Method for designing species specific primer for detecting species with known genome information in microbial community and method for measuring bacterium content
A microbial community and primer design technology, applied in the field of determining the content of the corresponding bacterial species in the flora, and the design of species-specific primers, can solve the problems of lack of effective use of genomic information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 6
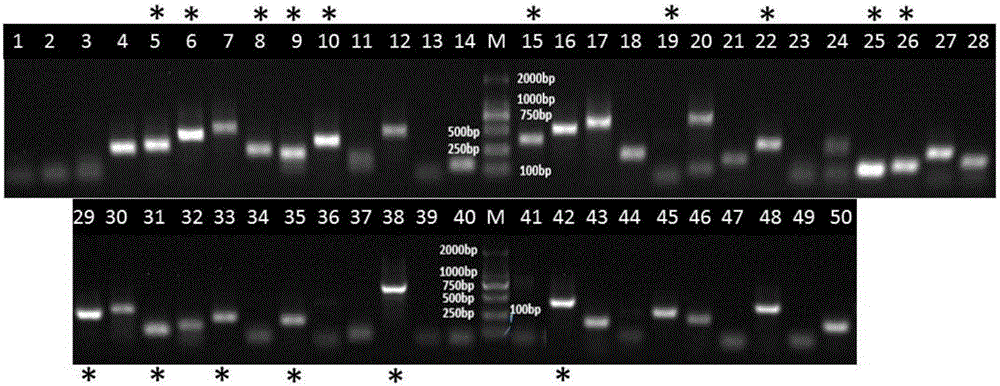
[0040] Example 1 16S rRNA gene TA clone sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
[0041] First, 200 mg of a soil sample was freshly weighed, and the genome was extracted using the Solarbio Soil Genome Kit or the Shanghai Sangon EZUP Column Soil Genome Extraction Kit, and the final elution volume was 100 μL. Genome template samples (10-50ng / ul) were refrigerated at -80°C for later use. Soil samples can be sealed in plastic bags and stored in a -80°C refrigerator for 1-2 years. Through the amplification of 16S rDNA in a soil sample, the amplification primers are 27F (5'-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AG-3') and 1492R (5'-GGT TAC CTT GTT ACG ACTT-3'). Augmented templates were metagenomics extracted from soil samples. After the PCR amplification product was purified, it was connected to the pMD-19T vector by TA cloning and transformed into competent DH5α Escherichia coli, and then the blue and white spots were screened by LBA culture, and the white spots were picked for sequencing, and ...
Embodiment 2
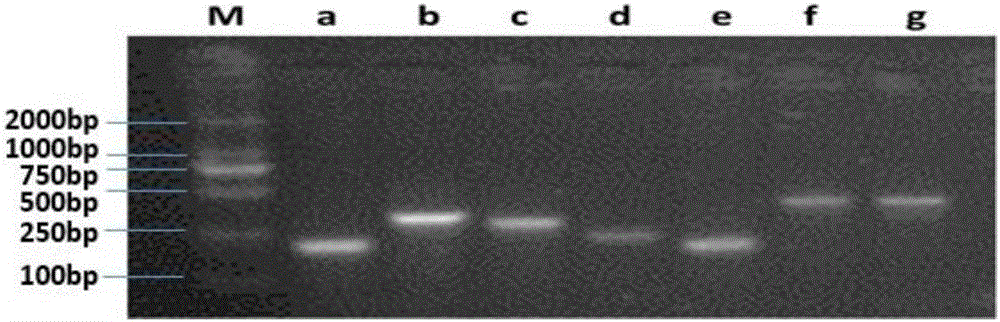
[0045] Embodiment two specific primer design and screening
[0046] According to the microbial species obtained in Example 1, the name of each microbial species is entered into the EBI genome website (www.ebi.ac.uk / genomes / ) to check whether it has (full) genome information (Table 1), and it ( The whole) genome sequence information was downloaded for subsequent species-specific primer design. The obtained (full) genome sequence information was used as a template for species-specific primer design on the Primer-Blast website (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / tools / primer-blast / ). Enter the (full) genome information of the target strain in the PCR Template box. Since the maximum sequence length here is 50,000bp, only 50kb can be entered each time; the annealing temperature is 60±3℃, and the primer length is 100-400bp. In the "Primer Pair Specificity Checking Parameters" box, select: Automatic, nr, and enter the names or taxonomy ids of all non-target species in the microbial communi...
Embodiment 3
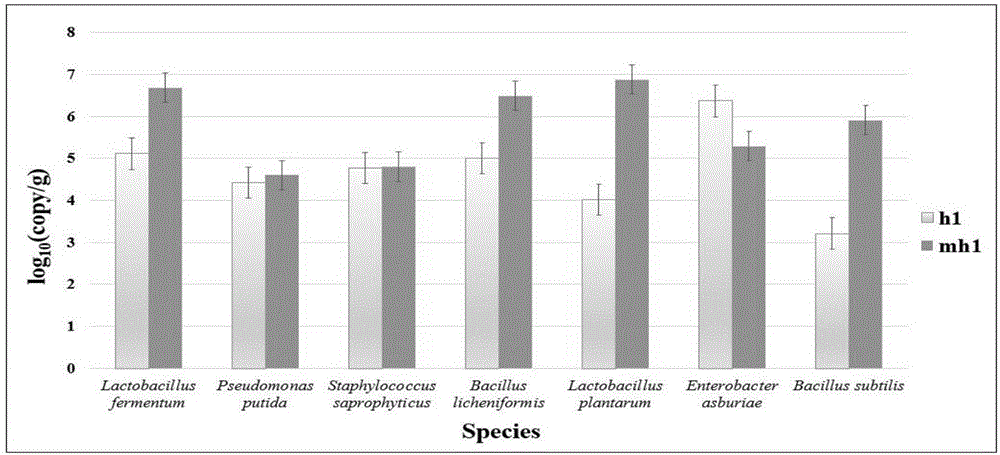
[0053] Configuration and qPCR quantitative determination of embodiment 3qPCR system
[0054] 1. The qPCR system can use a general qPCR kit. Taking GREDBIO's NPK62 kit (including 2×buffer) as an example, see Table 3 for the composition of the qPCR system.
[0055] Table 2 qPCR system composition of NPK62 kit (GREDBIO)
[0056] 2×PCR buffer (containing fluorescent dye and PCR booster)
6μL
Primer 1 (2 μM)
1μL
Primer 2 (2 μM)
1μL
Template+H 2 o
3.8μL
Taq enzyme (5U / μL)
0.2 μL
12 μL total volume
[0057] 2. Preparation of standards: In this experiment, qPCR uses a plasmid containing the target PCR product as a standard.
[0058] The preparation method is as follows: 7 PCR products are gel-cut and purified, connected to pMD-19T vector by TA cloning, and then transformed into competent DH5α Escherichia coli cells. Then the Escherichia coli engineering bacteria were shaken in liquid culture, and the plasmid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com