Protein (poly)peptides libraries
a technology of polypeptides and libraries, applied in the field of synthetic dna sequences, can solve the problems of not providing the possibility of improving the desired properties of the members in an easy and rapid manner, no general procedure available to improve the desired properties of the members, and winter invention does not provide for artificial variable regions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design of a Synthetic Human Combinatorial Antibody Library (HuCAL)
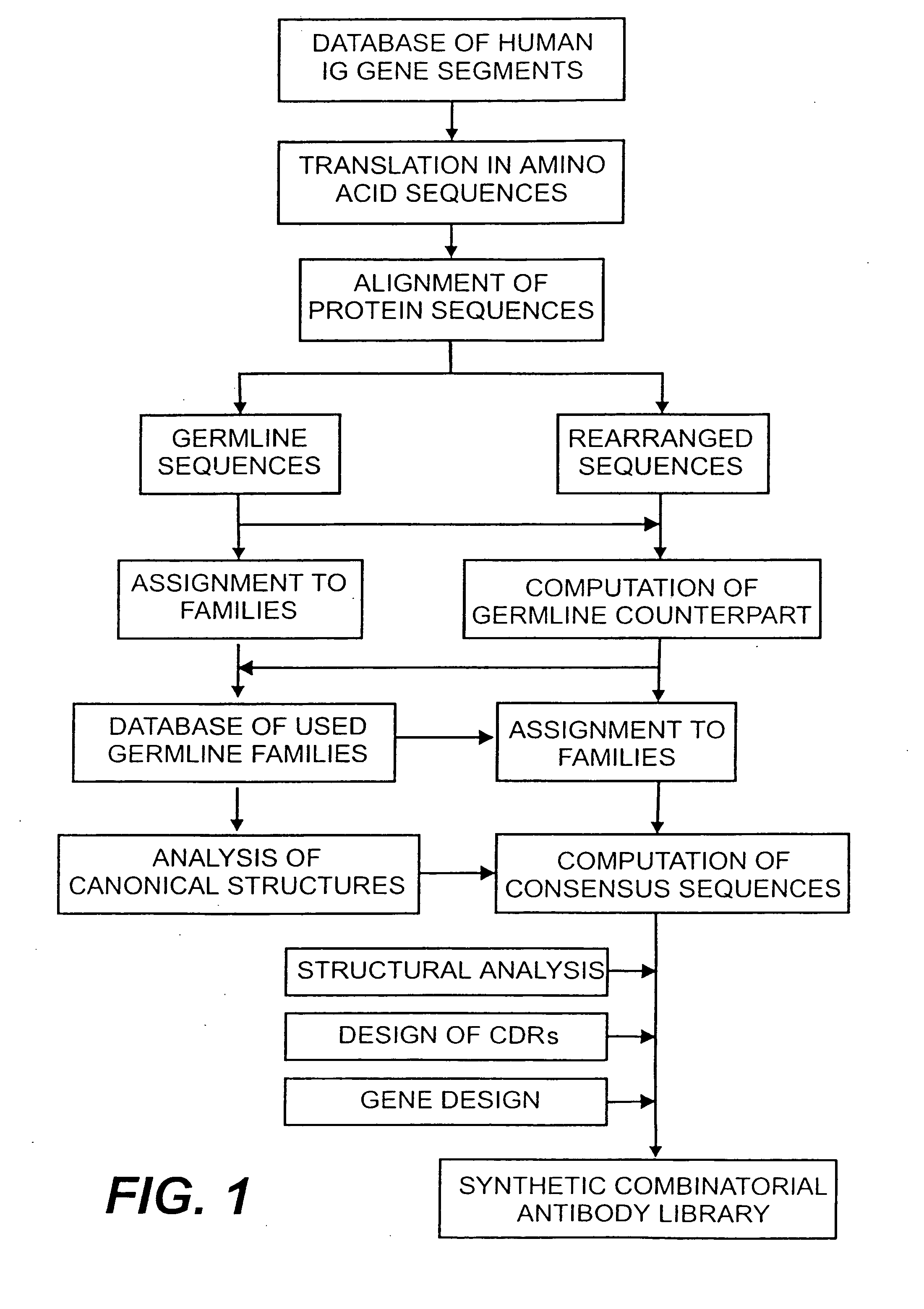
[0123] The following example describes the design of a fully synthetic human combinatorial antibody library (HuCAL), based on consensus sequences of the human immunoglobulin repertoire, and the synthesis of the consensus genes. The general procedure is outlined in FIG. 1.
1.1.1 Collection and Alignment of Human Immunoglobulin Sequences
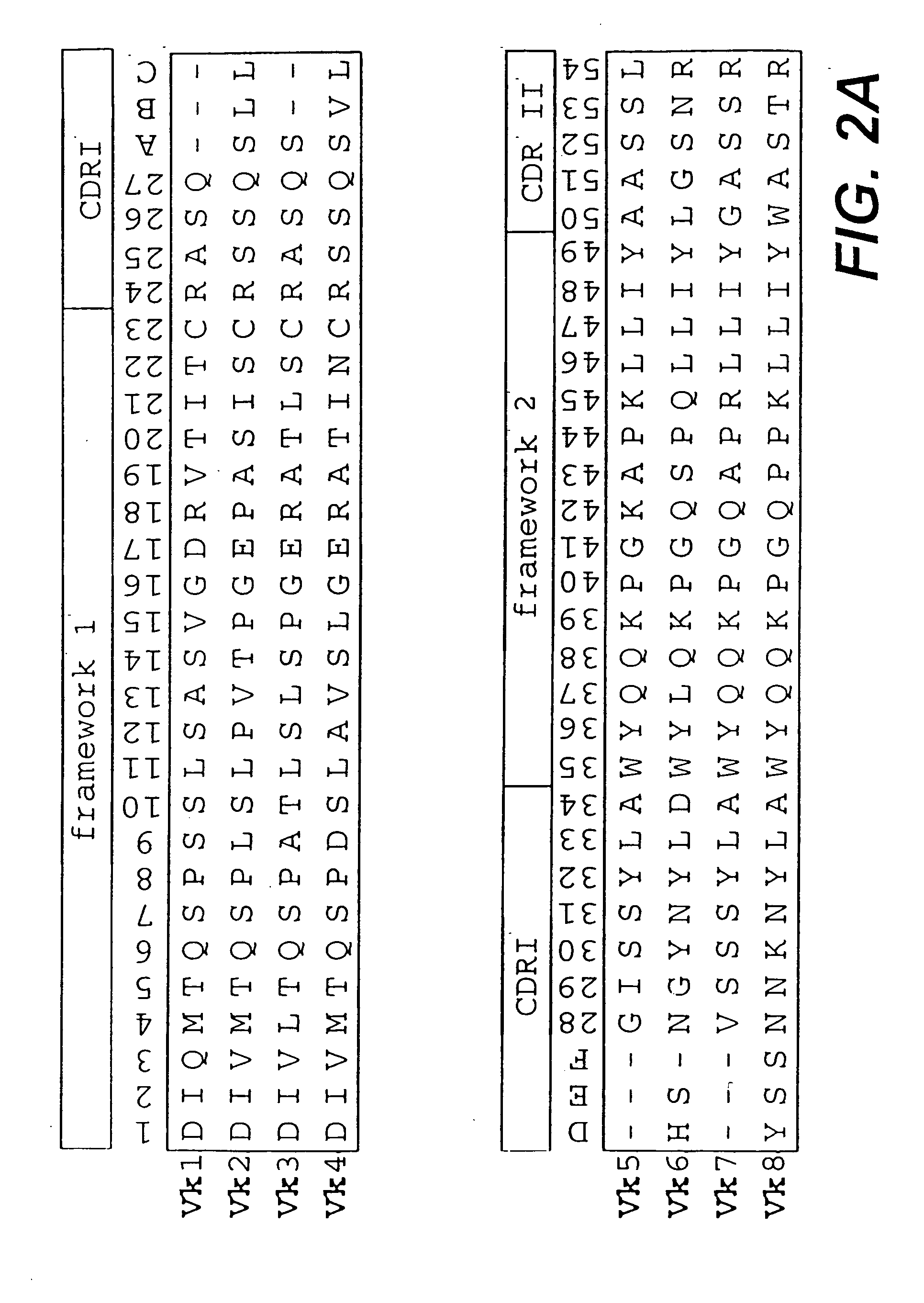
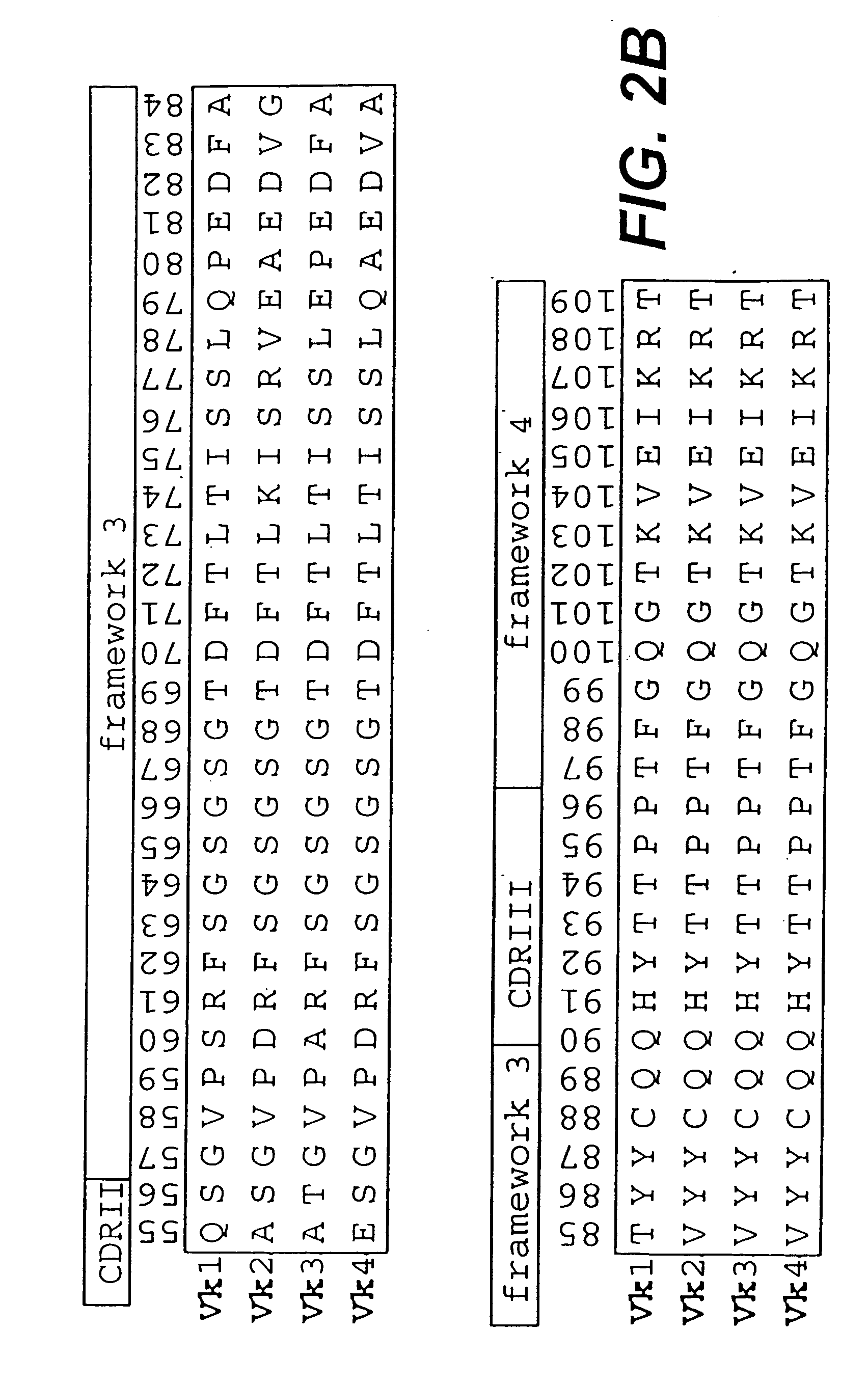
[0124] In a first step, sequences of variable domains of human immunoglobulins have been collected and divided into three sub bases: V heavy chain (VH), V kappa (Vκ) and V lambda (Vλ). For each sequence, the gene sequence was then translated into the corresponding amino acid sequence. Subsequently, all amino acid sequences were aligned according to Kabat et al. (1991). In the case of Vλ sequences, the numbering system of Chuchana et al. (1990) was used. Each of the three main databases was then divided into two further sub bases: the first sub base contained all...
example 2
Cloning and Testing of a HuCAL-Based Antibody Library
[0154] A combination of two of the synthetic consensus genes was chosen after construction to test whether binding antibody fragments can be isolated from a library based on these two consensus frameworks. The two genes were clones as a single-chain Fv (scFv) fragment, and a VH-CDR3 library was inserted. In order to test the library for the presence of functional antibody molecules, a selection procedure was carried out using the small hapten fluorescein bound to BSA (FITC-BSA) as antigen.
2.1 Cloning of the HuCAL VH3-Vk2 scFv Fragment
[0155] In order to test the design of the consensus genes, one randomly chosen combination of synthetic light and heavy gene (HuCAL-Vκ2 and HuCAL-VH3) was used for the construction of a single-chain antibody (scFv) fragment. Briefly, the gene segments encoding the VH3 consensus gene and the CH1 gene segment including the CDR3-framework 4 region, as well as the Vκ2 consensus gene and the Cκ gene se...
example 3
HuCAL H3κ2 Library Against a Collection of Antigens
[0166] In order to test the library used in Example 2 further, a new selection procedure was carried out using a variety of antigens comprising β-estradiol, testosterone, Lewis-Y epitope (LeY), interleukin-2 (IL-2), lymphotoxin-β (LT-β), E-selectin ligand-1 (ESL-1), and BSA.
3.1 Biopanning
[0167] The library and all procedures were identical to those described in Example 2. The ELISA plates were coated with β-estradiol-BSA (100 μg / ml), testosterone-BSA (100 μg / ml), LeY-BSA (20 μg / ml) IL-2 (20 μg / ml), ESL-1 (20 μg / ml) and BSA (100 μg / ml), LT-β (denatured protein, 20 μg / ml). In the first two rounds, bound phages were eluted with 0.1 M triethylamine (TEA) at RT for 10 minutes. In the case of BSA, elution after three rounds of panning was carried out with addition of BSA in a concentration of 100 μg / ml in PBS. In the case of the other antigens, third round elution was done with 0.1 M triethylamine. In all cases except LeY, enrichment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com