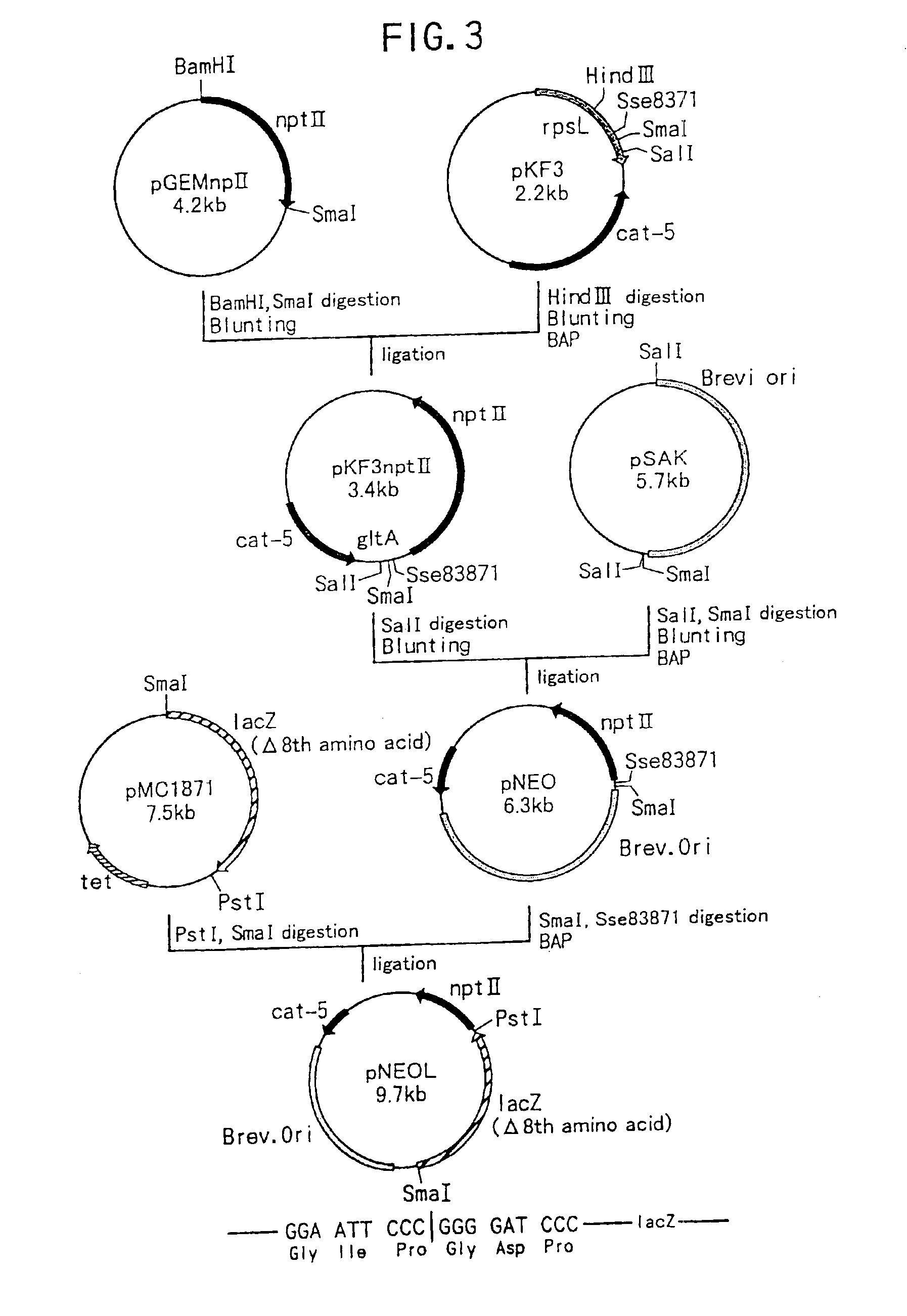
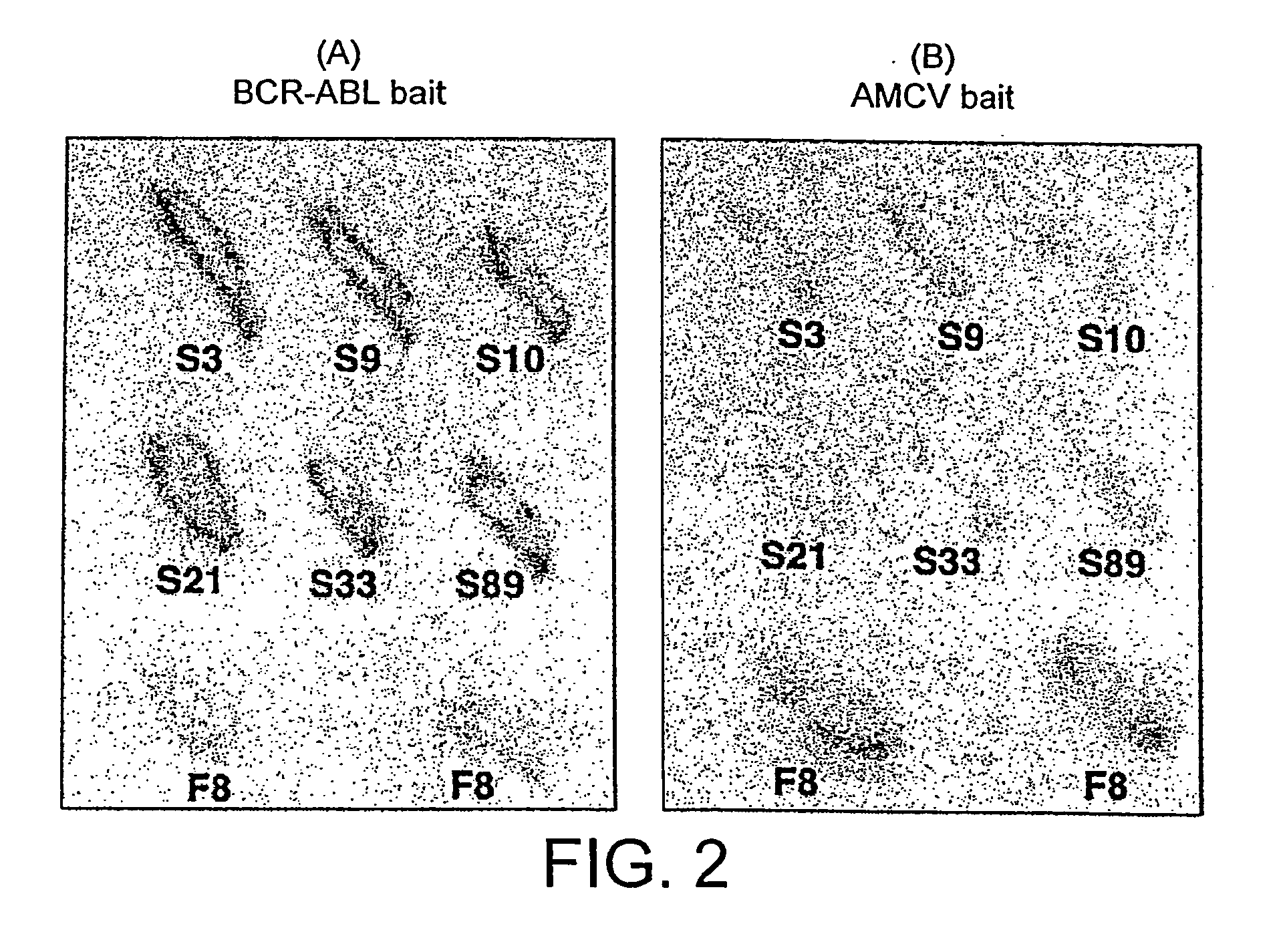
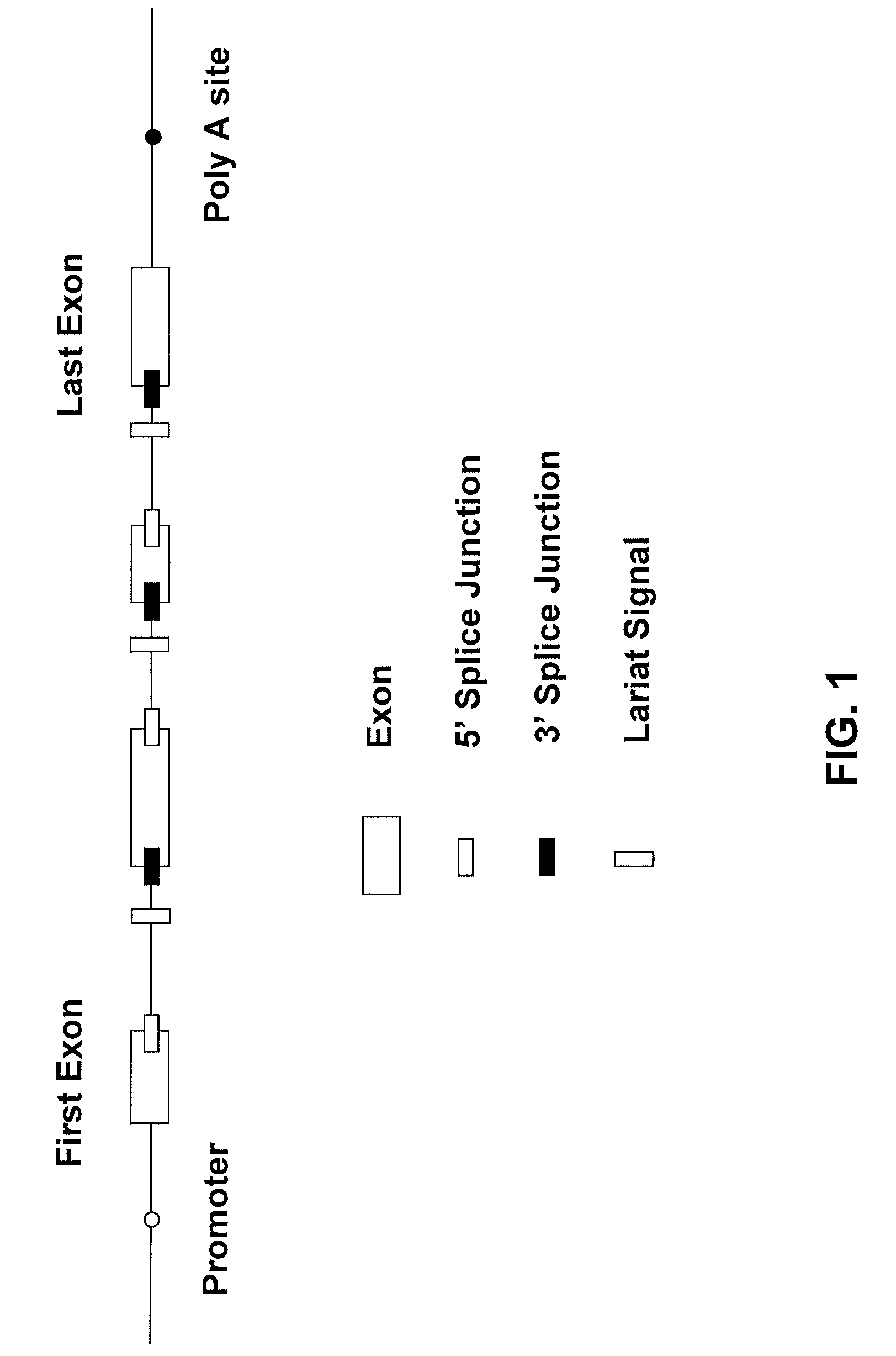
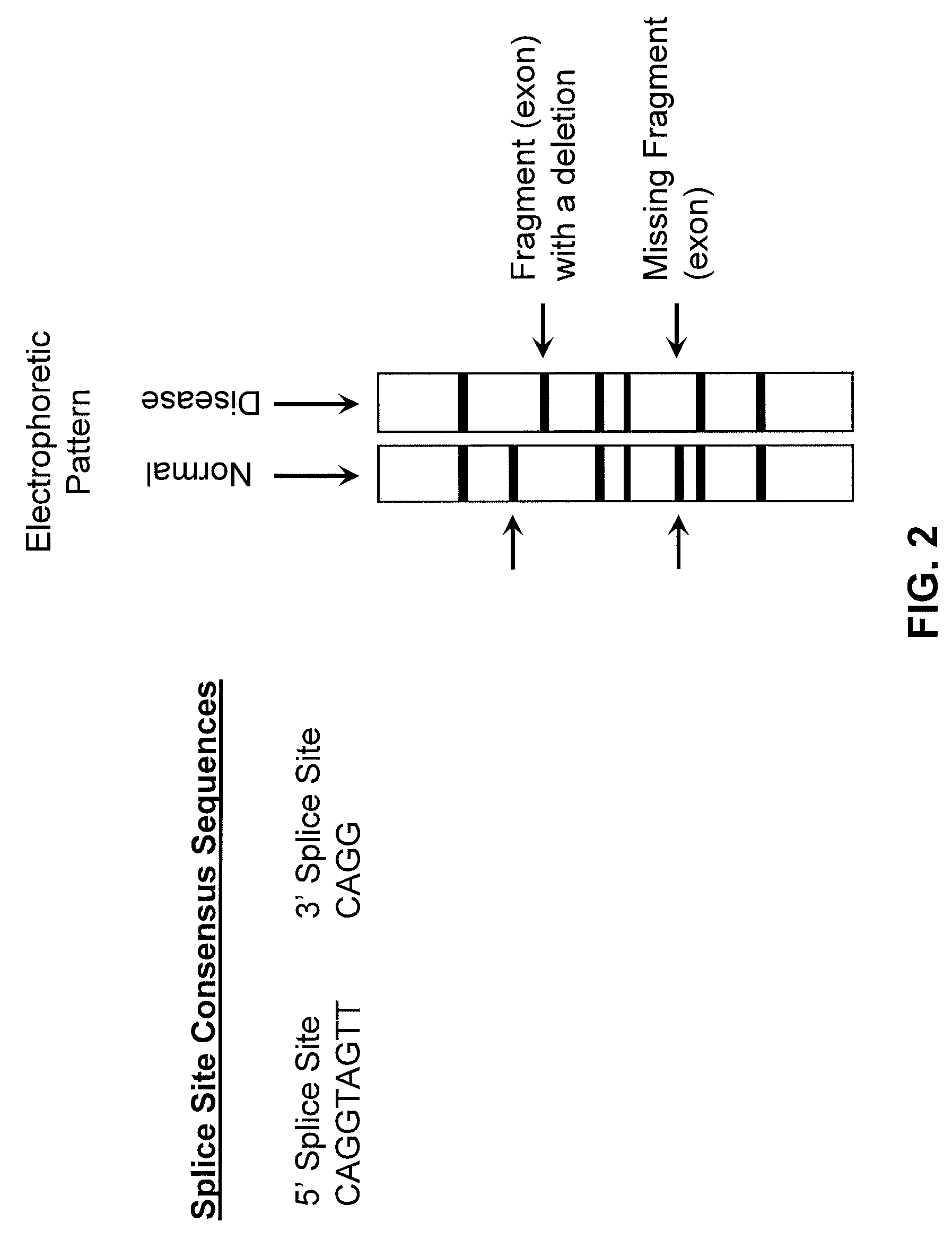
Patents
Literature
294 results about "Consensus sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
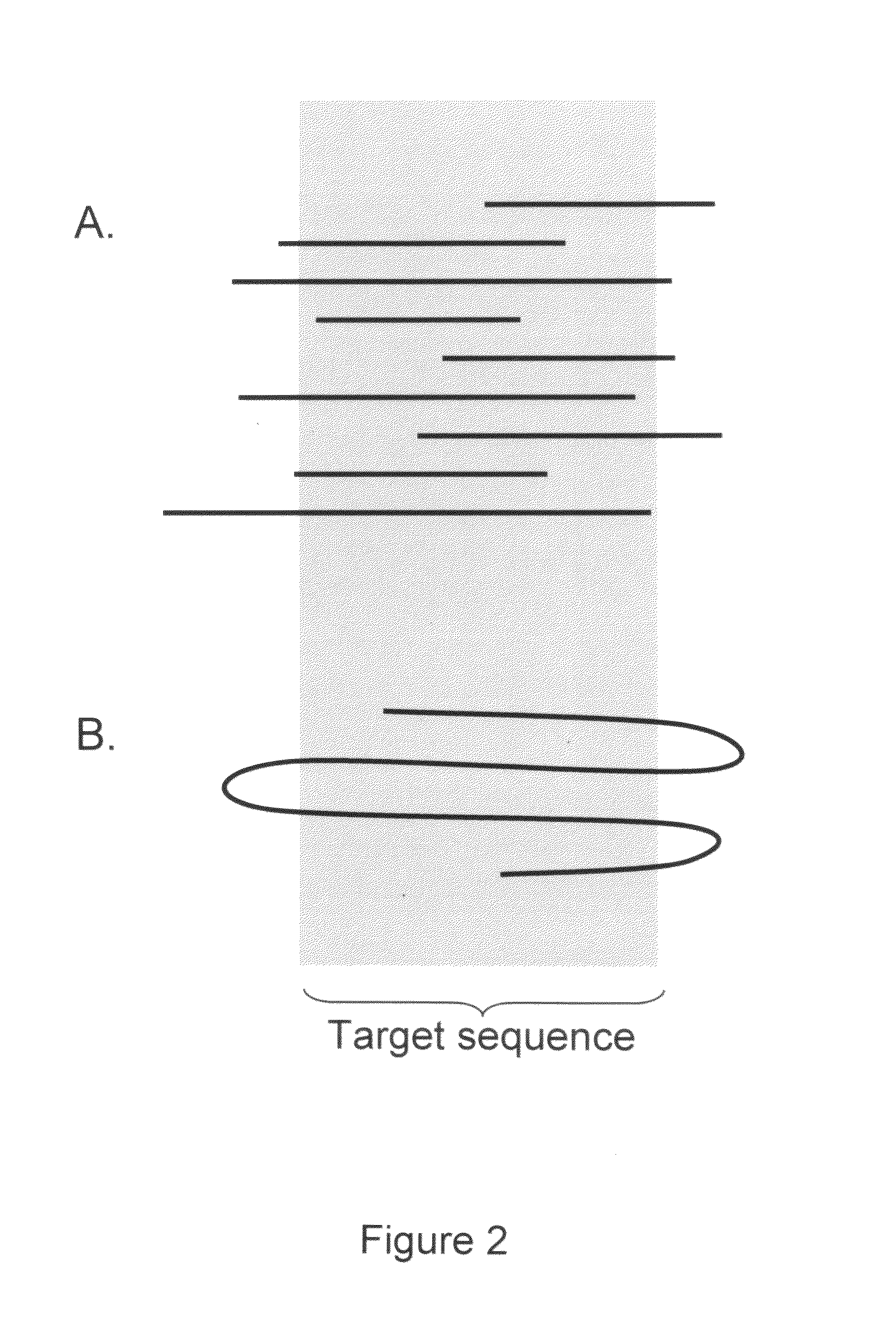
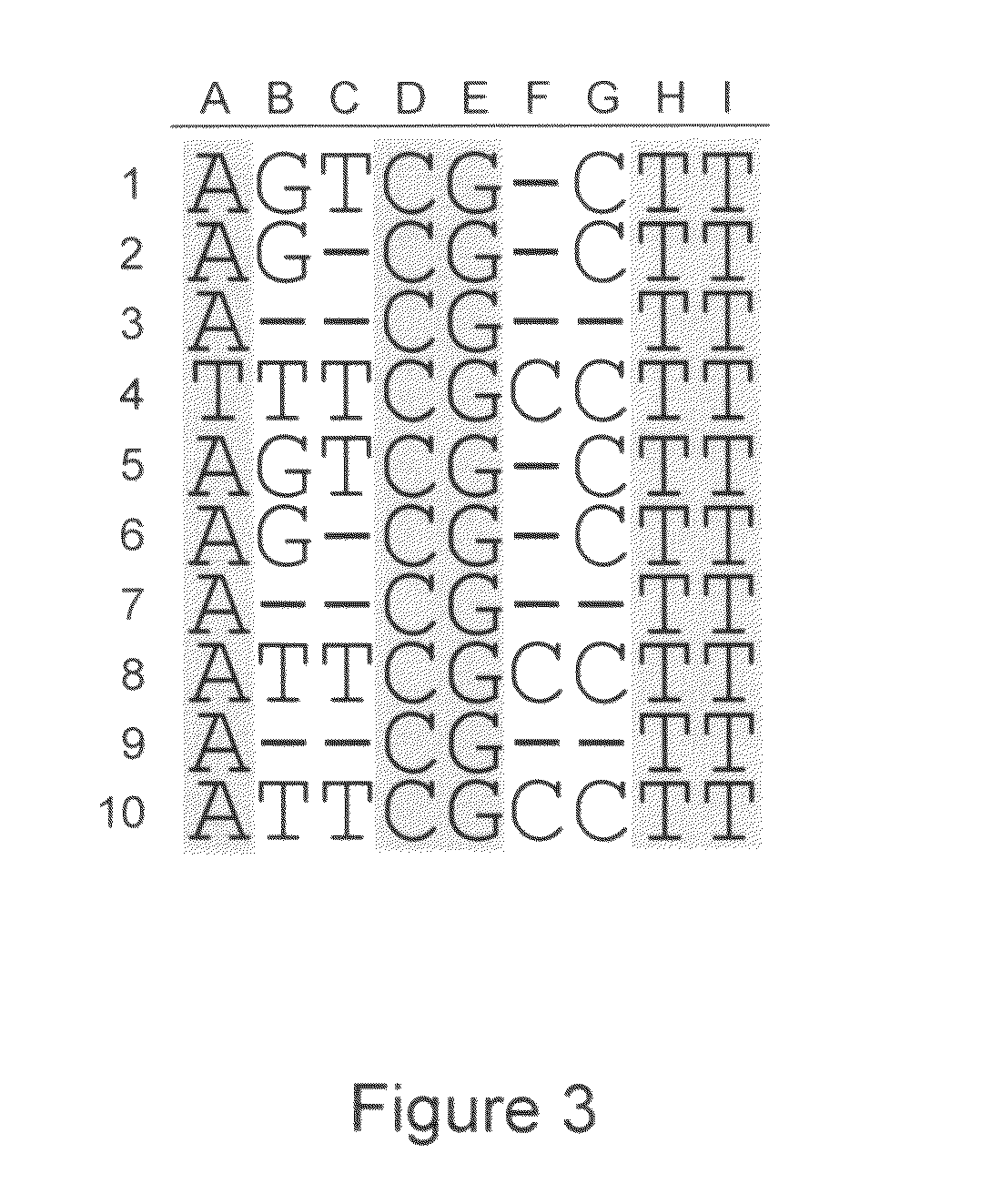
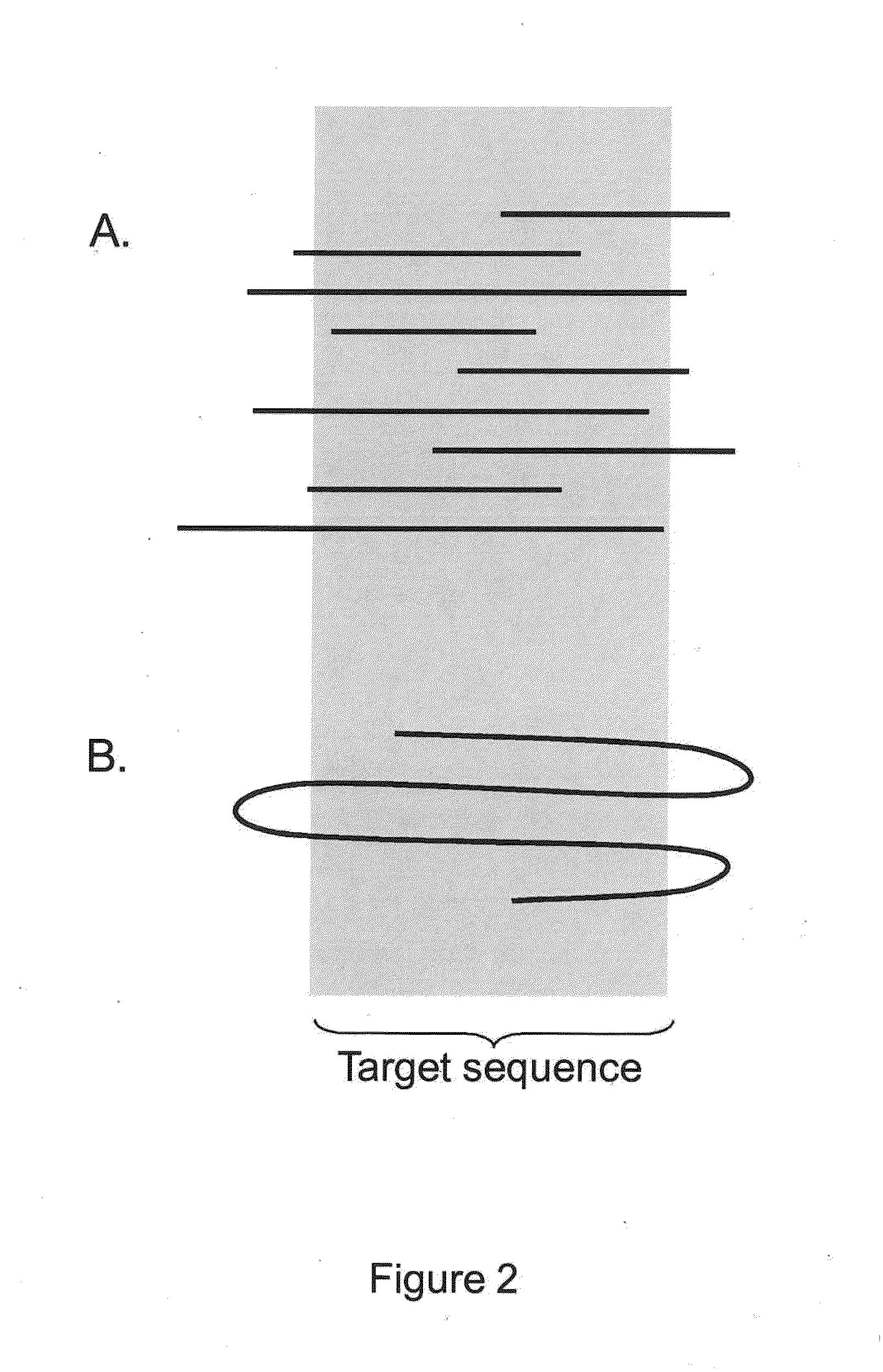
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, the consensus sequence (or canonical sequence) is the calculated order of most frequent residues, either nucleotide or amino acid, found at each position in a sequence alignment. It represents the results of multiple sequence alignments in which related sequences are compared to each other and similar sequence motifs are calculated. Such information is important when considering sequence-dependent enzymes such as RNA polymerase.
Protein/(poly)peptide libraries
InactiveUS6828422B1Reduce in quantityRemoving unwanted cleavages sitesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman DNA sequencingSynthetic DNA
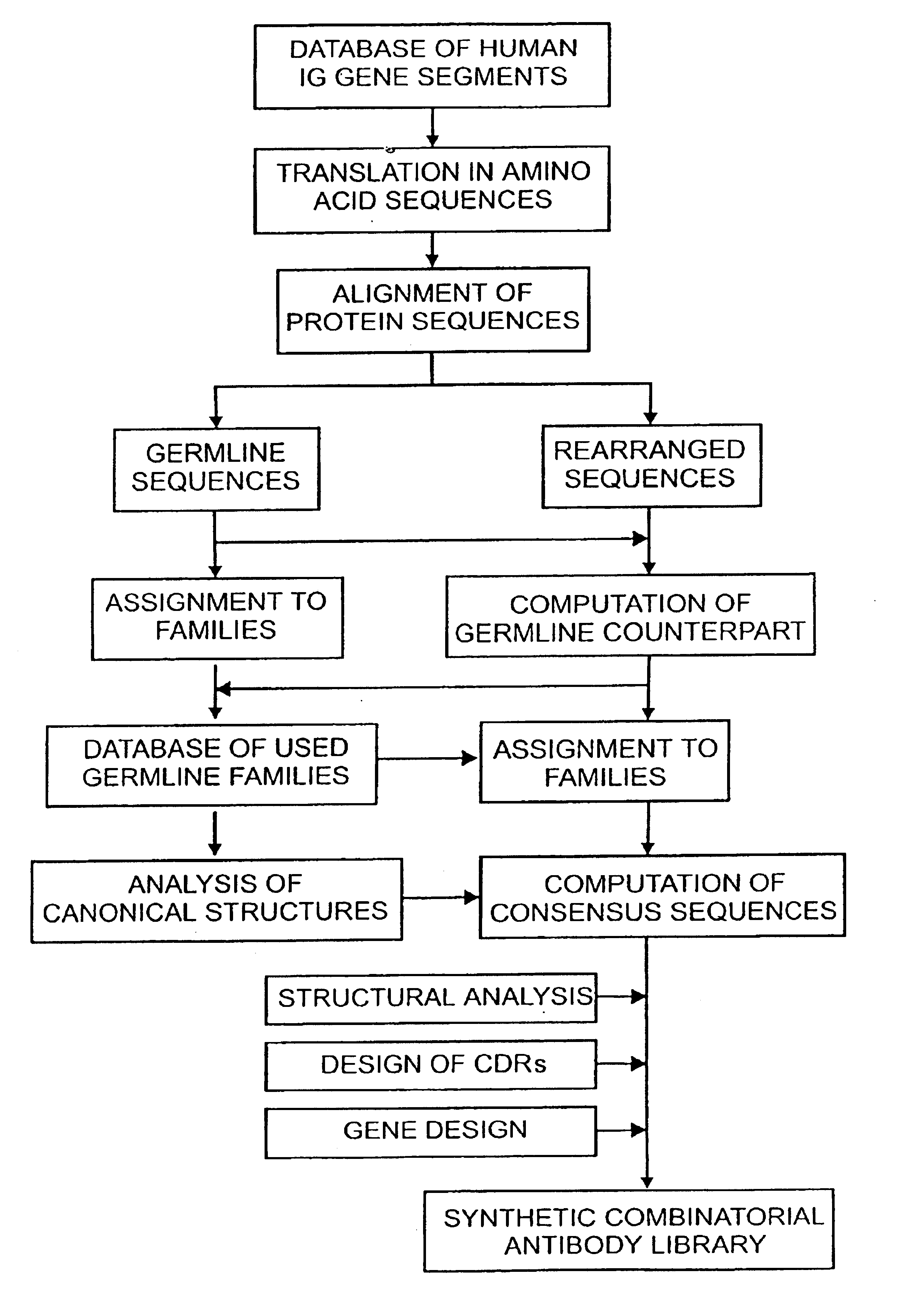
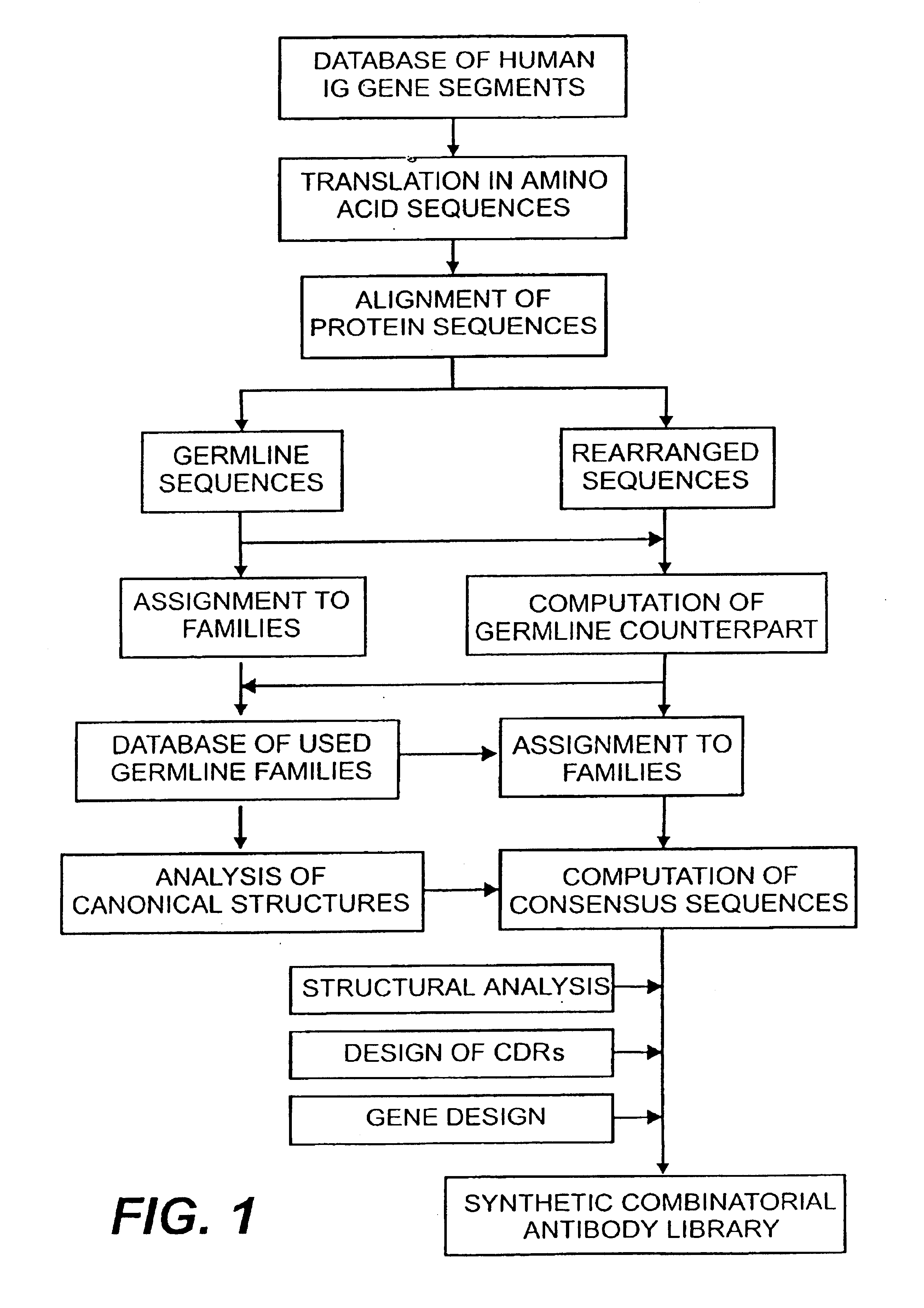
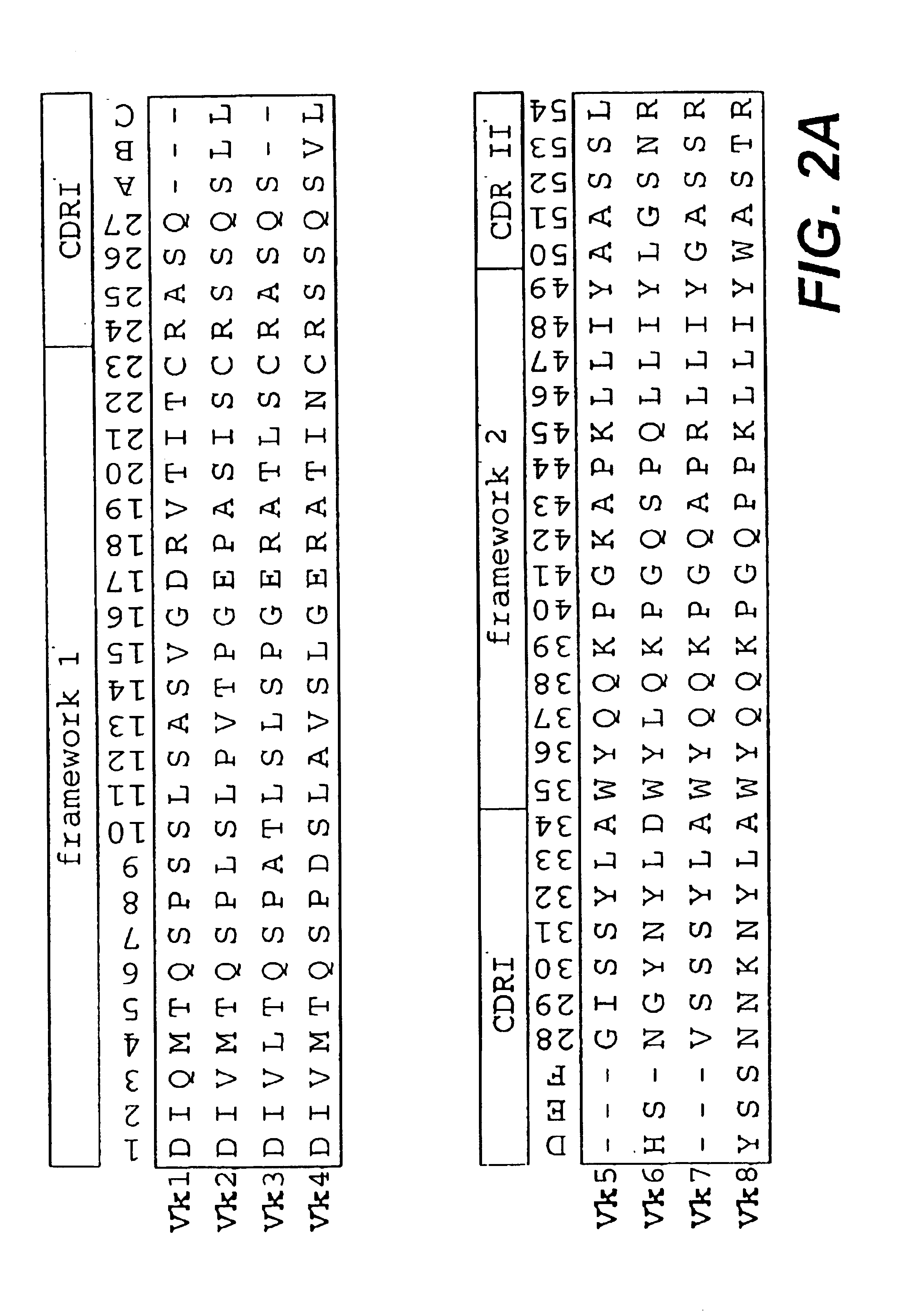
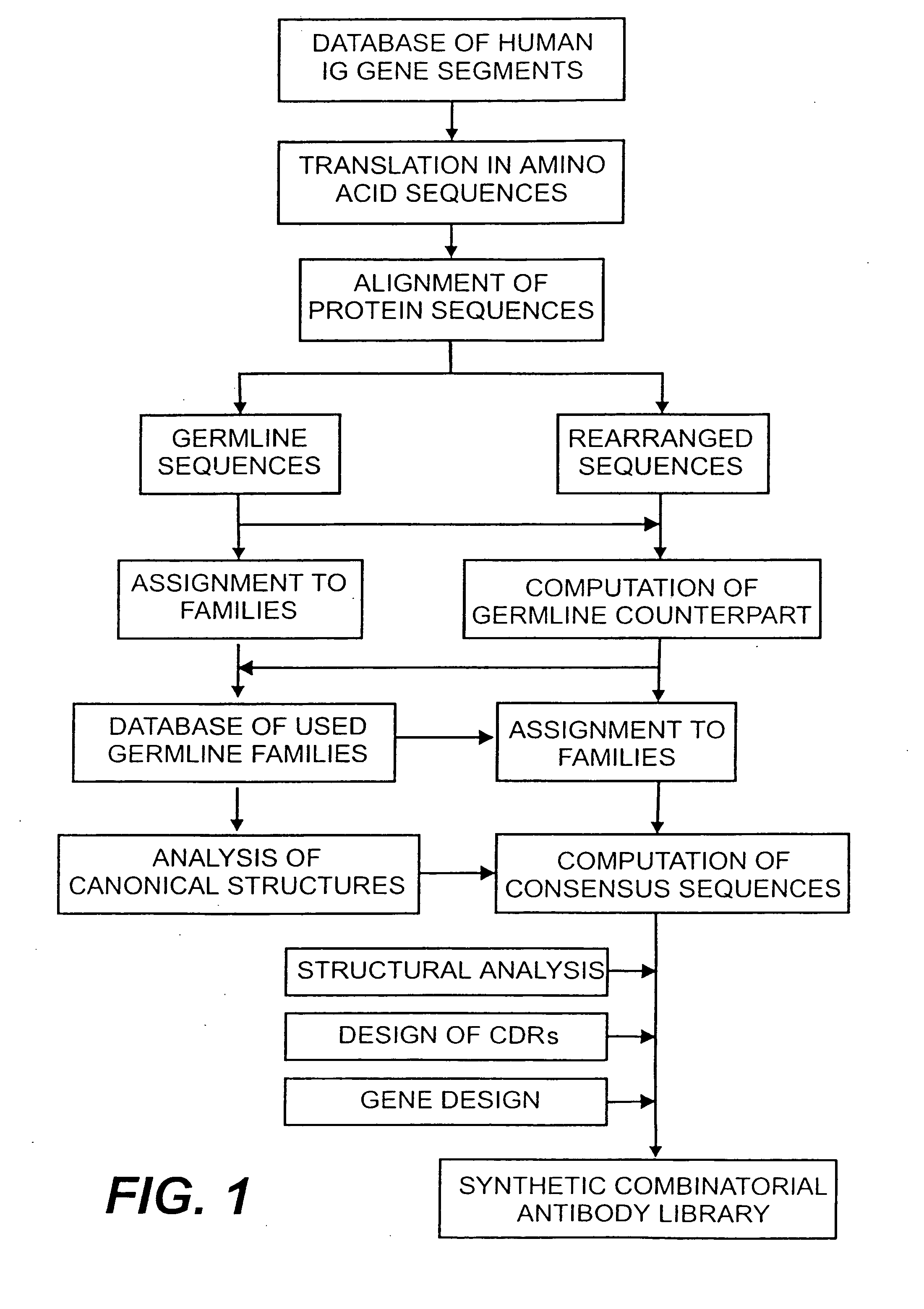
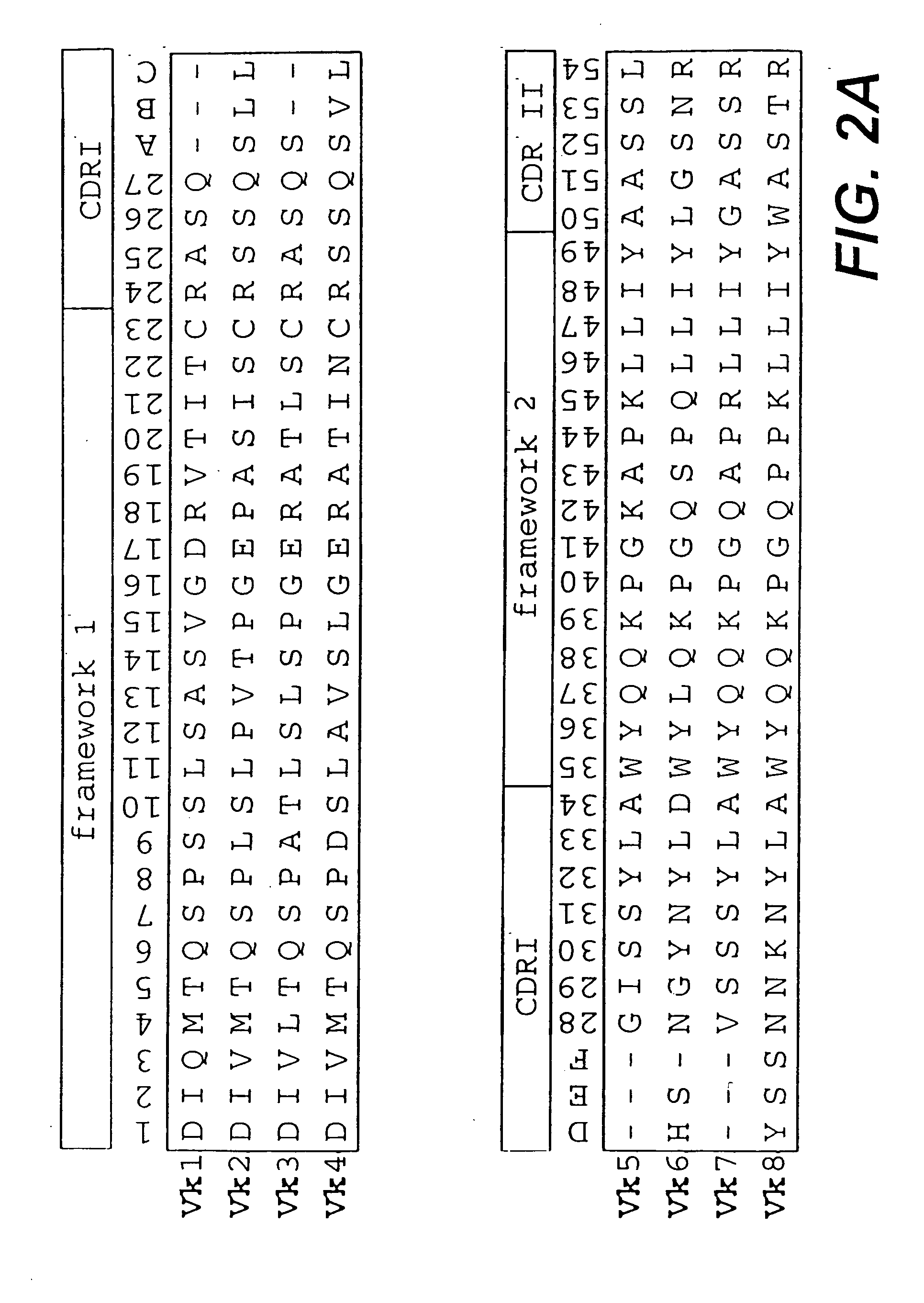
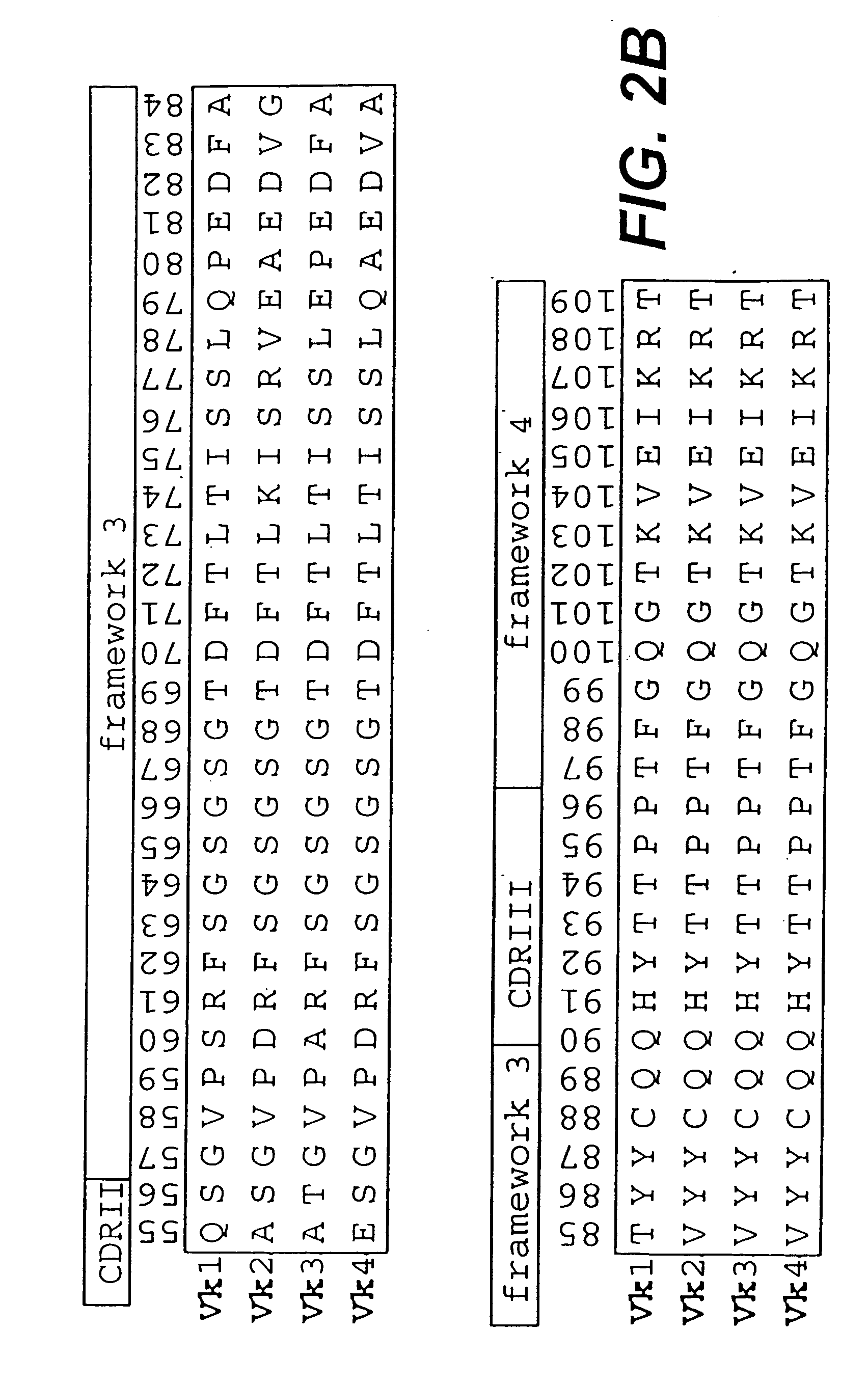
The present invention relates to synthetic DNA sequences which encode one or more collections of homologous proteins / (poly)peptides, and methods for generating and applying libraries of these DNA sequences. In particular, the invention relates to the preparation of a library of human-derived antibody genes by the use of synthetic consensus sequences which cover the structural repertoire of antibodies encoded in the human genome. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of a single consensus antibody gene as a universal framework for highly diverse antibody libraries.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
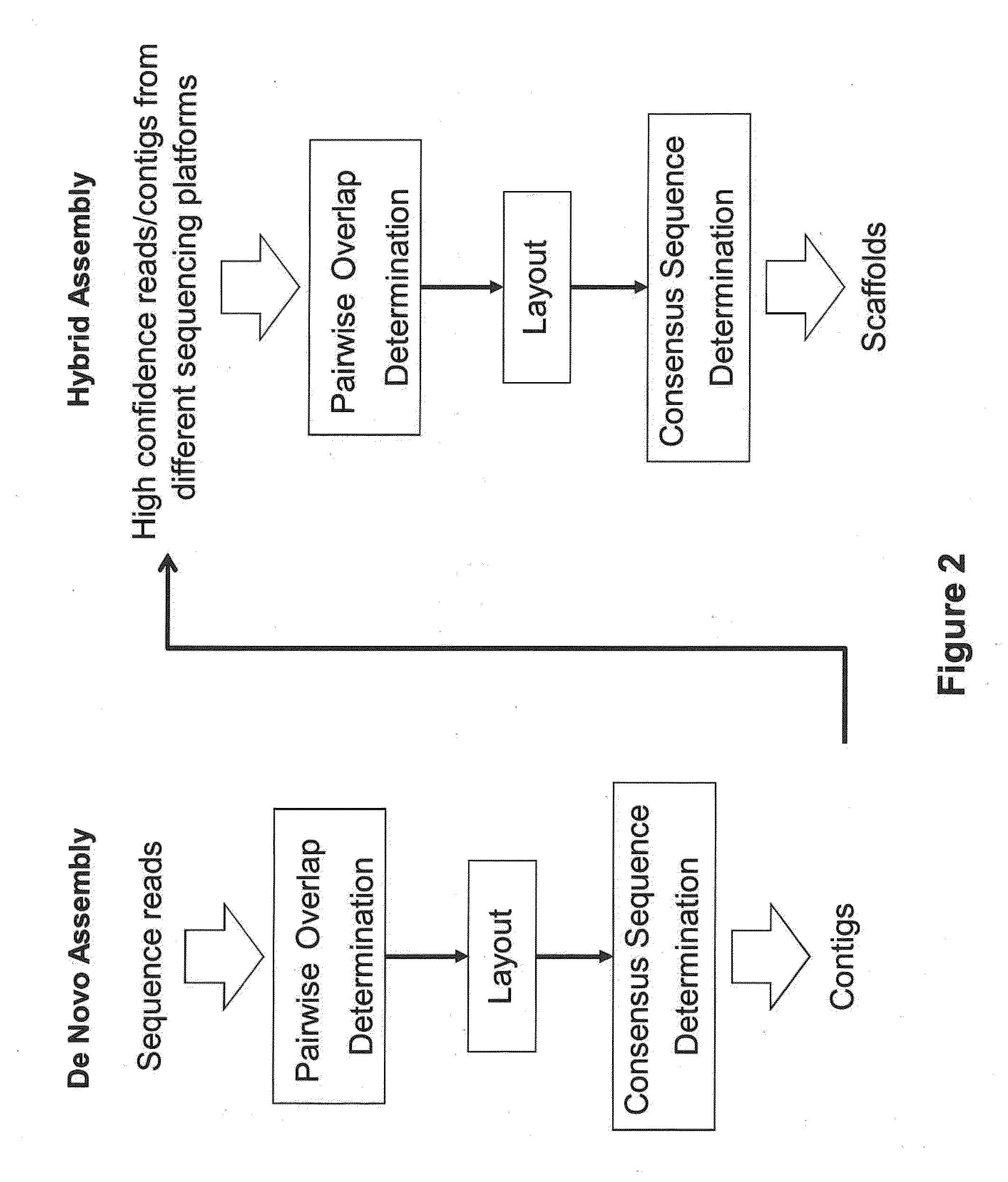
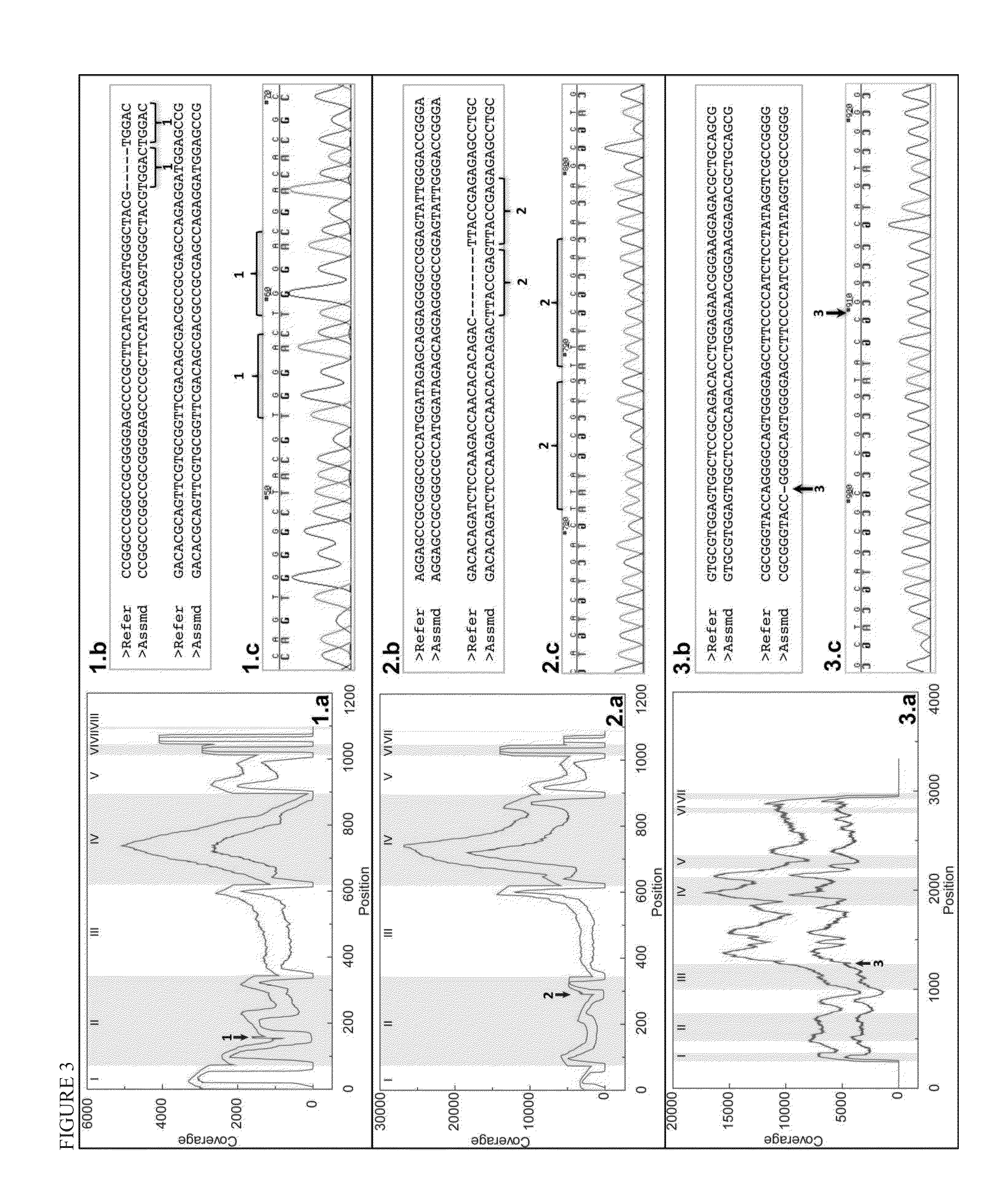
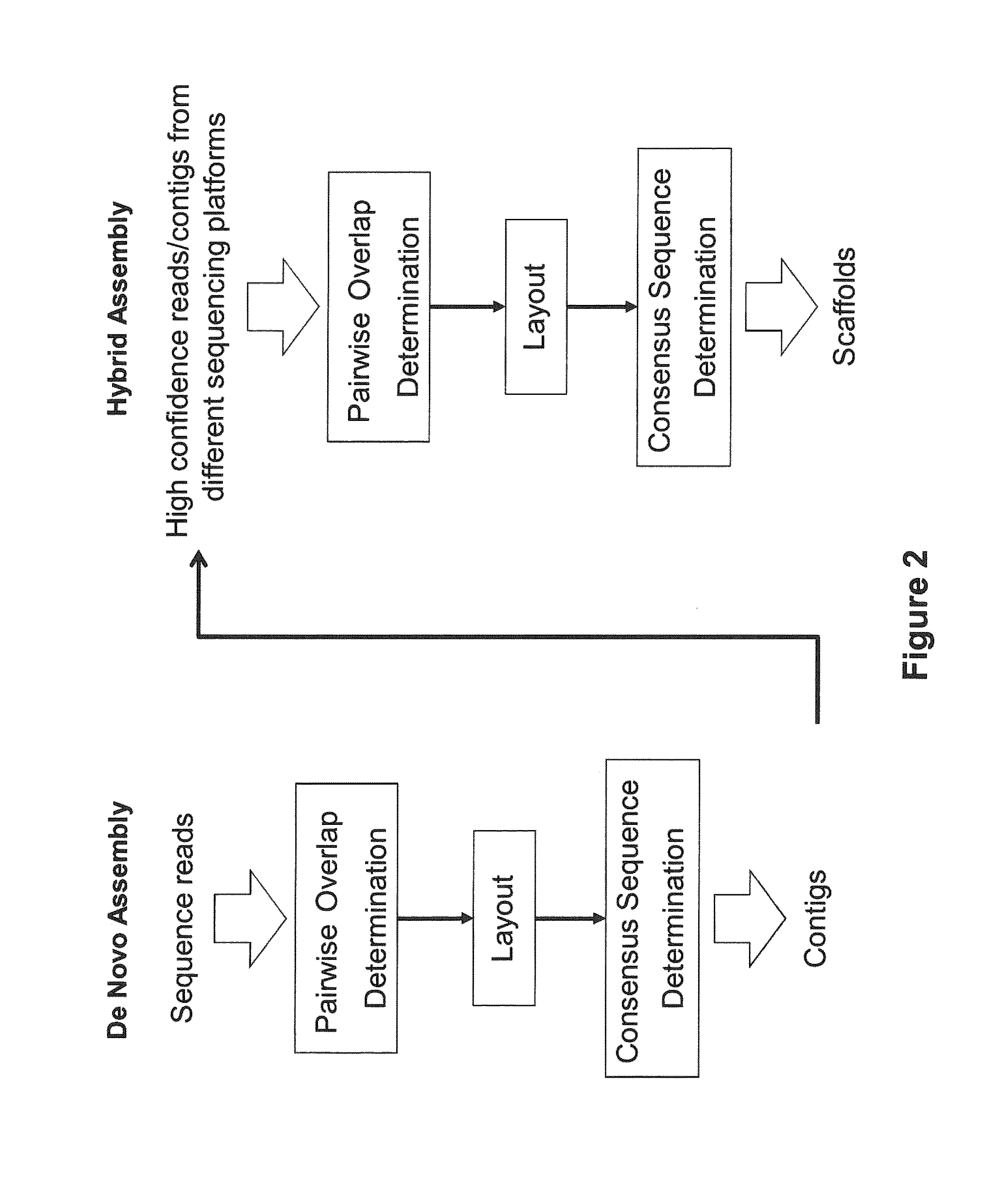
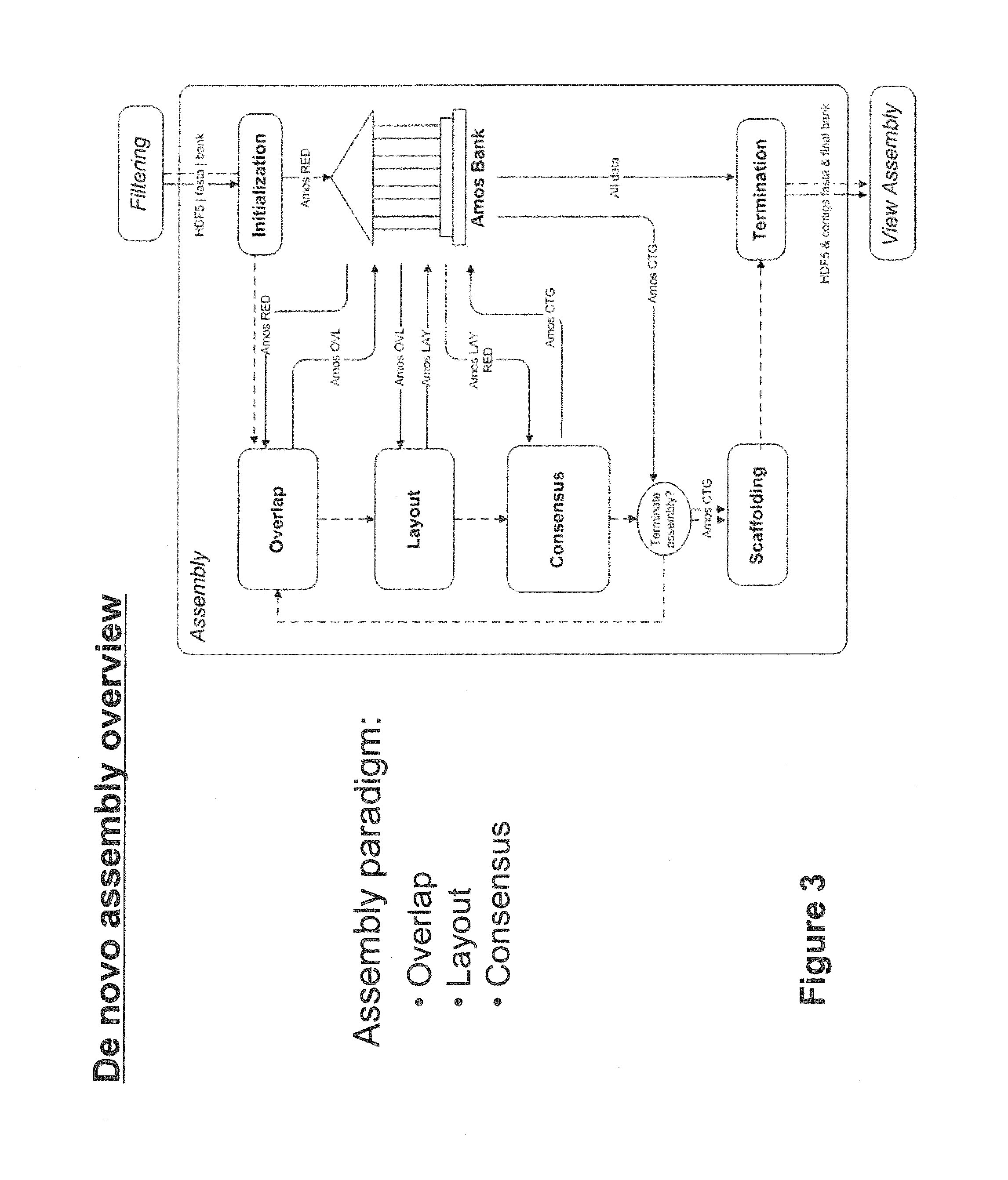
Sequence assembly and consensus sequence determination
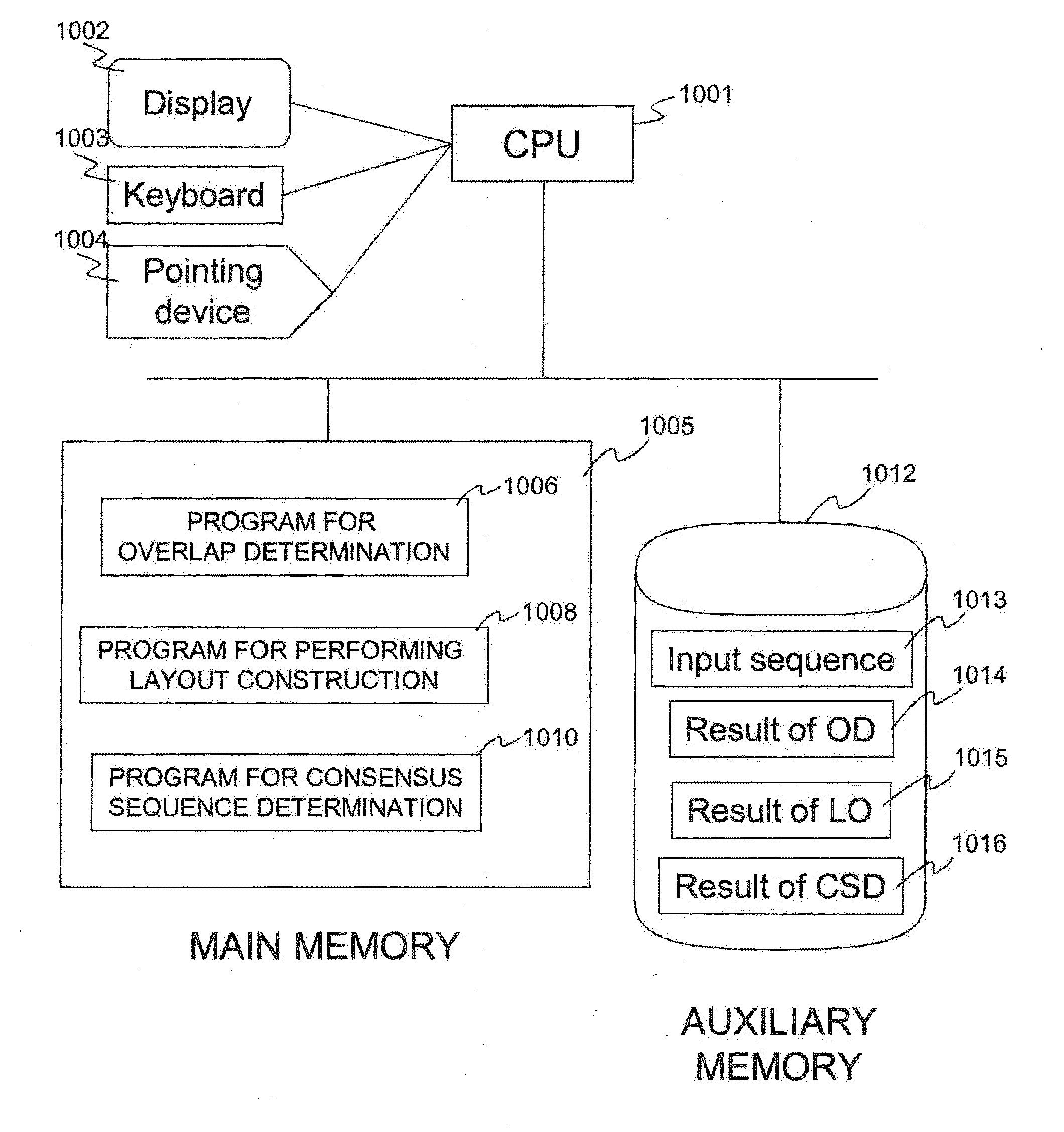
ActiveUS20120330566A1Maximum flexibilitySubstantial sensitivityBiostatisticsBiological testingNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
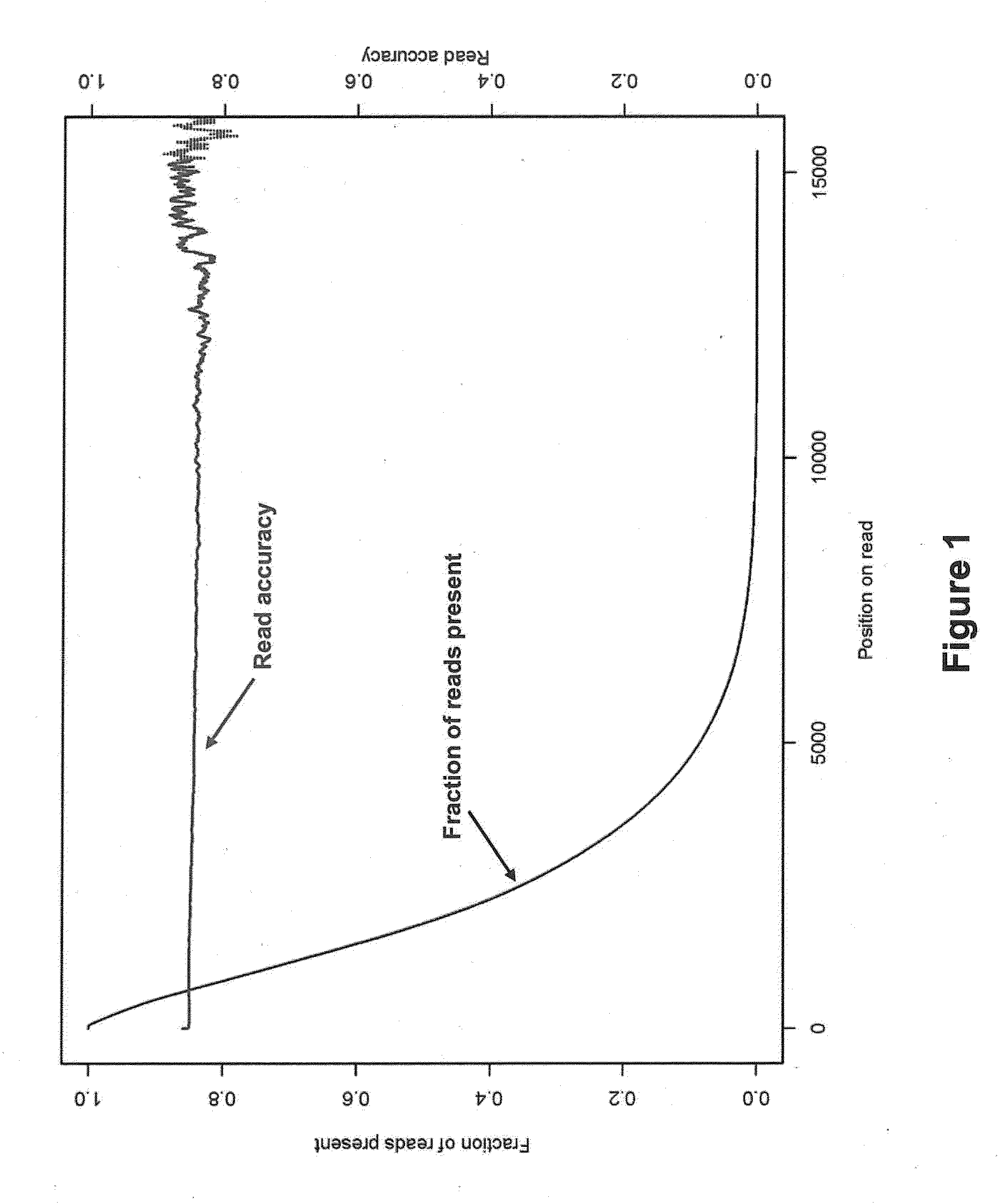
Computer implemented methods, and systems performing such methods for processing signal data from analytical operations and systems, and particularly in processing signal data from sequence-by-incorporation processes to identify nucleotide sequences of template nucleic acids and larger nucleic acid molecules, e.g., genomes or fragments thereof. In particularly preferred embodiments, nucleic acid sequences generated by such methods are subjected to de novo assembly and / or consensus sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method for Accurate Sequencing of DNA
ActiveUS20150275289A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationDNA formationComputational biology
DNA is sequenced by (a) independently sequencing first and second strands of a dsDNA to obtain corresponding first and second sequences; and (b) combining the first and second sequences to generate a consensus sequence of the dsDNA. By independently sequencing first and second strands the error probability of the consensus sequence approximates a multiplication of those of the first and second sequences.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method, computer-accessible medium and systems for score-driven whole-genome shotgun sequence assemble
ActiveUS20120041727A1Computation using non-denominational number representationSequence analysisHaplotypeData mining
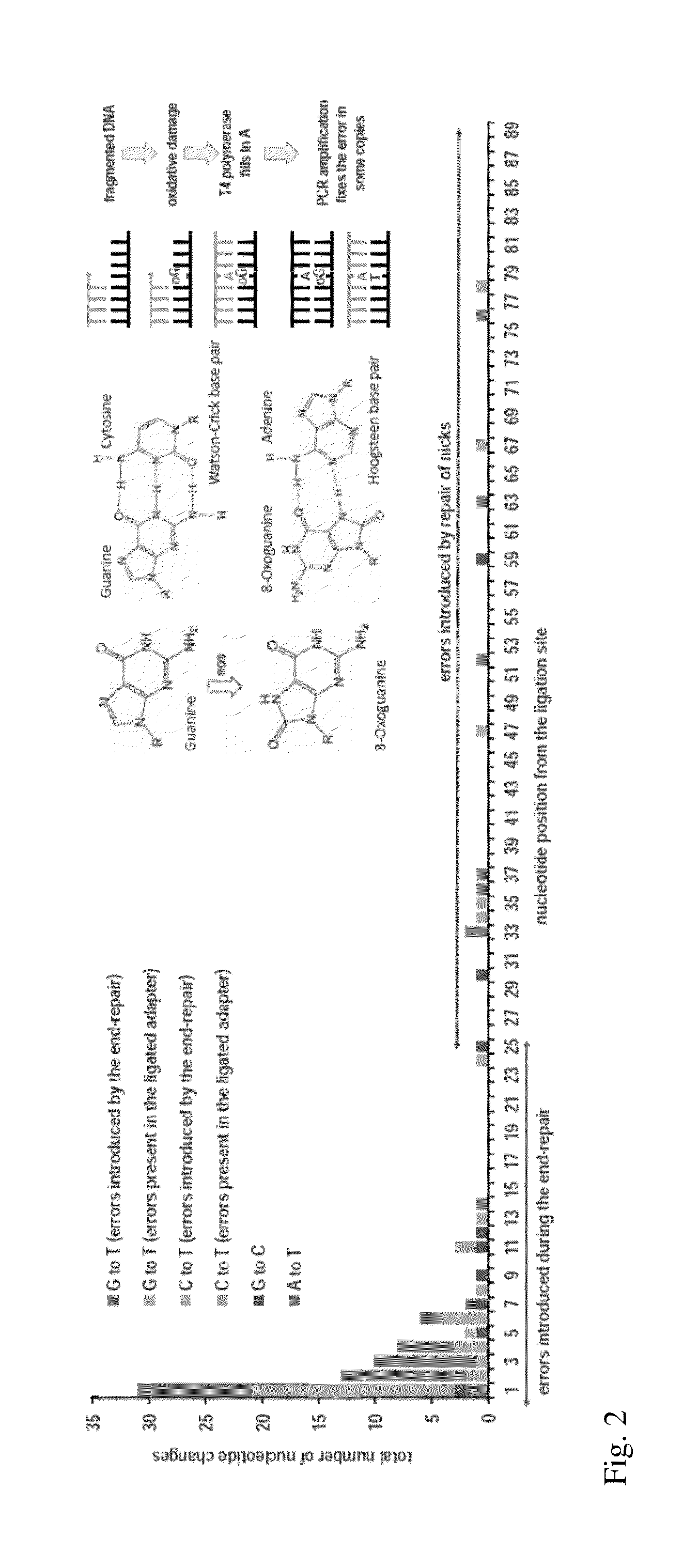
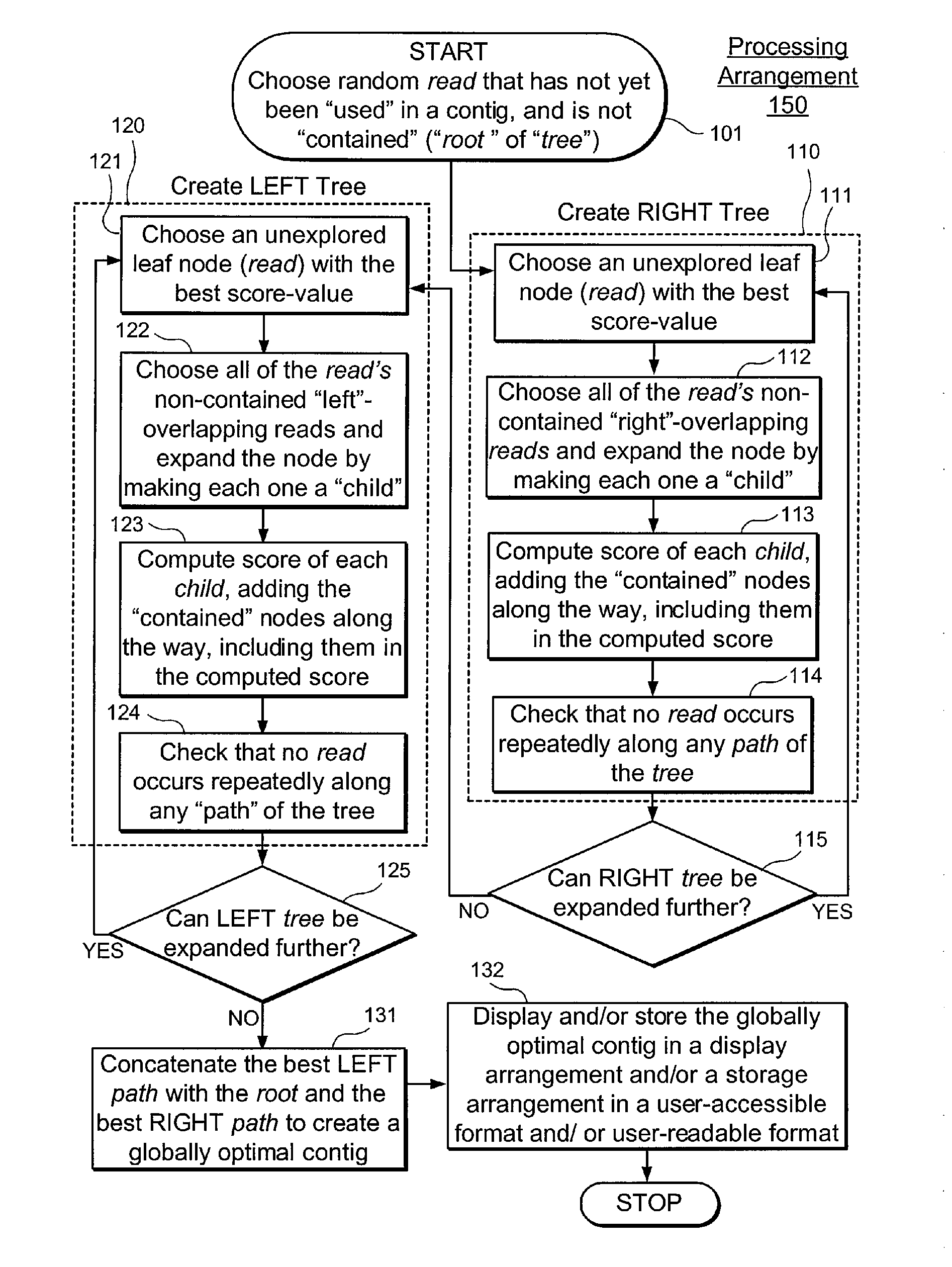
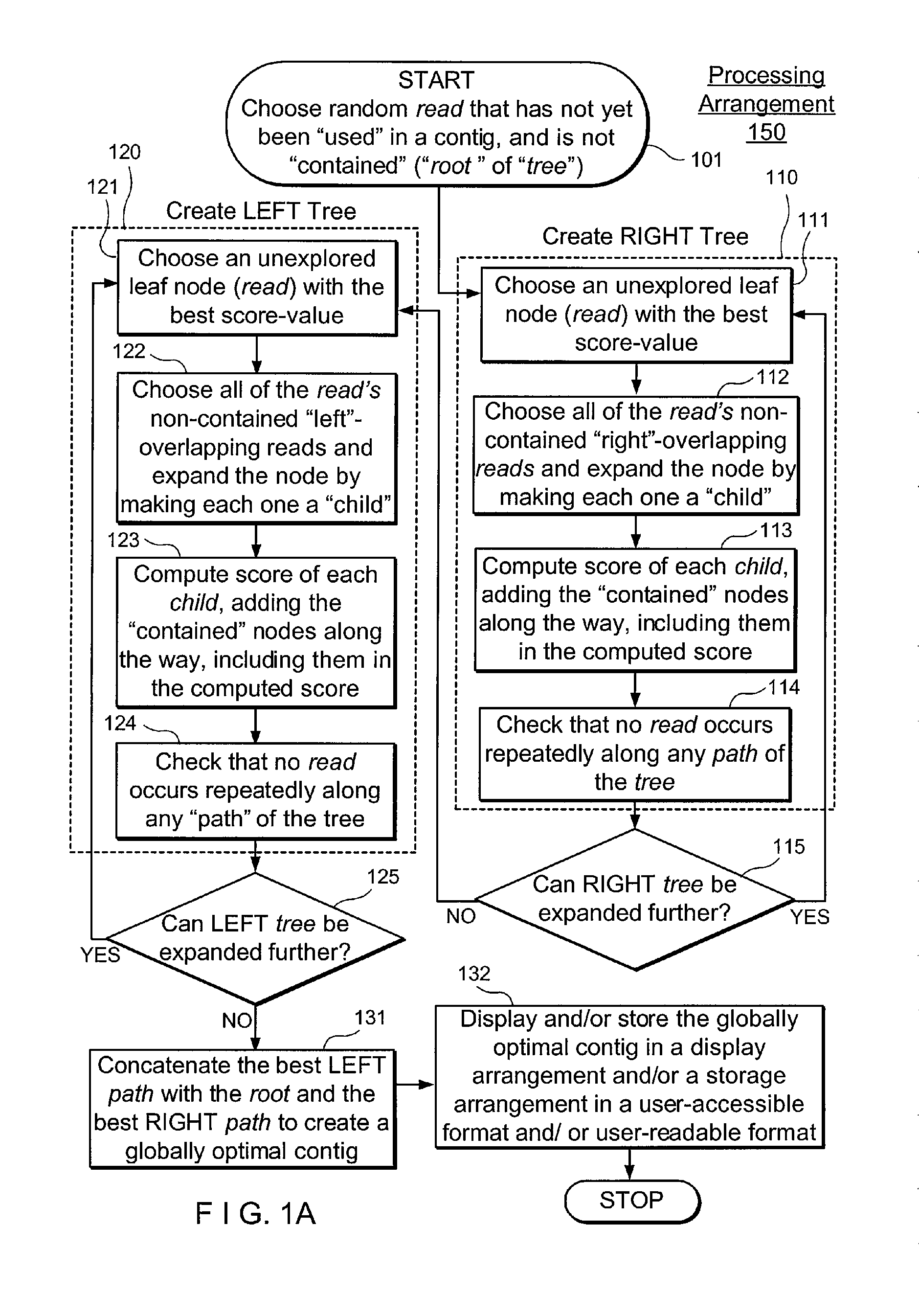
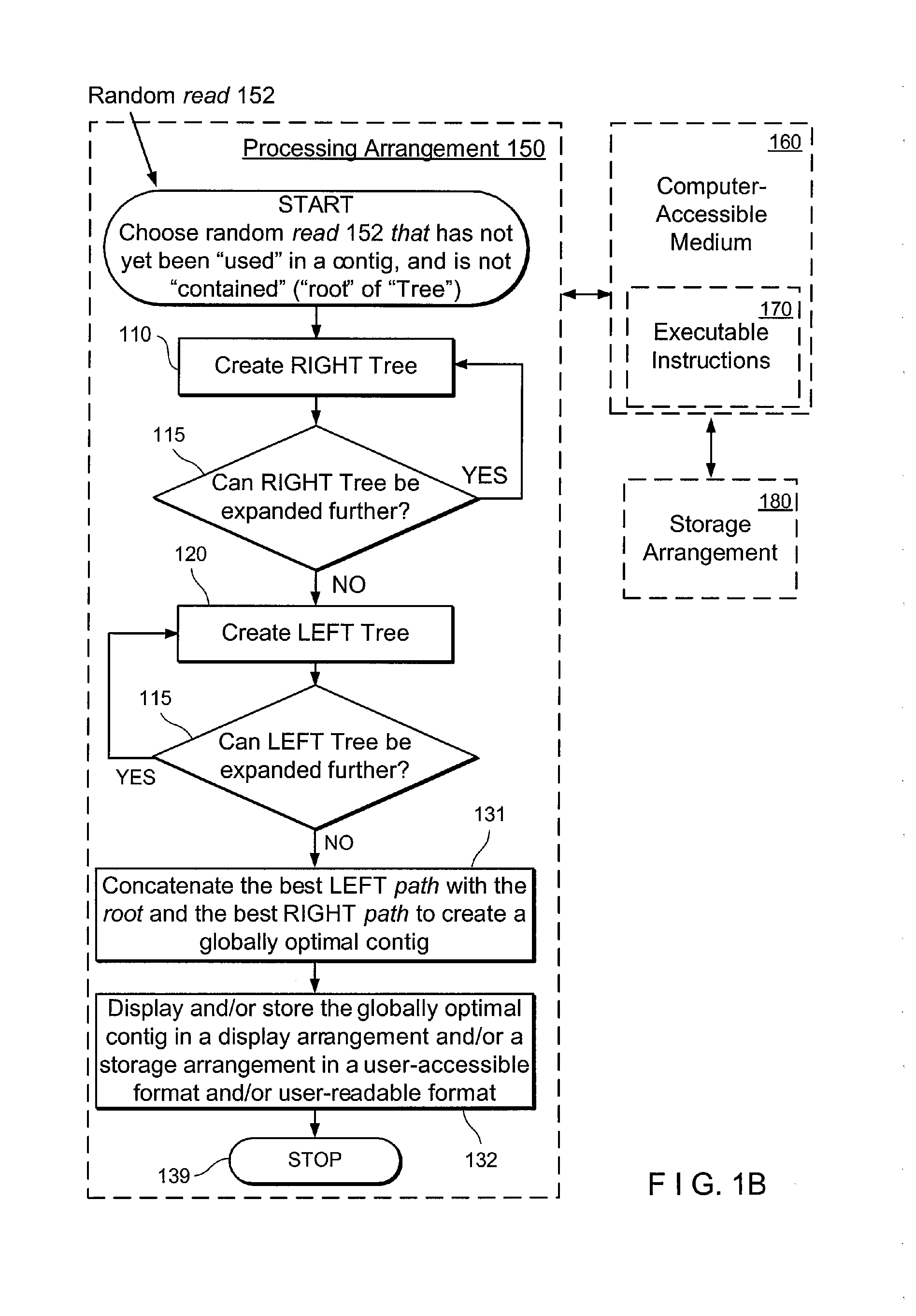
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to methods, computer-accessible medium and systems for assembling haplotype and / or genotype sequences of at least one genome, which can be based upon, e.g., consistent layouts of short sequence reads and long-range genome related data. For example, a processing arrangement can be configured to perform a procedure including, e.g., obtaining randomly located short sequence reads, using at least one score function in combination with constraints based on, e.g., the long range data, generating a layout of randomly located short sequence reads such that the layout is globally optimal with respect to the score function, obtained through searching coupled with score and constraint dependent pruning to determine the globally optimal layout substantially satisfying the constraints, generating a whole and / or a part of a genome wide haplotype sequence and / or genotype sequence, and converting a globally optimal layout into one or more consensus sequences.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
C-, S- and N-glycosylation of peptides
The present invention provides polypeptide conjugates wherein a modifying group such as a water-soluble polymer, a therapeutic agent or a biomolecule is covalently linked to the polypeptide through a glycosyl linking group. In one embodiment, the polypeptide includes a glycosylation consensus sequence, wherein glycosylation occurs at an aromatic amino acid residue, such as the C-2 or the N-1 position of a tryptophan side chain. Exemplary polypeptides of the invention are those in which the glycosylation consensus sequence has been introduced into the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide by mutation. In another aspect the invention provides polypeptide conjugates wherein the modifying group is covalently linked to the polypeptide via a glycosyl mimetic linking group. Also provided are methods of making and using as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing the polypeptide conjugates of the invention. Further provided are methods of treating, ameliorating or preventing diseases in mammals by administering an amount of a polypeptide conjugate of the invention sufficient to achieve the desired response.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
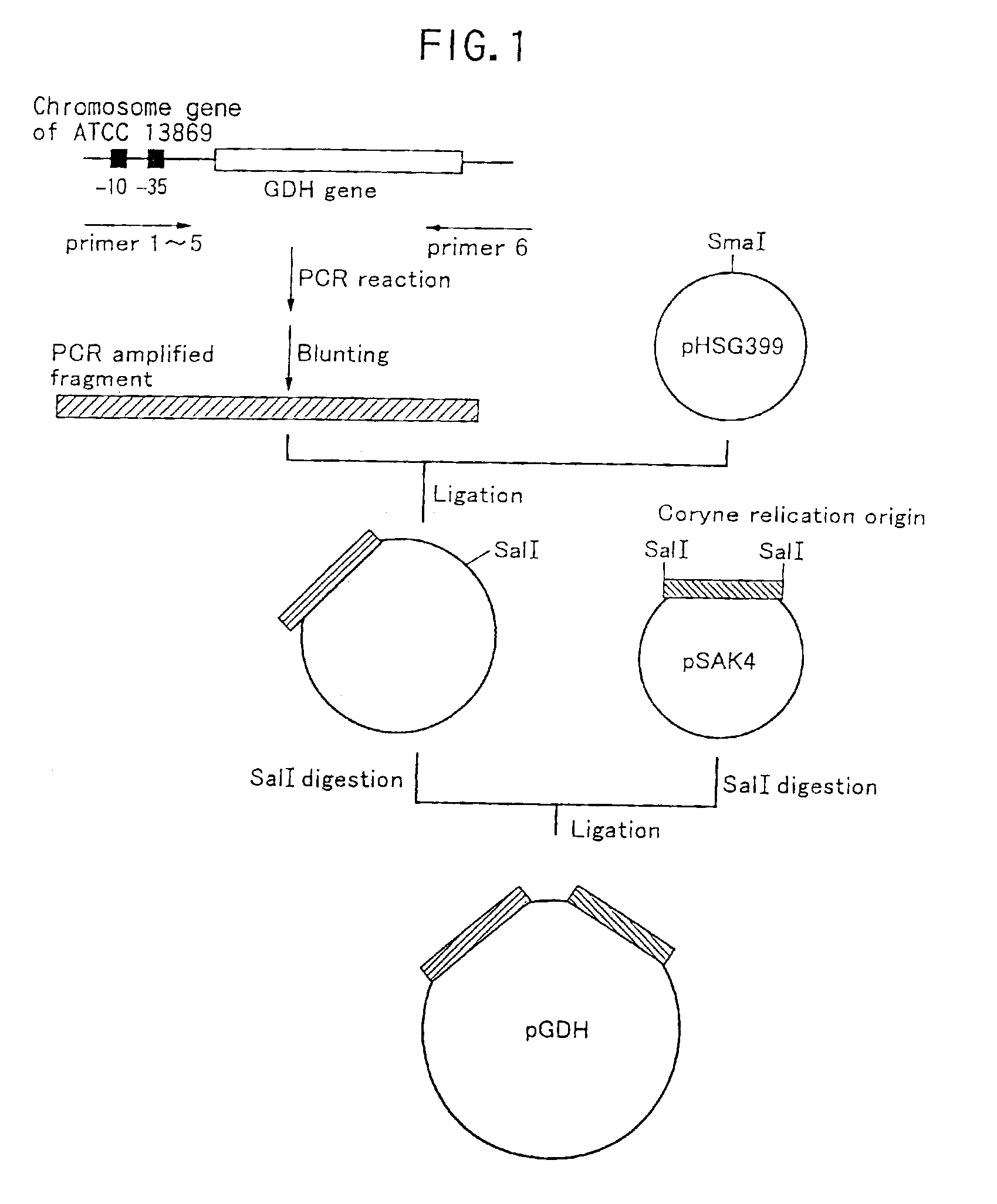
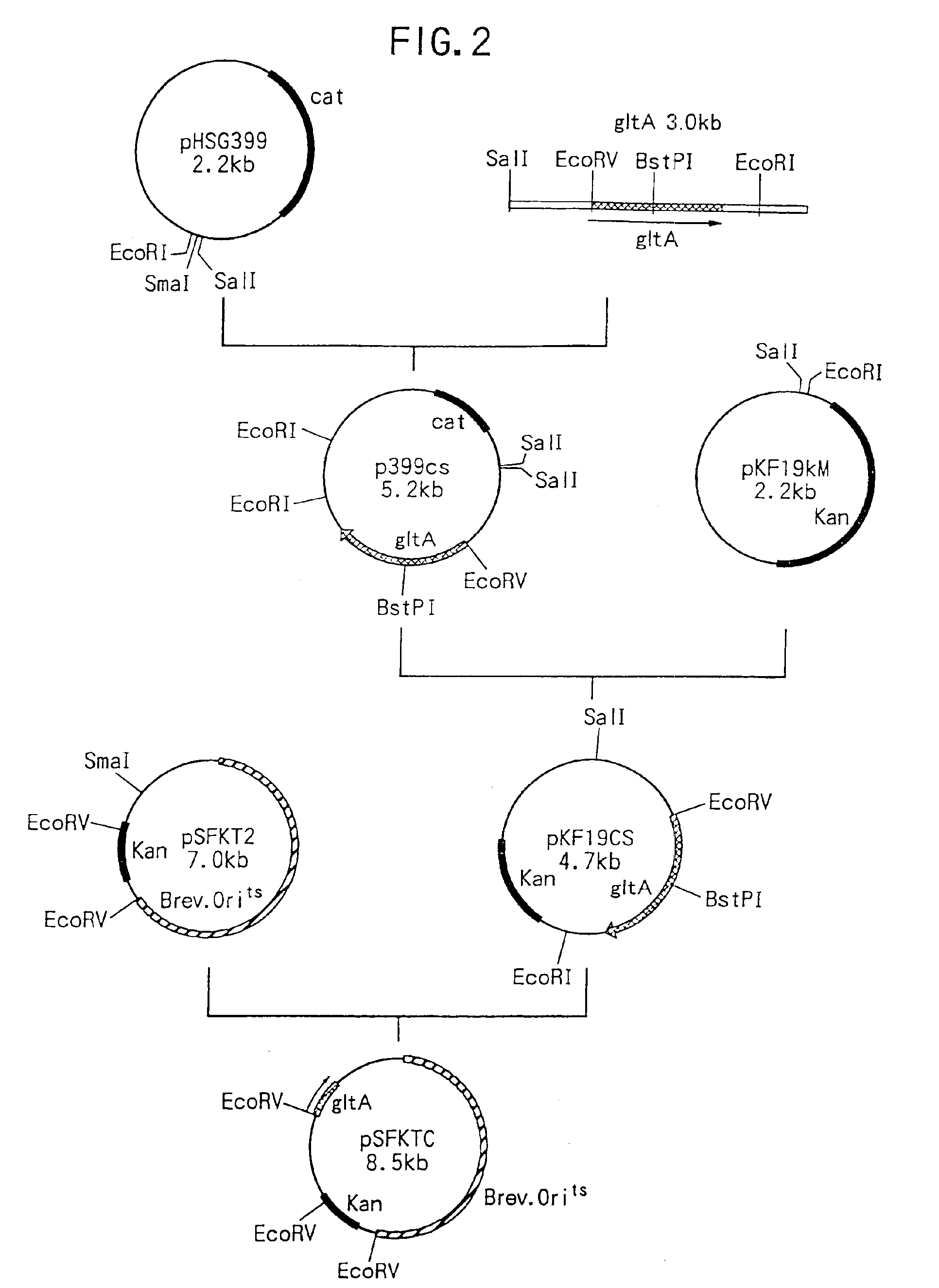
Method of constructing amino acid producing bacterial strains, and method of preparing amino acids by fermentation with the constructed amino acid producing bacterial strains
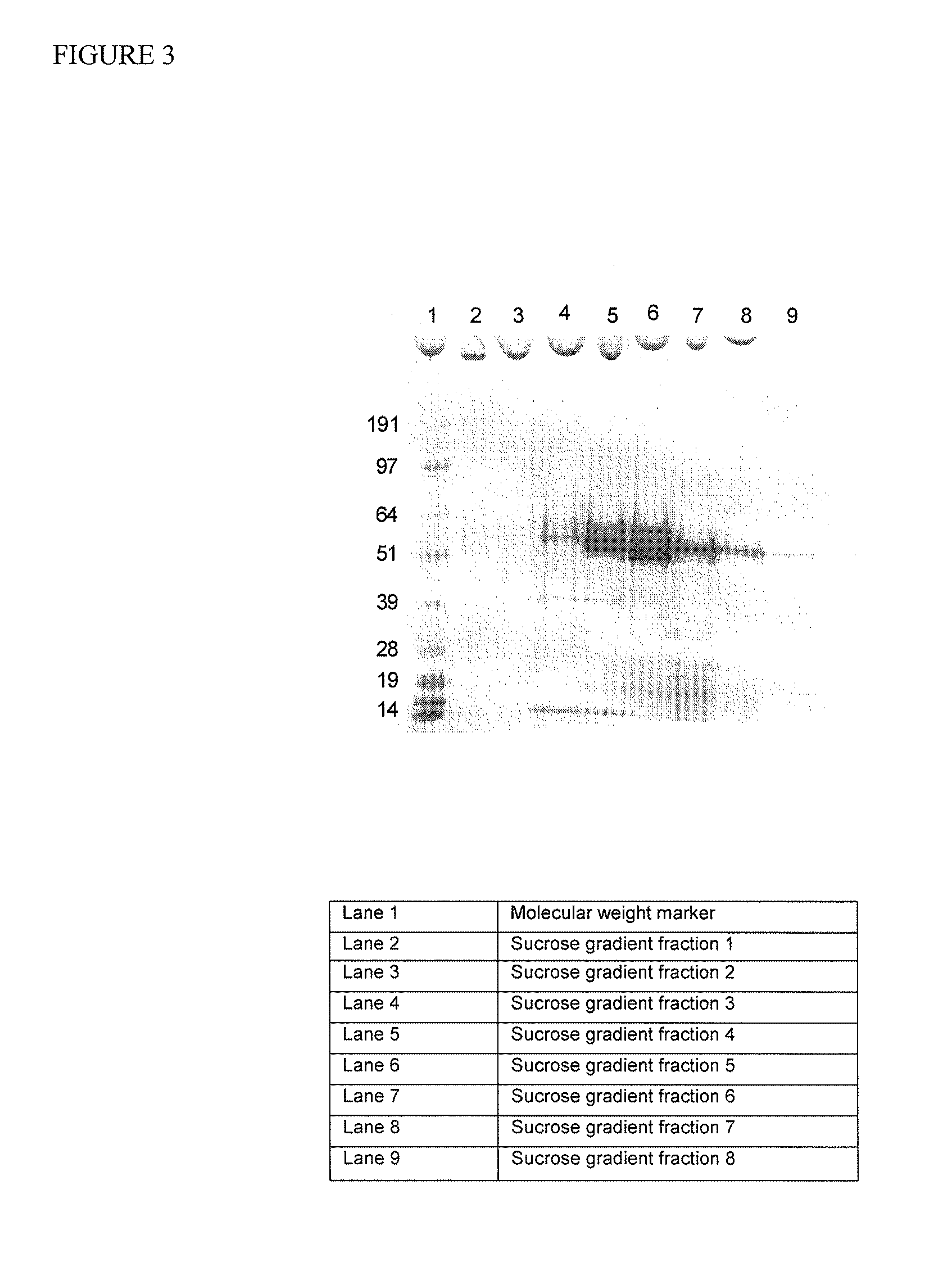
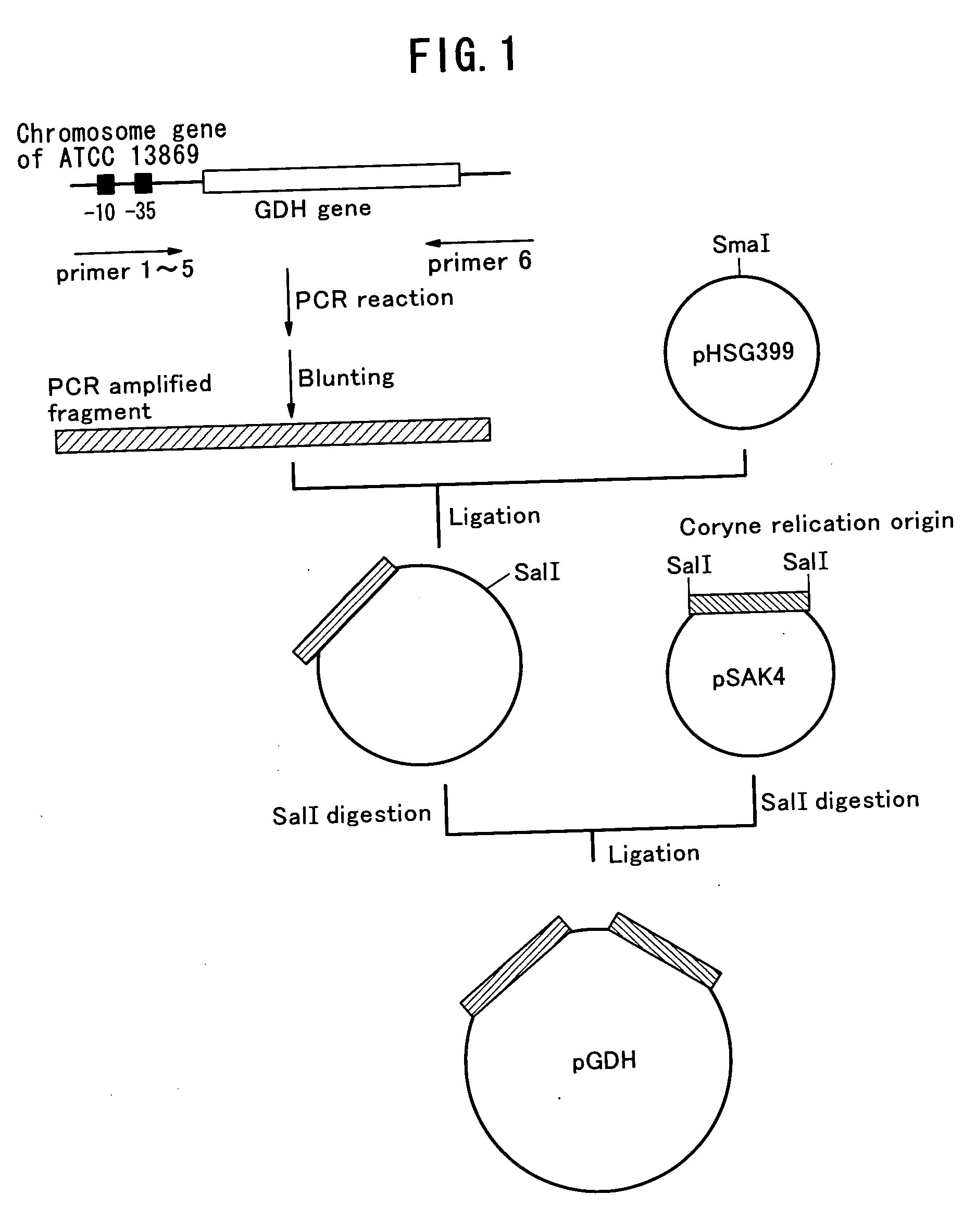
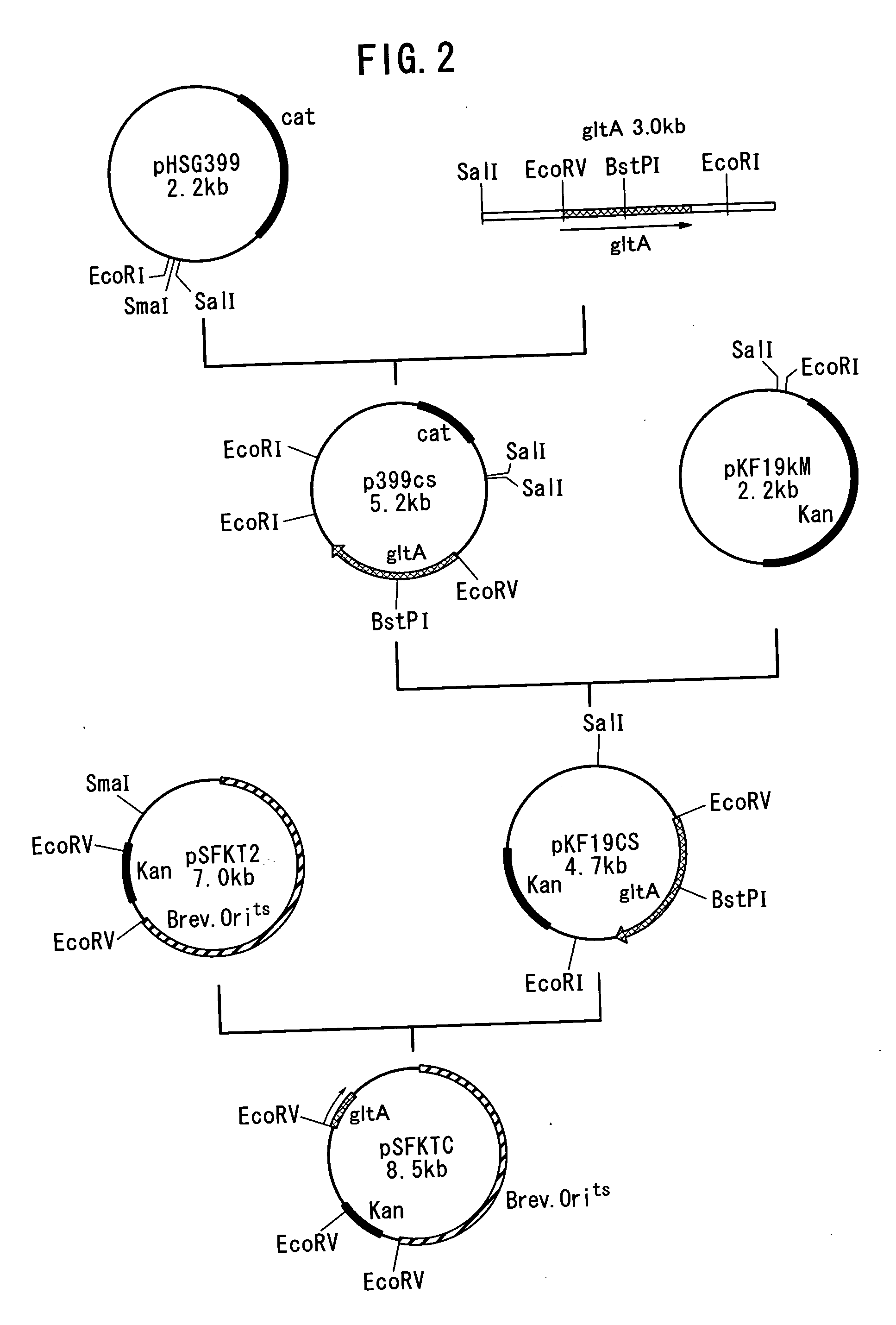
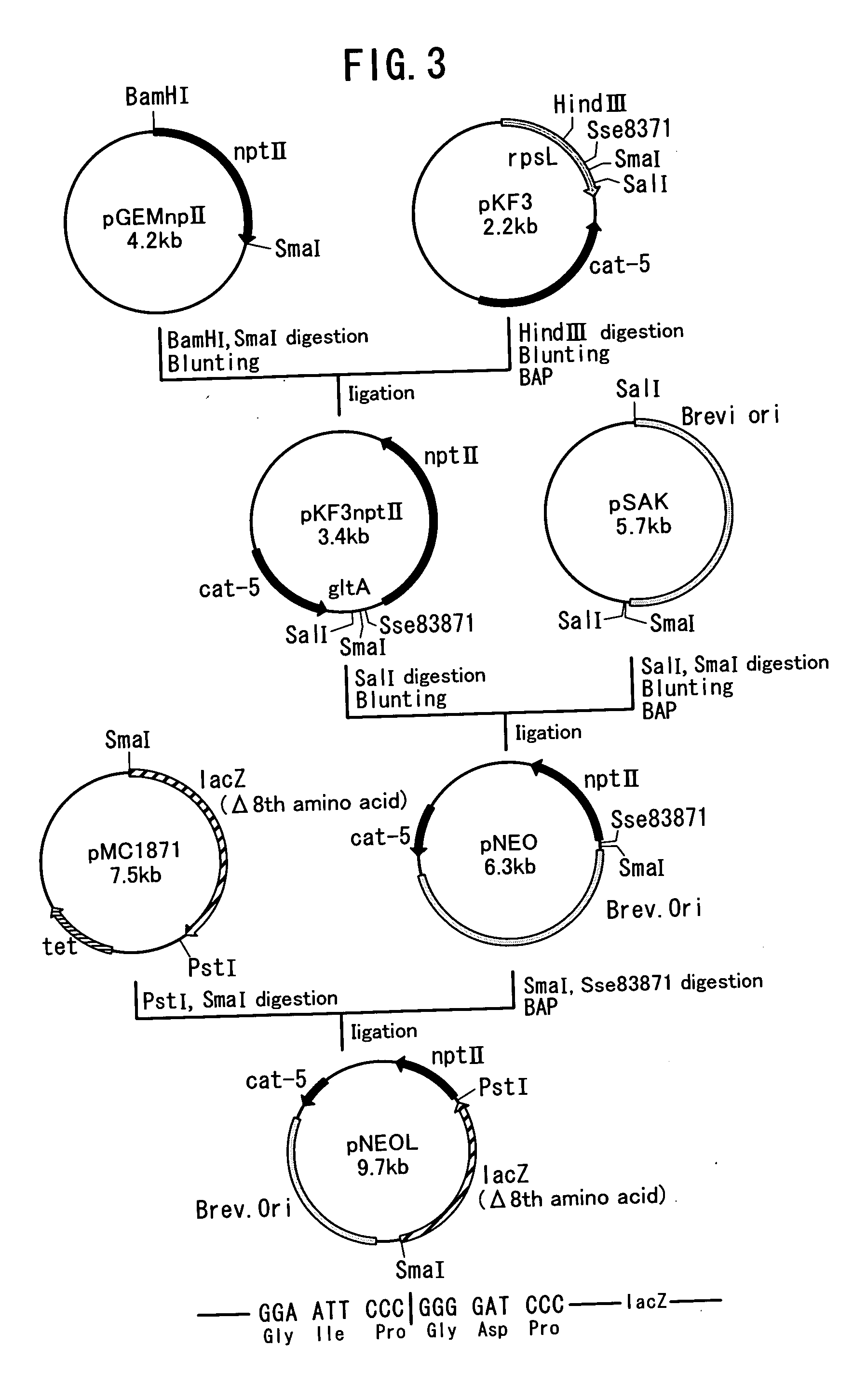
A method of producing coryneform bacteria having improved amino acid or nucleic acid productivity comprising the steps of introducing a mutation in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium to make it close to a consensus sequence, or introducing a change in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium by gene recombination to make it close to a consensus sequence, to obtain mutants of the coryneform amino acid- or nucleic acid-producing microorganism, culturing the mutants and selecting a mutant capable of producing the intended amino acid or nucleic acid in a large amount. This method allows the construction of a mutant capable of enriching or controlling the expression of an intended gene without using a plasmid and to promote production of amino acids in a high yield by recombination or mutation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Antibodies and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20080187966A1Speed up the processIncrease productionImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyDisulfide bondingAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides methods for producing humanized antibodies and increasing the yield of antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments when produced in cell culture. In one aspect of the invention, at least one framework region amino acid residue of the variable domain is substituted by a corresponding amino acid from a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain. In another aspect, an amino acid is placed at a position proximal to a cys residue that participates in an intrachain variable domain disulfide bond that corresponds to an amino acid found at that position in a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
2′-branched nucleosides and Flaviviridae mutation
ActiveUS7824851B2High sensitivityReduce Flaviviridae infectionBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAmino acidMutant strain
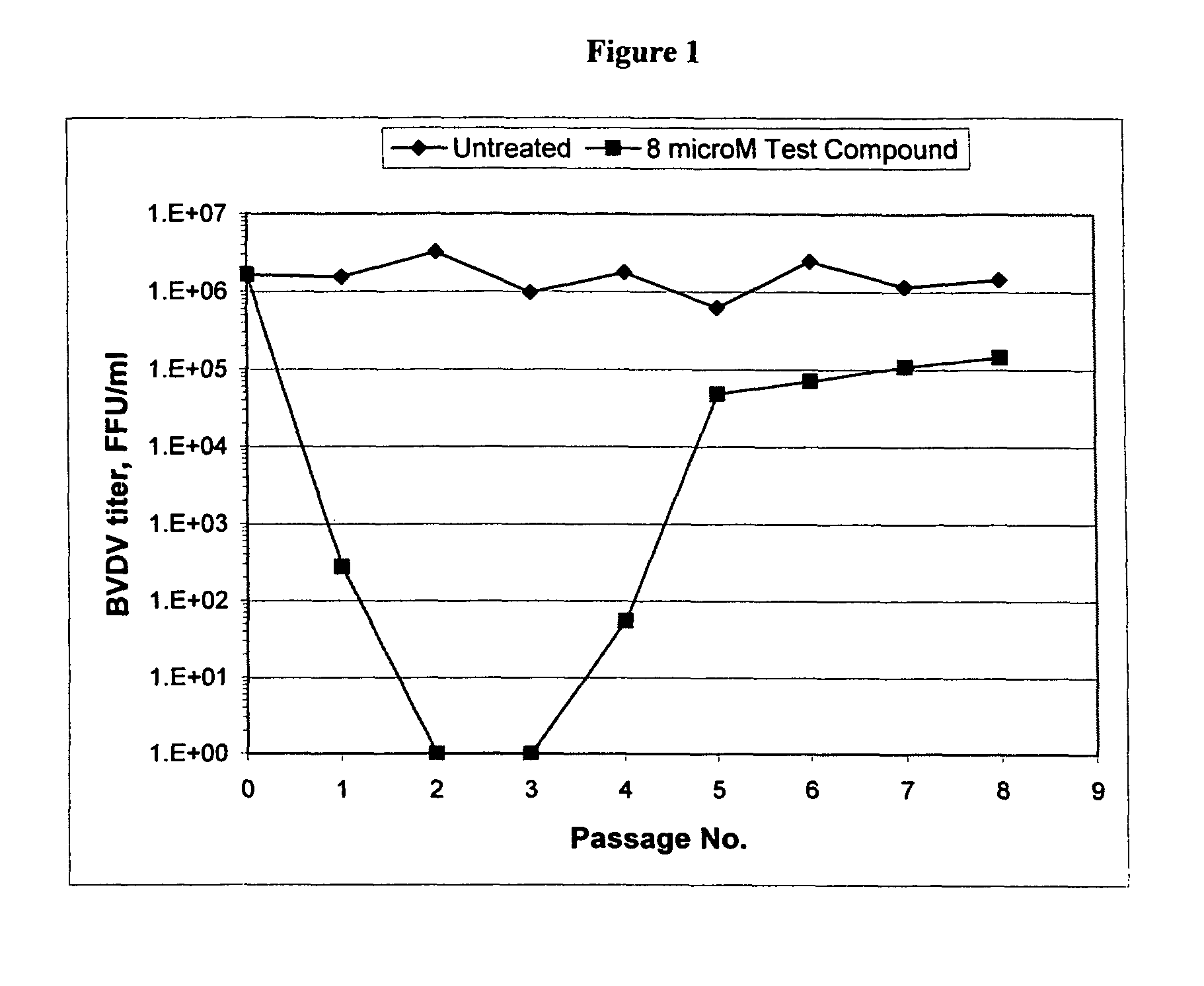
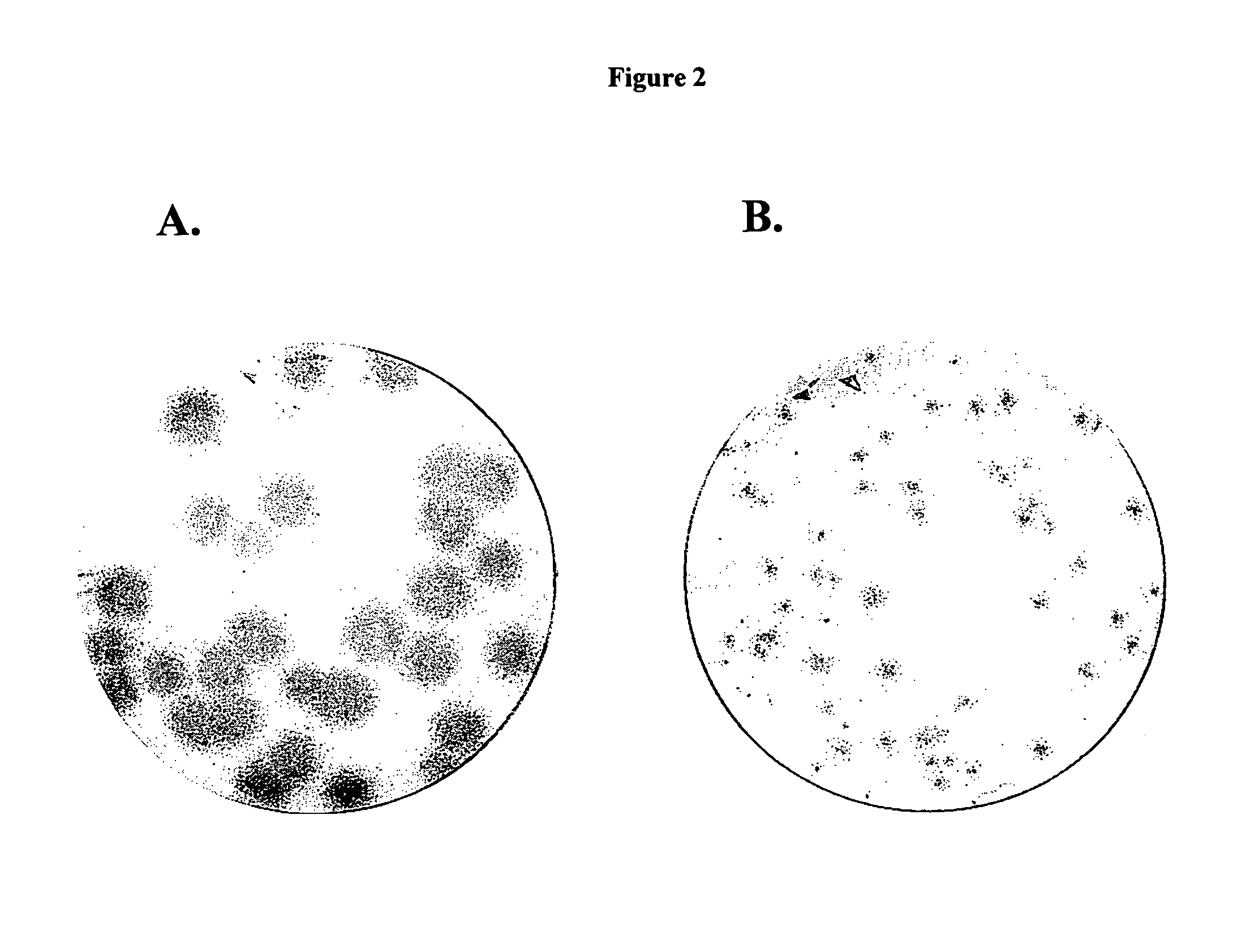
The present invention discloses a method for the treatment of Flaviviridae infection that includes the administration of a 2′-branched nucleoside, or a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug and / or salt thereof, to a human in need of therapy in combination or alternation with a drug that directly or indirectly induces a mutation in the viral genome at a location other than a mutation of a nucleotide that results in a change from seine to a different amino acid in the highly conserved consensus sequence, XRXSGXXXT (Sequence ID No. 63), of domain B of the RNA polymerase region, or is associated with such a mutation. The invention also includes a method to detect a mutant strain of Flaviviridae and a method for its treatment.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
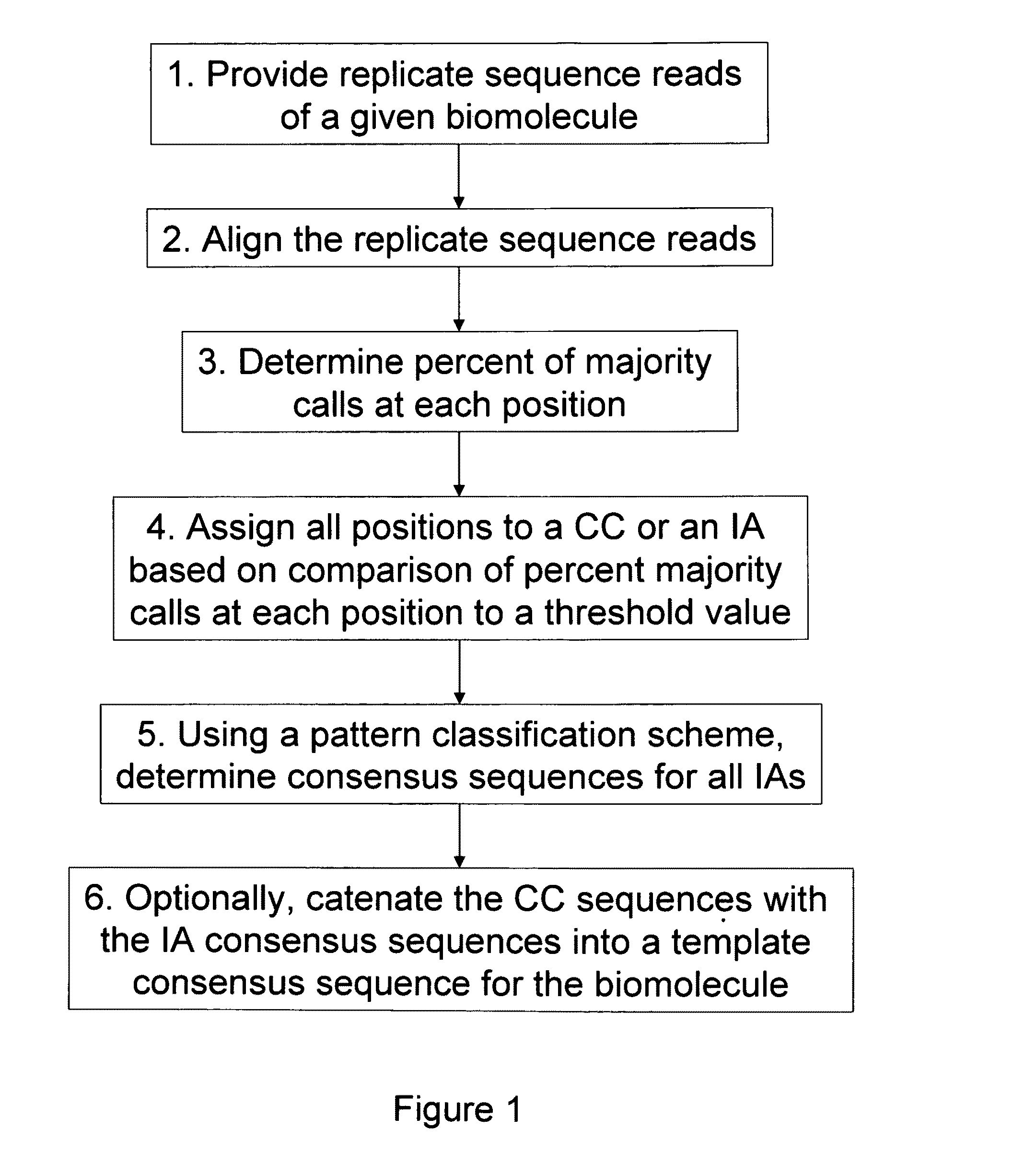
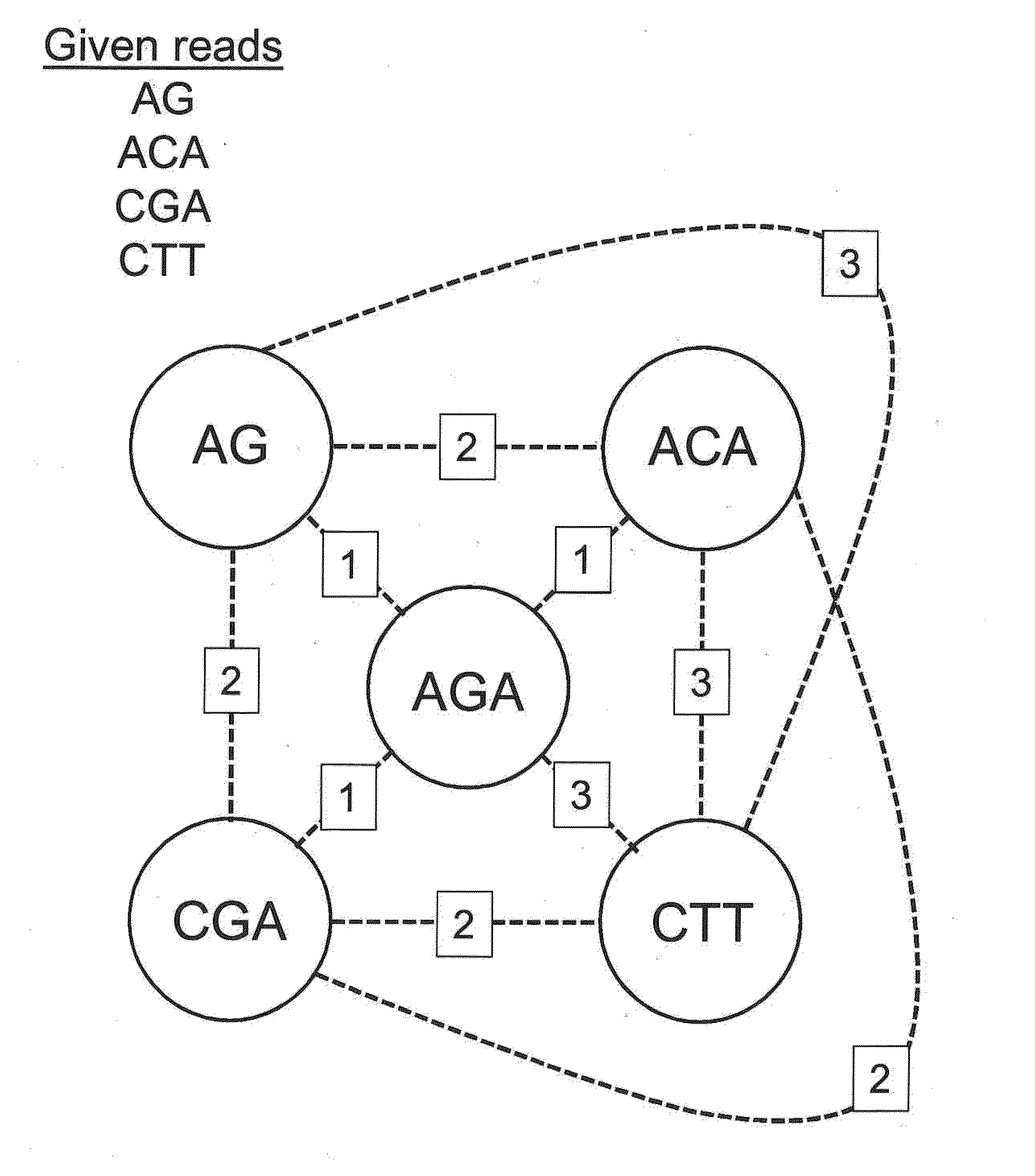
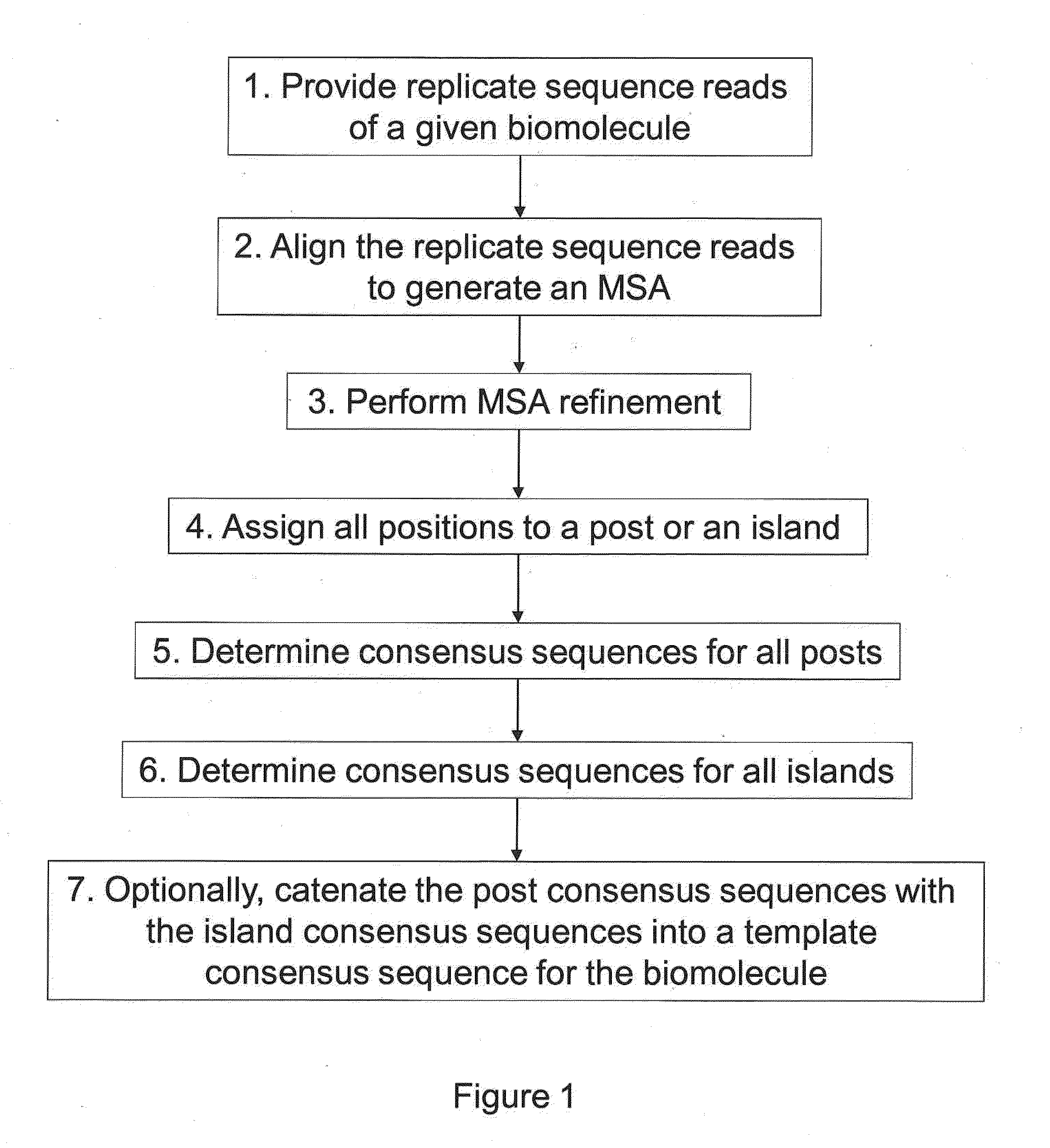
Algorithms for sequence determination
ActiveUS8370079B2Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyBiological testingSequence analysisOne passSequence analysis
The present invention is generally directed to powerful and flexible methods and systems for consensus sequence determination from replicate biomolecule sequence data. It is an object of the present invention to improve the accuracy of consensus biomolecule sequence determination from replicate sequence data by providing methods for assimilating replicate sequence into a final consensus sequence more accurately than any one-pass sequence analysis system.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
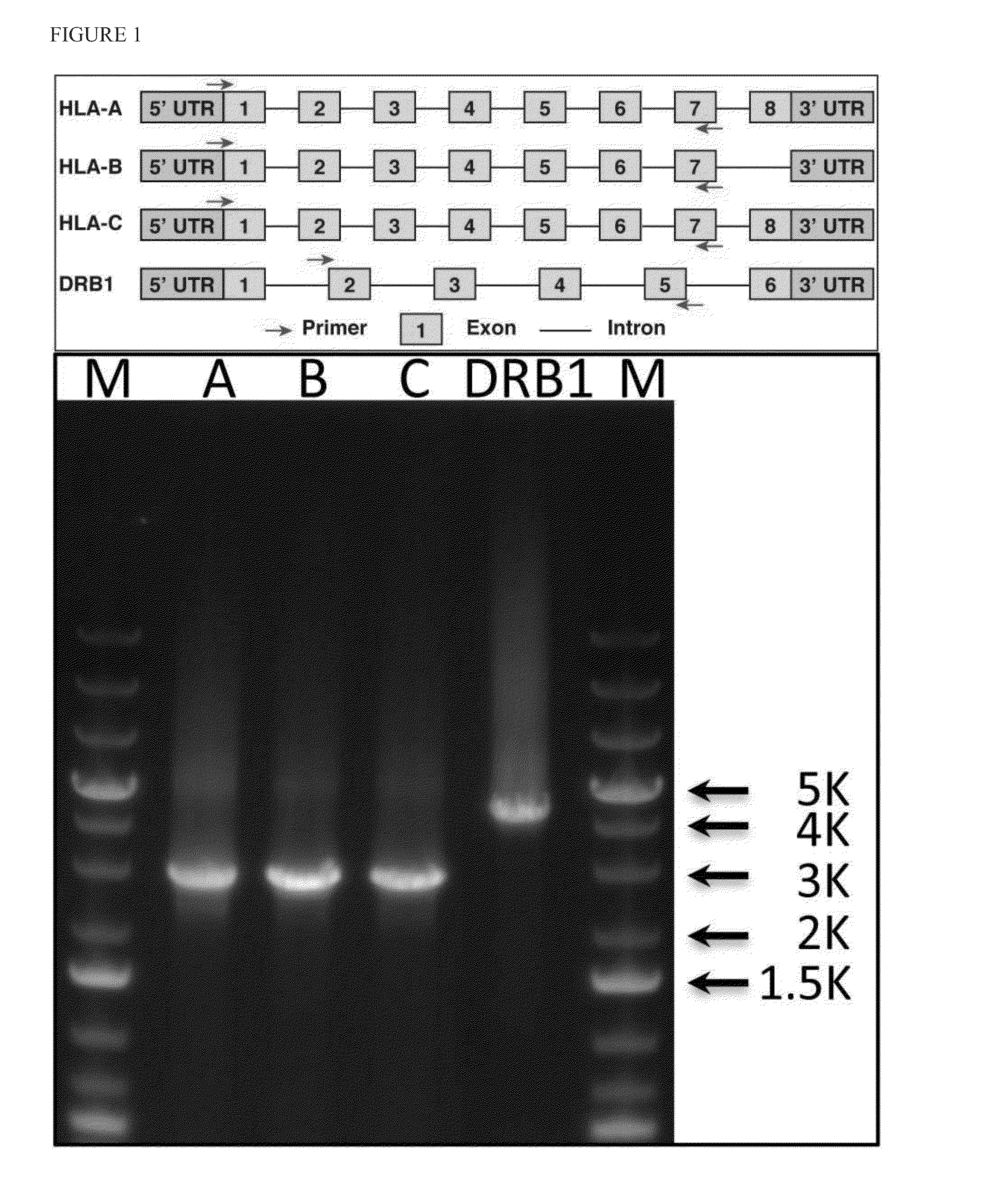
Haplotying of HLA loci with ultra-deep shotgun sequencing
ActiveUS20140206547A1Minimize biasEfficient reconstructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHaploidisationHaplotype
Methods are provided to determine the entire genomic region of a particular HLA locus including both intron and exons. The resultant consensus sequences provides linkage information between different exons, and produces the unique sequence from each of the two genes from the individual sample being typed. The sequence information in intron regions along with the exon sequences provides an accurate HLA haplotype.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Protein (poly)peptides libraries
InactiveUS20060003334A1High expressionMaximizes correspondenceFungiBacteriaHuman DNA sequencingSynthetic DNA
The present invention relates to synthetic DNA sequences which encode one or more collections of homologous proteins / (poly)peptides, and methods for generating and applying libraries of these DNA sequences. In particular, the invention relates to the preparation of a library of human-derived antibody genes by the use of synthetic consensus sequences which cover the structural repertoire of antibodies encoded in the human genome. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of a single consensus antibody gene as a universal framework for highly diverse antibody libraries.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
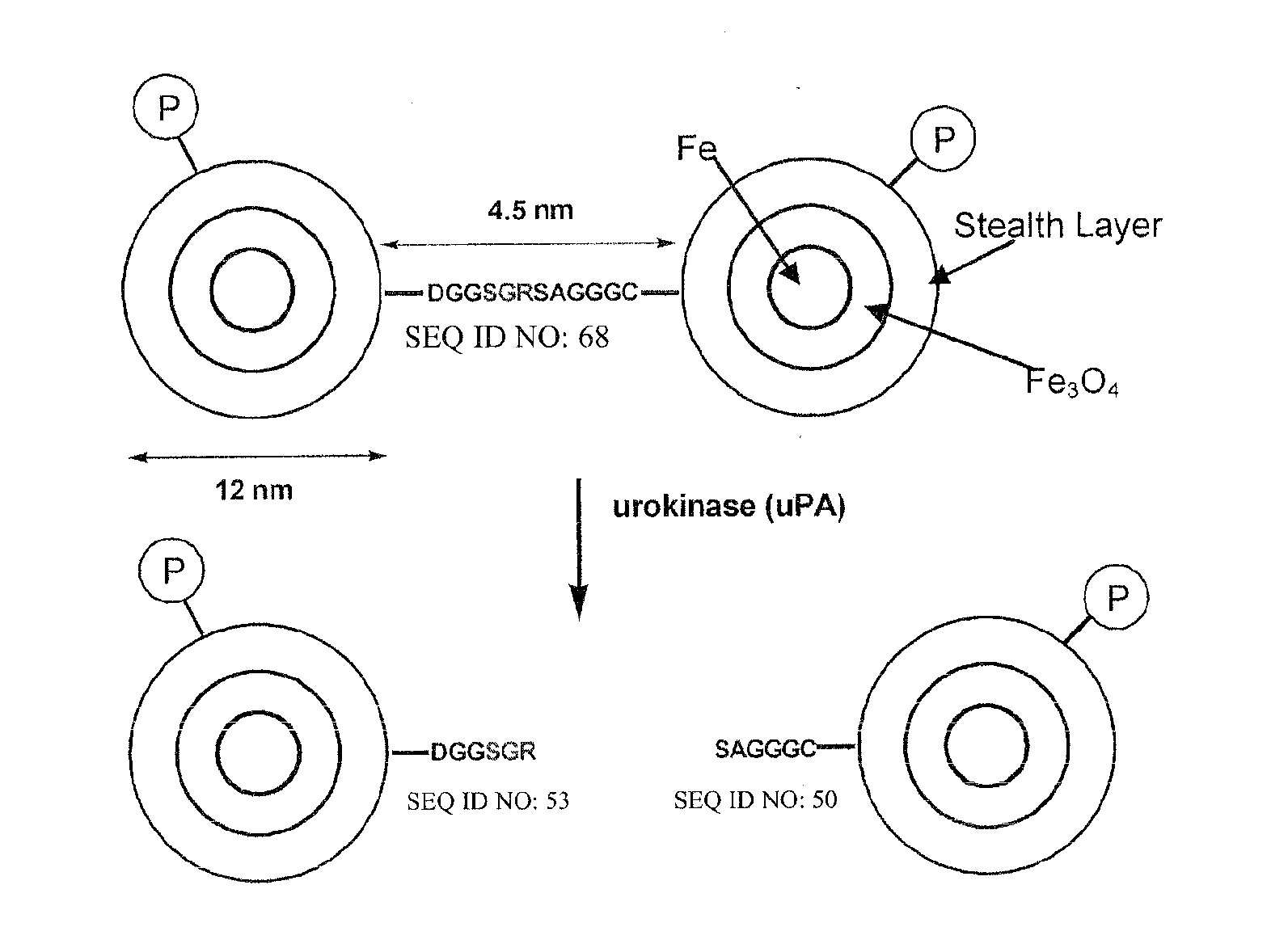
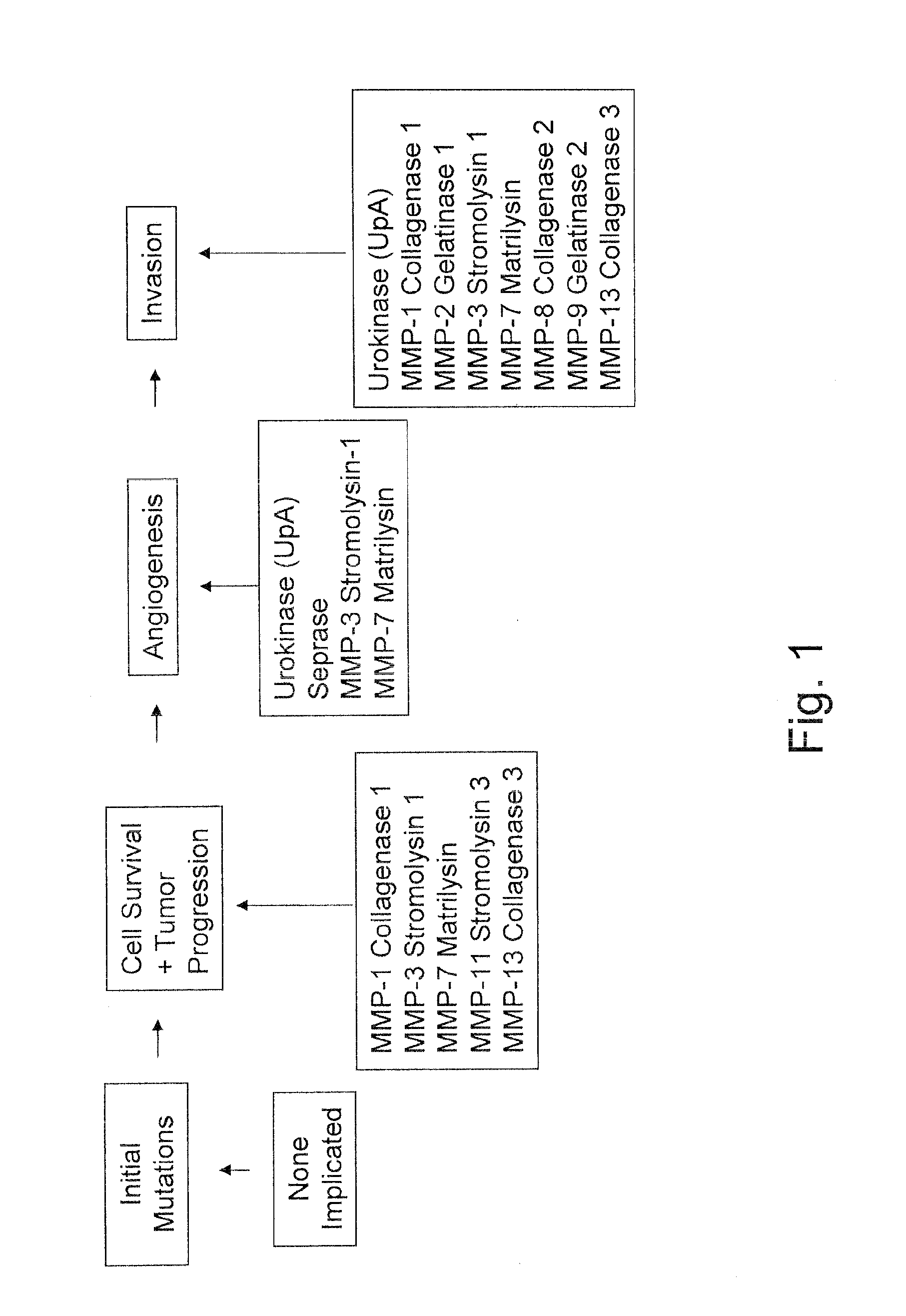
MRI and optical assays for proteases
The present invention provides multifunctional nanoplatforms for assessing the activity of a protease in vivo or in vitro, along with methods of imaging and detecting the presence of cancerous or precancerous tissues, and the therapeutic treatment thereof, including monitoring of treatment. The diagnostic nanoplatforms comprise nanoparticles and are linked to each other or other particles via an oligopeptide linkage that comprises a consensus sequence specific for the target protease. Cleavage of the sequence by the target protease can be detected using various sensors, and the diagnostic results can be correlated with cancer prognosis. Individual unlinked nanoplatforms are also adaptable for therapeutic hyperthermia treatment of the cancerous tissue.
Owner:NANOSCALE CORPORATION +1
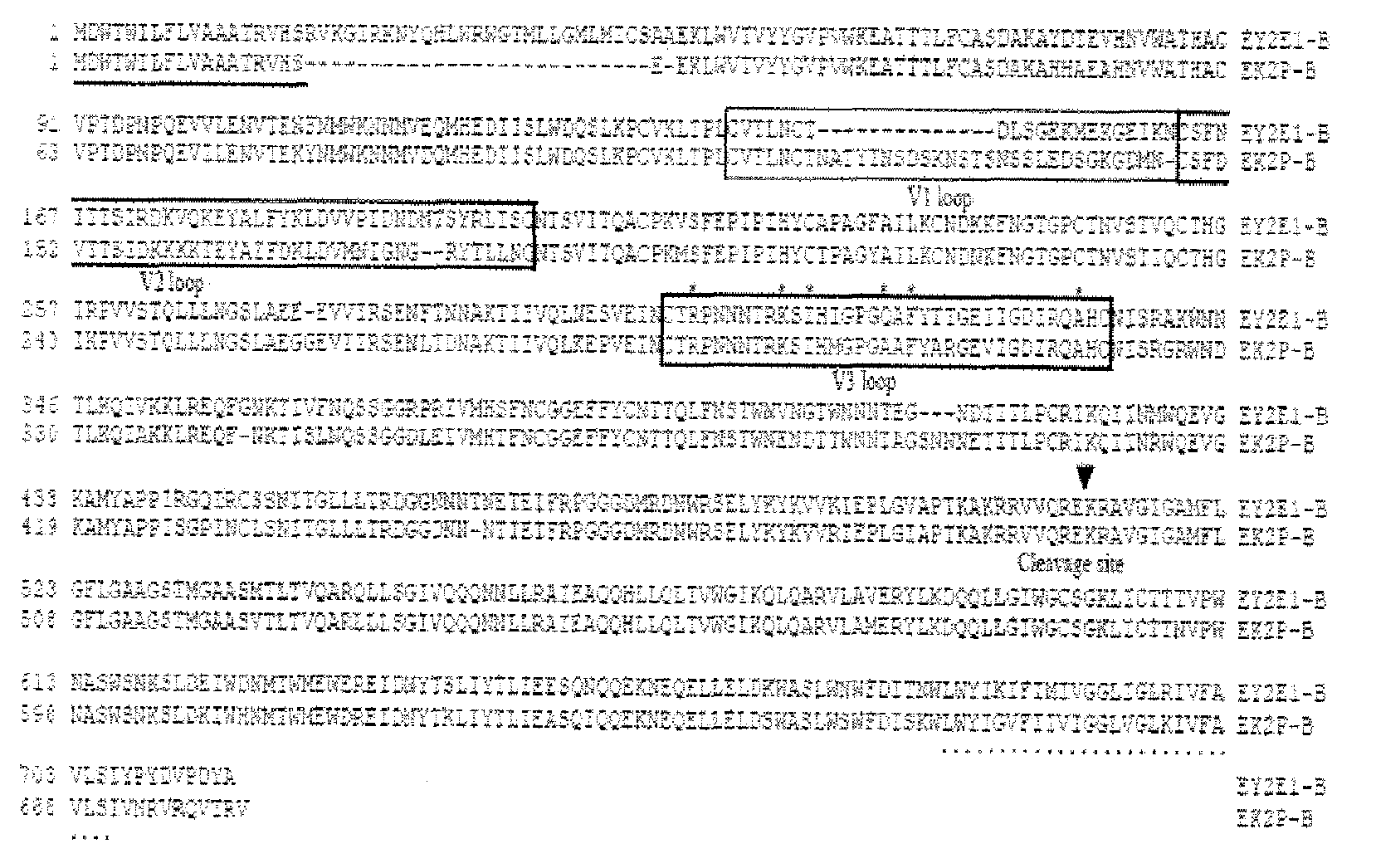
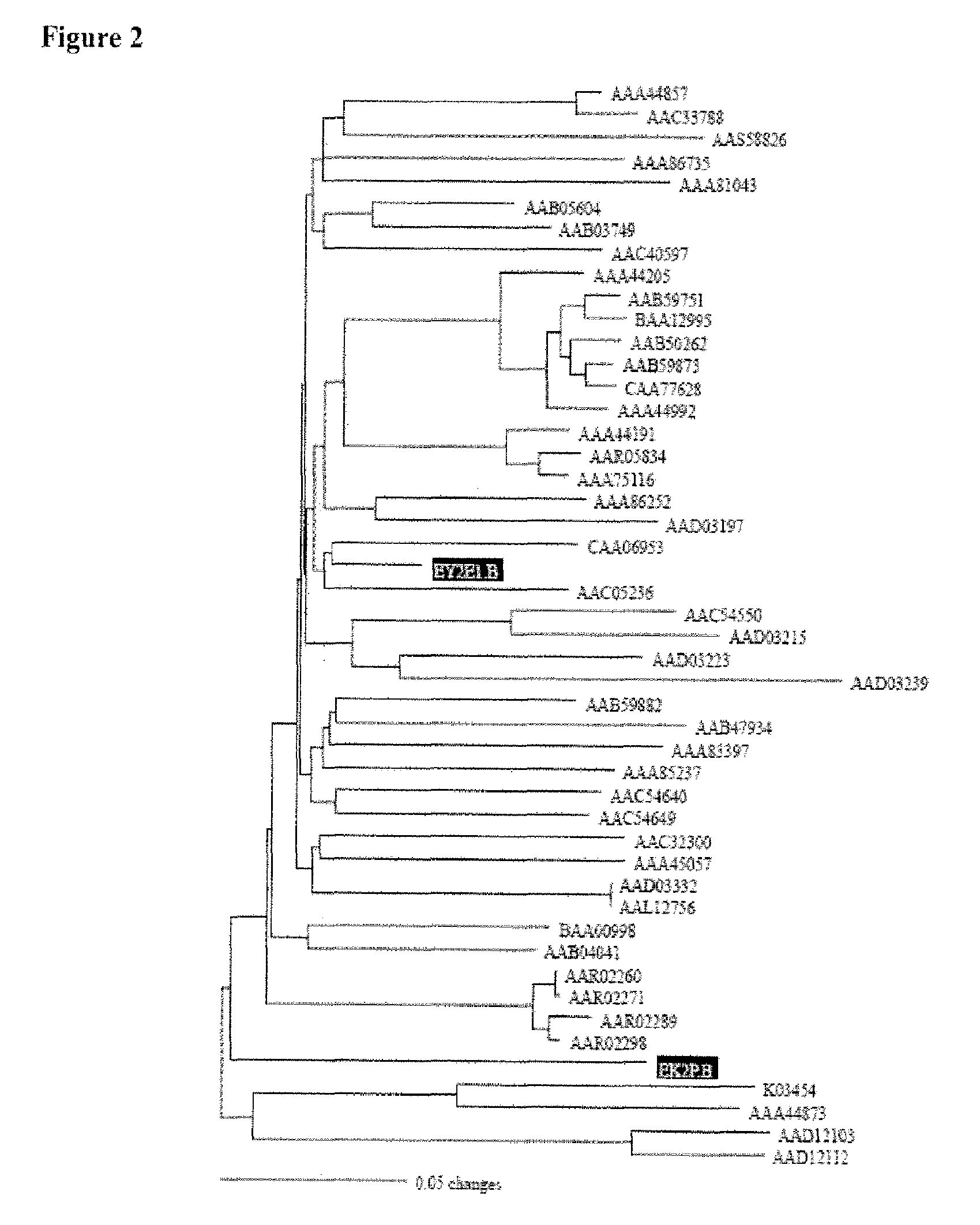
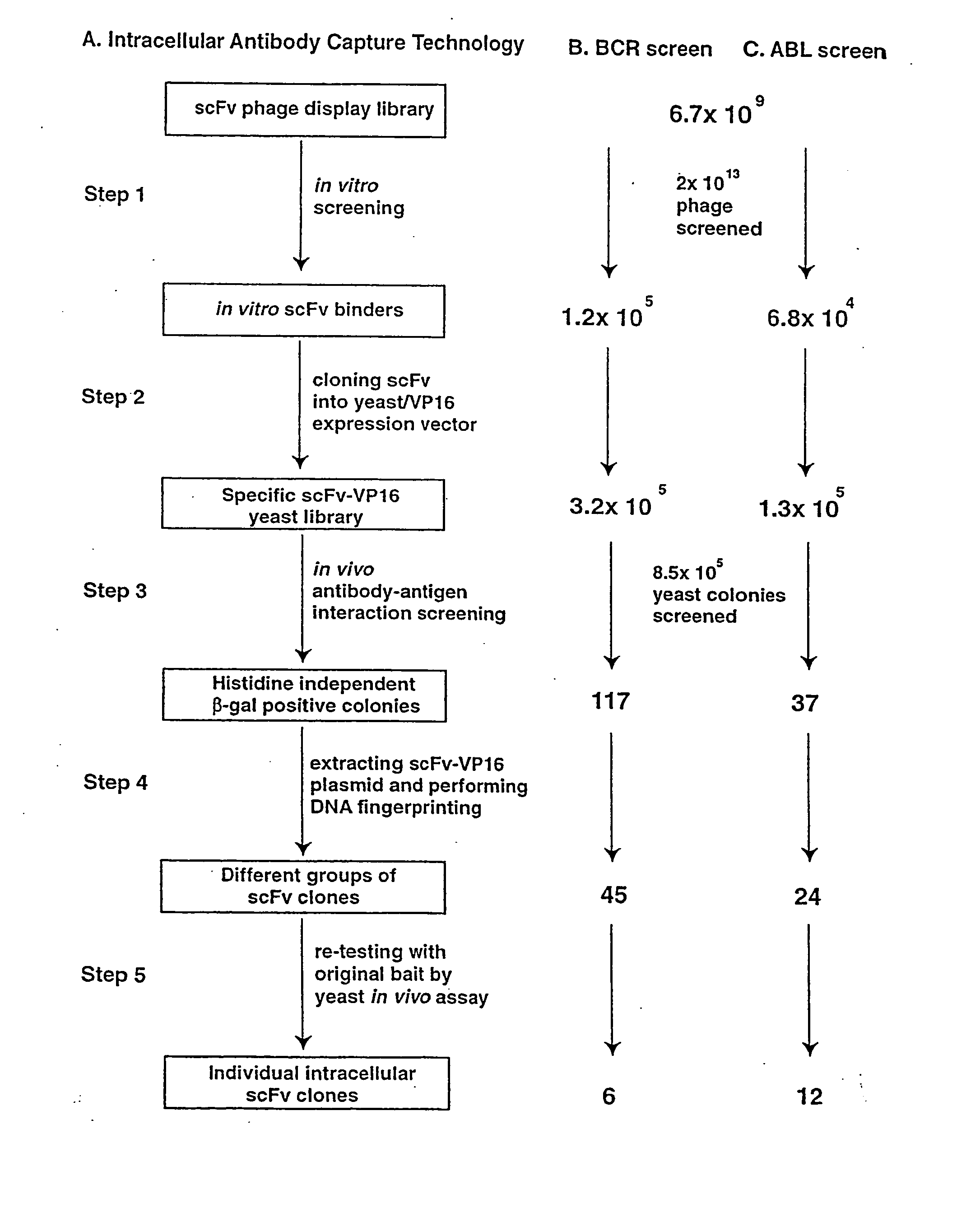
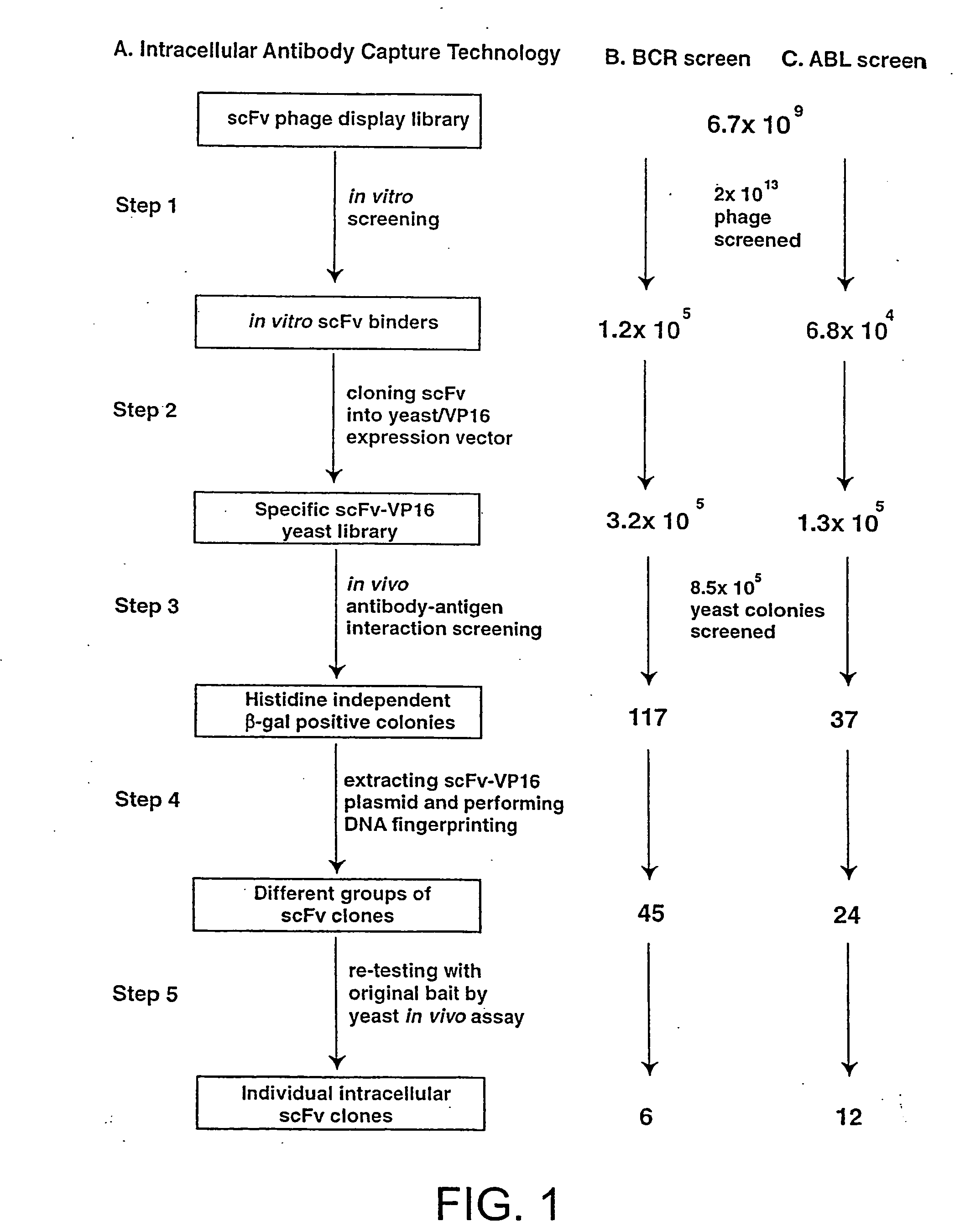
Immunoglobulin frameworks which demonstrate enhanced statbility in the intracellular envioronment and methods of identifying same
ActiveUS20060035320A1Improve solubilityImprove stabilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSolubilityAntibody fragments
Compositions are provided, which can be used as frameworks for the creation of very stable and soluble single-chain Fv antibody fragments. These frameworks have been selected for intracellular performance and are thus ideally suited for the creation of scFv antibody fragments or scFv antibody libraries for applications where stability and solubility are limiting factors for the performance of antibody fragments, such as in the reducing environment of a cell. Such frameworks can also be used to identify highly conserved residues and consensus sequences which demonstrate enhanced solubility and stability.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
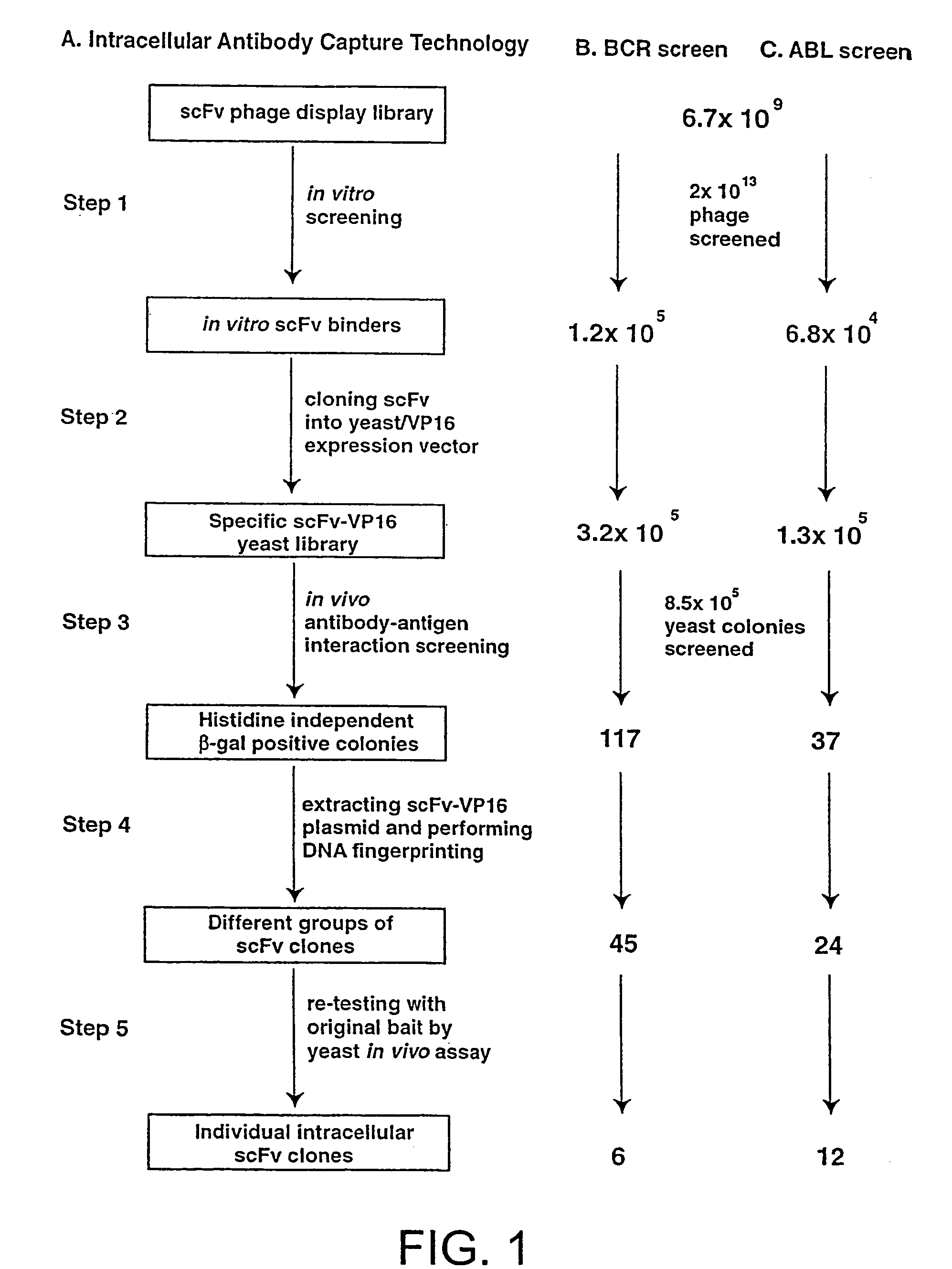
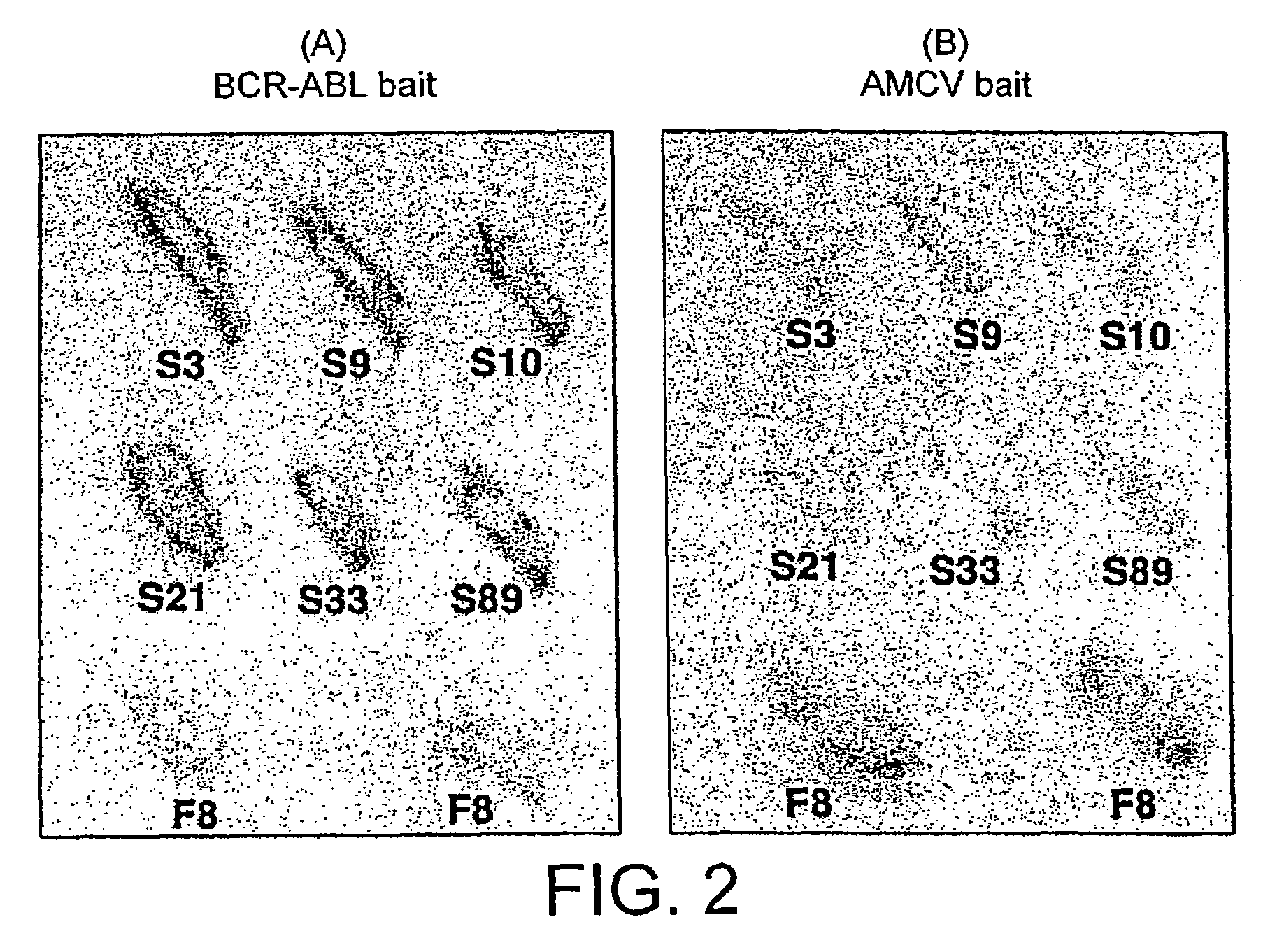
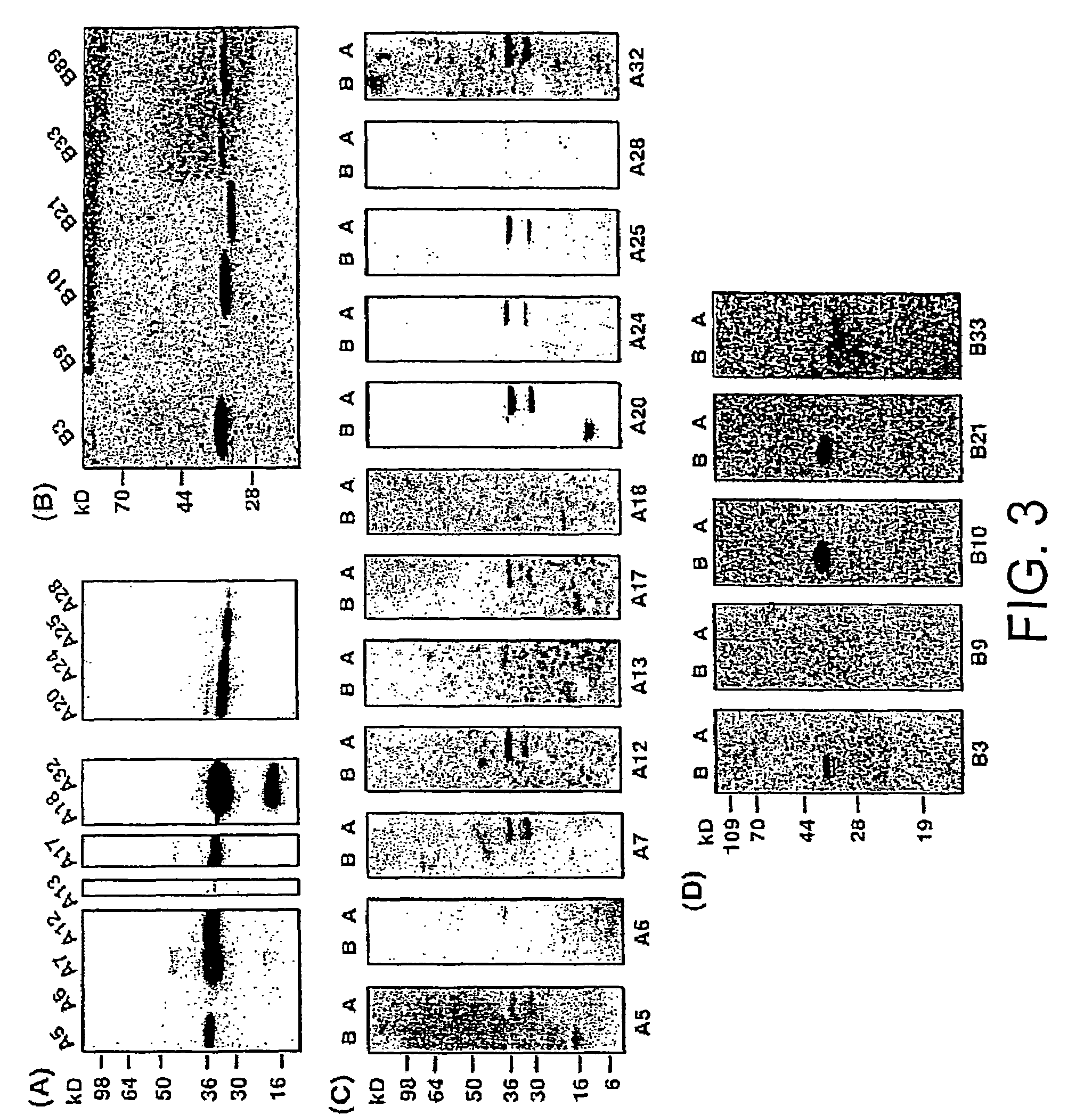
Intracellular antibodies
InactiveUS7608453B2Simple and efficient comparisonAnimal cellsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsIntracellularAmino acid
A method of identifying at least one consensus sequence for an intracellular antibody (ICS) comprising the steps of: creating a database comprising sequences of validated intracellular antibodies (VIDA database) and aligning the sequences of validated intracellular antibodies according to Kabat; determining the frequency with which a particular amino acid occurs in each of the positions of the aligned antibodies; selecting a frequency threshold value (LP or consensus threshold) in the range from 70% to 100%; identifying the positions of the alignment at which the frequency of a particular amino acid is greater than or equal to the LP value; and identifying the most frequent amino acid, in the position of said alignment.
Owner:SISSA SCUOLA INT SUPERIORE DE STUDI AVANZATI +1
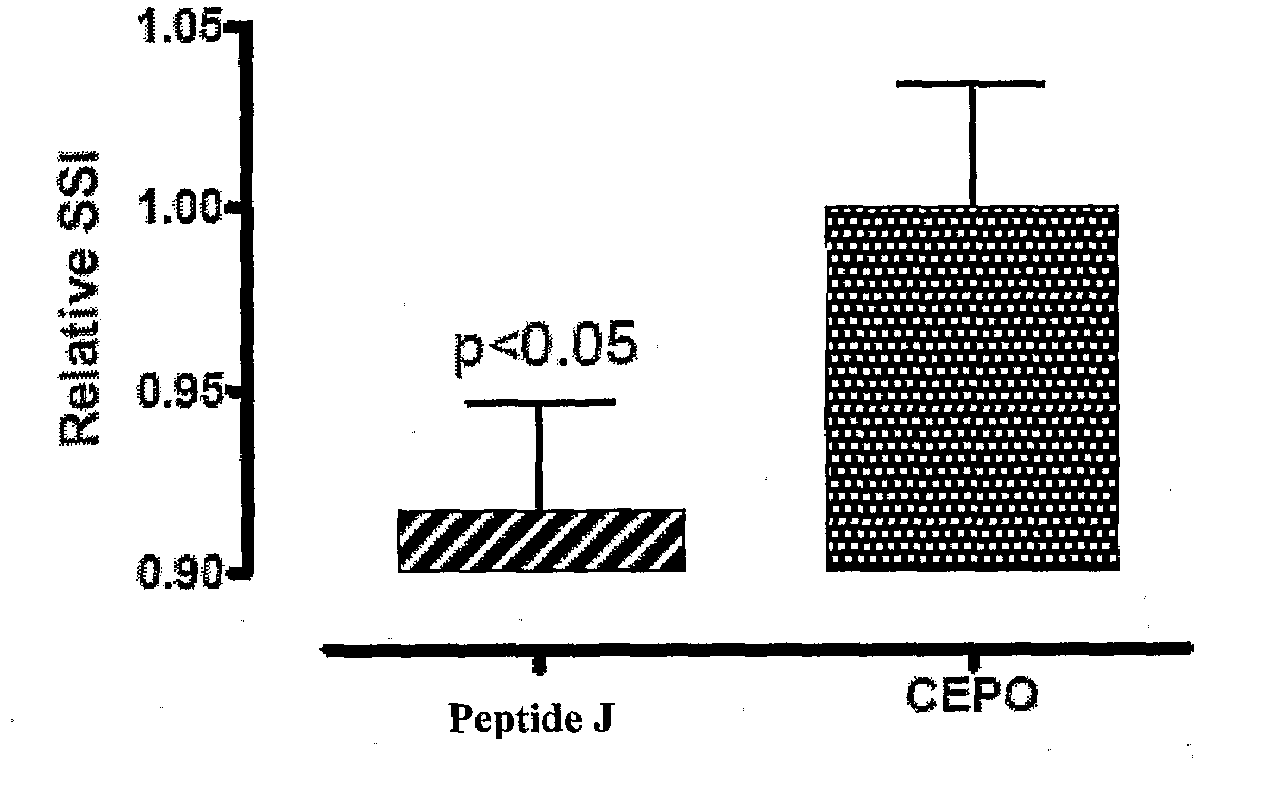
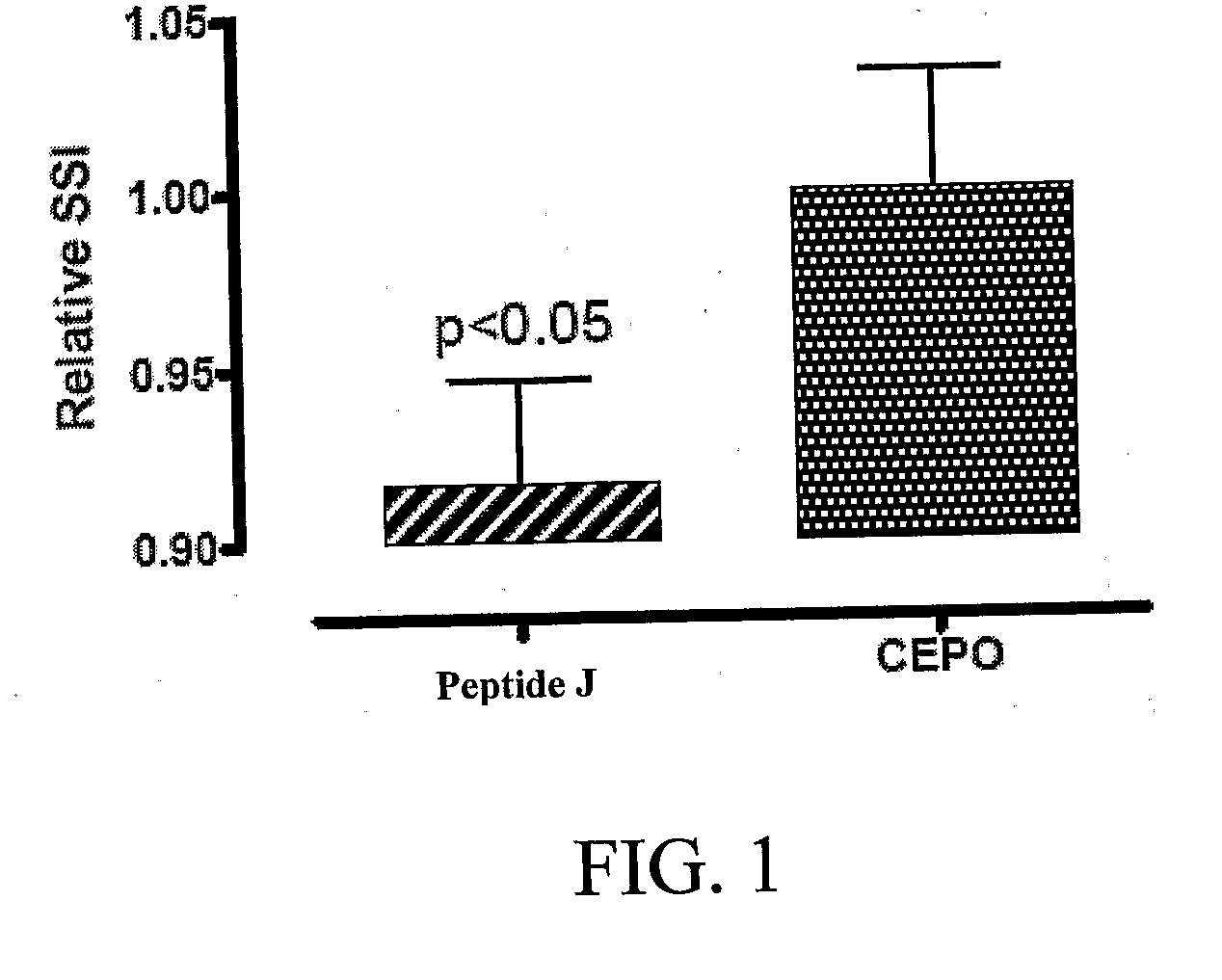
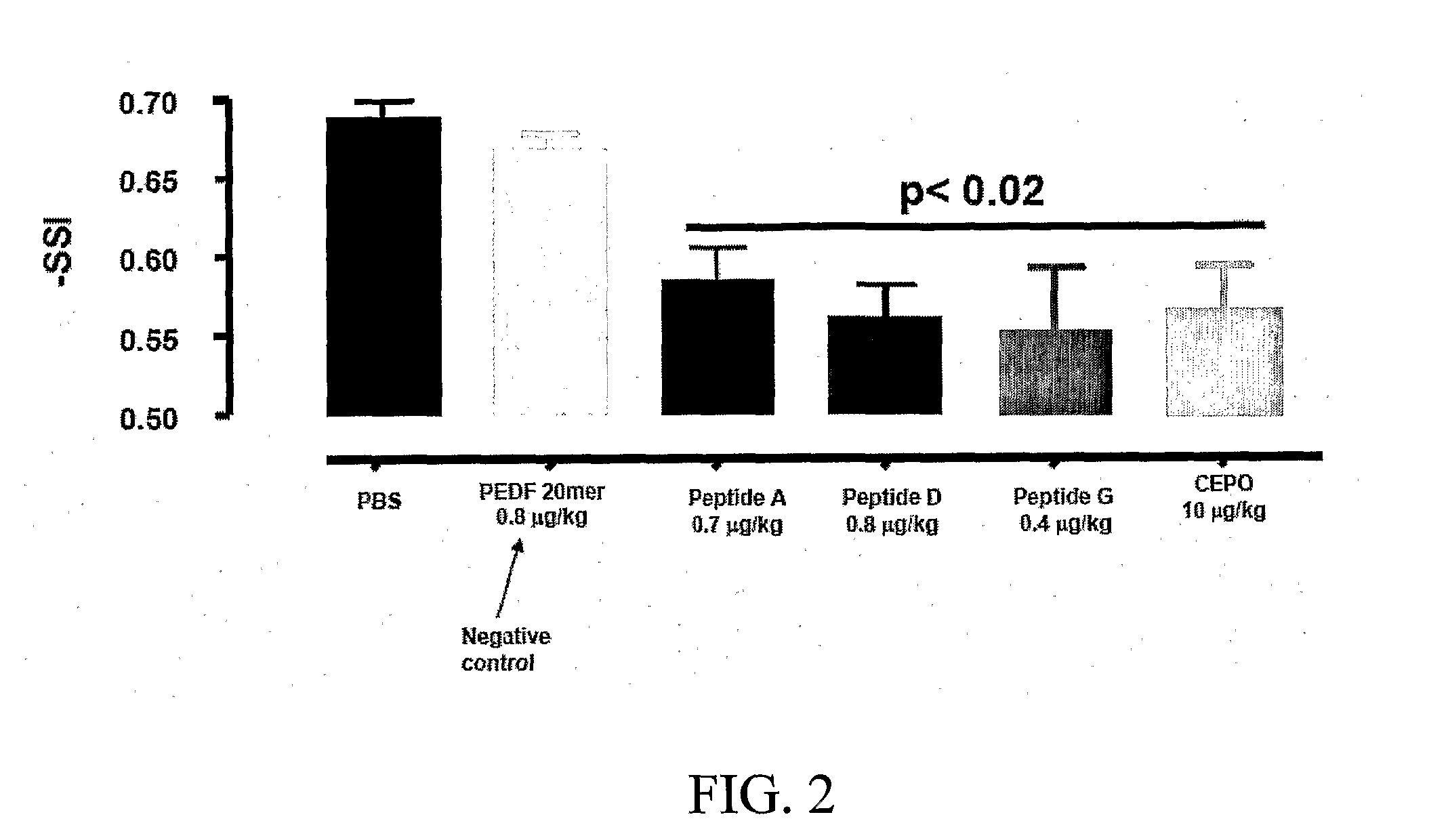
Tissue protective peptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090221482A1Avoid damageFacilitate optimal expressionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTissue protection
The present invention is directed to novel tissue protective peptides. The tissue protective peptides of the invention may bind to a tissue protective receptor complex. In particular, the present invention is drawn to tissue protective peptides derived from or sharing consensus sequences with portions of cytokine receptor ligands, including Erythropoietin (EPO), that are not involved in the binding of the ligand to the receptor complex, e.g., to the EPO receptor homodimer. Accordingly, the tissue protective peptides of the invention are derived from the amino acid sequences of regions of cytokine receptor ligands that are generally located on or within the region of the ligand protein that is opposite of the receptor complex, i.e., are generally derived from amino acid sequences of regions of the ligand protein that face away from the receptor complex while the ligand is bound to the receptor. The invention is further directed to the consensus sequences for use in engineering a synthetic tissue protective peptide. These tissue protective peptides also include fragments, chimeras, as well as peptides designed to mimic the spatial localization of key amino acid residues within the tissue protective receptor ligands, e.g., EPO. The invention further encompasses methods for treating or preventing a disease or disorder using tissue protective peptides of the current invention. The invention also encompasses methods for enhancing excitable tissue function using tissue protective peptides of the current invention.
Owner:ARAIM PHARMA INC
Algorithms for sequence determination
InactiveUS20130138358A1Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyBiological testingSequence analysisOne passSequence analysis
The present invention is generally directed to powerful and flexible methods and systems for consensus sequence determination from replicate biomolecule sequence data. It is an object of the present invention to improve the accuracy of consensus biomolecule sequence determination from replicate sequence data by providing methods for assimilating replicate sequence into a final consensus sequence more accurately than any one-pass sequence analysis system.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Protease assay
The present invention provides a diagnostic reagent or assay for assessing the activity of a protease in vivo or in vitro and methods of detecting the presence of a cancerous or precancerous cell. The assays are comprised of two particles linked via an oligopeptide linkage that comprises a consensus sequence specific for the target protease. Cleavage of the sequence by the target protease can be detected visually or using various sensors, and the diagnostic results can be correlated with cancer prognosis.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Vaccines and methods for using the same
ActiveUS20100166787A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsRecombinant vaccinesBioinformatics
Improved anti-HIV immunogens and nucleic acid molecules that encode them are disclosed, Immunogens disclosed include those having consensus sequences for HIV Subtype A Envelope protein, those having consensus sequences for HIV Subtype B Envelope protein, those having consensus sequences for HIV Subtype C Envelope protein, those having consensus sequences for HIV Subtype D Envelope protein, those having consensus sequences for HIV Subtype B consensus Nef-Rev protein, and those having consensus sequences form HIV Gag protein subtypes A, B, C and D. Improved anti-HPV immunogens and nucleic acid molecules that encode them; improved anti-HCV immunogens and nucleic acid molecules that encode them; improved hTERT immunogens and nucleic acid molecules that encode them; and improved anti-Influenza immunogens and nucleic acid molecules that encode them are disclosed. Pharmaceutical composition, recombinant vaccines comprising and live attenuated pathogens are disclosed as well methods of inducing an immune response in an individual against HIV, HPV, HCV, hTERT and Influenza are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Intracellular antibodies
InactiveUS20050288864A1Simple and efficient comparisonImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingIntracellularBioinformatics
A method of identifying at least one consensus sequence for an intracellular antibody (ICS) comprising the steps of: creating a database comprising sequences of validated intracellular antibodies (VIDA database) and aligning the sequences of validated intracellular antibodies according to Kabat; determining the frequency with which a particular amino acid occurs in each of the positions of the aligned antibodies; selecting a frequency threshold value (LP or consensus threshold) in the range from 70% to 100%; identifying the positions of the alignment at which the frequency of a particular amino acid is greater than or equal to the LP value; and identifying the most frequent amino acid, in the position of said alignment.
Owner:SISSA SCUOLA INT SUPERIORE DE STUDI AVANZATI +1
Method of genome-wide nucleic acid fingerprinting of functional regions
InactiveUS7691614B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
A method of specifically amplifying desired regions of nucleic acid from a sample is provided. The method uses a plurality of first and second PCR primers, each having a region of fixed nucleotide sequence identical or complementary to a consensus sequence of interest and a region of randomized nucleotide sequence located 5′ to, 3′ to, anywhere within, or flanking the region of fixed nucleotide sequence; and then amplifying the nucleic acid present in the sample via PCR using the plurality of first and second PCR primers; whereby a subset of the first primers binds to the consensus sequence of interest wherever it occurs in the sample, and a subset of the second primers binds to the sample at locations removed from the first primers such that DNA regions flanked by the first primer and the second primer are specifically amplified.
Owner:GENOME TECH
Treatment of diseases associated with the egr-1 enhancer element
InactiveUS20070099826A1Improve understandingImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFertility DisordersDisease cause
Compounds and methods are provided for treating patients suffering from health condition associated with an expression state of a gene such as fertility disorders, cancer, proliferative diseases, vascular diseases, wounds requiring therapeutic intervention, inflammation, and pulmonary disorders by administering to said patient a compound capable of modulating egr-1 and / or an egr-1 response element consensus sequence thereby altering the expression state of said gene. Also described are new methods for screening compounds to identify effectors of egr-1 and / or egr-1 consensus sequence elements and methods for treating patients by administering such effectors to modulate egr-1 and / or egr-1 consensus sequences to thereby modify expression of genes associated therewith to in turn treat diseases or other physiological conditions associated with such gene expression.
Owner:RESVERLOGIX
Polypeptide with brain targeted medicine delivery characteristic and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein polypeptides, relates to a polypeptide with a brain targeted medicine delivery characteristic, and provides a molecular structure of the polypeptide, and application of the polypeptide to brain targeted medicine delivery. A phage monoclonal antibody which has the function of penetrating a blood brain barrier and can be enriched in a brain is obtained through repeated in-vivo Sprague Dawley (SD) outbred stock rat screening by a phage display technology; deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing proves that the phase display polypeptides comprise a consensus sequence; meanwhile, an immunohistochemical method and in-vivo recovery rate comparison prove that the obtained polypeptide has the brain targeted medicine delivery characteristic. The polypeptide and derivative peptides thereof can be used for modifying medicine-carrying nanoparticles, liposomes, vesicles or micelles to construct a brain targeted medicine delivery system; and the delivery of medicines in the brain can be improved, the treatment effect on brain diseases is enhanced and systemic toxic and side effects are reduced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods for producing humanized antibodies and improving yield of antibodies or antigen binding fragments in cell culture
ActiveUS7575893B2Speed up the processIncrease productionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntigen Binding FragmentAmino acid substitution
The present invention provides methods for producing humanized antibodies and increasing the yield of antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments when produced in cell culture. In one aspect of the invention, at least one framework region amino acid residue of the variable domain is substituted by a corresponding amino acid from a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain. In another aspect, an amino acid is placed at a position proximal to a cys residue that participates in an intrachain variable domain disulfide bond that corresponds to an amino acid found at that position in a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequenc of the variable domain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Use of consensus sequence as vaccine antigen to enhance recognition of virulent viral variants
ActiveUS20090186045A1Reduce probabilitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsVaccine antigenPhases of clinical research
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Sequence assembly and consensus sequence determination
Computer implemented methods, and systems performing such methods for processing signal data from analytical operations and systems, and particularly in processing signal data from sequence-by-incorporation processes to identify nucleotide sequences of template nucleic acids and larger nucleic acid molecules, e.g., genomes or fragments thereof. In particularly preferred embodiments, nucleic acid sequences generated by such methods are subjected to de novo assembly and / or consensus sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Bioconjugates made from recombinant n-glycosylated proteins from procaryotic cells
The present invention is directed to a bioconjugate vaccine, such as an 01-bioconjugate vaccine, comprising: a protein carrier comprising a protein carrier containing at least one consensus sequence, D / E-X—N—Z—S / T, wherein X and Z may be any natural amino acid except proline; at least one antigenic polysaccharide from at least one pathogenic bacterium, linked to the protein carrier; and, optionally, an adjuvant. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a method of producing an O1-bioconjugate in a bioreactor comprising a number steps.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Virus-like particles comprising composite capsid amino acid sequences for enhanced cross reactivity
ActiveUS8841120B2Strong immune responseImprove protectionVirusesMicroorganismsEpitopeVirus-like particle
The present invention provides polypeptides having a composite amino acid sequence derived from a consensus sequence representing the capsid proteins of two or more circulating strains of a non-enveloped virus. In particular, the invention provides virus-like particles comprising at least one composite polypeptide. Such virus-like particles have antigenic epitopes of two or more circulating strains of a non-enveloped virus and produce an increase in antisera cross-reactivity to one or more circulating strains of the non-enveloped virus. Methods of making composite virus-like particles and vaccine formulations comprising composite virus-like particles are also disclosed.
Owner:TAKEDA VACCINES INC
Methods and compositions for treating a cell-proliferative disorder using CRE decoy oligomers, BCL-2 antisense oligomers, and hybrid oligomers thereof
InactiveUS20030176376A1Hinder and prevent bindingModulate transcriptional activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention is directed to hybrid oligomers comprising a cyclic AMP response element (CRE) sequence and a sequence that hybridizes to a bcl-2 pre-mRNA or mRNA, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such hybrids. The present invention is also directed to the use of CRE decoy oligomers, comprising a CRE consensus sequence, and bcl-2 antisense oligomers in combination therapies, and the use of bcl-2 / CRE hybrid oligomers, to treat or prevent cell-proliferative related disorders, including hyperplasias, cancers, tumors and carcinomas. In one embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a CRE decoy oligomer and a bcl-2 antisense oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders. In another embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a bcl-2 antisense / CRE decoy (bcl-2 / CRE) hybrid oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders.
Owner:GENTA INC
Method of constructing amino acid producing bacterial strains, and method of preparing amino acids by fermentation with the constructed amino acid producing bacterial strains
InactiveUS20060003424A1Enhancing and controlling expressionProducing amino acids in a high yieldBacteriaFermentationMicroorganismEukaryotic plasmids
A method of producing coryneform bacteria having an improved amino acid- or nucleic acid-productivity comprises the steps of introducing a mutation in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium to make it close to a consensus sequence or introducing a change in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium by gene recombination to make it close to a consensus sequence, to obtain mutants of the coryneform amino acid d- or nucleic acid-producing microorganism, culturing the mutants and select a mutant capable of producing the intended amino acid or nucleic acid in a large amount. This method can construct a mutant capable of suitably enriching or controling the expression of an intended gene without using a plasmid and also capable of producing amino acids in a high yield, by the recombination or mutation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Protease assay
The present invention provides a diagnostic reagent or assay for assessing the activity of a protease in vivo or in vitro and methods of detecting the presence of a cancerous or precancerous cell. The assays are comprised of two particles linked via an oligopeptide linkage that comprises a consensus sequence specific for the target protease. Cleavage of the sequence by the target protease can be detected visually or using various sensors, and the diagnostic results can be correlated with cancer prognosis.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com