Food-borne pathogen numerator detection mark establishing method
A food-borne pathogenic bacteria and molecular detection technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc. High, false detection methods, etc., to achieve the effect of large number and saving financial resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The concrete steps of embodiment one are as follows:
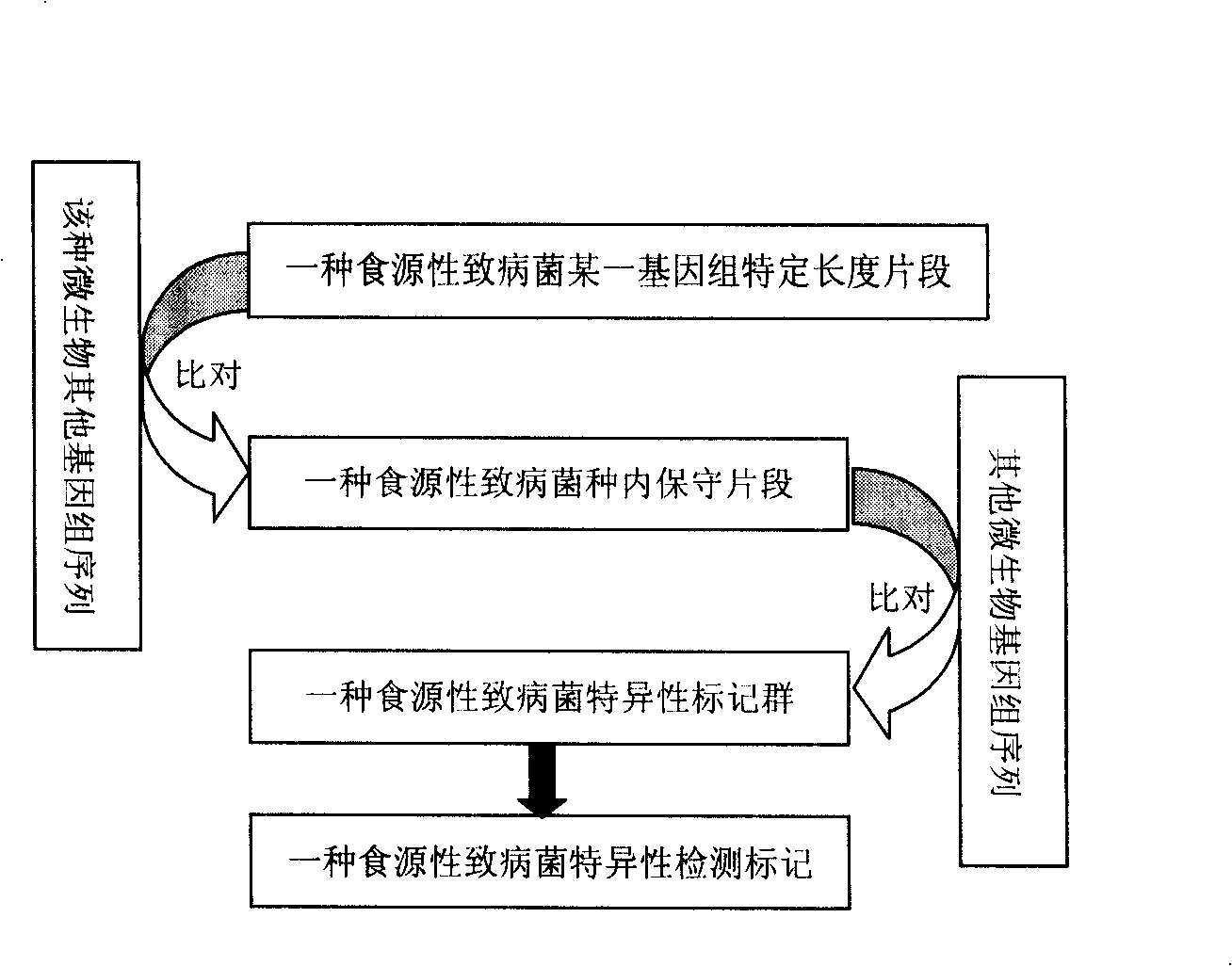
[0021] (1) Collection of gene sequences of Staphylococcus aureus and comparison strains; from GenBank (ftp: / / ftp.ncbi.nih.gov / genbank / genomes / Bacteria / ) all 14 genome sequences of Staphylococcus aureus that have been published ( Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 8325, USA300, RF122, COL, Mu50, N315, MRSA252, JH1, JH9, MSSA476 and MW2) and all other microbial genome sequences that have been sequenced.
[0022] (2) Analyze and obtain the conserved sequence fragments of Staphylococcus aureus: Segment the Staphylococcus aureus ATCC N315 genome according to the length of 500bp, compare and analyze each fragment with the genomes of other Staphylococcus aureus one by one using BLASTN, and retain Sequence fragments with a similarity of more than 98%.
[0023] (3) Acquisition of nucleic acid sequence fragments specific to food-borne pathogenic bacteria species: compare and analyze any fragment of the conserved nucleic acid fragmen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com