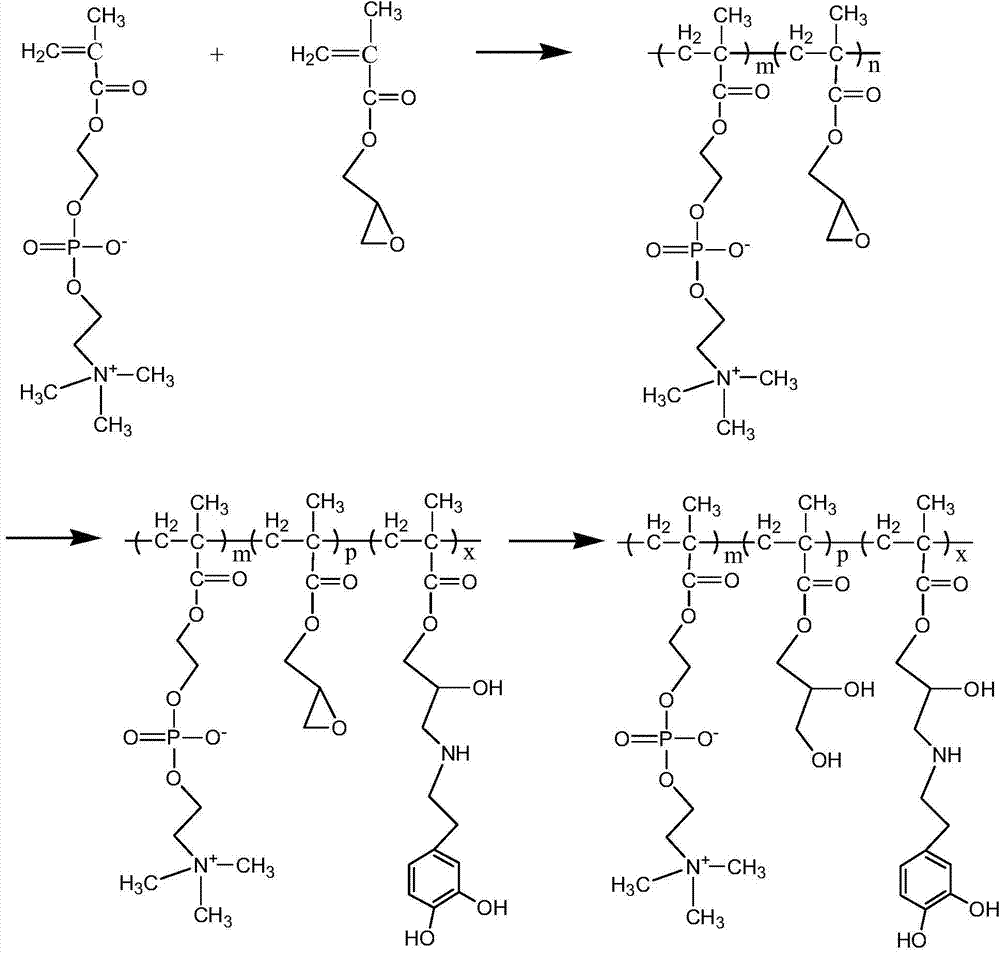
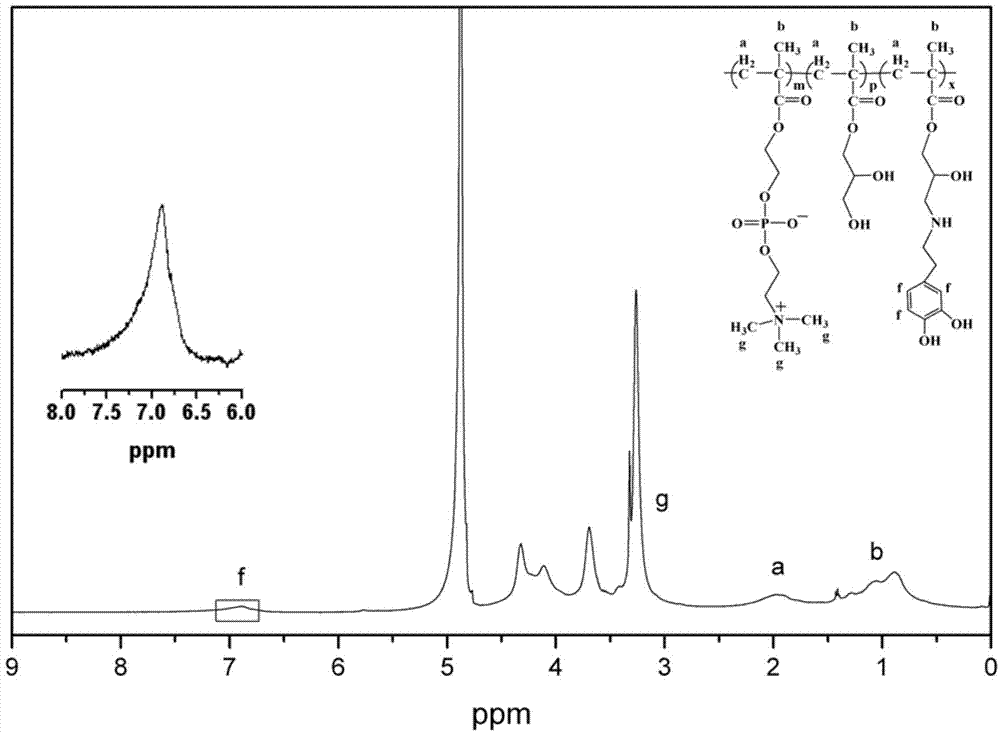
Preparation method of di-bionic polymer
A technology of polymer and polymer solution, applied in the field of material surface science and biomedical polymer materials, can solve problems such as difficulty in separation and purification, and achieve the effects of broad application prospects, high grafting rate and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. Weigh 5mmol 2-methacryloyloxyethylphosphorylcholine and 5mmol glycidyl methacrylate, dissolve and mix them with a solvent to obtain a mixed solution of monomers, and mix 0.1mmol azobisisobutyronitrile Dissolved with tetrahydrofuran to obtain the initiator solution, in N 2 Protection, under the condition of stirring at 70°C, add the mixed solution of monomers into the three-necked flask, preheat for 30 minutes, add the initiator solution to continue the reaction for 24 hours, after the reaction is completed, concentrate the reaction solution, and use a dialyzer with a molecular weight cut-off of 6000-8000D bag dialysis; finally, freeze-dry the dialyzed sample at -50°C to obtain a phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy groups; the solvent is formed by mixing methanol and tetrahydrofuran at a volume ratio of 7:1; NMR test results show that the molar content of epoxy groups in the polymer is about 57.7%;
...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0034] Step 1. Weigh 7 mmol of acryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine and 3 mmol of glycidyl acrylate, dissolve and mix them with a solvent to obtain a mixed solution of monomers, and dissolve 0.1 mmol of azobisisobutyronitrile with tetrahydrofuran to obtain an initiator solution, in N 2 Protection, under the condition of stirring at 60°C, add the mixed solution of monomers into the three-necked flask, preheat for 30 minutes, add the initiator solution and continue the reaction for 24 hours. Dialyze the concentrated reaction solution in the bag; finally, freeze-dry the dialyzed sample at -50°C to obtain a phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy groups; the solvent is composed of methanol and tetrahydrofuran in a volume ratio of 6:1 It is mixed; NMR test results show that the molar content of epoxy groups in the polymer is about 39.2%;
[0035] Step 2, the phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy group described in 0.40m...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1. Weigh 6 mmol of 2-methacrylamide ethyl phosphorylcholine and 4 mmol of glycidyl acrylate, dissolve and mix them with a solvent to obtain a mixed solution of monomers, and dissolve 0.1 mmol of azobisisobutyronitrile in tetrahydrofuran to obtain Initiator solution, in N 2 Protection, under the condition of stirring at 80°C, add the mixed solution of monomers into the three-necked flask, preheat for 30 minutes, add the initiator solution and continue the reaction for 12 hours. Bag dialysis; finally, freeze-dry the dialyzed sample at -50°C to obtain a phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy groups; the solvent is formed by mixing methanol and tetrahydrofuran at a volume ratio of 8:1; NMR test results show that the molar content of epoxy groups in the polymer is about 48.1%;
[0040] Step 2, the phosphorylcholine polymer containing epoxy group described in 0.5mmol step 1 is dissolved in 20mL methanol to obta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com