Method for in-situ determination of wood fiber biomass enzyme accessibility
A lignocellulosic and biomass technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc. Effective site and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] (1) Take a 6mm×4mm×1mm small fragment of dewaxed straw in a low-protein adsorption tube (dewaxed straw components: cellulose 38.44, hemicellulose 33.60, lignin 5.73, ash and others 22.23), add pH The value was 6.0, 500 μL of phosphate buffer solution with a concentration of 100 mM, and the initial concentration Et of cellulosomal fluorescent protein probe GFP-CBM3 was 4.0 μM / L, and labeled in the dark for 1.5 h at a constant temperature of 55 °C.
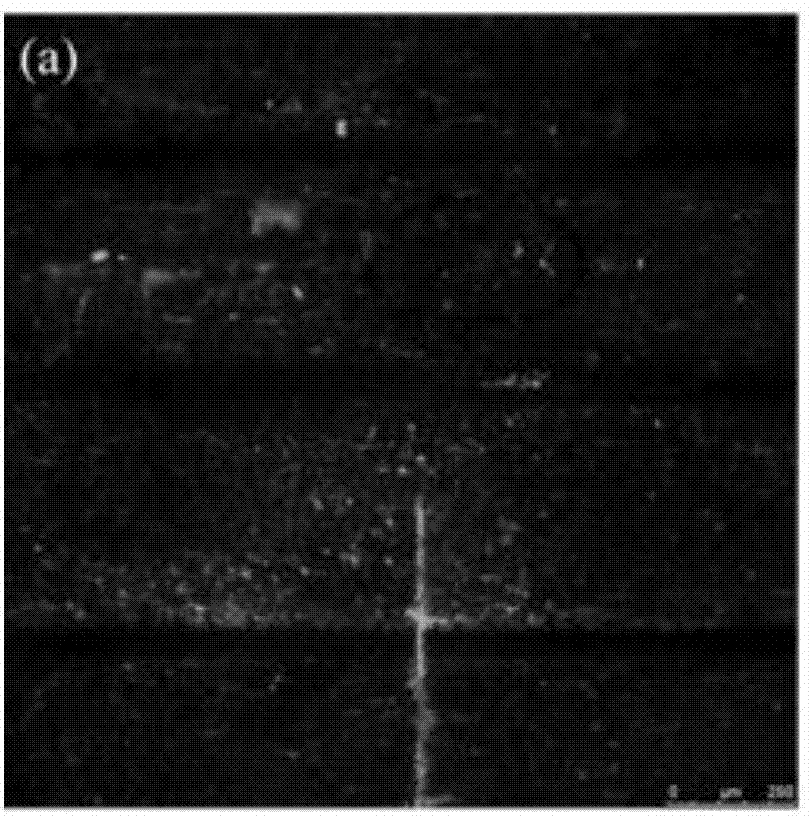
[0063] (2) In situ observation and analysis of dewaxed rice straw samples using laser confocal microscopy (LCSM, Leica TCS SP5) and fluorescent microplate reader, to obtain the total enzyme binding site distribution and cellulosomal fluorescent protein probe adsorption amount of the sample ; The distribution of the total enzyme-binding sites is shown in Figure 1(b), with an average fluorescence value of 34.6; the concentration of free cellulosomal fluorescent protein probes in the supernatant of the labeling solution E fa 2.7...
Embodiment 2
[0068] (1) Take a 3mm×8mm×200μm small fragment of pretreated straw in a low-protein adsorption tube (pretreated straw components: cellulose 50.04, hemicellulose 5.74, lignin 14.45, ash and others 24.77), add pH The value was 5.0, 1 mL of sodium citrate buffer with a concentration of 50 mM, and the initial concentration of cellulosomal fluorescent protein probe GFP-CBM3 was 2.0 μM / L, and labeled in the dark for 2.0 h at a constant temperature of 15°C.
[0069] (2) The measurement method is as described in step (2) in Example 1. The distribution of the total enzyme binding sites is shown in Figure 1(d), with an average fluorescence value of 31.8; the concentration of free cellulosomal fluorescent protein probes in the supernatant of the labeling solution E fa 0.90μM / L, E a is 1.10 μM / L (calculated using the Langmuir equation), and the adsorption amount of the cellulosomal fluorescent protein probe per unit area of the sample is E ua 4.58×10 4 μM / m 2 ;
[0070] (3) Add 0.5...
Embodiment 3
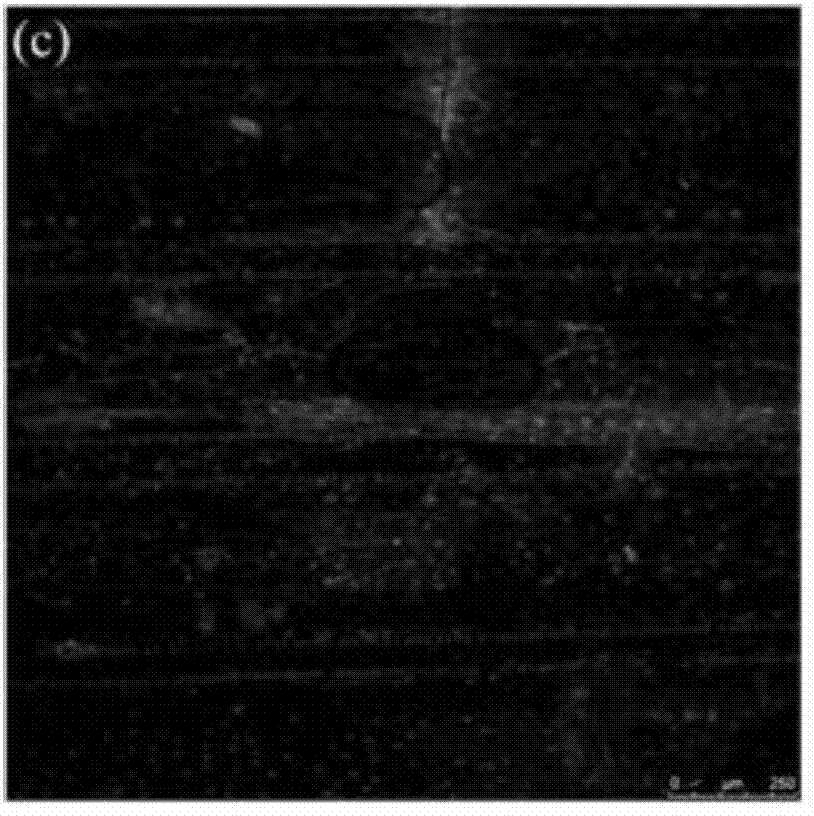
[0074] (1) Take a 5mm×5mm×100μm small fragment of pretreated straw in a low-protein adsorption tube (pretreated straw components: cellulose 69.30, hemicellulose 21.24, lignin 1.52, ash and others 7.80), add pH The value was 7.0, 200 μL of phosphate buffer solution with a concentration of 200 mM, and the initial concentration Et of cellulosomal fluorescent protein probe YFP-CBM was 8.0 μM / L, and labeled in the dark for 0.5 h at a constant temperature of 60 °C.
[0075] (2) In situ observation and analysis of dewaxed rice straw samples using laser confocal microscopy (LCSM, Leica TCS SP5) and fluorescent microplate reader, to obtain the total enzyme binding site distribution and cellulosomal fluorescent protein probe adsorption amount of the sample ; The distribution of the total enzyme-binding sites is shown in Fig. 1(f), with an average fluorescence value of 142.4; the concentration of free cellulosomal fluorescent protein probes in the supernatant of the labeling solution E f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com