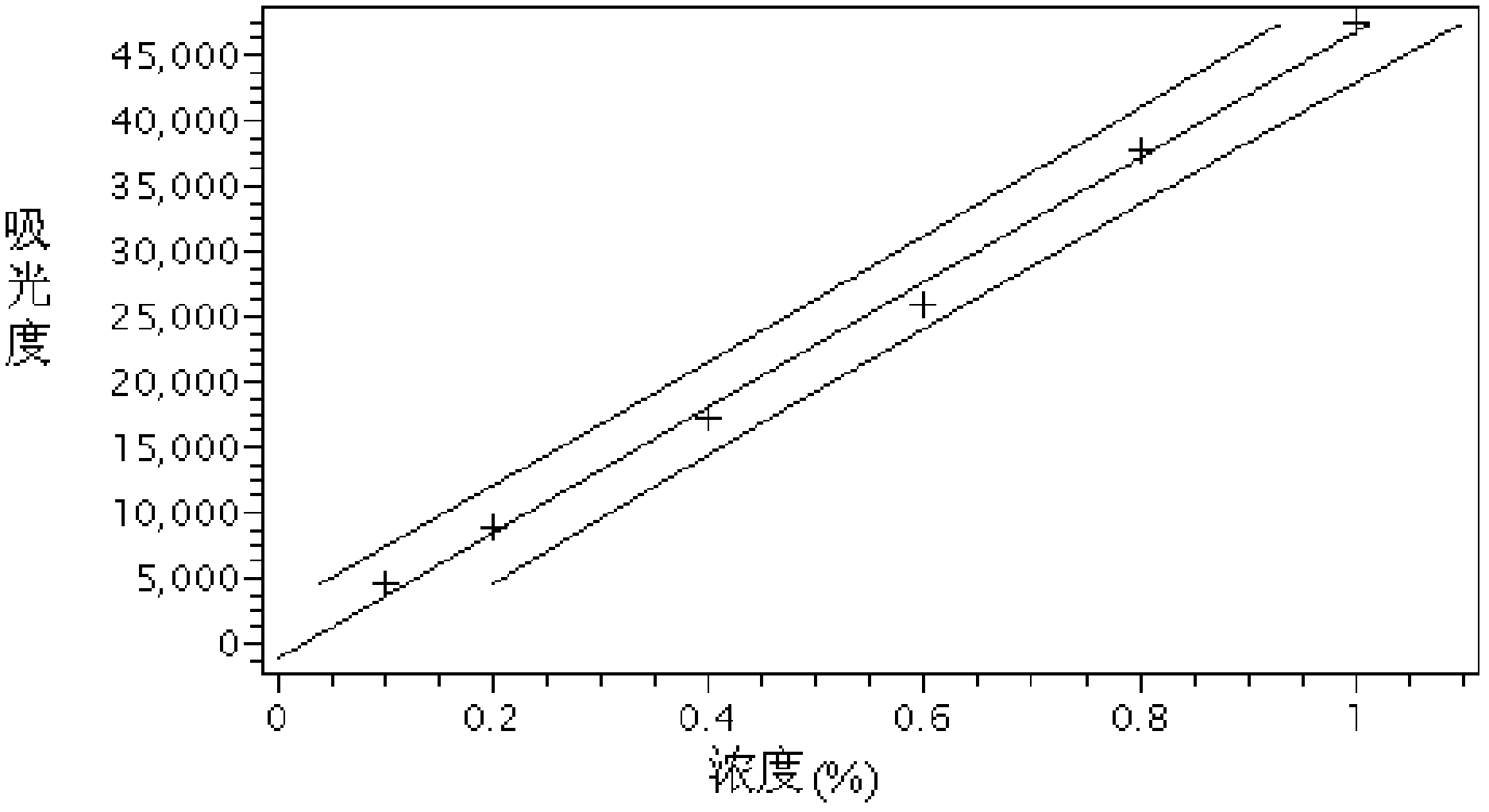
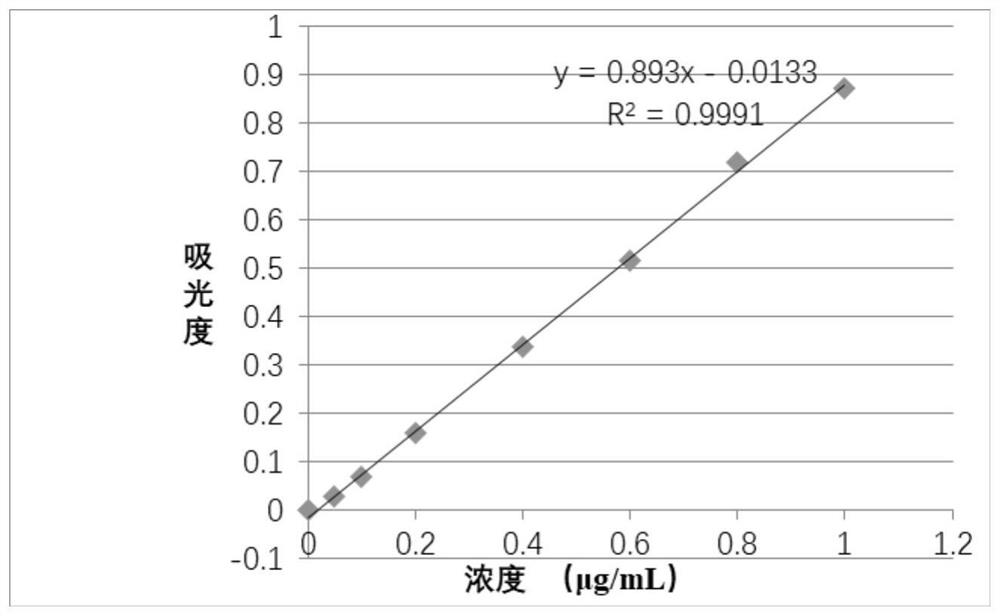
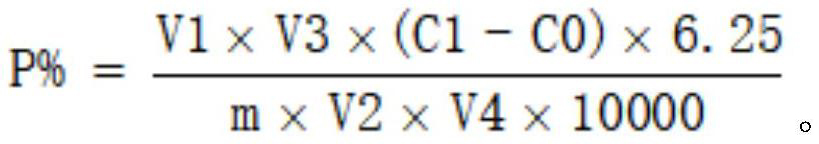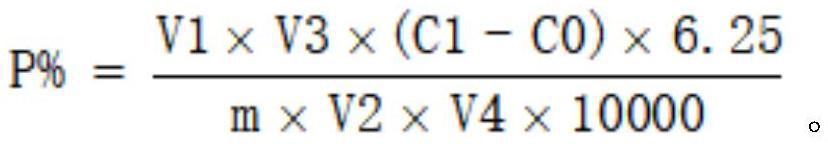Patents
Literature
76 results about "Protein nitrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
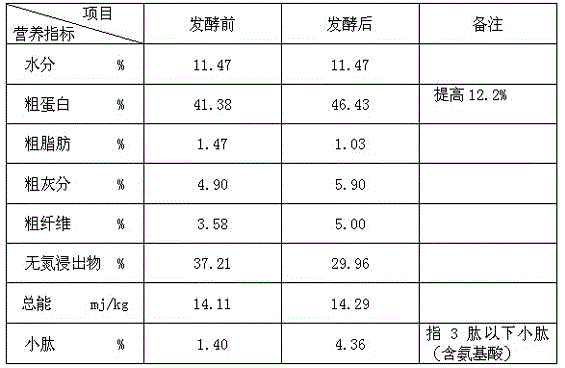
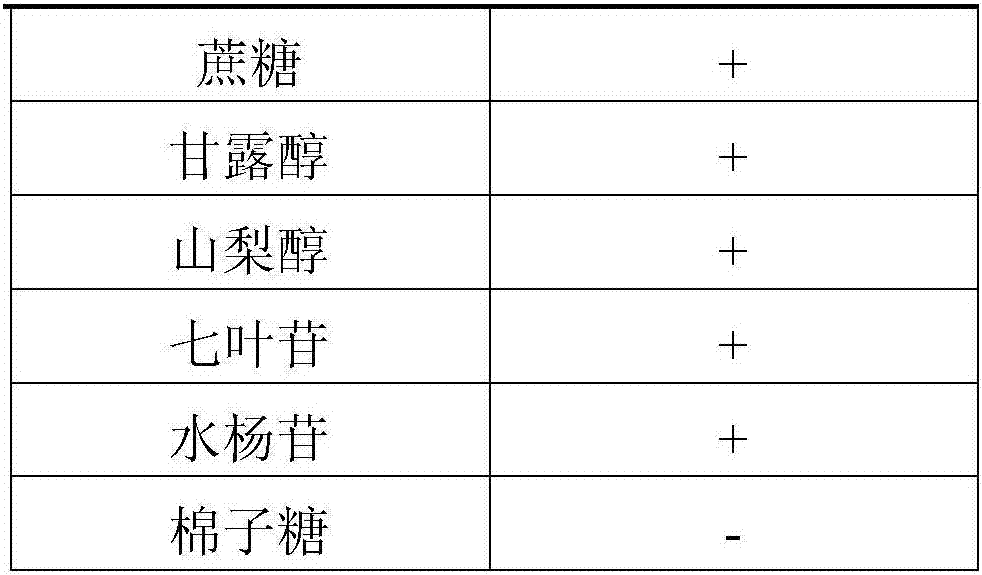
Nonprotein nitrogen (NPN) the nitrogenous constituents of the blood exclusive of the protein bodies, consisting of the nitrogen of urea, uric acid, creatine, creatinine, amino acids, polypeptides, and an undetermined part known as rest nitrogen.
Culture medium for haemophilus influenzae type b
ActiveUS20090017074A1Simple methodHigh biosecurityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaPolyribosyl phosphateProtoporphyrin IX
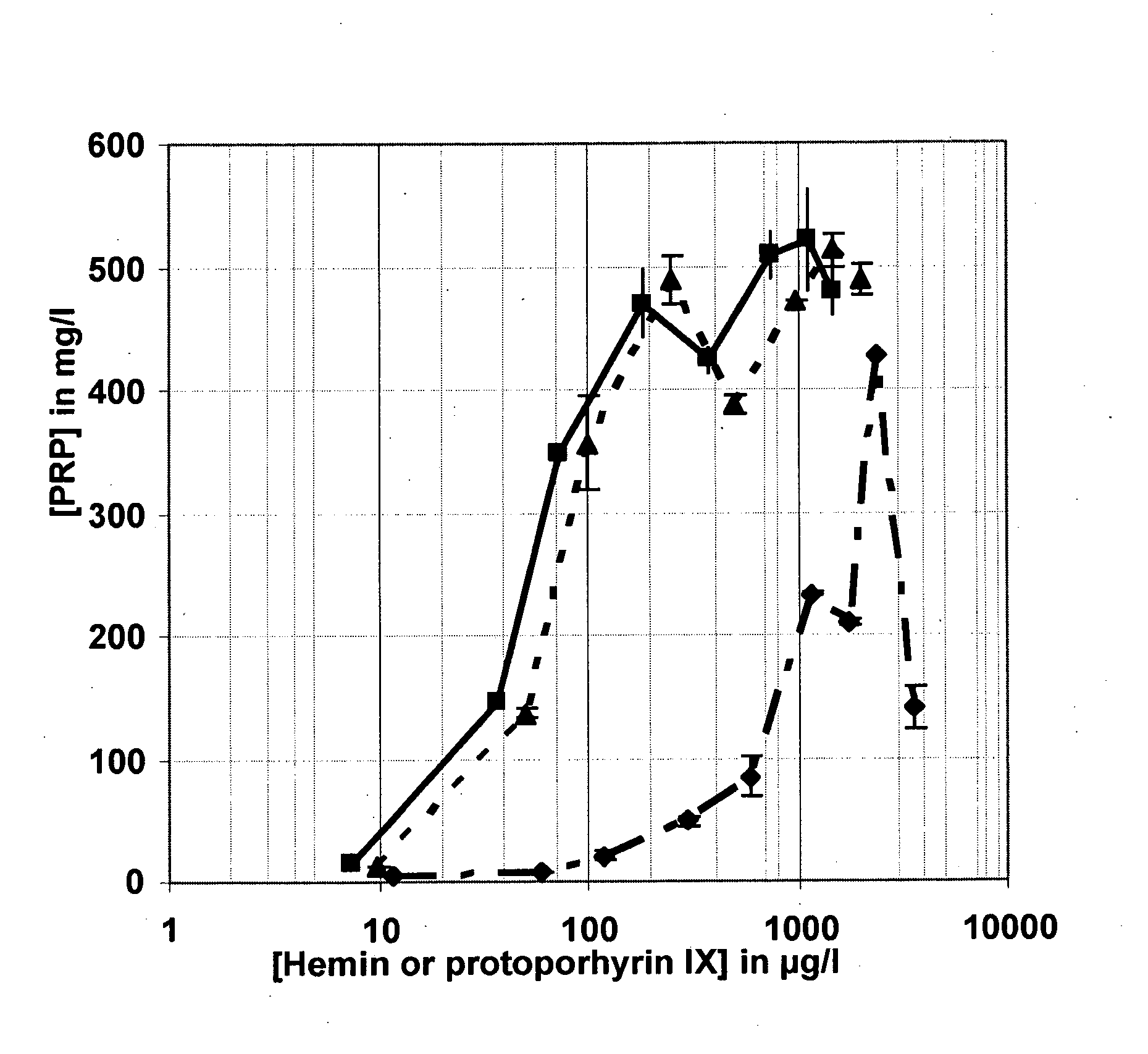
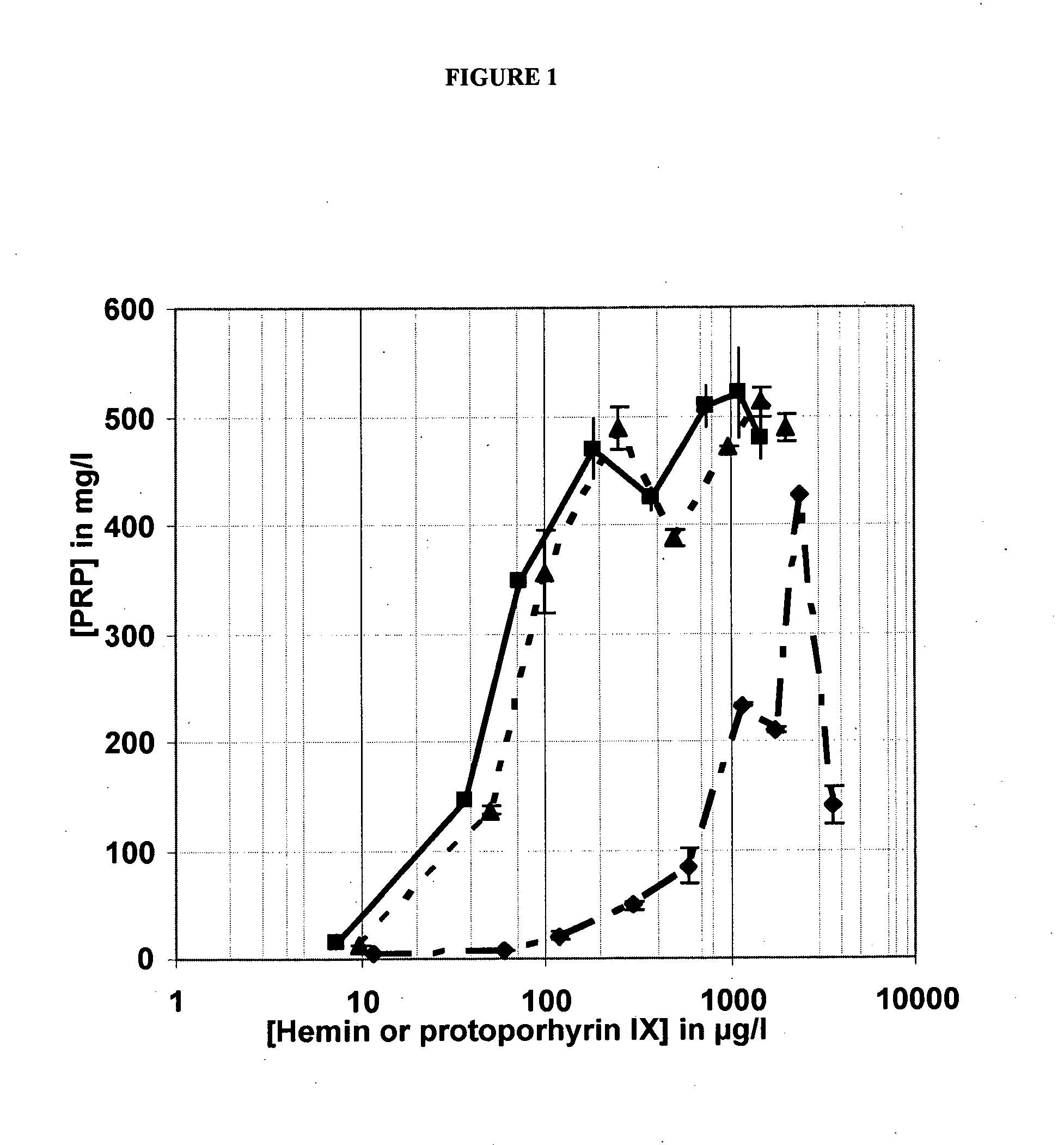
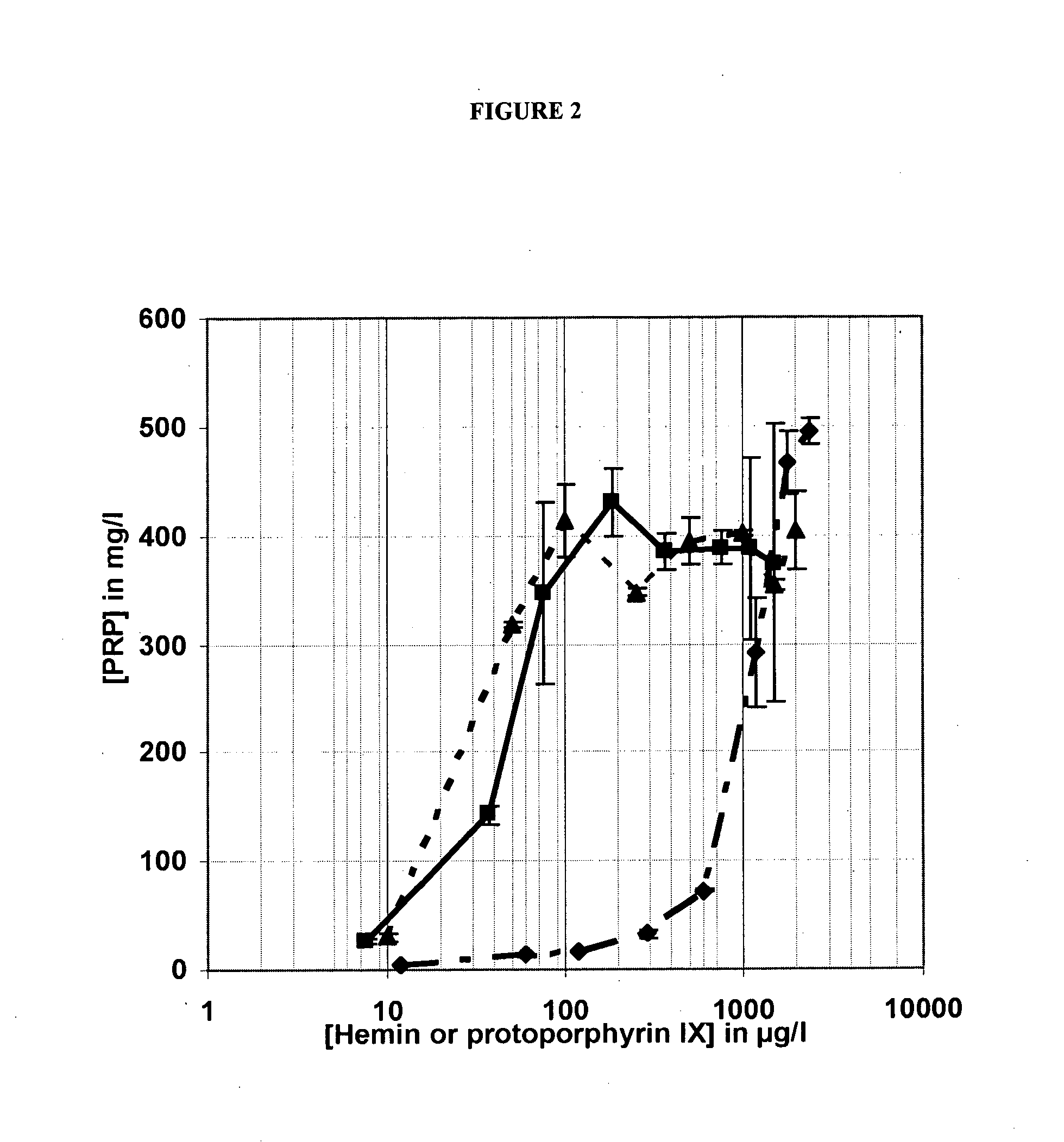
The invention relates to a culture medium for Haemophilus influenzae type b, characterized in that the source of protein nitrogen is of non-animal origin and comprises at least one plant peptone and in that the heme source consists of protoporphyrin IX. This medium serves in particular for the production of polyribosyl phosphate (PRP) and for the manufacture of a vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR SA
Method for recovering coin protein sugar dregs and preparing protein nitrogen sources and nitrogen-containing syrup
The invention discloses a method for recovering coin protein sugar dregs and preparing protein nitrogen sources and nitrogen-containing syrup in the production of enzymatic corn starch sugar, comprising the steps of size mixing, liquefying, saccharifying, standing separation, centrifugal separation, proteolysis, concentration, drying, compounding, and the like. In the invention, protein is condensed under the heat flash of liquefying, the protein sugar dregs concentrate and float upwards in saccharifying, the sugar dregs are recovered through the steps of standing separation and centrifugal separation, the sugar dregs are dried into protein, or the sugar dregs are hydrolyzed to prepare protein nitrogen sources, and the nitrogen sources can be compounded with syrup to form nitrogen-containing starch syrup for fermenting. Clarified saccharification liquid after centrifugal separation is decolored, filtered, refined and concentrated, and starch syrup products are obtained. The majority of lentous sugar dregs in the saccharification liquid are removed before the treatment of decoloring and filtering, and the decoloring and filtering performance of the material is better. The use level of active carbon, and the like can be properly reduced, the production capability of filtering equipment is improved, and the frequency of the loading and unloading of filters as well as the consumption of washing waste water and various kinds of loss are greatly reduced.
Owner:广州双桥(重庆)有限公司
Method for preparing protein nitrogen source applicable to fermentation and food by rice
The invention discloses a method for preparing organic nitrogen source applicable to fermentation and food by taking rice or rice flour as raw material and carrying out acid process or enzymatic hydrolysis for scum left through pressing and filtering in the process of filtering starch syrup produced in an enzymatic method. The method comprises the following steps: the rice or the rice flour is washed and ground to be milk, calcium chloride and liquefying amylase are added to the milk for consecutive spraying liquefaction to obtain liquefied liquid, various saccharifying enzymes and / or germinating malts and lipase are added to the liquefied liquid for synergistic saccharification, the starch syrup is obtained by filtering saccharified product and refining and concentrating filtrate; the scum obtained by filtering and pressing is washed by water, the residual sugar in the scum is obtained by filtering and pressing, and the washing liquor is used for size mixing; alkaline lipase is added to the left washed sugar-free grains to further hydrolyze the fat in material, rice sugar-free grains protein with higher protein content is obtained by filtering and washing, and rice sugar-free grains protein is hydrolyzed by edible hydrochloric acid or protease to prepare the organic nitrogen source which can be used as the fermentation raw material of a biopharmaceutical process.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHUANGQIAO +1
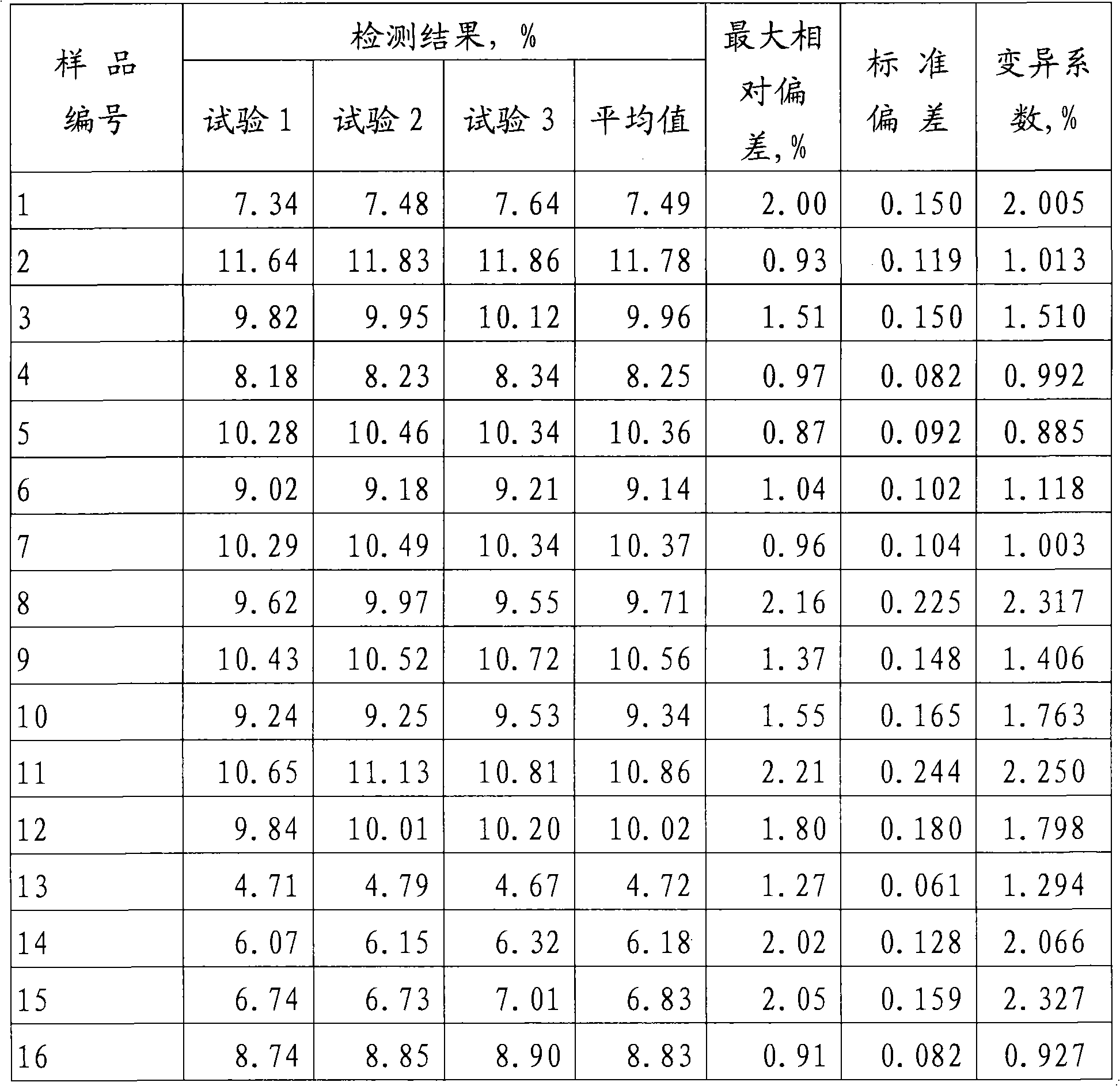
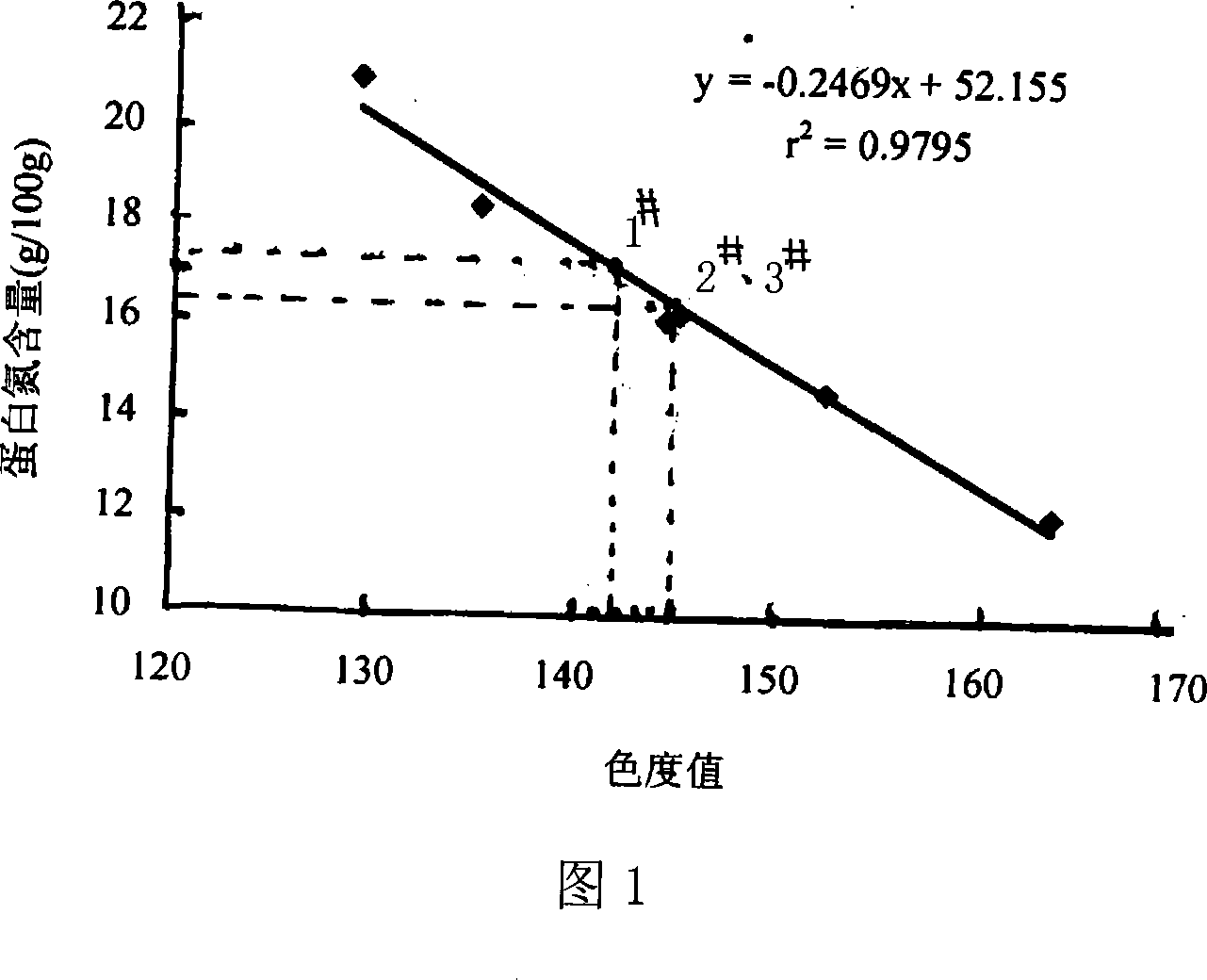
Method for measuring protein nitrogen content in tobacco
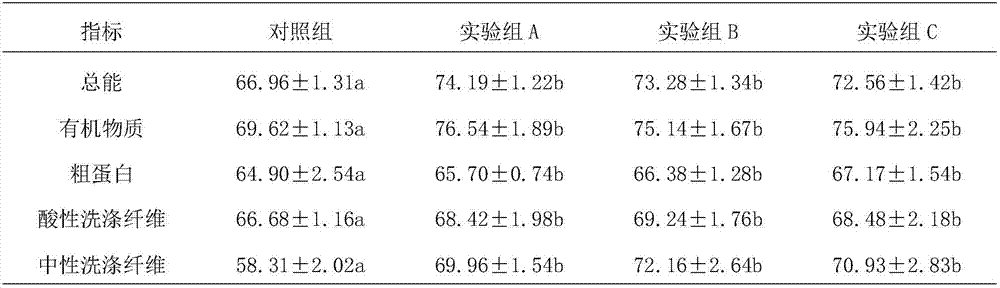
InactiveCN101354349AFew stepsReduce operating errorsColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingComplete proteinProtein nitrogen
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Fermenting enzymolysis agent for soybean meal fermentation and application thereof
ActiveCN105614023AIncrease nutritionImprove digestion and absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffMycoproteinAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a fermenting enzymolysis agent for soybean meal fermentation and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of feed fermenting agents. The fermenting enzymolysis agent consists of microorganism strains, enzyme preparations, an accessory ingredient and a carrier. According to the fermenting enzymolysis agent, seven types of beneficial bacteria and three types of enzyme preparations are combined, 72-hour aerobiotic, microaerobic and anaerobic fermentation and enzymolysis are performed on crushed soybean meal and a small amount of corn flour, so that antinutritional factors in the soybean meal are eliminated, cell walls are broken, non-protein nitrogen is converted into mycoprotein, proteins are decomposed into polypeptide and small peptide, more Vitamin B is generated, the nutrition performance of the soybean meal is comprehensively improved, and thus the soybean meal becomes a feed protein source capable of partially replacing a feed protein source for import fish meal feed.
Owner:湖州环农微生物技术研究所 +1
Sheep feed and the manufacturing technique thereof
InactiveCN101081061AOsmotic pressure equalizationImprove absorption rateFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSodium bicarbonateHigh absorption
The present invention discloses one kind of sheep feed and its production process. Pre-mixed material is first produced with zinc sulfate, ferrous sulfate, anhydrous cupric sulfate, potassium iodide, sodium selenite, cobalt chloride, manganese sulfate, vitamin A, vitamin D3 and vitamin E; and then mixed with slow released non-protein nitrogen, calcium biphosphate, alcoholic dregs, feather powder, cotton seed dregs, sunflower seed dregs, tree leaf powder, calcium carbonate, anhydrous sodium sulfate, sodium bicarbonate and yeast through stirring homogeneously to produce the sheep feed. The sheep feed has balanced nutrients, protein capable of being decomposed directly in the rumen of sheep, high absorption rate and raised sheep growing speed.
Owner:齐庆文
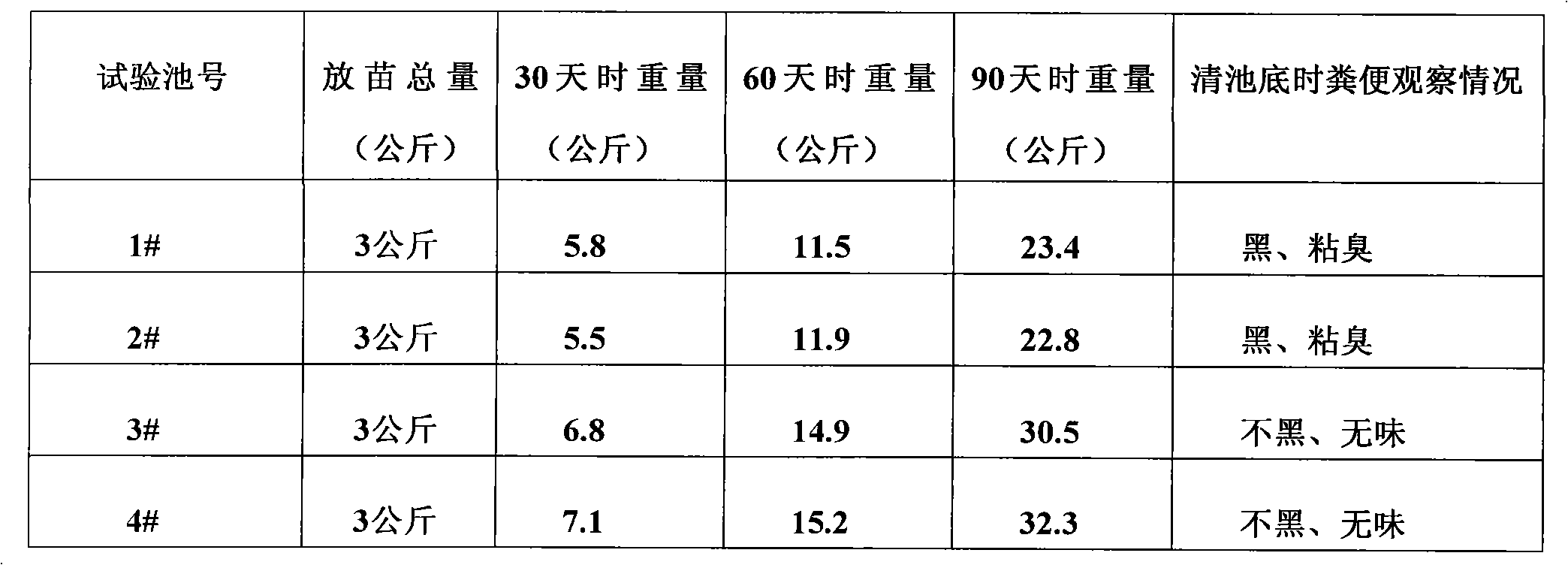
Biological feeds for sea cucumber
The invention discloses biological feeds for sea cucumber, which comprise the following components by weight portion: vegetable protein accounting for 10 to 20 parts, straws accounting for 30 to 50 parts, bur clover accounting for 10 to 20 parts, pomace and peelings accounting for 10 to 30 parts, pot ale accounting for 5 to 10 parts, zymocyte accounting for 0.02 to 0.05 parts and complex enzyme accounting for 0.02 to 0.05 parts. The sea cucumber biological feeds can resolve polysaccharide substances such as robust fibers to produce low-molecular monosaccharide, hexabiosa and the like, can improve nutritional components of the feeds, can accelerate the feed acidation, can promote vegetable protein to convert to microbial protein nitrogen, can improve the digestion utilization ratio, can reduce feed coefficient, can achieve good food calling performance, and can accelerate the growth rate; the sea cucumber biological feeds contain a great amount of probiotics groups and active enzyme, so that propagation and growth of destructive bacteria, mixed bacteria and putrefying bacteria can be inhibited, water contamination caused by putrefaction of residual bait can be controlled, water environment with sufficient oxygen can be provided to sea cucumber, the immunization and the disease resistance of sea cucumber can be improved, the survival rate is improved, and output benefits can be improved further; in addition, raw materials are abundant and are easy to get, and the cost of the feeds is low.
Owner:山东清源致远智能工程有限公司
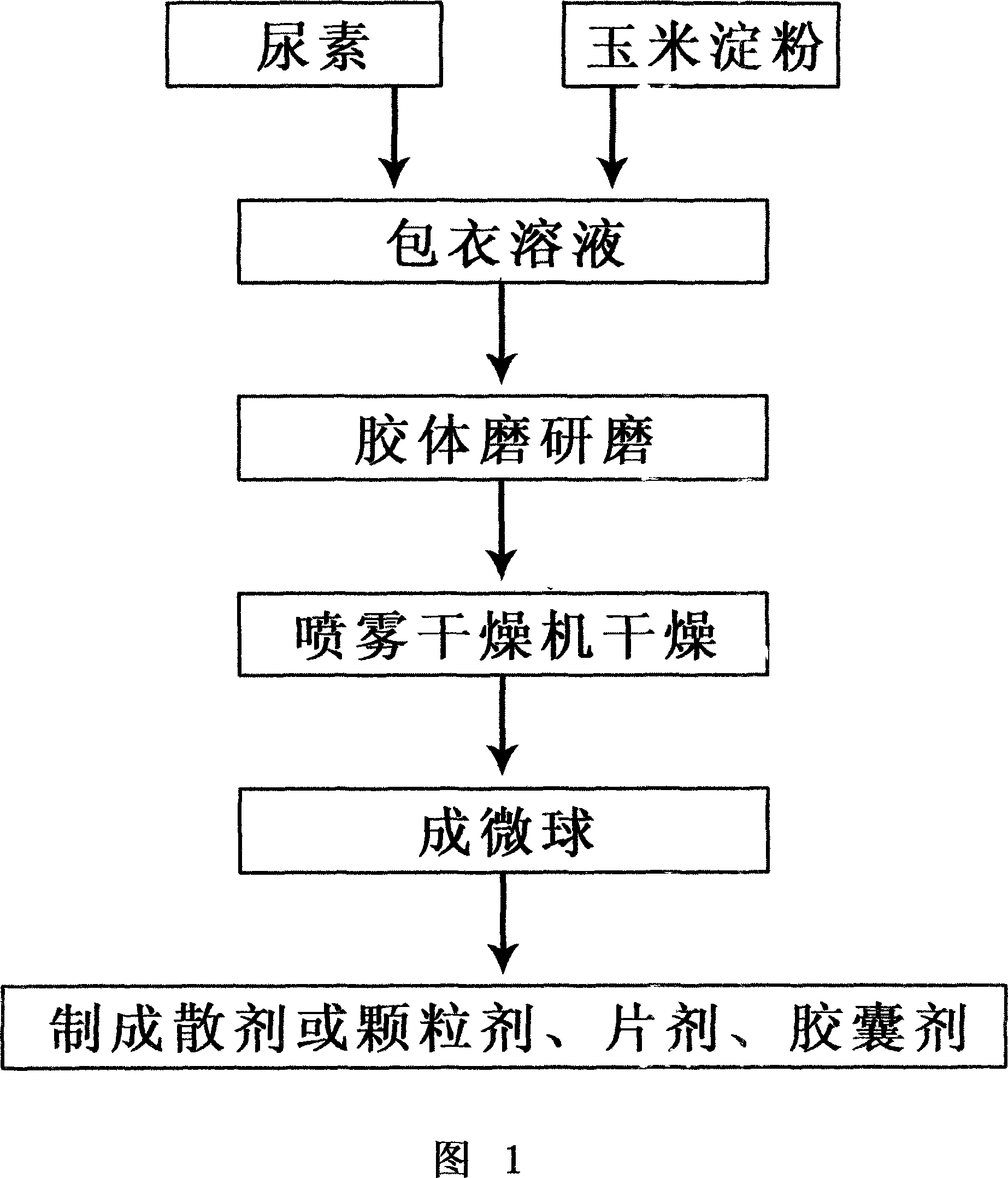
Nonprotein nitrogen feed additive suitable for ruminant and its producing process
InactiveCN101077126ASolve the problem that the decomposition speed is too fastDecomposition will not causeAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsRumenFeed additive
The present invention discloses one kind of non-protein nitrogen feed additive for ruminant and its production process. The non-protein nitrogen feed additive has reasonable recipe, easy production, low cost, high decomposition speed, urea decomposing speed matching the utilization speed of rumen to avoid ammonia accumulation in blood and good taste. The non-protein nitrogen feed additive consists of urea 35-50 wt%, corn starch 35-48 wt%, and coating material 2-20 wt%, and its production process includes the steps of dispersing urea and corn starch in coating material solution, grinding in a colloid mill to form emulsion, and spray drying at normal temperature to form microspherical feed additive. It may be also produced into powder, granule, tablet or capsule.
Owner:史义林 +1
Milk cattle feedstuff and manufacturing technique
InactiveCN101081062AIncrease milk productionImprove absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsSodium bicarbonateVegetable oil
The present invention discloses one kind of milk cow feed. Pre-mixed material is first produced with zinc sulfate, ferrous sulfate, anhydrous cupric sulfate, potassium iodide, sodium selenite, cobalt chloride, manganese sulfate, molybdenum chloride, vitamin A, vitamin D3 and vitamin E and through mixing; and then mixed with slow released non-protein nitrogen, calcium biphosphate, feather powder, cotton seed dregs, tree leaf powder, calcium carbonate, table salt, anhydrous sodium sulfate, sodium bicarbonate, yeast and vegetable oil through stirring homogeneously to produce the milk cow feed. The milk cow feed has balanced nutrients, protein capable of being decomposed directly in the rumen of milk cow, high absorption rate and capacity of raising milk yield.
Owner:齐庆文
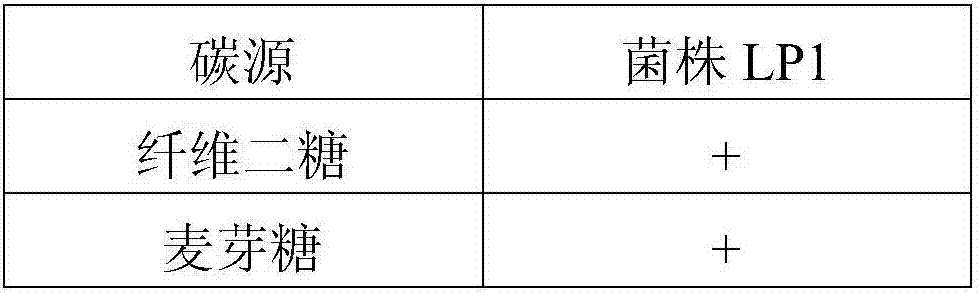
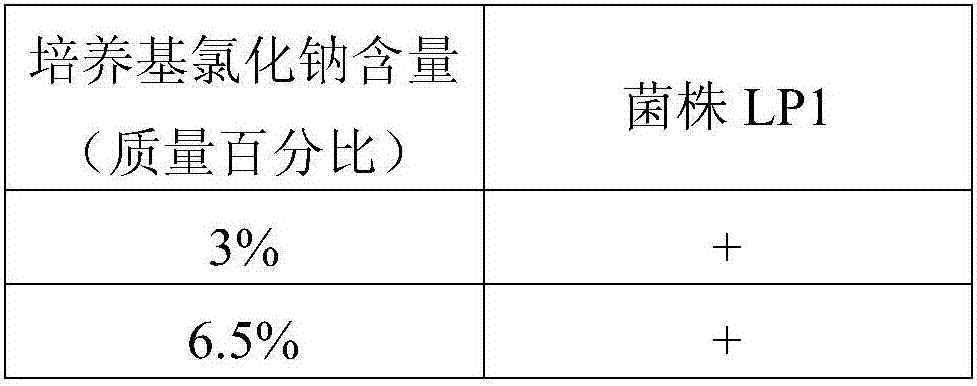
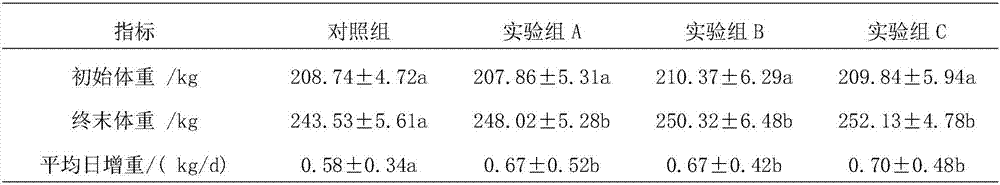
Lactobacillus plantarum Lp1 and application thereof in preparation of feed additive
InactiveCN107475147AImprove filtration efficiencyLow costBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffGeneticsFeed additive
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum Lp1 and an application thereof in preparation a feed additive. The disclosed lactobacillus plantarum Lp1 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 10473. The invention discloses the application of the lactobacillus plantarum Lp1 in preparing alfalfa silage. The lactobacillus plantarum LP1 can be used as the alfalfa silage additive, and has the advantages of significantly increasing output of lactic acid, reducing the pH value significantly and effectively improving fermentation quality of the alfalfa silage; the content of non-protein nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen can be reduced, degradation of protein in the alfalfa silage is inhibited, and feed value of the alfalfa silage is increased effectively; meanwhile, the lactobacillus plantarum LP1 has the advantages of high fermentation efficiency, low cost and the like and can be applied to production of green bio-feed.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fermented crop straw composition and application thereof
InactiveCN105053535AImprove palatabilityHigh nutritional valueFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyCellulose
The present invention relates to a fermented composition, and particularly relates to a fermented crop straw composition and an application thereof. The fermented crop straw composition includes the following components in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of molasses, 8-10 parts of compound bacteria, 2.5-4.5 parts of compound enzyme, 4-6.5 parts of compound trace elements, 0.5-2 parts of non-protein nitrogen, and 0.5-1.0 part of edible salt. The compound bacteria are cultured and blended by 12%-17% of candida utilis, 7%-12% of bacillus subtilis, and 8%-12% of trichoderma viride. The composition is used to ferment crop straws and to prepare ruminant feed, the crop straws contain a large amount of cellulose which is decomposed, the crude fiber content is decreased, the fermented feed crude protein content is enhanced, the palatability is improved, the digestibility is improved, and at the same time, the cost of feed is reduced .
Owner:黄吉森
Method for analyzing protein nitrogen content of milk powder
InactiveCN101059447AHigh measurement accuracyAssay time optimizationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingProtein detectionProtein insertion
The invention discloses a milk powder protein nitrogen content analysis method belonging to protein check technique. Based on the chromatometry theory combined with that trichloroacetic acid can deposit protein and biuret can make protein into violet complex compound, that the sample with different protein contents via trichloroacetic acid can deposit the protein nitrogen, and the protein nitrogen under alkali condition can form bluish violet complex compounds with different color degrees via the biuret agent, and the chromatic value is linearly correlative with the protein content, the invention uses a computer software automatic analysis to obtain the value to be compared with the absorbance tested by a spectrophotometer, to calculate out the protein content. The invention uses general computer and scanner to replace special lab precision device as spectrophotometer, with the processes as accuracy, time, and cost test but without artificial standard curvature drafting, to make operation quick and simple, save device, reduce cost, and reduce condition demand, without pollution, while the invention can be used to detect milk powder in batch.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Ox feed and producing process thereof
InactiveCN1439283AImprove qualityImprove absorption rateFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSulfateChloride
A feed for meat cattle is prepared from zinc sulfate, ferrous sulfate, manganese sulfate, copper sulfate, potassium iodide, sodium selenite, cabalt chloride, Mo, VA, VB, VD3, VB5, antioxidizing agent, fine wheat bran, slowly-releasing non-protein nitrogen, leaf powder, light calcium, stone powder, salt, CT No.1, and anhydrous sodium sulfate. Its advantage are easy decomposing, high absorptivity (95-98%), low cost, and high speed to increase weight of meat cattle.
Owner:CHANGDA INDAL CHANGCHUN CITY
Composite premixed feed lick brick for grazing yak
InactiveCN107242363AAdapt to needsAvoid nutritional deficienciesAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBrickCalcium formate
The invention relates to a lick brick for a ruminant animal, and specifically discloses a composite premixed feed lick brick for a grazing yak. The composite premixed feed lick brick for grazing yak comprises salt, cement, bentonite, urea, ammonium chloride, calcium formate, a flavoring agent, calcium hydrophosphate, ferrous sulfate, copper sulfate, zinc sulfate, magnesium sulfate, manganese sulfate, sodium selenite, cobalt chloride, calcium iodate, rumensin and composite multi-vitamins; and the density of the lick brick is 1.8-2.1 g / cm<3>. The composite premixed feed lick brick is researched and developed according to the physiological property of the grazing yak, provides sufficient microelements and vitamins for the grazing yak, and additionally complements part of the non-protein nitrogen, so that the defect of lack of a protein source for the grazing yak fed with forage grass is avoided, the feed intake and the digestive efficiency of the grazing yak are effectively improved, the growing and fattening speed of the yak is increased, the quality of beef is improved, the immunity of the yak is strengthened, the deficiency disease and the metabolic disease of the yak are effectively prevented, and the culture benefit is improved.
Owner:GUANGHAN LONGDA FEED
Method for manufacturing raw materials of fodder with rich proteins from amino acid fermentation residual liquor
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing raw materials of fodder with rich proteins from amino acid fermentation residual liquor. The method includes inoculating and cultivating candida tropicalis or candida utilis and inoculating the candida tropicalis or the candida utilis into the amino acid fermentation residual liquor to obtain fermentation mash; adding honey into soybean meal and the like to manufacture solid fermentation raw materials; proportionally mixing the fermentation mash and the solid fermentation raw materials with one another, then carrying out solid-state fermentation on the fermentation mash and the solid fermentation raw materials, and drying and crushing the fermentation mash and the solid fermentation raw materials. The method has the advantages that a characteristic that residual non-protein nitrogen and residual sugar in the amino acid fermentation residual liquor can be converted into microbial cells by the candida tropicalis or the candida utilis is utilized, and the candida tropicalis or the candida utilis is inoculated into the amino acid fermentation residual liquor, so that the non-protein nitrogen and carbon sources which remain in the amino acid fermentation residual liquor during amino acid production can be converted into proteins of the microbial cells by the aid of the candida tropicalis or the candida utilis, and resources of the amino acid fermentation residual liquor can be sufficiently utilized; the non-protein nitrogen utilization rate further can be increased owing to solid-state fermentation, accordingly, the cost of the fodder can be reduced, and the method for efficiently manufacturing the raw materials of the fodder with the proteins is provided for developing the breeding industries.
Owner:河南双成生物科技有限公司 +1
Megasse non-protein nitrogen urea sustained-release particle feed
InactiveCN101485386ASolve the problem of seasonal imbalanceSolve the problem of safe and anti-corrosion storage for many yearsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAdditive ingredientBeet pulp
The invention discloses a beet pulp non-protein nitrogen urea slow-release granular fodder, relates to an animal fodder, and solves the problems of imbalance between deficient nutrient components of the beet pulp fodder and animal demands, and imbalance between production seasonal nature of beet pulp and perennial demands of ruminant fodder, or environmental problem due to untimely beet pulp treatment, huddle and misplacing pollution, and also solves the problems of safety and corrosion protection for preserving the beet pulp all around the year. The fodder consists of beet pulp, urea, zeolite powder, maize meal, secondary calcium phosphate, stone powder, salt, trace elements and vitamin additives. Due to the combination of the beet pulp, non-protein nitrogen urea and slow-release agent, the fodder not only meets nutrient demand of ruminants, but also solves the problems of reasonable utilization of the beet pulp and scientific utilization of non-protein nitrogen, lowers fodder cost, and remarkably improves economic benefit of ruminant cultivation.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Detection method for on-site fast detection protein nitrogen
InactiveCN101368971AQuality improvementLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingProtein nitrogenReagent
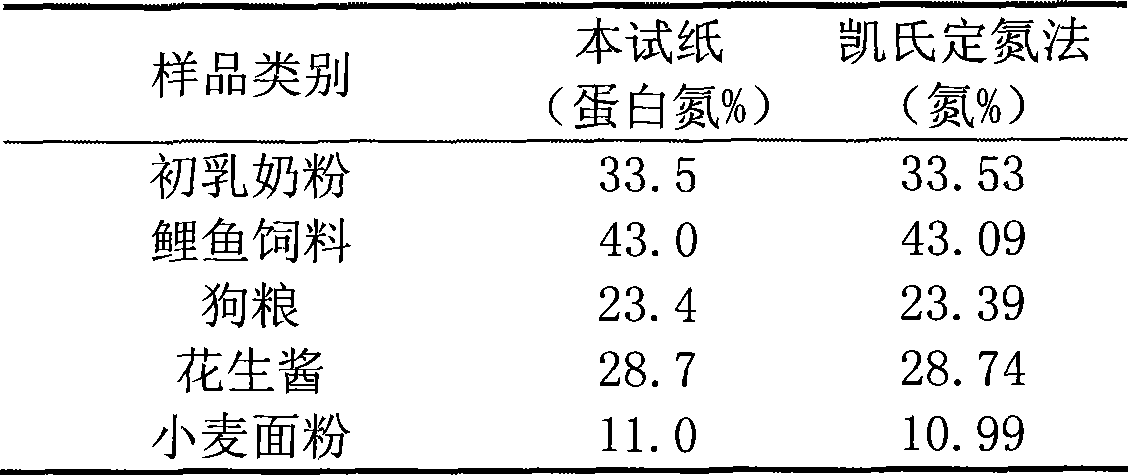
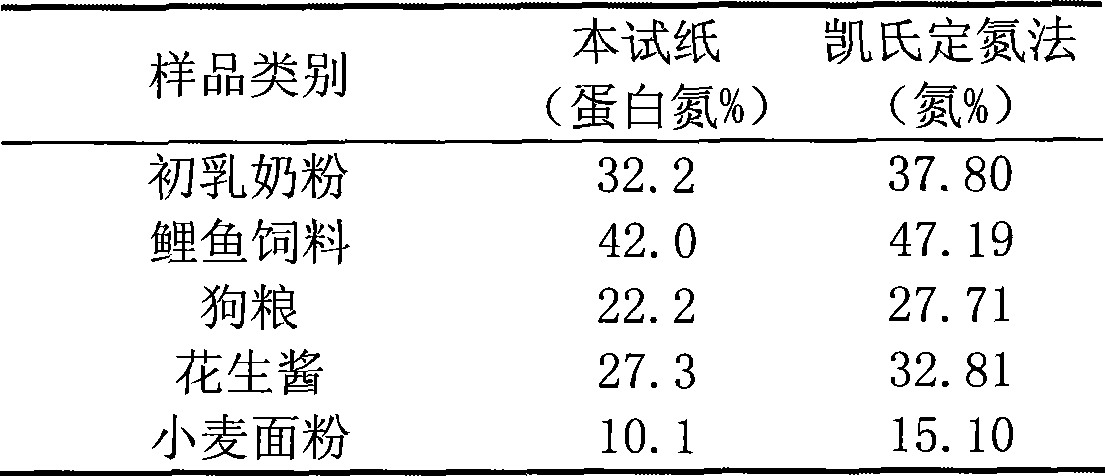
Disclosed is a detection method of swiftly detecting protein nitrogen in situ, after the iTAG reagent which adopts the iTAG protein-labeled technique, or the coomassie brilliant blue method dyeing reagent, or the Folin- hydroxybenzene reagent swiftly reacts on the sample to be tested and presents color, the content of the protein nitrogen in the sample can be obtained through comparing the presented color with the standard colourimetric card. The cost of the detecting method is greatly lower than that of large-scale precision instrument, and the operation is simple and swift; although the precision is not enough, the content of protein nitrogen in milk from different batches can be swiftly obtained when food enterprises purchase mass raw material such as milk in situ, according to coloring result of the sample, whether the true protein (protein nitrogen) reaches the standard or not can be directly obtained; thereby being suitable for rough detection of mass sample in situ.
Owner:崔杰
Feed for ruminant animals (ox, sheep, deer, etc) and its production technology
InactiveCN1390471AImprove qualityImprove absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsHigh absorptionDecomposition
A feed for ruminant animal (ox, sheep, deer, etc) contains the pre-mixture of ferrous sulfate, zinc sulfate, calcium carbonate, VA, VB, straw, etc, the concentrated material of non-protein nitrogen, pine needle powder, stone powder, etc. trace elements, and thionitrogen. Its advantages are high absorption rate (95-100%), low cost, and high quality of meat.
Owner:齐庆文
Slow release non protein nitrogen feed and its production process
A slow-releasing non-protein nitrogen feed for domestic animals and fowls is prepared from corn flour, urea, bentonite, brown sugar and soybean through pulverizing, proportionally mixing, puffing, cooling and breaking. It features that the urea particles are wrapped by starch membrane to elongate its hydrolyzing time to 3-4 hr, so preventing poisoning.
Owner:吉林省禾合农业高新技术开发有限公司
Detection reagent, detection method and detection instrument for proteins
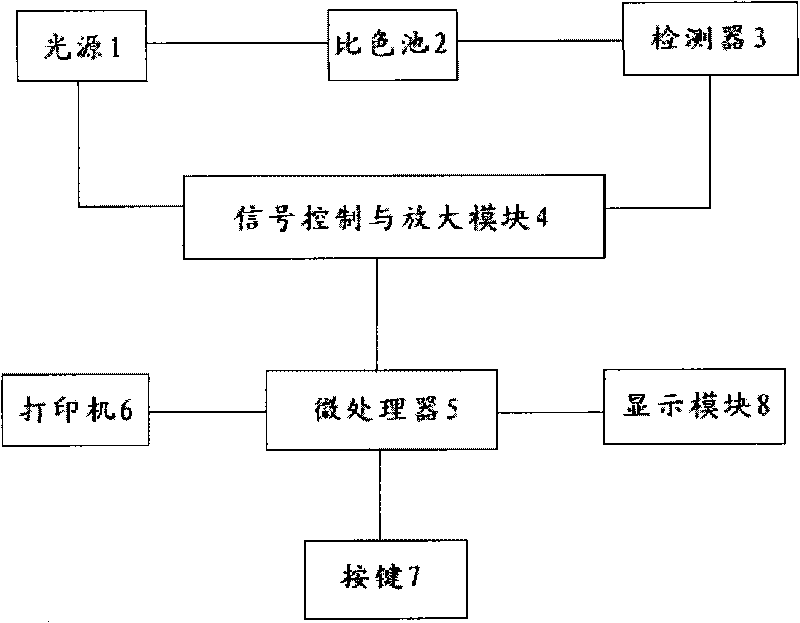
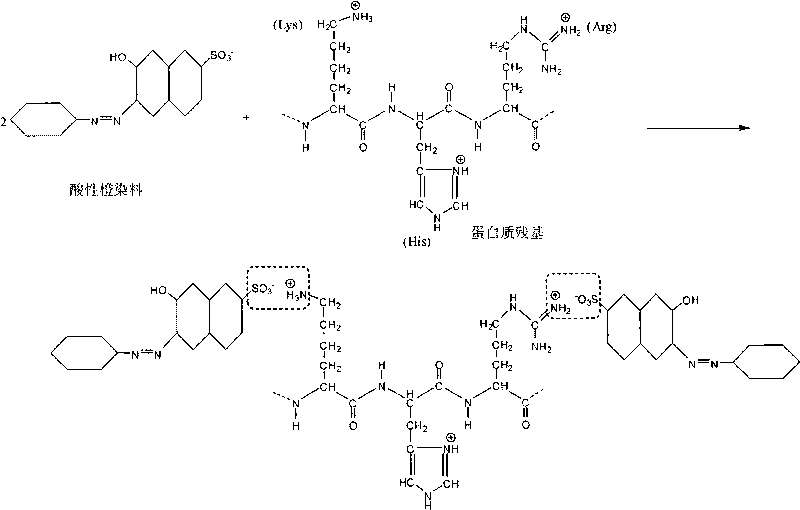
InactiveCN101718790AEfficient detectionDoes not interfere with accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAcetic acidPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a detection reagent, a detection method and a detection instrument for proteins. The reagent is prepared by the following steps: dissolving 0.1 to 10 weight parts of acid orange-12 into 1 to 500 weight parts of buffer solution of phosphoric acid; adding 1 to 500 weight parts of glacial acetic acid; and finally, diluting with 1 to 5,000 weight parts of water, and oscillating and mixing to obtain the detection reagent for the proteins. Compared with the traditional method, the detection method can effectively detect the content of true proteins, and detect the proteins in a wide range; and the detection accuracy is basically not interfered by non-protein nitrogen-containing compounds such as carbamide and melamine. The instrument has small structure, and is convenient to carry. The detection reagent, the detection method and the detection instrument can be widely applied to quick detection of milk products in the basic level and on the spot.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Method for measuring protein nitrogen content in tobaccos
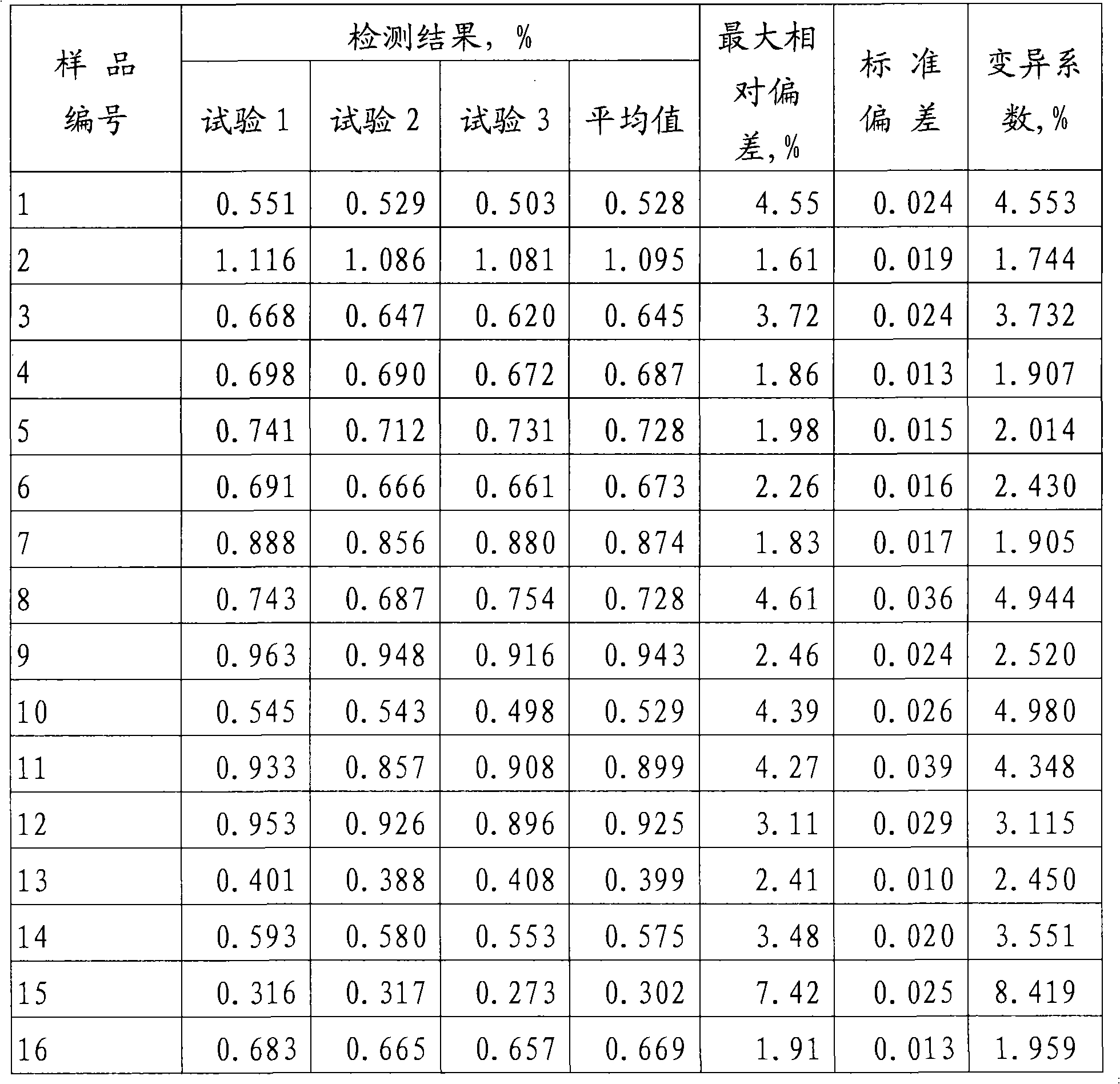
ActiveCN102565425AThe coefficient of variation of the data is smallImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingPeroxydisulfateProtein nitrogen
The invention provides a method for measuring the protein nitrogen content in tobaccos. The method comprises the following steps of: separating protein nitrogen in the tobaccos to obtain a sample to be measured, wherein the sample to be measured contains non-protein nitrogen; adding potassium peroxydisulfate to the sample to be measured under the heating condition to obtain a mixed solution; carrying out ultraviolet catalysis and high-temperature heating on the mixed solution in sequence to obtain a digestion product; detecting the digestion product to obtain the non-protein nitrogen content in the tobaccos; and obtaining the protein nitrogen content in the tobaccos according to the preset total nitrogen content in the tobaccos and the non-protein nitrogen content in the tobaccos. The method provided by the invention has the capability of digesting nitrogenous substances in the tobaccos more completely and thoroughly and has a favorable digestion effect; and according to the method provided by the invention, reducible components in the tobaccos are also digested at the same time that the nitrogenous substances in the tobaccos are digested, so that the tobaccos lose the reducing action, the interference of the reducing components to the digestion of the nitrogenous substances is reduced, the homogeneity of digestion results is improved, and the accuracy of measuring the protein content in the tobaccos is also improved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Parenteral nutrition formulation with optimized amino acid and glucose content
ActiveUS20210069138A1Improve balanceMalnutrition is issueOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryAmino acid uptakePN - Parenteral nutrition
The present disclosure relates to a sterile medical product for parenteral nutrition comprising a polymeric container having at least a first and a second chamber which are separated by a non-permanent peel seal, wherein the first chamber contains a composition of amino acids and optionally electrolytes, and wherein the second chamber contains a dextrose solution, and wherein the product is characterized by a high protein (nitrogen) content per volume. The reconstituted solution is configured to be administered peripherally or centrally for the treatment of patients suffering from malnutrition and / or having a need for increased uptake of amino acids.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
<15>N SIP (stable isotope probing) vibrio parahaemolyticus culture medium and cultivation method thereof
InactiveCN104560813ASimple componentsLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSimple componentVibrio parahaemolyticus
The invention discloses a <15>N SIP (stable isotope probing) vibrio parahaemolyticus culture medium and a cultivation method thereof. A formula of the culture medium comprises components as follows: 1-5 g / L of a nitrogen source, 5-18 g / L of a carbon source, 0.5-2.0 g / L of KH2PO4, 0.6-2.0 g / L of K2HPO4, 0.1-1.0 g / L of MgSO4, 10-30 g / L of NaCl and 1L of distilled water, the pH is in a range from 7.0 to 7.5, and nitrogen atoms of the nitrogen source are labeled by adopting <15>N. The cultivation method of the <15>N SIP vibrio parahaemolyticus comprises steps as follows: 1), continuously and repeatedly cultivating the vibrio parahaemolyticus through transferring; 2), verifying the labeling efficiency of protein nitrogen atoms in labeled vibrio parahaemolyticus cells with LC-MS / MS (high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry). The process is simple and reasonable, the culture medium has simple components and is low in cost, and the novel culture medium preparation method is provided for industrial preparation of the <15>N SIP vibrio parahaemolyticus culture medium.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for preparing fatty acid-rich protein feed raw material from amino acid fermentation residual liquor
InactiveCN104855689AIncrease profitReduce drying costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAmino acid fermentation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a fatty acid-rich protein feed raw material from amino acid fermentation residual liquor. The method comprises the following steps: performing inoculated culture on trichosporon mucoides first and then inoculating a trichosporon mucoides seed solution into the amino acid fermentation residual liquor to obtain fermented liquor; adding a proper amount of molasses into bean pulp and the like, and mixing uniformly to prepare a solid-state fermentation raw material; mixing the fermented liquor with the solid-state fermentation raw material at a certain ratio, and performing aerobic solid-state fermentation; drying a fermented material and grinding. Wastes are reasonably utilized, the utilization rate of the fermentation residual liquor in amino acid production is increased, the trichosporon mucoides capable of efficiently utilizing non-protein nitrogen is applied to the fermentation of the amino acid fermentation residual liquor, and residual non-protein nitrogen and sugar in the amino acid fermentation residual liquor are fully utilized for microbial conversion. Moreover, in combination with solid-state fermentation, the utilization rate of non-protein nitrogen is further increased, the drying cost is greatly reduced, the environment is protected, resources are saved, and the low-cost and fatty acid-rich protein feed raw material is obtained.
Owner:河南双成生物科技有限公司 +1
Method for preparing mycoprotein by taking glycerin residue as raw material
The invention discloses a method for preparing mycoprotein by taking glycerin residue as a raw material, belonging to the field of biological feed. The method takes the glycerin residue as the main raw material, and concretely comprises the steps of diluting the glycerin residue by water to form glycerin residue solution with a certain concentration; adjusting the potential of hydrogen (pH) of the solution to be within the range from 6.5 to 7.5 by hydrochloric acid; then, adding non-protein nitrogen source, phosphate, magnesium salt and sodium chloride into the solution; carrying out liquid fermentation by microorganism; culturing for 72-96 hours at the temperature of 30-32 DEG C to obtain the mycoprotein. After the mycoprotein is added into the feed, the nutritive value of the basic feed can be enhanced, and the quality of animal products can be improved. The method takes the glycerin residue with low price as the main raw material, and can convert the glycerin residue waste produced in the glycerin distillation preparation into the mycoprotein by microbial fermentation, thus avoiding the environmental pollution caused by the glycerin residue on the one hand, and improving the economic benefit of the glycerin residue on the other hand.
Owner:惠州长龙生物技术有限公司
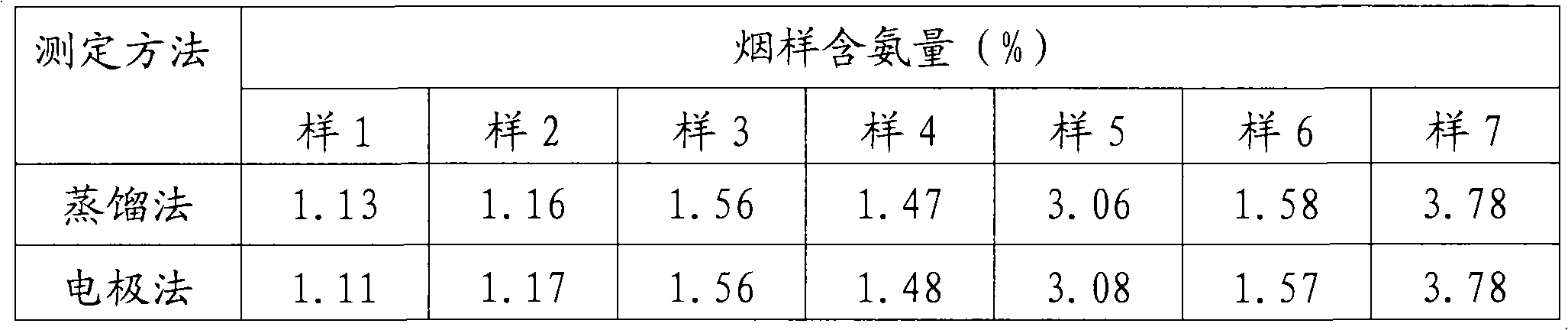
Method for measuring nonprotein nitrogen content in liquid
InactiveCN102519901AMild digestion conditionsEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsPotassium persulfateAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a method for measuring nonprotein nitrogen content in liquid, which includes the following steps: separating protein nitrogen from liquid so as to obtain a to-be-measured sample containing nonprotein nitrogen; adding potassium persulfate in the to-be-measured sample to obtain a mixed solution under the heating condition; performing ultraviolet catalysis and high-temperature heating to the mixed solution sequentially, so as to obtain a digestion product; detecting the digestion product to obtain ultraviolet spectrum data; and obtaining the nonprotein nitrogen content in the liquid as per the ultraviolet spectrum data and a predetermined standard curve. Through the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the digestion of the nitrogenous ingredient in the liquid sample is more complete, the digestion effect is better, the digestion of the nonprotein nitrogen as well as the digestion of the reductive ingredient in the liquid can be realized, the reductive function of the to-be-measured sample is lost, the interference in the nonprotein nitrogen digestion is reduced, so that the digestion effect becomes more uniform, the recovery rate of the nonprotein nitrogen measurement is improved, and the accuracy of the measurement result is improved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Detection method for non-protein nitrogen-containing compound in feed protein raw material
InactiveCN101464415AQuick checkLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDecompositionKetone
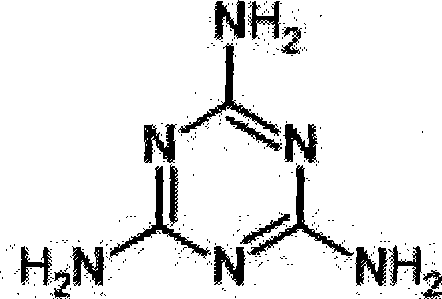
The invention provides a method for detecting non-protein nitrogen-containing compounds in a feed protein raw material. Compared with other aldehyde, ketone and carbohydrate, formaldehyde produced in the decomposition of an ureaformaldehyde polymer, which is one of the non-protein nitrogen-containing compounds (NPN), under the action of hot sulfuric acid, has the characteristic that formaldehyde can form a purplish red substance with chromotropic acid, and the characteristic can be utilized for verifying whether the raw material is adulterated. The method comprises the following steps: after degreasing and drying the protein raw material with petroleum ether, placing the sample under a stereo microscope; picking out and placing suspicious materials into a 50ml beaker with a pair of tweezers; adding 1ml of chromotropic acid into the beaker; heating the beaker with an electric stove until fume starts rising; and taking the beaker off from the electric stove, and adding 50ml of water into the beaker instantly. The fact that the liquid turns purplish red shows that a non-protein nitrogen (NPN)-containing compound, called unreaformaldehyde polymer, is present in the sample, so that whether the sample is adulterated can be verified accurately.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW HOPE LIUHE GROUP
Method for measuring content of protein nitrogen in liquid
ActiveCN102539367AThe measurement result is accurateMild digestion conditionsPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPotassium persulfateProtein nitrogen
The invention provides a method for measuring content of protein nitrogen in liquid, which includes the following steps: separating protein nitrogen in liquid to obtain a to-be-measured sample containing nonprotein nitrogen; adding potassium persulfate into the to-be-measured sample that is being heated to obtain a mixed solution; ultraviolet catalyzing and high-temperature heating the mixed solution sequentially to obtain a digestion product; measuring the digestion product to obtain the content of nonprotein nitrogen in the liquid; and obtaining the content of protein nitrogen in the liquid as per the predeterminate total nitrogen content in the liquid and the content of nonprotein nitrogen obtained through measurement. Through adopting the method provided by the invention, the nitrogenous component in the liquid can be radically and completely digested, the digestion effect is better, the nitrogenous component as well as the reducing component in the liquid are digested, so that the liquid loses the reducing action, the interference in the digestion of the nitrogenous component is reduced, the uniformity of the digestion result is improved, the recovery rate in the content measurement of the protein nitrogen is improved, and the accuracy of the testing result is improved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Method for rapidly detecting protein content in tobacco leaves
PendingCN114414513APromote exudationEfficient precipitationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting the content of protein in tobacco leaves, which comprises the following steps: taking a certain amount of tobacco leaf powder to be detected in a homogenizer, adding 0.05 mol / L phosphate buffer solution containing SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) with the pH value of 6.8, fully grinding to obtain homogenate, carrying out ultrasonic oscillation on the homogenizer, then carrying out centrifugal separation, then carrying out centrifugal separation at the rotating speed of 4800r / min, taking the supernatant, filtering, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain the protein content in the tobacco leaves. According to the method, cell tissues are fully damaged in the homogenizing process, exudation of protein is facilitated, protein can be efficiently separated out from the screened protein precipitation solution, the influence of non-protein nitrogen is avoided, and the result is more accurate; compared with a Kendall method and a continuous flow analysis method, the method has the advantages that the steps are simplified, the digestion time is obviously shortened, and the total consumed time is less; the ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometer can realize simultaneous detection of a plurality of samples and has the characteristics of high efficiency and large flux, and other devices such as a centrifugal machine and a water bath kettle are standing devices in a laboratory.
Owner:GANSU TOBACCO IND
Sheep feed and its production technology
InactiveCN104247863AOsmotic pressure equalizationImprove absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffSodium bicarbonateWeight gaining
The invention discloses a sheep feed and its production technology. The production technology of the sheep feed mainly comprises the following steps: using zinc sulfate, ferrous sulfate, anhydrous copper sulfate, potassium iodide, sodium selenite, cobalt chloride, manganese sulfate, VA, VC and VD to prepare a premix, and uniformly mixing slow-release non-protein nitrogen with calcium hydrogen phosphate, distiller's grains, feather meal, cottonseed meal, sunflower meal, leaf powder, calcium carbonate, anhydrous sodium sulfate, sodium bicarbonate, yeast and the premix to prepare the sheep feed. A slow-release non-protein nitrogen technology and trace elements are adopted to realize sulfur and nitrogen balance, electrolyte balance, calcium and phosphorus balance, amino acid balance and osmotic pressure balance in order to make protein sources directly decomposed by sheep rumens, and the release of the slow-release non-protein nitrogen is synchronous with the development and absorption of thalli in the rumens, so the absorption rate increases to 96-98%, and the feeding cost is reduced; and beneficial bacteria are decomposed and absorbed by the rumen under the action of acetic acid, so long wool, rapid weight gain and economic benefit increase are reached.
Owner:郁东
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com