Method for detecting staphylococcus aureus live bacteria in milk
A staphylococcus and aureus technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of overestimation of the risk of pathogenic bacteria, inability to effectively distinguish dead bacteria from live bacteria, etc., to avoid mistakes Evaluate and detect effects with high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
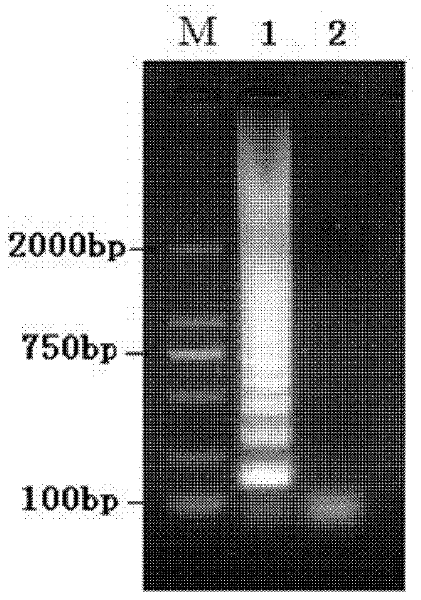
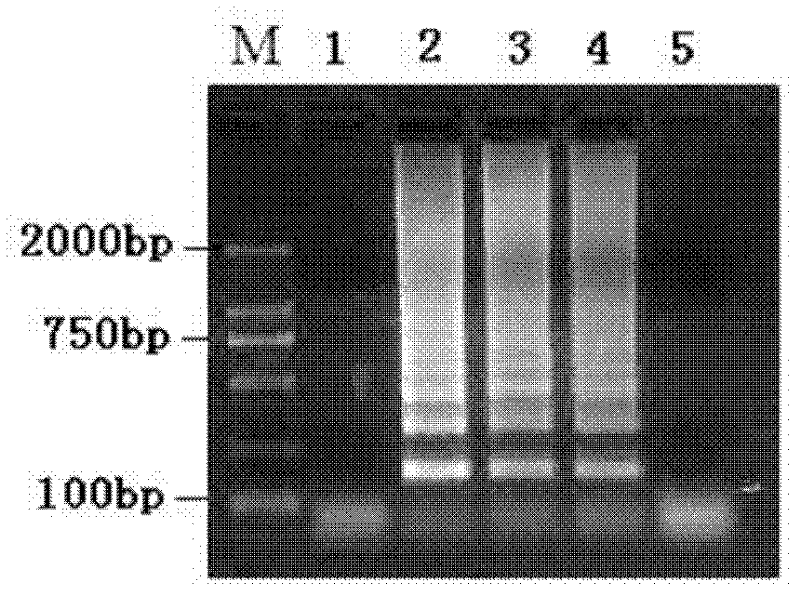
[0010] Specific embodiment 1: the method for detecting Staphylococcus aureus viable bacteria in milk according to this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps: 1. Pretreatment of the tested milk sample: add PMA to 1 mL of the tested milk so that the concentration of PMA is 3 μg / mL, then placed on ice in a dark place for 5-30min, then placed 15-20cm away from a 650W halogen lamp, and exposed for 3-5min; 3. Use the extract as a template to carry out LAMP amplification to obtain the LAMP amplification product; 4. Identification: Take 5 μL of the LAMP amplification product, spot it on an agarose gel with a mass concentration of 2%, and use a voltage of 100V at 1 Electrophoresis in ×TAE electrophoresis buffer for 30 minutes, and then imaged in a gel imaging system, the detection is completed.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0011] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: in step 1, place it on ice in a dark place for 5 minutes. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0012] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that: in step 1, place it on ice in a dark place for 30 minutes. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com