Enzyme biosensor for detecting inosine monophosphate(IMP) and preparation method and application thereof
A biosensor and inosinic acid technology, applied in the field of biosensors, can solve the problems of long time-consuming, complicated operation, high detection cost, etc., and achieve the effects of improved reaction speed, simple preparation process, and strong anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
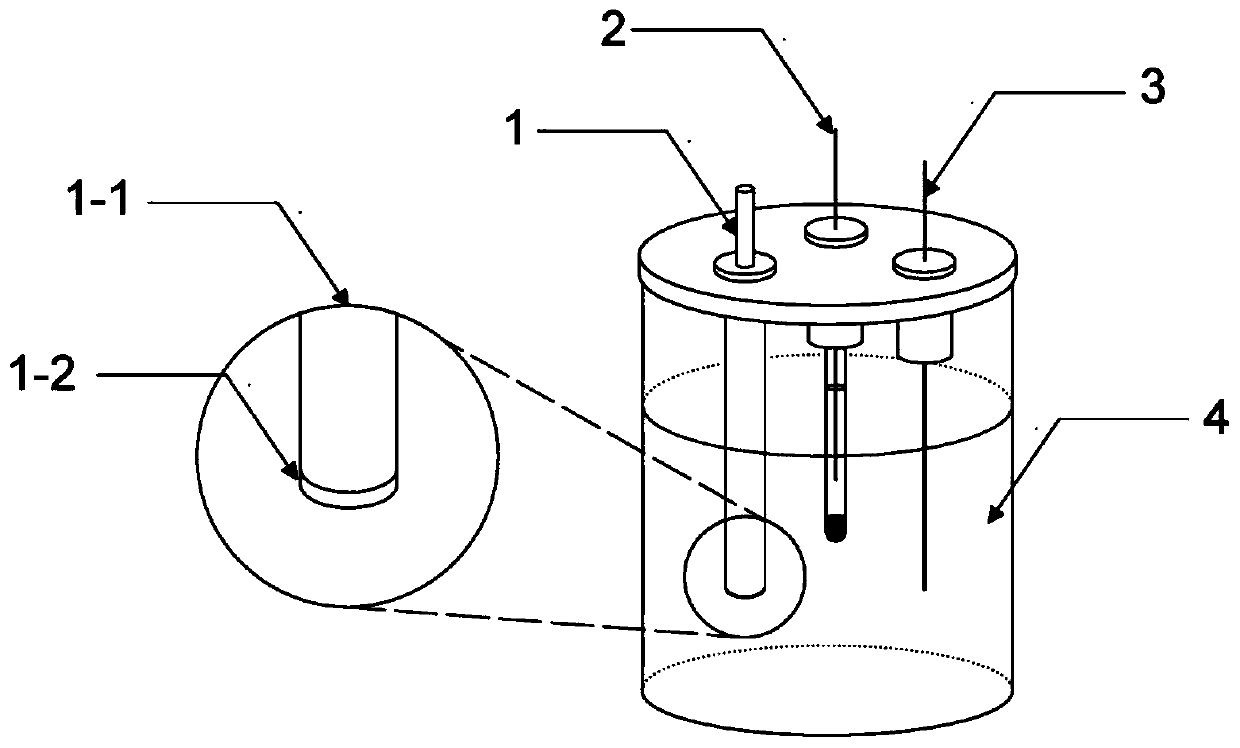
[0042] Enzyme biosensor for detecting inosinic acid, its overall structure is as follows figure 1 As shown, it is composed of a reference electrode 2, a counter electrode 3 and a modified electrode 1. The modified electrode 1 is composed of a working electrode 1-1 and a substance recognition film 1-2 solidified on the surface of the working electrode. Among them, the inosinic acid-sensitive Substance recognition membrane 1-2 made of MXene-Ti 3 C 2 Prepared from Tx solution, chitosan solution, chloroauric acid solution, chloroplatinic acid solution, 5'-nucleotidase solution, xanthine oxidase solution and bovine serum albumin solution, put the above enzyme biosensor into the In the test solution 4, the content of inosinic acid in the test solution 4 can be detected.
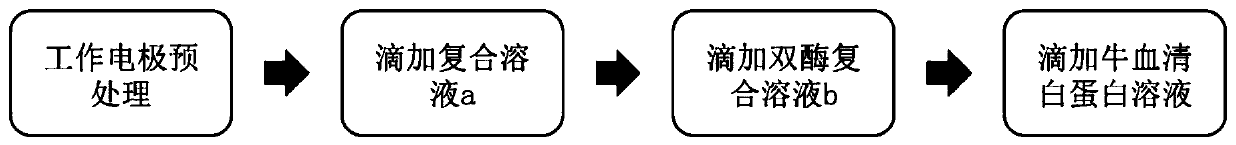
[0043] The preparation process of the modified electrode 1 is as follows: figure 2 Shown, concrete preparation method step is:
[0044] (1) Working electrode pretreatment. The working electrode was polished t...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The enzyme biosensor for detecting inosinic acid, its preparation steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) A glassy carbon electrode with a diameter of 3 mm was polished to a mirror surface on a polishing cloth with alumina powders with a diameter of 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm in sequence, then rinsed with ultrapure water, and then ultrasonically treated in ultrapure water for 1 min, and left to dry After drying, the glassy carbon electrode was placed in potassium ferricyanide solution (made by K 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ], K 4 [Fe(CN) 6 ] and KCl in a molar ratio of 1:1:100), at -0.2 to 0.6V, use cyclic voltammetry to scan 4 circles to activate the electrode, take it out and rinse it with ultrapure water, and dry it with nitrogen to get Pretreated glassy carbon electrodes.
[0052] (2) 125mgMXene-Ti 3 C 2 The Tx material was dispersed in 100mL ultrapure water to obtain MXene-Ti with a concentration of 1.25mg / mL 3 C 2 Tx solution; Adopt 1wt% acetic acid solution preparation concentration ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The enzyme biosensor for detecting inosinic acid, its preparation steps are as follows:
[0061] (1) A glassy carbon electrode with a diameter of 3 mm was polished to a mirror surface on a polishing cloth with alumina powders with a diameter of 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm in sequence, then rinsed with ultrapure water, and then ultrasonically treated in ultrapure water for 1 min, and left to dry After drying, the glassy carbon electrode was placed in potassium ferricyanide solution (made by K 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ], K 4 [Fe(CN) 6 ] and KCl in a molar ratio of 1:1:100), at -0.2 to 0.6V, use cyclic voltammetry to scan 4 circles to activate the electrode, take it out and rinse it with ultrapure water, and dry it with nitrogen to get Pretreated glassy carbon electrodes.
[0062] (2) 125mgMXene-Ti 3 C 2 The Tx material was dispersed in 100mL ultrapure water to obtain MXene-Ti with a concentration of 1.25mg / mL 3 C 2 Tx solution; Adopt 1wt% acetic acid solution preparation concentration ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com