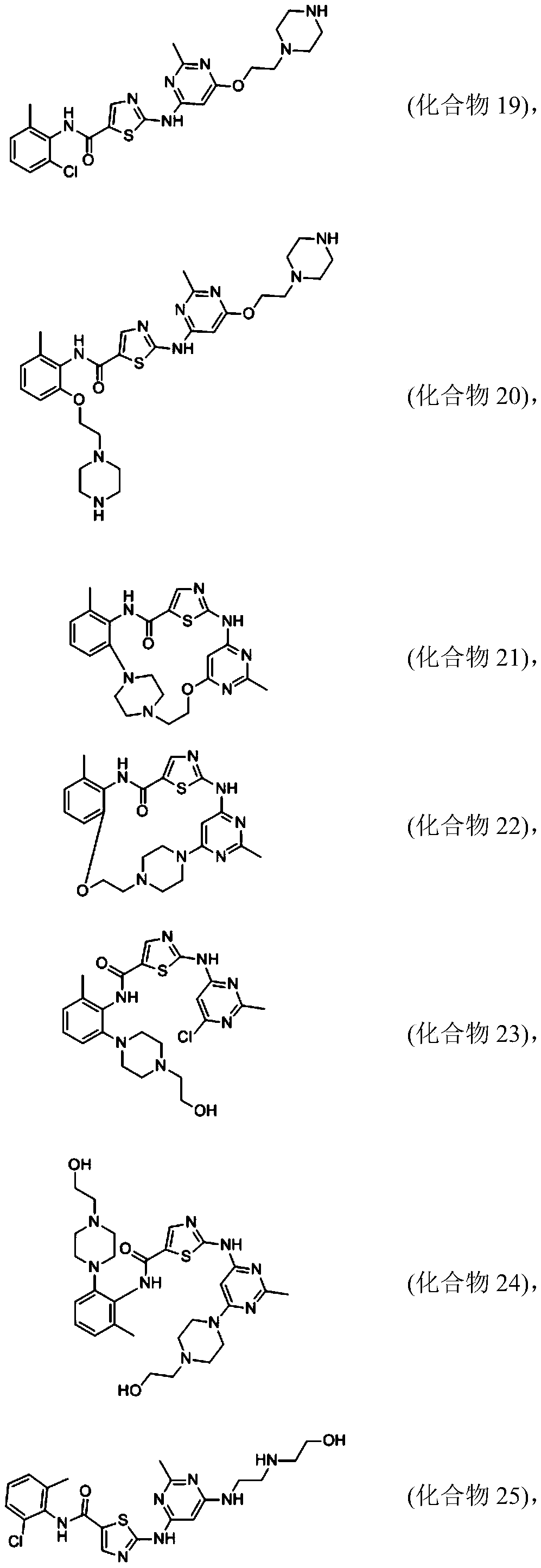
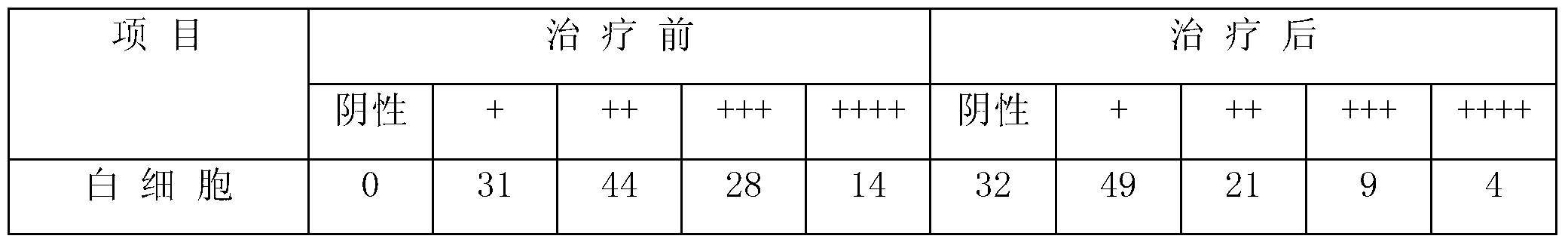
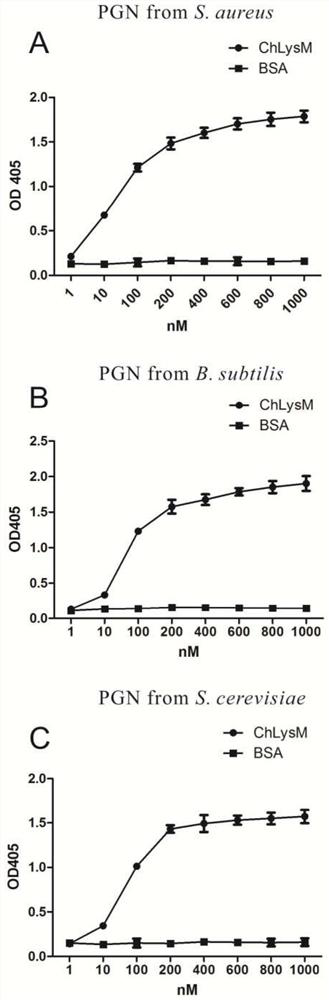
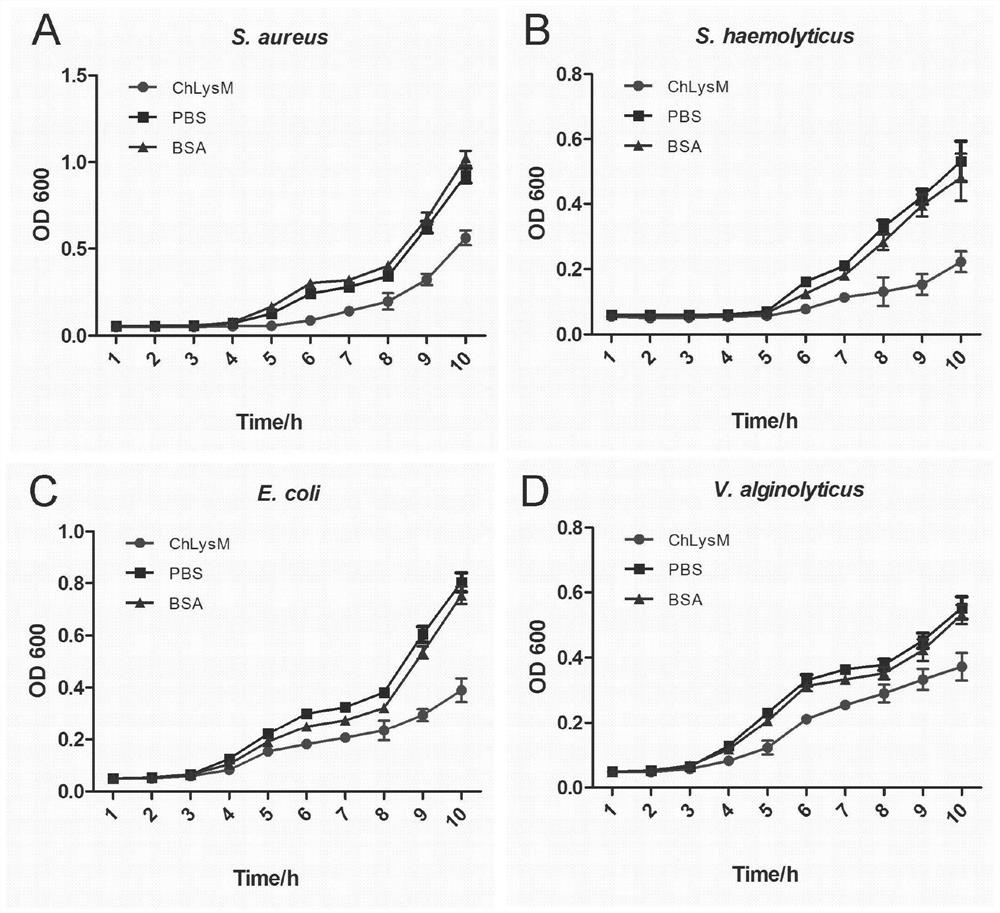
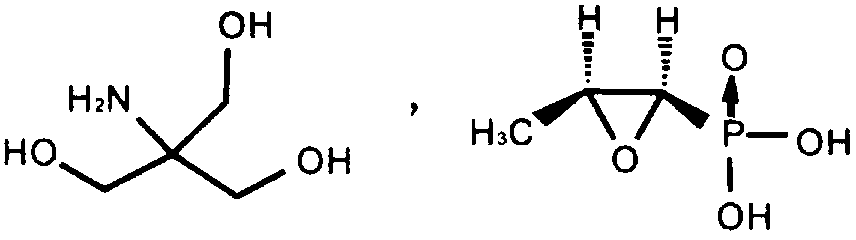Patents
Literature
39 results about "Staphylococcus haemolyticus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS (S. epidermidis is the first). Infections can be localized or systemic, and are often associated with the insertion of medical devices. The highly antibiotic-resistant phenotype and ability to form biofilms make S. haemolyticus a difficult pathogen to treat.
Kit used for staphylococcus aureus detection
InactiveCN110079586ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention provides a kit used for staphylococcus aureus detection. The kit used for staphylococcus aureus detection contains guide RNA of a specific targeted staphylococcus aureus rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), Ribonuclease Inhibitor and buffer liquid. By using the kit for staphylococcus aureus detection, the detection specificity is high, and staphylococcus aureus and other staphylococcus, including staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri,staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus, can be separated. Meanwhile, by using a RNA sequence for detection, elapsed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instruments are used, the equipment requirements are low, and are significantly lower than that of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical application valve is large.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
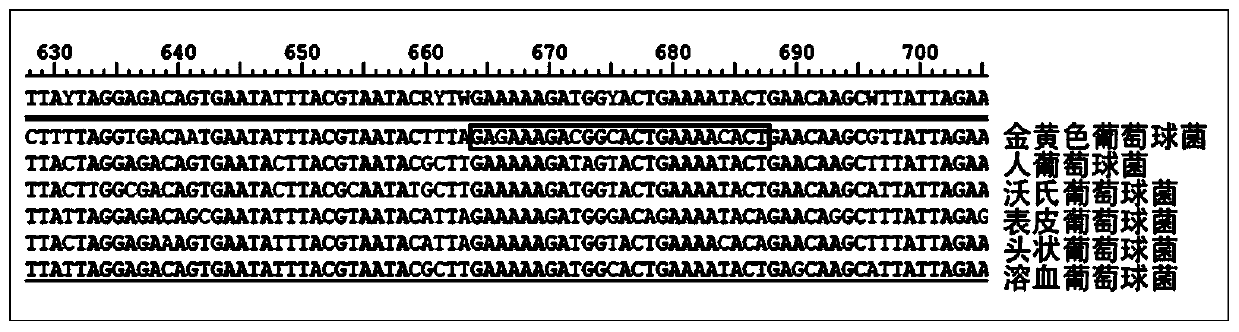
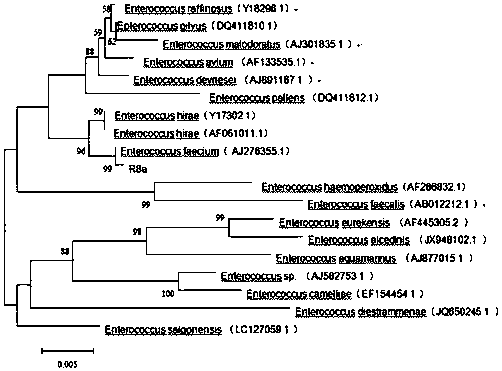
Screening and application of fish-derived enterococcus faecium R8
ActiveCN108660097AHigh activityIncrease weight gainAntibacterial agentsBacteriaStaphylococcus haemolyticusVibrio parahaemolyticus
The invention provides enterococcus faecium R8 that is screened and separated from a crucian intestinal tract and has safe and prebiotic characteristics. The enterococcus faecium is collected in ChinaGeneral Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on January 17, 2018 and has a collection number of CGMCC NO. 15229. The enterococcus faecium is high in heat resistance, acid-base resistance and stress resistance and more significant in probiotic performance, has a relatively obvious inhibiting effect on common aquatic pathogenic bacteria such as aeromonas veronii, staphylococcus haemolyticus, vibrio parahaemolyticus and vibrio vulnificus and can be widely applied to aquaculture as a feed additive.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
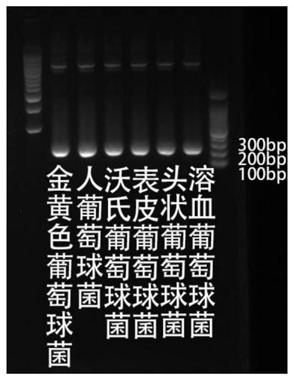
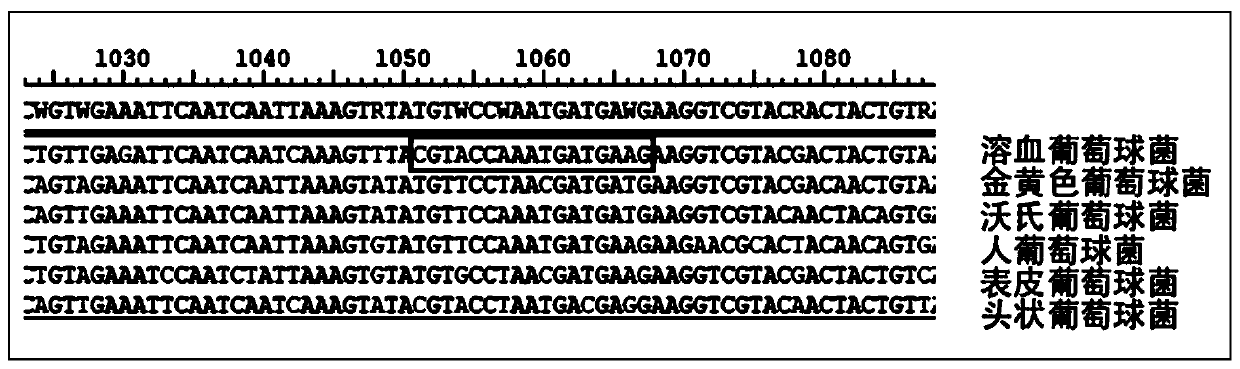
Novel specific molecular targets for four common pathogenic staphylococci and rapid detection method thereof
ActiveCN111154899AImprove practicalityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesStaphylococcus haemolyticusStaphylococcus aureus bacteria
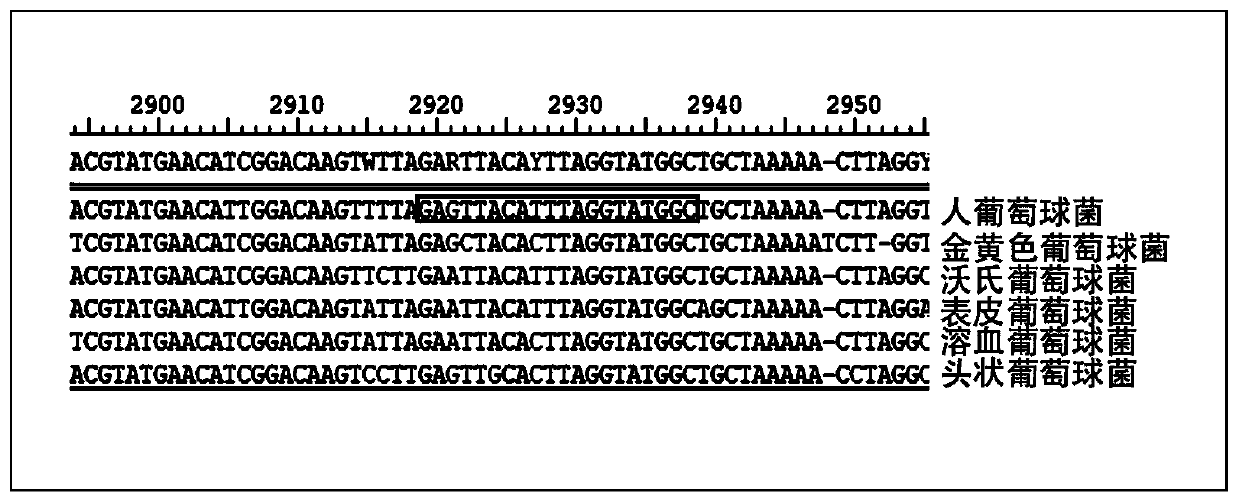
The invention discloses novel specific molecular targets for four common pathogenic staphylococci and a rapid detection method thereof. Nineteen novel specific molecular detection targets for identifying four common pathogenic staphylococci-staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcu sepidermidis, staphylococcus haemolyticus and staphylococcus hominis, and corresponding PCR primer sets and a PCR rapid detection method are provided. The detection method can be used for detecting some strains with insensitive biochemical reaction, so that the defects of biochemical identification can be made up, and practicability can be enhanced; and the detection method also has the advantages of being simple in operation, easy in result determination, short in detection time, strong in specificity and low in cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
Genetically engineered lysin with function of killing staphylococcus, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110684760AEfficient killingBroad cracking spectrumAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiOrganomercurial lyase
The invention discloses a genetically engineered lysin with a function of killing staphylococcus and a preparation method. According to the preparation method, a lysin LysGH15 is subjected to genetically engineered modification to obtain a novel bacteriophage lysin LysGH15(+). The bacteriophage lysin LysGH15(+) shows stronger bactericidal activity and wider host spectrum, in comparison with a lysin before modification, can kill staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus haemolyticus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus saprophyticus, staphylococcus cohnii, fermented staphylococcus xylosus and the like, provides a potential novel medicine to prevention and treatment of diseases caused by staphylococcal infection, and has a good application value.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus hominis
InactiveCN110157821ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus hominis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus hominis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus hominis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus hominis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
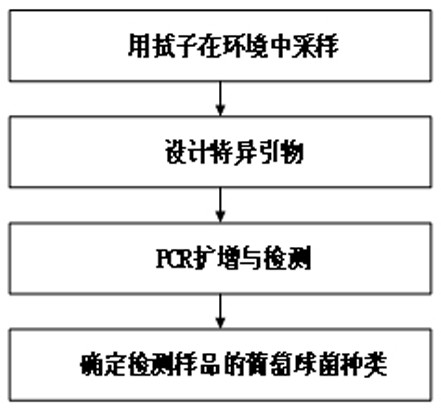
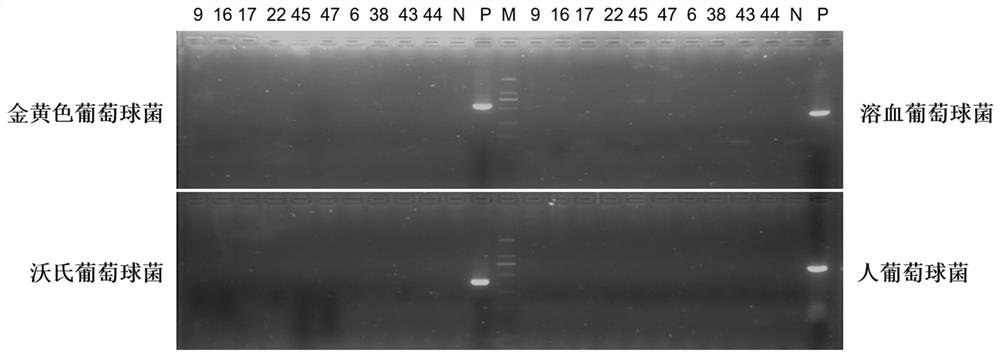
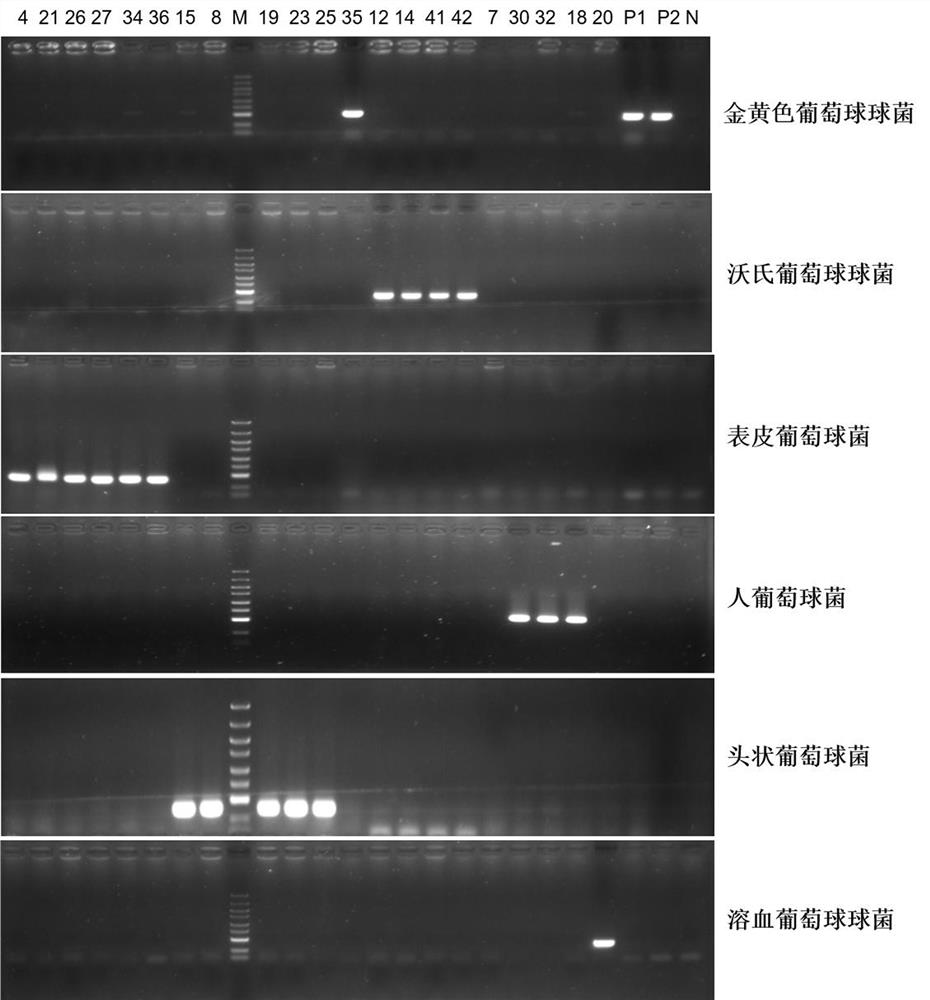
Primer group, kit and method for identifying staphylococcus in environment at in-species level
ActiveCN112961929AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStaphylococcus haemolyticusNucleotide
The invention provides a primer group, kit and method for identifying staphylococcus in an environment at an in-species level, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection. The primer group comprises primers F1 and R1 for amplifying staphylococcus aureus, primers F2 and R2 for amplifying staphylococcus warneri, primers F3 and R3 for amplifying staphylococcus epidermidis, primers F4 and R4 for amplifying staphylococcus hominis, primers F5 and R5 for amplifying staphylococcus capitis, and primers F6 and R6 for amplifying staphylococcus haemolyticus; and the nucleotide sequences of the primers F1, R1, F2, R2, F3, R3, F4, R4, F5, R5, F6 and R6 are respectively as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 to SEQ ID No. 12. The primer group, kit and method are easy to operate and high in sensitivity, and can complete the detection of environmental staphylococcus in a short time; and the method is low in cost, can identify various staphylococcus species, and is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:至微生物智能科技(厦门)有限公司
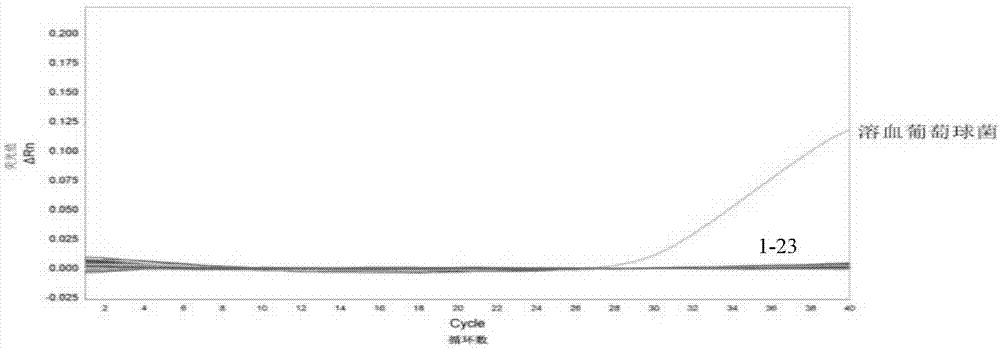
Complete set reagent for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus
InactiveCN107988400AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a complete set reagent for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus. The complete set reagent for detecting the staphylococcus haemolyticus disclosed by the invention is composedof a primer pair for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus and a probe, wherein the primer pair consists of single-chain DNA with names of F and R; F is a single-chain DNA molecule shown in sequence 1of a sequence table; R is a single-chain DNA molecule as shown in sequence 2 of the sequence table; and a sequence of the probe is sequence 3 of the sequence table. According to the experiment, the complete set reagent for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus has high specificity, high sensitivity and very good repeatability and amplification efficiency while detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus, is simple and convenient, quick and accurate in detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus, and is a reagent used for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus and preparing staphylococcus haemolyticus.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Kit for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus
InactiveCN110129462ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus. The kit comprises guide RNA specifically targeting staphylococcus haemolyticus rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-chain DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus haemolyticus, high detection specificity is achieved, and the staphylococcus haemolyticus can be distinguished from other staphylococcus such as staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus epidermidis. Meanwhile, when the RNA sequence is used to perform detection, detection time is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, equipment requirements are evidently lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and a high clinical practical value is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Primers and detection kit for identifying various staphylococci based on pheS gene and application of primers and detection kit
ActiveCN112980982AQuick checkRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteria identificationStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention provides primers and a detection kit for identifying various staphylococci based on a pheS gene and application of the primers and the detection kit, and belongs to the technical field of bacterial identification. The invention provides a primer group for identifying various staphylococci based on a pheS gene. The primer group comprises the following two or more primer pairs: a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus aureus, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus warneri, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus epidermidis, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus hominis, a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus capitis, and a primer pair for specifically amplifying staphylococcus haemolyticus. The primer group has the characteristics of good amplification specificity, high detection sensitivity and simultaneous identification of various staphylococci. A method for detecting various staphylococci in the environment based on the primer group can realize simultaneous identification of various staphylococci, and has the characteristics of short detection time, low detection cost and an accurate and reliable detection result.
Owner:至微生物智能科技(厦门)有限公司
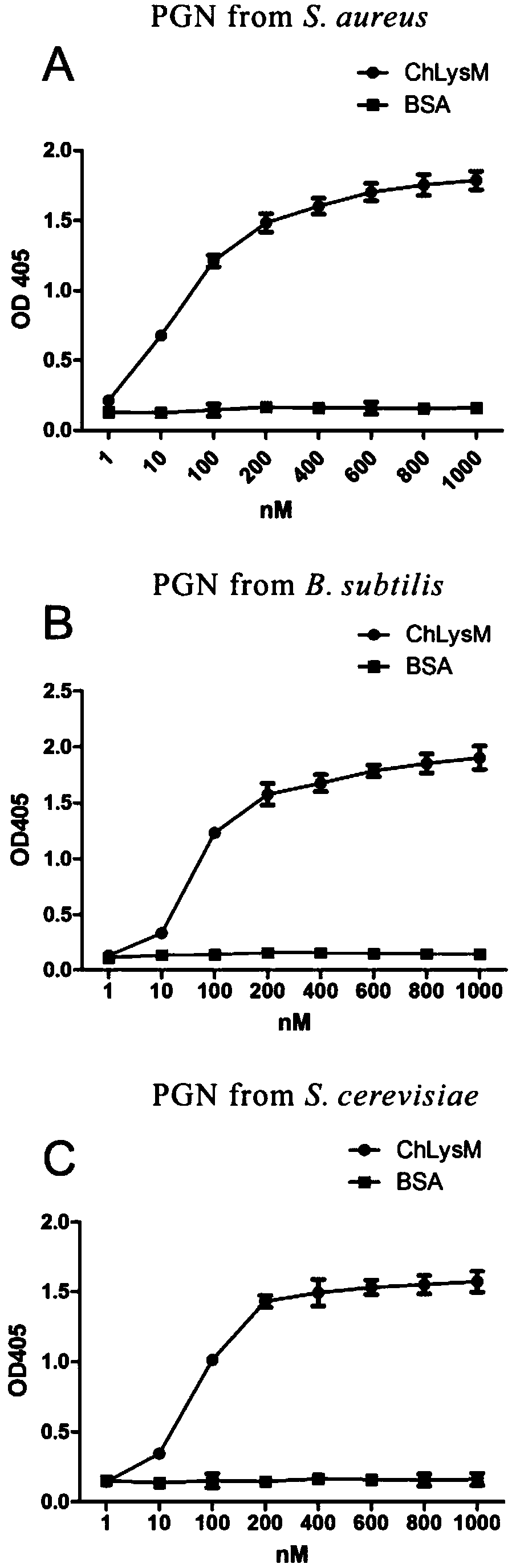
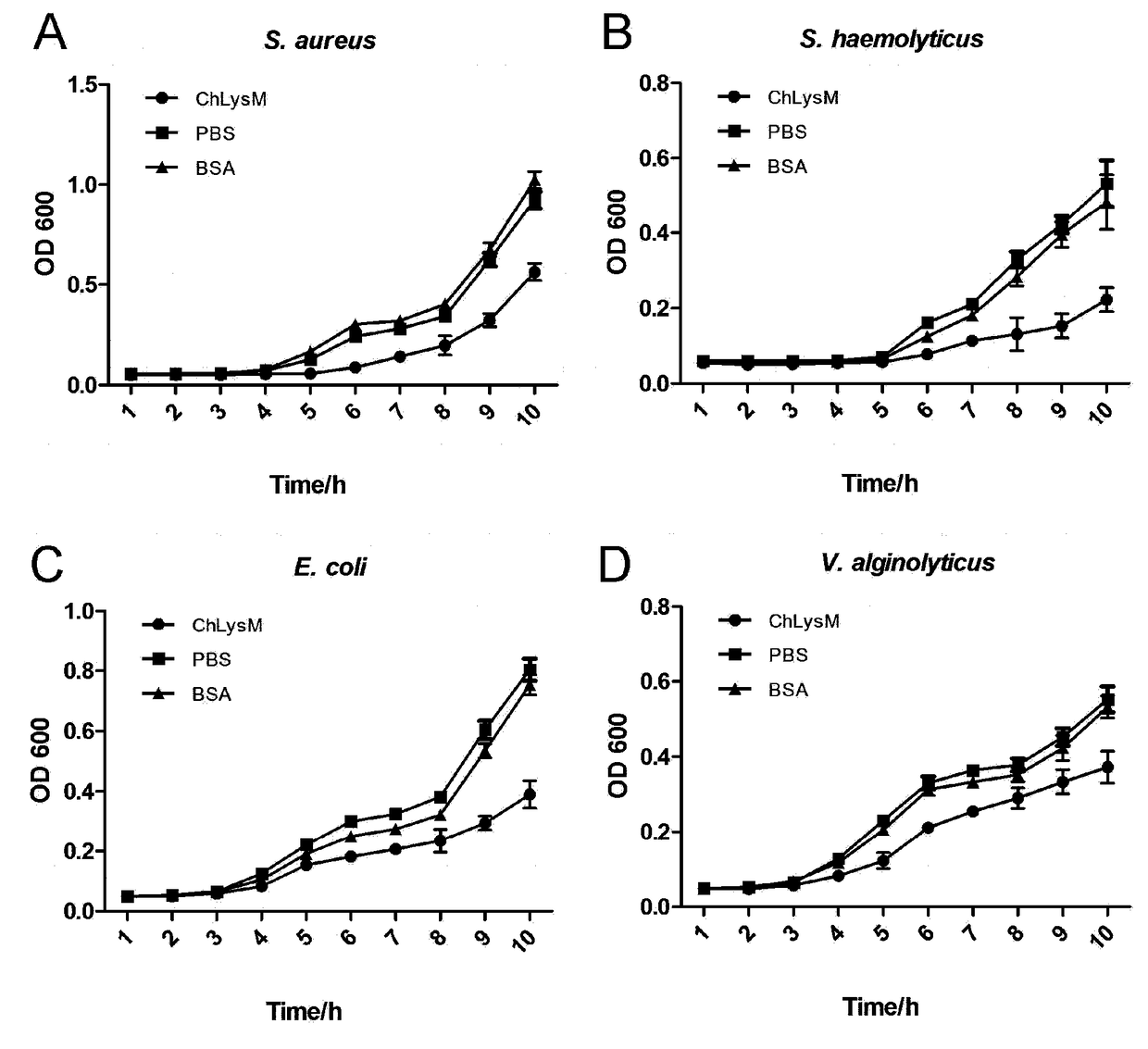
Crassostrea hongkongensis LysM protein having bacteriostatic activity, and encoding gene and application of crassostrea hongkongensis LysM protein
ActiveCN108794613AEfficient identificationGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention discloses a crassostrea hongkongensis LysM protein having a bacteriostatic activity, and an encoding gene and an application of the crassostrea hongkongensis LysM protein. The LysM protein is separated from crassostrea hongkongensis for the first time, PGN is effectively recognized, and the LysM protein has an obvious bacteriostatic effect on the growth of alginolyticus, staphylococcus haemolyticus, staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli. The LysM protein plays important roles in immunological recognition of the crassostrea hongkongensis and the antibacterial activity, provides evidences for developing broad-spectrum antibiotics and screening an immunopotentiator, and also provides an application guide for the disease resistance and breeding of the shellfish.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Uses of Phyllanthus emblica, and Phyllanthus emblica composition and uses thereof
InactiveCN109276602AExpand the scope of antibacterial applicationGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses applications of Phyllanthus emblica or Phyllanthus emblica and a Phyllanthus emblica composition in preparation of products for preventing and / or treating at least one of mastitis, diarrhea and porcine respiratory diseases, and further provides antibacterial effects of Phyllanthus emblica or Phyllanthus emblica extract and the Phyllanthus emblica composition, wherein the Phyllanthus emblica or Phyllanthus emblica extract and the Phyllanthus emblica composition can effectively inhibit the growth of one or a variety of bacteria selected from Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Pseudomonas, Salmonella choleraesuis, Escherichia coli, Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, Streptococcus suis, Bordetella, Pasteurella multocida, Salmonella enterica, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Enterococcus faecalis and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, and the effectiveness of the uses are proved through experiments so as to expanded the applications of Phyllanthus emblica andthe Phyllanthus emblica composition.
Owner:SICHUAN ANIMAL SCI ACAD
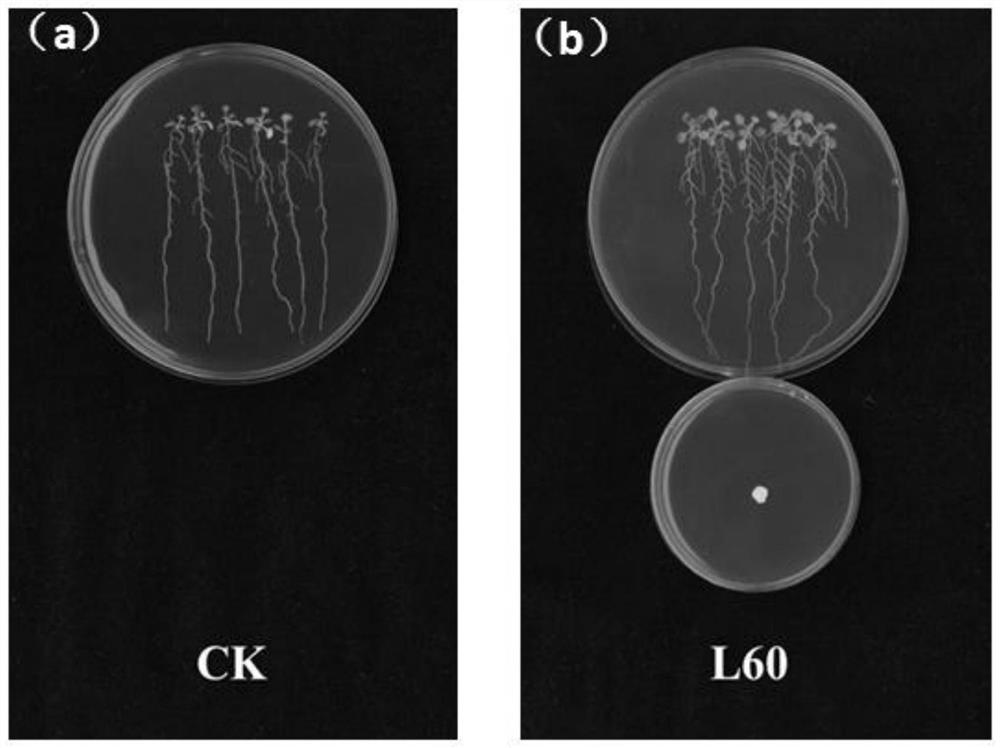
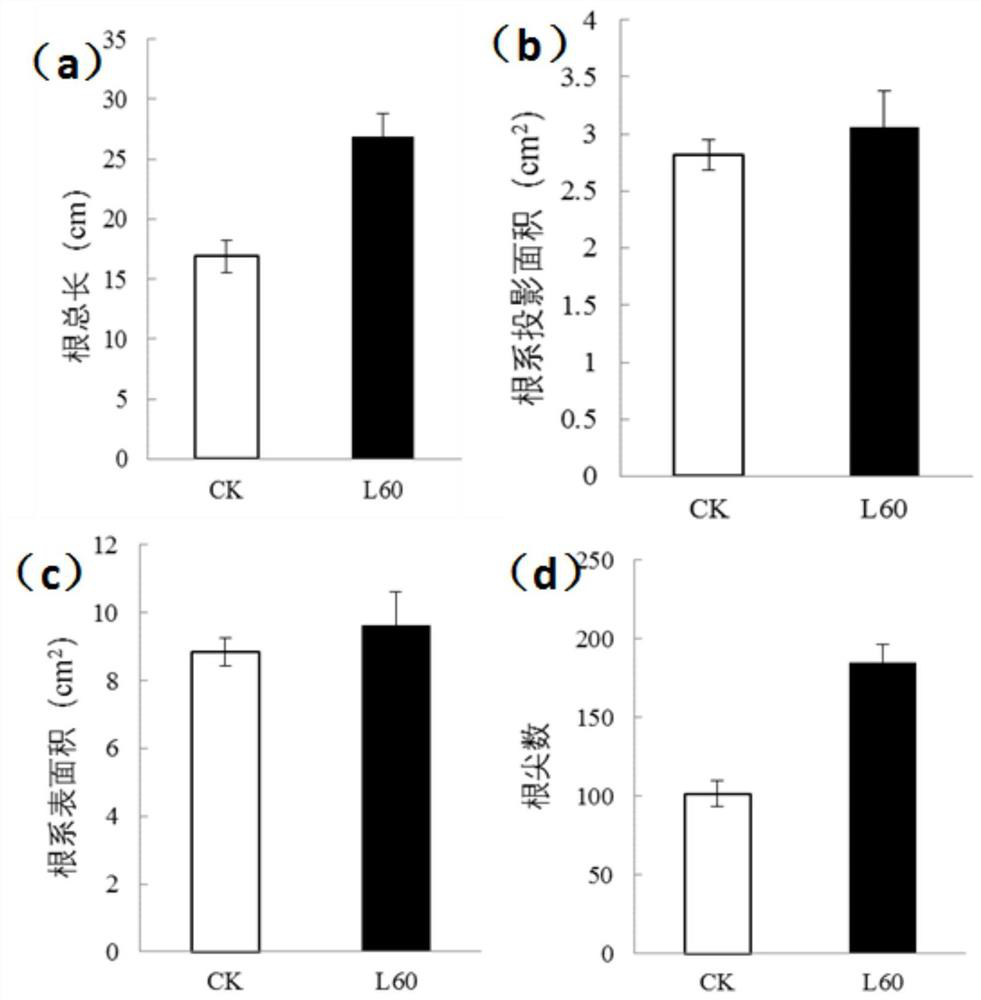
Applications of corn growth promoting rhizobacteria in promoting growth of plants
ActiveCN112680386APromote growthIncrease the projected areaBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial application, and specifically discloses applications of corn rhizosphere growth promoting bacteria in promoting growth of plants. The corn rhizosphere growth promoting bacteria are staphylococcus haemolyticus and can be used for promoting the growth of corns and arabidopis thaliana. Volatile substances produced by the strains can promote the growth of the corns and arabidopis thaliana, especially have efficient promotion effects on the roots of the corns and arabidopis thaliana.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Staphylococcus lyase and preservation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110117587AHigh expressionLow cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention relates to a lyase capable of killing staphylococcus, in particular to staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus sciuri, staphylococcus equorum, staphylococcus haemolyticus, staphylococcus saprophyticus and other staphylococcus, and a preservation method and application of the lyase. The amino acid sequence of the staphylococcal lyase is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the nucleotide sequenceof a gene for encoding the staphylococcal lyase is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The pH range of the lyase for effect exertion is wide, the activity for lysing the staphylococcus is kept at the pH of 6-10, and a recombinant protease constructed by the encoding gene can be subjected to soluble expression in escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). The lyase can be used as an antibiotic for treating in-vivo and in-vitro staphylococcal infection and can also quickly lyse the cell walls of the staphylococcus to release substances in cells, and therefore the lyase is used for nucleic acid extraction and preparation ofmedicaments for staphylococcal detection and identification. It is proved through tests that after the staphylococcus lyase is lyophilized, the bactericidal activity of the protein of the staphylococcus lyase is not reduced, and therefore the staphylococcus lyase can be prepared into lyophilized powder for storage.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cyclic hexadepsipeptide compound desotamide A4 and application thereof in preparation of antibacterial drugs
ActiveCN113150077AStrong inhibitory activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsPeptidesCyclic peptideStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention discloses a cyclic hexapeptide compound desotamide A4 and an application thereof in preparation of antibacterial drugs. The structural formula of the compound desotamide A4 is as shown in formula (I) . The cyclic hexapeptide desotamide A4 disclosed by the invention has a broad-spectrum anti-gram pathogenic bacterium effect. The test result shows that the desotamide A4 has good inhibitory activity (MIC is 8-32 [mu] g / mL) on a plurality of clinical drug-resistant staphylococcus aureus, enterococcus faecalis, micrococcus luteus, bacillus subtilis, simulated staphylococcus and staphylococcus haemolyticus including methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus; compared with an unmodified parent natural cyclic peptide compound desotamide A, the activity of the cyclic hexapeptide desotamide A4 disclosed by the invention is enhanced by 2-4 times, and the cyclic hexapeptide desotamide A4 has an important value in research and development of antibacterial drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Staphylococcus haemolyticus applied to preventing and treating xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and application thereof
ActiveCN107201330AStrong antagonistic effectReduce usageBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention discloses staphylococcus haemolyticus applied to preventing and treating xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and application thereof. The staphylococcus haemolyticus is named as staphylococcus haemolyticus JS-1, a preservation number is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2017308, and the staphylococcus haemolyticus is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University in Wuhan of China on June 6th 2017. The staphylococcus haemolyticus has an excellent antagonism effect on the xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, further field experiments can be performed based on the xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, and mature microbial organic fertilizer can be developed; thus, use of a lot of fertilizer and pesticides is reduced, and the staphylococcus haemolyticus has important significance on reducing agricultural non-point source pollution.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus epidermidis
InactiveCN110157822ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus epidermidis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus epidermidis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydratedTwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus epidermidis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus epidermidis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus capitis
InactiveCN110129463ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusStaphylococcus lentus
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus capitis. The kit comprises guide RNA specifically targeting staphylococcus capitis rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmpbasic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-chain DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus capitis, high detection specificity is achieved, and the staphylococcus capitis can be distinguished from other staphylococcus such as staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus epidermidis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. Meanwhile, when the RNA sequence is used to perform detection, detection time is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, equipment requirements are evidently lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and a high clinical practical value is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus warneri
InactiveCN110144416ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The present invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus warneri. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus warneri rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying spheres, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), an ribonuclease inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcuswarneri and high in detection specificity, and can separate the staphylococcus warneri from other staphylococci, including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. At the same time, the use of the RNA sequence for the detection takes about 1 hour, does not require a PCR instrument, has low requirements on equipment, and is significantly lower than a conventional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method and large in clinical practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant bacterium capable of using whole-cell transformation method to produce N-acetylneuraminic acid in high-yield manner and application
InactiveCN109971696ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesN-acetylneuraminic acid aldolaseStaphylococcus haemolyticus
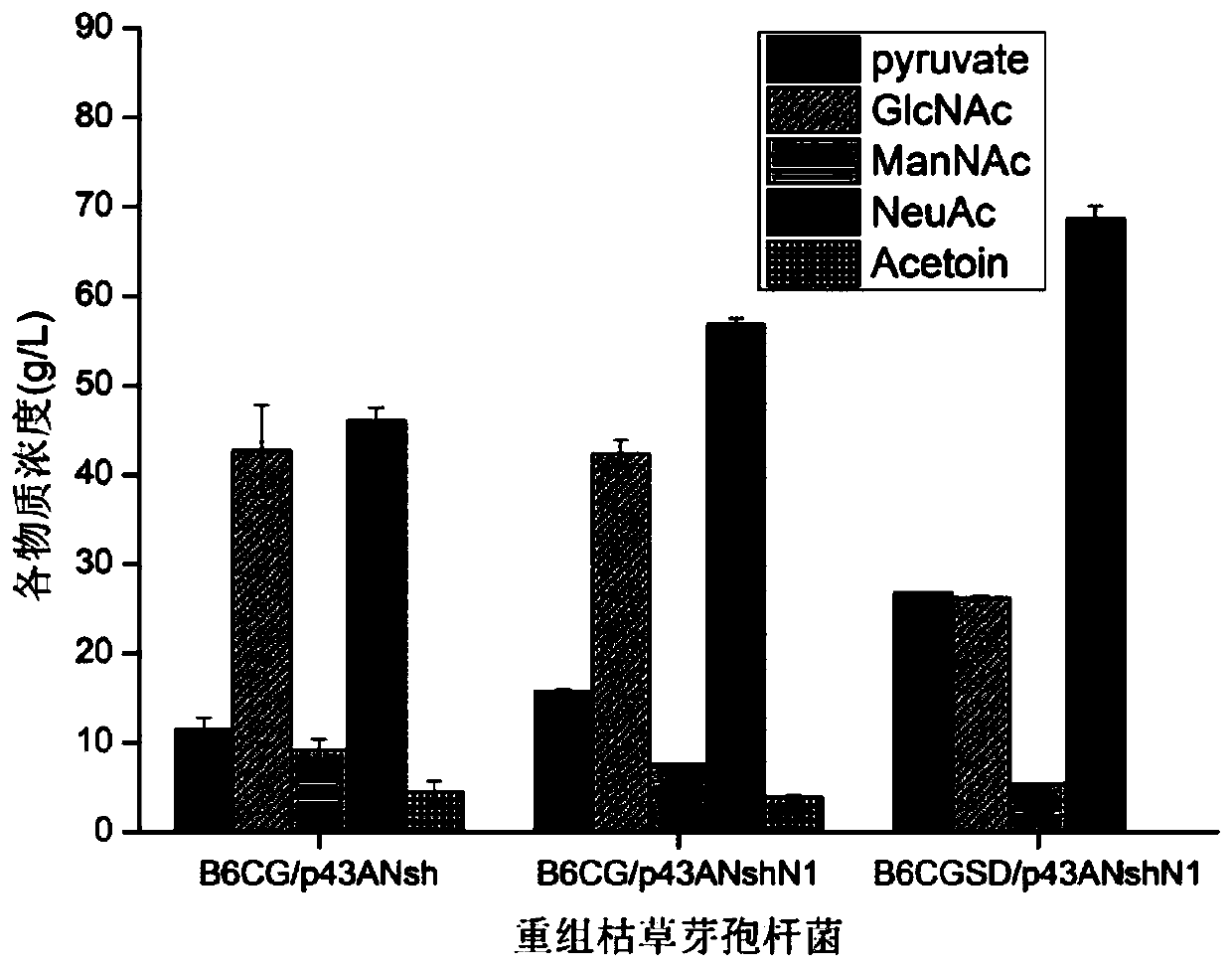
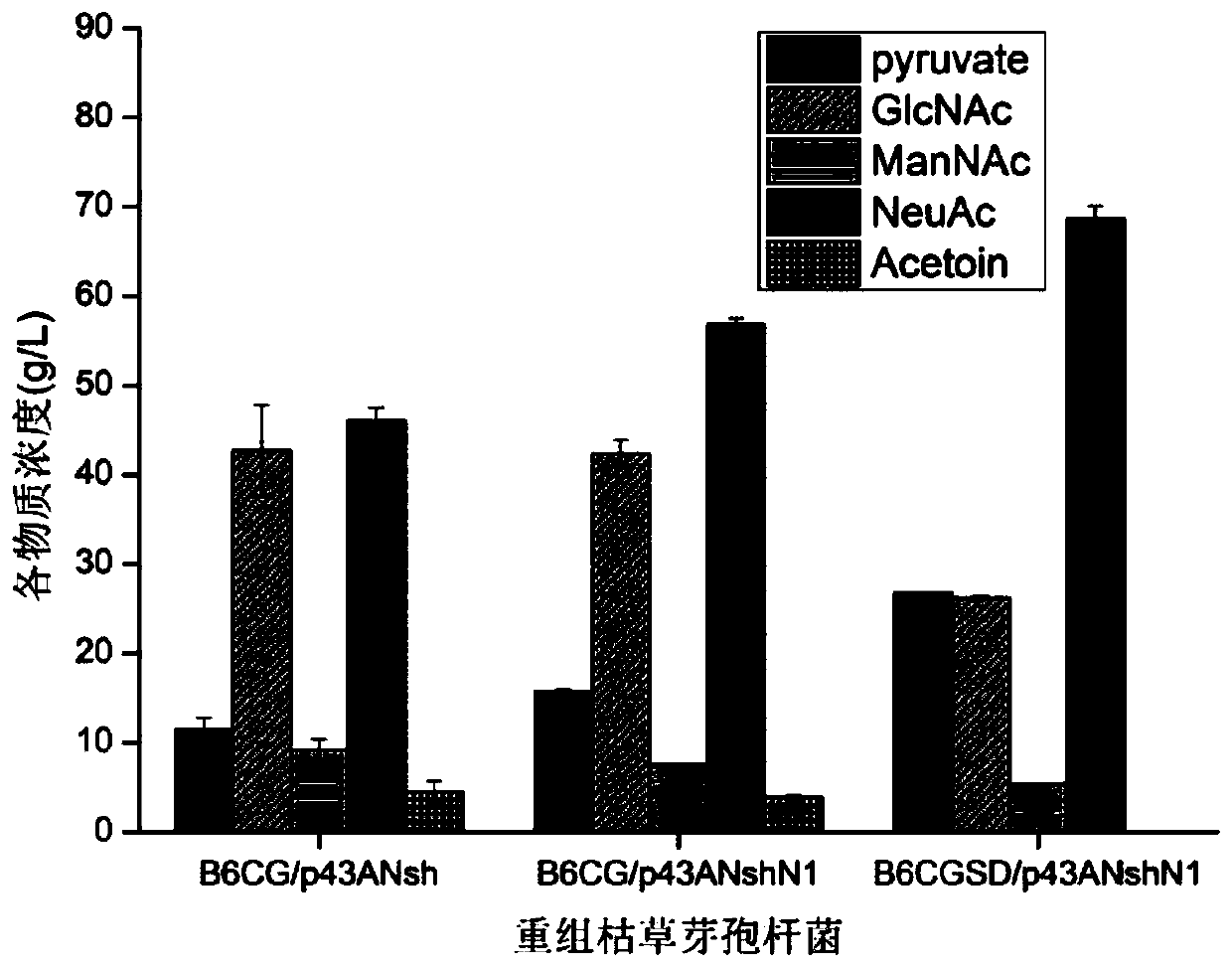
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium capable of using a whole-cell transformation method to produce N-acetylneuraminic acid in a high-yield manner and application and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The recombinant bacterium is characterized in that bacillus subtilis is used as the expression host to overexpress N-acetylglucosamine isomerase (AGE) from anabaena and N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase (ShNanA) from staphylococcus haemolyticus, the N terminal encoding sequence of gene tufA is further fused to the 5'-terminla of the ShNanA encoding sequence, and the recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of producing the N-acetylneuraminic acid in a high-yield manner is obtained by knocking out the related genes alsS and alsD for generating byproduct acetoin. The recombinant bacterium has the advantages that the recombinant bacterium can be used to produce the N-acetylneuraminic acid through whole-cell transformation, the yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid reaches 93.78g / L, the mole transformation rate of the N-acetylglucosamine is 50.54%, and a foundation is laid for the N-acetylneuraminic acid production using bacillus subtilis engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
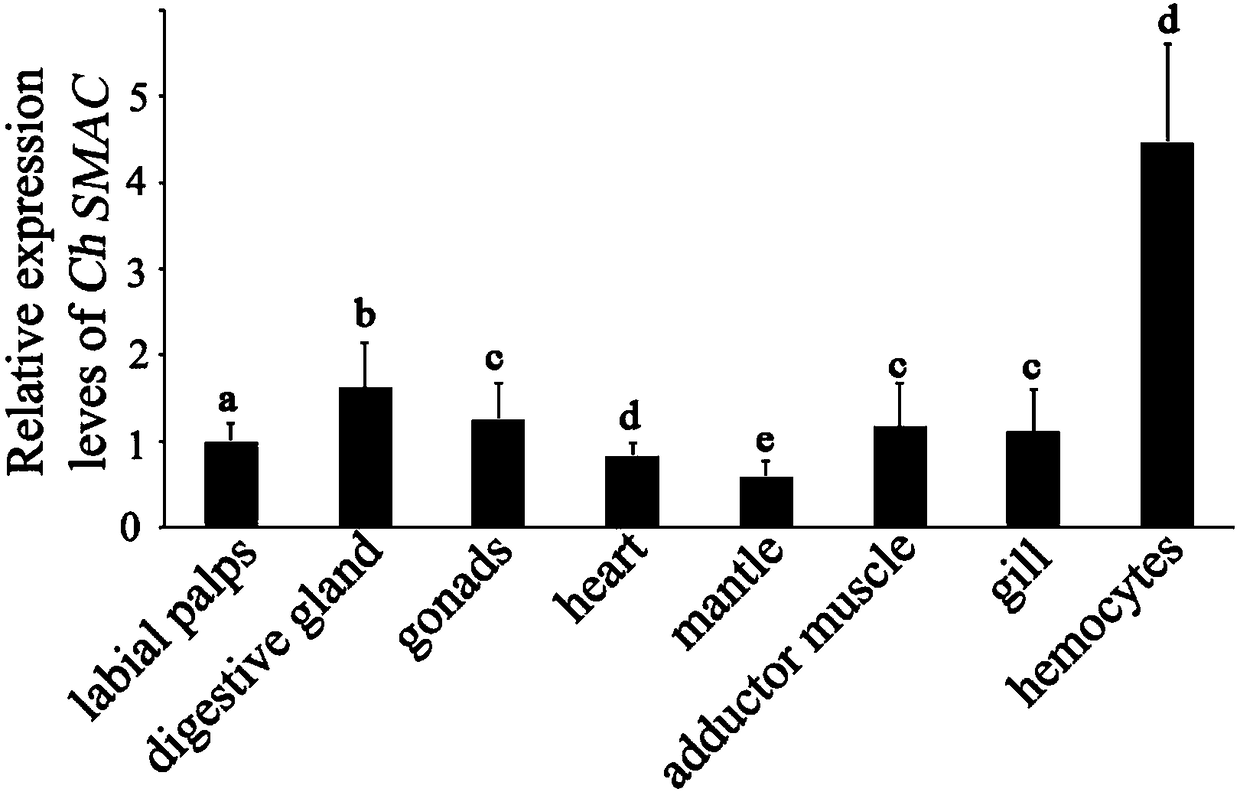
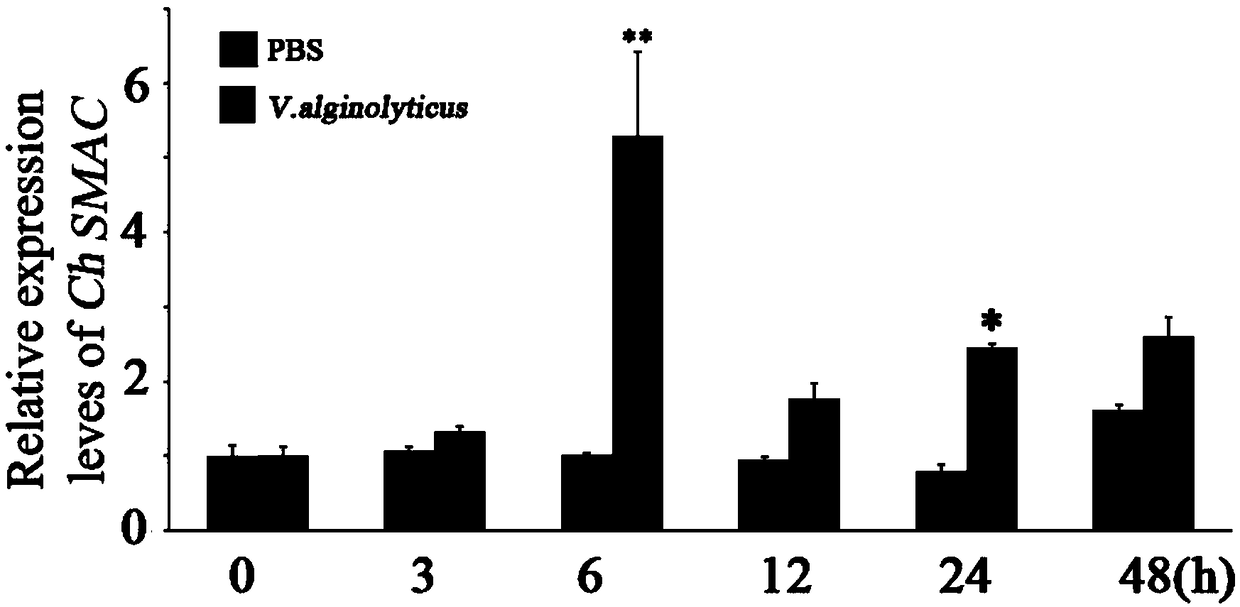
Oyster cell apoptosis gene SMAC gene and application thereof in preparation of pathology detecting and diagnostic reagent
ActiveCN108586596AAvoid elevationEnhance germplasm innovation abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAntigenStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention discloses an oyster cell apoptosis gene SMAC gene and an application thereof in the preparation of a pathology detecting and diagnostic reagent. The invention discovers the symbolic geneSMAC gene of the cell apoptosis of the species, and the nuclear antigen sequence is shown as from the 50th bp to the 1006th bp of the SEQ ID NO.1. The amino acid sequence (the amino acid sequence isshown in the SEQ ID NO. 2) of the gene coding has high species specificity, the similarity of the amino acid sequence in ostrea is 60%-88%, the evolution relationship is close, and the similarity withthe homologous proteins of other species is 30% or below, so that the evolution relationship is far. The quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) experiment shows that the SMAC gene is up-regulated after the infection of vibrio alginolyticus and staphylococcus haemolyticus, can be used as a standard for detecting the apoptosis of the oyster cells, provides a positive and accurate warning signal for the prevention of oyster diseases, and prevents the expansion of the disaster.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Probes, chip, primers and kit for rapid detection of ophthalmic clinical microorganisms and application thereof
ActiveCN112626244AQuick checkEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention relates to probes, a chip, primers and a kit for rapid detection of ophthalmic clinical microorganisms and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of clinical microorganism detection. The probes disclosed by the invention comprise probes for detecting staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus haemolyticus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus hominis, serratia marcescens, escherichia coli, bacillus subtilis and enterobacter cloacae, respectively. The invention also discloses the primers for amplifying the target strains, and the primers can be used to amplify gene sequence fragments with the intraspecific homology of the target strains > 95% and with the interspecific homology < 75%. The invention further discloses a method for synthesizing hybridization probes on the chip, a method for hybridization reaction and a method for scanning detection. The probes disclosed by the invention are high in specificity, high in positive rate of detecting microorganisms in ophthalmic clinical samples, high in accuracy and short in diagnosis time.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
Composition containing phenyl-carbamoyl thiazole derivative mixture and application of composition
InactiveCN110772522AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRalstonia pickettiiStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention provides a composition containing a mixture of a first phenyl-carbamoyl thiazole derivative and a second phenyl-carbamoyl thiazole derivative which are different from each other. Together with extracts of plants such as crotalaria assamica, star anise fruits, calophyllum membranaceum, schisandrae virides caulis, cycas leaves and the like, the mixture can generate synergistic antibacterial action on staphylococcus hominis, pantoea agglomerans, kocuria kristinae, serratia liquefaciens, ralstonia pickettii, peptostreptococcus anaerobius, klebsiella oxytoca, corynebacterium macginleyi, listeria monocytogens, simulation corynebacterium, clostridium perfringens, staphylococcus haemolyticus, aeromonas hydrophila, acinetobacter baumannii, streptococcus sanguis, peptostreptococcus prevotii, propionibacterium acnes, pseudomonas oryzihabitans, staphylococcus warneri, and legionella pneumophila.
Owner:黄泳华
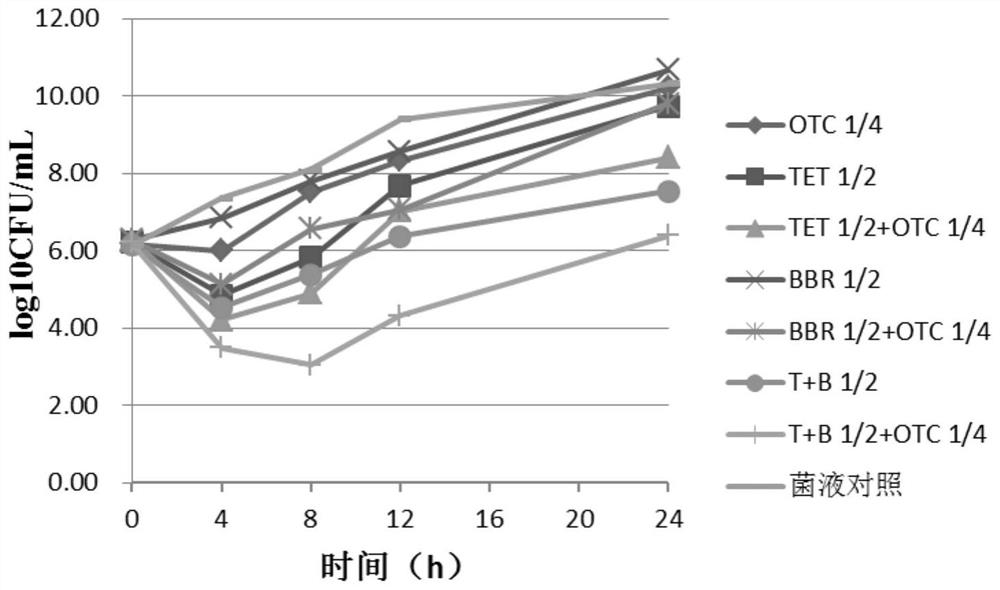
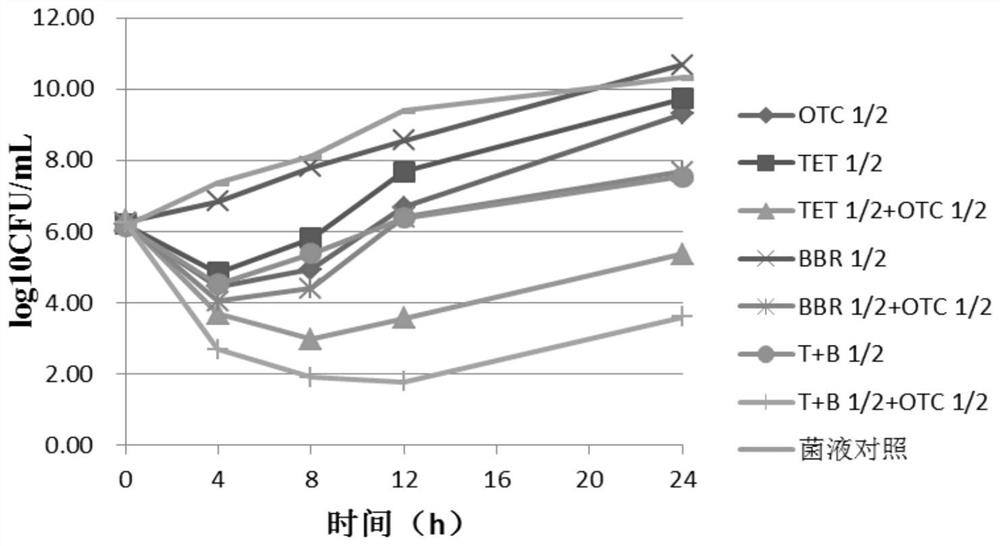
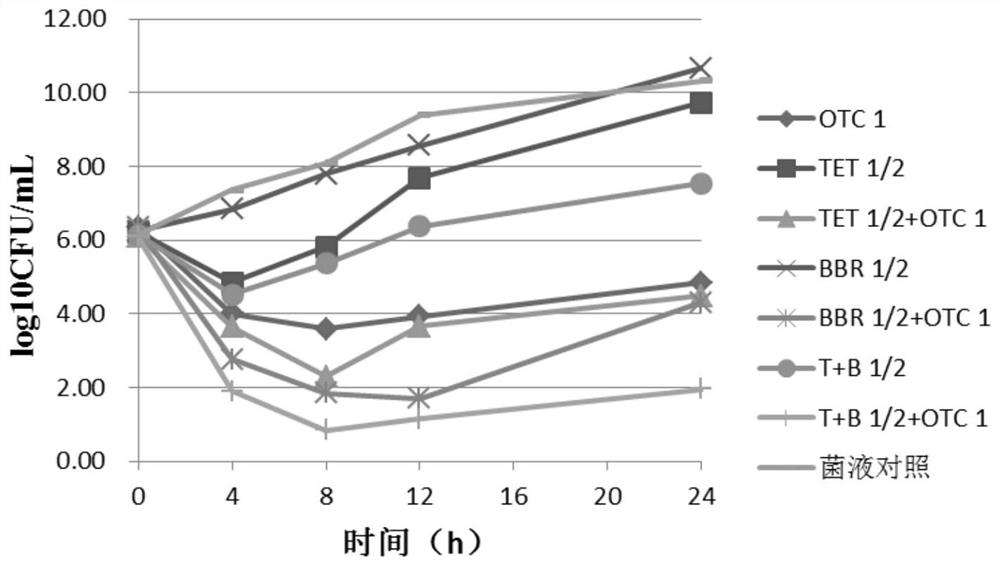
Application of isoquinoline alkaloid in preparation of staphylococcus haemolyticus drug resistant to drug resistance
ActiveCN111888356ALow minimum inhibitory concentrationIncreased sensitivityAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsStaphylococcus haemolyticusQuinoline
The invention discloses an application of isoquinoline alkaloid in preparation of a staphylococcus haemolyticus drug resistant to drug resistance. The isoquinoline alkaloid has lower minimum inhibitory concentration, and the sensitivity of staphylococcus haemolyticus to OTC can be improved after the isoquinoline alkaloid is combined with OTC; the isoquinoline alkaloid can also increase the accumulation amount of the OTC in the staphylococcus hemolyticus, has a certain inhibition effect on the gene transcription level of an efflux pump, and shows a good efflux inhibition effect; and therefore,the isoquinoline alkaloid can be prepared into the staphylococcus haemolyticus drug resistant to drug resistance independently or in combination with antibiotics.
Owner:CHONGQING BULL ANIMAL PHARMA
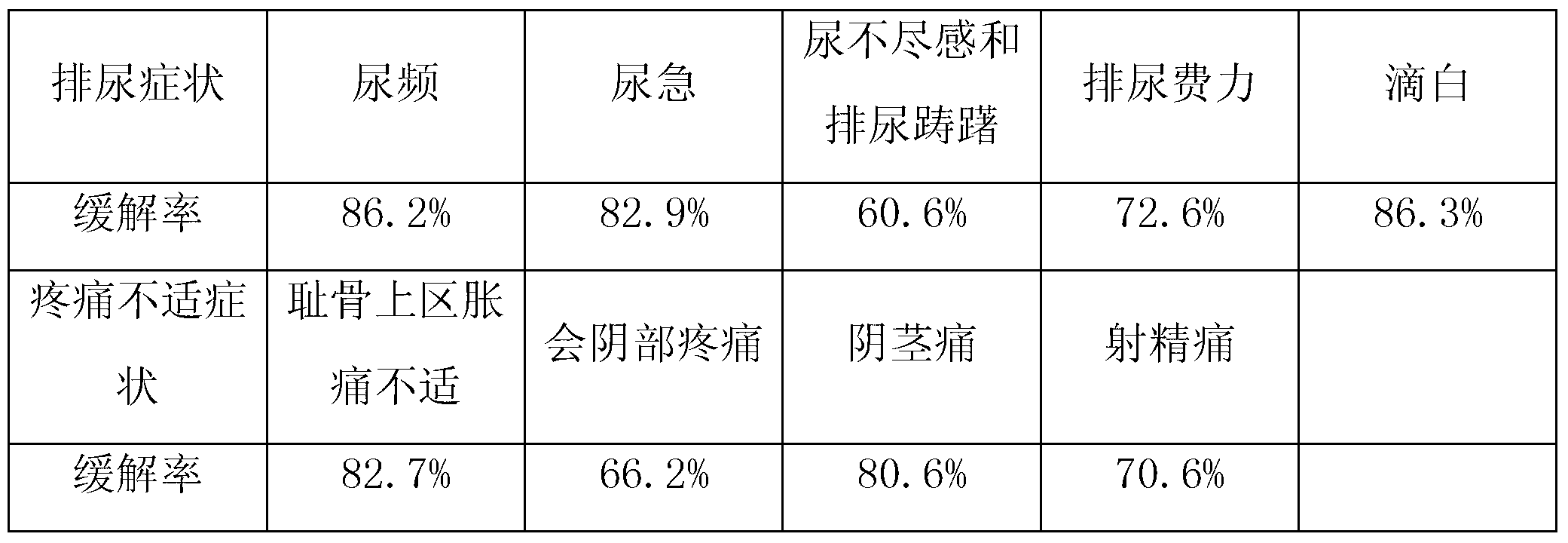
Application of fosfomycin trometamol to preparation of drug for treating chronic bacterial prostatitis
ActiveCN103263425AImprove medication complianceDefinite curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses an application of fosfomycin trometamol to the preparation of a drug for treating chronic bacterial prostatitis in the field of chemical drug applications. The chronic bacterial prostatitis goes with bacterial infection in seminal fluid; bacteria include one or more selected from staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, streptococcus agalactiae, streptococcus faecium, streptococcus viridans, enterococcus faecalis and staphylococcus haemolyticus; the drug is an oral drug; the oral drug is in a form of powder, granules, dry suspension or effervescent tablets; 5.631g of fosfomycin trometamol is contained in the unit dose of the oral drug; the chronic bacterial prostatitis goes with a pain and discomfort symptom and a micturition symptom; and the pain and discomfort symptom includes one or more selected from suprapubic swelling pain and discomfort, perineum pain, phallalgia pain and ejaculation pain. In the new application, the product disclosed by the invention is exact in curative effect, few in adverse effects and good in compliance of patient in taking a medicine.
Owner:SHENYANG NO 1 PHARMA FACTORY DONGBEI PHARMA GRP
A Hong Kong oyster lysm protein with antibacterial activity and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN108794613BEfficient identificationGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a crassostrea hongkongensis LysM protein having a bacteriostatic activity, and an encoding gene and an application of the crassostrea hongkongensis LysM protein. The LysM protein is separated from crassostrea hongkongensis for the first time, PGN is effectively recognized, and the LysM protein has an obvious bacteriostatic effect on the growth of alginolyticus, staphylococcus haemolyticus, staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli. The LysM protein plays important roles in immunological recognition of the crassostrea hongkongensis and the antibacterial activity, provides evidences for developing broad-spectrum antibiotics and screening an immunopotentiator, and also provides an application guide for the disease resistance and breeding of the shellfish.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A test kit for human staphylococcus detection
InactiveCN110157821BLower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus hominis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus hominis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus hominis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus hominis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
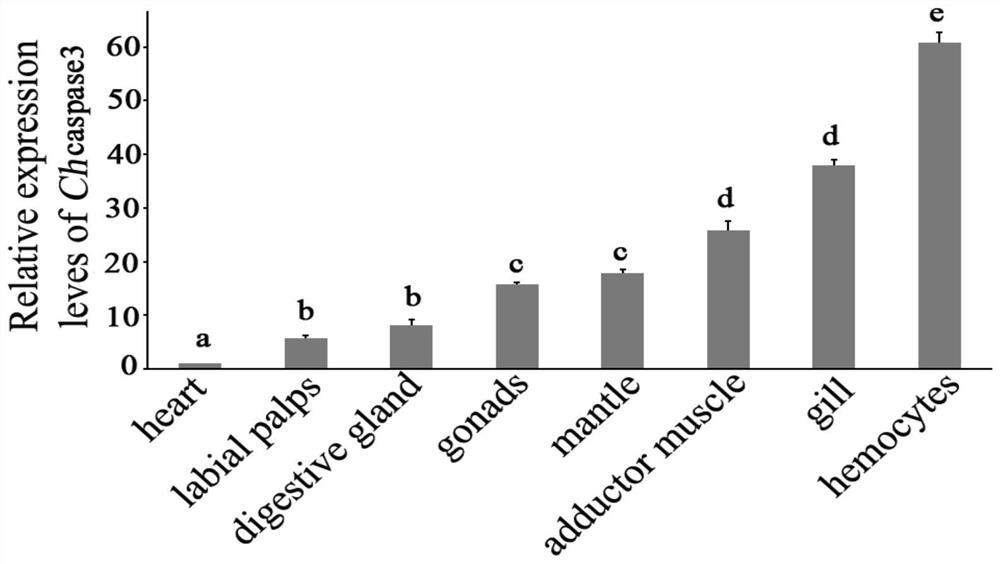
A kind of oyster cell apoptosis gene caspase 3 gene and its application in the preparation of pathological detection diagnostic reagents
ActiveCN108610406BAvoid elevationEnhance germplasm innovation abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationStaphylococcus haemolyticusNucleotide
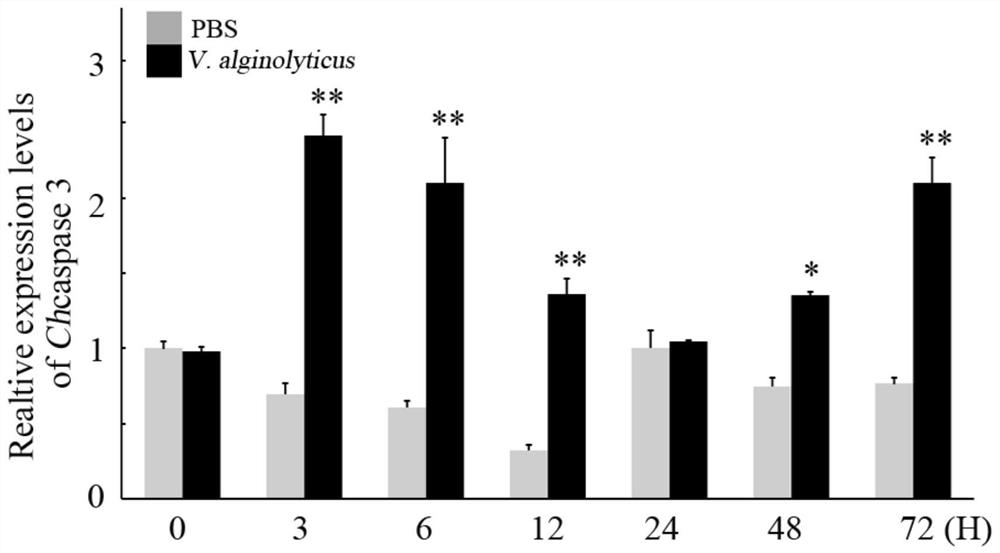
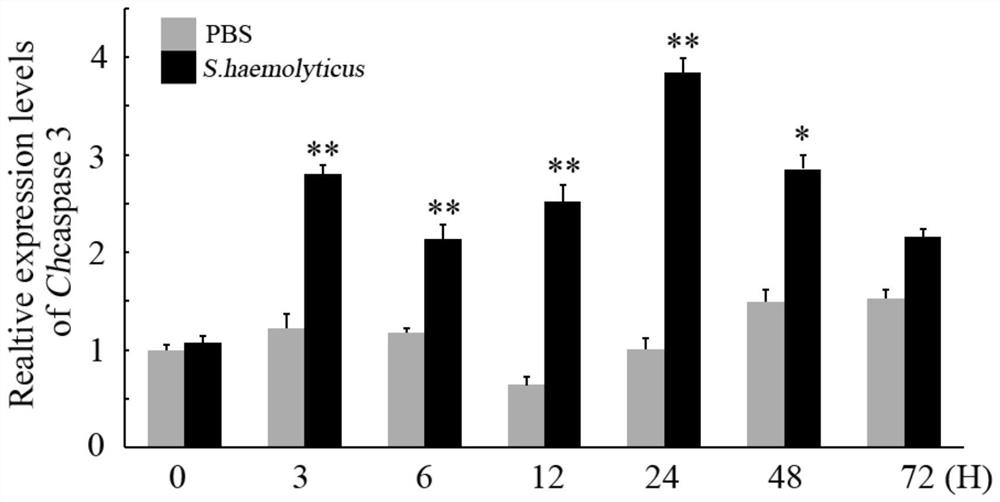
The invention discloses an oyster cell apoptosis gene caspase 3 gene and an application thereof in preparation of a pathological detection and diagnosis reagent. A Hong Kong crassostrea gigas cell apoptosis marker gene-caspase 3 gene is found out, has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, is significantly up-regulated after being infected by vibrio alginolyticus and staphylococcus haemolyticus, and can be used as a standard for detection of oyster cell apoptosis conditions; a positive and accurate warning signal is provided for prevention of oyster disease, and the expansion of disasters is prevented. With the application of the oyster cell apoptosis gene caspase 3 gene, the germplasm innovation ability of cultured shellfishes can be further enhanced and the efficient and sustainable development of the industry is supported.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Autophagy protein beclin-1 as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN112300259AInhibition formationRapid response to infectionAntibacterial agentsGenetic engineeringDiseaseStaphylococcus haemolyticus
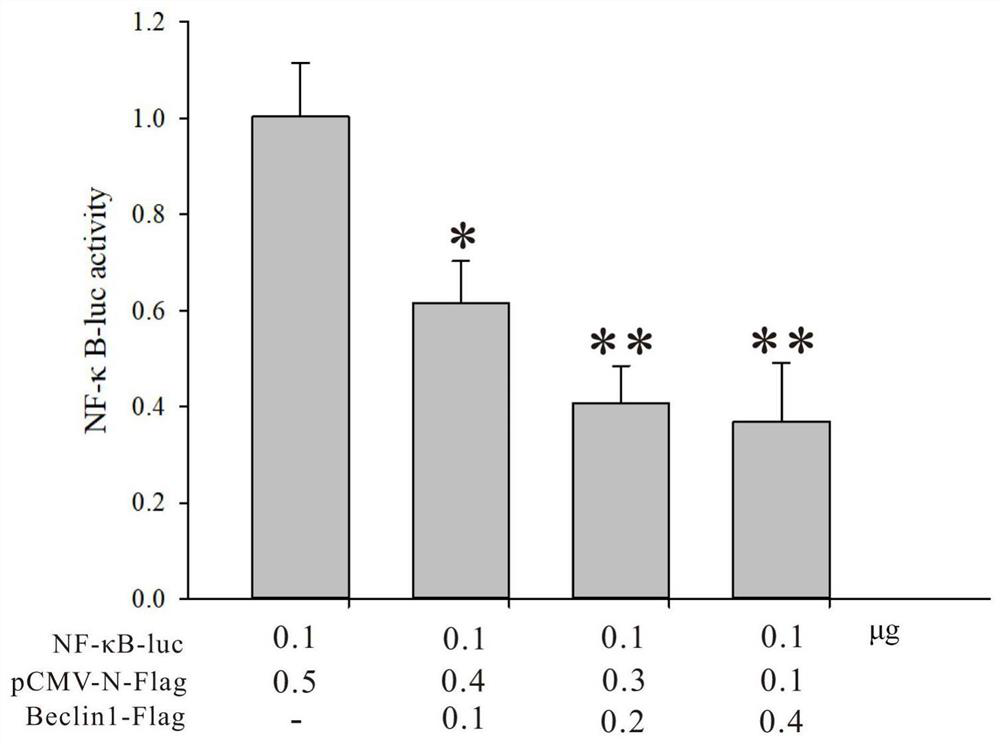
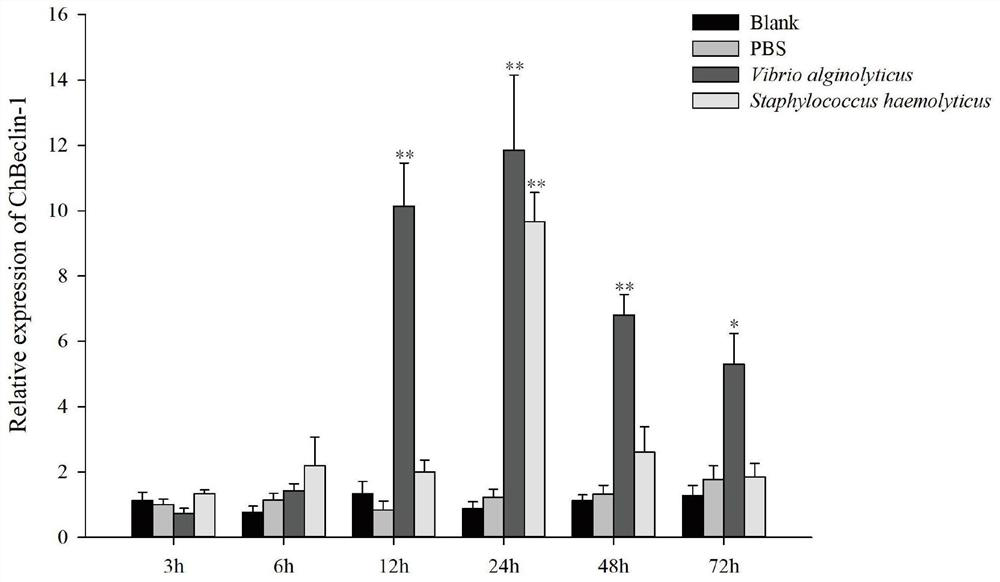
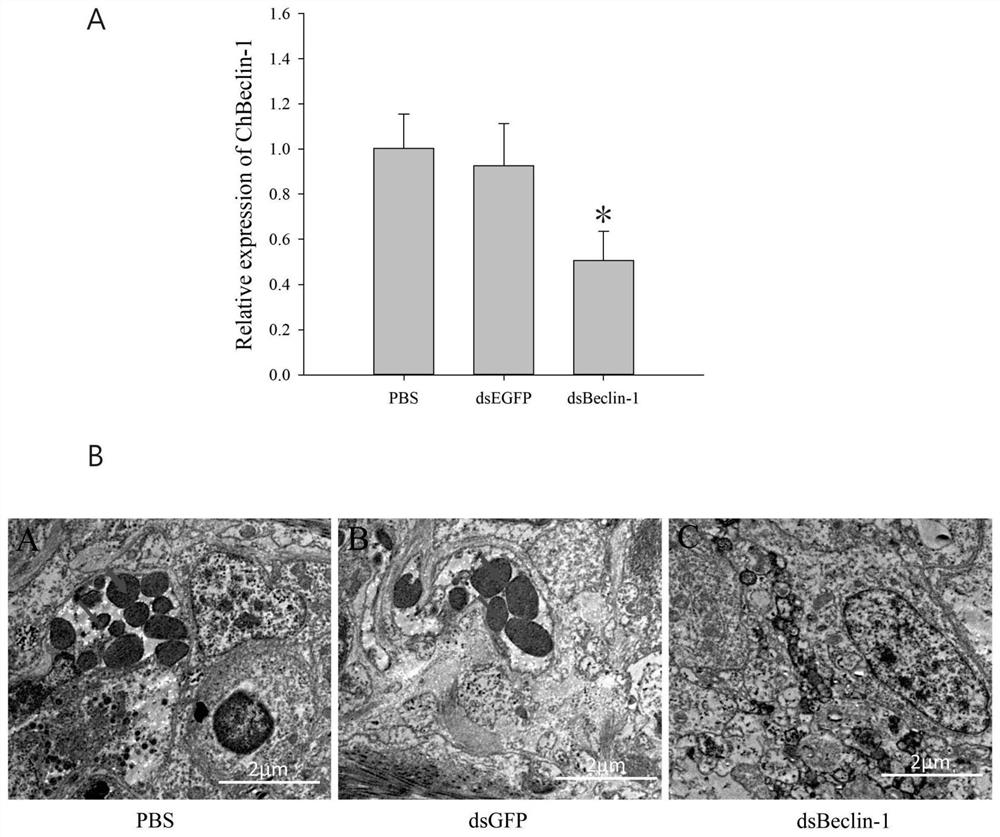
The invention discloses an autophagy protein beclin-1 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the autophagy protein beclin-1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. A Beclin-1 gene is obtained through identification from crassostrea hongkongensis for the first time, formation of autophagosome can be inhibited by interfering expression of Beclin-1, an NF-kappaB signal channel is inhibited, and infection of vibrio alginolyticus and staphylococcus haemolyticus can be quickly responded. The Beclin-1 plays an important role in immune defense of the crassostrea hongkongensis, and provides application guidance for disease control and disease-resistant breeding of the crassostrea hongkongensis and other mariculture shellfishes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Staphylococcus haemolyticus Prophage PhiSH2 Endolysin is Lytic for Staphylococcus aureus
InactiveUS20140065127A1Readily apparentBacteriaSugar derivativesStaphylococcus haemolyticusStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
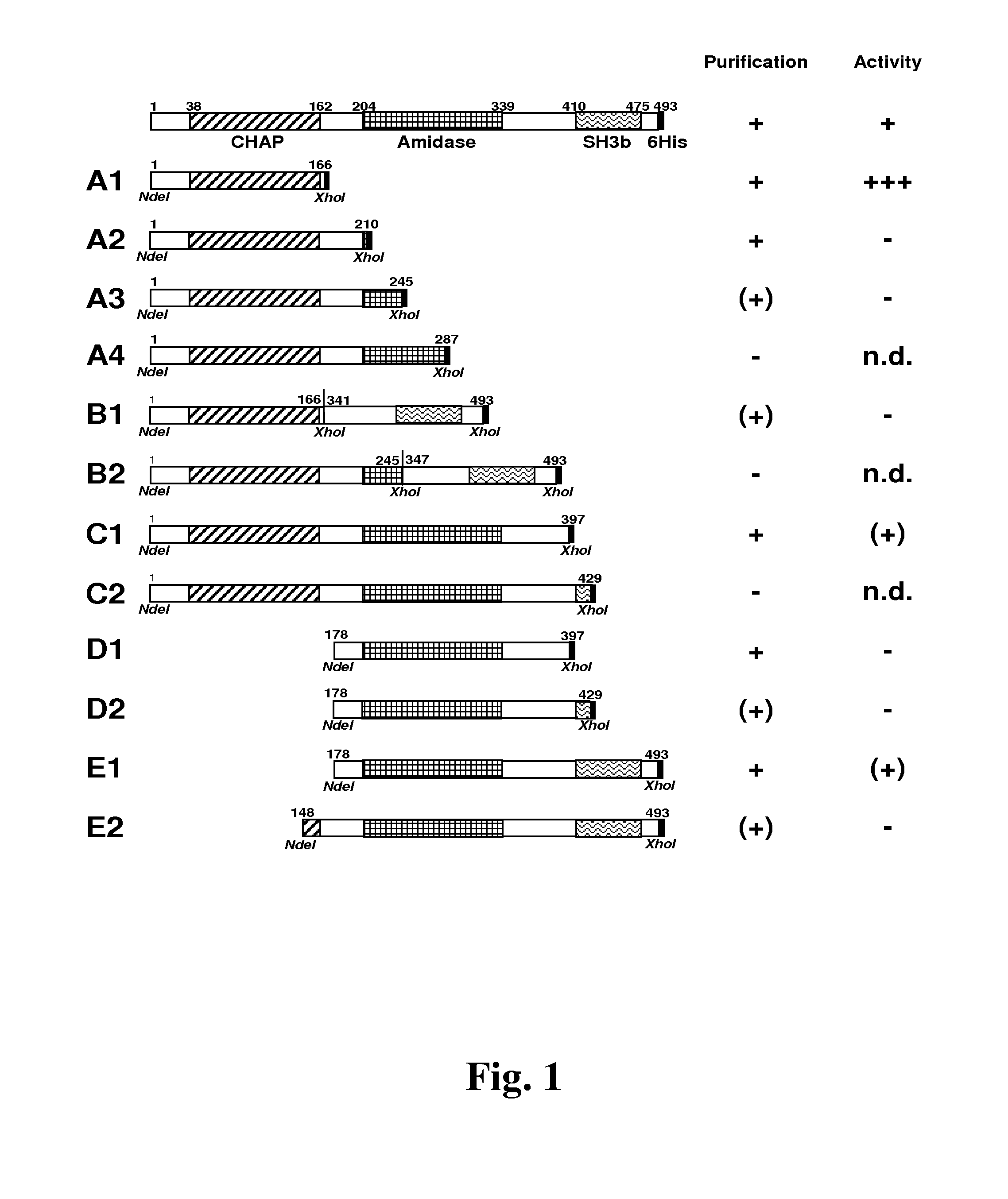
Methicillin-resistant (MRSA) and multi-drug resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus are becoming increasingly prevalent in both human and veterinary clinics. S. aureus-causing bovine mastitis yields high annual losses to the dairy industry. Treatment of mastitis by broad range antibiotics is often not successful and may contribute to development of antibiotic resistance. Bacteriophage endolysins are a promising new source of antimicrobials. The endolysin of prophage φSH2 of Staphylococcus haemolyticus strain JCSC1435 (φSH2 lysin) shows lytic activity against live staphylococcal cells. Deletion constructs were tested in zymograms and turbidity reduction assays to evaluate the contribution of each functional module to lysis. The CHAP domain exhibited three-fold higher activity than the full length protein. Activity was further enhanced in the presence of bivalent calcium ions. The full length enzyme and the CHAP domain showed activity against multiple staphylococcal strains, including MRSA strains, mastitis isolates, and coagulase negative staphylococcal (CoNS) strains.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
A kit for detecting hemolytic staphylococcus
InactiveCN110129462BLower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus. The kit comprises guide RNA specifically targeting staphylococcus haemolyticus rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-chain DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus haemolyticus, high detection specificity is achieved, and the staphylococcus haemolyticus can be distinguished from other staphylococcus such as staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus epidermidis. Meanwhile, when the RNA sequence is used to perform detection, detection time is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, equipment requirements are evidently lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and a high clinical practical value is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com