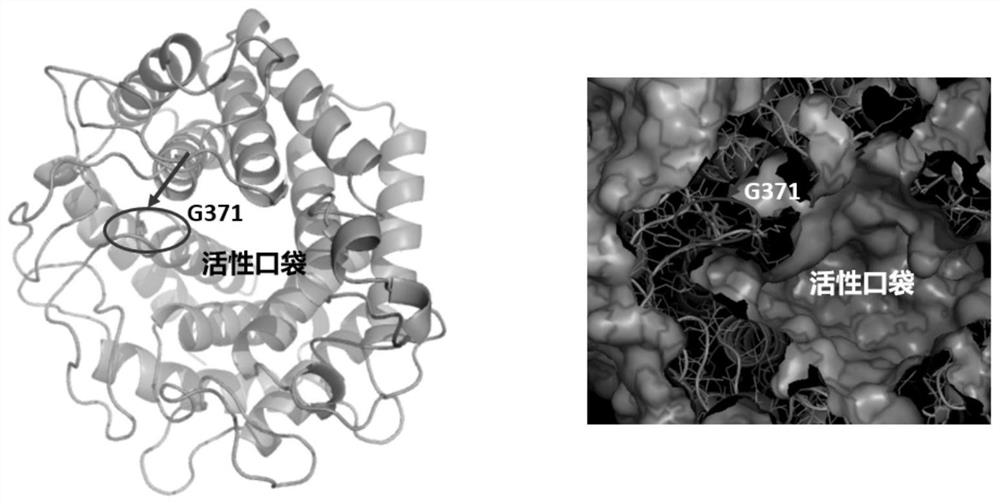
Method for increasing yield of sialic acid and application
A sialic acid and amino acid technology, applied in the fields of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering, can solve the problems of low sialic acid yield, low N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase catalytic efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Construction of recombinant bacteria containing N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase mutant
[0049] The specific method is as follows:
[0050] (1) Chemically synthesize a gene encoding N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3;
[0051] (2) Use Extaq enzyme to amplify the N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase gene, connect it to the T vector, transform Escherichia coli JM109, screen to obtain recombinant bacteria, and extract to obtain N-acetylglucosamine-2-containing - T vector for the epimerase gene.
[0052] (3) Utilize the primer sequence, take the T carrier containing N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase gene as template PCR, carry out site-directed mutation at N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase gene; The primer sequences involved are as follows:
[0053] G371C-FW:AAATGGAAATGTTGCTTCCAC;
[0054] G371C-RS: TGGAAGCAACATTTCCATTT;
[0055] G371A-FW:AAATGGAAAGCTTGCTTCCAC;
[0056] G371A-RS: GTGGAAGCAAGCTTTCCATTT.
[0057] PCR rea...
Embodiment 2
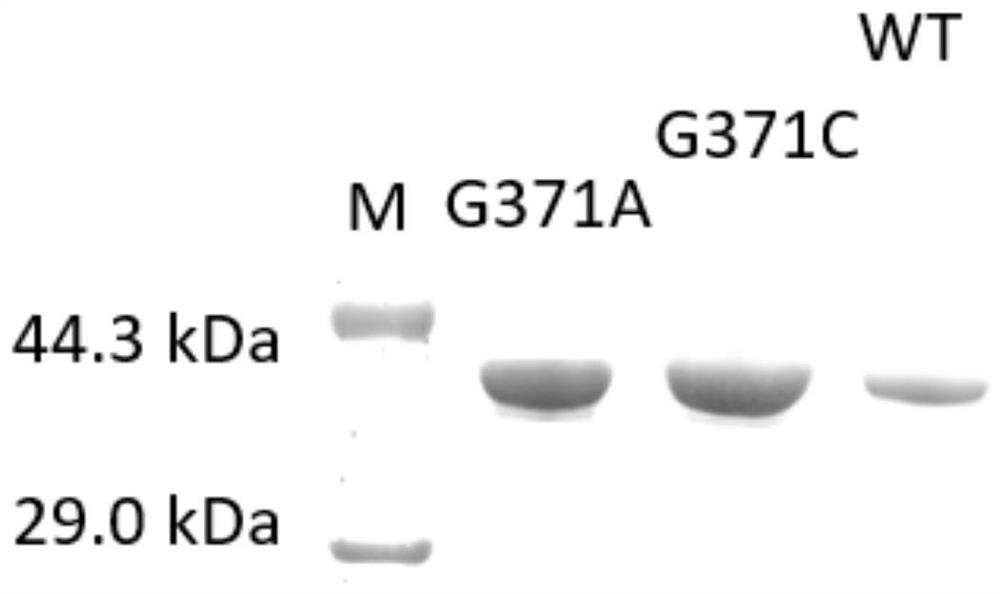
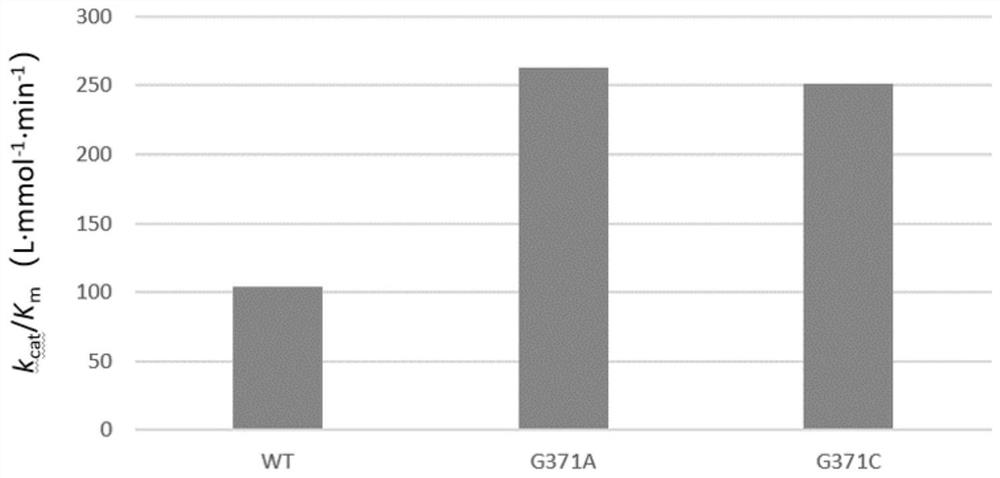
[0063] Example 2: Expression, purification and analysis of N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase
[0064] Specific steps are as follows:
[0065] (1) Pick single colonies of E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-G371C, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-G371A and E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-WT prepared in Example 1 Inoculate to 50 μg·mL -1 Kanamycin liquid LB medium, 37°C, 200r min -1 After culturing for 12 hours, the seed solution was prepared.
[0066] (2) Inoculate the prepared seed liquid into LB liquid medium with an inoculation volume of 1% by volume, at 37°C, 200r min -1 Continue to culture to OD 600 When it is 0.8, add 1.0mmol·L -1 IPTG was cultured at 28°C for 8 hours to induce the expression of recombinant protein, and the crude enzyme solutions containing N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase mutants were obtained respectively: namely, the crude enzyme solutions containing G371A and the crude enzyme solutions containing G371C were respectively obtained , and a crude enzyme solution containing N-acety...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3: the preparation of sialic acid
[0087] Specific steps are as follows:
[0088] 1. Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli
[0089] (1) Chemically synthesize the nucleotide sequence of the N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase gene shnal shown in SEQ ID NO.8, add NdeI and EcoRI restriction sites at both ends, and insert it into the vector plasmid pET28a after synthesis Between the cloning sites EcoRI and NdeI, the recombinant plasmid pET28a-shnal was obtained.
[0090] (2) The N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase mutant G371C gene and G371A gene and nucleotide sequence obtained in the step (4) of Example 2 are shown in SEQ ID NO.3 respectively N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase WT was digested by restriction enzymes NdeI and EcoRI and connected to the recombinant plasmid pET28a-shnal prepared in step (1) to obtain recombinant plasmids pET28a-shnal respectively. shnal-G371C, pET28a-shnal-G371A and pET28a-shnal-WT.
[0091] (3) Construction of recombinant Escher...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com