Patents
Literature
160 results about "Staphylococcus pseudintermedius" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus. Its type strain is LMG 22219ᵀ (=ON 86ᵀ=CCUG 49543ᵀ). It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well.
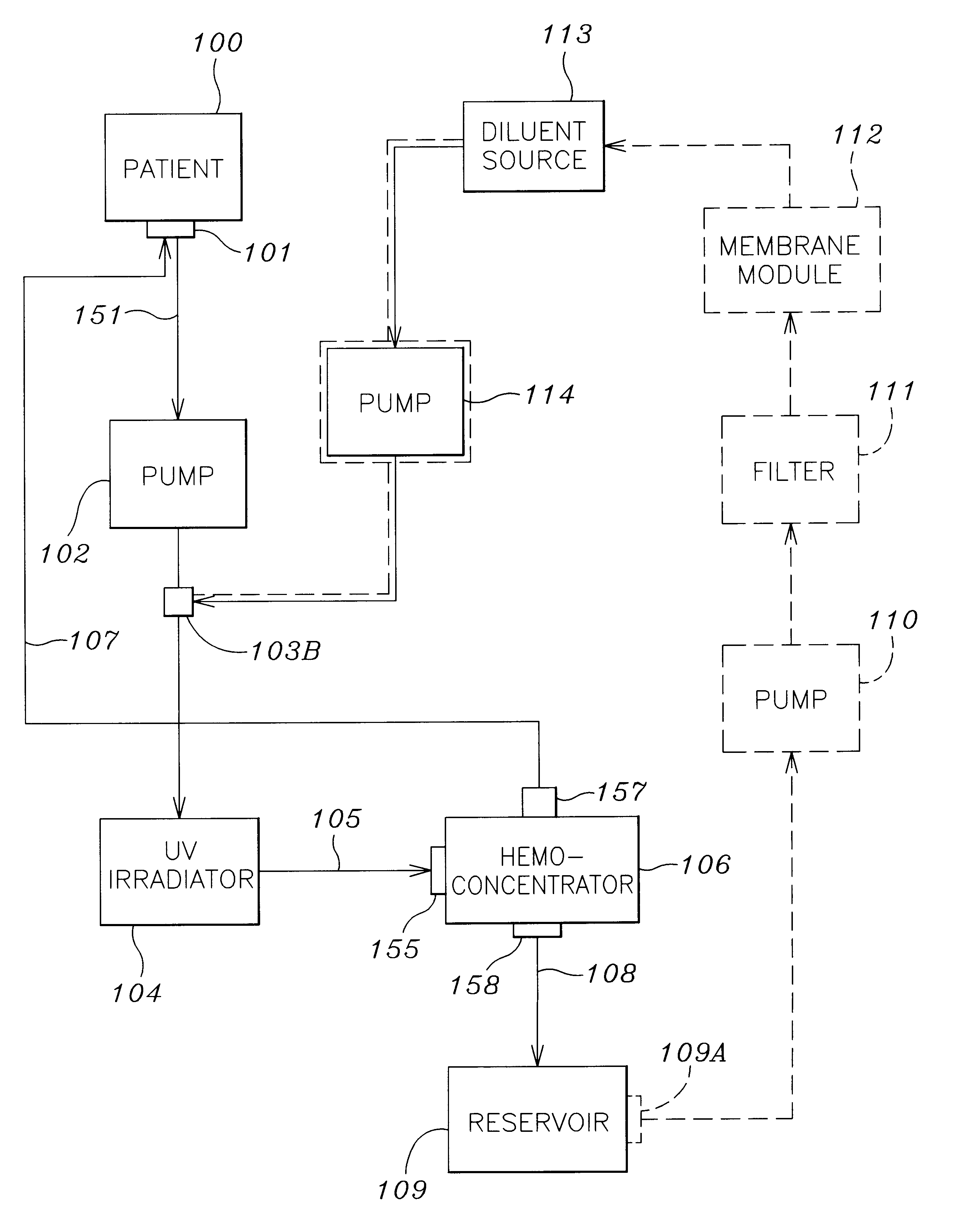
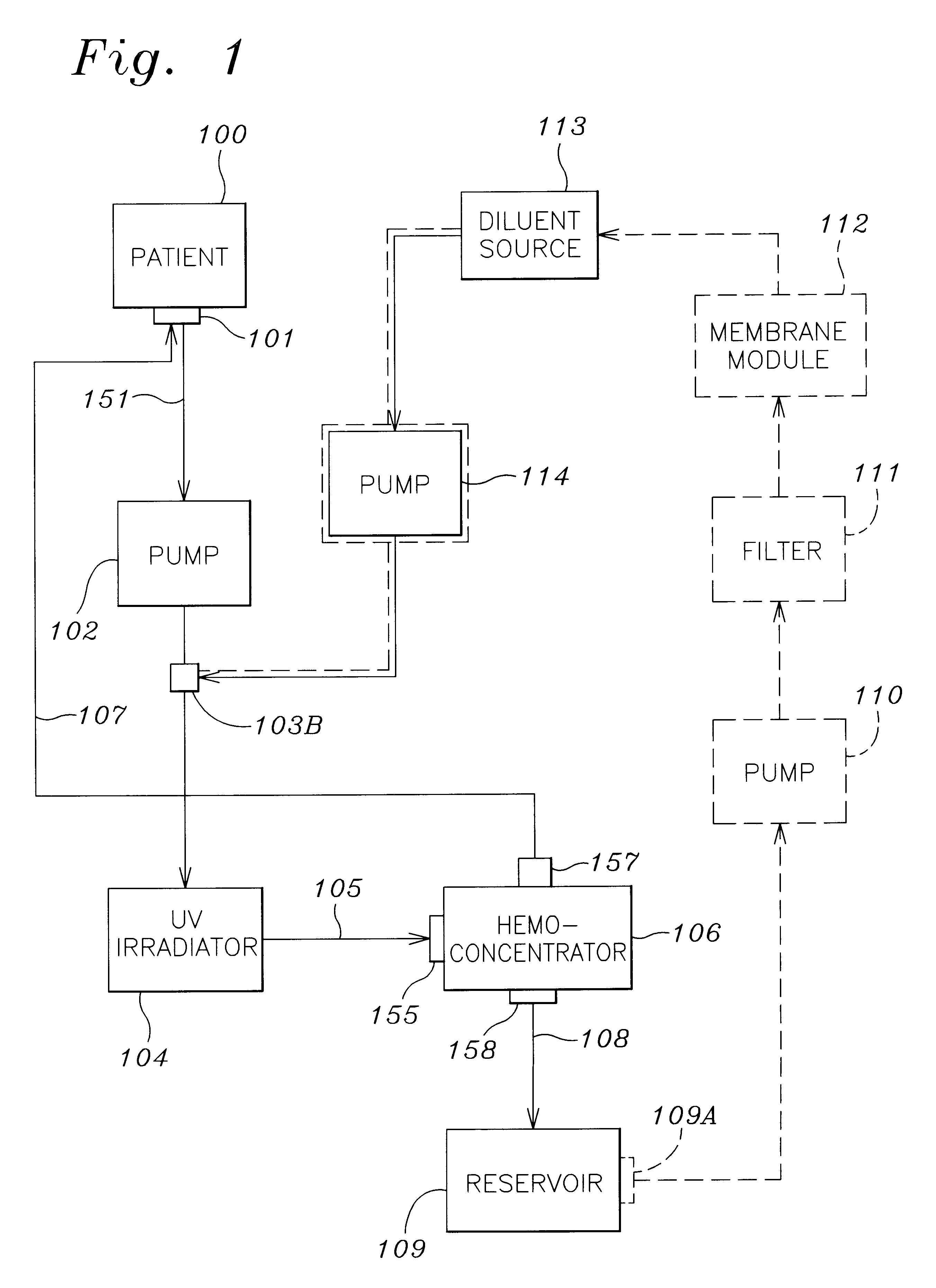
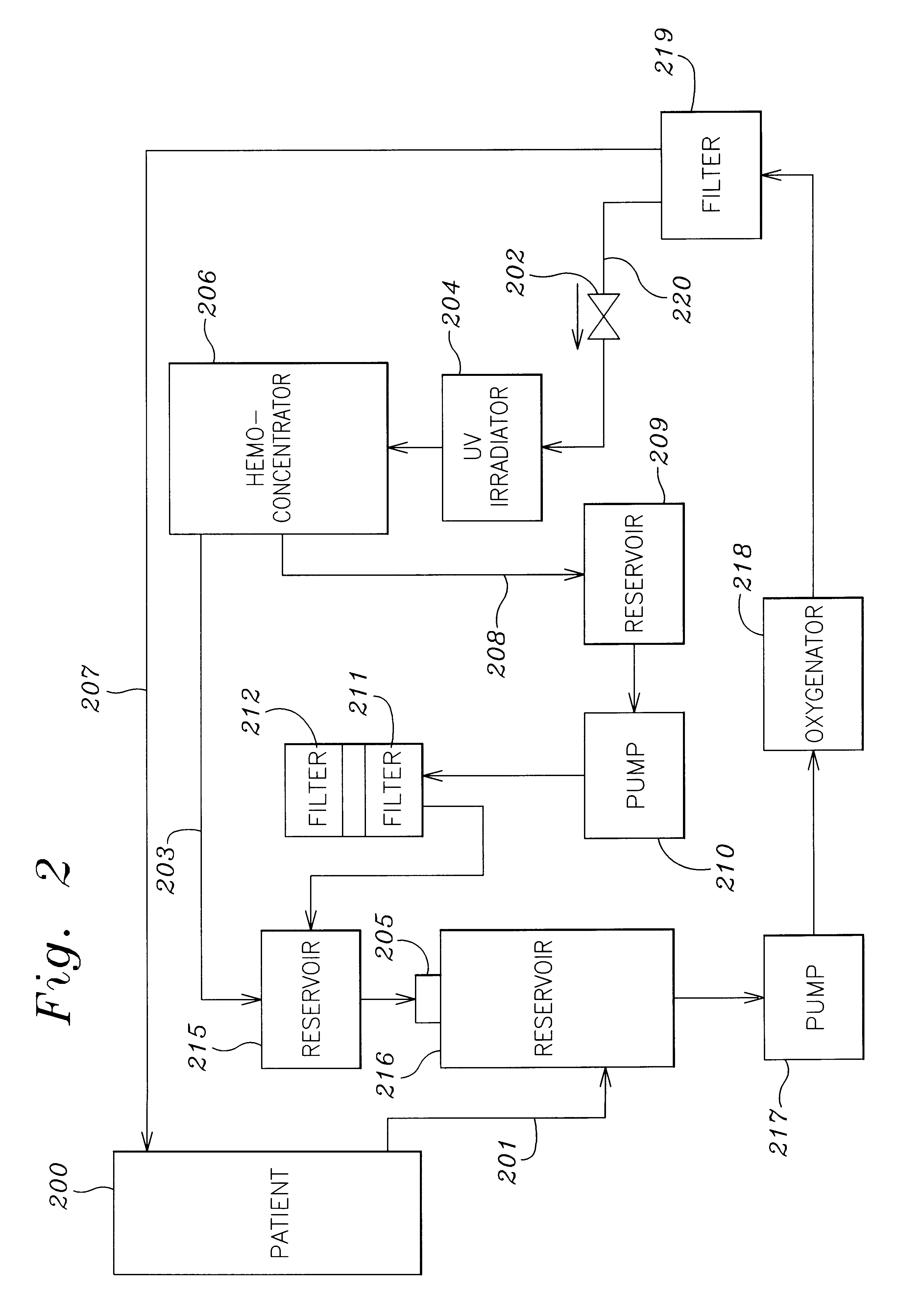
Septicemia prevention and treatment system
InactiveUS6193681B1Electrolysis componentsOther blood circulation devicesStaphylococcus cohniiFiltration
A method and apparatus for preventing and treating septicemia in patient blood. The extracorporeal system includes an anti-microbial device to kill at least 99% of bloodborne microorganisms, a hemoconcentrator / filtration unit to remove approximately 90% of target molecules from the patient blood and a filter unit to remove target molecules from patient blood from the sieved plasma filtrate. Target molecules are produced by microorganisms as well as the patient's cells and include endotoxins from gram negative bacteria, exotoxins from gram negative and gram positive bacteria, as well as RAP protein mediator from Staphylococcus aureus, and cell mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin 1-beta, complement proteins C3a and C5a, and brandykinin.
Owner:HEMAVATION
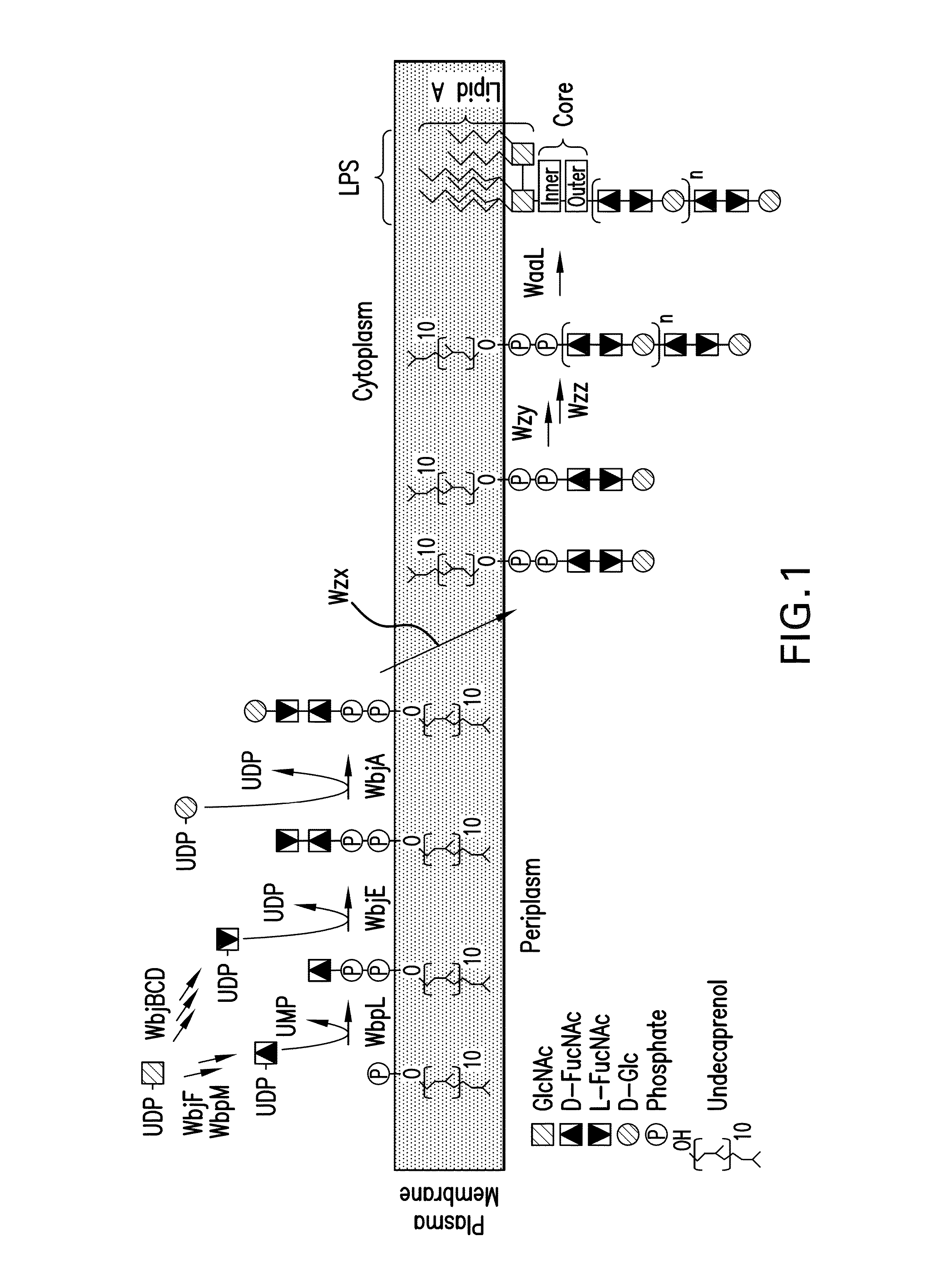
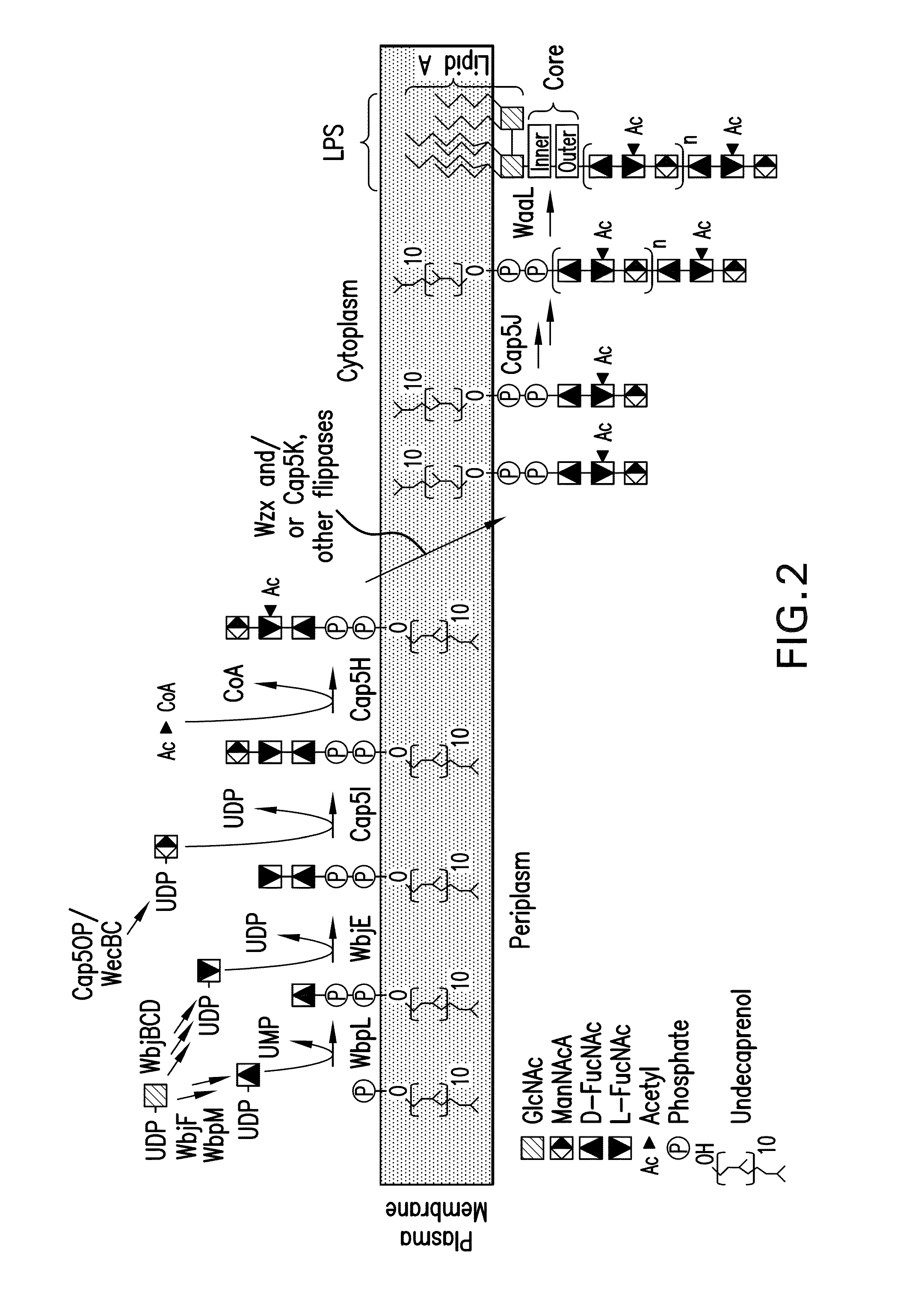
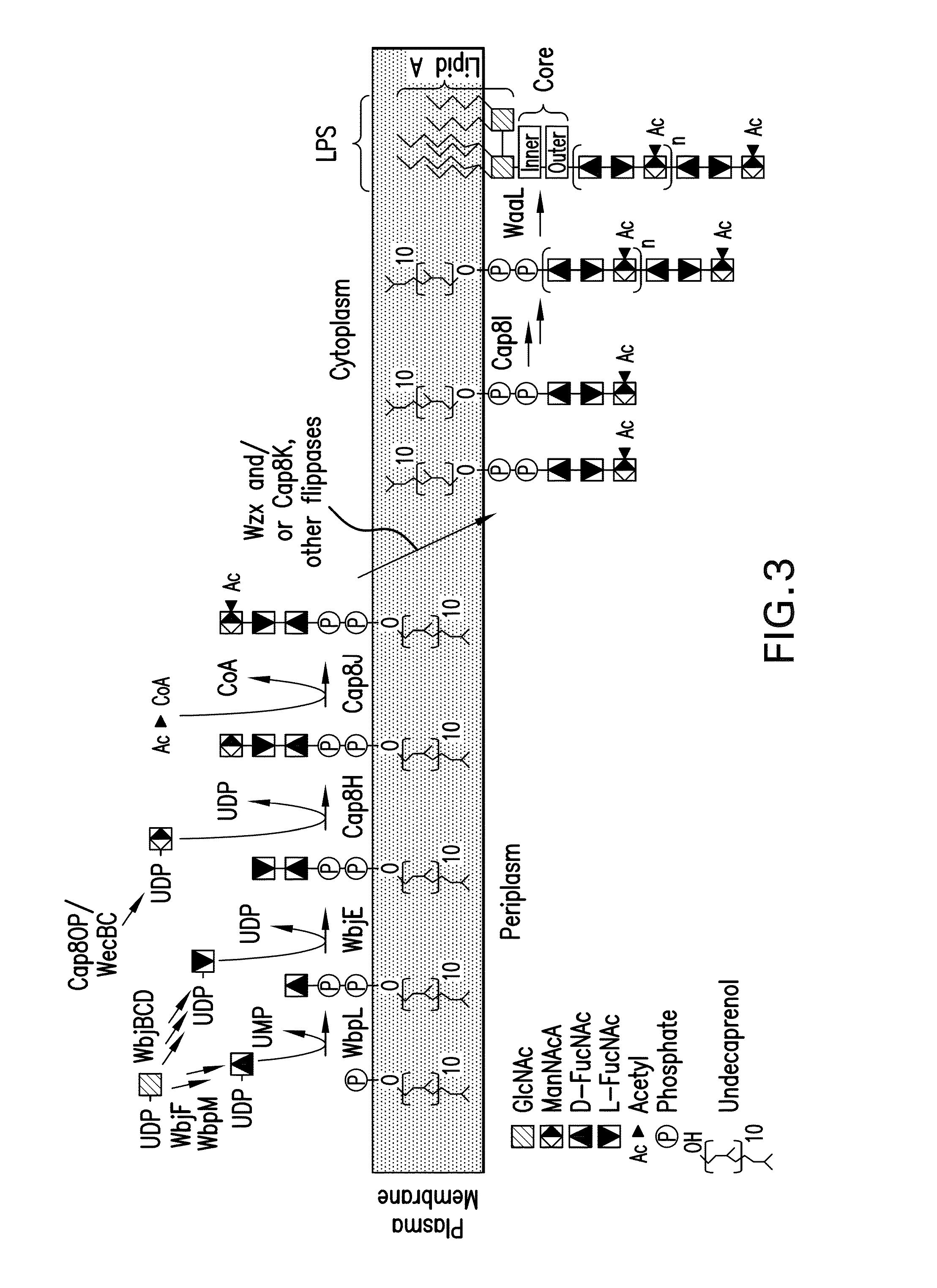
Capsular gram-positive bacteria bioconjugate vaccines
The present invention encompasses a novel S. aureus bioconjugate vaccine. More generally, the invention is directed to Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines containing a protein carrier, at least one polysaccharide such as a capsular Gram-positive polysaccharide, and, optionally, an adjuvant or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The instant invention also includes methods of producing Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines. An N-glycosylated protein is also provided that contains one or more polysaccharides such as Gram-positive polysaccharides. The invention is additionally directed to engineered prokaryotic organisms comprising nucleotide sequences encoding a glycosyltransferase of a first prokaryotic organism and a glycosyltransferase of a second prokaryotic organism. The invention further includes plasmids and prokaryotic cells transformed with plasmids encoding polysaccharides and enzymes which produce an N-glycosylated protein and / or bioconjugate vaccine. Further, the invention is directed to methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal comprising administering said bioconjugate vaccines.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Detection of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus in biological samples
ActiveUS20090035780A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMethicillin resistance geneCytosine
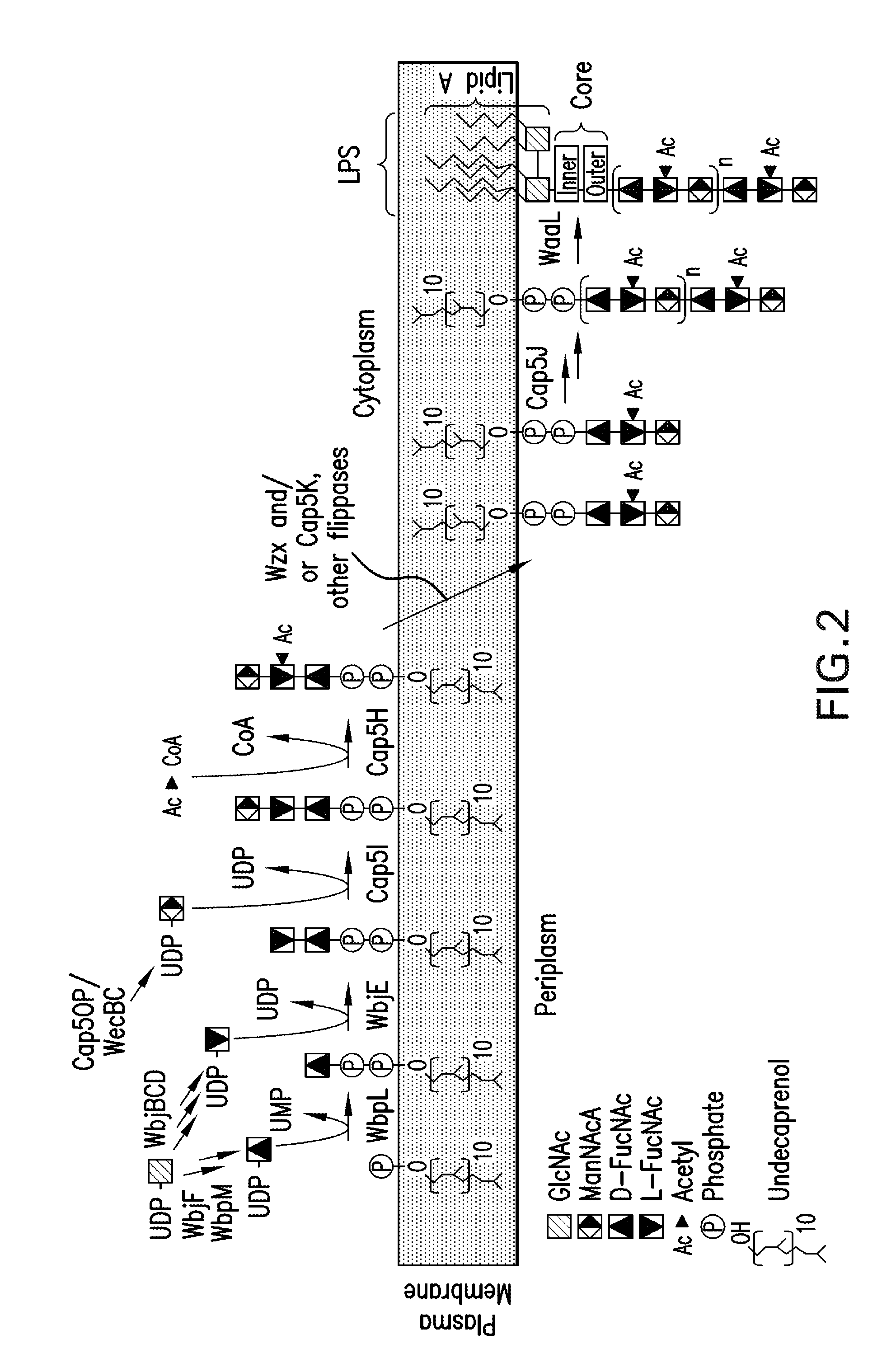
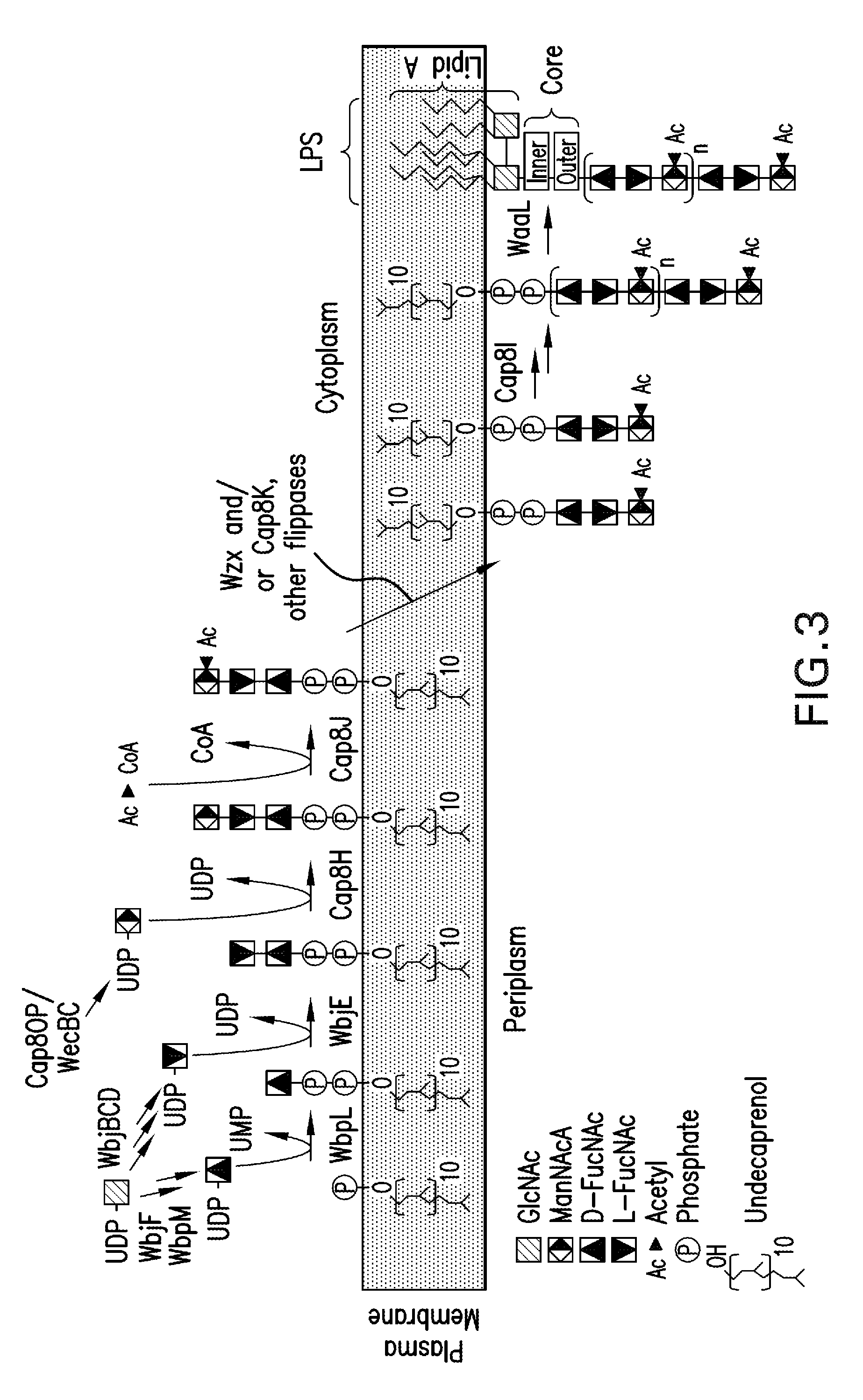
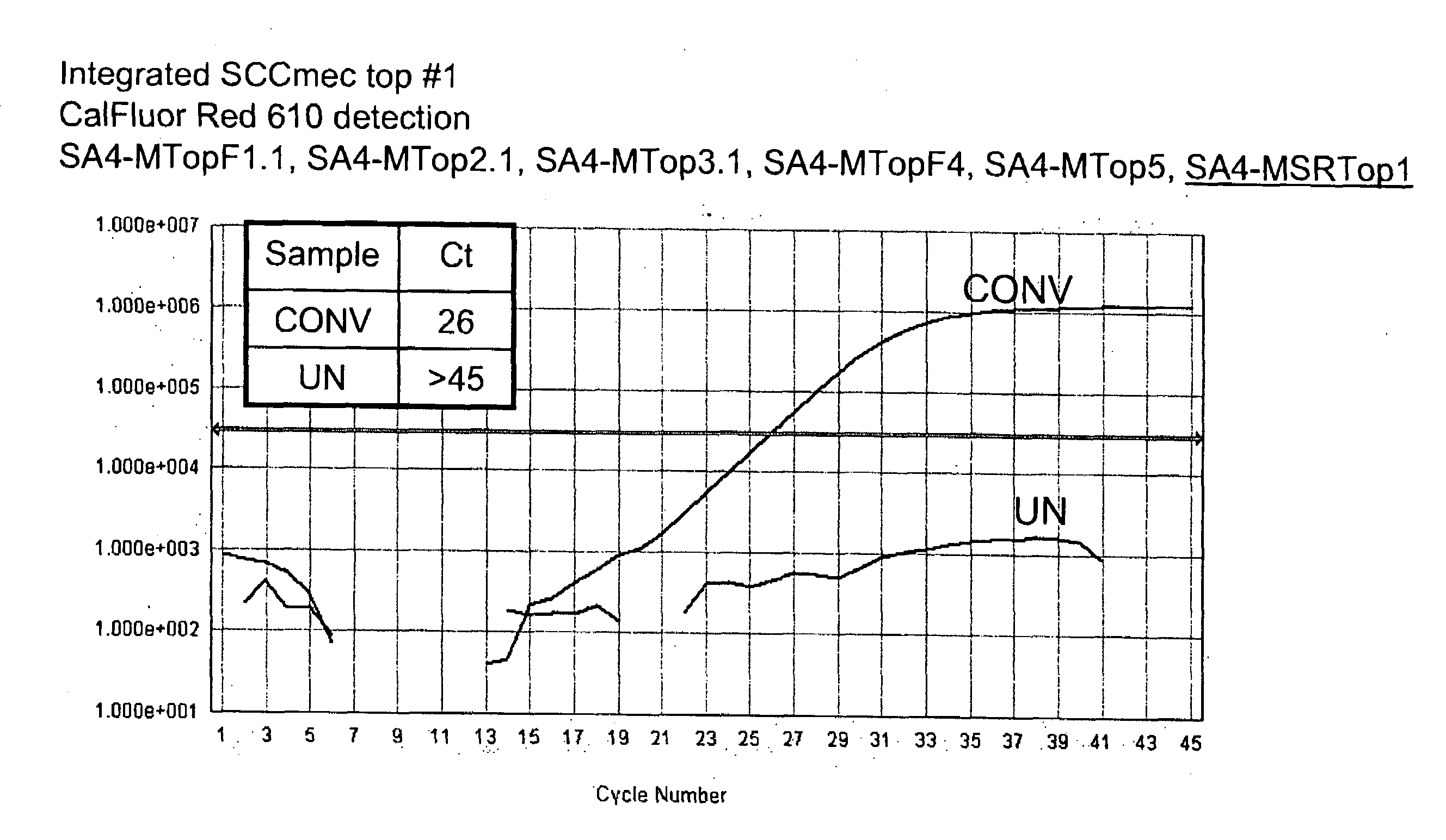
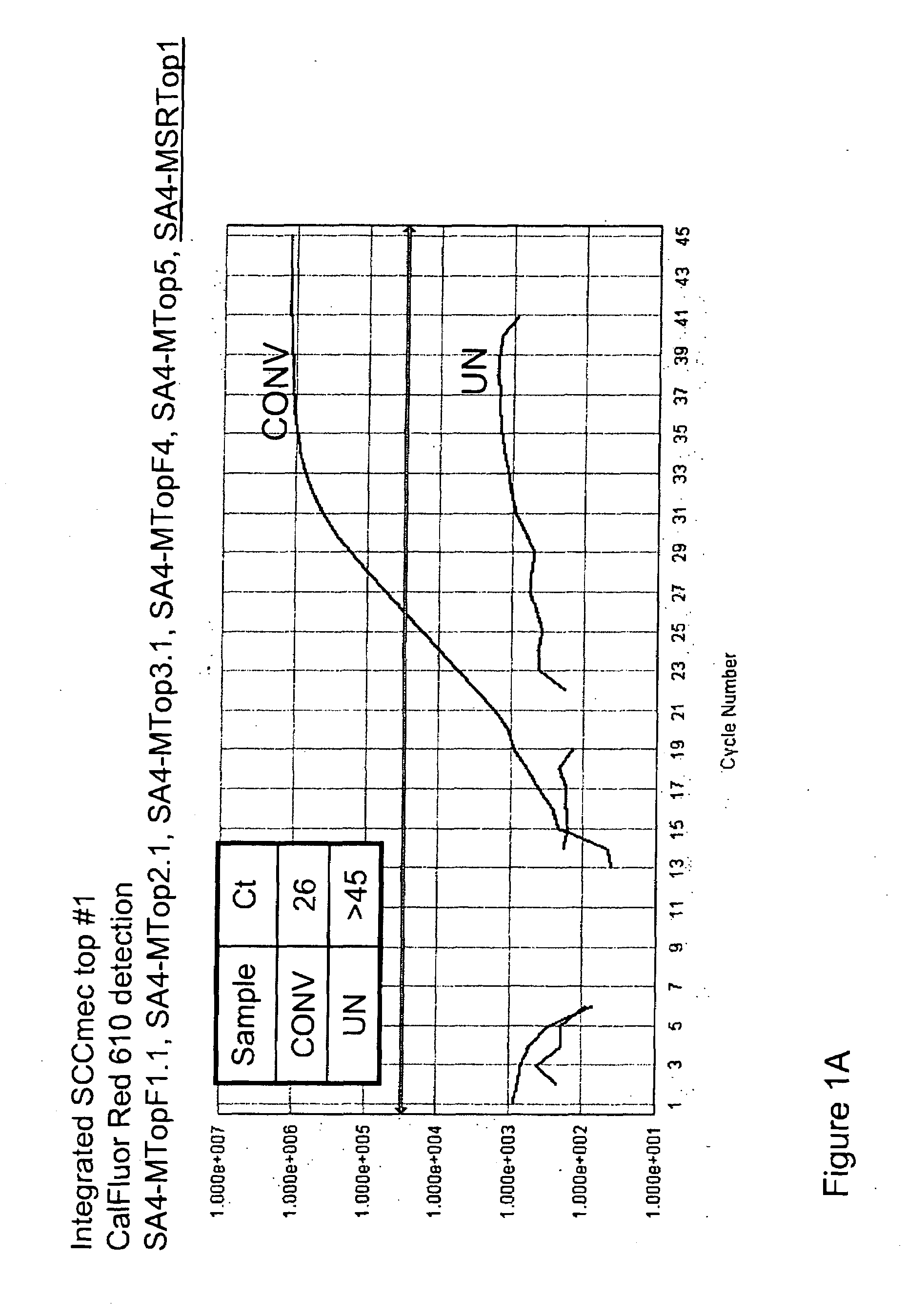
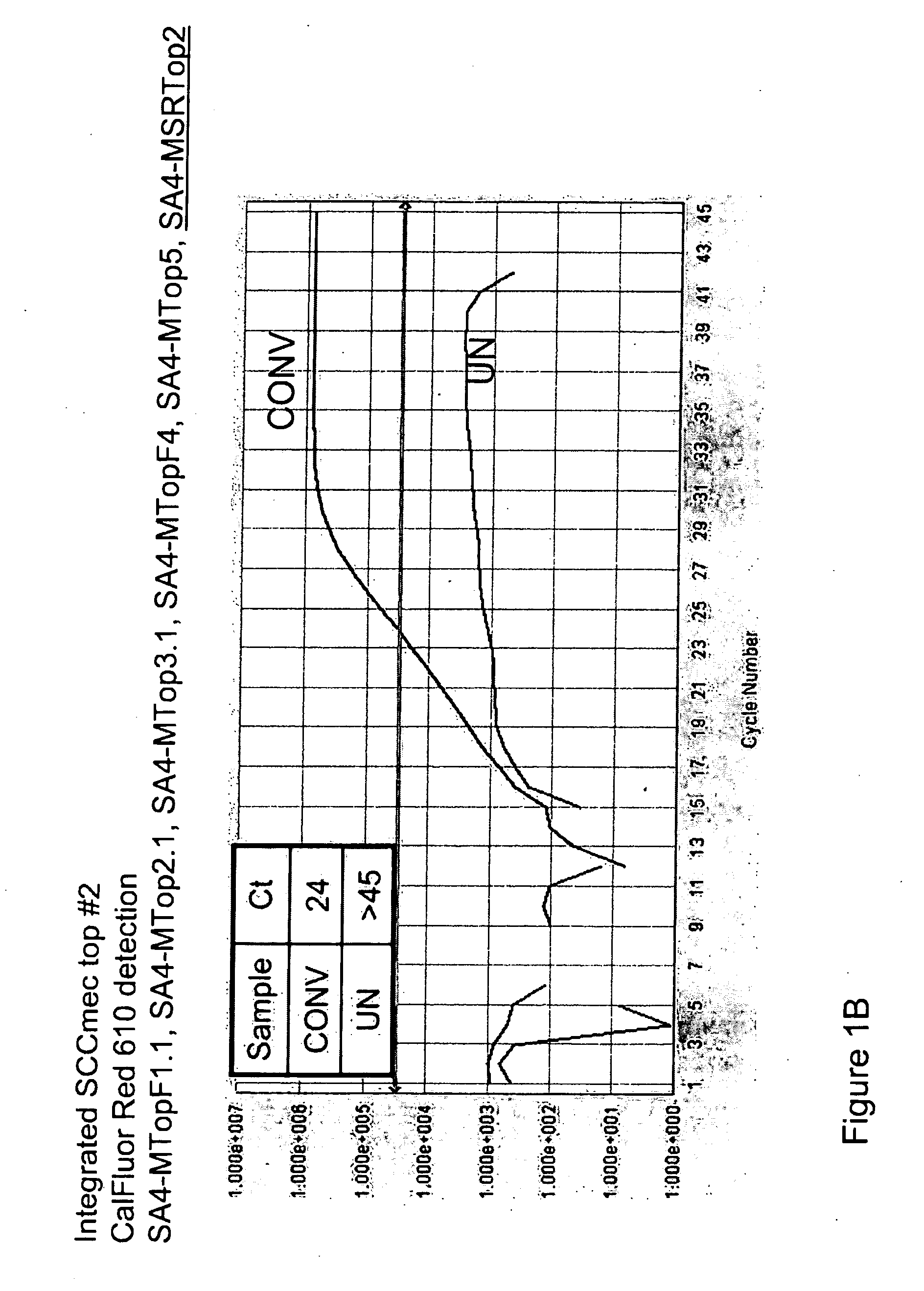
Disclosed are methods of identifying a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) in a sample. The present invention provides a diagnostic method comprising modification of sequences of S. aureus by converting non-methylated cytosine residues ultimately into thymidine residues in the target nucleic acid. The invention further provides for the detection of modified sequences derived from the spa gene, the mecA gene, and the integrated SCCmec cassette of S. aureus.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Culture medium for composite enrichment of salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101412978AShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLithium chlorideStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses a complex enrichment medium used for salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and staphylococcus aureus and a method for preparing the same. The complex enrichment medium comprises the following components in weight portion: 15 to 19 portions of tryptone, 2 to 4 portions of peptone, 2 to 3 portions of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 to 3 portions of glucose, 0.5 to 1.5 portions of aesculin, 1, 000 portions of distilled water, 1 to 2.5 portions of sodium pyruvate, 3 to 10.0 portions of mannitol, 1.0 to 25.0 portions of sodium chloride, 1 to 2.5 portions of lithium chloride, 0.0001 to 0.0002 portion of potassium tellurite, and 0.005-0.015 portion of nalidixic acid, wherein the pH value is between 7.1 and 7.5. The complex enrichment medium can inhibit the growth of other pathogenic microorganisms while performing enrichment on three target pathogens, thus the complex enrichment medium can be directly applied to the isolation culture and the biological assay test of target bacteria, and can also be directly applied to a detection technology of a plurality of pathogens based on one detection platform for multiple PCR and the like to make a diagnostic report.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of infections caused by staphylococcus aureus bacteria
InactiveUS20090130082A1Preventing and inhibiting growthAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesMicroorganism
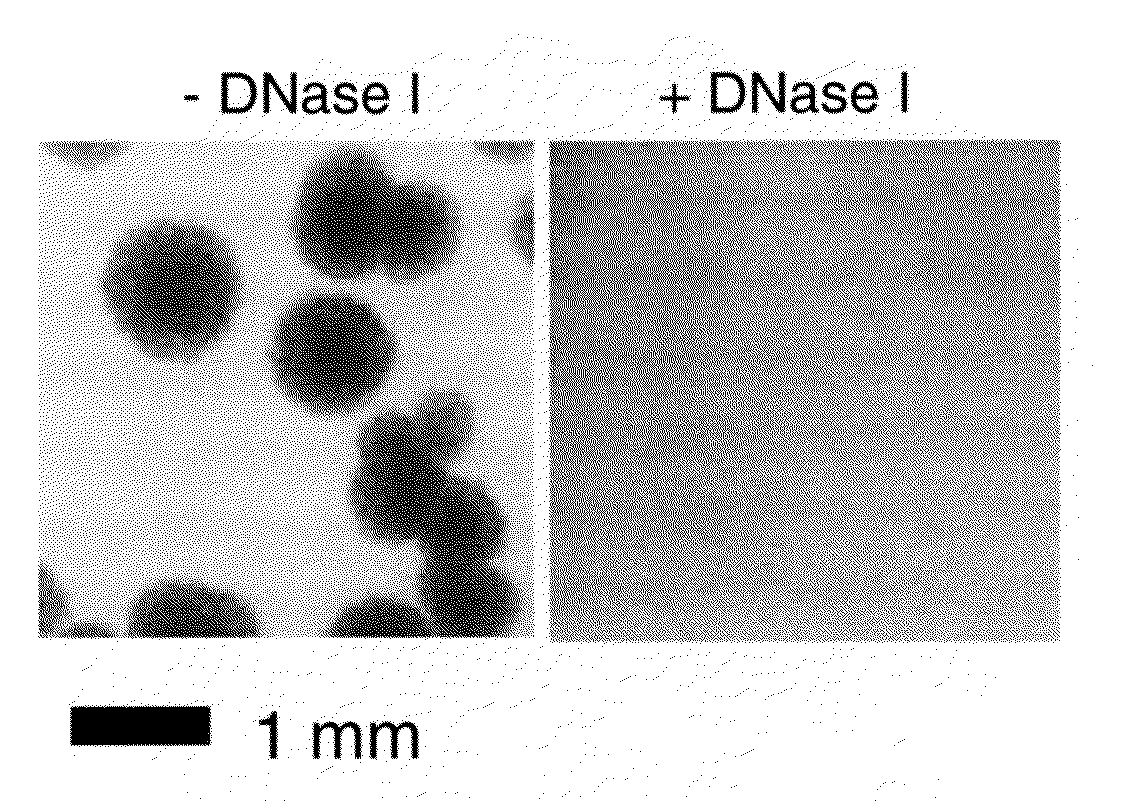
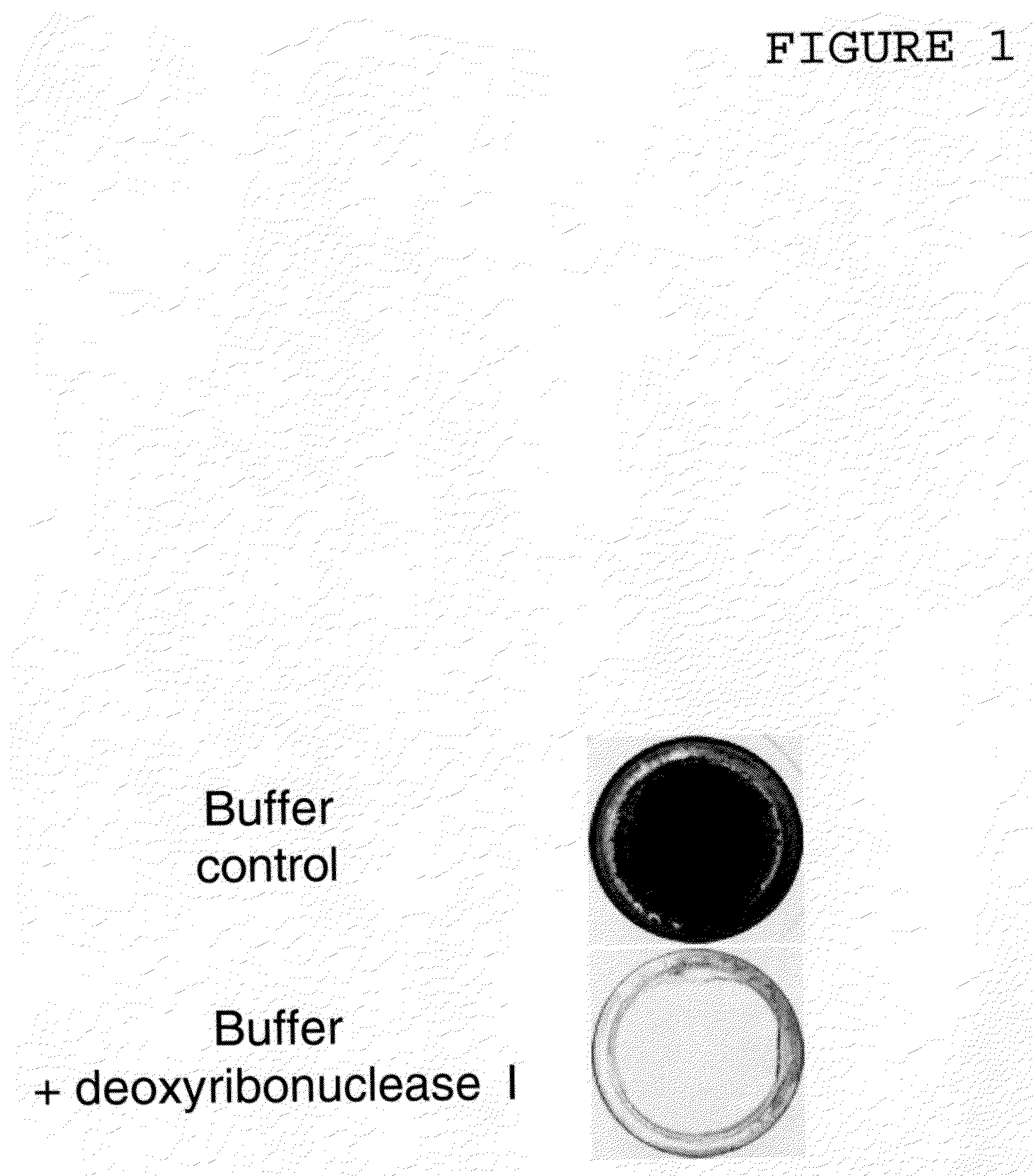
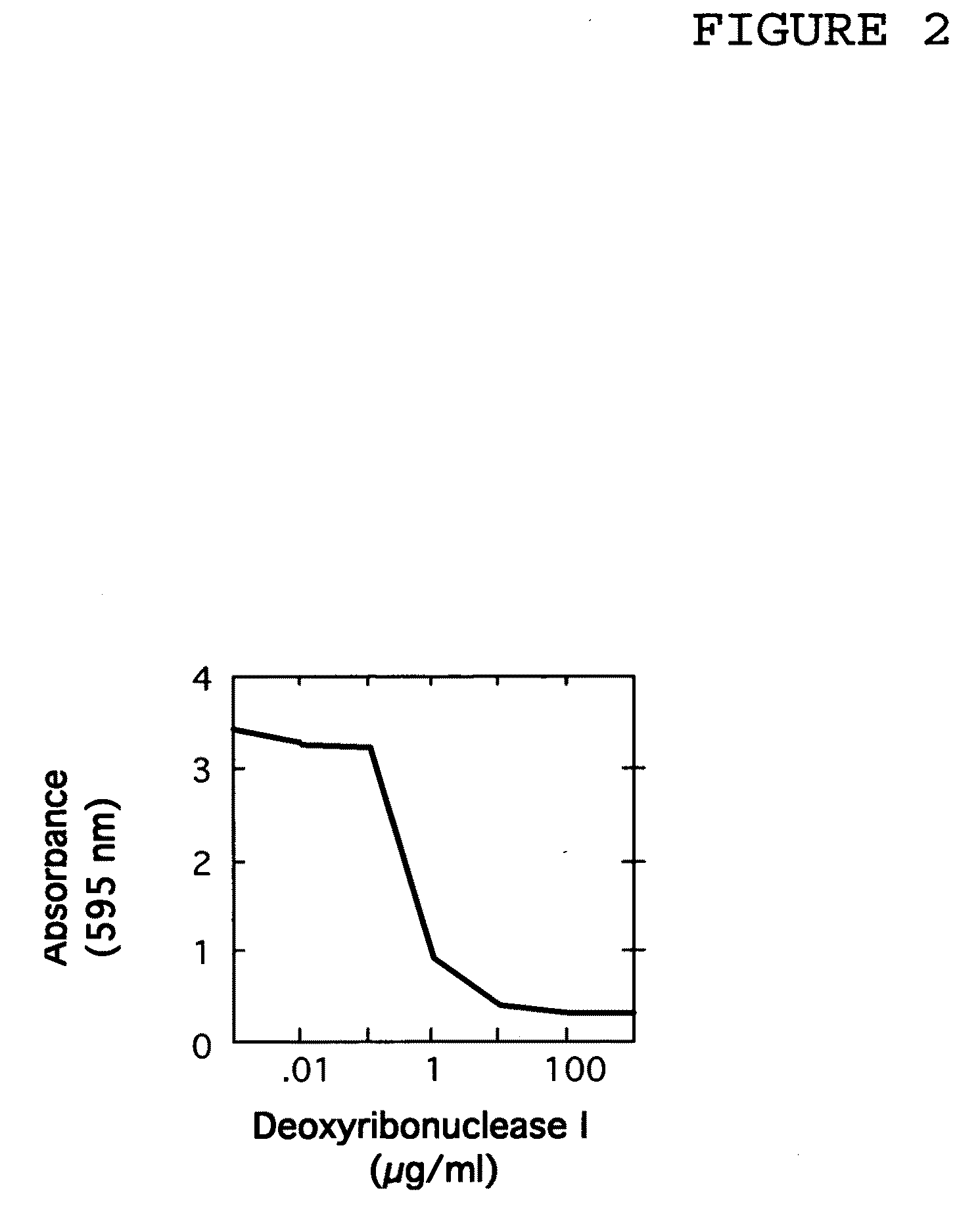
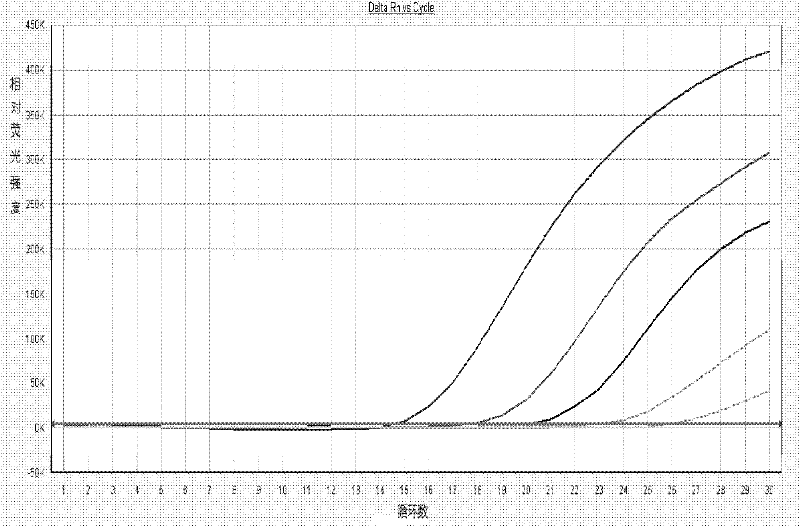
The present invention relates to antimicrobial deoxyribonuclease-based compositions that inhibit growth and proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. The present invention also relates to methods of administering the compositions in the treatment and prevention of S. aureus infections. The present invention also relates to methods of administering the compositions in the eradication of S. aureus nasal carriage, in order to prevent the transmission of S. aureus bacteria
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
Staphylococcus aureus methicillin resistant strain PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit
ActiveCN102399877AGuaranteed credibilityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMethicillin resistance geneStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention relates to the field of microorganism detection, in particular to a staphylococcus aureus methicillin resistant strain PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit. The invention has the technical scheme of amplifying and detecting a highly conservative specific nucleic acid sequence nuc gene in the staphylococcus aureus gene by using the polymerase chain reaction and molecular beacon and fluorescent probe technologies and simultaneously amplifying and detecting the drug resistant nucleic acid sequence mecA gene to judge whether the strain is a methicillin resistant strain of staphylococcus aureus. The invention also provides PCR amplification primers of the nuc gene and the mecA gene and the sequence of the probe. The kit is applicable to the rapid detection of the staphylococcus aureus methicillin resistant strain in a clinical specimen of a suspect staphylococcus aureus infector and has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, stability, timeliness, convenience for operation and the like.
Owner:福州泰普生物科学有限公司
Bacteriophage or lytic protein derived from the bacteriophage which effective for the treatment of staphylococcus aureus biofilm
ActiveUS20100254950A1Eliminate effectiveGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseBiofilm
The present invention relates to compositions for removing a biofilm formed by Staphylococcus aureus, comprising a bacteriophage, such as Myoviridae family T4-like phage genus bacteriophage (Accession No: KCTC 11153BP, SAP-I) or Podoviridae family φ29-like virus genus bacteriophage (Accession No: KCTC11154BP, SAP-2), and lytic protein derived therefrom, that destroys the biofilm. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus capable of forming biofilm.
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Culture medium and method for detecting thermonuclease-positive staphylococci
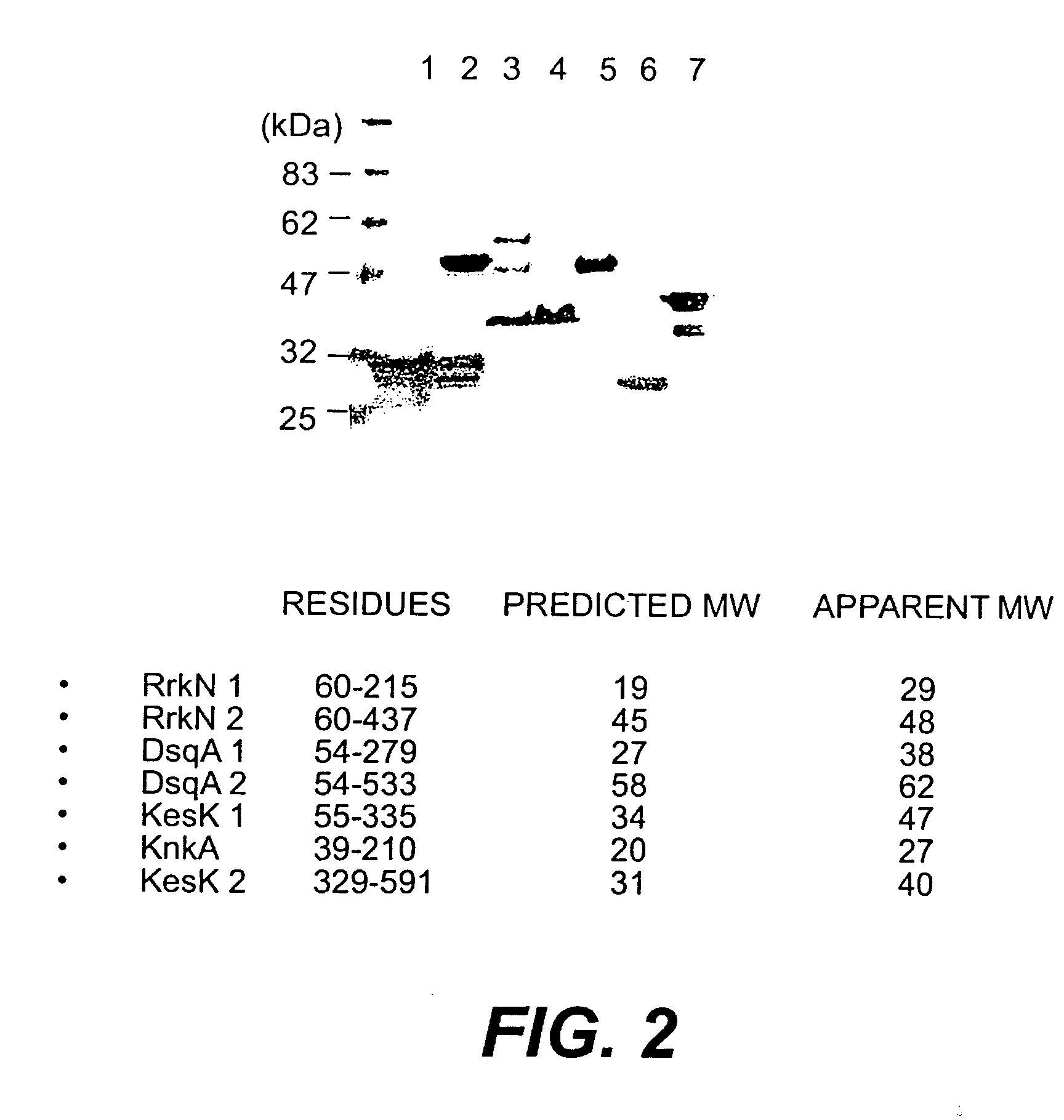
ActiveUS7087401B2Promote growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelect agentStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
The present invention provides a method of detecting thermonuclease-positive staphylococci that does not require inactivation of DNase-positive / TNase-negative bacteria with heat. The method includes (a) providing a culture medium selective for growing staphylococci; (b) inoculating the culture medium with a sample; (c) incubating the inoculated culture medium under conditions effective to promote the growth of staphylococci; (d) providing an indicator system that produces a differentiable, detectable signal in the presence of thermonuclease-positive staphylococci; (e) contacting the indicator system with the inoculated, incubated culture medium, thereby forming a detection assembly; (f) incubating the detection assembly under conditions effective for generating the differentiable, detectable signal; and (g) detecting the detectable signal.The present invention also provides a culture medium for the selective identification of Staphylococcus aureus. The culture medium includes at least one first selective agent that selects for growth of staphylococci; at least one second selective agent for differentiating Staphylococcus aureus from other staphylococci; at least one first indicator for indicating the presence of staphylococci; and at least one second indicator for differentially indicating the presence of non-staphylococci bacteria. The present invention also provides a method of selectively identifying Staphylococcus aureus in a sample by using the culture medium of the present invention.
Owner:NEOGEN FOOD SAFETY US HOLDCO CORP
LAMP primer combination for detecting 6 infectious pathogens of dairy cow mastitis and application thereof
ActiveCN107541509AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStreptococcus pyogenesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses an LAMP primer combination for detecting 6 infectious pathogens of dairy cow mastitis and application thereof. The invention first provides a primer combination consisting of 36 DNA molecules shown in sequence 1 to sequence 36. The primer combination can be used for detecting whether a to-be-detected bacterium is Mycoplasma bovis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Corynebacterium bovis or Staphylococcus epidermidis, and can be used for detecting whether a to-be-detected sample contains Mycoplasma bovis and / or Staphylococcus aureusand / or Streptococcus agalactiae and / or Streptococcus pyogenes and / or Corynebacterium bovis and / or Staphylococcus epidermidis. The primer combination provided by the invention is used for identifying and detecting the 6 infectious pathogens of dairy cow mastitis, has high specificity and high sensitivity, and can realize simple, rapid and accurate detection, thus having great popularization value.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP
Primers and method of detecting bacteria
InactiveUS7326779B2Easily and rapidlyEasily and rapidly and absenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
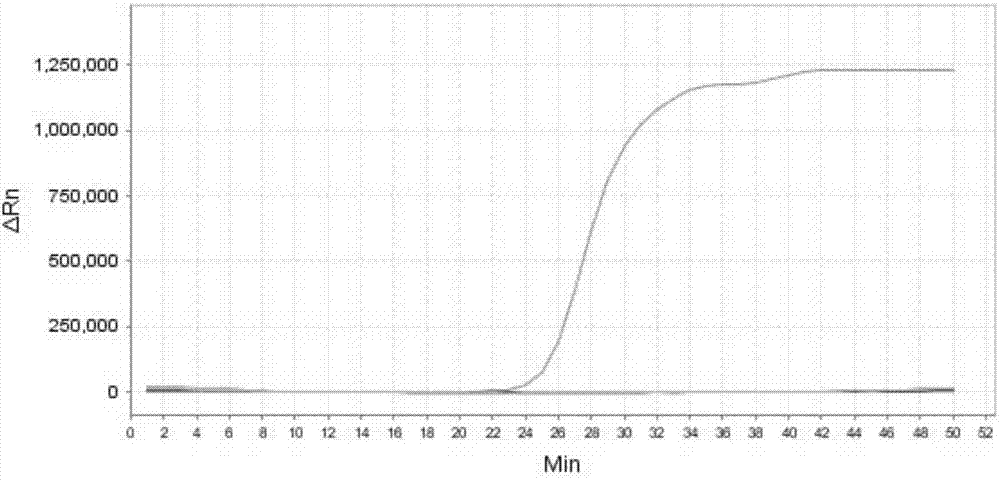
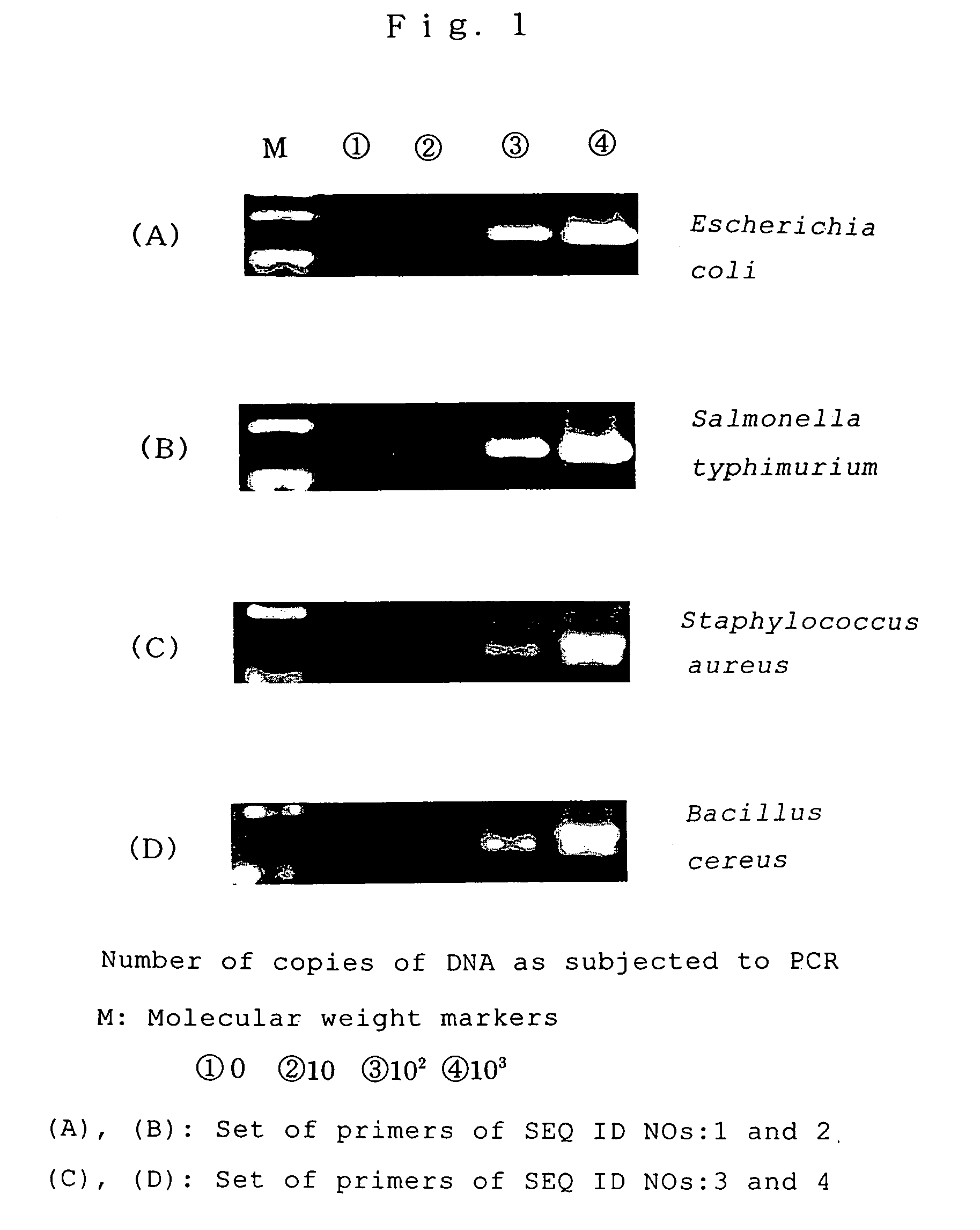
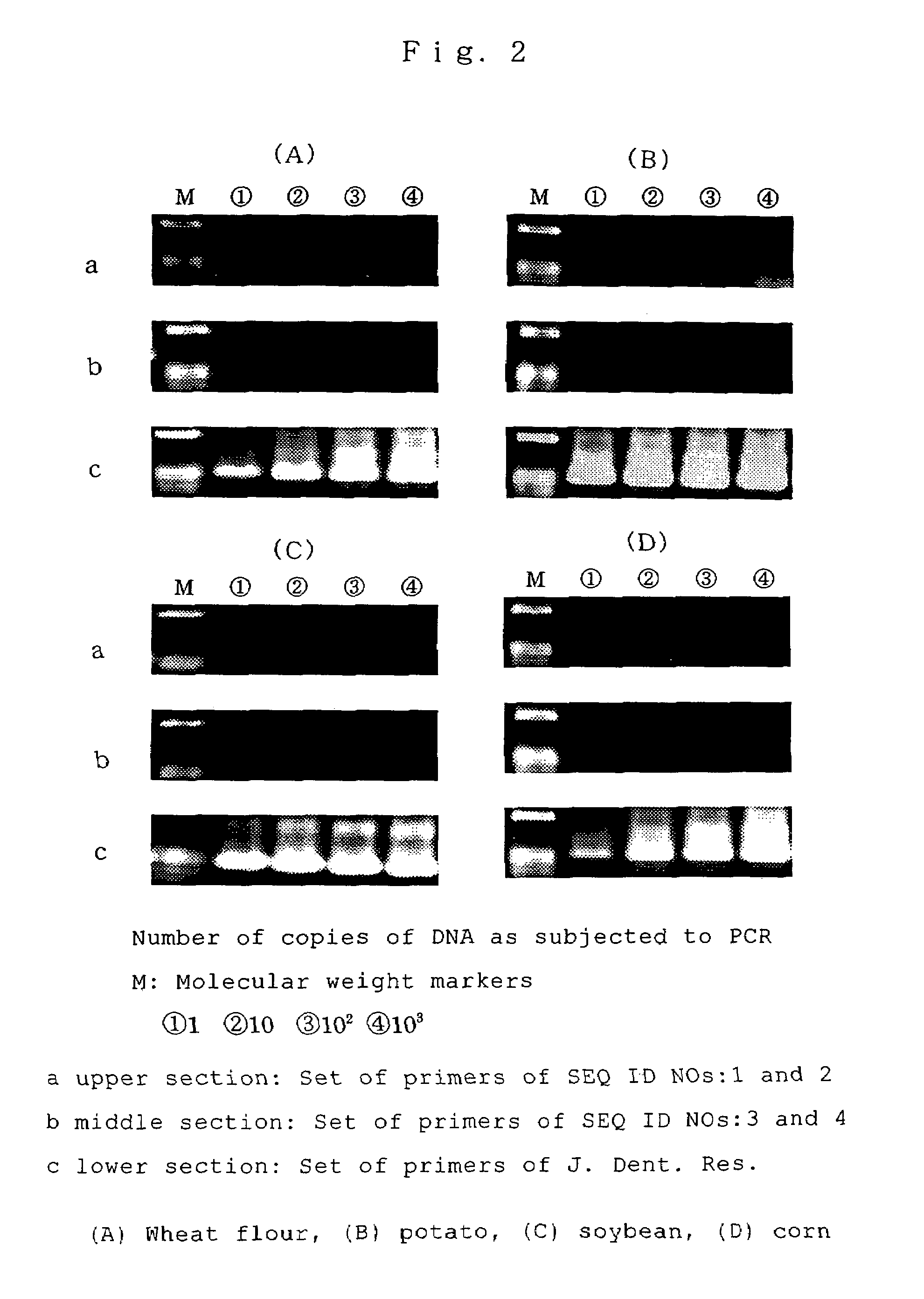
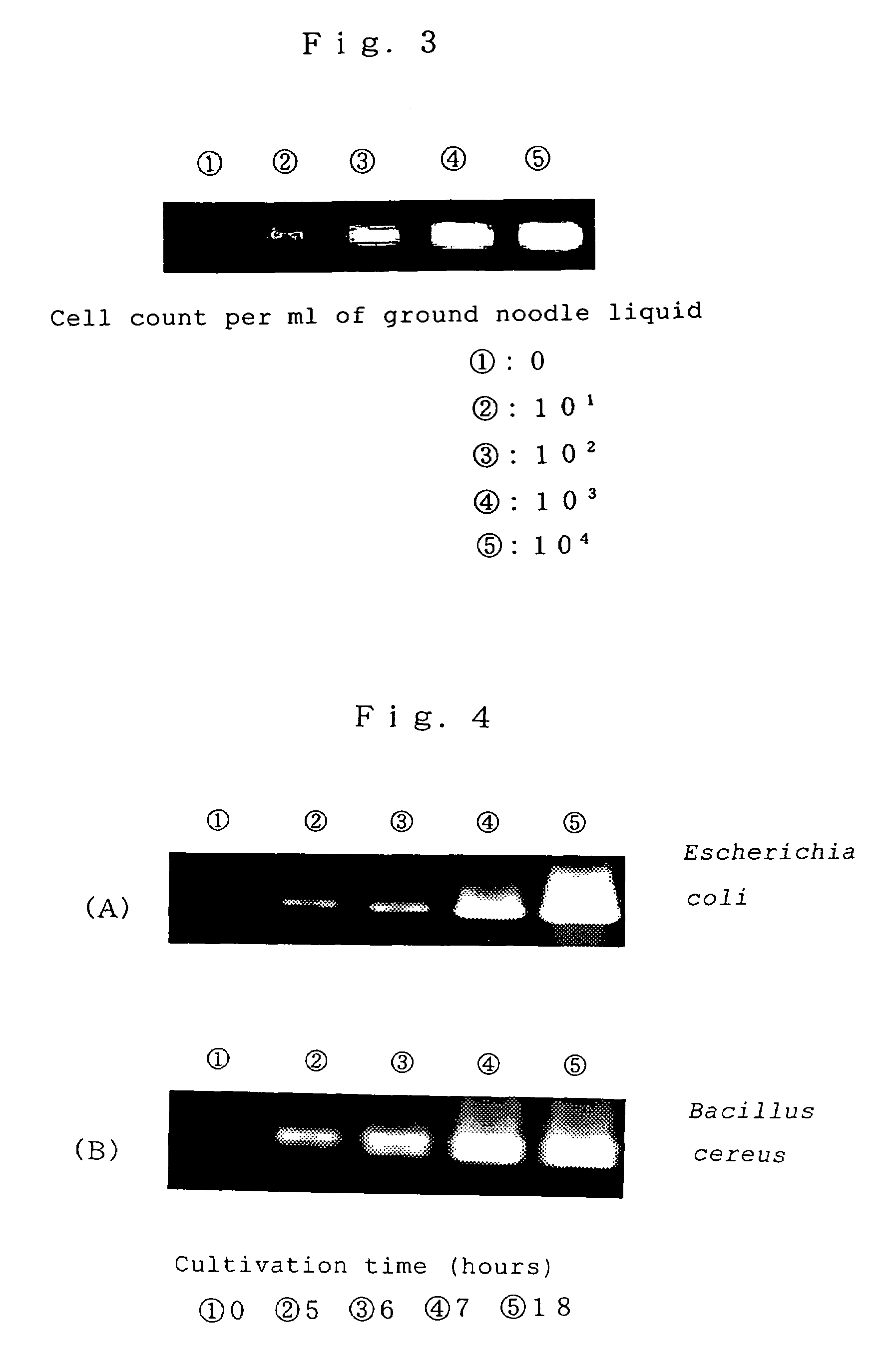
The first primer of the invention is a primer which, when used in PCR under appropriate conditions, serves to detectably amplify 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs of bacteria of the Escherichia, Salmonella and Vibrio genera, but when used in PCR under the same conditions, does not serve to detectably amplify either chloroplast 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs or mitochondrial 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs. The second primer of the invention is a primer which, when used in PCR under appropriate conditions, serves to detectably amplify 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs of Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus, but when used in PCR under the same conditions, does not serve to detectably amplify either chloroplast 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs or mitochondrial 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs.
Owner:NISSIN YORK
Sequences for detection and identification of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) of mrej type xxi
InactiveUS20130266942A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiSCCmec
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the detection and identification of Staphylococcus aureus strains harboring polymorphic SCCmec right extremity (MREP) type xxi sequences.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
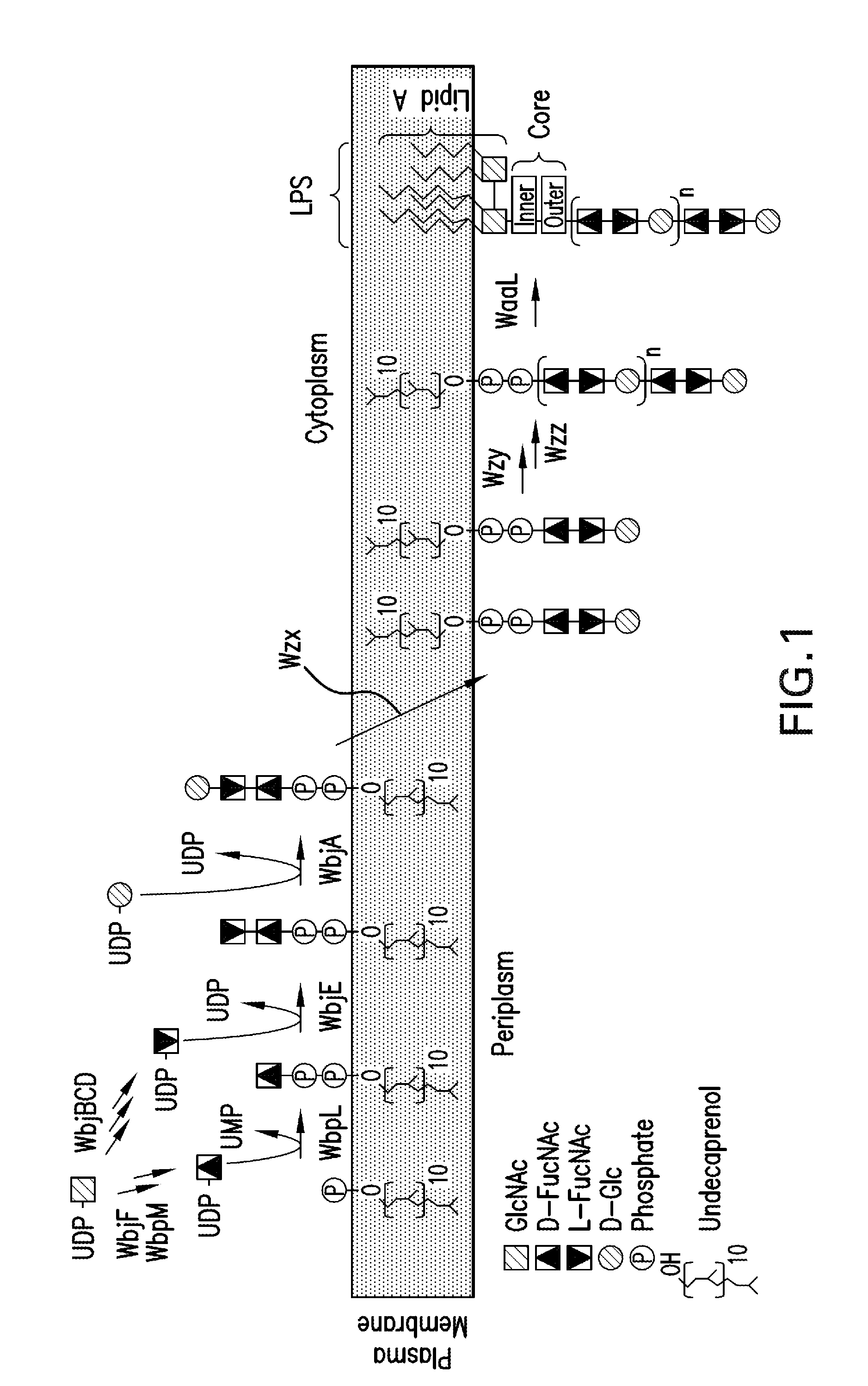
Anther-specific expression promoter in plant and application thereof
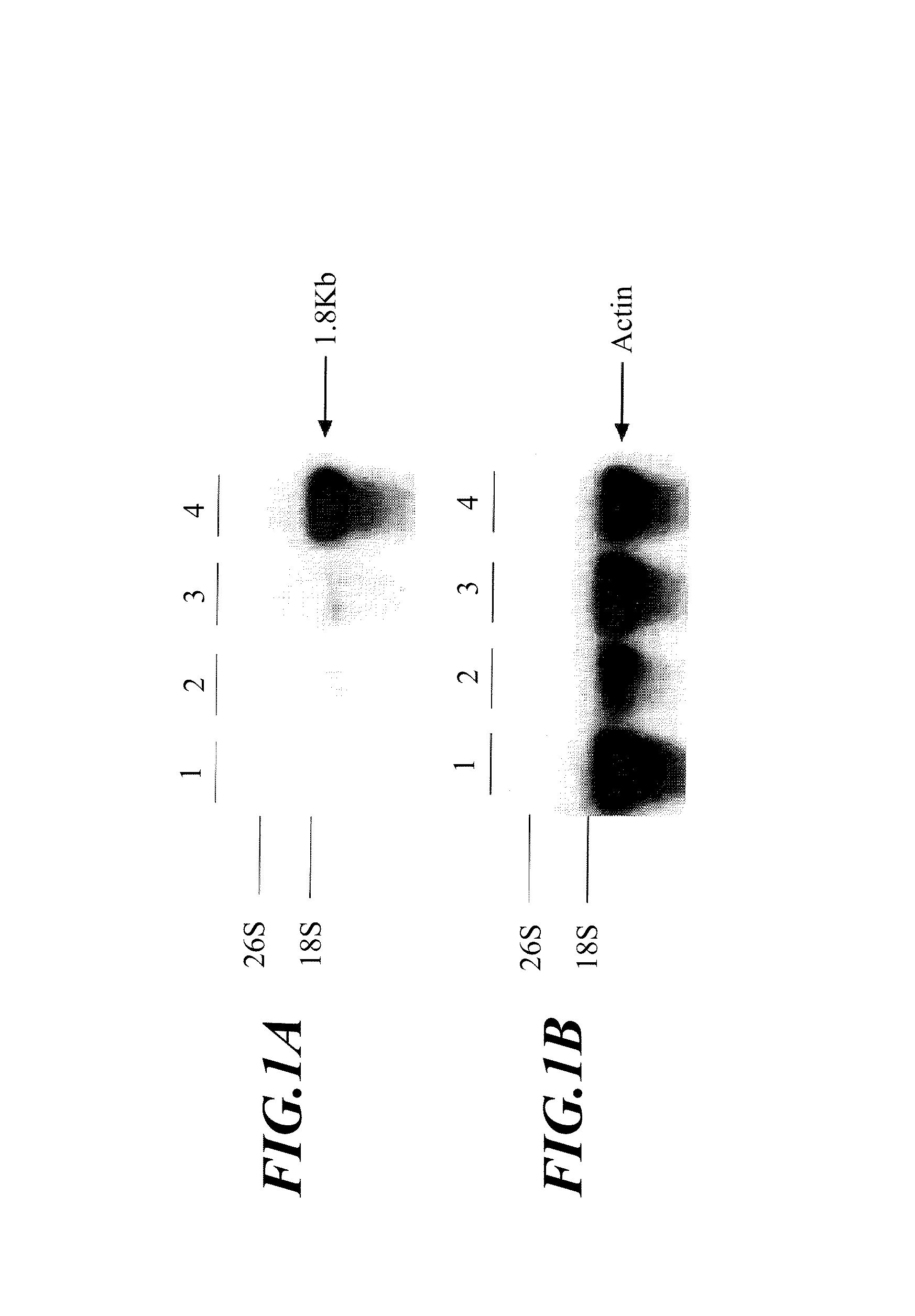
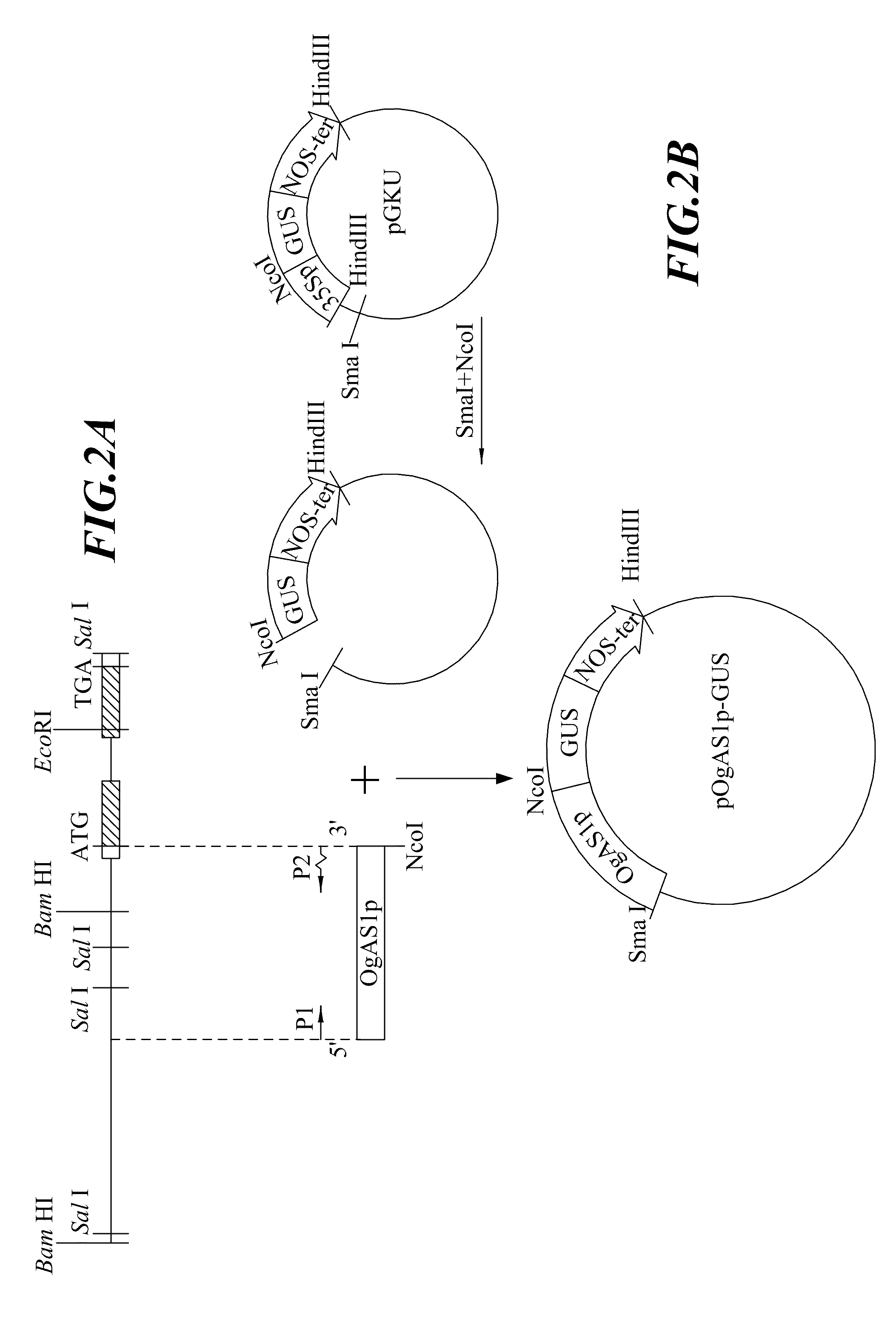
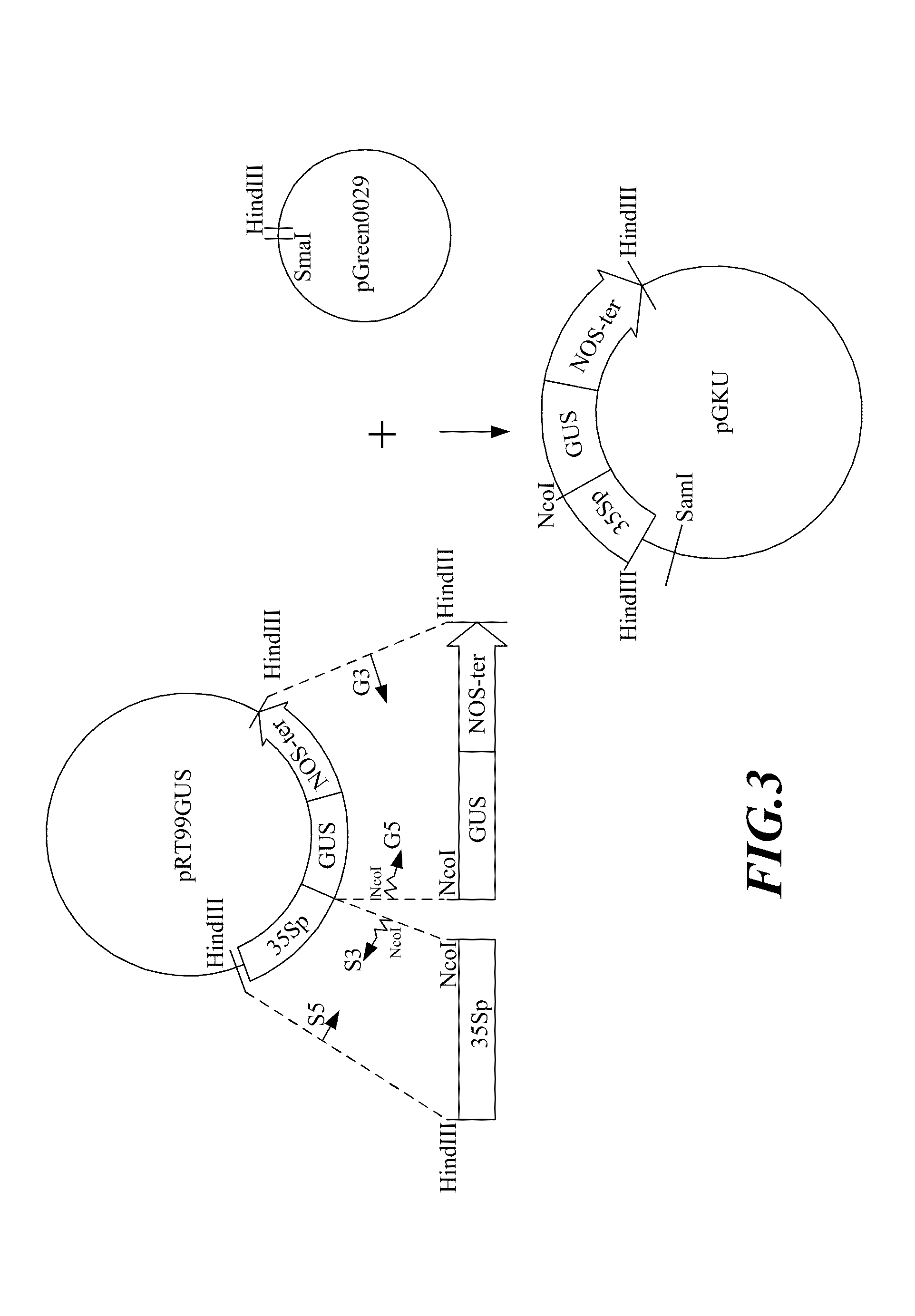
ActiveUS7750208B2Genomic constitution of the transgenic plant might be alteredEfficient expressionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesOpen reading frameAureusidin synthase
The invention provides an anther-specific expression promoter in plant, wherein said promoter is a promoter of Oncidium aureusidin synthase gene OgAS1, and has a sequence as SEQ ID No: 3. The invention provides further a gene expression cassette that comprised a promoter having a DNA sequence as SEQ ID No: 3, and a polynucleotide that encode an open reading frame and is linked to the 3′ end of said promoter, wherein said promoter can activate the transcription of said polynucleotide in an organism containing said gene expression cassette. The invention provides also a gene expression vector that contains a promoter having DNA sequence as SEQ ID No: 3. The invention provides further a process for producing a transgenic plant or part of organ, tissue or cell of said transgenic plant containing the above-described gene expression cassette.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Antibodies recognizing a highly expressed putative antigen of ca-mrsa and methods of use
ActiveUS20090130115A1Avoid infectionInhibit growthAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
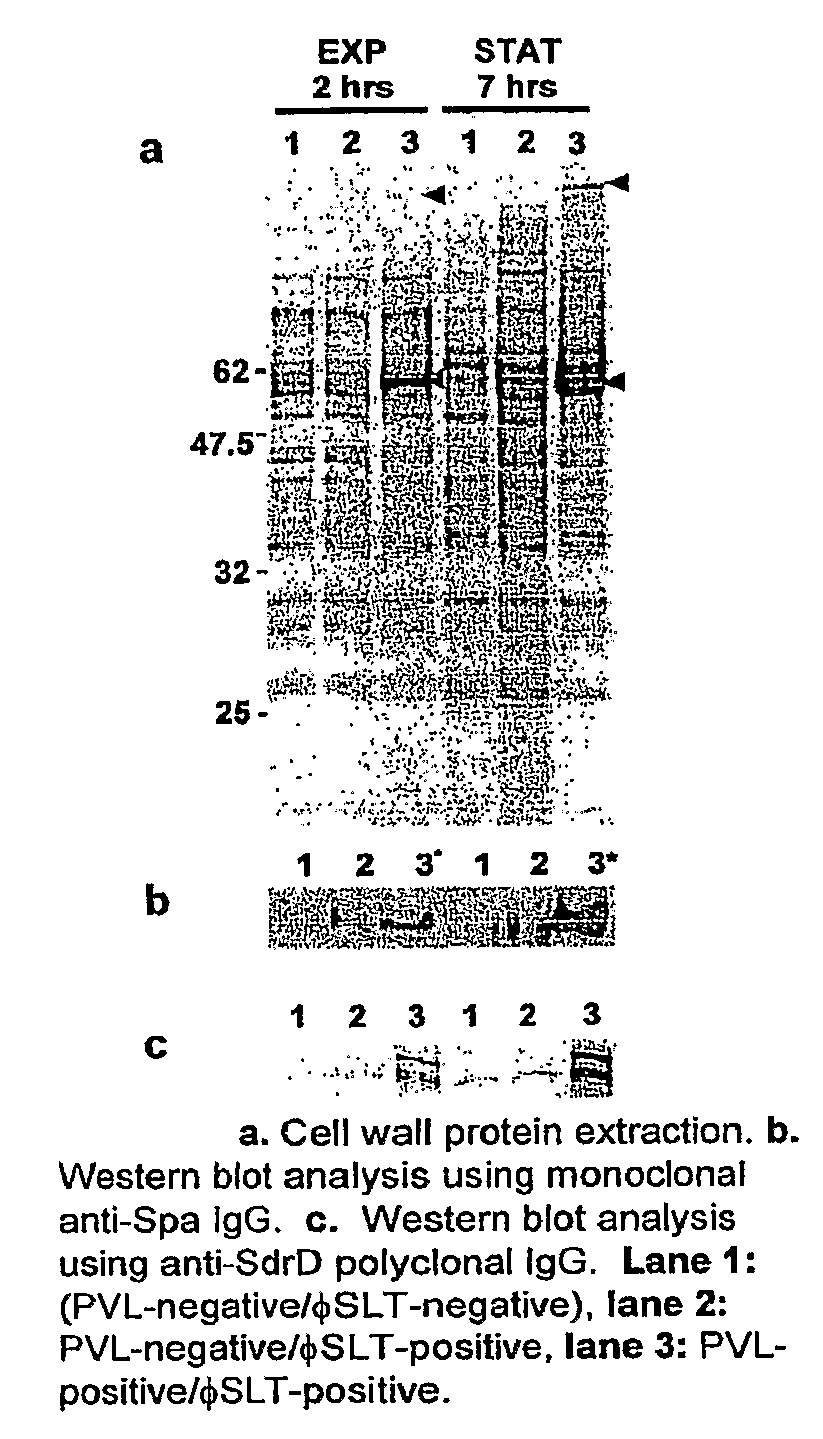
The present invention provides MSCRAMM® proteins from S. aureus which are putative highly-expressed antigens from methicillin-resistant S. aureus, including communit-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA), and these antigens can thus be utilized in methods of generating antibodies capable of binding these antigens which can be useful in methods of treating or preventing infection from MRSA. The present invention is directed to these proteins, antibodies capable of binding these proteins, methods of generating said antibodies, nucleic acids coding for said proteins, and pharmaceutical compositions or vaccines which include the proteins or antibodies of the present invention in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle, carrier or excipient.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Cross-reactive monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies which recognize surface proteins from coagulase-negative staphylococci and staphylococcus aureus
InactiveUS20050106648A1Preventing and treating staphylococcal infectionWide rangeAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcal infections
Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies which are cross-reactive to both coagulase-positive staphylococcus bacteria, such as S. aureus and to coagulase-negative bacteria, such as S. epidermidis and S. hemolyticus, are provided which can recognize surface proteins from both coagulase-positive and coagulase negative staph bacteria. The antibodies may be generated from surface proteins that have been isolated on the basis of characteristics that may be common between S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci, and these recombinant surface proteins are used to generate the antibodies of the invention. There is also provided vaccines and methods which utilize these proteins and antibodies for the treatment or protection against a wide variety of staphylococcal infections.
Owner:FOSTER TIMOTHY +5
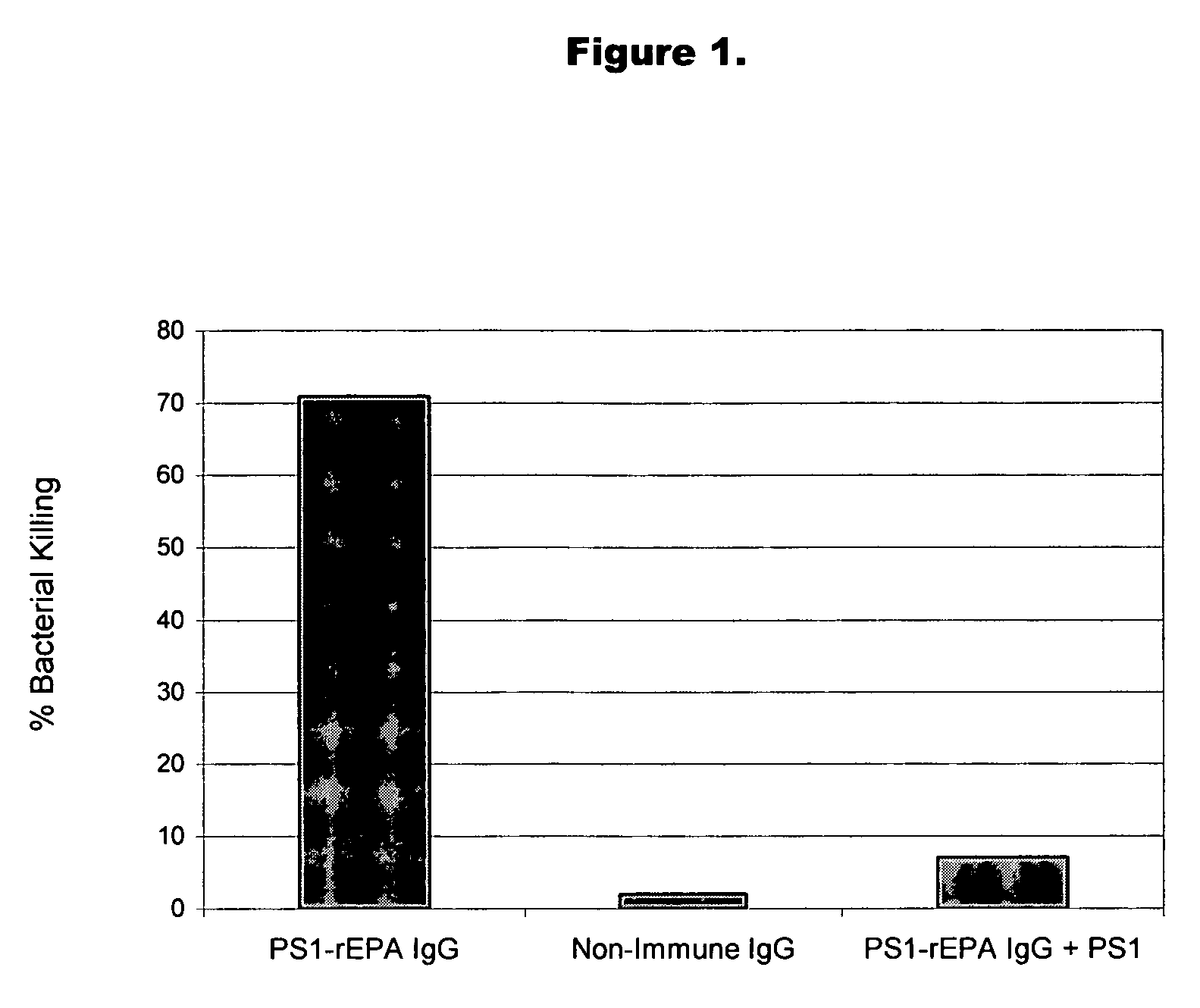
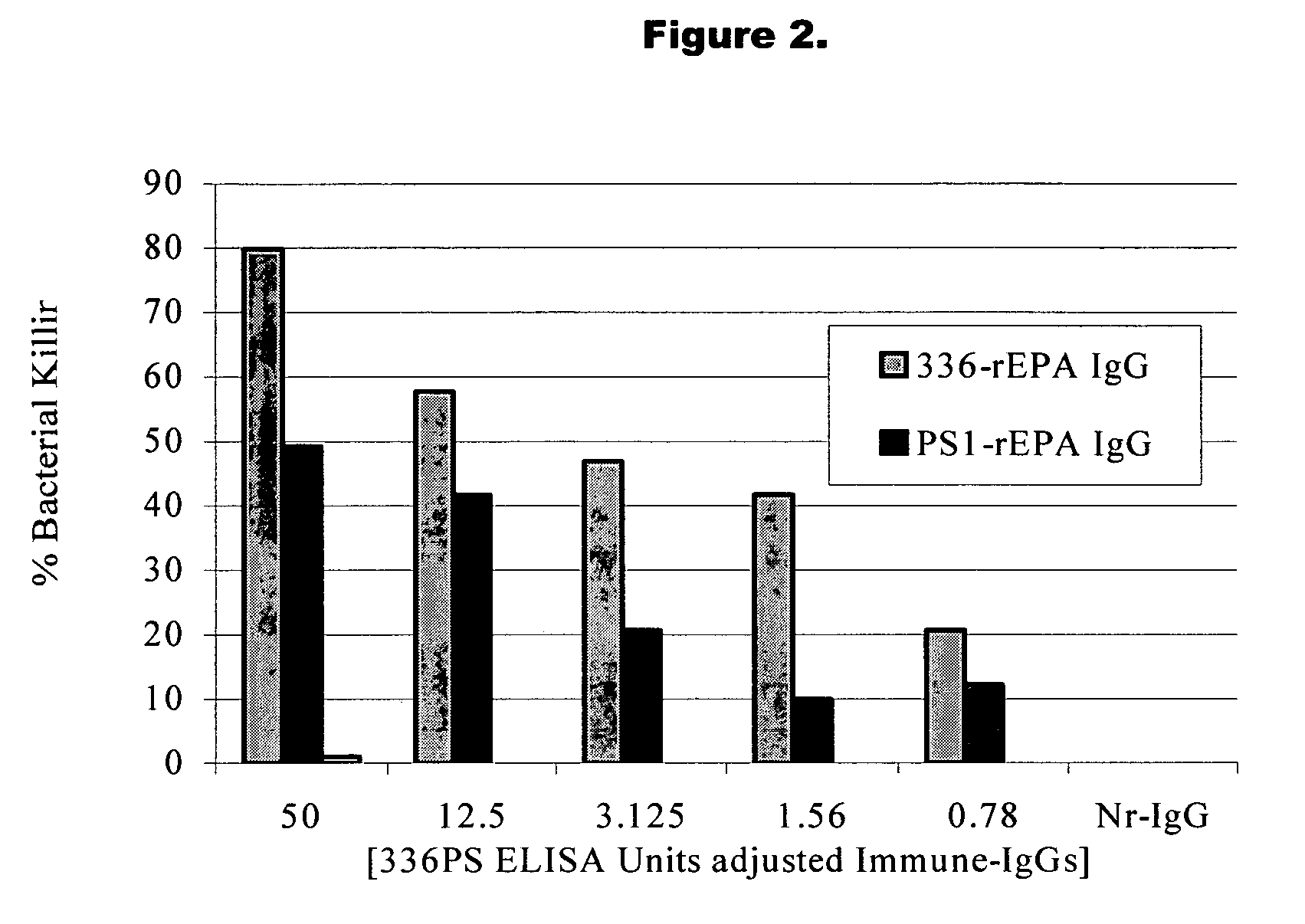
Method of protecting against staphylococcal infection
A method of preventing or treating staphylococcal bacterial infection in an individual is disclosed. A vaccine based on a conjugate of PS1 polysaccharide antigen can be used for active protection in individuals who are to be subjected to conditions that place them at immediate risk of developing a bacterial infection, as would be case in the context of a catheterization or a surgical procedure. Alternatively, antibodies raised in response to the antigen can be used to treat or to provide passive protection to individuals. The method can be used in a population of patients at risk for infection by various species of Staphylococcus or various types of Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Method for distinguishing between species within the genus staphilococcus
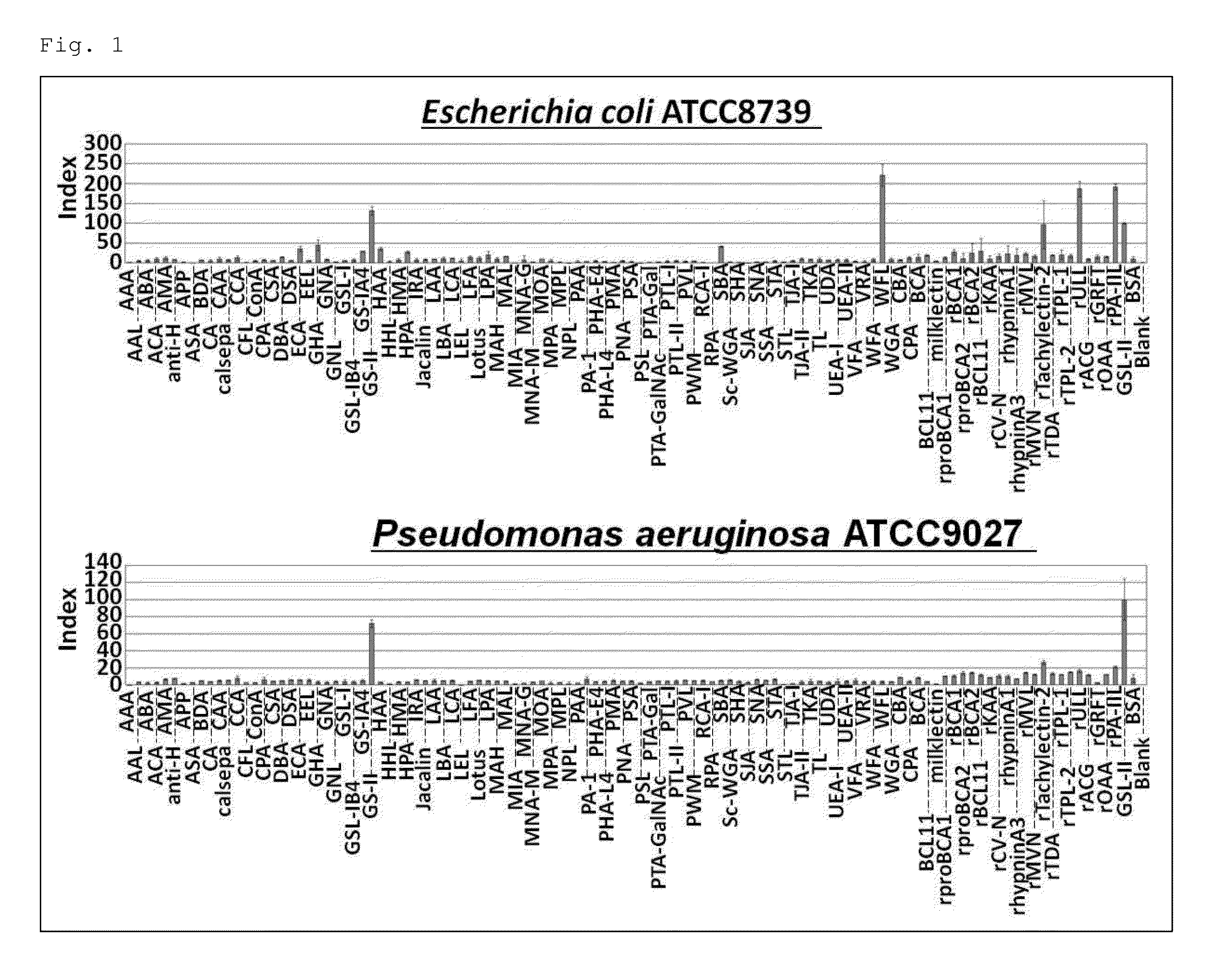
InactiveUS20140087395A1Distinguishing specieThe process is convenient and fastSugar derivativesLectin superfamilyBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
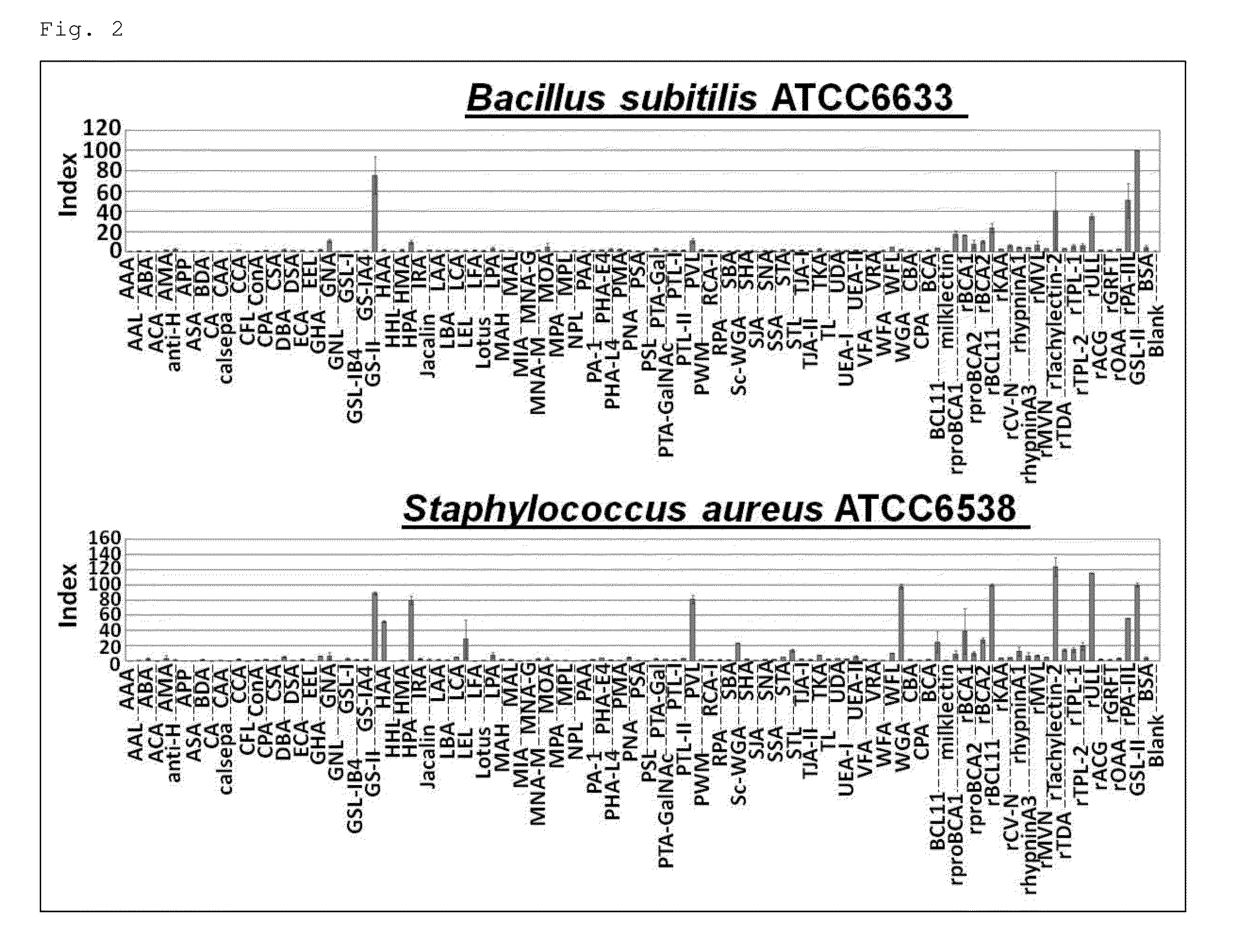
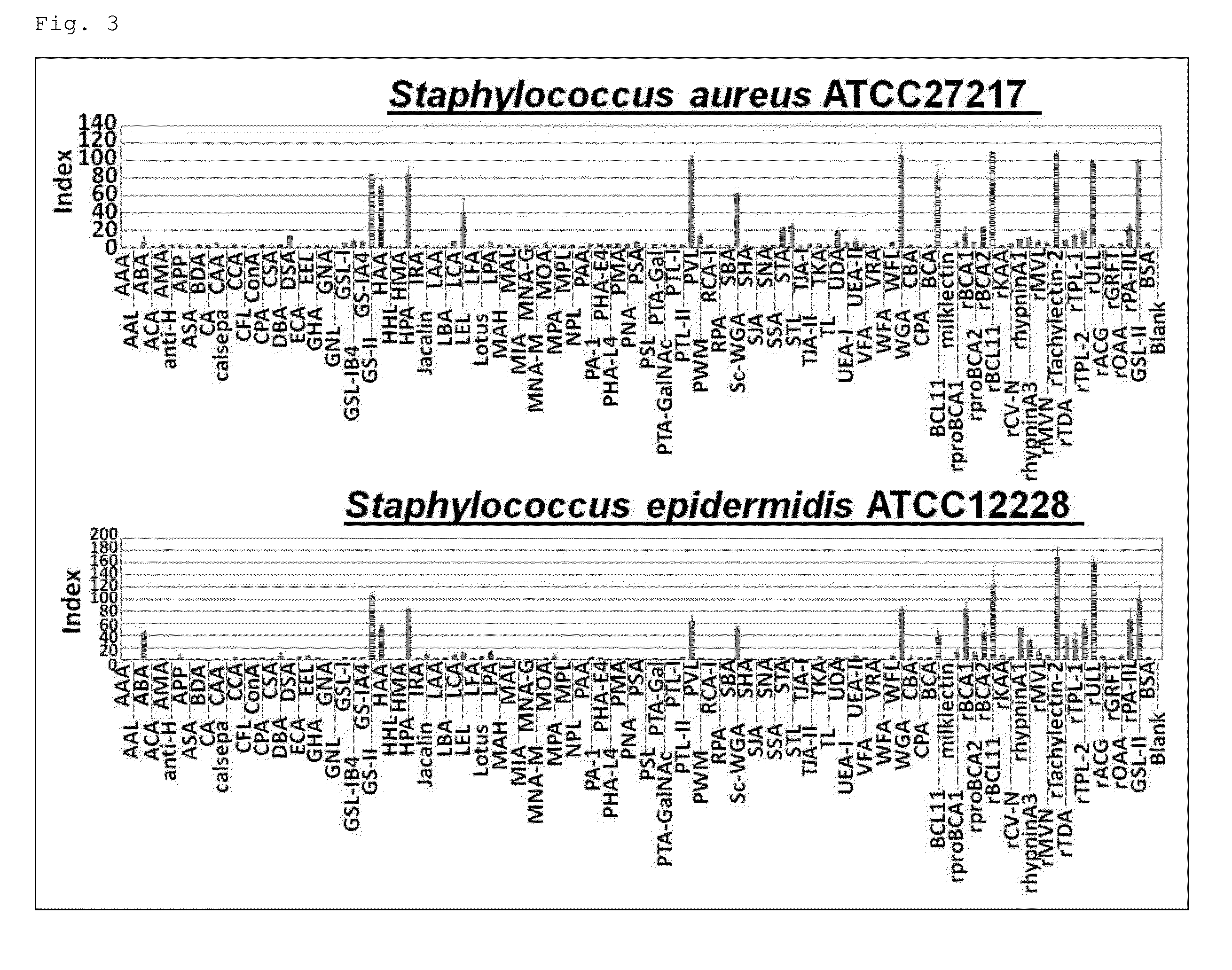
The object was to provide a method for distinguishing between species within the genus Staphylococcus; binding affinities between many types of lectins and bacteria belonging to the genus Staphylococcus were examined; and lectins of Tachylectin-2, LEL, KAA1, BCL11, CBA, HAA, HPA, STL, proBCA1, proBCA2, ULL, DSA, PWM, UDA, WFL, hypninA3, BCL11d, CFA1, CFA2, CLA, MPA1, MPA2, AC-avranin, algCSA, BML11b, BML11c, etc. were selected. Further, it was found that these lectins could be used to distinguish between species within the genus Staphylococcus.
Owner:GLYENCE
Construction of bacteria ghost vector PMAL-E-SN and its application in bacillus coli
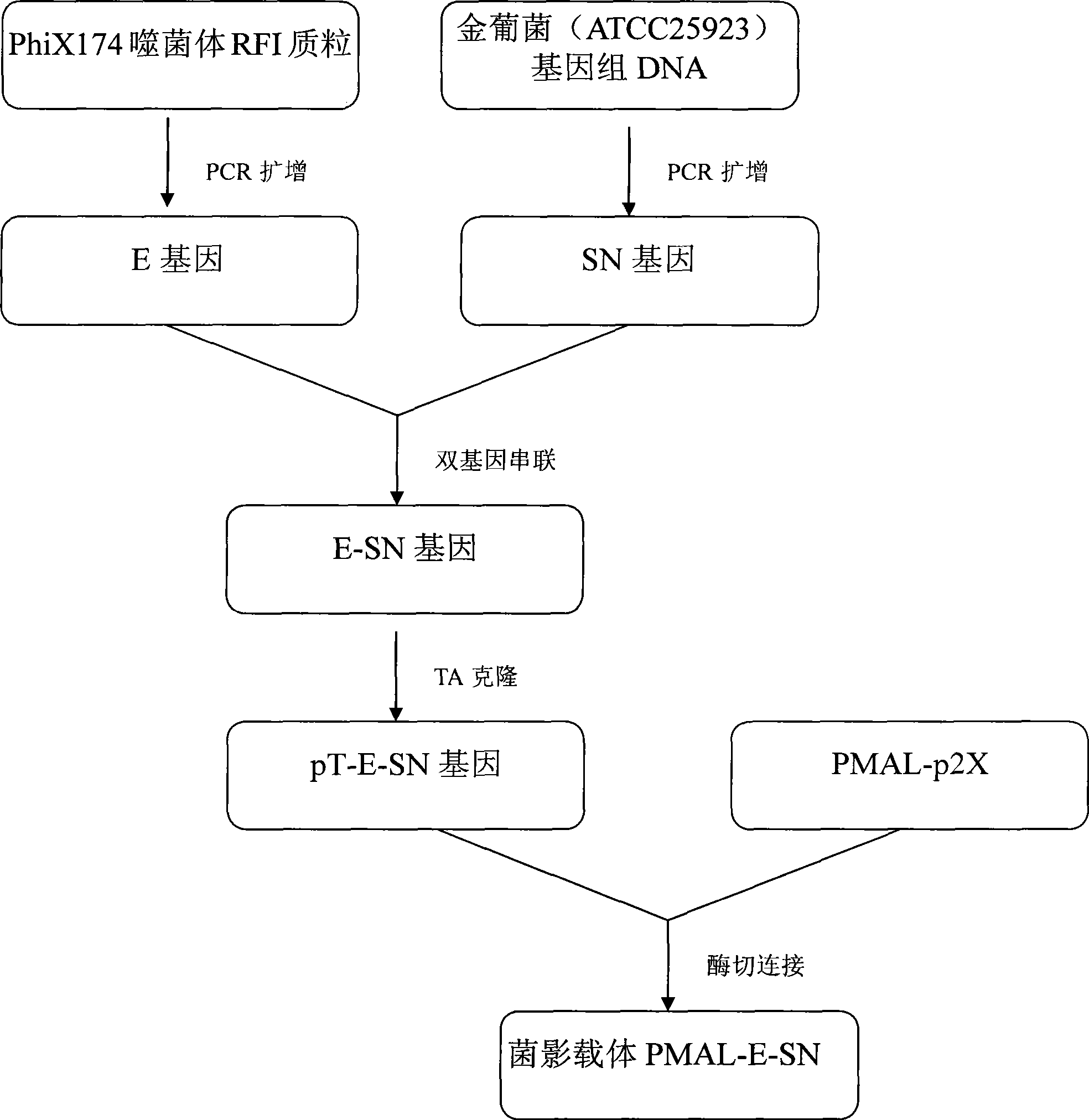
InactiveCN101457231ASame protection rateImprove cracking efficiencyBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses a bacterial ghost vector PMAL-E-SN construction and application thereof in an escherichia coli comprising an E gene obtained by PCR amplification using a PhiX174 phage RFI plasmid as a template; an SN gene obtained by PCR amplification using a staphylococcus aureus standard strain ATCC25923 genome DNA as a template; an E-SN gene obtained by serial connecting the E gene and the SN gene by the Linker of the fifteen flexible amino acids; a positive plasmid pT-E-SN sequencing screened by coupling an E-SN gene PCR amplification outcome and a pMD18-T vector and the bacterial ghost vector PMAL-E-SN constructed by the recombinant plasmid pT-E-SN with right sequencing and the plasmid vector PMAL-p2X. The bacterial ghost vector PMAL-E-SN of the invention enables the E gene and the SN gene to obtain the high efficiency expression through a ''tac'' strong promoter and a malE start signal, successfully prepares the escherichia coli bacterial ghost and the degradation efficiency can reach 99.99 The invention induces a secondary killing gene SN, obtains good effect by combining the E gene and the SN gene to a high efficiency expression vector PMAL-p2X and is widely used in preparation of the escherichia coli bacterial ghost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Capsular gram-positive bacteria bioconjugate vaccines
The present invention encompasses a novel S. aureus bioconjugate vaccine. More generally, the invention is directed to Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines containing a protein carrier, at least one polysaccharide such as a capsular Gram-positive polysaccharide, and, optionally, an adjuvant or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The instant invention also includes methods of producing Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines. An N-glycosylated protein is also provided that contains one or more polysaccharides such as Gram-positive polysaccharides. The invention is additionally directed to engineered prokaryotic organisms comprising nucleotide sequences encoding a glycosyltransferase of a first prokaryotic organism and a glycosyltransferase of a second prokaryotic organism. The invention further includes plasmids and prokaryotic cells transformed with plasmids encoding polysaccharides and enzymes which produce an N-glycosylated protein and / or bioconjugate vaccine. Further, the invention is directed to methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal comprising administering said bioconjugate vaccines.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
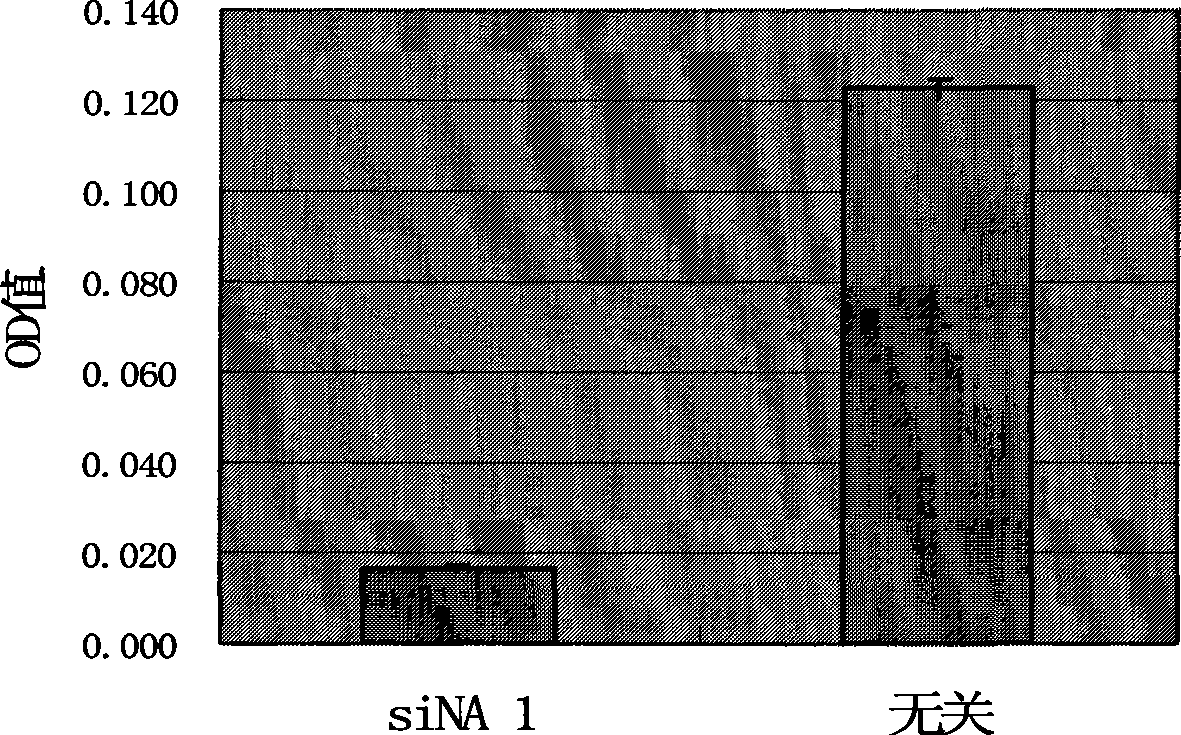
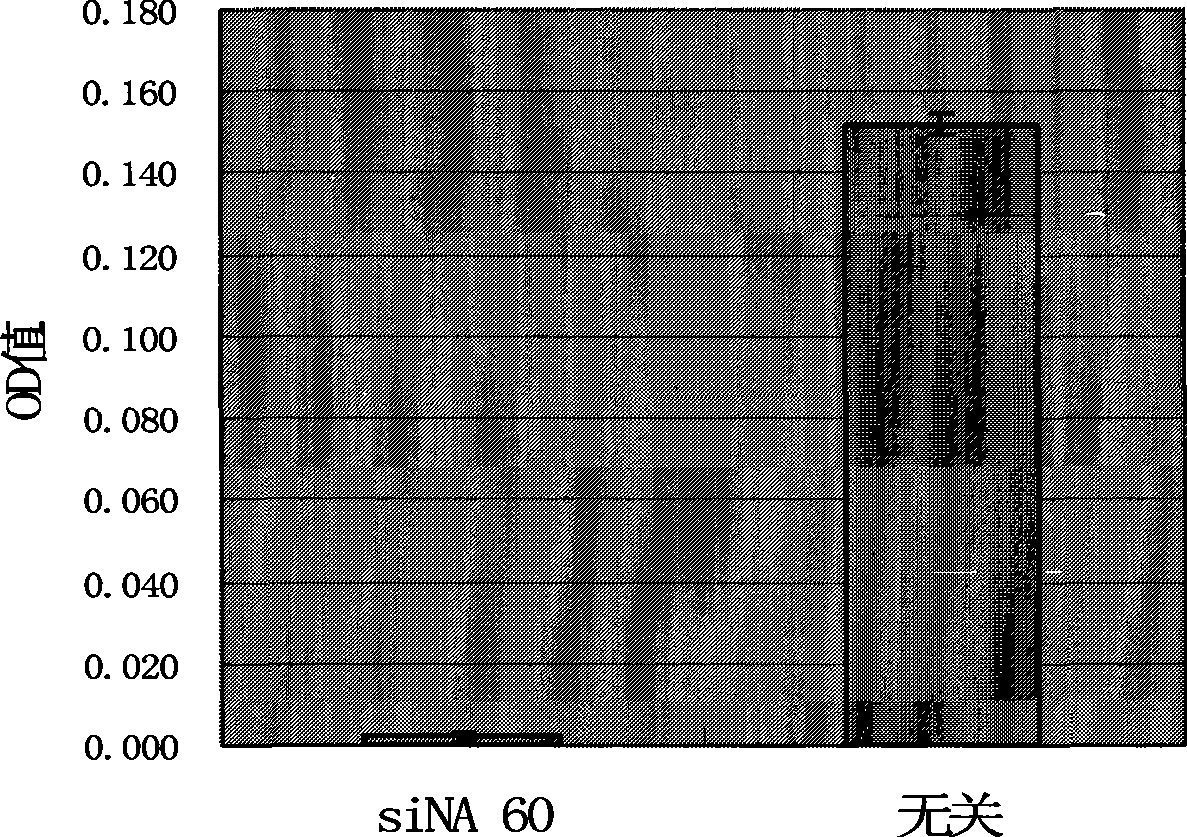
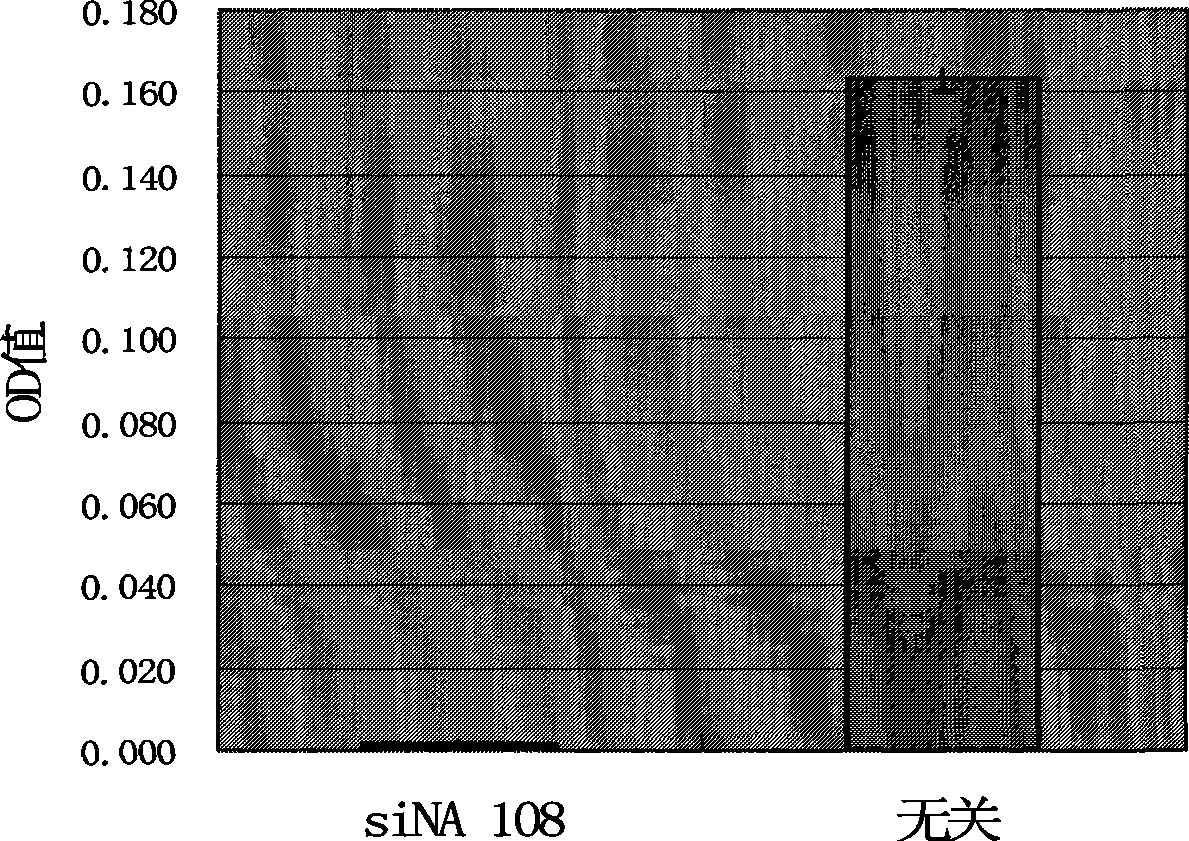
Double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing drug tolerant bacteria and composition thereof
InactiveCN101457222ADrug resistance is reversibleInhibition is effectiveAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesMethicillin resistance geneHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing various drug tolerance bacteria using methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aurous as represents. The siNA of the invention is a double-chain molecule with 19 base pairs. A sense strand and a antisense strand respectively have two overhanging bases dT at 5' terminals, the GC content is 40-55; the aimed target sequence is selected from the genes relative with the vital movements of copy, transcription and translation in the staphylococcus aurous genome and an mecA gene correlative with the drug tolerance; said target sequence is preserved in 900f staphylococcus aurous; said target sequence is in a conservative sequence area in more than 900f staphylococcus aurous with distinct source with all the gene sequences in the human genome; the target sequence of the said siNA double-chain molecule is selected from SEQ ID NO. 1-325, the sense strand is a corresponding DNA or RNA sequence with the target sequence and the antisense strand is a corresponding RNA or DNA with the sense strand according to the complementary base law.
Owner:李宝健
Genetic engineering-modified staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a genetic engineering-modified staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase, the amino acid sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase, comprising the following concrete steps: (1) cloning the amino acid sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO:1 into a prokaryotic expression vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid; (2) transforming the recombinant plasmid obtained in the step (1) into host bacteria to obtain recombinant bacteria; (3) expressing the staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase by the recombinant plasmid; and (4) purifying the staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase obtained in the step (3). Multiple staphylococcus aureus can be specifically inactivated by independently using the genetic engineering-modified staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase or matching the genetic engineering-modified staphylococcus aureus staphylophage lyase with other compounds, thus providing a safe enzymic preparation source without toxic and side effects for staphylococcus aureus infection, particularly staphylococcus aureus caused dairy mastitis in the existing dairy farm control.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method and medium for detecting the presence or absence of staphylococcus aureus in a test sample
InactiveUS20110269160A1Facilitates handling and packaging and storingFavorable source of coagulase substrateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLesion swabTest sample
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) kit for rapid detection of staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN102864226AQuick checkThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerSerodiagnoses
The invention discloses an LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) kit for rapid detection of staphylococcus aureus. The LAMP kit for rapid detection of staphylococcus aureus comprises LAMP reaction fluid, a standard positive template and a negative quality control standard. The LAMP reaction fluid contains large fragments in Bst DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, primers, LAMP 10Xbuffer, dNTPs (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates) solution, MgSO4 solution and betaine. The primers include forward primers and reverse primers. The LAMP kit for rapid detection of staphylococcus aureus has the advantages that the LAMP kit is high in specificity, high in sensitivity, high in speed, simple and high in reliability, results are recognizable to naked eyes, and the like. The LAMP kit is applicable to rapid qualitative detection of staphylococcus aureus in industrial foods, and can be a substitute for commonly used traditional culture methods and serodiagnosis methods.
Owner:WUHAN ZHENFU PHARMA CO LTD
Method and medium for detecting the presence or absence of staphylococcus aureus in a test sample
InactiveUS20090191577A1Small amountFacilitates handling and packaging and storingBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLesion swabTest sample
A presence / absence test for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) involves placing a first generation test sample in a solution that will clot in the presence of S. aureus. The solution contains components that will selectively grow S. aureus and also contains clotting factors that will react with S. aureus, if S. aureus is present in the sample, to clot the solution. Examples of specimen samples that can be tested include nasal swabs and lesion swabs, among others. The test can also be modified to detect the presence or absence of methicillin resistant S. Aureus (MRSA).
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
Method for detecting Candida on skin
InactiveUS20080057532A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliSpectral response
A method and system for rapidly detecting Candida on the skin of a host, such as an infant with diaper rash, is provided. The method includes contacting a dermal sample with a colorant that exhibits a certain spectral response (e.g., color change) in the presence of Candida. For example, the colorant may change from a first color to a second color, from colorless to a color, or from a color to colorless. The colorant is typically capable of differentiating between Candida (e.g., Candida albicans) and other microorganisms commonly associated with diaper rash, such as S. aureus and E. coli. Thus, when a dermal sample is placed into contact with the colorant, the color change may simply be observed to determine whether the infection is caused by Candida. If the color change occurs to a certain extent (e.g., from yellow to bright red), it may be determined that the test sample contains Candida. Likewise, if a color change occurs to a lesser extent (e.g., from yellow to faint orange) or not at all, it may be determined that the dermal sample contains other microorganisms (e.g., S. aureus or E. coli), no infection is present, or that the infection is simply due to other causes. Regardless, it will become readily apparent whether or not treatment for Candida is needed.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
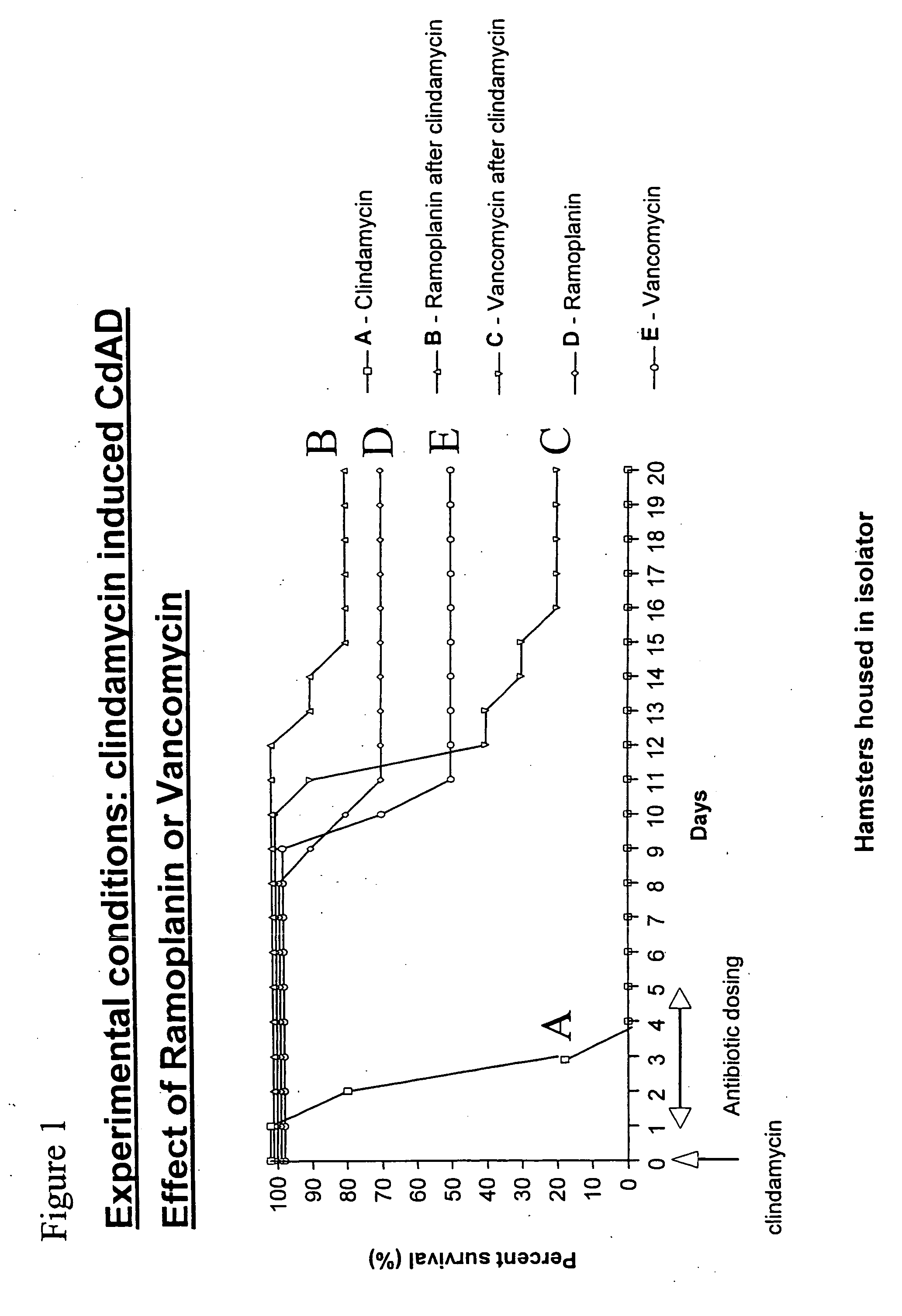
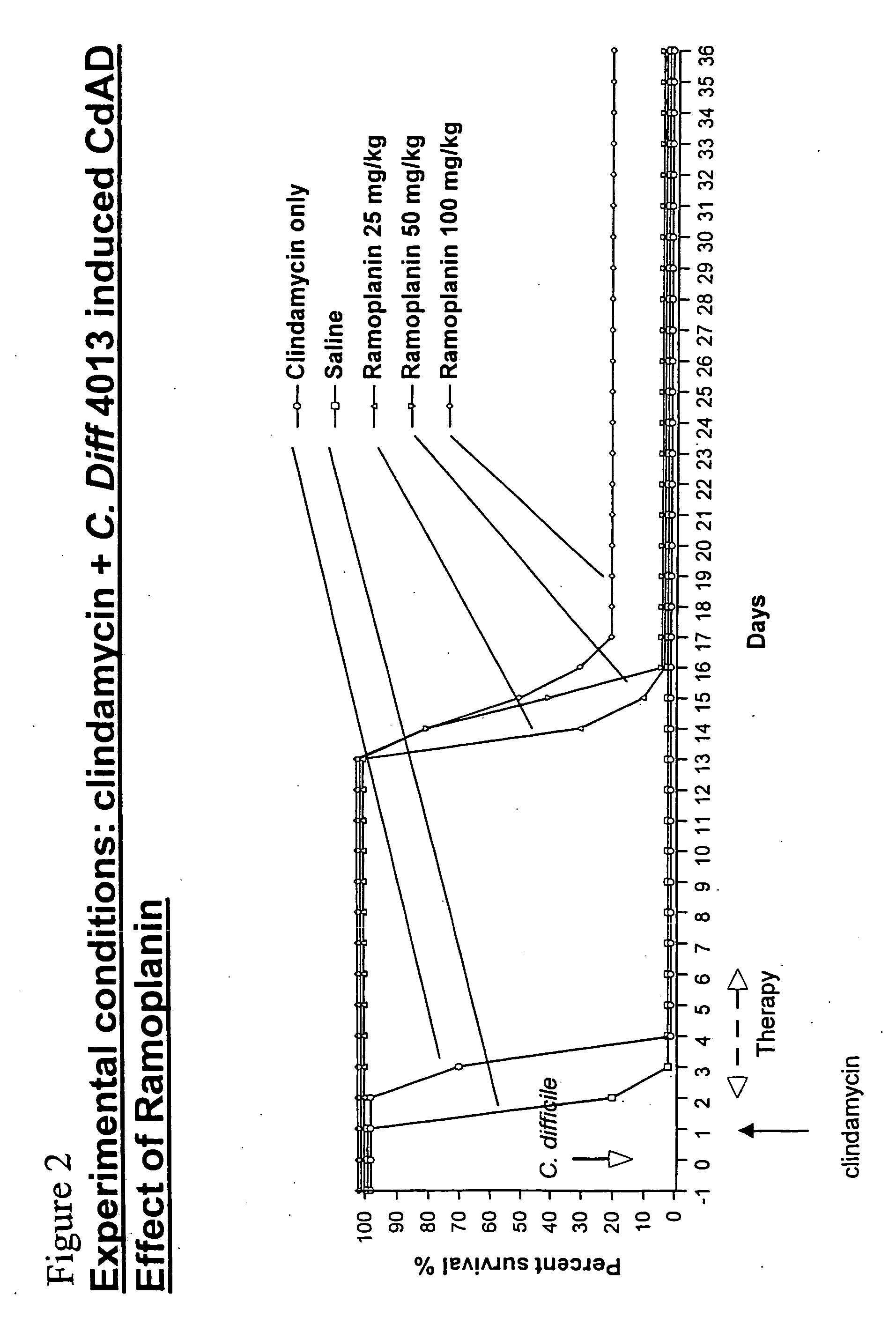
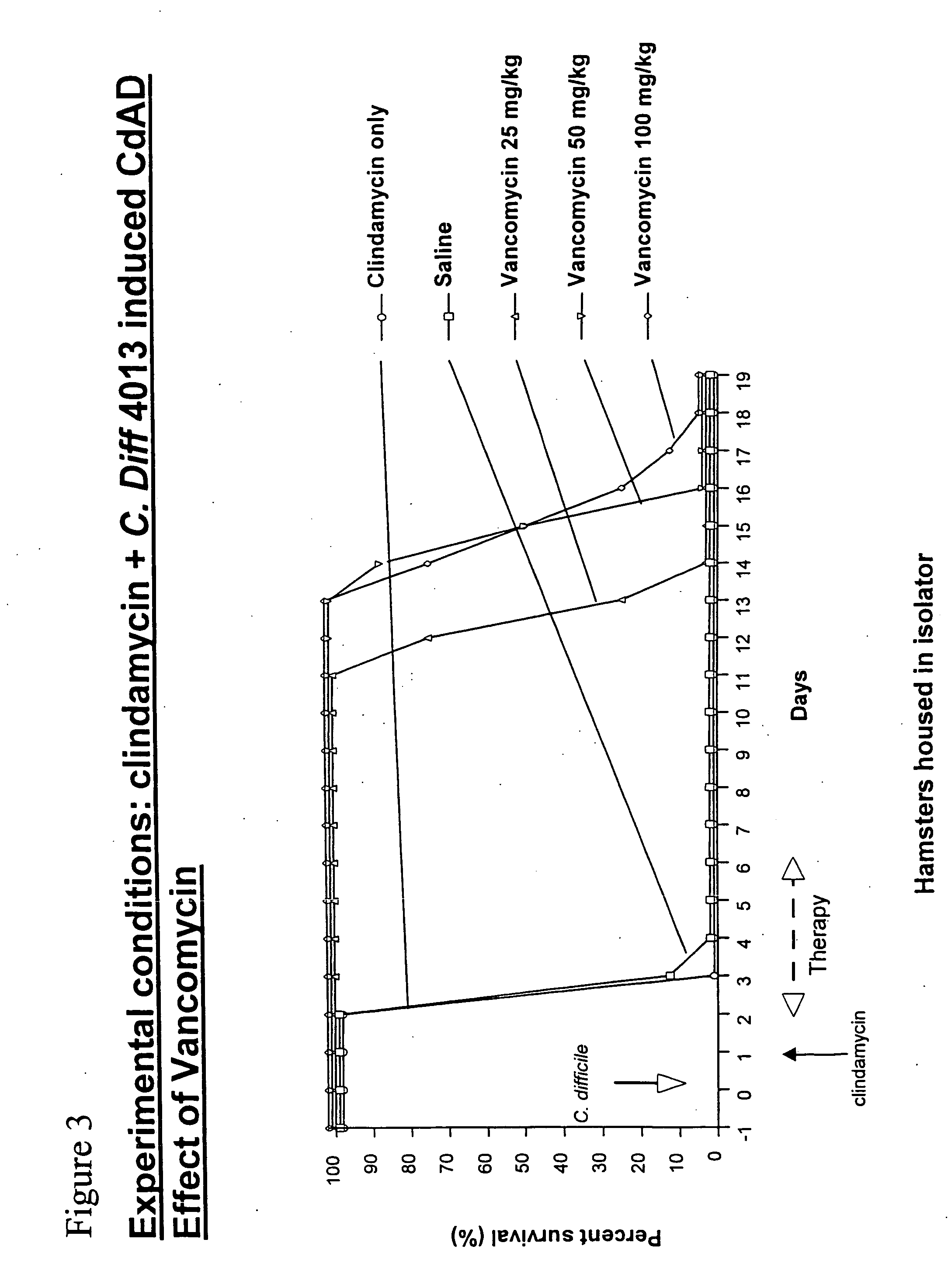
Use of ramoplanin to treat diseases associated with the use of antibiotics
InactiveUS20070014849A1Prevent relapseInhibit relapse of antibiotic-associated diarrheaAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseBacteroides
The invention features a method of treating or preventing a disease associated with the use of antibiotics in a patient in need thereof by administering to the patient ramoplanin in an amount and for a duration effective to treat said disease. The disease may be caused, for example, by the presence of a bacterium such as enterotoxin producing strains of C. difficile, C. perfringens, or S. aureus.
Owner:NANOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for detecting bacterial pathogens
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
Small-molecule adjuvants for antibiotics to address antibiotic resistance
PendingUS20190125825A1Improve efficiencyAvoid problemsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdjuvantHalogen
Methods for treating a bacterial infection and for suppressing antibiotic resistance in a patient are described herein. Certain such methods generally involve administering an antibiotic and an adjuvant compound to a patient with a bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus, wherein the adjuvant compound comprises a fused tricyclic ring system with at least one halogen substituent. Compositions and kits containing such components are also described.
Owner:HIGH POINT UNIVERSITY
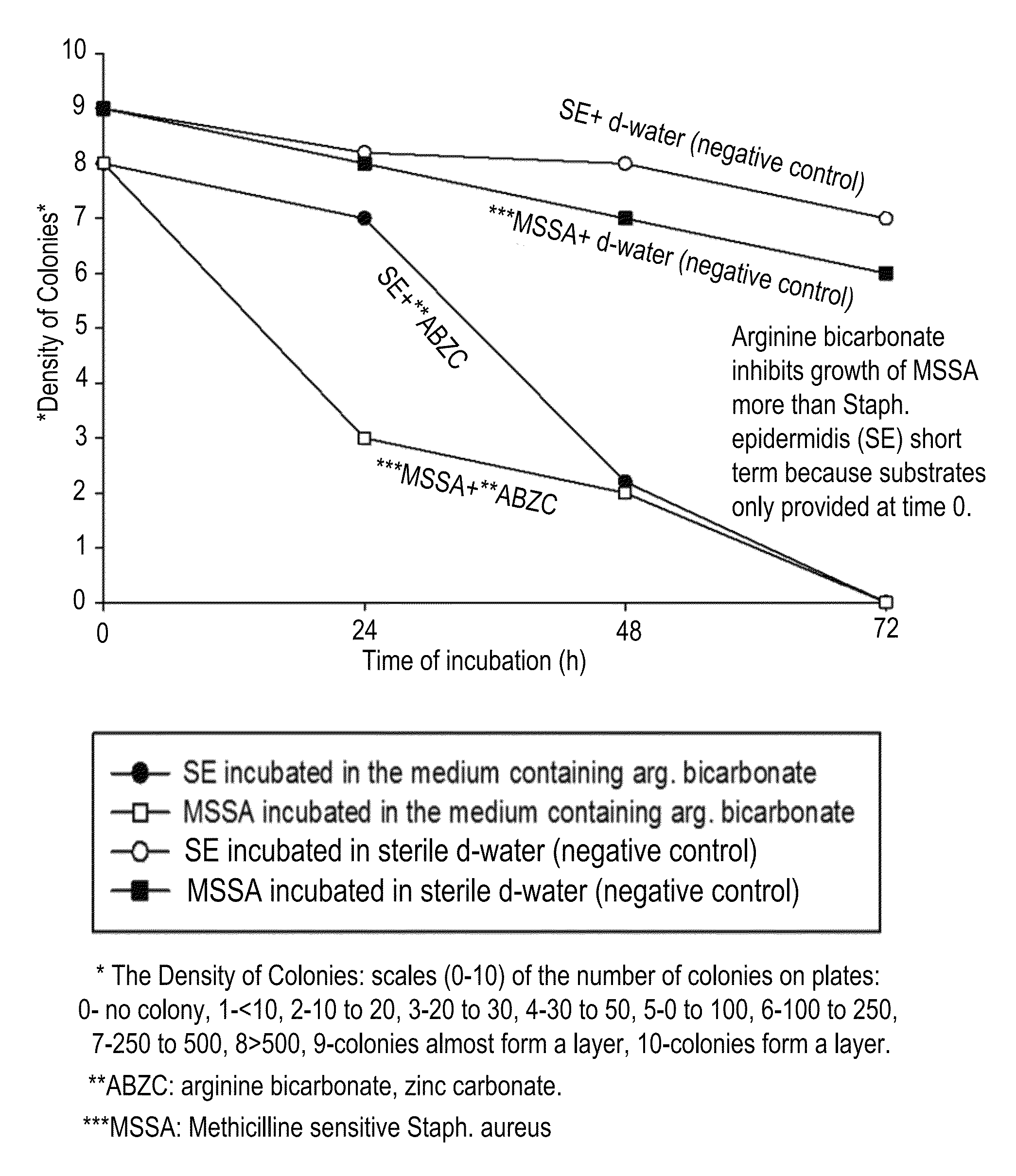
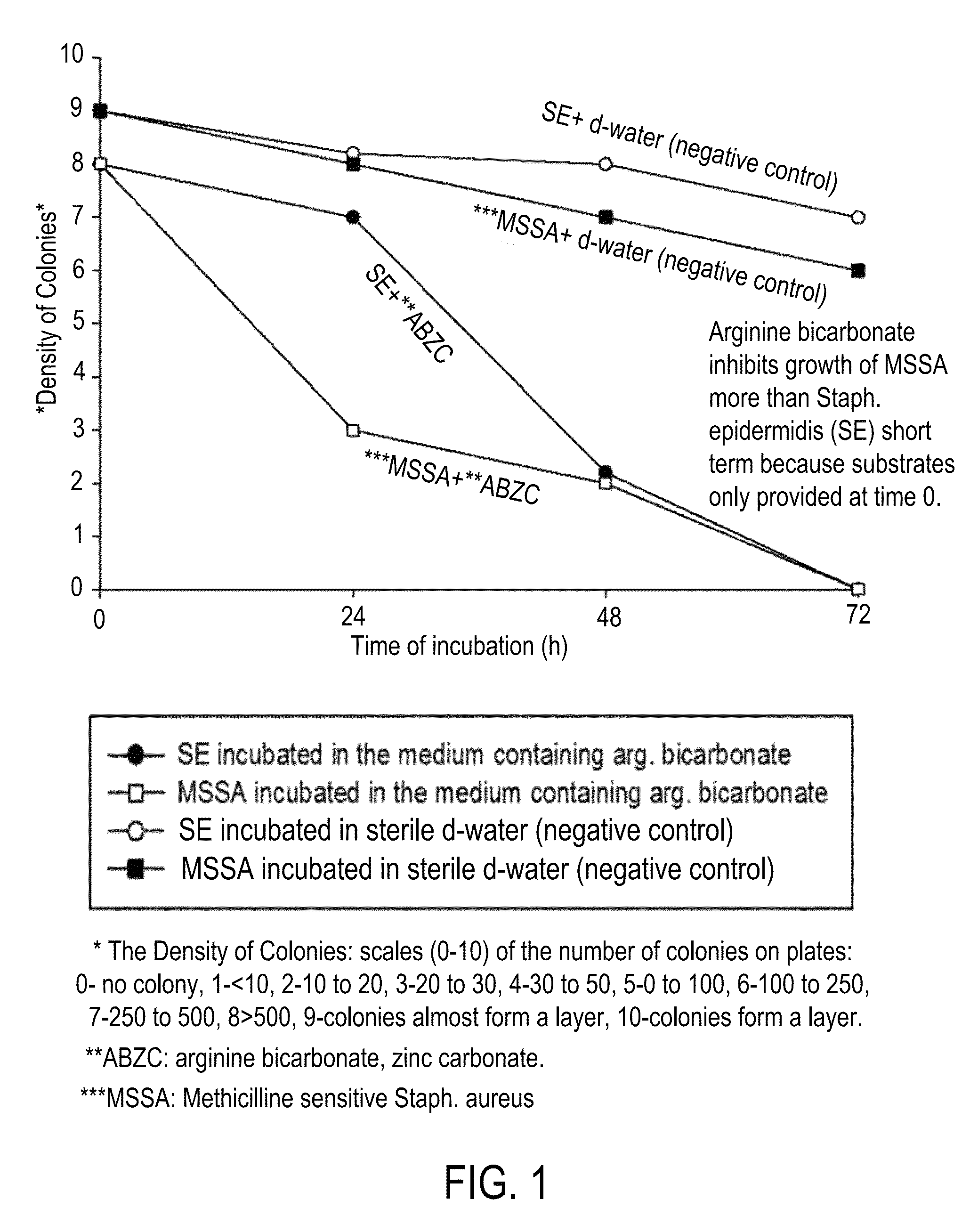
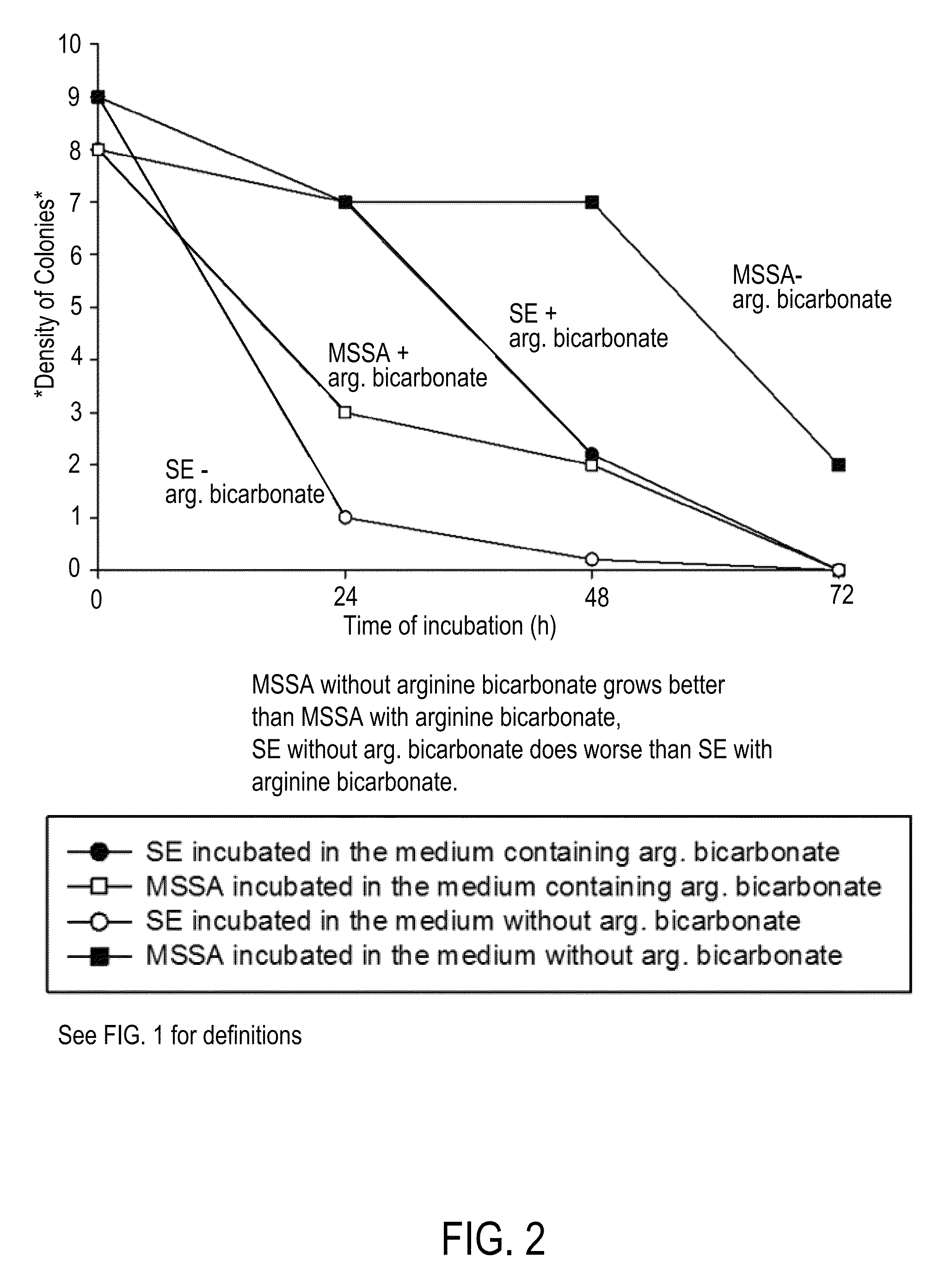
Compositions and methods for altering human cutaneous microbiome to increase growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and reduce Staphylococcus aureus proliferation
ActiveUS9370476B2Selectively inhibiting growthImprove scalabilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsArginineStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
A composition including arginine or a salt thereof, a zinc salt, preferably arginine bicarbonate and zinc carbonate (ABZC), in combination, plus one or more physiologically acceptable excipients, administered for the modification of cutaneous microfloras, generally to inhibit the growth of pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus bacteria and also promote the growth of non-pathogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria, and methods for using such composition.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
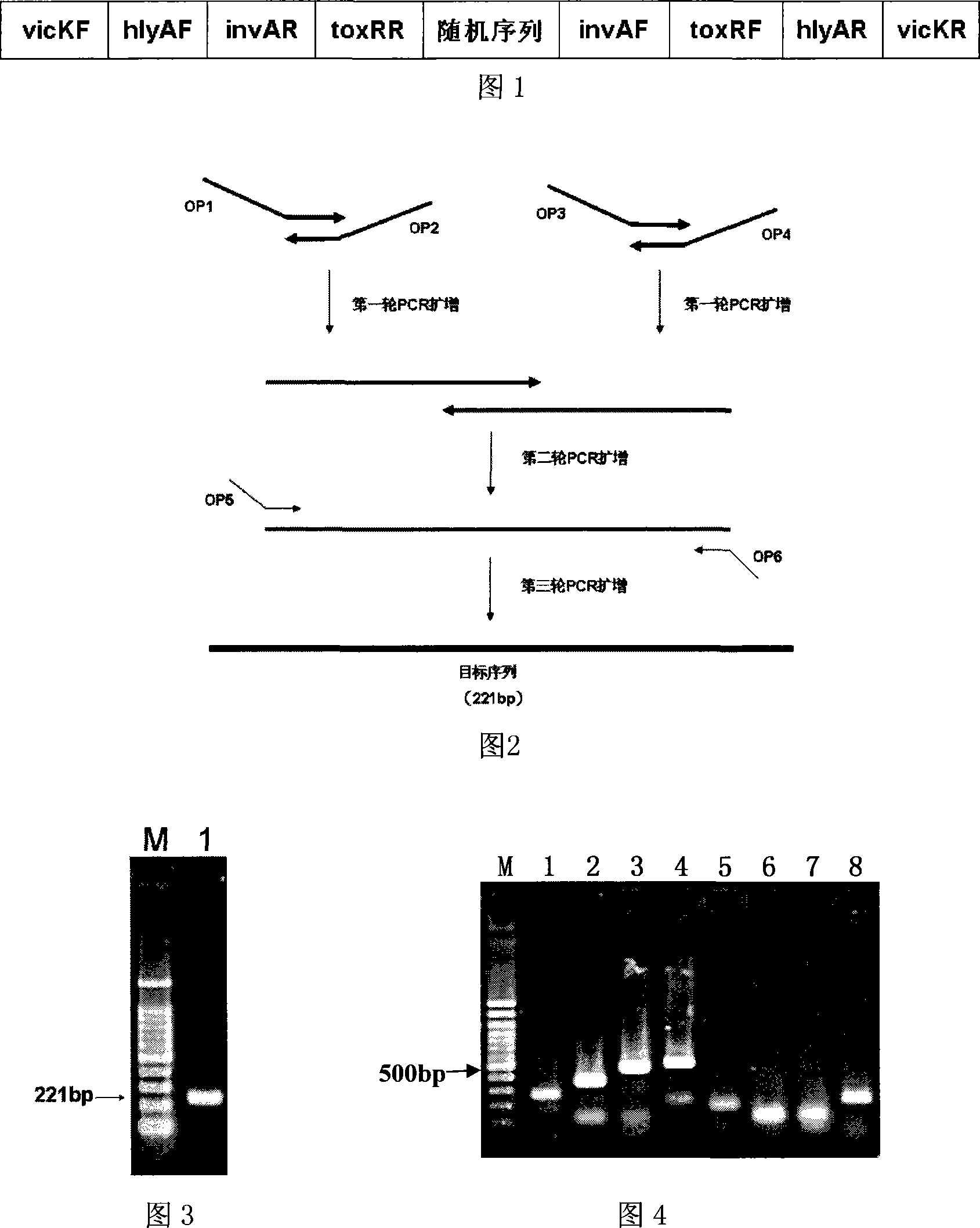
Method for manufacturing multiple amplification internal mark for four-bacteria PCR test
InactiveCN101220393AImprove accuracyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionStaphylococcus cohniiNucleotide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a multiple amplification internal standard used for the PCR detection of four bacteria of the technical field of food safety, the steps are that: a specific detection primer is designed according to a staphylococcus aureus vicK gene, a salmonella invA gene, a listeria monocytogene hlyA gene and vibrio parahaemolyticus toxR gene; the invention adopts an overlap PCR technology for assembling the sequence of the specific detection primer of the staphylococcus aureus vicK gene, the salmonella invA gene, the listeria monocytogene hlyA gene and the vibrio parahaemolyticus toxR gene into a nucleotide segment so as to construct the multiple amplification internal standard; the artificial sequence is cloned to a plasmid vector pMD-18T to constitute a plasmid pMD-mIAC which comprises the sequence of the multiple amplification internal standard; the multiple amplification internal standard is respectively verified in the detections of staphylococcus aureus, salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and vibrio parahaemolyticus. The invention can greatly reduce the detection cost and ensure the accuracy and the high efficiency of the detection at the same time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for detecting staphylococcus aureus live bacteria in milk
InactiveCN102311997AHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a method for detecting staphylococcus aureus live bacteria in milk. The invention aims to solve the problem of overestimation of pathogenic bacteria risk due to the ineffective distinction between dead bacteria and live bacteria by present LAMP detection methods. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: 1, pretreating a tested milk sample; 2, extracting DNA of the tested milk sample treated by Step 1 to obtain an extract; 3, performing LAMP amplification by using the extract as a template; 4, loading a LAMP amplification product into agarose gel for electrophoresis and imaging in a gel imaging analysis system to finish the detection. The method provided by the invention has high detection sensitivity with the minimal measminimal detectable limit of staphylococcus aureus being 100fg, and can be widely applied in the field of foodborne pathogens detection.
Owner:黑龙江省乳品工业技术开发中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com