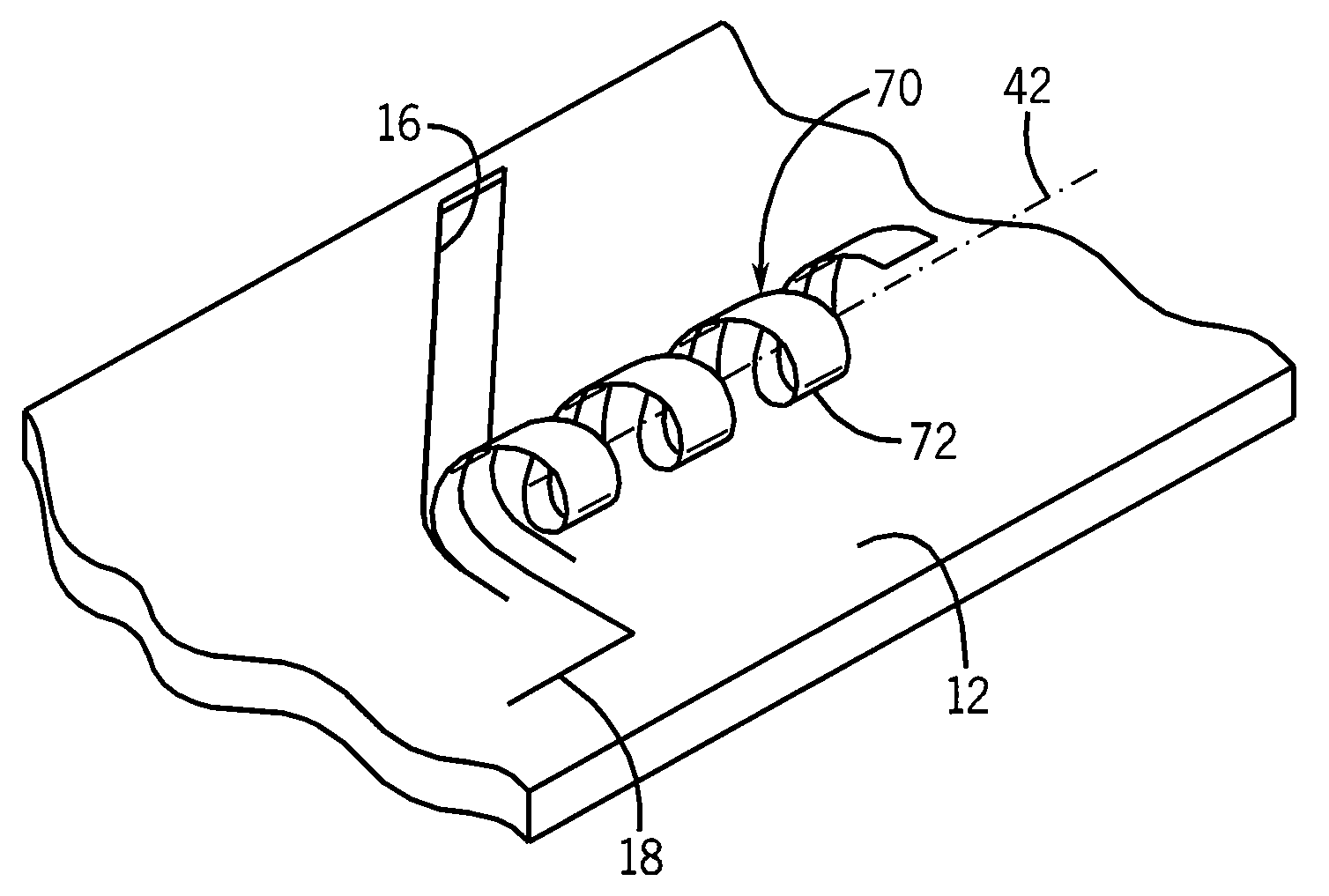
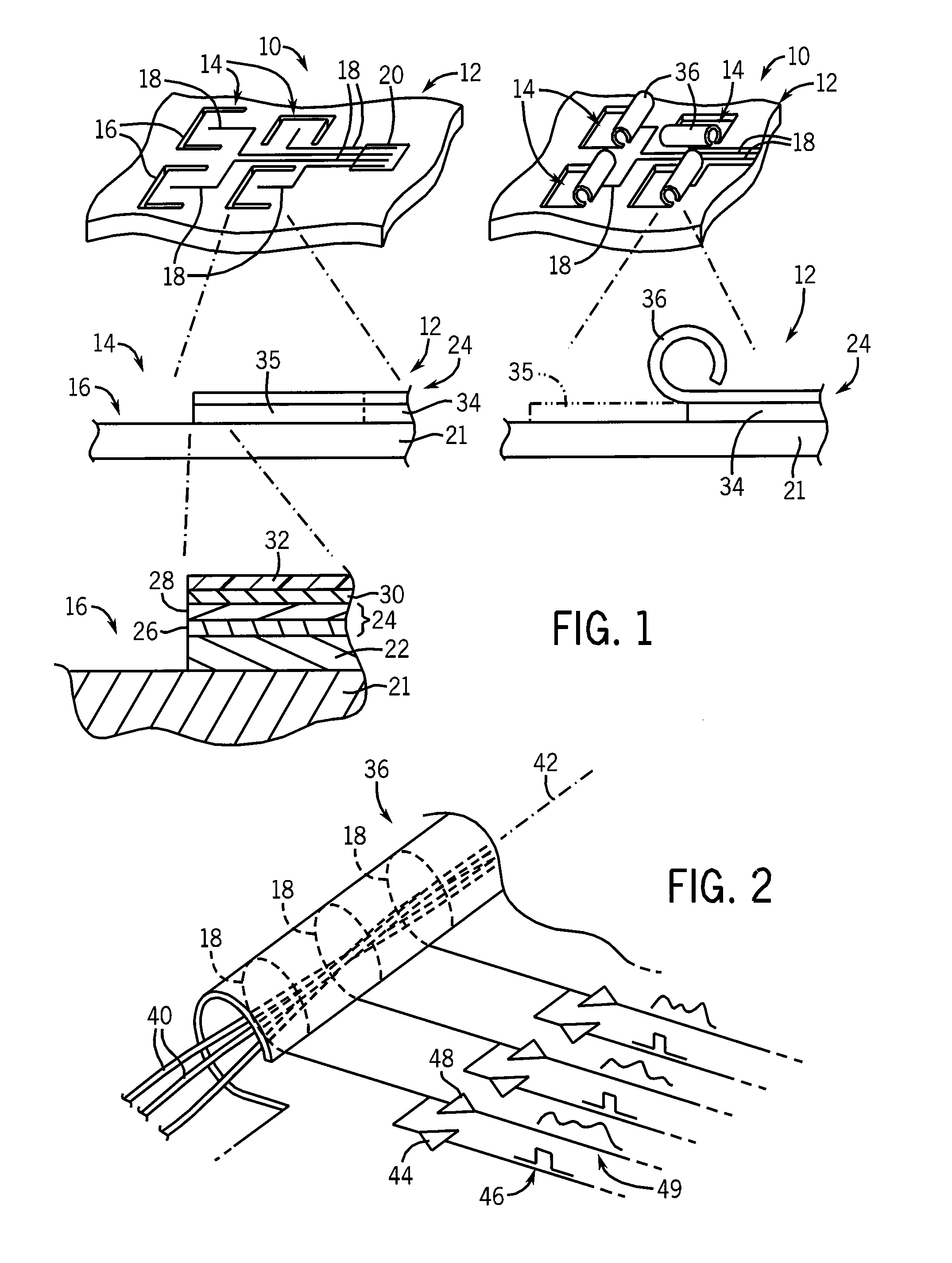
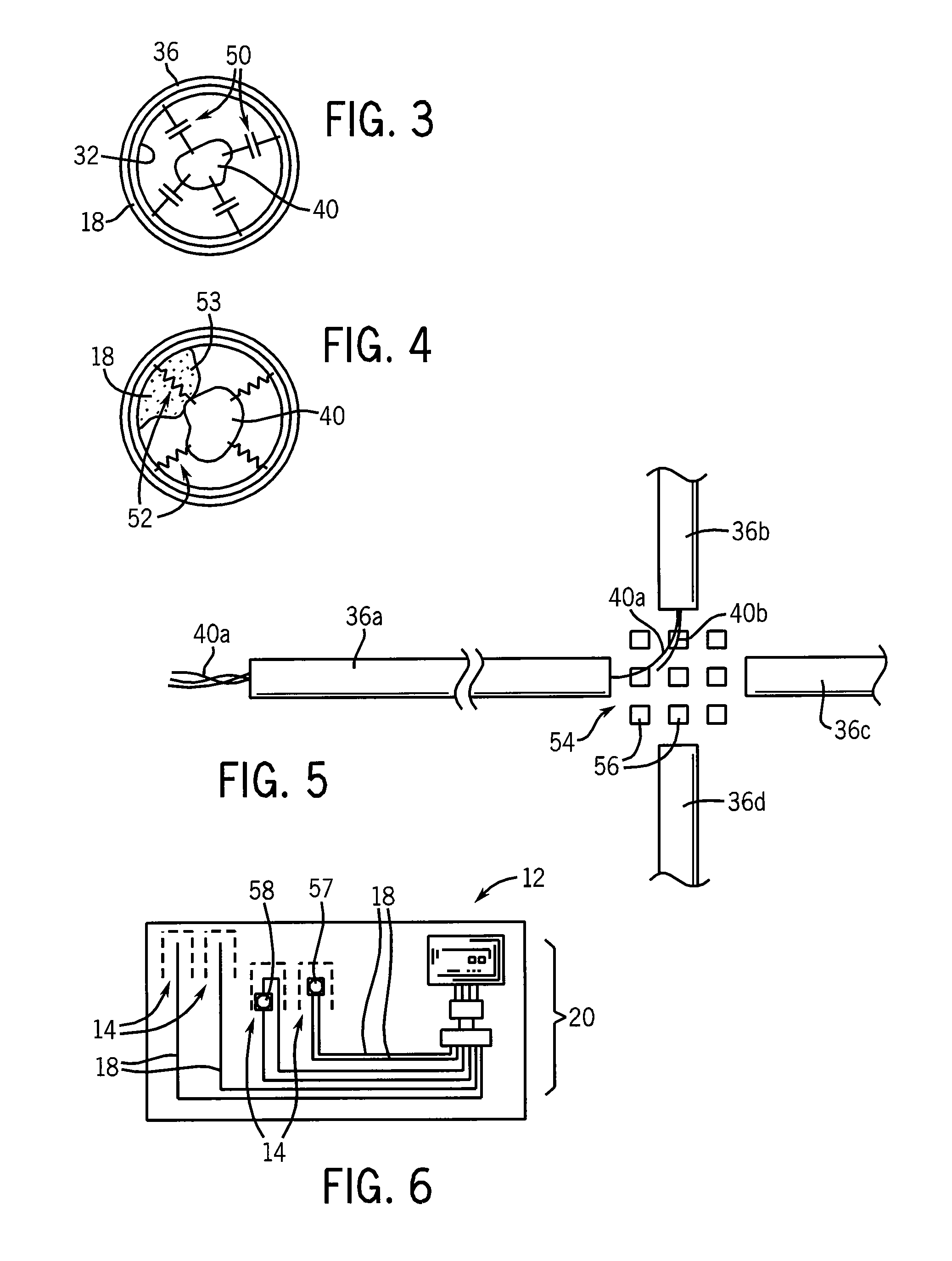
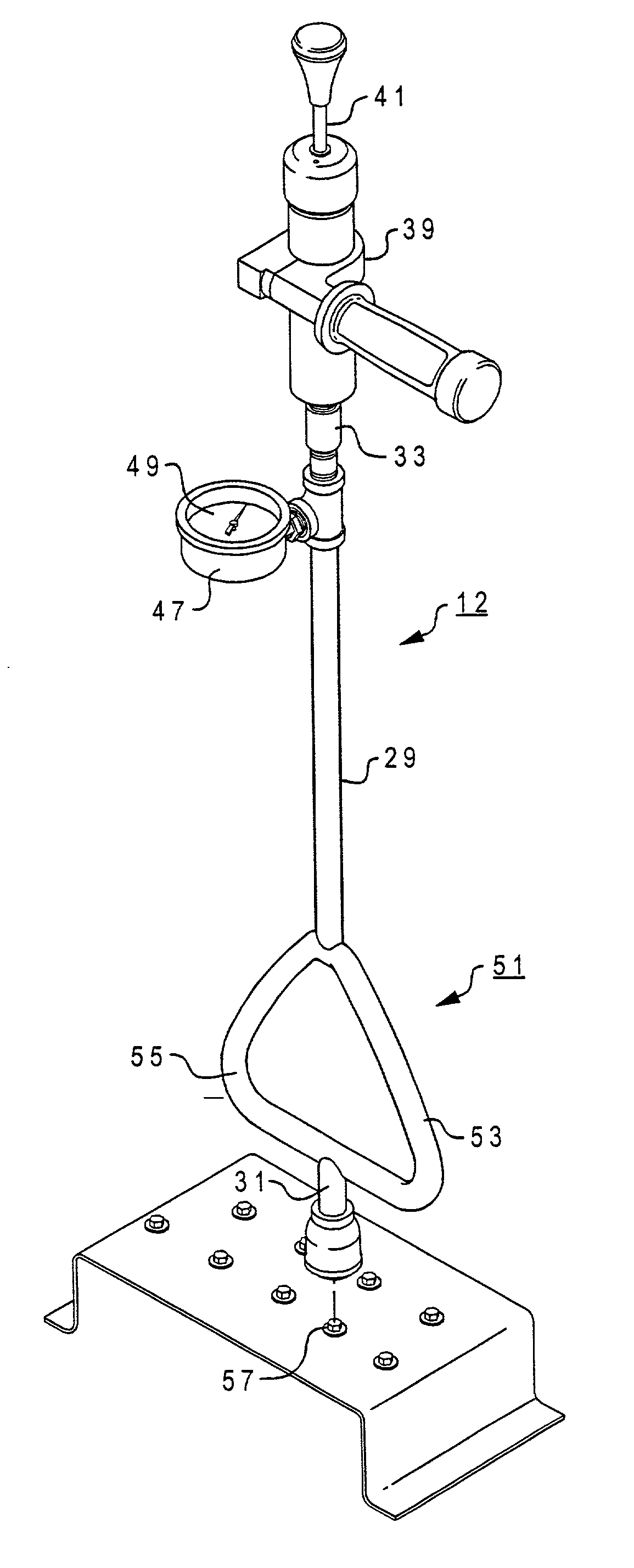
Patents
Literature
103 results about "Tubular scaffold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tubular Scaffolding. Tubular scaffolding is also referred to as steel scaffolding, tube and clamp scaffolding, tube and fitting scaffolding, or tube and coupler scaffolding. It is a traditional scaffolding system which is still in use by many because of the total flexibility that it provides.
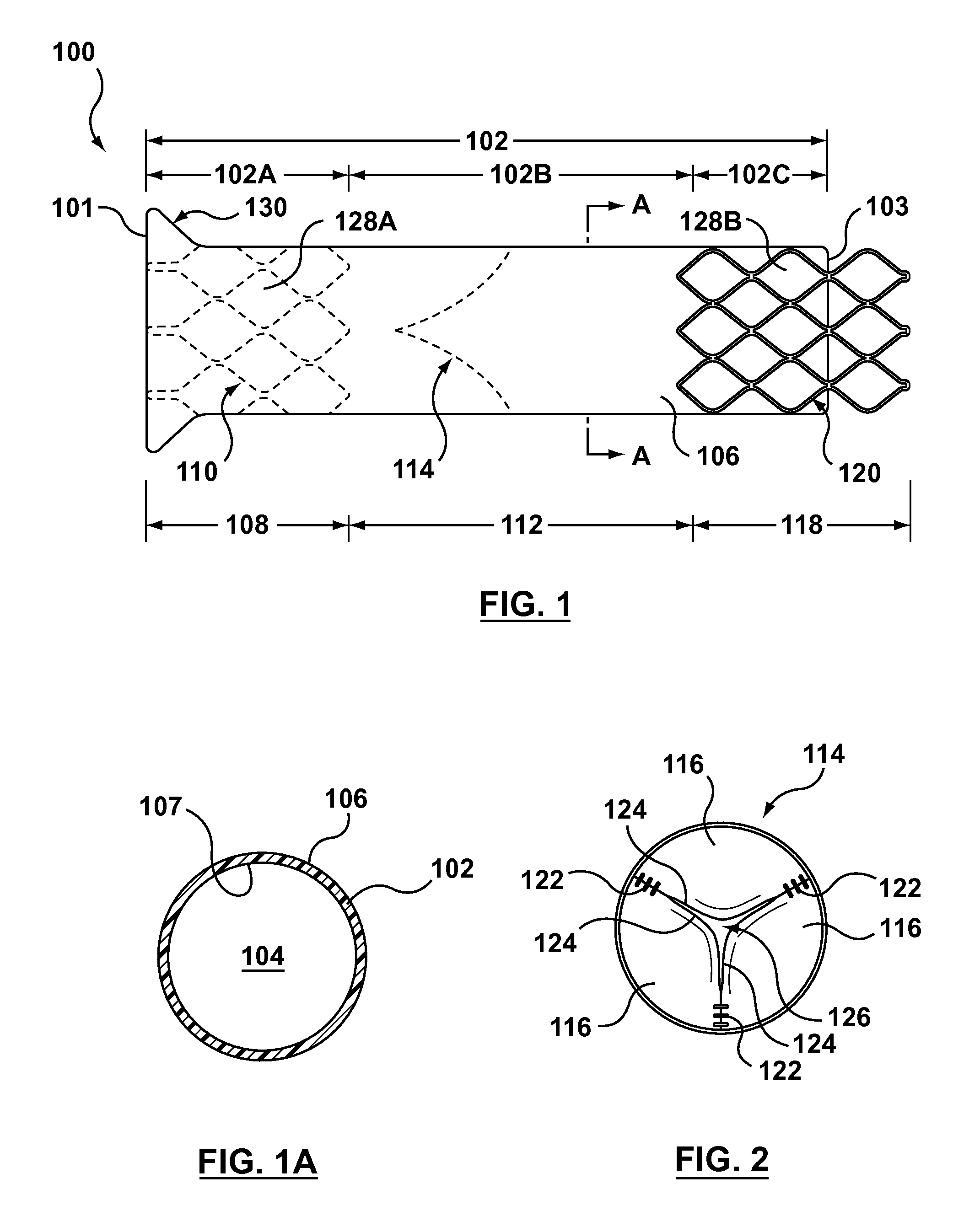
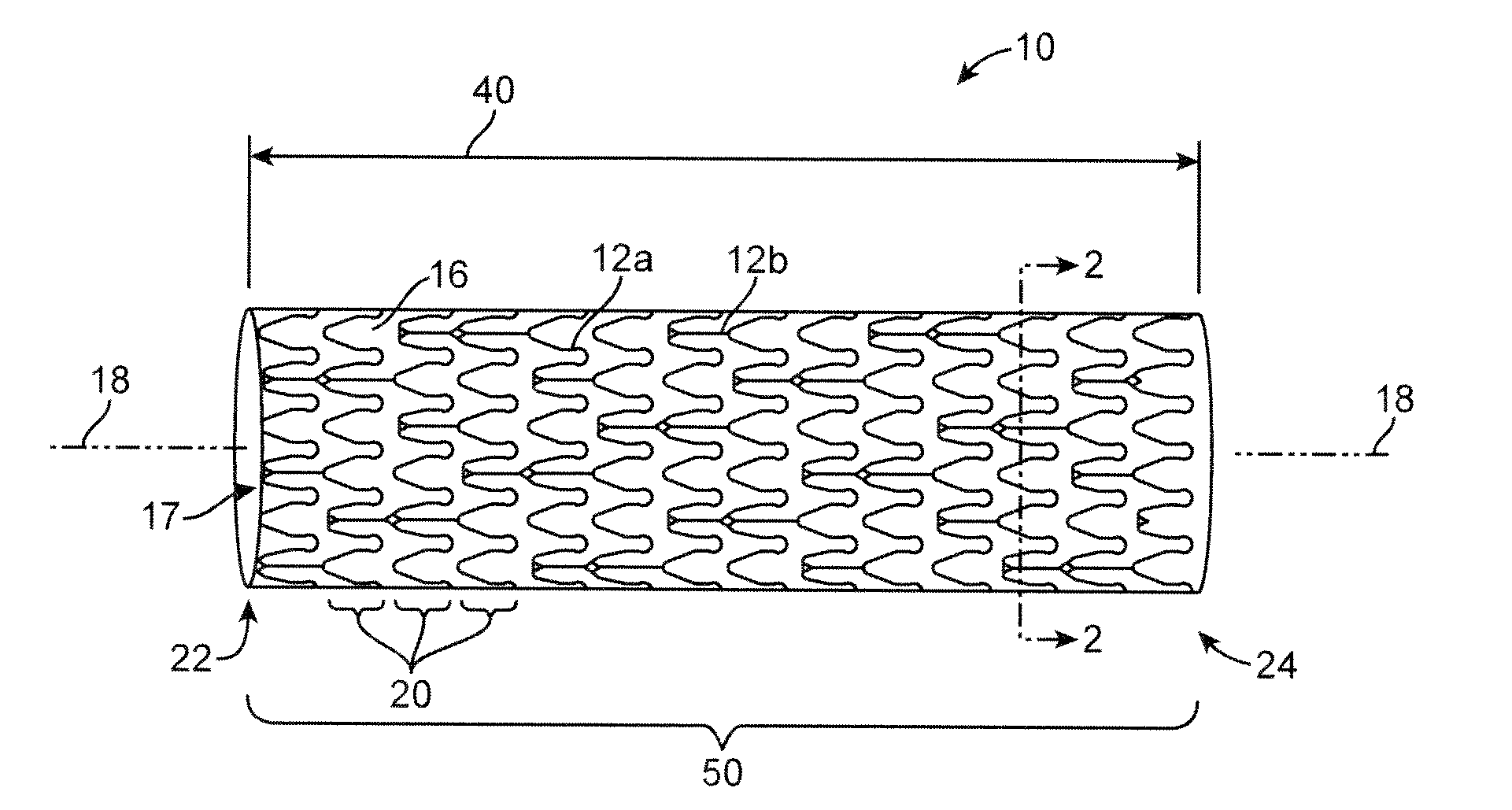
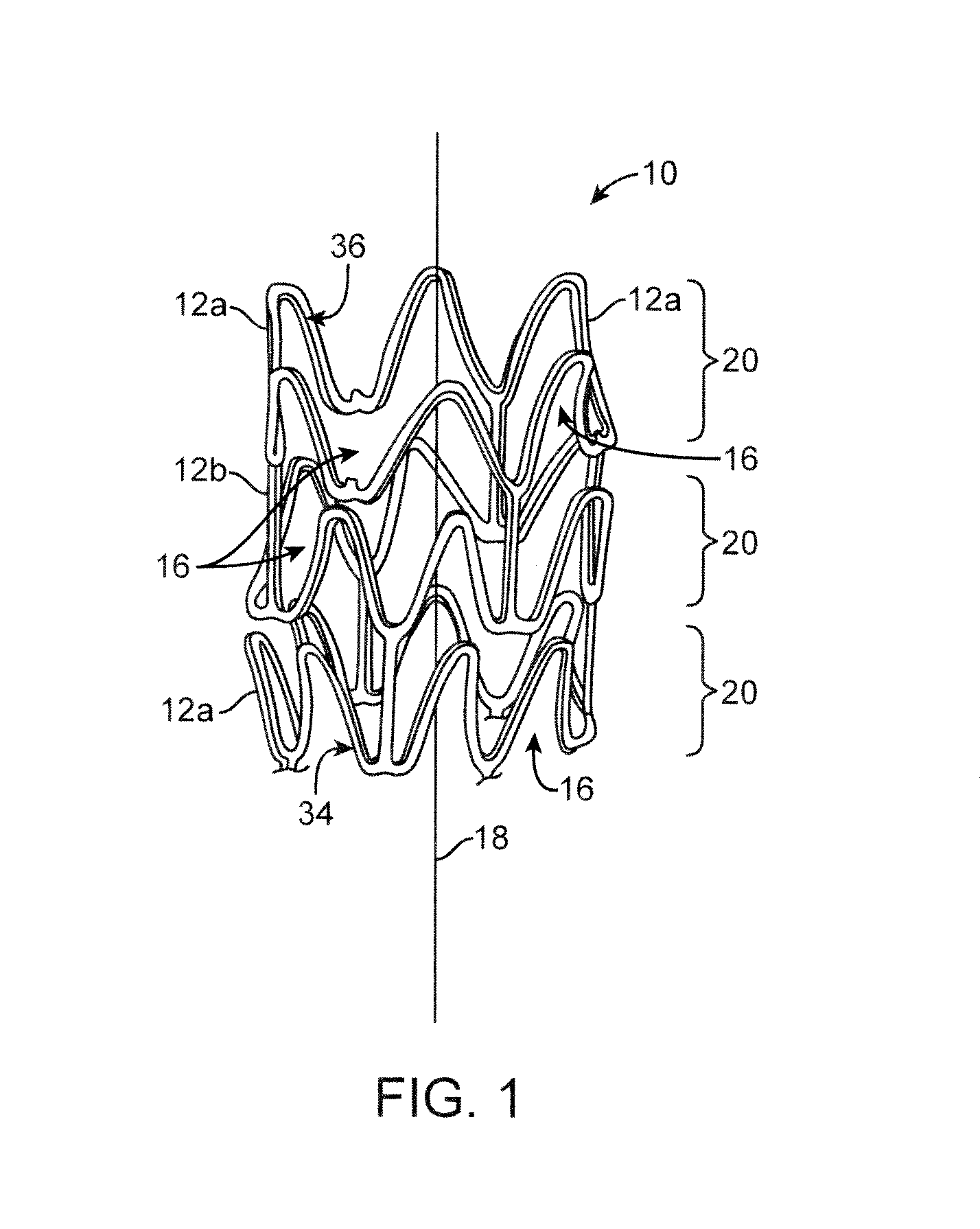
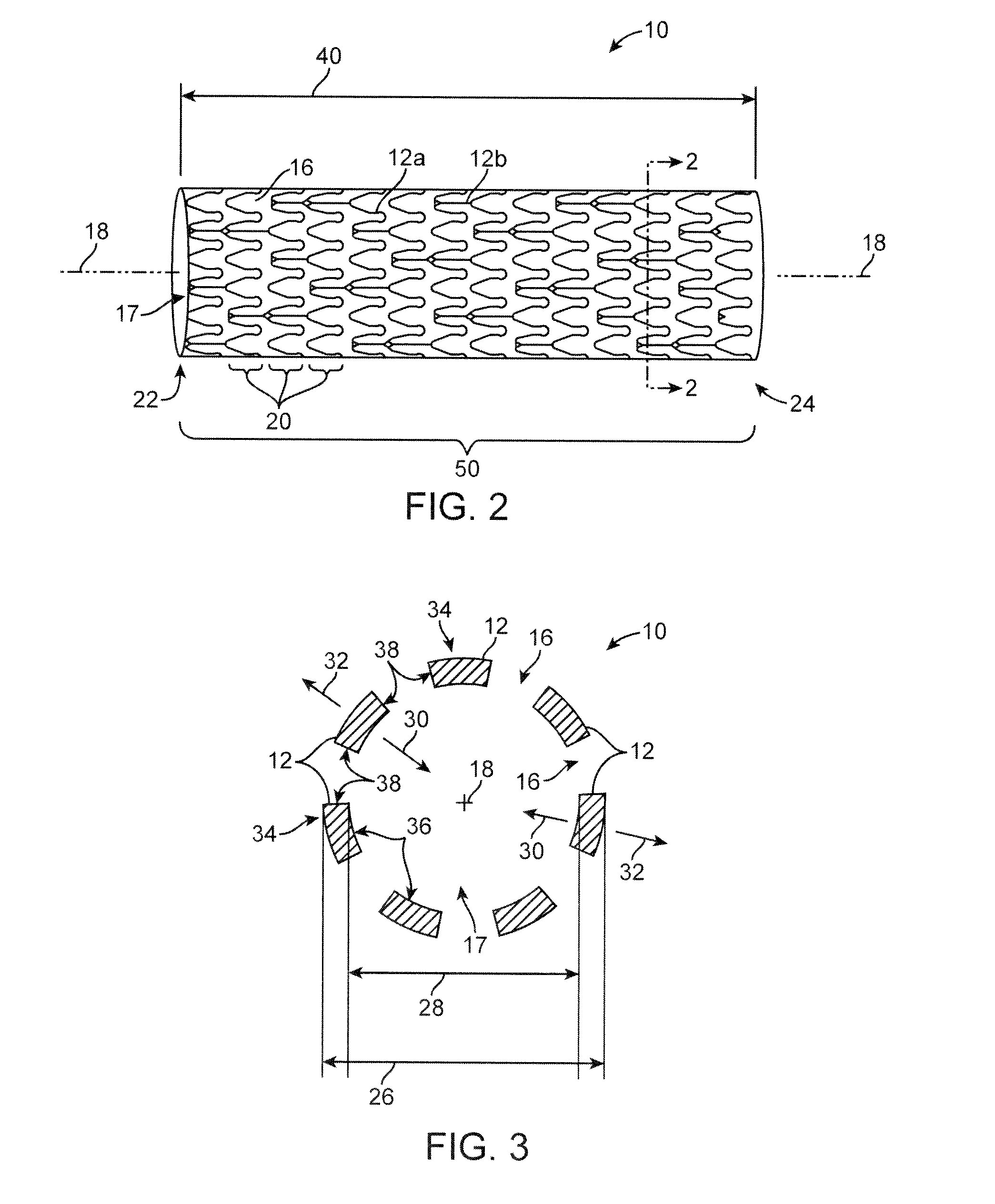
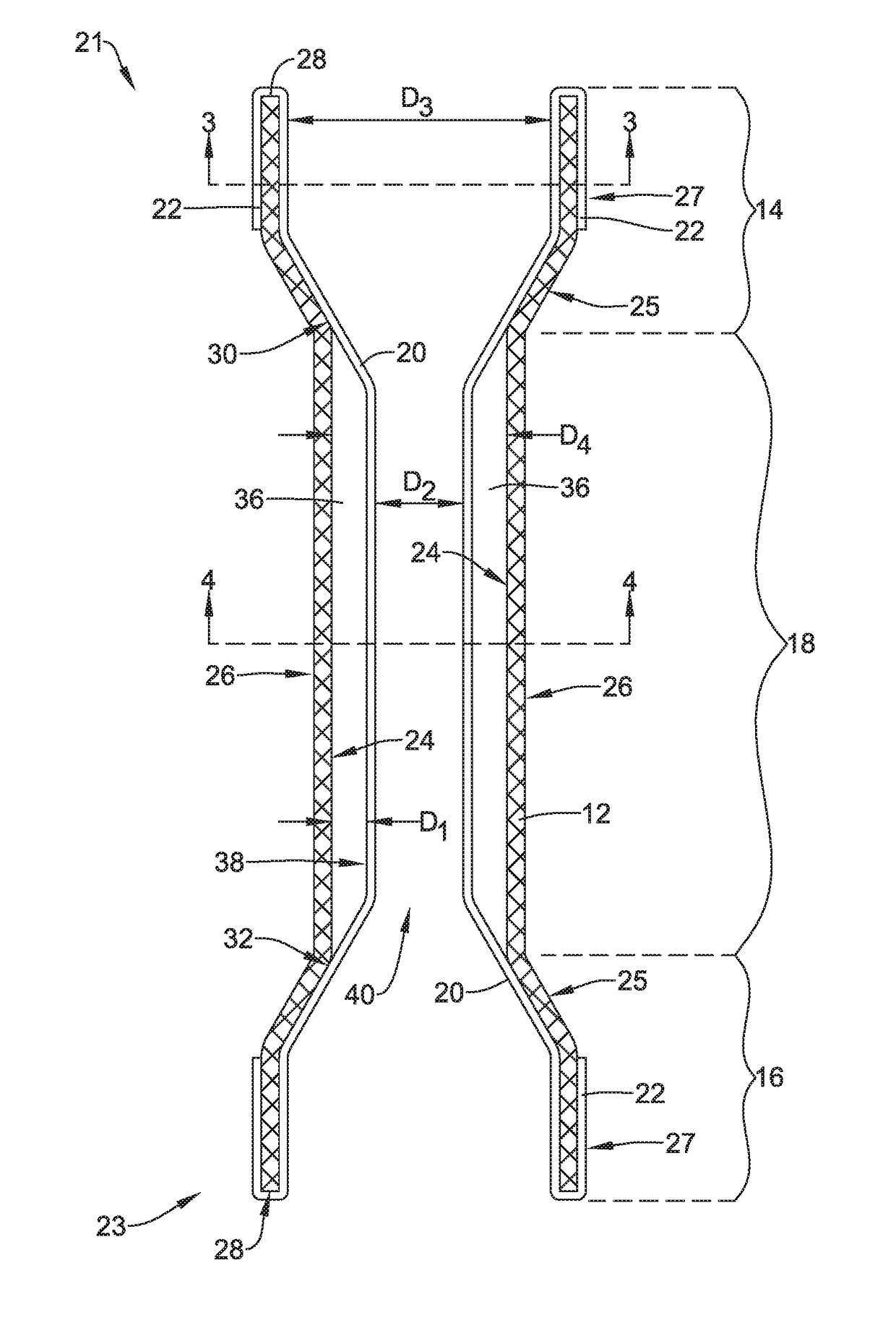
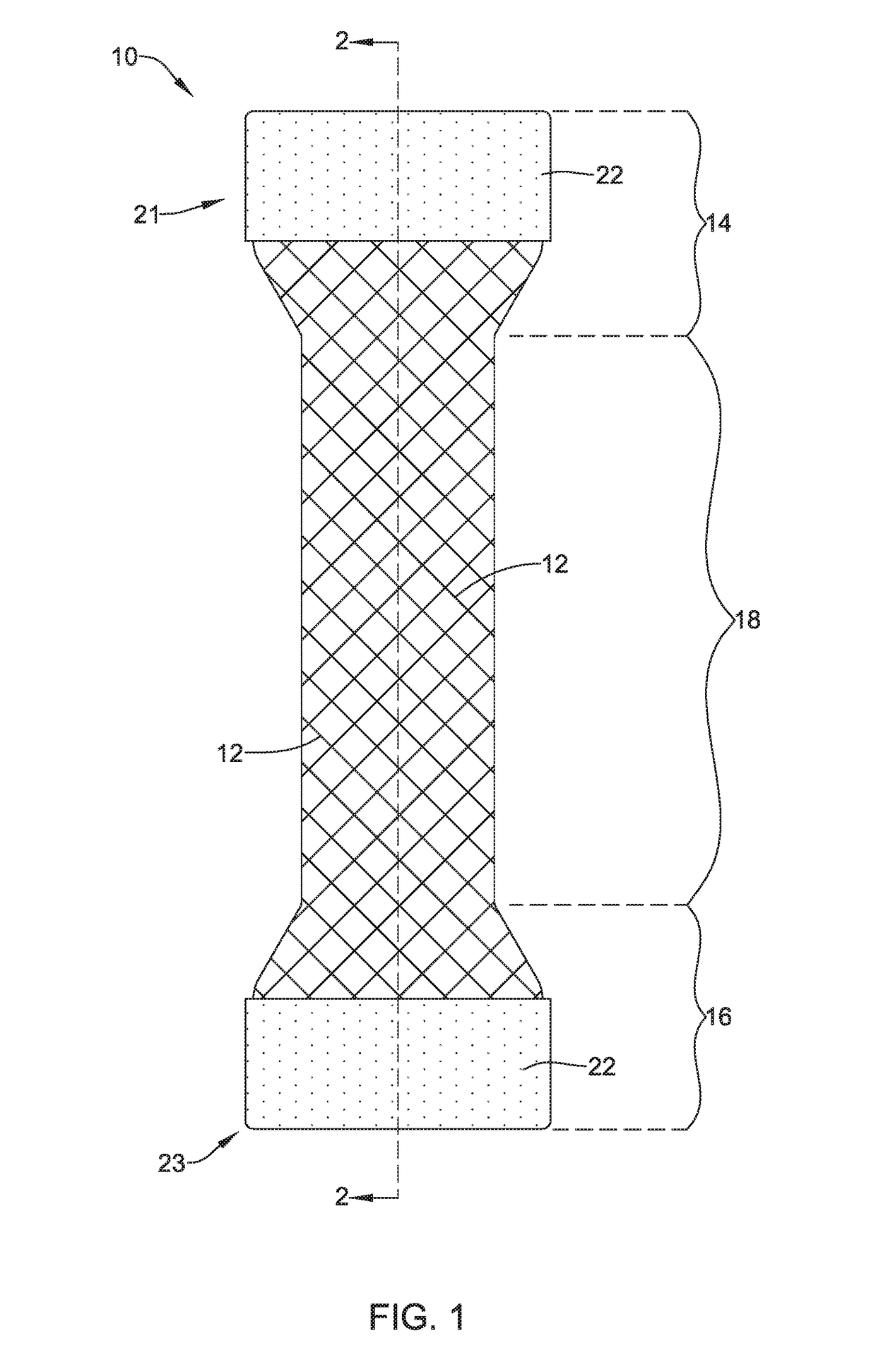
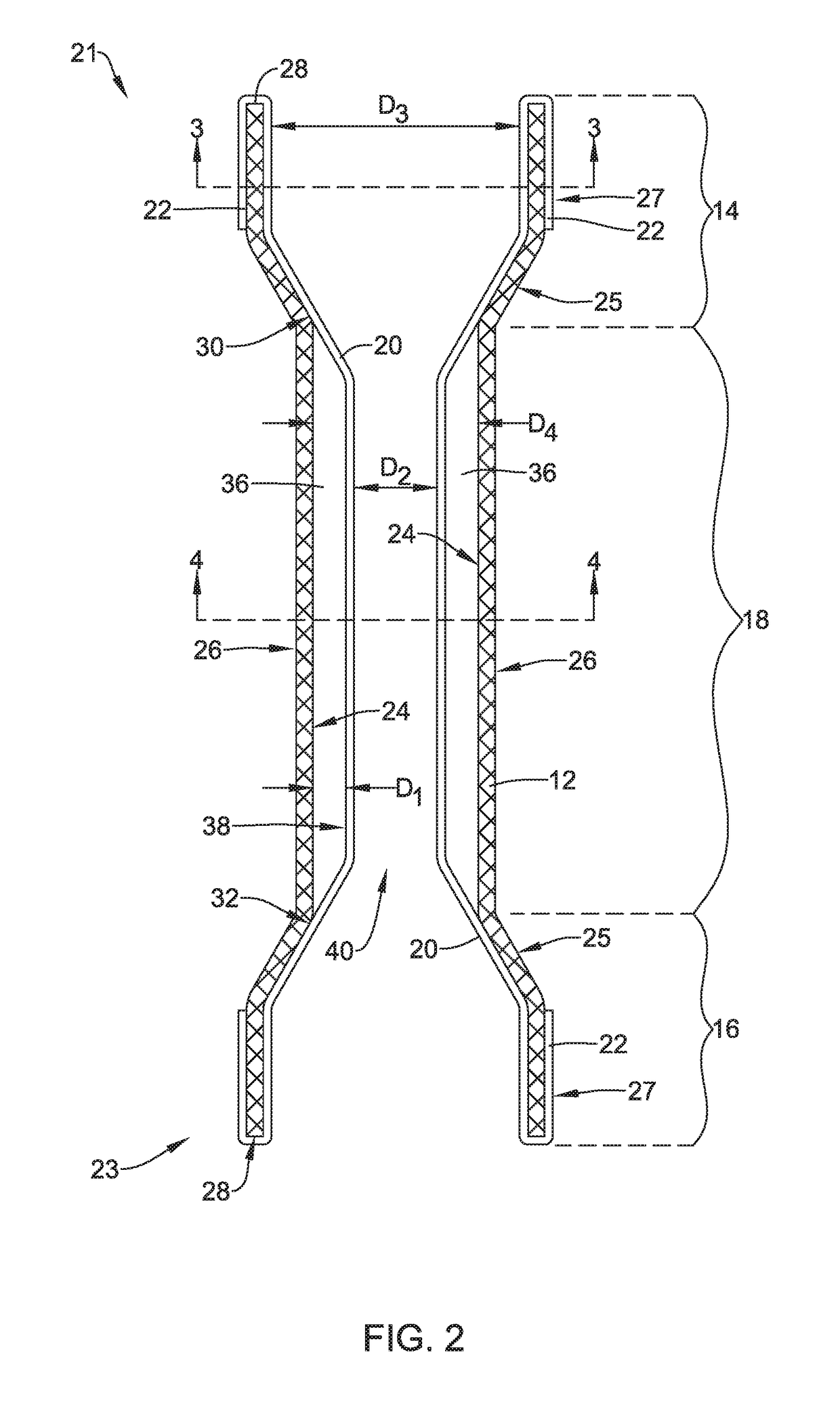
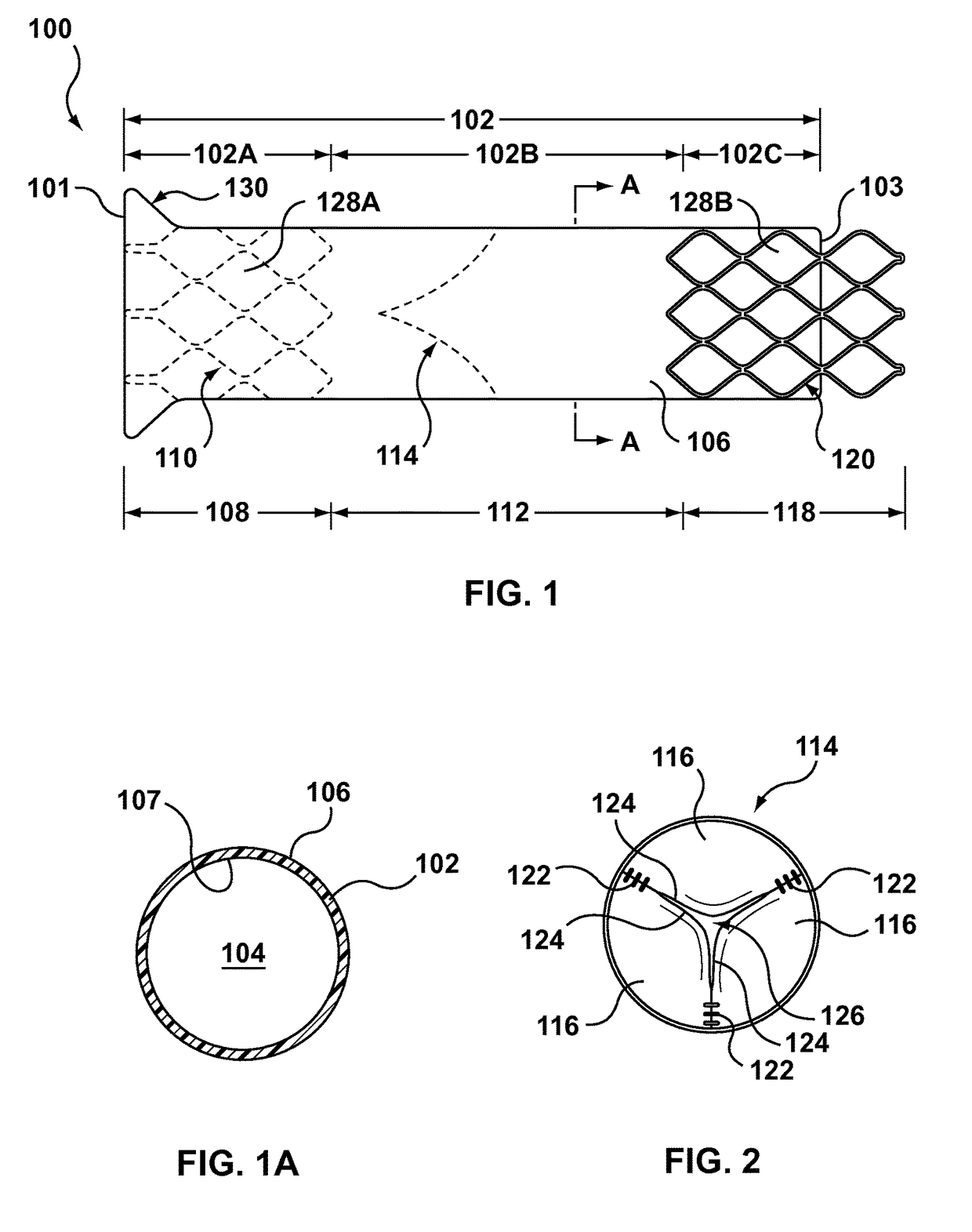
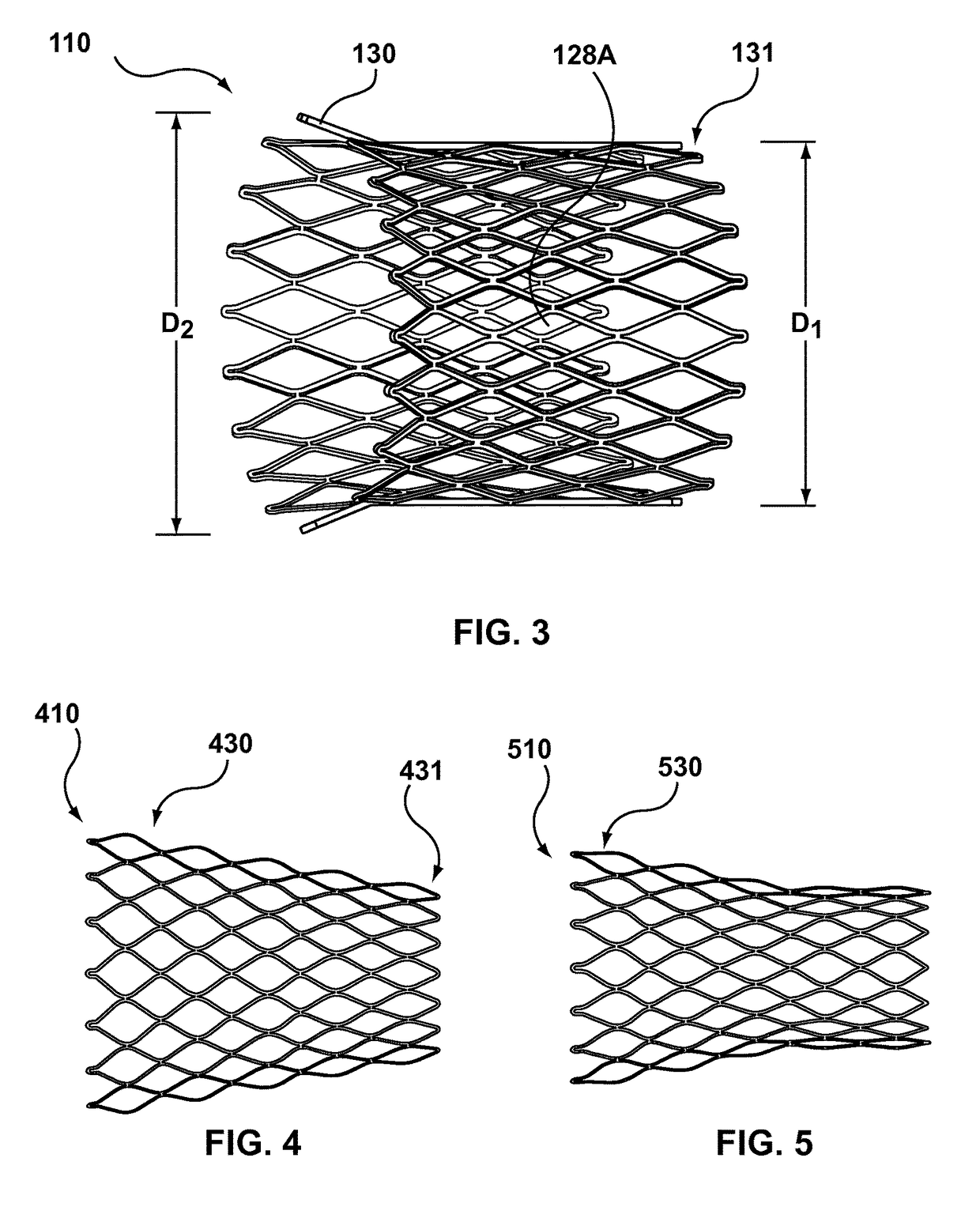
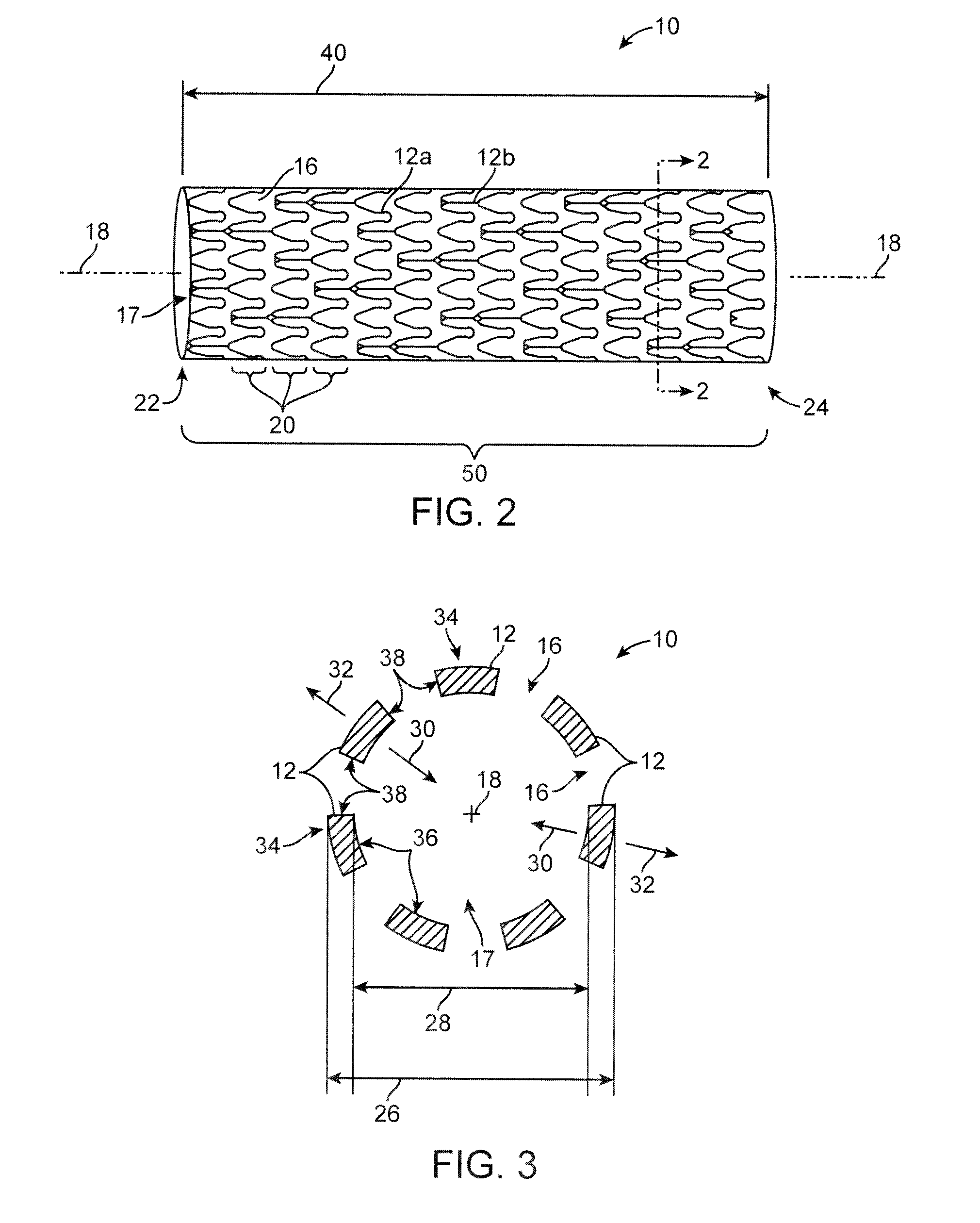
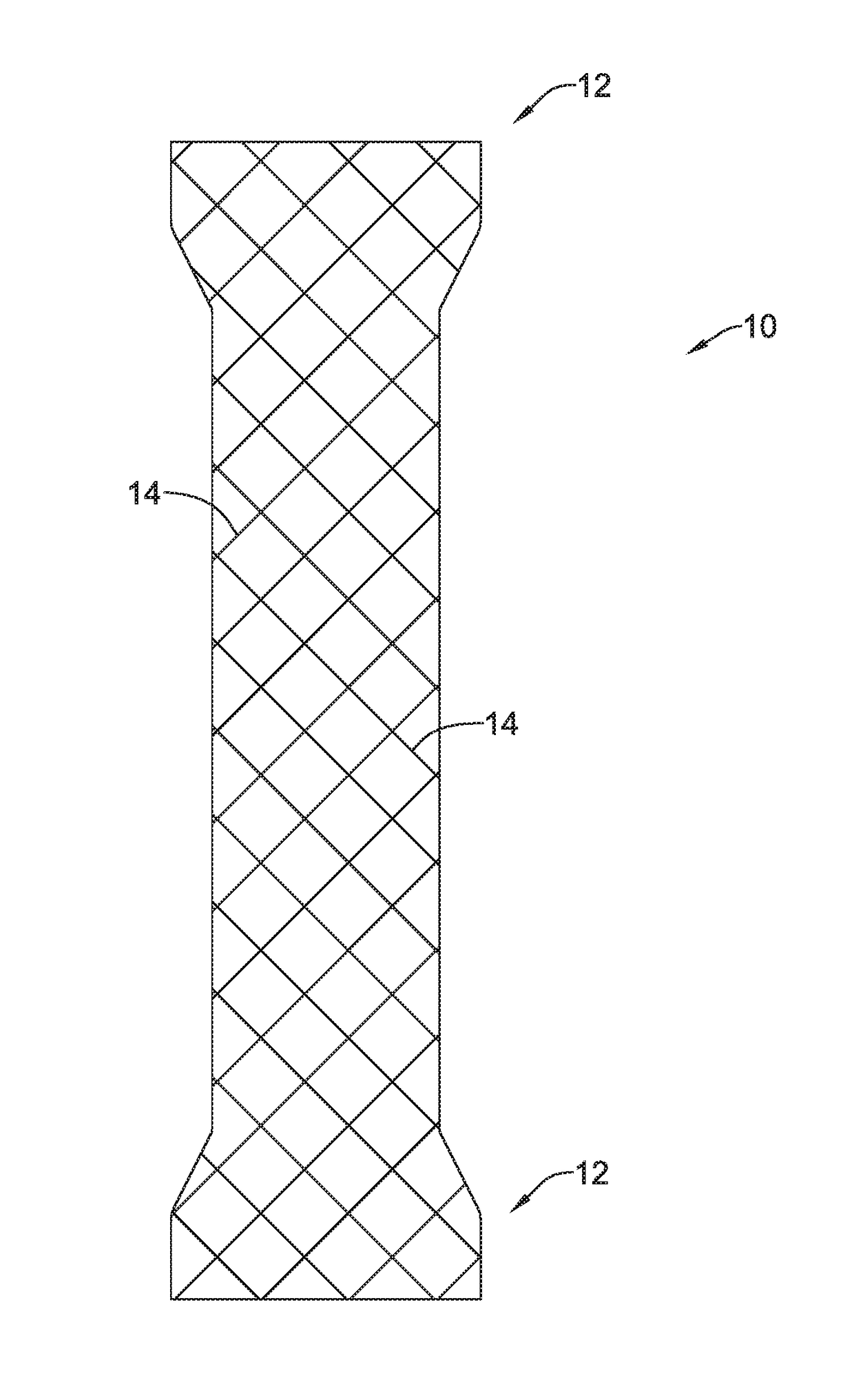
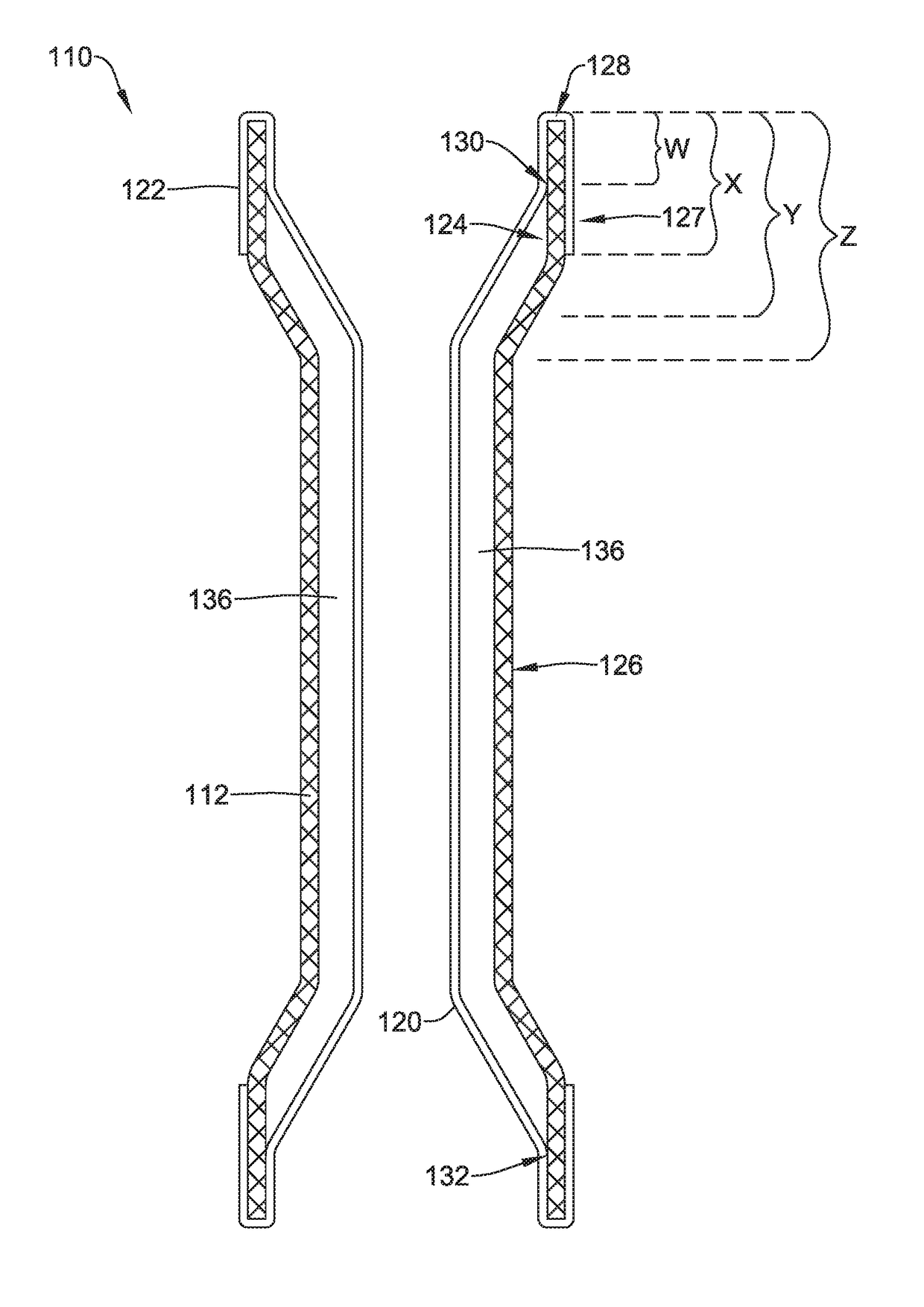
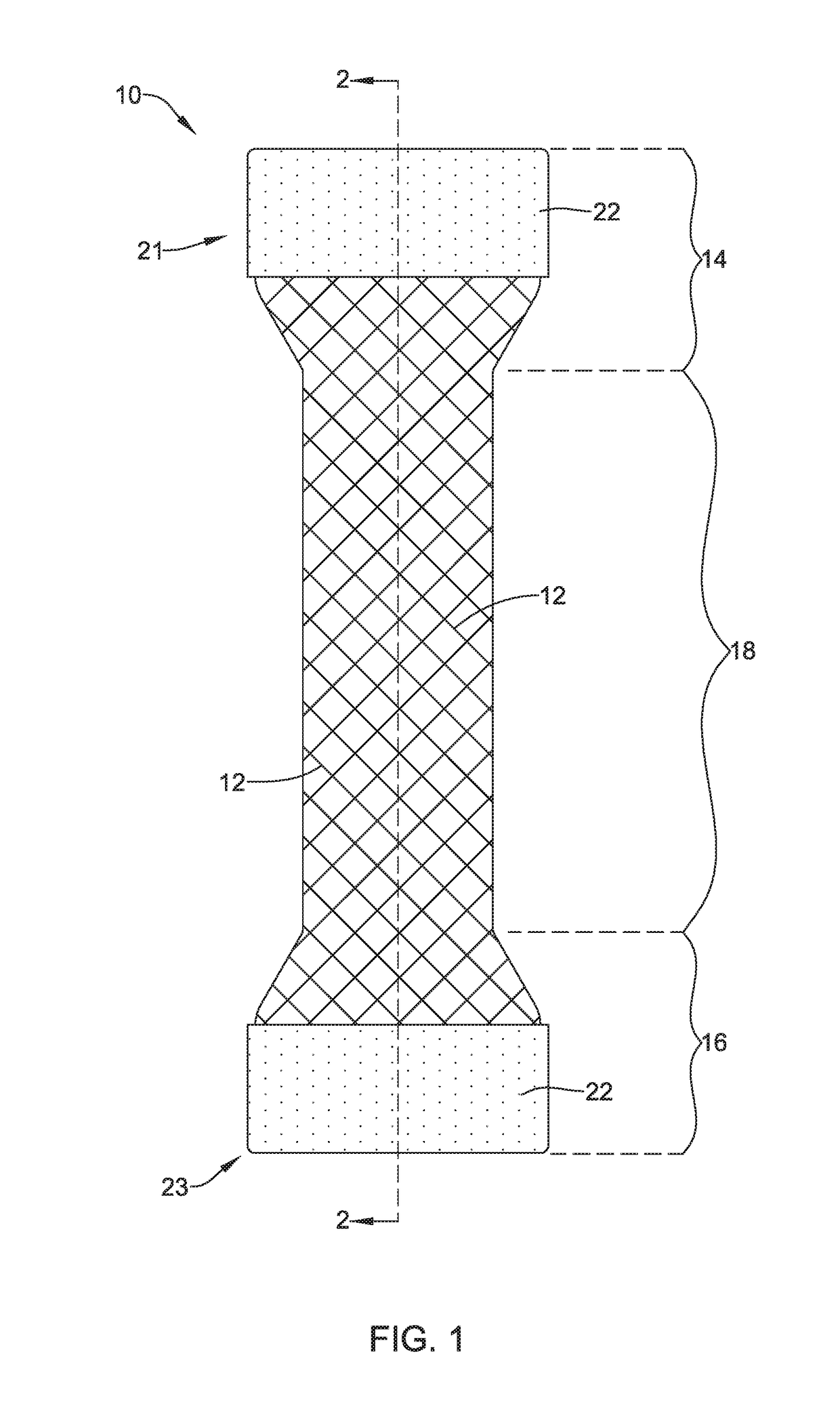
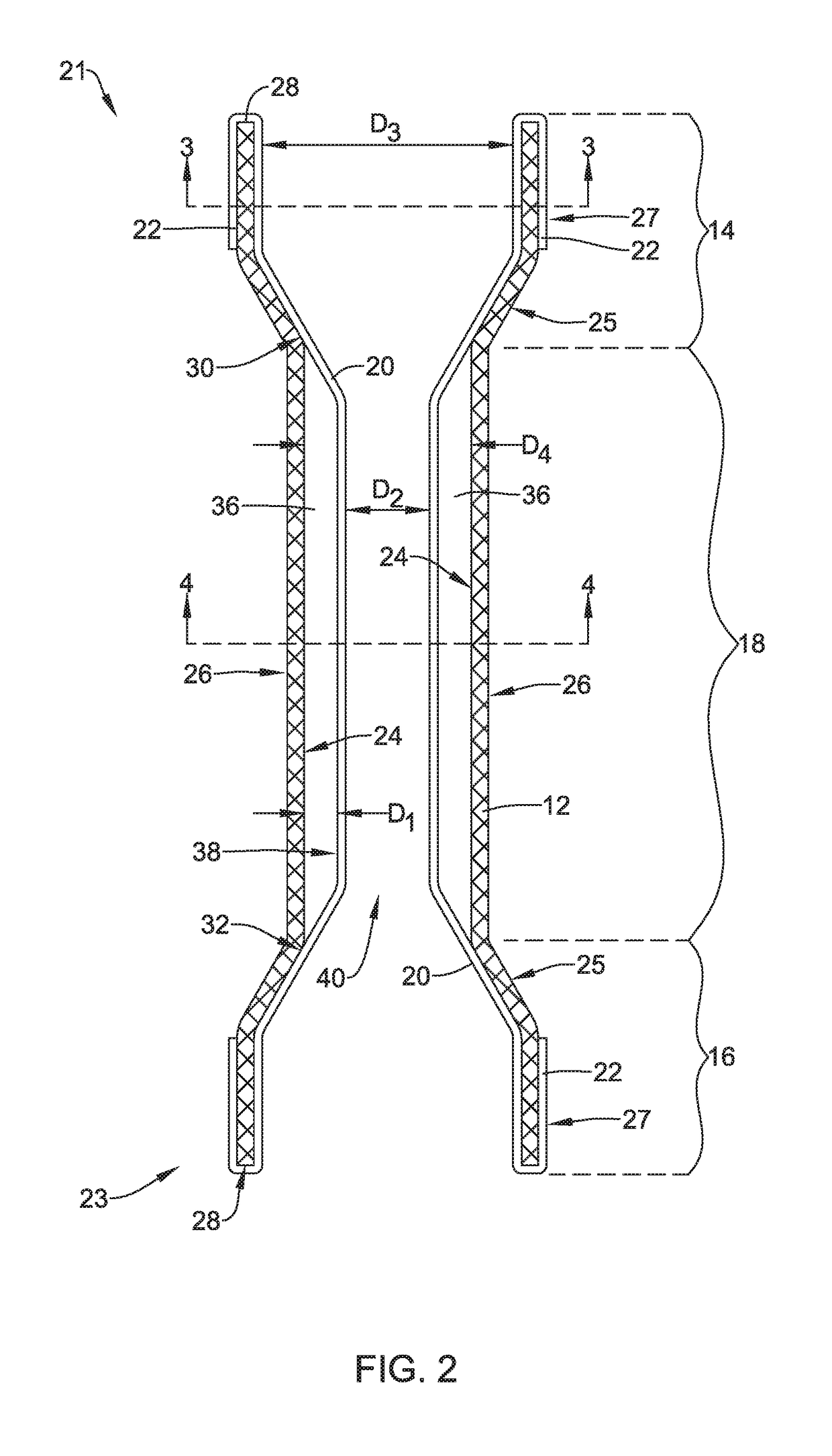
Tubular stent with oval struts
InactiveUS7153322B2Enhance crimping and symmetric expansion of stentLength of tubeStentsBlood vesselsLongest DiameterEndoluminal stent
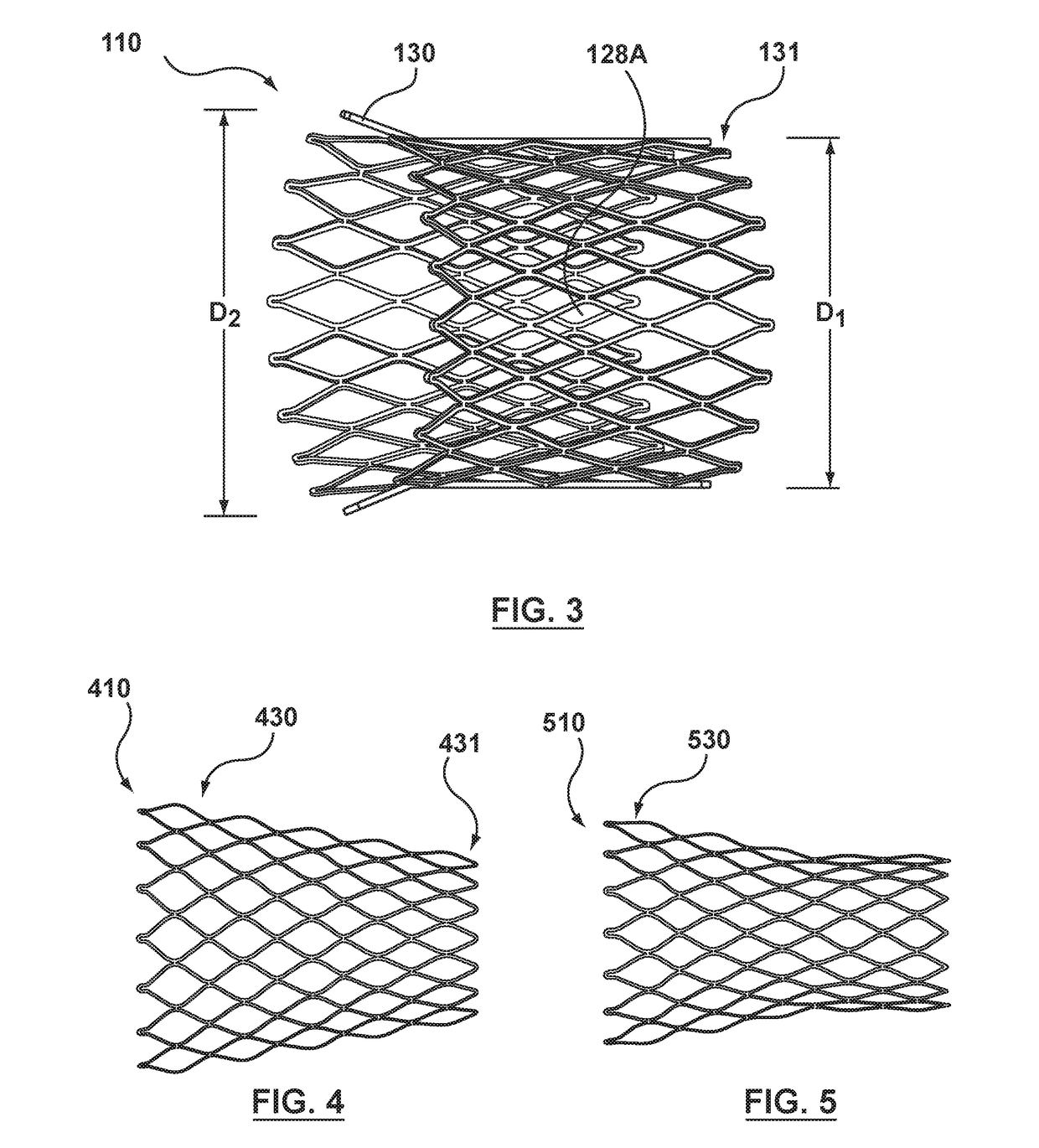
A vascular or endoluminal stent is adapted for deployment in a vessel or tract of a patient to maintain an open lumen. The stent constitutes a scaffold formed from a single open-ended tube having a multiplicity of through-holes in its wall. The through-holes are defined by a plurality of struts that bound the holes. Each of the struts has an optimized cross-section of oval shape with a long diameter generally aligned with the length or circumference of the tube wall and a short diameter generally aligned with the thickness of the tube wall. The oval shape of the struts provide several advantages including enhancing flexibility of the stent, easing advancement of the stent through a lumen of the vessel or tract for deployment at a target site therein, protecting the balloon of a balloon catheter on which the stent is tightly crimped, and enhancing expansion of the stent during deployment while maintaining its capability to withstand compression in response to recoil of the vessel or tract following deployment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Bio-acceptable conduits and method providing the same
InactiveUS20100047310A1Reduced dimensionLow costElectric discharge heatingFilament/thread formingFiberFluorescence
Disclosed is a bio-electrospinning technique for preparing a cell-containing, oriented, continuous tubular scaffold, made of biodegradable polymer, designed for use as a nerve guide conduit (NGC) in nerve regeneration. With a coaxial spinneret, the PC-12 cell medium solution was co-electrospun into a core of tubular fibers, with PLA on the outer shell. The resulted fibers' morphology was characterized via SEM and optical microscopy, and following structural characteristics were found: 1. the larger, hollow fibers had diameters in tenth of microns and wall thicknesses around few microns, 2. an orientation in a preferred direction with the aid of a high-rotating collection device. The fluorescent PC12 cells embedded within the scaffold were cultured and nerve growth factor was added. We observed cells could not only survive the process, but also sustain their viability by undergoing differentiation process, extending neurite along the micro tubular scaffold in the desired direction. All these results demonstrate its potential application for advanced NGC.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
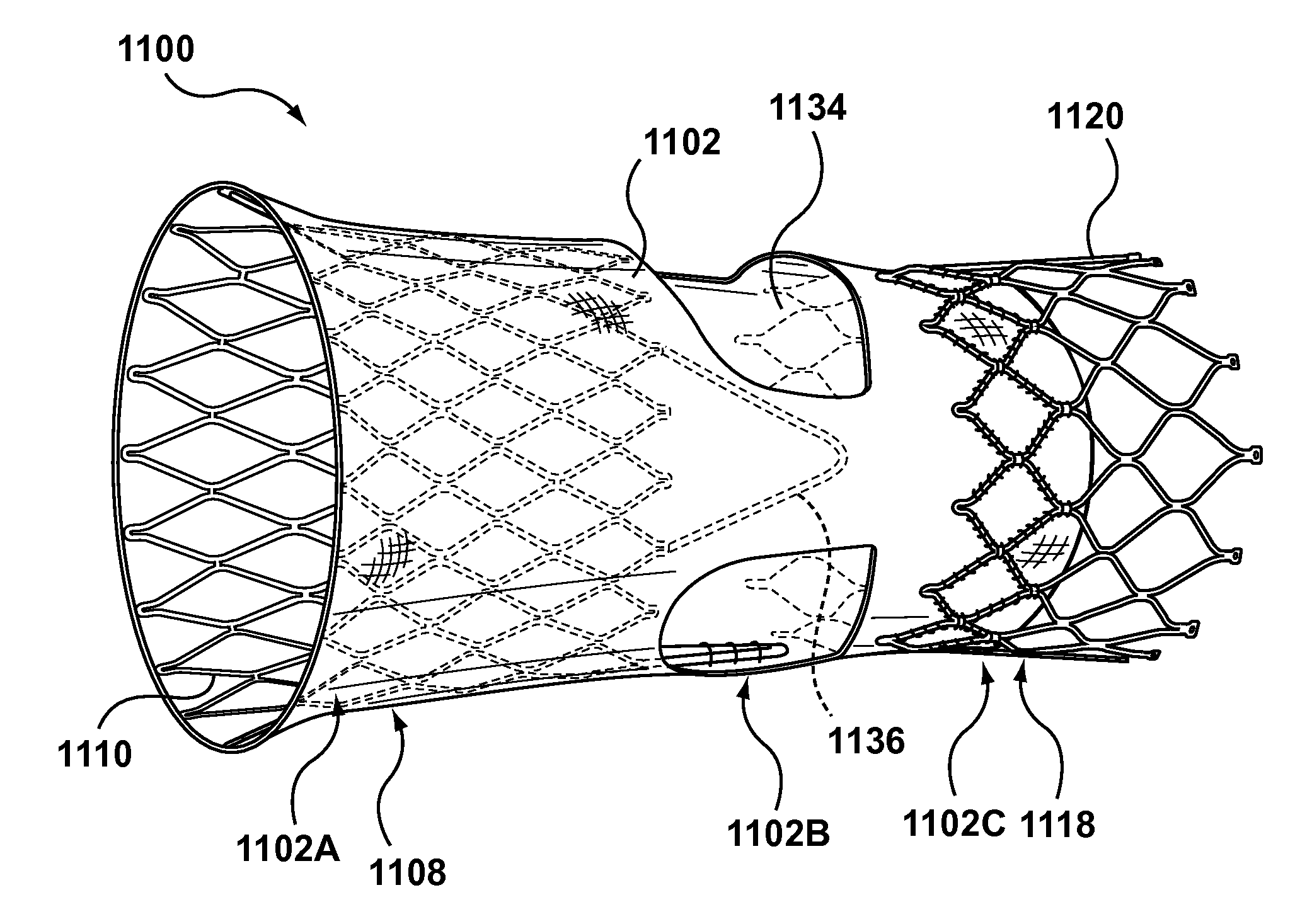
Segmented transcatheter valve prosthesis having an unsupported valve segment
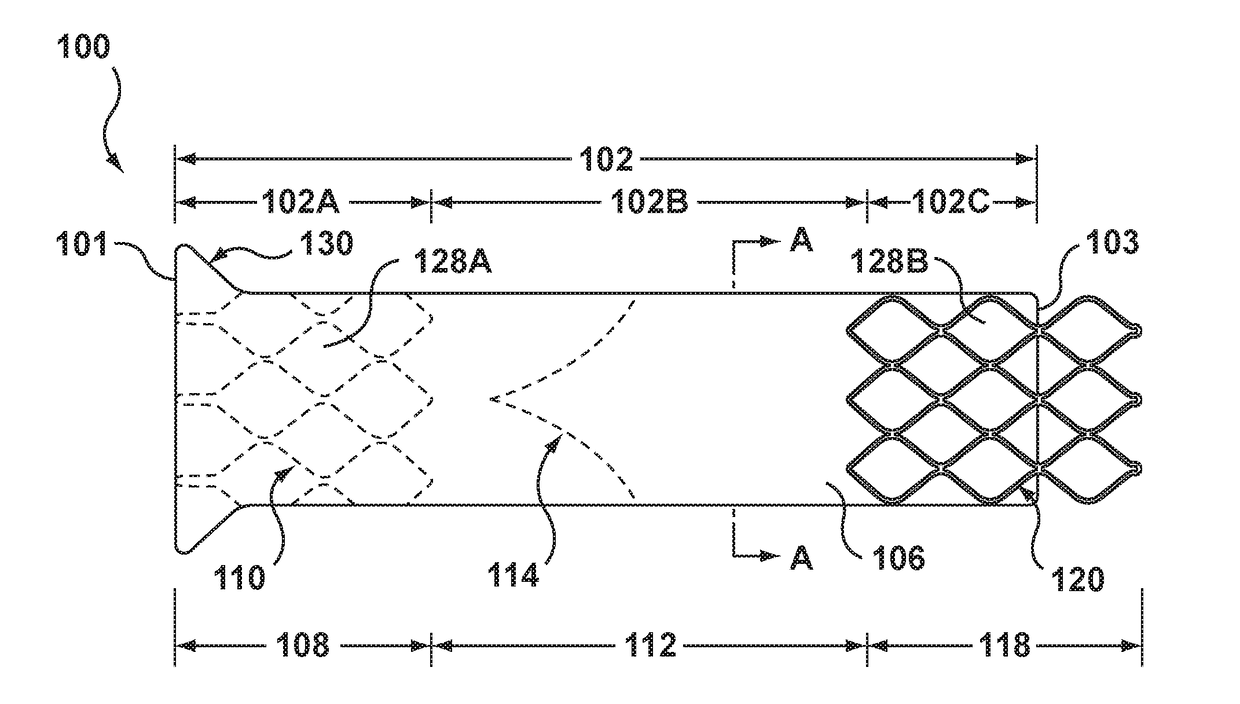
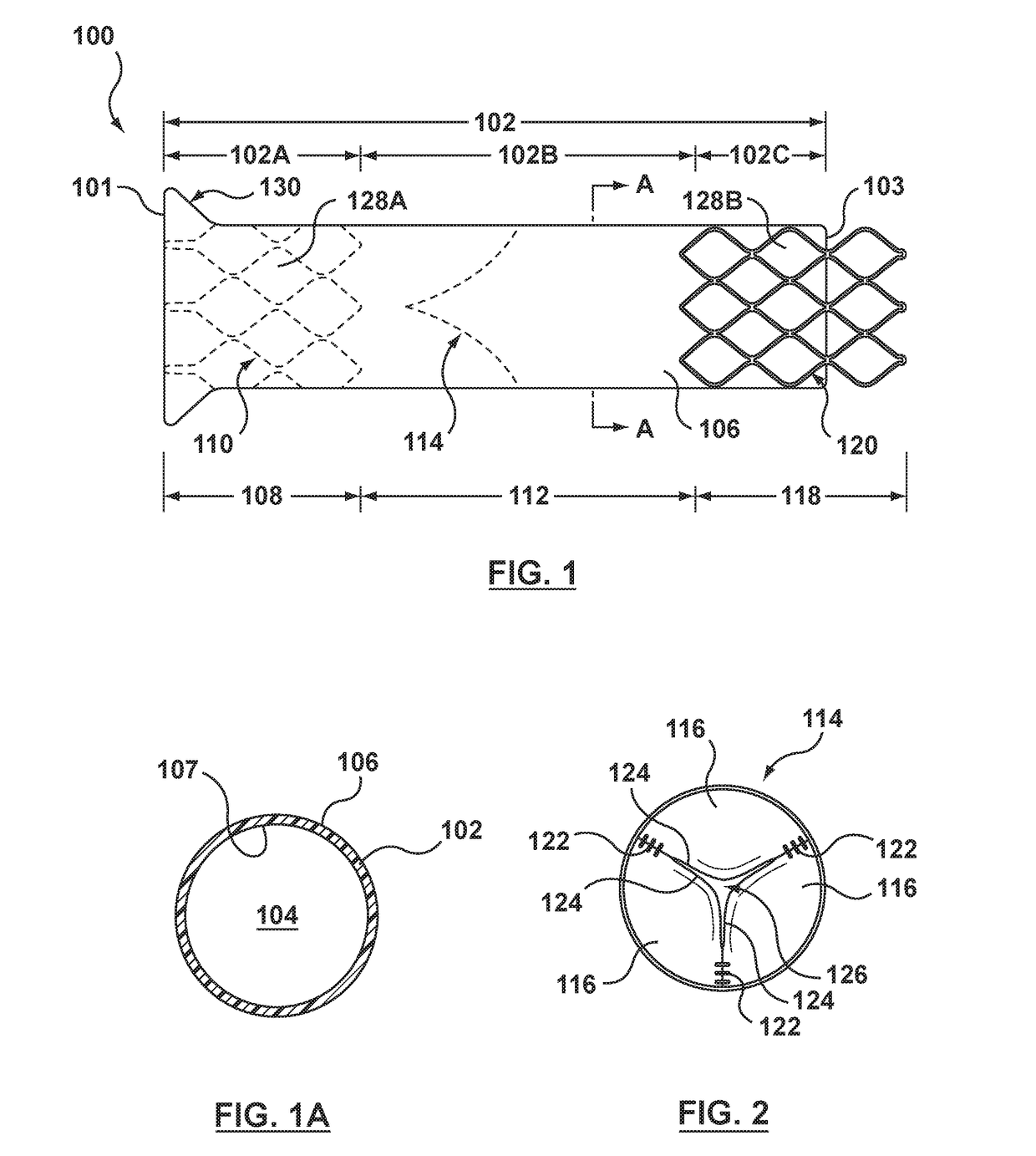
Embodiments hereof relate to a transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular fabric body, a first or inflow tubular scaffold attached to a first end portion of the tubular fabric body, and a second or outflow tubular scaffold attached to a second end portion of the tubular fabric body. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to an intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body that longitudinally extends between the first and second end portions of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion is unsupported such that neither of the first and second tubular scaffolds surrounds the intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion may include one or more windows for coronary access and may include one or more commissure reinforcement members coupled thereto to provide support for the prosthetic valve component.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
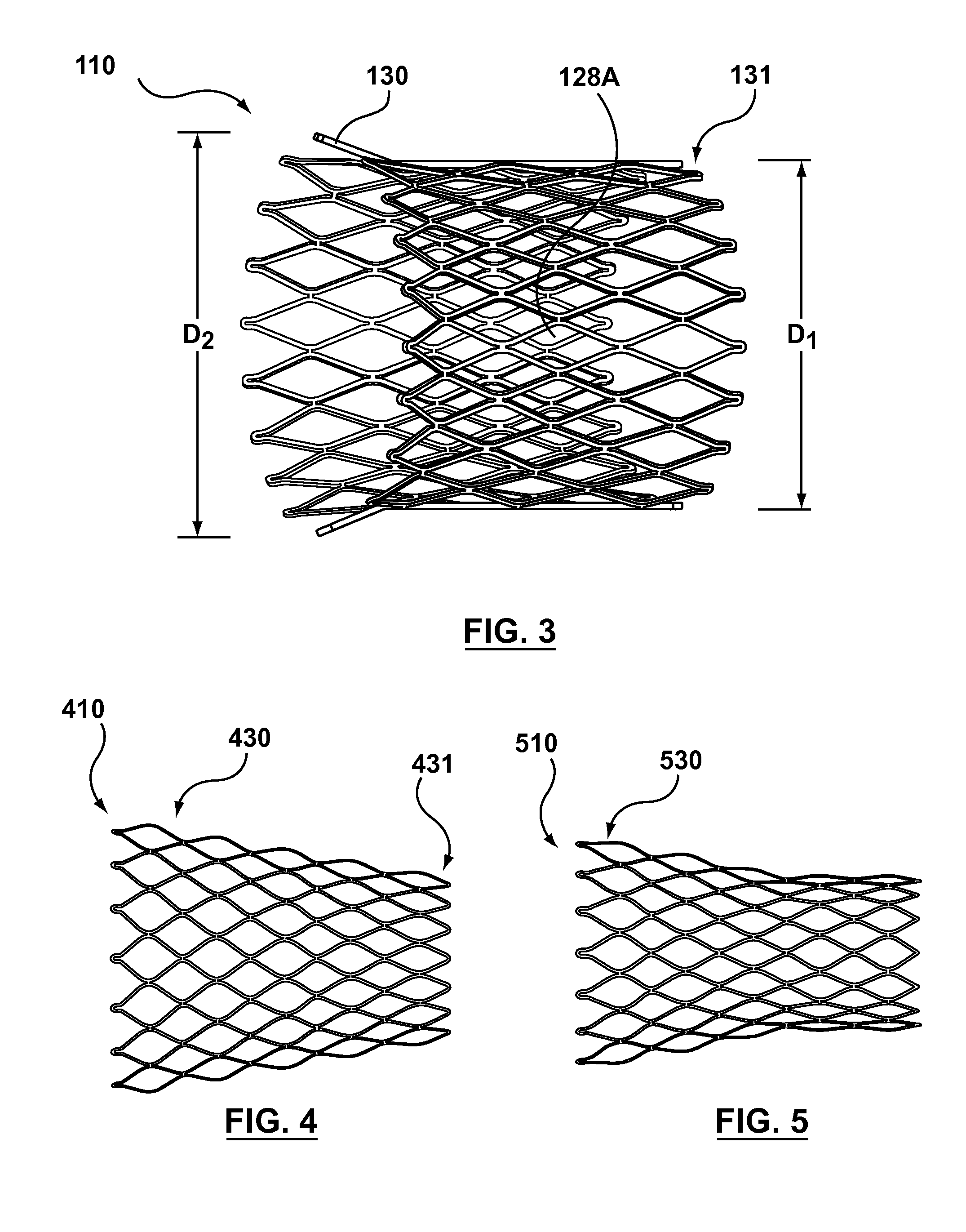
Barbed stent vascular occlusion device
A vascular occlusion device for occluding a body cavity. The device includes a tubular scaffold extending from a proximal end to a distal end. The scaffold is formed from a plurality of interconnected and articulated members configured to self-expand into an open configuration. A plurality of barbs extend from the articulated members, each barb including an anchoring end. The anchoring end is disposed radially outward from the scaffold in the open configuration and adapted to embed into the cavity walls. A radially expandable substance is disposed within a device lumen. The substance is configured to promote body tissue growth within the body cavity to occlude the body cavity. In one example, the body cavity includes a patent foramen ovale.
Owner:COOK INC
Implantable Prosthesis With Depot Retention Feature
InactiveUS20110245904A1StentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiomedical engineeringPolymer composition
A prosthesis for intraluminal drug delivery can comprise a plurality of interconnected struts that form a tubular scaffold structure. The struts include through-holes with an inner surface configured to retain a bioabsorbable depot. The bioabsorbable depot includes a drug-polymer composition that hydrolytically degrades upon implantation. The inner surface of the through-hole can be an entirely smooth and continuous area that is concave or convex, with no geometric discontinuities. The inner surface of the through-hole can include any number of constricted and distended regions to form grooves of a size and shape carefully selected to engage a corresponding geometric feature of the bioabsorbable depot.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
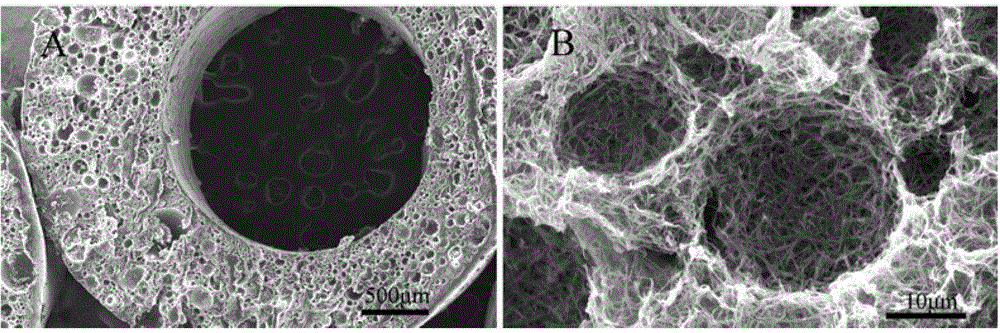
Methods and Apparatus for Fabricating Porous Three-Dimensional Tubular Scaffolds
ActiveUS20100330144A1Reduce porosityProperties be controlledEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsIntestinal structureBile fluid
Owner:BEIJING ADVANCED MEDICAL TECH
Construction method of anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material
InactiveCN102961783AInduce and promote regenerationPromote regenerationStentsBlood vesselsFiberSignalling molecules
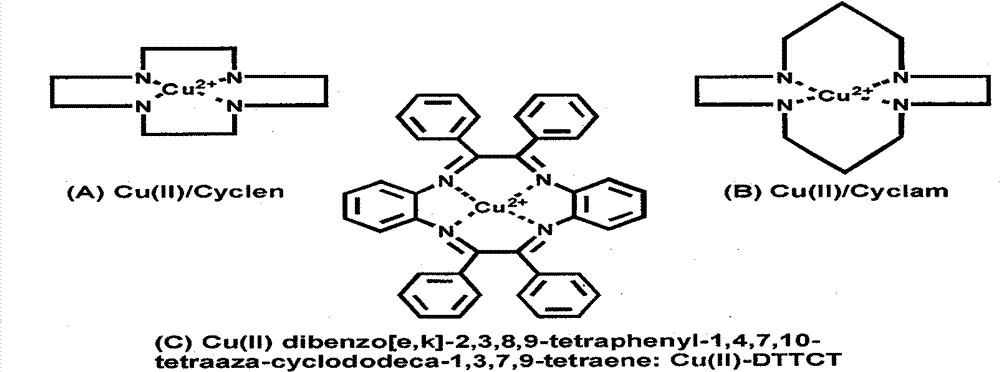
The invention discloses a construction method of an anticoagulant artificial blood vessel scaffold material. The method includes: taking a rotating stainless steel pipe as a receiver, employing an electrospinning technology to prepare an organic macromolecular polymer, a mixture of a Cu2<+> complex catalyst and the organic macromolecular polymer, and the organic macromolecular polymer successively into a three-layer structured superfine fiber porous tubular scaffold material; and regulating the types and proportion of the Cu2<+> complex catalyst and the organic macromolecular polymer, as well as the electrospinning time of a three-layer electrospinning solution so as to control the release rate of NO. With a three-layer structure, the blood vessel scaffold material formed by the invention not only realizes loading of the Cu2<+> organic complex catalyst, but also improves the phenomenon of NO burst release catalyzed by an ordinary hybrid electrospun structure scaffold material, improves the loading stability of the Cu2<+> complex catalyst, and can leave the biological signal molecule NO to play a better role in inhibiting platelet adhesion, resisting platelet activation and inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation so as to improve its anticoagulant property.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
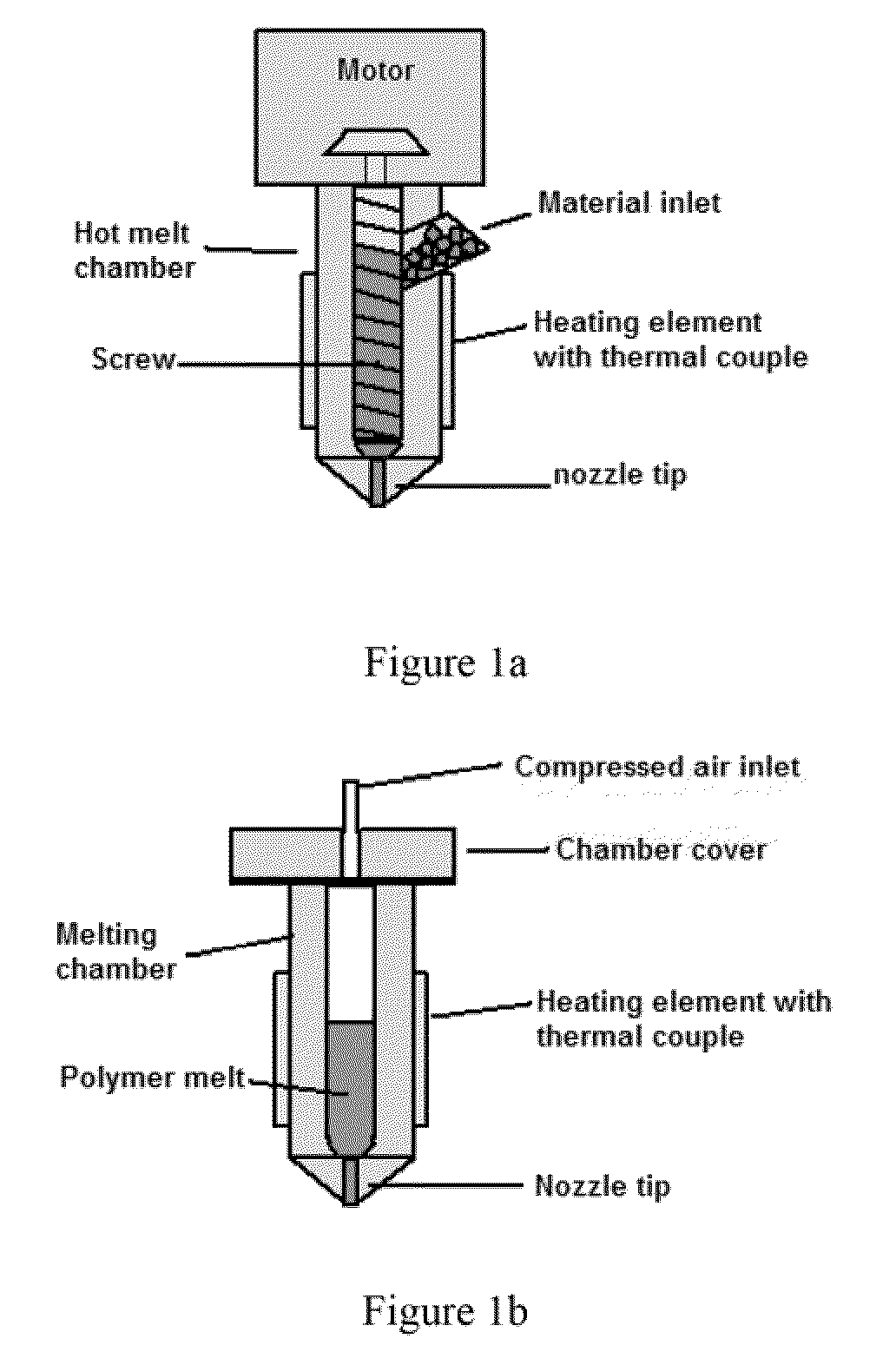
Method of forming micro-tubular polymeric materials
The present invention discloses the design and fabrication of highly porous (up to 97%) scaffolds from biodegradable polymers with a novel phase-separation technique to generate controllable parallel array of micro-tubular architecture. The porosity, diameter of the micro-tubes, the tubular morphology and their orientation may be controlled by the polymer concentration, solvent system and temperature gradient. The mechanical properties of these scaffolds are anisotropic. Osteoblastic cells are seeded in these 3-D scaffolds and cultured in vitro. The cell distribution and the neo-tissue organization are guided by the micro-tubular architecture. The method has general applicability to a variety of polymers, therefore the degradation rate, cell-matrix interactions may be controlled by the chemical composition of the polymers and the incorporation of bioactive moieties. These micro-tubular scaffolds may be used to regenerate a variety of tissues with anisotropic architecture and properties.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Preparation method of porous nano-fiber tubular scaffold
InactiveCN102908208AImprove toughnessIncrease elasticityTubular organ implantsPorosityPolymer dissolution
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous nano-fiber tubular scaffold, which comprises the steps that (1) PLLA (Poly L Lactic Acid) and other polymers are dissolved in a solvent to get a polymer solution; (2) the polymer solution is injected into a tubular mold and rapidly placed at a low temperature for phase separation, then the polymer solution is taken out, a tubular mold housing is removed, polymer gel after the phase separation and a core mold are immersed in ice water together, then the core mold is taken out, the polymer gel is immersed in deionized ice water to exchange the solvent, and the tubular scaffold is obtained; and (3) finally, the tubular scaffold obtained is frozen and dried for 48-120 hours, and then the porous nano-fiber tubular scaffold is obtained. The preparation method is simple to operate, and requires no additional hole-foaming agent, is suitable for volume production, and is lower in preparation cost; the prepared tubular scaffold has a nano-fiber structure similar to an extracellular matrix of a human tissue, and a porous structure with the diameter and porosity capable of being adjusted, and facilitates growth of cells and reconstruction of a cambium.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
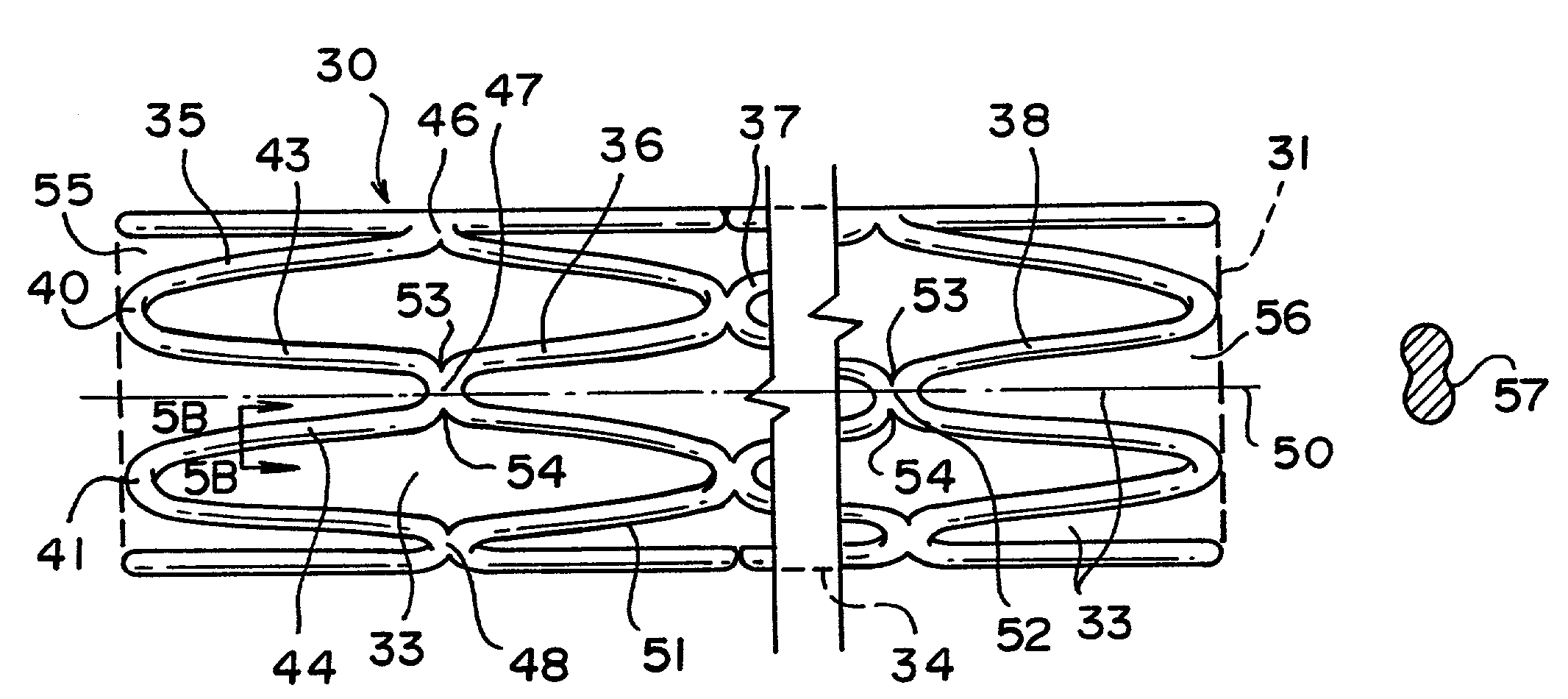
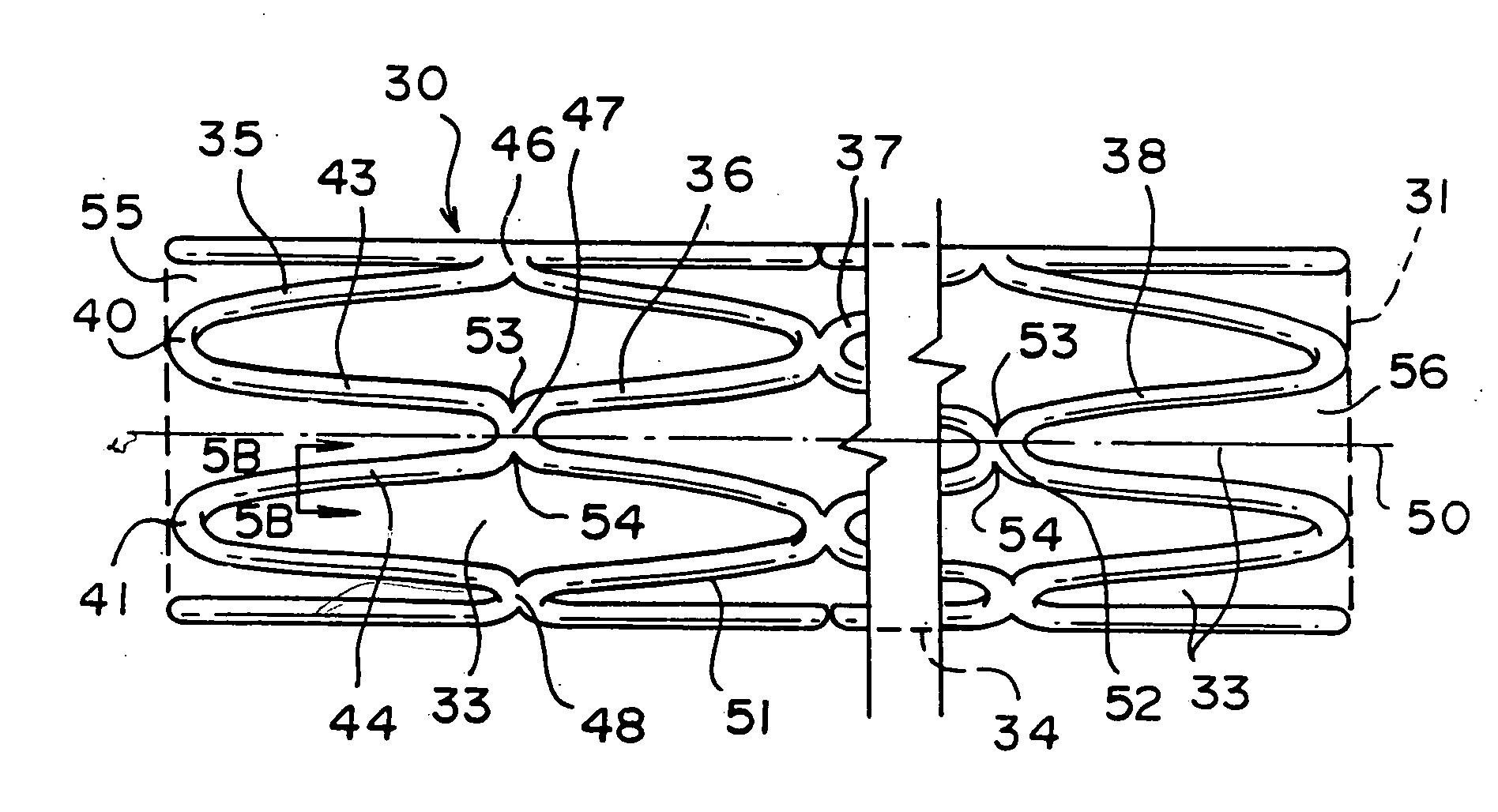
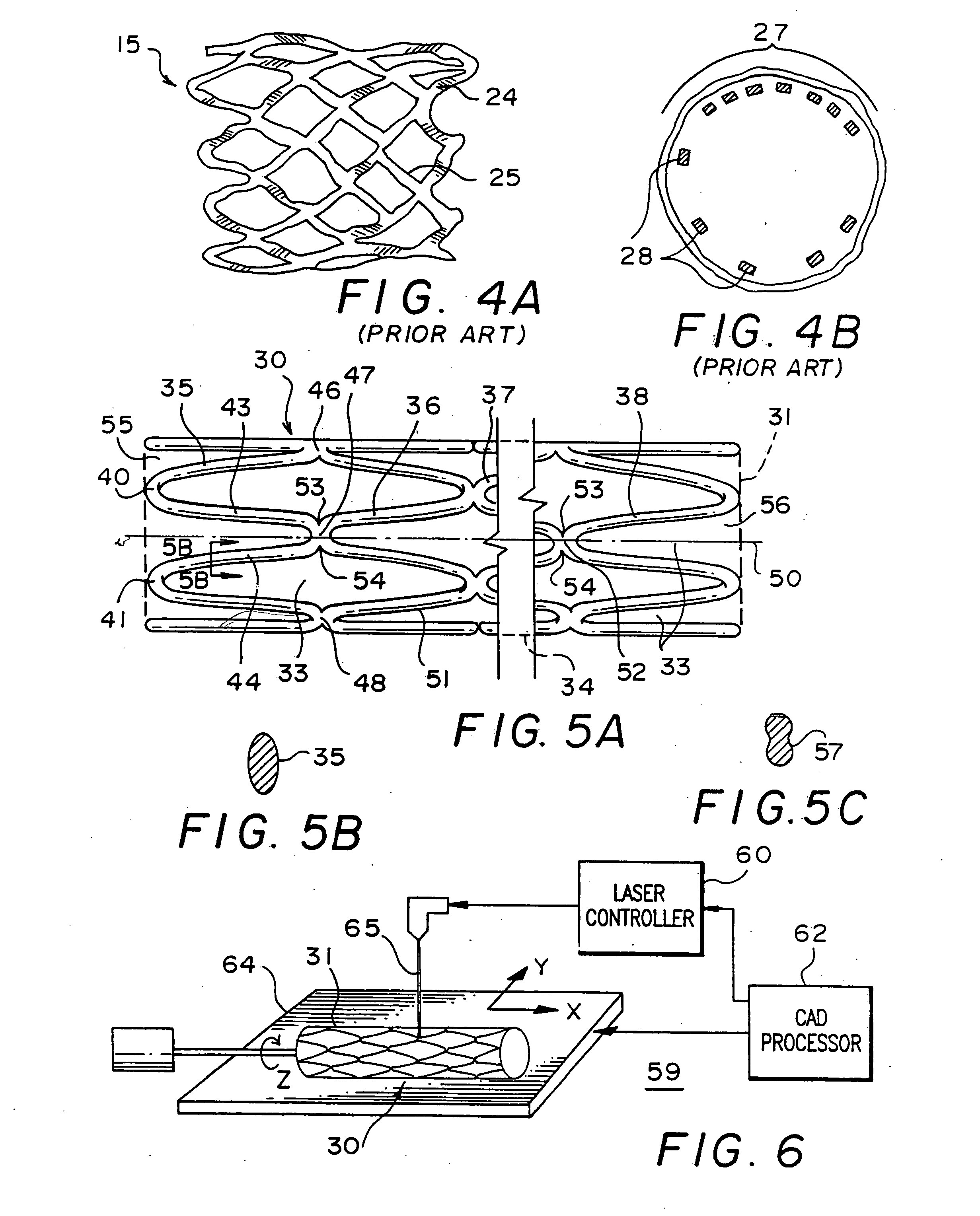
Tubular stent with oval struts
InactiveUS20070010870A1Enhance crimping and symmetric expansion of stentLength of tubeStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentProsthesis
An expandable tubular endoluminal prosthesis for maintaining the patency of a bodily vessel has a plurality of axially spaced serpentine bands. Each serpentine band has a proximal and distal end and a plurality of interconnected struts. Serpentine bands which are adjacent one another are connected one to the other. The prosthesis has a flow path therethrough and is capable of radial outward expansion from a first diameter to a second enlarged diameter. In a cross-section perpendicular to the flowpath, the struts have thicker portions with a narrower portion therebetween and have a greater width than thickness.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fabricated scaffold and using method thereof
InactiveCN101844612AImprove utilizationShorten the timeDry-dockingSlipwaysWork patternGeneral assembly
The invention discloses a fabricated scaffold and a using method thereof. The fabricated scaffold comprises a plurality of fixing parts, bearing parts and a plurality of scaffold platforms, wherein the plurality of fixing parts are vertical to a mounting surface; one bearing part is arranged on each fixing part; and the plurality of scaffold platforms are paved between two or among more than two bearing parts. The using method thereof comprises the following steps of: a ship segment stage, namely vertically and fixedly arranging the plurality of fixing parts on the mounting surface at preset intervals; and a general assembly and carrying phase, namely arranging one bearing part on each fixing part and arranging one scaffold platform on the adjacent bearing part. In the invention, a conventional operating mode that a tubular scaffold is needed to be erected in a whole cabin space so as to help a worker reach a higher operation point is changed, a method for extendedly arranging the scaffold clung to the mounting surface is adopted so as to release most of the space in the cabin, shorten the construction period, improve the use ratio of a dock, and reduce the hazard index of workersbelow the scaffold; and the fabricated scaffold has very obvious effect on backing construction in the ship building.
Owner:SHANGHAI WAIGAOQIAO SHIP BUILDING CO LTD
A kind of silk fibroin tubular scaffold and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102274089AImprove mechanical propertiesGood tissue compatibilityBlood vesselsAdhesiveInsertion stent
The invention provides a silk fibroin tubular support and a preparation method thereof. The tubular stent includes an outer layer, a core layer and an inner layer arranged in sequence, the outer layer and the inner layer are silk fibroin films, and the silk fibroin films include cross-linked silk fibroin and an adhesive; the core layer is Bombyx mori cooked silk thread tubular braid. The bending inner diameter of the tubular stent provided by the present invention is 5mm-7mm. The tubular scaffold provided by the invention has no cytotoxicity and has excellent biomechanical properties.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Beta type titanium alloy for vascular stent
A beta-type Ti alloy used for the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular scaffold, the tubular scaffold of other organs, and surginal implant contains Zr (0.5-9.5 wt%), Mo (0.5-6.5), Nb (8.5-28.5), C (0-0.03), N (0-0.04), H (0-0.003), O (0-0.12) and Ti (rest). Its advantages are moderate strength, lower modulus of elasticity, high plasticity and low cost.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Tubular stent with oval struts
InactiveUS7632301B2Enhance crimping and symmetric expansion of stentLength of tubeStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentProsthesis
An expandable tubular endoluminal prosthesis for maintaining the patency of a bodily vessel has a plurality of axially spaced serpentine bands. Each serpentine band has a proximal and distal end and a plurality of interconnected struts. Serpentine bands which are adjacent one another are connected one to the other. The prosthesis has a flow path therethrough and is capable of radial outward expansion from a first diameter to a second enlarged diameter. In a cross-section perpendicular to the flowpath, the struts have thicker portions with a narrower portion therebetween and have a greater width than thickness.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Nano-fiber tubular scaffold with multi-stage porous structure
The invention relates to a tissue engineering tubular scaffold with a multi-stage porous structure. The scaffold comprises at least one channel which is axially arranged, the area of the cross section of the channel is 300 mu m2-300 mm2, the non-channel part of the scaffold has micropores which are interconnected, the volume range of the micropores is 1 mu m3-5000 mu m3, the pore diameter distribution curve of the micropores is serrated, and the microporous wall of the scaffold is a nano-fiber three-dimensional network. Simultaneously, drugs with the function of changing physiological actionsof cells and tissues are contained in the scaffold, the functional drugs are released according to a certain rule to the environment located by the scaffold during the application process, and the types, the loading quantities and the release rate of the drugs can be set according to the actual needs. The tissue engineering scaffold with a fine topological structure and the physiological functionhas broad prospects.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUN SHING BIOTECH CO LTD
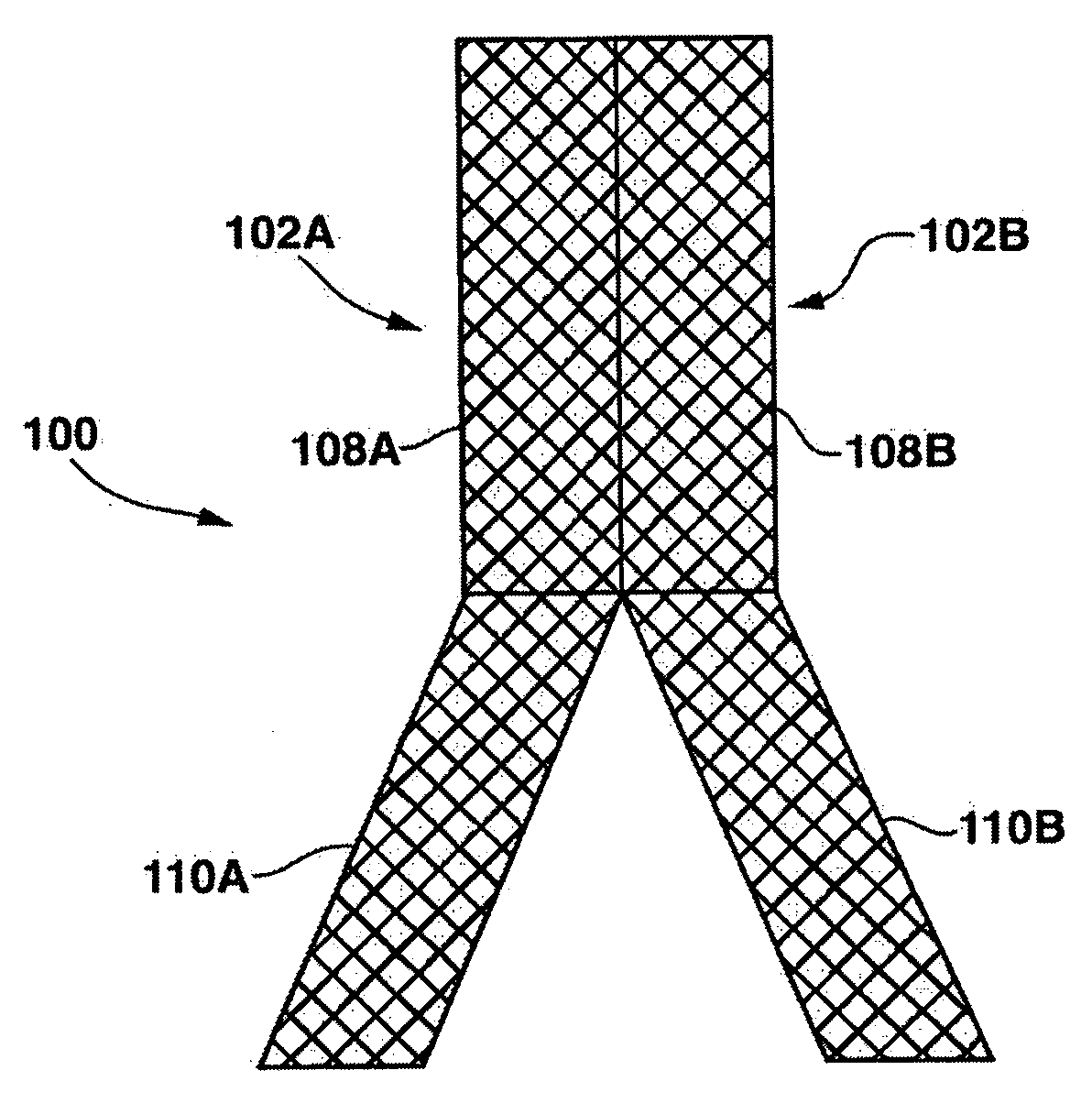
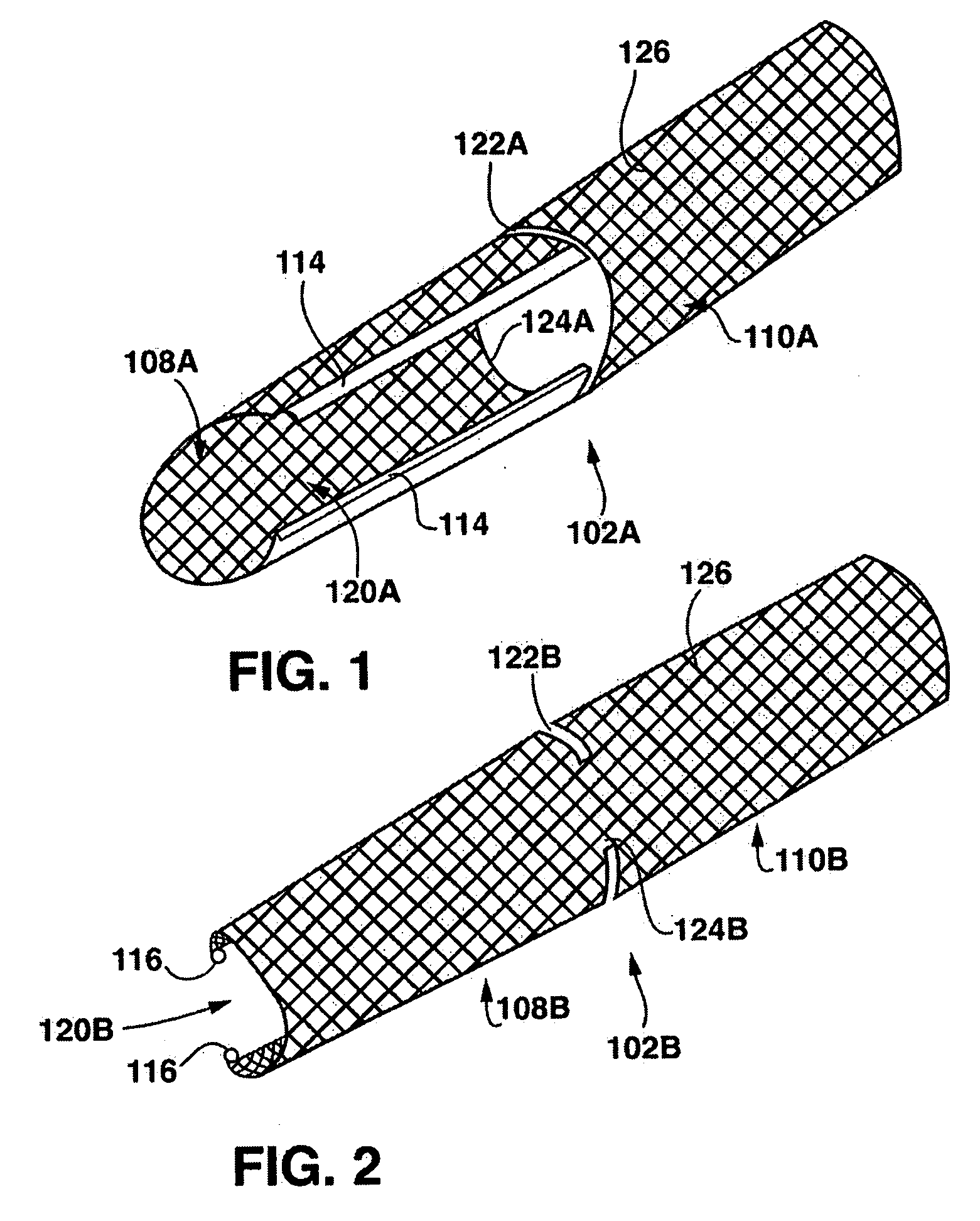
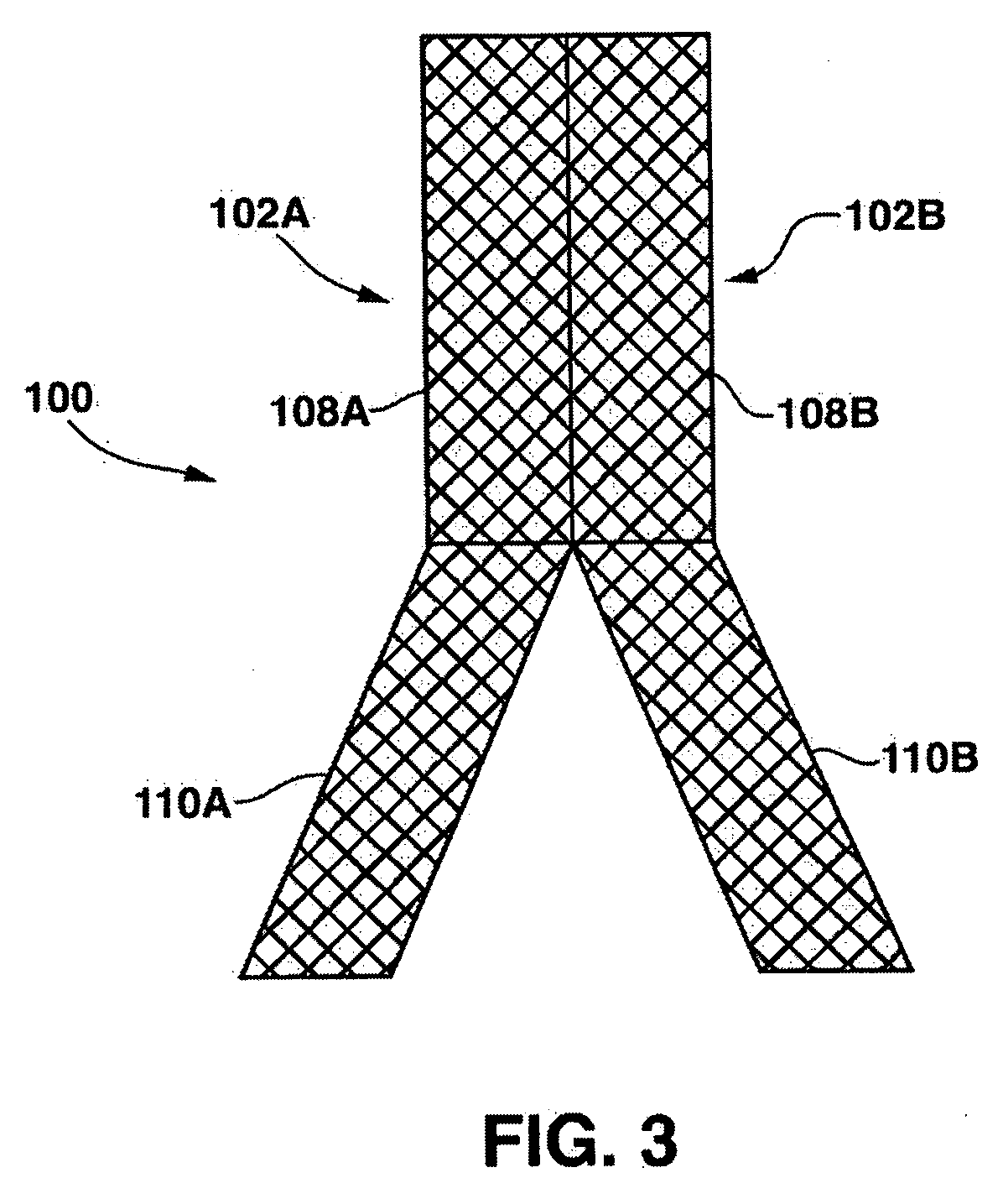
Stent having a C-shaped body section for use in a bifurcation
A bifurcation stent system includes a pair of self-expanding stents. Each stent has a C-shaped body section having a generally semicircular cross-section along its length and an O-shaped body section having a circular cross-section along its length. The stents are deployed in vivo such that the edges of the C-shaped body sections abut each other to form a tubular scaffold in a Y-shaped formation that conforms to the bifurcation. In order to connect the stents in vivo, the C-shaped body sections are configured to include a ball and socket connection there between. The C-shaped body sections align and abut to form a tubular scaffold that extends in the main vessel of the bifurcation, while the O-shaped body sections are tubular scaffolds that extend into the respective branch legs of the bifurcation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Segmented transcatheter valve prosthesis having an unsupported valve segment
Embodiments hereof relate to a transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular fabric body, a first or inflow tubular scaffold attached to a first end portion of the tubular fabric body, and a second or outflow tubular scaffold attached to a second end portion of the tubular fabric body. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to an intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body that longitudinally extends between the first and second end portions of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion is unsupported such that neither of the first and second tubular scaffolds surrounds the intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion may include one or more windows for coronary access and may include one or more commissure reinforcement members coupled thereto to provide support for the prosthetic valve component.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Esophageal stent including an inner liner
An example medical device is disclosed as an expandable stent. The stent includes a tubular scaffold having an inner surface, an outer surface, and a lumen extending therein. The expandable stent also includes a liner disposed within the lumen of the tubular scaffold. Further, the liner is radially spaced from a medial region of the tubular scaffold to define a tissue ingrowth region along an uncovered portion of the medial region. Additionally, the liner extending along the tissue ingrowth region is configured to limit the amount of tissue ingrowth along the medial region of the scaffold.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Segmented transcatheter valve prosthesis having an unsupported valve segment
Embodiments hereof relate to a transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular fabric body, a first or inflow tubular scaffold attached to a first end portion of the tubular fabric body, and a second or outflow tubular scaffold attached to a second end portion of the tubular fabric body. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to an intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body that longitudinally extends between the first and second end portions of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion is unsupported such that neither of the first and second tubular scaffolds surrounds the intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion may include one or more windows for coronary access and may include one or more commissure reinforcement members coupled thereto to provide support for the prosthetic valve component.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable prosthesis with depot retention feature
A prosthesis for intraluminal drug delivery can comprise a plurality of interconnected struts that form a tubular scaffold structure. The struts include through-holes with an inner surface configured to retain a bioabsorbable depot. The bioabsorbable depot includes a drug-polymer composition that hydrolytically degrades upon implantation. The inner surface of the through-hole can be an entirely smooth and continuous area that is concave or convex, with no geometric discontinuities. The inner surface of the through-hole can include any number of constricted and distended regions to form grooves of a size and shape carefully selected to engage a corresponding geometric feature of the bioabsorbable depot.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Esophageal stent including a valve member
An example medical device is disclosed. The example medical device includes a tubular scaffold. The scaffold includes a longitudinal axis, an inner surface and an outer surface. The medical device also includes a flexible valve extending radially inward from the inner surface of the scaffold. The valve includes an annular chamber extending circumferentially around the inner surface of the scaffold and is configured to shift from a closed configuration to an open configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Preparation method of anti-coagulating composite tubular scaffold with good compliance
InactiveCN104524632AGood blood compatibilityImprove compliancePharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPoly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl etherHaemodialysis machine
The invention provides a preparation method of an anti-coagulating composite tubular scaffold with good compliance. The tensile property of the tubular scaffold can be improved by the composite tubular scaffold by virtue of braided fabric; the tubular scaffold with sponge layers can be prepared by modification of silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin by polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether; the compliance of the tubular scaffold is improved; the anti-permeability of the tubular scaffold can be improved by the silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin tubular scaffold with double sponge layers; meanwhile, the anti-coagulating property of the tubular scaffold can be improved by the sulfated silk fibroin; the composite tubular scaffold with good tensile property, compliance, anti-permeability and blood compatibility can be prepared by the combination; the pipe diameter is controllable; and the composite tubular scaffold can be applied to repair and reconstruction of a small-caliber blood vessel and building of hemodialysis vascular access. The preparation method is simple to operate and low in cost; and commercial production can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Tubular scaffold for neural growth
ActiveUS20120064628A1Promote neural growthSimple methodSolid-state devicesNervous system cellsEngineeringInterconnection
A scaffold for neurons consists of tubes sized to promote neural growth through the tubes. The tubes may be fixed to a substrate providing electrical or optical paths out from the interior of the tubes from sensors or stimulating probes at one or more locations along the length of the coaxial axons. Steering electrodes at spaces between tubes may be used to selectively promote the growth of interconnections of different axons in a one, two, or three-dimensional fashion.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for detecting leaks in metal roofs
InactiveUS20030167826A1Detection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain ratePositive pressureEngineering
An apparatus and method are shown for detecting leaks in metal roofs which are made up of metal roof panels secured in position to form a roof structure by metal screws. The apparatus includes an elongate tubular stand having a lower extent and an upper extent connected by an internal bore, the lower extent terminating in a bore end opening. A hand operated pump communicates with the internal bore for supplying positive pressure or drawing a vacuum on the internal bore. The bore end opening is sealed by an elastomeric seal which is used to form a pressure tight seal about one of the metal screw to be tested. A pressure gauge on the stand communicates with the internal bore for measuring a change in pressure within the internal bore, such pressure change being indicative of a leak present at the metal screw being tested.
Owner:HOLT JESSE E
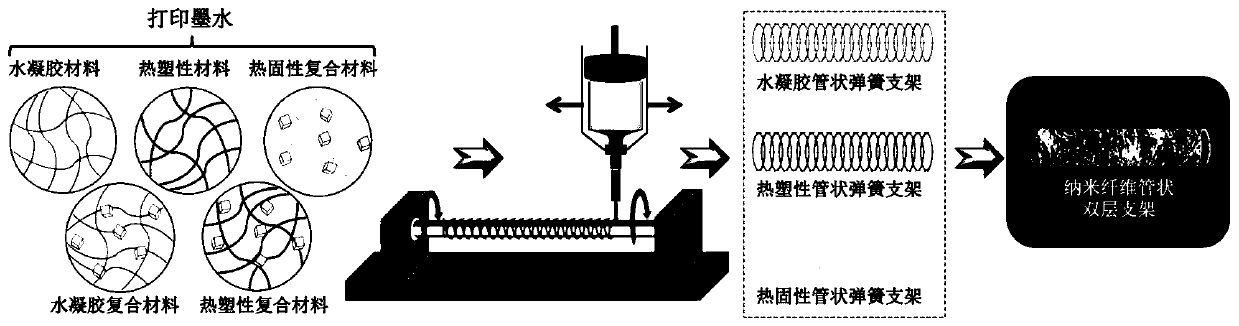
4-axis 3D-printing tubular medical stent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109701080APrecisely controllable multi-level pore structureSimple methodAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberTissue repair
The invention relates to a 4-axis 3D-printing tubular medical stent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The 4-axis 3D-printing tubular medical stent comprises a tubular stent witha multi-stage pore structure; and the surface of the stent is coated with nanofibers so as to form a double-layer tubular stent used for tubular tissue repair, extravascular stents, artificial tracheal stents and the like. The 4-axis 3D-printing tubular medical stent solves the problem of difficult direct construction of porous tubular stents by extrusion-type, especially fused-deposition-molding-type (FDM-type), 3D printing; and the prepared medical stent has the advantages of being possessed of a precise and controllable multi-stage pore structure, simple in application method, quick to useand suitable for multiple materials. And thus, the 4-axis 3D-printing tubular medical stent has good application prospects in the field of repair of tubular tissues and organs, including blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, urethra and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Preparation method of silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin composite tubular scaffold
InactiveCN103861158AGood cell compatibilityGood blood compatibilitySurgeryEngineeringHemodialysis access
The invention provides a preparation method of a silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin composite tubular scaffold. The composite tubular scaffold is characterized in that the composite tubular scaffold is composed of an elastic bonding layer, a fabric reinforcing layer and a compact coating layer, and the fabric reinforcing layer is embedded in the elastic bonding layer, and the outer surface of the compact coating layer is covered with the elastic bonding layer, wherein the compact coating layer and the fabric enhancing layer are made of silk fibroin, and the elastic bonding layer is made a silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin mixture. The elastic bonding layer can improve the compliance and the anticoagulation property of the tubular scaffold, the fabric reinforcing layer can improve the mechanical properties of the scaffold, and the compact coating layer can improve the impermeability of the scaffold. The tubular scaffold prepared in the invention has excellent mechanical properties, has good impermeability, cell compatibility and blood compatibility, has a controllable diameter, and can be used for restoring and reconstructing small caliber vessels and constructing a hemodialysis access. The preparation method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and commercial production realization.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
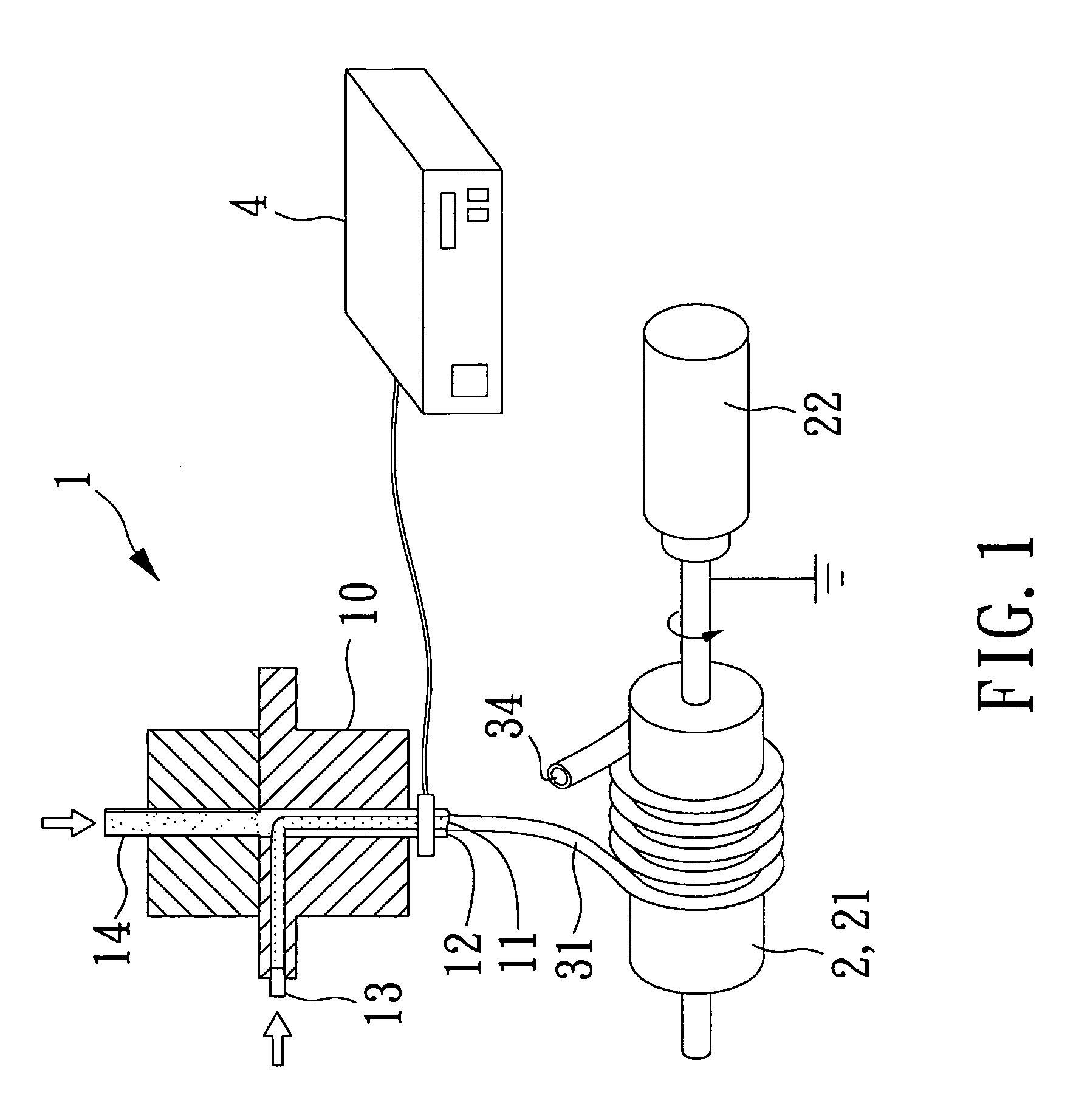
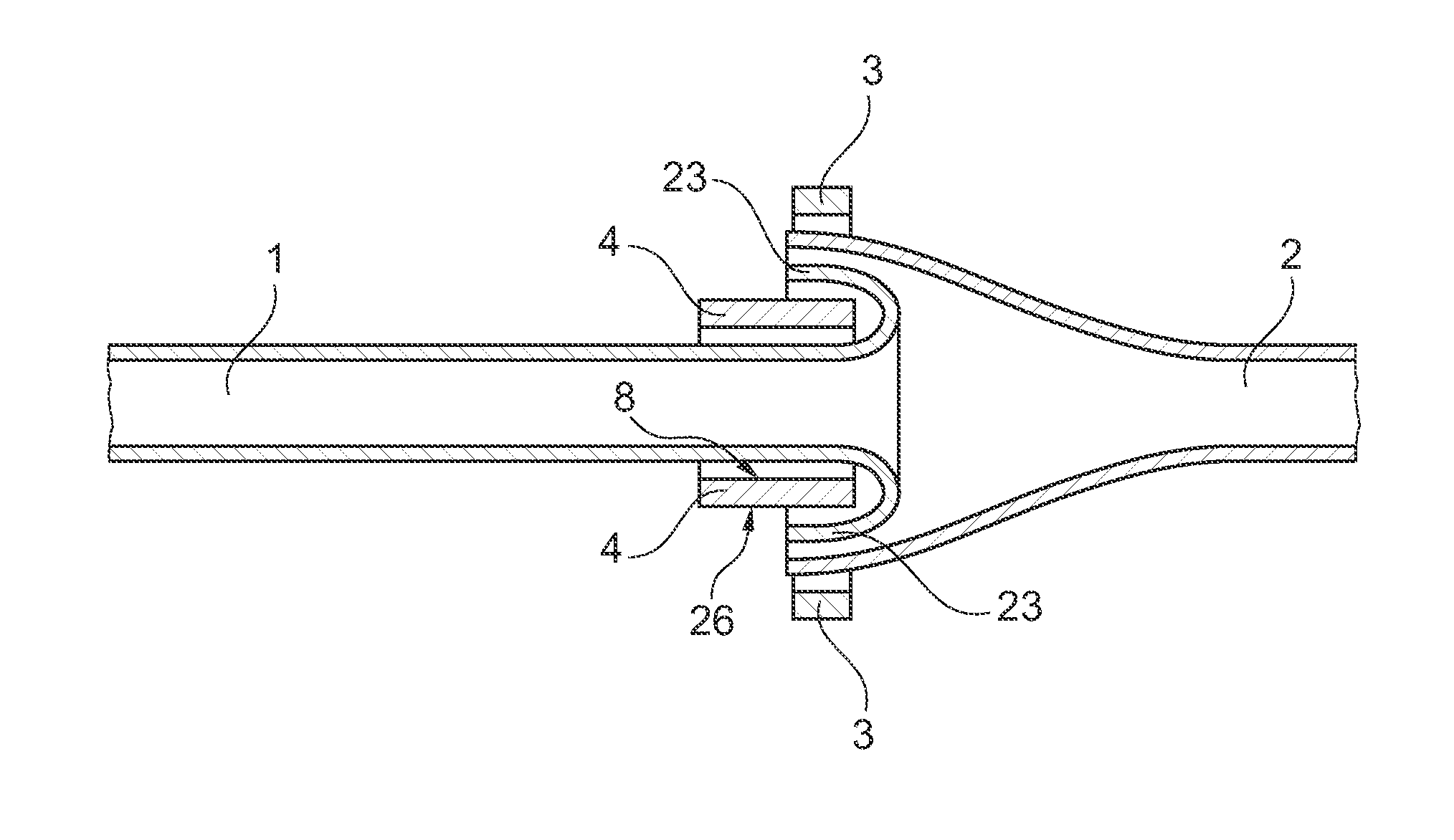
Medical device
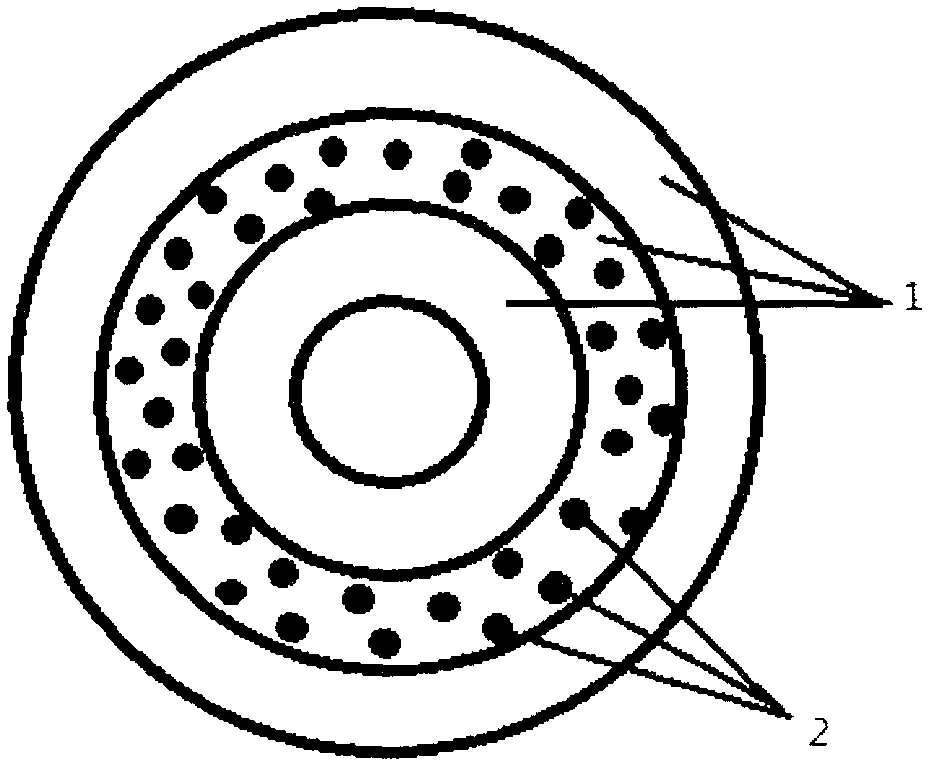
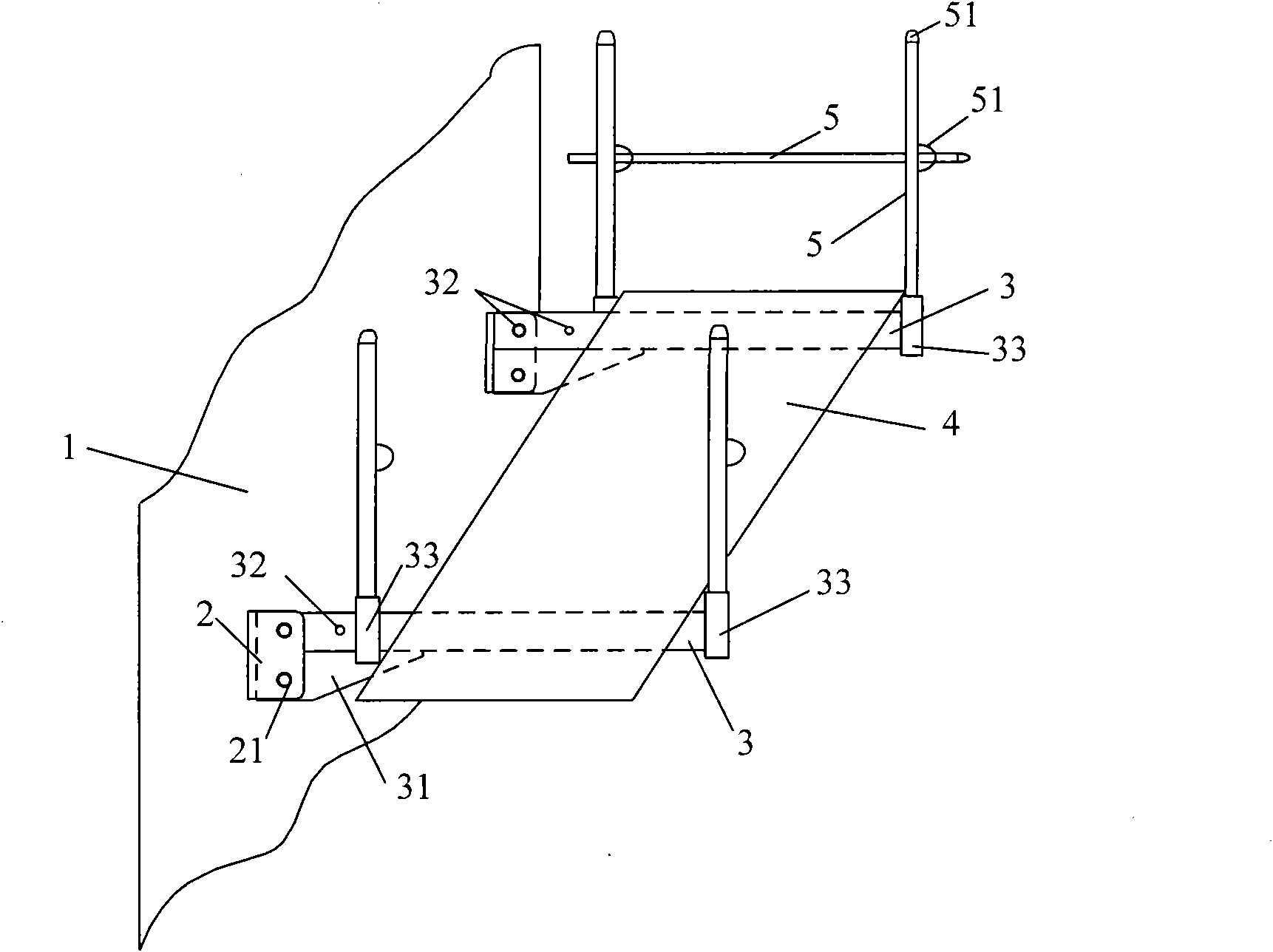
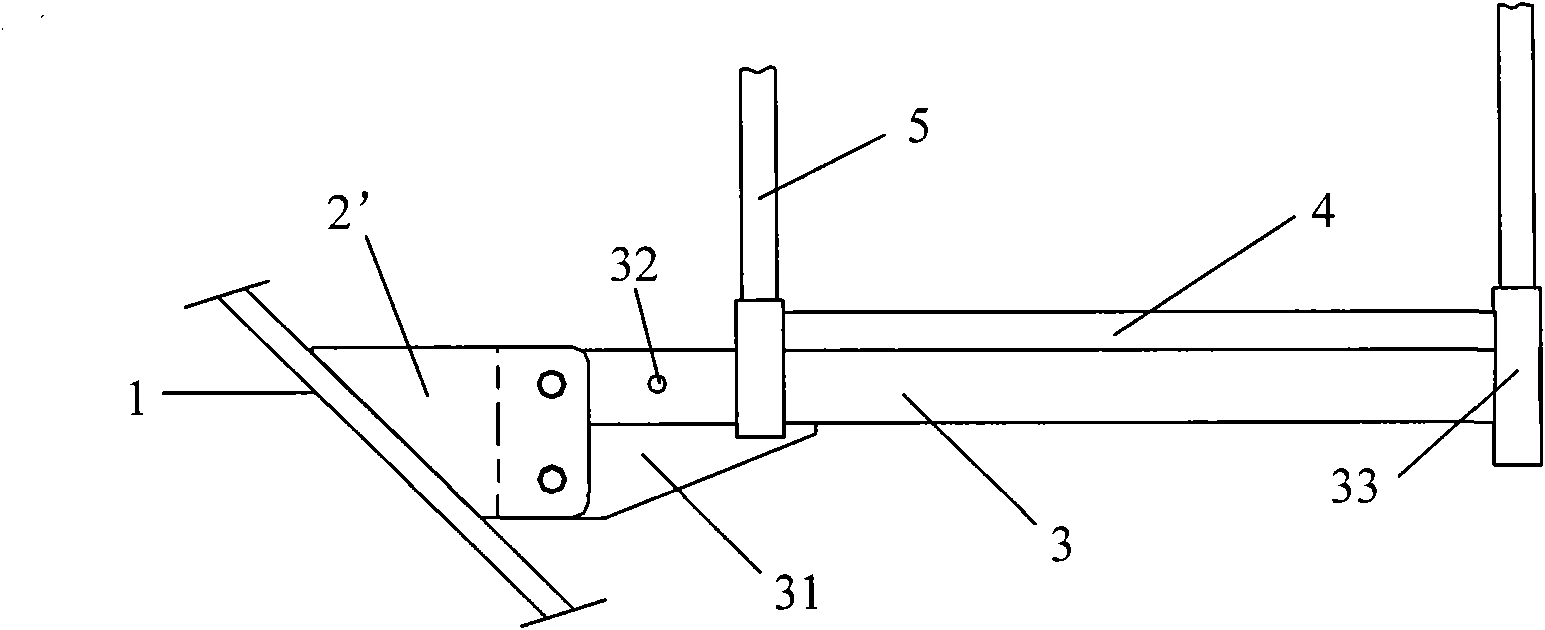
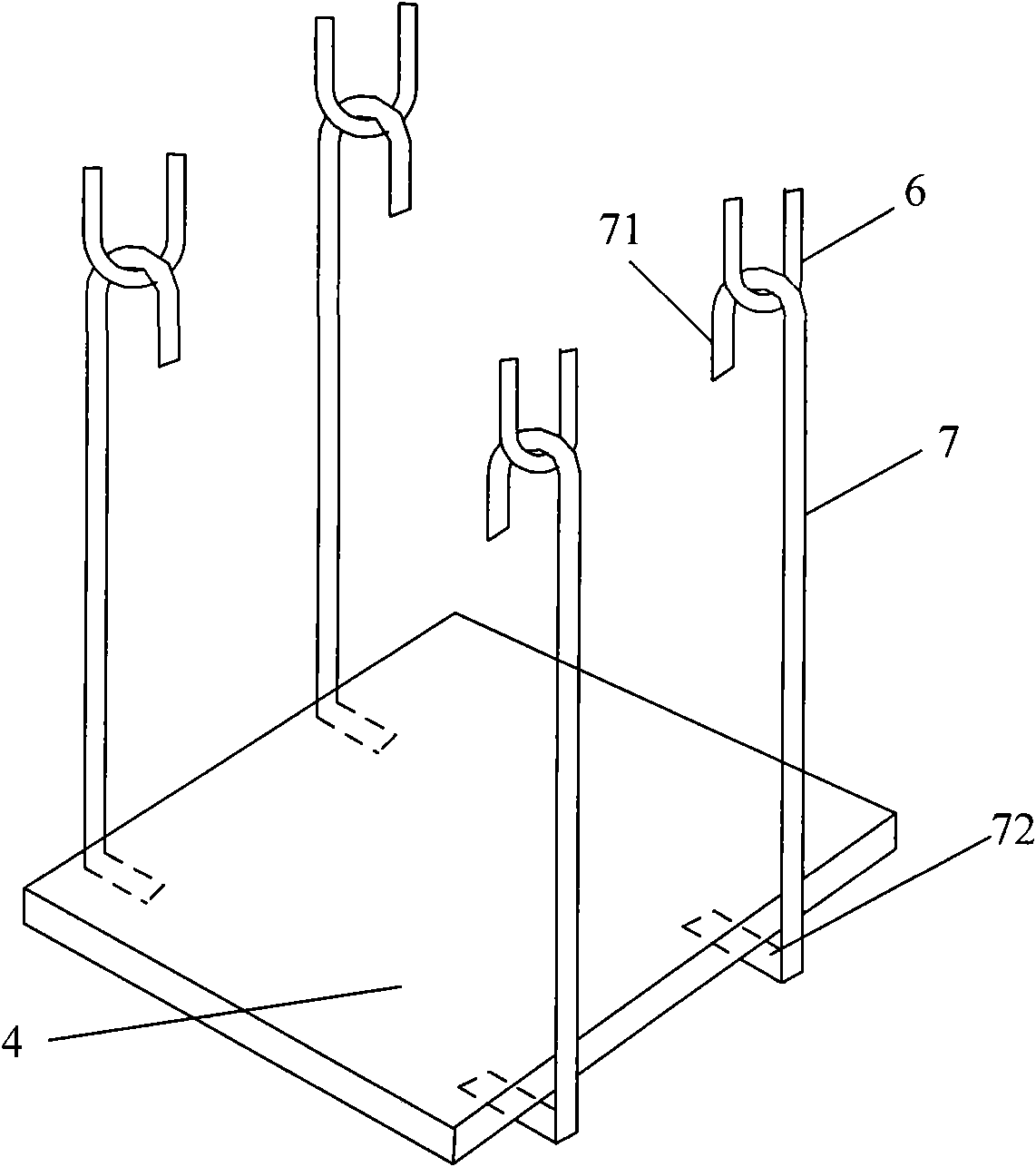
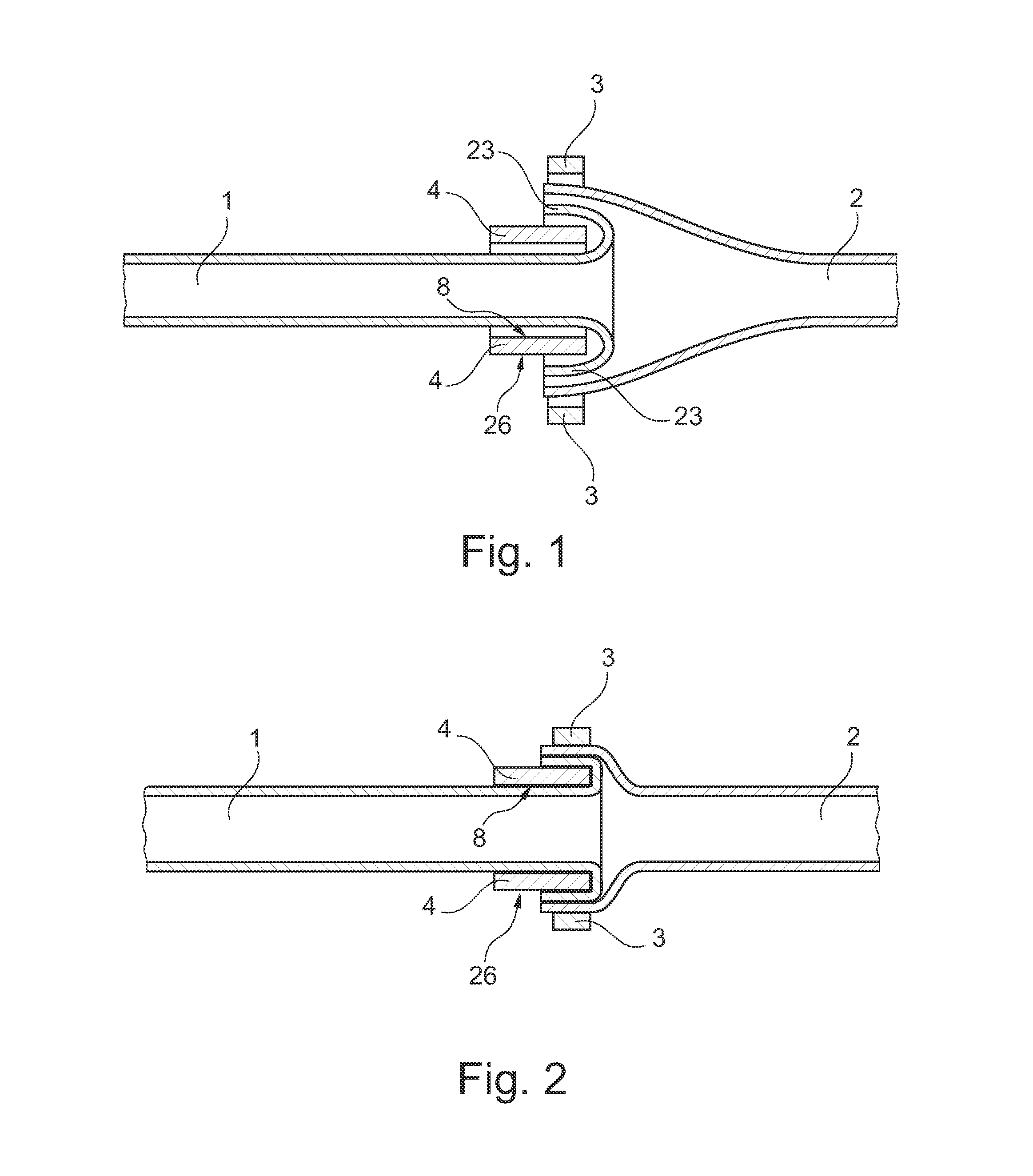
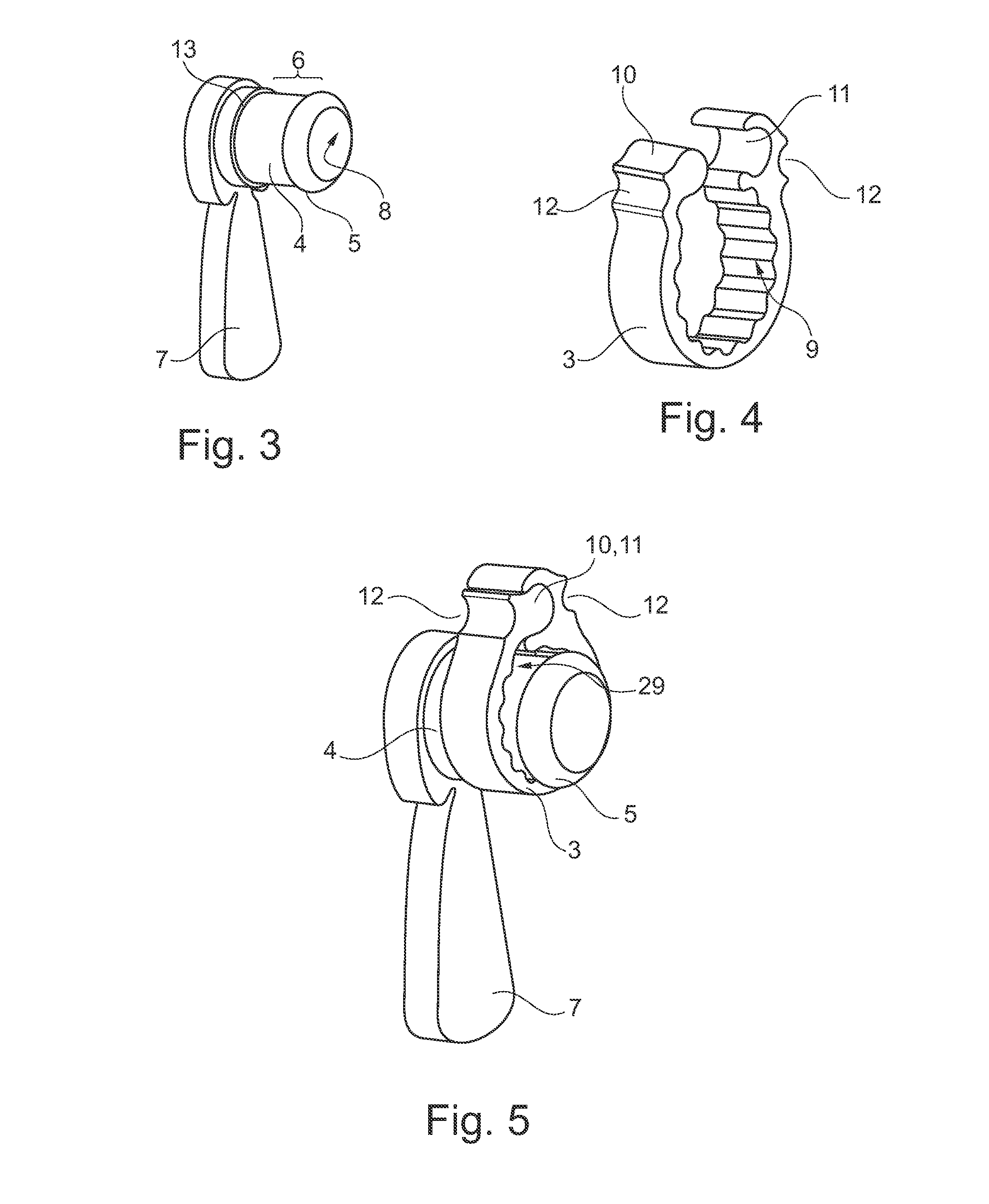
ActiveUS20130296890A1Simple and relatively fast to applyAnastomosisWound clampsMedical deviceBlood vessel
A medical device is disclosed for joining a first tubular organ (1), such as a blood vessel, to a second tubular organ (2), such as a blood vessel. The kit includes an external tubular scaffold (4) with a removable scaffold handle (7,18,19) and a clip (3). In use, the clip (3) and the external tubular scaffold (4) remain outside of the tubular organs (1,2) being joined. The clip (3) embraces a first longitudinal tubular section (6) of the external tubular scaffold (4) thereby holding together a longitudinal segment of an intima of the first tubular organ (1) and a longitudinal segment of an intima of the second tubular organ (2).
Owner:METESO
Furniture arch beam arm structure and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a furniture arch beam arm structure and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method mainly adopts the stamping mode to ensure metal plates are used to separately form different components and connectors; the components and connectors adapt to the curvatures and shapes of different parts of a preset beam arm, wherein each component contains an opening of which width is expanded slantways to one side, the connectors are connected at the openings to form a plurality of sealed hollow tubular scaffolds; and the scaffolds are connected mutually and dressed properly to form a beam arm structure with the preset and complete curvature and shape which is used to connected with other furniture component. The tubular structure formed by metal material is used to replace the original wooden beam arm structure, thus reducing the material cost, simplifying the processing procedure of the arch beam arm structure in the furniture and increasing the overall production efficiency.
Owner:NEW CHANNEL
Innervation of engineered structures
Methods of generating an innervated muscle structures are disclosed as well as bioengineered structures for tissue repair or regeneration. The methods can include the steps of obtaining populations of smooth muscle cells and neuronal progenitor cells and then seeding the cells together onto a matrix material, followed by culturing the seeded cells to form an innervated smooth muscle cell construct of directionally oriented smooth muscle cells. In one embodiment, the neuronal progenitor cells can be seeded first as neurospheres in a biocompatible solution, e.g., a collagen / laminin solution, and allowed to gel. Next, a second suspension of smooth muscle cells can be deposited as separate layer. Multiple layer structures of alternating muscle or neuron composition can also be formed in this manner. Differentiation of the neuronal progenitor cells can be induced by exposure to a differentiation medium, such as Neurobasal A medium and / or exposure to a differentiating agent, such as B-27 supplement. The innervated muscle structures can be disposed around a tubular scaffold, e.g., a chitosan-containing tube and further cultured to form tubular, bioengineered structures and two or more innervated muscle structures can be joined together to form an elongate composite structure.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Retrievable stent system
A system for treating a body lumen including a first stent configured to be positioned in a body lumen and a second stent configured to be positioned in the lumen of the first stent prior to removing the first stent from the body lumen. The first stent includes a liner disposed radially inward of the tubular scaffold of the first stent to permit tissue ingrowth within a tissue ingrowth region defined between the liner and the tubular scaffold. The retrieval stent is configured to be expanded within the previously implanted first stent to cause tissue to recede from the tissue ingrowth region to facilitate removal of the first stent from the body lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com