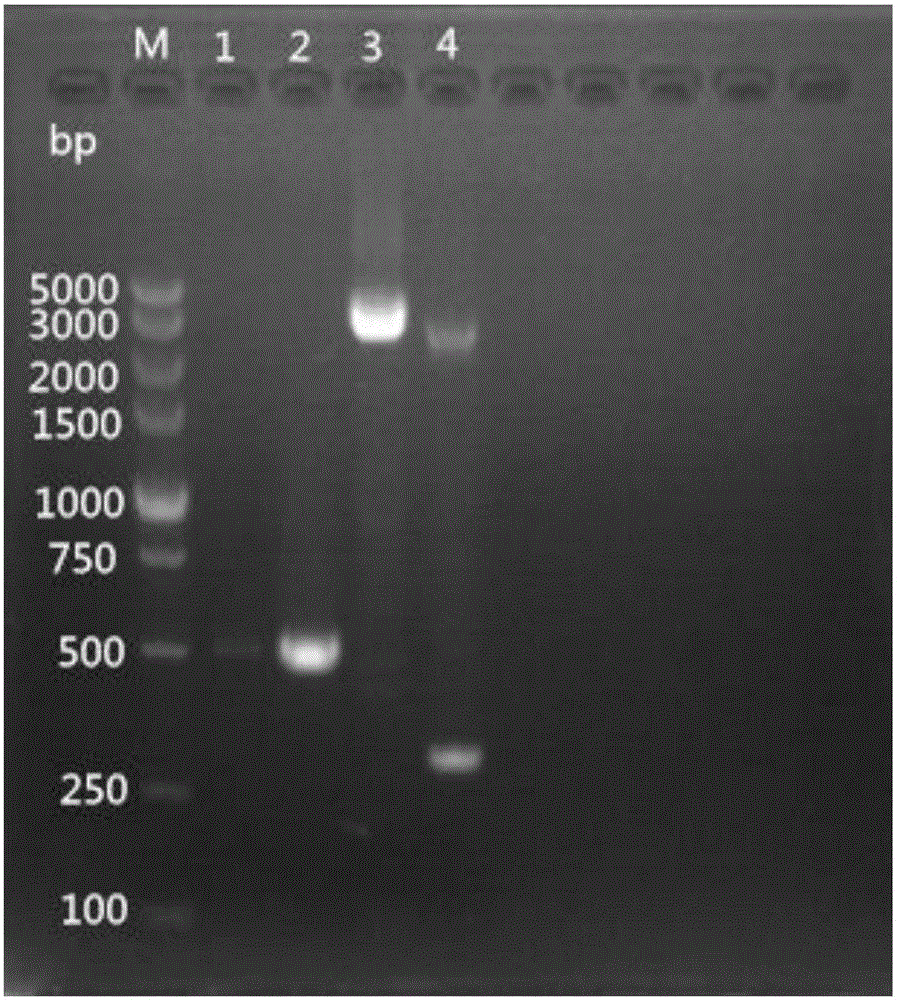
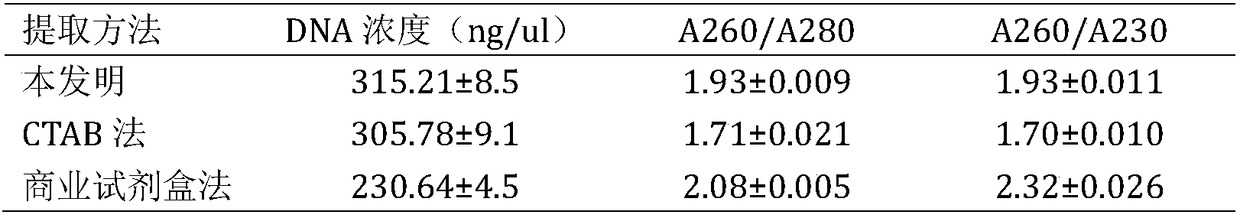
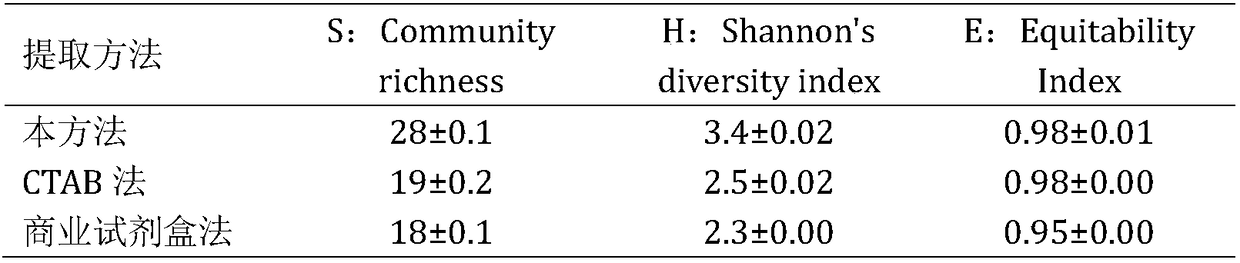
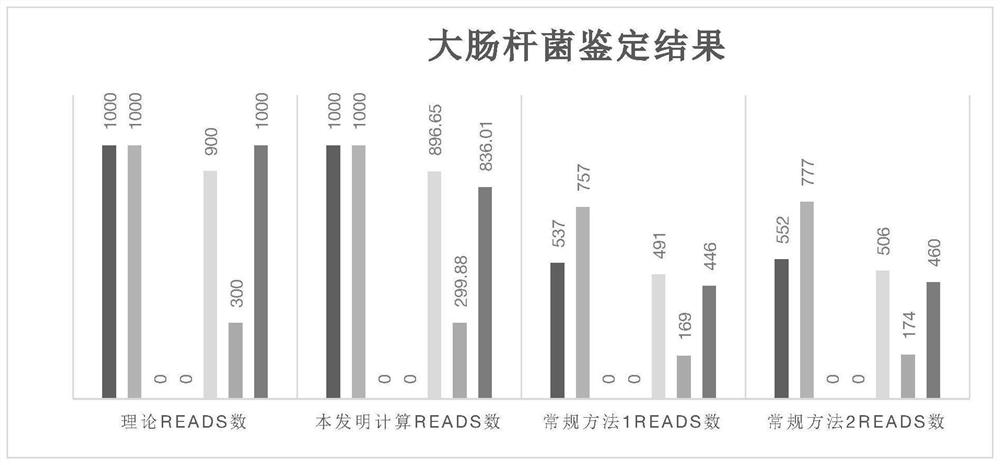
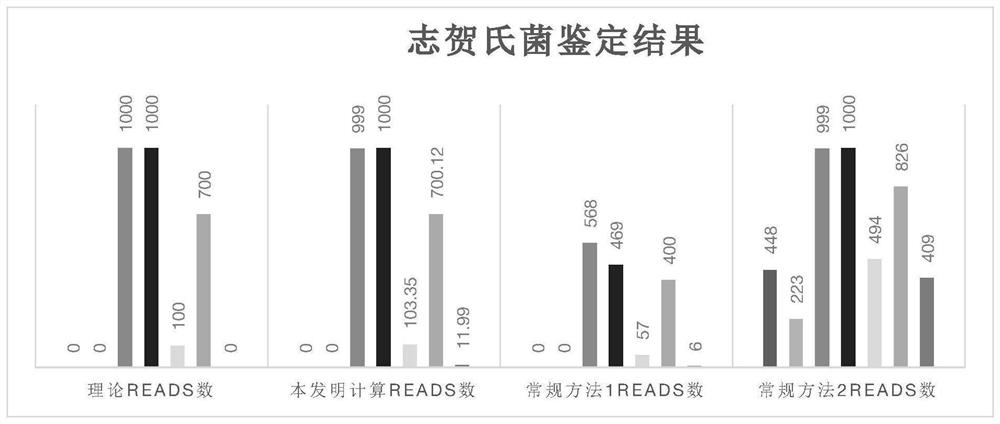
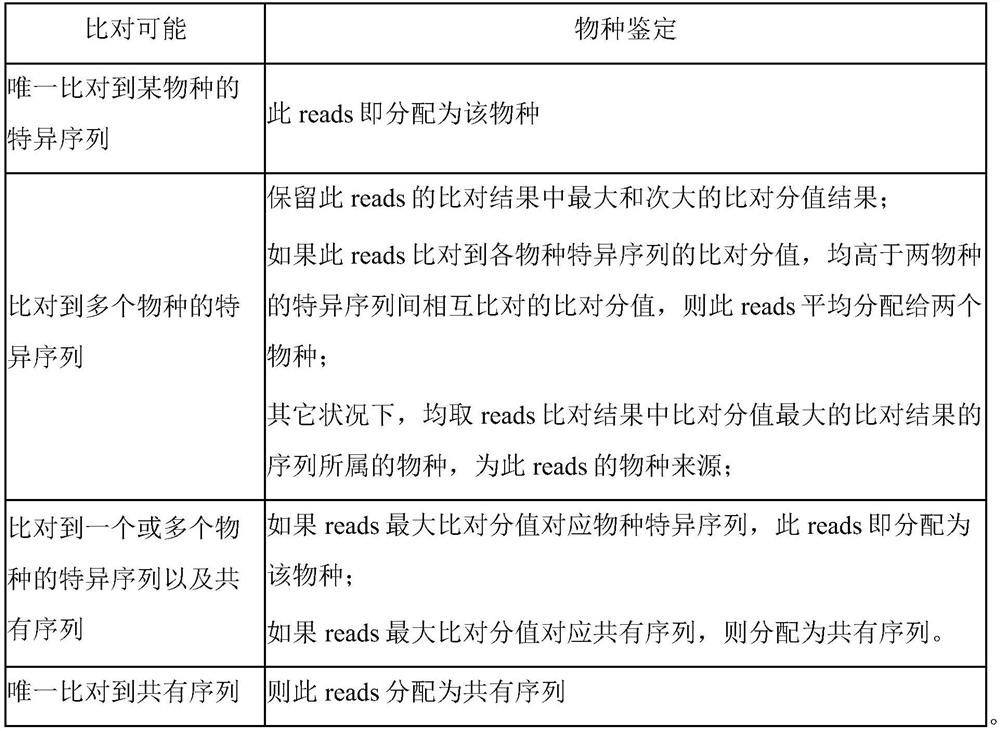
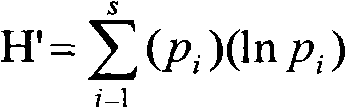Patents
Literature
78 results about "Microbial Genomes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial genomes are widely variable and reflect the enormous diversity of bacteria, archaea and lower eukaryotes. Bacterial genomes usually consist of a single circular chromosome, but species with more than one chromosome (eg.
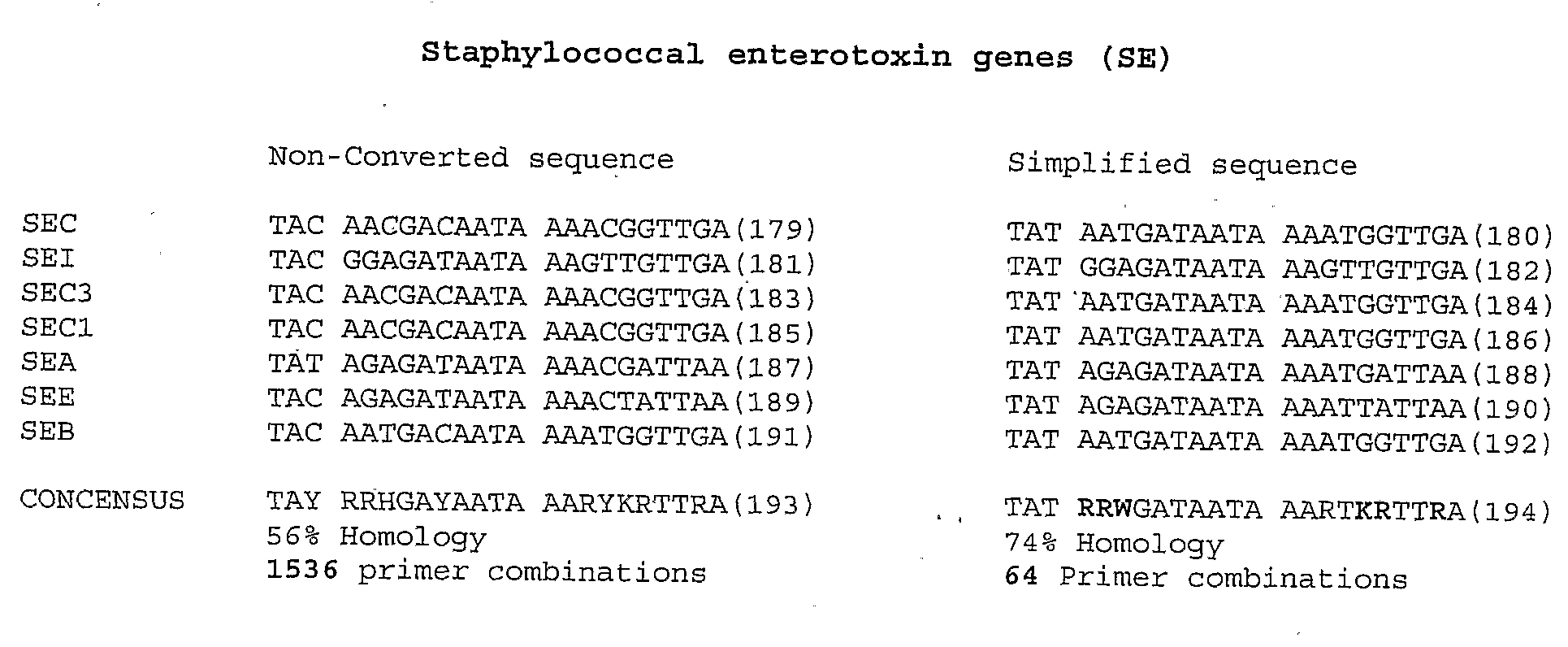
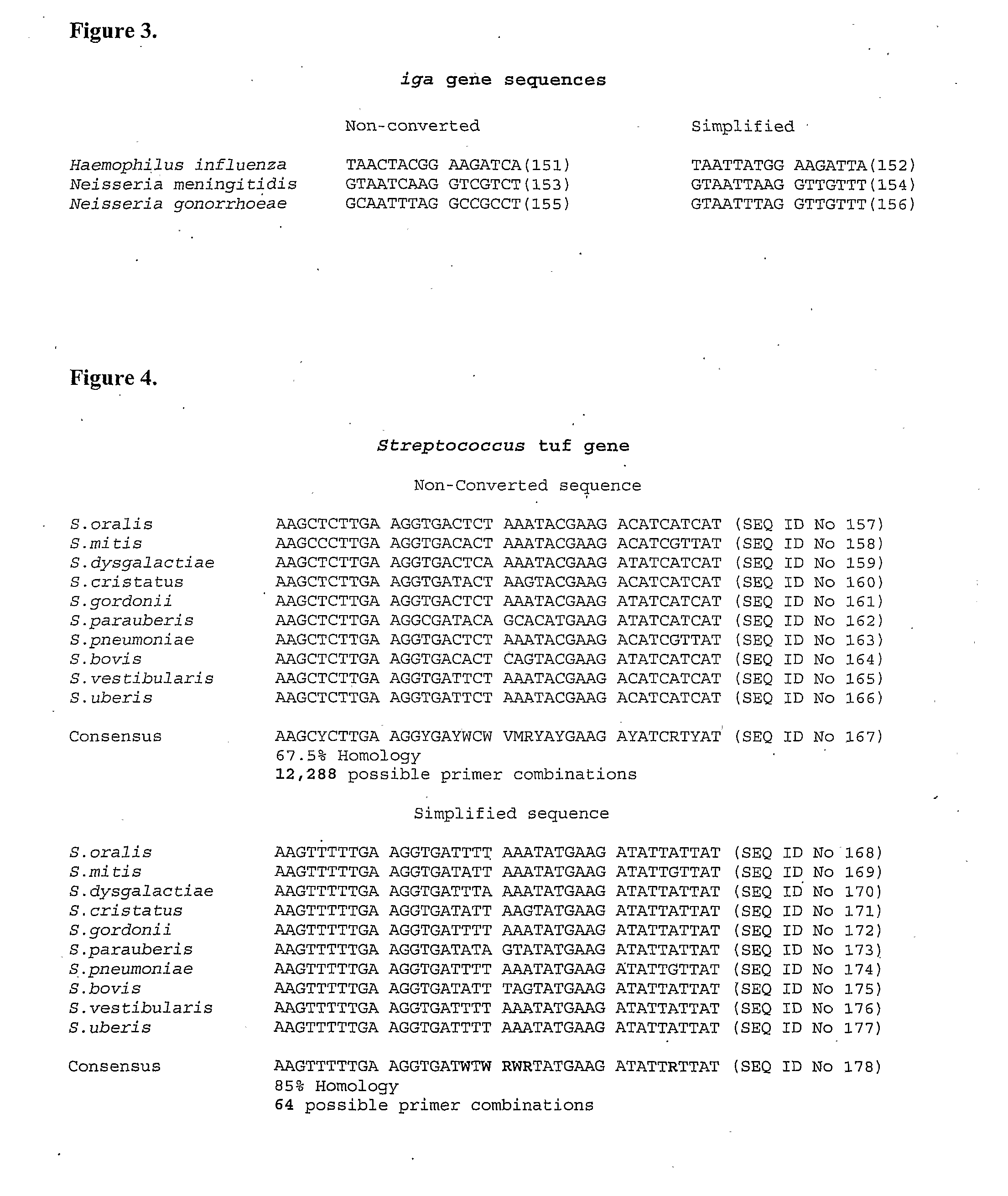
Methods for simplifying microbial nucleic acids by chemical modification of cytosines
ActiveUS20090042732A1High similaritySimplify the differenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismCytosine
A method for simplification of a microbial genome or microbial nucleic acid comprising treating microbial genome or nucleic acid with an agent that modifies cytosine to form derivative microbial nucleic acid and amplifying the derivative microbial nucleic acid to produce a simplified form of the microbial genome or nucleic acid.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Kit and extraction method for quickly extracting microbial genome DNA from animal fecal microorganisms
InactiveCN104531680AReduce extraction timeSimplify the experimental stepsDNA preparationDecompositionAnimal feces
The invention discloses a kit and an extraction method for quickly extracting microbial genome DNA from animal fecal microorganisms. The extraction method for extracting microbial genome DNA from animal fecal microorganisms comprises the following five steps: pre-treatment of feces; splitting decomposition of microbial cells in feces; dissociation of DNA and abstraction of impure proteins; DNA adsorption by a DNA adsorption column and removal of impurities; and elution of DNA. The kit disclosed by the invention is capable of absorbing the genome DNA by a silicone mold adsorption column and removing impurities such as proteins by using special deproteinization liquid and wash liquid. Compared with conventional extraction methods for extracting microbial genome DNA from animal fecal microorganisms, the microbial genome DNA from animal fecal microorganisms can be extracted within 4 hours, so that not only is a lot of extraction time shortened, but also the experimental steps are simplified. Therefore, the microbial genome DNA from animal fecal microorganisms can be effectively, quickly and economically extracted.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Microbial genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) indirect extraction method for evaluating diversity of animal intestinal microflora
The invention relates to a microbial genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) indirect extraction method for evaluating diversity of animal intestinal microflora. Before cell lysis, the method performs pretreatment on a sample and separates microbial cells from the excrement sample to avoid the problems that pollutants are difficult to remove and the DNA recovery rate is low in a purification step. According to the invention, phenol and chloroform are not used in the extraction process, thus harm to the physical health of experimenters is reduced. The OD260 / OD230 and OD260 / OD280 of the extracted intestinal microorganism DNA are approximate to standard values, and the intestinal microorganism DNA can be directly applied to molecular operation to evaluate the diversity of animal intestinal microflora.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods for simplifying microbial nucleic acids by chemical modification of cytosines
ActiveUS7833942B2High similaritySimplify the differenceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMicrobial GenomesCytosine
A method for simplification of a microbial genome or microbial nucleic acid comprising treating microbial genome or nucleic acid with an agent that modifies cytosine to form derivative microbial nucleic acid and amplifying the derivative microbial nucleic acid to produce a simplified form of the microbial genome or nucleic acid.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Method for designing species specific primer for detecting species with known genome information in microbial community and method for measuring bacterium content
InactiveCN106222249AAccurate understandingLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInformation analysisFermentation
The invention relates to a method for designing a species specific primer for detecting the species with known genome information in a microbial community and a method for measuring the bacterium content. The designing method is based on a species specific primer of some species with known genome information in a microbial community. The method comprises the following steps: cloning and sequencing a nearly full-length ribosomal gene library; carrying out biological information analysis (BLAST, etc.) to determine the species in a bacterial community and relative abundance of the species; inquiring the species with known genome sequences; based on a PRIMER-BLAST tool, designing a species specific primer, and detecting the specificity of the primer. The bacterium content is measured through a QPCR method: the provided species specific primer is used to quantitatively measure the content of corresponding species in a microbial community. The provided method for measuring the content of known microbes in a microbial community can trace and inspect the number change of some important microbial species in an important biological process (liquor fermentation, for example) in the species level. The provided method can measure the copy number of non-ribosomal gene sequence of species specificity in some microbial genome and cannot obtain the specific number of cells of species in a microbial community.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
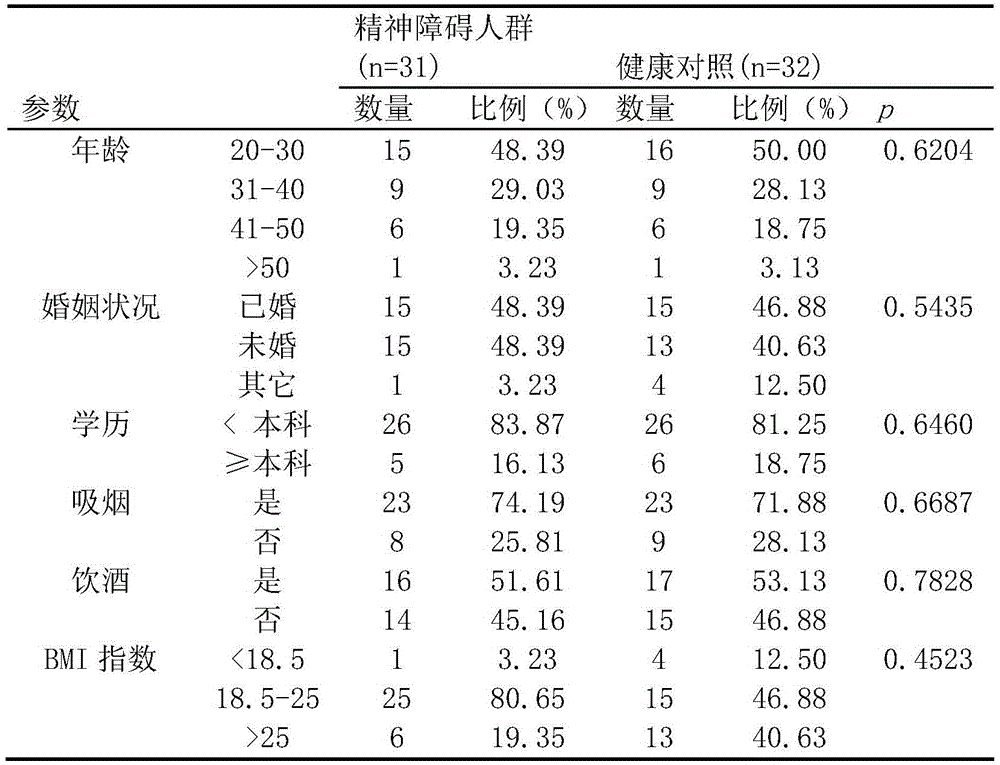
Mental disorder biomarker and application thereof
ActiveCN105543369AMonitoring the Effects of InterventionsMaster recoveryNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementFecesGut flora
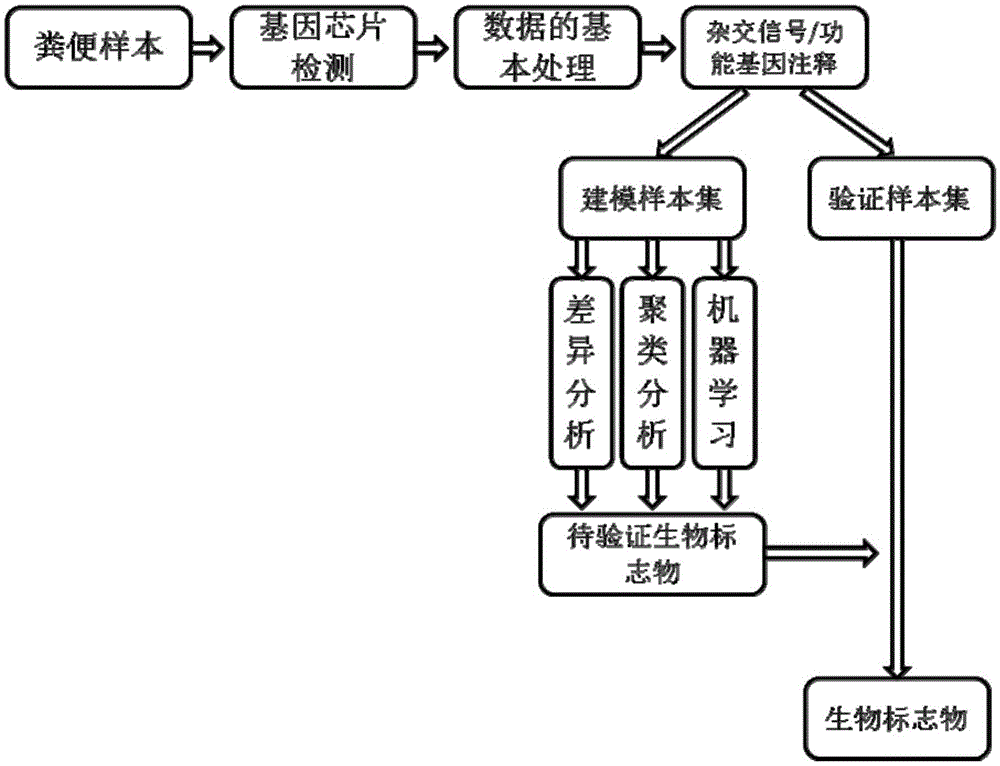
The invention discloses a mental disorder biomarker and application thereof. Microorganism gene chip hybridization research is conducted on intestinal flora microbial genomes in fecal samples of a mental disorder group and fecal samples of a healthy control group to describe characteristics of fecal microflorae and functional genes. By means of difference testing, discriminant analysis and machine learning, fifteen functional genes are recognized finally and can serve as biomarkers to highly accurately distinguish the mental disorder group. The biomarker is selected from at least ten genes in the fifteen functional genes. The fifteen functional genes have obvious differences in mental disorder people and the healthy people. The invention further discloses a drug which is capable of changing the number or expression of genes and is used for treating mental disorder, a method for producing or screening the drug for treating mental disorder and a kit for detecting mental disorder.
Owner:金锋 +1
Method and device for microbiological analysis of host sample
ActiveCN111009286AFast and accurate analysisFast and accurate detectionProteomicsGenomicsMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of microbiological detection, in particular to a method and a device for microbiological analysis of a host sample. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing first filtering processing on a sequencing data set from a host sample by adopting a host genome database so as to remove sequencing data which can be compared with the host genome database from the sequencing data set; (2) performing second filtering processing on the sequencing data set by adopting a homologous database so as to remove the sequencing data which can be compared with the homologous database from the sequencing data set; and (3) comparing the sequencing data set subjected to the first filtering treatment and the second filtering treatment with a microbial genome database so as to determine microbial sequencing data from the microorganisms in the sequencing data set. By applying the method and the device provided by the invention, rapid and accurate analysis and detection of microorganisms in a host can be realized.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +1
Method for constructing environmental microbial genome draft
ActiveCN105420375AExcellent analysis resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
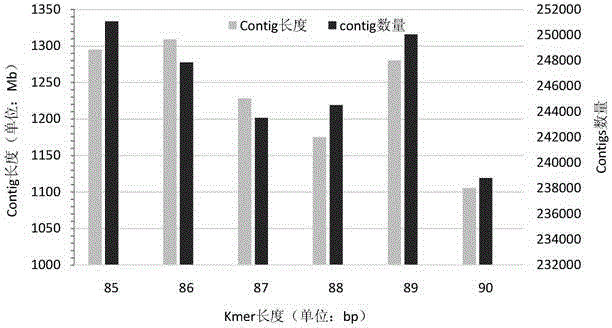
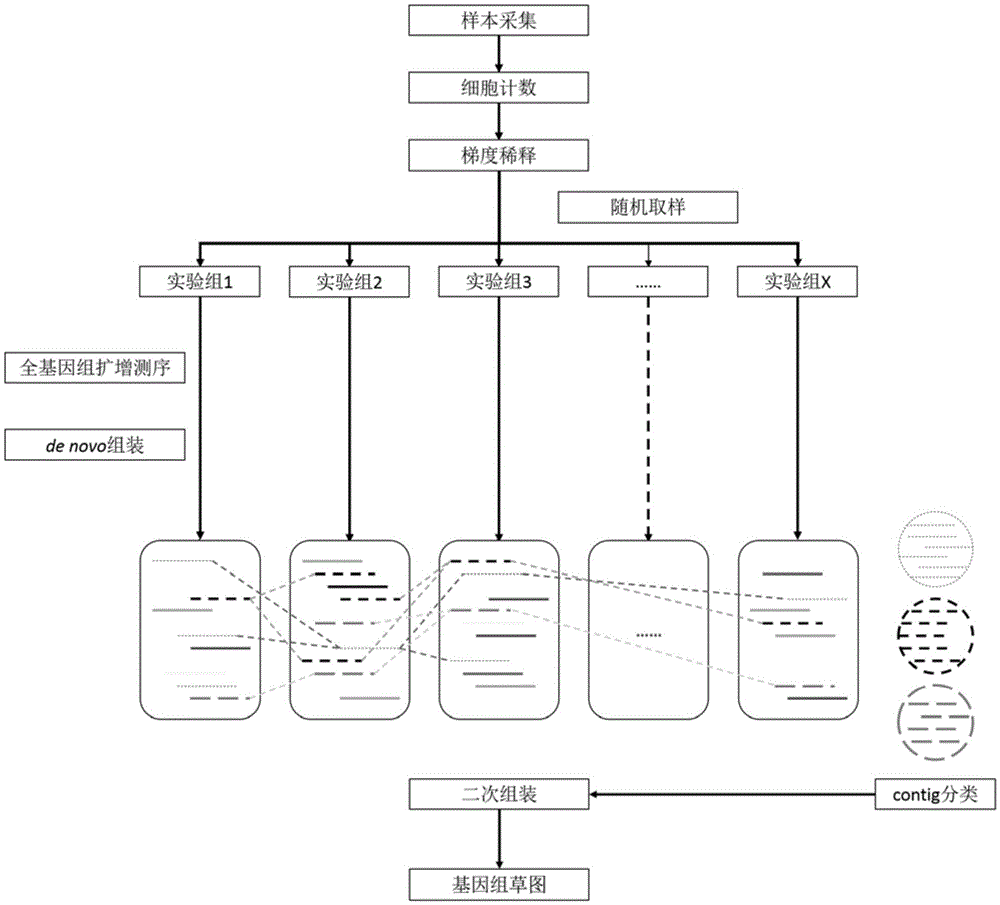
The invention discloses a method for constructing an environmental microbial genome draft based on micro-cell whole genome sequencing. The method comprises the steps of conducting nucleic acid isolation and amplification on multiple environmental microorganism micro metagenome samples, constructing a high-pass sequencing library, conducting filtration, de novo assembly and open reading frame prediction on sequencing data, conducting sequence classification with the algorithm based on a Hidden Markov model, and obtaining the microbial genome draft. According to the method, the number of times of parallel tests is adjusted according to the complexity of an environment sample microflora, so that the optimal analysis result is obtained. The method can be applied to research of microflorae of various environments such as soil, air, water and human bodies.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for simultaneously cloning multiple exogenous genes to microbial genome
ActiveCN104404077AFast expressionEfficient expressionFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously cloning multiple exogenous genes to a microbial genome. The method comprises steps of introducing a plurality of exogenous genes to a plurality of bidirectional gene expression carriers, and then simultaneously introducing the plurality of bidirectional gene expression carriers into a host microbe. Each bidirectional gene expression carrier comprises a bidirectional terminator and a bidirectional promoter. Except for the first bidirectional gene expression carrier and the last bidirectional gene expression carrier, the 3' ends of the bidirectional terminators of other bidirectional gene expression carriers and the 5' ends of the bidirectional terminators of the next bidirectional gene expression carriers have the same homologous arm. The 5' end of the bidirectional terminator of the first bidirectional gene expression carrier and the 3' end of the bidirectional terminator of the last bidirectional gene expression carrier can both carry out homologous recombination with the genomes of a host microbe. Through the provided method, established is a novel technology that can organically integrate the whole gene expression process such as expression design, clone design, host cell modification, and the like.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
High-throughput mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification method and application thereof
ActiveCN106636433AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseRibosomal DNA
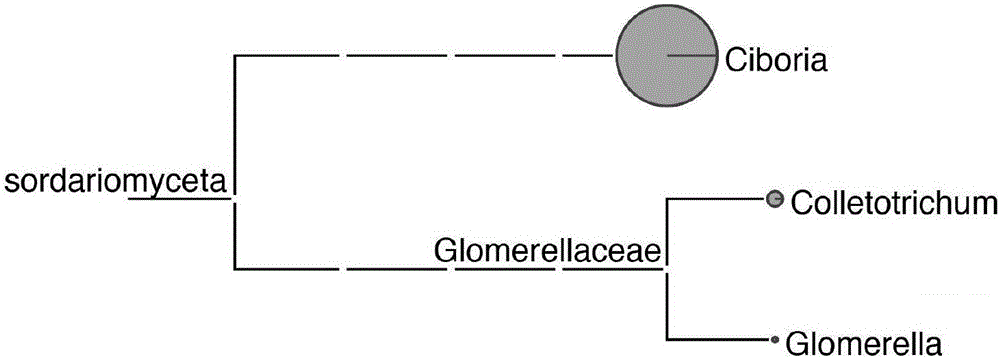
The invention discloses a high-throughput mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification method. The method comprises the following steps that diseased mulberries are collected; the total DNA of the diseased mulberries is extracted; an Illumina DNA library is created; Illumina high-throughput sequencing is carried out; a mulberry genome sequence in sequencing data is removed; microbial genome sequences are assembled; complete ribosomal DNA sequences are assembled; microbial ribosomal DNA sequences are screened and labeled; the ribosomal DNA sequences are comparatively analyzed to classify species, and thereby the mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification are fulfilled. A result shows that three species of fungi are identified in total when the method disclosed by the invention is applied to carry out the identification of pathogenic bacteria of popcorn disease and species classification, wherein the Ciboria pathogenic bacteria has the highest relative abundance, hereby the pathogenic Ciboria shiraiana is determined as Ciboria, and according to a comparison result, the pathogenic Ciboria shiraiana is determined as Ciboria carunculoides. Most of the species are phytopathogenic bacteria, and can lead to symptoms, such as mummification and swelling, appearing on fruits and seeds of plants, which are identical with the symptoms of the popcorn disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting enteric microbial genome DNA
InactiveCN108179145AReduce usageHigh purity of total DNADNA preparationFecesIntestinal microorganisms
The invention discloses a method for extracting enteric microbial genome DNA. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) coprophilous fungi sample collection; (2) thallus acquisition;and (3) coprophilous fungi genome DNA extraction and purification. According to the method disclosed by the invention, usage of an organic solvent is reduced, the cost is low, and the extracted microbial total DNA has high purity; guanidinium isothiocyanate is capable of rapidly breaking cells and inhibiting ribozyme released from the cells, and the obtained DNA has high quality; enriched DNA population information can be obtained, the diversity and community composition of enteric microorganisms can be comprehensively reflected, the operating steps are less, the stability is excellent, and the method is a practical and reliable fecal microorganism DNA extraction method and can be widely applied to study on intestinal microecology.
Owner:北京凡知医学科技有限公司
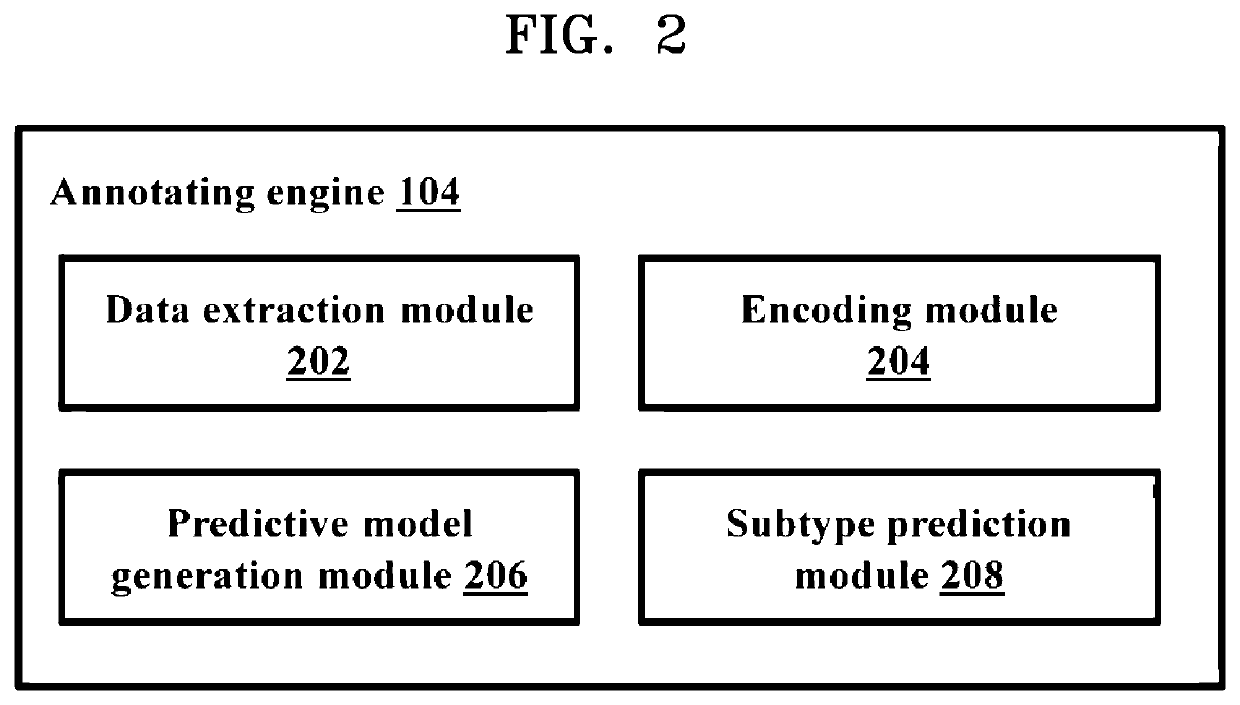
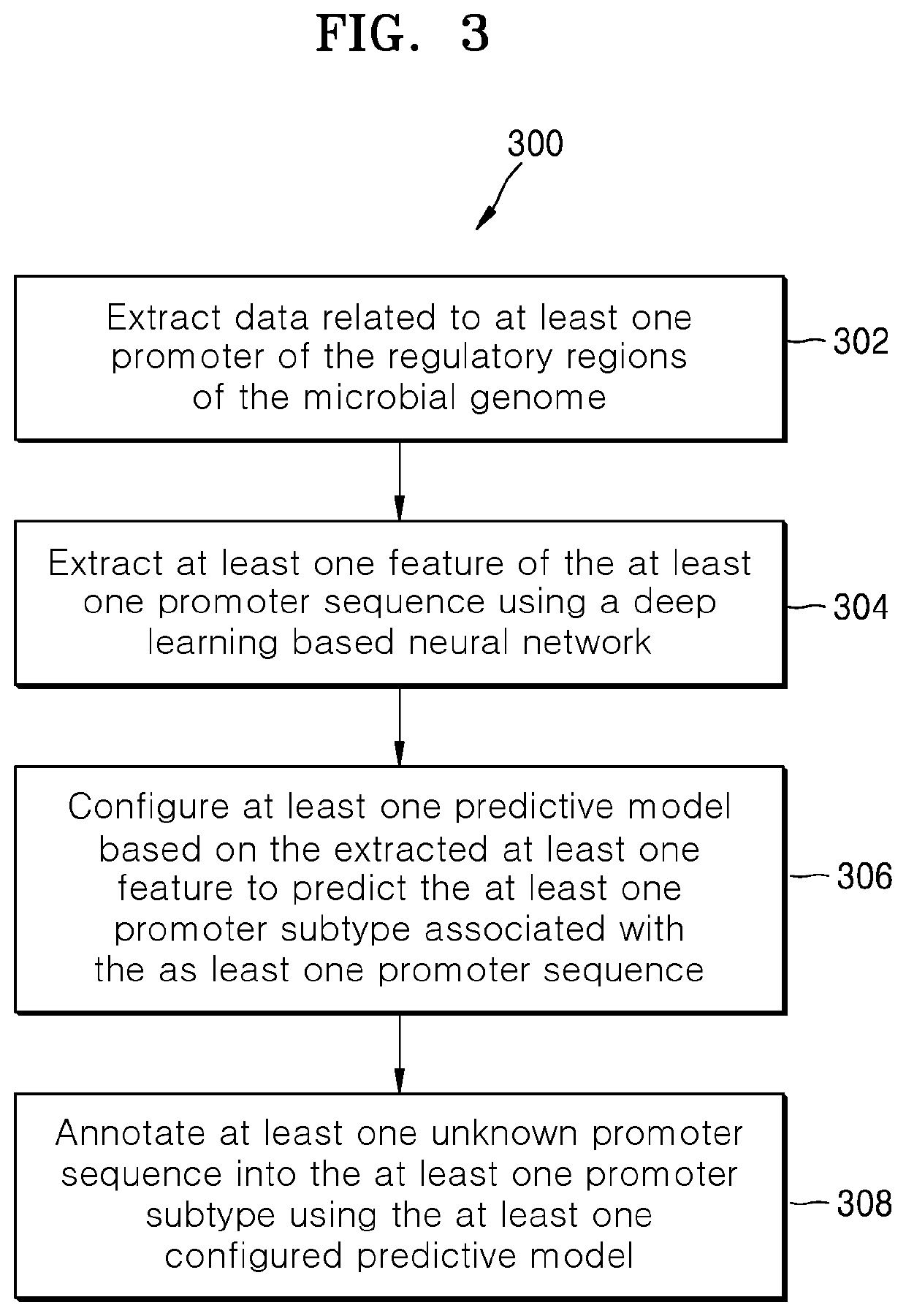
Methods and systems for annotating regulatory regions of a microbial genome
Methods and systems for annotating regulatory regions of a microbial genome. A method disclosed herein includes extracting data related to at least one promoter of the regulatory regions of the microbial genome, wherein the data includes at least one promoter sequence and data available for at least one promoter subtype. Based on extracted at least one feature of the at least one promoter sequence, the method further includes configuring at least one predictive model using the deep learning based neural network to predict the at least one promoter subtype associated with the at least one promoter sequence. The method further includes annotating at least one unknown promoter sequence into the at least one promoter subtype using the at least one configured predictive model.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-similarity microorganism identifying and classifying method
ActiveCN107577923AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsMicrobial GenomesClassification methods
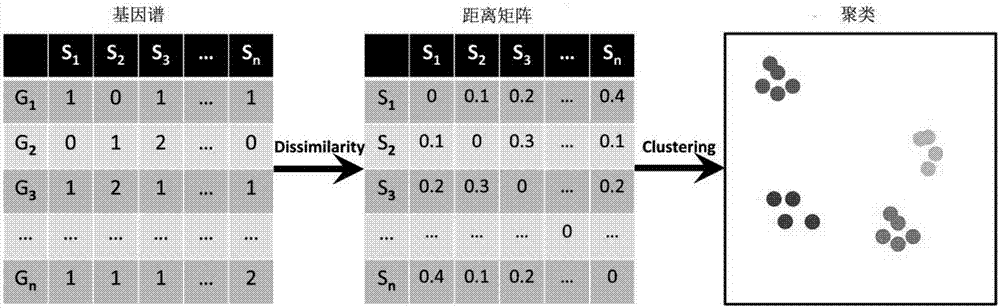
The invention discloses a method for identifying and classifying highly similar microorganisms, which comprises: (1) using eggNOG database to compare the protein sequences encoded by the microbial genomes, assigning an eggNOG gene ID to each microbial genome, and generating an eggNOG database based on eggNOG database (2) Calculate the gene content dissimilarity between different microorganisms to be tested in the gene spectrum to obtain a dissimilarity matrix; (3) Perform cluster analysis on the matrix, and cluster microorganisms with similar gene content as A cluster, judged as the same type of microorganisms, completes the identification and classification of microorganisms. Aiming at highly similar microorganisms, the method of the present invention creatively proposes that the main driving factor for differences at the level of microorganisms is the gain and loss of genes, rather than the nucleic acid site mutation that is often considered by traditional methods. The invention has extremely high accuracy for the identification and classification of highly similar microorganisms, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:广东美格基因科技有限公司
Method for simultaneously transferring multiple genes into microbial genome
InactiveCN102719481AAvoid multiple conversionsAvoid the hassle of vector constructionFungiStable introduction of DNAMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously transferring multiple genes into microbial genome. The invention provides a method for preparing recombinant microorganism expressing multiple exogenous genes; the method comprises the following steps of: transferring expression cassettes of all genes into the host microorganism to obtain the recombinant microorganism combining multiple exogenous genes into the genome and expressing the multiple exogenous genes, wherein the 5' end of the expression cassette of the first gene has a homologous arm A, the 3' end of the expression cassette of the last gene has a homologous arm B, and the 3' tail end of the expression cassette of each gene and the 5' tail end of the expression cassette of the next gene have the same homologous arm; and the homologous arm A and the homologous arm B can be subjected to homologous recombination with the genome of the host microorganism. Through the method, multiple genes contained in a target metabolic pathway can be transferred into the host strain at one step and arranged according to a set sequence, the required engineering strain is directly obtained, and the troubles caused by multiple times of transformation and vector construction are avoided.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection method of symbiotic bacteria in sponge cell based on quantum dot fluorescence in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN101974626AEasy accessAvoid interference from autofluorescenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexSymbiotic bacteria
The invention provides a detection method of symbiotic bacteria in sponge cells based on quantum dot fluorescence in-situ hybridization, which relates to the technical field of bacterial detection. The detection method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a sponge single cell; according to a classical fluorescence in-situ hybridization method, adopting an oligonucleotide probe marked by biotin to hybridize microbial genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in the sponge single cell; finally, adopting a quantum dot marked by streptavidin to carry out incubation treatment; and obtaining blue sponge cells in a fluorescence microscope with exciting light as an ultraviolet band and red bacteria. The invention combines a mechanical method and a chemical method, can quickly obtain sponge cells, avoids the autofluorescence interference of the sponge cells and successfully detects the bacteria in the sponge cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
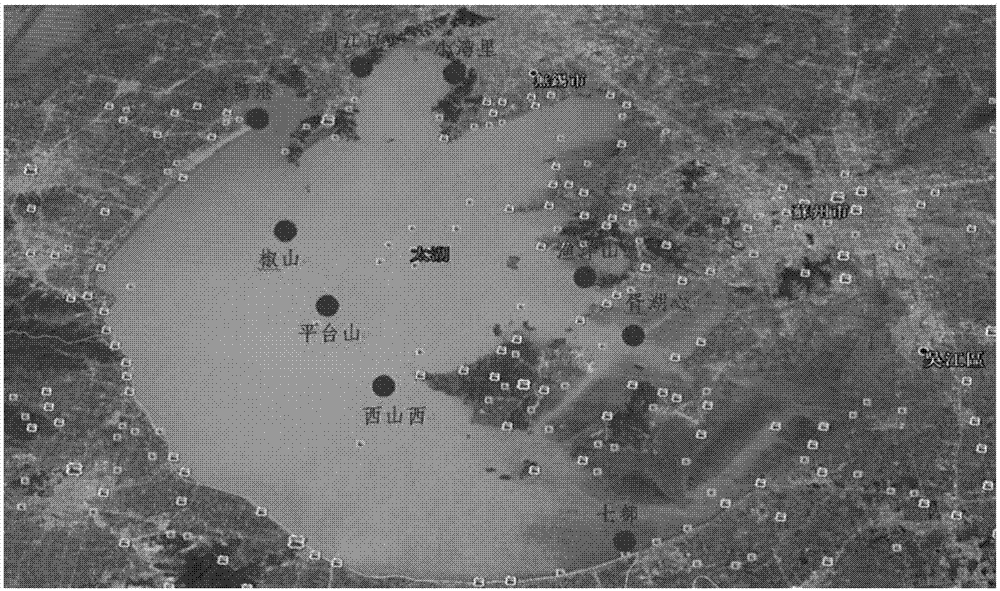
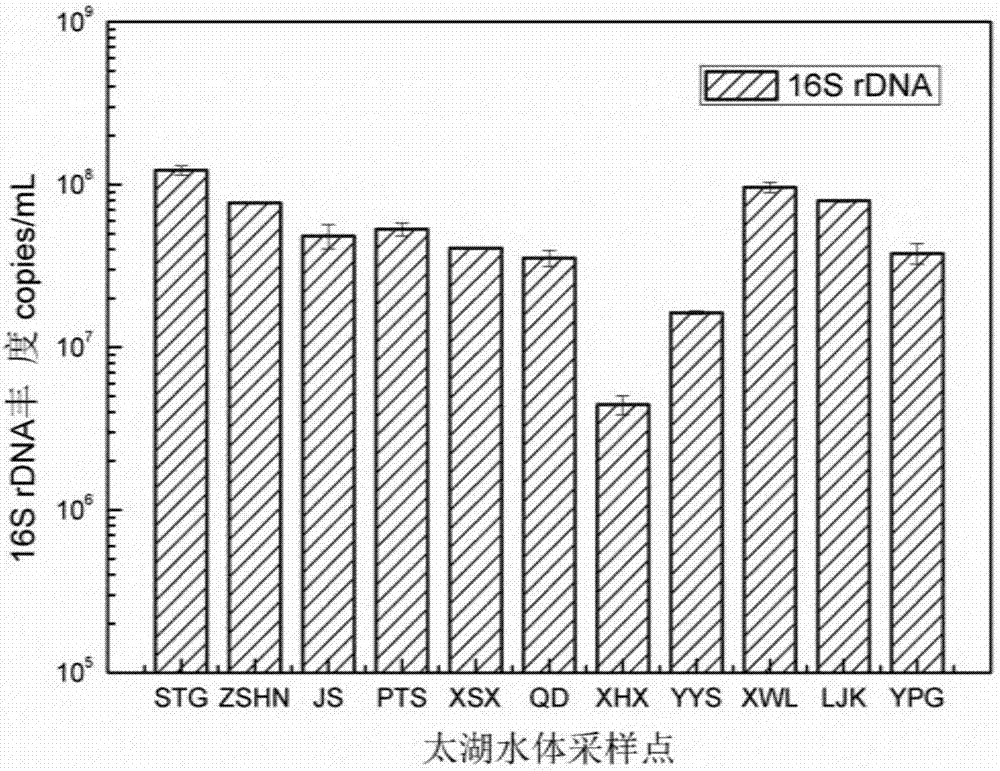
Evaluating method of bacterioplankton community in Taihu Lake water body
InactiveCN106929578AAuxiliary analysis structureAuxiliary analysis of the corresponding abundanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceBacterioplankton
The invention provides an evaluating method of a bacterioplankton community in a Taihu Lake water body. The evaluating method comprises the steps of carrying out microbial genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) extraction on water samples at 11 sampling points of a Taihu Lake area, quantitatively analyzing 16S rDNA (Ribosomal Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) abundance in samples through carrying out common PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and real-time fluorescence quantification PCR on the extracted DNAs; purifying products subjected to rRNA (Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid) gene PCR amplification of 16S, sequencing the purified products by adopting a second generation of high throughput sequencing technology, and after carrying out data processing and analysis on a sequencing result, analyzing the bacterioplankton community in the water body. The method genetically reveals a community structure of cyanobacterial bloom and the interaction with the environment, and predicates the phenomenon that an environment change may cause the change of the community structure; a second generation of high throughput sequencing Miseq platform is adopted for determining a microbial community structure in the Taihu Lake water body and bottom mud, so that the analysis of the community structure and the corresponding abundance of microorganisms in the Taihu Lake water body is more symmetrically assisted.
Owner:CHANGZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENT
Kit for rapidly extracting genomes of animal excrement by virtue of CTAB method
InactiveCN104975004AQuick extractionEfficient extractionDNA preparationMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention provides a kit for rapidly extracting genomes of animal excrement by virtue of a CTAB method. The kit is utilized for carrying out pretreating the excrement, splitting microbial cells in the excrement, dissociating DNA, abstracting impurity protein, adsorbing DNA by virtue of a DNA adsorption column, removing impurities and eluting DNA; after cells are disrupted, protein impurities are removed by virtue of a CTAB solution, meanwhile, genome DNA is adsorbed by virtue of a silicone mold adsorption column, and finally, the residual protein impurities are eluted by virtue of special deproteinization liquid and rinsing liquid. A conventional animal excrement microbial genome extraction method needs to be finished within 14 hours or longer, and the genomes are easily degraded due to the long-playing operation. Compared with the conventional animal excrement microbial genome extraction method, the kit has the advantages that the animal excrement genomes can be extracted within only 4 hours, so that plenty of extraction time is saved, meanwhile, experimental steps are simplified, and the microbial genomes of the animal excrement can be relatively effectively, rapidly and economically extracted.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Microbial genome database construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112992277ALow chance of false positivesImprove compatibilitySequence analysisInstrumentsMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention provides a microbial genome database construction method and application thereof. According to the invention, the construction method of the microbial genome database comprises the steps: constructing the database in a manner of labeling after genome breaking, labelling consensus sequences and specific sequences of multiple species, and constructing a comparison score matrix among the specific sequences of the species, so a sequence source is quickly and accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING SIMCERE MEDICAL LAB CO LTD +2
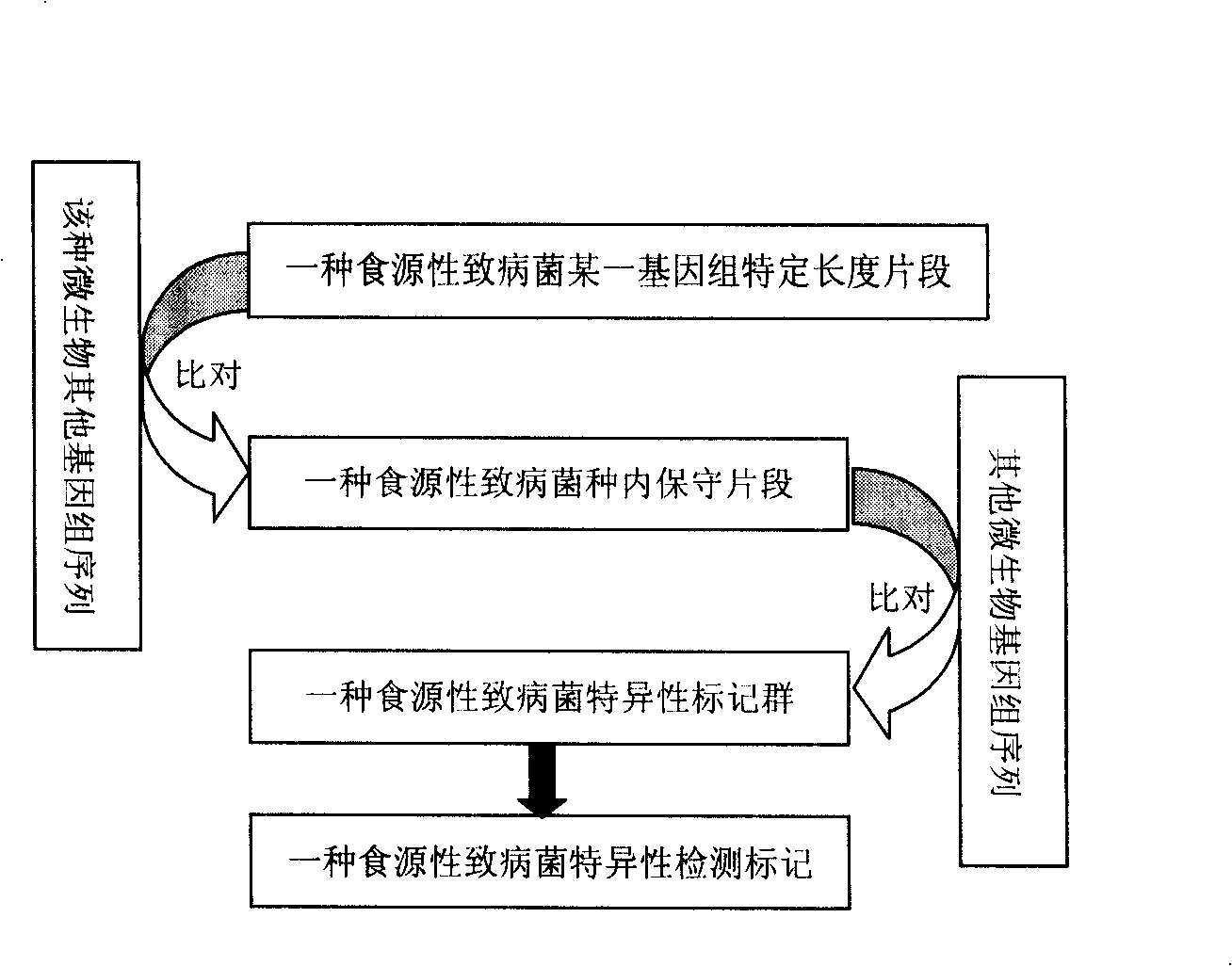
Food-borne pathogen numerator detection mark establishing method
InactiveCN101343662AStrong specificitySave moneyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicroorganismMicrobial Genomes
The invention relates to a building method for a food borne pathogen molecule detecting marker. The method adopts the following steps: all genome sequences of a food borne pathogen are collected; one genome selected from the genome sequences is divided into segments with a length of 500 bp to 1000 bp, each divided segment is compared with other genome sequences of the food borne pathogen, the divided segments with the similarity above 98 percent are retained, and conservative sequence segments of the food borne pathogen can be obtained; when one segment in the conservative sequence segments is compared with other microbial genome sequences, segments in conservative sequence segments which are identical with other microbial genome sequences are eliminated, so the retained sequence segments serve as a specific marker group for the food borne pathogen; and sieving is performed on the data information in the specific marker group for obtaining the molecule detecting marker of the food borne pathogen. The invention provides the molecule detecting and labeling method by using the combination of Bioinformatics and microbial Genomics for exploring the food borne pathogen for the first time, the obtained detecting marker has a higher specificity in comparison with the existing molecule detecting marker, and experiments of molecular biology such as molecular cloning, gene sequence testing and PCR are not required to be conducted, so the financial resources are saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Kit for rapidly extracting sludge microbial genome DNA and extracting method
The invention discloses a kit for rapidly extracting sludge microbial genome DNA and an extracting method. The sludge microbial genome DNA is extracted by the following steps: breaking sludge microbial cells, removing impurity proteins, adsorbing DNA by using a DNA adsorption column, and removing impurities and eluting the DNA. The conventional method for extracting the sludge microbial genome DNA often uses a method for precipitating the genome by using anhydrous ethanol, the operating time is above 12 hours, and the genome DNA is easily degraded. The kit mainly uses a silicone mould adsorption column for absorbing the genome DNA, and then uses a specific protein-removing solution and a specific bleaching solution for removing the proteins and other impurities; the kit can extract the sludge microbial genome DNA within 4 hours, so that the kit is more convenient and quicker.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
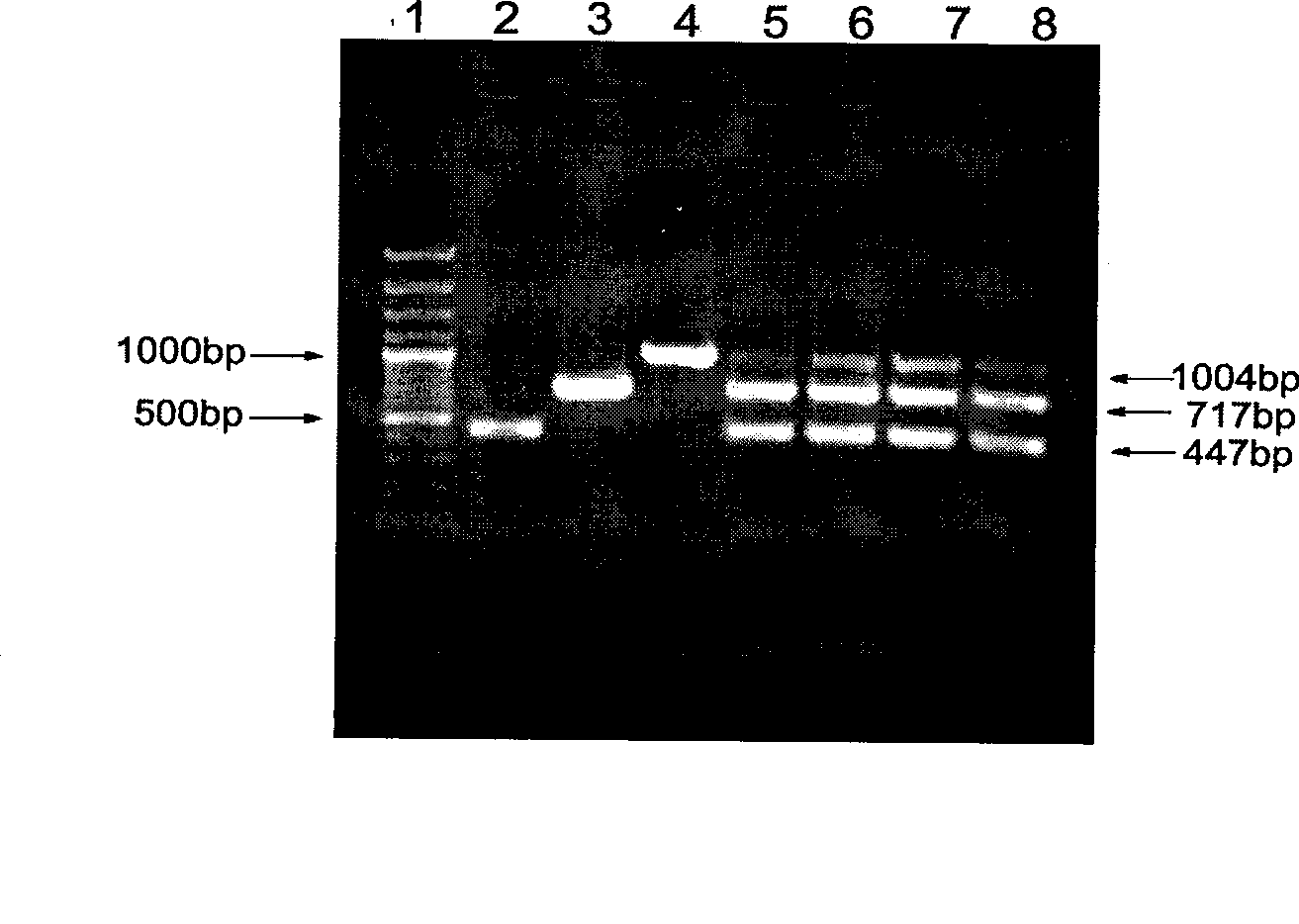
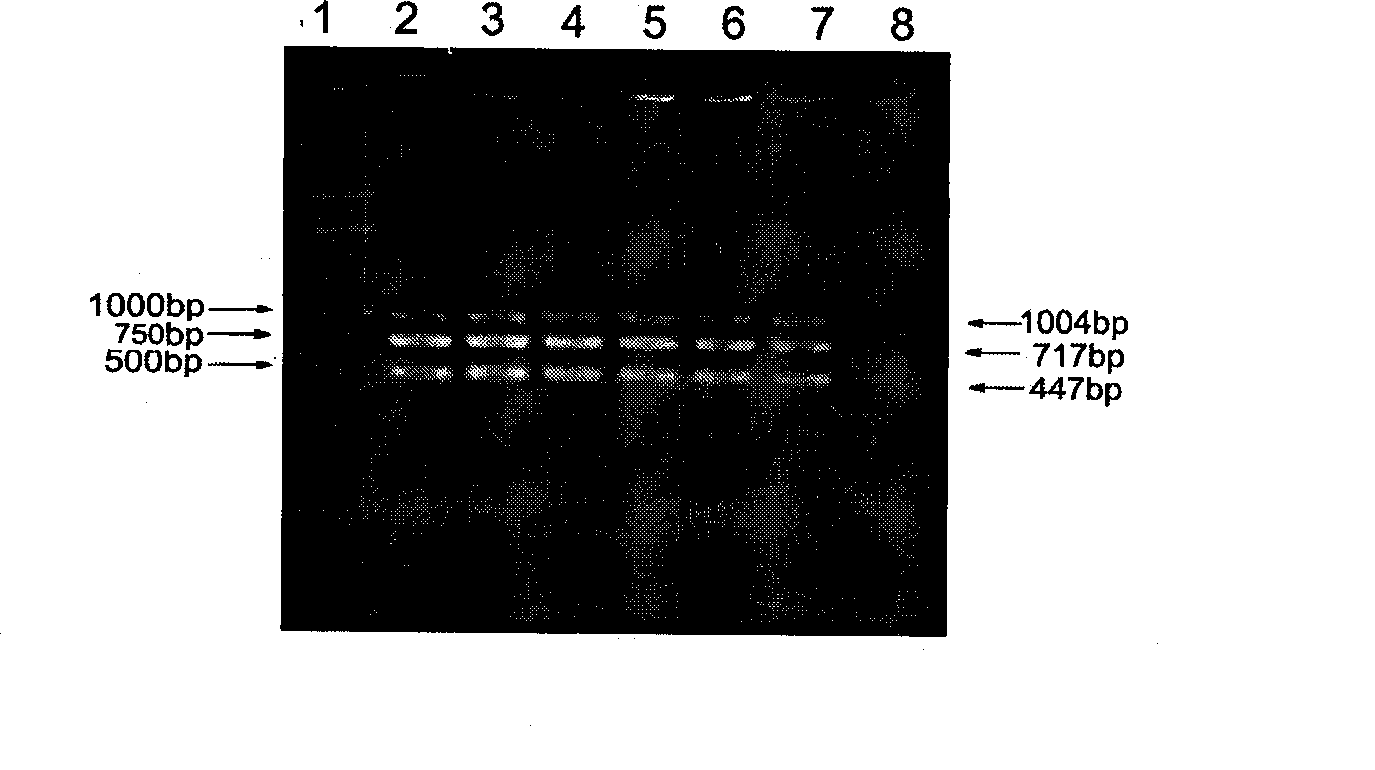
Method for detecting Francisella tularensis using multiple PCR technology
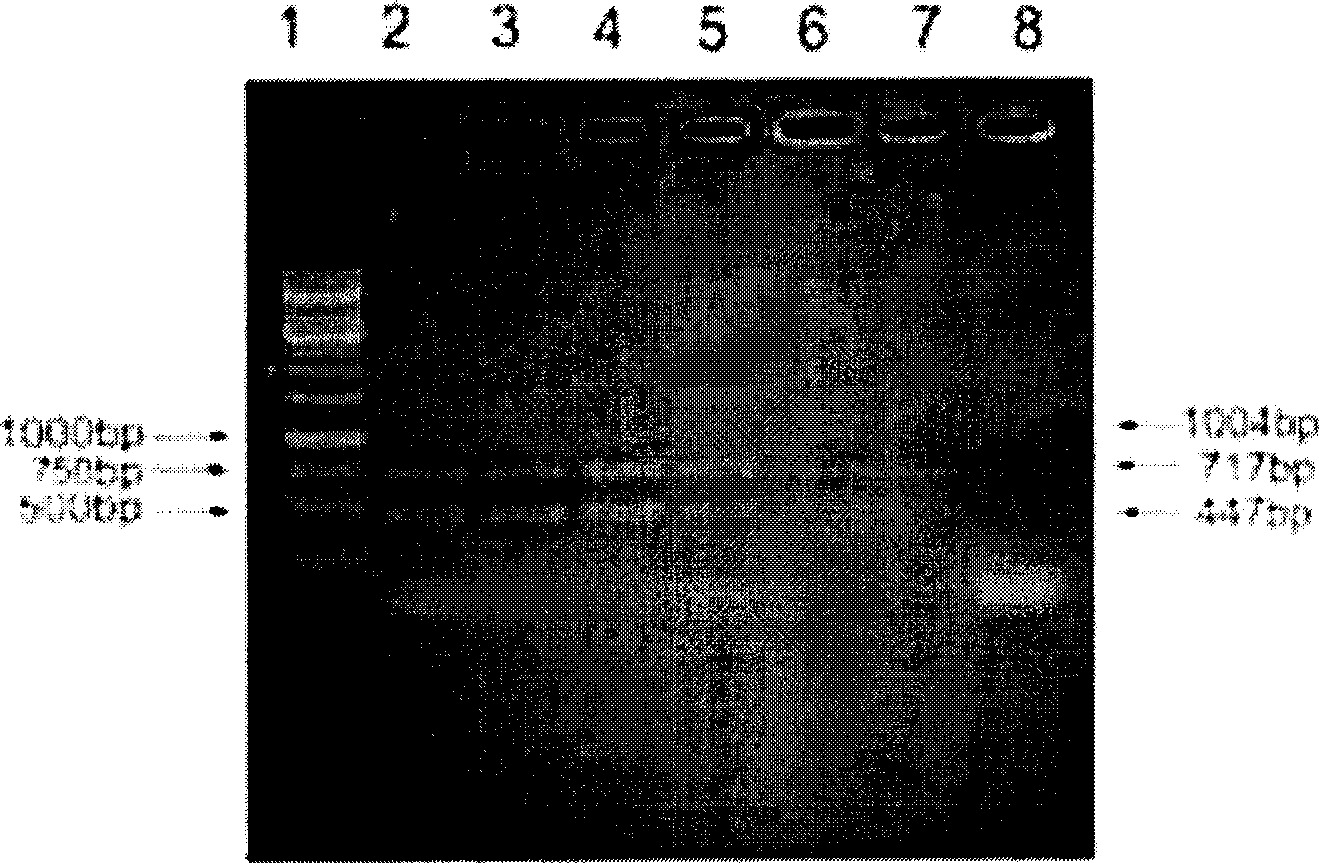
InactiveCN101372713ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisComplete sequence
The invention relates to a method of detecting Francisella tularensis by a multiple PCR technique, belonging to the technical field of detecting biological agent. The invention comprises steps of: using the related genes lpxF, lpxE and flmK of the endotoxin of the Francisella tularensis as the specificity targets, carrying out comparison by complete sequence Blastp of NCBI microbial genome to determine the specificities of the three genes, designing the related primer and conducting detection by the multiple PCR technique; after three strips, which are 447bp,717bp and 1004bp in turn, appear in the electrophoresis detection, judging the strips to be masculine according to the appearance of three specificity strips, otherwise, judging the strips to be feminine. The invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, easy promotion and application, short detecting cycle, high sensitivity, good specificity and higher detecting rate, wherein, with respect to 5 to 7 days needed to obtain the result by the traditional detecting method, the detecting cycle of the method, which is 3 hours, is much shorter than that of the traditional method, thus greatly improving the detecting efficiency; moreover, the detecting limit, which is 0.01ng / [mu]L and 5X10<5>cfu / mL, reaches or exceeds that of the traditional detecting method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
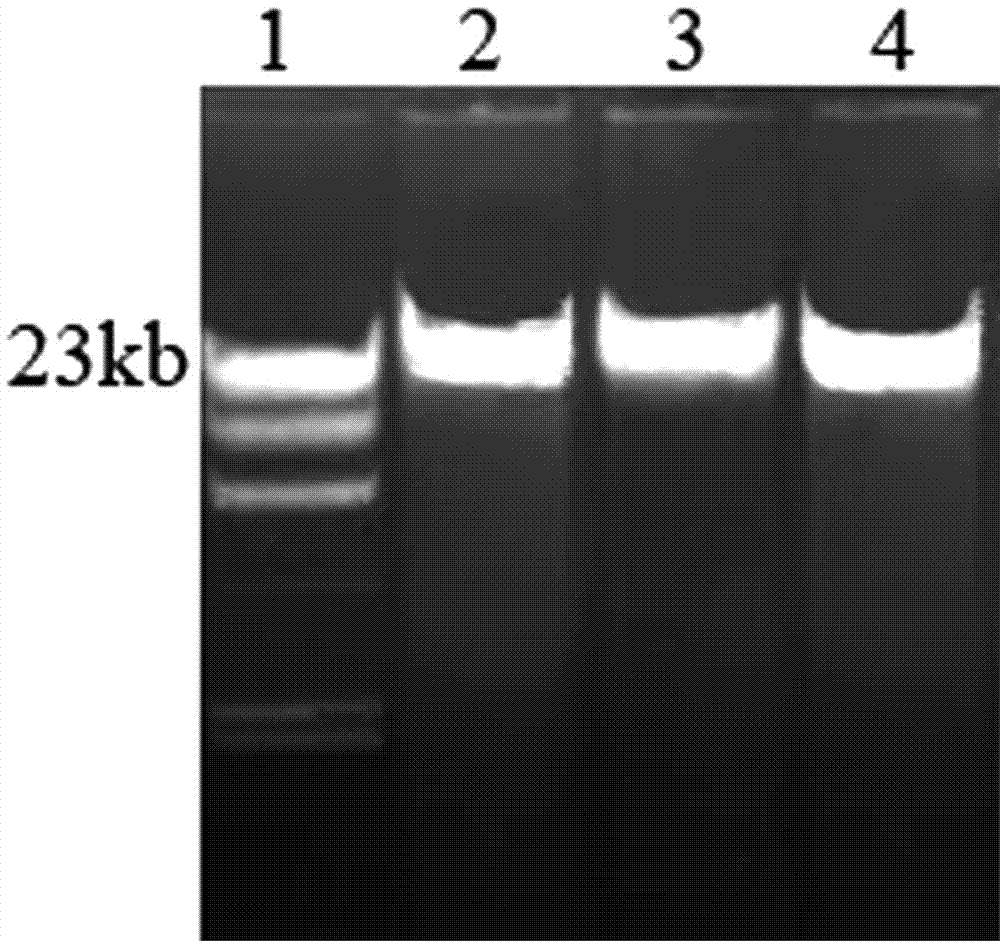
Method for rapidly extracting microbial genomes from soil sample
The invention discloses a method for rapidly extracting microbial genomes from a soil sample. The method comprises the steps that the soil sample is ground and smashed in liquid nitrogen, a genome extraction buffer solution is added to the smashed sample, and incubation is conducted for 30 min in a water bath of 37 DEG C; a protease K solution and an SDS solution are added, water bath is conducted for 30 min at 55 DEG C, centrifugation is conducted, and precipitation is discarded, supernatant is collected and extracted for the first time through phenol; centrifugation is conducted, supernatant is collected and extracted for the second time through mixed liquid of phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol, centrifugation is conducted, and supernatant is collected; ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol is added to the supernatant, total liquid is subjected to centrifugation and passes through a DNA recovery and purification column, high-speed centrifugation is conducted on the recovery and purification column again, drying is conducted, DNA eluant is added, and a microbial genome sample is obtained after centrifugation is conducted. The yield of the extracted microbial genomes can reach 80 micrograms / gram, the integrity of DNA is high, the size is 23 kb or above, pollution of RNA or protein does not exist, and OD260 / OD280 is close to the standard value.
Owner:ANHUI YUANDA MACHINERY MFG
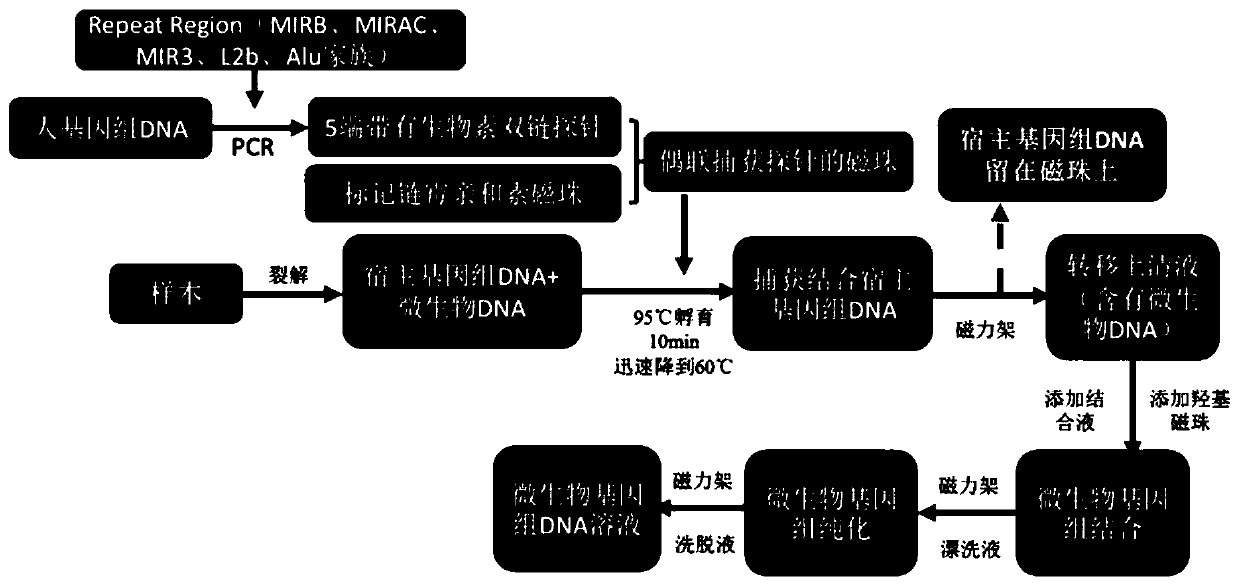
Microbial nucleic acid extraction method with host genome DNA removal function and kit
PendingCN111057747AIncrease concentrationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention discloses a microbial nucleic acid extraction method with a host genome DNA removal function and a kit. The invention provides a complete set of primer pairs, including one or more primer pairs. Each primer pair correspondingly amplifies one highly repetitive sequence in host genome DNA, wherein the highly repetitive sequence is selected from at least one gene in the following gene family: the gene family includes an MIR family gene and / or an ALu family gene. The microbial DNA extraction method with the host genome DNA removal function has the advantage that the microbial genomeDNA enrichment effect is stronger. According to the method, the host genome DNA is removed after the nucleic acid is released through lysis, then the microbial genome DNA is enriched for purificationand recovery, and meanwhile, viral nucleic acid in host cells can be enriched without changing the metagenome flora structure.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
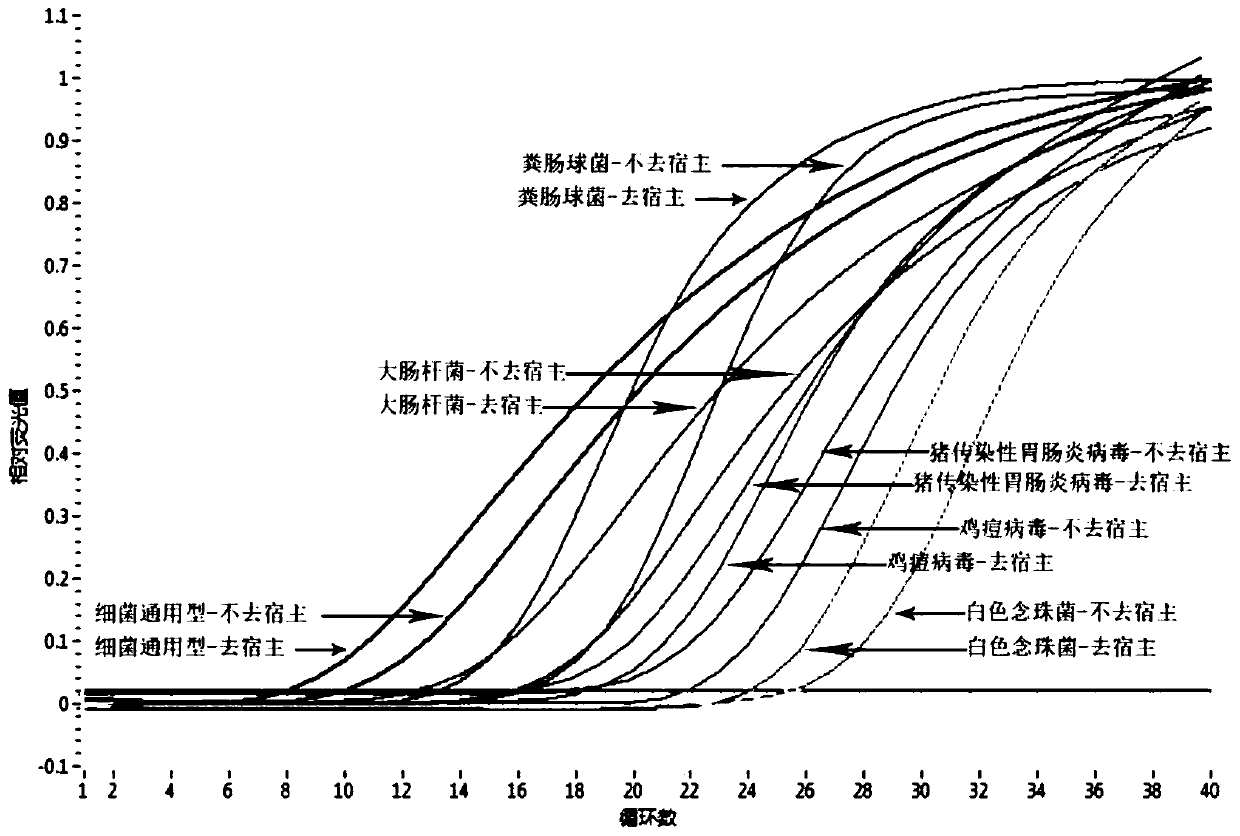
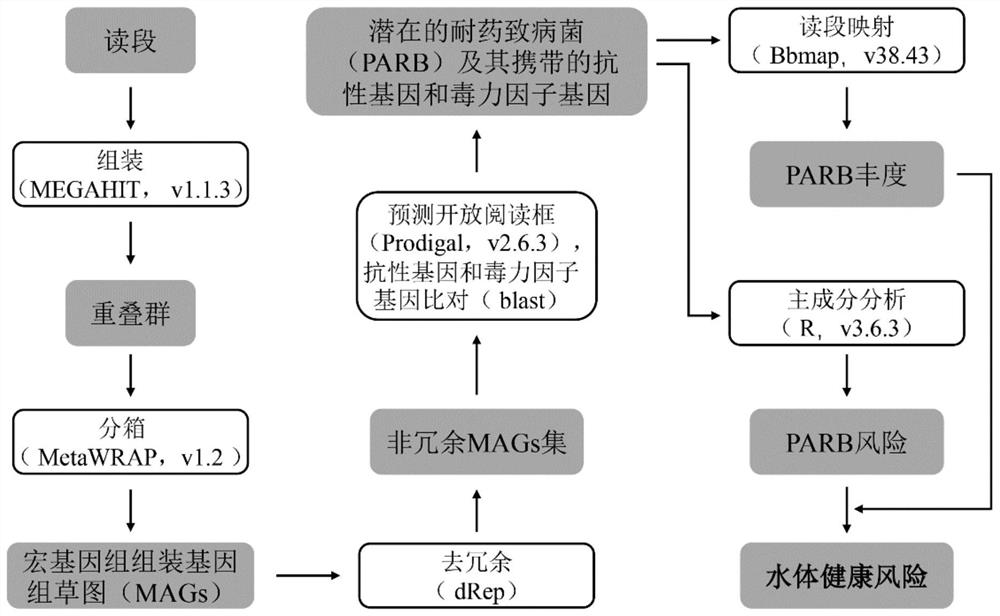
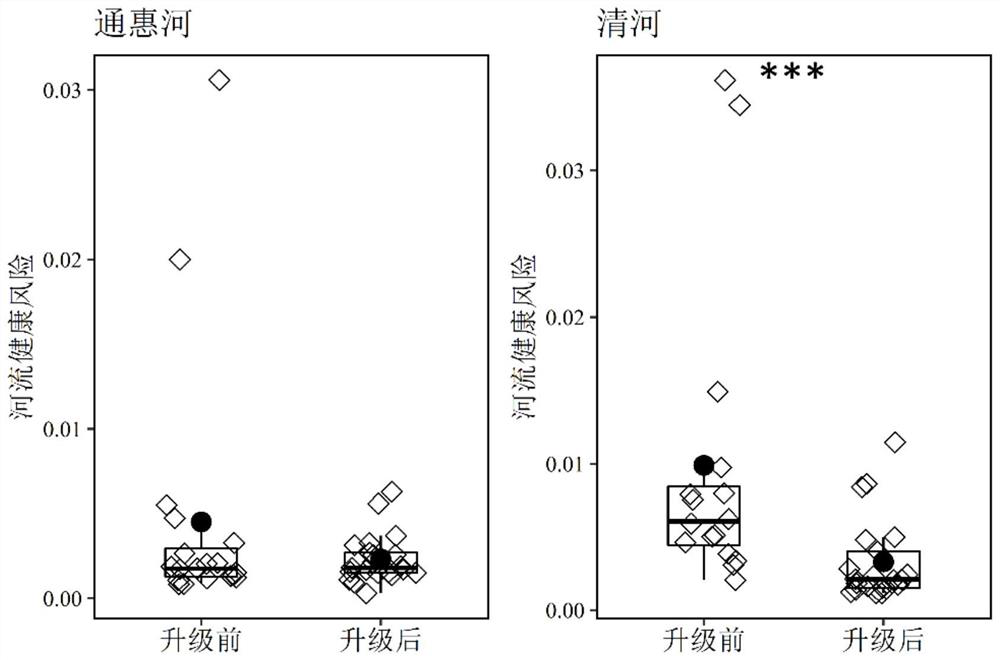
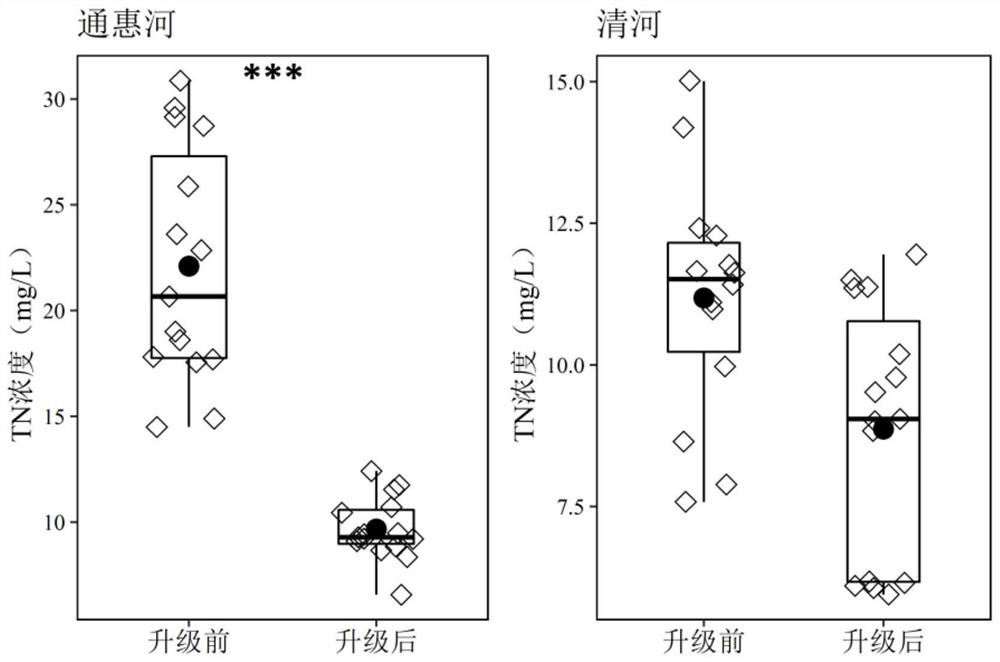
Method for evaluating water body health risk based on resistance gene and virulence factor gene
PendingCN111944914AAvoid time consumingAvoid conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic sequencingPure culture
The invention provides a method for evaluating water body health risk based on a resistance gene and a virulence factor gene. The method is based on metagenome sequencing analysis, and comprises the following steps of: obtaining a microbial genome sketch by assembling and binning sequencing data, identifying potential drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria (PARB) from the microbial genome sketch, evaluating the abundance, diversity and risk level of the potential PARB in the sample, and evaluating the quantity and types of ARGs and VFGs contained in the PARB, thereby determining the quantity and health risk level of the potential PARB in the environment. The method of the invention is based on metagenome sequencing, potential PARB can be recognized on genome level, a high degree of credibilityis shown, the limitations that a traditional pure culture method consumes time and is prone to being affected by culture conditions are avoided, and the method can be widely applied to water body health risk evaluation.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
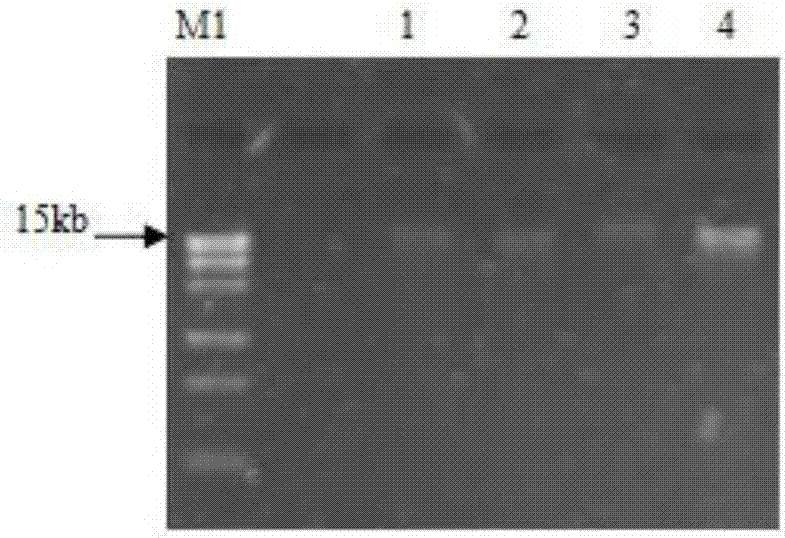
Method for constructing metagenomic Fosmid library of soil microorganisms in tropical rainforest
InactiveCN107475244AEasy to digEfficient use ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFosmidLow voltage
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a method for constructing a metagenomic Fosmid library of soil microorganisms in a tropical rainforest. The method comprises the following steps: washing by using cross-linked polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVPP), removing impurities, and then adopting a lysozyme-protease K-SDS-CTAB lysis method to extract and purify deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in large fragments of soil microbial genomes; carrying out agarose gel low-voltage electrophoresis detection and pulsed electrophoresis detection; carrying out tail end repairing on the metagenomic DNA, cutting off a marker and a small sample, and using ligase to enable a recycled product to be ligated with pCC1FOS of a Fosmid carrier; carrying out a ligation reaction within 2h; packing a ligation product with a lambda packaging extract, carrying out transfection by using an EPI300-T1R strain, coating an LB flat plate, which contains 12.5mu g / ml of chloramphenicol, with a product of the transfection, and culturing overnight at the temperature of 37 DEG C. The method provided by the invention reflects that in the extreme environment of the tropical rainforest, the microorganisms and genetic resources thereof are extremely rich and abundant; the method is beneficial to the excavation and utilization of functional genes of the microorganisms.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HAINAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
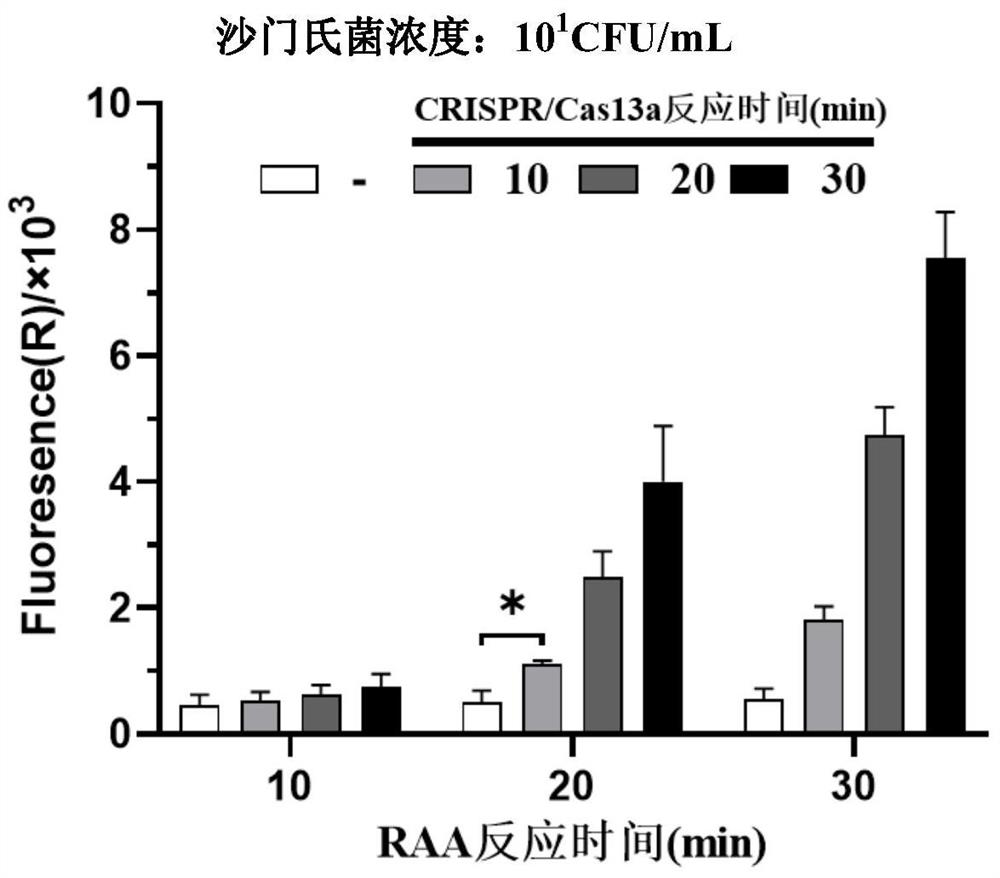
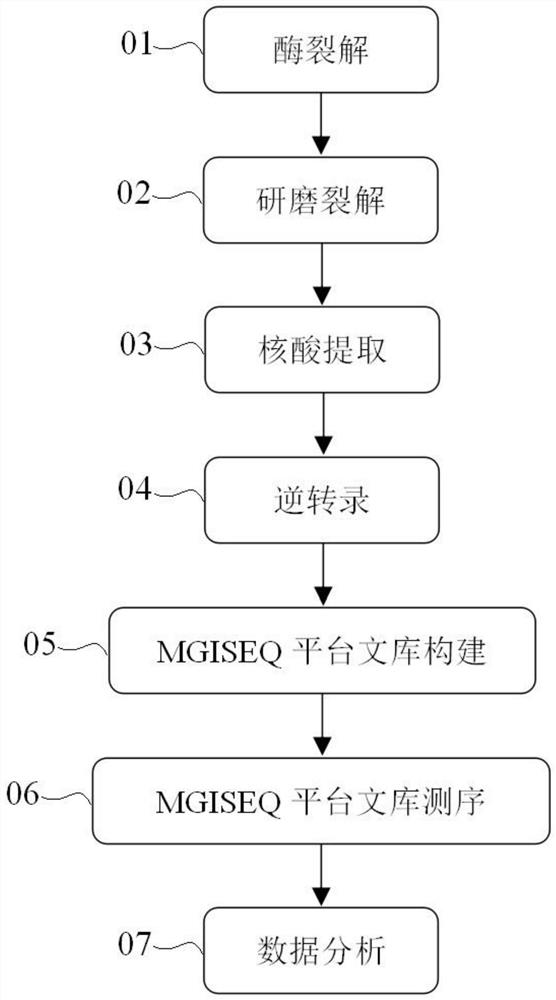
Method for jointly detecting microorganisms through combination of nucleic acid isothermal amplification and CRISPR/Cas13a, and application of method
PendingCN113462796AShorten the timeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesA-DNARecombinase
The invention relates to a method for detecting microorganisms through combination of recombinase-mediated nucleic acid isothermal amplification and CRISPR / Cas13a, and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out RAA isothermal amplification on microbial genome DNA to obtain a DNA product with a T7 promoter (referred as T7-DNA), and then jointly carry out T7 transcription and CRISPR / Cas13a detection. When a Cas13a-crRNA compound recognizes and specifically bind to RNA obtained by transcription of the T7-DNA, Cas13a randomly cuts surrounding irrelevant single-chain RNA fluorescent reporter molecules, and a fluorescent signal is generated. The method disclosed by the invention can specifically detect 10<1> CFU / mL of microorganisms only in 30 minutes, is short in time, high in sensitivity and good in specificity, only needs a common metal bath and a portable fluorescence detector, and is suitable for field detection of food-borne pathogens, medicine and veterinary pathogenic microorganisms or suitable for use in primary laboratories.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for acquiring high-quality soil microbial genome DNA with pretreatment means
InactiveCN102080076AQuality improvementGood removal effectSugar derivativesDNA preparationHigh concentrationGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to a method for acquiring high-quality soil microbial genome DNA through re-extraction by pretreating a soil sample. In the invention, a solution of calcium carbonate and the like is used for pretreating a soil sample to be subjected to genome DNA extraction, the extracted DNA has clear appearance color, and the DNA with OD260 / OD280 of 1.81 has high purity. The extracted DNA can be used for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification directly, and a DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) map indicates that an amplified product has high concentration and sharp banding patterns. Shannon index indicates that the amplified product has great diversity and can effectively reflect the microorganism diversity of a soil microbial community. The pretreatment technology provided by the invention is simple and feasible, has the advantages of low cost, obvious effect on removing humic acid substances and high quality of extracted genome DNA, and is suitable for the extensive research field of molecular ecology.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method, solution and kit for simultaneously detecting multiple microbial genomes
PendingCN112011596ALow costReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementCell wallEnzyme inhibitor
The invention discloses a method, solution and kit for simultaneously detecting multiple microbial genomes. The method comprises the following steps: high-throughput sequencing is carried out on a to-be-detected sample by adopting a microbial RNA detection process; before the sequencing, microbial cell lysis treatment is performed on a sample to be detected in advance, i.e., fungal cell wall lyticenzyme is adopted to perform cell wall lysis treatment on the sample to be detected, and meanwhile, an RNA enzyme inhibitor and dithiothreitol are added into a treatment solution; after cell wall cracking treatment is completed, physical grinding is further conducted; and then nucleic acid extraction and microbial RNA detection processes are carried out. According to the method disclosed by the invention, microbial genome nucleic acid including RNA and DNA in one sample can be comprehensively detected only through one process; the microbial genome detection cost and workload are reduced, andthe detection efficiency is improved; and the sample consumption is reduced, so that the microbial genome nucleic acid information of special samples or precious samples with a relatively small sampleamount can be obtained more completely.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +2
Method and device for screening primer design template and application
ActiveCN110970093ASimple designDifficulty of SimplificationProteomicsGenomicsMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
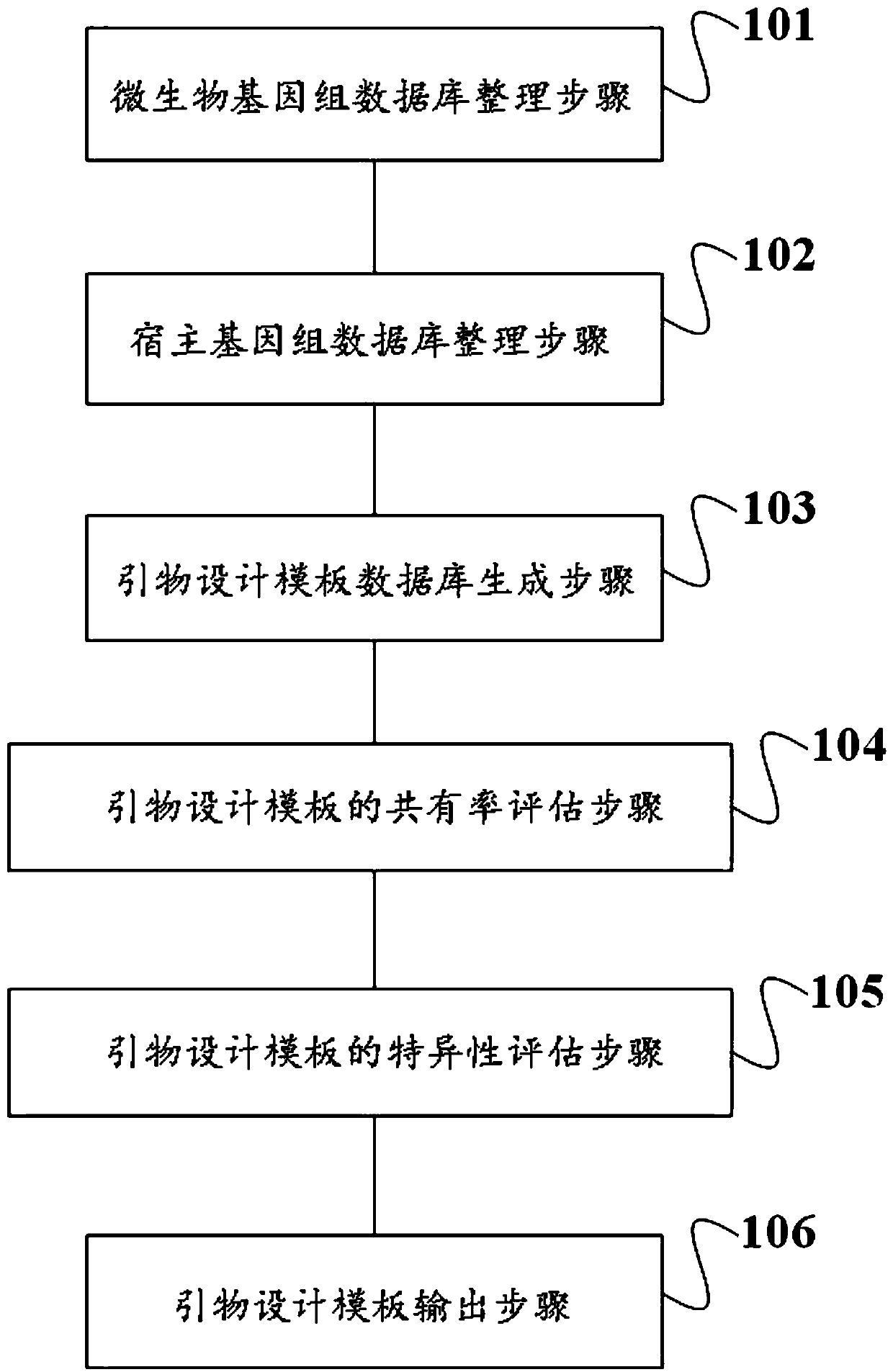
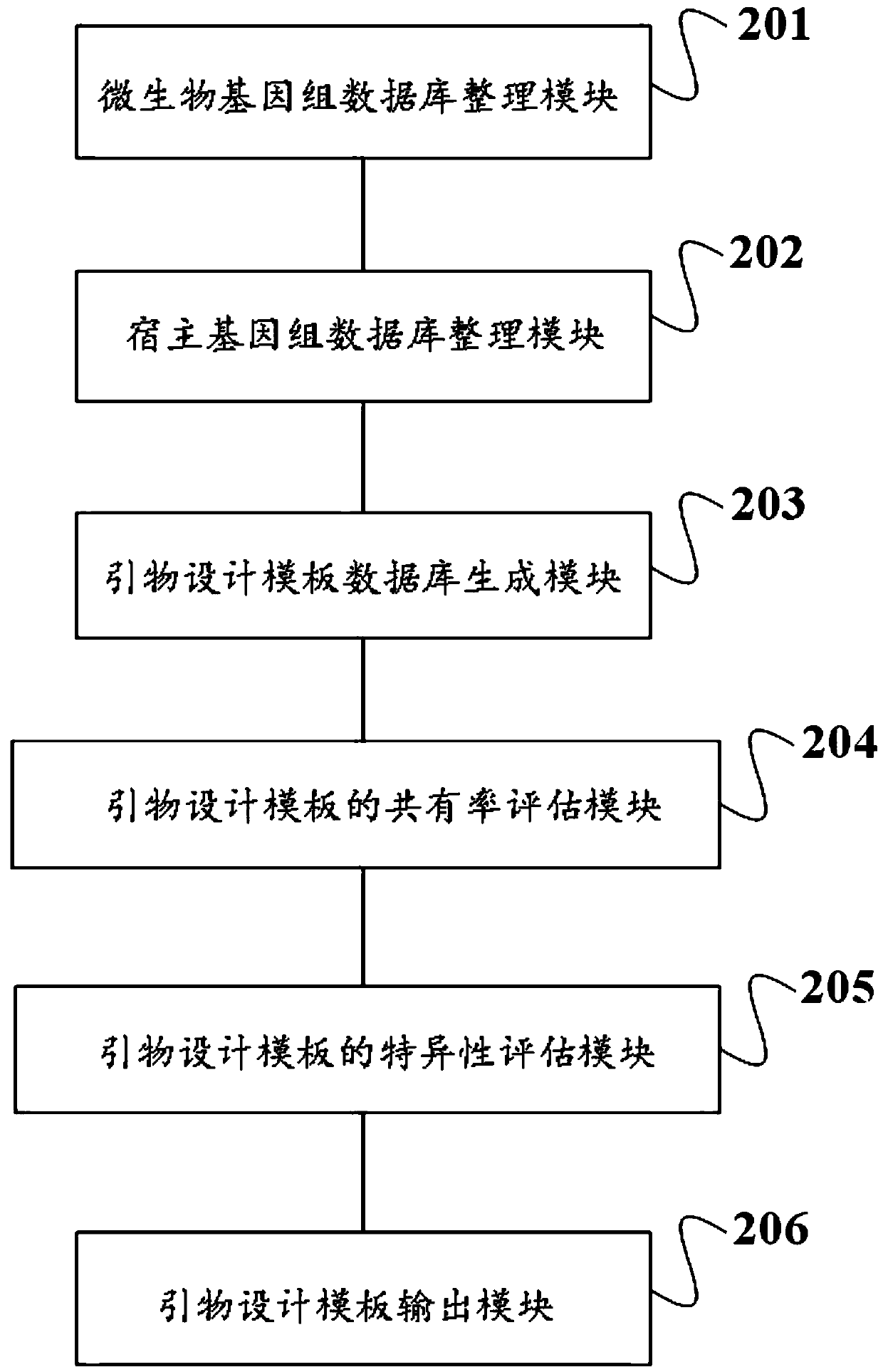
The invention discloses a method and device for screening a primer design template and an application. The method comprises a microbial genome database arrangement step, a host genome database arrangement step, a primer design template database generation step, a primer design template consensus rate evaluation step, a primer design template specificity evaluation step and a primer design templateoutput step. The method is simple and convenient to operate, and primer design templates can be screened in batches; the device for screening the primer design template is high in automation degree,high in operation speed, low in cost and capable of efficiently and accurately outputting the primer design templates of one or more species in batches. The method and the device provided by the invention have the advantage of high precision, the screened primer design template has the characteristics of high consensus rate and high specificity, the target detection primer or probe with strong applicability and good specificity can be designed, and a solid foundation is laid for the technical scheme of detection based on the primer or probe.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +1
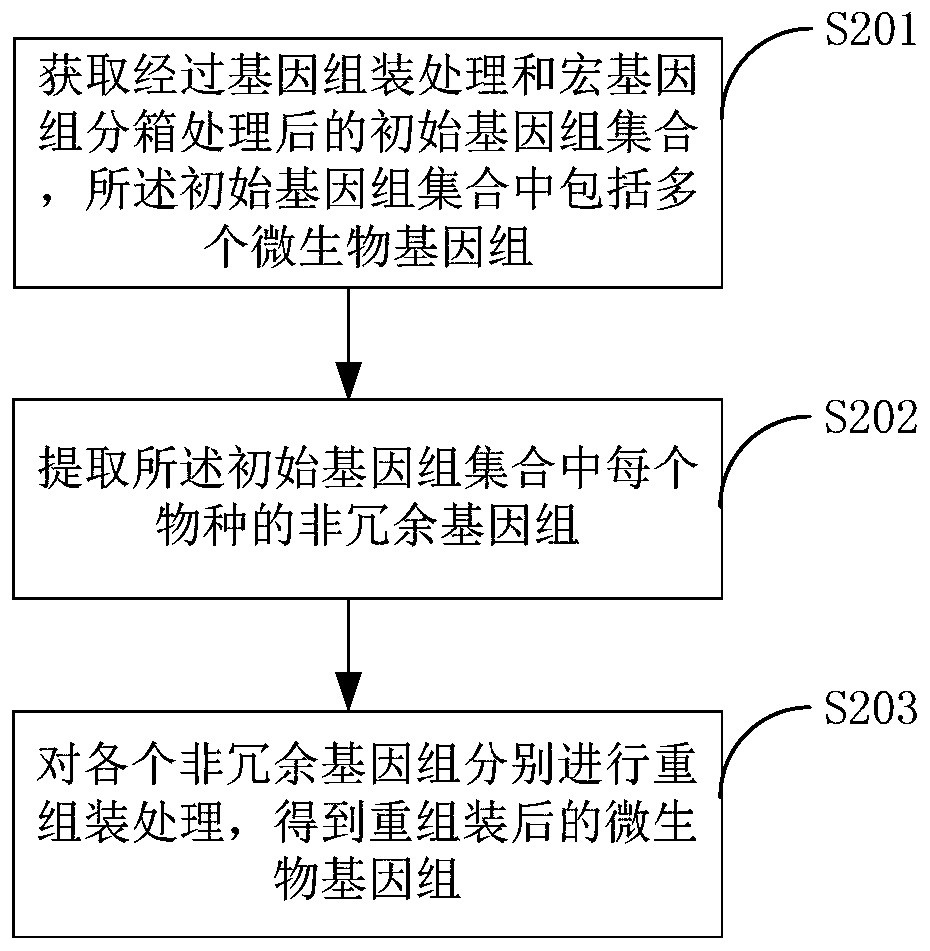
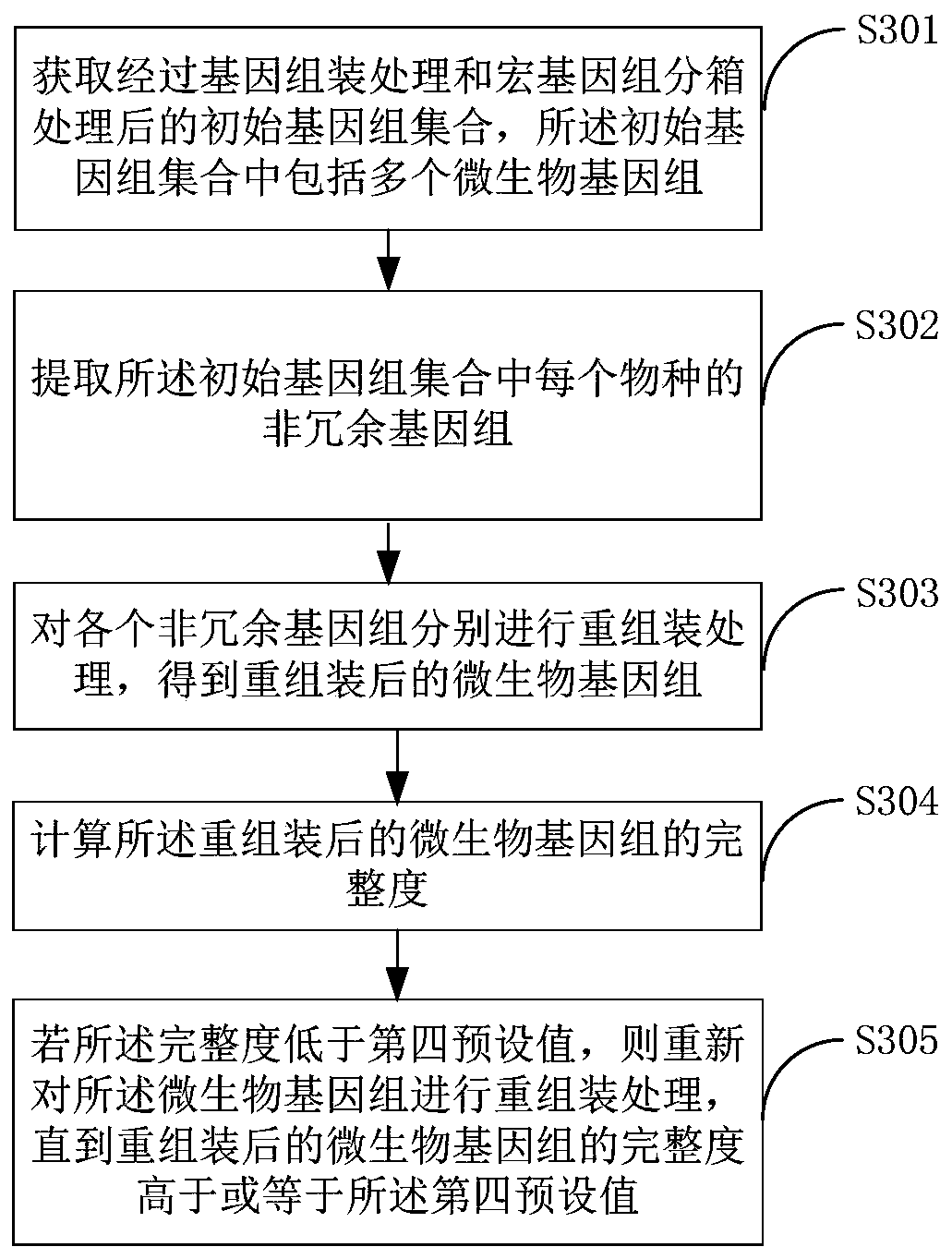
Metagenome reassembling method, a metagenome reassembling device and terminal equipment
PendingCN111161798AQuality improvementReliable research objectProteomicsGenomicsMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological information, and relates to a metagenome reassembling method, a metagenome reassembling device and terminal equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an initial genome set after genome assembling processing and metagenome binning processing, wherein the initial genome set comprises a plurality of microbial genomes; extracting a non-redundant genome of each species in the initial genome set, wherein each non-redundant genome is a microbial genome with the largest number of target genes corresponding to the species to which the non-redundant genome belongs; and separately carrying out reassembling treatment on each non-redundant genome to obtain reassembled microbial genomes. By means of the method, the microbialgenomes with high quality can be obtained, and reliable research objects are provided for subsequent gene research.
Owner:余珂
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com