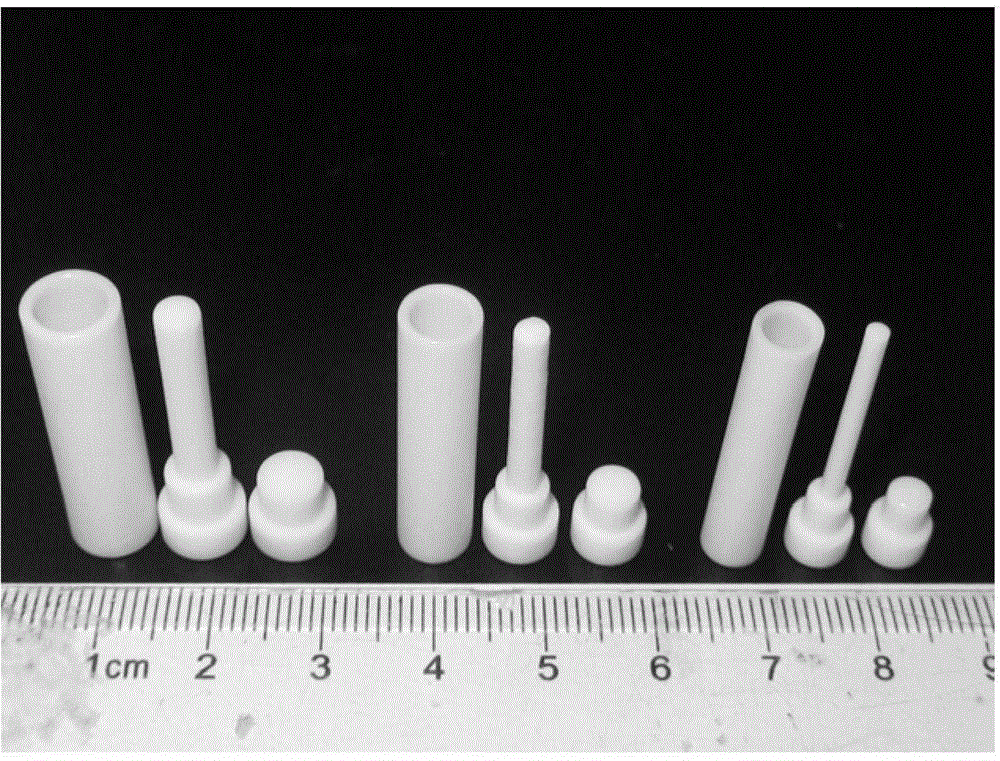
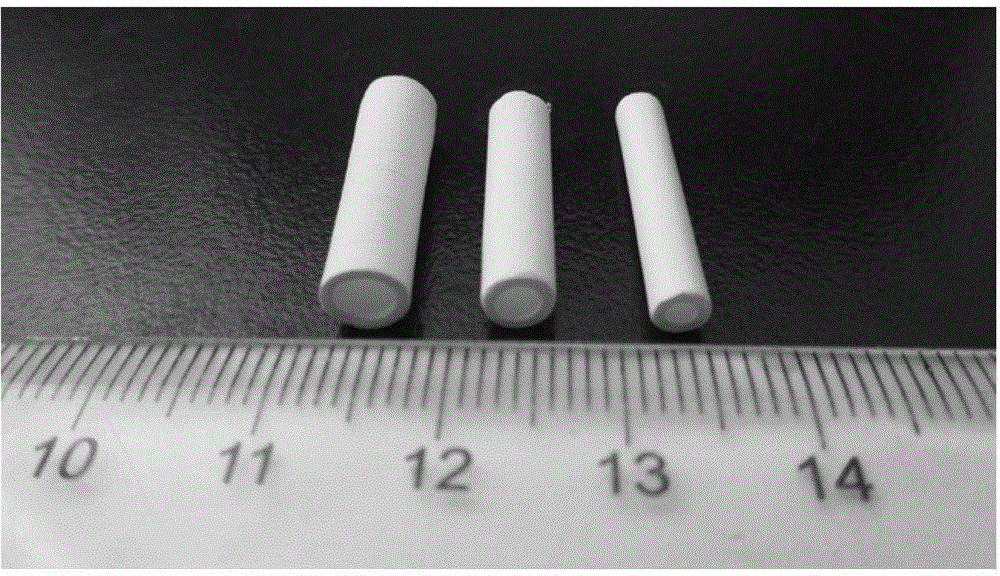
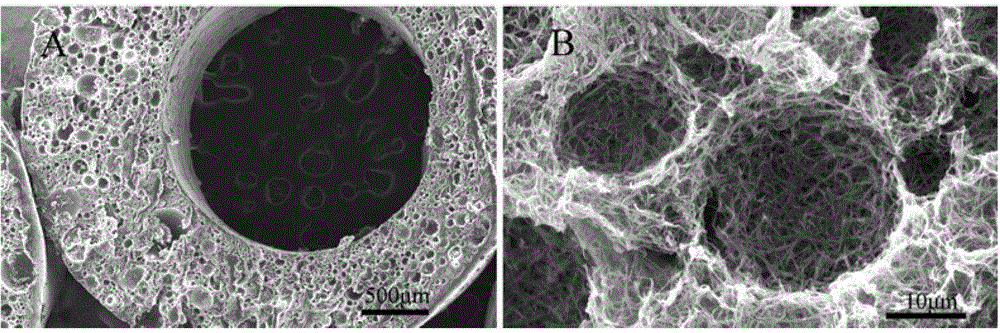
Preparation method of porous nano-fiber tubular scaffold
A nanofiber and tubular technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of tubular tissue engineering scaffolds, can solve the problems of high brittleness of PLLA scaffolds and difficulty in providing toughness and elasticity of tubular tissues, and achieve low equipment requirements, improved toughness and elasticity, and simple preparation process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The nanofibrous tubular scaffold with porous structure was prepared under the condition of mass ratio PLLA:PCL=70:30 and total polymer concentration of 0.05 g / mL.
[0033] (1) Dissolve PLLA and PCL in tetrahydrofuran at 55°C at a ratio of 70:30 to form a homogeneous solution;
[0034] (2) Inject the polymer solution into the polytetrafluoroethylene mold, and quickly place it at -80°C to allow phase separation to occur overnight;
[0035] (3) Take it out from the low temperature, and remove the shell of the mold, soak the gelled polymer and the core mold in deionized ice water for 30 minutes, take out the core mold, and soak the polymer in deionized Exchange the solvent in ice water for 2 days, and change the deionized ice water three times a day;
[0036] (4) The tubular scaffold is taken out from the deionized water and freeze-dried to obtain a nanofiber tubular scaffold with a porous structure.
Embodiment 2
[0038] The porous nanofibrous tubular scaffold was prepared under the condition of mass ratio of PLLA:PU=70:30 and total polymer concentration of 0.1g / mL.
[0039] (1) Dissolve PLLA and PU in tetrahydrofuran at 60°C at a ratio of 70:30 to form a homogeneous solution;
[0040] (2) Inject the polymer solution into the polytetrafluoroethylene mold, and quickly place it at -100°C to allow phase separation to occur overnight;
[0041] (3) Take it out from the low temperature, and remove the shell of the mold, soak the gelled polymer and the core mold in deionized ice water for 30 minutes, take out the core mold, and soak the polymer in deionized Exchange the solvent in ice water for 3 days, and change the deionized ice water three times a day;
[0042] (4) The tubular scaffold is taken out from the deionized water and freeze-dried to obtain a nanofiber tubular scaffold with a porous structure.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The porous nanofiber tubular scaffold was prepared under the condition of mass ratio of PLLA:PLGA=60:40 and total polymer concentration of 0.15g / mL.
[0045] (1) Dissolve PLLA and PLGA in tetrahydrofuran at 70°C at a ratio of 60:40 to form a homogeneous solution;
[0046] (2) Inject the polymer solution into the polytetrafluoroethylene mold, and quickly place it at -50°C to allow phase separation to occur overnight;
[0047] (3) Take it out from the low temperature, and remove the shell of the mold, soak the gelled polymer and the core mold in deionized ice water for 30 minutes, take out the core mold, and soak the polymer in deionized Exchange the solvent in ice water for 3 days, and change the deionized ice water three times a day;
[0048] (4) The tubular scaffold is taken out from the deionized water and freeze-dried to obtain a nanofiber tubular scaffold with a porous structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com