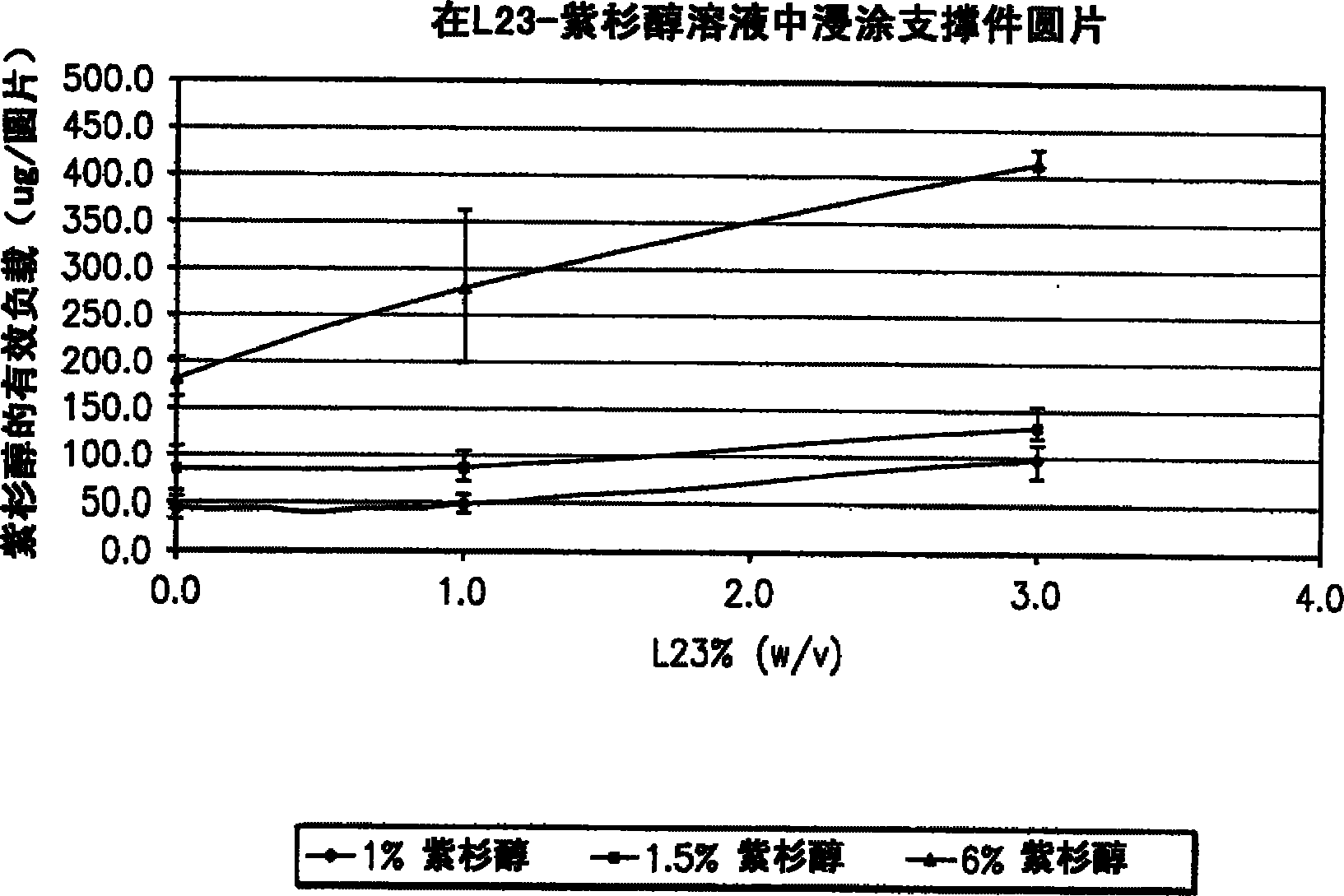
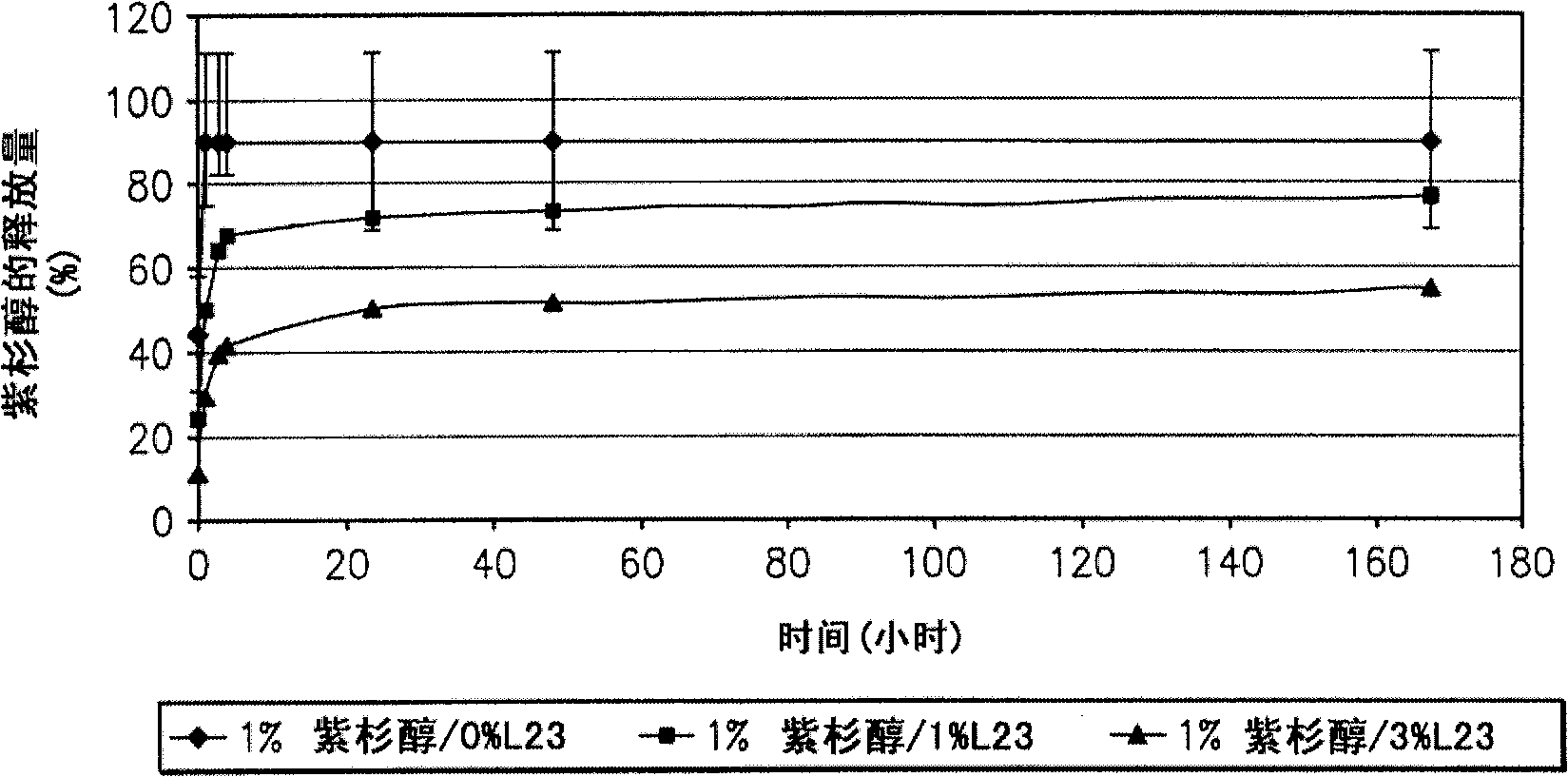
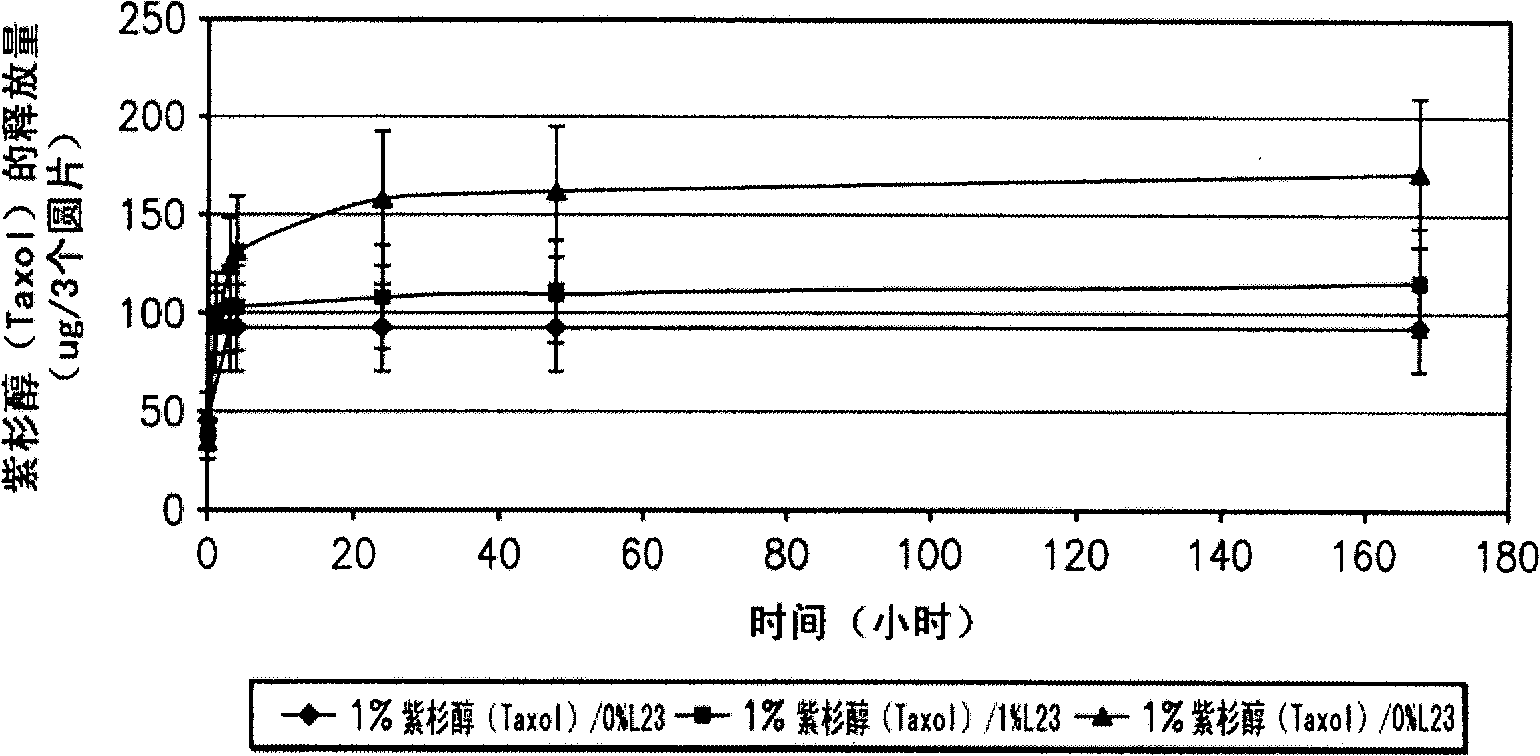
Wound closure material
A technology of polymer materials and products, applied in the field of polymer materials products, can solve the problems of material damage, fracture or tearing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084]Films were prepared from a polymer comprising about 60 wt% glycolide, about 14 wt% de-p-dioxanone, and about 26 wt% trimethylene carbonate. The polymer pellets were placed in a hot water press (Carver Laboratory Press, Model 2626). The heated press is heated to a temperature of about 125-165°C. The particles were placed in the center of a polytetrafluoroethylene-coated stainless steel hot press plate with stainless steel shims to control the thickness of the resulting film. The pellets are melted and spread onto the heated platen, applying a pressure of less than about 100 psi to the polymer melt. All equipment is rapidly cooled by running water passing through the hot plate. Films with a thickness of approximately 0.002 inches to 0.012 inches were obtained. The film is multidirectionally oriented.
Embodiment 2
[0086] Membranes were prepared using a random copolymer comprising about 17 wt% caprolactone, about 7 wt% lactide, about 7 wt% trimethylene carbonate, and about 69 wt% glycolide. The copolymer was extruded through a slot die from a 3 / 4 inch general purpose extruder. Thick tapes were made. The resulting tape was placed on a Teflon-coated stainless steel hot plate with appropriate spacers in a hot water press as described in Example 1 to produce a film of the desired thickness. The heated press is heated to about 105-120°C and a pressure of less than about 100 psi is applied. Similar to the film prepared using the particles in Example 1, the film produced by this method had a thickness of about 0.002 inches to 0.012 inches. Because the extruded film has a less crystalline structure than the pellets of Example 1, lower temperatures can be used to form polymer streams. The film is multidirectionally oriented.
Embodiment 3
[0088] Films were prepared from the polymers described in Example 2 using the blown film method. Incorporate polymer particles into the
[0089] in a rod / barrel configuration and jacketed extruder (Randcastle Extrusion System, Inc., Cedar Grove, New Jersey) equipped with external heating elements. The barrel had three zones set at three different temperatures, zone 1 being the part of the barrel closest to where the polymer pellets were introduced, zone 2 being the middle part of the barrel, and zone 3 being the tail end of the barrel from where the polymer was extruded . The barrel has a length / diameter ratio of 24 to 1 and a 3 / 4 inch rod is provided inside the barrel. A die, approximately 1.25 inches in diameter, was placed at the end of the barrel from which the polymer melt was extruded.
[0090] The barrel temperature in zone 1 is about 344°F; the temperature in zone 2 is about 347°F-350°F; the temperature in zone 3 is about 294°F; the temperature of the adapter betwee...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com