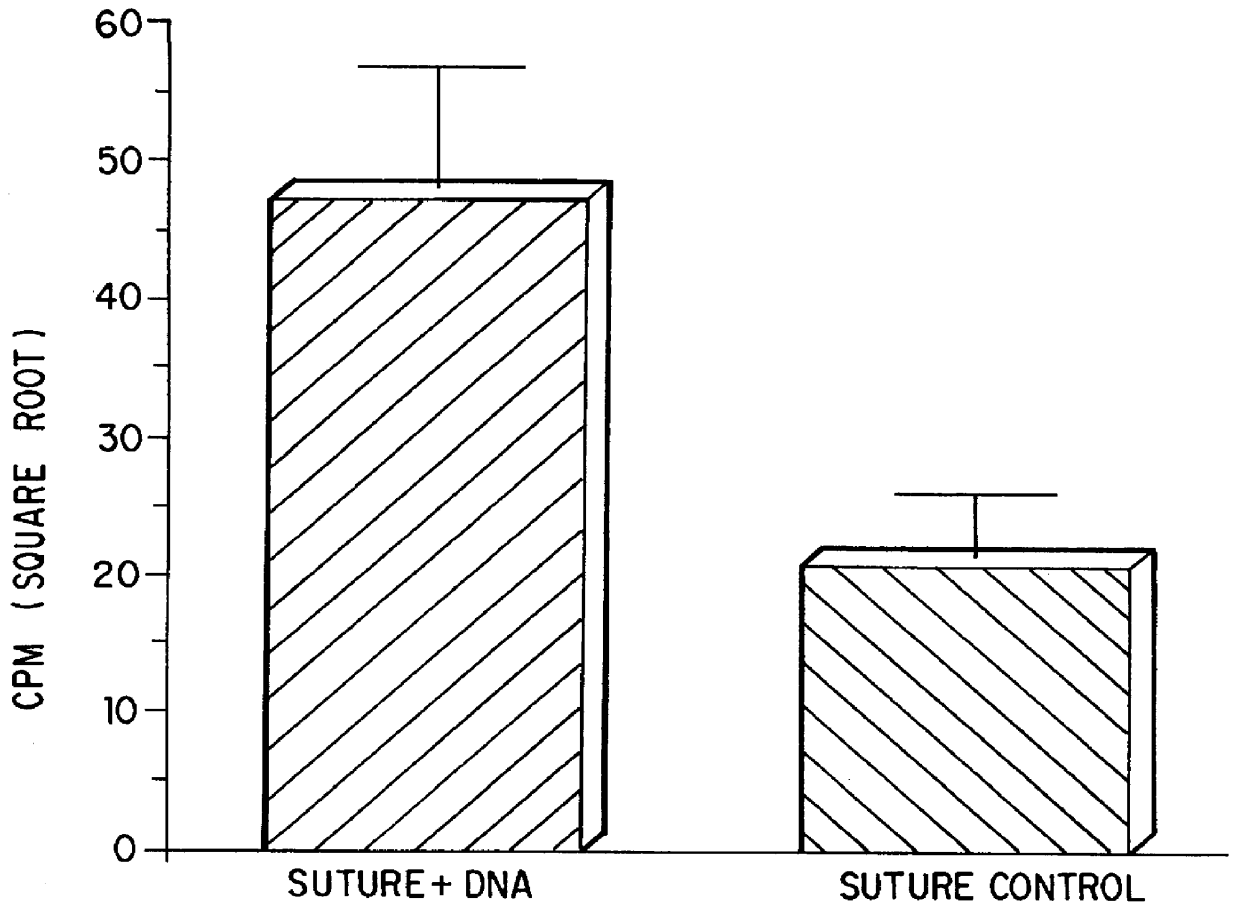
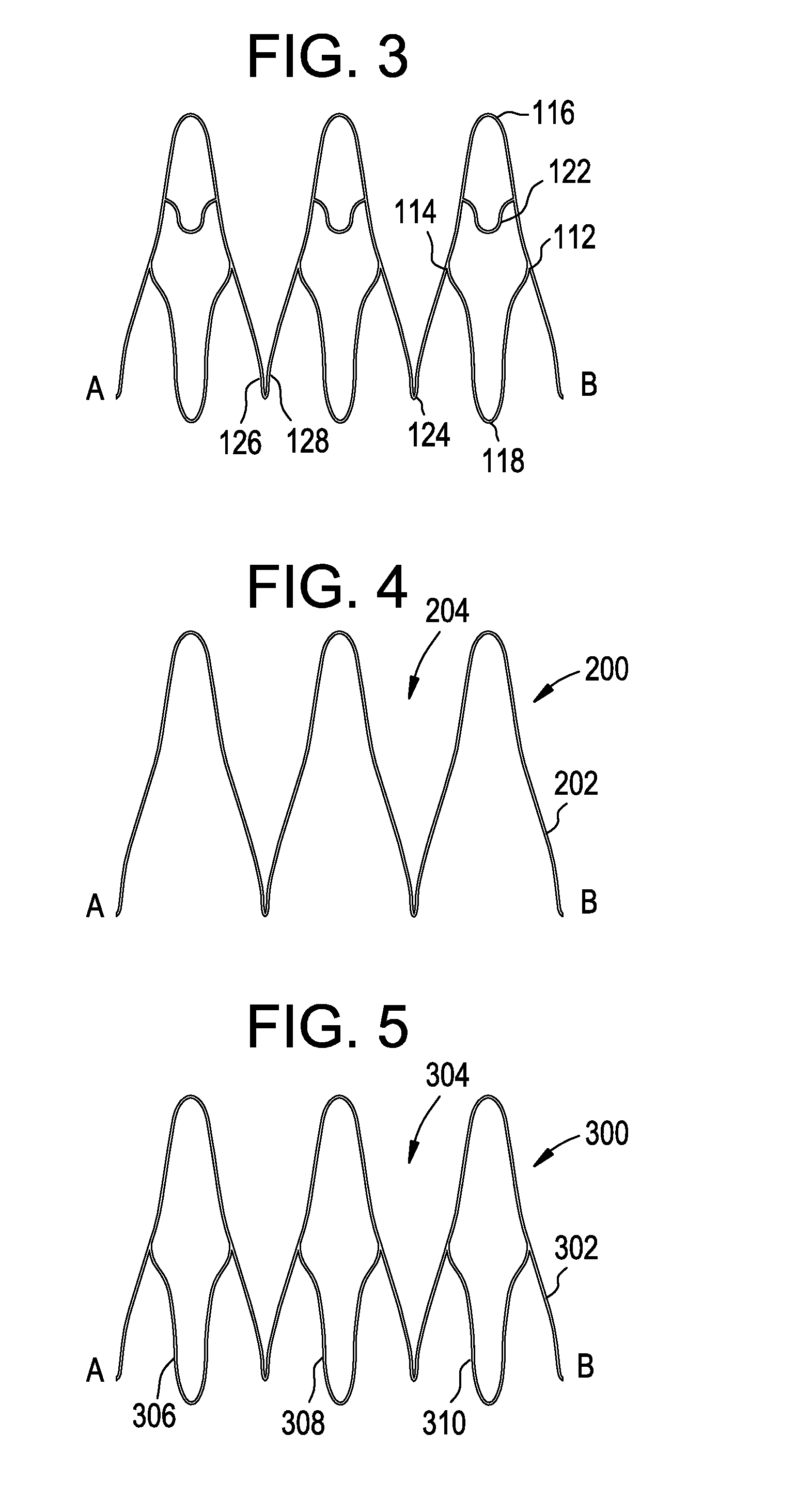
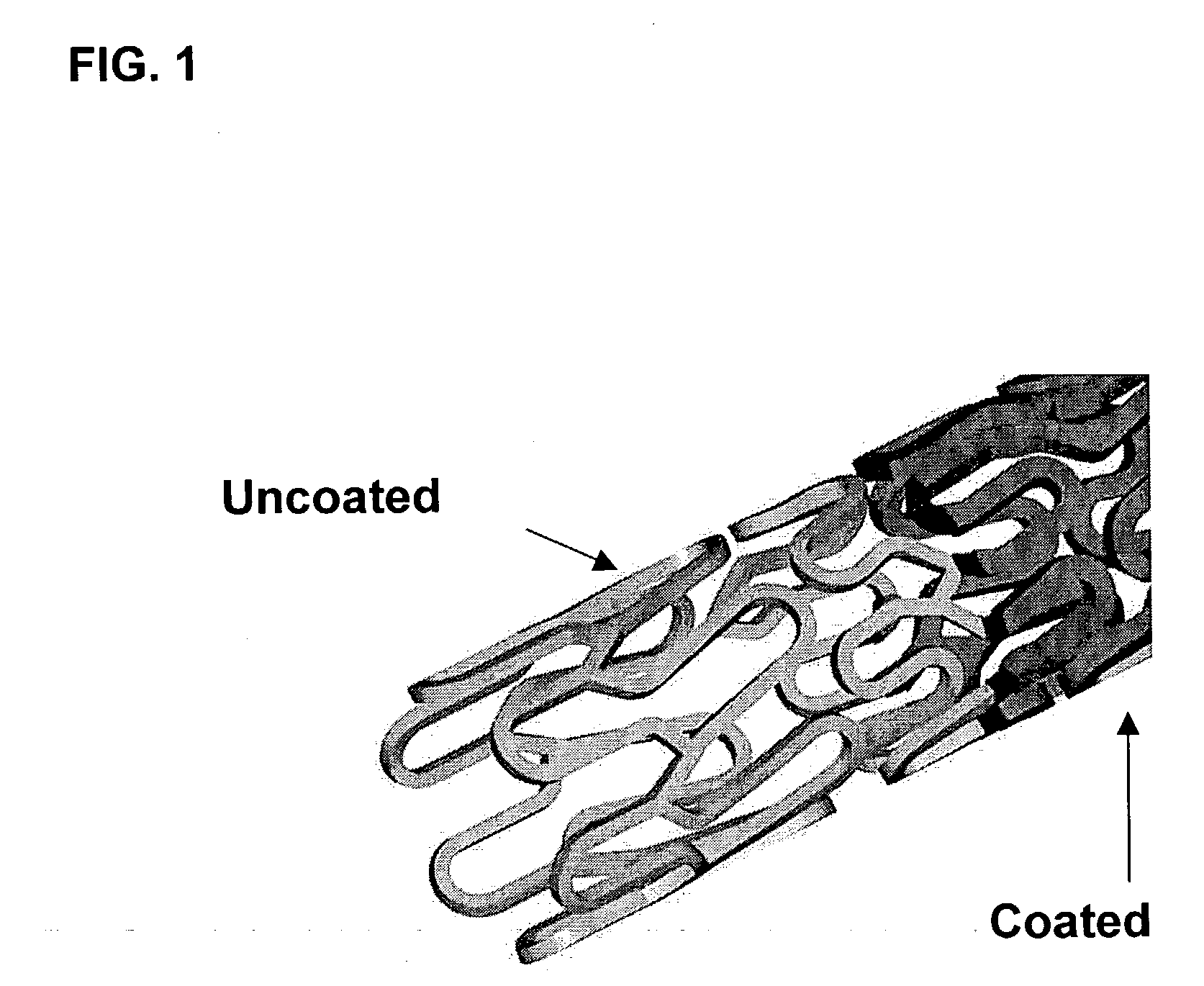
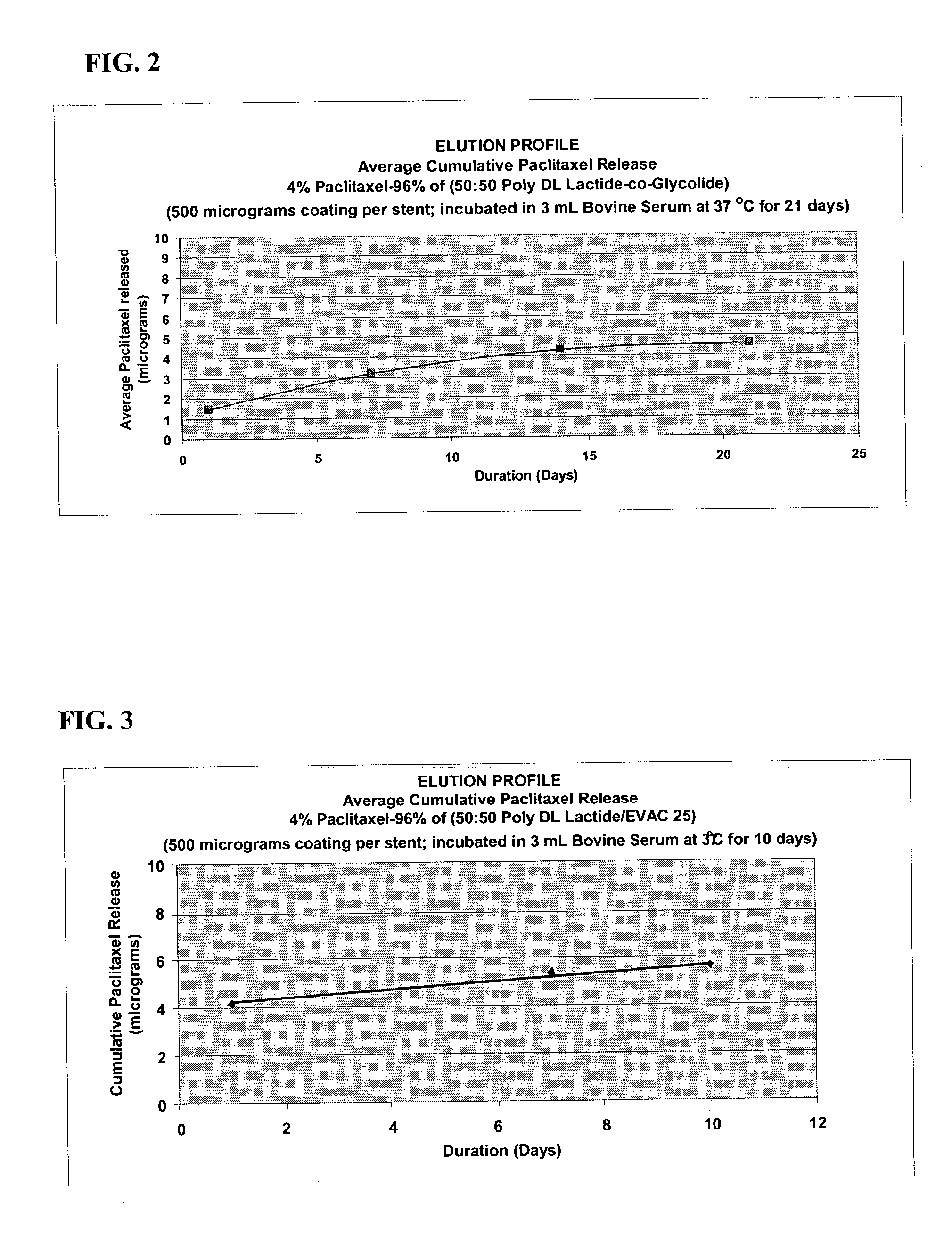
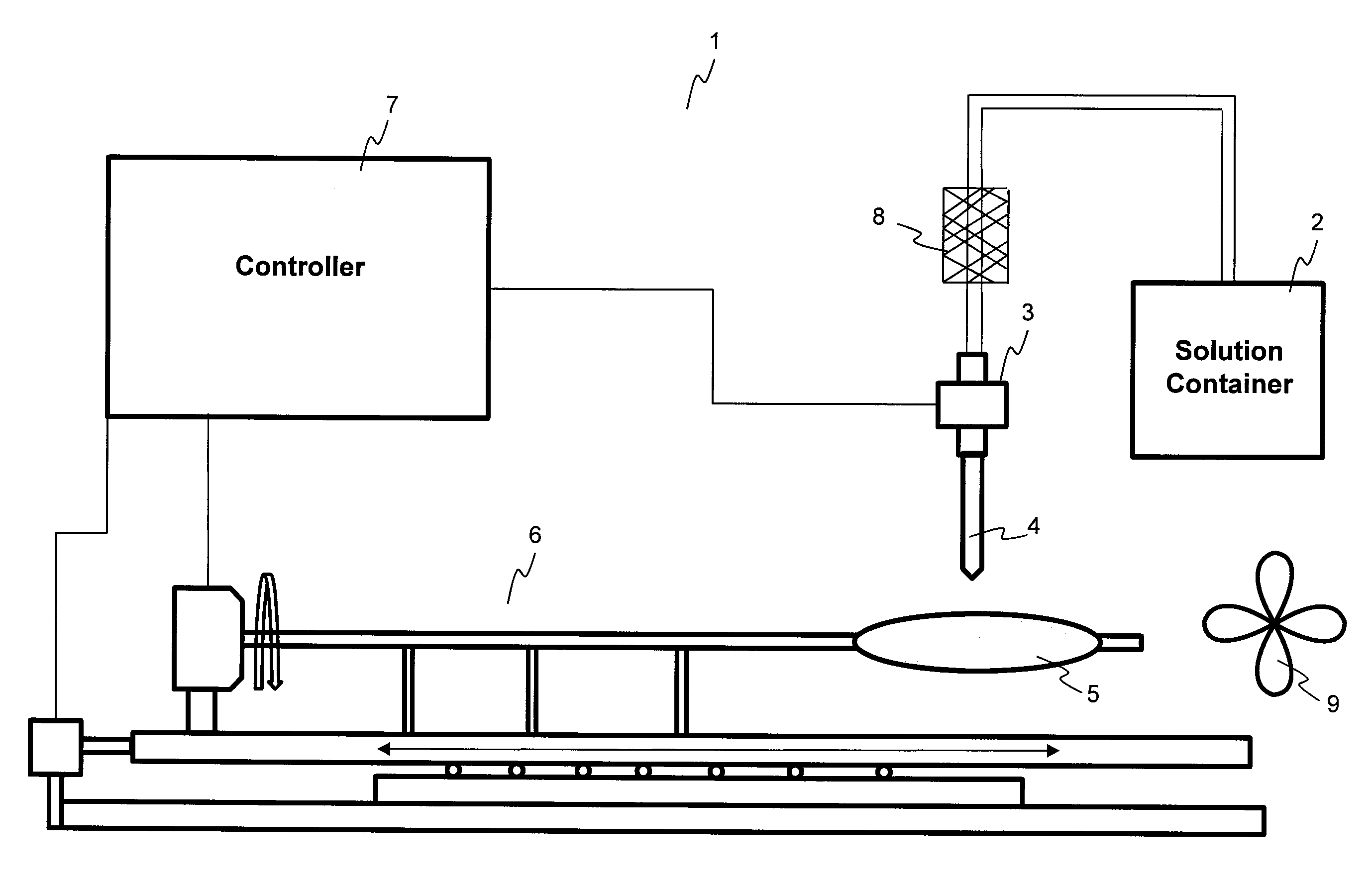
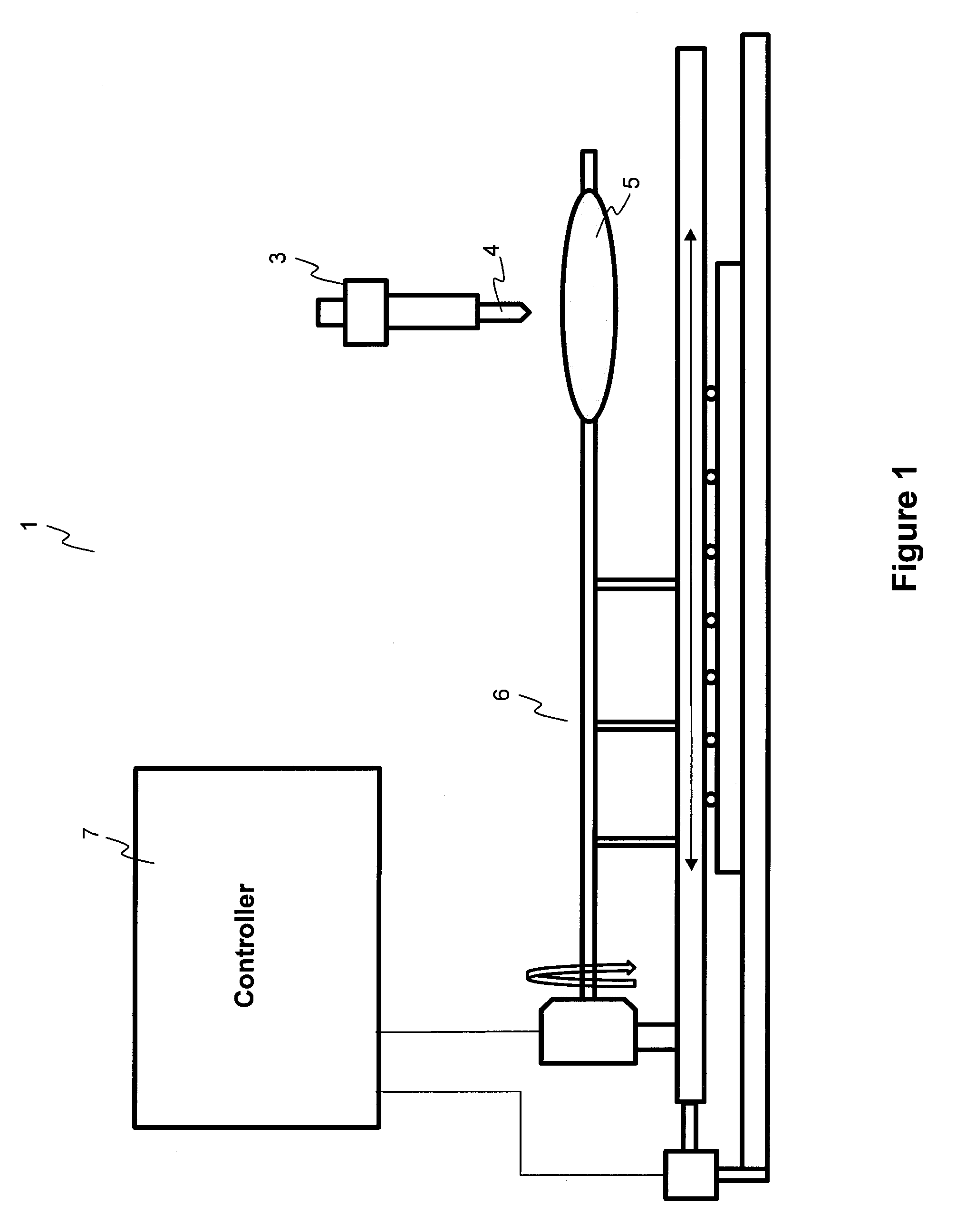
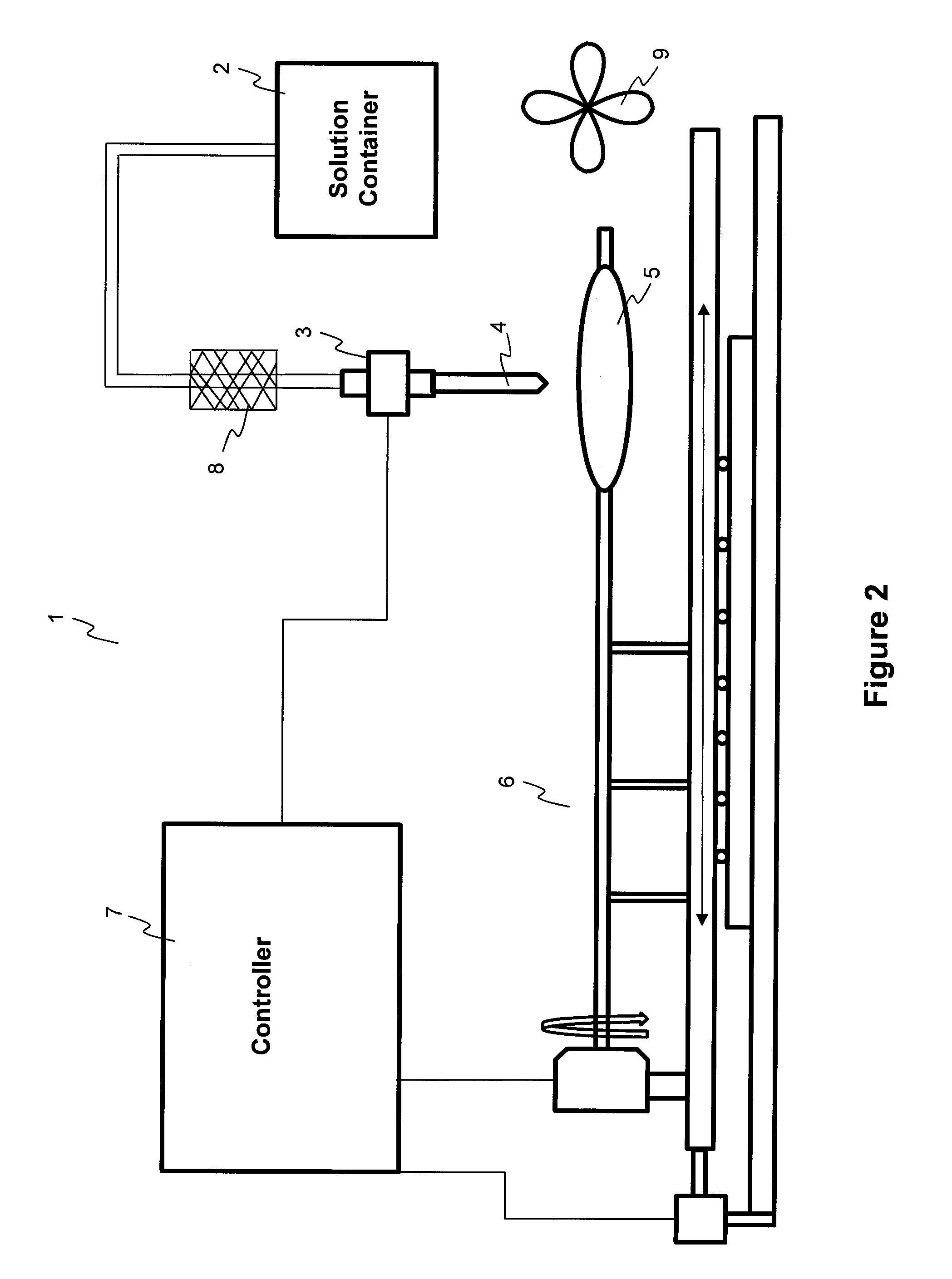
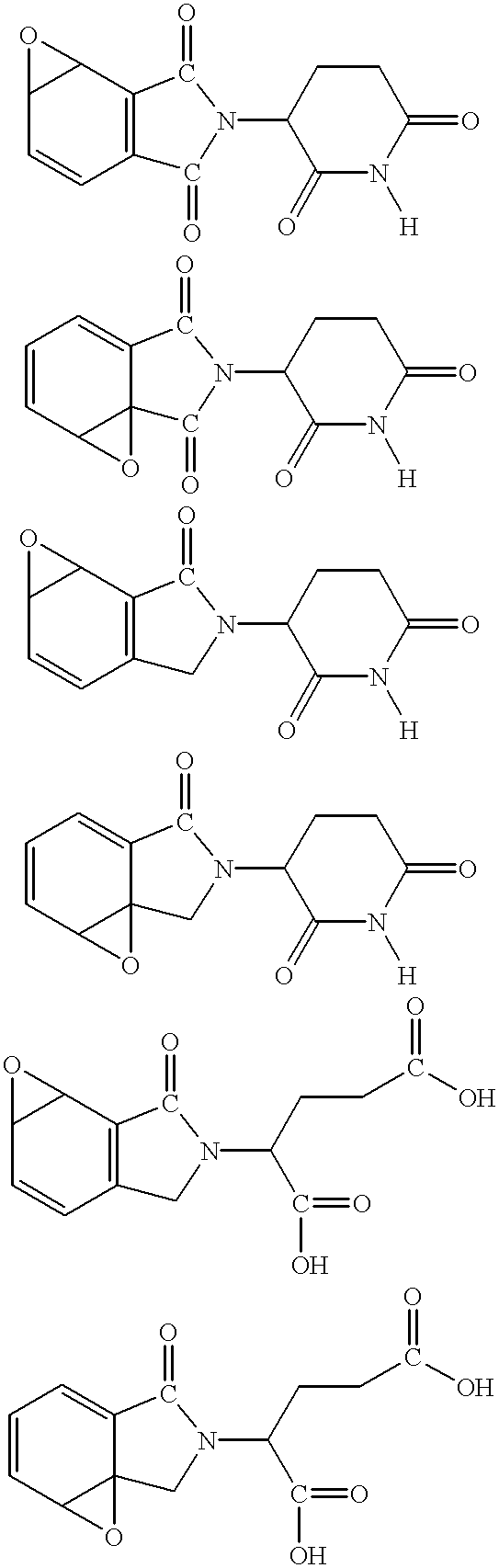
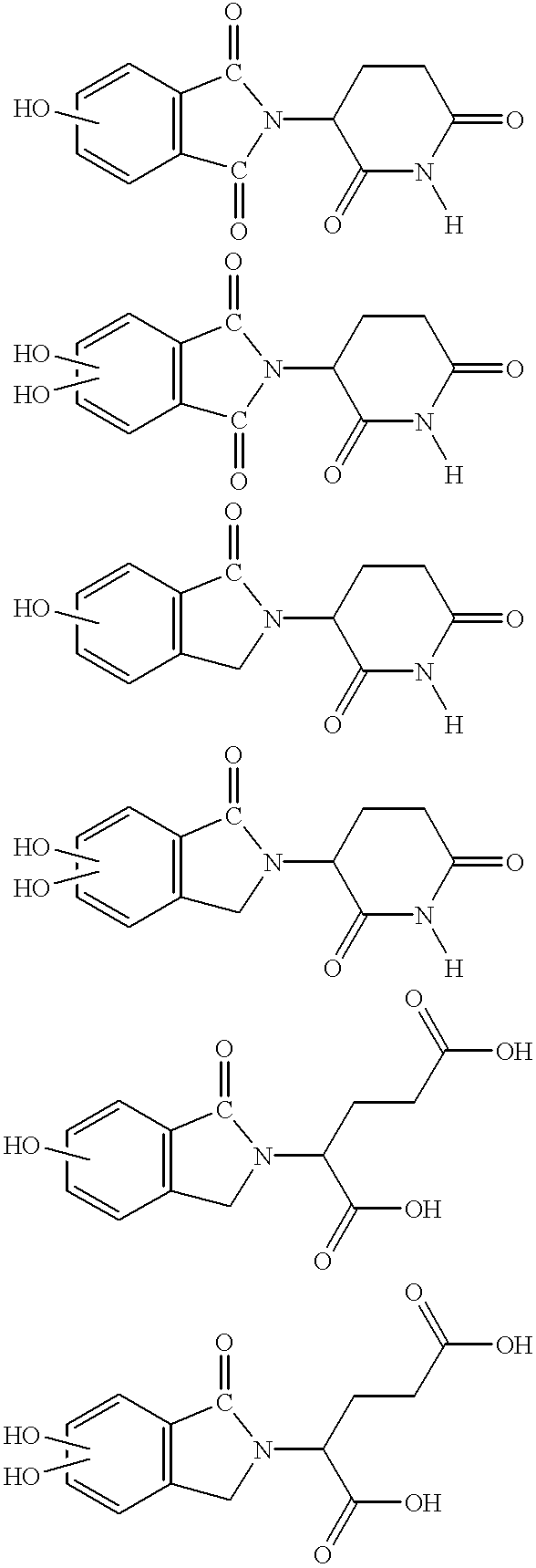
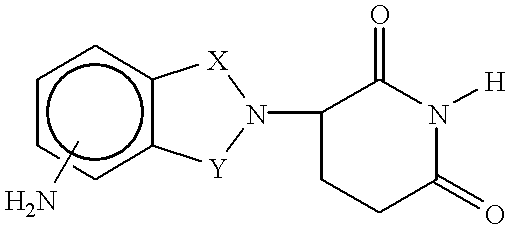
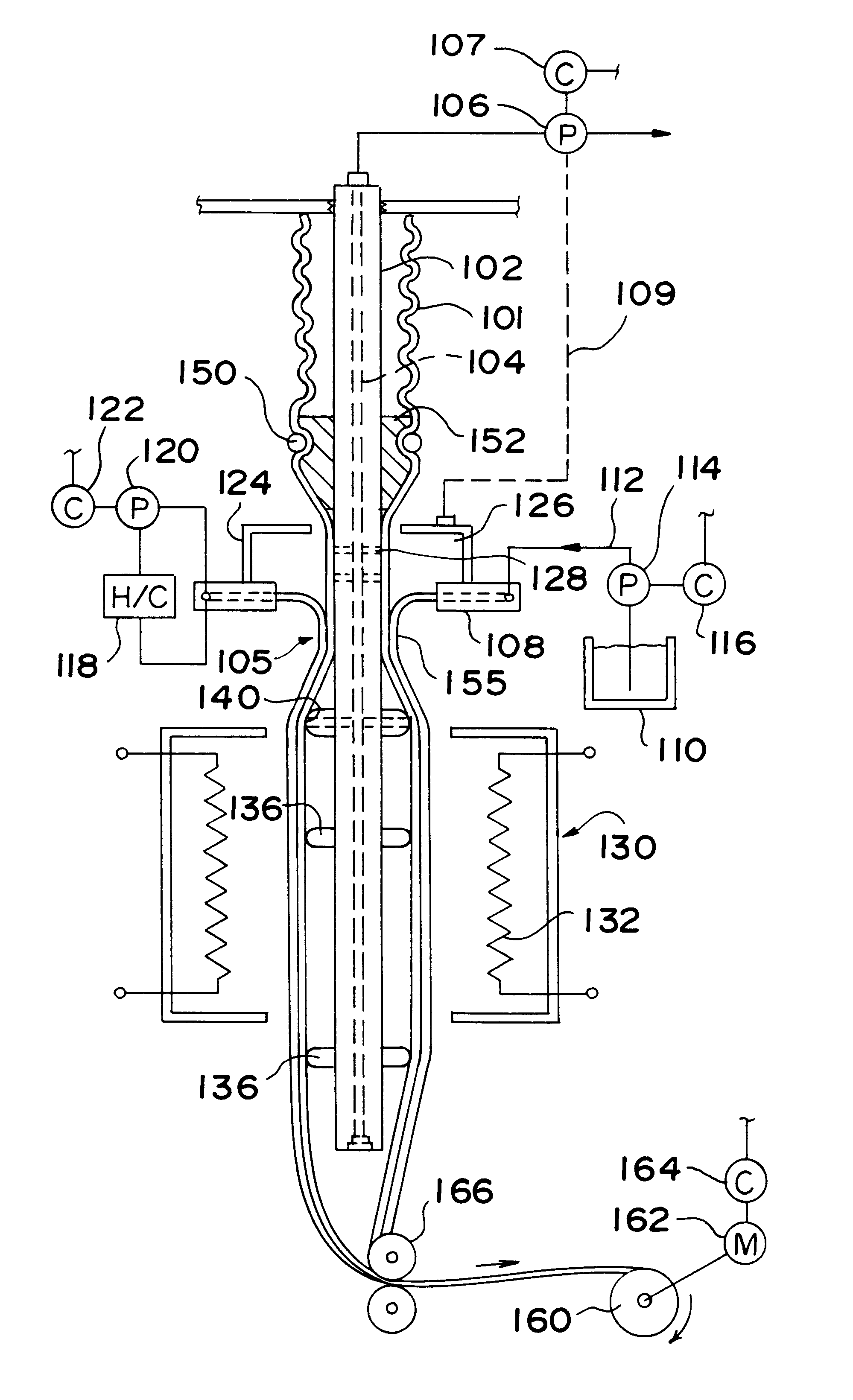
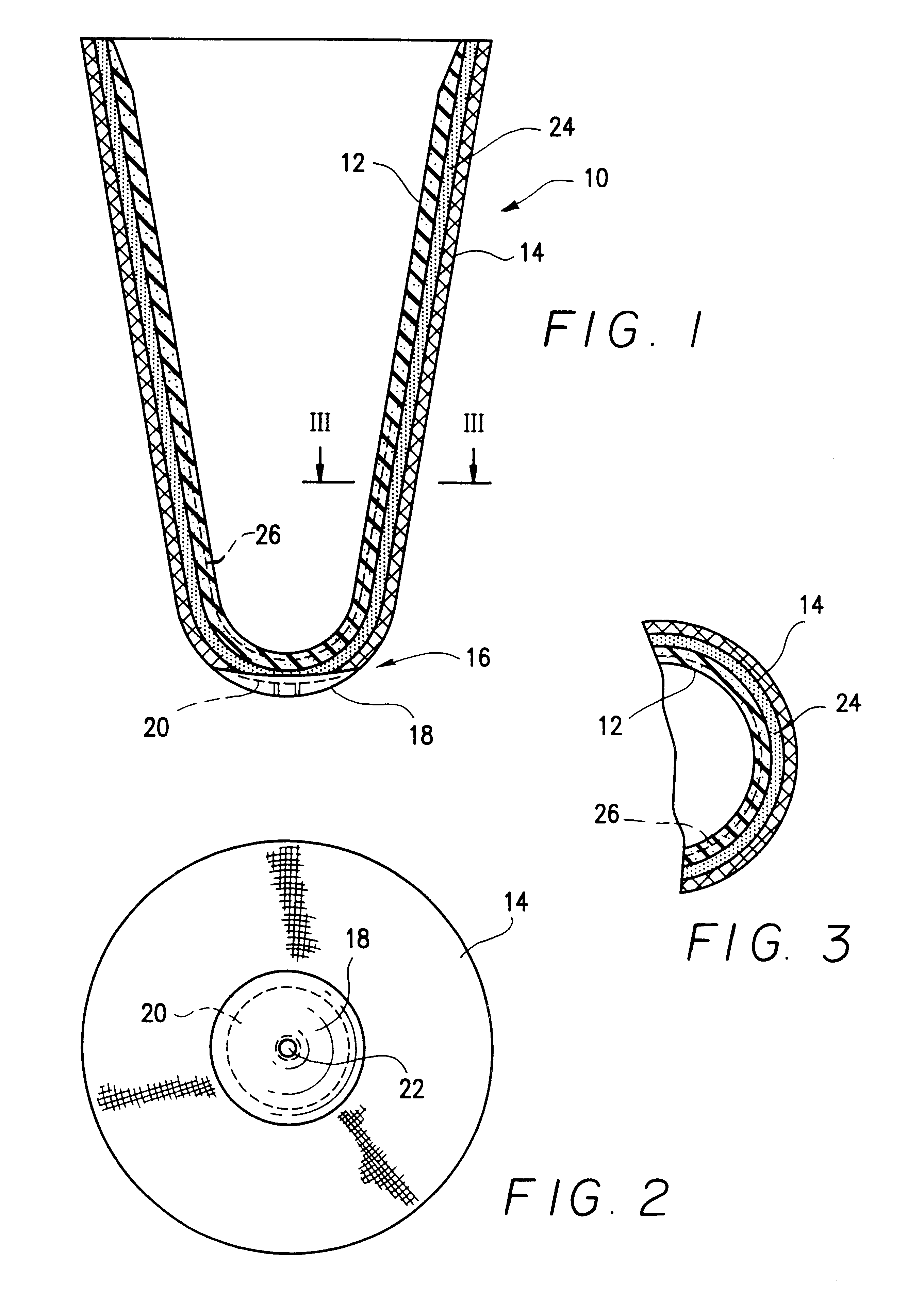
Patents
Literature
2991results about "Antithrombogenic treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
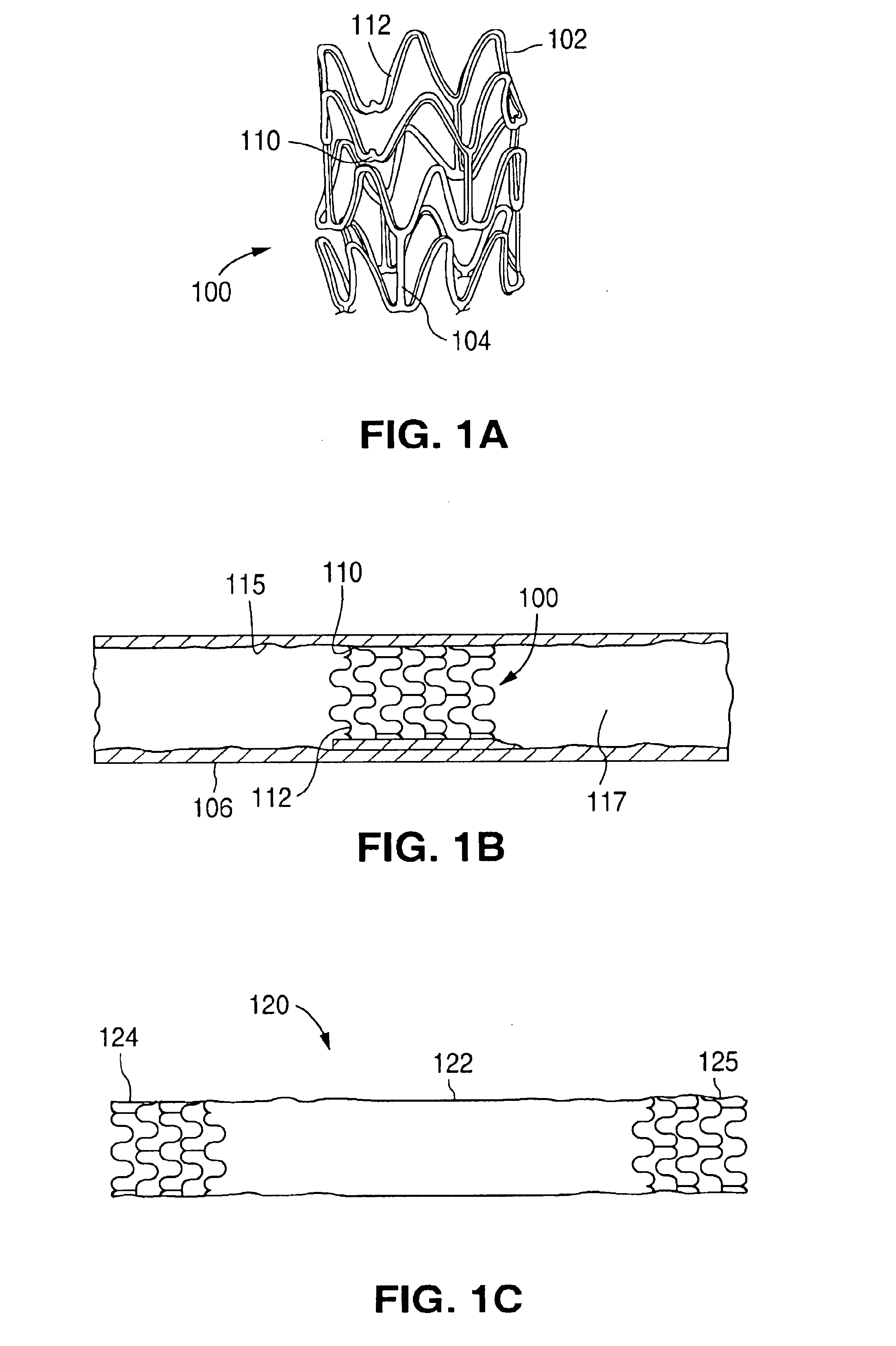
Method for preparing two-layer bicomposite collagen material for preventing post-operative adhesions
InactiveUS6596304B1Improve propertiesAvoid stickingPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgerySurgical operationPost operative
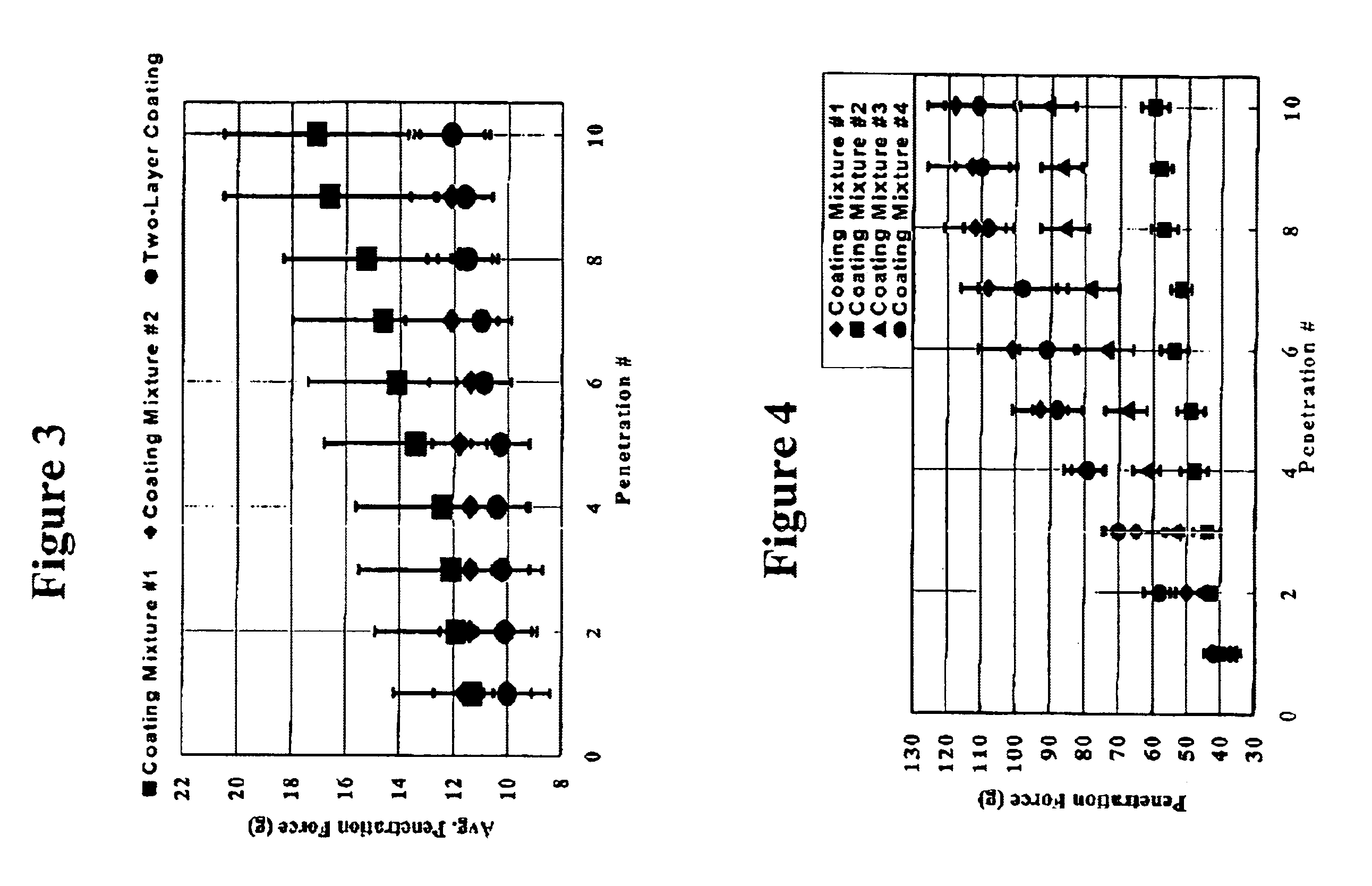
A bicomposite material based on collagen is prepared which has two closely bound layers and is biocompatible, non-toxic, hemostatic and biodegradable in less than a month, and can be used in surgery to achieve hemostasis and prevent post-surgical adhesion. To prepare the material, a solution of collagen or gelatin, which may contain glycerine and a hydrophilic additive such as polyethylene glycol or a polysaccharide, is poured onto an inert support to form a layer 30 .mu.m to less than 100 .mu.m thick. Then a polymeric porous fibrous layer is applied during gelling of the collagen or gelatin, and the resultant material is dried. The polymeric porous fibrous layer may be made of collagen or a polysaccharide, and have a density of not more than 75 mg / cm.sup.2, a pore size from 30 .mu.m to 300 .mu.m and a thickness of 0.2 cm to 1.5 cm.
Owner:IMEDEX BIOMATERIAUX CHAPONOST
Extraction of solvents from drug containing polymer reservoirs
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
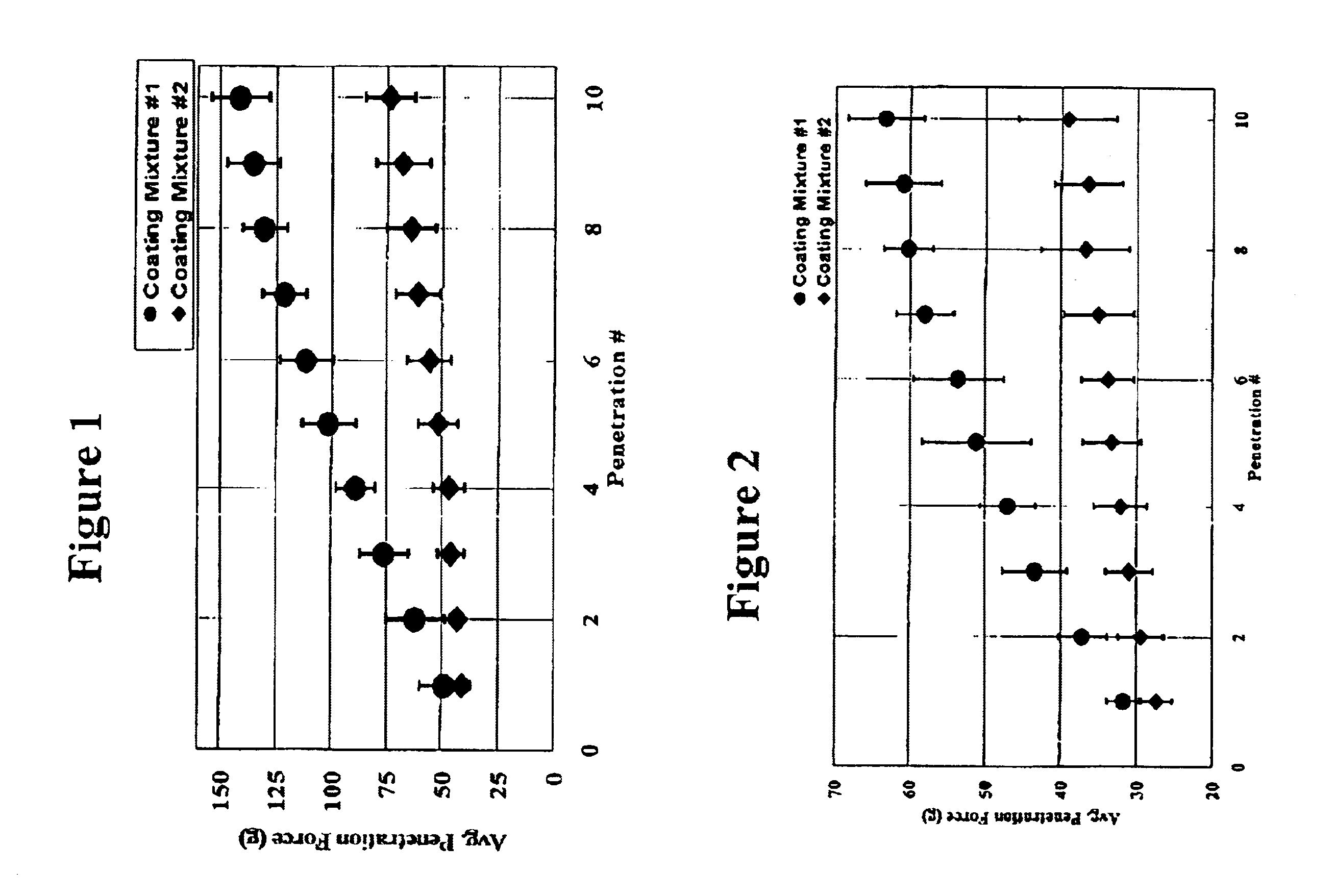
Medical devices having durable and lubricious polymeric coating
A medical device having a contact surface exposed repeatedly to bodily tissue is disclosed. The contact surface is coated with a silicone polymer and one or more non-silicone hydrophobic polymers. The preferred medical device is a surgical needle, and the preferred coating is a polydimethylsiloxane and polypropylene wax hydrocarbon mixture. The incorporation of the non-silicone hydrophobic polymer increases the durability of the coating on the device without sacrificing lubricity.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Agents and devices for providing blood clotting functions to wounds
InactiveUS20070190110A1Promote healingShorten the timePhysical treatmentAntithrombogenic treatmentNitrogen dioxideMedicine
Hemostatic agents and devices are made from oxidized cellulose fiber, the oxidized cellulose having a carboxylation content increased by the action of nitrogen dioxide on virgin cellulose fiber. A composition may be incorporated into the oxidized cellulose fiber to cause a pharmacological effect on a wound to which the hemostatic agents and devices are applied. When applied, the oxidized cellulose fiber causes blood emanating from the wound to clot. The oxidized cellulose fiber can either be resorbed into the wound or removed from the wound after healing. A hemostatic bandage includes a pad of unwoven oxidized cellulose fibers mounted on a substrate. Methods of arresting a flow of blood emanating from a wound using such devices are also disclosed. Methods of fabricating oxidized cellulose are also disclosed.
Owner:PAMEIJER CORNELIS H +1
Fiber strand and implantable supporting body having a fiber strand
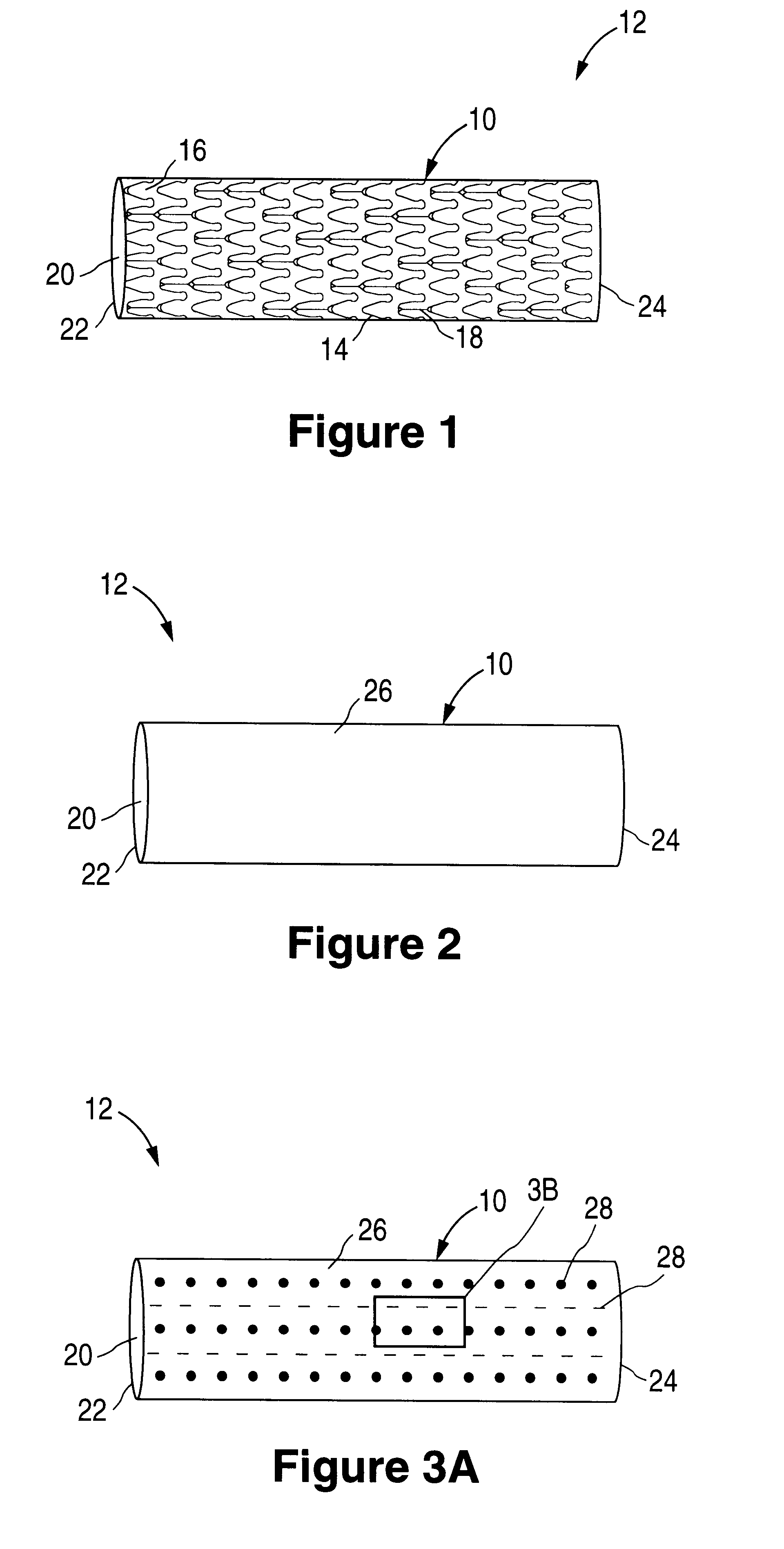
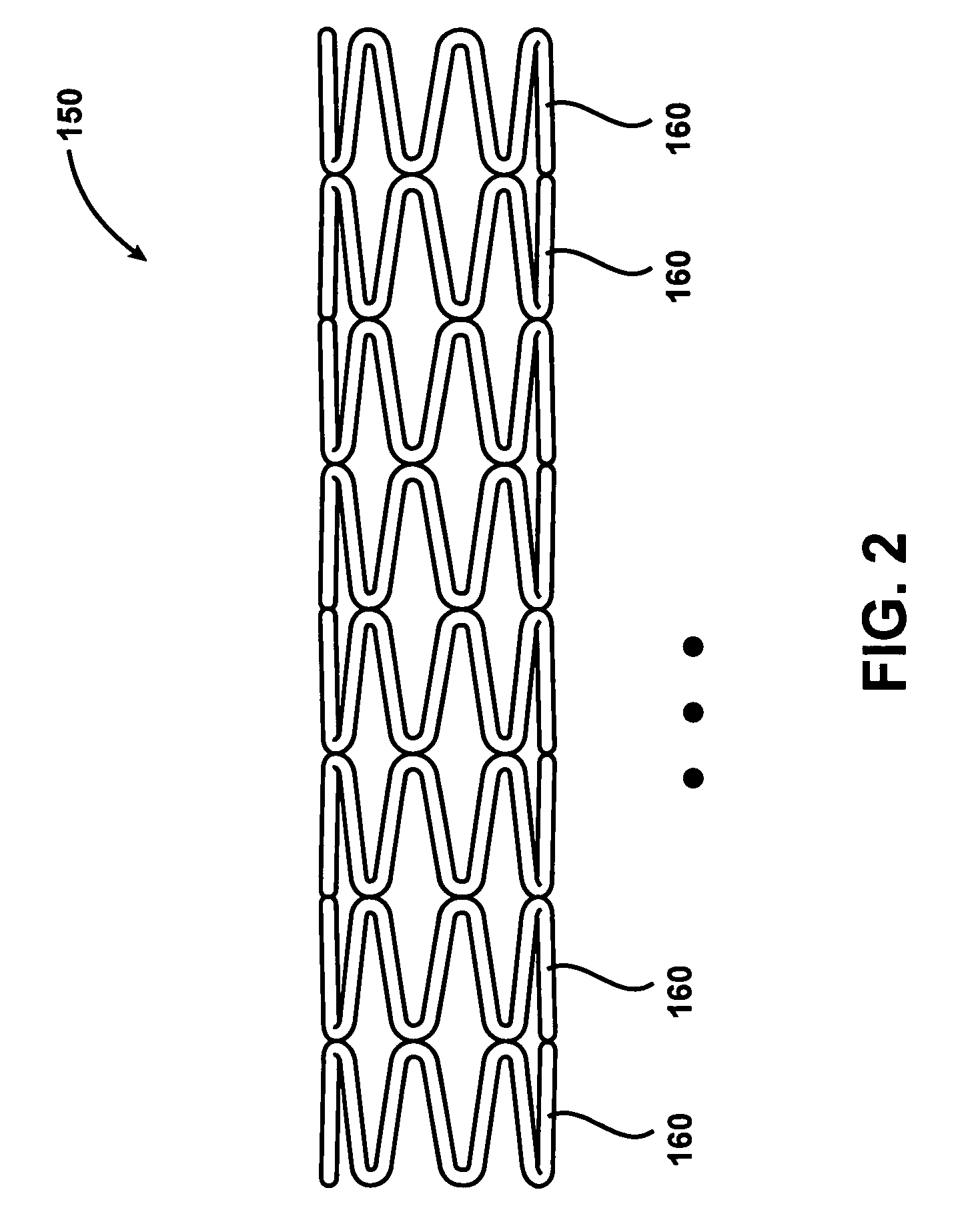
InactiveUS7997054B2Desired mechanical properties can be adjusted especially easilySignificant positive effectPowder deliveryStentsFiberBiomedical engineering
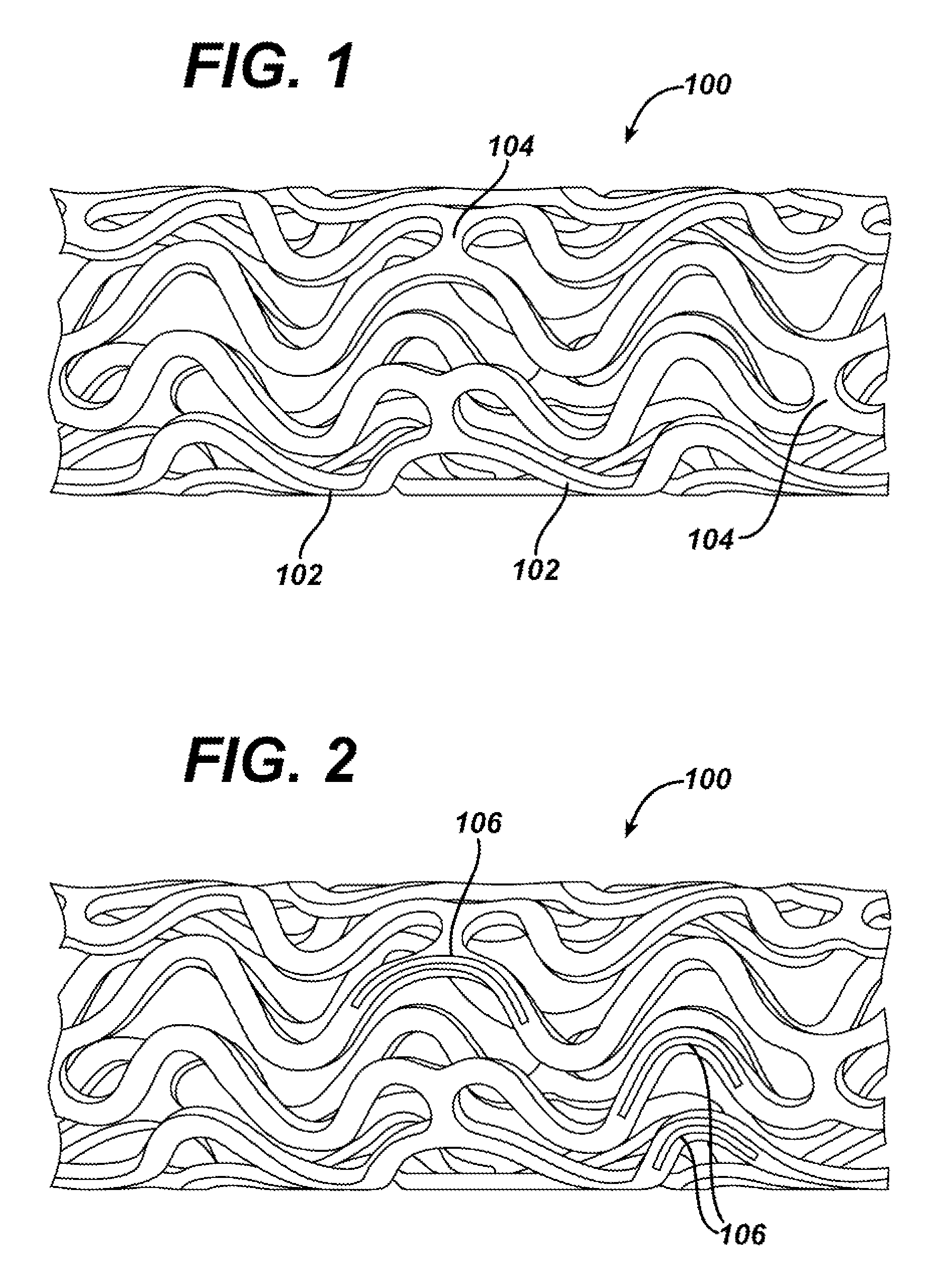
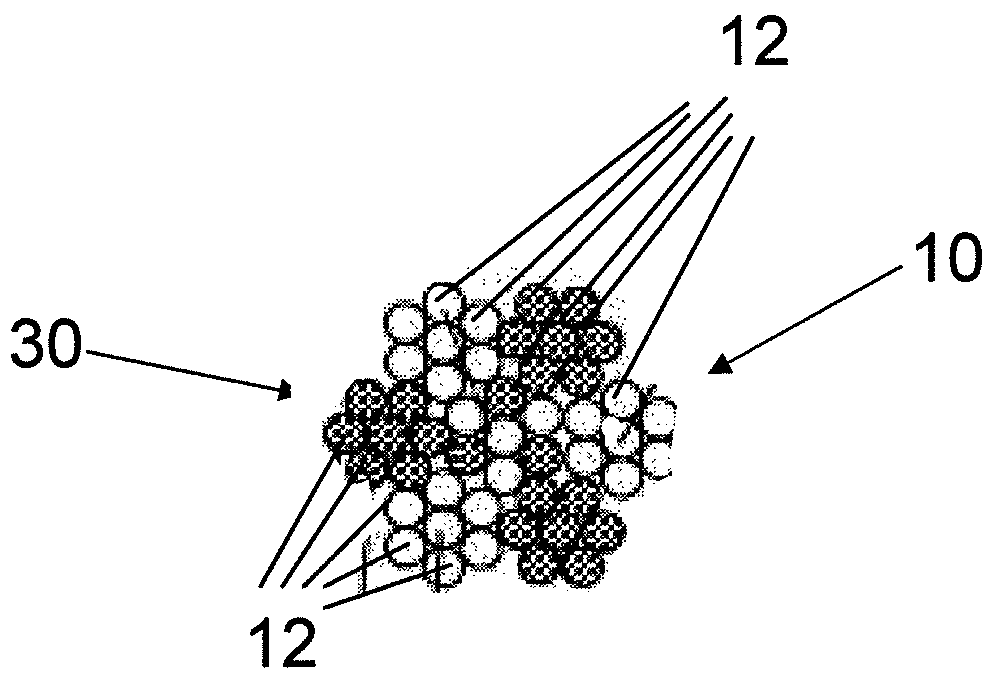
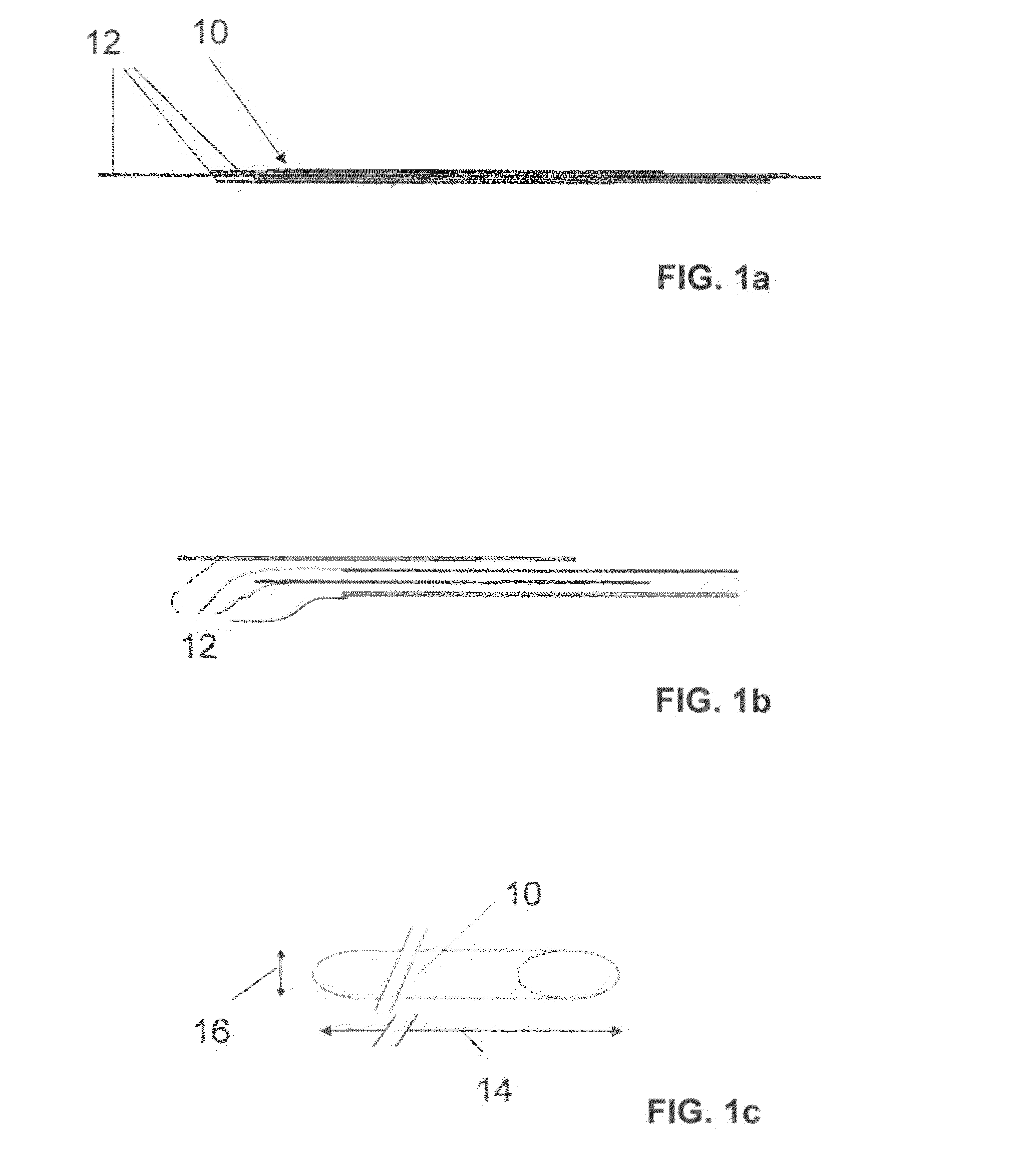
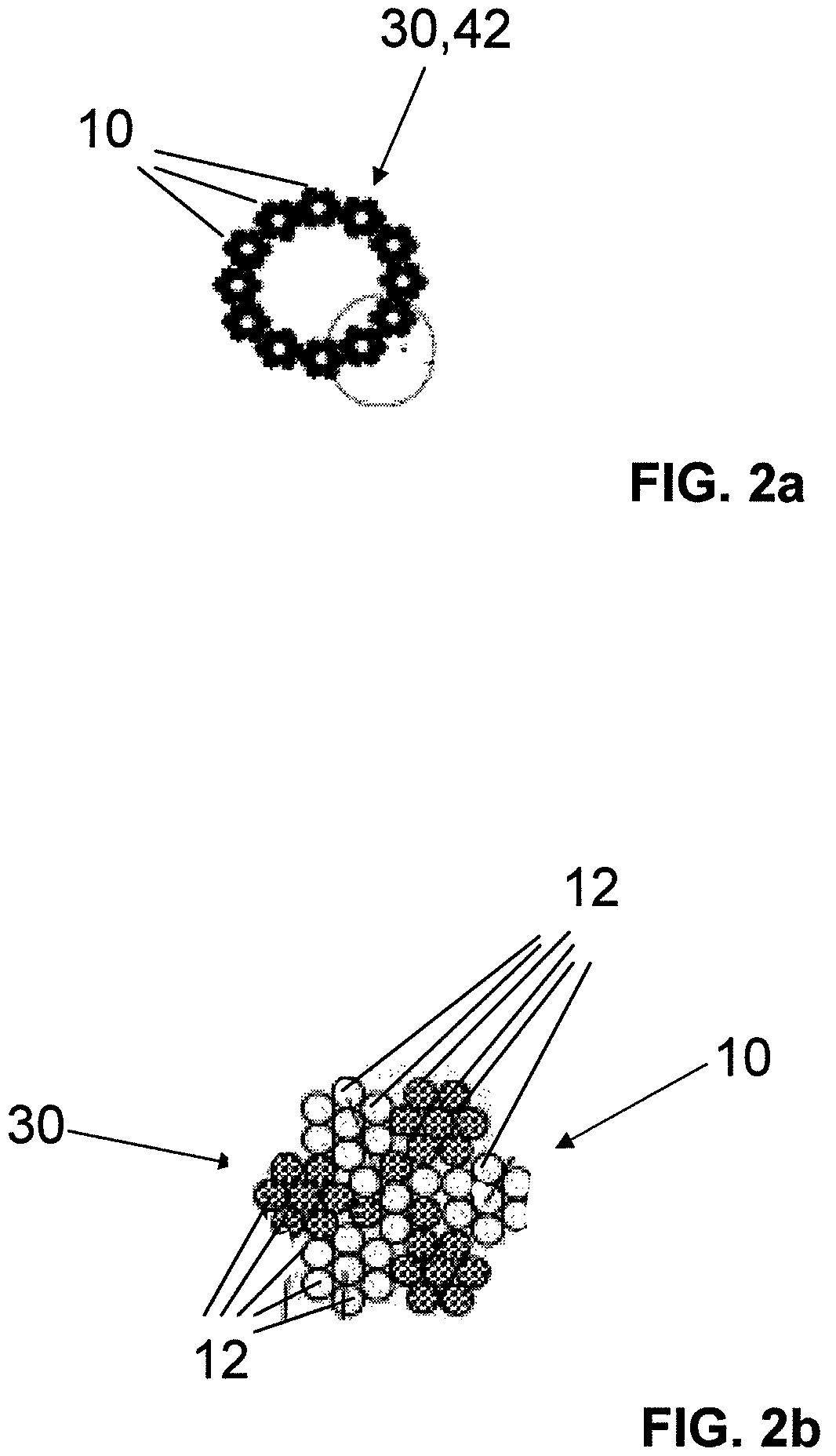
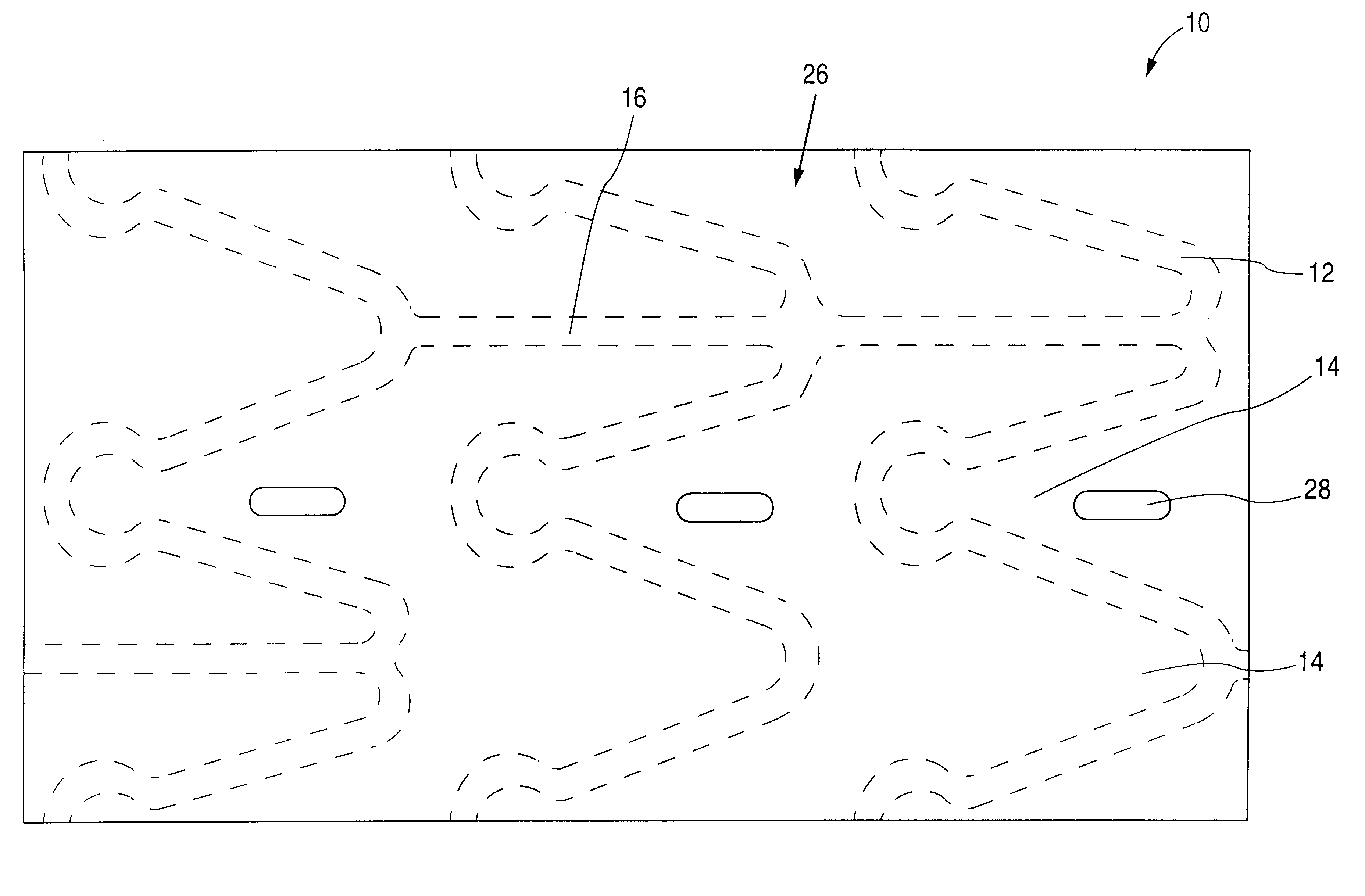
The invention relates to a fiber strand (10) for an implantable supporting body (100) comprising at least two individual fibers (12). The at least two individual fibers (12) are each shorter in their longitudinal extent than the longitudinal extent (14) of the fiber strand, and in their transverse extent they are each thinner than the transverse extent (16) of the fiber strand.
Owner:BIOTRONIK AG
Methods of forming a coating for a prosthesis
InactiveUS6503556B2Increase the amount addedIncrease the number ofRadiation applicationsGlovesProsthesisImplanted device
Methods of forming a coating onto an implantable device or endoluminal prosthesis, such as a stent, are provided. The coating may be used for the delivery of an active ingredient. The coating may have a selected pattern of interstices for allowing a fluid to seep through the coating in the direction of the pattern created.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
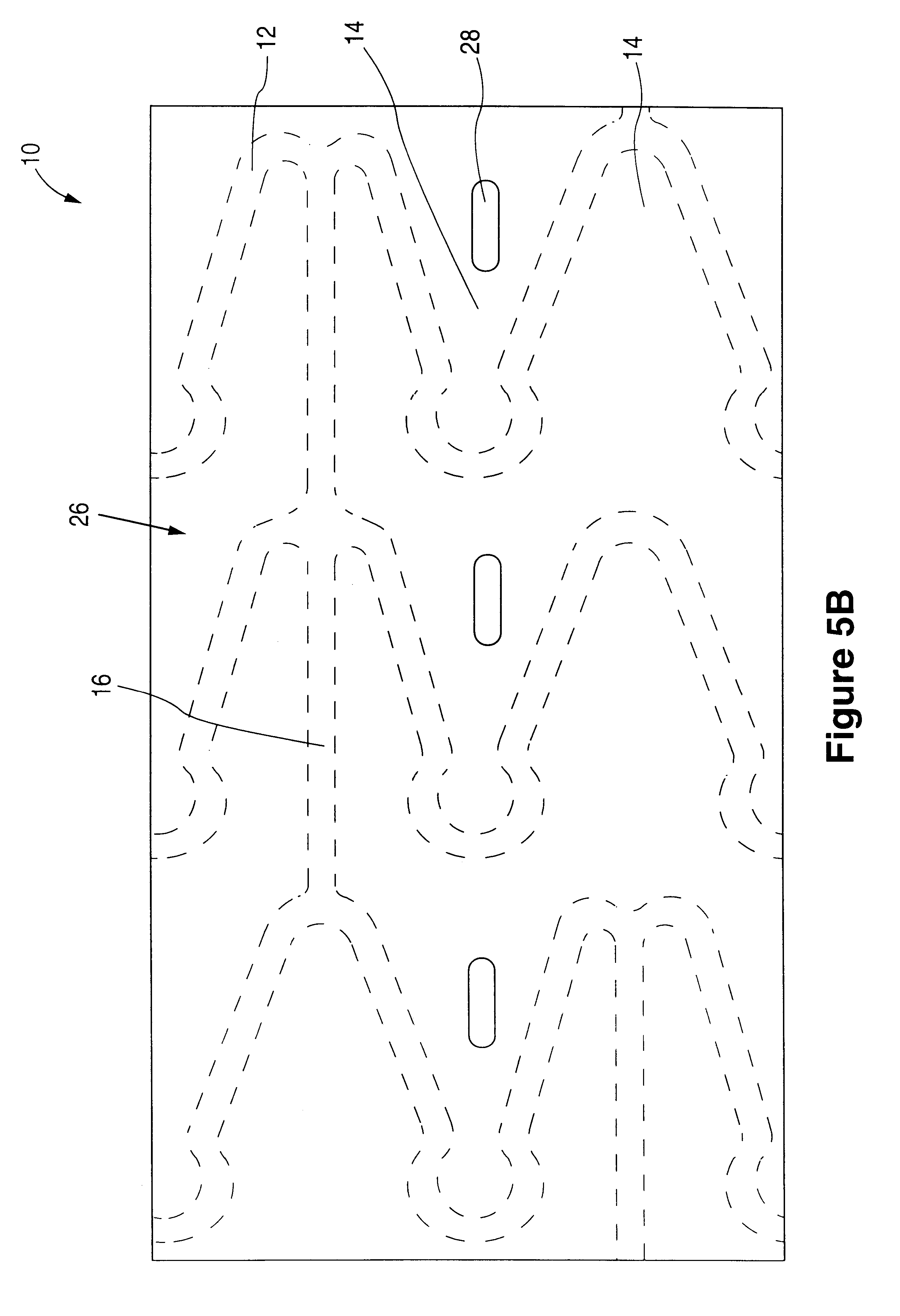
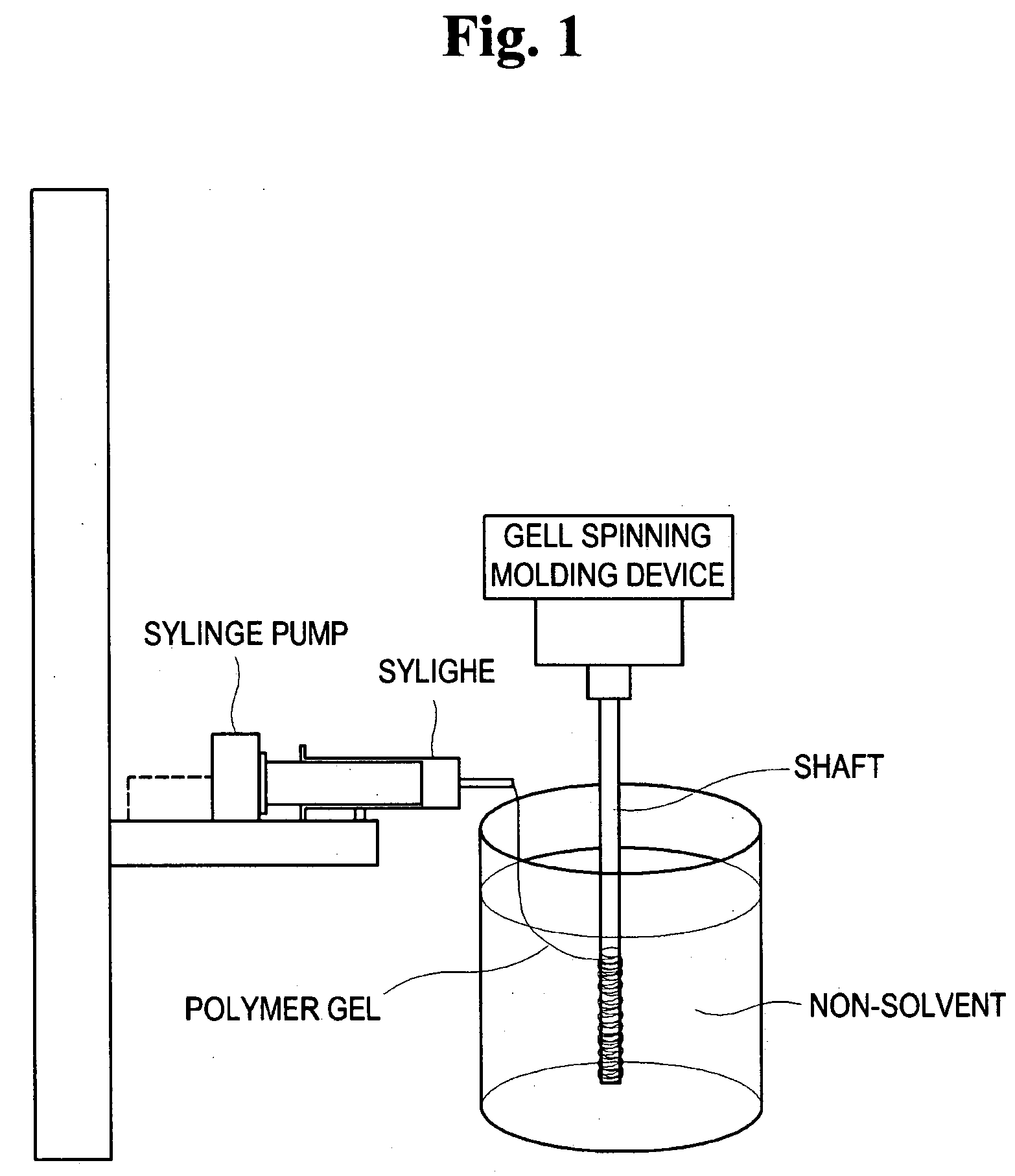
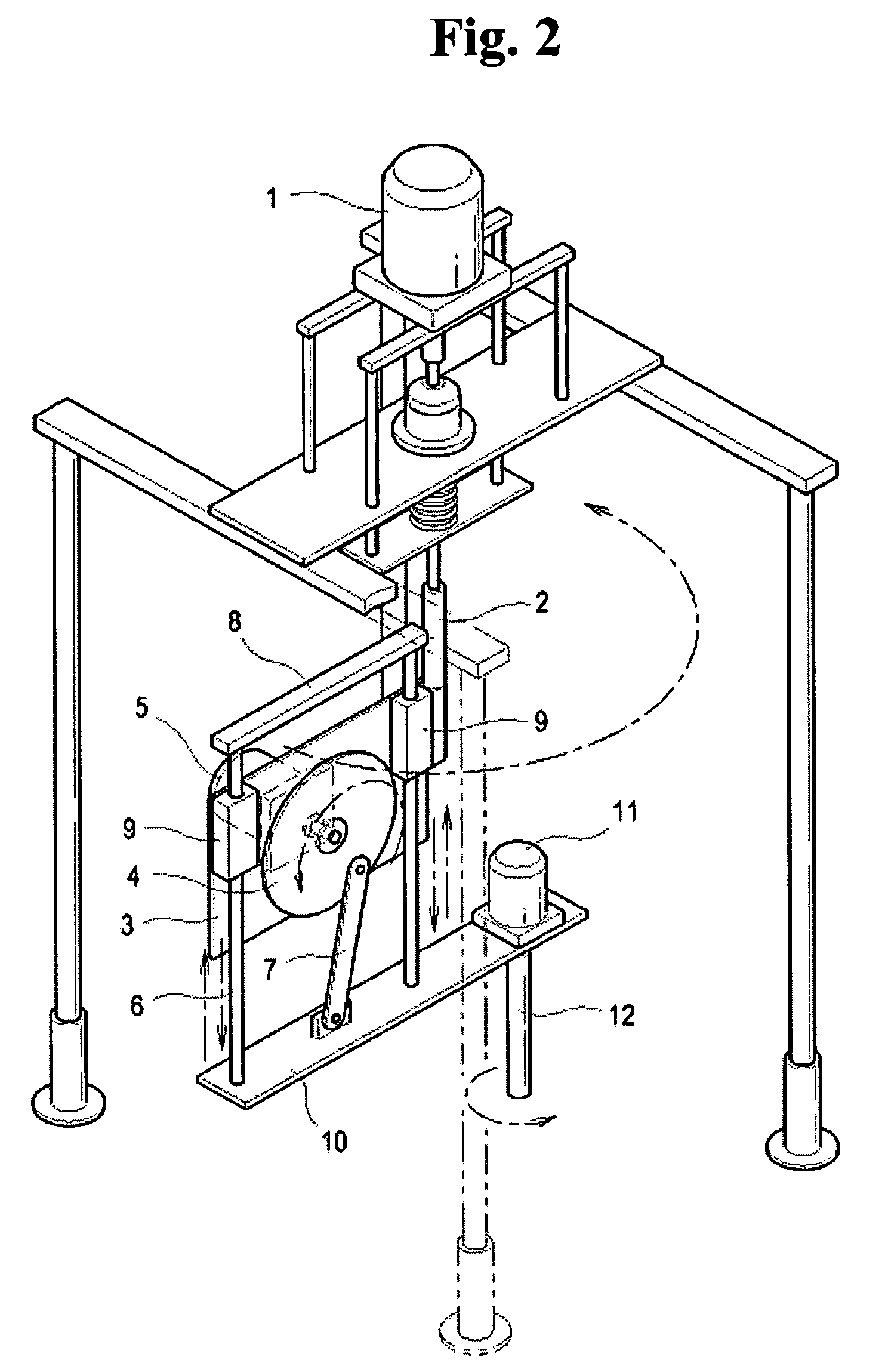
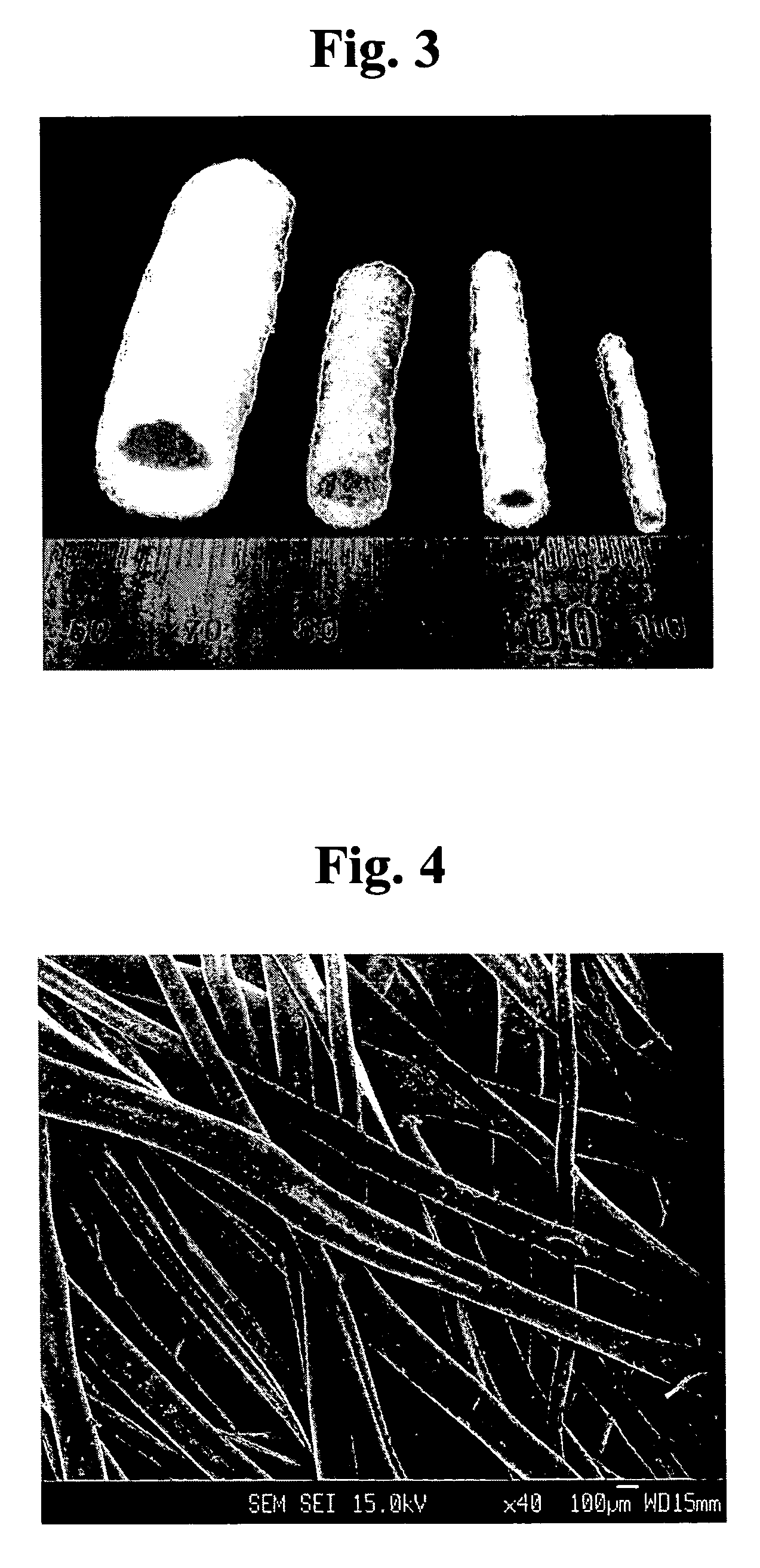
Method for preparing porous polymer scaffold for tissue engineering using gel spinning molding technique
InactiveUS20070009570A1Uniform pore sizeImprove interconnectivitySuture equipmentsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceSpinning
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a porous polymer scaffold for tissue engineering using a gel spinning molding technique. The method of the present invention can prepare a porous polymer scaffold having a uniform pore size, high interconnectivity between pores and mechanical strength, as well as high cell seeding and proliferation efficiencies, which can be effectively used in tissue engineering applications. Further, the method of the present invention can easily mold a porous polymer scaffold in various types such as a tube type favorable for regeneration of blood vessels, esophagus, nerves and the like, as well as a sheet type favorable for regeneration of skins, muscles and the like, by regulating the shape and size of a template shaft.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Compositions and methods for coating medical devices
InactiveUS6143037AStimulates and promotesImproved wound healing characteristicSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisDiseaseMedical device
Owner:MICHIGAN REGENTS THE UNIV OF
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110027453A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesPharmaceutical containersAnalyteSolvent
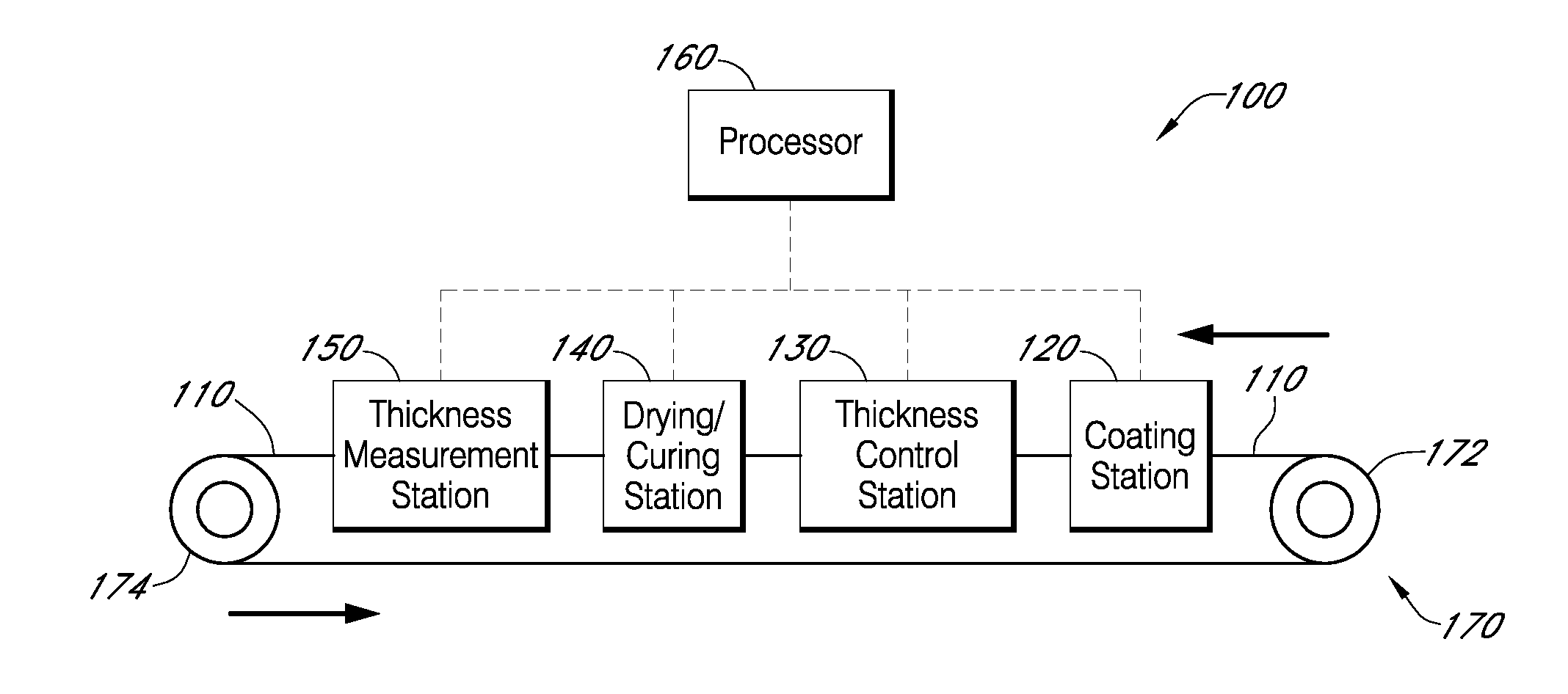
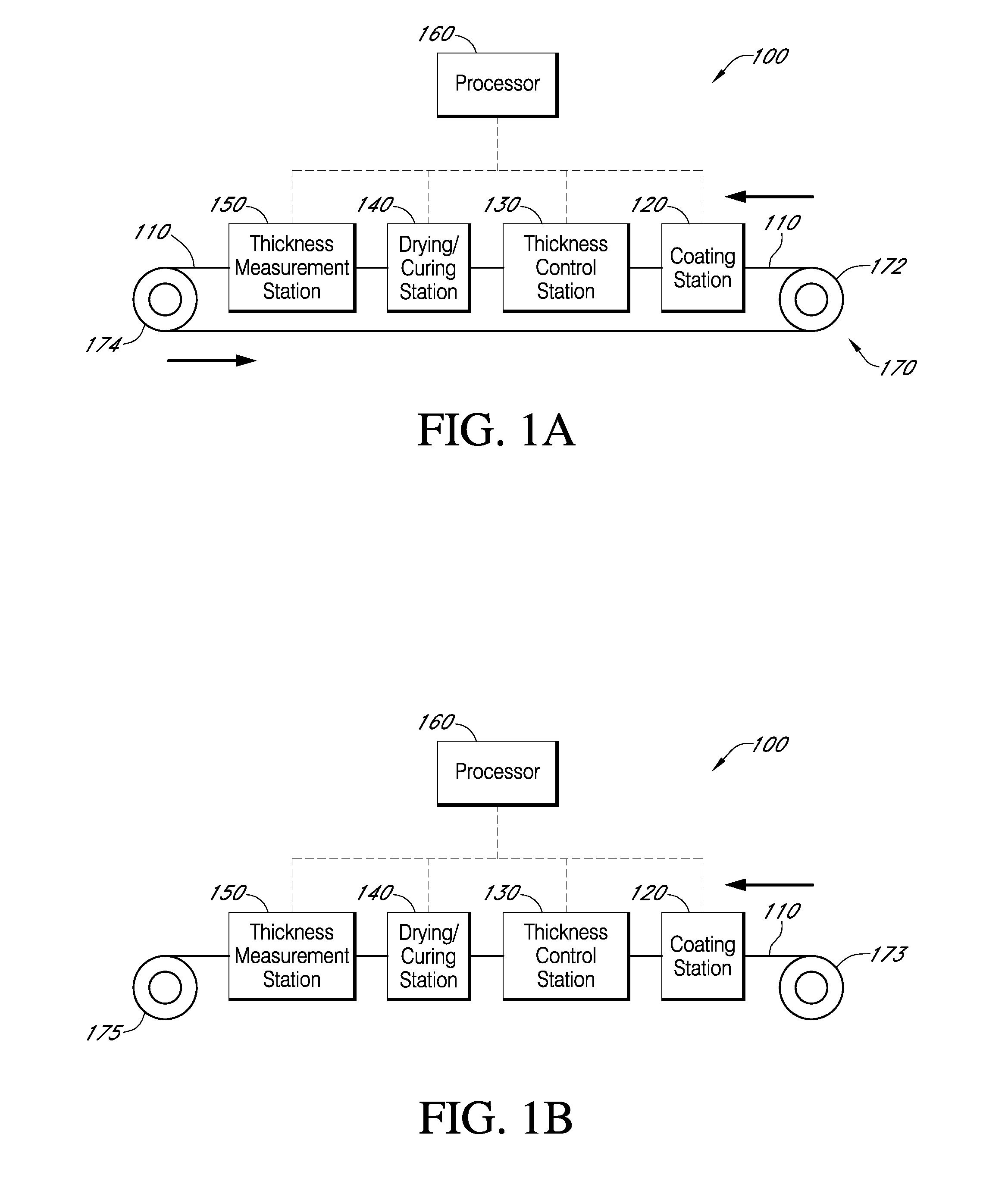
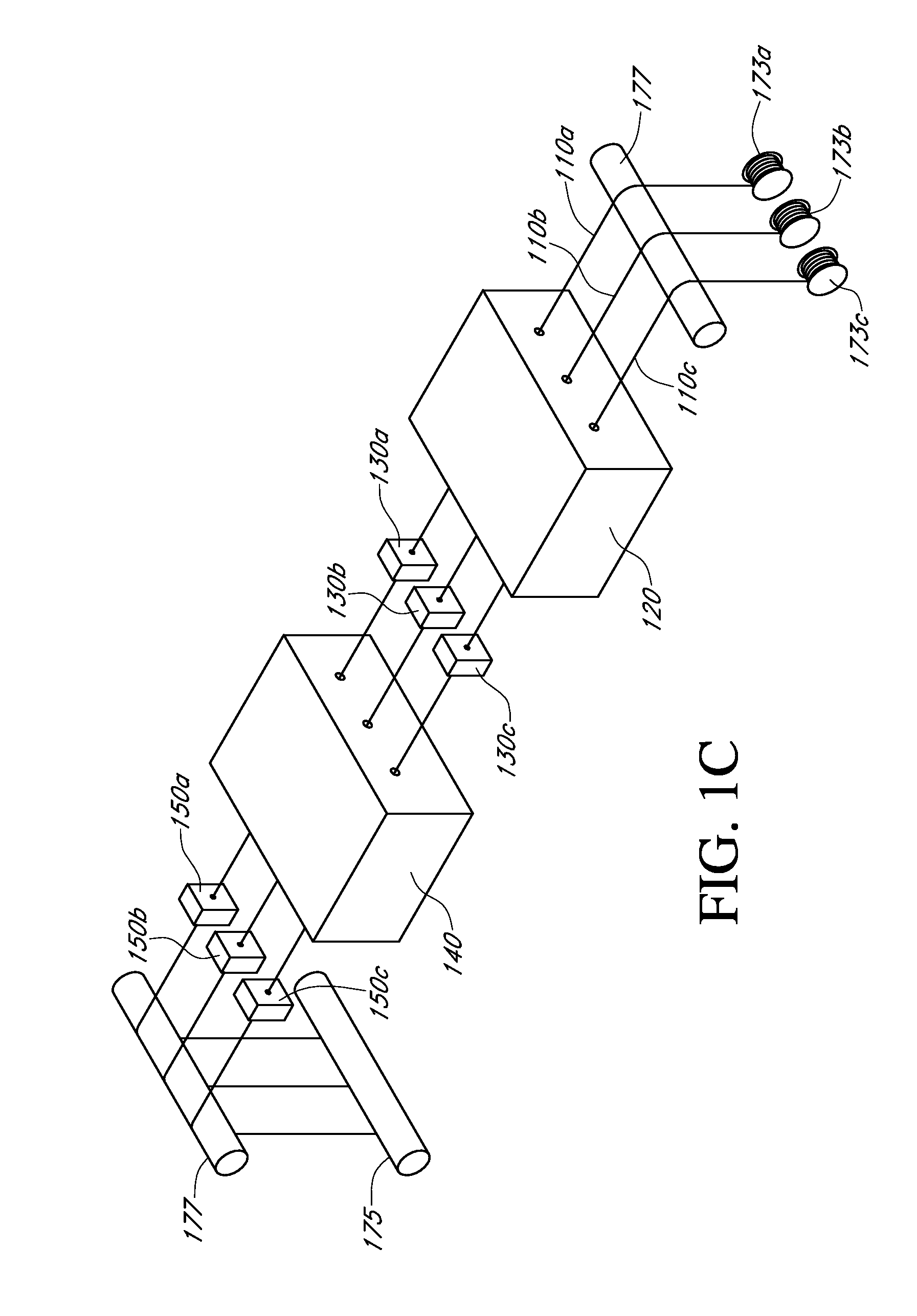
Described here are embodiments of processes and systems for the continuous manufacturing of implantable continuous analyte sensors. In some embodiments, a method is provided for sequentially advancing an elongated conductive body through a plurality of stations, each configured to treat the elongated conductive body. In some of these embodiments, one or more of the stations is configured to coat the elongated conductive body using a meniscus coating process, whereby a solution formed of a polymer and a solvent is prepared, the solution is continuously circulated to provide a meniscus on a top portion of a vessel holding the solution, and the elongated conductive body is advanced through the meniscus. The method may also comprise the step of removing excess coating material from the elongated conductive body by advancing the elongated conductive body through a die orifice. For example, a provided elongated conductive body 510 is advanced through a pre-coating treatment station 520, through a coating station 530, through a thickness control station 540, through a drying or curing station 550, through a thickness measurement station 560, and through a post-coating treatment station 570.
Owner:DEXCOM
Surface features of an implantable medical device
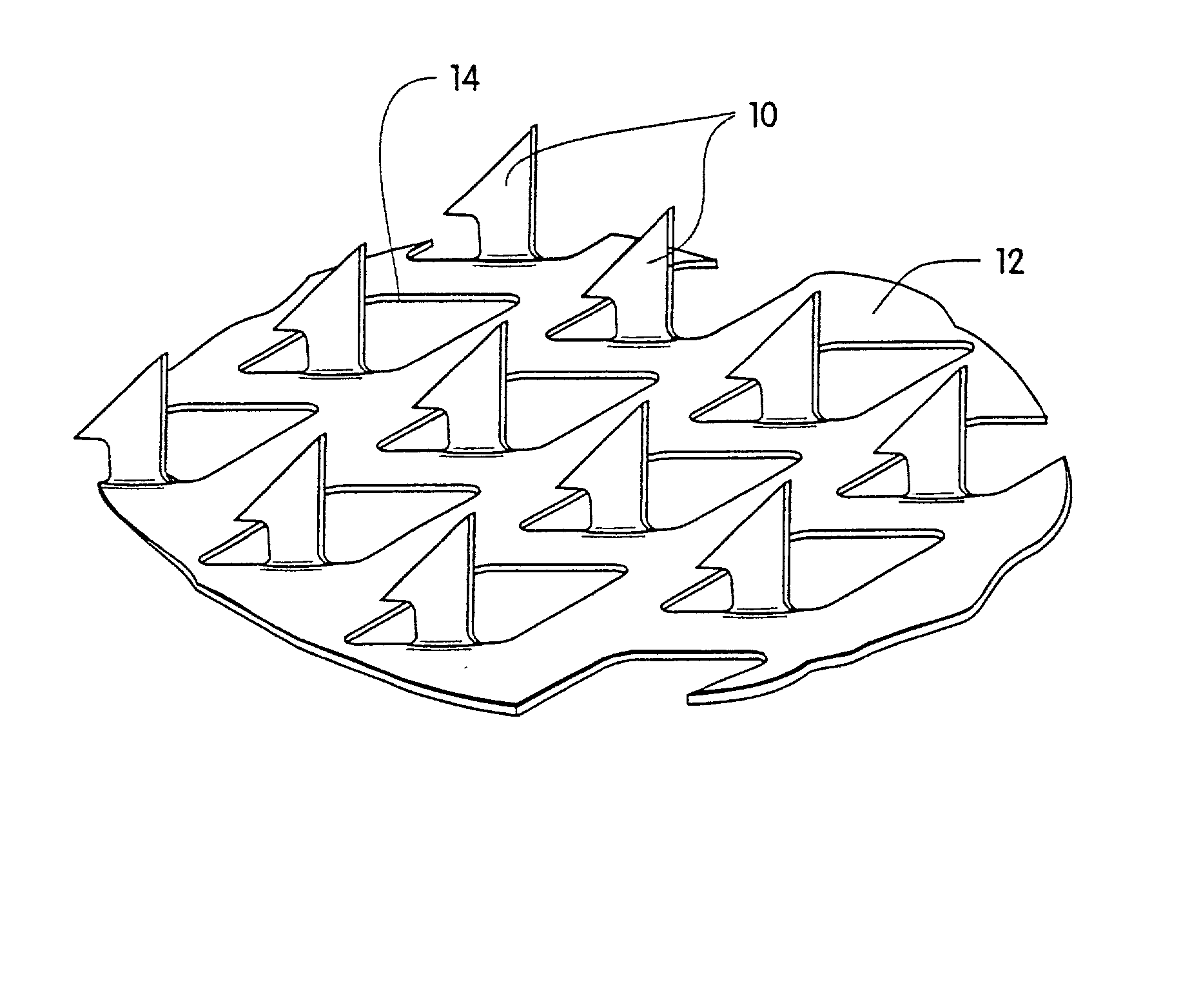
An implantable medical device, such as a stent or graft, having asperities on a designated region of its outer surface is disclosed. The asperities can serve to improve retention of one or more layers of a coating on the device and to increase the amount of coating that can be carried by the device. The asperities can be formed by using a stream of pressurized grit to roughen the surface. The asperities can also be formed by removing material from the outer surface, for example, by chemical etching with or without a patterned mask. Alternatively, the asperities can be formed by adding material to the outer surface, for example, by welding powder particles to the outer surface or sputtering.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Prosthetic valves and related inventions
ActiveUS20140214159A1Low height to width profilePrevent perivalvular leakSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
This invention relates to the design and function of a compressible valve replacement prosthesis, collared or uncollared, which can be deployed into a beating heart without extracorporeal circulation using a transcatheter delivery system. The design as discussed focuses on the deployment of a device via a minimally invasive fashion and by way of example considers a minimally invasive surgical procedure preferably utilizing the intercostal or subxyphoid space for valve introduction. In order to accomplish this, the valve is formed in such a manner that it can be compressed to fit within a delivery system and secondarily ejected from the delivery system into the annulus of a target valve such as a mitral valve or tricuspid valve.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Wound closure material
Articles are provided having no orientation or a multi-directional orientation. Such articles may be in the form of films, ribbons, sheets, and / or tapes and may be utilized as buttresses with a surgical stapling apparatus or as reinforcing means for suture lines. The articles may be produced with a polymeric material having an agent, such as a chemotherapeutic agent or a radiotherapeutic agent, incorporated therein or applied as a coating thereon.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Biocompatibly coated medical implants
InactiveUS20050079200A1Easy to controlProperty variableStentsHeart valvesCarbon layerBiocompatible coating
Implantable medical devices with biocompatible coatings and processes for their production are described. The present invention relates in particular to medical implantable devices coated with a carbon-containing layer which devices are produced by at least partially coating the device with a polymer film and heating the polymer film in an atmosphere which is essentially free from oxygen to temperatures in the region of 200° C. to 2500° C., a carbon-containing layer being produced on the implantable medical device.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Sheath for a prosthesis and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS6540776B2Increase the amount addedIncrease the number ofStentsPharmaceutical containersProsthesisImplanted device
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
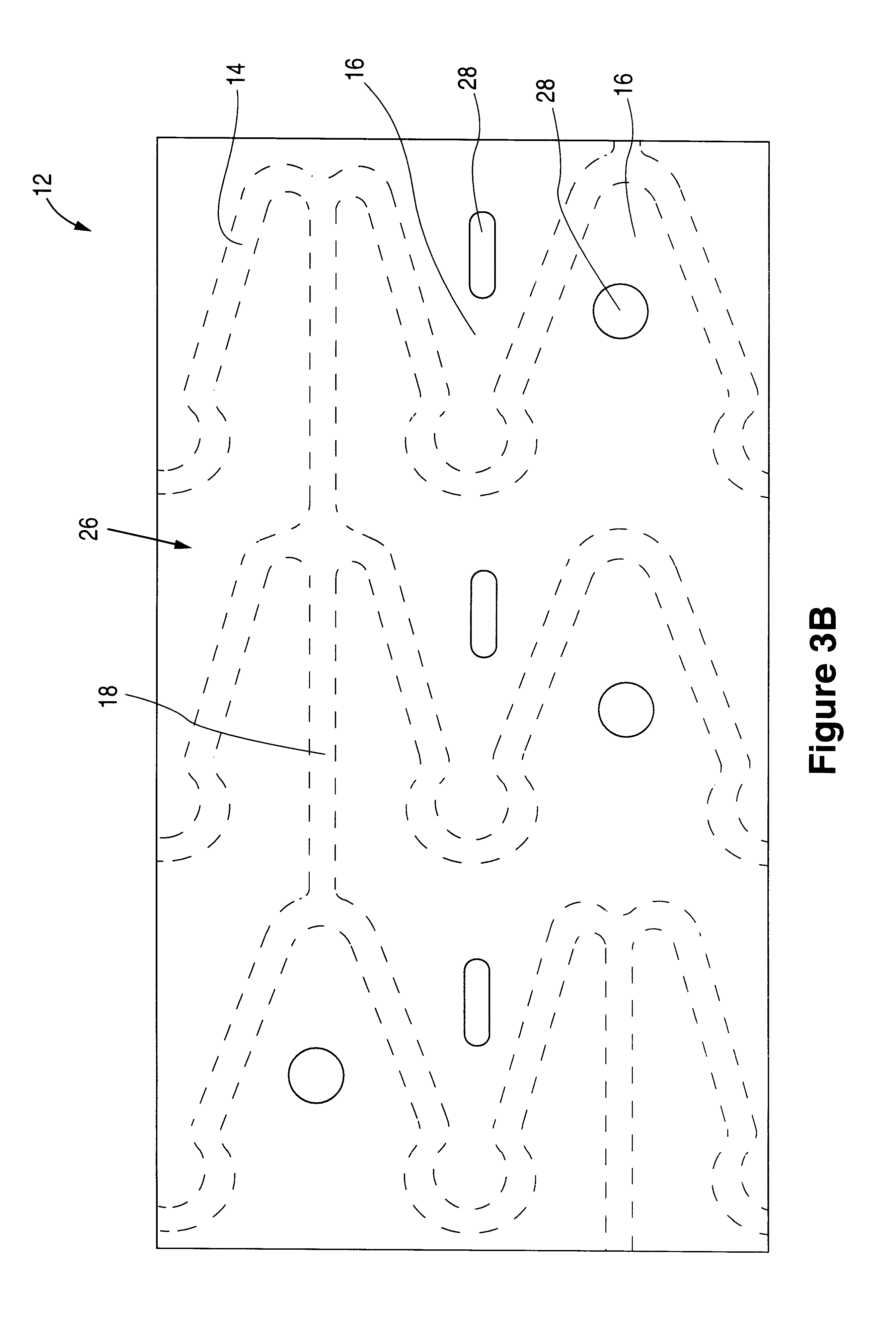
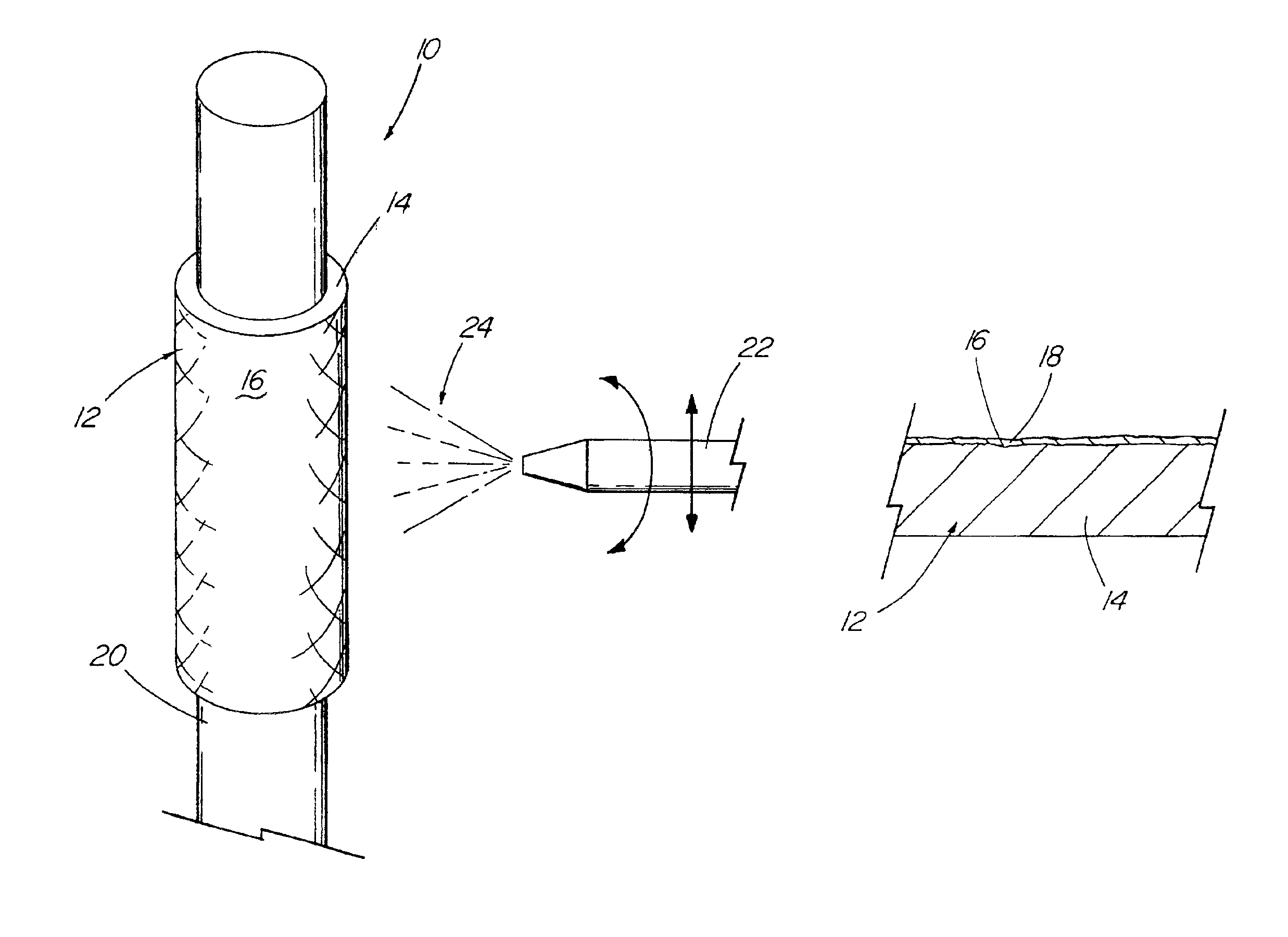
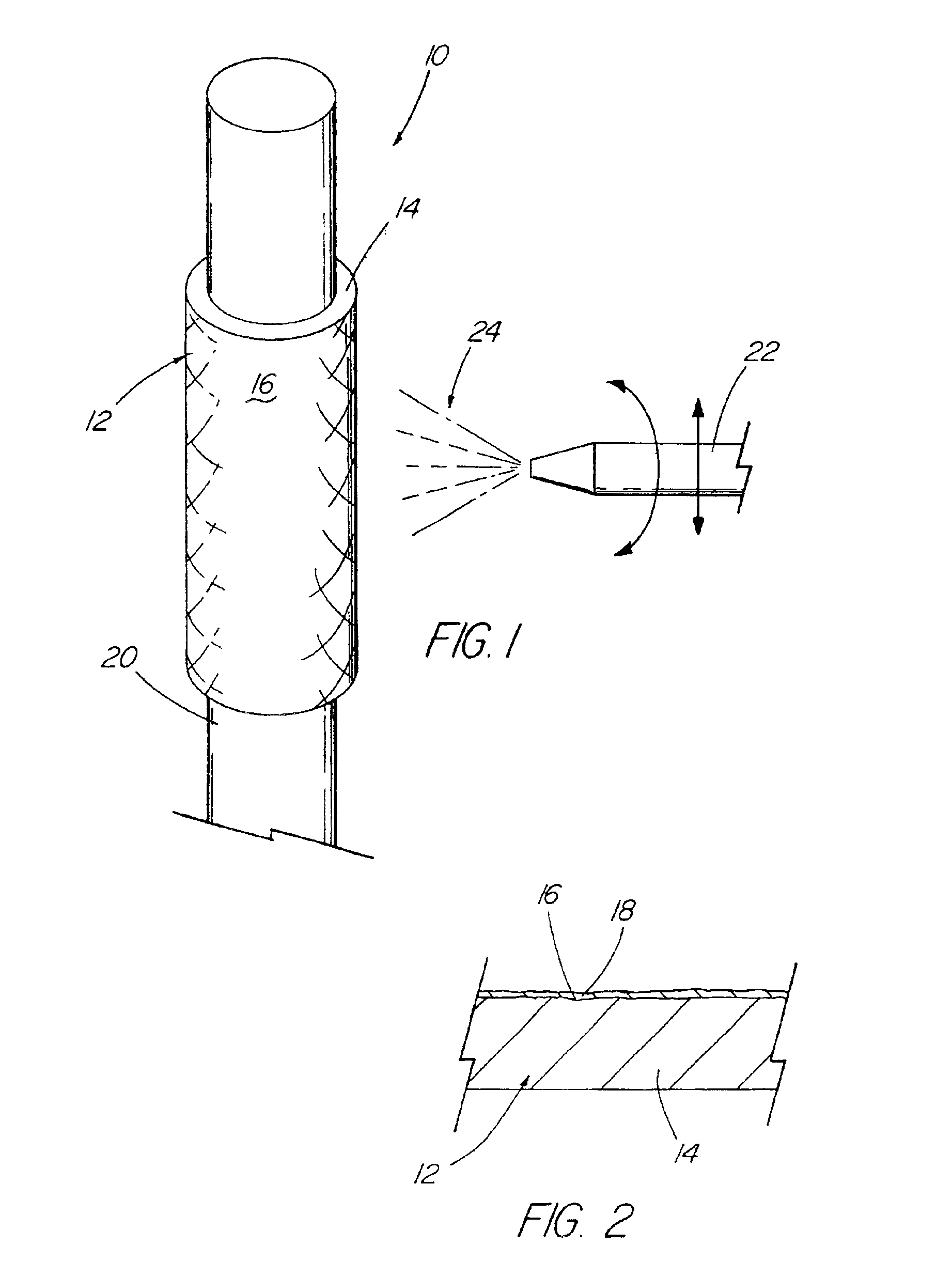
Coated implantable medical device
InactiveUS6918927B2Good worker safetyLow costOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySodium bicarbonateMedicine
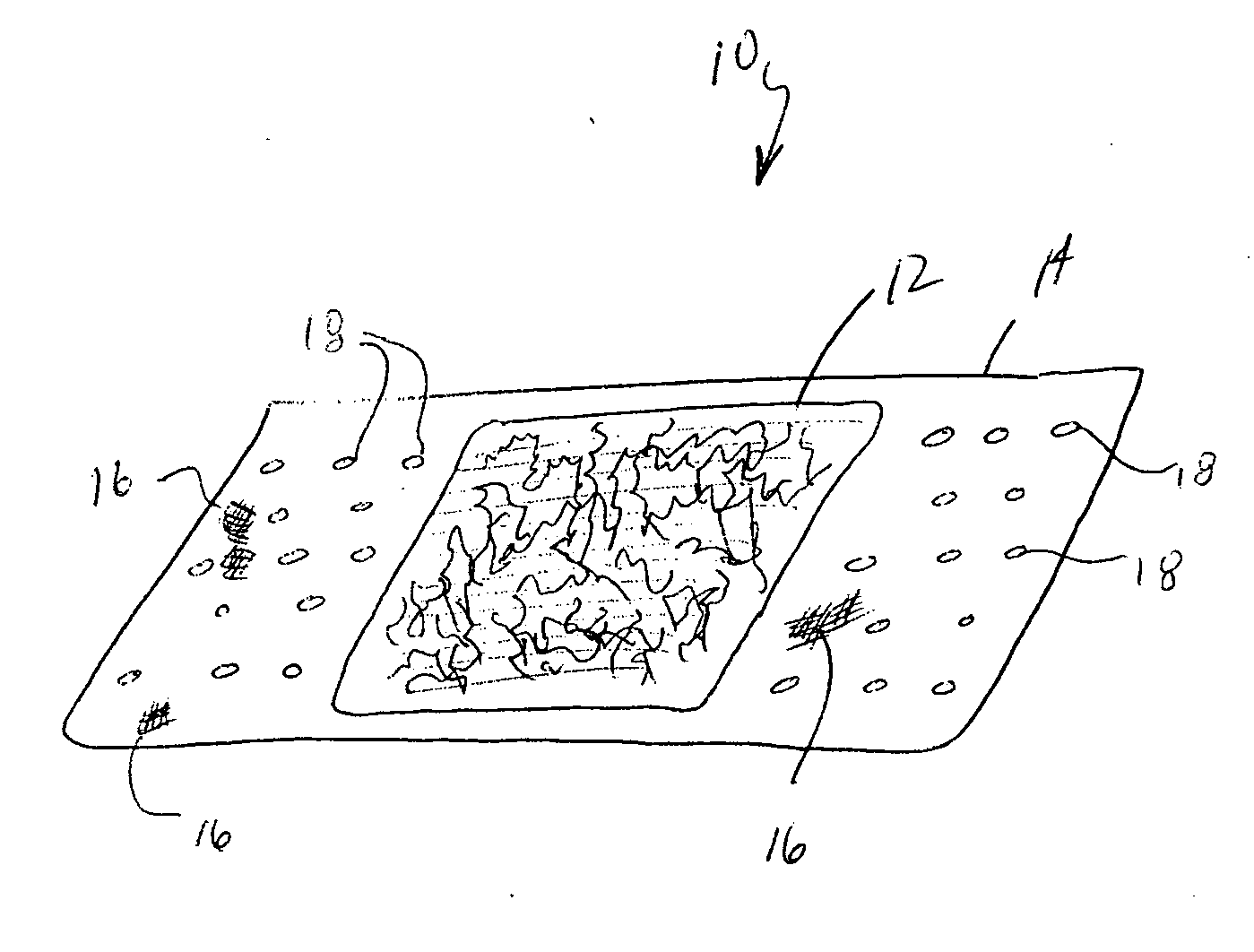
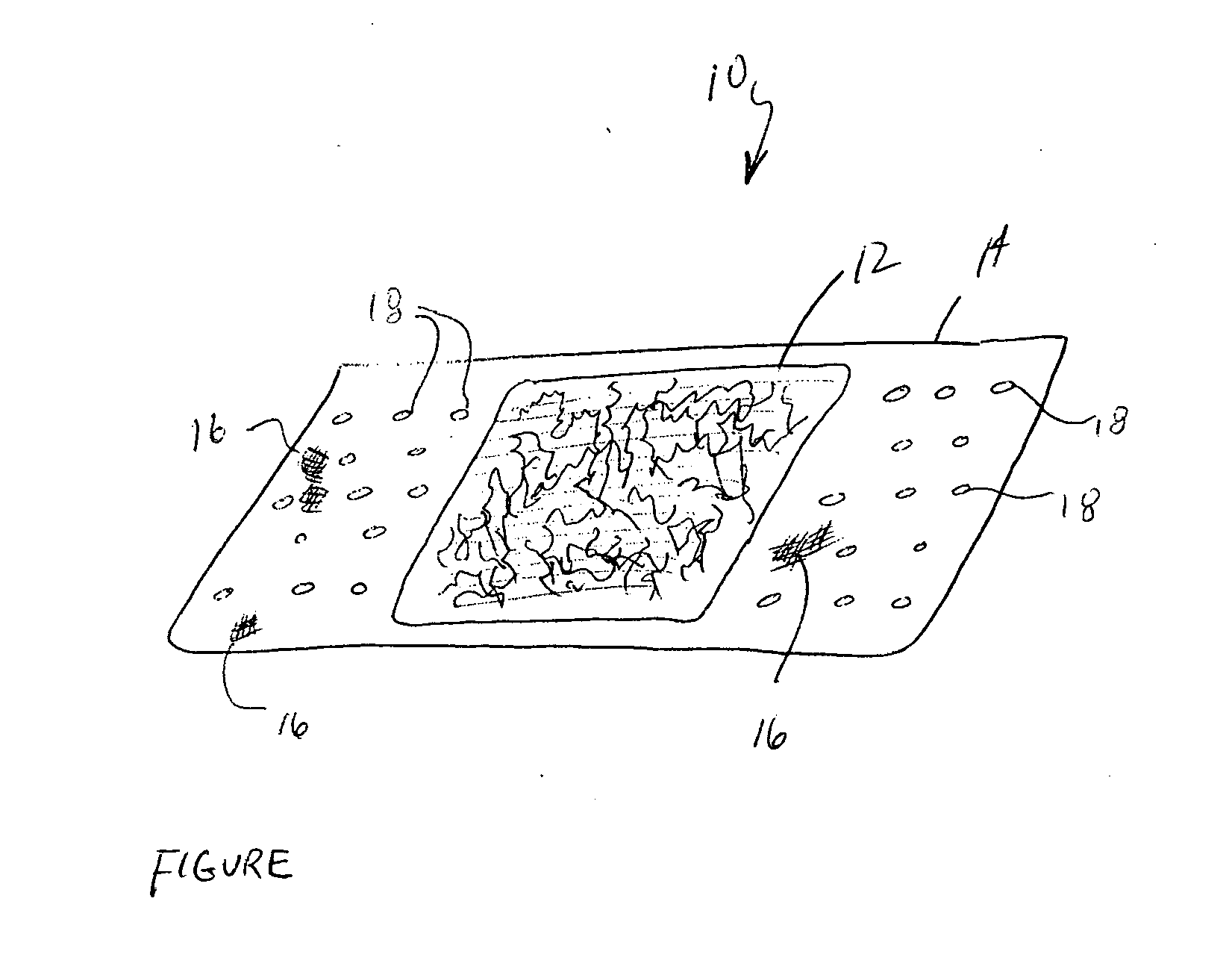
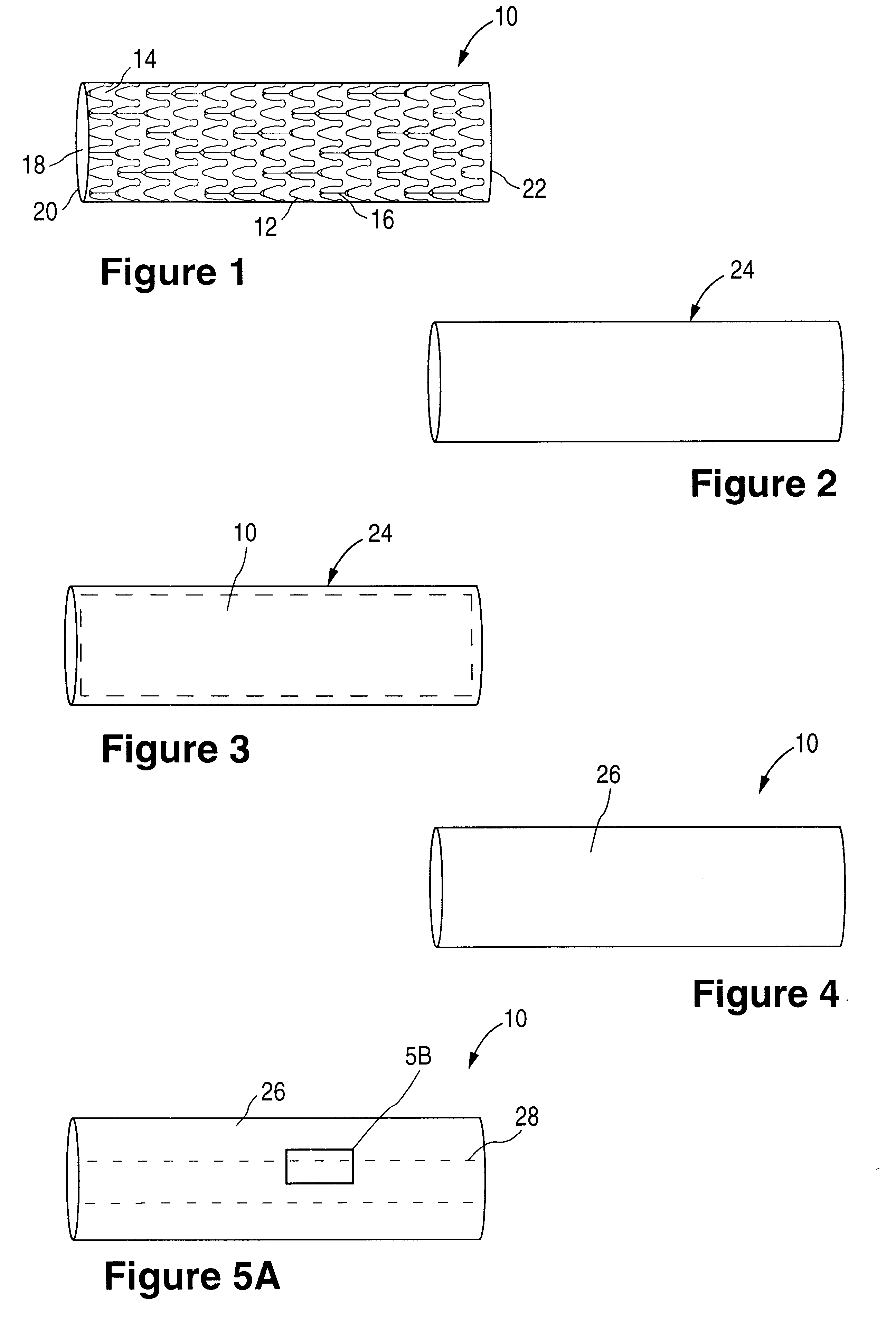
A medical device (10) includes a structure (12) adapted for introduction into a patient, the structure (12) being formed of a preferably non-porous base material (14) having a roughened or textured surface (16). The structure (12) is conveniently configured as a vascular stent with a base material (14) of stainless steel, nitinol or another suitable material. The medical device (10) also includes a layer (18) of a bioactive material posited directly upon the roughened or textured surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12). The surface (16) of the base material (14) is roughened or textured by etching or by abrasion with sodium bicarbonate or another suitable grit. A preferred roughened or textured surface (16) is thought to have a mean surface roughness of about 10 μin. (about 250 nm) and a surface roughness range between about 1 μin. and about 100 μin. (about 25 nm and about 2.5 μm). The particularly preferred use of sodium bicarbonate as the abrasive to provide roughness or texture to the surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12) is additionally advantageous in the low toxicity of the sodium bicarbonate to production workers, the ease of product and waste cleanup, and the biocompatibility of any residual sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
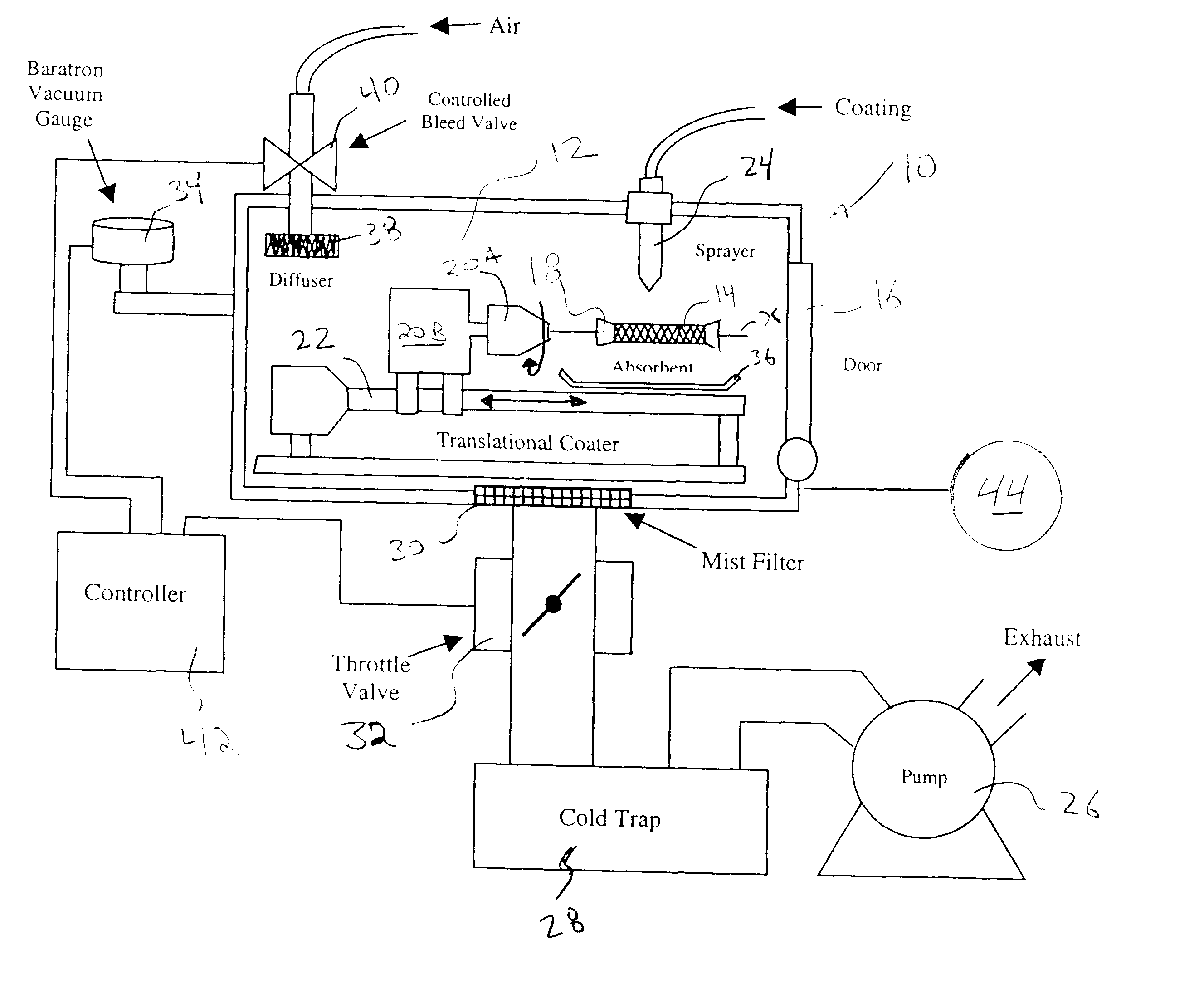
Apparatus and method for coating implantable devices
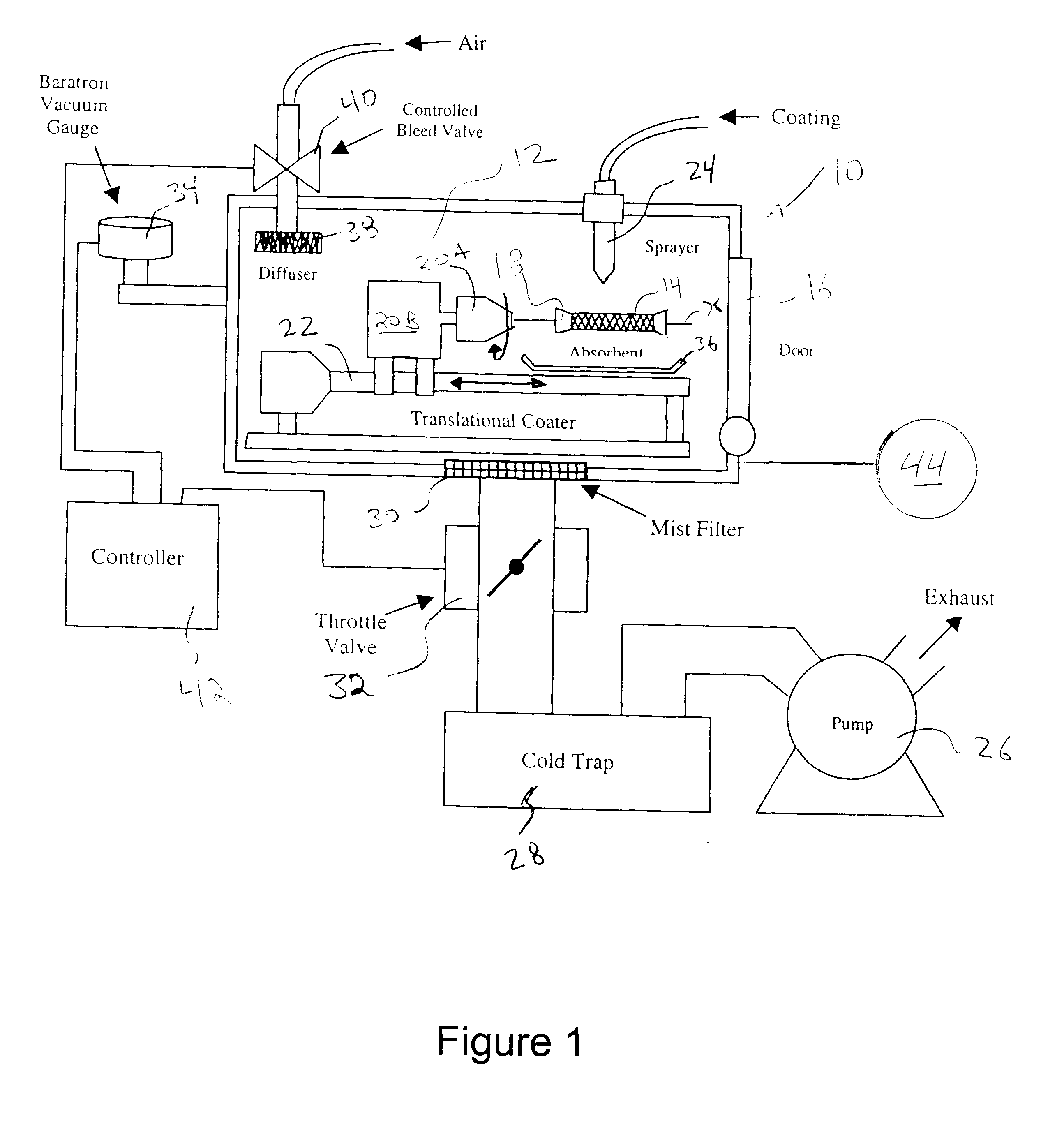
A method of forming a coating for an implantable medical device, such as a stent, is provided which includes applying a composition to the device in an environment having a selected pressure. An apparatus is also provided for coating the devices. The apparatus comprises a chamber for housing the device wherein the pressure of the chamber can be adjusted during the coating process.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for applying an LbL coating onto a medical device
The present invention provides an improved LbL-coating process for modifying the surface of a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens. An LbL coating on a contact lens, which is prepared according to the process of the invention, can have increased hydrophilicity characterized by an averaged contact angle of about 80 degree or less, preferably about 50 degrees or less, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material.
Owner:ALCON INC
Medical device
InactiveUS20050002981A1Reduce connective tissue hyperplasiaReduce restenosisStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological propertyConnective tissue fiber
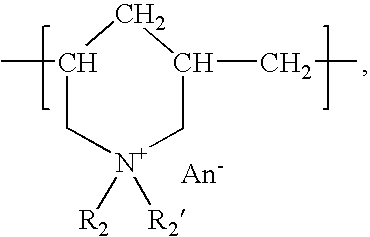
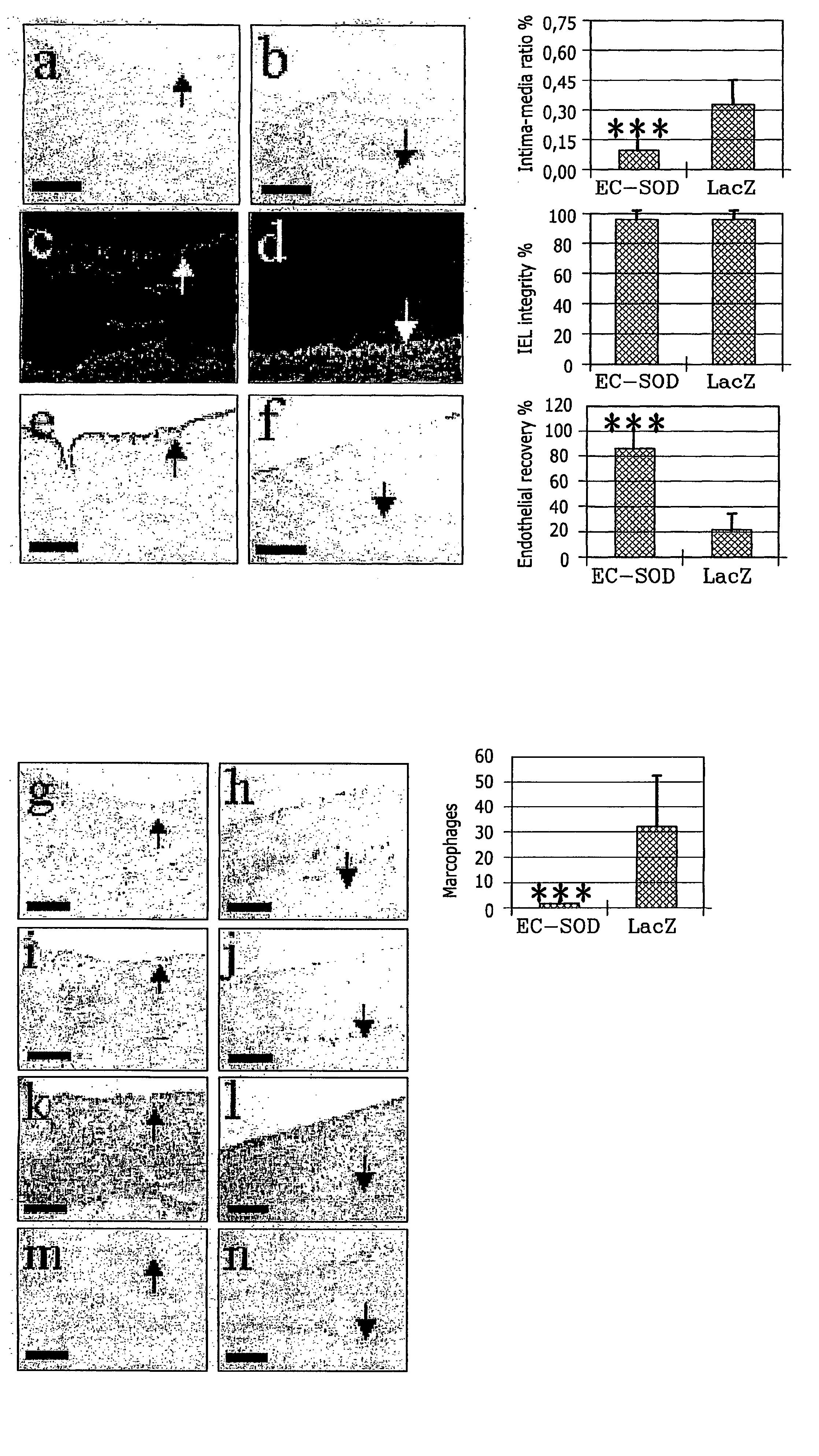
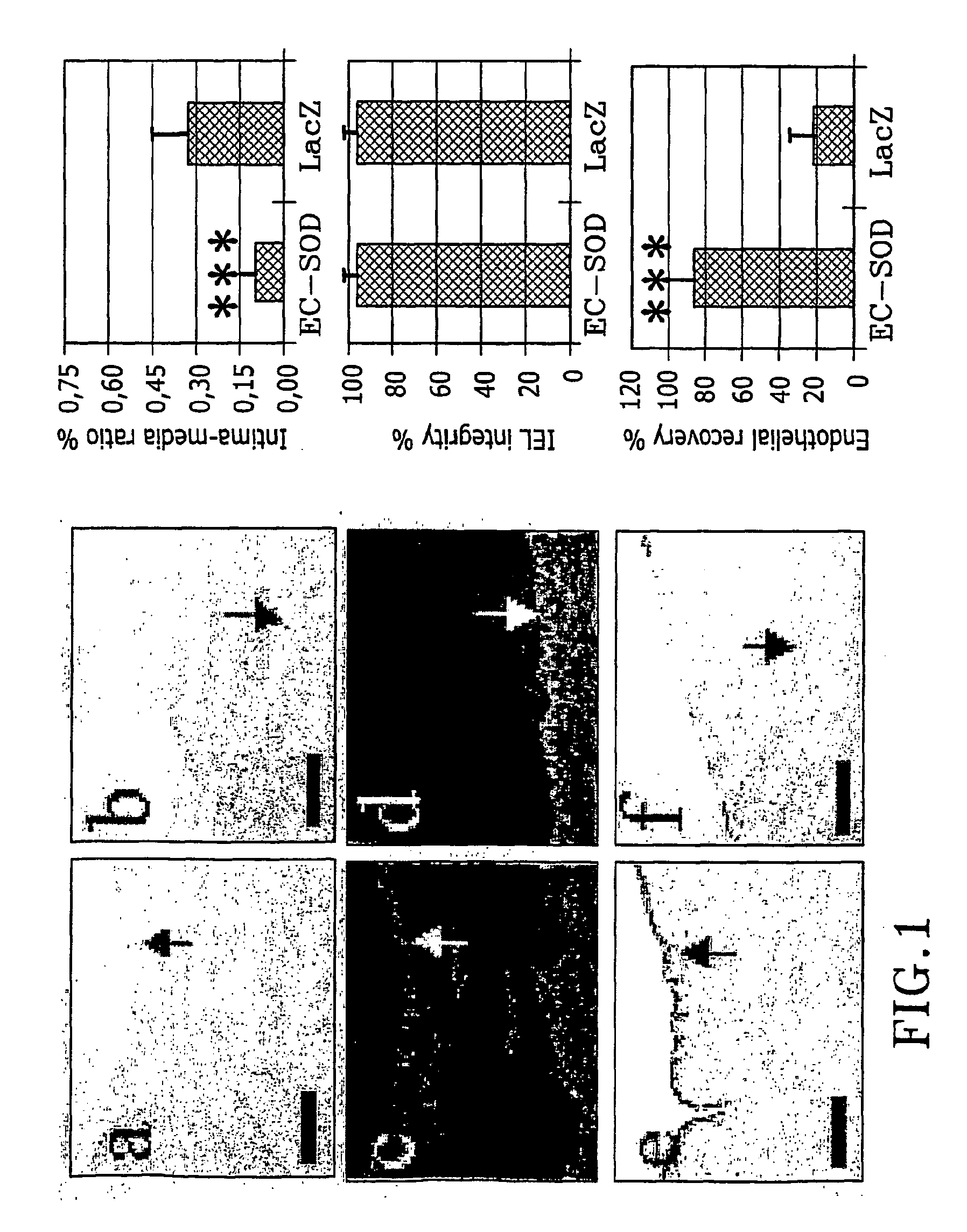
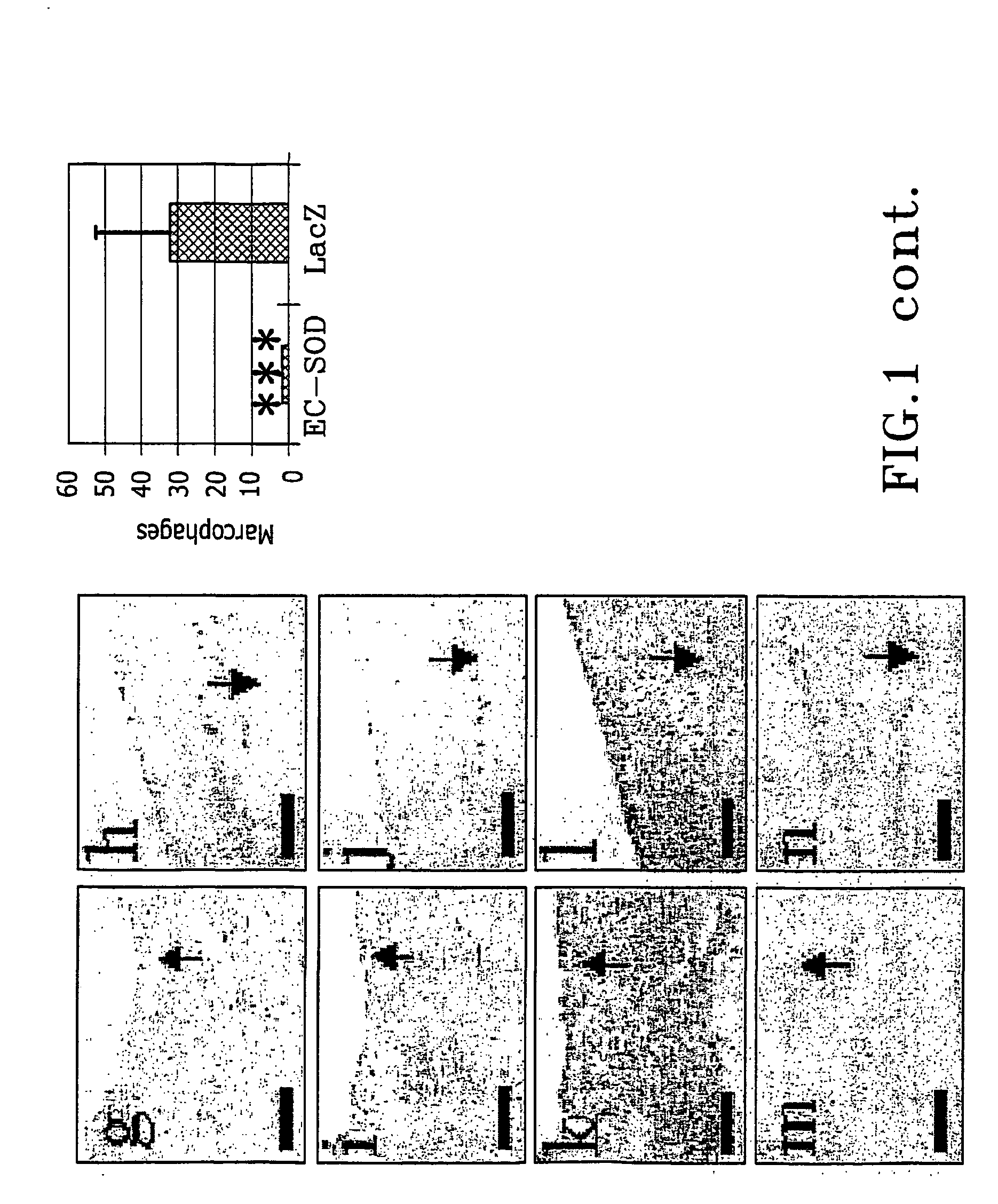
The present invention relates to the use of a gene transfer product to reduce hyperplastic connective tissue growth after tissue trauma or implantation of a medical device. The present invention also relates to a medical device with improved biological properties for an at least partial contact with blood, bodily fluids and / or tissues when introduced in a mammalian body, which device comprises a core and a nucleic acid, encoding a product capable of leading to production of extracellular superoxide dismutase present in a biologically compatible medium. Said nucleic acid encodes a translation or transcription product, which is capable of inhibiting hyperplastic connective tissue growth and promoting endothelialisation in vivo at least partially on a synthetic surface of said core. The present invention also relates to a method of producing a medical device according to the invention.
Owner:FIT BIOTECH OY PLC
Implantable or insertable medical device resistant to microbial growth and biofilm formation
InactiveUS6887270B2Prevent preferential partitioningPrevent chemical modificationAntipyreticAnalgesicsActive agentMicrobial adhesion
Disclosed are implantable or insertable medical devices that provide resistance to microbial growth on and in the environment of the device and resistance to microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on the device. In particular, the invention discloses implantable or insertable medical devices that comprise at least one biocompatible matrix polymer region, an antimicrobial agent for providing resistance to microbial growth and a microbial adhesion / biofilm synthesis inhibitor for inhibiting the attachment of microbes and the synthesis and accumulation of biofilm on the surface of the medical device. Also disclosed are methods of manufacturing such devices under conditions that substantially prevent preferential partitioning of any of said bioactive agents to a surface of the biocompatible matrix polymer and substantially prevent chemical modification of said bioactive agents.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Adhesion barriers applicable by minimally invasive surgery and methods of use thereof
Biocompatible crosslinked polymers, and methods for their preparation and use with minimally invasive surgery applicators are disclosed. The disclosure includes compositions and methods for in situ formation of hydrogels using minimally invasive surgical techniques.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Articles having bioactive surfaces and solvent-free methods of preparation thereof
Methods for preparing articles having a bioactive surface comprising treating a substrate to form free reactive groups, depositing a monomer onto the treated substrate, and covalently immobilizing a biologically functional molecule onto the deposited monomer. Additional embodiments include methods for the deposition of the monomer onto the treated substrate in a solvent-free environment. Further embodiments include articles having surfaces prepared using the methods described herein. Additional embodiments include articles prepared using the methods described herein.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Circumferential ablation device assembly and methods of use and manufacture providing an ablative circumferential band along an expandable member
InactiveUS6954977B2Strong connectionConsistent positionElectrotherapyDiagnosticsFluoropolymerBalloon catheter
A medical balloon catheter assembly includes a balloon having a permeable region and a non-permeable region. The balloon is constructed at least in part from a fluid permeable tube such that the permeable region is formed from a porous material which allows a volume of pressurized fluid to pass from within a chamber formed by the balloon and into the permeable region sufficiently such that the fluid may be ablatively coupled to tissue engaged by the permeable region. The non-permeable region is adapted to substantially block the pressurized fluid from passing from within the chamber and outwardly from the balloon. The porous material may be a porous fluoropolymer, such as porous polytetrafluoroethylene, and the pores may be created by voids that are inherently formed between an interlocking node-fibril network that makes up the fluoropolymer. Such voids may be created according to one mode by expanding the fluoropolymer. The balloon may be formed such that the porous material extends along both the permeable and non-permeable regions. In one mode of this construction, the porous material is porous along the permeable region but is non-porous along the non-permeable region, such as for example by expanding only the permeable region in order to render sufficient voids in the node-fibril network to provide permeable pores in that section. The voids or pores in the porous material may also be provided along both permeable and non-permeable sections but are substantially blocked with an insulator material along the non-permeable section in order to prevent fluid from passing therethrough. The insulator material may be dip coated, deposited, or extruded with the porous material in order to fill the voids. The insulator material may in one mode be provided along the entire working length of the balloon and then selectively removed along the permeable section, or may be selectively exposed to only the non-permeable sections in order to fill the voids or pores there.
Owner:MAGUIRE MARK A +1
Six cell inner stent device for prosthetic mitral valves
InactiveUS20140358224A1Prevent perivalvular leakHeart valvesSurgeryProsthesisPROSTHETIC MITRAL VALVE
This invention relates to a self-expanding wire frame for a pre-configured compressible transcatheter prosthetic cardiovascular valve, a combined inner valve-outer collar component system, and methods for deploying such a valve for treatment of a patient in need thereof.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Drug eluting implantable medical device
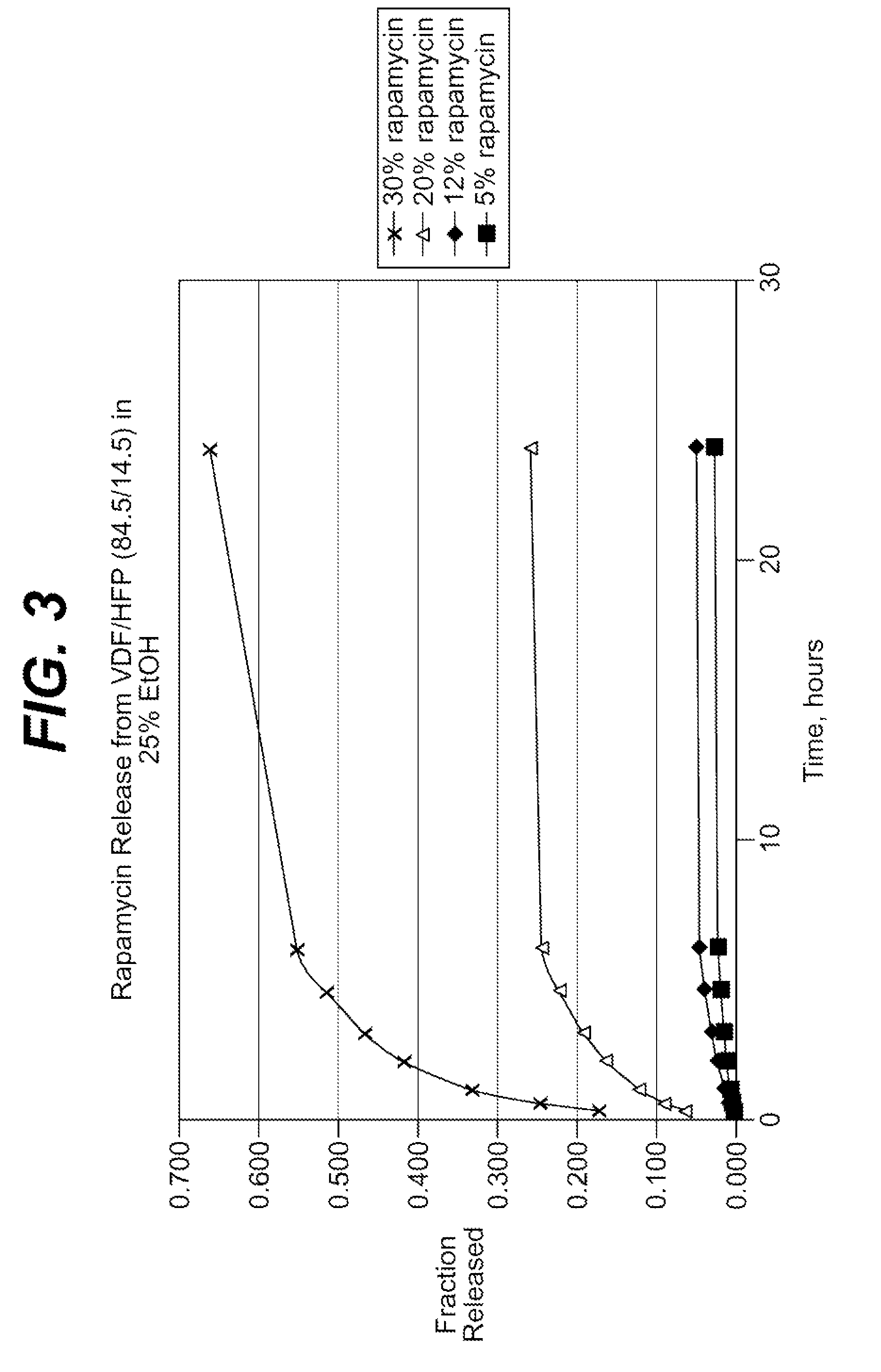
A drug eluting medical device is provided for implanting into vessels or luminal structures within the body of a patient. The coated medical device, such as a stent, vascular, or synthetic graft comprises a coating consisting of a controlled-release matrix of a bioabsorbable, biocompatible, bioerodible, biodegradable, nontoxic material, such as a Poly(DL-Lactide-co-Glycolide) polymer, and at least one pharmaceutical substance, or bioactive agent incorporated within the matrix or layered within layers of matrix. In particular, the drug eluting medical device when implanted into a patient, delivers the drugs or bioactive agents within the matrix to adjacent tissues in a controlled and desired rate depending on the drug and site of implantation.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Methods and apparatuses for coating balloon catheters
ActiveUS20100055294A1Destroy surface tensionUniform coatingBalloon catheterGlovesTransverse axisSolvent
Embodiments of the invention relate to a method and apparatus for coating a medical device. In one embodiment, the method for preparing a substantially uniform coated medical device includes (1) preparing a coating solution comprising a solvent, a therapeutic agent, and an additive; (2) loading a metering dispenser with the coating solution; (3) rotating the medical device about the longitudinal axis of the device and / or moving the medical device along the longitudinal or transverse axis of the device; (4) dispensing the coating solution from the metering dispenser onto a surface of the medical device and flowing the coating solution on the surface of the medical device while the medical device is rotating and / or linearly moving; and (5) evaporating the solvent, forming a substantially uniform coating layer on the medical device.
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, restenosis and related disorders
Methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of all forms of atherosclerosis are described. Administration of compounds such as thalidomide, its analogs, hydrolysis products, metabolites, derivatives and precursors as well as additional compounds capable of inhibiting tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) are used in the invention. Also disclosed is the coating of prosthetic devices, such as stents, with the compounds of the invention for the prevention and / or treatment of restenosis.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
Apparatus and process for making prosthetic suction sleeve
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Therapeutic agent delivery device with protective separating layer
Owner:CONOR MEDSYST
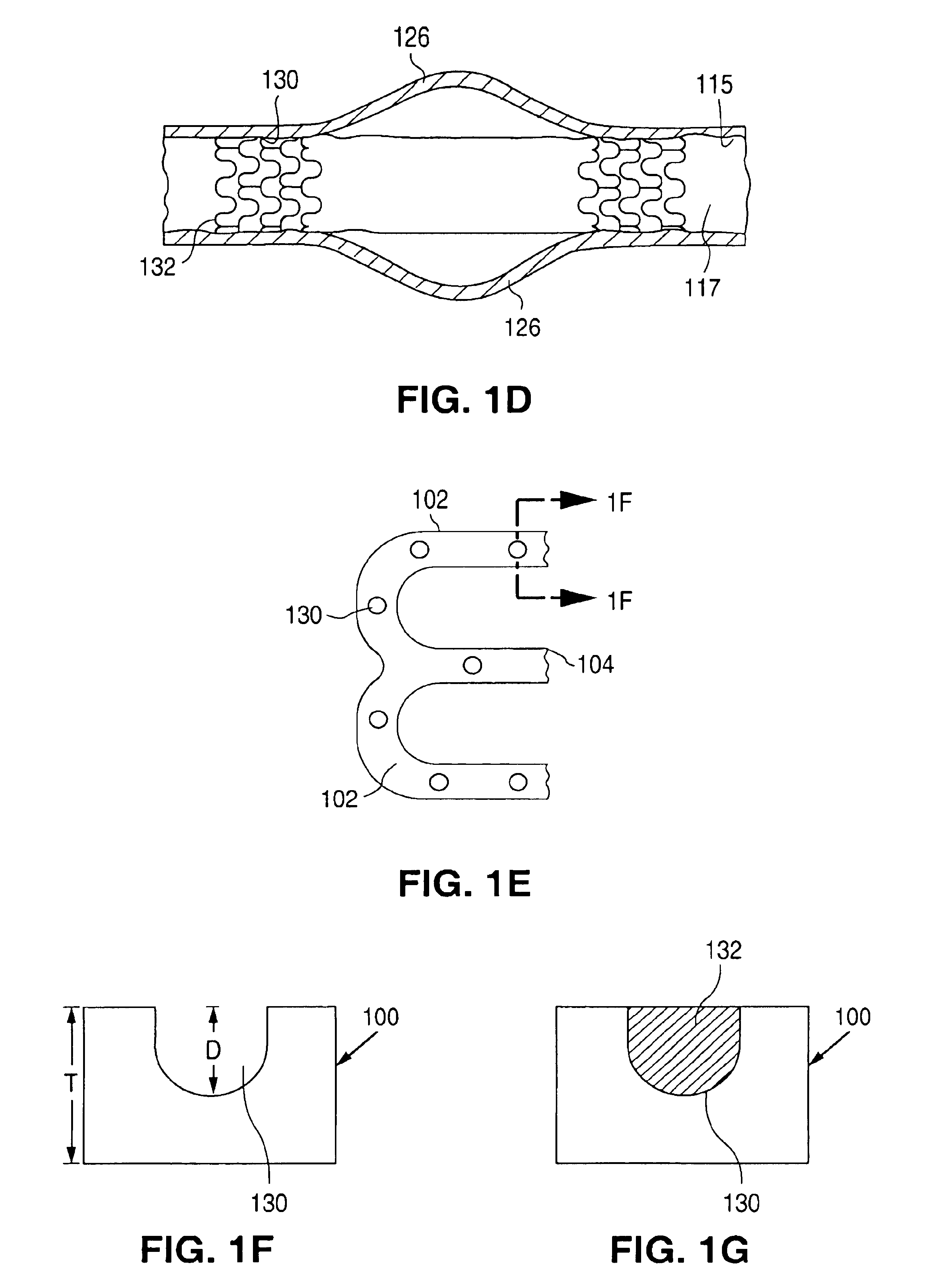
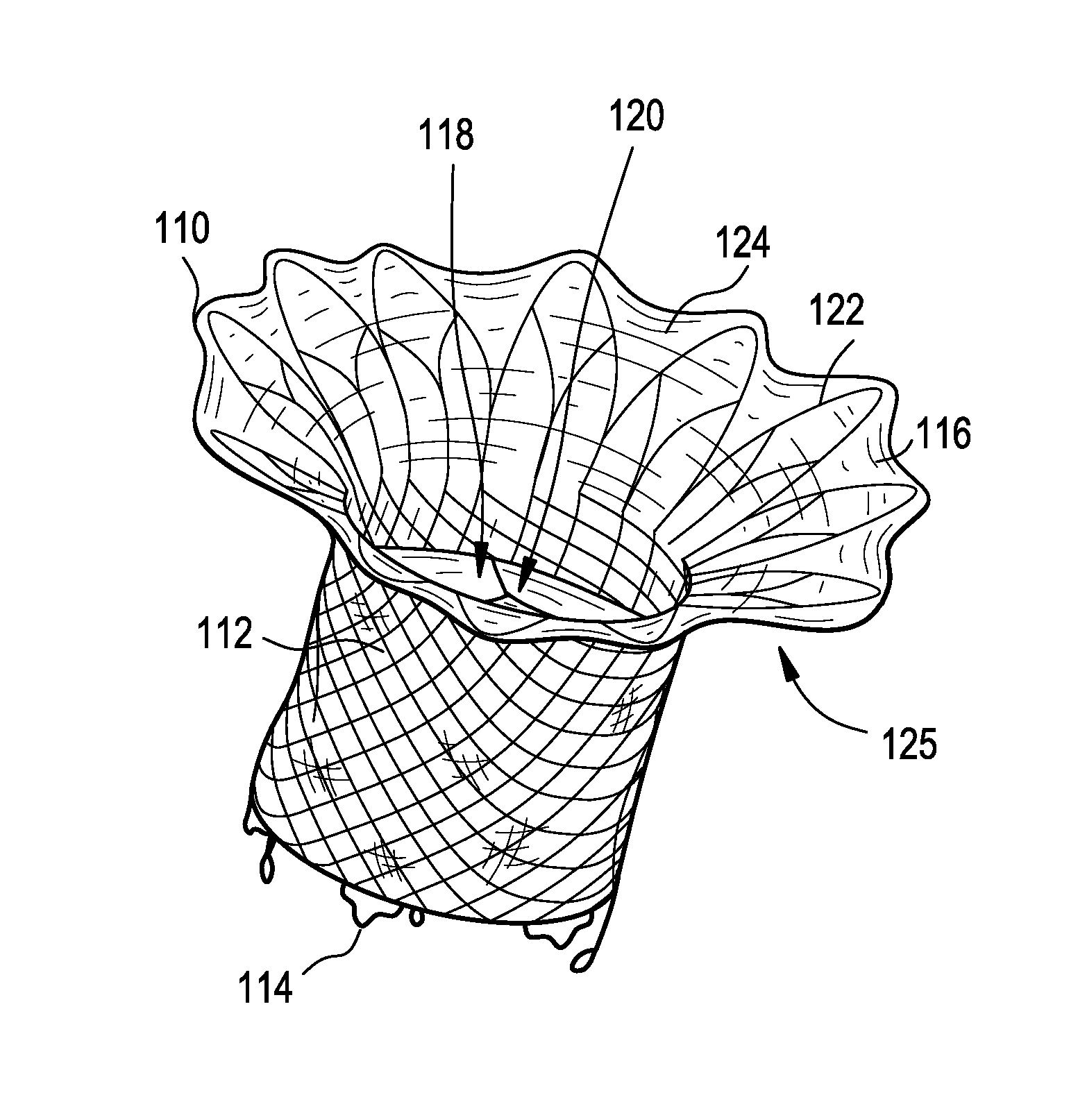
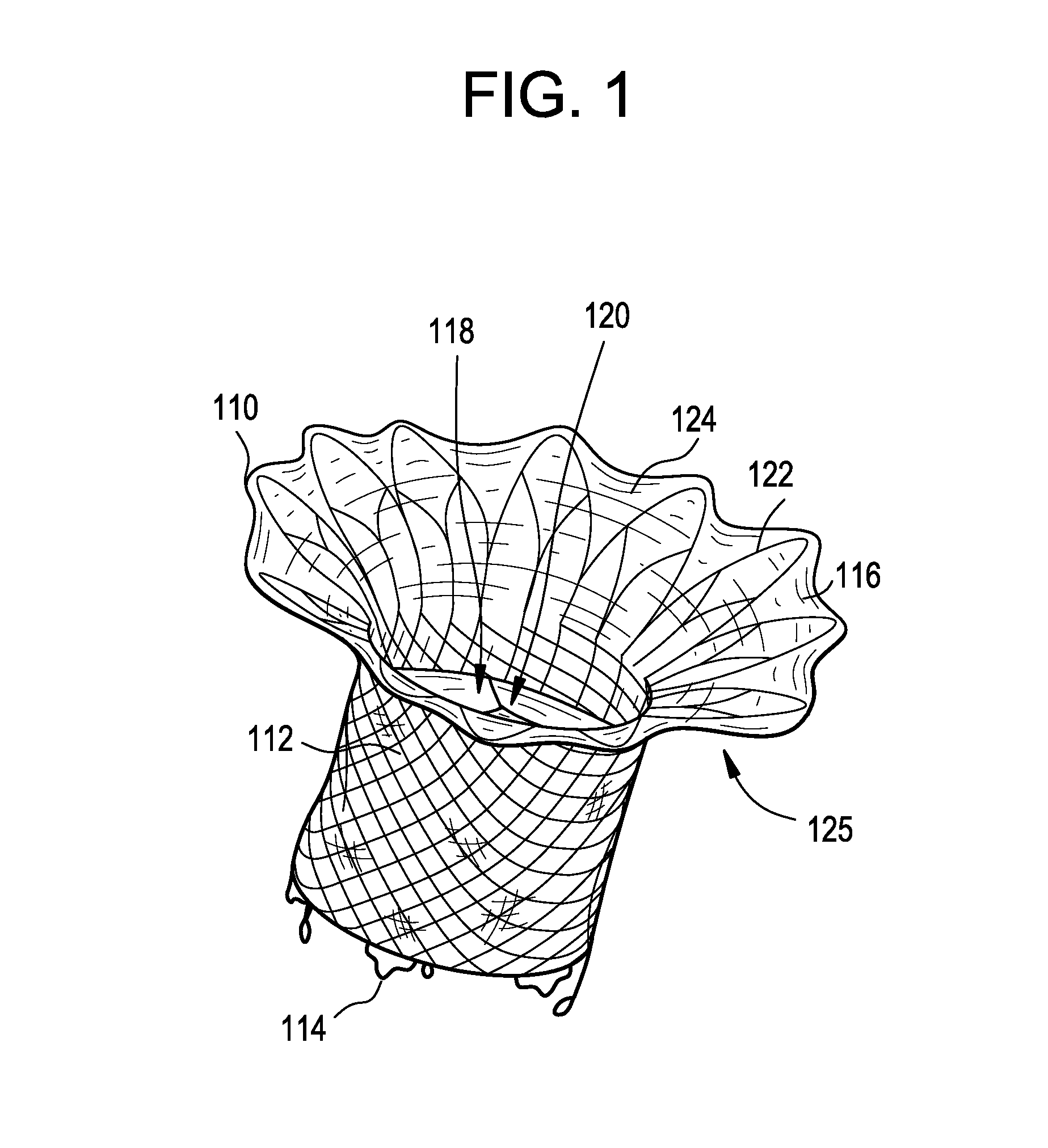
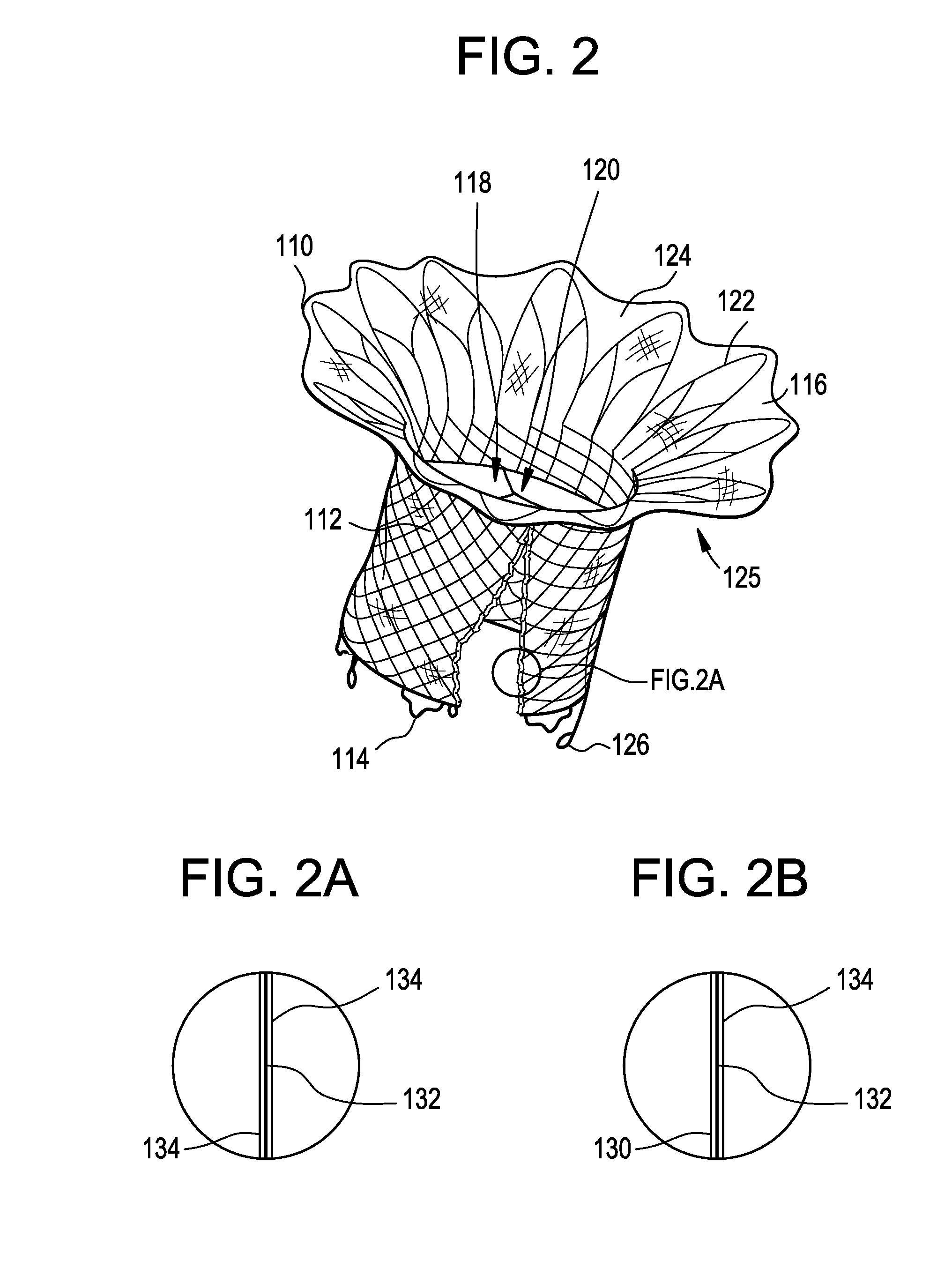
Stent with outer slough coating
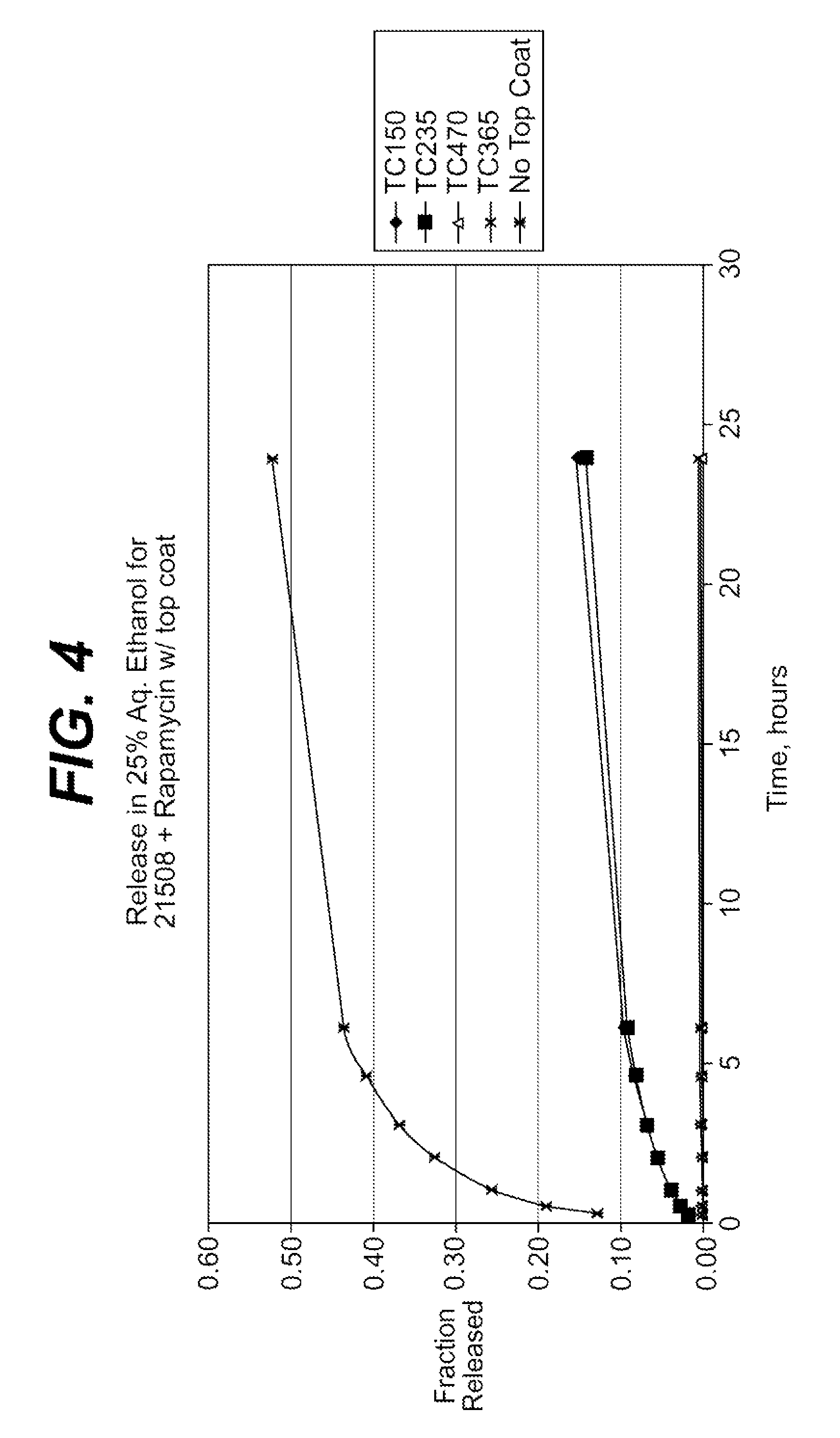
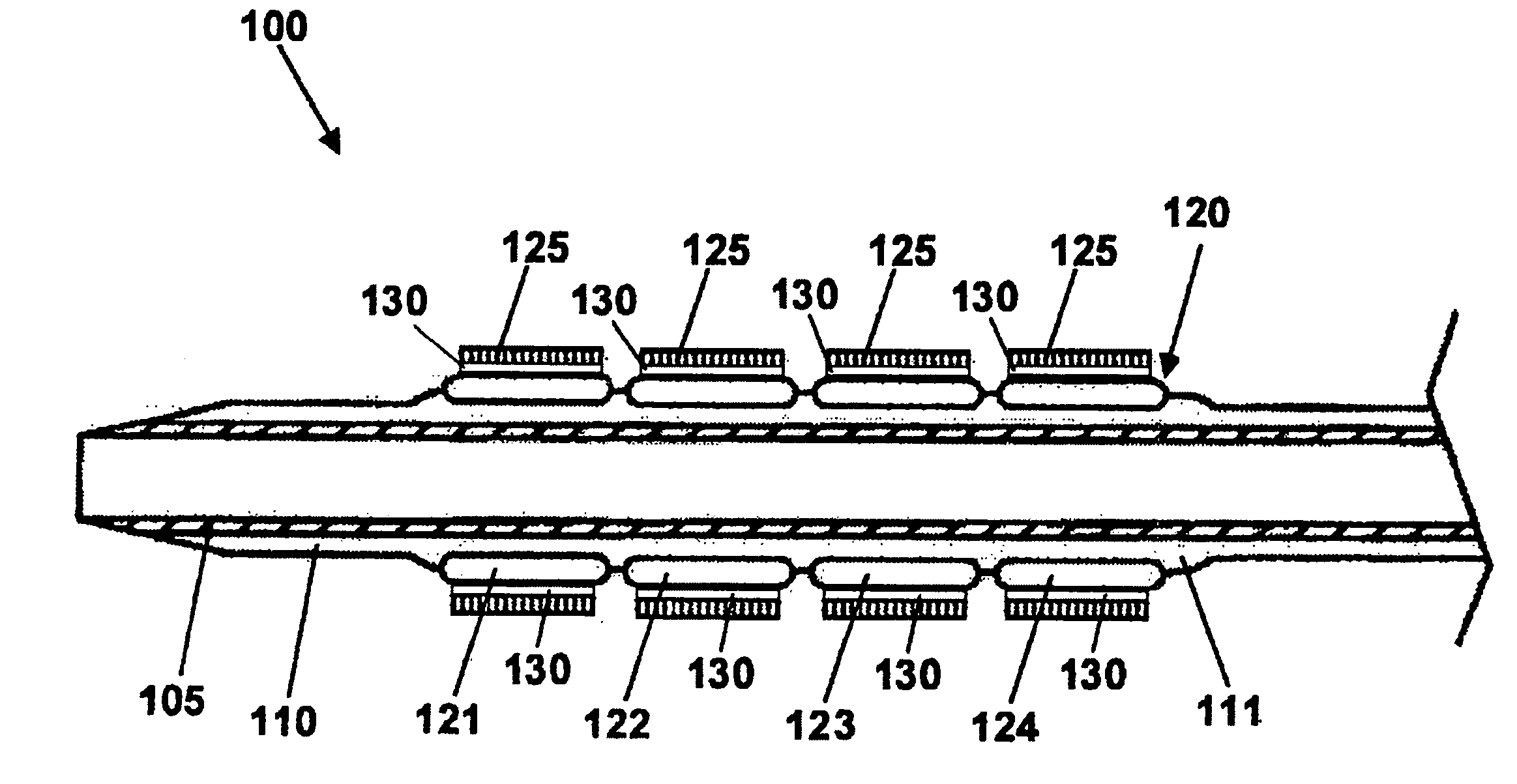
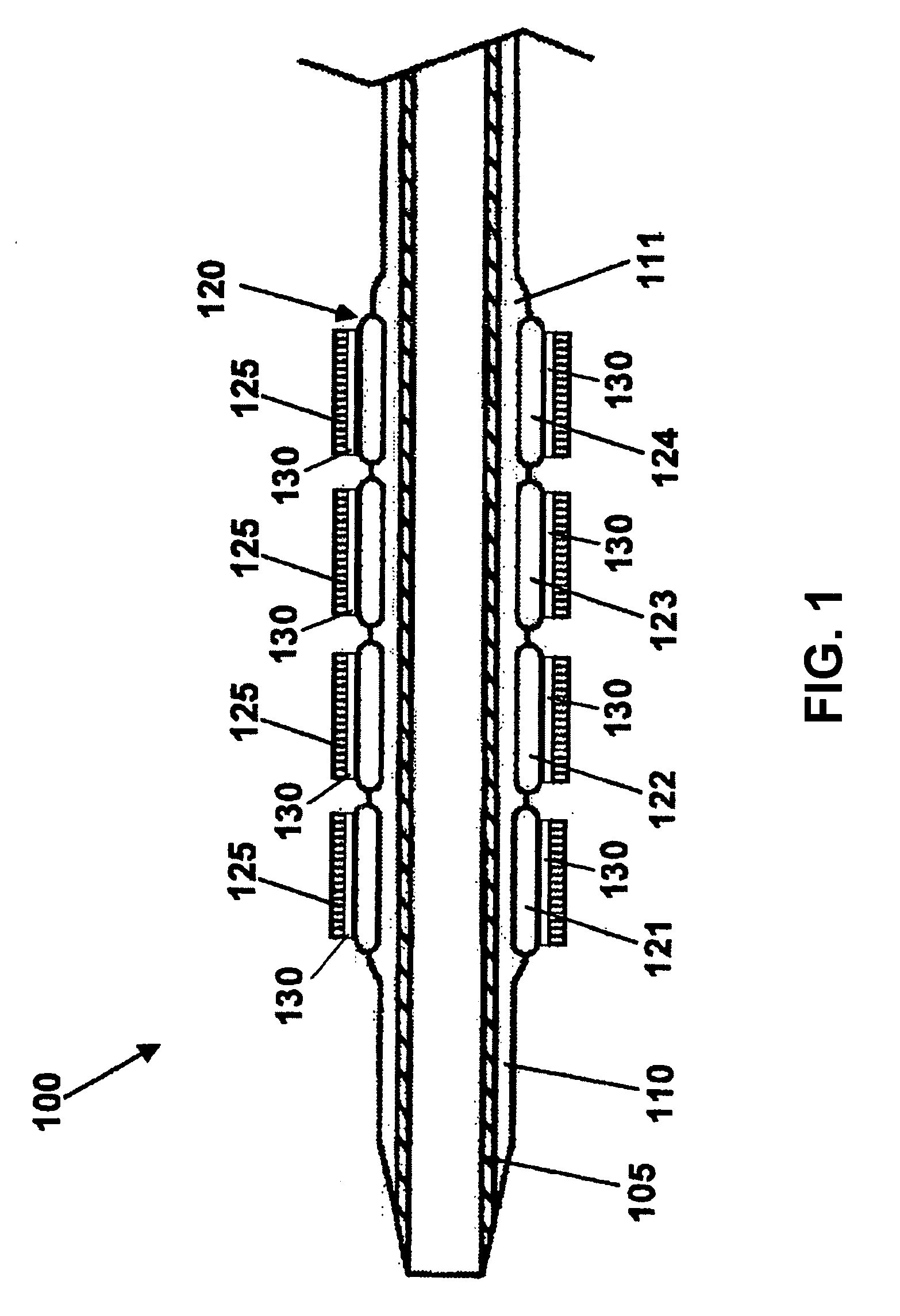
The stent with an outer slough coating 125 of the present invention provides a coated stent having a permanent coating 130 disposed on the stent and a slough coating 125 disposed on the permanent coating 130. The permanent coating 130 includes an anti-proliferative agent and the slough coating 125 includes an anti-inflammatory agent. The slough coating 125 erodes shortly after stent implantation to deliver the anti-inflammatory agent, which treats tissue trauma from the angioplasty and the presence of the stent. Once the slough coating 125 has substantially eroded, the permanent coating 130 delivers the anti-proliferative agent long-term to prevent tissue growth on the stent or within the body lumen, and prevent restenosis. The permanent coating 130 can also include an anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
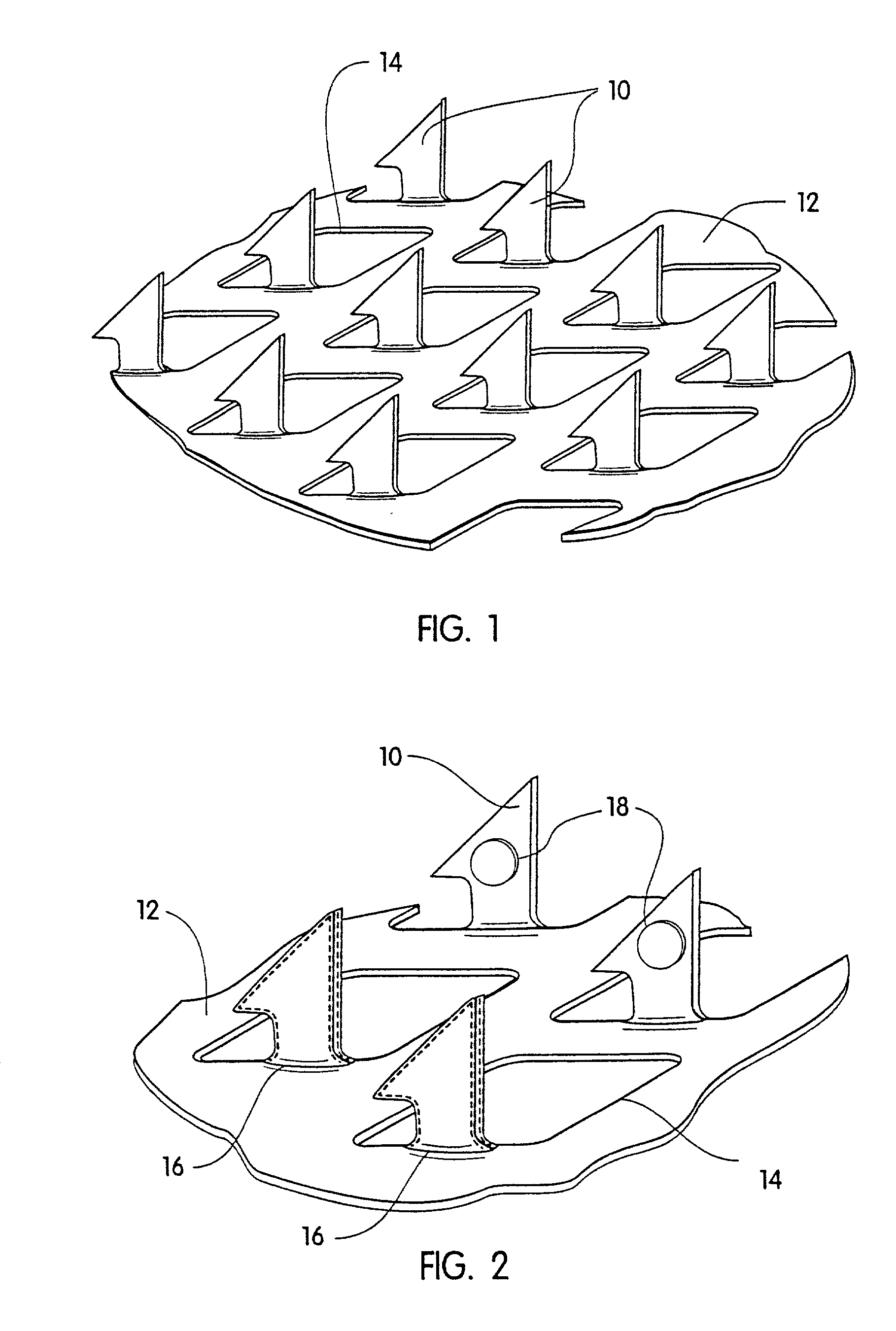
Transdermal drug delivery devices having coated microprotrusions
A device (12) and method are provided for percutaneous transdermal delivery of a potent pharmacologically active agent. The agent is dissolved in water to form an aqueous coating solution having an appropriate viscosity for coating extremely tiny skin piercing elements (10). The coating solution is applied to the skin piercing elements (10) using known coating techniques and then dried. The device (12) is applied to the skin of a living animal (e.g., a human), causing the microprotrusions (10) to pierce the stratum corneum and deliver a therapeutically effect dose of the agent to the animal.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com