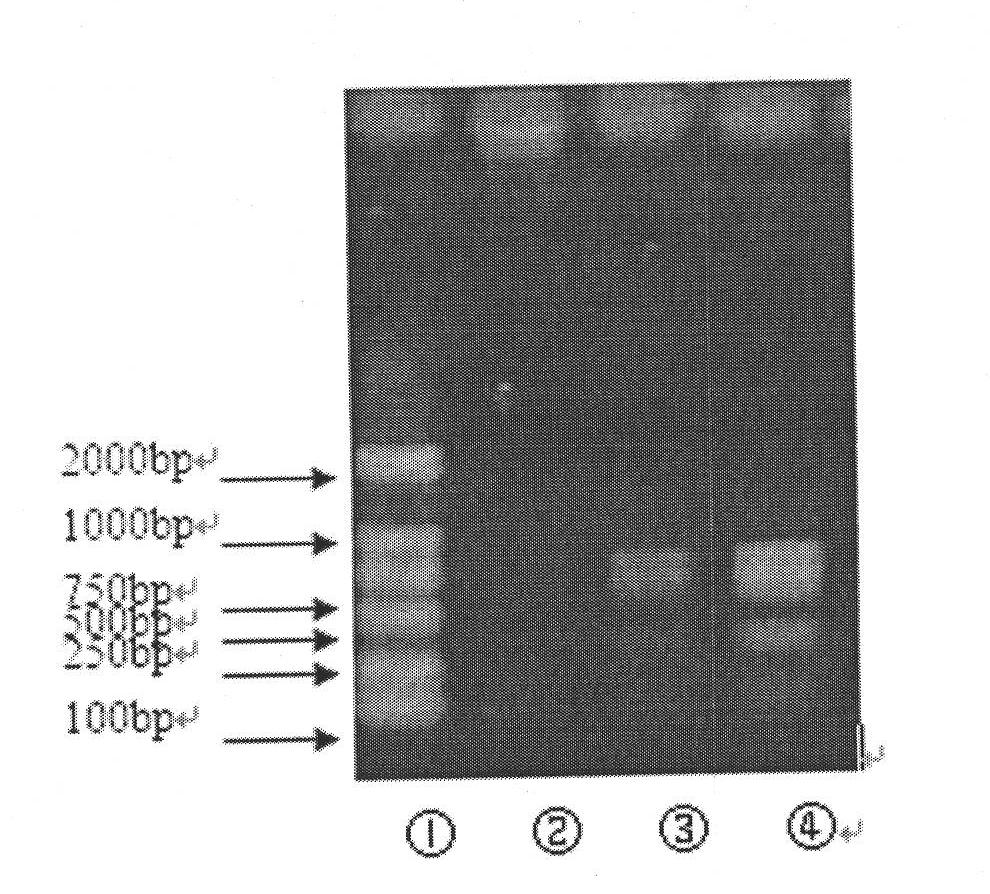
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Molecular ecology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular ecology is a field of evolutionary biology that is concerned with applying molecular population genetics, molecular phylogenetics, and more recently genomics to traditional ecological questions (e.g., species diagnosis, conservation and assessment of biodiversity, species-area relationships, and many questions in behavioral ecology). It is virtually synonymous with the field of "Ecological Genetics" as pioneered by Theodosius Dobzhansky, E. B. Ford, Godfrey M. Hewitt and others. These fields are united in their attempt to study genetic-based questions "out in the field" as opposed to the laboratory. Molecular ecology is related to the field of Conservation genetics.
Kit for extracting aquatic animal fecal like bacteria DNA and method thereof
InactiveCN1824809AReduce physical health damageIncrease productionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSolubilityHigh concentration
This invention provides an aquatic dung bacteria DNA distilling kit and its method. In this invention, the dung is disposed by ethanol and TritonX-100 to increase sensitivity of the bacteria to cracking liquid. Then cell is cracked by cracking liquid with SDS, the liquid also has PVP that with absorption to PCR restrictor. Then a high concentration GuSCN, low pH environment is provided for further denaturation of protein in the solution, and the water solubility is reinforced, and the DNA can be binding on silica gel column. Finally, DNA is eluted from the column in low concentration buffer solution or water. The goal of the maximum diversities information, high quality and higher output DNA of aquatic dung bacteria community can be reached by using this kit and its distilling method. The DNA got can be used to molecular ecology, system evolution and other researches.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA
The invention relates to a method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA, and belongs to the fields of microbiology and molecular ecology. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding by using liquid nitrogen; breaking cell walls by using mechanical force; cracking cells by adopting lysozyme and SDS lysate; obtaining DNA deposit through separation and precipitation; and finally dissolving the DNA deposit with TE to obtain the DNA with good quality. The product DNA fragment obtained by the method is greater than 20Kb; and can be subjected to gene magnification and sequencing. The method has good generality and is used for extracting the intestinal microbial DNA of various crustacean aquatic animals. High-quality template DNA can be obtained through extraction at one time without repeated experiment; and the obtained DNA can be applied to the research of molecular ecology, system evolution and the like.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Kit for extracting aquatic animal fecal like bacteria DNA and method thereof
InactiveCN100368566CReduce physical health damageIncrease productionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSolubilityHigh concentration
This invention provides an aquatic dung bacteria DNA distilling kit and its method. In this invention, the dung is disposed by ethanol and TritonX-100 to increase sensitivity of the bacteria to cracking liquid. Then cell is cracked by cracking liquid with SDS, the liquid also has PVP that with absorption to PCR restrictor. Then a high concentration GuSCN, low pH environment is provided for further denaturation of protein in the solution, and the water solubility is reinforced, and the DNA can be binding on silica gel column. Finally, DNA is eluted from the column in low concentration buffer solution or water. The goal of the maximum diversities information, high quality and higher output DNA of aquatic dung bacteria community can be reached by using this kit and its distilling method. The DNA got can be used to molecular ecology, system evolution and other researches.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for oil-gas resource exploration indicating by utilizing molecular ecology
InactiveCN104101914AAccurate exception divisionImprove the success rate of explorationGeological measurementsEarth surfaceSediment
The invention relates to the field of microorganism oil-gas resource exploration and discloses a method for oil-gas resource exploration indicating by utilizing molecular ecology. The method includes utilizing a molecular ecology studying means to calibrate fingerprint spectra of microorganism species in topsoil or sediment; comparing the fingerprint spectra with references of point locations where underlaying oil-gas reservoirs exist in a known manner to complete dividing of potential abnormality areas and background areas of oil-gas resources. By the method, abnormality dividing of potential oil-gas-resource-containing areas can be realized more accurately, so that exploration success rate is increased.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL TECH INC
Method for fast identifying harmful algae
InactiveCN101824481AQuick and easy preliminary identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementRed tideRestriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention discloses a method for fast identifying harmful algae. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: a, preparation of experimental algae f / 2 and derivative culture media of the experimental algae; b, design and verification of primers; c, obtaining of 18s rDNA fragment of the experimental algae; d, optimization and propagating of (polymerase chain reaction) PCR; e, control experiment of simulated enzyme cutting and practical enzyme cutting; and f, identification of the harmful algae by using restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). As a molecule ecological means for identifying the harmful algae, the method can serve as the supplementary means and auxiliary means of the conventional identification methods. The method establishes a characteristic map based on FELP, standardizes the whole flow, and is favorable for initially identifying the harmful algae fast, easily and conveniently and pre-alarming the outbreak of the red tide of phytoplankton.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
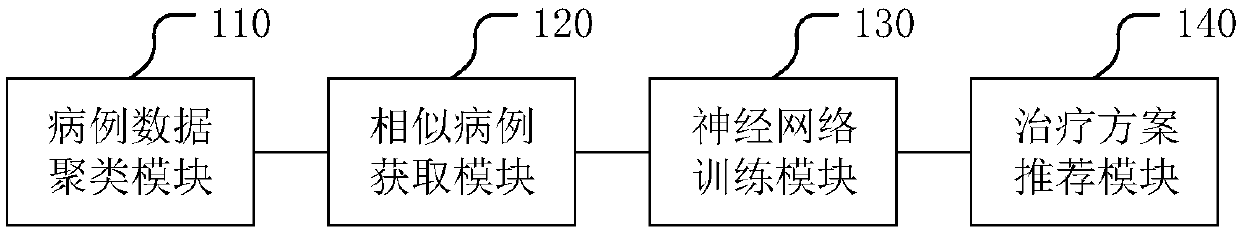
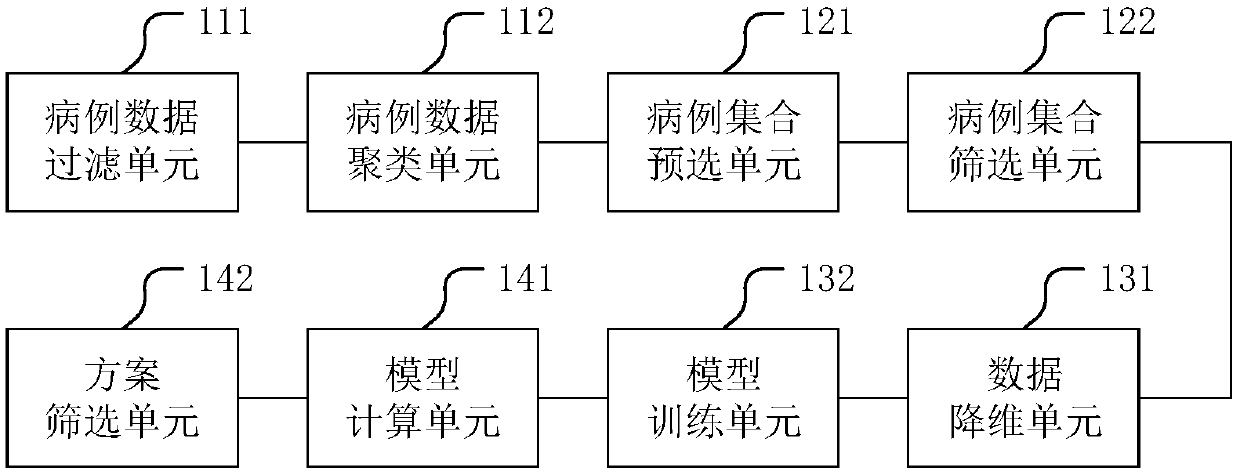
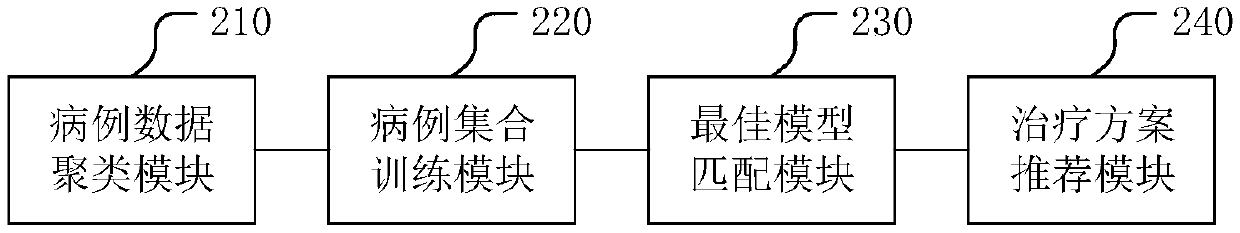
Gene target therapy scheme recommendation system and related system
PendingCN109599182AReduce complexityReduce data volumeTherapiesMedical automated diagnosisRecommendation modelMachine learning
The invention discloses a gene target therapy scheme recommendation system. The system comprises a case data cluster module, a similar case acquisition module, a neural network training module and a therapy scheme recommendation module, wherein the case data cluster module is used for classifying multiple case data according to molecular ecology network analysis to obtain multiple case sets, wherein case data comprise gene data and case feature data; the similar case acquisition module is used for screening cases according to similarity between the current case and each case set to obtain similar case sets; the neural network training module is used for neural network training according to the similar case sets and corresponding therapy schemes to obtain a scheme recommendation model; thetherapy scheme recommendation module is used for calculating the current case according to the scheme recommendation model to obtain a target therapy scheme. Useless data are reduced by screening andthe model accuracy is improved. The invention further discloses another gene target therapy scheme recommendation system with the benefits.
Owner:湖南金特尔信息技术有限公司
Bio-augmentation technology for fermentation process of solid-state brewing vinegar
ActiveCN102226142AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBio engineeringFood flavor
The invention discloses a bio-augmentation technology for fermentation process of solid-state brewing vinegar, belonging to the technical field of biological Engineering. The operation procedures of the method comprise: (1) determining functional microorganisms for brewing vinegar: analyzing the structure of the microflora in vinegar fermented grains with molecular ecology technology such as PCR-DGGE, determining the functional microorganisms in the process of brewing vinegar by combining the key physicochemical indexes related to the quality and functionality of vinegar; (2) pure culture of the functional microorganisms for brewing vinegar: using microorganism pure culture technique to get the functional microorganisms for brewing vinegar from the vinegar fermented grains; and (3) bio-augmentation in the vinegar fermentation process: selecting the functional microorganisms or a combination thereof, and carrying out bio-augmentation in the solid-state fermentation stage of vinegar. The method has the advantages of shortening brewing cycle of vinegar, improving and controlling the flavor, quality and functionality of vinegar products, improving the utilization rate of raw material and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for extraction and purification of microbial total DNA of compost and buffer solution thereof
InactiveCN101550413AReduce pollutionIdeal anti-corrosion effectSugar derivativesDNA preparationMicroorganismDNA Solutions
The invention discloses a method for the extraction and the purification of microbial total DNA of a compost and a buffer solution thereof, the method comprises the following steps of: adding a dehumification solution in an amount of 8-15ml / g of the compost into a sample of the compost in which the DNA is to be extracted, for dehumification; then adding a DNA extraction buffer solution in an amount of 1.0-1.5ml / g of the compost for the crude extraction of the microbial total DNA; and finally, purifying the crudely-extracted DNA solution with a kit so as to obtain the microbial total DNA of the compost. The inventive method can reduce the influence of humic acids and effectively improve the yield and the purity of the DNA extracted from the compost, thus better facilitating compost microbial molecular ecology and researches of other functional genes.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for distinguishing soil N2O microorganism emission source
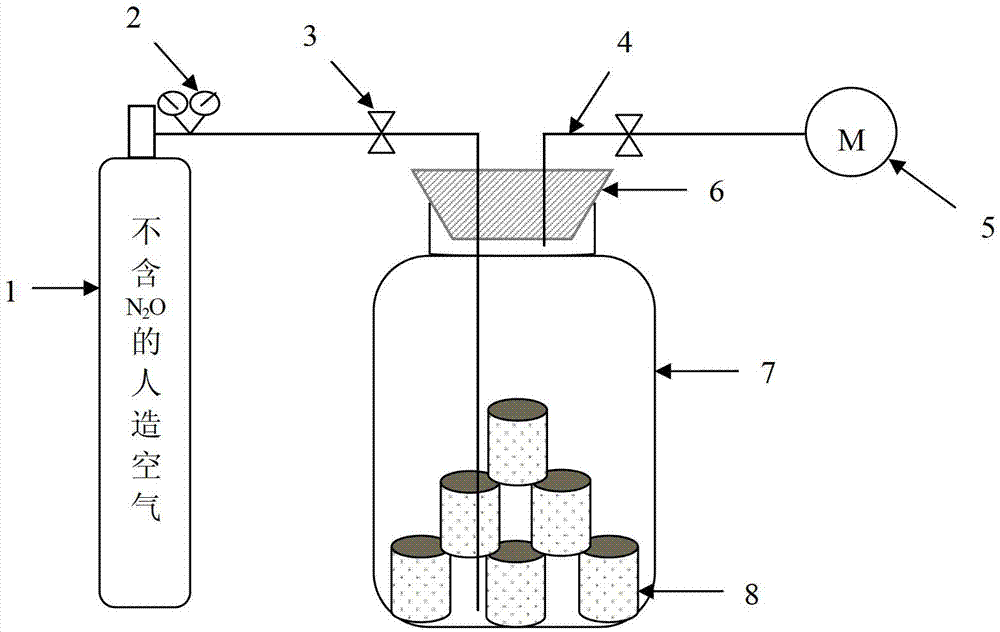
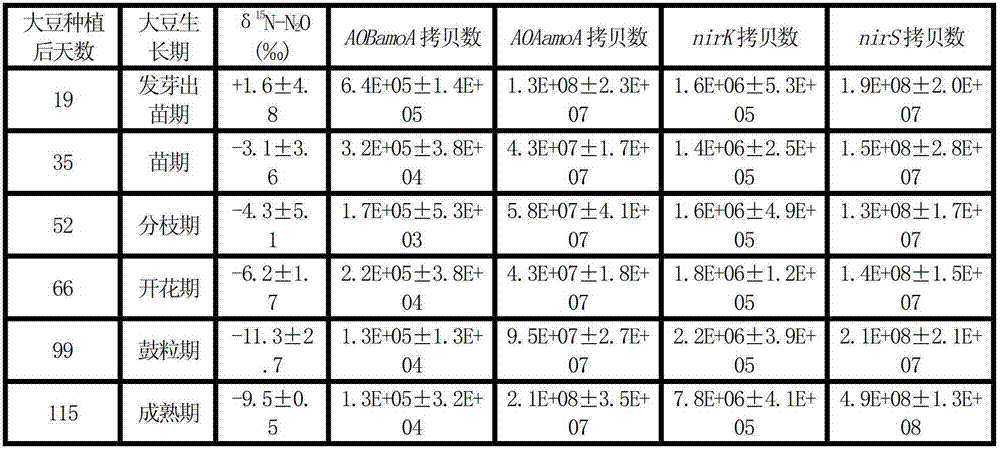
ActiveCN102758017AAccelerate emissionsReduce disturbanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroorganismIsotope
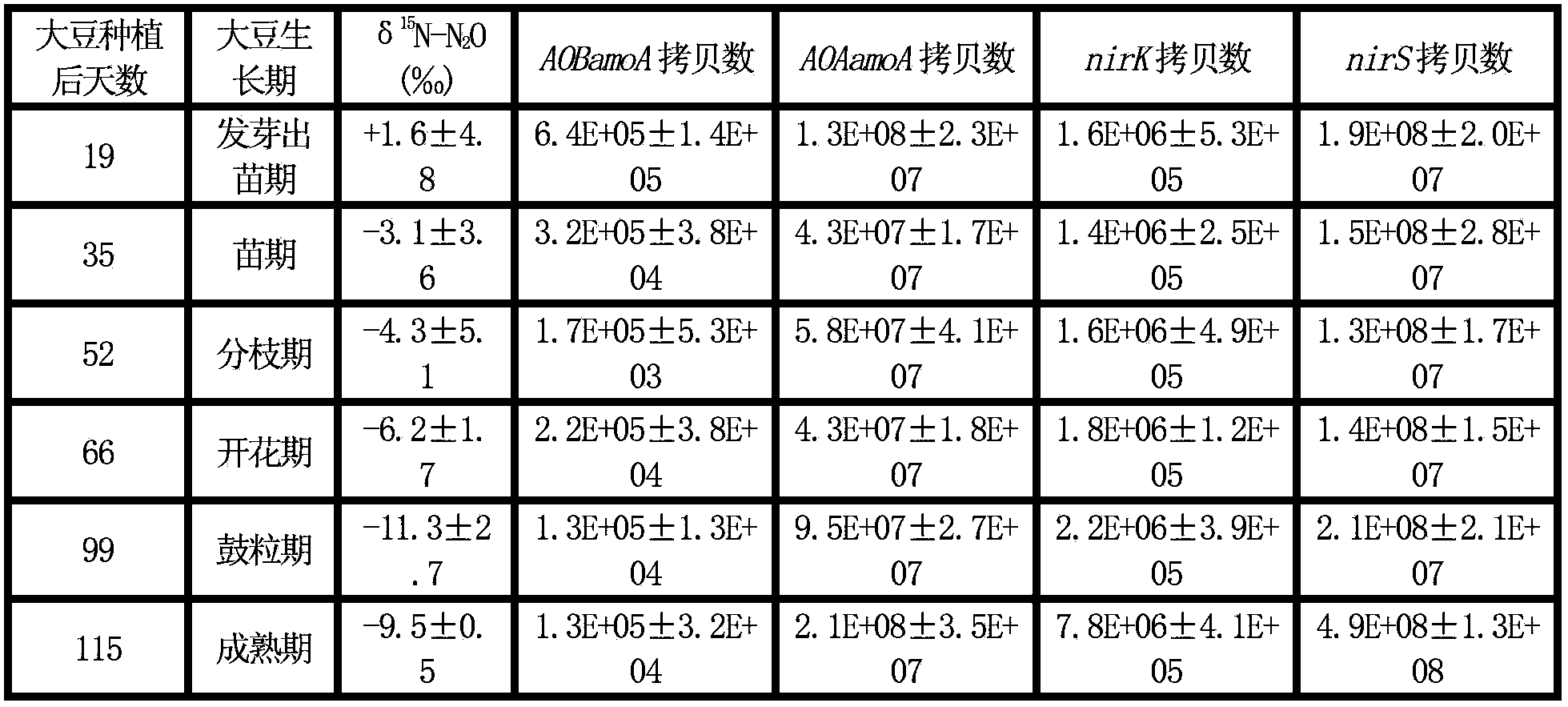
The invention relates to soil microbial molecular ecology and particularly relates to a method for distinguishing a soil N2O emission source. The method comprises the following steps of: after treating soil to be analyzed, determining the isotope delta 15N value of N2O emitted by the soil and the copy number of related microbial genes in the process that the soil produces the N2O, and judging that functional microbial groups with correlation test p <0.05 between gene abundance and delta 15N-N2O abundance value are microbial groups which play an important role in soil N2O emission. The method is applicable to the distinguishing of the microbial groups with N2O emission function in certain soil.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Kit and method for rapidly detecting archaea
PendingCN112646902AReduce experiment costSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroorganismExperimental laboratory
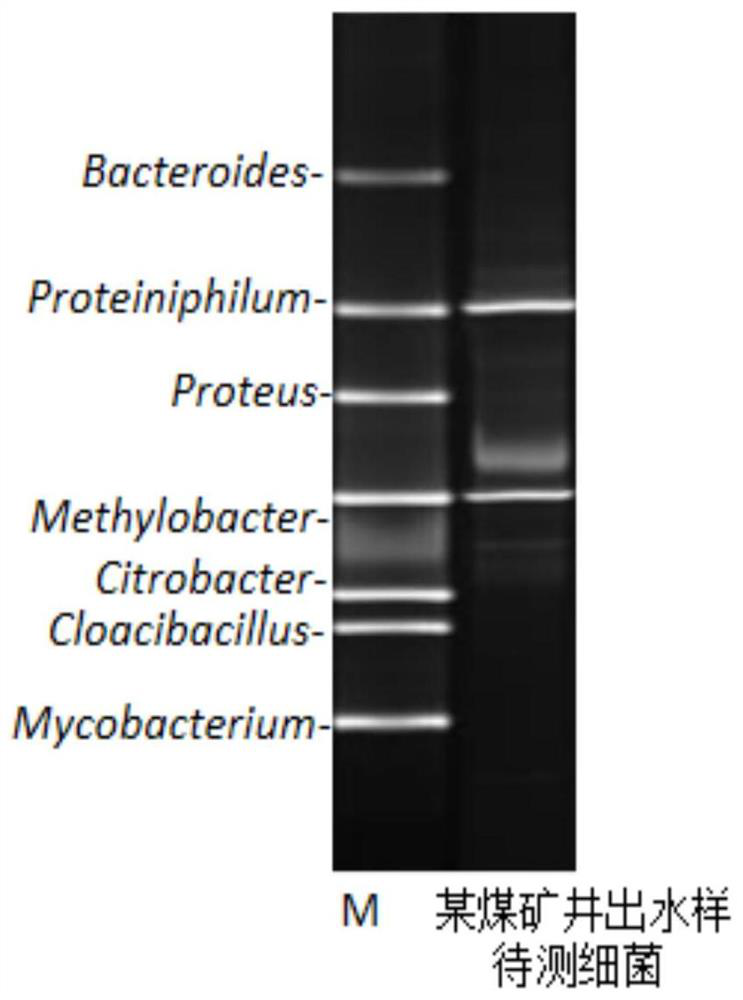
The invention belongs to the field of microbial molecular ecology detection, and particularly relates to a kit and a method for rapidly detecting archaea. According to the kit and the method for rapidly detecting archaea, the problems existing in abundance, diversity, composition and structure of archaea communities under different environments in real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR and high-throughput sequencing at present are solved, and the kit for quickly detecting archaea comprises a primer group, a DNA fragment, a PCR buffer solution and an STE buffer solution; in addition, the DGGE technology is used for rapidly detecting the archaea, the experiment cost is low, operation is easy and convenient, and meanwhile the method has the advantages of being high in specificity, easy to popularize in a laboratory, independent of large experiment equipment and the like; and the method is an efficient, rapid, economical and convenient detecting method.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Reagent case for extracting zooxanthellae genom from ledge rock coral and method thereof
InactiveCN101250521AIncrease productionReduce physical injuryDNA preparationSilica gelChromatography column
The invention provides a reagent kit which extracts zooxanthella genome DNA from reef building coral and a method of the reagent kit. The reagent kit comprises: reagent A (lysis buffer), reagent B (protease E), reagent C (RNAase A), reagent D (supersaturation NaC1 solution), reagent E (DNA cleaning mixture) and reagent F (DNA eluent). The method of the invention comprises: firstly, using the lysis buffer which contains SDS to crack tissue cells, then, providing a high salt low PH circumstance, enabling protein in solution to degenerate further, but combining DNA on a silica gel column, and finally, quantitatively reclaiming the DNA from a chromatography column in water-soluble buffer solution. The zooxanthella genome DNA can be rapidly and conveniently extracted from varous reef building coral, the DNA which is obtained can be used to research molecular ecology, systematic evolution and the like, and thereby the demands of regular monitoring tasks in coral reef nature reserves can be satisfied.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for acquiring high-quality soil microbial genome DNA with pretreatment means
InactiveCN102080076AQuality improvementGood removal effectSugar derivativesDNA preparationHigh concentrationGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to a method for acquiring high-quality soil microbial genome DNA through re-extraction by pretreating a soil sample. In the invention, a solution of calcium carbonate and the like is used for pretreating a soil sample to be subjected to genome DNA extraction, the extracted DNA has clear appearance color, and the DNA with OD260 / OD280 of 1.81 has high purity. The extracted DNA can be used for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification directly, and a DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) map indicates that an amplified product has high concentration and sharp banding patterns. Shannon index indicates that the amplified product has great diversity and can effectively reflect the microorganism diversity of a soil microbial community. The pretreatment technology provided by the invention is simple and feasible, has the advantages of low cost, obvious effect on removing humic acid substances and high quality of extracted genome DNA, and is suitable for the extensive research field of molecular ecology.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Improved CTAB method for extracting nucleic acid of paulownia fordii
PendingCN113584018APrevent browningBrown avoidDNA preparationAgainst vector-borne diseasesSodium acetatePaulownia
The invention belongs to the field of molecular ecology experiments, and particularly provides a CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) extraction method for an improved genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) version of an endangered semi-mangrove plant tung paulownia. The endangered semi-mangrove plant paulownia fortunei is rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol, so that the tissue grinding fluid is extremely viscous, and the extraction of nucleic acid with good quality is extremely difficult. On the basis of a traditional CTAB method, cells are split by adopting an improved lysis solution, and extraction is carried out through a mixed solution of Tris balanced phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol in a certain proportion. The DNA is precipitated by using sodium acetate-isopropanol with improved volume, and then the DNA is purified so as to obtain the high-quality genome DNA. The DNA extracted by adopting the method for extracting the nucleic acid of the endangered semi-mangrove plant tung paulownia, provided by the invention, is high in concentration and purity and is not easy to degrade, and most importantly, polysaccharide and polyphenol can be effectively removed. A foundation is laid for subsequent molecular biology experiments such as PCR amplification, molecular marker technology development, genome library construction and the like.
Owner:HAINAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for establishing RFLP characteristic map of red tide algae
InactiveCN101864485AQuick and easy preliminary identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementRed tideMolecular ecology
The invention discloses a method for establishing a RFLP characteristic map of red tide algae, which comprises the following steps: a, the establishment of simulated experimental data tables; b, simulated enzyme digestion electrophoretogram; c, simulated enzyme digestion and actual enzyme digestion control experiments; d, an actual enzyme digestion experiment; e, a simulated digestion experiment; f, contrast between results of the simulated digestion experiment and the actual enzyme digestion experiment; g, the optimization of digestion experiment conditions; h, the establishment of RFLP map; and i, the identification of red tide algae species based on RFLP technology. The invention is used as a molecular ecology means for identifying the red tide algae species, and can be used as a complementary and auxiliary means of the traditional identification method. Based on FELP, the invention establishes a characteristic map, standardizes the entire process, and can be favorable for rapid and simple preliminary identification of the red tide algae species.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for detecting diversity of fish species by using environmental DNA technology
PendingCN113355403AEliminate the effects ofThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerNucleotide
The invention provides a method for detecting fish species diversity by using environmental DNA, and relates to the technical field of molecular ecology. The method for detecting fish species diversity by using the environmental DNA comprises the following steps: collecting a water sample of a place to be detected, filtering, extracting eDNA to obtain eDNA of the water sample to be detected, carrying out PCR amplification by using a primer group to obtain an amplification product, carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the amplification product to obtain sequence fragments, splicing the sequence fragments, and carrying out OTU cluster analysis on the species diversity. The primer group comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer, the nucleotide sequence of the forward primer is as shown in SEQID.NO 1, and the nucleotide sequence of the reverse primer is as shown in SEQID.NO 2. The method has the advantages that the method can be used for detecting the diversity of fish species, especially the diversity of lake aquatic organisms, the detection result is accurate, and multiple species can be detected.
Owner:邢迎春 +1
Tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus, as well as amplification primer and application thereof
InactiveCN109371151AGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTetraena mongolicaMicrosatellite
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides a tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus and a primer sequence thereof. The tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-10. The tetraena mongolica microsatellite locus can be used in molecular ecological research, pedigree analysis, germplasm resources investigation, assistant breeding and individual recognition of tetraena mongolica, and provides basic materials to studying plant drought resisting mechanisms.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +2
Dasyatis zugei microsatellite sites, primers and application thereof
InactiveCN104087584AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmPolymorphic microsatellites
The invention discloses dasyatis zugei microsatellite sites, primers and application thereof. The dasyatis zugei microsatellite sites include 10 stable polymorphic microsatellite sites, wherein the sequences of the 10 stable polymorphic microsatellite sites are respectively as shown in SEQ ID NO:1-SEQ ID NO:10. The sequences of the primers of the dasyatis zugei microsatellite sites are respectively as shown in SEQ ID NO:11-SEQ ID NO:30. The application of the dasyatis zugei microsatellite sites or the primers comprises molecular ecology study, pedigree analysis, germplasm resource survey, assistant breeding and individual identification. The genotyping result of 10 pairs of primers in 15 dasyatis zugei individuals shows that the allelic gene number is 3-24, and the average allelic gene number is 13.6; the expected heterozygosity He is 0.5-0.984, and the observed heterozygosity Ho is 0.429-1, so that the 10 pairs of primers are indicated to have high polymorphism and meet the requirement for individual identification of dasyatis zugei.
Owner:张洁
Spodoptera frugiperda polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers and primers thereof
InactiveCN111424099AContribute to molecular ecology researchGood polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetics
The invention discloses spodoptera frugiperda polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers and primers thereof. Nucleotide sequences of the microsatellite molecular markers are correspondingly shown as SEQ ID NO.1-12, and primer pairs of the microsatellite molecular marker are shown as SEQ ID NO.13-36. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the polymorphic microsatellite molecularmarker. According to the invention, polymorphism experimental verification is carried out on 33 sites by predicting four-base microsatellite sites with polymorphism in the genome of spodoptera frugiperda, and twelve four-base microsatellite markers with good polymorphism are obtained through screening for the first time, wherein the four-base microsatellite markers comprise four moderate polymorphism markers and eight high polymorphism markers, so that molecular technical support is provided for genetic research on invasion of spodoptera frugiperda, and molecular ecological research on the highly-multiphagous species, namely the grassland spodoptera litura, is facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
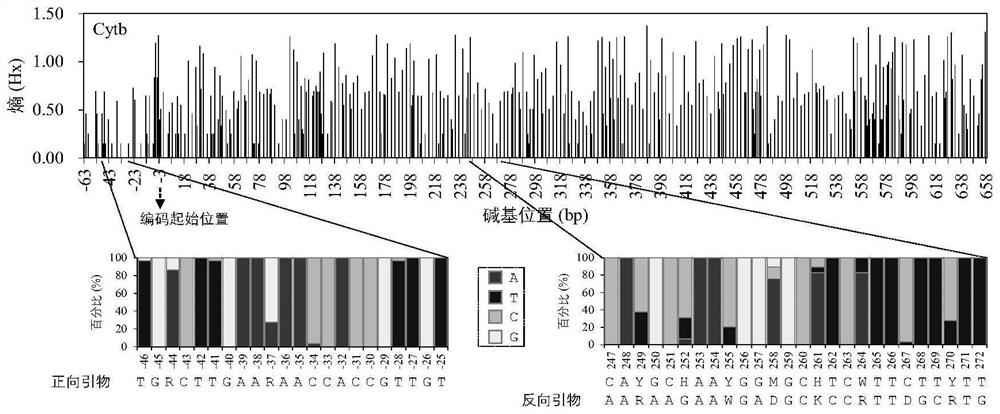
Primer for monitoring DNA of fish environment at middle and upper reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River
PendingCN113881781AAccurate and comprehensive detection effectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHigh throughput sequenceZoology
The invention relates to a primer for monitoring DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a fish environment in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River and an application method thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular ecology. The primers comprise the following components of YZR-Cytb-F:TGRCTTGAARAACCACCGTTGT and YZR-Cytb-R: AARAAGAAWGADGCKCCRTTDGCRTG. The method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting a water sample and extracting eDNA; (2) slightly transforming the primer and then carrying out primary PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) on eDNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); (3) carrying out secondary PCR on the purified product of the primary PCR by using an Illumina library building primer; (4) performing high-throughput sequencing on the purified product of the second PCR; and (5) analyzing the fish species composition in the water sample according to the sequencing data. The primer has an identification effect on the species level of all fishes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, and the method can be used for accurately and completely monitoring the species diversity of the fishes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River on the premise of not damaging the environment and fish populations.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
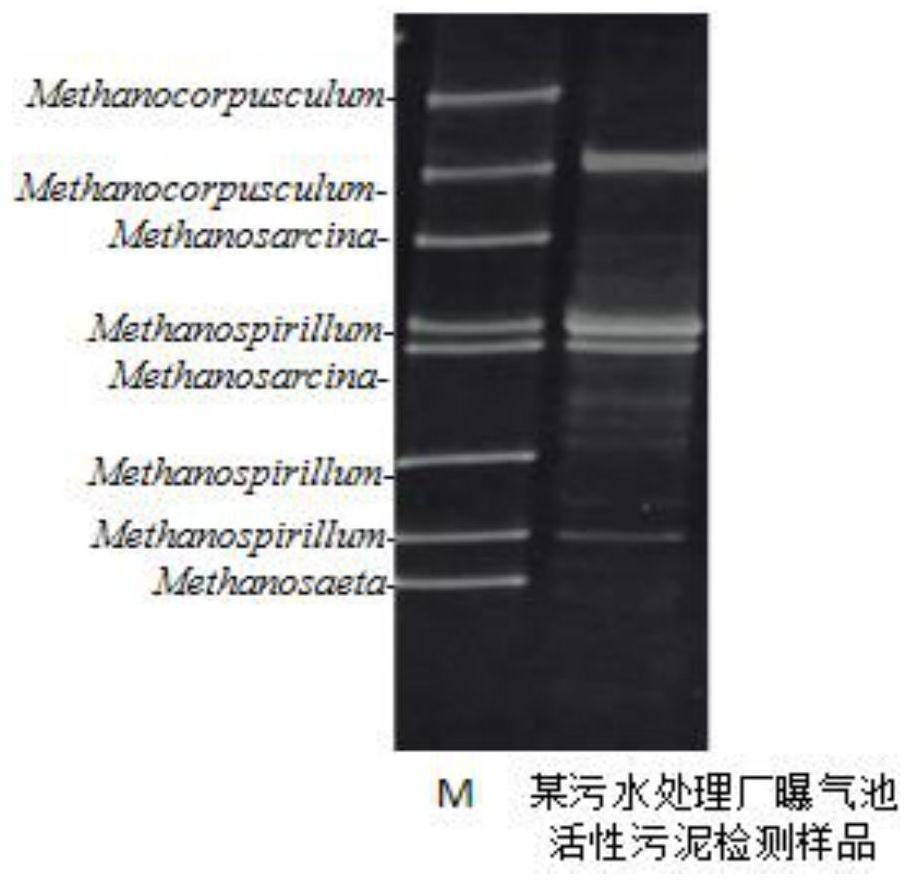
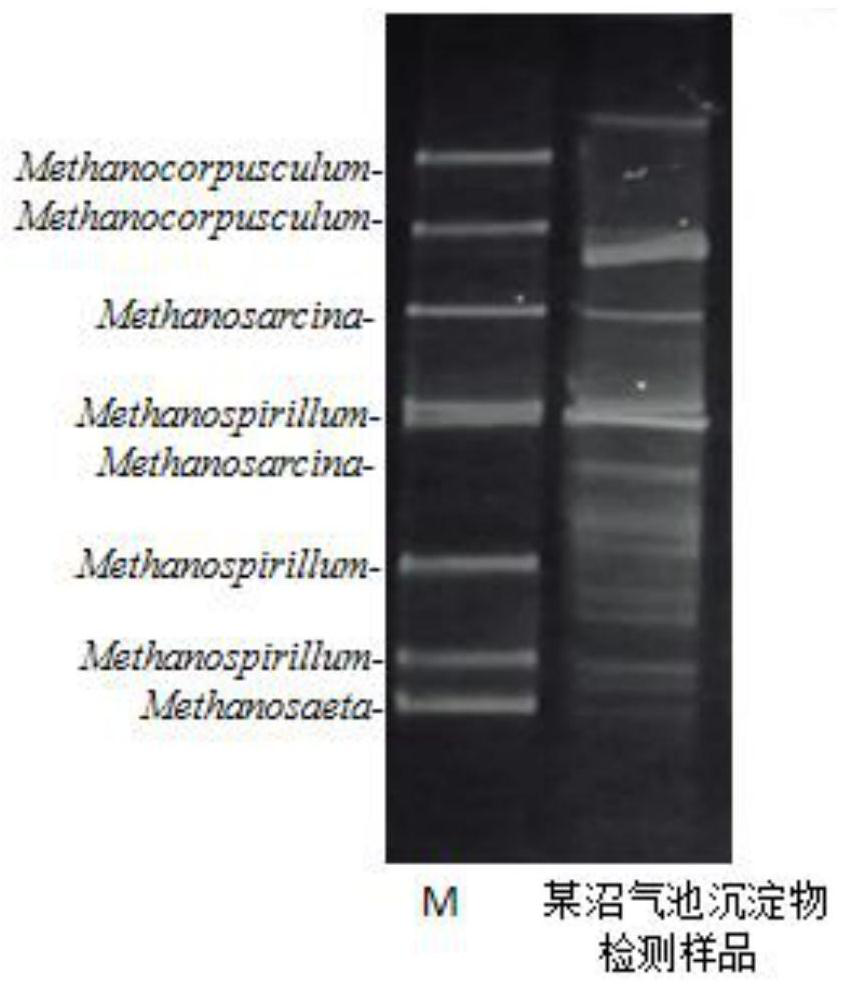
PCR-DGGE (Polymerase Chain Reaction Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) analysis method of microbial diversity in bioremediation process of soil polluted by petroleum
InactiveCN102174648APromote growthIncrease brightnessMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBioremediationGel electrophoresis
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil microbial community diversity analysis and discloses optimal conditions and reagent dosage in a PCR-DGGE (Polymerase Chain Reaction Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) method used for analyzing microbial community diversity of soil polluted by petroleum. The analysis method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting enough DNA from 0.4g of soil samples; 2, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) on 1 microliter of purified DNA; 3, performing a DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) experiment on 3-5 microliters of PCR products; 4, adding 9 microliter of TEMED (tetramethylethylenediamine) and 40 microliter of 10% APS (ammonium sulfate) into 18ml of modified acrylamide glue solution for preparing gel; 5, filling the gel, covering the top with a preservative film, standing still overnight to finally obtain excellent modified gel; 6, performing electrophoresis for 5 hours at the voltage of 120V and the electrophoresis temperature of 60 DEG C to obtain a good DGGE map; and 7, performing silver staining, wherein a stop solution is not used necessarily. The method is mainly used in the molecular ecology researches in the bioremediation process of soil polluted by petroleum, and also can provide references for molecular ecology researches of other environmental samples.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microorganism bacterium species, and preparation method and application
ActiveCN107119130AStrip sharpUniform brightnessMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismNucleotide
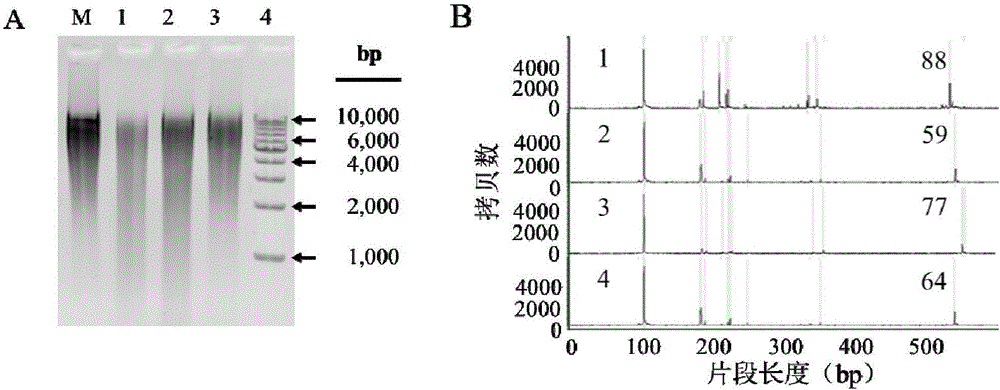
The invention relates to a DNA Marker specially used for coal geology environment bacteria species in molecular detection of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) for coal geology environment microbial flora, and belongs to the field of microorganism molecular ecology. According to the DNA Marker for detecting the coal geology microorganism bacterium species, the DNA Marker consists of 11 DNA segments a to k, wherein the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment a is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.1; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment b is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.2; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment c is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.3; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment d is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.4; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment e is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.5; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment f is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.6; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment g is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.7; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment h is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.8; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment i is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.9; the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment j is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.10; and the nucleotide sequence of DNA segment k is as shown in SEQ. ID. No.11.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Phomopsis RPB2 gene amplification primer and design method and application thereof
InactiveCN105567680AAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhomopsis sp.High throughput sequence
The invention discloses a phomopsis RPB2 gene amplification primer and a design method and application thereof. The phomopsis RPB2 gene amplification primer is a universal primer aiming at phomopsis fungi. The upstream primer PR2-F of the phomopsis RPB2 gene amplification primer has 44 bases, to be more specific, CGCCAGGGTTTTCCCAGTCACGACATGGCCTACATGAAGCGATG, and the downstream primer PR2-R of the phomopsis RPB2 gene amplification primer has 46 bases, to be more specific, AGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAATCTCACAATGCGTGTACATGT. The phomopsis RPB2 gene amplification primer has the advantages that the primer is high in universality to phomopsis, high in amplification sequencing success rate, appropriate in fragment length and convenient in high-throughput sequencing and analysis, and an important tool is provided for the molecular ecology researches and quarantine and identification of the phomopsis.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Kit and method for rapidly detecting coal geological environment bacteria
PendingCN112626243AReliable resultsFast experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
The invention belongs to the field of microbial molecular ecology detection, and particularly relates to a kit and a method for rapidly detecting coal geological environment bacteria. Aiming at the problem of limitation of environment bacteria detection in the prior art, the invention provides the kit for rapidly detecting the coal geological environment bacteria. The kit comprises a primer group and a DNA fragment for rapidly detecting the coal geological environment bacteria, a PCR buffer solution and an STE buffer solution. In addition, the geological environment bacteria are rapidly detected by using a DGGE technology, the result is reliable, the experiment speed is high, the specificity is good, the sensitivity is high, and a plurality of samples can be analyzed at the same time. The price of experimental consumables is low, and the experimental technology is easy to popularize and simple to operate. Compared with a general detection method, the detection method is efficient, rapid, economical and convenient.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for distinguishing soil N2O microorganism emission source
ActiveCN102758017BAccelerate emissionsReduce disturbanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroorganismGeneration process
The invention relates to soil microbial molecular ecology, specifically a method for distinguishing soil N2O emission sources. Measure the isotope δ15N value of N2O emitted by the soil to be analyzed after treatment, and the copy number of related microbial genes in the process of soil N2O production, and the correlation between gene abundance and the abundance value of δ15N-N2O is tested for functional microbial groups with p<0.05 , which is the microbial population that plays an important role in soil N2O emission. This method is suitable for differentiating N2O-emitting microbial populations in a certain soil.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extracting method of cellulose degradation flora metagenome
ActiveCN105821033AEasily brokenFacilitated releaseMicroorganism lysisDNA preparationCelluloseCell wall
The invention discloses an extracting method of cellulose degradation flora metagenome and provides an extracting method of cellulose degradation flora metagenome DNA. The extracting method comprises the following steps that cellulose degradation florae are sequentially subjected to thallus wall breaking, DNA organic solution extraction, DNA isoamylol sediment and DNA solution so that the metagenome DNA can be obtained. Experiments prove that a high-salt solution is adopted for carrying out eluting before extraction, lysozyme and mechanical homogenate are added to reinforce cell wall breaking, proteinase K is adopted for wall breaking, cell walls of microorganisms can be broken more easily, and DNA molecules can be released more easily. Meanwhile, the process repeatability is effectively ensured, and then integrity and purity of extracted metagenome DNA fragments and flora structure integrity are ensured. The extracting method provides an effective technology support for study and application of the natural cellulose utilizing florae and the microorganism molecular ecology study.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A kind of mussel environmental DNA metabarcoding primer, identification method and application
ActiveCN113512593BProtected speciesSave human and financial resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementInvasive species monitoringMicrobiologyZoology
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method for constructing Copepoda full-length cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) library
InactiveCN104278023ASmall amount of sampleSimple methodLibrary creationDNA preparationEcologic studyComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a method for constructing a Copepoda full-length cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) library. The method comprises the following steps: extracting high-quality RNA (ribonucleic acid) from a small amount of Copepoda individual, and carrying out reverse transcription to obtain a first chain cDNA by using Modified oligo dT as a primer; and on the basis of the sequence of a messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid) transsplicing precursor spliced leader (SL for short) of the Copepoda, designing a forward degenerate primer Copepod SL, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification for 25-35 cycles by using a Modified oligo dT upper adaptor sequence as a reverse primer and the first chain cDNA as a template, and carrying out the conventional connection-transformation-cloning process to obtain the full-length cDNA library of Copepoda. The method has the advantages of small required sample quantity and high efficiency, is simple and easy to operate, is suitable for Copepoda molecular ecology research, and facilitates and promotes the quick and accurate screening of the functional gene.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for extracting microbial total DNA of cotton dreg fermentation sample
The invention discloses a method for extracting microbial total DNA of a cotton dreg fermentation sample, which belongs to the technical field of bio-genetic engineering. The method aims at the adverse effects caused by protein, polysaccharide and phenol substances contained in a cotton dreg and a fermentation product in the process of extracting the microbial total DNA and the subsequent molecular operations, and is a method which is used for extracting the microbial total DNA at high quality and consists of key techniques of phenol removal through decolorization, protein and polysaccharide removal through repeated extraction, moderate wall breaking of microbial cells and the like. The method has the characteristics of strong pertinence, simplicity, practicability, lower extraction cost and the like, and the obtained DNA can be directly applied to PCR amplification and enzyme cutting reaction, thus the method establishes a foundation for researching microbial fermentation cotton dregdetoxification by using a molecular ecological method. The method can be applied to units or fields relating to cotton dreg comprehensive development technical study.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Mussel environment DNA macro bar code primer, identification method thereof, and application of primer and identification method
ActiveCN113512593AProtected speciesSave human and financial resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementInvasive species monitoringBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention particularly relates to a mussel environment DNA macro bar code primer, an identification method thereof, and application of the primer and identification method, and belongs to the field of molecular ecology. The mussel environment DNA macro bar code primer is named 16SPP300 or 16SPP147; the primer 16SPP300 is composed of an upstream primer as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and a downstream primer as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; and the primer 16SPP147 is composed of an upstream primer as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 and a downstream primer as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. The invention further discloses the identification method of environment DNA macro bar code for mussel community structure research, and application thereof. According to the method, abundance data of mussel animals which are difficult to collect and endangered in a traditional investigation method can be supplemented, male mussel species can be identified, the identification level, the species detection rate and the abundance evaluation accuracy of the mussels are effectively improved, and the method is an effective and reliable new mussel community structure investigation method and has practical value.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Reagent case for extracting zooxanthellae genom from ledge rock coral and method thereof
InactiveCN101250521BIncrease productionReduce physical injuryDNA preparationSilica gelChromatography column
The invention provides a reagent kit which extracts zooxanthella genome DNA from reef building coral and a method of the reagent kit. The reagent kit comprises: reagent A (lysis buffer), reagent B (protease E), reagent C (RNAase A), reagent D (supersaturation NaC1 solution), reagent E (DNA cleaning mixture) and reagent F (DNA eluent). The method of the invention comprises: firstly, using the lysis buffer which contains SDS to crack tissue cells, then, providing a high salt low PH circumstance, enabling protein in solution to degenerate further, but combining DNA on a silica gel column, and finally, quantitatively reclaiming the DNA from a chromatography column in water-soluble buffer solution. The zooxanthella genome DNA can be rapidly and conveniently extracted from varous reef building coral, the DNA which is obtained can be used to research molecular ecology, systematic evolution and the like, and thereby the demands of regular monitoring tasks in coral reef nature reserves can be satisfied.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com