Antibodies and methods for making and using them
a technology of antigen binding fragments and cell culture, which is applied in the field of cell culture production of can solve the problems of not providing an antibody that can be produced in high yield in cell culture, and reducing the time to prepare humanized antibodies or antigen binding fragments, so as to and improve the yield of antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Heavy Chain Aggregation During Expression and Folding of Antibodies
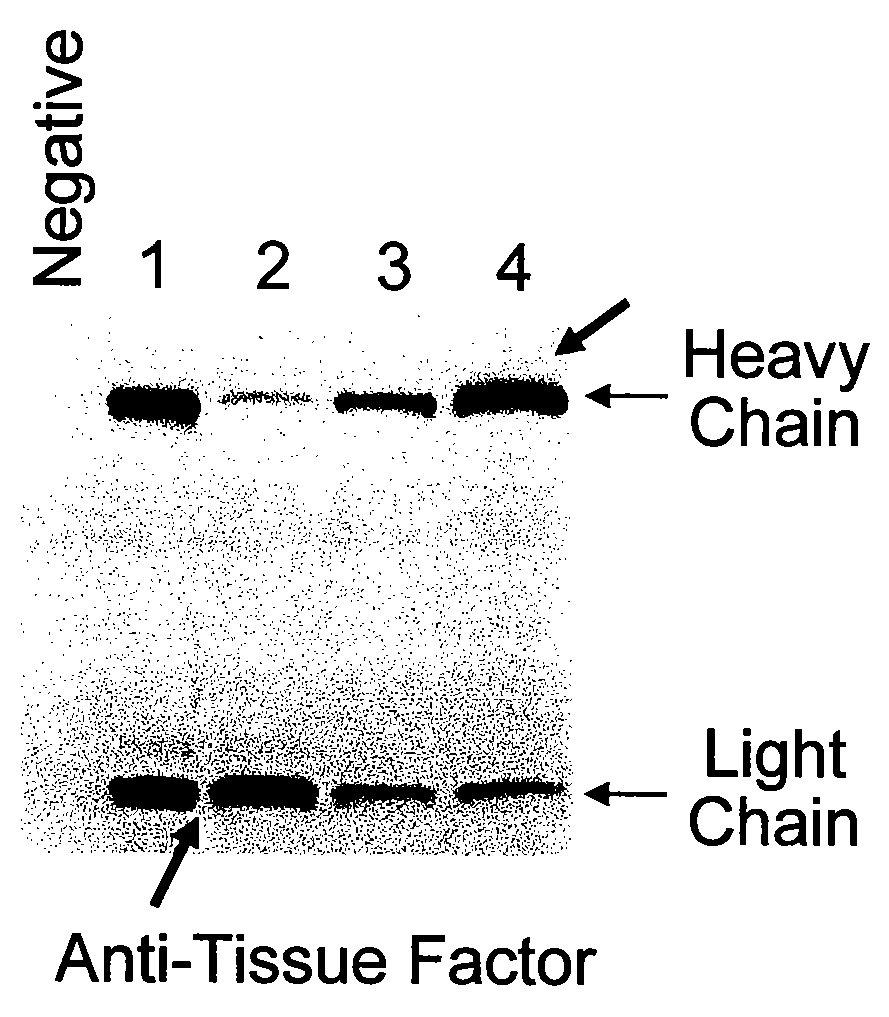
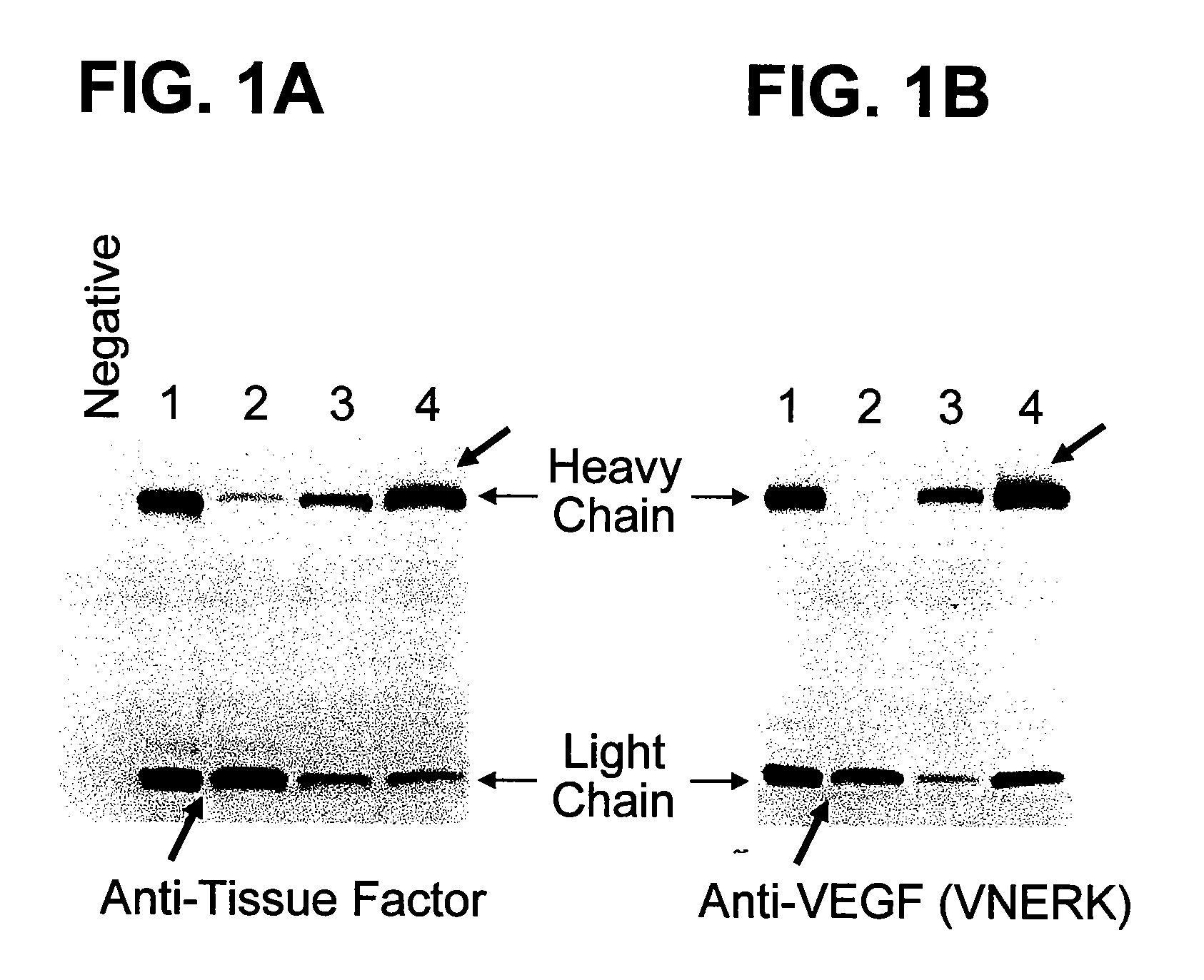
[0210]Antibodies produced in cell culture can accumulate intracellularly, in the periplasm or in the extracellular medium. Antibody production typically involves expression of the light and heavy chains in the cytoplasm, secretion into the periplasmic space, folding of the light and heavy chains, and assembly of the folded light and heavy chains to form an antibody molecule. Multiple covalent and non-covalent interactions occur between and within the heavy and light chains during these folding and assembly processes. Antibody yield can be greatly affected by the efficiency and fidelity of these processes. Following synthesis of the heavy and light chains, protein aggregation or proteolysis can occur thereby reducing the yield of the antibody. Solubility experiments were carried out in order to assess the efficiency of steps in the antibody production pathway in bacterial cells for the purpose of improving antibody yi...
example 2
Preparation of Anti-VEGF Antibodies with Improved Yield
[0226]The yield of antibodies or antigen binding fragments from cells can be influenced by the in vivo folding and / or assembly of the antibody. In order to increase antibody or antigen binding fragment yield, the sequence of the antibody or fragment was modified and the effect on folding and yield on the antibody was examined. As described in Example 1, aggregation of heavy chains may contribute to a decrease in antibody folding, assembly and yield. Targeted modification of the heavy chain variable region FR1 of anti-VEGF antibodies was performed. Antibody variants with different human variable domain subgroup consensus sequences in the FR1 were prepared and the yield of completely assembled antibody products was examined.
Materials and Methods
A. Preparation of Expression Vectors Encoding Modified Anti-VEGF Antibodies
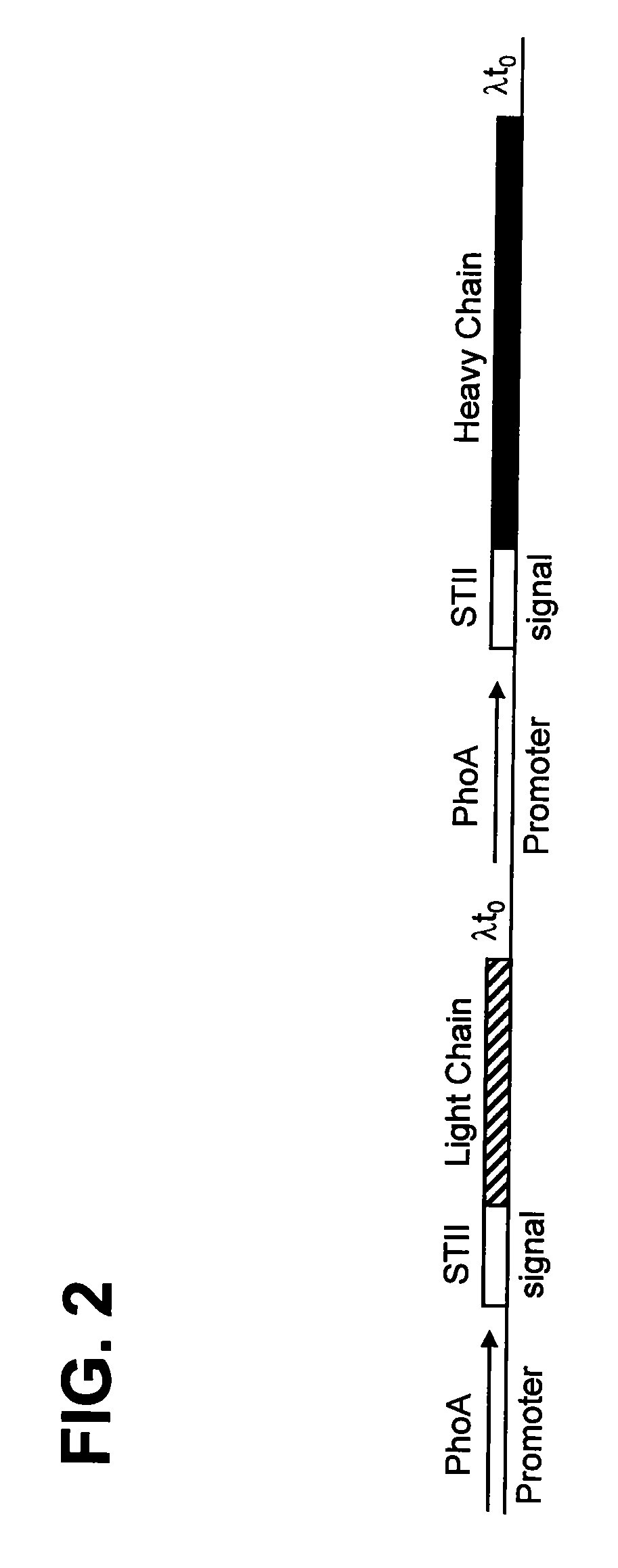
[0227]To evaluate the effect of different heavy chain FR1 human subgroup consensus sequences on the expression, fo...
example 3
Selection of a Heavy Chain FR1 Sequence for Antibodies Based on Comparison of HVR1 Antibody Sequences to HVR1 Consensus Subgroup I-III Sequences
[0278]Substitution of heavy chain FR1 consensus sequence subgroup III with consensus sequence subgroup I in anti-VEGF antibodies increased assembled antibody yield, presumably due to improved folding efficiency. Framework region sequences that provide for improved yield for other antibodies or antigen binding fragments can be identified based upon identifying the consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity in the HVR1 region of the variable domain when the HVR1 region of the antibody or fragment is compared to the corresponding HVR1 sequences of each of the subgroup consensus sequences. The method of identifying a heavy chain FR1 sequence for increasing the yield of antibodies based on HVR1 consensus subgroup I-III comparisons was tested for an anti-IgE antibody, E25.
A. Identification of a Heavy Chain FR1 Sequence for Hum...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com