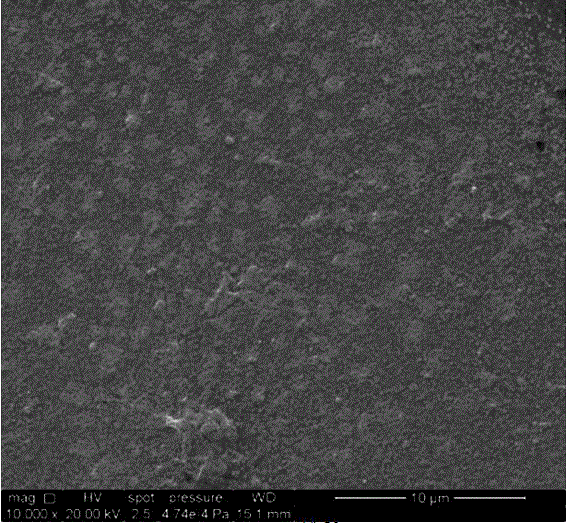
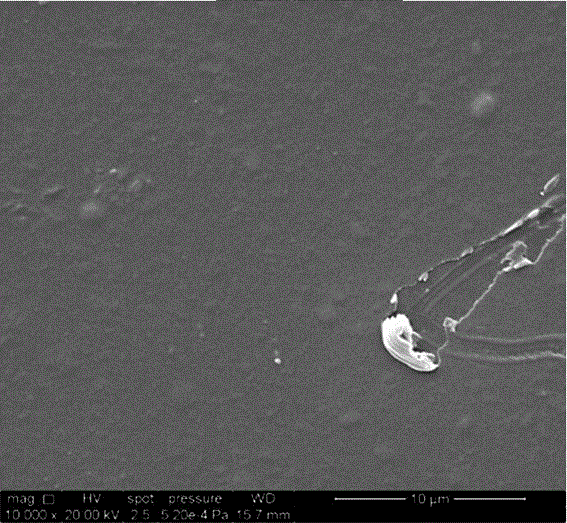
Preparation method of polyester material capable of preventing platelet adhesion without affecting platelet function
A polyester material, anti-platelet technology, applied in anti-coagulation treatment, packaging item types, special packaging items, etc., can solve the problem of increased leukocyte removal during filtration, the influence of platelet function has not been paid attention to, and platelet adhesion and platelet function. Affect unresearched problems, and achieve the effect of improving blood compatibility, improving hydrophilicity and blood compatibility, and inhibiting platelet activation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Preparation method of polyester material that resists platelet adhesion and does not affect platelet function:
[0035] S1. Soak the polyester material in 3 mg / mL polyethyleneimine solution for 1 hour, and carry out amination treatment on the material;
[0036] S2. Soak the polyester material in a dopamine solution (prepared in PBS, pH=7.4, concentration 2mg / mL), add hydrogen peroxide (wt5%-15%), and shake at a constant temperature for 12 hours to make dopamine self-polymerize on the surface of the polyester material to form polydopamine coating;
[0037] S3. Soak the aminated polyester material obtained in S1 or the dopamine-coated polyester material obtained in S2 in sodium heparin solution (prepared in acetate buffer solution, pH=4.0, concentration 1 mg / mL), shake at constant temperature for 15 minutes, Loading heparin on the surface of the material through electrostatic interaction, and then rinsing with acetate buffer solution with pH=4.0 for 2-4 times;...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Changing the reaction conditions to construct a hydrophilic polyester material through layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembly
[0041] S1. Soak the polyester material in a dopamine solution (prepared in PBS, pH=7.4, concentration 1mg / mL), add hydrogen peroxide (wt5%-15%), and shake at a constant temperature for 6 hours to make dopamine self-polymerize on the surface of the polyester material to form polydopamine coating;
[0042] S2. Soak the dopamine-coated polyester material obtained in S1 in sodium heparin solution (prepared in acetate buffer solution, pH=4.0, concentration 1 mg / mL), shake at constant temperature for 15 minutes, so that heparin can be loaded on the surface of the material through electrostatic action , and then rinsed 2-4 times with acetate buffer solution of pH=4.0;
[0043] S3. Soak the polyester material of surface self-assembled polyanionate obtained in S2 in a solution of dopamine (prepared in PBS, pH=7.4, concentration 2mg / mL), ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Regulating the hydrophilicity and surface heparin content of polyester materials through the number of assembled layers
[0046] The layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembled polyester material was prepared according to the method of Example 1 and Example 2, and the hydrophilicity of the polyester material assembled with different layers and different polyelectrolytes was characterized by static water contact angle. The toluidine blue method was used to detect the heparin content on the surface of the material, and the specific method was as follows:
[0047] S1 draw standard curve
[0048] Prepare 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 μg / mL heparin standard solutions, and accurately pipette 0.25 mL of 0.005% toluidine blue solution (prepared with 0.01 mol HCl solution containing 0.2% NaCl) to 8 Into a clean test tube, add 0.1mL of heparin standard solution of different concentrations, then add 1mL of 0.2% NaCl solution, immediately vortex vigorously, then im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com