Microbial genome database construction method and application thereof
A construction method and database technology, applied in the construction method of microbial genome database and its application in microbial identification, can solve problems such as false positives, and achieve the effect of good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1 method is established
[0053] 1. Microbial genome database construction method:
[0054] 1) Data acquisition: Obtain representative genome data of microbial species. Each strain of each species may have multiple genome sequences. For example, when genome data is obtained from NCBI, the RefSeq category marked as "reference genome" and " The genome sequence of "representative genome" is used as the genome sequence of the strain of the species; if there is no genome of "reference genome" or "representative genome", the genome marked with "na" is selected as the genome sequence.
[0055] 2) Plasmid sequence removal: In order to avoid the influence of the plasmid sequence on the identification, the plasmid sequence existing in the above-mentioned genome was removed to obtain the genome sequence after plasmid removal.
[0056] 3) Identification of the consensus sequence set and the specific sequence set: the above-mentioned plasmid-removed genomes of each speci...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2 Escherichia coli and Shigella data construction
[0069] The following uses Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri as examples to construct the database.
[0070] 1 Data Acquisition:
[0071] The microbial genome sequences were downloaded from NCBI, and the genome sequences GCF_000008865.2 and GCF_003697165.2 of two strains of Escherichia coli, and the genome sequences of two strains of Shigella, GCF_000006925.2 and GCF_007197595.1 were obtained.
[0072] 2 Remove the plasmid sequence: remove the sequence with Plasmid (plasmid) according to the sequence name in the genome sequence file.
[0073] 3 Identification of consensus and specific sequence sets: Merge the two genome sequences of Escherichia coli, and then use jellyfish to interrupt according to the length of 76bp, step size 1bp, jellyfish includes the process of removing redundancy, and obtain sequence set 1; The genome sequences were merged, and then jellyfish was used to cut them according to the le...
Embodiment 3
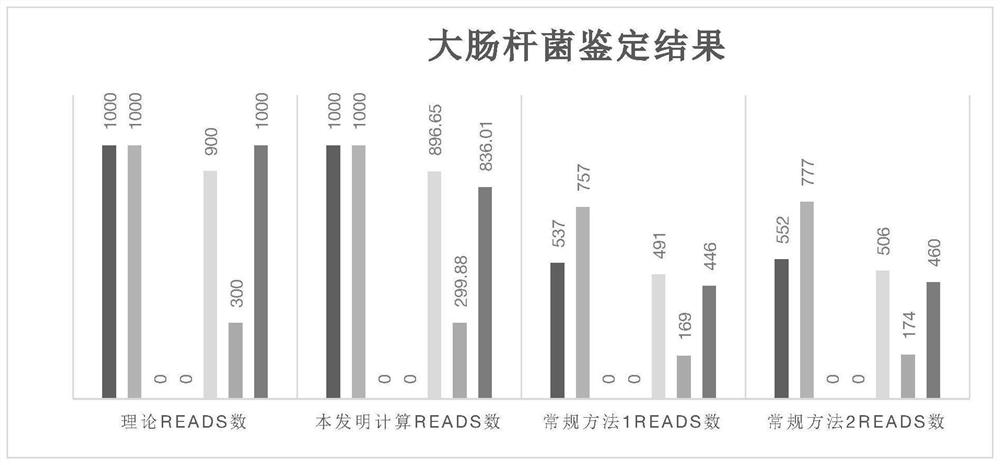
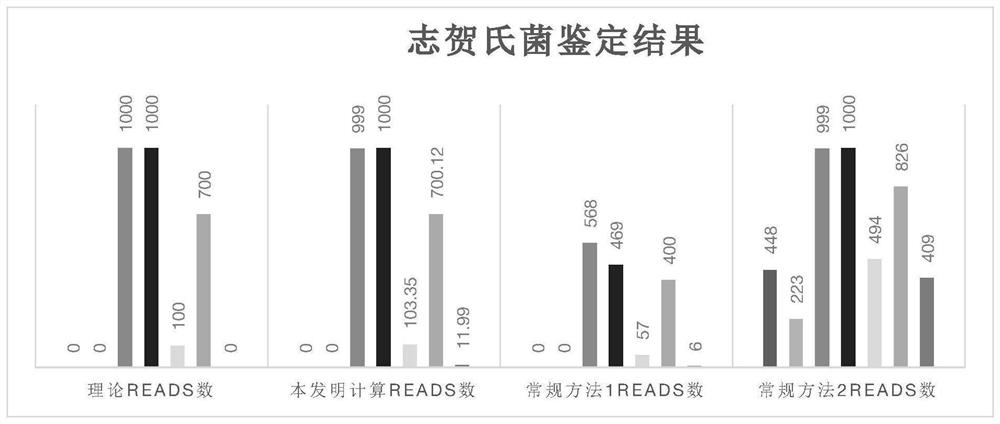
[0089] Embodiment 3 is compared with conventional library building and screening methods
[0090] The database was constructed according to the conventional method, that is, the genome sequences of 4 downloaded E. coli and Shigella species were used, and after removing the plasmid sequences, the sequences were merged together as the microbial genome reference database of the 4 species of bacteria.
[0091] For this database, use the blast software command makeblastdb to build a comparison library. Using the above 7 simulated data, perform blast comparison with this comparison library, and screen the comparison results.
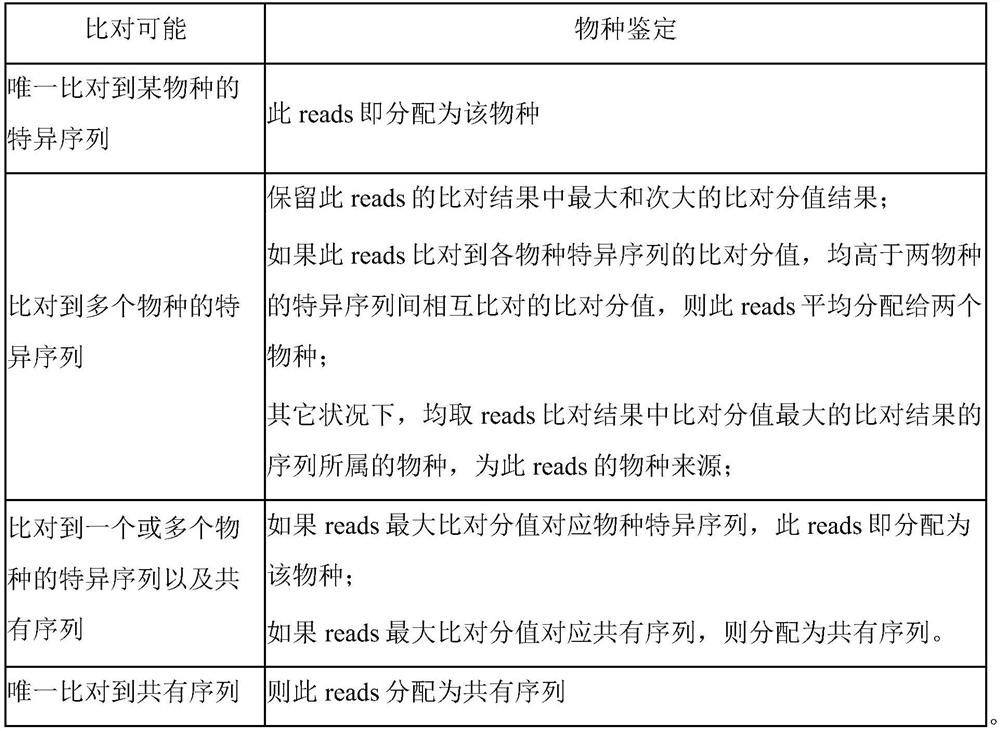
[0092] In the first method, when all the comparison results of each read are the same species, it is the source species of the reads; if all the comparison results of a single read are not the same species, the reads are discarded. The result is as follows:
[0093]
[0094] In the second method, each reads only retains the alignment result with the highe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com