Application of chlorosis seedling lethality 1 (CSL1) gene to regulation of development of rice chloroplasts
A chloroplast and gene technology, applied in the application field of CSL1 gene in regulating rice chloroplast development, can solve problems such as unclear MAPK cascade
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
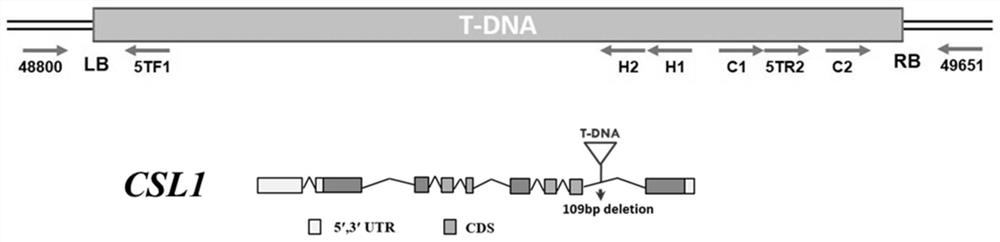
[0044] Example 1: Isolation and Identification of T-DNA Insertion Mutants
[0045] (1) An etiolated seedling lethal rice mutant was isolated from the transformed population of japonica rice Zhonghua 11 transformed with plasmid pDsBar1300 (provided by the Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Academy of Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences), and it was named csl1 mutant. Then the csl1 mutant genomic DNA was extracted, the genomic DNA was digested with HindIII restriction endonuclease, and the fragment was then cyclized with DNA ligase. Then, the circularized DNA was used as a template, and the left border primers H1 and H2 of the T-DNA fragment, and the right border primers C1 and C2 were used as nested PCR primers to amplify the T-DNA flanking sequence of the csl1 mutant. Among them, the sequences involved are as follows:
[0046] C1:5'-TGGCGTAATAGCGAAGAGGCC-3' (SEQ ID NO.3);
[0047] C2: 5'-AATGGCGAATGCTAGAGC-3' (SEQ ID NO.4);
[0048] H1: 5'-AATA...
Embodiment 2
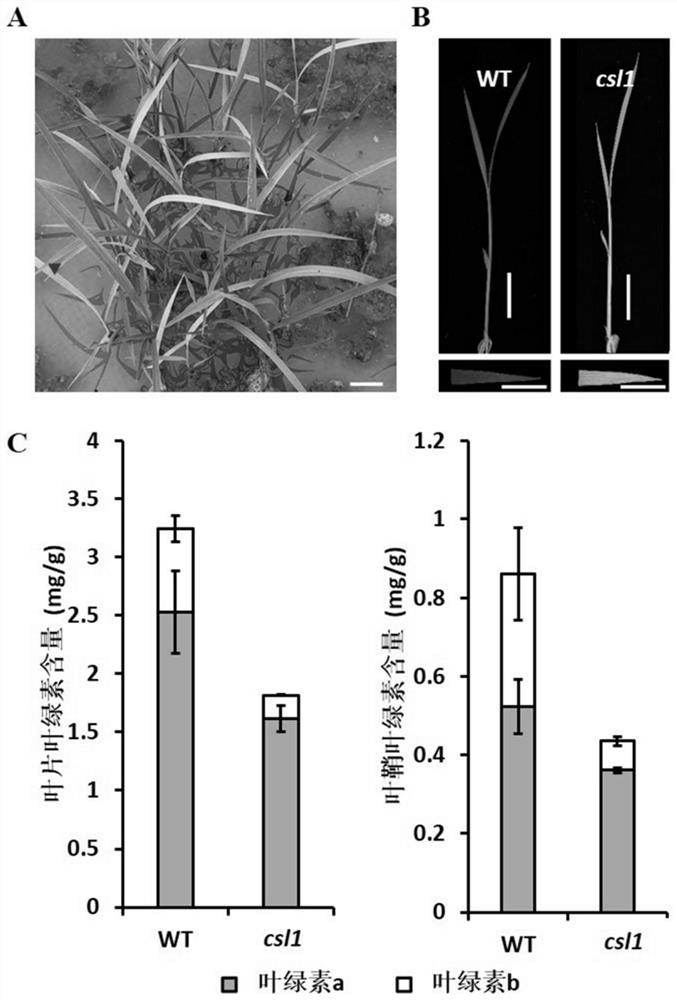
[0059] Embodiment 2: Determination of chlorophyll content
[0060] The japonica rice Zhonghua 11 seeds of csl1 mutant plants were sown in the field (mutations include homozygous mutation (homozygous mutation lethal) and heterozygous mutation, and the seeds here are seeds of heterozygous mutation) to observe the phenotype of the materials, and wild-type japonica rice Zhonghua 11 (WT) was used as the control. Some plants showed yellowing in the field, and these plants died after the three-leaf stage in follow-up observation.
[0061] Use ultraviolet spectrophotometry to detect the chlorophyll a and b contents in the mutants respectively. The specific measurement methods are as follows: cut 0.1g of fresh rice leaves or leaf sheaths (three-leaf stage) into small pieces and place them in a 10ml centrifuge tube, add 2ml of extraction buffer (ethanol :propanol:H 2 0, volume ratio=4.5:4.5:1), and stood at 4° C. in the dark for 12 hours until the green leaves precipitated and the lea...
Embodiment 3
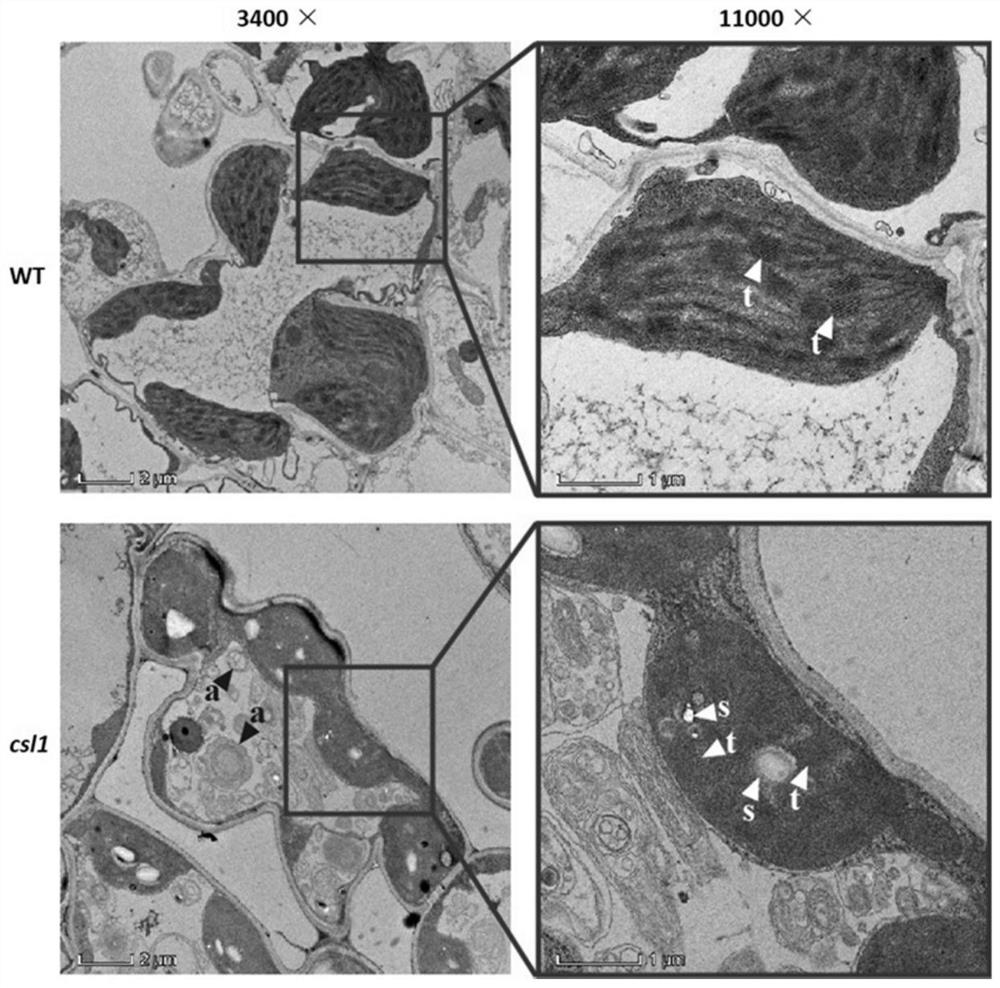
[0067] Embodiment 3: Chloroplast Ultrastructure Electron Microscopic Observation
[0068] The csl1 mutant rice leaves at the three-leaf stage (mutant plants isolated in Example 1) were fixed in glutaraldehyde and embedded in resin to observe the ultramicroscopic structure of chloroplasts with a transmission electron microscope. The specific experimental method is as follows:
[0069] The second leaf of rice at the three-leaf stage was taken, cut into small pieces with a width of 0.5 mm and a length of 2 mm, and fixed with 2.5% (v / v) glutaraldehyde at 4° C. for 24 hours. After washing 3 times with 0.1M PBS buffer, wash with 1% (w / v) OsO 4 (osmium tetroxide) for secondary fixation, and washed 3 times with 0.1M PBS buffer after 2 hours. Then use 30%, 50%, 70%, 80, 90%, 100%, 100% acetone solution by volume percentage to carry out gradient dehydration at room temperature, each gradient is 15 minutes. Utilize 6 gradients to gradually carry out resin infiltration to the material,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com