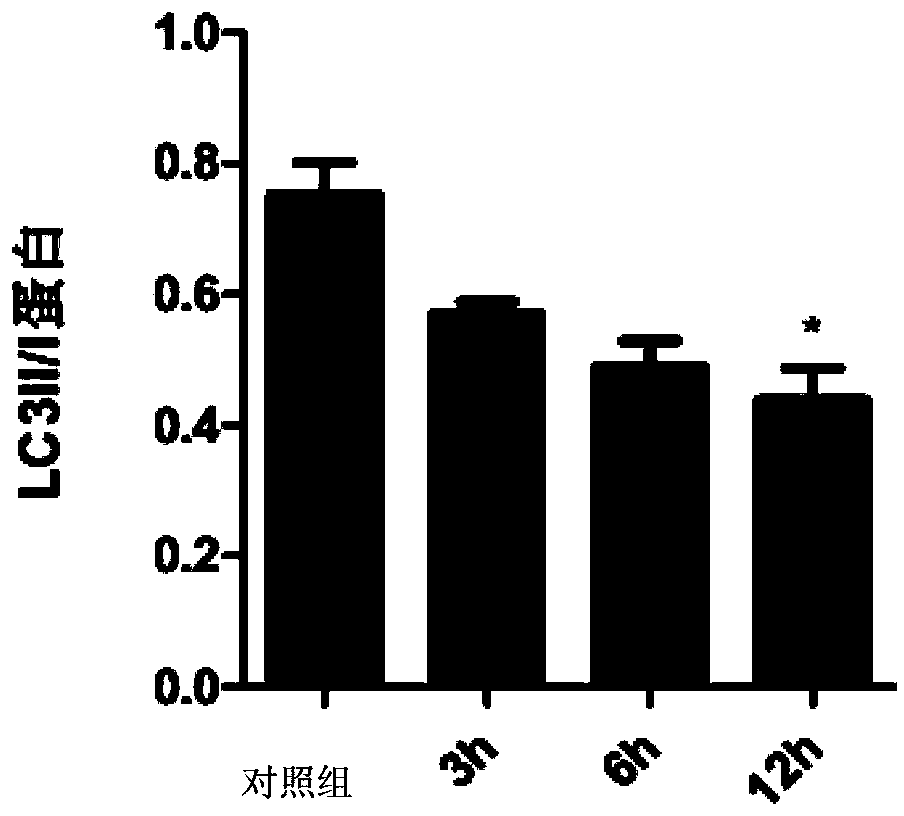
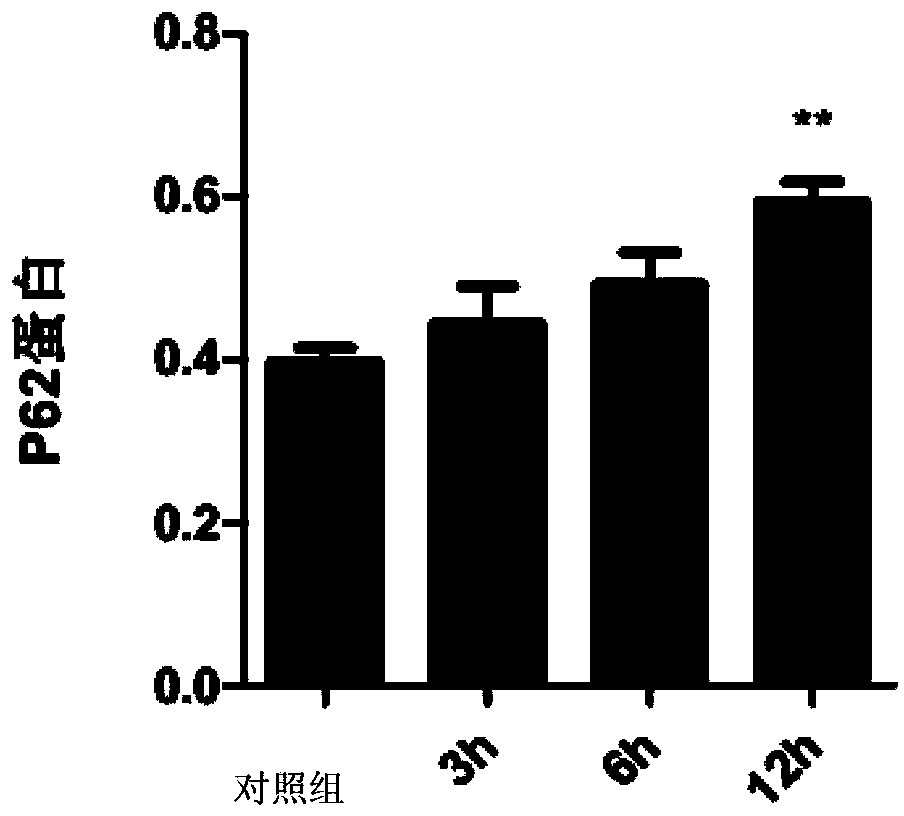
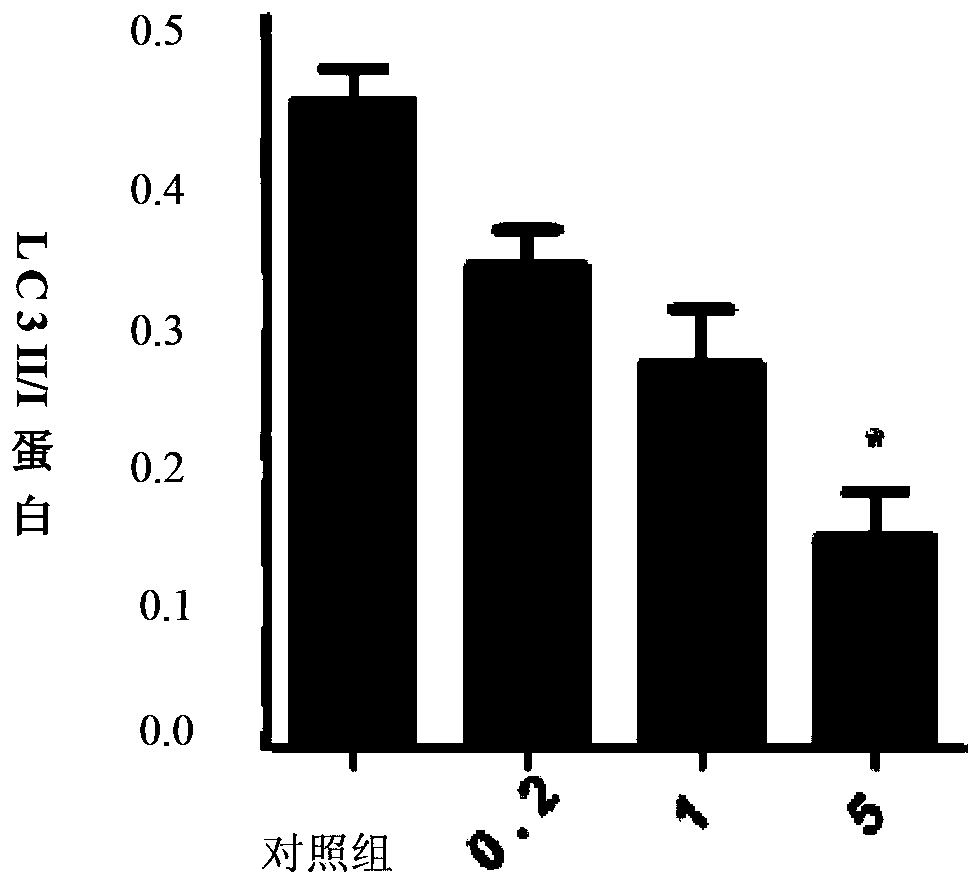
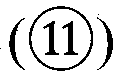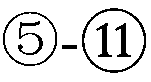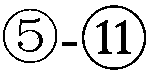Patents
Literature
36 results about "Autophagosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
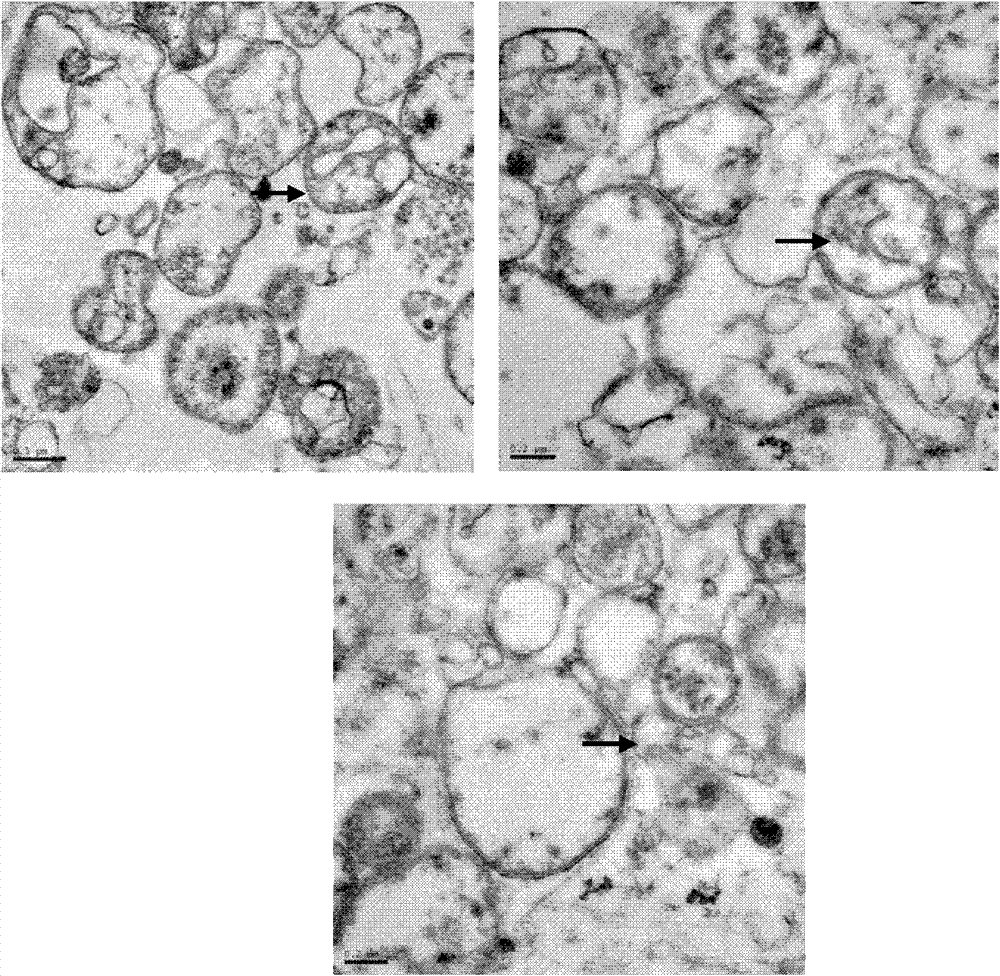
An autophagosome is a spherical structure with double layer membranes. It is the key structure in macroautophagy, the intracellular degradation system for cytoplasmic contents (e.g., abnormal intracellular proteins, excess or damaged organelles, invading microorganisms). After formation, autophagosomes deliver cytoplasmic components to the lysosomes. The outer membrane of an autophagosome fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome. The lysosome's hydrolases degrade the autophagosome-delivered contents and its inner membrane.
Application of H22 liver cancer cell autophagosome to preparation of liver cancer therapeutic vaccine
ActiveCN102430118AConform to the characteristicsEffective recruitmentTumor/cancer cellsAntibody medical ingredientsOncologyTumor antigen
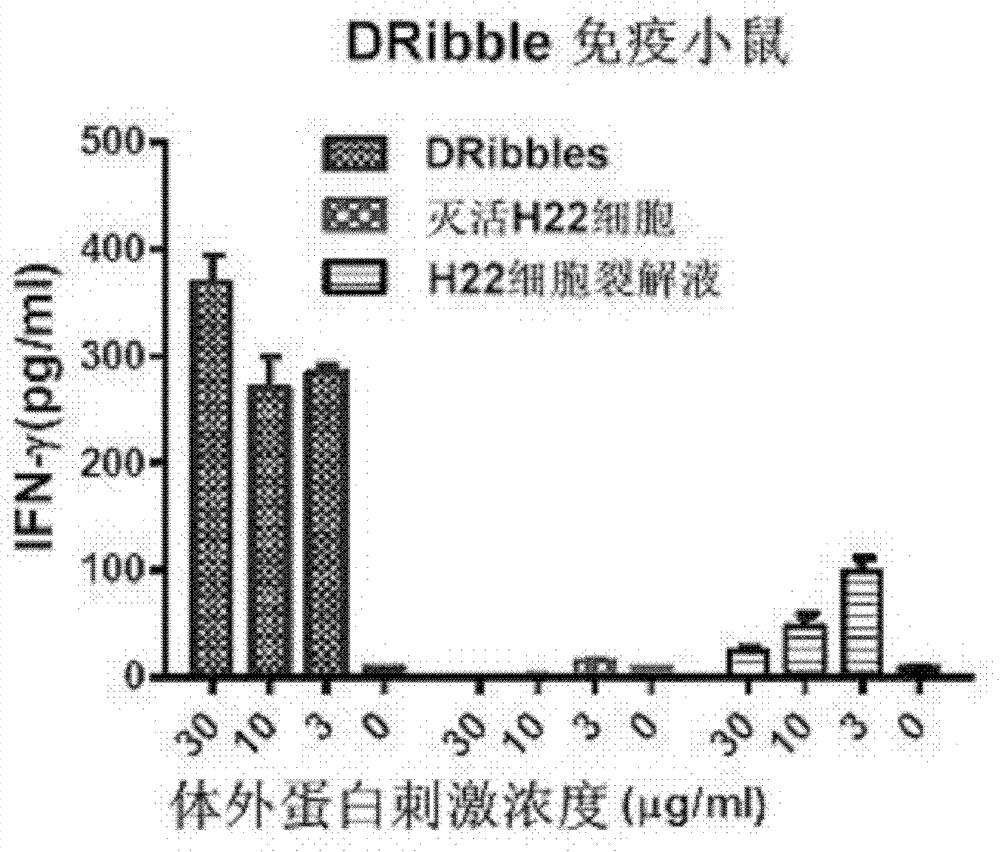
The invention discloses application of H22 liver cancer cell autophagosome DRibbles to the preparation of a liver cancer therapeutic vaccine. Liver cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in China and can be effectively prevented by developing a liver cancer vaccine; and years of research results prove that tumor cell autophagosome is one of effective vectors for tumor antigen cross-presentation. The application comprises a core technology for extracting the autophagosome DRibbles from human liver cancer cells and proves that the autophagosome can effectively induce anti-tumor immune response of organisms and has a good biotherapy prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Allogeneic autophagosome-enriched composition for the treatment of disease
ActiveUS9226955B2Easy to produceReducing and inhibiting protein degradationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
Owner:PROVIDENCE HEALTH SYST OREGON +1
Application of sinomenine to preparation of medicament for treating human brain glioma
InactiveCN106860456ABroaden medical applicationsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHuman gliomaBrain section
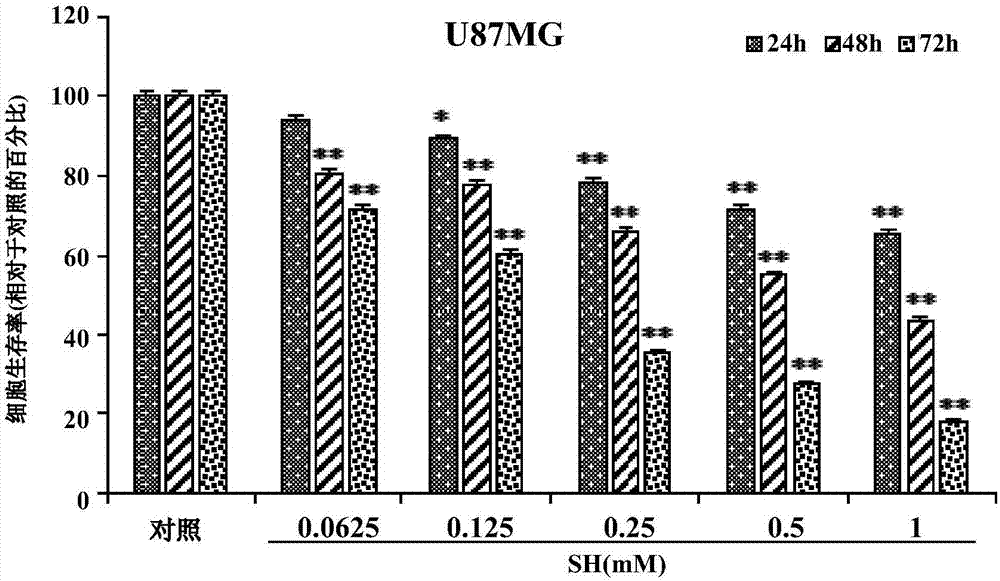
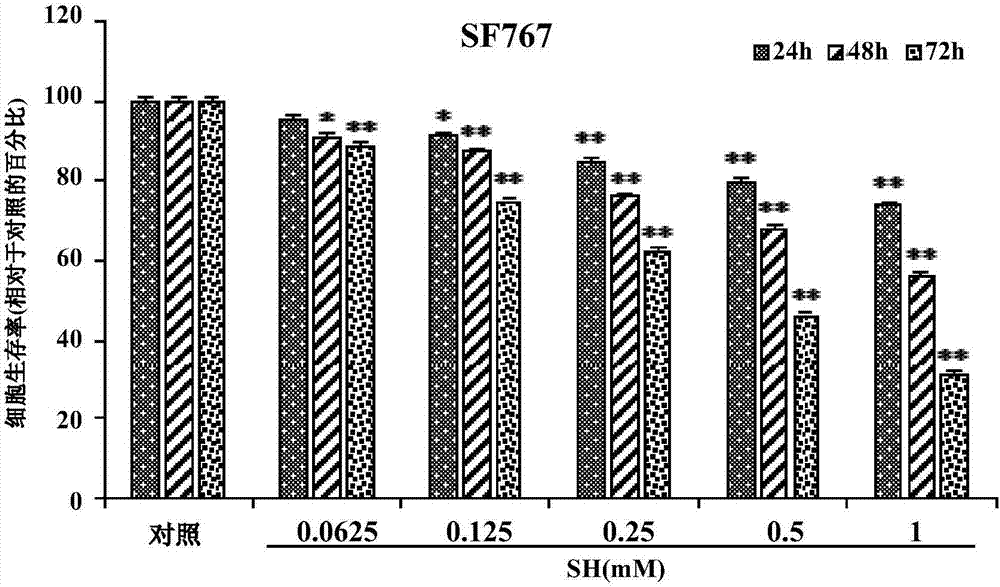
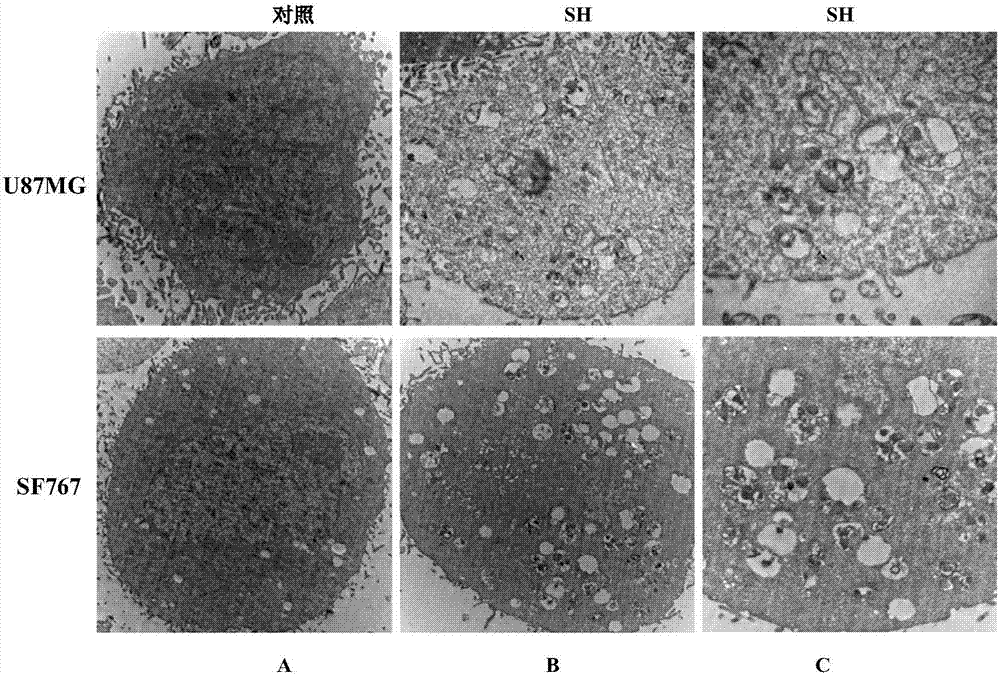
The invention provides application of sinomenine to preparation of a medicament for treating human brain glioma. As proved by experiments, the sinomenine has a function of restraining human-derived glioma U87MG and SF767 cell strains, and the function is improved along with the increase of dose and time. Moreover, the sinomenine can induce the increase of autophagosomes, increase the quantity of autophagic vesicles, prompt the expression increase of human glioma cells LC3B-II, induce autophagic death of human glioma cells, and restrain the growth of U87MG cell xenograft tumors. The sinomenine is a novel and effective glioma-resisting medicament with a great potential, and can be used for preparing a human brain glioma medicament; by adopting the sinomenine, a new way is created for medical treatment of human brain glioma, and the medical application of the sinomenine is expanded.
Owner:EXPERIMENTAL RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
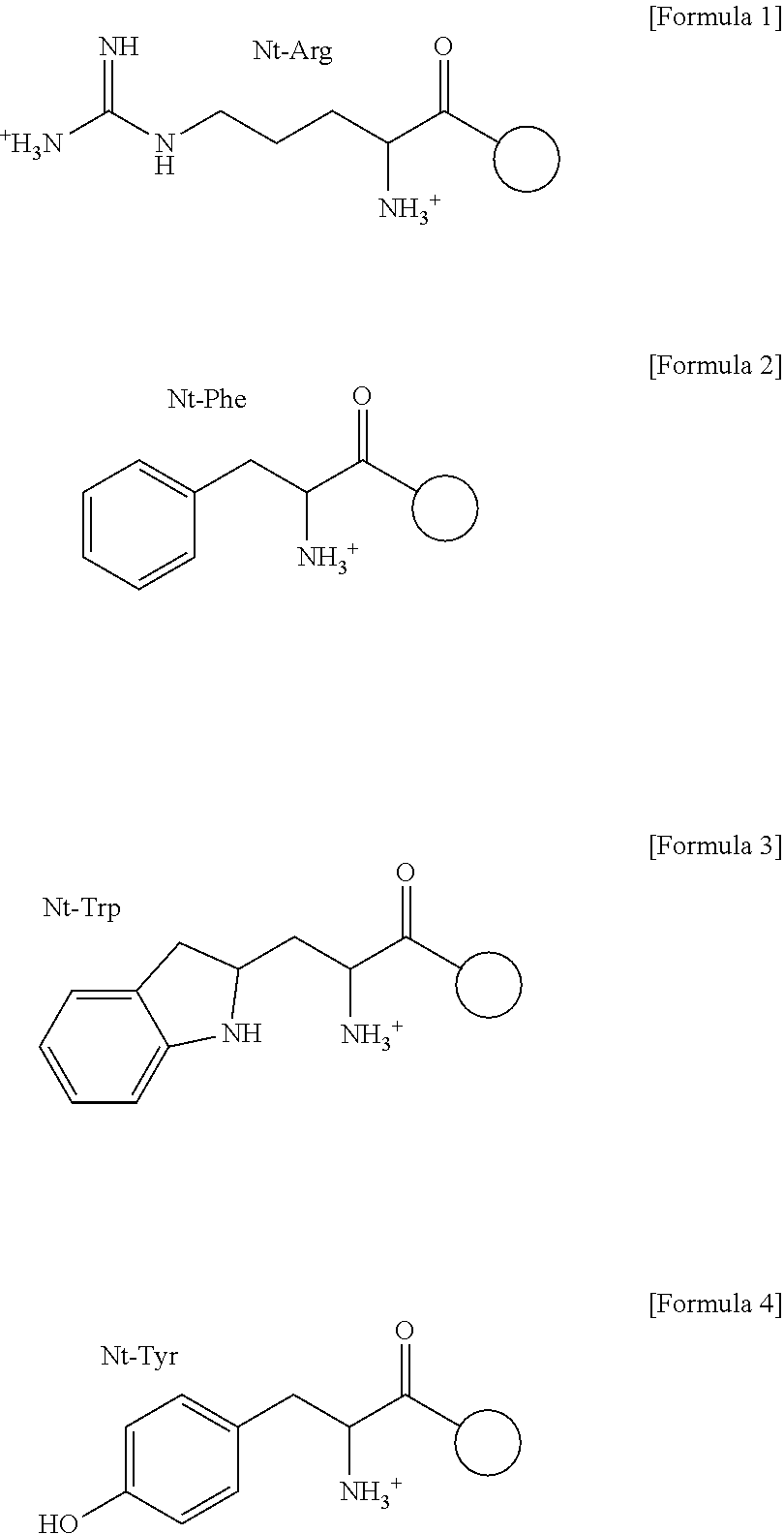
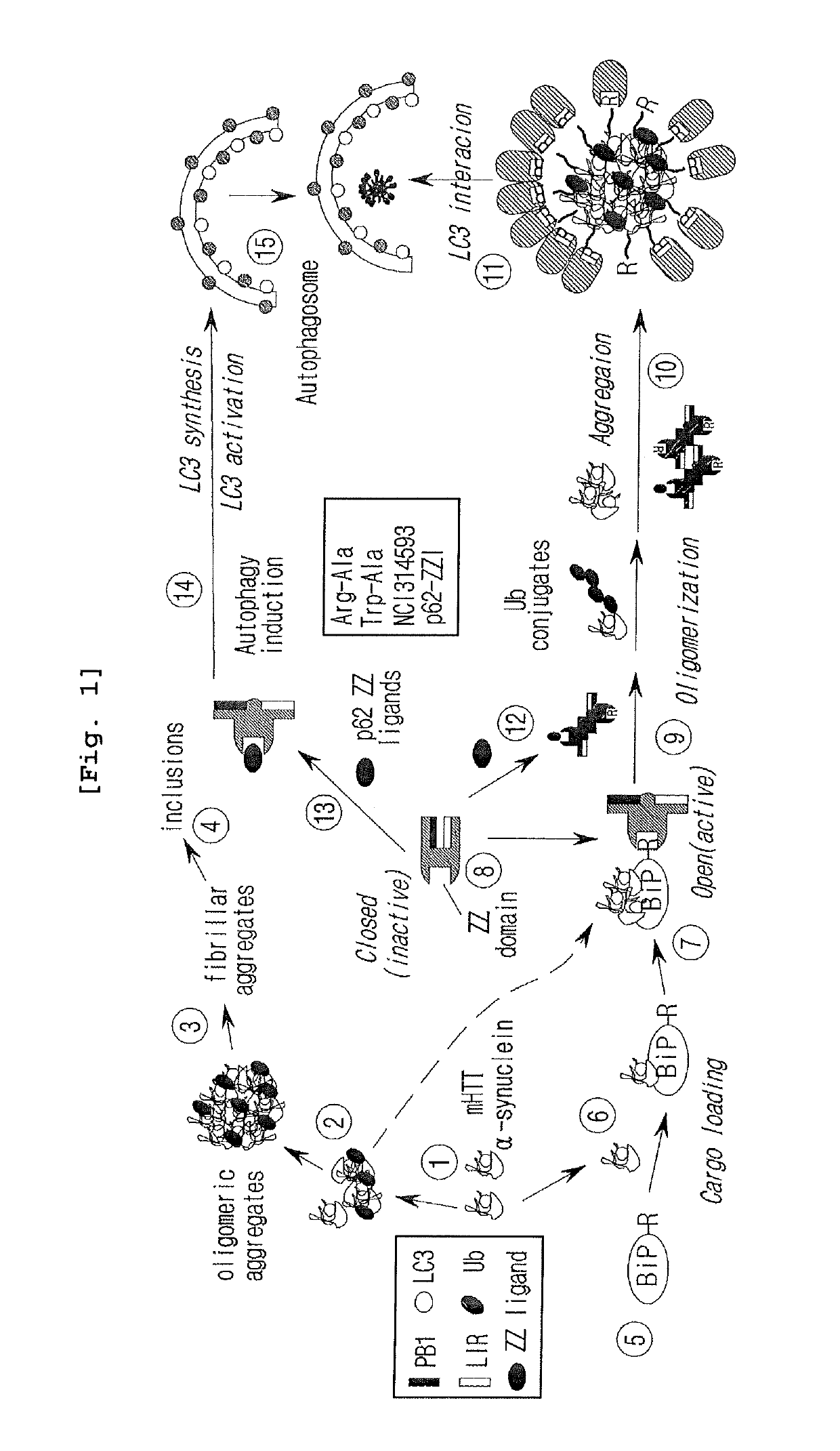
Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through autophagy activity mediated by ligand or arginylated bip binding to p62 zz domain
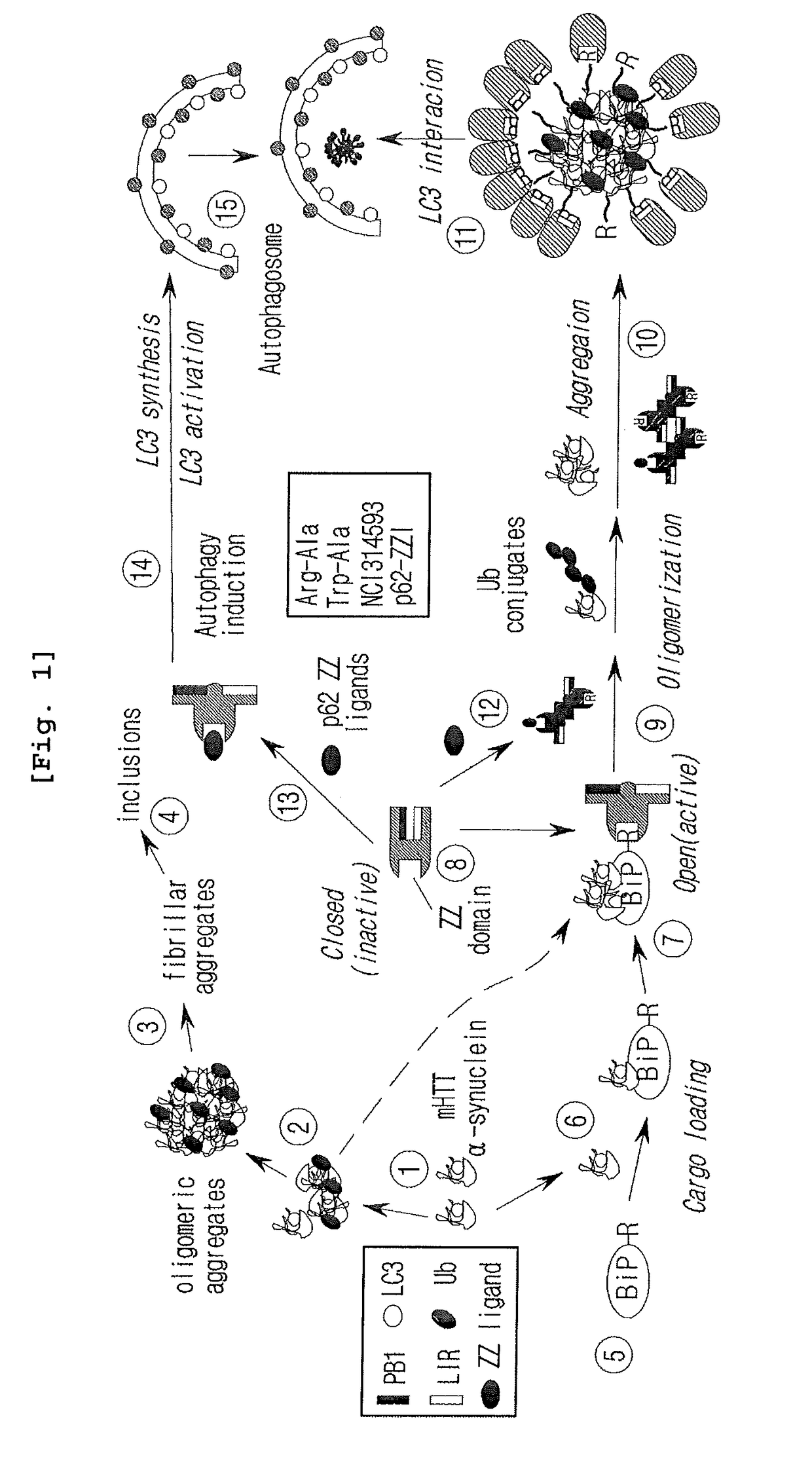
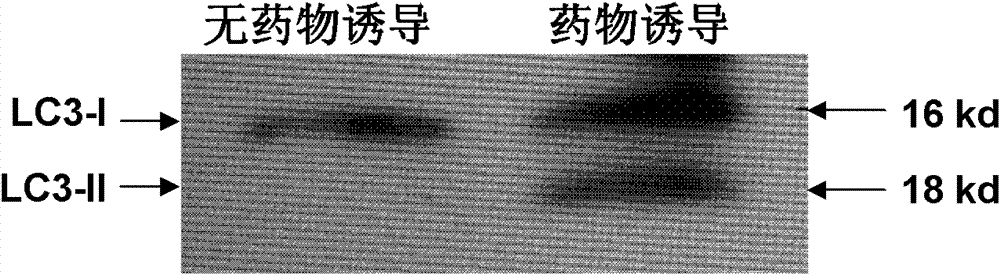
The drug action mechanisms and core techniques of the present invention are summarized in figure 1. Specifically, the invention provides malignant denatured proteins, such as mutant Huntingtin proteinor alpha-synuclein, stick together to grow into oligomer aggregates (1, 2), fibrillar aggregates (3), and ultimately inclusion bodies (4). Young neuronal cells produce a large quantity of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (5) of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones, such as BiP, and thereafter, arginylated BiP (R-BiP) comes into the cytoplasm and binds with denatured proteins (6). Nt-Arg of R-BiP, as a ligand, binds with the ZZ domain of p62 (7) to induce the structural activation of p62 (8) while the ordinarily closed inactive form of p62 is changed with an open form thereof, and thus PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. On the basis of oligomerization (9) by the PB1 domain, p62 binds with the denatured protein aggregates to be concentrated to autophagically degradable aggregates, that is, p62 bodies (10). Thereafter, p62 completes autophagy targeting (11) and lysosomal proteolysis through binding with LC3 protruding on the autophagosomal membranes. In young neuronal cells, theautophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is strong, and thus the cytotoxic protein aggregates (1-5) do not accumulate, but in aged neuronal cells, the autophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is weakened, and thus the protein aggregates (1-5) accumulate, resulting in a vicious cycle. The present invention attempts to effectively remove Huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein aggregates and the like by artificially activating p62 using low-mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain (12, 13). Specifically, p62 binding the ligands through step 12 promotes p62-R-BiP-denatured protein oligomerization (9) and autophagy aggregate formation (10). In addition, the ligand-62 conjugates step 13 act as autophagy activators (14), to promote LC3 synthesis, the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II, and the like, thereby promoting the formation of autophagosomes (15).
Owner:奧土择破利悟
Application of berberine in preparation of weight-loss drug
InactiveCN103356611AEnhanced inhibitory effectDecreased number of autophagosomesOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBerberineMedicine
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparation, and particularly provides an application of berberine in preparation of a medicine used for inhibiting autophagy of adipocyte and a medicine used for treating obesity. According to the application, C3H10T1 / 2 cell is cultured and induced to be differentiated into mature adipocyte, then the test for the impact of berberine to the mature C3H10T1 / 2 adipocyte autophagy marker protein LC3 and an autophagy substrate P62, and the test for detecting the C3H10T1 / 2 flat autophagy flux variation through chloroquine serving as a lysosomal inhibitor are performed, and the variation of the quantity of autophagosome can be observed through a transmission electron microscope; the results of various tests show that the berberine can effectively inhibit the autophagy of C3H10T1 / 2 adipocyte and provides theoretical basis for clinically reasonably applying the berberine to the treatment of obese patients; in addition, the berberine also can be applied to the preparation of the medicine for inhibiting the autophagy of adipocyte.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Electrochemical immunosensor for measuring secretory autophagosome and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110632148ANo complex processing requiredImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingSurface markerMedicine
The invention discloses an electrochemical immunosensor for measuring a secretory autophagosome as well as a preparation method and an application of the electrochemical immunosensor, and belongs to the technical field of biomedical detection. A substrate electrode is modified by a GH-MB solution, a surface marker LC3B first antibody solution of the autophagosome is covalently bound to the modified substrate electrode, and the electrochemical immunosensor is prepared. The invention further provides a method for detecting the secretory autophagosome in human peripheral blood and mouse peripheral blood by using the electrochemical immunosensor based on GH-MB signal amplification. The secretory autophagosome is captured by a Fe3O4-Au modified LC3B second antibody and then specifically bound to the LC3B first antibody. The detection method is high in sensitivity, good in specificity, wide in linear range, low in detection limit and low in cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Antiaging nutrient composition and application
PendingCN107982280AIncrease the number ofRaise the potentialHeavy metal active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsHydroxytyrosolArginine
The invention discloses an antiaging nutrient composition. The antiaging nutrient composition is prepared from nucleotide, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, arginine, histidine, glycine, aspartic acid, leucine, isoleucine, valine, serine, glutamine, glutamic acid, proline, tyrosine, cysteine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, taurine, orotic acid, granulesten, egg yolk lecithin, cephalin, alpha-linolenic acid, gamma-linolenic acid, inositol, hydroxytyrosol, vitamin A, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, niacin, folic acid, iron, zinc, manganese, copper, selenium, chromium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, choline, L-carnitine, pentose, sodium carbonate and freeze-dried powder of chick embryos hatched for three days. The antiaging nutrient composition has the advantages that neural stem cell proliferation is accelerated, amount of autophagosome is increased and activity of mesenchymal stem cells telomerase is improved.
Owner:吴文国 +2
Autophagy monitoring method for fat cells
InactiveCN103060421ANot easily transfectedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnimal scienceMature Fat Cell
The invention discloses an autophagy monitoring method for fat cells. Due to the adoption of a special structure, mature fat cells are full of plenty of lipid droplets, so that organelle and nucleus are displaced towards the periphery, and a typical autophagosome is hard to be seen under an electron microscope. Proved by a plurality of experiments, the method disclosed by the invention finally and successfully observes autophagy structures in various autophagy stages in mature 3T3-L1 fat cells by continuously improving the experiment condition. Besides, mature fat has a characteristic of being not easy to be transfected, so common plasmid transfection is hard to play an expectant effect. Therefore, the method disclosed by the invention utilizes a GFP-LC3 lentivirus method to infect 3T3-L1 fat cells, and the infection efficiency is as high as 80% or greater by observation under a fluorescence microscope. At nutrition and hunger condition, by the method disclosed by the invention, GFP-LC3 point-like aggregation phenomenon is successfully observed. The establishment of the autophagy monitoring method for mature fat cells lays the foundation of research on the relationship between autophagy and fat metabolism for us.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR ENDOCRINE & METABOLIC DISEASES
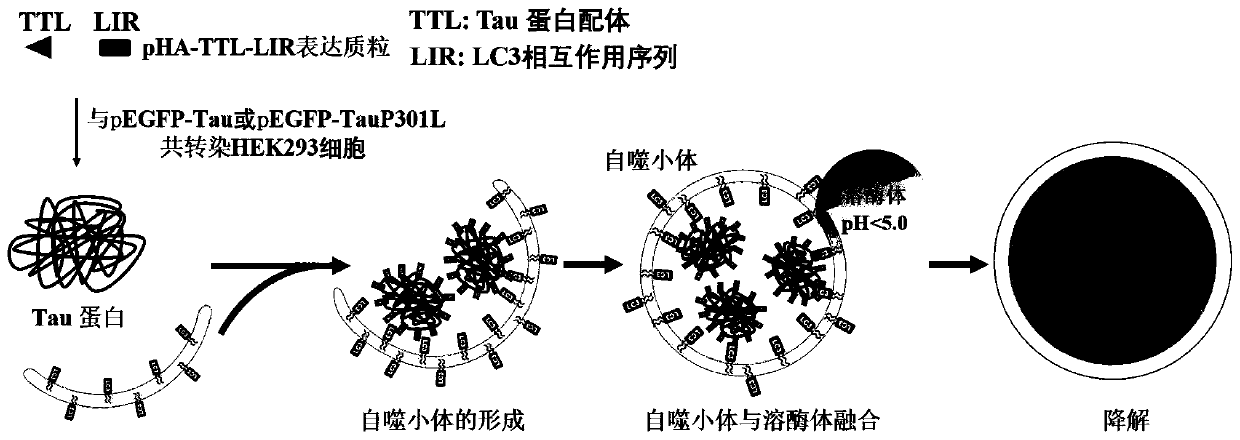
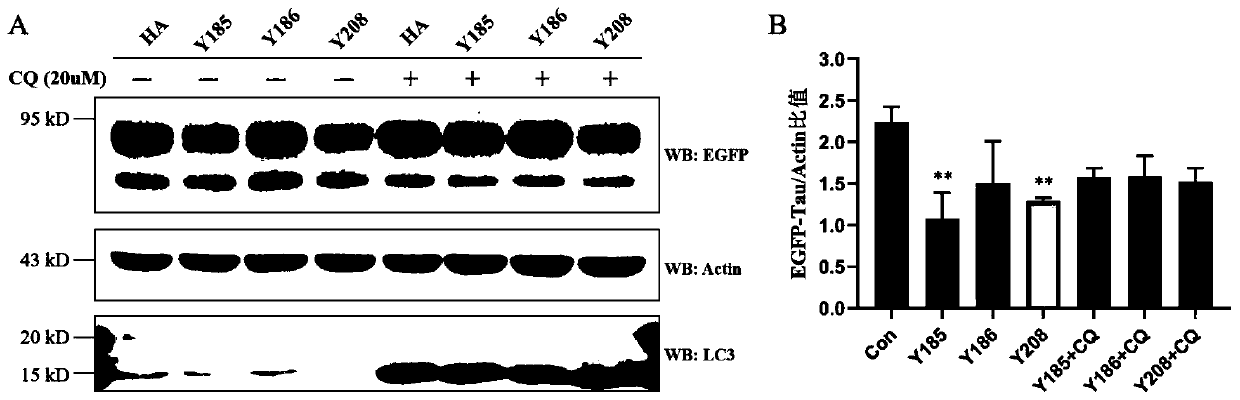
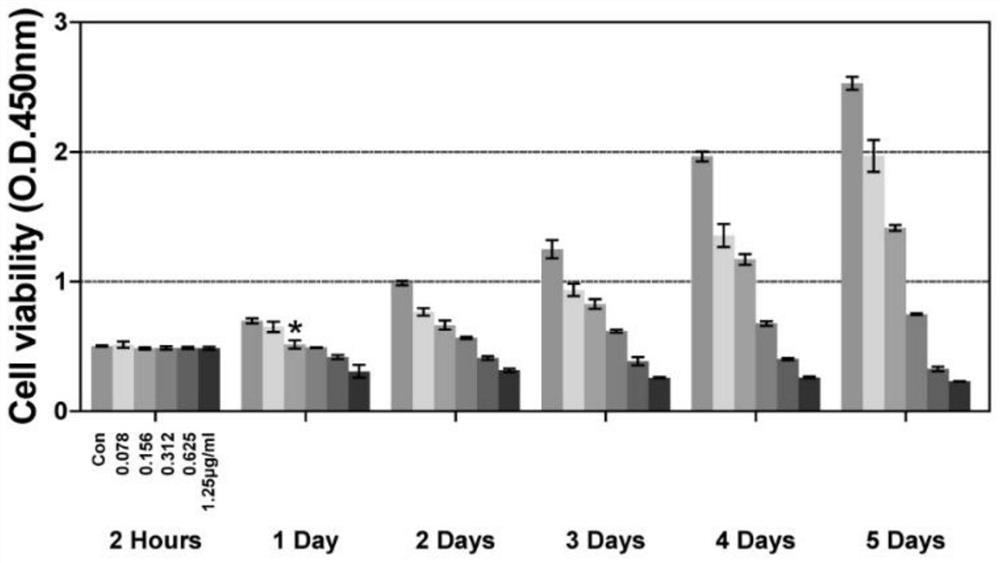
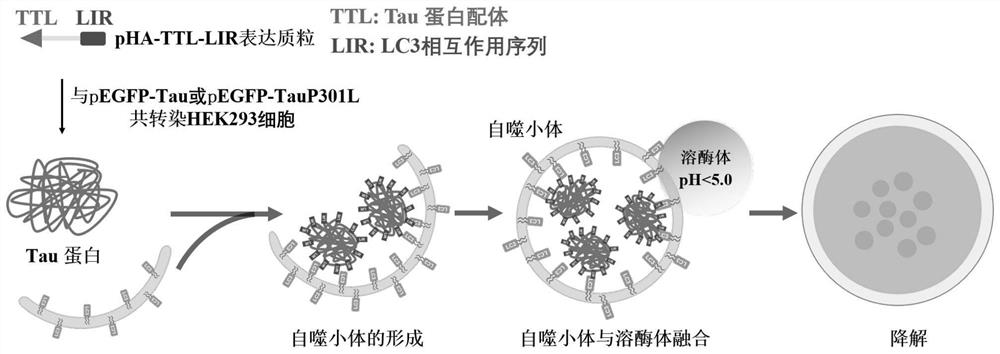
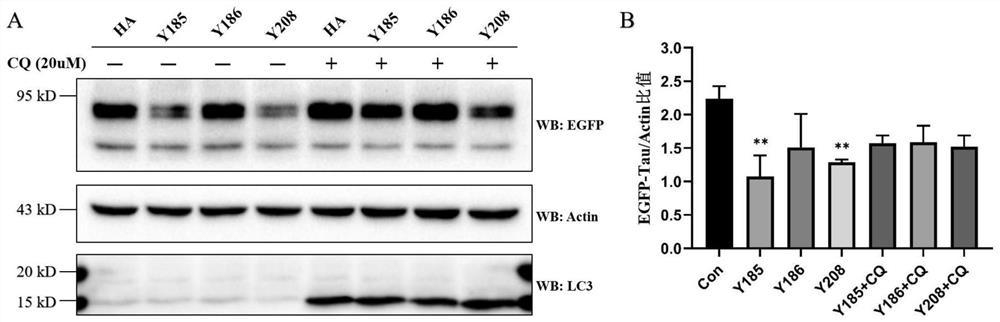
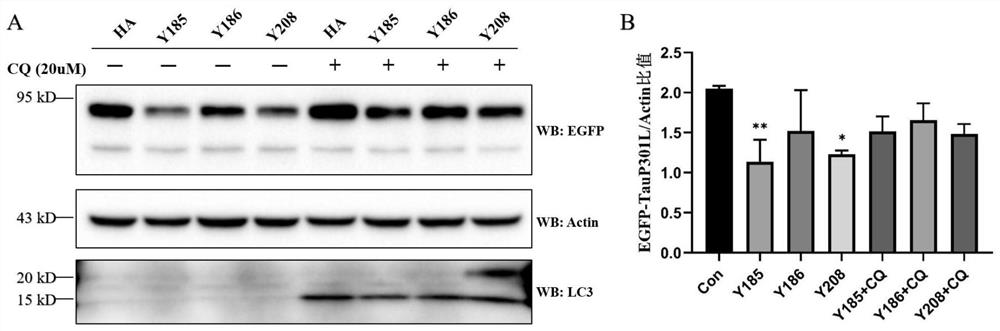
Chimeric molecule for mediating Tau protein degradation based on autophagy mechanism and application of chimeric molecule
ActiveCN111410695APromote degradationOvercome the defect of not being able to efficiently degrade intracellular macromolecular componentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsProtein targetMolecular binding
The invention discloses a chimeric molecule for mediating Tau protein degradation based on an autophagy mechanism, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:5 or 7. The invention also discloses a nucleic acid molecule and an expression vector; and the nucleic acid molecule is used for encoding the chimeric molecule for mediating Tau protein degradation based on the autophagy mechanism, andthe expression vector comprises the nucleic acid molecule. The invention also discloses an application of the chimeric molecule for mediating Tau protein degradation based on the autophagy mechanism,the nucleic acid molecule and the expression vector in degradation of Tau protein. The novel targeted chimeric molecule is developed in the invention, and the chimeric molecule is bound to the surface of the aggregate protein Tau, so that the Tau protein is recruited into cell autophagosome and is promoted to be degraded through the cell autophagy pathway. The novel protein targeted degradation technology provided by the invention is expected to be applied to different target proteins, so as to overcome the defect that a current ubiquitin-proteasome pathway-based protein targeted degradationtechnology cannot efficiently degrade intracellular macromolecules.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
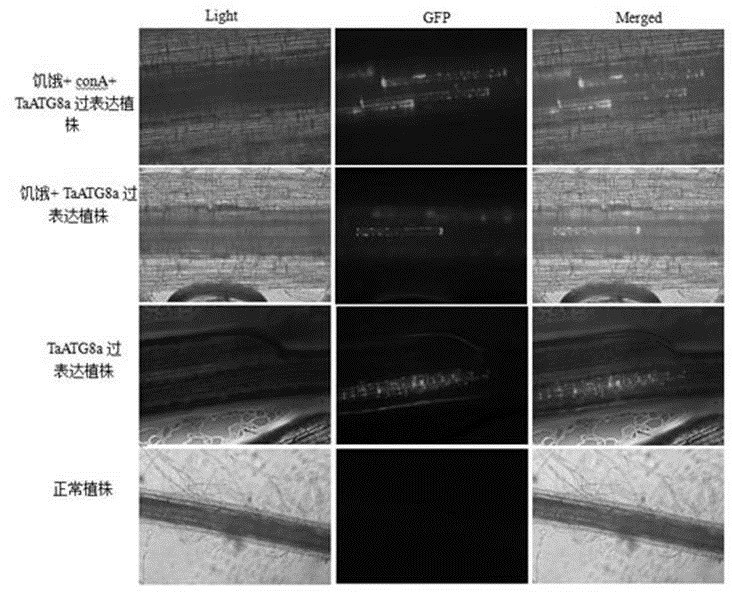
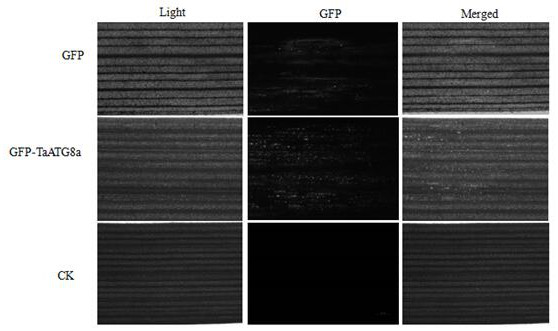
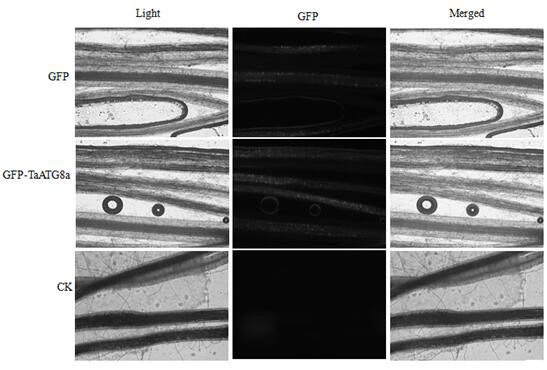
FoMV-mediated GFP-ATG8 expression vector and application thereof
PendingCN112430619AEasy to operateSuitable for gene function researchHydrolasesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyAutophagosome
The invention constructs a FoMV-mediated GFP-ATG8 expression vector and application thereof. A method takes TaATG8a as a target for monitoring autophagy, a VOX technology based on FoMV is adopted forexpressing GFP-TaATG8a fusion protein on a wheat plant, the expression situation and subcellular localization situation of the fusion protein in leaves and root tissues are observed through fluorescence, and a technical platform for monitoring the autophagy level on a wheat living plant with overexpression GFPTaATG8 as the target is established. The platform is successfully applied to observationof representation autophagosomes and autophagovesicles in leaf epidermis, mesophyll cells and root cells under hunger and drug treatment, and the invention shows that the vector can be applied to autophagy level monitoring and autophagy function research in the wheat growth and development process or the environmental factor response process. Research results provide technical support for deep exploration of autophagy regulation and control mechanisms and physiological functions of important crop wheat.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
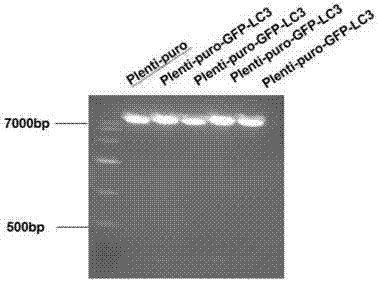
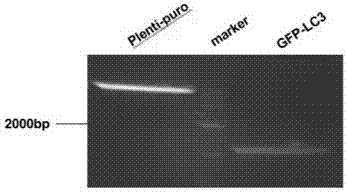
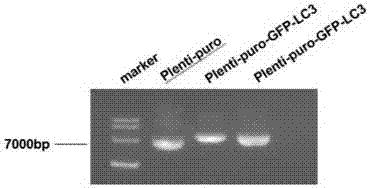
Slow virus green fluorescence autophagy report vector and building method thereof
InactiveCN107236764AWide applicabilityLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionLentivirusGreen fluorescent protein
The invention belongs to the field of cell research, and relates to a lentiviral green fluorescent autophagy reporter carrier based on a lentiviral carrier skeleton, which is used for screening stable strains and observing changes in autophagosomes in cells and a construction method. The invention discloses a lentiviral green fluorescent autophagy reporter carrier, which comprises ampicillin resistance, puromycin selection marker and green fluorescent autophagy marker protein LC3 gene sequence. The green fluorescent autophagy marker protein LC3 plasmid of the present invention uses lentivirus as the backbone, which is conducive to the establishment of stably expressing green fluorescent cell lines, and due to the wide applicability of lentivirus to mammalian cells, the green fluorescent plasmid of the present invention can be used for various cells. Compared with the expensive price and specificity of using common vectors, the cost is very low.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL OF SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method and application of nervous system neoplasm cell autophagosome to preparing vaccine
PendingCN109402058AImprove acquisition efficiencyFacilitated releaseCulture processCancer antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthFreeze thawing
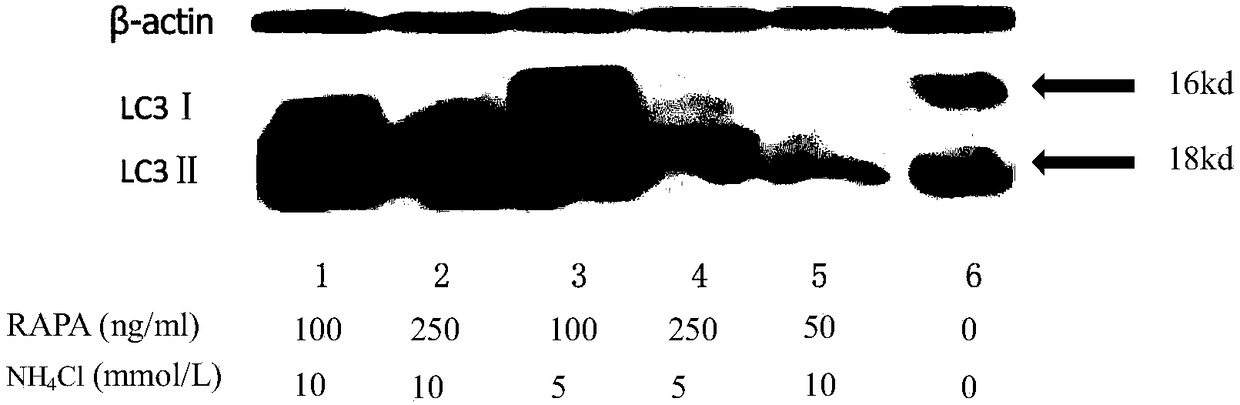
The invention belongs to the technical field of biologics and relates to a preparation method and application of nervous system neoplasm cell autophagosome to preparing a vaccine. Sirolimus and ammonium chloride are adopted to induce and culture nervous tumor cells, autophagosome generation is promoted, and autophagosome is extracted through repeated blowing and beating and high-speed centrifugation at different steps. A great deal of autophagosome can be rapidly prepared by using the method provided by the invention, after the autophagosome is carried by DCs (Dendritic Cells), DC maturation can be effectively promoted, T lymphocyte can be activated, proliferation of the T lymphocyte can be promoted, a remarkable killing function on tumor cells can be achieved, and the killing effect is remarkably better than tumor freeze thawing splitting antigen prepared in the prior art. The autophagosome prepared by using the method can be further adopted to prepare a nervous system tumor vaccine,and the vaccine is a dendritic cell tumor vaccine for nervous system derived tumor cell autophagosome.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
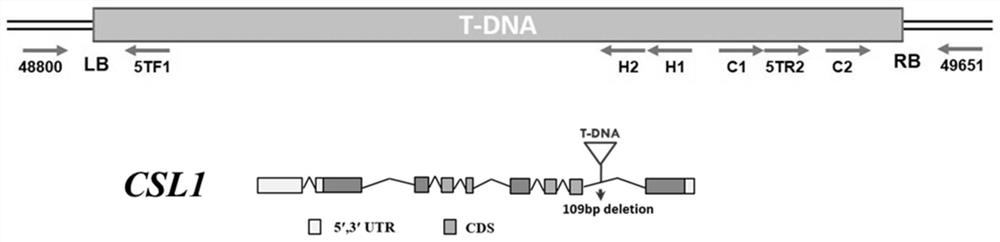
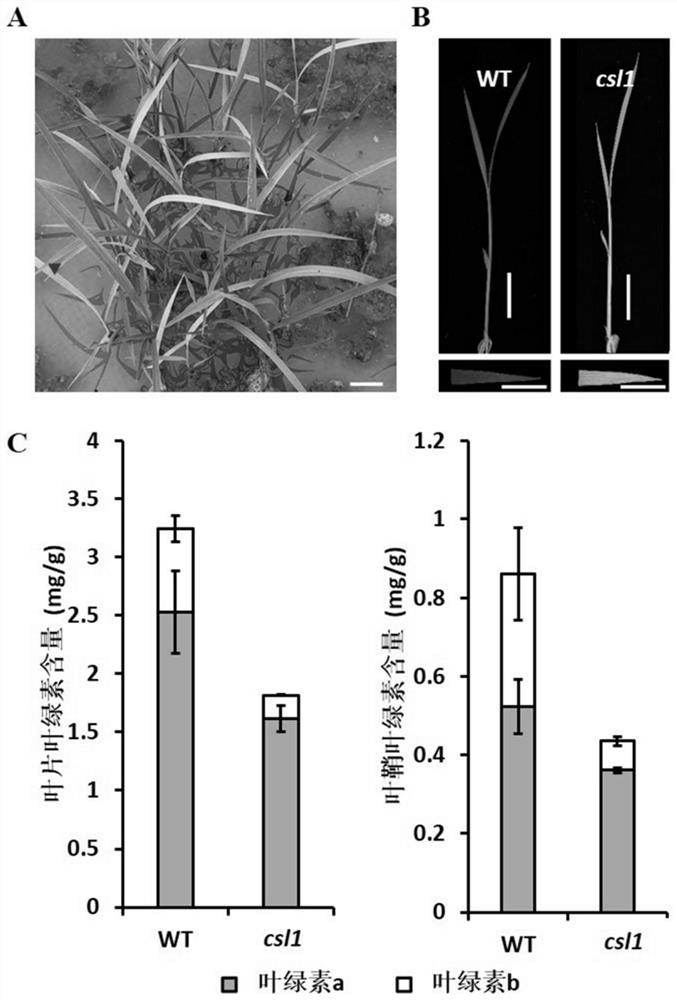
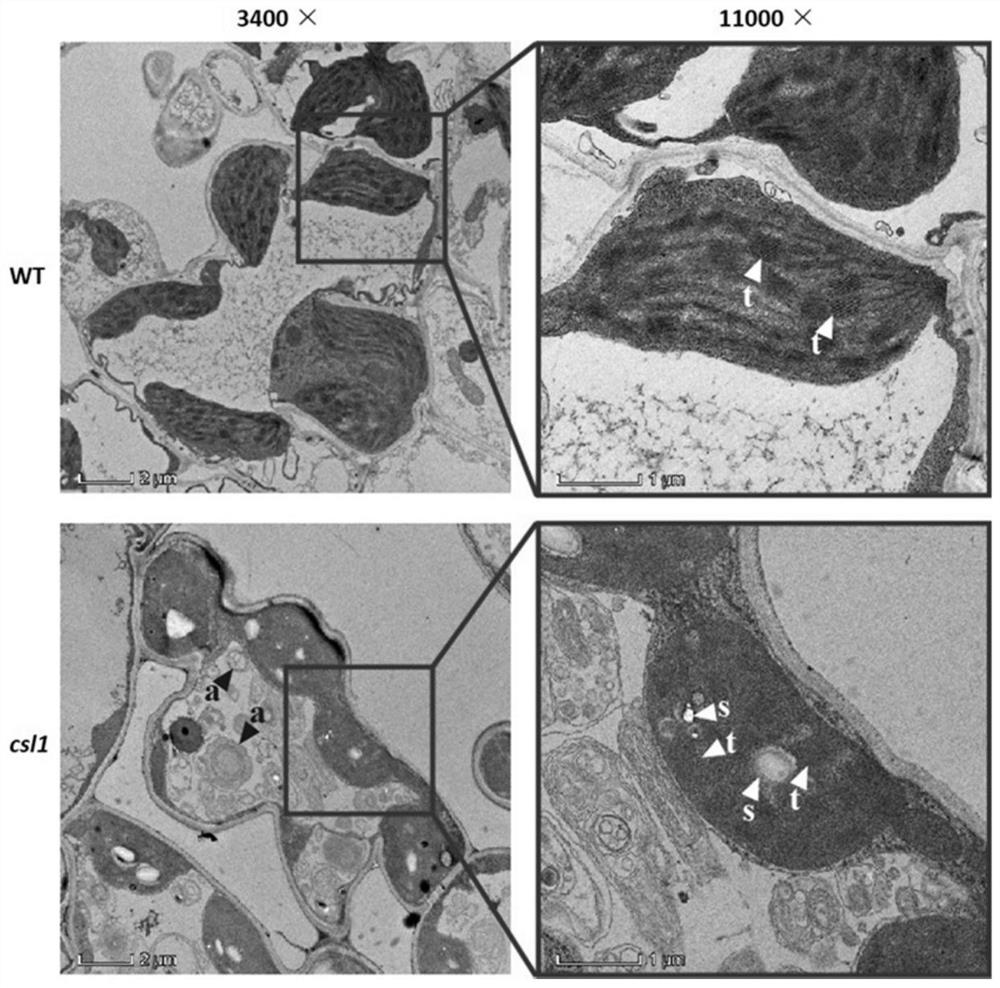
Application of chlorosis seedling lethality 1 (CSL1) gene to regulation of development of rice chloroplasts
The invention discloses application of a chlorosis seedling lethality 1 (CSL1) gene to regulation of development of rice chloroplasts. According to the invention, a lethal rice mutant at an etiolatedseedling stage is isolated from a rice T-DNA mutant library; the lethal rice mutant is inserted into a seventh intron of the CSL1 gene by means of T-DNA insertion; a 109bp sequence is deleted at a T-DNA insertion position; the chlorophyll content of the CSL1 mutant decreases; single-layer or multi-layer autophagosomes appear in the mesophyll cells; starch grains in the chloroplasts increase; a thylakoid structure is disordered; and the expression quantity of chloroplast-related genes is changed. meanwhile, the invention further constructs a knockout plant (the CSL1 gene has a deletion of one base A at the site 46 of exon 5, or a deletion of one base A at the site 47 and substitution of the base A with the base T at the site 48) by means of gene knockout, and the knockout plant has the samephenotype as the CSL1 mutant, thus showing that the CSL1 gene is involved in regulation of development of the rice chloroplasts.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Prevention and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Autophagy Activity Mediated by A Synthetic Ligand or Arginylated BIP Binding to the P62 ZZ Domain
ActiveUS20180243244A1Easy to useNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsLysosomal proteolysisInclusion bodies
The pharmacokinetics and key technologies of the present invention are summarized in FIG. 1. Particularly, malignant misfolded proteins such as mutant huntingtin and alpha-synuclein are coagulated and grow into oligomeric coagulum (①, ②, fibrillar coagulum (③) and eventually inclusion body (④). Young neurons produce a large amount of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (⑤) of vesicle chaperones such as BiP secreted into the cytoplasm, and then arginylated BiP (R-BiP) is secreted binds to the misfolded proteins (⑥). As a ligand, the Nt-Arg of R-BiP binds to the p62 ZZ domain (⑦), and the normally inactivated closed form of p62 is changed to an open form, leading to structural activation (⑧). As a result, PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. The PB1 domain induces oligomerization (⑨), leading to the concentration as a p62 body (⑩) that is a coagulum capable of being degraded by autophagy. Then, p62 binds to LC3, which is protruding from the autopagosomal membranes, leading to the completion of autophagy targeting (⑪) and lysosomal proteolysis. Since autophagy proteolysis including steps (⑤)-(⑪) is strong in young neurons, cytotoxic protein coagulums (①-⑤) do not accumulate. However in aged neurons, autophagy proteolysis including steps ⑤-⑪ is weakened, and protein coagulums (①-⑤) accumulate and become cytotoxic. In this invention, p62 is intentionally activated (⑫, ⑬) by using low mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain to effectively remove huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein coagulums. Particularly, in step ⑫, p62 ligated with a ligand accelerates the oligomerization of p62-R-BiP-misfolded protein (⑨) and the formation of autophagy coagulum (⑩). In step (⑬), the ligand-p62 conjugate acts as an autophagy activator (⑭) to induce the synthesis of LC3 and the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II in order to accelerate the formation of autophagosomes (⑮).
Owner:AUTOTAC BIO
Double-fluorescent-protein positioning detection system for detecting mitochondrial autophagy of cells and application
PendingCN112162096AEasy to operateFast trackAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological testingMitophagyAutophagosome
The invention discloses a double-fluorescent-protein positioning detection system for detecting mitochondrial autophagy of cells. The detection system at least comprises (1) fusion protein composed offluorescent protein A and indicating protein A; and (2) fusion protein composed of a fluorescent protein B and an indicator protein B, wherein the fluorescent protein A and the fluorescent protein Bhave different fluorescence colors, the indicating protein A is used for indicating autophagosome, and the indicating protein B is used for indicating mitochondria. The invention provides a quicker, more convenient and more accurate way for researching the observation of mitochondrial autophagy. The system is a good supplement for methodology of mitochondrial autophagy research, and opens up a newidea for methodology of mitochondrial autophagy research.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOCHIP
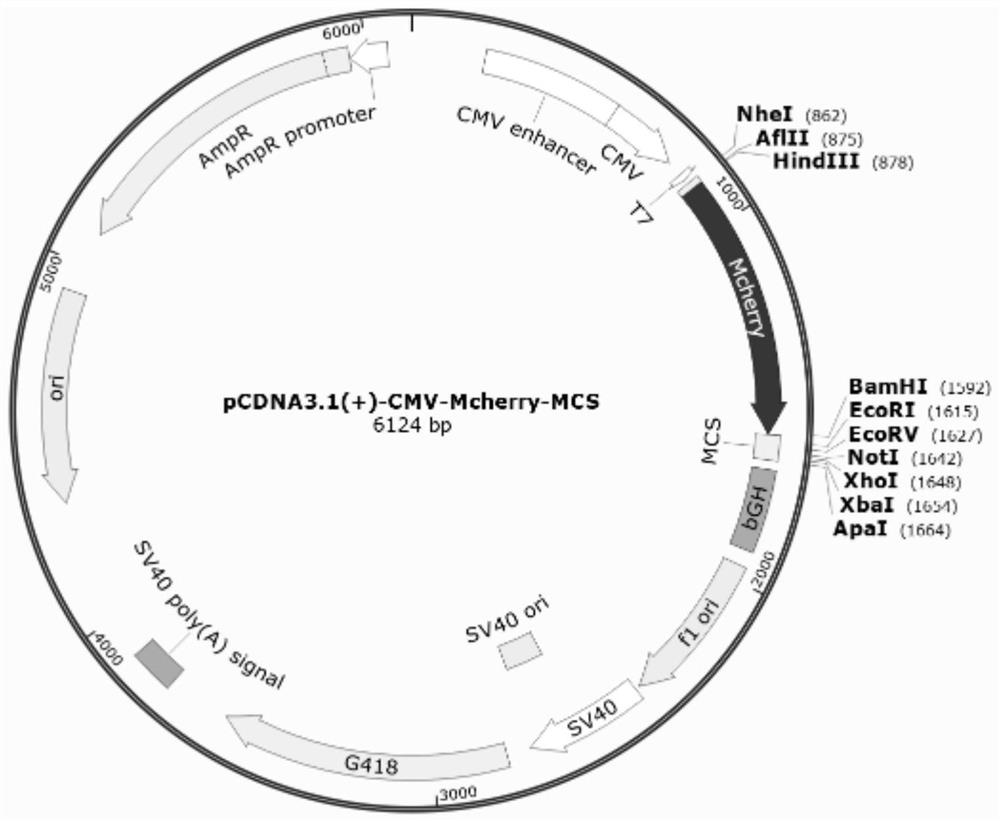
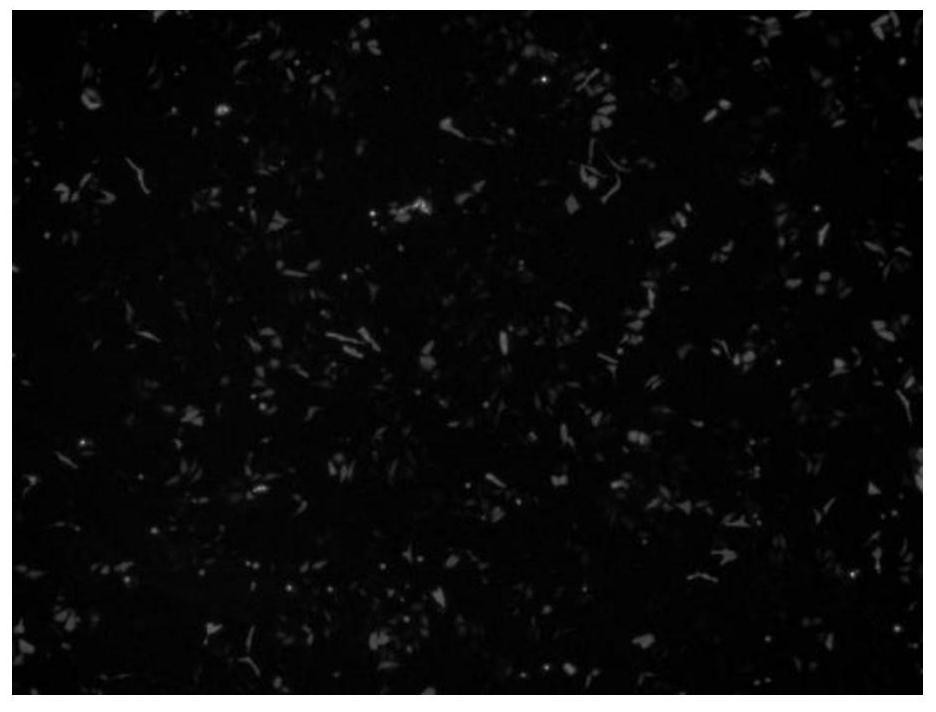
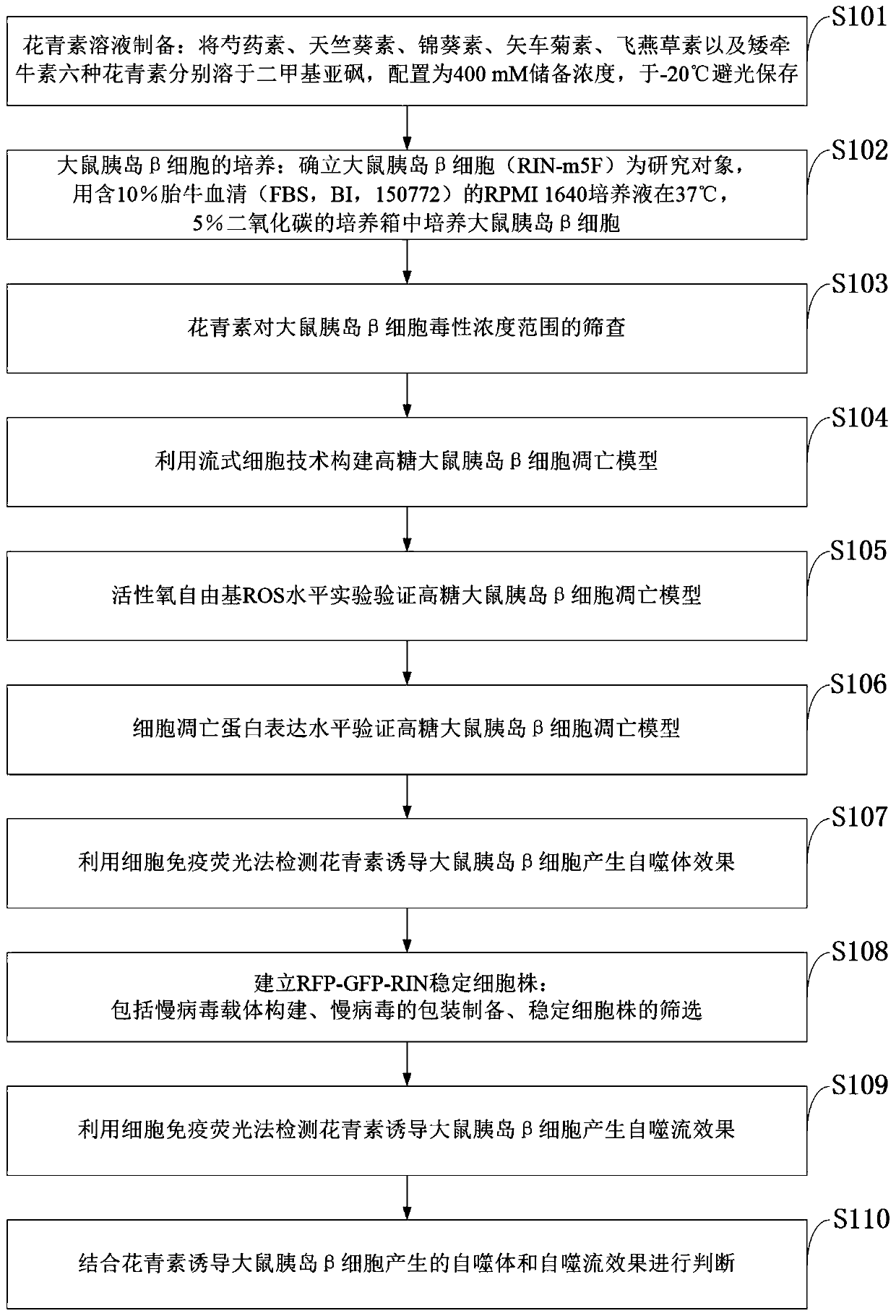
Method for detecting anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell autophagy effect
ActiveCN110551791AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisReactive oxygen radicalsScreening method
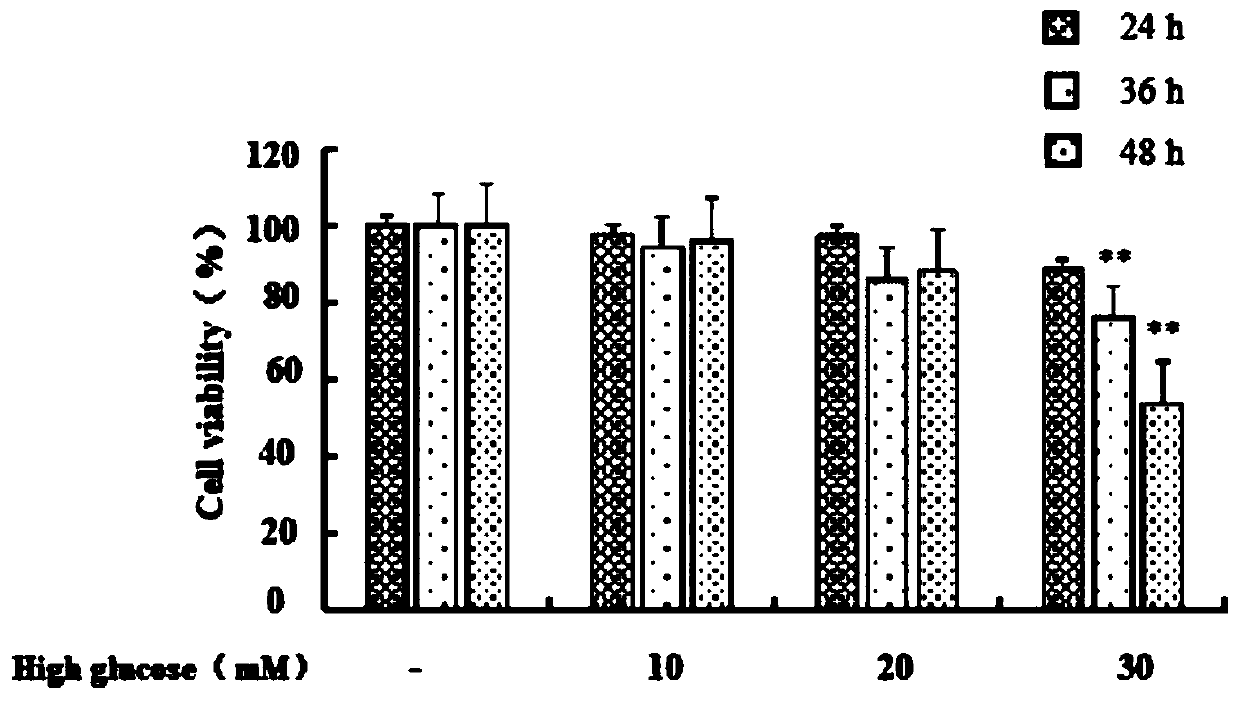
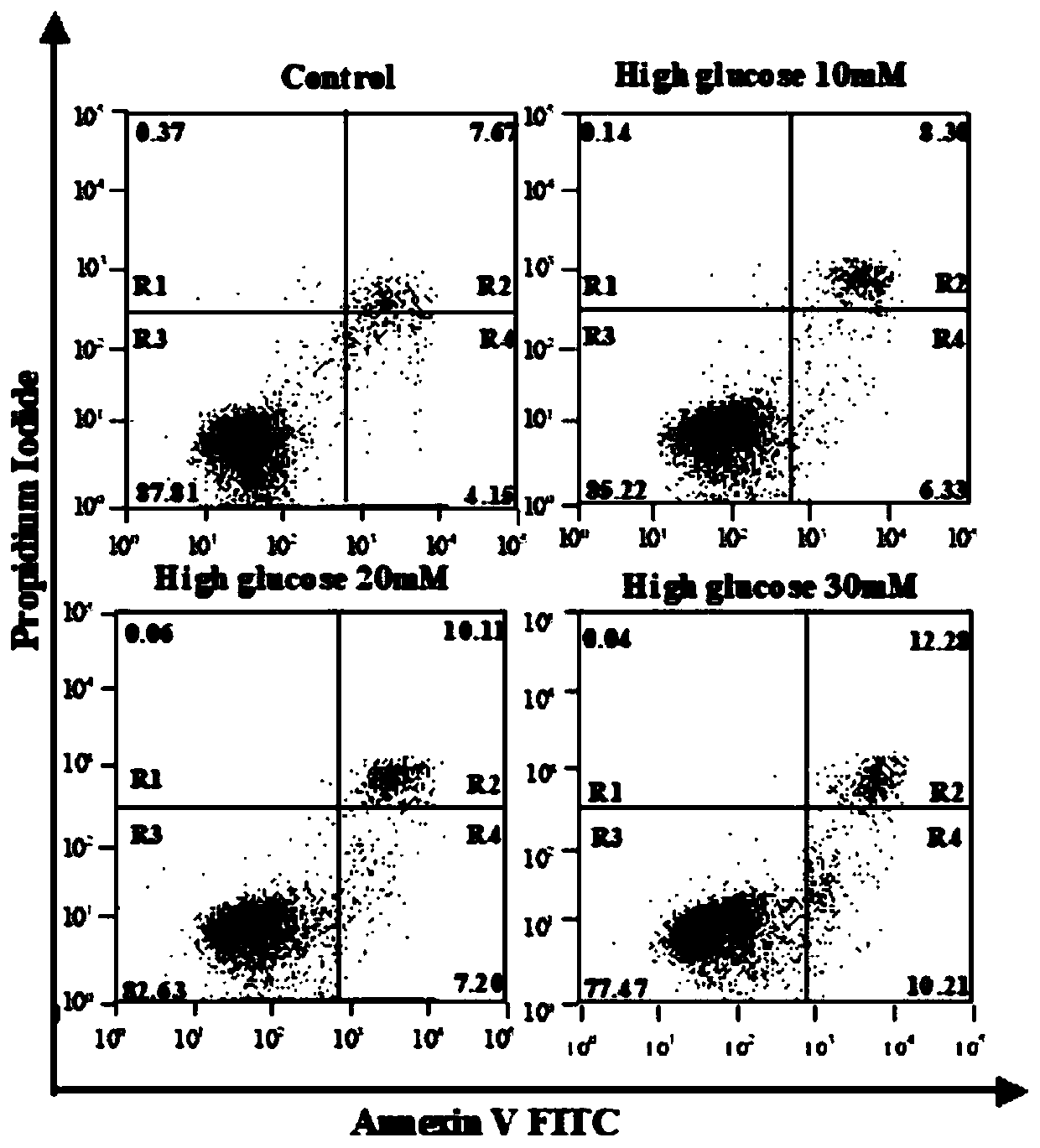
The invention belongs to the technical field of cytobiology detection and discloses a method for detecting an anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell autophagy effect. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an anthocyanin solution, culturing a rat islet beta cell, screening a concentration range of anthocyanin upon the toxicity of the rat islet beta cell, establishing a high-sugar ratislet beta cell apoptosis model by using a flow cytometry technique, performing an active oxygen free radical level experiment and a western blotting method so as to verify the high-sugar rat islet beta cell apoptosis model, detecting the anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell autophagy effect by using a cell immumofluorescence method, establishing an RFP-GFP-RIN (red fluorescence protein-greenfluorescent protein-rat islet beta cell) stable cell line to detect the anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell autophagy effect, generating autophagosome from the anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell, and performing autophagy flux effect judgment. A high-flux screening method is established for the anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell autophagy effect, and theoretic bases are provided for preventing diabetes according to the anthocyanin-induced rat islet beta cell autophagy effect.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Cloning and application of tomato ATG8f gene
InactiveCN105802977AEasy to detectQuick checkPlant peptidesFermentationBiologyAutophagosome formation
The invention discloses cloning and application of a tomato ATG8f gene. The gene plays an important role in a tomato autophagosome formation process. The tomato ATG8f gene is cloned, and an agrobacterium tumefaciens engineering bacterium A containing a tomato ATG8f gene over-expression vector is constructed; the agrobacterium tumefaciens engineering bacterium A is used for carrying out mediated transformation on an explant of a target plant to prepare an ATG8f gene transgenic plant; the vegetative growth of the plant is vigorous; the agrobacterium tumefaciens engineering bacterium A is infected with nicotiana benthamiana and a point-shaped autophagosome can be observed. The tomato ATG8f gene disclosed by the invention has important application value in cultivation of good tomato varieties and autophagosome detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of H22 liver cancer cell autophagosome to preparation of liver cancer therapeutic vaccine
ActiveCN102430118BConform to the characteristicsEffective recruitmentTumor/cancer cellsAntibody medical ingredientsOncologyTumor antigen
The invention discloses application of H22 liver cancer cell autophagosome DRibbles to the preparation of a liver cancer therapeutic vaccine. Liver cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in China and can be effectively prevented by developing a liver cancer vaccine; and years of research results prove that tumor cell autophagosome is one of effective vectors for tumor antigen cross-presentation. The application comprises a core technology for extracting the autophagosome DRibbles from human liver cancer cells and proves that the autophagosome can effectively induce anti-tumor immune response of organisms and has a good biotherapy prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
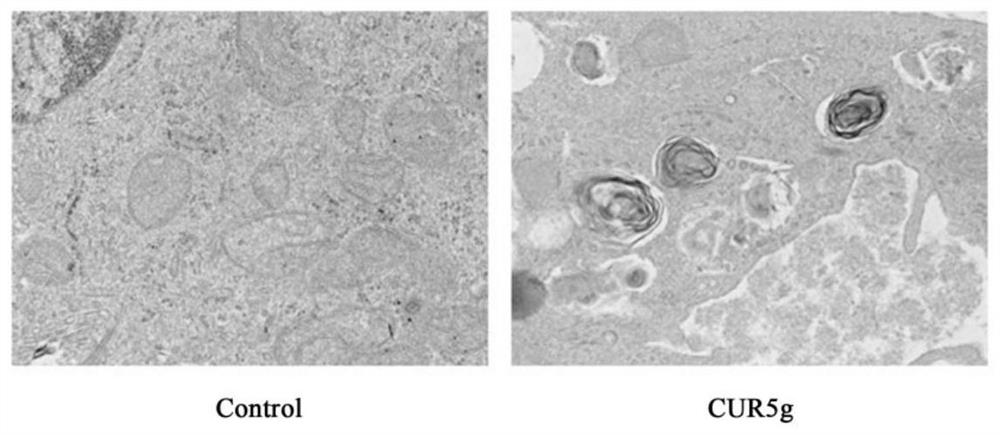
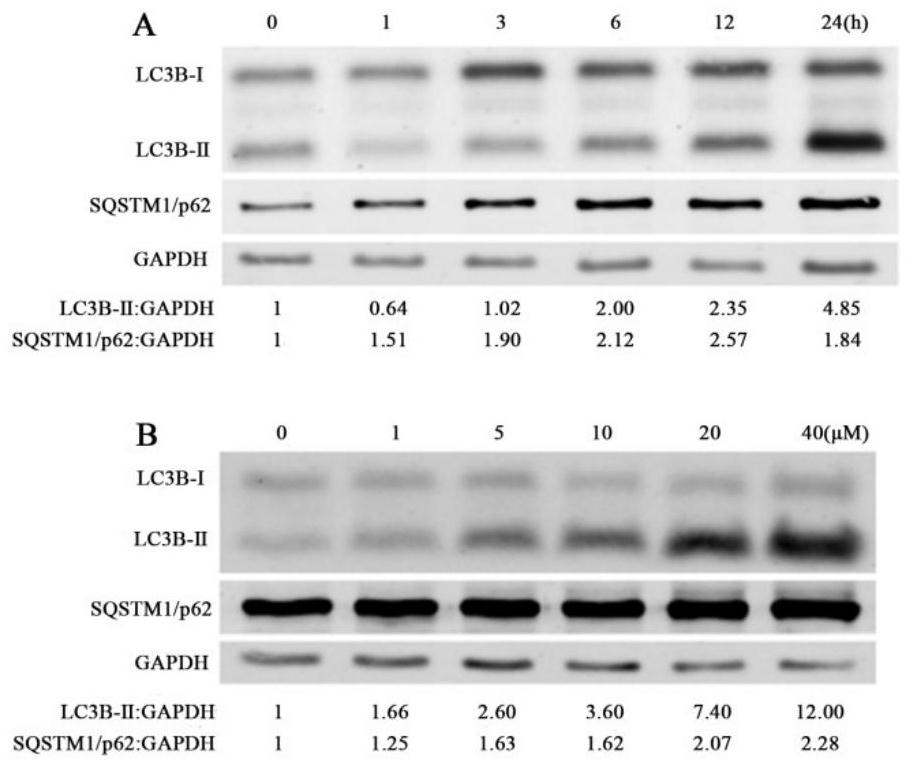
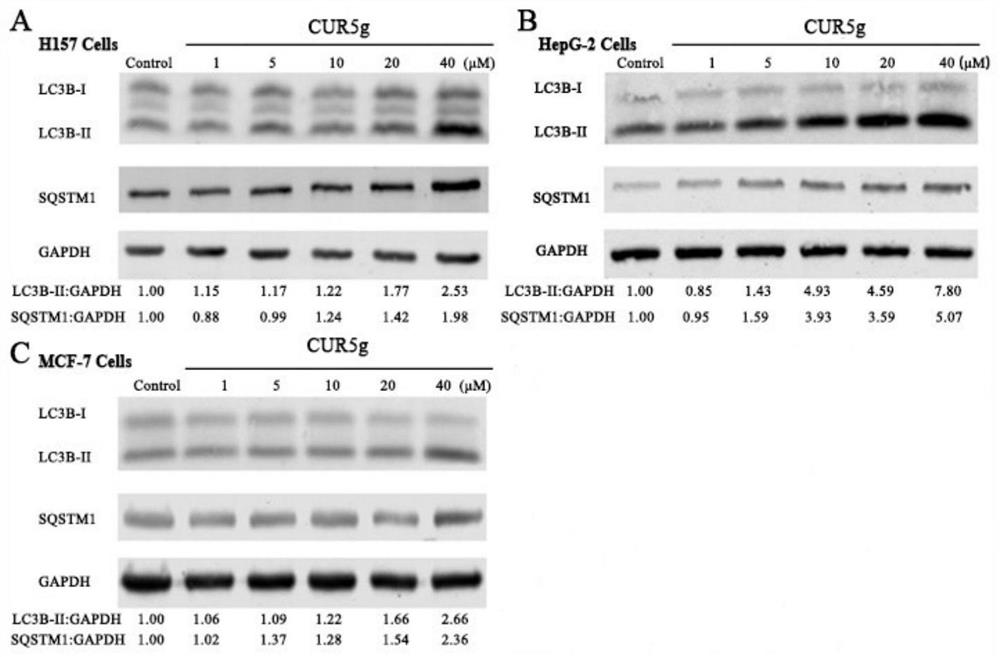
Application of curcumin analogue CUR5g as novel autophagy inhibitor
The invention discloses an application of a curcumin analogue CUR5g as an autophagy inhibitor. According to the invention, the influence of 5g of CURR on A549 cell autophagy is detected through a transmission electron microscope experiment, the influence of 5g of CURR on A549 cell autophagy marker protein level is detected through a protein immunoblotting method, and the influence of 5g of CURR on H157, HepG-2 and MCF-7 cell autophagy marker protein levels is detected through the protein immunoblotting method. The effects of cur5g on autophagy marker protein level of A549 cells under autophagy inhibition and activation conditions were detected by Western blotting, and the effects of cur5g on autophagy initiation protein level of A549 cells were detected by Western blotting. It was proved that cur5g can effectively inhibit the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes in vitro, so as to inhibit the autophagy. 5g of CUR5 has a remarkable effect as an autophagy inhibitor, and an attractive prospect is provided for development and application of the autophagy inhibitor.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
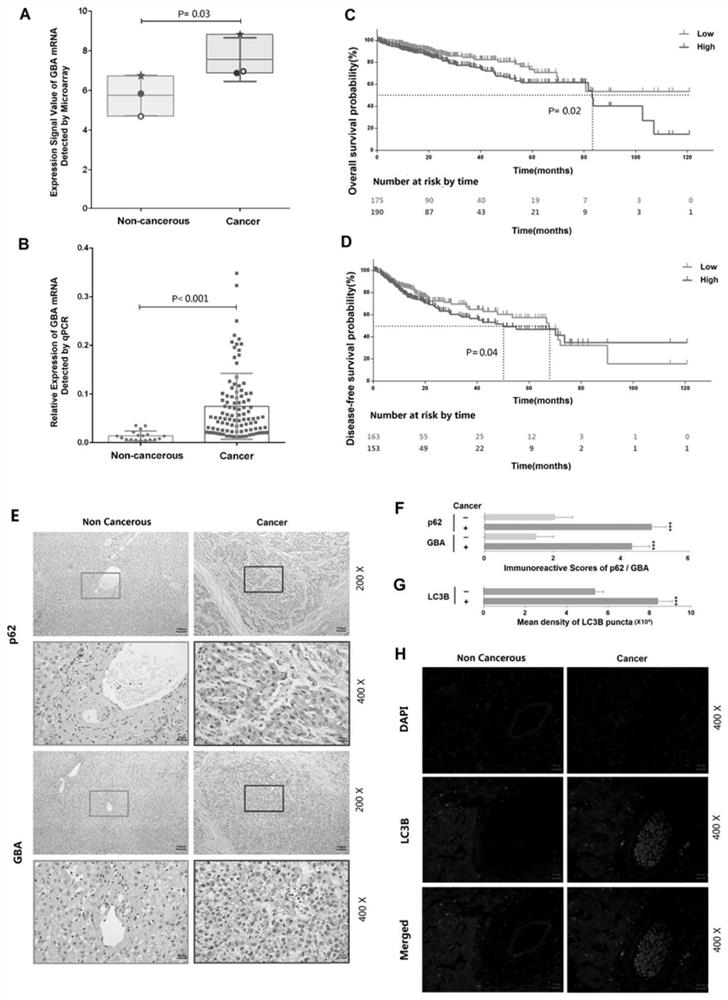
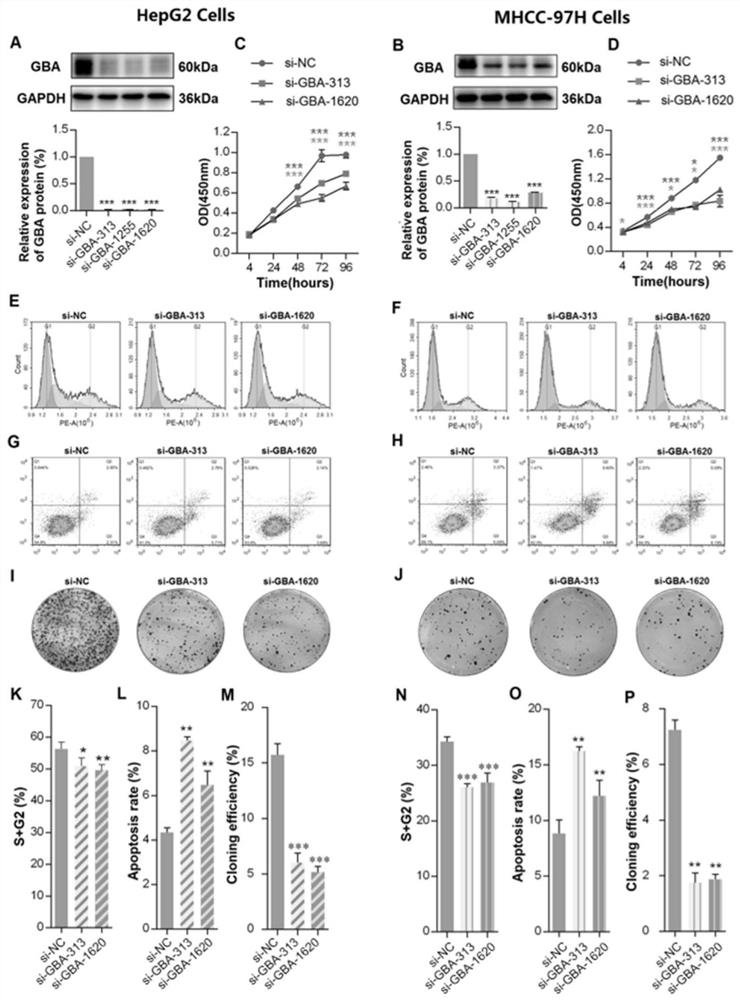
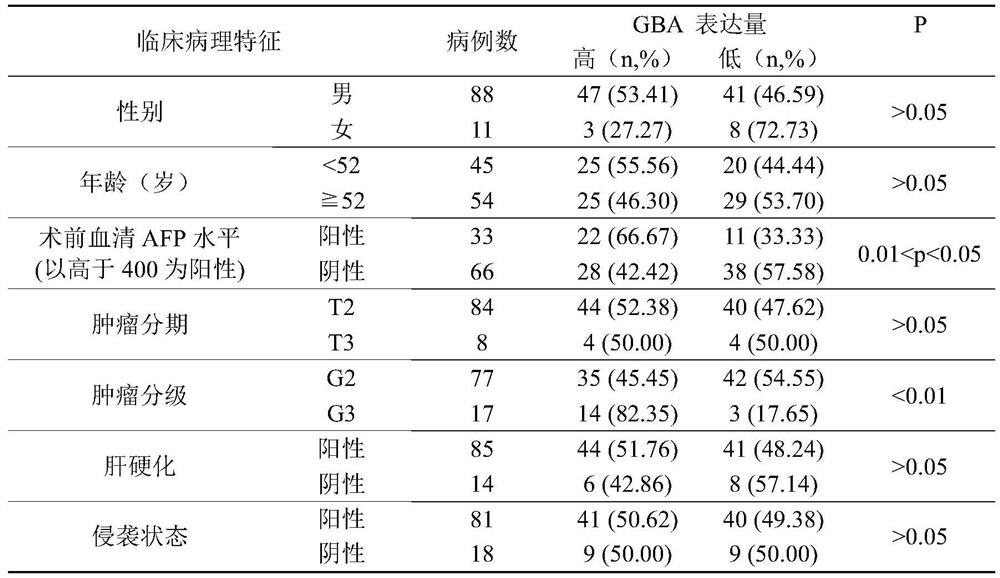
Application of reagent targeting biomarker in preparation of medicine for relieving/treating liver cancer
ActiveCN113198016AAvoid degradationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPharmaceutical drugBiomarker (medicine)
The invention relates to an application of a reagent targeting a biomarker in preparation of a medicine for relieving / treating liver cancer, wherein the biomarker is GBA. The reagent targeting the biomarker inhibits the overexpression of GBA, the overexpression of GBA is closely related to the malignant development and poor prognosis of liver cancer, and the mechanism can be that the overexpression of GBA induces autophagy of liver cancer cells and promotes the proliferative activity of the liver cancer cells, thereby promoting the malignant development of liver cancer. The reagent targeting the biomarker prevents degradation of autophagosome in the liver cancer cells by inhibiting abnormal high expression of GBA, so that the downstream of autophagy flow is blocked, and the anti-liver cancer drug effect of the reagent is exerted.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI +1
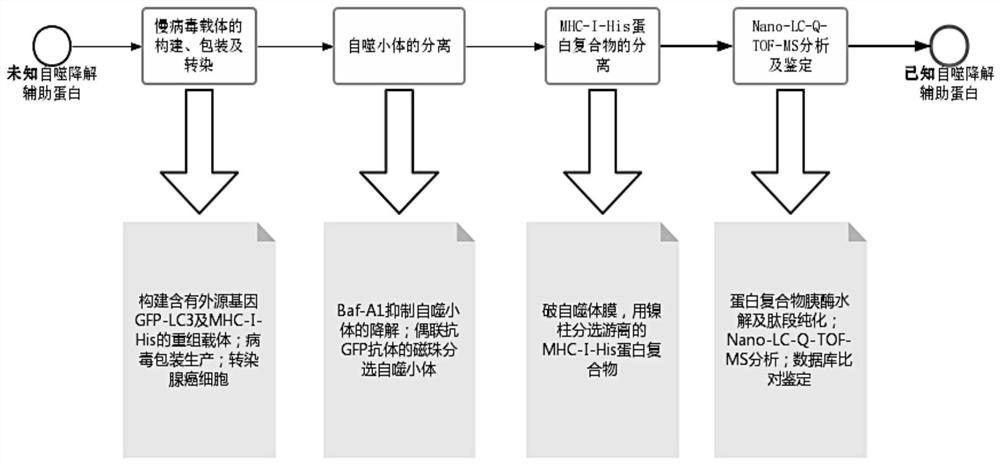
Method for screening autophagy degradation helper protein
PendingCN114196706AAccurate identificationBiological testingTumor/cancer cellsPancreas CancersSeparation technology
The pancreatic cancer cells overexpressing GFP-LC3 and MHC-I-His protein are constructed by adopting lentivirus, autophagosome is separated by a magnetic separation technology under the condition of inhibiting autophagy degradation, an MHC-I-His protein binding compound in the autophagosome is separated by a nickel column separation technology, and after trypsin hydrolysis, the pancreatic cancer cells are separated by using the MHC-I-His protein binding compound. And carrying out mass spectrometry on the purified hydrolysis peptide fragment by using Nano-LC-Q-TOF-MS, and finally determining the type of the separated protein by searching a database, thereby realizing the screening of the MHC-I autophagy degradation auxiliary protein. The auxiliary protein for MHC-I autophagy degradation can be accurately screened out, and a new target spot is provided for blocking MHC-I autophagy degradation and improving body anti-tumor immunity research.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
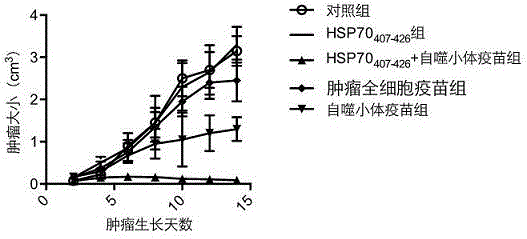
Vaccine adopting subcellular structure and preparation method of vaccine
InactiveCN105641712AAbility to enhance anti-tumor immune responseStrong tumor growth inhibitionCancer antigen ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumour-associated antigenBortezomib
The invention discloses a vaccine adopting the subcellular structure and a preparation method of the vaccine. On the basis that short-lived protein in tumor cells is induced by bortezomib and ammonium chloride and a defective ribosome product is used as antigen protein, the vaccine adopting the subcellular structure enters autophagic vacuoles adopting the double-membrane structure through an autophagy pathway, the autophagic vacuoles coating tumor antigens are collected and then modified by HSP70 immune activation peptide fragments, modified autophagic vacuoles are the vaccine adopting the subcellular structure, and the vaccine is delivered through lymph glands, can effectively induce cross presentation of a body immune system and activate CD4+ and CD8+ T lymph cells and CTL cells, and has the better tumor killing effect.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Application of triacetyl andrographolide as medicine for regulating degradation of autophagosome
PendingCN114028386AImprove learning and memory abilityReduce aggregationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGene modelPhosphorylation
The invention belongs to the field of medicines, and relates to application of andrographolide, in particular to application of triacetyl andrographolide as a medicine for regulating autophagosome degradation. The invention relates to an application of triacetyl andrographolide in preparation of a medicine for promoting autophagosome clearance. The invention also discloses application of triacetyl andrographolide as a medicine for simultaneously reducing the expression levels of LC3-II and P62 in the brain. Triacetyl andrographolide also can be used as a medicine for reducing phosphorylation levels of Akt and mTOR, improving learning and improving memory. An APP / PS1 / Tau triple transgenic model mouse and an ApoE4 transgenic mouse are utilized to prove that the triacetyl andrographolide can effectively improve the learning and memory ability of a model animal and reduce the levels of A[beta]1-40 and A[beta]1-42 in the brain of a model animal. Triacetyl andrographolide can inhibit the activation of Akt-mTOR signals in both in-vivo and in-vitro models, relieve the excessive accumulation of LC3-II and P62, and reduce the aggregation of autophagosome.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
An electrochemical immunosensor for detecting secreted autophagosomes and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110632148BNo complex processing requiredImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingSurface markerSecretion
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Autophagy monitoring method for fat cells
InactiveCN103060421BNot easily transfectedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnimal scienceMature Fat Cell
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR ENDOCRINE & METABOLIC DISEASES
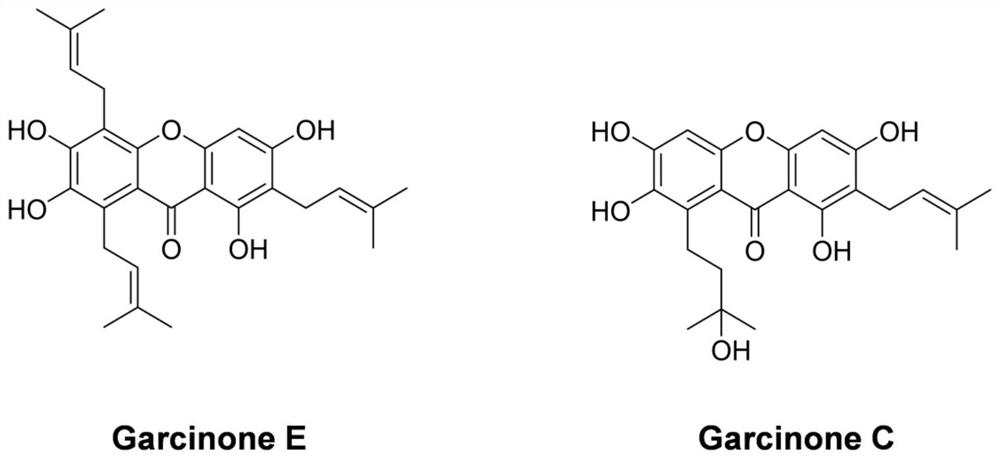
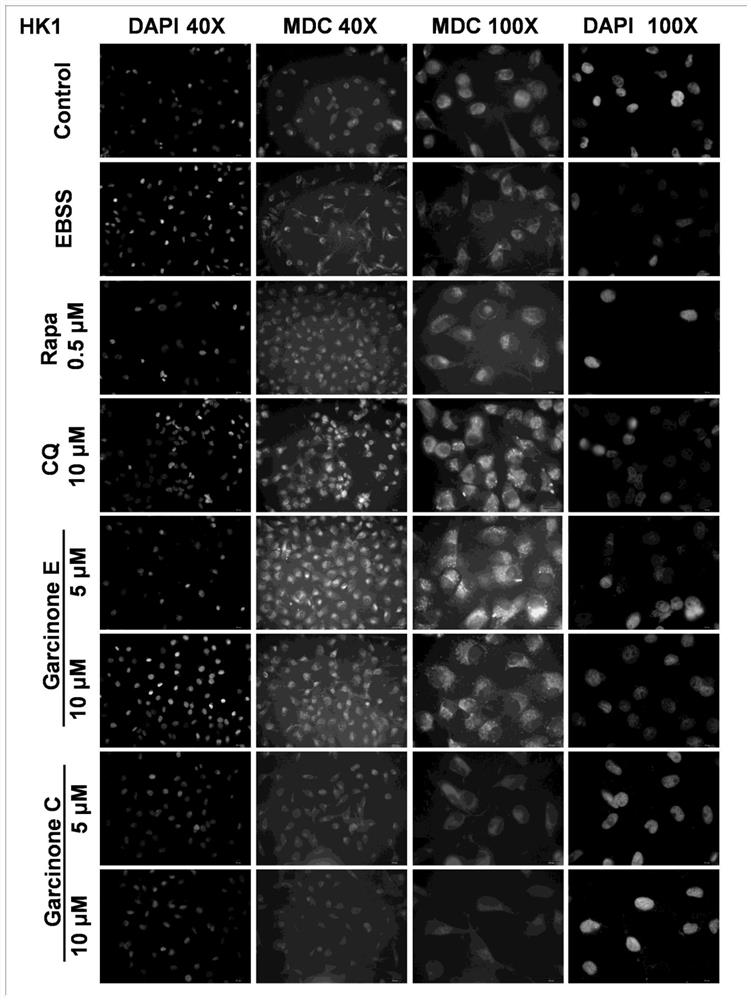
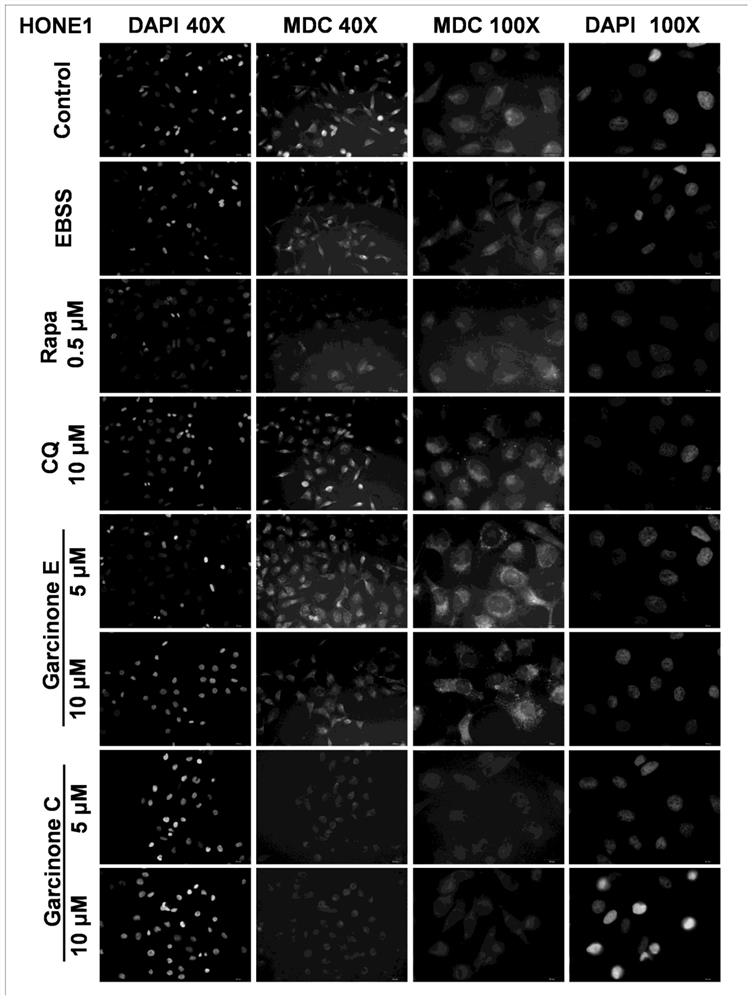
Application of Garcinone E in preparation of tumor cell autophagosome inducer
The invention discloses application of Garcinone E in preparation of a tumor cell autophagosome inducer. It is found for the first time that Garcinone can effectively induce increase of autophagosomesof nasopharyngeal carcinoma and ovarian carcinoma cells, induce increase of expression levels of autophagy marker proteins LC3A / B-I and LC3A / B-II in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, and reduce the expression level of p62. A negative control compound Garcinone C which has the same mother ring structure as Garcinone E and has an inhibition effect on proliferation activity of tumor cells does not induce the increase of the number of autophagosomes of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma and ovarian carcinoma cells, induces increase of the expression levels of autophagy related proteins Beclin-1, LC3A / B-II, Atg7 and other proteins of the ovarian cancinoma cells, and induces no increase of the expression quantity of LC3A / B-I. It is prompted that Garcinone E can play an important role in preparation ofa novel autophagosome inducer for antitumor research.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through autophagy activity mediated by a synthetic ligand or arginylated BIP binding to the P62 ZZ domain
ActiveUS10391067B2Easy to useNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsLysosomal proteolysisInclusion bodies
Owner:AUTOTAC BIO
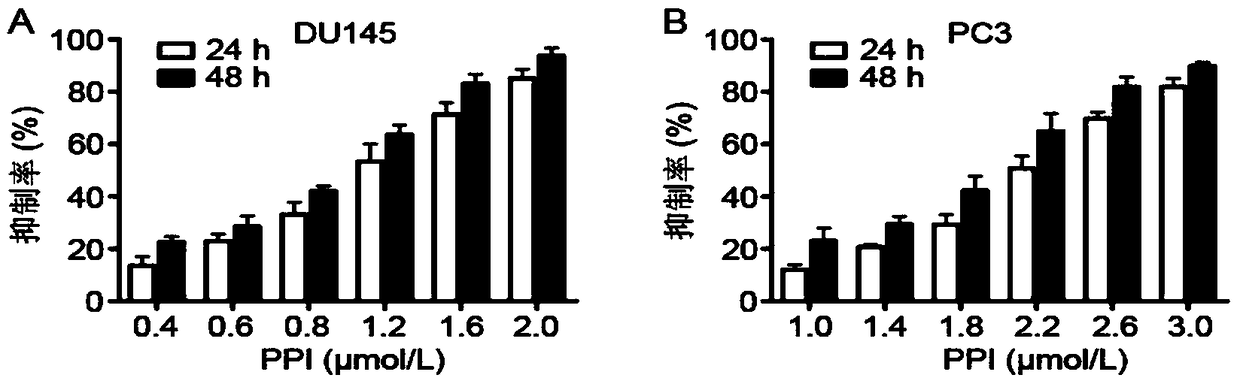
Application of rhizoma paridis extract in preparation of drugs for treating human prostate cancer
InactiveCN108853128AGrowth inhibitionHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderDU145Autophagosome
The invention discloses application of a rhizoma paridis extract in preparation of drugs for treating human prostate cancer. According to the application, experiments shows that polyphyllin I has an inhibition effect on the human prostate cancer DU145 and PC3 cell lines, and the inhibition effect is improved along with the increase of dosage and time; in addition, the polyphyllin I can induce theincrease of autophagosomes and promote the expression increase of human prostate cancer cells LC3B-II, and therefore the growth of xenografted tumors of DU145 cells can be inhibited; and the polyphyllin I is a potential, novel and effective anti-prostate-cancer drug and can be used for preparing drugs for treating the human prostate cancer, a new way for treating the human prostate cancer is opened up, and the medical application range of the polyphyllin I is widened.
Owner:HUBEI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE
Application of loranoside C as Beclin1 activator in preparation of anti-hepatoma drugs
PendingCN114272256AProliferation inhibitoryOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellPharmaceutical Substances
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicine, and particularly relates to application of erioside C serving as an activator of Beclin1 in preparation of anti-liver cancer drugs. By up-regulating expression of Beclin1 protein, the chaenoside C promotes conversion from LC3I to LC3II and promotes formation of cell autophagosome, so that proliferation of liver cancer Huh-7 cells is inhibited. It is found in tests that the erioside C has an inhibiting effect on liver cancer Huh-7 cells, shows good time and concentration dependence, provides a new candidate drug for treating liver cancer by targeting Beclin1, and has important clinical significance.
Owner:广西皓智科技有限公司
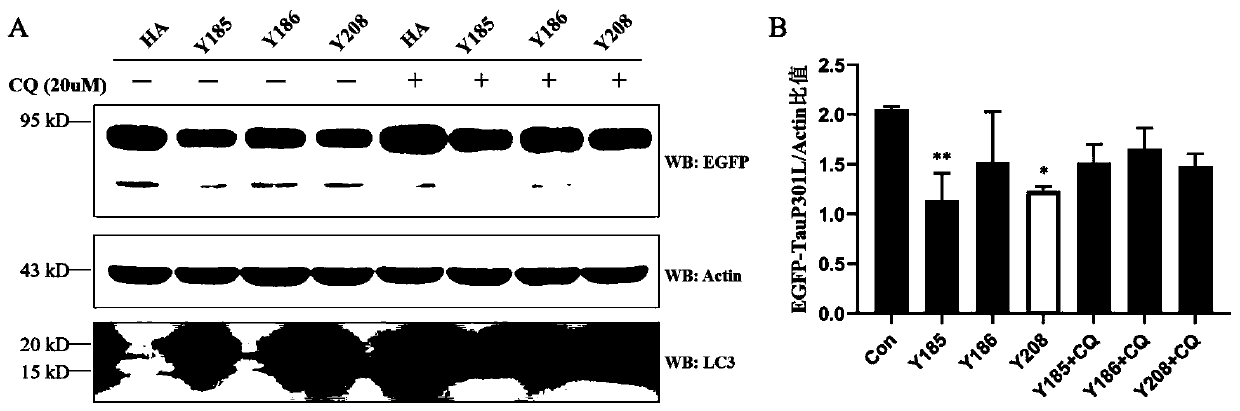
Chimeric molecules mediating tau protein degradation based on autophagy mechanism and their applications
ActiveCN111410695BPromote degradationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsProtein targetMolecular binding
The invention discloses a chimeric molecule that mediates the degradation of Tau protein based on an autophagy mechanism, and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:5 or 7. Also disclosed is a nucleic acid molecule encoding the chimeric molecule that mediates Tau protein degradation based on an autophagy mechanism; an expression vector comprising the nucleic acid molecule. Also disclosed are the applications of the chimeric molecules, nucleic acid molecules and expression vectors that mediate Tau protein degradation based on autophagy mechanism in degrading Tau protein. The invention develops a novel targeting chimeric molecule, which is combined on the surface of the aggregation protein Tau, thereby recruiting the Tau protein into the cell autophagosome and promoting its degradation through the cell autophagy pathway. The new protein targeted degradation technology provided by the present invention is expected to apply this new technology to different target proteins, thereby overcoming the inability of the current protein targeted degradation technology based on the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to efficiently degrade intracellular macromolecules point defects.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com