Method for jointly detecting microorganisms through combination of nucleic acid isothermal amplification and CRISPR/Cas13a, and application of method
An isothermal amplification and combined detection technology, applied in the biological field of pathogenic microorganism and food-borne pathogen detection, can solve the problems of expensive instruments and cannot be used in basic laboratories, and achieve the effect of high sensitivity, good specificity and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1. Establishment of a system based on RAA isothermal amplification and CRISPR / Cas13a detection of Salmonella
[0052] 1. Design and synthesis of RAA primers
[0053] 1. Design principles
[0054] Different from PCR primers, RAA primers are in the range of 30-35nt in length, and there is no palindromic sequence, continuous single-base repeat sequence and internal secondary structure in the sequence, so it is usually not necessary to consider the Tm value of the primer. Specificity and conservation need to be confirmed by NCBI Blast screening.
[0055] 2. Design RAA Primers
[0056] Preferably, the well-conserved invA gene of Salmonella is selected. According to the above principles, after NCBI Blast screening, the RAA primer sequence was determined to be:
[0057]
[0058] (Note: the underlined sequence is the T7 promoter.)
[0059] 2. Design and synthesize crRNA
[0060] 1. Design principles
[0061] The function of crRNA is to specifically recognize t...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2. Feasibility analysis is carried out to the system
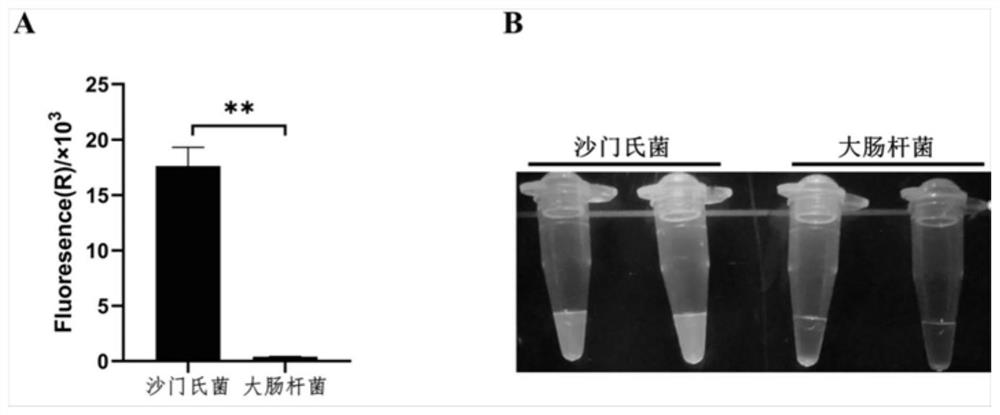
[0080] Cultivate fresh Salmonella and Escherichia coli, and detect according to the steps described in Example 1.
[0081] The test results are attached figure 1 As shown, when the template is Salmonella, the reaction tube will produce a strong fluorescent signal, while Escherichia coli has no fluorescent signal, which proves that the detection system is feasible and can specifically detect Salmonella.
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3. Sensitivity detection is carried out to the system
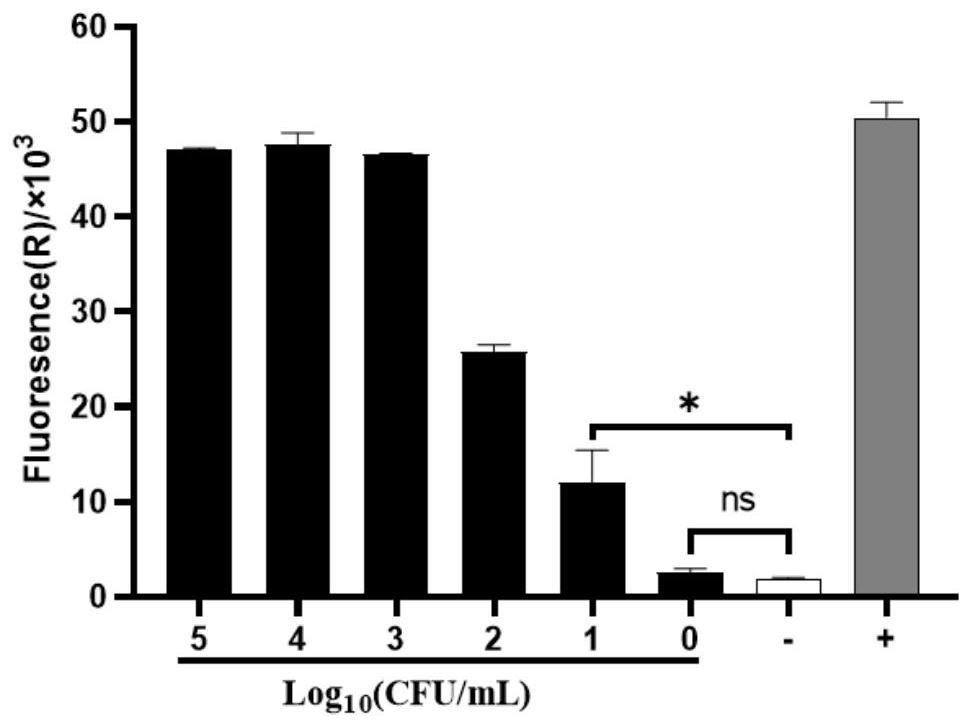
[0083] Take fresh Salmonella, adjust OD 620 to the range of 0.05-0.09 (about 10 8 CFU / mL), using PBS for ten-fold serial dilution, take 1mL 10 5 -10 0 The CFU / mL bacterial liquid was detected according to the steps described in Example 1 (at the same time, a suitable gradient bacterial liquid was taken for plate counting), and DEPC water was set up as a negative control, and the high-concentration Salmonella genome was used as a positive control.
[0084] The test results are attached figure 2 As shown, the detection limit of the proof system is 10 1 CFU / mL, with strong sensitivity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com