Patents
Literature
99 results about "Catheter valves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
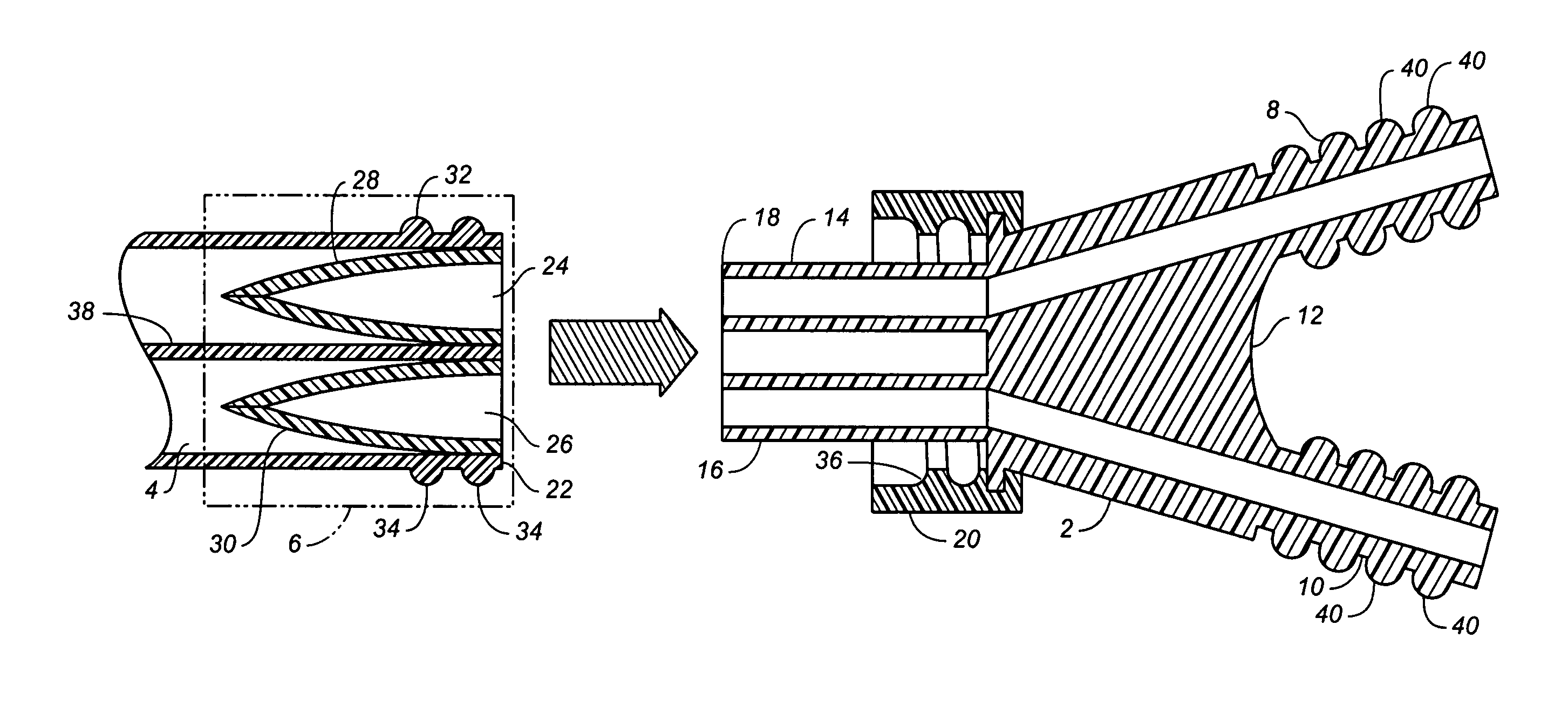
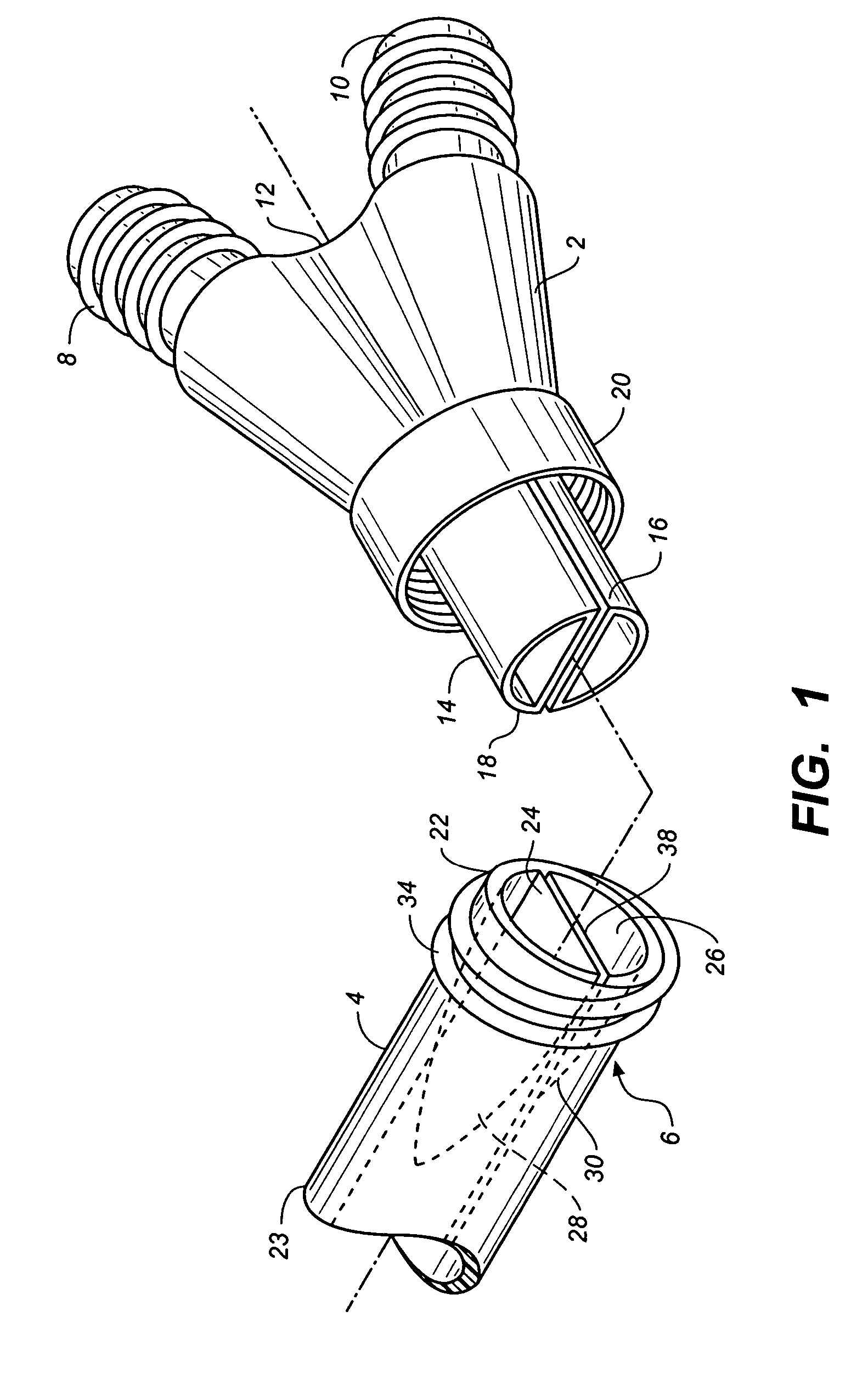
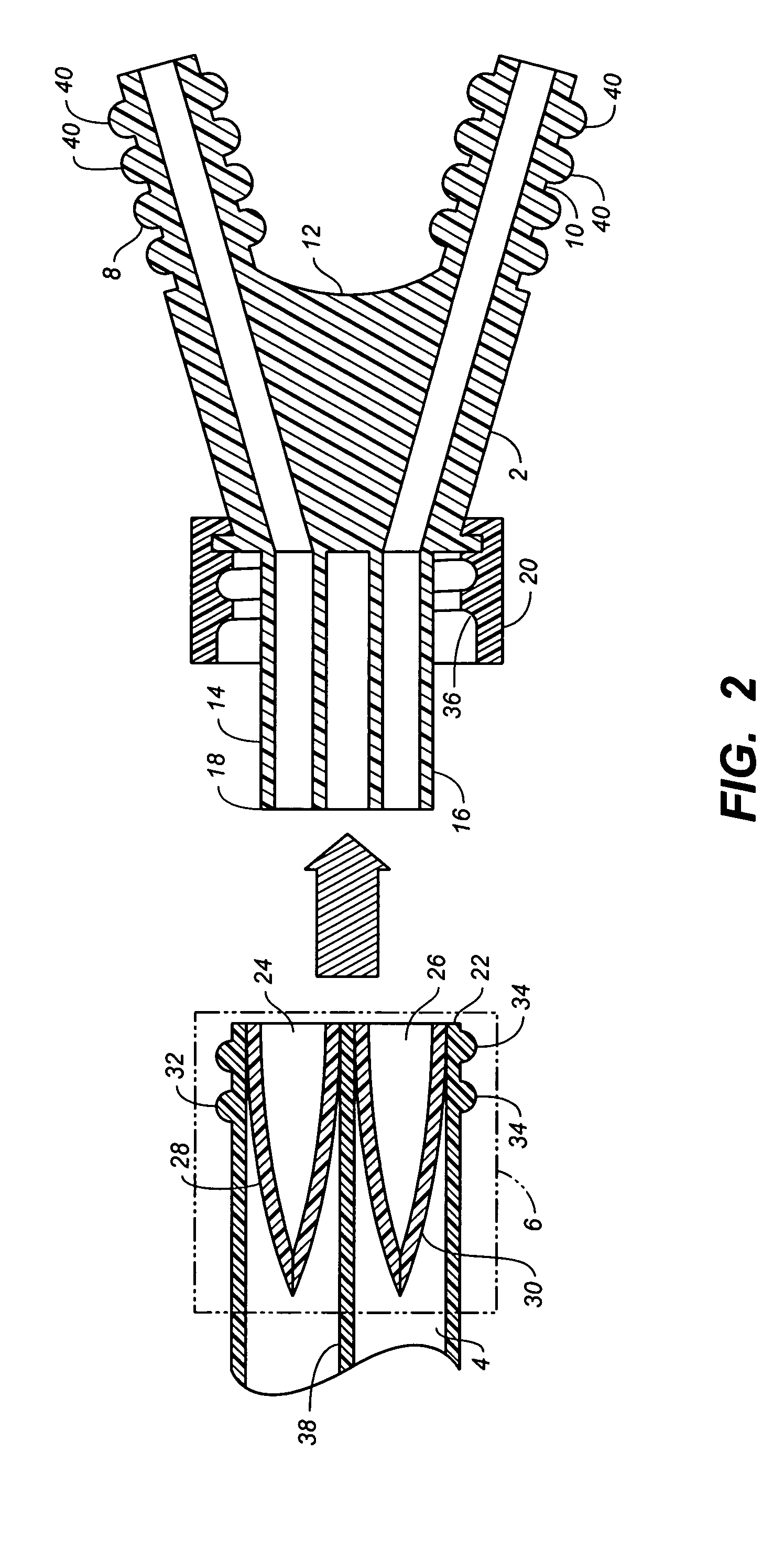
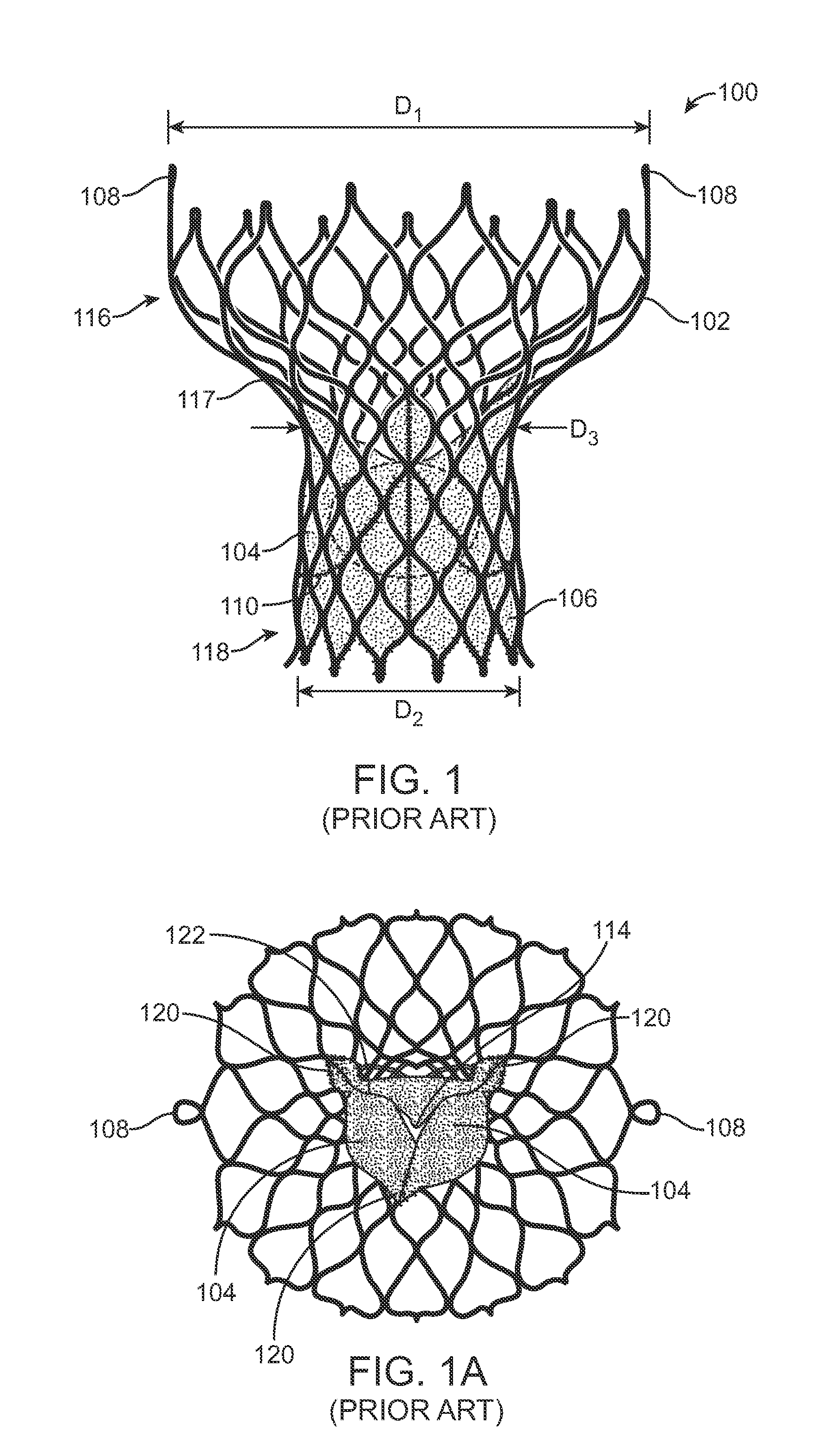
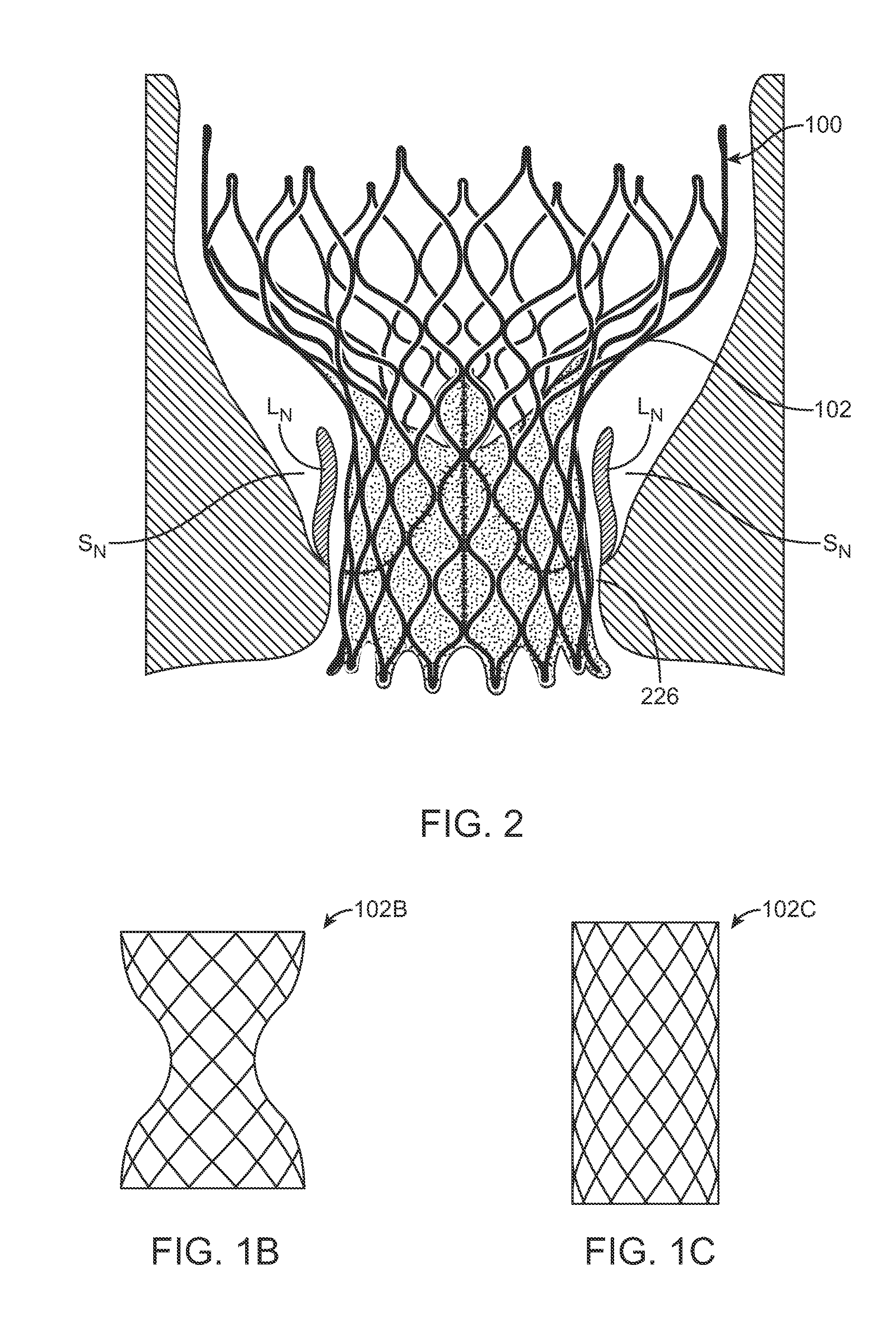
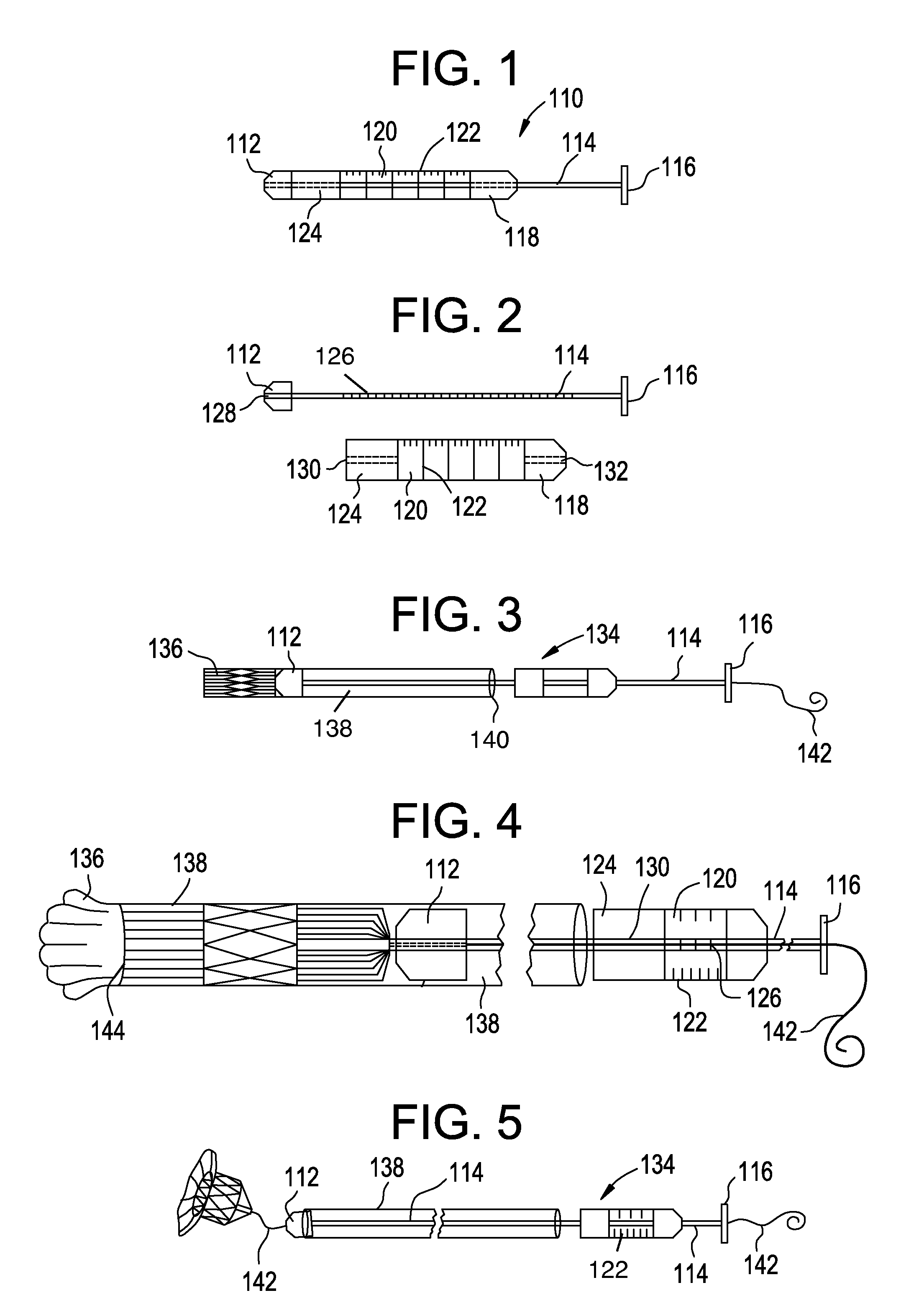
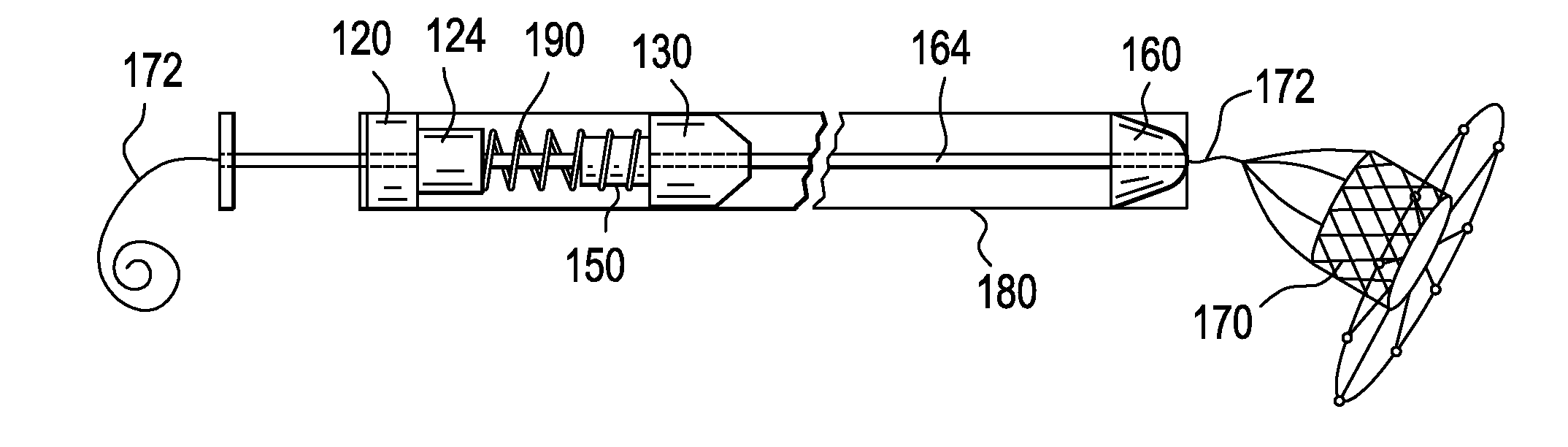
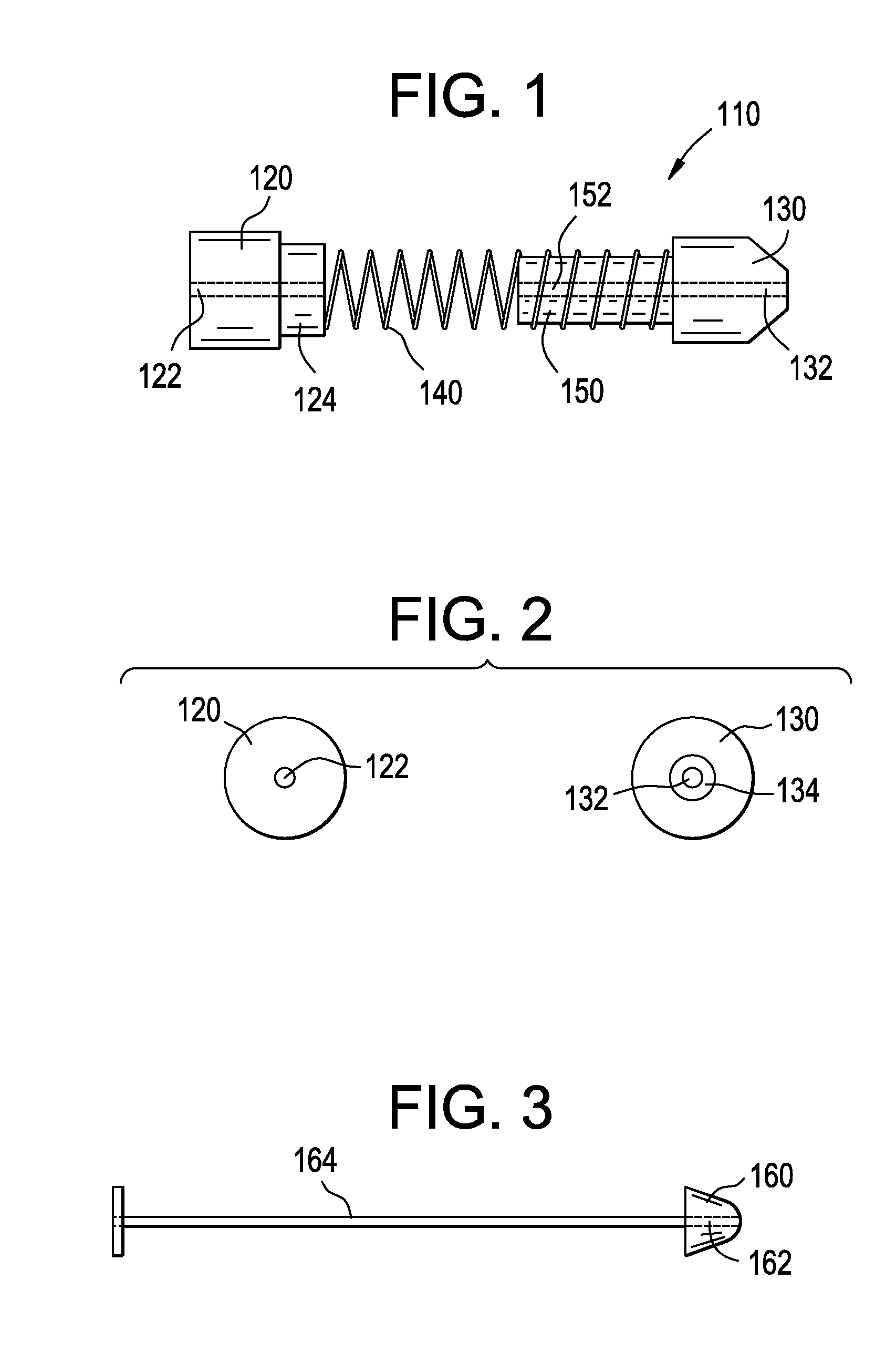
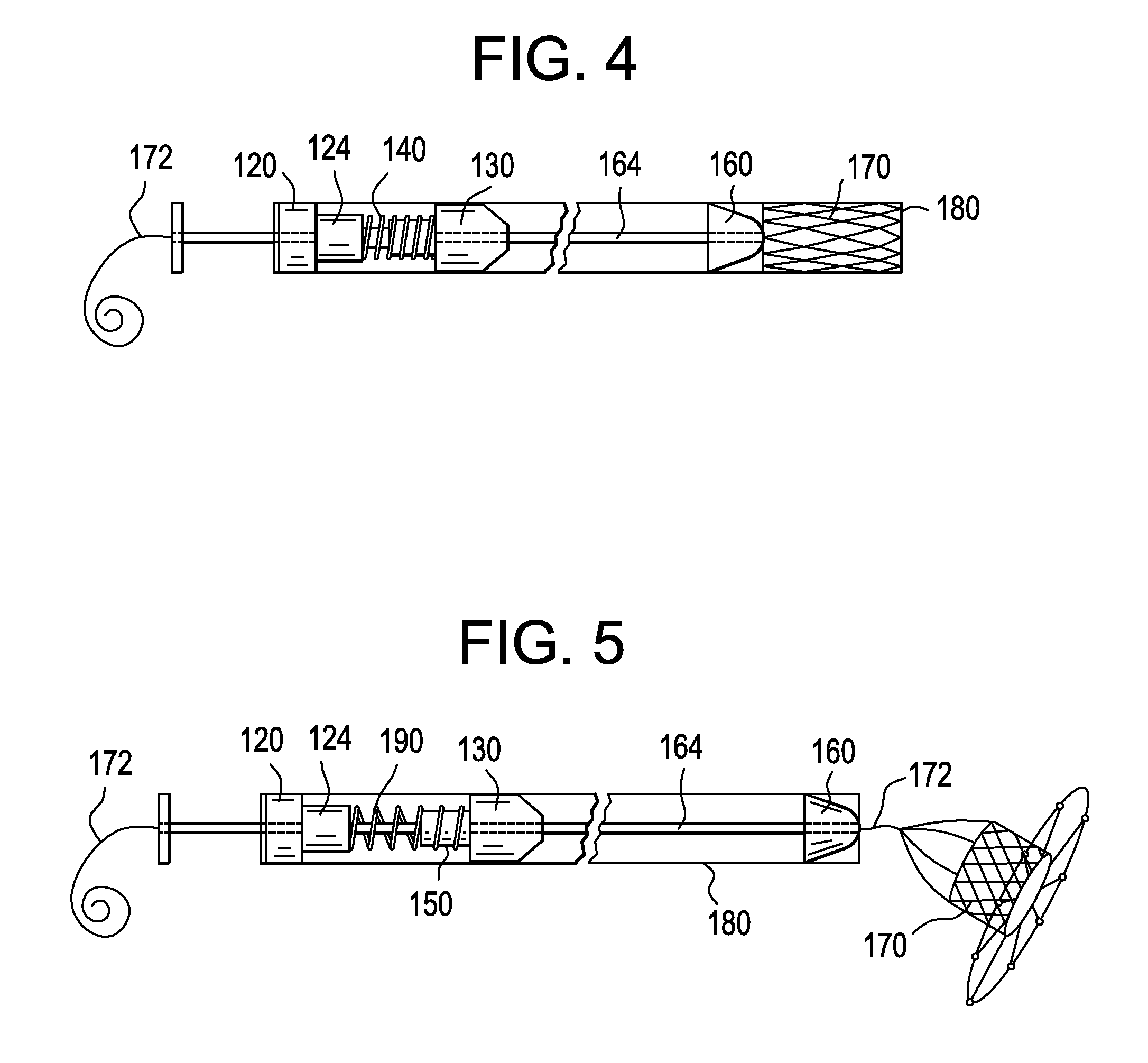
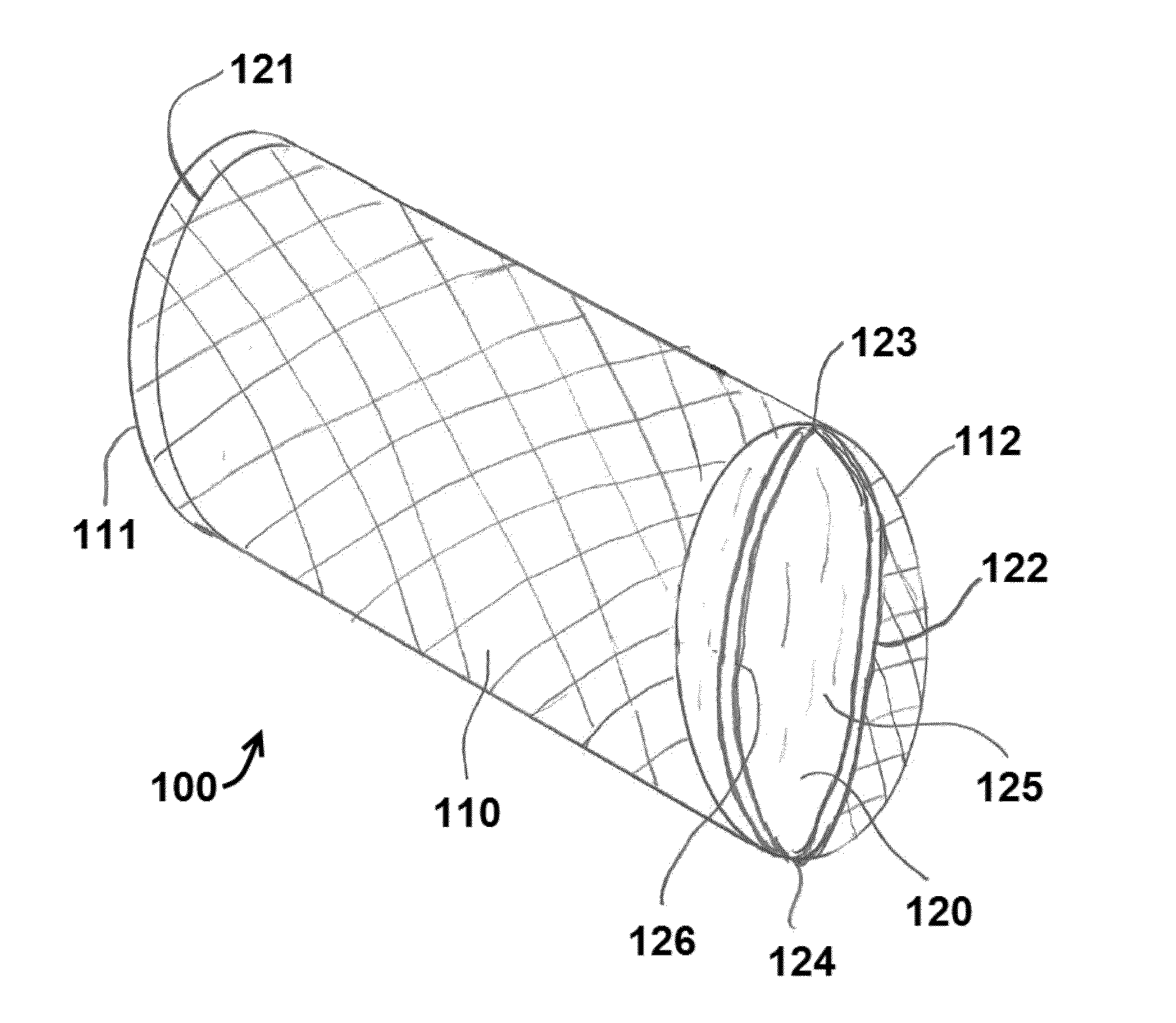
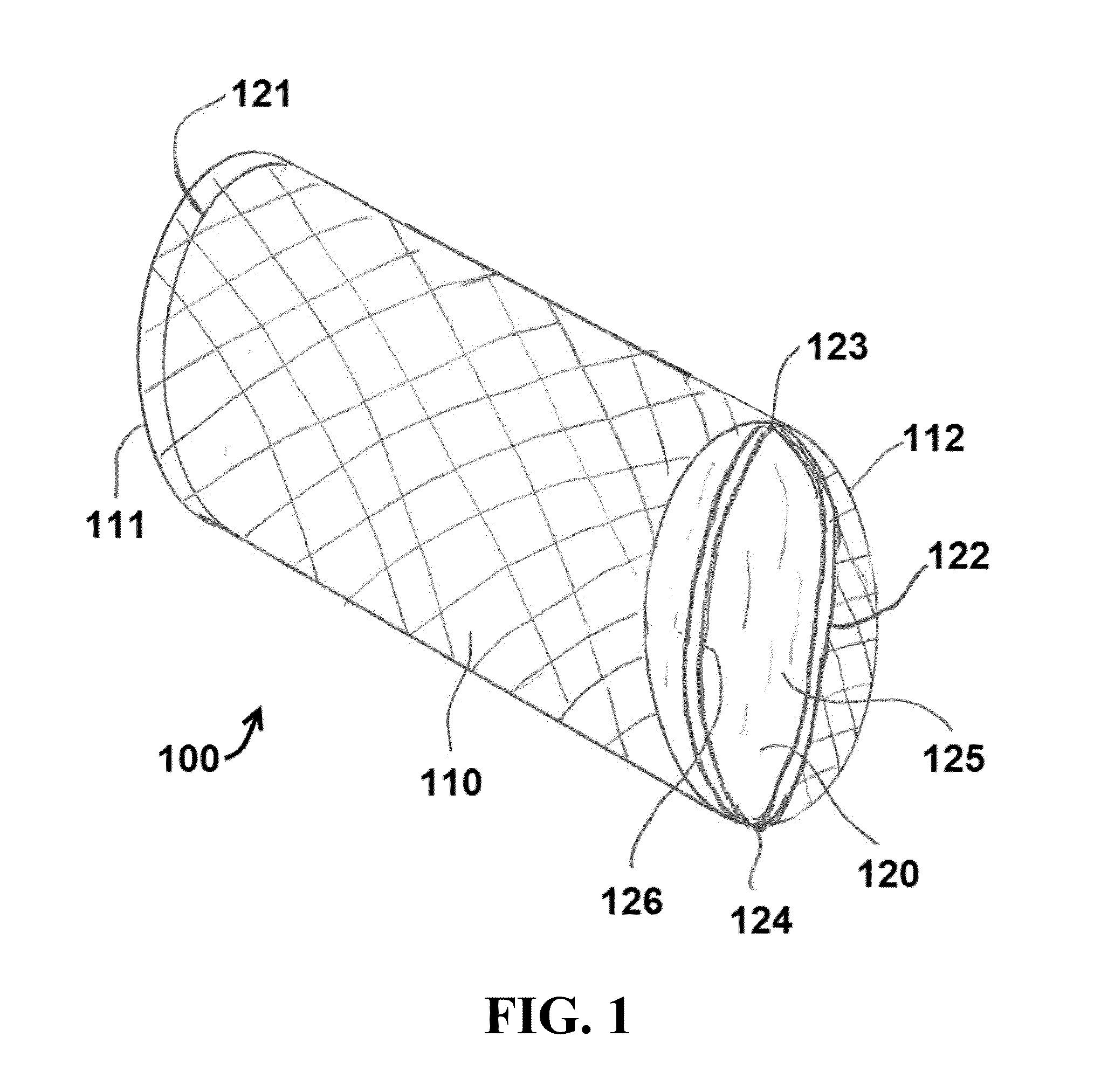
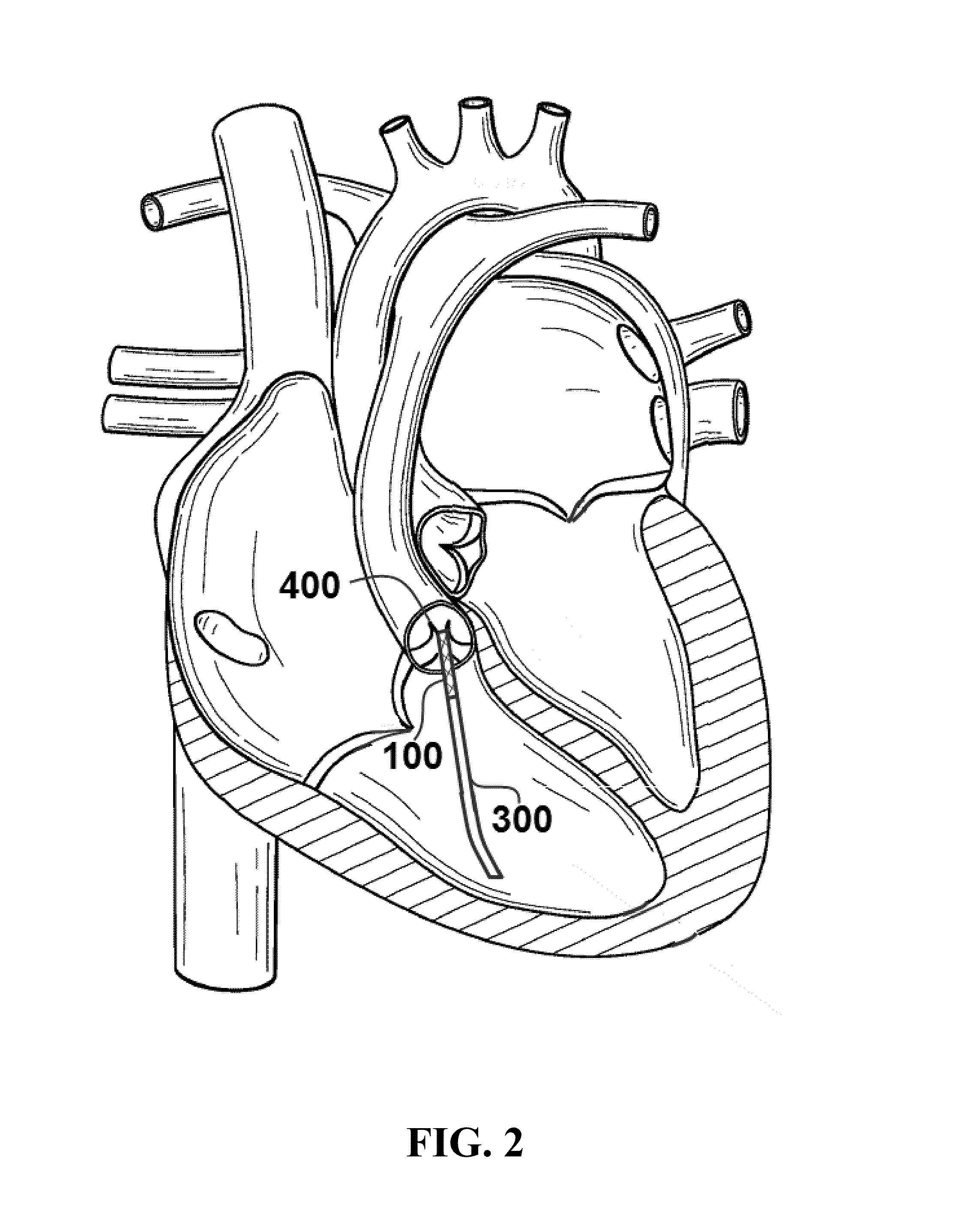
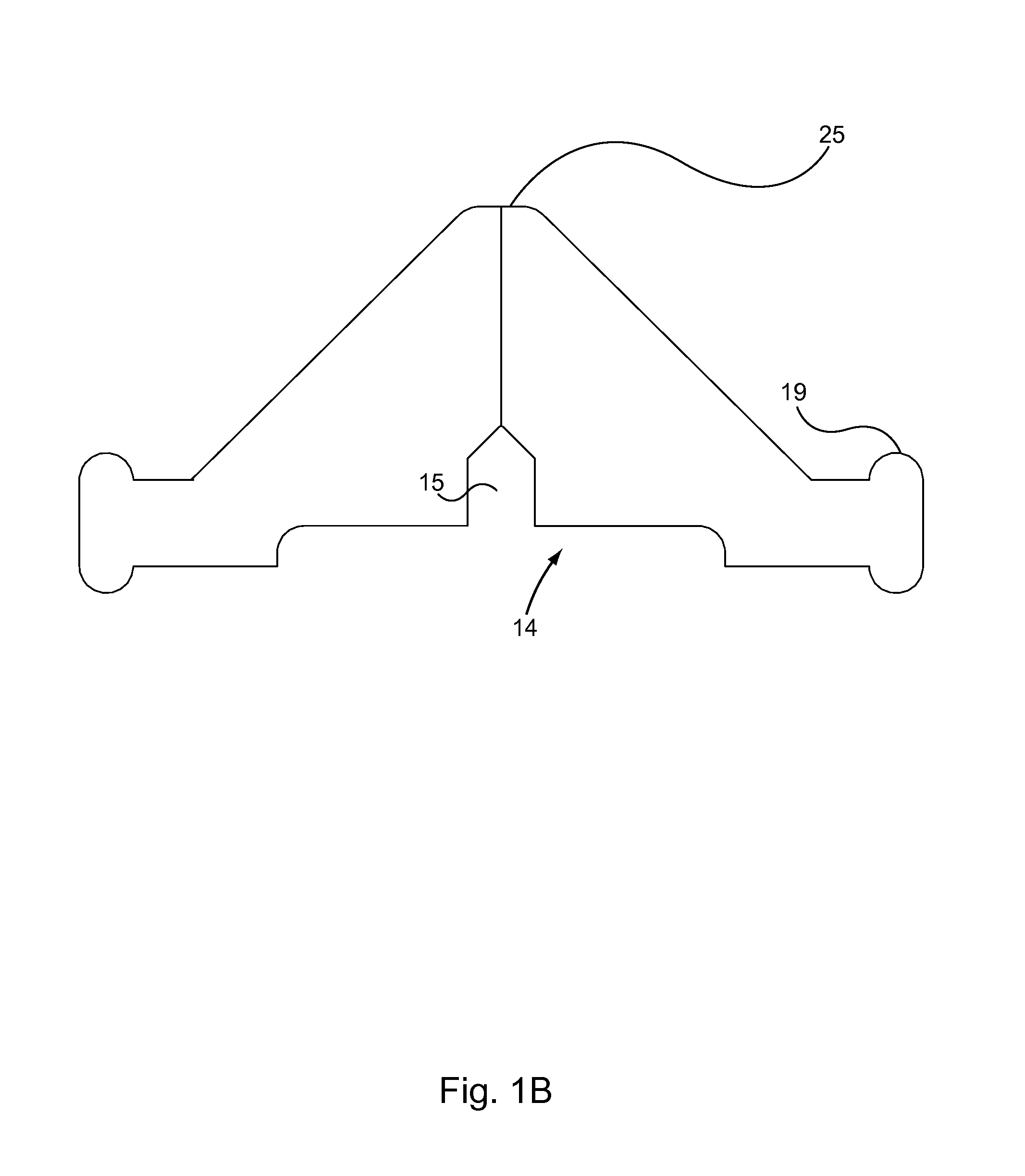
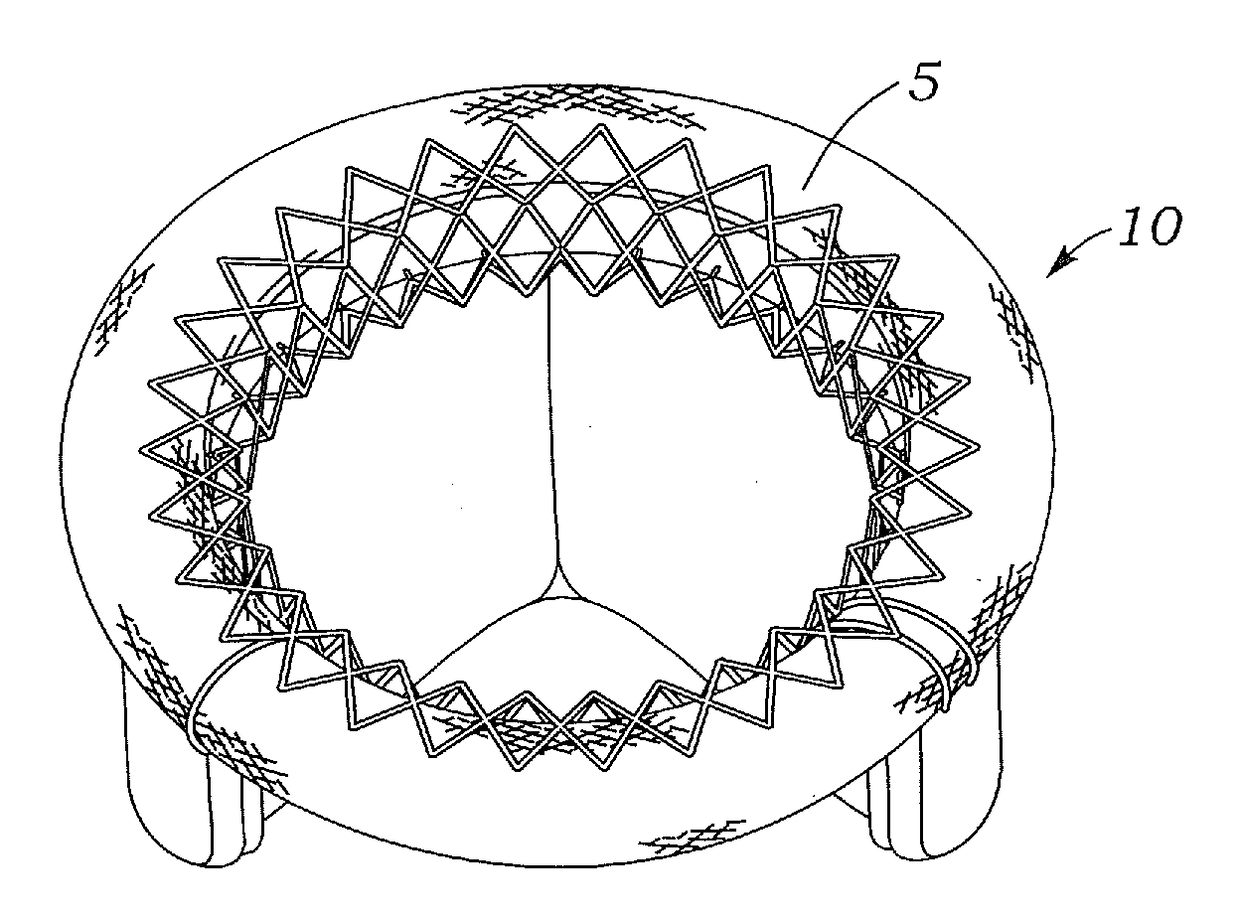
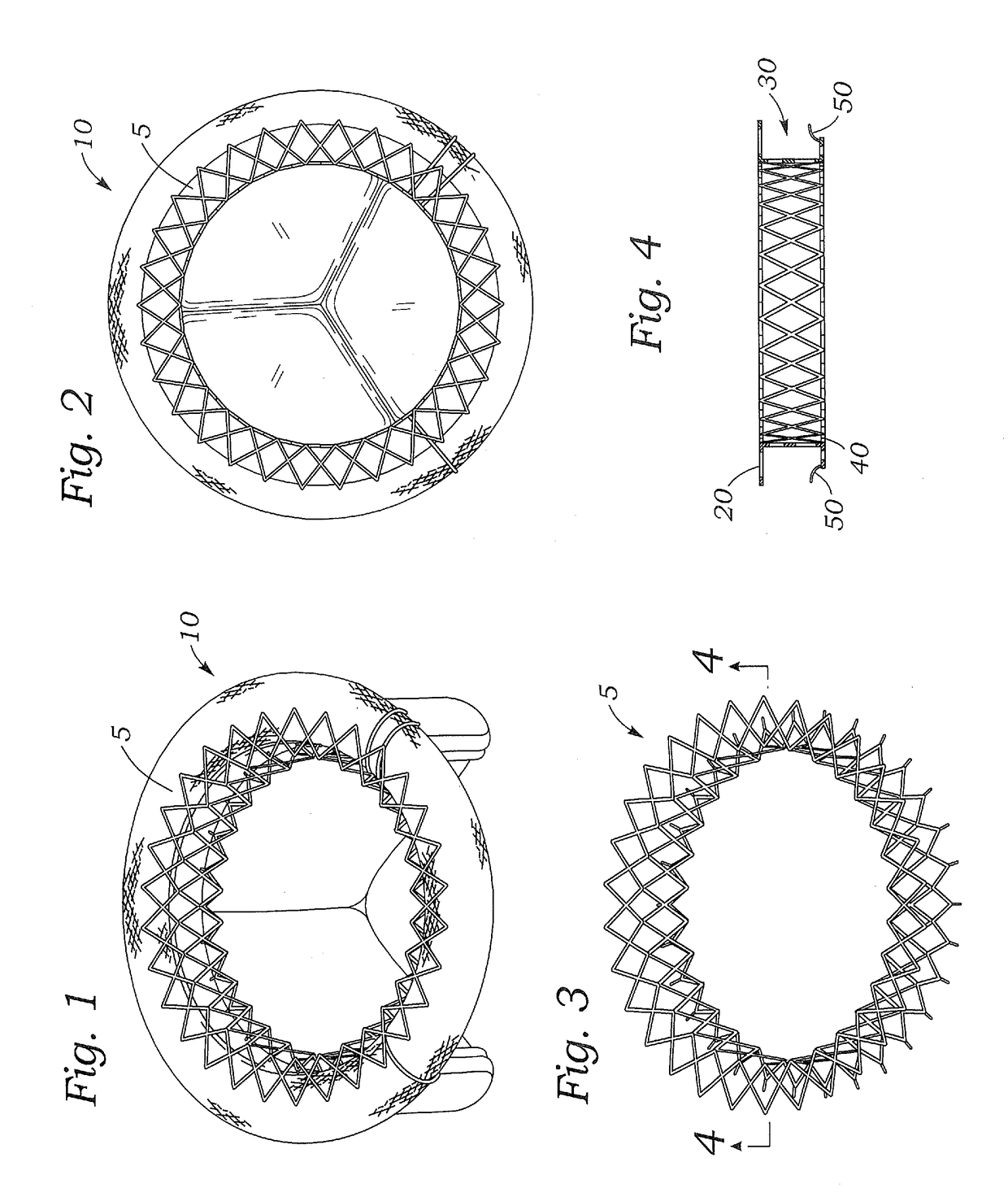
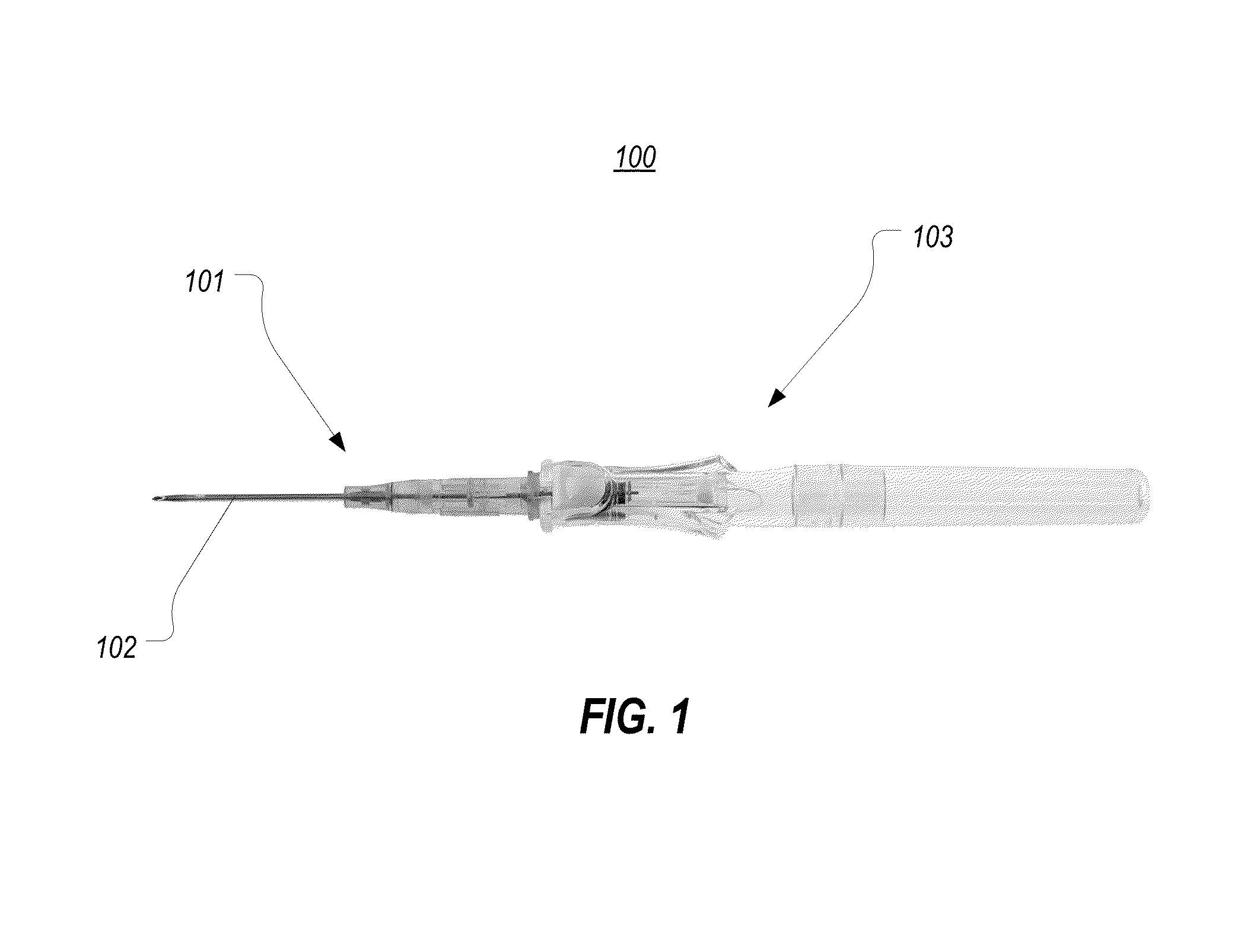
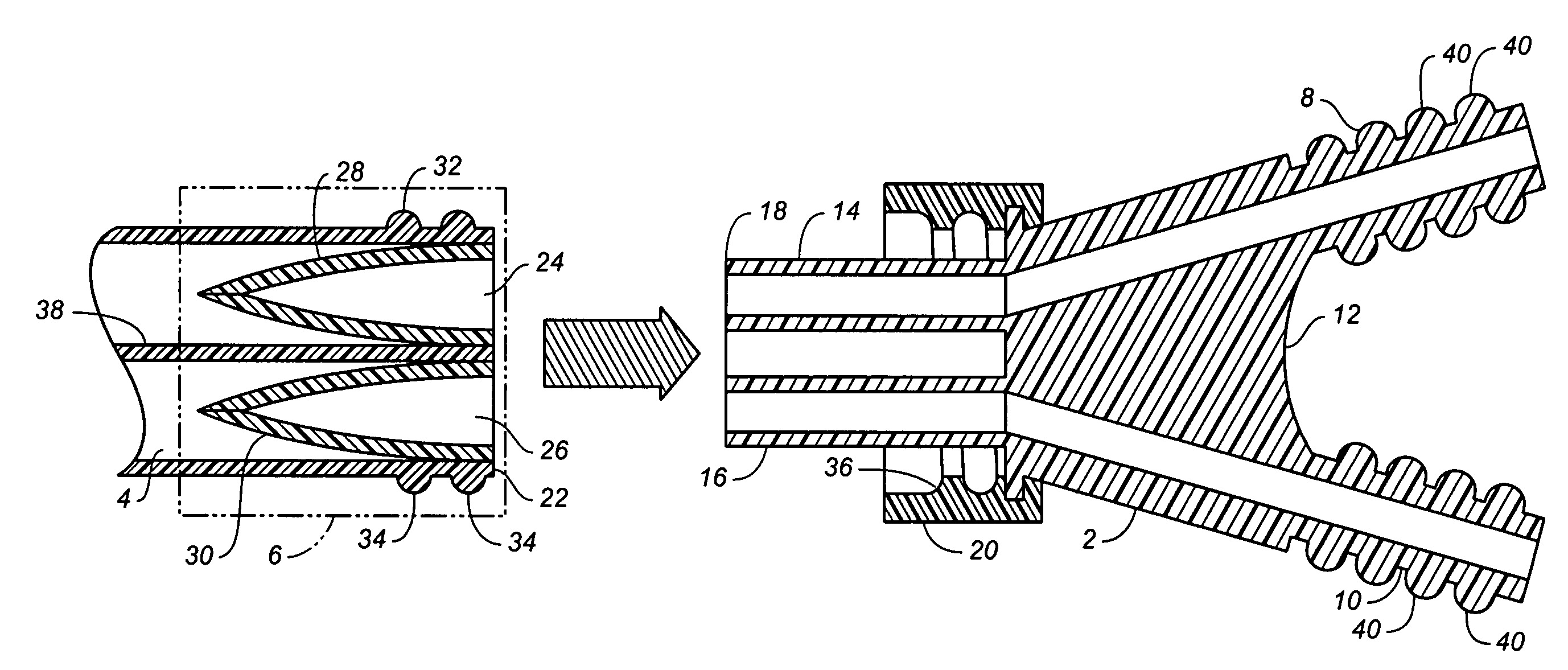
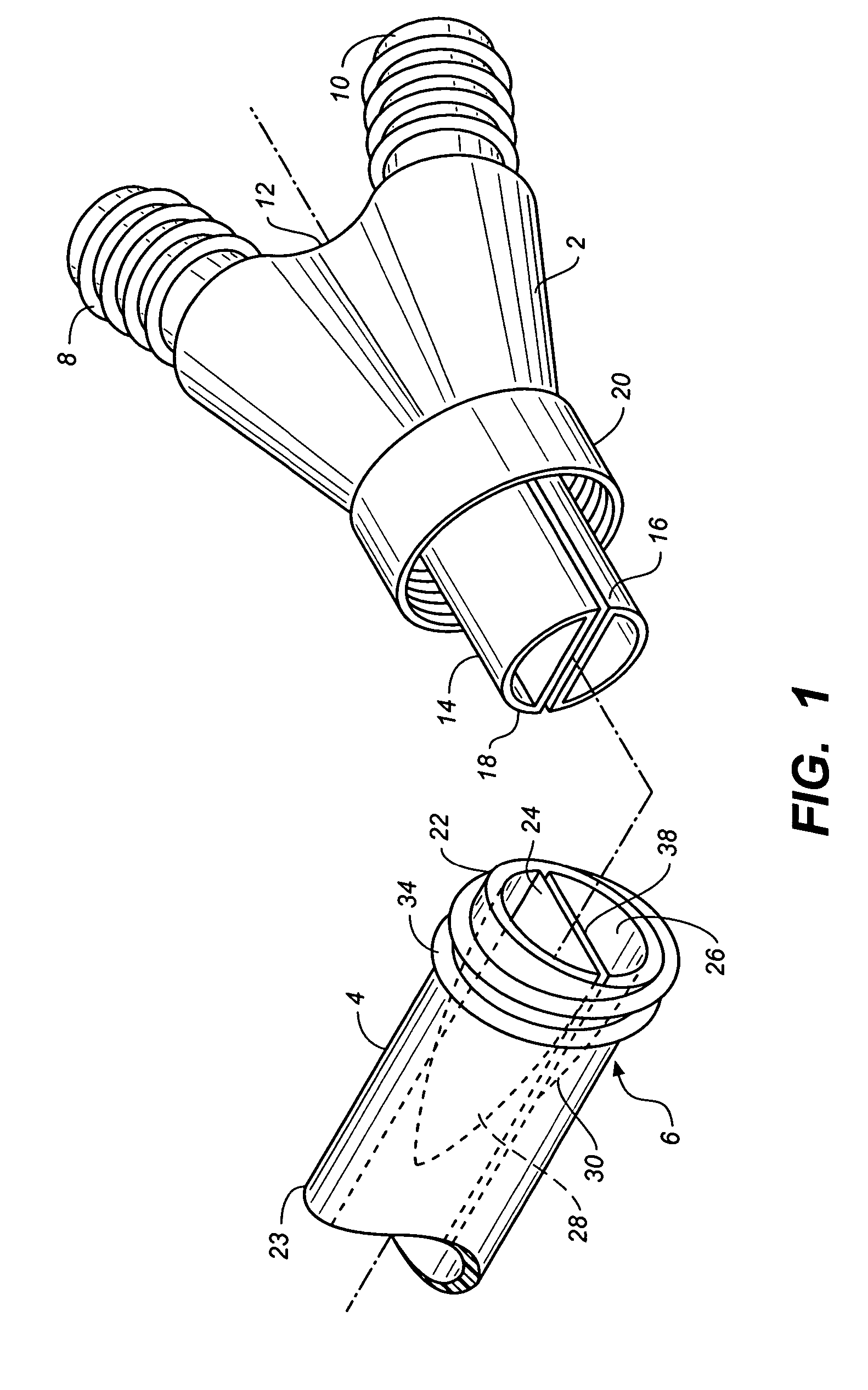
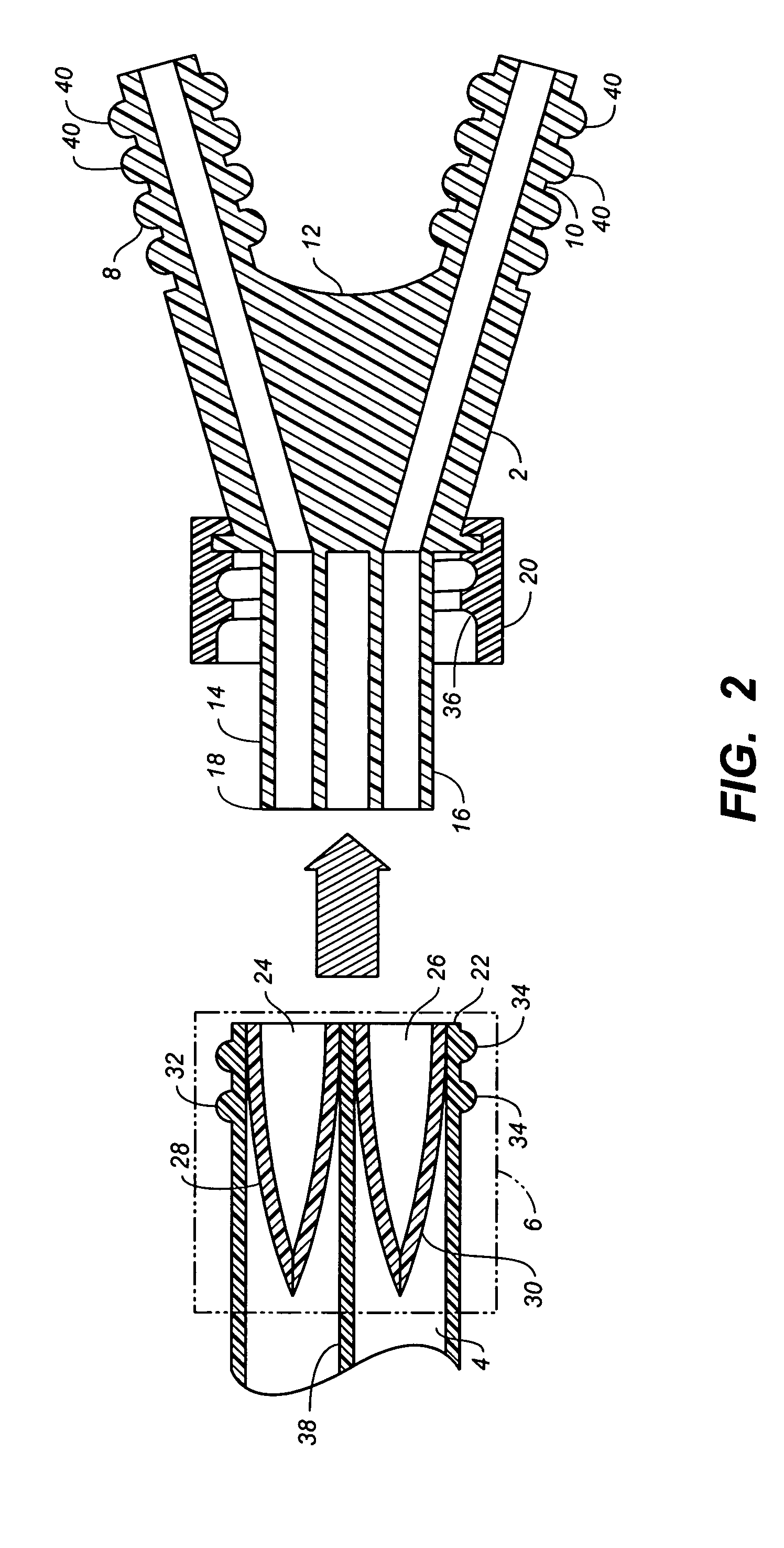
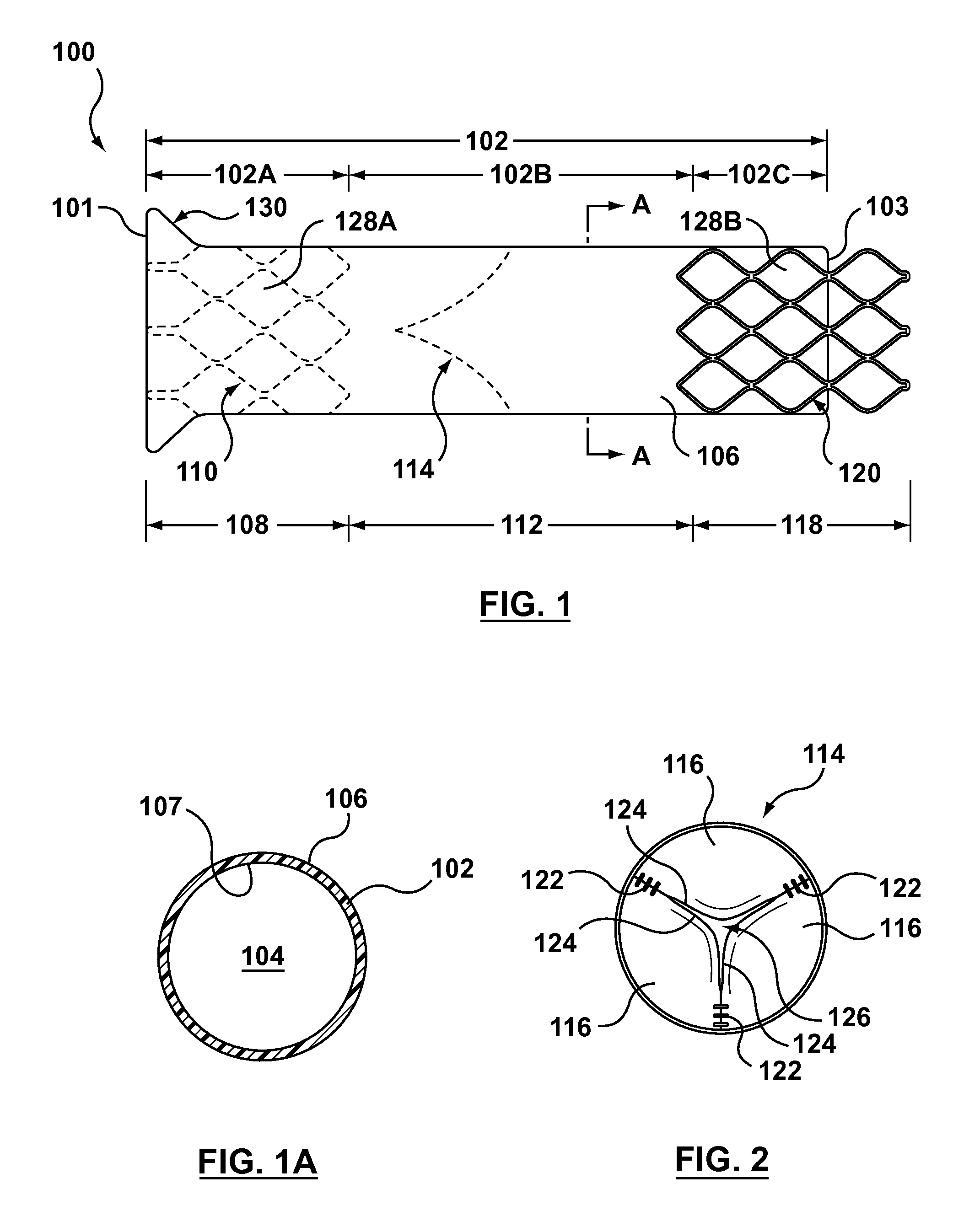
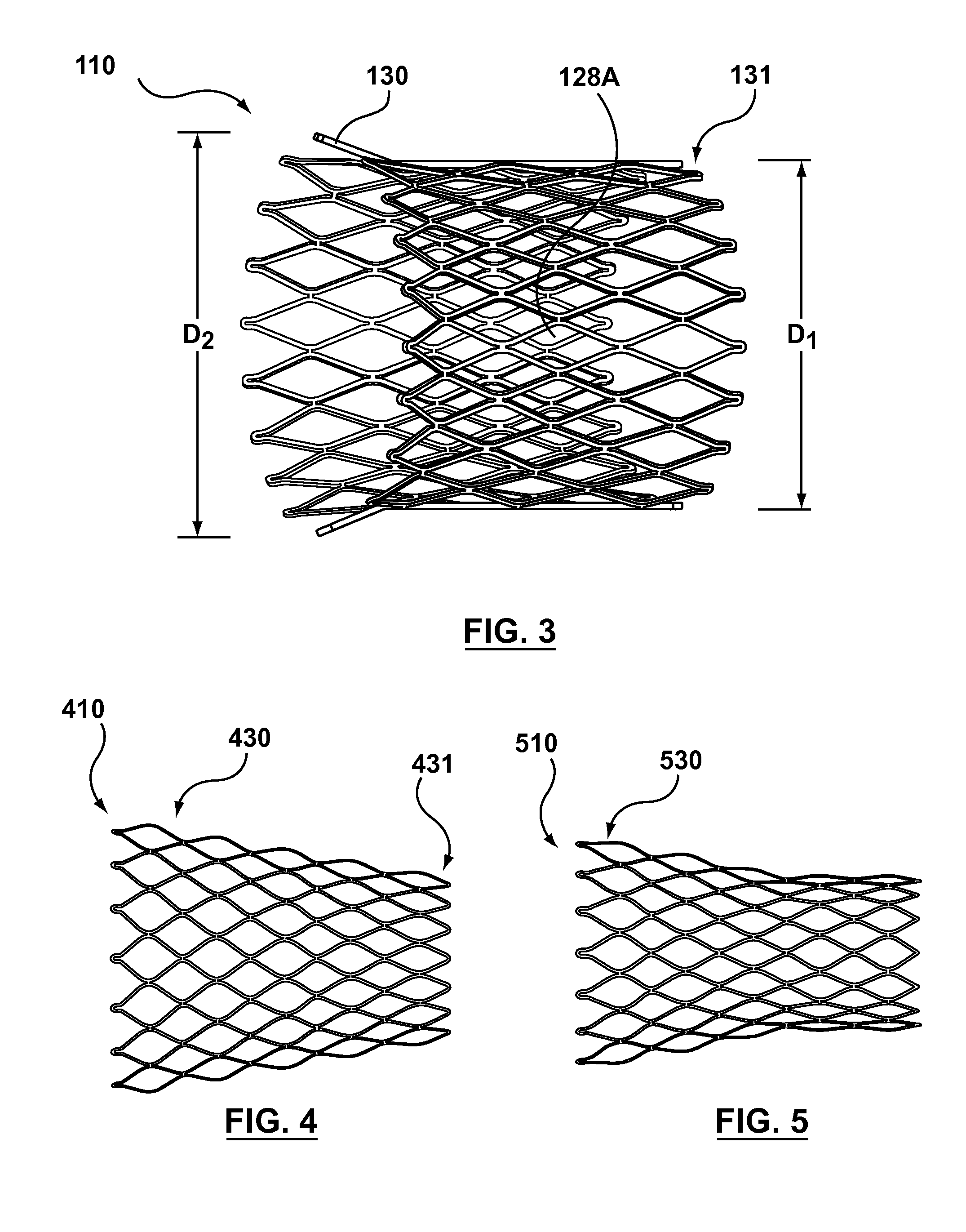
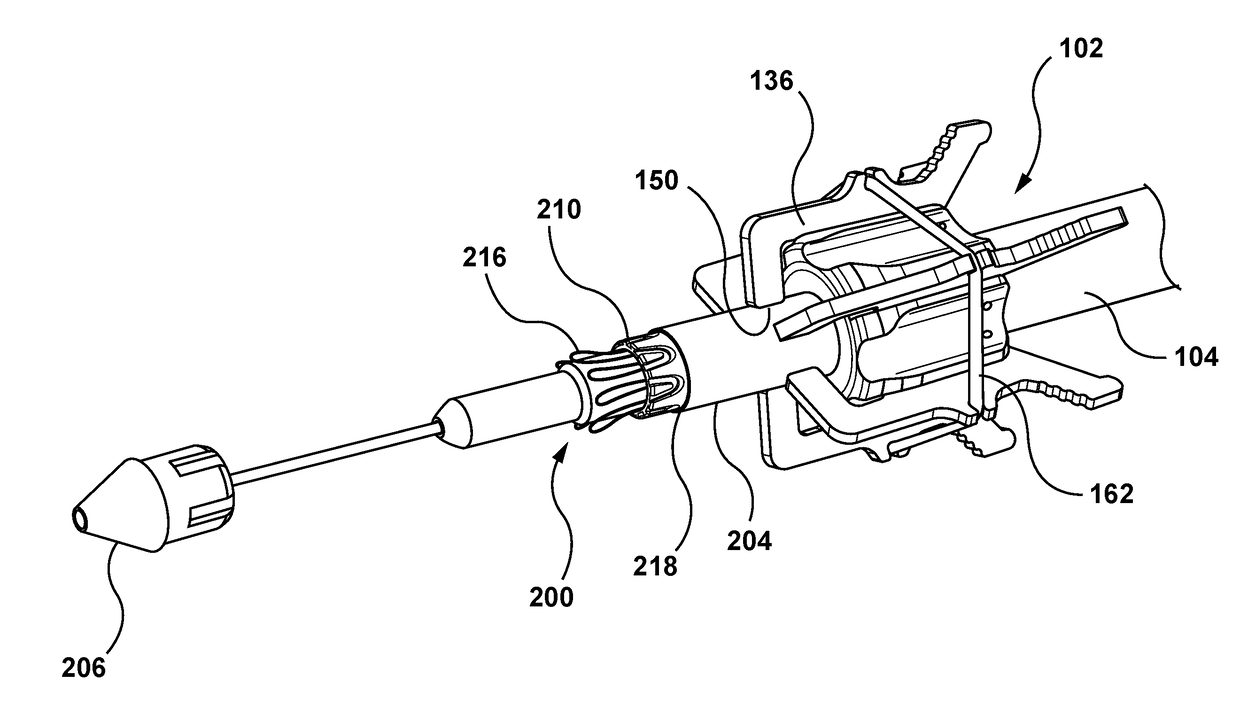
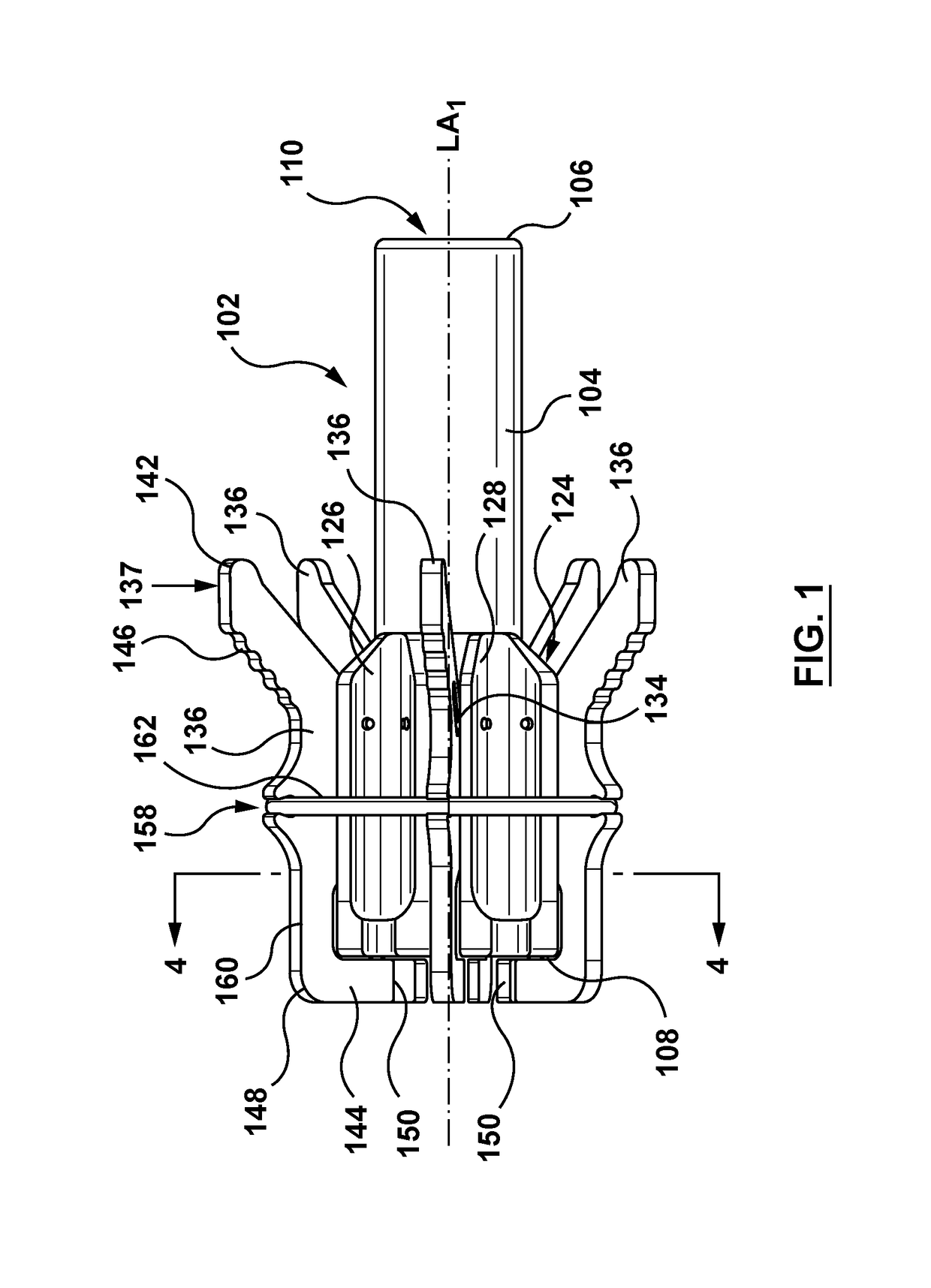
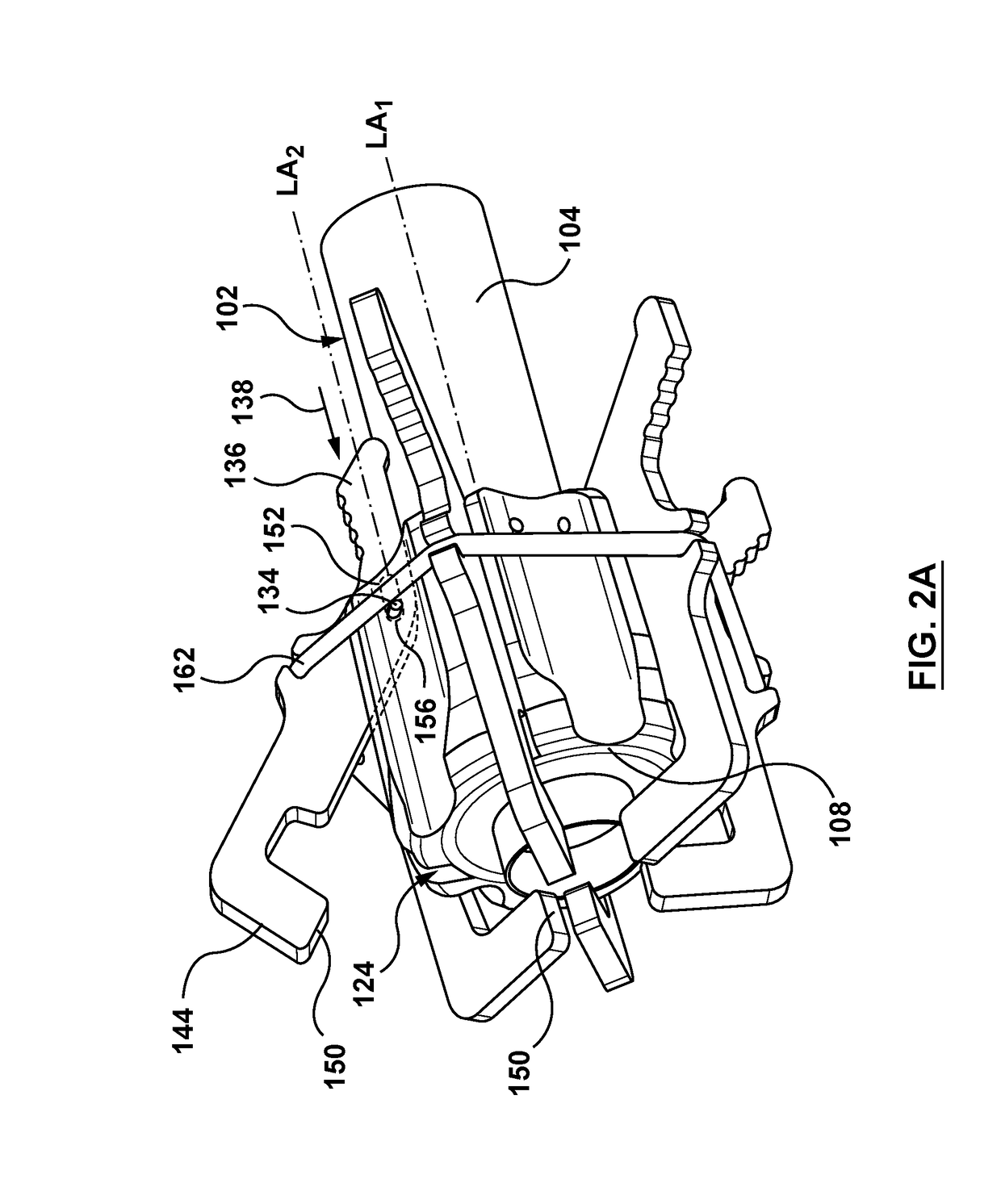
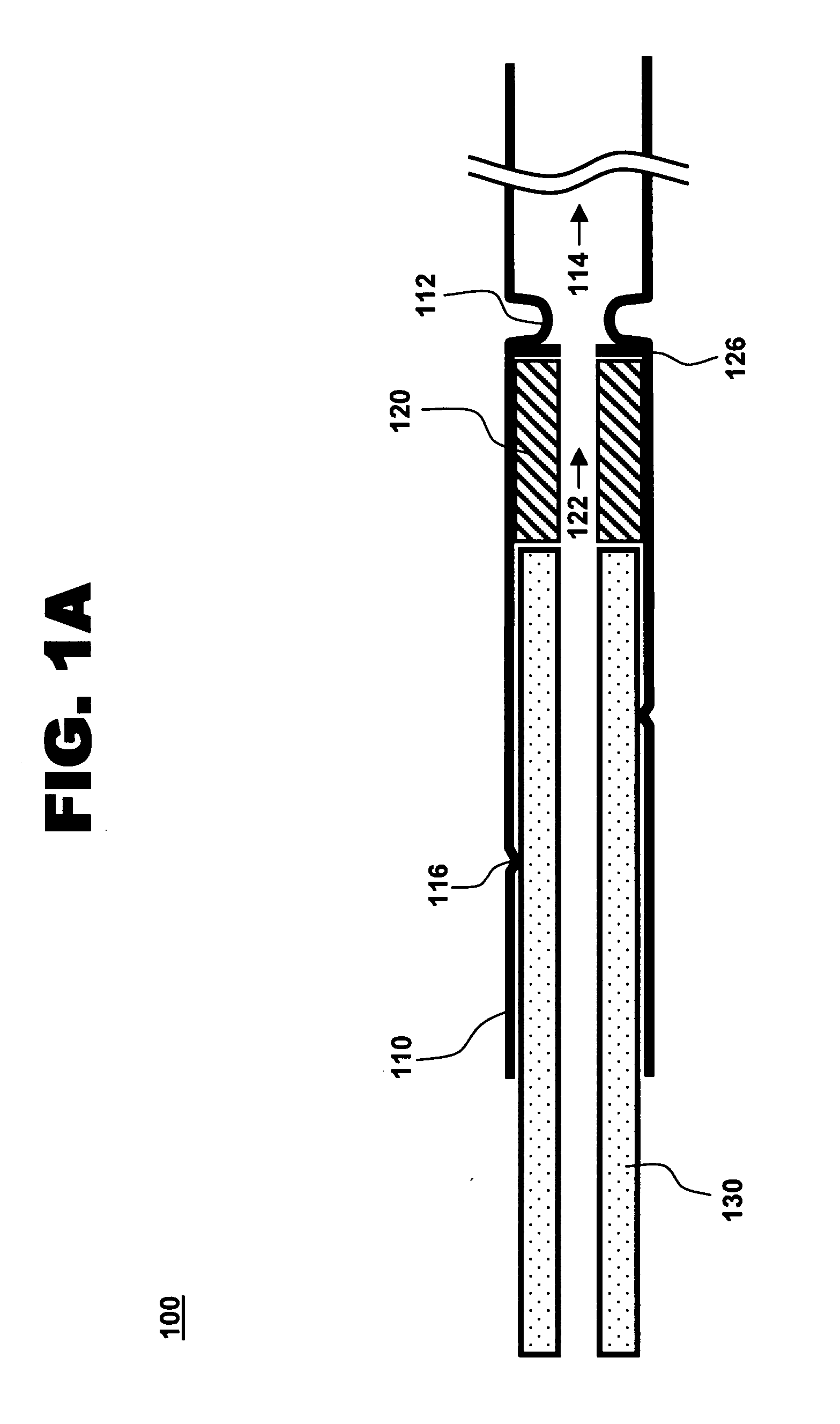
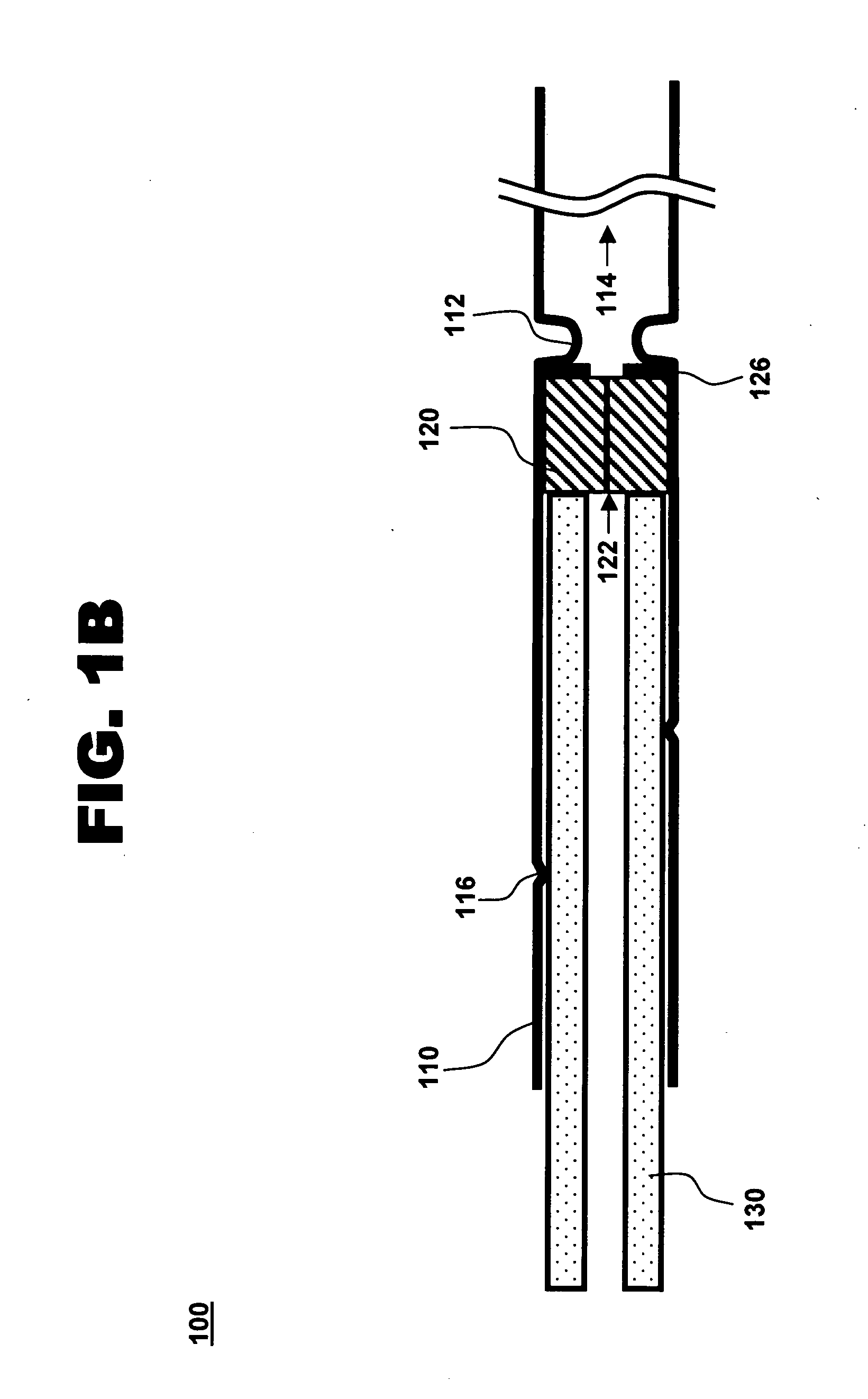
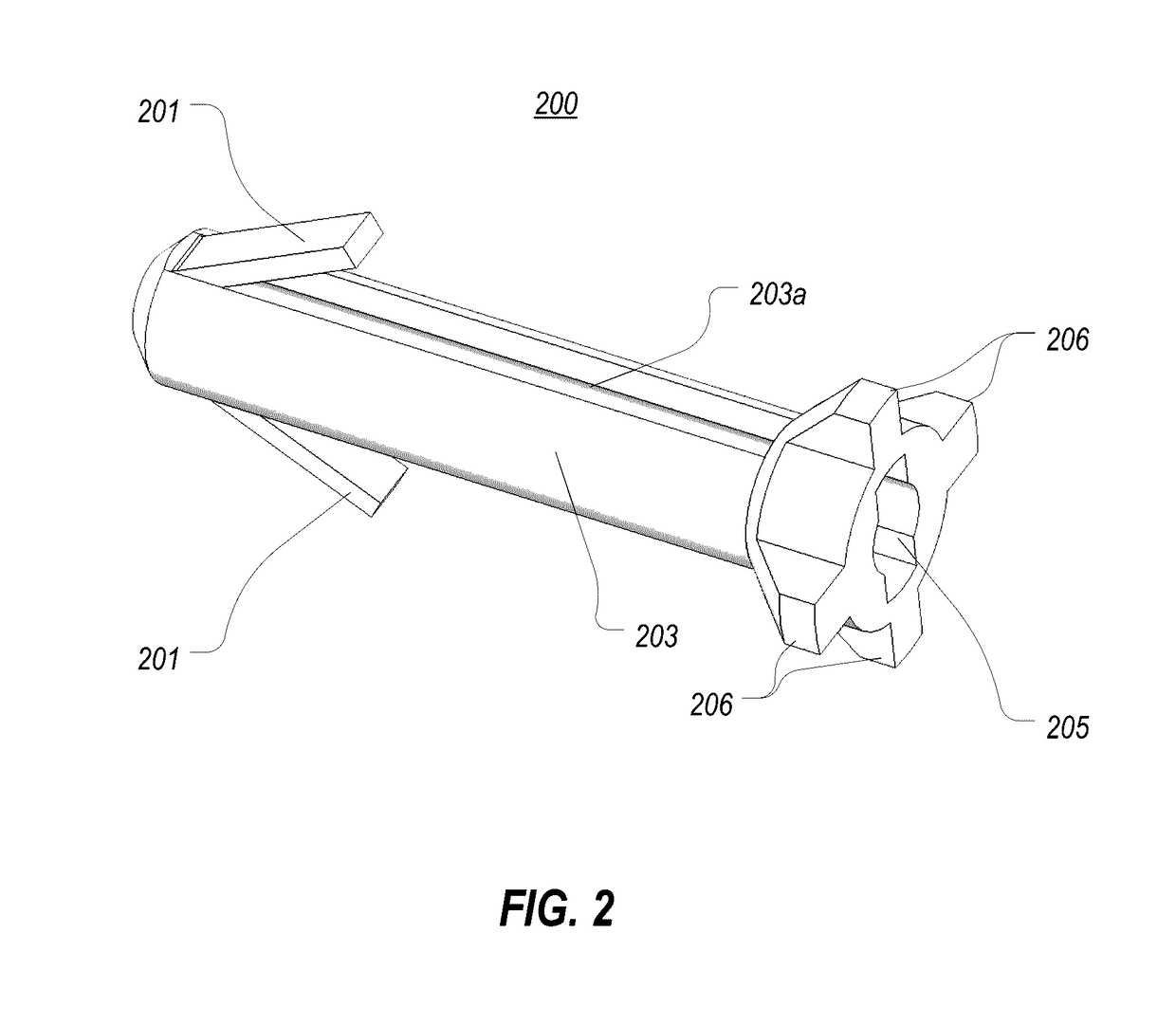
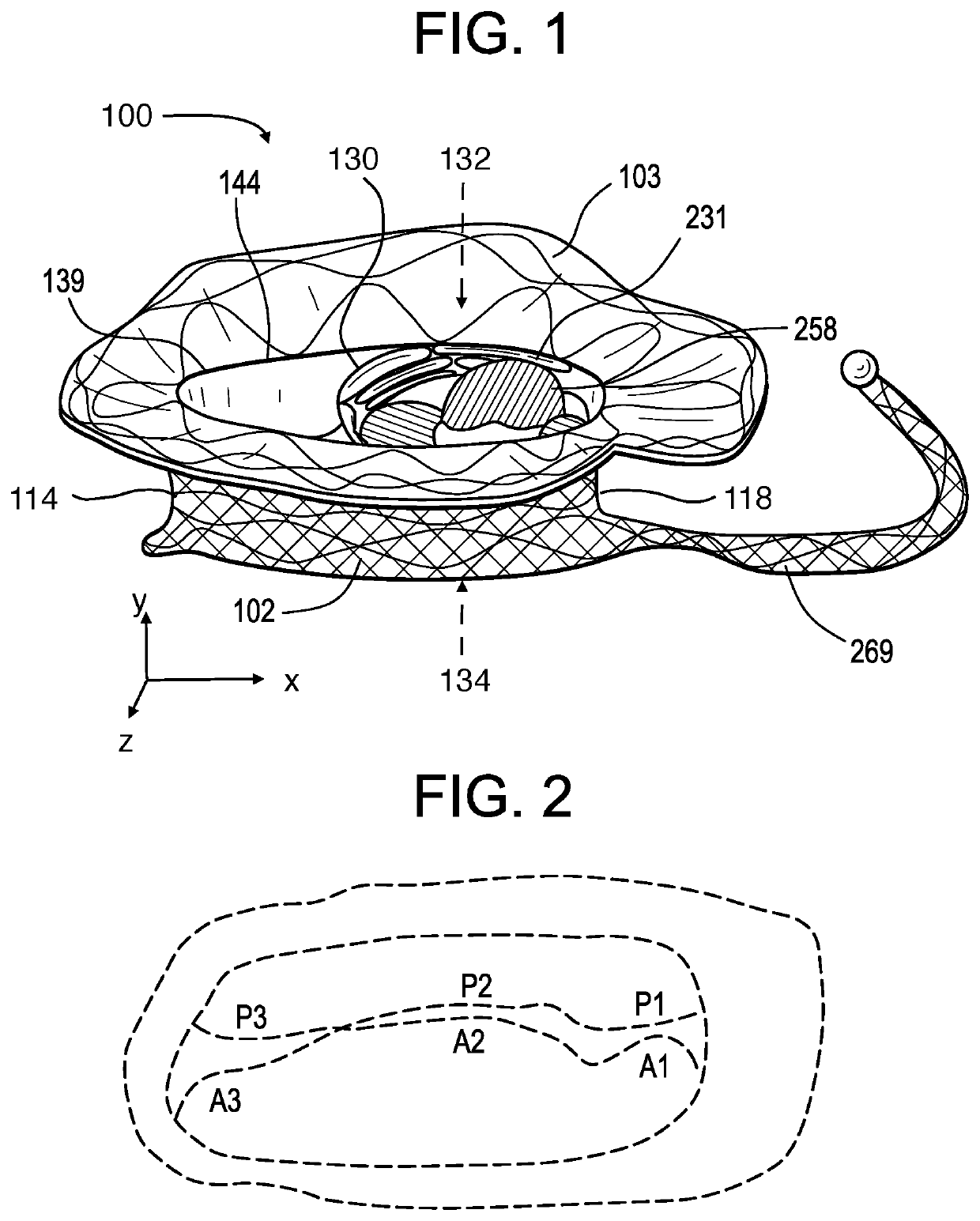
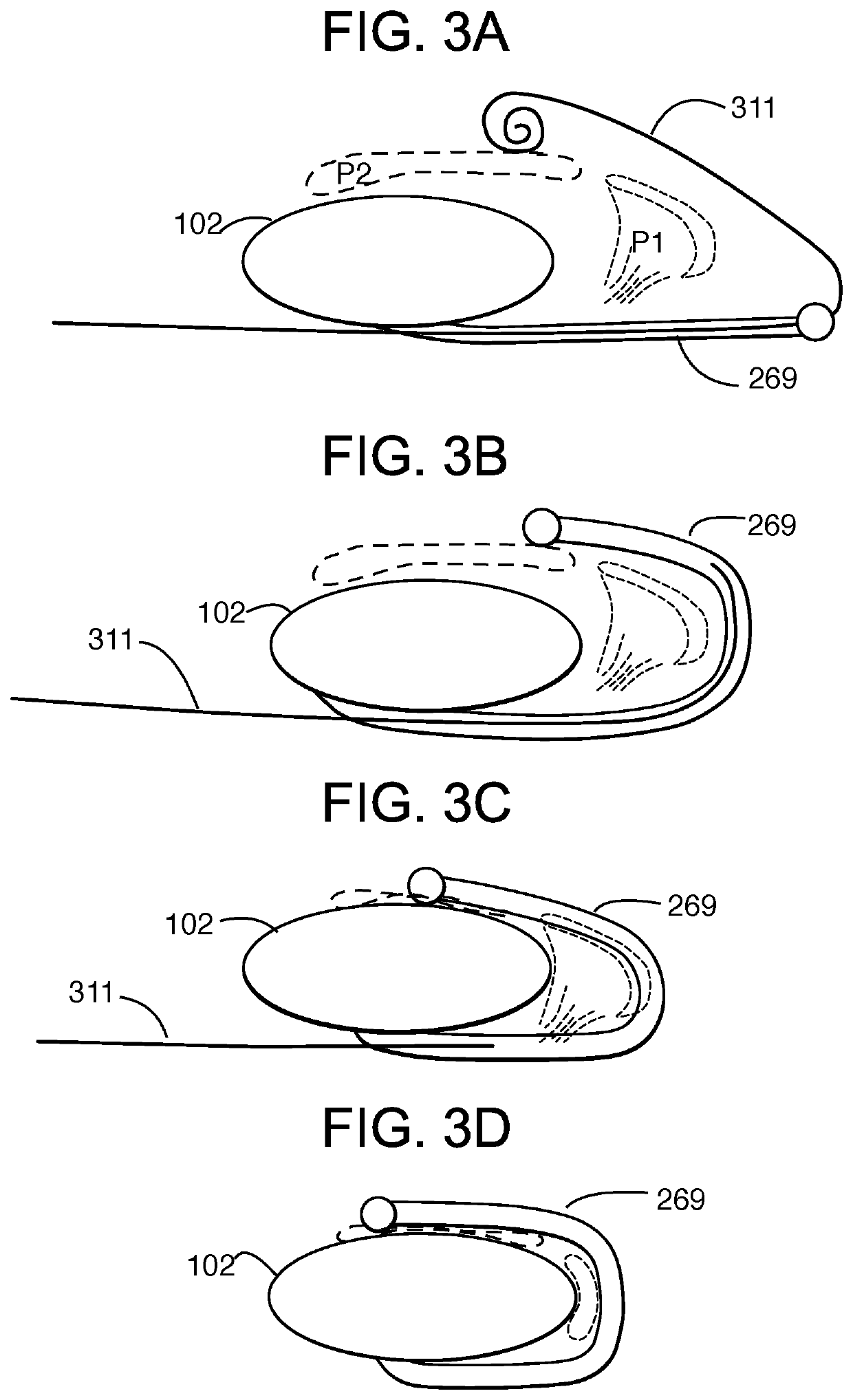
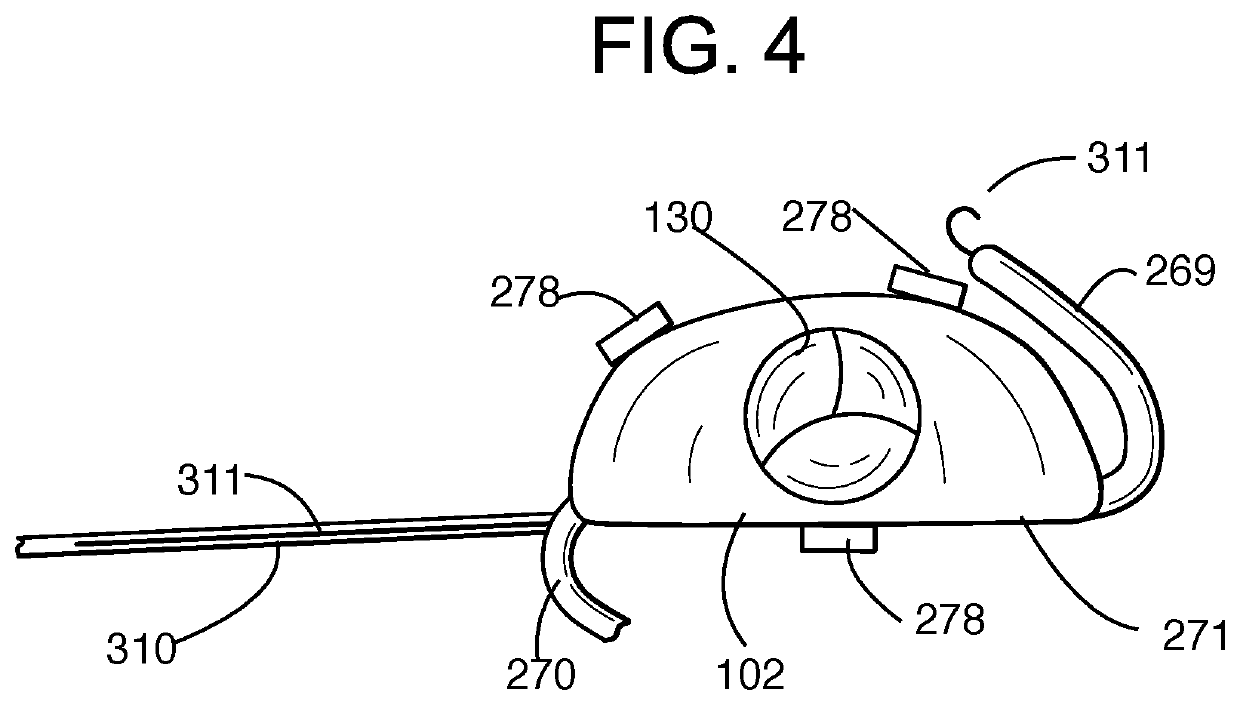
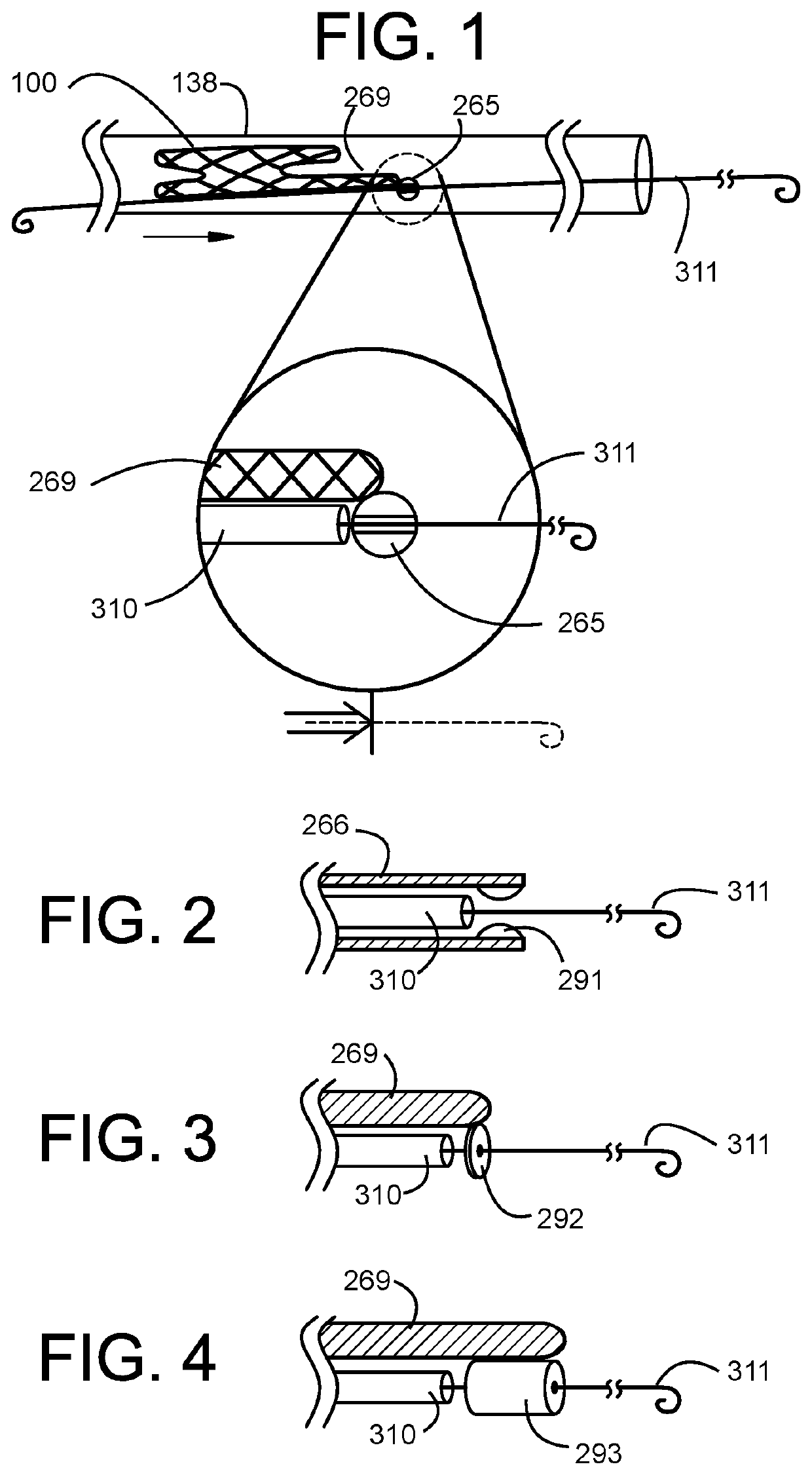
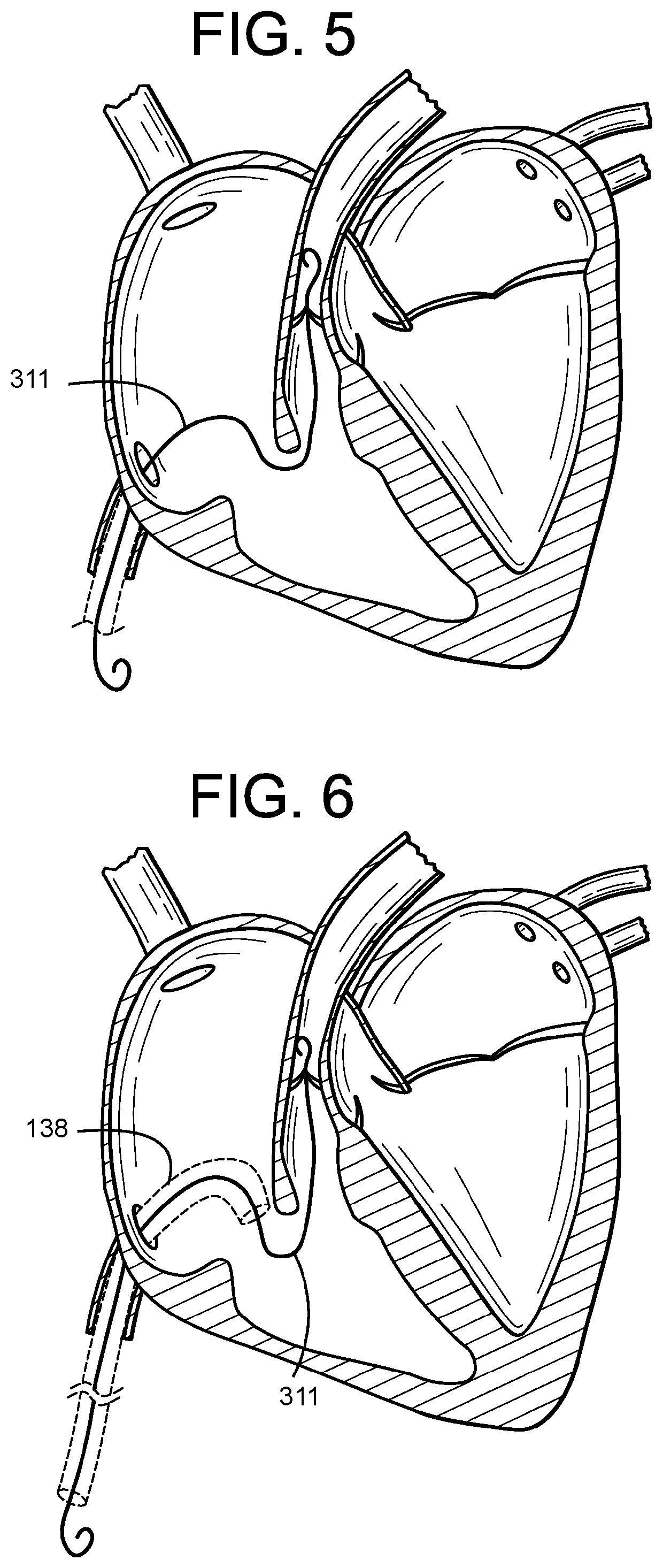
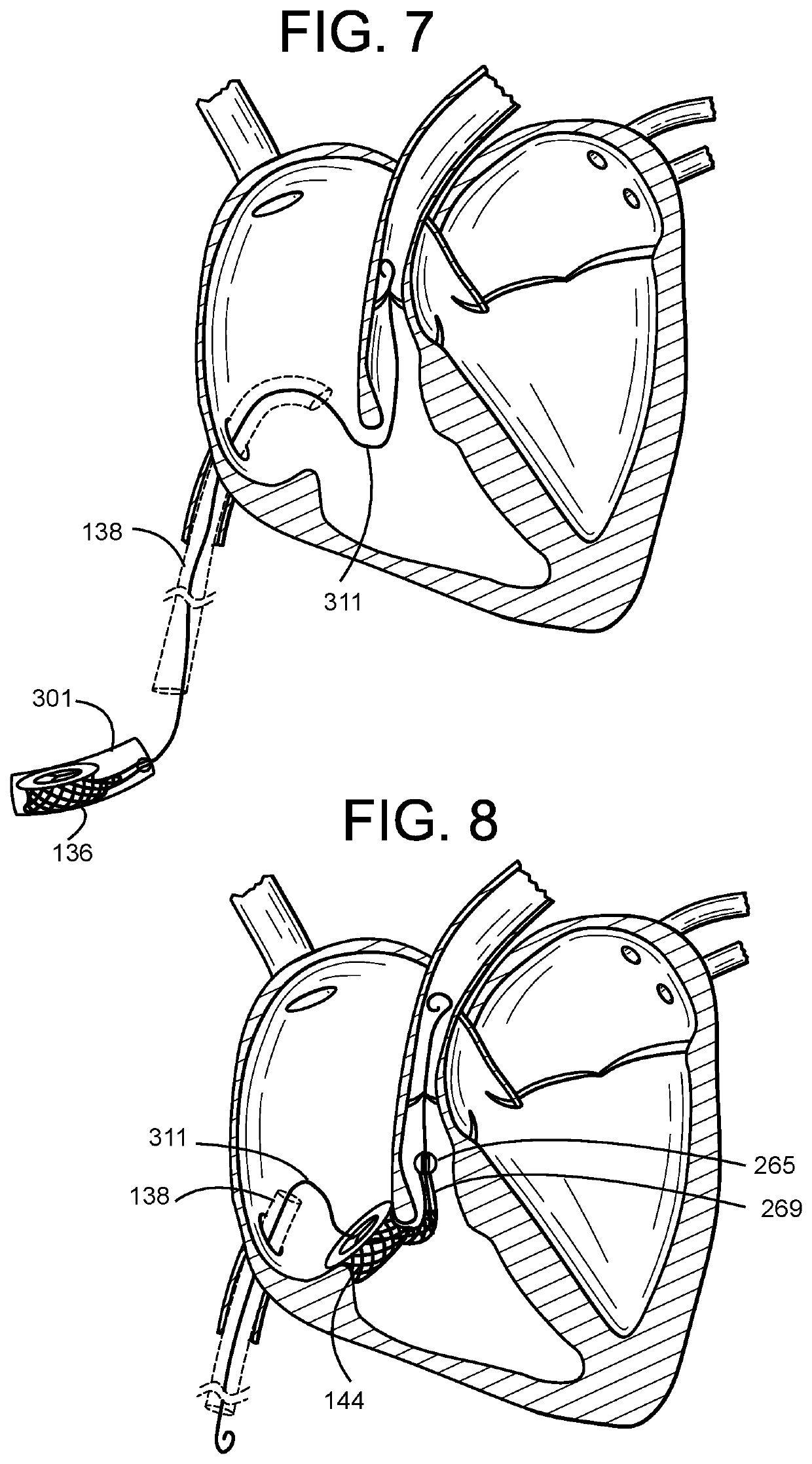
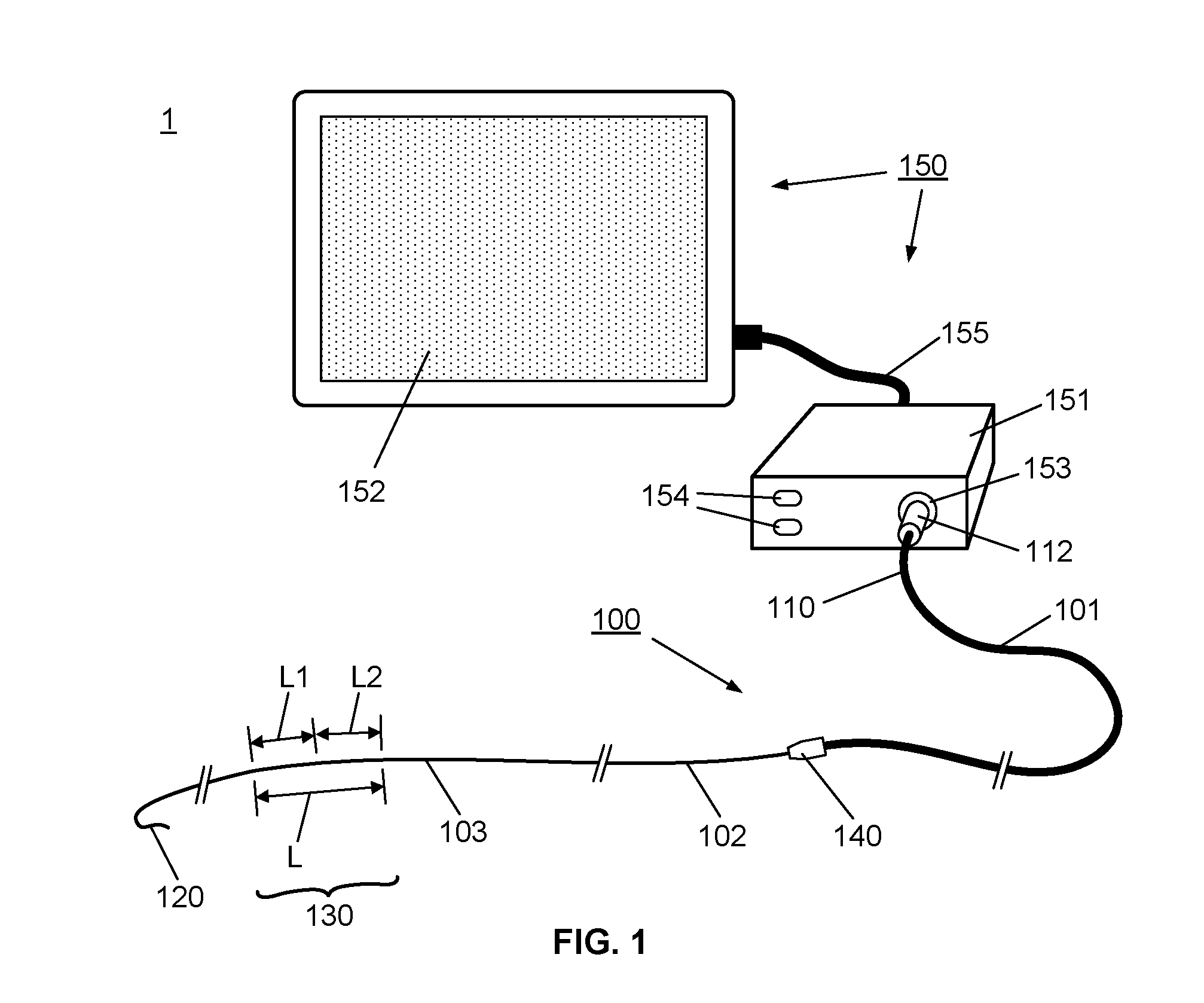
Catheter with removable extension
ActiveUS20050256461A1Easy to disengageAvoid infectionInfusion devicesCatheterGuide tubeCatheter valves
Catheter valve assemblies and methods for connecting catheters and / or providing fluid access to catheters. In one variation, a device comprises a catheter valve assembly and an extension leg unit. The extension leg unit includes lumen inserts for engaging valves positioned within the catheter valve assembly. In another variation, the valve assembly comprises a depressable plunger which may be engaged by an access cannula. Various connectors with integrated valve assemblies are also disclosed.
Owner:CR BARD INC
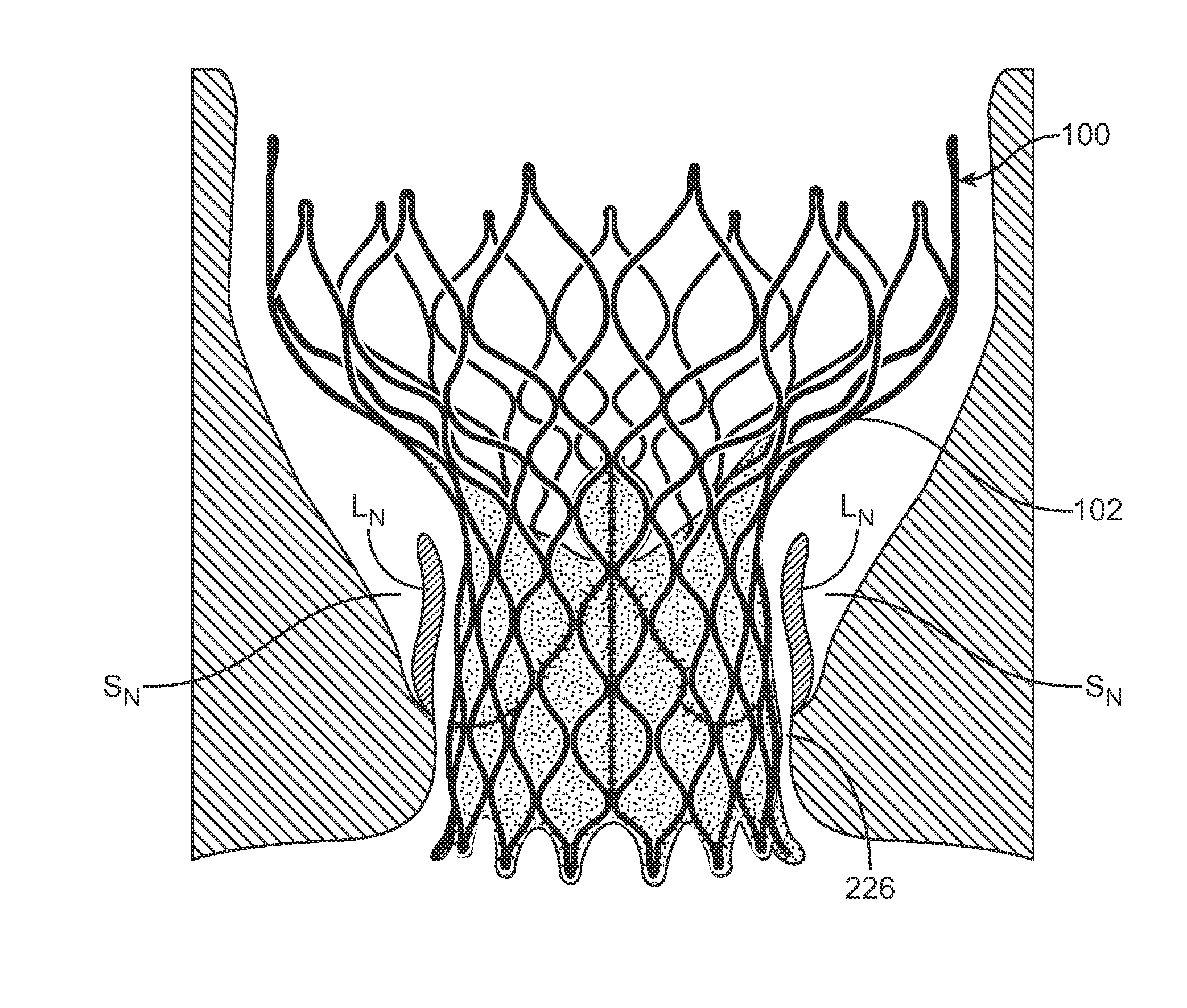
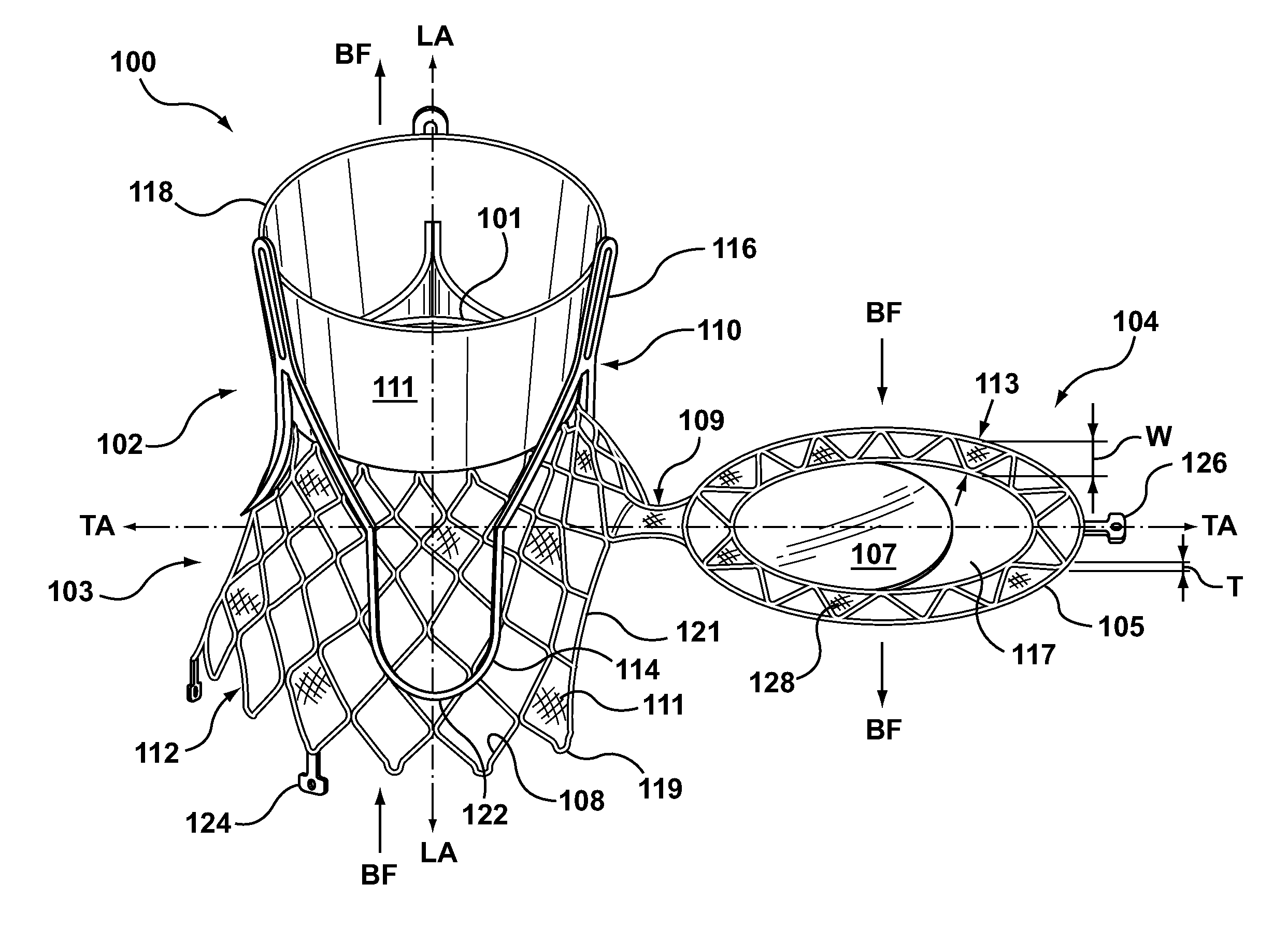
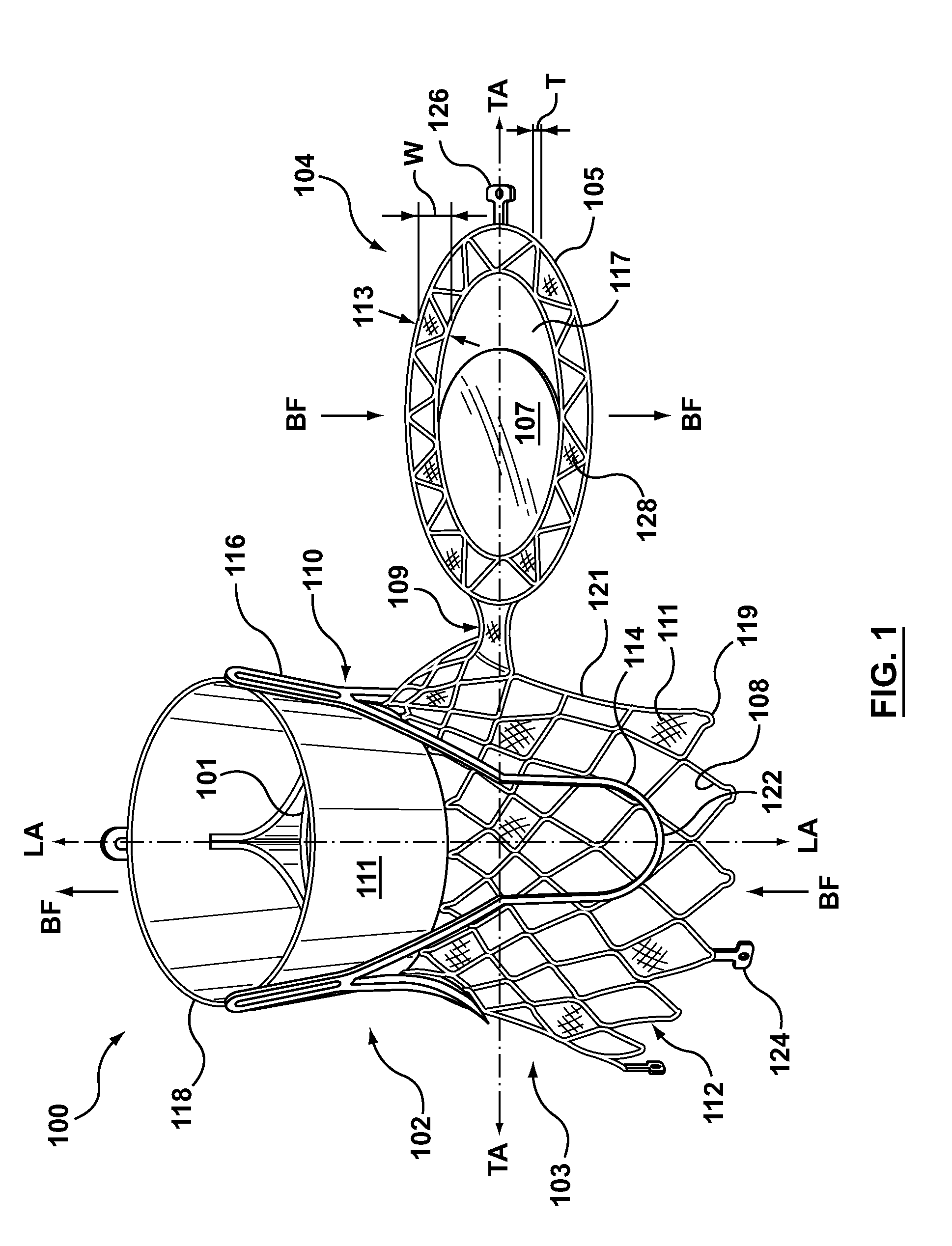
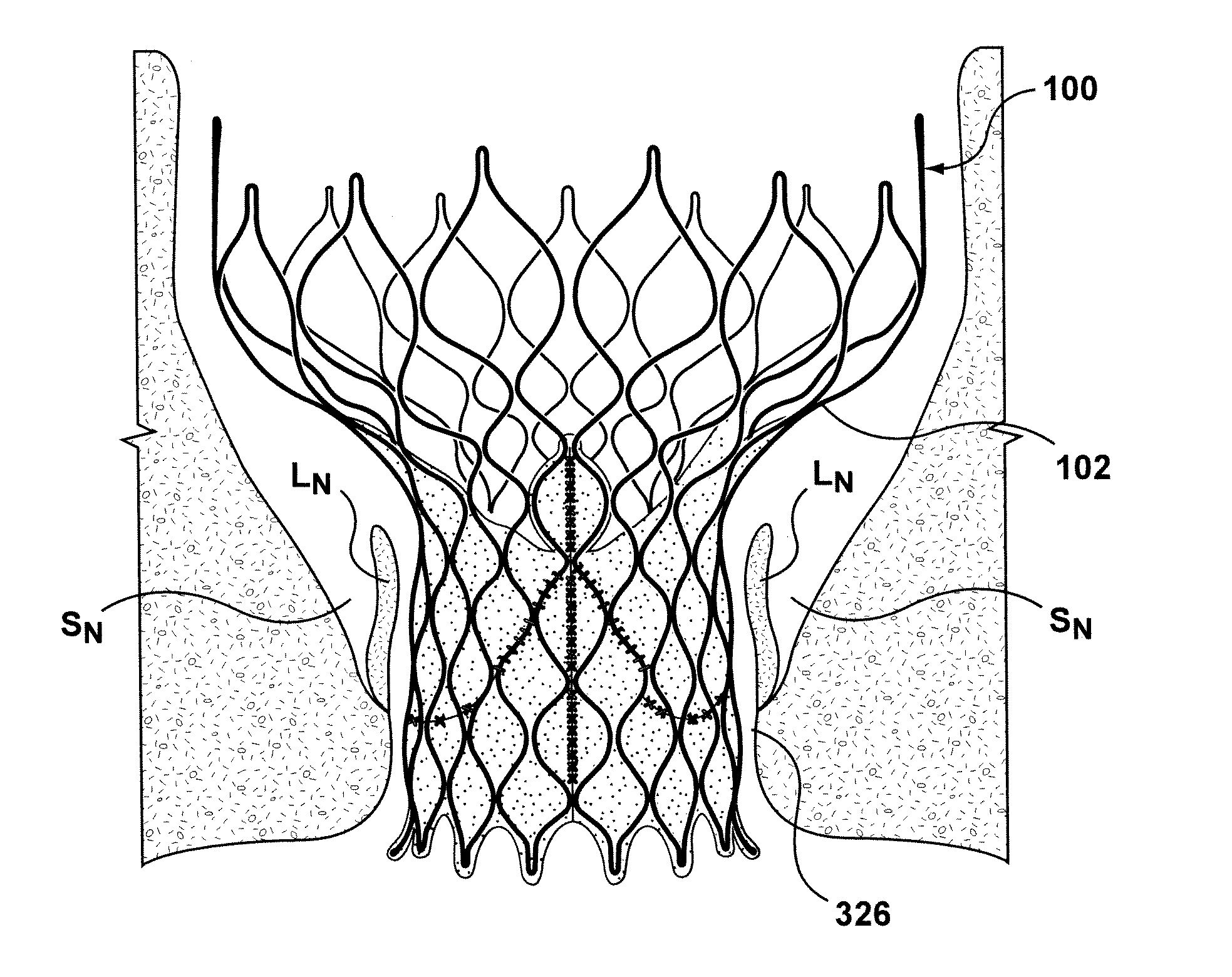
Anti-Paravalvular Leakage Component for a Transcatheter Valve Prosthesis
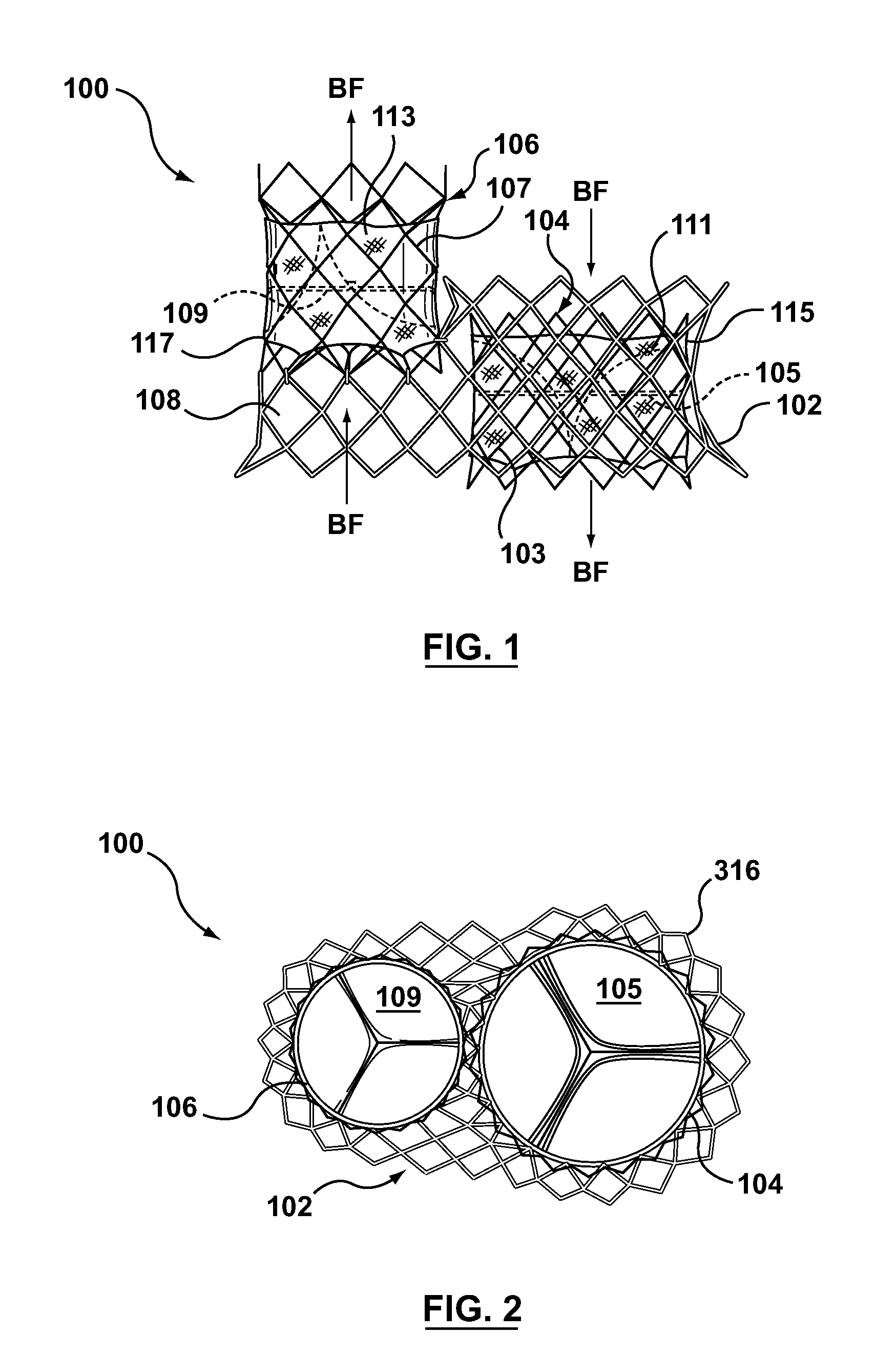
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes an expandable tubular stent, a prosthetic valve within the stent, and an anti-paravalvular leakage component coupled to and encircling the stent which includes a plurality of self-expanding struts and an annular sealing membrane. Each strut has a first end coupled to a distal end of the stent and a second end not coupled to the stent. Each anti-paravalvular leakage component is moveable between a compressed configuration and a deployed configuration. In the compressed configuration, each strut extends distally away from the distal end of the stent. In the deployed configuration, each strut extends proximally away from the distal end of the stent. In an embodiment hereof, the deployed strut has a C-shape and is twisted such that the C-shape lies in a plane substantially along or tangential with the outer surface of the stent. In another embodiment hereof, the deployed strut is rolled-up and extends radially away from the outer surface of the stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
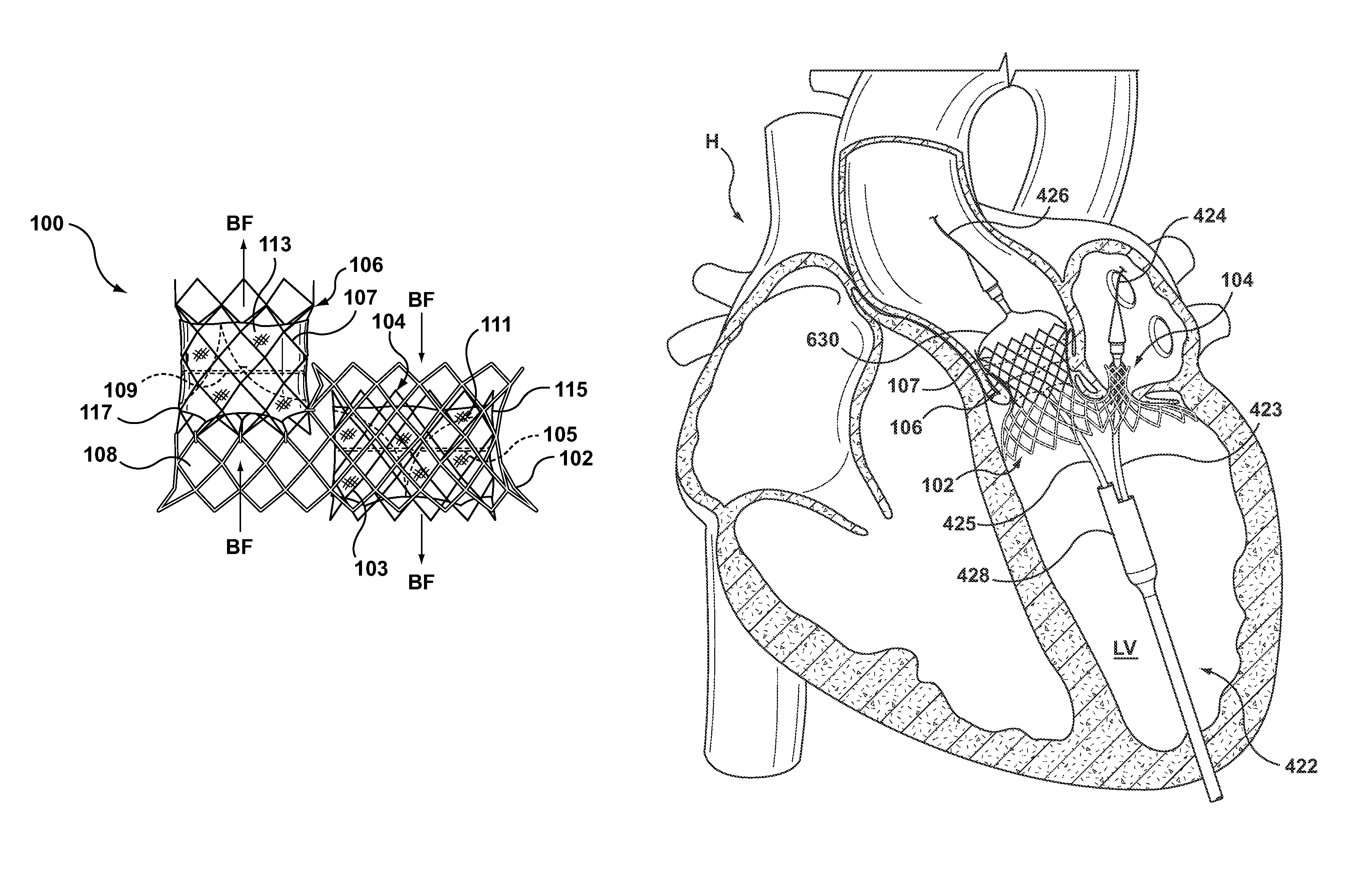
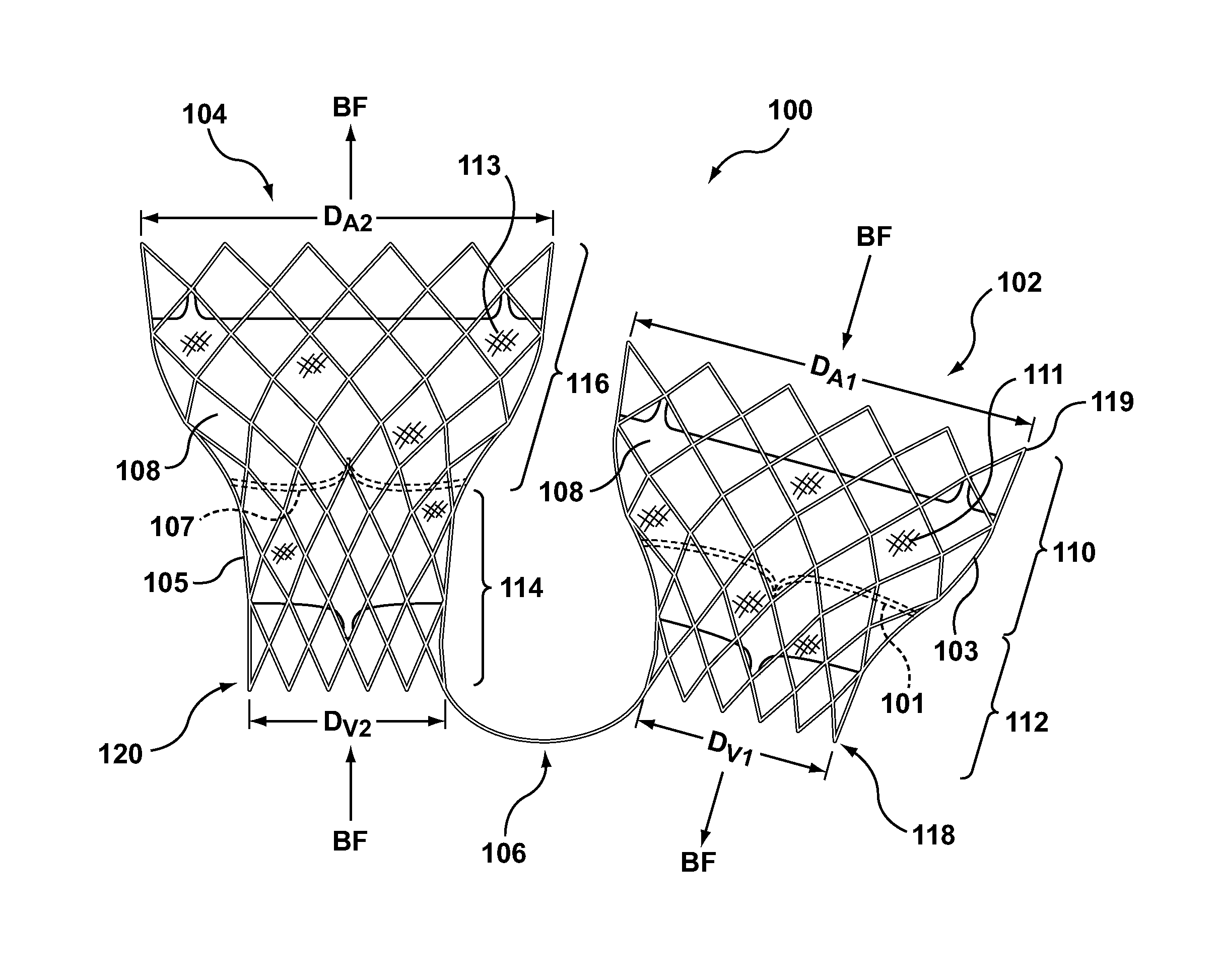
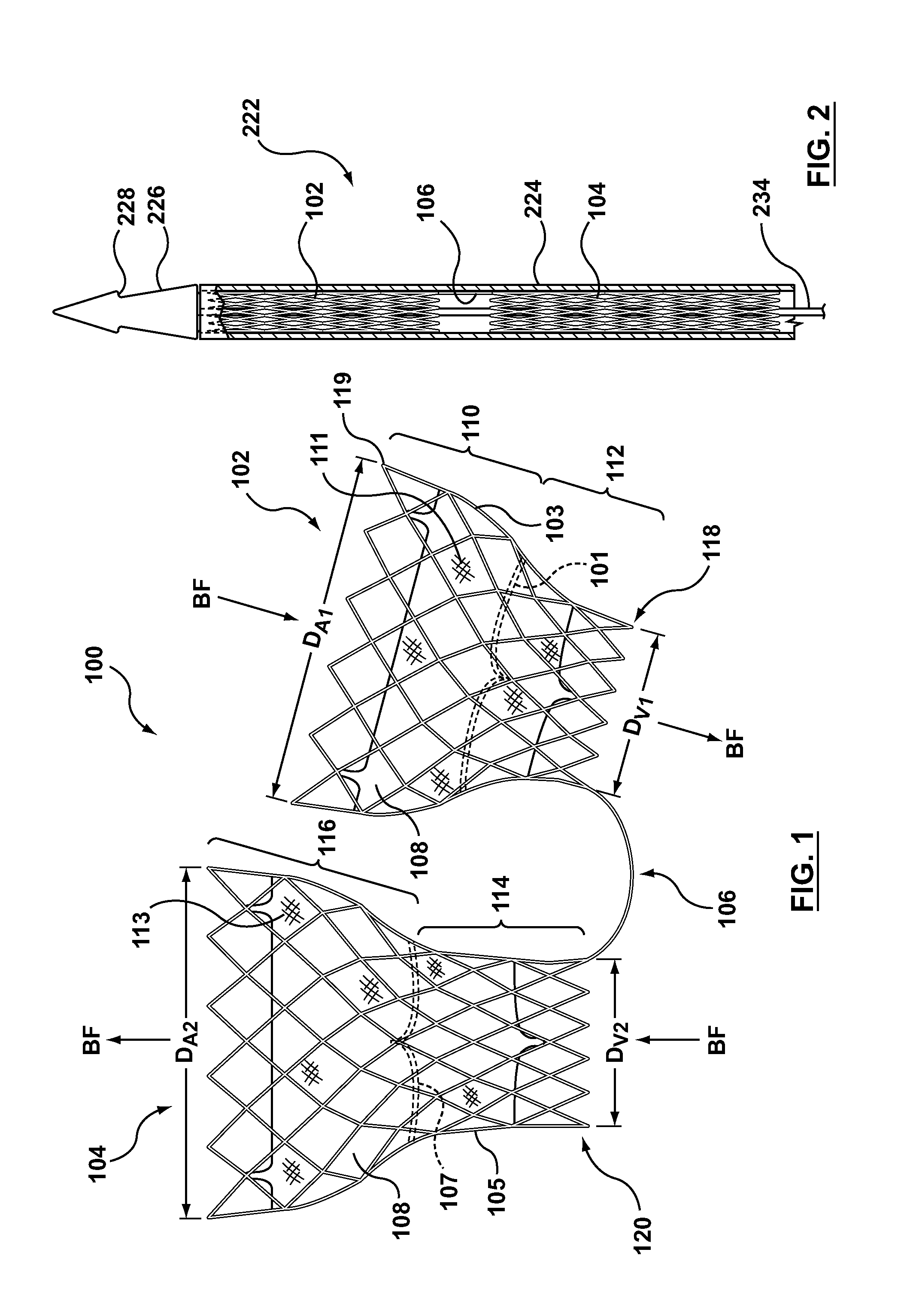
Dual Valve Prosthesis for Transcatheter Valve Implantation
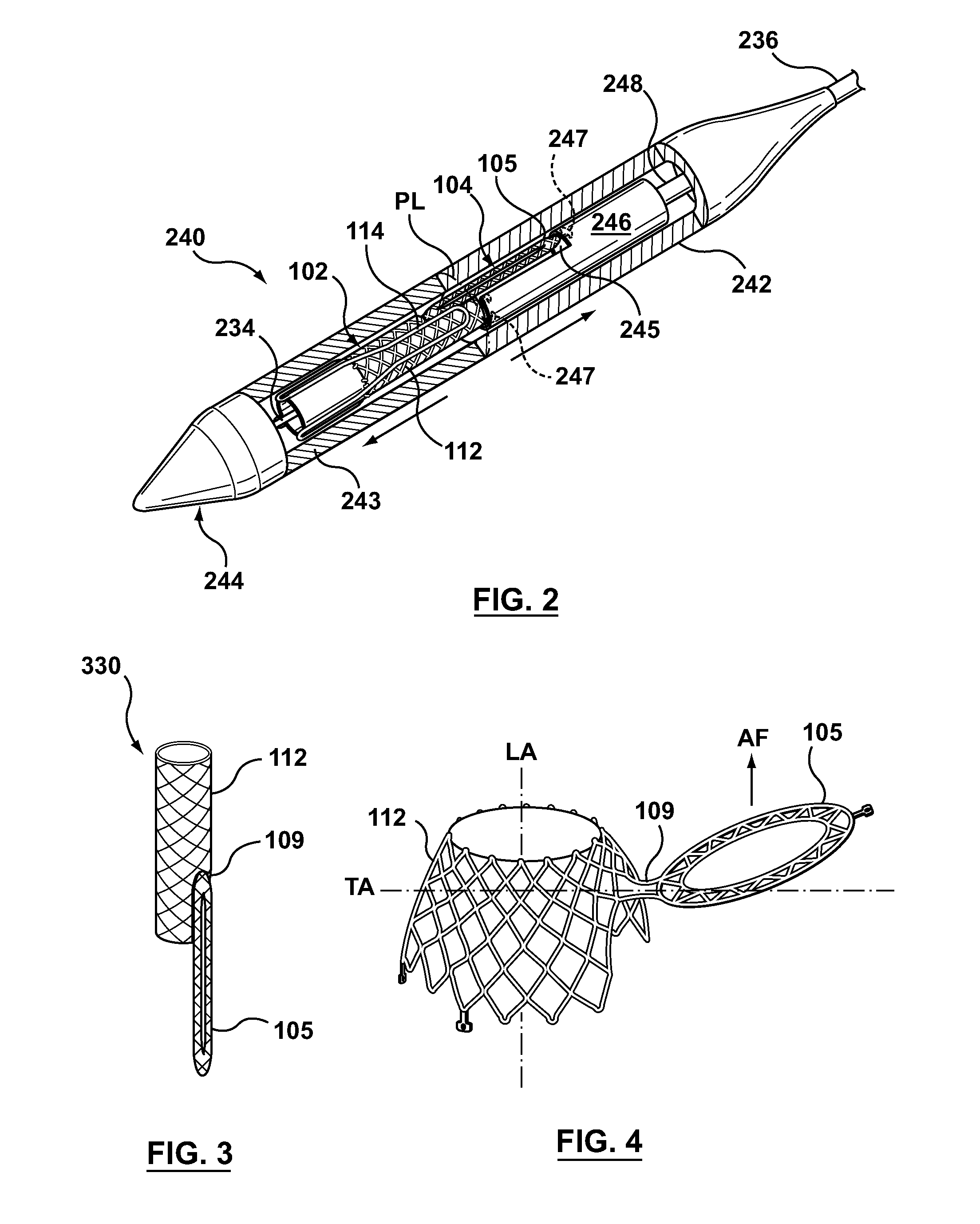
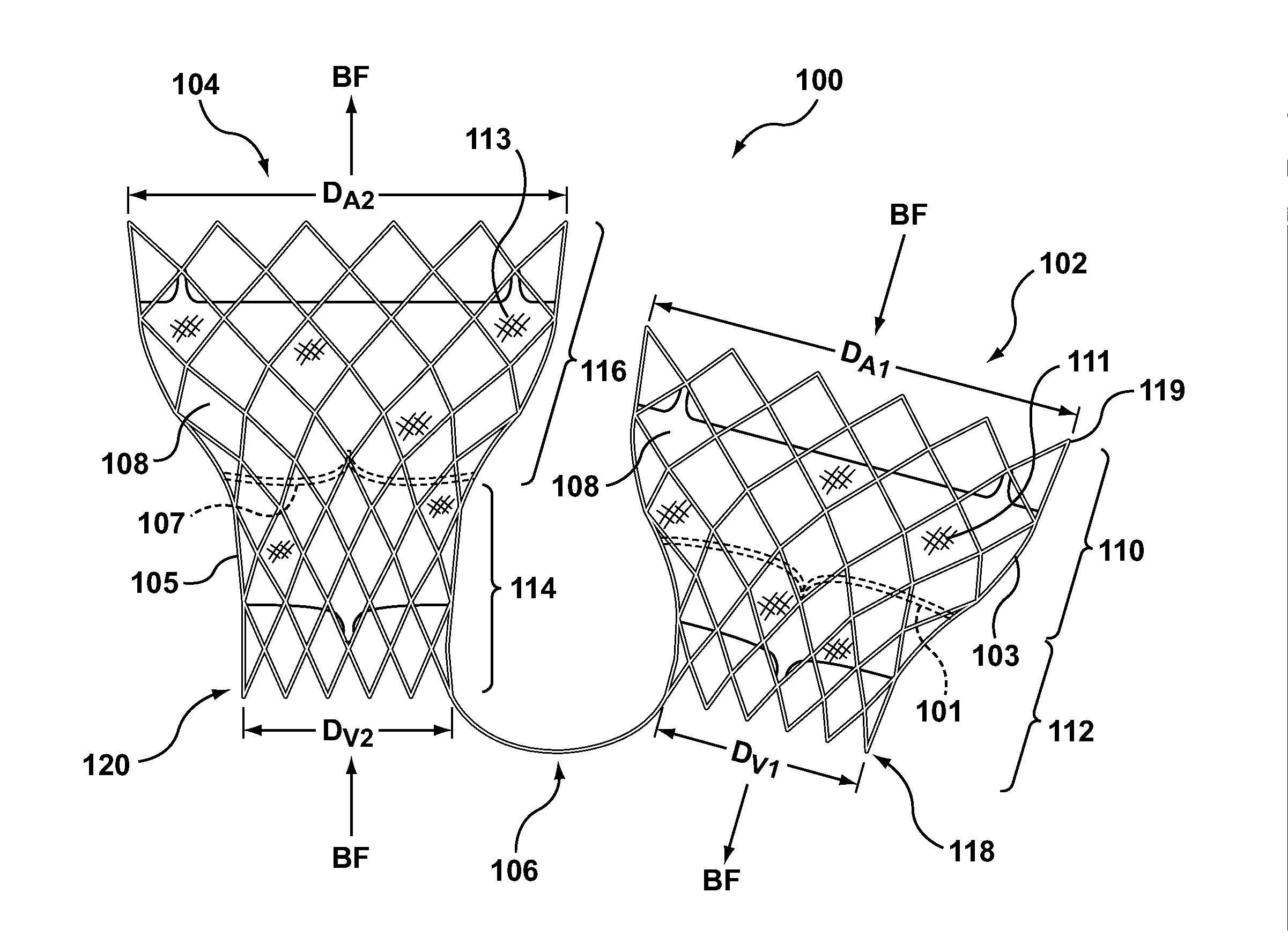
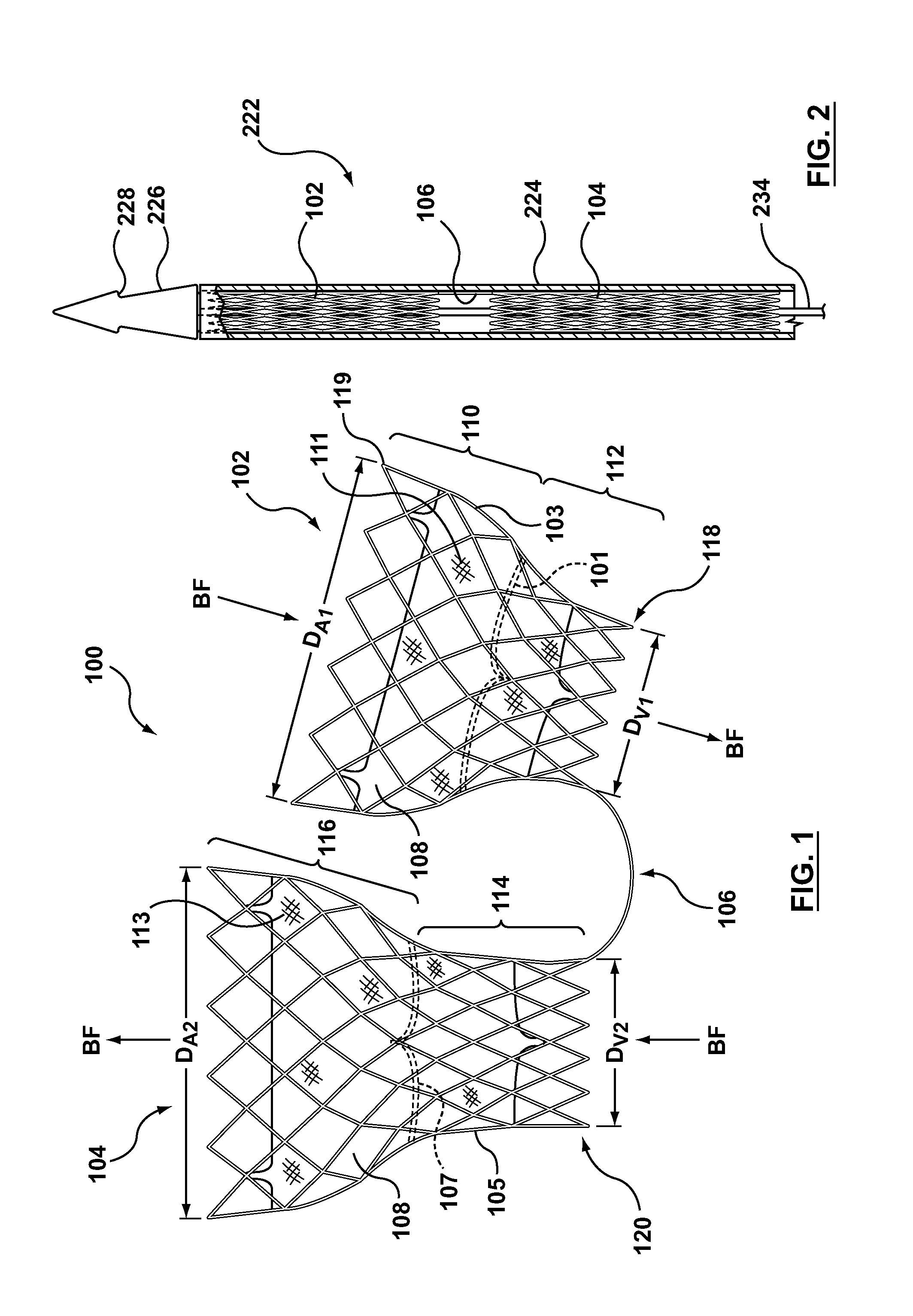
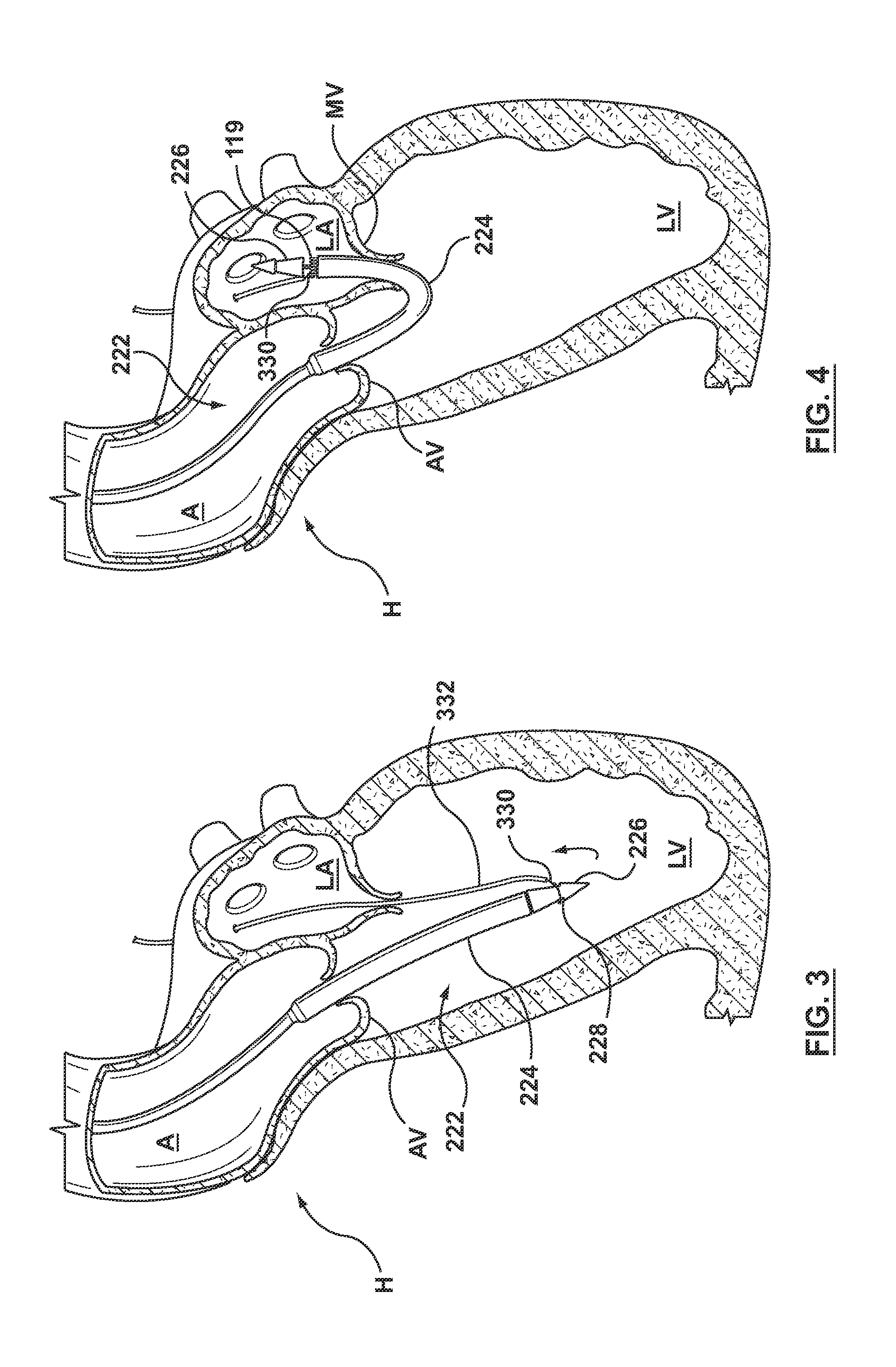
A dual valve prosthesis having first and second prosthetic valve sections is disclosed. The first prosthetic valve section includes a stent structure with a first prosthetic valve secured therein and the second prosthetic valve section includes an annular frame with a second prosthetic valve secured therein. When the dual valve prosthesis is in an expanded configuration, the annular frame extends from the stent structure such that the first and second prosthetic valves are laterally offset from each other. In a method in accordance herewith, the first and second prosthetic valve sections include prosthetic aortic and mitral valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native aortic and mitral valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VSACULAR GALWAY
Dual Valve Prosthesis for Transcatheter Valve Implantation
A dual valve prosthesis having first and second prosthetic valve components with a linkage that connects the first and second prosthetic valve components together is disclosed. Each of the first and second prosthetic valve components includes a stent structure with a prosthetic valve secured therein. In a disclosed method, the first and second prosthetic valve components include prosthetic mitral and aortic valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native mitral and aortic valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure. The linkage between the first and second prosthetic valve components is configured to secure the anterior mitral valve leaflet against a wall of the left ventricle when the dual valve prosthesis is implanted within the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Dual valve prosthesis for transcatheter valve implantation
A dual valve prosthesis having first and second prosthetic valve sections is disclosed. The first prosthetic valve section includes a stent structure with a first prosthetic valve secured therein and the second prosthetic valve section includes an annular frame with a second prosthetic valve secured therein. When the dual valve prosthesis is in an expanded configuration, the annular frame extends from the stent structure such that the first and second prosthetic valves are laterally offset from each other. In a method in accordance herewith, the first and second prosthetic valve sections include prosthetic aortic and mitral valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native aortic and mitral valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VSACULAR GALWAY
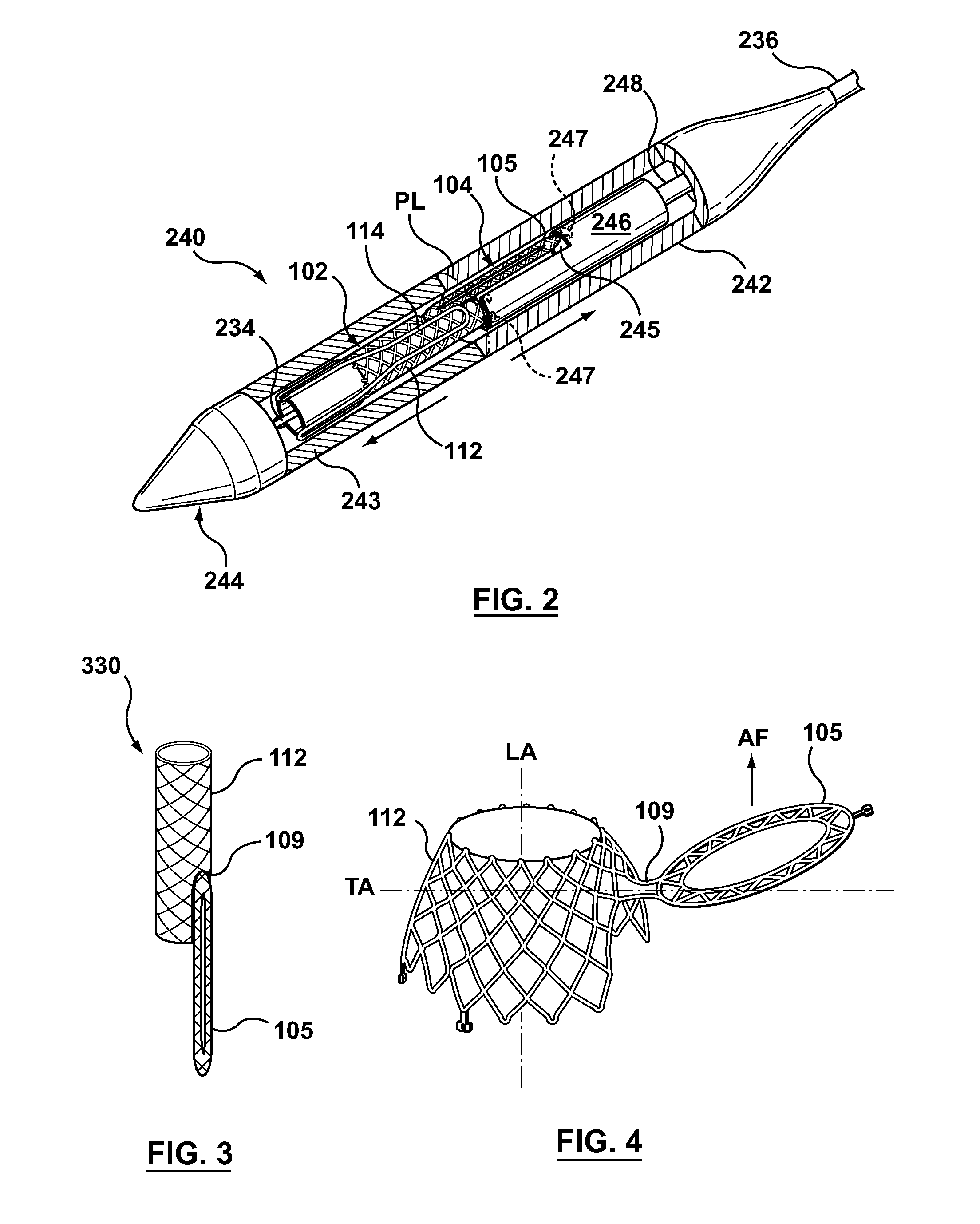
Positioning Tool for Transcatheter Valve Delivery
This invention relates to a positioning device for delivery of a transcatheter prosthetic heart valve that comprises a ratchet rod with reference scale for accurate positioning a valve during deployment, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
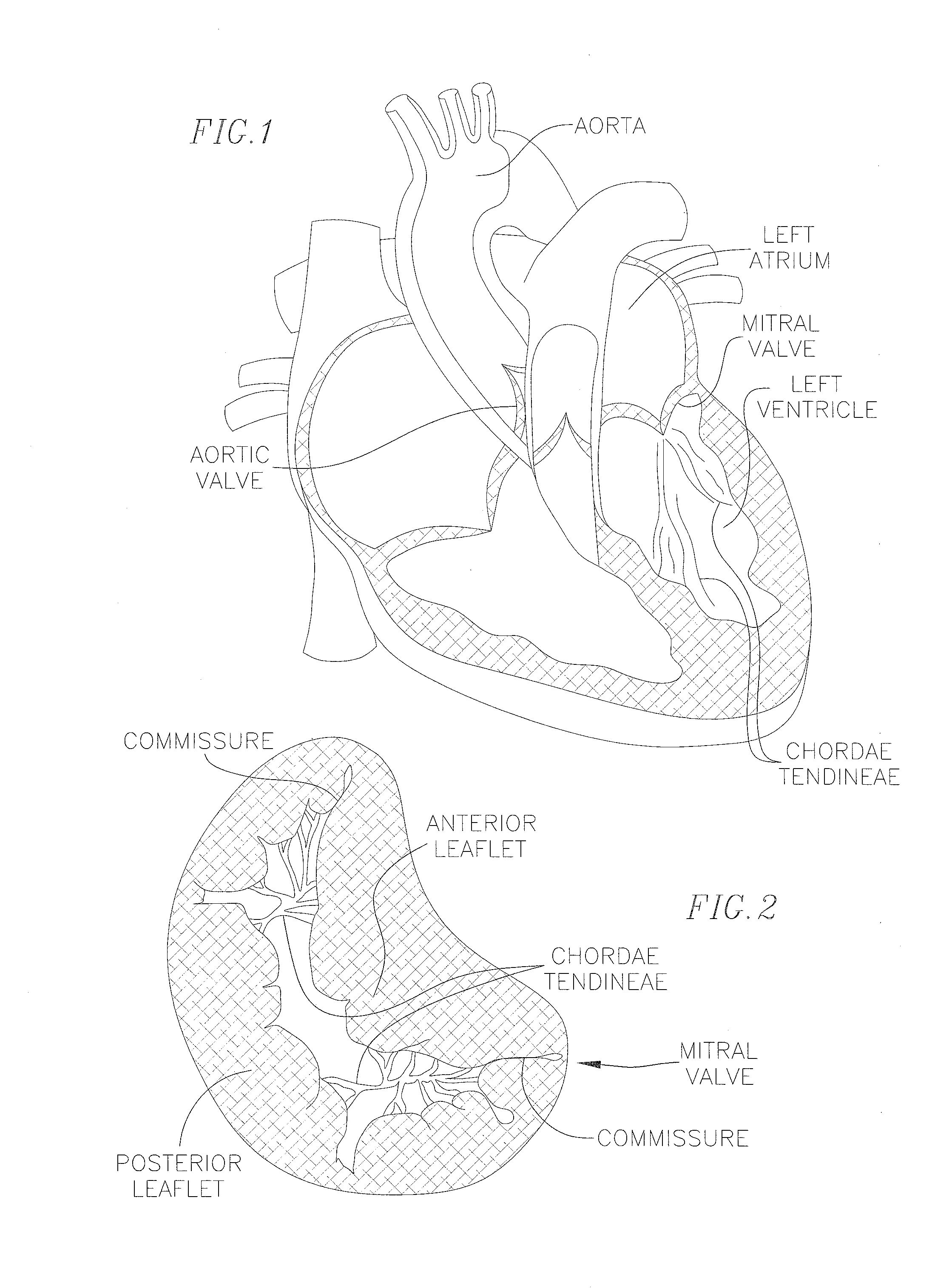
Heart Valves Prostheses and Methods for Percutaneous Heart Valve Replacement
ActiveUS20170100236A1Prevent retrograde blood flowHeart valvesHeart valve replacement (procedure)Heart valve replacement
Prosthetic heart valve devices and associated methods for percutaneous heart valve replacement are disclosed herein. A transcatheter valve prosthesis configured in accordance herewith includes a frame having a valve support and one or more support arms coupled thereto. The one or more support arms are configured to extend from the second end of the valve support toward the first end when the valve prosthesis is in an expanded configuration. When deployed in the expanded configuration, the one or more support arms have a curvilinear shape, such as a substantially S-shape, that at least partially engages tissue at the native heart valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Deployment Compensator for Transcatheter Valve Delivery
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Systems and methods utilizing expandable transcatheter valve
Apparatus and methods for transcatheter valves. Specific embodiments relate to transcatheter flutter valves configured for pediatric use.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Pressure Actuated Catheter Valve
InactiveUS20130204226A1Reduce physical stressReduce overall outer diameterInfusion syringesCheck valvesCatheter hubCatheter valves
This invention provides catheter assemblies and methods for insertion of a catheter into a vessel. The assemblies include a resilient valve in the hub of the catheter that can be opened by pressure from a male luer fitting. The methods include piercing a vessel with the needle and catheter of the assembly, retraction of the needle component thus closing the resilient valve. Finally the catheter can be accessed by applying a male luer fitting to the catheter hub and a shoulder of the resilient valve.
Owner:I V ACCESS TECH
Dual valve prosthesis for transcatheter valve implantation
A dual valve prosthesis having a self-expanding anchoring frame with first and second prosthetic valve assemblies attached to the anchoring frame is disclosed. Each of the first and second prosthetic valve assemblies includes a balloon-expandable stent structure with a prosthetic valve secured therein. In a disclosed method, the first and second prosthetic valve assemblies include prosthetic mitral and aortic valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native mitral and aortic valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Spacer for securing a transcatheter valve to a bioprosthetic cardiac structure
InactiveUS20170281337A1Reduce the overall diameterBalloon catheterAnnuloplasty ringsDocking stationProsthesis
A spacer for creating a docking station for a transcatheter heart valve is provided. The spacer changes an effective diameter and / or a shape of an implanted bioprosthetic structure such as a bioprosthetic heart valve or annuloplasty ring, providing a supporting structure into which the transcatheter valve expands without over expanding. The spacer may be deployed through an interventional technique either through transseptal access, transfemoral access, or transapical access and is typically deployed at least in part on an inflow portion of the implanted bioprosthetic structure.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Blood control catheter valve employing actuator with flexible retention arms
ActiveUS20150038910A1Avoid flowTolerance requirement can be reducedGuide needlesInfusion syringesCATHETER ADAPTERActuator
The present invention extends to a blood control catheter valve for use in a catheter adapter. The blood control catheter value employs an actuator for bypassing a septum to open the blood control catheter valve. The actuator includes flexible retention arms positioned on one end which retract into the body of the actuator while the end of the actuator passes through the septum, and then expand outwardly to maintain the actuator positioned within the septum. This design facilitates the manufacturing of catheter adapters (as well as blood control catheter valves and other components that attach to the catheter adapter) because the design can reduce the tolerance requirements of such components. Further, the design provides a reliable blood control catheter valve that does not require the catheter adapter to be increased in size to accommodate the valve.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Dual valve prosthesis for transcatheter valve implantation
A dual valve prosthesis having first and second prosthetic valve components with a linkage that connects the first and second prosthetic valve components together is disclosed. Each of the first and second prosthetic valve components includes a stent structure with a prosthetic valve secured therein. In a disclosed method, the first and second prosthetic valve components include prosthetic mitral and aortic valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native mitral and aortic valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure. The linkage between the first and second prosthetic valve components is configured to secure the anterior mitral valve leaflet against a wall of the left ventricle when the dual valve prosthesis is implanted within the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Filtered sealing components for a transcatheter valve prosthesis
A transcatheter valve prosthesis includes a stent having a compressed configuration for delivery within a vasculature and an expanded configuration for deployment within a native heart valve and a prosthetic valve component disposed within and secured to the stent. A compartment is coupled to the stent, and a filtered opening into the compartment is configured to permit blood flow there-through and to trap emboli in the blood flow within the compartment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
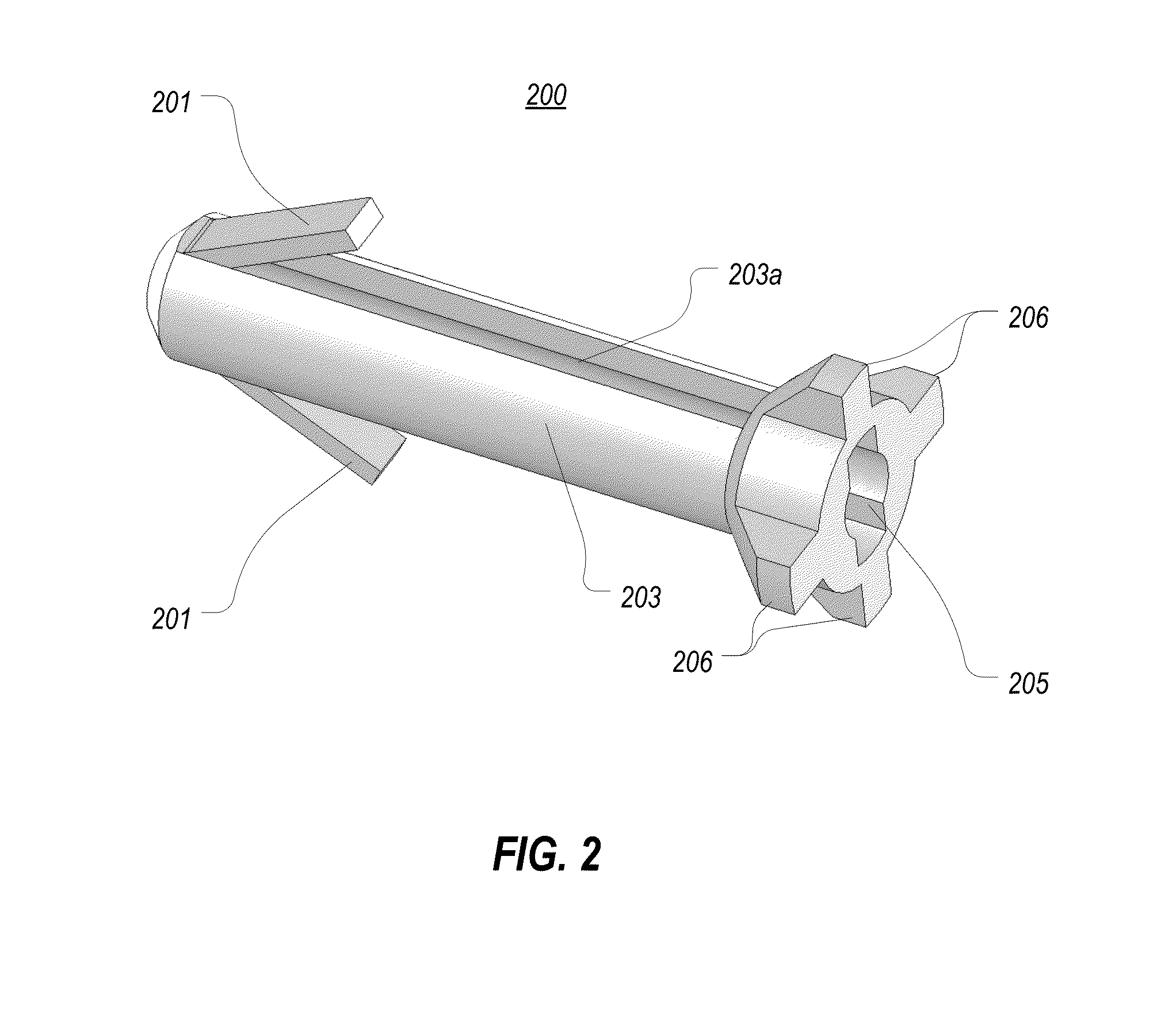
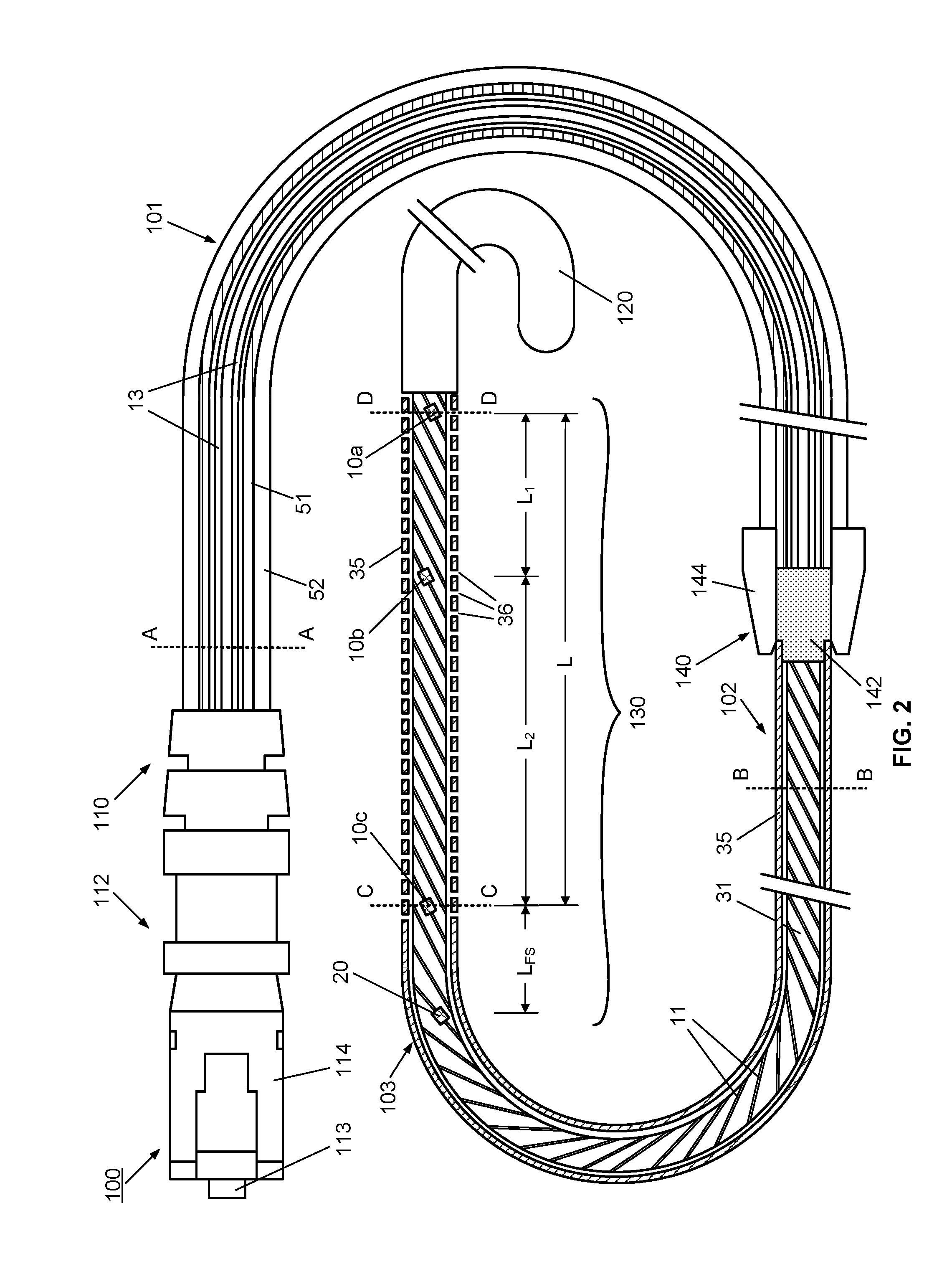
Catheter with removable extension
ActiveUS7347853B2Easy to disengageAvoid infectionInfusion devicesHaemostasis valvesCatheter valvesVALVE PORT
Catheter valve assemblies and methods for connecting catheters and / or providing fluid access to catheters. In one variation, a device comprises a catheter valve assembly and an extension leg unit. The extension leg unit includes lumen inserts for engaging valves positioned within the catheter valve assembly. In another variation, the valve assembly comprises a depressable plunger which may be engaged by an access cannula. Various connectors with integrated valve assemblies are also disclosed.
Owner:CR BARD INC
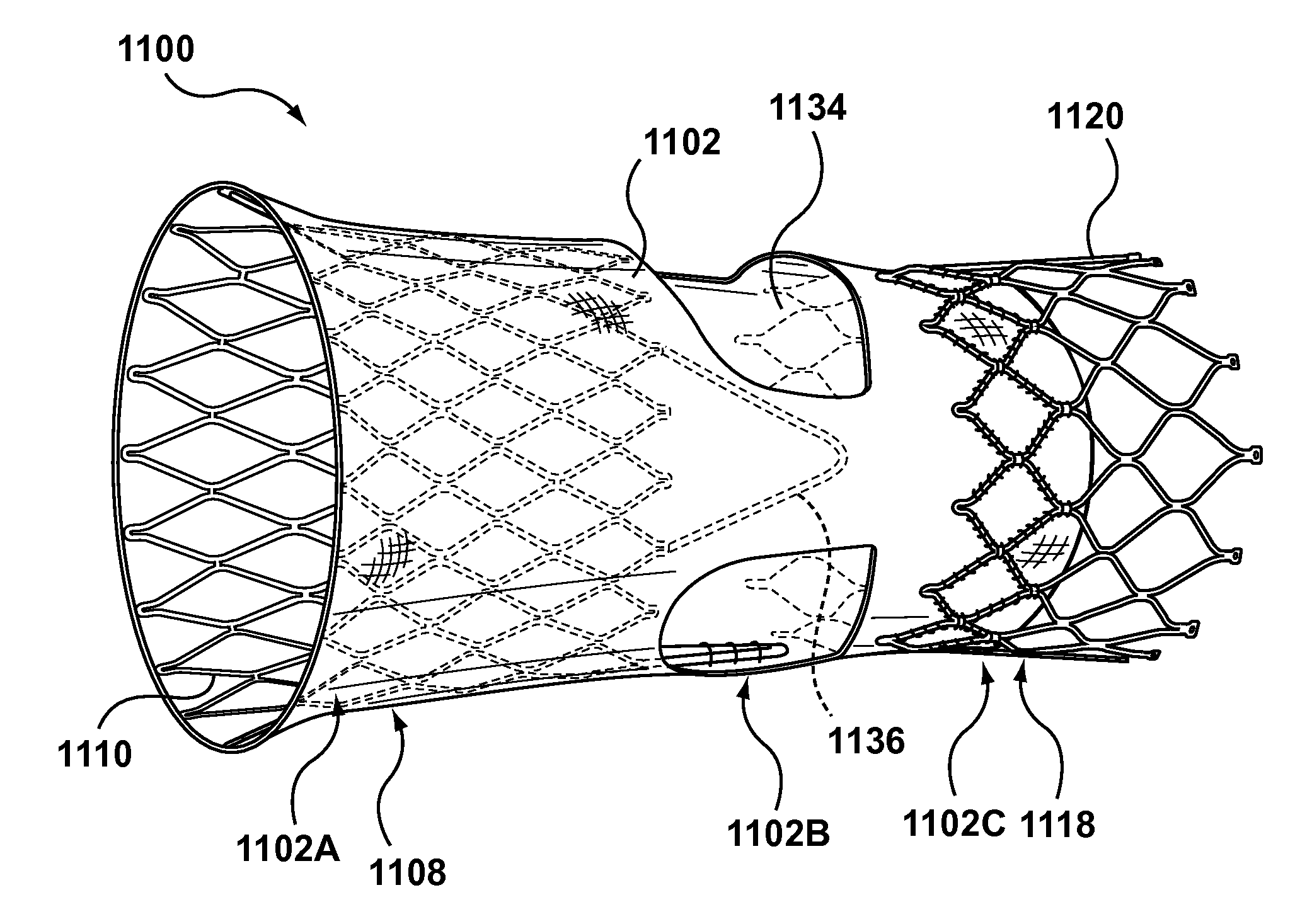
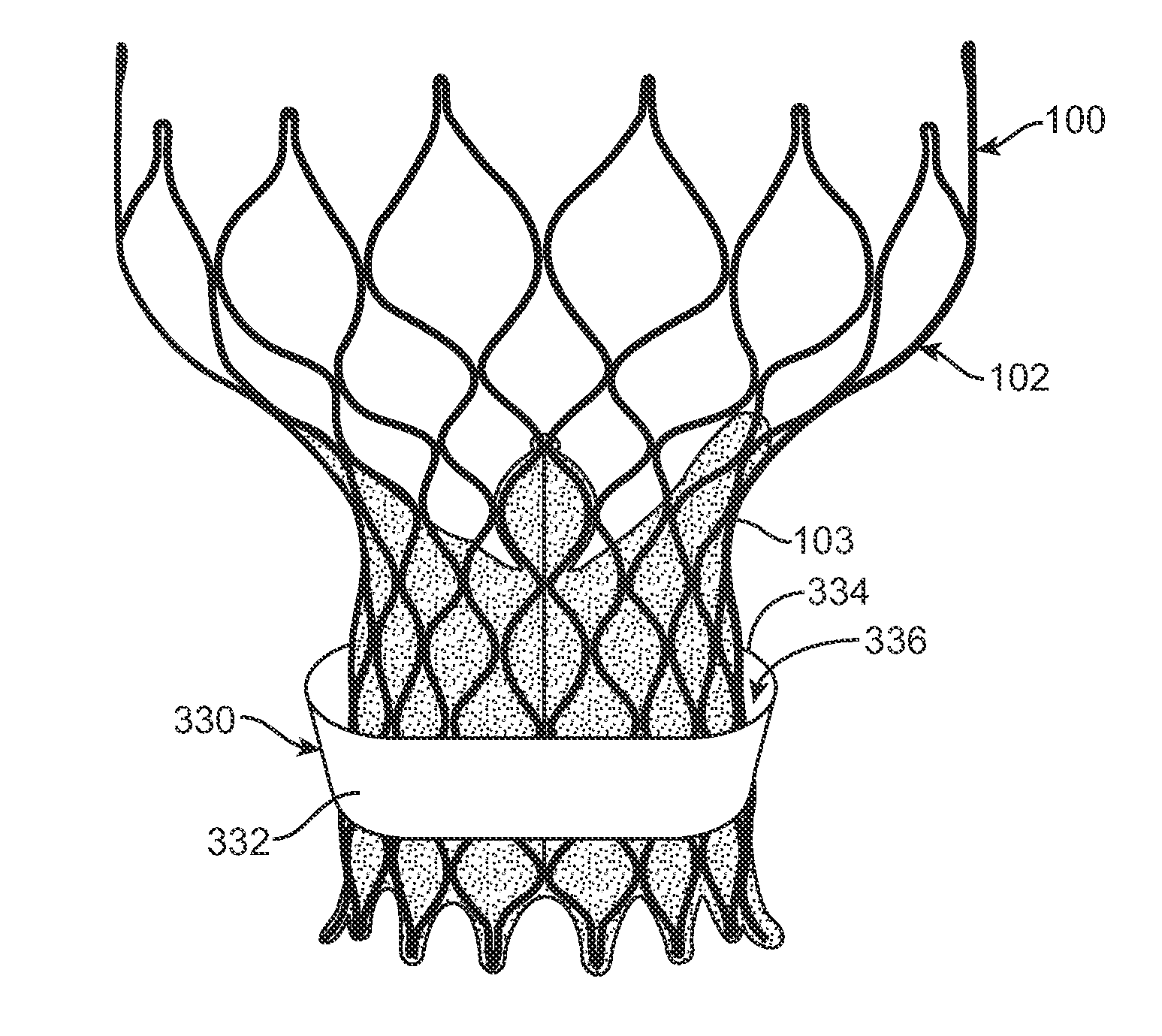
Segmented transcatheter valve prosthesis having an unsupported valve segment
Embodiments hereof relate to a transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular fabric body, a first or inflow tubular scaffold attached to a first end portion of the tubular fabric body, and a second or outflow tubular scaffold attached to a second end portion of the tubular fabric body. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to an intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body that longitudinally extends between the first and second end portions of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion is unsupported such that neither of the first and second tubular scaffolds surrounds the intermediate portion of the tubular fabric body. The intermediate portion may include one or more windows for coronary access and may include one or more commissure reinforcement members coupled thereto to provide support for the prosthetic valve component.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Transcatheter valve prosthesis having an external skirt for sealing and preventing paravalvular leakage
A transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular stent includes an interior skirt or skirt portion is coupled to and covers an inner circumferential surface of the stent, and an exterior skirt or skirt portion is coupled to and covers an outer circumferential surface of the stent. A prosthetic valve component is disposed within and secured to the interior skirt or skirt portion. The interior and exterior skirts or skirt portions may overlap to form a double layer of skirt material on the stent, or may be portions of a skirt that do not overlap such that only a single layer of skirt material covers the stent. When the stent is in at least the compressed configuration, at least one endmost crown may be positioned radially inwards with respect to the remaining endmost crowns formed at the inflow end of the stent in order to accommodate the exterior skirt.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
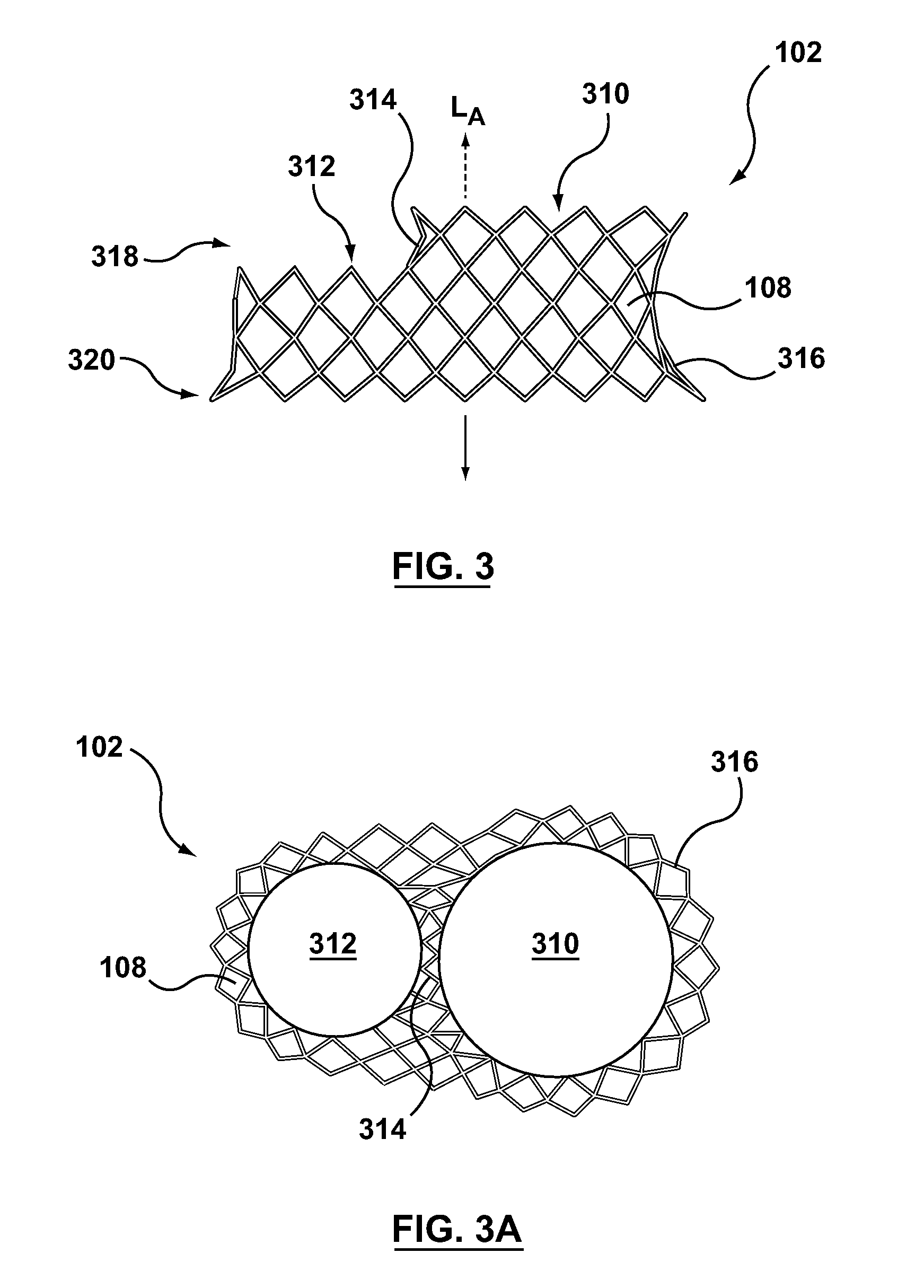
Cut pattern transcatheter valve frame
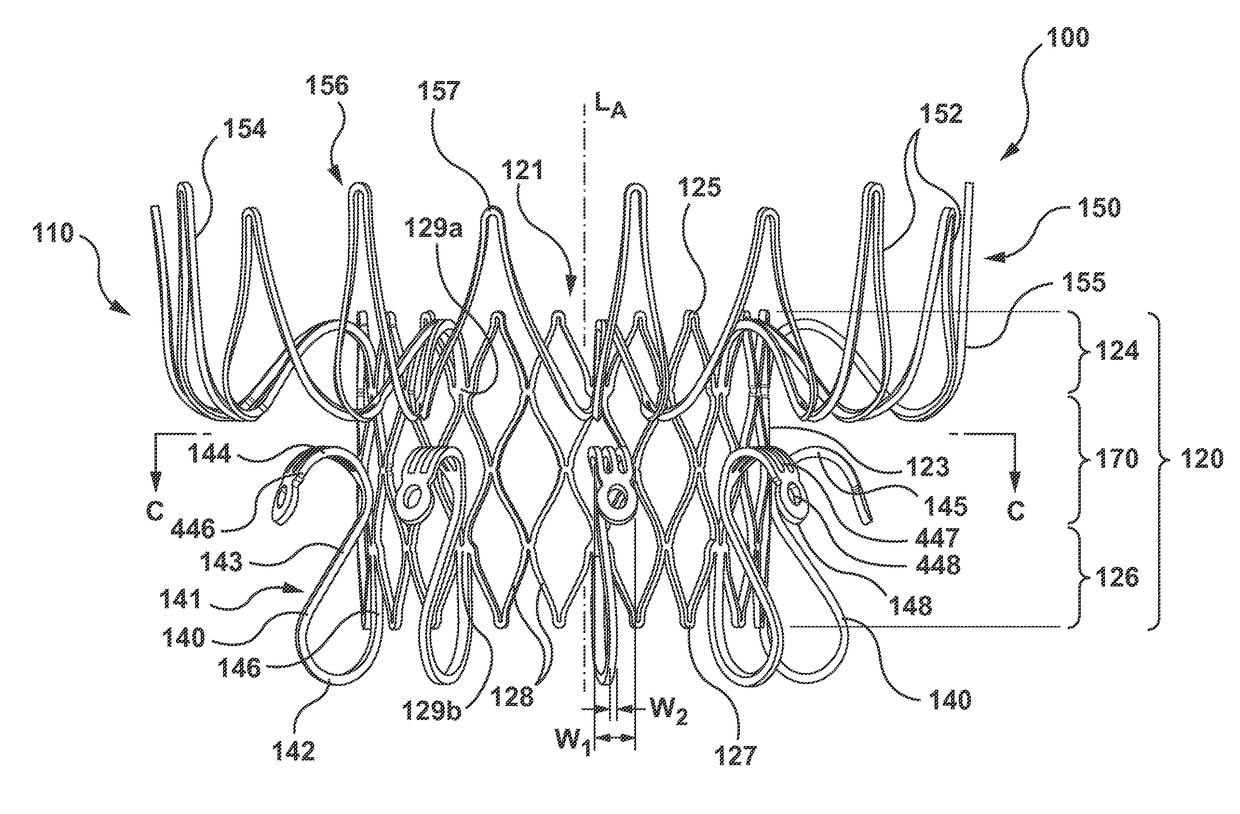
A transcatheter valve frame comprising a valve frame comprising an elongate tubular member having a longitudinal axis and a circumference, the elongate tubular member comprising a plurality of struts interconnected by peaks and valleys that define a closed cell construction comprising a plurality of interconnected cells, the valve frame is formed from a single piece of material comprising a metal or metal alloy, the valve frame having a diameter that increases upon axial compression and the valve frame comprising a locking mechanism integral with the valve frame configured to fix the diameter of the valve frame.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
System for loading a transcatheter valve prosthesis into a delivery catheter
A tool for use in loading a transcatheter valve prosthesis within a delivery catheter includes a body portion, a pivotable element and a biasing element. The body portion includes a central passageway extending form a proximal end to a distal end of the body portion. The central passageway is configured to receive a distal portion of a delivery catheter therethrough. The pivotable element is attached to the body portion and is configured to secure a tether during loading of a transcatheter valve prosthesis within the delivery catheter. The biasing element compresses the pivotable element against the body portion such that the pivotable element holds a second end against the delivery catheter and secures the tether thereto. The pivotable element may be two or more pivotable elements.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
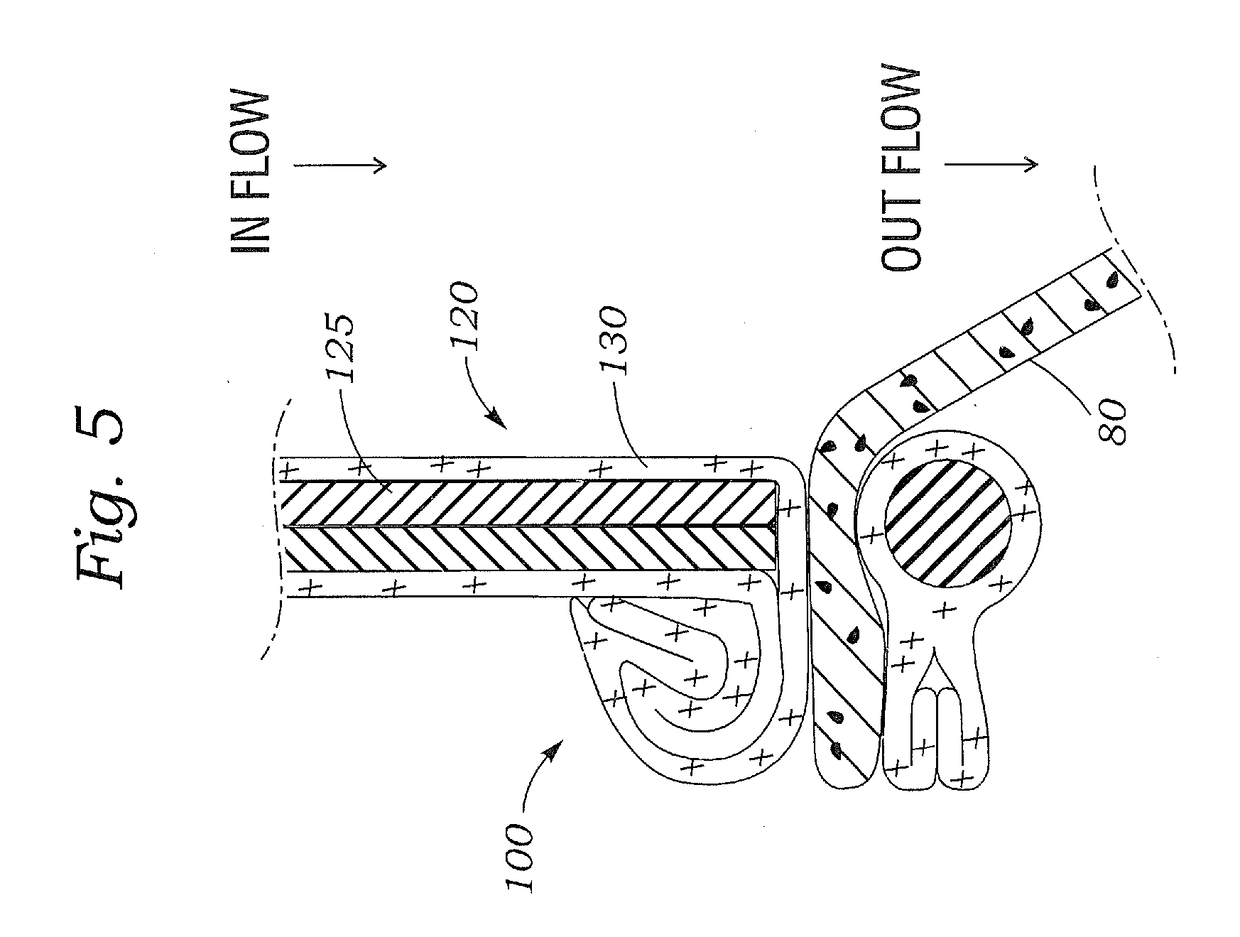
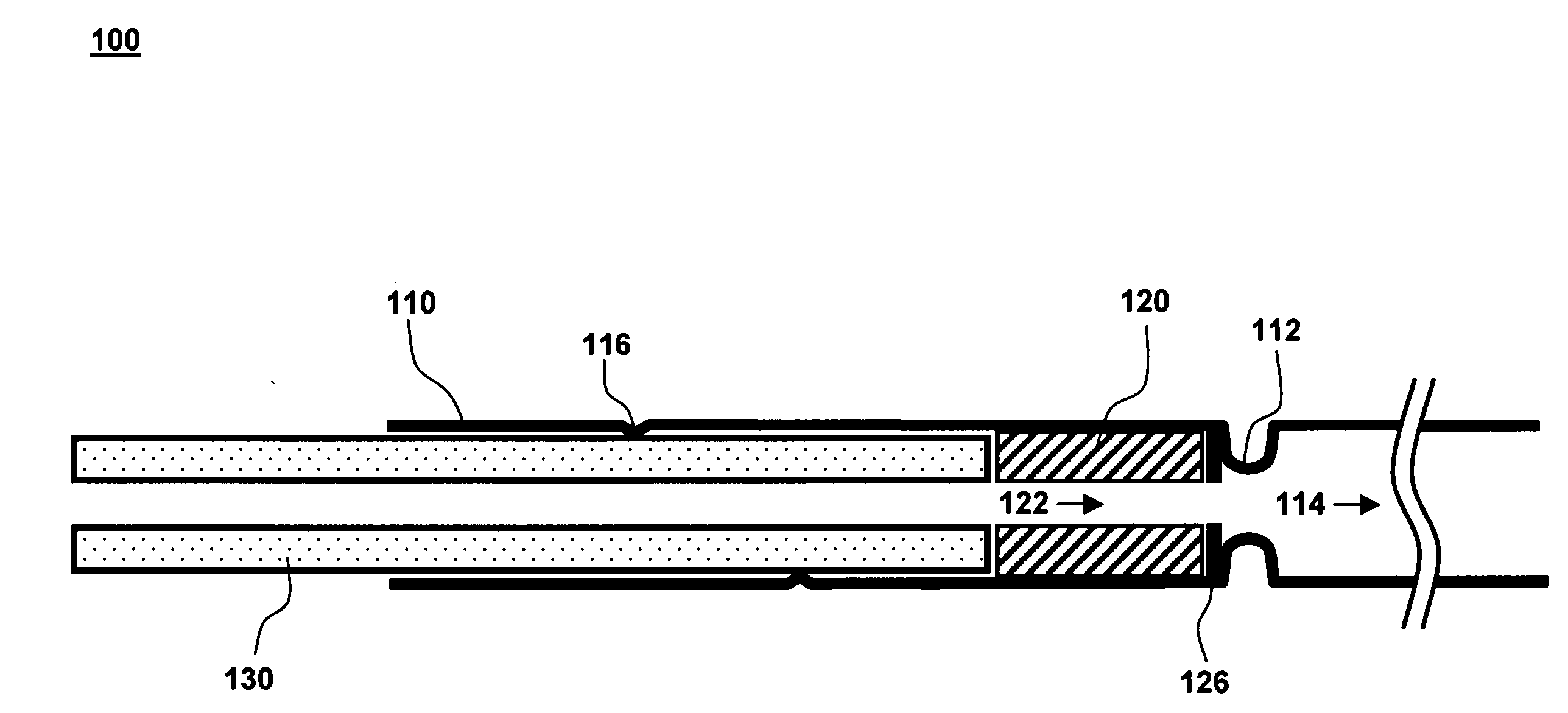
Low-profile valve contained within a catheter lumen
A low-profile catheter valve includes a catheter, an elastomeric plug having a channel, and a hollow stem. The catheter has at least one stop extending into a central lumen of the catheter adjacent to the catheter's proximal end. The elastomeric plug is received within the central lumen of the catheter and seated against the stop. The hollow stem is slidably received within the central lumen of the catheter. An axial force applied to the elastomeric plug via the stem compresses the plug and closes the channel. The stem is maintained in a position within the catheter by an interference fit between the stem and the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Blood control catheter valve employing actuator with flexible retention arms
ActiveUS9592367B2Tolerance requirement can be reducedEasy to manufactureGuide needlesInfusion syringesCATHETER ADAPTERActuator
The present invention extends to a blood control catheter valve for use in a catheter adapter. The blood control catheter value employs an actuator for bypassing a septum to open the blood control catheter valve. The actuator includes flexible retention arms positioned on one end which retract into the body of the actuator while the end of the actuator passes through the septum, and then expand outwardly to maintain the actuator positioned within the septum. This design facilitates the manufacturing of catheter adapters (as well as blood control catheter valves and other components that attach to the catheter adapter) because the design can reduce the tolerance requirements of such components. Further, the design provides a reliable blood control catheter valve that does not require the catheter adapter to be increased in size to accommodate the valve.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Covering and assembly method for transcatheter valve
A covering layer for a transcatheter heart valve is in various embodiments configured to prevent or reduce damage to the native valve tissue around the site where the prosthetic valve is implanted. In some cases, prosthetic valves are manufactured with the covering layer attached. Other covering layers are stand-alone accessories that can be mounted onto pre-existing prosthetic valves by an end user. Covering layers that can be mounted by an end user are provided with various features that can facilitate easier attachment of the covering layer to the prosthetic valve, which further reduces the possibility of damage to the covering layer or to the valve. Another covering is provided with two layers in order to insulate and protect the native tissue surrounding the implant from damage due to friction or abrasion, and / or other movement driven wear.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
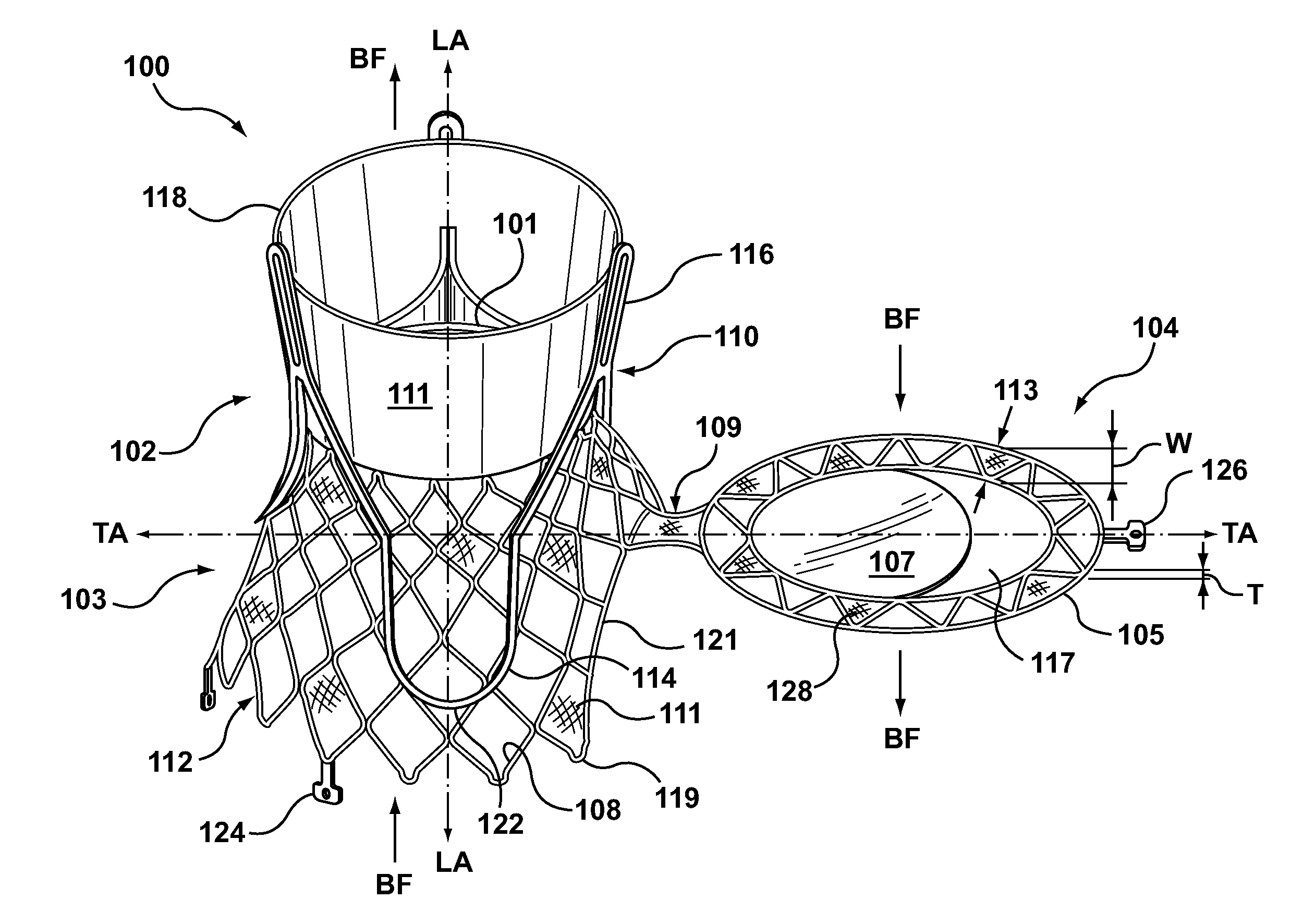
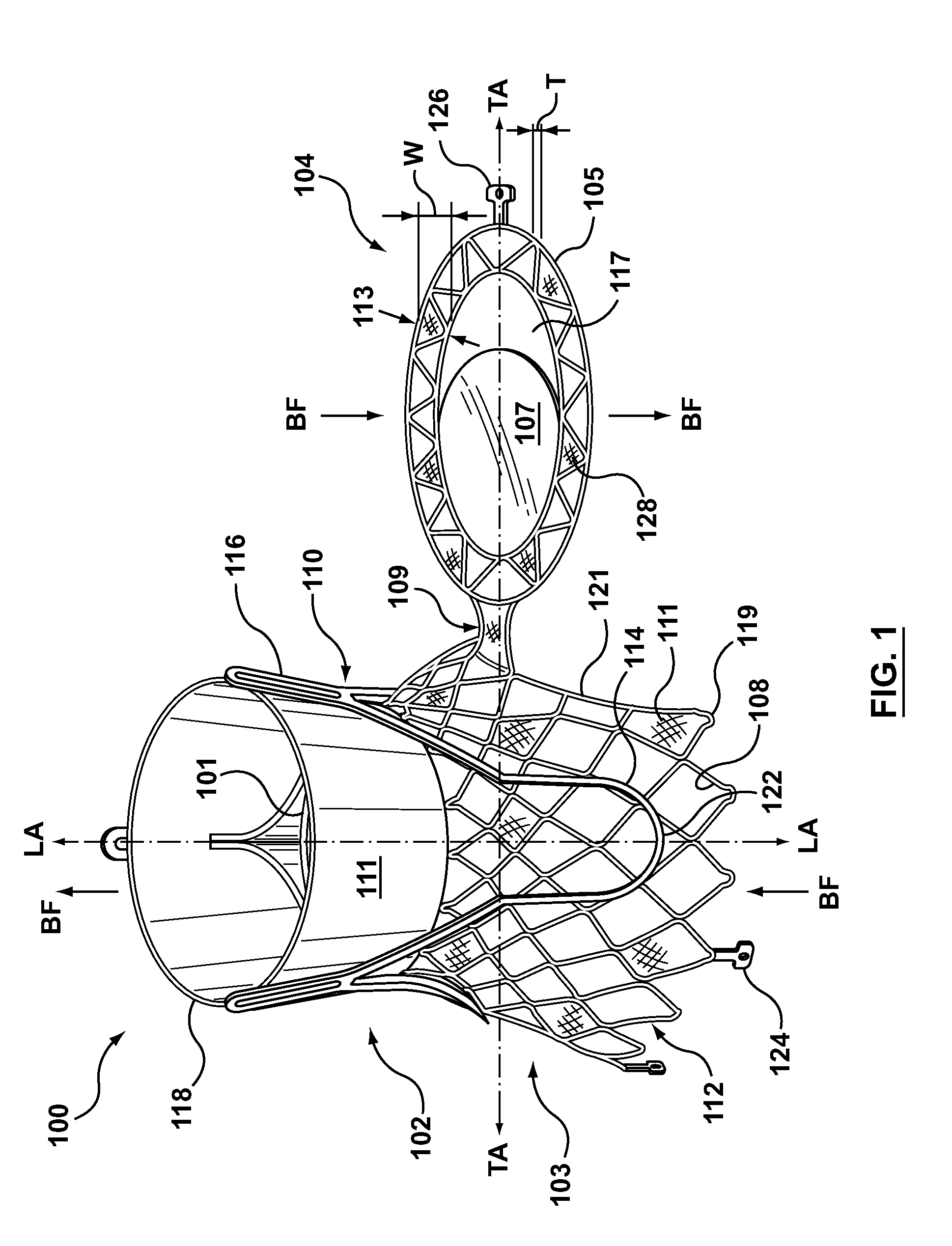
Distal subannular anchoring tab for side-delivered transcatheter valve prosthesis
The invention relates to a distal anchoring tab for an orthogonally delivered prosthetic mitral valve where the tab is extended using a guide wire to capture native mitral leaflet and / or chordae tissue and withdrawing the guide wire contracts the tab and pins the native tissue against the subannular sidewall of the prosthetic valve.
Owner:VDYNE INC
Anti-paravalvular leakage components for a transcatheter valve prosthesis
A valve prosthesis includes one or more anti-paravalvular leakage components coupled to a stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may encircle the stent and include a radially expandable control ring coupled to an unattached edge of a flexible skirt which extends the unattached skirt edge outwardly away from the stent and against the native heart valve to form an open-ended annular pocket around the stent. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may encircle the perimeter of the stent and include a flexible skirt having opposing edges coupled to the stent to form one or more enclosed compartments around the stent. Each compartment includes a one-way valve which allows for blood flow into the compartment but prevents blood flow out of the compartment. The anti-paravalvular leakage component may be at least one flap that is coupled to an inner surface of the stent and formed of a flexible material moveable by blood flow.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
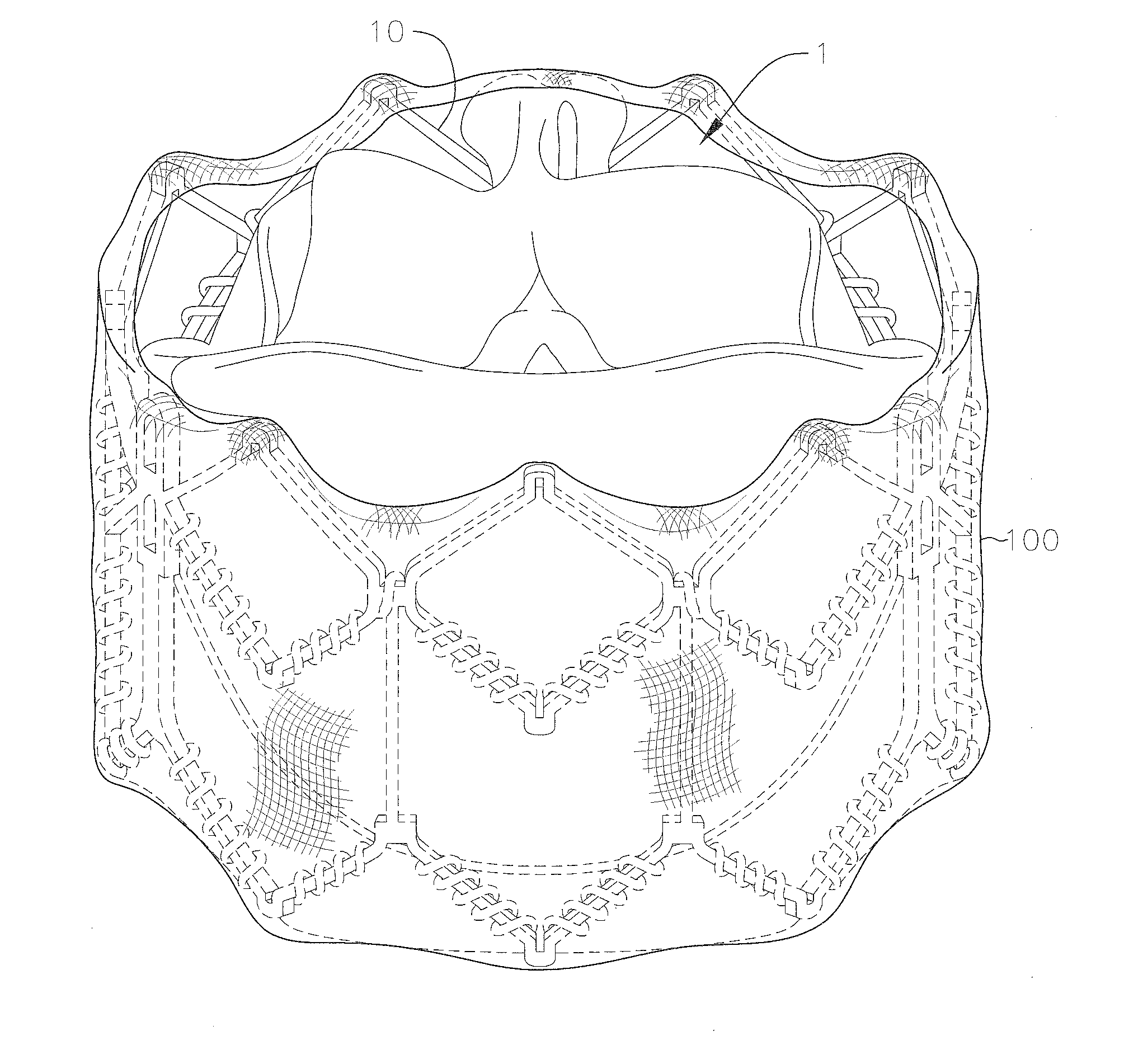
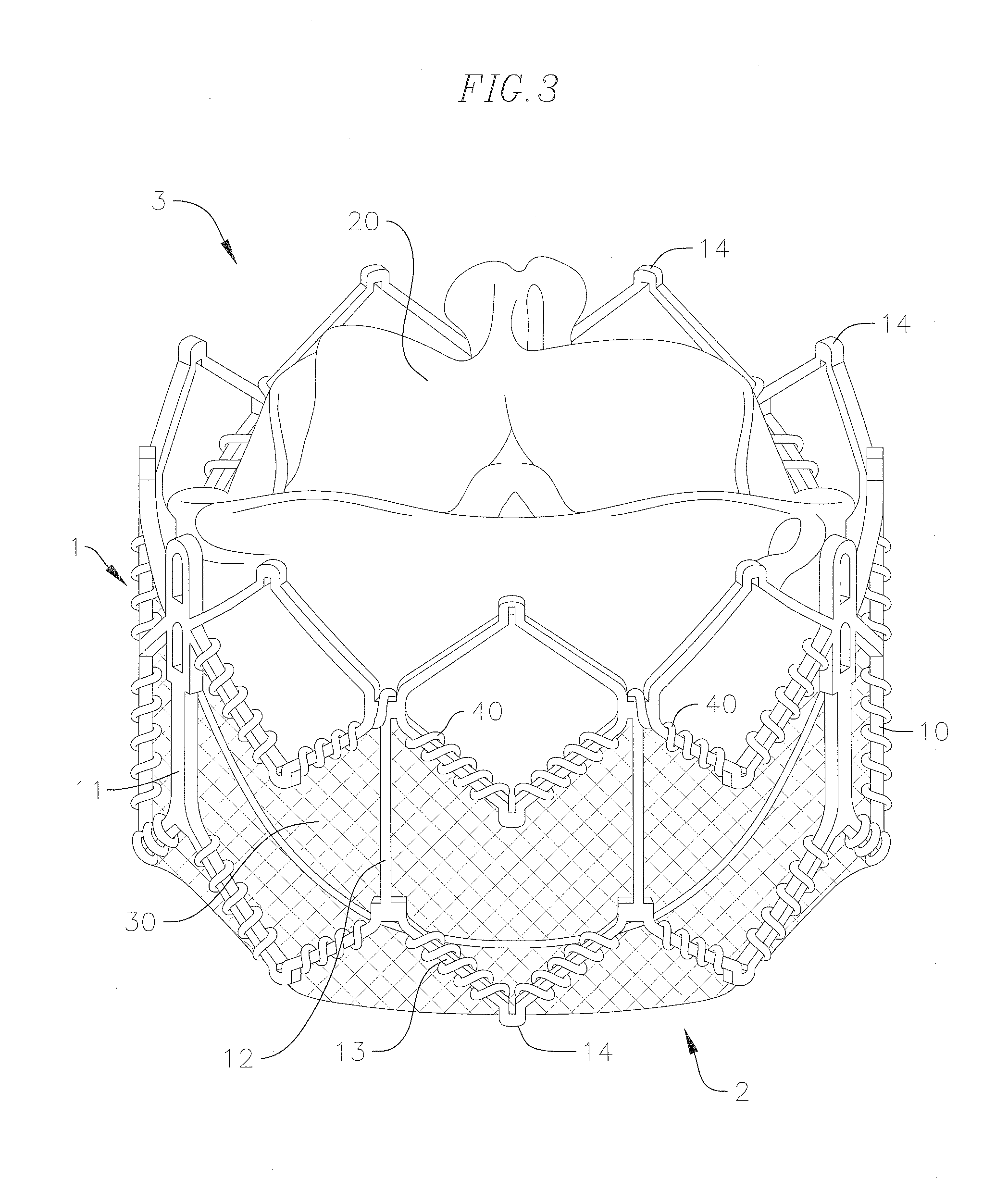
Valve prostheses having an integral centering mechanism and methods of use thereof
A transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular stent, a prosthetic valve component disposed within and secured to the stent, and a centering mechanism coupled to and encircling an outer surface of the tubular stent. The centering mechanism includes a self-expanding centering ring having an expanded diameter in the expanded configuration that is greater than an expanded diameter of the tubular stent in the expanded configuration and a plurality of self-expanding spokes radially extending between the tubular stent and the centering ring. The centering mechanism may include a base ring and / or a skirt. Alternatively, the centering mechanism includes a plurality of self-expanding loops. When each loop is in a delivery configuration the loop has a straightened profile that proximally extends from a proximal end of the tubular stent. When each loop is in an expanded configuration the loop has a U-shaped profile radially spaced apart from the tubular stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Valve prostheses having an integral centering mechanism and methods of use thereof
A transcatheter valve prosthesis including a tubular stent, a prosthetic valve component disposed within and secured to the stent, and a centering mechanism coupled to and encircling an outer surface of the tubular stent. The centering mechanism includes a self-expanding centering ring having an expanded diameter in the expanded configuration that is greater than an expanded diameter of the tubular stent in the expanded configuration and a plurality of self-expanding spokes radially extending between the tubular stent and the centering ring. The centering mechanism may include a base ring and / or a skirt. Alternatively, the centering mechanism includes a plurality of self-expanding loops. When each loop is in a delivery configuration the loop has a straightened profile that proximally extends from a proximal end of the tubular stent. When each loop is in an expanded configuration the loop has a U-shaped profile radially spaced apart from the tubular stent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
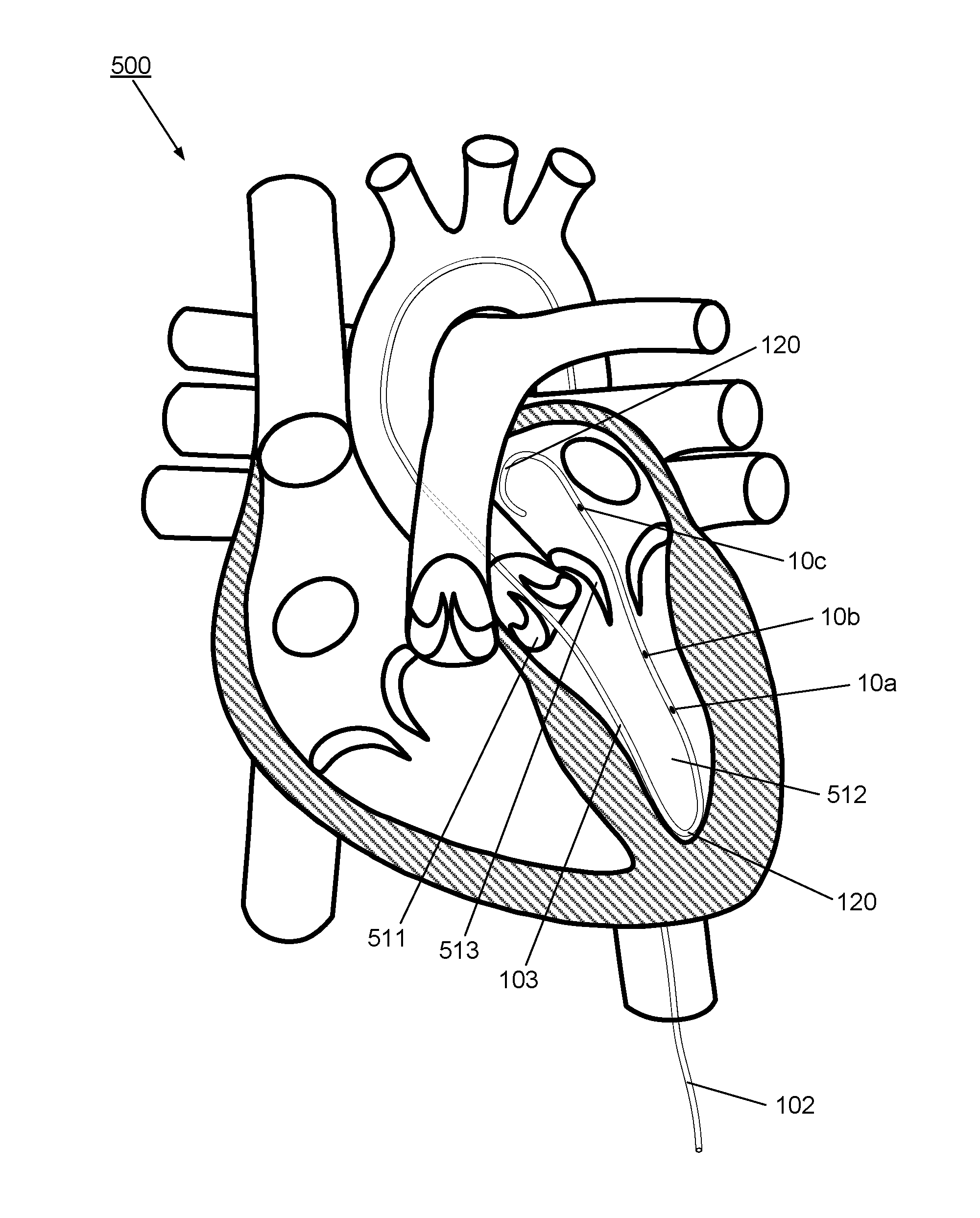
Guidewire Delivery of Transcatheter Heart Valve
The invention relates to delivery system for deployment of a prosthetic valve, having a hypotube sheathed guidewire assembly having an outer sheath and an inner guidewire shaft that pushes against a guidewire collar on a tension arm of a compressed transcatheter valve to deliver the valve and position the valve to the RVOT or other location in the body.
Owner:VDYNE INC
System and apparatus comprising a multisensor guidewire for use in interventional cardiology
InactiveUS20160128583A1Reduce disadvantagesAvoiding tissue trauma or perforationHeart valvesCatheterControl systemMultiple sensor
A system and apparatus comprising a multisensor guidewire for use in interventional cardiology, e.g. for Transcatheter Valve Therapies (TVT), comprises a plurality of optical sensors for direct measurement of cardiovascular parameters, e.g. transvalvular blood pressure gradients and flow. A conventional outer coil contains a shaped core wire having a cross-section defining helical grooves extending along its length, which accommodate optical fibers and optical sensors within a diameter Dcore of the core wire. Advantageously, the diameter and material of the core wire provides the guidewire with sufficient stiffness for use as a support guidewire for valve replacement, e.g. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), while accommodating multiple sensors and optical fibers within a guidewire of outside diameter ≦0.89 mm. An optical connector couples the guidewire to a control system. Optionally, the guidewire includes a contact force sensor; a pre-formed tip; and / or a separable micro-connector for proximal mounting of over-the-guidewire components.
Owner:THREE RIVERS CARDIOVASCULAR SYST
System and method for assessing dimensions and eccentricity of valve annulus for trans-catheter valve implantation
A system for detecting the dimensions and geometry of a native valve annulus for trans-catheter valve implantation includes a compliant balloon and a shaft within the balloon. One or more drive electrodes may be affixed to a surface of the balloon, and one or more sense electrodes may be affixed to the shaft. After insertion of the balloon into the native valve annulus, the drive electrodes may be energized with a predetermined voltage. Using a trained statistical model and the voltages measured at the sense electrodes, initial estimates of the cross-section of the valve annulus may be obtained. The initial estimates may then be provided to an optimization model of the valve annulus to obtain a highly accurate prediction of the cross-section of the valve annulus.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com